Page 1

XM-120 Eccentricity Module
User Guide
Firmware Revision 5
1440-VST02-01RA
Page 2
Important User Information
WARNING
IMPORTANT
ATTENTION
SHOCK HAZARD
BURN HAZARD
Solid state equipment has operational characteristics differing from those of electromechanical equipment. Safety Guidelines for the
Application, Installation and Maintenance of Solid State Controls (publication SGI-1.1 available from your local Rockwell Automation sales
office or online at http://literature.rockwellautomation.com
wired electromechanical devices. Because of this difference, and also because of the wide variety of uses for solid state equipment, all
persons responsible for applying this equipment must satisfy themselves that each intended application of this equipment is acceptable.
In no event will Rockwell Automation, Inc. be responsible or liable for indirect or consequential damages resulting from the use or
application of this equipment.
The examples and diagrams in this manual are included solely for illustrative purposes. Because of the many variables and requirements
associated with any particular installation, Rockwell Automation, Inc. cannot assume responsibility or liability for actual use based on the
examples and diagrams.
No patent liability is assumed by Rockwell Automation, Inc. with respect to use of information, circuits, equipment, or software described in
this manual.
Reproduction of the contents of this manual, in whole or in part, without written permission of Rockwell Automation, Inc., is prohibited.
Throughout this manual, when necessary, we use notes to make you aware of safety considerations.
Identifies information about practices or circumstances that can cause an explosion in a
hazardous environment, which may lead to personal injury or death, property damage, or
economic loss.
) describes some important differences between solid state equipment and hard-
Identifies information that is critical for successful application and understanding of the product.
Identifies information about practices or circumstances that can lead to personal injury or death,
property damage, or economic loss. Attentions help you identify a hazard, avoid a hazard, and
recognize the consequence
Labels may be on or inside the equipment, for example, a drive or motor, to alert people that
dangerous voltage may be present.
Labels may be on or inside the equipment, for example, a drive or motor, to alert people that
surfaces may reach dangerous temperatures.
Allen-Bradley, Rockwell Automation, and XM are trademarks of Rockwell Automation, Inc.
Trademarks not belonging to Rockwell Automation are property of their respective companies.
Page 3
Safety Approvals
WARNING
AVERTISSEMENT
IMPORTANT
The following information applies when operating
this equipment in hazardous locations.
Products marked "CL I, DIV 2, GP A, B, C, D" are suitable
for use in Class I Division 2 Groups A, B, C, D, Hazardous
Locations and nonhazardous locations only. Each product
is supplied with markings on the rating nameplate
indicating the hazardous location temperature code.
When combining products within a system, the most
adverse temperature code (lowest "T" number) may be
used to help determine the overall temperature code of
the system. Combinations of equipment in your system
arfe subject to investigation by the local Authority Having
Jurisdiction at the time of installation.
EXPLOSION HAZARD -
•Do not disconnect equipment unless power
has been removed or the area is known to be
nonhazardous.
•Do not disconnect connections to this
equipment unless power has been removed
or the area is known to be nonhazardous.
Secure any external connections that mate to
this equipment by using screws, sliding
latches, threaded connectors, or other means
provided with this product.
•Substitution of components may impair
suitability for Class I, Division 2.
•If this product contains batteries, they must
only be changed in an area known to be
nonhazardous.
Informations sur l’utilisation de cet équipement en
environnements dangereux.
Les produits marqués "CL I, DIV 2, GP A, B, C, D" ne
conviennent qu'à une utilisation en environnements de
Classe I Division 2 Groupes A, B, C, D dangereux et non
dangereux. Chaque produit est livré avec des marquages
sur sa plaque d'identification qui indiquent le code de
température pour les environnements dangereux. Lorsque
plusieurs produits sont combinés dans un système, le
code de température le plus défavorable (code de
température le plus faible) peut être utilisé pour
déterminer le code de température global du système. Les
combinaisons d'équipements dans le système sont
sujettes à inspection par les autorités locales qualifiées
au moment de l'installation.
RISQUE D’EXPLOSION –
•Couper le courant ou s'assurer que
l'environnement est classé non dangereux
avant de débrancher l'équipement.
•Couper le courant ou s'assurer que
l'environnement est classé non dangereux
avant de débrancher les connecteurs. Fixer
tous les connecteurs externes reliés à cet
équipement à l'aide de vis, loquets
coulissants, connecteurs filetés ou autres
moyens fournis avec ce produit.
•La substitution de composants peut rendre
cet équipement inadapté à une utilisation en
environnement de Classe I, Division 2.
•S'assurer que l'environnement est classé non
dangereux avant de changer les piles.
Wiring to or from this device, which enters or leaves the system enclosure, must
utilize wiring methods suitable for Class I, Division 2 Hazardous Locations, as
appropriate for the installation in accordance with the product drawings as
indicated in the following table.
Model Catalog Number Haz Location Drawings* Model Catalog Number Haz Location Drawings*
w/o
Barriers
XM-120 1440-VST0201RA
XM-121 1440-VLF0201RA XM-360 1440-TPR0600RE
XM-122 1440-VSE0201RA XM-361 1440-TUN0600RE
XM-123 1440-VAD0201RA XM-361 1440-TTC0600RE
XM-160 1440-VDRS0600RH
XM-161 1440-VDRS0606RH XM-441 1440-REX0004RD 48241-HAZ N/A
XM-162 1440-VDRP0600RH XM-442 1440-REX0304RG 48642-HAZ N/A
XM-220 1440-SPD0201RB 48640-HAZ 48641-HAZ
48178-HAZ 48179-HAZ
51263-HAZ 51264-HAZ
* Drawings are available on the included CD
w/
Barriers
w/o
Barriers
XM-320 1440-TPS0201RB 48238-HAZ 48239-HAZ
48295-HAZ 48299-HAZ
XM-440 1440-RMA0004RC 48240-HAZ N/A
w/
Barriers
Page 4

Page 5

Introduction
Installing the XM-120 Eccentricity
Module
Table of Contents
Chapter 1
Introducing the Eccentricity Module . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Eccentricity Module Components. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Using this Manual. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Organization. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Document Conventions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Chapter 2
XM Installation Requirements. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Wiring Requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Power Requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Grounding Requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Mounting the Terminal Base Unit. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
DIN Rail Mounting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Interconnecting Terminal Base Units . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Panel/Wall Mounting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Connecting Wiring for Your Module . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Terminal Block Assignments. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Connecting the Power Supply. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Connecting the Relays . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Connecting the Tachometer Signal. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Connecting the Buffered Outputs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Connecting a Non-Contact Sensor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Connecting the Remote Relay Reset Signal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Connecting the 4-20 mA Outputs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Serial Port Connection. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
DeviceNet Connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Mounting the Module . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Module Indicators . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Basic Operations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Powering Up the Module . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Manually Resetting Relays . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Installing the XM-120 Eccentricity Firmware. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Chapter 3
Configuration Parameters
v Publication GMSI10-UM010C-EN-P - May 2010
Channel Transducer Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Measurement Parameters. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Eccentricity Measurement Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Waveform Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Speed Measurement Parameter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Tachometer Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Tachometer Transducer Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Tachometer Signal Processing Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
Alarm Parameters. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Relay Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
4-20 mA Output Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
Page 6

Table of Contents vi
Specifications
DeviceNet Information
I/O Data Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
Data Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
Monitor Data Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
Alarm and Relay Status Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
Device Mode Parameters. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
Appendix A
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
Appendix B
Electronic Data Sheets. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
Changing Operation Modes. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
Transition to Program Mode. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
Transition to Run Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
XM Services . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
Invalid Configuration Errors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
Eccentricity I/O Message Formats . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
Poll Message Format . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
COS Message Format . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
ADR for XM Modules. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
DeviceNet Objects
Appendix C
Identity Object (Class ID 01H) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
Class Attributes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
Instance Attributes. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
Status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
Services. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
DeviceNet Object (Class ID 03H) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80
Class Attributes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80
Instance Attributes. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80
Assembly Object (Class ID 04H) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
Class Attribute . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
Instances. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
Instance Attributes. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
Assembly Instance Attribute Data Format. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
Services. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
Connection Object (Class ID 05H). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
Class Attributes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
Instances. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
Instance Attributes. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
Services. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
Publication GMSI10-UM010C-EN-P - May 2010
Page 7

Table of Contents vii
Analog Input Point Object (Class ID 0AH). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
Class Attributes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
Instances. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
Instance Attributes. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
Services. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
Parameter Object (Class ID 0FH). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90
Instances. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90
Instance Attributes. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 92
Services. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 92
Acknowledge Handler Object (Class ID 2BH) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 93
Class Attributes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 93
Instances. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 93
Instance Attributes. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 93
Alarm Object (Class ID 31DH) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94
Class Attributes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94
Instances. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94
Instance Attributes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94
Services. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 95
Device Mode Object (Class ID 320H) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 96
Class Attributes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 96
Instance Attributes. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 96
Services. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 96
Relay Object (Class ID 323H) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 97
Class Attributes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 97
Instances. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 98
Instance Attributes. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 98
Spectrum Waveform Measurement Object (Class ID 324H) . . . . . . . 99
Class Attributes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 99
Instances. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100
Instance Attributes. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100
Services. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100
Get_Waveform_Chunk . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 101
Speed Measurement Object (Class ID 325H). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 102
Class Attributes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 102
Instance Attributes. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 103
Services. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 103
Tachometer Channel Object (Class ID 326H) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 103
Class Attributes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 103
Instance Attributes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 104
Services. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 104
Transducer Object (Class ID 328H) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 105
Class Attributes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 105
Instances. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 105
Instance Attributes. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 105
Services. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 106
Publication GMSI10-UM010C-EN-P - May 2010
Page 8

Table of Contents viii
Wiring Connections for Previous
Module Revisions
4-20 mA Output Object (Class ID 32AH) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 106
Class Attributes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 106
Instances. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 106
Instance Attributes. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 107
Services. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 107
Appendix D
Terminal Block Assignments. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 109
Connecting the Transducer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 112
Glossary
Index
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 115
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 119
Publication GMSI10-UM010C-EN-P - May 2010
Page 9

Chapter
IMPORTANT
1
Introduction
This chapter provides an overview of the XM-120 Eccentricity module. It also
discusses the components of the module.
For information about See page
Introducing the Eccentricity Module 1
Eccentricity Module Components 2
Using this Manual 3
This manual only describes how to install and use the
XM-120 Eccentricity module. For information about the
dynamic measurement and low frequency dynamic
measurement modules, refer to the XM-120/121 Dynamic
Measurement Module User Guide.
Introducing the Eccentricity Module
The XM-120 Eccentricity module is a 2-channel eccentricity monitor. It is a
member of the Allen-Bradley™ XM
condition monitoring and protection modules that operate both in stand-alone
applications or integrate with Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) and
control system networks.
Eccentricity is the measure of the amount of bow in a rotor. The lower the
eccentricity value the more straight the shaft. Rotor bow can be a fixed
mechanical bow, or it can be a temporary bow caused by uneven thermal
heating or simply by the weight of the rotor (gravity bow).
The Eccentricity module is suitable for virtually all types of rotating and
reciprocating machinery where rotor bow must be measured prior to or during
startup. It accepts input from non-contact eddy current probe systems to
provide peak-to-peak eccentricity, maximum instantaneous DC voltage (max
gap), minimum instantaneous DC voltage (min gap), and instantaneous DC
voltage (gap) measurements. In addition to the transducer inputs, the module
can accept one tachometer input to provide speed measurement, which can, if
desired, be used to disable eccentricity alarms after startup.
®
Series, a family of DIN rail mounted
1 Publication GMSI10-UM010C-EN-P - May 2010
Page 10

2 Introduction
XM-940 Dynamic Measurement Module Terminal Base Unit
Cat. No. 1440-TB-A
XM-120 Dynamic Measurement Module
Cat. No. 1440-VST02-01RA
IMPORTANT
The Eccentricity module includes a single on-board relay, expandable to five,
making it a complete monitoring system. It can operate stand-alone, or it can
be deployed on a standard or dedicated DeviceNet network where it can
provide real-time data and status information to other XM modules, PLCs,
distributed control systems (DCS), and Condition Monitoring Systems.
The Eccentricity module can be configured remotely via the DeviceNet
network, or locally using a serial connection to a PC or laptop. Refer to
Chapter 3 for a list of the configuration parameters.
Eccentricity Module Components
The Eccentricity module consists of a terminal base unit and an instrument
module. The XM-120 Dynamic Measurement Module and the XM-940
Terminal Base are shown below.
Figure 1.1 Eccentricity Module Components
• XM-940 Dynamic Measurement Module Terminal Base - A DIN rail
mounted base unit that provides terminations for all field wiring
required by XM Dynamic Measurement and Eccentricity modules.
Publication GMSI10-UM010C-EN-P - May 2010
• XM-120 Dynamic Measurement Module - The XM-120 mounts on the
XM-940 terminal base via a keyswitch and a 96-pin connector. The
XM-120 contains the measurement electronics, processors, relay, and
serial interface port for local configuration.
The XM-441 Expansion Relay module may be connected
to the XM-120 module via the XM-940 terminal base.
When connected to the module, the Expansion Relay
module simply “expands” the capability of the XM-120 by
adding four additional epoxy-sealed relays. The module
controls the Expansion Relay module by extending to it the
same logic and functional controls as the on-board relay.
Page 11

Introduction 3
Using this Manual
This manual introduces you to the XM-120 Eccentricity module. It is intended
for anyone who installs, configures, or uses the XM-120 Eccentricity module.
Organization
To help you navigate through this manual, it is organized in chapters based on
these tasks and topics.
Chapter 1 "Introduction" contains an overview of this manual and the
XM-120 Eccentricity module.
Chapter 2 "Installing the XM-120 Eccentricity Module" describes how to
install, wire, and use the Eccentricity module. It also provides instructions on
how to install the Eccentricity firmware.
Chapter 3 "Configuration Parameters" provides a complete listing and
description of the Eccentricity parameters. The parameters can be viewed and
edited using the XM Serial Configuration Utility software and a personal
computer.
Appendix A "Specifications" lists the technical specifications for the
Eccentricity module.
Appendix B "DeviceNet Information" provides information to help you
configure the module over a DeviceNet network.
Appendix C "DeviceNet Objects" provides information on the DeviceNet
objects supported by the XM-120 Eccentricity module.
Appendix D "Wiring Connections for Previous Module Revisions" provides
terminal block assignments and wiring diagrams of earlier revisions of the
XM-120 module (before revision D01).
For definitions of terms used in this Guide, see the Glossary at the end of the
Guide.
Document Conventions
There are several document conventions used in this manual, including the
following:
Publication GMSI10-UM010C-EN-P - May 2010
Page 12
4 Introduction
TIP
EXAMPLE
The XM-120 Eccentricity module is referred to as XM-120, Eccentricity
module, device, or module throughout this manual.
A tip indicates additional information which may be
helpful.
This convention presents an example.
Publication GMSI10-UM010C-EN-P - May 2010
Page 13
Chapter
ATTENTION
2
Installing the XM-120 Eccentricity Module
This chapter discusses how to install and wire the XM-120 Eccentricity
module. It also describes the module indicators and the basic operations of the
modules.
For information about See page
XM Installation Requirements 6
Mounting the Terminal Base Unit 13
Connecting Wiring for Your Module 17
Mounting the Module 35
Module Indicators 37
Basic Operations 39
Installing the XM-120 Eccentricity Firmware 40
Environment and Enclosure
This equipment is intended for use in a Pollution Degree 2
Industrial environment, in overvoltage Category II applications
(as defined in IED publication 60664–1), at altitudes up to 2000
meters without derating.
This equipment is supplied as “open type” equipment. It must be
mounted within an enclosure that is suitably designed for those
specific environmental conditions that will be present, and
appropriately designed to prevent personal injury resulting from
accessibility to live parts. The interior of the enclosure must be
accessible only by the use of a tool. Subsequent sections of this
publication may contain additional information regarding specific
enclosure type ratings that are required to comply with certain
product safety certifications.
See NEMA Standards publication 250 and IEC publication
60529, as applicable, for explanations of the degrees of
protection provided by different types of enclosures.
5 Publication GMSI10-UM010C-EN-P - May 2010
Page 14
6 Installing the XM-120 Eccentricity Module
ATTENTION
ATTENTION
XM Installation Requirements
This section describes wire, power, and grounding requirements for an XM
system.
Wiring Requirements
Use solid or stranded wire. All wiring should meet the following specifications:
• 14 to 22 AWG copper conductors without pretreatment; 8 AWG
required for grounding the DIN rail for electromagnetic interference
(emi) purposes
• Recommended strip length 8 millimeters (0.31 inches)
• Minimum insulation rating of 300 V
• Soldering the conductor is forbidden
• Wire ferrules can be used with stranded conductors; copper ferrules
recommended
See the XM Documentation and Configuration Utility CD
for Hazardous Locations installation drawings. The XM
Documentation and Configuration Utility CD is packaged
with the XM modules.
Power Requirements
Before installing your module, calculate the power requirements of all modules
interconnected via their side connectors. The total current draw through the
side connector cannot exceed 3A. Refer to the specifications for the specific
modules for power requirements.
A separate power connection is necessary if the total
current draw of the interconnecting modules is greater than
3 A.
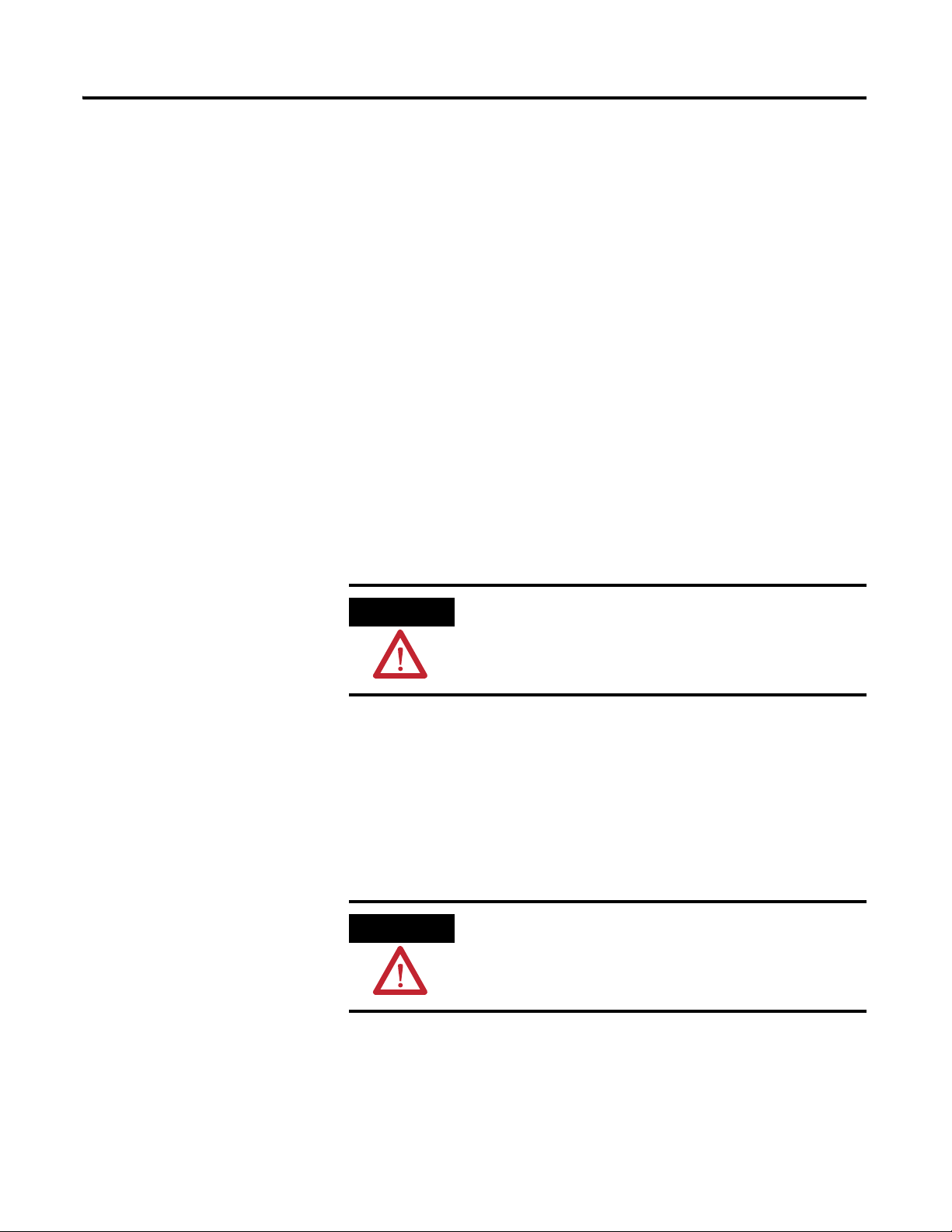
Figure 2.1 is an illustration of wiring modules using separate power
connections.
Publication GMSI10-UM010C-EN-P - May 2010
Page 15
Installing the XM-120 Eccentricity Module 7
Any limited power
source that satisfies
the requirements
specified below
Figure 2.1 XM Modules with Separate Power Connections
Power Supply Requirements
XM Power Supply Requirements
Listed Class 2 rated supply, or
Protection
Fused* ITE Listed SELV supply, or
Fused* ITE Listed PELV supply
Output Voltage 24 Vdc ± 10%
Output Power 100 Watts Maximum (~4A @ 24 Vdc)
Static Regulation ± 2%
Dynamic Regulation ± 3%
Ripple < 100mVpp
Output Noise Per EN50081-1
Overshoot < 3% at turn-on, < 2% at turn-off
Hold-up Time As required (typically 50mS at full rated load)
* When a fused supply is used the fuse must be a 5 amp, listed, fast acting fuse such as
provided by Allen-Bradley part number 1440-5AFUSEKIT
Publication GMSI10-UM010C-EN-P - May 2010
Page 16

8 Installing the XM-120 Eccentricity Module
IMPORTANT
See Application Technique "XM Power Supply Solutions",
publication ICM-AP005A-EN-E, for guidance in
architecting power supplies for XM systems.
Grounding Requirements
Use these grounding requirements to ensure safe electrical operating
circumstances, and to help avoid potential emi and ground noise that can cause
unfavorable operating conditions for your XM system.
DIN Rail Grounding
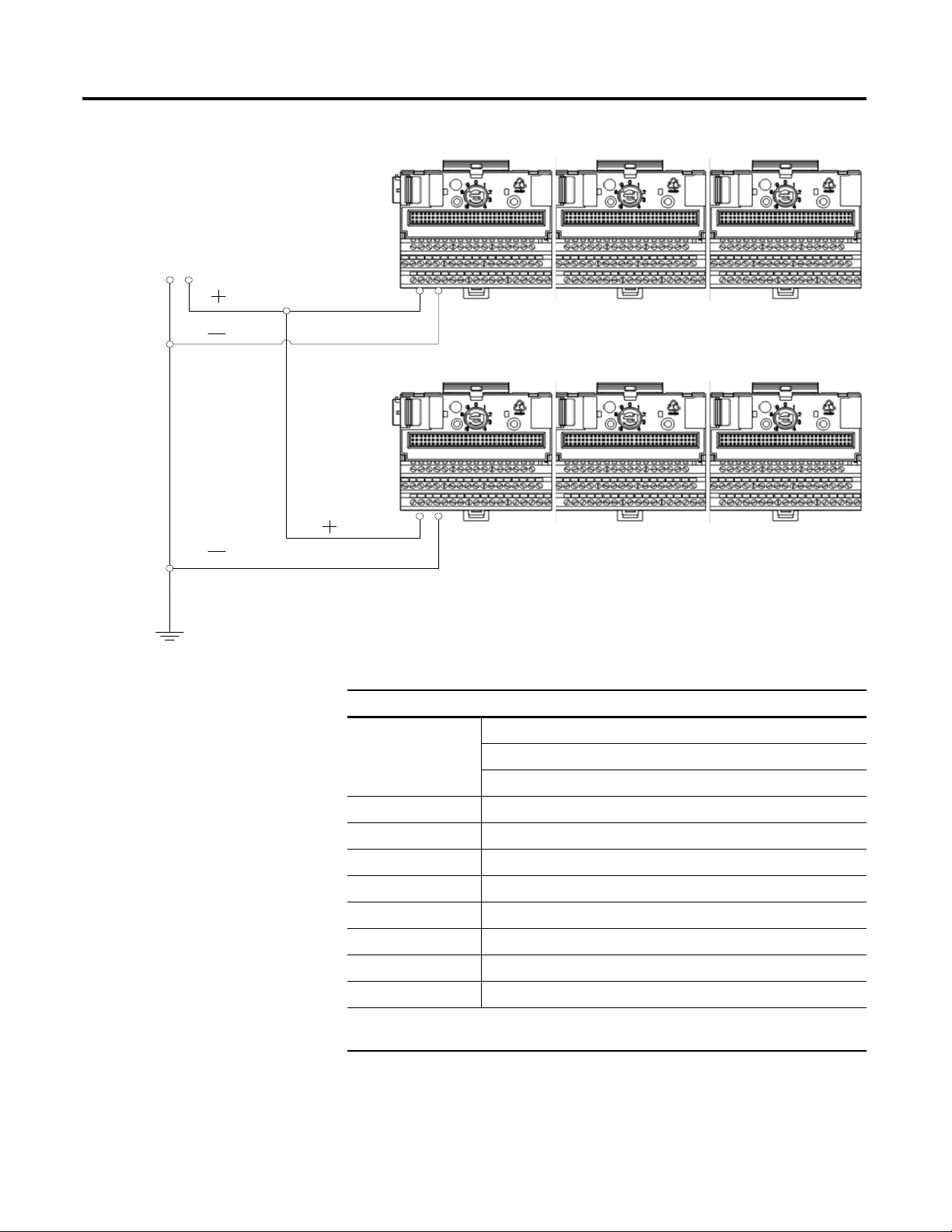
The XM modules make a chassis ground connection through the DIN rail.
The DIN rail must be connected to a ground bus or grounding electrode
conductor using 8 AWG or 1 inch copper braid. See Figure 2.2.
Use zinc-plated, yellow-chromated steel DIN rail (Allen-Bradley part no.
199-DR1 or 199-DR4) or equivalent to assure proper grounding. Using other
DIN rail materials (e.g. aluminum, plastic, etc.), which can corrode, oxidize, or
are poor conductors can result in improper or intermittent platform
grounding.
Publication GMSI10-UM010C-EN-P - May 2010
Page 17
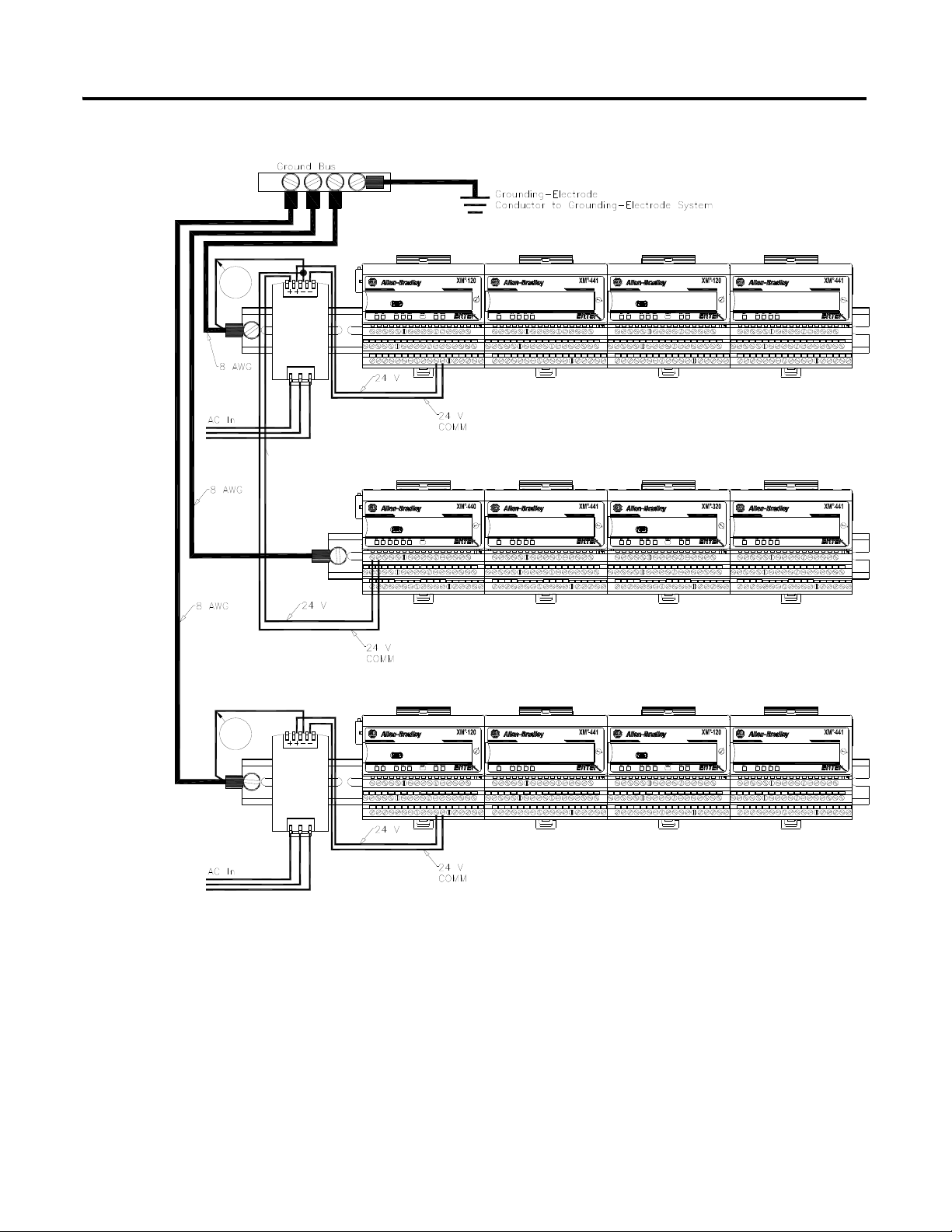
Figure 2.2 XM System DIN Rail Grounding
Power
Supply
DYNAMIC MEASUREMENT
1440-VST02-01RA
DYNAMIC MEASUREMENT
1440-VST02-01RA
POSITION
1440-TSP02-01RB
MASTER RELAY
1440-RMA00-04RC
EXPANSION RELAY
1440-REX00-04RD
EXPANSION RELAY
1440-REX00-04RD
EXPANSION RELAY
1440-REX00-04RD
EXPANSION RELAY
1440-REX00-04RD
Power
Supply
DYNAMIC MEASUREMENT
1440-VST02-01RA
DYNAMIC MEASUREMENT
1440-VST02-01RA
EXPANSION RELAY
1440-REX00-04RD
EXPANSION RELAY
1440-REX00-04RD
1
1
Installing the XM-120 Eccentricity Module 9
1Use 14 AWG wire.
The grounding wire can be connected to the DIN rail using a DIN Rail
Grounding Block (Figure 2.3).
Publication GMSI10-UM010C-EN-P - May 2010
Page 18
10 Installing the XM-120 Eccentricity Module
Figure 2.3 DIN Rail Grounding Block
Panel/Wall Mount Grounding
The XM modules can also be mounted to a conductive mounting plate that is
grounded. See Figure 2.5. Use the grounding screw hole provided on the
terminal base to connect the mounting plate the Chassis terminals.
Figure 2.4 Grounding Screw on XM Terminal Base
Publication GMSI10-UM010C-EN-P - May 2010
Page 19
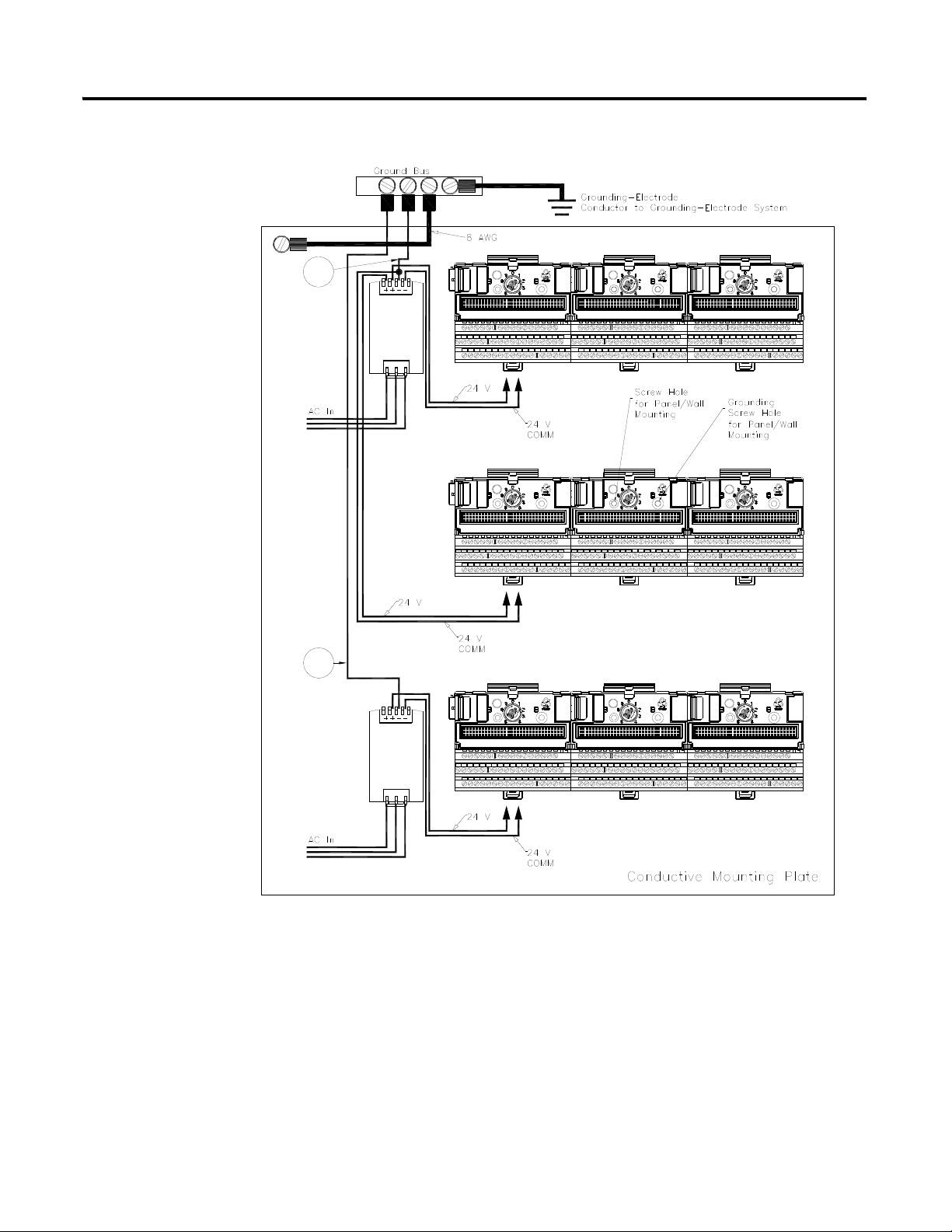
Figure 2.5 Panel/Wall Mount Grounding
Power
Supply
Power
Supply
1
1
Installing the XM-120 Eccentricity Module 11
1 Use 14 AWG wire.
Publication GMSI10-UM010C-EN-P - May 2010
Page 20
12 Installing the XM-120 Eccentricity Module
IMPORTANT
IMPORTANT
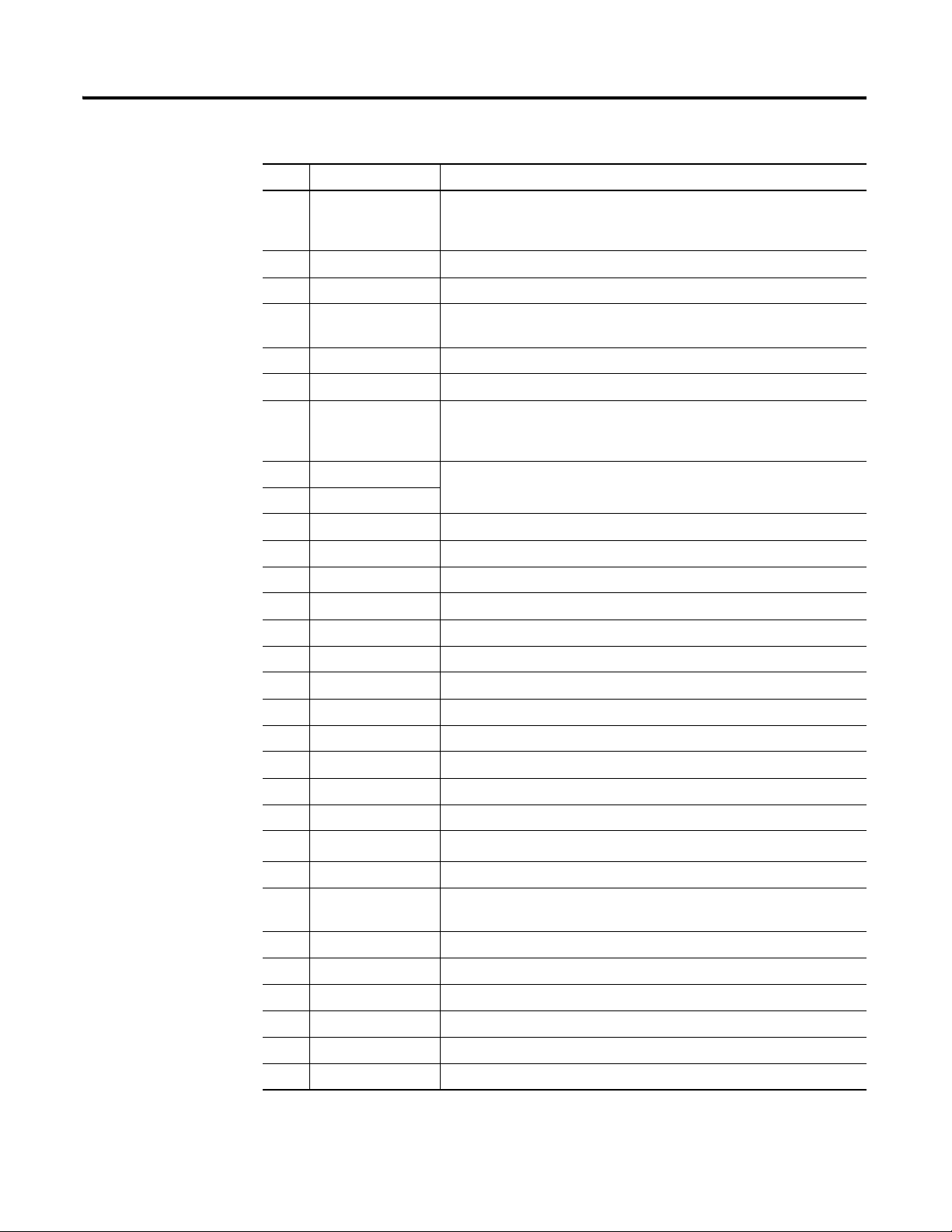
24V Common Grounding
24 V power to the XM modules must be grounded. When two or more power
supplies power the XM system, ground the 24 V Commons at a single point,
such as the ground bus bar.
If it is not possible or practical to ground the -24Vdc
supply, then it is possible for the system to be installed and
operate ungrounded. However, if installed ungrounded
then the system must not be connected to a ground
through any other circuit unless that circuit is isolated
externally. Connecting a floating system to a non-isolated
ground could result in damage to the XM module(s)
and/or any connected device. Also, operating the system
without a ground may result in the system not performing
to the published specifications regards measurement
accuracy and communications speed, distance or reliability.
The 24 V Common and Signal Common terminals are
internally connected. They are isolated from the Chassis
terminals unless they are connected to ground as described
in this section. See Terminal Block Assignments on page 18
for more information.
Transducer Grounding
Make certain the transducers are electrically isolated from earth ground. Cable
shields must be grounded at one end of the cable, and the other end left
floating or not connected. It is recommended that where possible, the cable
shield be grounded at the XM terminal base (Chassis terminal) and not at the
transducer.
DeviceNet Grounding
The DeviceNet network is functionally isolated and must be referenced to
earth ground at a single point. XM modules do not require an external
DeviceNet power supply. Connect DeviceNet V- to earth ground at one of the
XM modules, as shown in Figure 2.6.
Publication GMSI10-UM010C-EN-P - May 2010
Page 21
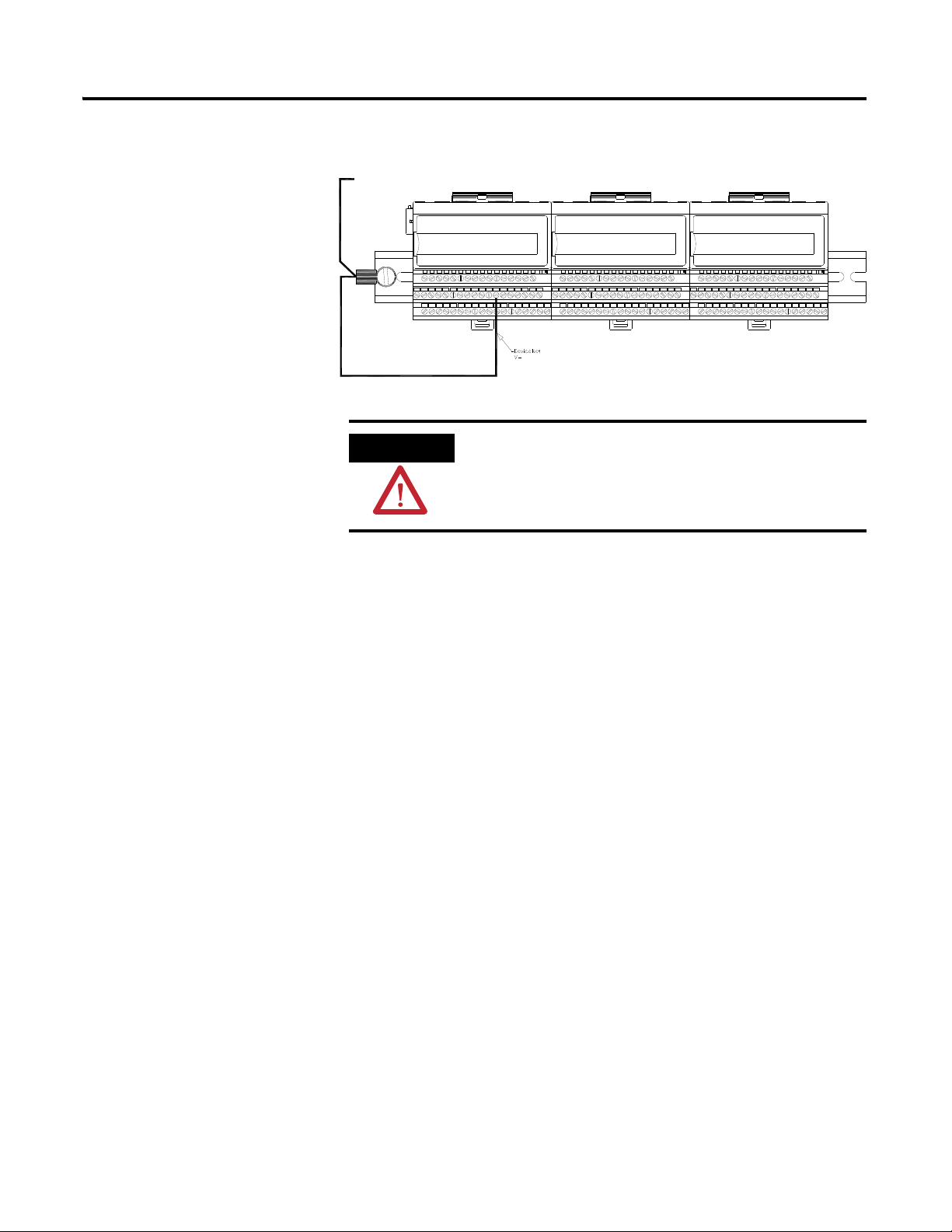
Installing the XM-120 Eccentricity Module 13
To
Ground
Bus
ATTENTION
Figure 2.6 Grounded DeviceNet V- at XM Module
Use of a separate DeviceNet power supply is not
permitted. See Application Technique "XM Power Supply
Solutions", publication ICM-AP005A-EN-E, for guidance
in using XM with other DeviceNet products.
Mounting the Terminal Base Unit
For more information on the DeviceNet installation, refer to the ODVA
Planning and Installation Manual - DeviceNet Cable System, which is available
on the ODVA web site (http://www.odva.org).
Switch Input Grounding
The Switch Input circuits are functionally isolated from other circuits. It is
recommended that the Switch RTN signal be grounded at a single point.
Connect the Switch RTN signal to the XM terminal base (Chassis terminal) or
directly to the DIN rail, or ground the signal at the switch or other equipment
that is wired to the switch.
The XM family includes several different terminal base units to serve all of the
XM modules. The XM-940 terminal base, Cat. No. 1440-TB-A, is the only
terminal base unit used with the Eccentricity module.
Publication GMSI10-UM010C-EN-P - May 2010
Page 22
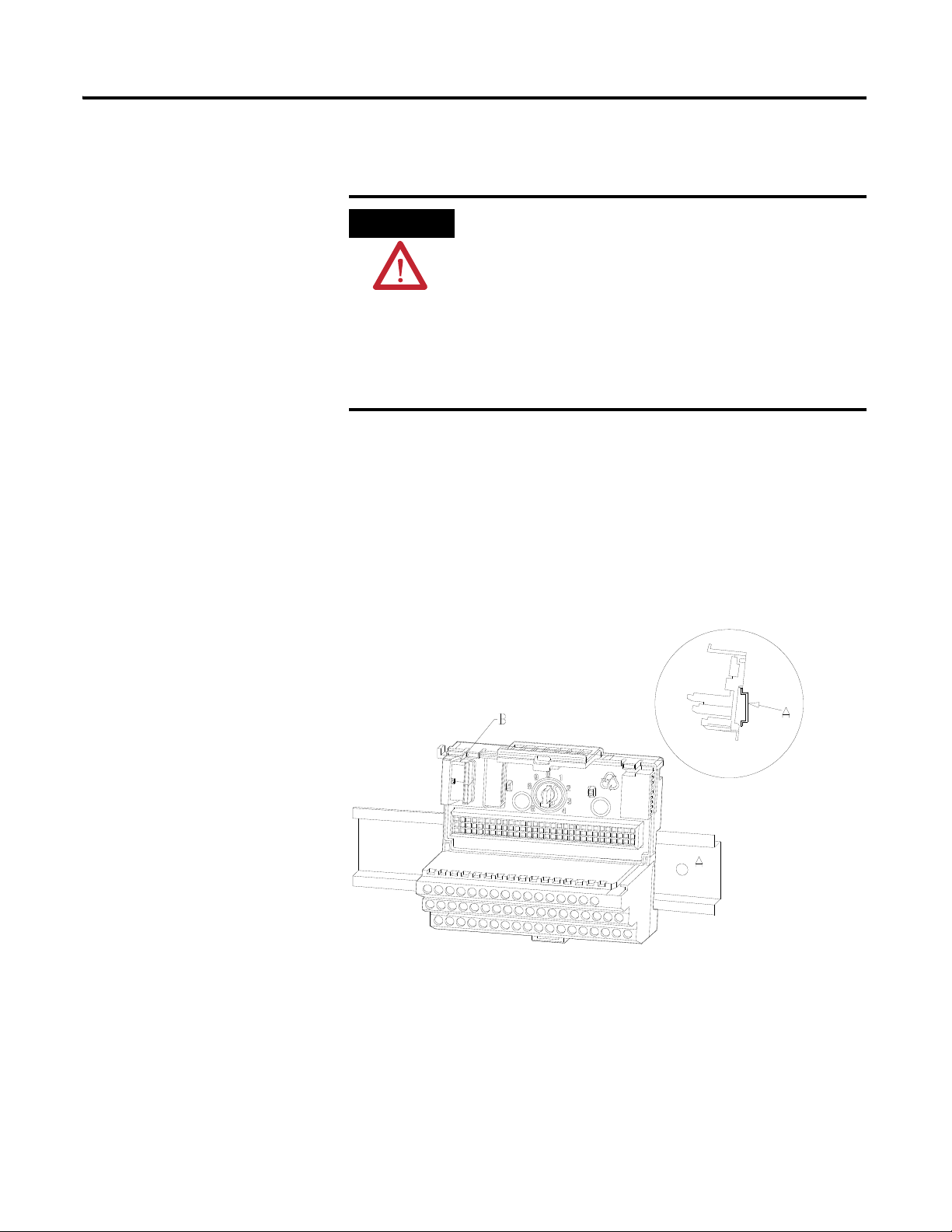
14 Installing the XM-120 Eccentricity Module
ATTENTION
Position terminal base at a slight angle and hook over the top of the DIN rail.
The terminal base can be DIN rail or wall/panel mounted. Refer to the
specific method of mounting below.
The XM modules make a chassis ground connection
through the DIN rail. Use zinc plated, yellow chromated
steel DIN rail to assure proper grounding. Using other
DIN rail materials (e.g. aluminum, plastic, etc.), which can
corrode, oxidize or are poor conductors can result in
improper or intermittent platform grounding.
You can also mount the terminal base to a grounded
mounting plate. Refer to Panel/Wall Mount Grounding on
page 10.
DIN Rail Mounting
Use the following steps to mount the XM-940 terminal base unit on a DIN rail
(A-B pt no. 199-DR1 or 199-DR4).
1. Position the terminal base on the 35 x 7.5 mm DIN rail (A).
2. Slide the terminal base unit over leaving room for the side
connector (B).
Publication GMSI10-UM010C-EN-P - May 2010
Page 23
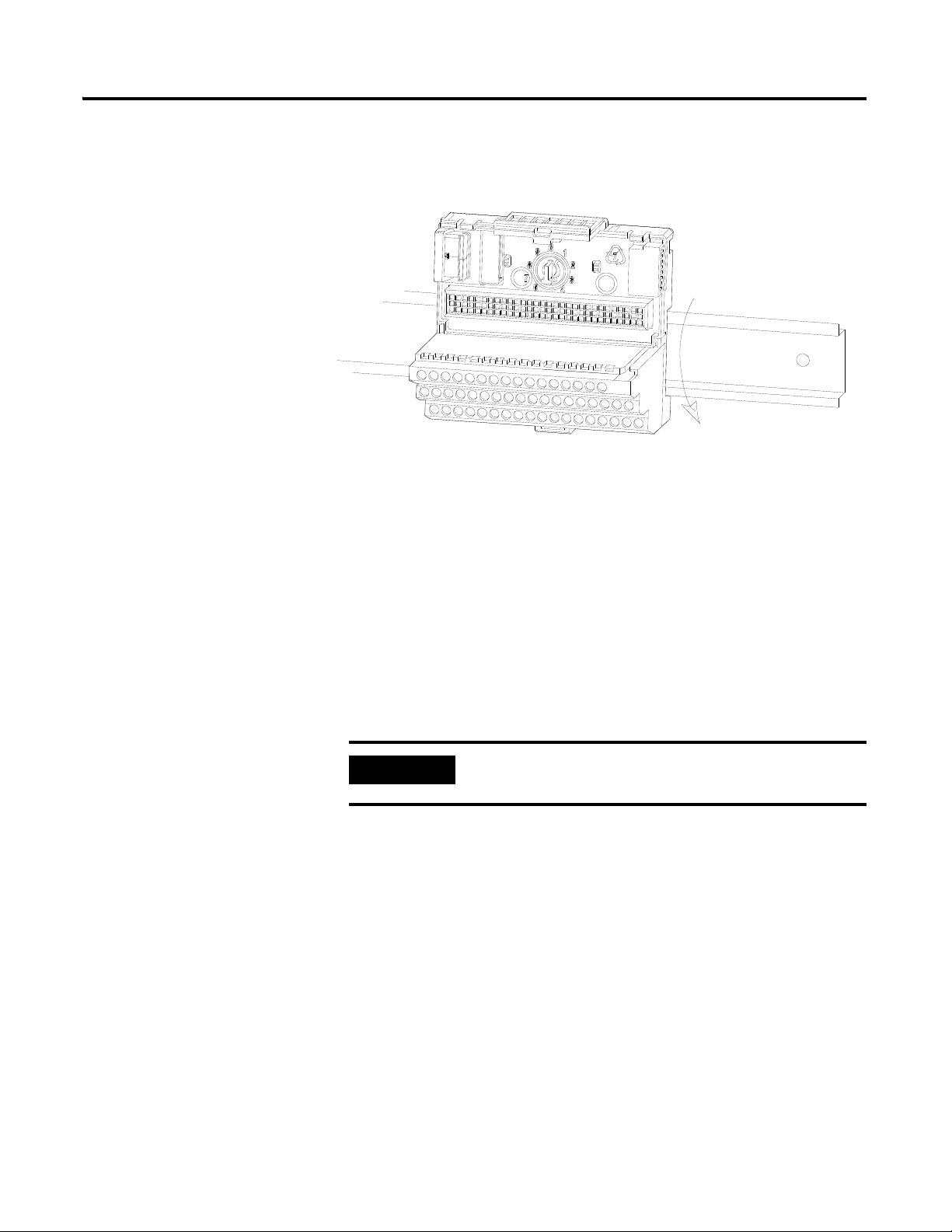
Installing the XM-120 Eccentricity Module 15
IMPORTANT
3. Rotate the terminal base onto the DIN rail with the top of the rail
hooked under the lip on the rear of the terminal base.
4. Press down on the terminal base unit to lock the terminal base on the
DIN rail. If the terminal base does not lock into place, use a screwdriver
or similar device to open the locking tab, press down on the terminal
base until flush with the DIN rail and release the locking tab to lock the
base in place.
Interconnecting Terminal Base Units
Follow the steps below to install another terminal base unit on the DIN rail.
Make certain you install the terminal base units in order of
left to right.
1. Position the terminal base on the 35 x 7.5 mm DIN rail (A).
2. Make certain the side connector (B) is fully retracted into the base unit.
3. Slide the terminal base unit over tight against the neighboring terminal
base. Make sure the hook on the terminal base slides under the edge of
the terminal base unit.
4. Press down on the terminal base unit to lock the terminal base on the
DIN rail. If the terminal base does not lock into place, use a screwdriver
or similar device to open the locking tab, press down on the terminal
base until flush with the DIN rail and release the locking tab to lock the
base in place.
Publication GMSI10-UM010C-EN-P - May 2010
Page 24
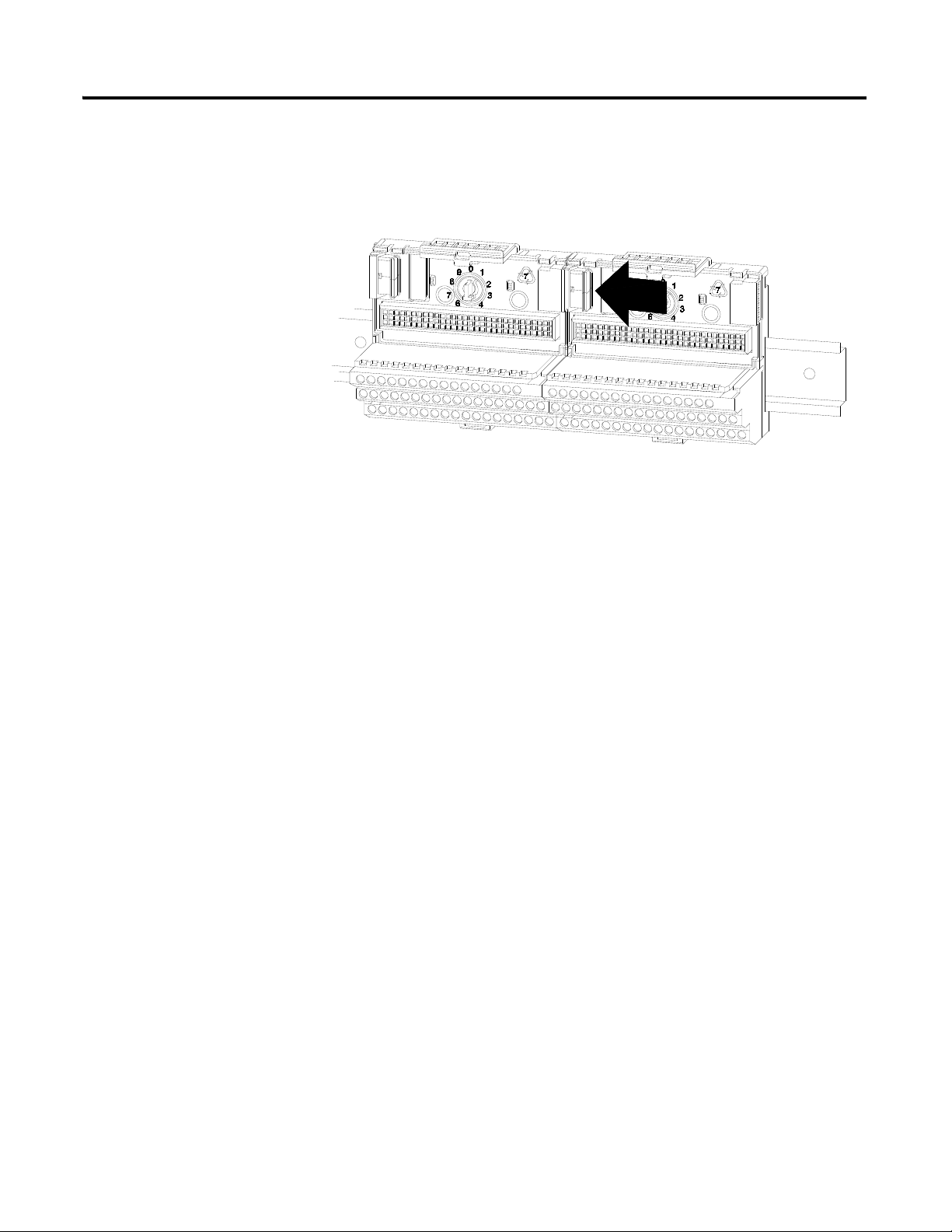
16 Installing the XM-120 Eccentricity Module
5. Gently push the side connector into the side of the neighboring terminal
base to complete the backplane connection.
Panel/Wall Mounting
Installation on a wall or panel consists of:
• laying out the drilling points on the wall or panel
• drilling the pilot holes for the mounting screws
• installing the terminal base units and securing them to the wall or panel
Use the following steps to install the terminal base on a wall or panel.
Publication GMSI10-UM010C-EN-P - May 2010
Page 25
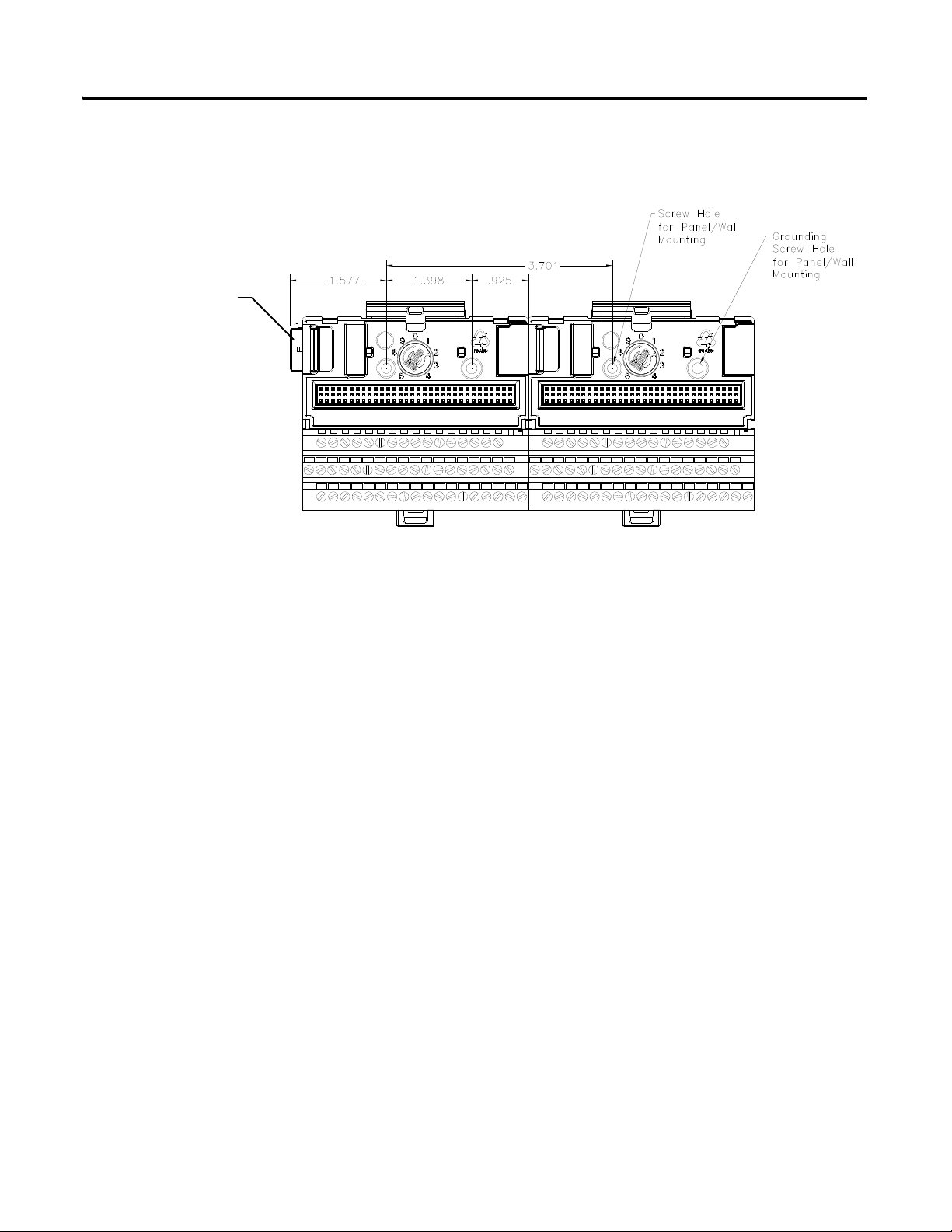
Installing the XM-120 Eccentricity Module 17
Side Connector
1. Lay out the required points on the wall/panel as shown in the drilling
dimension drawing below.
Connecting Wiring for Your Module
2. Drill the necessary holes for the #6 self-tapping mounting screws.
3. Secure the terminal base unit using two #6 self-tapping screws.
4. To install another terminal base unit, retract the side connector into the
base unit. Make sure it is fully retracted.
5. Position the terminal base unit up tight against the neighboring terminal
base. Make sure the hook on the terminal base slides under the edge of
the terminal base unit.
6. Gently push the side connector into the side of the neighboring terminal
base to complete the backplane connection.
7. Secure the terminal base to the wall with two #6 self-tapping screws.
Wiring to the module is made through the terminal base unit on which the
module mounts. The XM-120 is compatible only with the XM-940 terminal
base unit, Cat. No. 1440-TB-A.
Publication GMSI10-UM010C-EN-P - May 2010
Page 26
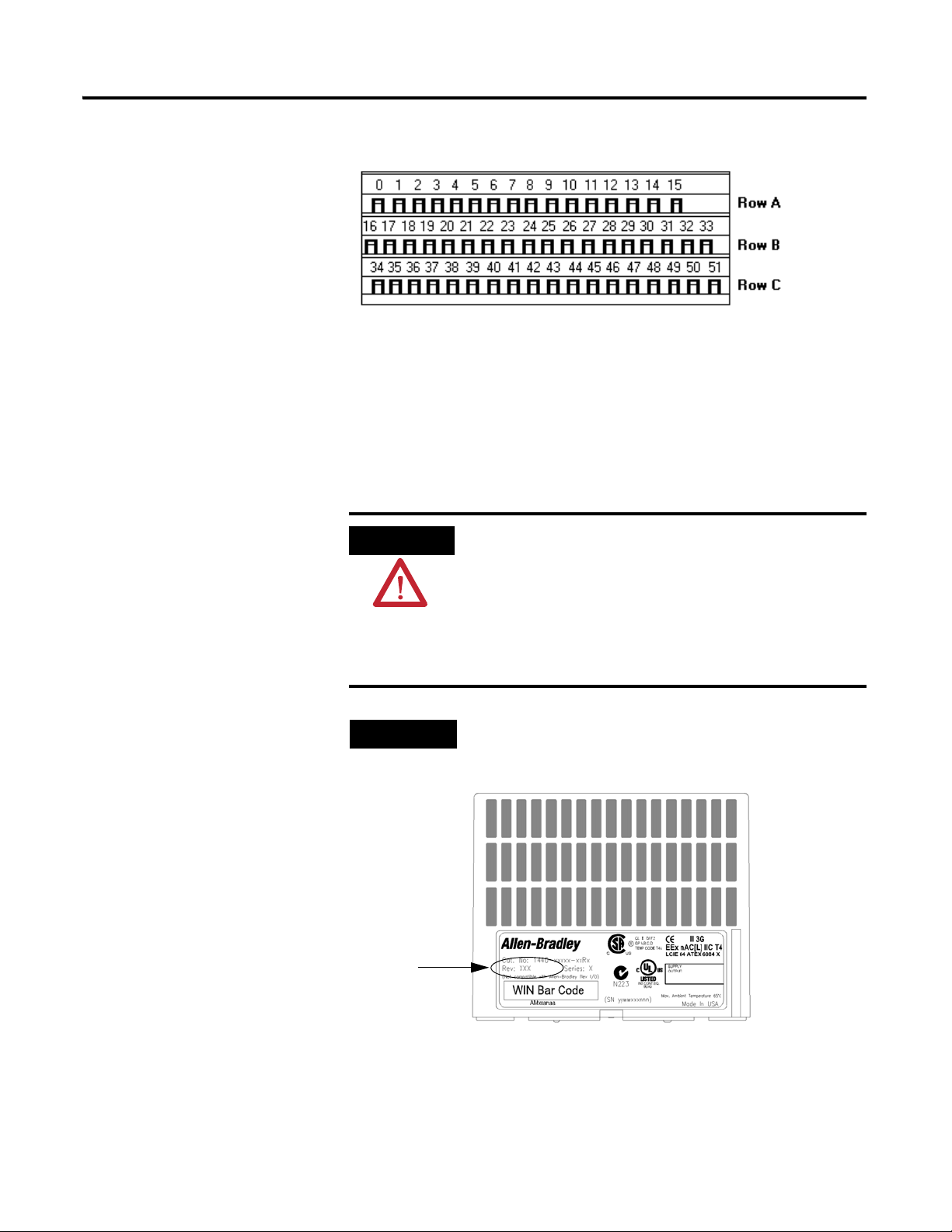
18 Installing the XM-120 Eccentricity Module
ATTENTION
TIP
XM-940 (Cat. No. 1440-TB-A)
Revision number
of XM module
Figure 2.7 XM-940 Terminal Base Unit
Terminal Block Assignments
The terminal block assignments and descriptions for the Eccentricity module
are shown below.
The terminal block assignments are different for different
XM modules. The following table applies only to the
XM-120 Eccentricity module revision D01 (and later). If
you have an earlier revision of the module, refer to
Appendix D for its terminal block assignments.
Refer to the installation instructions for the specific XM
module for its terminal assignments.
The XM module’s revision number is on the product label
(which is located on the front of the XM module, as shown
below).
Publication GMSI10-UM010C-EN-P - May 2010
Page 27

Installing the XM-120 Eccentricity Module 19
WARNING
EXPLOSION HAZARD
Do not disconnect equipment unless power has been
removed or the area is known to be nonhazardous.
Do not disconnect connections to this equipment unless
power has been removed or the area is known to be
nonhazardous. Secure any external connections that mate
to this equipment by using screws, sliding latches, threaded
connectors, or other means provided with this product.
Terminal Block Assignments
No. Name Description
0 Xducer 1 (+) Vibration transducer 1 connection
1 Xducer 2 (+) Vibration transducer 2 connection
2 Buffer 1 (+) Vibration signal 1 buffered output
3 Buffer 2 (+) Vibration signal 2 buffered output
4 Tach/Signal In (+) Tachometer transducer/signal input, positive side
5 Buffer Power 1 IN Channel 1 buffer power input
Connect to terminal 6 for positive biased transducers or terminal 21 for
negative biased transducers
6 Positive Buffer Bias Provides positive (-5 V to +24 V) voltage compliance to buffered outputs
Connect to terminals 5 (CH 1) or 22 (CH 2) for positive bias transducers
7 TxD PC serial port, transmit data
8 RxD PC serial port, receive data
9
XRTN
1
Circuit return for TxD and RxD
10 Chassis Connection to DIN rail ground spring or panel mounting hole
11 4-20 mA 1 (+) 4-20 mA output
12 4-20 mA 1 (-)
300 ohm maximum load
13 Chassis Connection to DIN rail ground spring or panel mounting hole
14 Chassis Connection to DIN rail ground spring or panel mounting hole
15 Chassis Connection to DIN rail ground spring or panel mounting hole
16
17
18
Xducer 1 (-)
Xducer 2 (-)
Signal Common
1
1
Vibration transducer 1 connection
Vibration transducer 2 connection
1
Vibration buffered output return
19 TACH Buffer Tachometer transducer/signal output
20 Tachometer (-) Tachometer transducer/signal return, TACH Buffer return
21 Buffer/Xducer Pwr (-) Provides negative (-24 V to +9 V) voltage compliance to buffered outputs
Connect to terminals 5 (CH 1) or 22 (CH 2) for negative bias transducers
Transducer power supply output, negative side; used to power external
sensor (40 mA maximum load)
Publication GMSI10-UM010C-EN-P - May 2010
Page 28
20 Installing the XM-120 Eccentricity Module
Terminal Block Assignments
No. Name Description
22 Buffer Power 2 IN Channel 2 buffer power input
23 CAN_High DeviceNet bus connection, high differential (white wire)
24 CAN_Low DeviceNet bus connection, low differential (blue wire)
25 +24 V Out Internally connected to 24 V In (terminal 44)
26 DNet V (+) DeviceNet bus power input, positive side (red wire)
27 DNet V (-) DeviceNet bus power input, negative side (black wire)
28
24 V Common
29 4-20 mA 2 (+) 4-20 mA output
30 4-20 mA 2 (-)
31 Chassis Connection to DIN rail ground spring or panel mounting hole
32 Chassis Connection to DIN rail ground spring or panel mounting hole
Connect to terminal 6 for positive biased transducers or terminal 21 for
negative biased transducers
Used to daisy chain power if XM modules are not plugged into each other
1
Internally connected to 24 V Common (terminals 43 and 45)
Used to daisy chain power if XM modules are not plugged into each other
If power is not present on terminal 44, there is no power on this terminal
300 ohm maximum load
33 Chassis Connection to DIN rail ground spring or panel mounting hole
34 Chassis Connection to DIN rail ground spring or panel mounting hole
35 Chassis Connection to DIN rail ground spring or panel mounting hole
36 Chassis Connection to DIN rail ground spring or panel mounting hole
37 Chassis Connection to DIN rail ground spring or panel mounting hole
38 Chassis Connection to DIN rail ground spring or panel mounting hole
39 Not Used
40 Switch RTN Switch return, shared between SetPtMult and Reset Relay
41 Reset Relay Switch input to reset internal relay (active closed)
42 Reserved
43
24 V Common
1
Internally DC-coupled to circuit ground
44 +24 V In Connection to primary external +24 V power supply, positive side
45
24 V Common
1
Connection to external +24 V power supply, negative side (internally
DC-coupled to circuit ground)
46 Relay N.C. 1 Relay Normally Closed contact 1
47 Relay Common 1 Relay Common contact 1
48 Relay N.O. 1 Relay Normally Open contact 1
49 Relay N.O. 2 Relay Normally Open contact 2
50 Relay Common 2 Relay Common contact 2
51 Relay N.C. 2 Relay Normally Closed contact 2
Publication GMSI10-UM010C-EN-P - May 2010
1 Terminals are internally connected and isolated from the Chassis terminals.
Page 29
Installing the XM-120 Eccentricity Module 21
IMPORTANT
IMPORTANT
ATTENTION
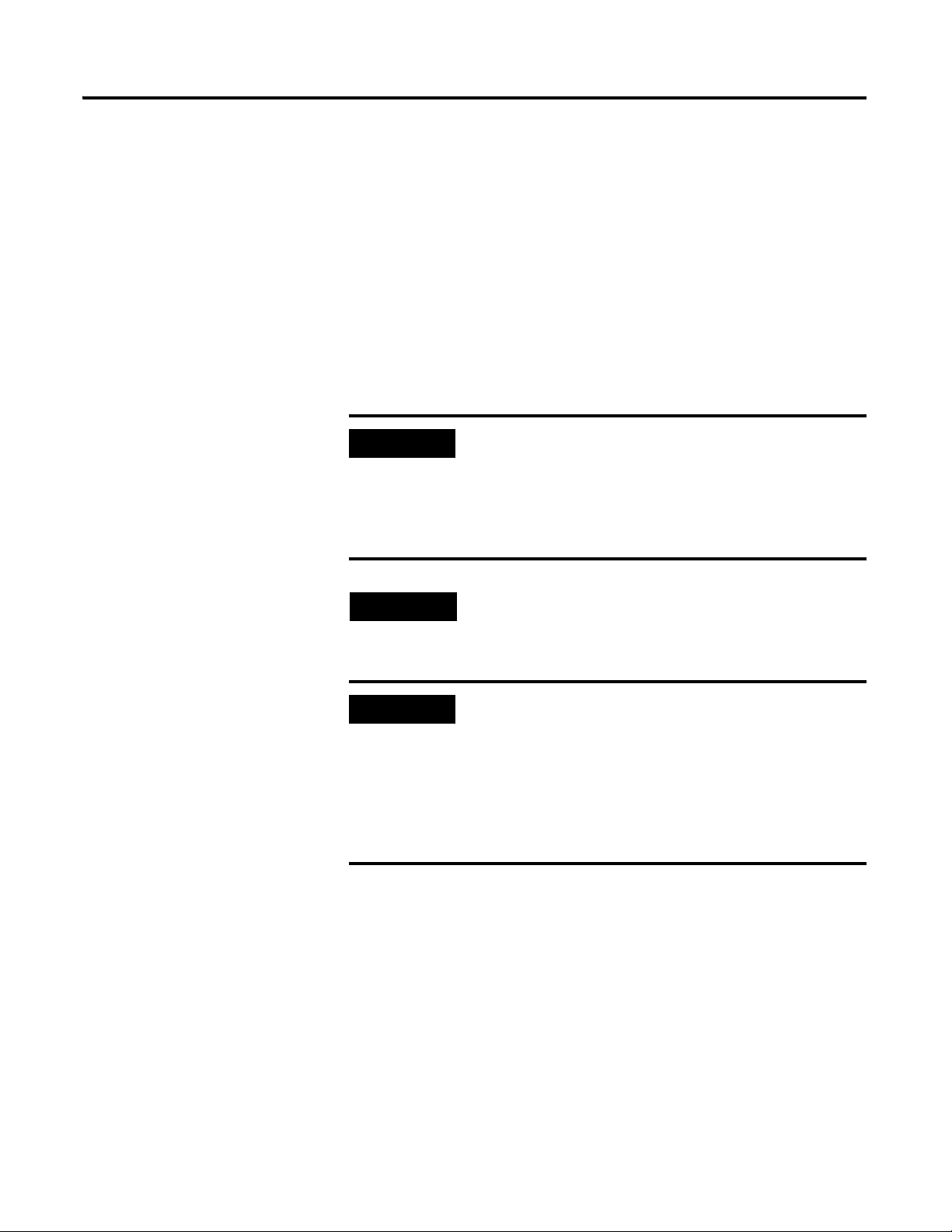
Connecting the Power Supply
Power supplied to the module must be nominally 24 Vdc (±10%) and must be
a Class 2 rated circuit.
Wire the DC-input power supply to the terminal base unit as shown in Figure
2.8.
Figure 2.8 DC Input Power Supply Connections
A Class 2 circuit can be provided by use of an NEC Class 2
rated power supply, or by using a SELV or PELV rated
power supply with a 5 Amp current limiting fuse installed
before the XM module(s).
24Vdc needs to be wired to terminal 44 (+24 V In) to
provide power to the device and other XM modules linked
to the wired terminal base via the side connector.
The power connections are different for different XM
modules. Refer to the installation instructions for your
specific XM module for complete wiring information.
Publication GMSI10-UM010C-EN-P - May 2010
Page 30
22 Installing the XM-120 Eccentricity Module
IMPORTANT
TIP
IMPORTANT
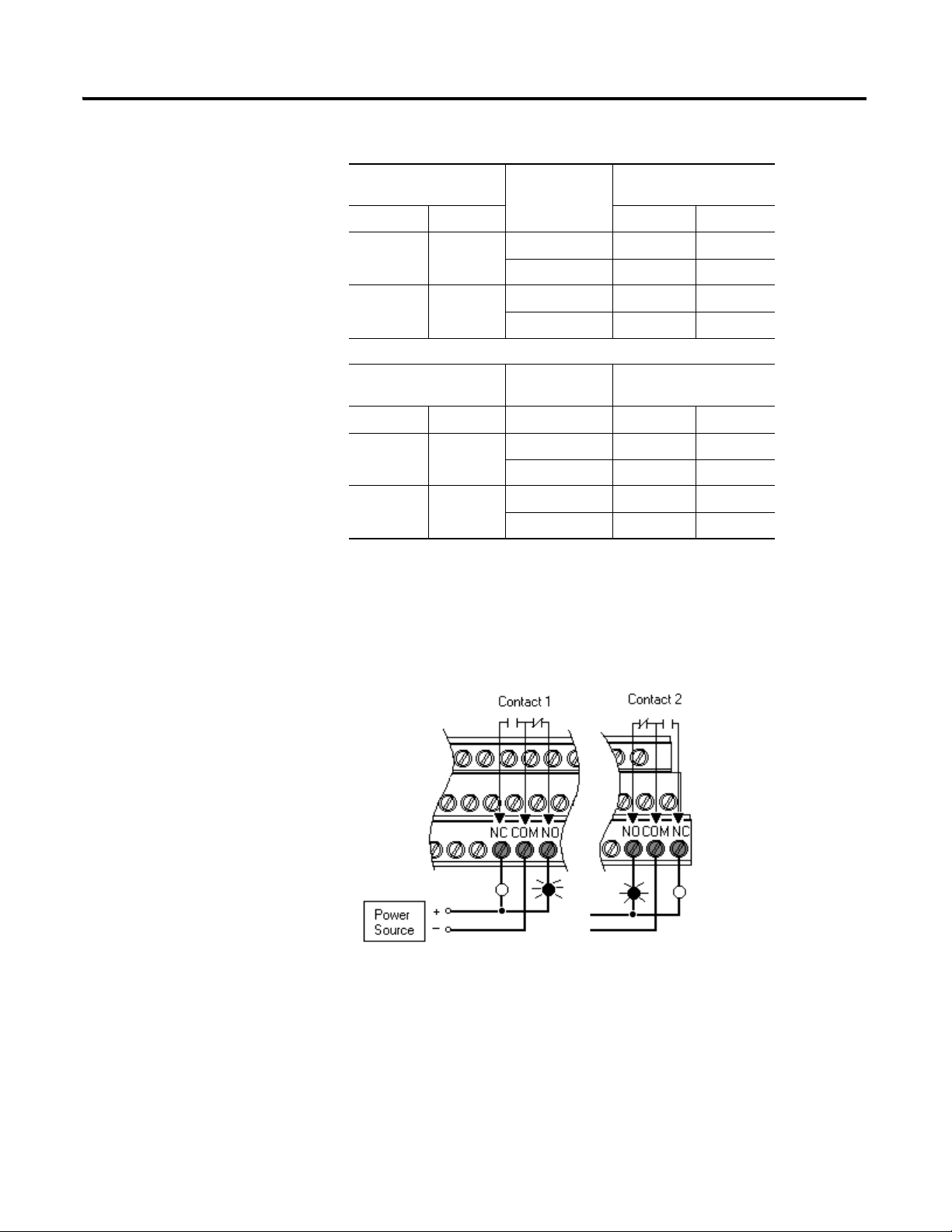
Connecting the Relays
The XM-120 has both Normally Open (NO) and Normally Closed (NC) relay
contacts. Normally Open relay contacts close when the control output is
energized. Normally Closed relay contacts open when the control output is
energized.
The alarms associated with the relay and whether the relay is normally
de-energized (non-failsafe) or normally energized (failsafe) depends on the
configuration of the module. Refer to Relay Parameters on page 52 for details.
Table 2.1 shows the on-board relay connections for the module.
All XM relays are double pole. This means that each relay
has two contacts in which each contact operates
independently but identically. The following information
and illustrations show wiring solutions for both contacts;
although, in many applications it may be necessary to wire
only one contact.
The Expansion Relay module may be connected to the
module to provide additional relays. Refer the XM-441
Expansion Relay Module User Guide for wiring details.
The NC/NO terminal descriptions (page 20) correspond
to a de-energized (unpowered) relay.
When the relay is configured for non-failsafe operation, the
relay is normally de-energized.
When the relay is configured for failsafe operation, the
relay is normally energized, and the behavior of the NC and
NO terminals is inverted.
Publication GMSI10-UM010C-EN-P - May 2010
Page 31
Installing the XM-120 Eccentricity Module 23
Table 2.1 Relay Connections for XM-120
Configured for
Failsafe Operation Relay 1 Terminals
Nonalarm Alarm Wire Contacts Contact 1 Contact 2
Closed Opened COM 47 50
NO 48 49
Opened Closed COM 47 50
NC 46 51
Configured for
Non-failsafe Operation Relay 1 Terminals
Nonalarm Alarm Wire Contacts Contact 1 Contact 2
Closed Opened COM 47 50
NC 46 51
Opened Closed COM 47 50
NO 48 49
Figures 2.9 and 2.10 illustrate the behavior of the NC and NO terminals when
the relay is wired for failsafe, alarm or nonalarm condition or non-failsafe,
alarm or nonalarm condition.
Figure 2.9 Relay Connection - Failsafe, Nonalarm Condition
Non-failsafe, Alarm Condition
Publication GMSI10-UM010C-EN-P - May 2010
Page 32

24 Installing the XM-120 Eccentricity Module
Figure 2.10 Relay Connection - Failsafe, Alarm Condition
Non-failsafe, Nonalarm Condition
Alternate Relay Wiring
Figures 2.11 and 2.12 show how to wire both ends of a single external
indicator to the XM terminal base for failsafe, nonalarm or alarm condition or
non-failsafe, nonalarm or alarm condition.
Figure 2.11 Relay Connection - Failsafe, Nonalarm Condition
Non-failsafe, Alarm Condition
Publication GMSI10-UM010C-EN-P - May 2010
Page 33

Installing the XM-120 Eccentricity Module 25
IMPORTANT
Figure 2.12 Relay Connection - Failsafe, Alarm Condition
Non-failsafe, Nonalarm Condition
Connecting the Tachometer Signal
The XM-120 provides a single tachometer input signal. The signal processing
performed on the tachometer signal depends on the configuration of the
module. See page 47 for a description of the tachometer parameters.
If you are not using the tachometer input, set the Pulses
Per Revolution parameter to zero (0). This will disable the
tachometer measurement and prevent the module from
indicating a tachometer fault (TACH indicator flashing
yellow). A tachometer fault occurs when no signal pulses
are received on the tachometer input signal for a relatively
long period.
Publication GMSI10-UM010C-EN-P - May 2010
Page 34

26 Installing the XM-120 Eccentricity Module
Connecting a Magnetic Pickup Tachometer
Figure 2.13 shows the wiring of a magnetic pickup tachometer to the terminal
base unit.
Figure 2.13 Magnetic Pickup Tachometer Signal Connection
Connecting a Hall Effect Tachometer Sensor
Figure 2.14 shows the wiring of a Hall Effect Tachometer Sensor, Cat. No.
EK-44395, to the terminal base unit.
Figure 2.14 Hall Effect Tachometer Signal Connection
Publication GMSI10-UM010C-EN-P - May 2010
Page 35

Installing the XM-120 Eccentricity Module 27
S
I
G
-
2
4
COM
Signal Common
Tach Input Signal
-24V DC
Shield
S hield Floating
Isolated Sensor Driver
20 21 31
4
18
Connecting a Non-Contact Sensor to the Tachometer Signal
Figure 2.15 shows the wiring of a non-contact sensor to the tachometer input
signal.
Figure 2.15 Non-Contact Sensor to Tachometer Signal Connection
Connecting the Buffered Outputs
The XM-120 provides buffered outputs of all transducer input signals. The
buffered output connections may be used to connect the module to portable
data collectors or other online systems.
Figure 2.16 shows the buffered output connections for the modules.
Publication GMSI10-UM010C-EN-P - May 2010
Page 36

28 Installing the XM-120 Eccentricity Module
IMPORTANT
Table 2.2 Configuring Buffered Output Input Range
Transducer Input Range Channel Connect Terminal To Terminal
Negative Bias -24 to +9 V 1 5 21
222 21
Positive Bias -5 to +24 V 1 5 6
222 6
Non-Bias -5 to +9 V 1 ---- ----
2 ---- ----
Figure 2.16 Buffered Output Connections
Applies only to XM-120 module revision D01 (and
later).
The voltage operating range of the buffered outputs must
be configured to coincide with the corresponding
transducer bias range. This operating range is configured by
placing a jumper from terminal 5 (channel 1) and terminal
22 (channel 2) to either terminal 6 (Positive Buffer Bias) or
terminal 21 (Buffer -), depending on the transducer. See
Table 2.2. Note the buffered output operating range is
configured independently per channel.
Publication GMSI10-UM010C-EN-P - May 2010
Page 37

Installing the XM-120 Eccentricity Module 29
IMPORTANT
ATTENTION
IMPORTANT
TYPICAL WIRING FOR NON-CONTACT SENSOR
TO XM-120 ECCENTRICITY MODULE CHANNEL 1
COM
SIG
-24
Channel 1 Input Signal
-24V DC
0
16
Signal Common
21
5
Jumpering terminal 5 to
terminal 21 configures
CH 1 buffer for -24V to +9V
(See Table 2.1)
Isolated Sensor Driver
Shield
Shield
Floating
37
Connecting a Non-Contact Sensor
The Eccentricity module accepts input from any Allen-Bradley non-contact
eddy current probe. The figures below show the wiring of a non-contact eddy
probe to the terminal base unit.
Figures 2.17 and 2.18 show the wiring to the XM-120
module revision D01 (and later). If you have an earlier
revision of the module, refer to Appendix D for wiring
information.
You may ground the cable shield at either end of the cable.
Do not ground the shield at both ends. Recommended
practice is to ground the cable shield at the terminal base
and not at the transducer. Any convenient Chassis terminal
may be used (see Terminal Block Assignments on page 18).
The internal transducer power supply is providing power to
the non-contact sensor.
Figure 2.17 Non-contact Sensor to Channel 1 Wiring
Publication GMSI10-UM010C-EN-P - May 2010
Page 38

30 Installing the XM-120 Eccentricity Module
TYPICAL WIRING FOR NON-CONTACT SENSOR
TO XM-120 ECCENTRICITY MODULE CHANNEL 2
COM
SIG
-24
Channel 2 Input Signal
-24V DC
1
17
22
Signal Common
21
Jumper ing terminal 21 to
terminal 22 configures
CH 2 buffer for -24V to +9V
(See Table 2.1)
Isolated Sensor Driver
Shield
Shield
Floating
38
TIP
TIP
Figure 2.18 Non-contact Sensor to Channel 2 Wiring
Connecting the Remote Relay Reset Signal
If you set the module relay to latching and the relay activates, the relay stays
activated even when the condition that caused the alarm has ended. The
remote relay reset signal enables you to reset your module relay remotely after
you have corrected the alarm condition. This includes latched relays in the
Expansion Relay module when it is attached to the XM-120.
If you set a module relay to latching, make sure that any
linked relays, such as relays in an XM-440 Master Relay
Module, are not configured as latching. When both relays
are set to latching, the relay in each module will have to be
independently reset when necessary.
You can discretely reset a relay using the serial or remote
configuration tool.
Wire the Remote Relay Reset Signal to the terminal base unit as shown in
Figure 2.19.
Publication GMSI10-UM010C-EN-P - May 2010
Page 39

Installing the XM-120 Eccentricity Module 31
ATTENTION
ATTENTION
Figure 2.19 Remote Relay Reset Signal Connection
The Switch Input circuits are functionally isolated from
other circuits. It is recommended that the Switch RTN
signal be grounded at a signal point. Connect the Switch
RTN signal to the XM terminal base (Chassis terminal) or
directly to the DIN rail, or ground the signal at the switch
or other equipment that is wired to the switch.
A single switch contact can also be shared by multiple XM modules wired in
parallel as shown in Figure 2.20.
The relay reset connections may be different for different
XM modules. Figure 2.20 applies only to the XM-120
module. Refer to the installation instructions for the
module for its terminal assignments.
Figure 2.20 Typical Multiple XM Modules Remote Relay Reset Signal Connection
Publication GMSI10-UM010C-EN-P - May 2010
Page 40

32 Installing the XM-120 Eccentricity Module
ATTENTION
-
Connecting the 4-20 mA Outputs
The module includes an isolated 4-20 mA per channel output into a maximum
load of 300 ohms. The measurements that the 4-20 mA output tracks and the
signal levels that correspond to the 4 mA and 20 mA are configurable. Refer
to 4-20 mA Output Parameters on page 55 for details.
Wire the 4-20 mA outputs to the terminal base unit as shown in Figure 2.21.
Figure 2.21 4-20mA Output Connections
The 4-20 mA outputs are functionally isolated from other
circuits. It is recommended that the outputs be grounded at
a single point. Connect the 4-20 mA (-) to the XM terminal
base (Chassis terminal) or directly to the DIN rail, or
ground the signal at the other equipment in the 4-20 mA
loop.
Serial Port Connection
The XM-120 includes a serial port connection that allows you to connect a PC
to it and configure the module’s parameters. There are two methods of
connecting an external device to the module’s serial port.
• Ter mi na l Ba s e U n it - There are three terminals on the terminal base
unit you can use for the serial port connection. They are TxD, RxD, and
RTN (terminals 7, 8, and 9, respectively). If these three terminals are
wired to a DB-9 female connector, then a standard RS-232 serial cable
with 9-pin (DB-9) connectors can be used to connect the module to a
PC (no null modem is required).
Publication GMSI10-UM010C-EN-P - May 2010
Page 41

Installing the XM-120 Eccentricity Module 33
mini connector
WARNING
IMPORTANT
The DB-9 connector should be wired to the terminal block as shown.
XM-120 Terminal Base Unit
(Cat. No. 1440-TB-A)
TX Terminal (terminal 7) ---------------------- Pin 2 (RD - receive data)
RX Terminal (terminal 8) ---------------------- Pin 3 (TD - transmit data)
RTN Terminal (terminal 9) --------------------- Pin 5 (SG - signal ground)
DB-9 Female Connector
• Mini Connector - The mini connector is located on the top of the
module, as shown below.
Figure 2.22 Mini Connector
A special cable (Cat. No. 1440-SCDB9FXM2) is required for this
connection. The connector that inserts into the PC is a DB-9 female
connector, and the connector that inserts into the module is a USB
Mini-B male connector.
If you connect or disconnect the serial cable with power
applied to the module or the serial device on the other end
of the cable, an electrical arc can occur. This could cause an
explosion in hazardous location installations. Be sure that
power is removed or the area is nonhazardous before
proceeding.
If 24 V Common is not referenced to earth ground, we
recommend you use an RS-232 isolator, such as Phoenix
PSM-ME-RS232/RS232-P (Cat. No. 1440-ISO-232-24), to
protect both the XM module and the computer.
Publication GMSI10-UM010C-EN-P - May 2010
Page 42
34 Installing the XM-120 Eccentricity Module
IMPORTANT
ATTENTION
ATTENTION
DeviceNet Connection
The XM-120 includes a DeviceNet™ connection that allows the module to
communicate with a programmable controller, DCS, or another XM module.
DeviceNet is an open, global, industry-standard communications network
designed to provide an interface through a single cable from a programmable
controller to a smart device such as the XM-120. As multiple XM modules are
interconnected, DeviceNet also serves as the communication bus and protocol
that efficiently transfers data between the XM modules.
Connect the DeviceNet cable to the terminal base unit as shown.
Connect To Terminal
Red Wire DNet V+ 26 (optional—see note)
White Wire CAN High 23
Bare Wire Shield (Chassis) 10
Blue Wire CAN Low 24
Black Wire DNet V- 27
The DeviceNet power circuit through the XM module
interconnect, which is rated at only 300 mA, is not intended
or designed to power DeviceNet loads. Doing so could
damage the module or terminal base.
To preclude this possibility, even unintentionally, it is
recommended that DeviceNet V+ be left unconnected.
You must ground the DeviceNet shield at only one
location. Connecting the DeviceNet shield to terminal 10
will ground the DeviceNet shield at the XM module. If you
intend to terminate the shield elsewhere, do not connect
the shield to terminal 10.
The DeviceNet network must also be referenced to earth at
only one location. Connect DNet V- to earth or chassis at
one of the XM modules.
Publication GMSI10-UM010C-EN-P - May 2010
Page 43

Installing the XM-120 Eccentricity Module 35
ATTENTION
IMPORTANT
IMPORTANT
ATTENTION
ATTENTION
The DNet V+ and DNet V- terminals are inputs to the XM
module. Do not attempt to pass DeviceNet power through
the XM terminal base to other non-XM equipment by
connecting to these terminals. Failure to comply may result
in damage to the XM terminal base and/or other
equipment.
Terminate the DeviceNet network and adhere to the
requirements and instructions in the ODVA Planning and
Installation Manual - DeviceNet Cable System, which is
available on the ODVA web site (http://www.odva.org).
The devices are shipped from the factory with the network node address
(MAC ID) set to 63. The network node address is software settable. You can
use the XM Serial Configuration Utility or RSNetWorx™ for DeviceNet
(Version 3.0 or later) to set the network node address. Refer to the appropriate
documentation for details.
Mounting the Module
The baud rate for the XM-120 is set by way of “baud
detection” (Autobaud) at power-up.
The XM-120 mounts on the XM-940 terminal base unit, Cat. No. 1440-TB-A.
We recommend that you mount the module after you have connected the
wiring on the terminal base unit.
The XM-120 module is compatible only with the XM-940
terminal base unit. The keyswitch on the terminal base unit
should be at position 1 for the modules.
Do not attempt to install XM-120 modules on other
terminal base units.
Do not change the position of the keyswitch after
wiring the terminal base.
This module is designed so you can remove and insert it
under power. However, when you remove or insert the
module with power applied, I/O attached to the module
can change states due to its input/output signal changing
conditions. Take special care when using this feature.
Publication GMSI10-UM010C-EN-P - May 2010
Page 44

36 Installing the XM-120 Eccentricity Module
WARNING
IMPORTANT
When you insert or remove the module while power is on,
an electrical arc can occur. This could cause an explosion in
hazardous location installations. Be sure that power is
removed or the area is nonhazardous before proceeding.
Install the overlay slide label to protect serial connector and
electronics when the serial port is not in use.
1. Make certain the keyswitch (A) on the terminal base unit (C) is at
position 1 as required for the module.
Publication GMSI10-UM010C-EN-P - May 2010
2. Make certain the side connector (B) is pushed all the way to the left. Yo u
cannot install the module unless the connector is fully extended.
3. Make sure that the pins on the bottom of the module are straight so they
will align properly with the connector in the terminal base unit.
4. Position the module (D) with its alignment bar (E) aligned with the
groove (F) on the terminal base.
5. Press firmly and evenly to seat the module in the terminal base unit. The
module is seated when the latching mechanism (G) is locked into the
module.
6. Repeat the above steps to install the next module in its terminal base.
Page 45

Installing the XM-120 Eccentricity Module 37
Module Indicators
Eccentricity LED
Module Indicators
The Eccentricity module has seven LED indicators, which include a module
status (MS) indicator, a network status (NS) indicator, a status indicator for
each channel (CH1, CH2, and TACH), an activation indicator for Eccentricity,
and a status indicator for the Relay. The LED indicators are located on top of
the module.
Figure 2.23 LED Indicators
The following tables describe the states of the LED status indicators.
Module Status (MS) Indicator
Color State Description
No color Off No power applied to the module.
Green Flashing Red Module performing power-up self test.
Flashing
Solid
Module operating in Program Mode
Module operating in Run Mode
Red Flashing • Application firmware is invalid or not loaded.
Download firmware to the module.
• Firmware download is currently in progress.
Solid An unrecoverable fault has occurred. The module may
need to be repaired or replaced.
1
.
2
.
1 Program Mode - Typically this occurs when the module configuration settings are being updated with the XM
Serial Configuration Utility. In Program Mode, the module does not perform its normal functions. The signal
processing/measurement process is stopped, and the status of the alarms is set to the disarm state to prevent
a false alert or danger status.
2 Run Mode - In Run Mode, the module collects measurement data and monitors each vibration measurement
device.
Publication GMSI10-UM010C-EN-P - May 2010
Page 46

38 Installing the XM-120 Eccentricity Module
Network Status (NS) Indicator
Color State Description
No color Off Module is not online.
• Module is autobauding.
• No power applied to the module, look at Module
Status LED.
Green Flashing Module is online (DeviceNet) but no connections are
currently established.
Solid Module is online with connections currently
established.
Red Flashing One or more I/O connections are in the timed-out state.
Solid Failed communications (duplicate MAC ID or Bus-off).
1 Normal condition when the module is not a slave to an XM-440, PLC, or other master device.
1
Channel 1, Channel 2, and Tachometer Status Indicators
Color State Description
No color Off • Normal operation within alarm limits on the channel.
• No power applied to the module, look at Module
Status LED.
Yellow Solid An alert level alarm condition exists on the channel
(and no transducer fault, tachometer fault, or danger
level alarm condition exists).
Flashing Tach
LED
Flashing CH1/2
LED
Red Solid A danger level alarm condition exists on the channel
Flashing A transducer fault condition exists on the channel.
A tachometer fault (no transducer fault) condition
exists on the tachometer channel
A tachometer fault condition exists and the channel’s
alarm speed range is enabled (and no transducer fault
on the channel’s transducer).
(and no transducer fault or tachometer fault condition
exists).
Publication GMSI10-UM010C-EN-P - May 2010
Eccentricity Indicator
Color State Description
Yellow Off Either alarm is actively monitoring the eccentricity
measurement.
Solid Neither alarm is actively monitoring the eccentricity
measurement. This occurs when both alarms have the
status of DISARM (alarms are disabled, the machine
speed is outside of the alarm’s speed range, or the
module is in Program mode).
Page 47
Installing the XM-120 Eccentricity Module 39
Relay Indicator
Color State Description
Red Off On-board relay is not activated.
Solid On-board relay is activated.
Basic Operations
Powering Up the Module
The module performs a self-test at power-up. The self-test includes an LED
test and a device test. During the LED test, the indicators will be turned on
independently and in sequence for approximately 0.25 seconds.
The device test occurs after the LED test. The Module Status (MS) indicator is
used to indicate the status of the device self-test.
MS Indicator State Description
Flashing Red and Green Device self-test is in progress.
Solid Green or Flashing Green Device self-test completed successfully,
and the firmware is valid and running.
Flashing Red Device self-test completed, the hardware is
OK, but the firmware is invalid. Or, the
firmware download is in progress.
Solid Red Unrecoverable fault, hardware failure, or
Boot Loader program may be corrupted.
Refer to Module Indicators on page 37 for more information about the LED
indicators.
Manually Resetting Relays
The XM-120 has an external reset switch located on top of the module, as
shown in Figure 2.24.
Publication GMSI10-UM010C-EN-P - May 2010
Page 48

40 Installing the XM-120 Eccentricity Module
IMPORTANT
Press the Reset
Switch to reset the
relays
TIP
Figure 2.24 Reset Switch
The switch can be used to reset all latched relays in the module. This includes
the relays in the Expansion Relay Module when it is attached to the XM-120.
Installing the XM-120 Eccentricity Firmware
The Reset switch resets the relays only if the input is no
longer in alarm or the condition that caused the alarm is no
longer present.
Before you can use the XM-120 Eccentricity module, you must install the
Eccentricity firmware onto the XM-120 Dynamic Measurement module. The
Eccentricity firmware is provided on the XM Documentation and
Configuration Utility CD (version 3.10 or later) that is packaged with the XM
modules.
XM firmware update files are available for download from
the XM Firmware Update page at
http://support.rockwellautomation.com
Complete the following steps to install the XM-120 Eccentricity firmware.
1. Make certain you have installed the XM Serial Configuration Utility onto
the computer that will be connected directly to the XM-120 module.
Refer to the XM-12X Dynamic Measurement Modules Installation
Instructions for assistance.
Publication GMSI10-UM010C-EN-P - May 2010
2. Insert the XM Documentation and Configuration Utility CD into the
CD-ROM drive of the computer.
3. Connect the computer to the XM-120 module using the special serial
cable. Refer to Serial Port Connection on page 32.
Page 49

Installing the XM-120 Eccentricity Module 41
Click this button to
update the device with
the Eccentricity
firmware
4. Power up the XM-120 module if you haven’t already done so, and start
the XM Serial Configuration Utility program. Click the Start program,
and then select Programs > Entek > XM > Serial Config Utility.
5. Click the Configure button on the XM Serial Configuration Utility
screen. The XM-120 Dynamic Measurement Module Configuration
Tool sc reen a ppea rs.
6. Click the Module tab.
7. In the Firmware Update group, click Update Firmware to initiate the
firmware update. The Open dialog box appears.
8. Navigate to the Firmware directory on the CD and select the
"xm12E.nvs" file.
Publication GMSI10-UM010C-EN-P - May 2010
Page 50

42 Installing the XM-120 Eccentricity Module
TIP
TIP
9. Click Open to start the firmware update and click Yes to confirm. The
Configuration Tool begins the update and shows its progress in the
Progress dialog box.
10. When the update completes, the message "The module is configured
with the factory defaults. You need to download a configuration."
appears. Click OK.
11. Click OK again to return to the XM Serial Configuration Utility screen.
Notice that the XM Module icon displays XM-12E instead of XM-120.
12. You are now ready to configure the Eccentricity module. Click the
Configure button to display the Eccentricity parameters in the
Configuration Tool. Refer to Chapter 3 for a complete list of the
Eccentricity configuration parameters.
Review and edit the Eccentricity parameters as necessary.
When you are finished, download the parameters to the
module. The module will remain in Program mode until
you download a configuration.
For assistance on how to use the XM Serial Configuration
Utility, refer to the online help.
Publication GMSI10-UM010C-EN-P - May 2010
Page 51

Chapter
IMPORTANT
3
Configuration Parameters
This chapter provides a complete listing and description of the Eccentricity
parameters. The parameters can be viewed and edited using the XM Serial
Configuration Utility software and a personal computer. If the module is
installed on a DeviceNet network, configuring can also be performed using a
network configuration tool such as RSNetWorx (Version 3.0 or later). Refer to
your configuration tool documentation for instructions on configuring a
device.
For information about See page
Channel Transducer Parameters 44
Measurement Parameters 45
Tachometer Parameters 47
Alarm Parameters 49
Relay Parameters 52
4-20 mA Output Parameters 55
I/O Data Parameters 56
Data Parameters 57
Device Mode Parameters 60
The appearance and procedure to configure the parameters
The
may differ in different software.
43 Publication GMSI10-UM010C-EN-P - May 2010
Page 52

44 Configuration Parameters
TIP
Channel Transducer
The channel transducer parameters define the characteristics of the
transducers you will be using with the module. Use the parameters to
Parameters
configure the transducer sensitivity, and operating range. There are two
instances of the channel transducer parameters, one for each channel.
The Channel LED will flash red when a transducer fault
condition exists on the channel even if you are not using
the channel. You can keep the Channel LED from flashing
red on unused channels by setting the unused channel’s
Fault High and Fault Low to greater than zero and less
than zero, respectively. For example, set Fault High to +18
volts and set Fault Low to -18 volts.
Transducer Parameters
Parameter Name Description Values/Comments
Channel Name (XM Serial
Configuration Utility only)
Sensitivity The sensitivity of the transducer in millivolts per
Eng. Units Defines the native units of the transducer. Options: mils
A descriptive name to help identify the channel in
the XM Serial Configuration Utility.
Eng. Unit.
Maximum 18 characters
The sensitivity value is included with
the transducer’s documentation or it
may be imprinted on the side of the
transducer.
µm
Fault Low The minimum, or most negative, expected DC
voltage from the transducer.
Fault High The maximum expected DC bias voltage from the
transducer.
Measured DC Bias (EDS File only) Shows the measured DC offset of the transducer
signal. This value is compared with Fault High and
Fault Low to determine whether the transducer is
working properly.
Transducer Status (EDS File only) States whether a transducer fault exists on the
associated channel.
Volts
Note: A voltage reading outside this
range constitutes a transducer fault.
Possible status values: No Fault
Fault
Publication GMSI10-UM010C-EN-P - May 2010
Page 53
Configuration Parameters 45
TIP
Measurement Parameters
Eccentricity Measurement Parameters
Use these parameters to configure the engineering units and update rate for
the eccentricity measurements. There are two instances of the eccentricity
measurement parameters, one for each channel.
The Eccentricity Update Rate parameter is for
installations where the tachometer signal is not available.
Eccentricity Measurement Parameters
Parameter Name Description Values/Comments
Eccentricity Units The data units of the measured values. Options: mils
Eccentricity Update Rate The update rate for the eccentricity, min gap, and
max gap measurements.
Enter a value from 1 to 255 seconds.
Note: This value is used when the
tachometer is disabled (Pulses Per
Revolution set to zero) or a fault
condition exists on the tachometer
channel.
µm
Waveform Parameters
There are two instances of the waveform parameters, one for each channel.
Use these parameters to set up the waveform measurements.
Waveform Parameters
Parameter Name Description Values/Comments
Waveform Period The total period of the waveform measurement. Seconds
Number of Points The number of samples in the waveform
measurement.
Options: 256
512
1024
2048
Publication GMSI10-UM010C-EN-P - May 2010
Page 54

46 Configuration Parameters
TIP
Number of Points
Requested
Period(s)
256 512 1024 2048
Actual
Sampling
Rate
Actual
Period
Actual
Sampling
Rate
Actual
Period
Actual
Sampling
Rate
Actual
Period
Actual
Sampling
Rate
Actual
Period
5 51.2 5.0 187.5 2.73 187.5 5.46 187.5 10.92
10 25.6 10.0 51.2 10.0 187.5 5.46 187.5 10.92
25 10.24 25.0 20.48 25.0 40.96 25.0 81.92 25.0
100 2.56 100.0 5.12 100.0 10.24 100.0 20.48 100.0
800 0.32 800 0.64 800.0 1.28 800.0 2.56 800.0
The Wavefor m Period and the Number of Points must
be configured such that the sampling rate (Number of
Points/Wavefor m Period) is from 0.32 Hz to 187.5 Hz.
The module will automatically use 187.5 Hz when the
sampling rate is above 93.75, resulting in waveforms
collected with a different period than specified.
The table below shows examples. The entries in the table
are the actual sampling rate (samples per second) and
period corresponding to the waveform period and number
of points.
Publication GMSI10-UM010C-EN-P - May 2010
Note that the signal processing hardware applies a low pass
filter of 20 Hz to the input signal. Therefore the
eccentricity measurements taken at sampling rates above
51.2 samples/second will reflect this low pass filter.
Page 55

Configuration Parameters 47
Time Constant
(milliseconds)
-3dB Frequency
(Hz)
Settling Time
(milliseconds)
5 31.8310 11
10 15.9155 22
20 7.9577 44
50 3.1831 110
100 1.5915 220
1200 0.1326 2640
Speed Measurement Parameter
Use the speed measurement parameter to configure the filtering performed on
the speed measurement.
Speed Measurement Parameter
Parameter Name Description Values/Comments
Exponential Averaging Time
Constant
Sets the 3-dB bandwidth for the digital filter used to
calculate the Speed Value. The 3-dB bandwidth is
roughly equal to 1 / (2
Time Constant). The greater the value entered, the
longer the response of the measured Speed Value to
a change in the input signal (less sensitive to noise
in the signal). See example table below.
π x Exponential Averaging
Milliseconds
Tachometer Parameters
Tachometer Transducer Parameters
Parameter Name Description Values/Comments
Tachometer Name (XM Serial
Configuration Utility only)
Fault Low The minimum, or most negative, expected DC
Fault High The maximum expected DC voltage from the
Transducer 3 Status (EDS File
only)
The tachometer parameters define the characteristics of the tachometer and
determine the signal processing that will be performed on the tachometer
signal.
Tachometer Transducer Parameters
A descriptive name to help identify the tachometer in
the XM Serial Configuration Utility software.
voltage from the transducer.
transducer.
States whether a transducer fault condition exists on
the tachometer channel. If a fault exists, the speed
value may not be accurate.
Maximum 18 characters
Volts
Note: A voltage reading outside this
range constitutes a transducer fault.
Possible status values: No Fault
Fault
Publication GMSI10-UM010C-EN-P - May 2010
Page 56

48 Configuration Parameters
IMPORTANT
XM Configuration
Utility
EDS File
Auto Trigger Trigger
Mode
XM Configuration
Utility
EDS File
Check = Auto Mode Auto
Clear = Manual
Mode
Manual
Tachometer Signal Processing Parameters
If you are not using the tachometer channel, set the Pulses
per Revolution to zero. This will disable the tachometer
measurement, and prevent the module from indicating a
tachometer fault.
Tachometer Signal Processing Parameters
Parameter Name Description Values/Comments
Pulses Per Revolution The number of tachometer signal pulses per
revolution of the shaft (number of gear teeth). This
setting is useful if a proximity probe located over a
gear or shaft with a multi-toothed speed sensing
surface is used to generate the input signal.
Fault Time-Out The number of seconds the module should wait after
the last valid tach pulse before it indicates a
tachometer fault.
Sets the trigger mode. In Auto Trigger mode, the
minimum signal amplitude for triggering is 2 volts
peak-to-peak and minimum frequency is 6 CPM (0.1
Hz).
In Manual Trigger mode, the value entered in
Trigger Threshold is used as the trigger point.
Minimum signal amplitude for triggering is 500
millivolts peak-to-peak and minimum frequency is 1
CPM.
Enter zero if you are not using the
tachometer channel to disable the
tachometer measurement.
Note: The Eccentricity, Min Gap,
and Max Gap measurements will be
updated after the number of Pulses
per Revolution has occurred on the
tachometer channel. If Pulses Per
Revolution is set to zero, the
measurements will be updated after
the Eccentricity Update Rate has
elapsed.
Enter a value from 1 to 64 seconds.
Trigger Hysteresis The amount of hysteresis around the trigger
Trigger Threshold
Publication GMSI10-UM010C-EN-P - May 2010
threshold. In Auto Trigger mode, the value entered is
a percentage of the peak-to-peak input signal. This
value can range from 0 to 50%.
In Manual Trigger mode, the value entered is a
voltage level. The hysteresis voltage is added to or
subtracted from the threshold voltage to determine
the hysteresis range. The minimum value is 0.12
volts.
The signal level to be used as the trigger value when
in Manual Trigger mode.
% in Auto Trigger mode
Volts in Manual Trigger mode
Enter a value from +16 to -16 volts dc.
Note: This value is not used in Auto
Trigger mode.
Page 57

Configuration Parameters 49
XM Configuration
Utility
EDS File
Check to Enable Enabled
Clear to Disable Disabled
Tachometer Signal Processing Parameters
Parameter Name Description Values/Comments
Trigger Slope The input signal slope to be used as the trigger value
when in Manual Trigger mode.
Options: Positive
Negative
Note: This value is not used in Auto
Trigger mode.
Alarm Parameters
The Alarm parameters control the operation of the alarms (alert and danger
level) and provide alarm status. The Eccentricity module provides two alarms,
one per eccentricity channel. Use the parameters to configure which
eccentricity measurement the alarm is associated with, as well as the behavior
of the alarm.
Alarm Parameters
Parameter Name Description Values/Comments
Number (1-2) (XM Serial
Configuration Utility only)
Name (XM Serial Configuration
Utility only)
Enable Enable/disable the selected alarm.
The alarm to be configured in the XM Serial
Configuration Utility. There are two alarms in the
Eccentricity module, one for each eccentricity
channel.
A descriptive name to identify the alarm in the XM
Serial Configuration Utility.
Note: The Alarm Status is set to "Disarm" when the
alarm is disabled.
Options: 1 (Channel 1 alarm)
Maximum 18 characters
2 (Channel 2 alarm)
Publication GMSI10-UM010C-EN-P - May 2010
Page 58
50 Configuration Parameters
Alarm Parameters
Parameter Name Description Values/Comments
Condition Controls when the alarm should trigger.
Options: Greater Than
• Greater than - Triggers the alarm when the
measurement value is greater than or equal to the
Alert and Danger Threshold values.
The Danger Threshold value must be greater than
or equal to the Alert Threshold value for the trigger
to occur.
• Less than - Triggers the alarm when the
measurement value is less than or equal to the
Alert and Danger Threshold values.
The Danger Threshold value must be less than or
equal to the Alert Threshold value for the trigger to
occur.
• Inside range - Triggers the alarm when the
measurement value is equal to or inside the range
of the Alert and Danger Threshold values.
The Danger Threshold (High) value must be less
than or equal to the Alert Threshold (High) value
AND the Danger Threshold (Low) value must be
greater than or equal to the Alert Threshold (Low)
value for the trigger to occur.
• Outside range - Triggers the alarm when the
measurement value is equal to or outside the
range of the Alert and Danger Threshold values.
The Danger Threshold (High) value must be greater
than or equal to the Alert Threshold (High) value,
AND the Danger Threshold (Low) value must be
less than or equal to the Alert Threshold (Low)
value for the trigger to occur.
Less Than
Inside Range
Outside Range
Publication GMSI10-UM010C-EN-P - May 2010
Page 59
Configuration Parameters 51
XM Configuration
Utility
EDS File
Check to Enable Enabled
Clear to Disable Disabled
Alarm Parameters
Parameter Name Description Values/Comments
Alert Threshold (High)
The threshold value for the alert (alarm) condition.
Note: This parameter is the greater threshold value
Same measurement unit as the
Eccentricity Unit selection for the
specified channel.
when Condition is set to "Inside Range" or "Outside
Range."
Danger Threshold (High) The threshold value for the danger (shutdown)
condition.
Note: This parameter is the greater threshold value
when Condition is set to "Inside Range" or "Outside
Range."
Alert Threshold (Low) The lesser threshold value for the alert (alarm)
condition.
Note: This parameter is not used when Condition is
set to "Greater Than" or "Less Than."
Danger Threshold (Low) The lesser threshold value for the danger (shutdown)
condition.
Note: This parameter is not used when Condition is
set to "Greater Than" or "Less Than."
Hysteresis The amount that the measured value must fall
(below the threshold) before the alarm condition is
cleared. For example, Alert Threshold = 120 and
Hysteresis = 2. The alarm (alert) activates when the
measured value is 120 and will not clear until the
measured value is 118.
Note: The Alert and Danger Thresholds use the
same hysteresis value.
Note: For the Outside Range condition, the
hysteresis value must be less than Alert Threshold
(High) – Alert Threshold (Low).
Speed Range Enable Controls whether the alarm is enabled only when the
measured speed is within a machine speed range.
Enter the machine speed range in Speed Range
High and Speed Range Low.
Note: The tachometer must be
enabled (Pulses Per Revolution set
to 1 or more) and a tachometer signal
must be provided at the tachometer
input when Speed Range Enable is
enabled.
Publication GMSI10-UM010C-EN-P - May 2010
Page 60

52 Configuration Parameters
IMPORTANT
Alarm Parameters
Parameter Name Description Values/Comments
Speed Range Low
Speed Range High The greater threshold of the machine speed range.
The lesser threshold of the machine speed range.
This value must be less than the Speed Range
High value.
This parameter is not used when Speed Range
Enabled is disabled.
This value must be greater than the Speed Range
Low value.
This parameter is not used when Speed Range
Enabled is disabled.
RPM
Relay Parameters
The Relay parameters control the operation of the on-board relay, as well as
the relays on the Expansion Relay (XM-441) module. Use these parameters to
configure which alarm(s) the relay is associated with, as well as the behavior of
the relay.
A relay can be defined, regardless of whether or not it is
physically present. A non-physical relay is a virtual relay.
When a relay (physical or virtual) activates, the module
sends a Change of State (COS) message to its master,
which acts on the condition as necessary. An XM-440
Master Relay Module can activate its own relays in response
to a relay (physical or virtual) activation at any of its slaves.
Relay Parameters
Parameter Name Description Options/Comments
Number (XM Serial Configuration
Utility only)
Sets the relay to be configured in the XM Serial
Configuration Utility.
Relay Number 1 is the on-board relay.
Numbers 2 through 5 are either relays
on the Expansion Relay module when
it’s connected to the module or virtual
relays.
Virtual relays are non-physical relays.
Use them when you want the effect of
the relay (monitor alarms, delay, and
change status) but do not need an
actual contact closure. For example, a
PLC or controller monitoring the relay
status.
Publication GMSI10-UM010C-EN-P - May 2010
Note: The Relay Installed parameter
indicates whether a relay is a virtual
relay or a physical relay on a module.
Page 61

Configuration Parameters 53
XM Configuration
Utility
EDS File
Check to Enable Enabled
Clear to Disable Disabled
XM Configuration
Utility
EDS File
Latching Latching
Option
XM Configuration
Utility
EDS File
Check means
latching (relay must
be explicitly reset)
Latching
Clear means
non-latching (relay
is reset once the
alarm condition has
passed)
Nonlatching
XM Configuration
Utility
EDS File
Activation Logic Logic
XM Configuration
Utility
EDS File
Alarm A/B Alarm
Identifier
A/B
Relay Parameters
Parameter Name Description Options/Comments
Name (XM Serial Configuration
Utility only)
A descriptive name to help identify the relay in the
XM Serial Configuration Utility.
Maximum 18 characters
Enable Enable/disable the selected relay.
Note: The Relay Current Status is set to "Not
Activated" when the relay is disabled. See page 57.
Controls whether the relay must be explicitly reset
after the alarm subsides.
Activation Delay Enter the length of time for which the Activation
Logic must be true before the relay is activated. This
reduces nuisance alarms caused by external noise
and/or transient vibration events.
Sets the relay activation logic.
• A or B - Relay is activated when either Alarm A or
Alarm B meets or exceeds the selected Alarm
Status condition(s).
• A and B - Relay is activated when both Alarm A
and Alarm B meet or exceed the selected Alarm
Status condition(s).
• A Only - Relay is activated when Alarm A meets
or exceeds the selected Alarm Status
condition(s).
Sets the alarm(s) that the relay will monitor. The
alarm must be from the same device as the relay.
When the Activation Logic is set to "A and B" or "A
or B," you can select an alarm in both Alarm A and
Alarm B. The system monitors both alarms. When
the Activation Logic is set to "A Only," you can
select an alarm only in Alarm A.
Enter a value from 0 to 25.5 seconds,
adjustable in increments of 0.1
seconds.
Default is 1 second
Options: A only
A or B
A and B
Alarm Number 1 or 2
Note: You can only select an alarm
that is enabled.
Publication GMSI10-UM010C-EN-P - May 2010
Page 62
54 Configuration Parameters
XM Configuration
Utility
EDS File
Alarm Status to
Activate On
Alarm Levels
XM Configuration
Utility
EDS File
Check = Physical
Relay
Installed =
Physical Relay
Clear = Virtual Relay Not Installed =
Virtual Relay
Relay Parameters
Parameter Name Description Options/Comments
Sets the alarm conditions that will cause the relay to
Options: Normal
activate. You can select more than one.
• Normal - The current measurement is not within
excess of any alarm thresholds.
• Alert - The current measurement is in excess of
the alert level threshold(s) but not in excess of the
danger level threshold(s).
• Danger - The current measurement is in excess of
the danger level threshold(s).
Check to enable.
Clear to disable.
• Disarm-The alarm is disabled or the device is in
Program mode.
• Xdcr Fault - A transducer fault is detected on the
associated transducer.
• Module Fault - Hardware or firmware failure, or
an error has been detected and is preventing
proper operation of the device.
• Ta ch o Fault - A required tachometer signal has
not been detected. Note that there is no
transducer fault either.
Relay Installed Indicates whether the relay is a physical relay on a
module or a virtual relay. If the relay is a physical
relay, then you can set the Failsafe parameter.
Danger
Xdcr Fault
Tacho Fault
Alert
Disarm
Module Fault
If the relay is a virtual relay, the Failsafe parameter
is not used or it is disabled.
Publication GMSI10-UM010C-EN-P - May 2010
Page 63
Configuration Parameters 55
XM Configuration
Utility
EDS File
Failsafe Relay Failsafe
Option
XM Configuration
Utility
EDS File
Check means
failsafe
Failsafe
Clear means
non-failsafe
Nonfailsafe
XM Configuration
Utility
EDS File
Check to enable Enabled
Clear to disable Disabled
Relay Parameters
Parameter Name Description Options/Comments
Determines whether the relay is failsafe or
non-failsafe.
Failsafe operation means that when in alarm, the
relay contacts are in their "normal," de-energized, or
"shelf-state" positions. In other words, normally
closed relays are closed in alarm, and normally open
relays are open in alarm. With failsafe operation, a
power failure equals an alarm.
The following are true of a relay in failsafe
operation:
• The relay is energized when power is applied to
the module.
• The relay in a nonalarmed condition has power
applied to the coil.
• In alarm condition, power is removed from the
relay coil, causing the relay to change state.
For non-failsafe operation, the following are true:
• Under nonalarm conditions, the relay closes the
circuit between the common and the N.C.
(normally closed) terminals.
• Under alarm conditions, the relay changes state to
close the circuit between the common and the
N.O. (normally open) terminals.
4-20 mA Output Parameters
4-20 mA Parameters
Parameter Name Description Options/Comments
Enable Enables/disables the 4-20 mA output.
Min Range The measured value associated with the 4 mA. Same measurement unit as the
Max Range The measured value associated with the 20 mA.
For failsafe operation, the following are true:
• Under nonalarm (with power applied to the unit)
conditions, the relay closes the circuit between the
common and the N.O. terminals.
• Under alarm or loss-of-power conditions, the relay
changes state to close the circuit between the
common and the N.C. terminals.
The 4-20 mA output parameters define the characteristics of the two 4-20 mA
output signals. The parameters are the same for each output.
Eccentricity Unit selection for the
specified channel.
Publication GMSI10-UM010C-EN-P - May 2010
Page 64

56 Configuration Parameters
IMPORTANT
IMPORTANT
IMPORTANT
Measured values between Min Range and Max Range are
scaled into the range from 4.0 to 20.0 to produce the
output value. The Min Range value does not have to be
less than the Max Range value. If the Min Range value is
greater than the Max Range value, then the output signal
is effectively inverted from the input signal.
The 4-20 mA outputs are either on or off. When they are
on, the 4-20 mA outputs overshoot the 4 and 20 mA limits
by 10% when the measurement exceeds the minimum and
maximum range. This means the minimum current
produced is 3.6 mA and the maximum current produced is
22 mA.
When the 4-20 mA outputs are off, they produce a current
approximately 2.9 mA. The 4-20 mA outputs are off under
the following conditions:
• The 4-20 mA outputs are set to "Disable" (see Enable on
the previous page).
I/O Data Parameters
• The module is in Program mode.
• A transducer fault or tachometer fault occurs that affects
the corresponding measurement.
The I/O data parameters are used to configure the content and size of the
DeviceNet I/O Poll response message.
The XM-120 must be free of Poll connections when
configuring the Poll Output (Poll Response Assembly)
and Poll Size. Any attempt to download the parameters
while a master device has established the Poll connection
with the Eccentricity module will result in an error.
To close an existing Poll connection with an XM-440,
switch the XM-440 from Run mode to Program mode.
Refer to Changing Operation Modes on page 67.
To close an existing Poll connection with other master
devices, remove the module from the scan list or turn off
the master device.
Publication GMSI10-UM010C-EN-P - May 2010
I/O Data Parameters
Parameter Name Description Values/Comments
COS Size (XM Serial
Configuration Utility only)
The size (number of bytes) of the Change of State
(COS) message.
The COS Size cannot be changed.
Page 65
Configuration Parameters 57
XM Configuration
Utility
EDS File
Poll Output Poll
Response
Assembly
TIP
I/O Data Parameters
Parameter Name Description Values/Comments
COS Output (XM Serial
Configuration Utility only)
Poll Size Sets the size (number of bytes) of the Poll response
The Assembly instance used for the COS message.
The COS message is used to produce the Alarm and
Relay status for the module.
message. Decreasing the maximum size will truncate
data from the end of the Assembly structure.
Important: If you set the Poll Output to "Custom
Assembly," the poll size is automatically set to the
actual size of the customized Poll response.
The COS Output cannot be changed.
Refer to COS Message Format on
page 73 for more information.
The minimum size is 4 bytes and the
maximum size is 124 bytes.
Assembly Instance Table (XM
Serial Configuration Utility only)
Custom Assembly (XM Serial
Configuration Utility only)
Data Parameters
Sets the Assembly instance used for the Poll
response message. Each Assembly instance contains
a different arrangement of the Poll data.
The Poll response message is used by the XM
module to produce measured values. It can contain
up to 31 REAL values for a total of 124 bytes of data.
Displays the format of the currently selected COS or
Poll Assembly instance.
Defines a custom data format for the Poll response.
The custom assembly can contain any of the
measurement parameters included in Assembly
instance 101, as well as alarm and relay
configuration parameters.
Options: Assembly Instance 101
Assembly Instance 102
Assembly Instance 103
Assembly Instance 104
Custom Assembly
Refer to Poll Message Format on
page 71 for more information.
The highlighted (yellow) Assembly
structure bytes are included in the I/O
message.
You can select up to 20 parameters.
Refer to Poll Message Format on
page 71 for the more information.
The Data parameters are used to view the measured values of the input
channels, as well as to monitor the status of the channels, alarms, and relays.
To view all the data parameters in the XM Serial
Configuration Utility, click the View Data tab.
Publication GMSI10-UM010C-EN-P - May 2010
Page 66

58 Configuration Parameters
XM Configuration
Utility
EDS File
Xdcr DC Bias Transducer 3
Measured
DC Bias
Monitor Data Parameters
Monitor Data Parameters
Parameter Name Description Values/Comments
Channel Status (XM Serial
Configuration Utility only)
Eccentricity Shows the measured eccentricity value. These values get updated after:
Maximum Gap The maximum measured transducer gap value.
Minimum Gap The minimum measured transducer gap value.
Gap Value Shows the measured transducer gap value. This
Speed Status (XM Serial
Configuration Utility only)
States whether a fault condition exists on the
associated channel. If a fault exists, the eccentricity
measurement may not be accurate.
The following conditions can cause a fault:
• a transducer fault on the associated channel
• no tachometer signal or a transducer fault exists
on the tachometer channel
• the module is in Program mode
value is compared with Fault High and Fault Low
to determine whether the transducer is working
properly.
States whether a fault condition (no tachometer
signal or transducer fault) exists on the tachometer
channel. If a fault exists, the speed and DC Bias
values may not be accurate.
Shows the measured average DC offset of the
tachometer signal. This value is compared with
Fault High and Fault Low to determine whether
the tachometer is working properly.
Possible status values: No Fault
• the number of Pulses per
Revolution has occurred, or
• the Eccentricity Update Rate has
elapsed
Possible status values: No Fault
Fault
Fault
Speed Value Shows the measured speed value.
Publication GMSI10-UM010C-EN-P - May 2010
Page 67

Configuration Parameters 59
XM Configuration
Utility
EDS File
Alarm Alarm Status
Alarm and Relay Status Parameters
Alarm and Relay Status Parameters
Parameter Name Description Values/Comments
States the current status of the alarm. Possible status values:
• Normal - The alarm is enabled, the
device is in Run mode, there is no
transducer fault, and the current
measurement is not within the Alert
or Danger Threshold value(s).
• Alert - The alarm is enabled, the
device is in Run mode, there is no
transducer fault, and the current
measurement is in excess of the
Alert Threshold value(s) but not in
excess of the Danger Threshold
value(s).
• Danger - The alarm is enabled, the
device is in Run mode, there is no
transducer fault, and the current
measurement is in excess of the
Danger Threshold value(s).
• Disarm-The alarm is disabled or the
device is in Program mode.
• Transducer Fault - The alarm is
enabled, the device is in Run mode,
and a transducer fault is detected on
the associated transducer.
• Tachometer Fault - The alarm is
enabled, the device is in Run mode,
a tachometer fault exists, but there
is no transducer fault.
• Module Fault - Hardware or
firmware failure, or an error has
been detected and is preventing
proper operation of the device.
Relay Status States the current status of the relay. Possible status values: Activated
Not Activated
Publication GMSI10-UM010C-EN-P - May 2010
Page 68

60 Configuration Parameters
IMPORTANT
Device Mode Parameters
The Device Mode parameters are used to control the functions and the
behavior of the device.
The XM Serial Configuration Utility handles these
parameters automatically and transparently to the user.
Device Mode Parameters
Parameter Name Description Values/Comments
Device Mode Sets the current operation mode of the device. Refer
to Changing Operation Modes on page 67 for more
information.
Autobaud Enables/disables autobaud.
When autobaud is set to "Enabled," the module will
listen to other devices on the network to determine
the correct baud rate to use for communications.
When autobaud is set to "Disabled," the module
baud rate must be set manually.
Options: Run Mode
Options: Enabled
Program Mode
Disabled
Publication GMSI10-UM010C-EN-P - May 2010
Page 69

Appendix
A
Specifications
The Appendix lists the technical specifications for the Eccentricity module.
XM-120 Eccentricity Technical Specifications
Product Feature Specification
Communications
DeviceNet
Standard DeviceNet protocol for all
functions
NOTE: The XM-120 uses only the DeviceNet
protocol, not power. Module power is provided
independently.
Available Electronic Data Sheet (EDS) file
provides support for most DeviceNet
compliant systems
Baud rate automatically set by bus master
to 125 kb, 250 kb, 500 kb
Configurable I/O Poll Response message
helps optimize space utilization within
scanner input tables.
Selectable Poll Response Assembly
Selectable Poll Response Size
(bytes)
Side Connector
Serial
All XM measurement and relay modules
include side connectors that allow
interconnecting adjacent modules, thereby
simplifying the external wiring
requirements.
The interconnect provides primary power,
DeviceNet communication, and the circuits
necessary to support expansion modules,
such as the XM-441 Expansion Relay
module.
RS-232 via mini-connector or terminal base
unit
Baud rate fixed at 19200.
NOTE: Local configuration via Serial
Configuration Utility.
61 Publication GMSI10-UM010C-EN-P - May 2010
Page 70

62 Specifications
XM-120 Eccentricity Technical Specifications
Product Feature Specification
Inputs
2 Channels
Eddy current transducer signals
Tachometer
Outputs
Transducer Power
Voltage Range
Sensitivity
Input Impedance
1 Tachometer Input
Input Impedance
Speed/Frequency Range
Speed Measurement Error
4-20 mA Outputs
Constant voltage (+24V dc)*
None (voltage input)
*Tachometer may be powered, constant voltage,
or configured as voltage input.
Selectable in software as 0 to ±20 V (min)
40 V max. peak-to-peak
User configurable in software
Greater than 100kohms
±25 V (50 V max. peak to peak)
1 to 50,000 events per revolution
120 kohms minimum
1 to 1,200,000 RPM
0.0167 to 20,000 Hz
1 to 12,000 RPM* +/- 1 RPM
12,001 to 120,000 RPM* +/- 6 RPM
120,001 to 1,200,000 RPM* +/- 50 RPM
* Exponential Averaging Time Constant
parameter set to ≥ 120ms
Two isolated outputs (one per eccentricity
channel)
300 ohm max load
Publication GMSI10-UM010C-EN-P - May 2010
Indicators
Buffered Outputs
7 LEDs Module Status - red/green
1 active buffer per vibration input channel
Resistive buffer for tachometer
Network Status - red/green
Channel 1 Status - yellow/red
Channel 2 Status - yellow/red
Tachometer Status - yellow/red
Eccentricity -yellow
Relay - red
Page 71

XM-120 Eccentricity Technical Specifications
Product Feature Specification
Signal Conditioning
Frequency Response
Peak-to-peak Eccentricity, Max Gap, Min
Gap: 0.0039 to 20 Hz (0.235 to 1200 cpm)
Gap: 0 to 20 Hz (0 to 1200 cpm)
Specifications 63
Accuracy
±1% of measurement
Noise Floor: 8 mV RMS
Specified at ambient temperature of +25°C
(+77°F)
Gap Resolution
Waveform
5.2mV
Block Size: 256, 512, 1024, 2048
Periods: 5 to 800 seconds
Amplitude Range
±21 V
Complex Data Waveform (asynchronous)
Measured Parameters
Speed
Peak-to-peak eccentricity
RPM
Peak-to-peak eccentricity is the difference
between the positive and the negative
extremes of the rotor bow.
µm or mils
Gap (or transducer bias voltage)
Min Gap
Max Gap
Volts
Volts
Volts
Alarms
Number
2 alarm and danger pairs (one each for the
eccentricity measurements)
Operators
Hysteresis
Speed Inhibit
Greater than
Less than
Inside range
Outside range
User configurable in software
A speed range may be specified for each
alarm. When applied, the alarm is disabled
when speed is outside of the defined range.
Publication GMSI10-UM010C-EN-P - May 2010
Page 72

64 Specifications
XM-120 Eccentricity Technical Specifications
Product Feature Specification
Relays
Number
Single on-board relay, two sets of contacts -
DPDT (2 Form C)
Four additional relays when interconnected
to an XM-441 Expansion Relay module, or
Four virtual relays whose status can be
used by remote Control Systems or the
XM-440 Master Relay module
On-board Relay Rating
Failsafe
Latching
Time Delay
Voting Logic
Reset
Maximum Voltage: 120V dc, 125V ac
Maximum Current: 3.5 A*
Minimum Current: 0
Maximum Power: 60 W, 62.5 VA
*Max current is up to 40°C, then derates to 2 A
at 65°C
Agency Rating:
120V ac @ 0.5 A
110V dc @ 0.3 A
30V dc @ 1.0 A
Normally energized (failsafe), or
Normally de-energized (non-fail-safe)
Latching, or
Non-latching
0 to 25.5 seconds, adjustable in 100msec
increments
Single or paired "And" or "Or" logic applied
to any alarm
Local reset switch on top of module
Remote reset switch wired to terminal base
Digital reset command via serial or
DeviceNet interface
Publication GMSI10-UM010C-EN-P - May 2010
Activation On
Alarm Status:
Normal
Alert
Danger
Disarm
Transducer fault
Module fault
Tacho fault
Page 73

Specifications 65
XM-120 Eccentricity Technical Specifications
Product Feature Specification
Non-Volatile Configuration A copy of the module configuration is
retained in non-volatile memory from where
it is loaded upon power up*.
*The configuration stored in non-volatile
memory can be deleted only by a module-reset
command sent via the serial interface, using
the Serial Configuration Utility, or via
DeviceNet from any compliant software
application.
Accuracy (minimum) ±1% of full scale range for the channel
±1% of alarm setpoint for speed
Power
Module
+21.6 to +26.4V dc
Environmental
Physical
Consumption
Heat Production
Transducer
Operating Temperature
Storage Temperature
Relative Humidity
Conformal Coating
Dimensions
Terminal Screw Torque
Maximum: 300 mA
Typical: 175 mA
Maximum: 7 Watts (24 BTU/hr)
Typical: 4 Watts (14 BTU/hr)
Isolated 24V dc, user configurable with
wiring
-20 to +65°C (-4 to +149°F)
-40 to +85°C (-40 to +185°F)
95% non-condensing
All printed circuit boards are conformally
coated in accordance with IPC-A-610C.
Height: 3.8 in (97 mm)
Width: 3.7 in (94 mm)
Depth: 3.7 in (94 mm)
7 pound-inches (0.6 Nm)
Publication GMSI10-UM010C-EN-P - May 2010
Page 74
66 Specifications
UL UL Listed for Ordinary
Locations
UL UL Listed for Class I, Division 2
Group A, B, C, and D Hazardous
Locations
CSA CSA Certified Process Control
Equipment
CSA CSA Certified Process Control
Equipment for Class I, Division
2 Group A, B, C, and D
Hazardous Locations
EEX* European Union 94/9/EEC ATEX
Directive, compliant with EN
50021; Potentially Explosive
Atmospheres, Protection “n”
CE* European Union 89/336/EEC
EMC Directive
C-Tick* Australian
Radiocommunications Act,
compliant with:
AS/NZS 2064, Industrial
Emissions
XM-120 Eccentricity Technical Specifications
Product Feature Specification
Approvals
(when product or packaging is marked)
Publication GMSI10-UM010C-EN-P - May 2010
*See the Product Certification link at
www.rockwellautomation.com for Declarations
of Conformity, Certificates and other
certification details.
Page 75
DeviceNet Information
IMPORTANT
Appendix
B
Electronic Data Sheets
Changing Operation Modes
Electronic Data Sheet (EDS) files are simple text files used by network
configuration tools such as RSNetWorx (Version 3.0 or later) to help you
identify products and easily commission them on a network. The EDS files
describe a product’s device type, product revision, and configurable parameters
on a DeviceNet network.
The EDS files for the XM modules are installed on your computer with the
XM configuration software. The latest EDS files can also be obtained at
http://www.ab.com/networks/eds/ or by contacting your local Rockwell
Automation representative.
Refer to your DeviceNet documentation for instructions on registering the
EDS files.
XM modules operate in two modes.
Mode Description
Run The XM measurement modules collect measurement data and
monitor each measurement device.
The XM-440 establishes I/O connections with the XM
measurement modules in its scan list and monitors their alarms,
and controls its own relay outputs accordingly.
Program The XM module is idle.
The XM measurement modules stop the signal
processing/measurement process, and the status of the alarms
is set to the disarm state to prevent a false alert or danger
status.
The XM-440 closes the I/O connections with the XM
measurement modules in its scan list and stops monitoring their
alarms, relays are deactivated unless they are latched.
Configuration parameters can be read, updated and downloaded
to the XM module.
To change the operation mode of the module, use the Device Mode parameter
in the EDS file. Note that the Stop and Start services described on page 69 can
also be used to change the operation mode.
The XM Serial Configuration Utility software automatically
puts XM modules in Program mode and Run mode
without user interaction.
67 Publication GMSI10-UM010C-EN-P - May 2010
Page 76

68 DeviceNet Information
TIP
TIP
TIP
TIP
Transition to Program Mode
Parameter values can only be downloaded to an XM module while the module
is in Program mode. Any attempt to download a parameter value while the
module is in Run mode will result in a Device State Conflict error.
To transition an XM module from Run mode to Program mode on a
DeviceNet network, set the Device Mode parameter to "Program mode" and
click Apply. Note that you cannot change any other parameter until you have
downloaded the Program mode parameter.
The Module Status indicator flashes green when the
module is in Program mode.
Refer to your DeviceNet documentation for specific instructions on editing
EDS device parameters.
You can also use the Stop service described on page 69 to
transition XM modules to Program mode.
Transition to Run Mode
In order to collect data and monitor measurement devices, XM modules must
be in Run mode. To transition an XM module from Program mode to Run
mode on a DeviceNet network, set the Device Mode parameter to "Run
mode" and click Apply.
The Module Status indicator is solid green when the
module is in Run mode.
Refer to your DeviceNet documentation for specific instructions on editing
EDS device parameters.
You can also use the Start service described on page 69 to
transition XM modules to Run mode.
Publication GMSI10-UM010C-EN-P - May 2010
Page 77
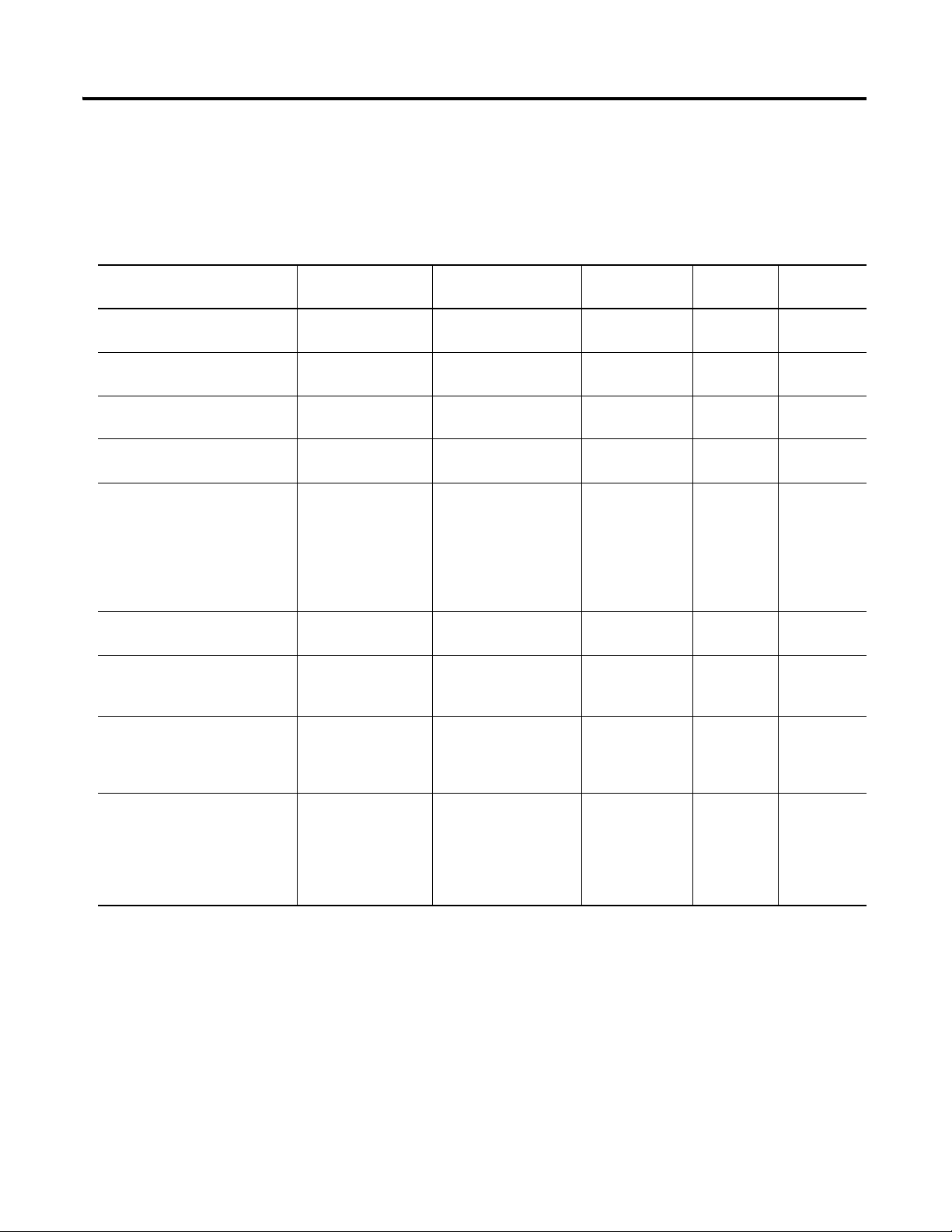
DeviceNet Information 69
XM Services
XM Services
Action
Transition to Run Mode Start
Transition to Program Mode Stop
Save configuration to
non-volatile memory (EEPROM)
Delete saved configuration from
non-volatile memory (EEPROM)
Reset a specific latched relay Reset
Reset all latched relays Reset
The table below defines services supported by the XM modules. The table
includes the service codes, classes, instances, and attributes by their
appropriate hexadecimal codes. Use the Class Instance Editor in RSNetWorx
to execute these services, as illustrated in the example below.
Service Code
(Hex)
(06)
(07)
Save
(16)
Delete
(09)
(05)
(05)
Class
(Hex) Instance Attribute Data
Device Mode Object
(320)
Device Mode Object
(320)
Device Mode Object
(320)
Device Mode Object
(320)
Relay Object
(323)
Relay Object
(323)
1 None None
1 None None
1 None None
1 None None
Relay number
1-C for XM-440,
1-5 for XM-12X,
XM-320 and
XM-220, 1-8 for
XM-36X and
XM-16X
0 None None
None None
Reset the Peak Speed (XM-12X
only)
Close the virtual setpoint
multiplier switch to activate the
alarm setpoint multipliers (not
applicable to all XM modules)
Open the virtual setpoint
multiplier switch to start the
setpoint multiplier timers and
eventually cancel alarm setpoint
multiplication (not applicable to
all XM modules)
Reset
(05)
Other
(33)
Other
(32)
Speed Measurement
Object
(325)
Discrete Input Point
Object
(08)
Discrete Input Point
Object
(08)
1, 2 for XM-220 None None
1 None None
1 None None
Publication GMSI10-UM010C-EN-P - May 2010
Page 78

70 DeviceNet Information
Select the Save
service code
Clear Send the attribute
ID and then enter the
Class (320
hex
) and
Instance (1)
Click Execute to
initiate the
action
Example
To save the configuration parameters to the non-volatile memory (EEPROM),
fill in the Class Instance Editor as shown below.
Invalid Configuration Errors
A Start or Save service request to an XM module may return an Invalid Device
Configuration error when there is a conflict amongst the configuration
settings.
The general error code for the Invalid Device Configuration error is D0
hex
.
An additional error code is returned with the general error code to specify
which configuration settings are invalid. The table below lists the additional
error codes associated with the Invalid Device Configuration error.
Additional Error Codes returned with the Invalid Device Configuration Error (0xD0)
Error Code
(Hex) Description
01 No specific error information is available.
02 Mismatched transducer, channel, and/or measurement unit.
03 Inverted transducer fault high/low values.
04 Alarm thresholds conflict with the alarm condition.
05 Alarm speed range is invalid.
06 Band minimum frequency is greater than maximum frequency. Or,
07 Relay is associated with an alarm that is not enabled.
08 Tachometer must be enabled for alarm or channel settings.
09 A senseless speed range is enabled on a speed alarm.
maximum frequency is greater than FMAX.
Publication GMSI10-UM010C-EN-P - May 2010
Page 79

DeviceNet Information 71
Additional Error Codes returned with the Invalid Device Configuration Error (0xD0)
Error Code
(Hex) Description
0A Too many alarms associated with a single measurement.
0B Invalid node address in the alarm list.
0C Too many alarms in the alarm list. Or, no alarms in the alarm list.
0D Alarm levels cannot be zero for alarms that are enabled.
0E Too many slaves in the scanner’s input data table.
0F The FMAX and Number of Lines do not yield correct vector calculations.
10 Phase (vector) alarms prohibited with synchronous sampling and more
than 1 tachometer pulse per revolution.
11 Can’t have order based band on asynchronous channel.
12 Unsupported Sensor Type and Channel ID combination.
13 Invalid Alarm Type for the associated measurement ID.
14 Synchronous sampling is required for alarm on synchronous
measurements.
15 Integration is not supported with the Bypass High Pass Filter option.
Eccentricity I/O Message Formats
The Eccentricity module supports Poll and Change of State (COS) I/O
messages. The Poll response message is used by the XM module to produce
measured values and the COS message is used to produce the Alarm and Relay
Status.
Poll Message Format
The Eccentricity module Poll request message contains no data. The Poll
response message can contain up to 31 REAL values for a total of 124 bytes.
The Eccentricity module provides four pre-defined (static) data formats of the
Poll response, as defined in Assembly instance 101–104. It also provides a
dynamic Assembly instance, instance 199, with which you can define a custom
data format for the Poll response. The dynamic Assembly instance can contain
any of the measurement parameters included in Assembly instance 101, as well
as several of the alarm and relay configuration parameters.
The default Assembly instance is 101 and the default size is 36 bytes. You can
change the Assembly instance and define the custom Assembly instance using
the configuration software. Refer to I/O Data Parameters on page 56 for
details.
Publication GMSI10-UM010C-EN-P - May 2010
Page 80

72 DeviceNet Information
The Poll response data can also be requested explicitly through Assembly
Object (Class ID 0x4), Instance 101 (0x65), Data Attribute (3).
The following tables show the static data format of Assembly instances 101–
104.
Eccentricity Assembly Instance 101 Data Format
Byte Definition
0–3 Speed
4–7 Channel 1 Eccentricity value
8–11 Channel 2 Eccentricity value
12–15 Channel 1 Gap value
16–19 Channel 2 Gap value
20–23 Channel 1 Maximum Gap value
24–27 Channel 2 Maximum Gap value
28–31 Channel 1 Minimum Gap value
32–35 Channel 2 Minimum Gap value
Eccentricity Assembly Instance 102 Data Format
Byte Definition
0–3 Channel 1 Gap value
4–7 Channel 2 Gap value
8–11 Channel 1 Maximum Gap value
12–15 Channel 2 Maximum Gap value
16–19 Channel 1 Minimum Gap value
20–23 Channel 2 Minimum Gap value
24–27 Channel 1 Eccentricity value
28–31 Channel 2 Eccentricity value
32–35 Speed
Eccentricity Assembly Instance 103 Data Format
Byte Definition
0–3 Channel 1 Eccentricity value
4–7 Channel 2 Eccentricity value
8–11 Channel 1 Minimum Gap value
12–15 Channel 2 Minimum Gap value
16–19 Speed
20–23 Channel 1 Gap value
Publication GMSI10-UM010C-EN-P - May 2010
Page 81

Eccentricity Assembly Instance 103 Data Format
Byte Definition
24–27 Channel 2 Gap value
28–31 Channel 1 Maximum Gap value
32–35 Channel 2 Maximum Gap value
Eccentricity Assembly Instance 104 Data Format
Byte Definition
0–3 Channel 1 Eccentricity value
4–7 Channel 1 Gap value
8–11 Channel 1 Minimum Gap value
12–15 Channel 1 Maximum Gap value
16–19 Speed
20–23 Channel 2 Eccentricity value
24–27 Channel 2 Gap value
28–31 Channel 2 Minimum Gap value
32–35 Channel 2 Maximum Gap value
DeviceNet Information 73
COS Message Format
The Eccentricity COS message contains five bytes of data as defined in the
table below. The COS data can also be requested explicitly through Assembly
Object (Class ID 0x4), Instance 100 (0x64), Data Attribute (3).
XM-120 COS Message Format
Byte Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
0 Relay 1
Status
1 Relay 2
Status
2 Relay 3
Status
3 Relay 4
Status
4 Relay 5
Status
Reserved
Alarm 2 Status Alarm 1 Status
Reserved Reserved Reserved
Reserved Reserved Reserved
Reserved Reserved Reserved
Reserved Reserved Reserved
Publication GMSI10-UM010C-EN-P - May 2010
Page 82

74 DeviceNet Information
IMPORTANT
XM Status Values
The following tables describe the XM Status values that are included in the
COS messages.
Alarm Status Descriptions
Alarm Status Value Description
0Normal
1Alert
2 Danger
3Disarm
4 Transducer Fault (Sensor OOR)
5 Module Fault
6 Tachometer Fault
7 Reserved
Relay Status Descriptions
ADR for XM Modules
Relay Status Value Description
0 Not Activated
1 Activated
Automatic Device Replacement (ADR) is a feature of an Allen-Bradley
DeviceNet scanner. It provides a means for replacing a failed device with a
new unit, and having the device configuration data set automatically. Upon
replacing a failed device with a new unit, the ADR scanner automatically
downloads the configuration data and sets the node address.
It is recommended that ADR not be used in safety related
applications. If the failure of the ADR server, and a
subsequent power cycle, would result in the loss of
protection for a machine, then ADR should not be
implemented.
ADR can be used with XM modules but keep the following in mind when
setting up the XM modules.
Publication GMSI10-UM010C-EN-P - May 2010
Page 83

DeviceNet Information 75
TIP
• The ADR scanner can not download the configuration data to an XM
module if the module has a saved configuration in its non-volatile
memory. This happens because the saved configuration is restored and
the module enters Run mode when the power is cycled. (Configuration
parameters cannot be downloaded while an XM module is in Run
mode.) XM modules must be in Program mode for the ADR
configuration to be downloaded and this occurs only when there is no
saved configuration.
To delete a saved configuration from non-volatile
memory, use the Delete service in RSNetWorx for
DeviceNet or perform the following steps in the XM
Serial Configuration Utility.
1. Save the current configuration to a file. From the
File menu, click Save As and enter a file name for
the configuration.
2. Reset the module to factory defaults. Click the
Module tab and click the Reset button.
3. Reload the saved configuration. From the File
menu, click Open and select the configuration file.
4. Make certain to disable auto save. From the Device
menu, clear the Auto Save Configuration check
mark.
• An XM module will enter Run mode automatically after the ADR
scanner restores the module’s configuration only if the module is in Run
mode at the time the configuration is saved to the scanner. If the
module is in Program mode when the configuration is saved, then the
module will remain in Program mode after the configuration is
downloaded by the ADR scanner.
• The ADR scanner saves and restores only the configuration parameters
contained in the module’s EDS file. Some XM parameters are not
included in the EDS file because they are not supported by either the
EDS specification or the tools that read the EDS files, for example
RSNetWorx for DeviceNet. These configuration parameters will not be
restored with ADR.
Below is a list of the configuration parameters that are not included in
the EDS file and can not be saved or restored with ADR.
– Channel Name
– Tachometer Name
– Alarm Name
– Relay Name
– All Triggered Trend related parameters
Publication GMSI10-UM010C-EN-P - May 2010
Page 84

76 DeviceNet Information
– All SU/CD Trend related parameters
– Custom Assembly structure (see page 56)
• The ADR and trigger group functions cannot be used together. A
module can have only one primary master so a module cannot be both
configured for ADR and included in a trigger group. The ADR scanner
must be the primary master for the modules configured for ADR. The
XM-440 Master Relay module must be the primary master for modules
included in a trigger group.
Publication GMSI10-UM010C-EN-P - May 2010
Page 85

Appendix
TIP
C
DeviceNet Objects
Appendix C provides information on the DeviceNet objects supported by the
Eccentricity module.
For information about See page
Identity Object (Class ID 01H) 78
DeviceNet Object (Class ID 03H) 80
Assembly Object (Class ID 04H) 81
Connection Object (Class ID 05H) 86
Analog Input Point Object (Class ID 0AH) 88
Parameter Object (Class ID 0FH) 90
Acknowledge Handler Object (Class ID 2BH) 93
Alarm Object (Class ID 31DH) 94
Device Mode Object (Class ID 320H) 96
Relay Object (Class ID 323H) 97
Spectrum Waveform Measurement Object (Class ID 324H) 99
Speed Measurement Object (Class ID 325H) 102
Tachometer Channel Object (Class ID 326H) 103
Transducer Object (Class ID 328H) 105
4-20 mA Output Object (Class ID 32AH) 106
Refer to the DeviceNet specification for more information
about DeviceNet objects. Information about the
DeviceNet specification is available on the ODVA web site
(http://www.odva.org).
77 Publication GMSI10-UM010C-EN-P - May 2010
Page 86

78 DeviceNet Objects
Identity Object
(Class ID 01
)
H
The Identity Object provides identification and general information about the
device.
Class Attributes
The Identity Object provides no class attributes.
Instance Attributes
Table C.1 Identity Object Instance Attributes
Access
Attr ID
1 Get Vendor ID UINT 668 = Entek
2 Get Device Type UINT 109 (Specialty I/O)
3 Get Product Code UINT 33 (0x21)
4 Get Revision:
5 Get Status WORD
Rule Name Data Type Default Value
STRUCT OF
Major
Minor
USINT
USINT
Value varies with each firmware revision.
Value varies with each firmware revision.
6 Get Serial Number UDINT
7 Get Product Name SHORT_
STRING
Status
The Status is a 16 bit value. The following bits are implemented.
Table C.2 Identity Object Status
Bit Name Description
0 Owned TRUE indicates that the module has an owner. More
specifically, the Predefined Master/Slave Connection Set
has been allocated to a master.
1 Reserved, set to 0
2 Configured This bit is set whenever a saved configuration is
successfully loaded from non-volatile memory. This bit is
cleared whenever the default configuration is restored or
loaded.
3 Reserved, set to 0
"XM-120 Eccentricity Module"
Publication GMSI10-UM010C-EN-P - May 2010
Page 87

DeviceNet Objects 79
Table C.2 Identity Object Status
Bit Name Description
4 Boot Program Vendor-specific, indicates that the boot program is
running. The Main Application must be corrupt or
missing.
5 - 7 Vendor-specific, not implemented
8 Minor Recoverable
Set whenever there is a transducer or tachometer fault.
Fault
9 Minor Unrecoverable
Not implemented
Fault
10 Major Recoverable
Fault
Set when the module detects a major problem that the
user may be able to recover from. The Module Status
LED will flash red. An example of this condition is when
the boot program is running.
11 Major Unrecoverable
Fault
Set when there is a module status fault (Module Status
LED is solid red).
12 - 15 Reserved, set to 0
Services
Table C.3 Identity Object Services
Service
Code Class/Instance Usage Name
01
05
0E
10
h
h
h
h
Instance Get_Attributes_All
Instance Reset
Instance Get_Attribute_Single
Instance
Set_Attribute_Single
1
1 Attributes can only be set while the device is in Program Mode. See the description of the Device Mode Object
for more information.
Publication GMSI10-UM010C-EN-P - May 2010
Page 88

80 DeviceNet Objects
DeviceNet Object
(Class ID 03
)
H
Table C.4 DeviceNet Object Class Attributes
Attr ID
1 Get Revision UINT 2
Table C.5 DeviceNet Object Instance Attributes
Attr ID
1 Get/Set
2 Get/Set
3 Get Bus-Off Interrupt BOOL 0
4 Get/Set Bus-Off Counter USINT 0
The DeviceNet Object is used to provide the configuration and status of a
physical attachment to DeviceNet.
Class Attributes
Access
Rule Name Data Type Default Value
Instance Attributes
Access
Rule Name Data Type Default Value
1
MAC ID
Baud Rate
2
USINT 63
USINT 0
5 Get Allocation Information STRUCT of
BYTE
USINT
100 Get/Set Autobaud Disable BOOL 0 (Ignore attribute 2 and always autobaud)
1 Setting the MAC ID causes the device to reset automatically, after which it will go online with the new MAC
ID.
2 The Baud Rate setting can not be set while Autobaud Disable is equal to 0. Applying the Baud Rate does not
occur until the Reset service to the Identity Object.
0 255
The MAC ID, Baud Rate, and Autobaud Disable settings are stored in
non-volatile memory so they do not reset to the default with each power cycle.
The Baud Rate attribute supports the following settings:
• 0 = 125 kbps
• 1 = 250 kbps
• 2 = 500 kbps
The Baud Rate setting is used only when automatic baud rate detection is
disabled (Autobaud Disable = 1). When Autobaud Disable is set to zero
(0), the module ignores its Baud Rate setting and performs automatic baud
Publication GMSI10-UM010C-EN-P - May 2010
Page 89

DeviceNet Objects 81
rate detection instead. This means that the module will determine the network
baud rate by listening for network traffic before attempting to go online.
Services
Table C.6 DeviceNet Object Services
Service
Code Class/Instance Usage Name
0E
10
h
h
Class/Instance Get_Attribute_Single
Instance
Set_Attribute_Single
1
Assembly Object (Class ID 04H)
Table C.7 Assembly Object Class Attributes
Attr ID
1 Get Revision UINT Revision of the
4B
h
4C
h
1 Attributes can only be set while the device is in Program Mode. See the description of the Device Mode Object
for more information.
Instance Allocate_Master/Slave_Connetion_Set
Instance Release_Group_2_Identifier_Set
The Assembly Object binds attributes of multiple objects to allow data to or
from each object to be sent or received in a single message.
The Eccentricity module provides both static and dynamic assemblies.
Class Attribute
Access
Rule Name Data Type Description Semantics
2
implemented object.
Instances
Table C.8 Assembly Object Instances
Instance Name Type Description
100 Default COS Message Input Alarm and Relay Status values
Publication GMSI10-UM010C-EN-P - May 2010
Page 90
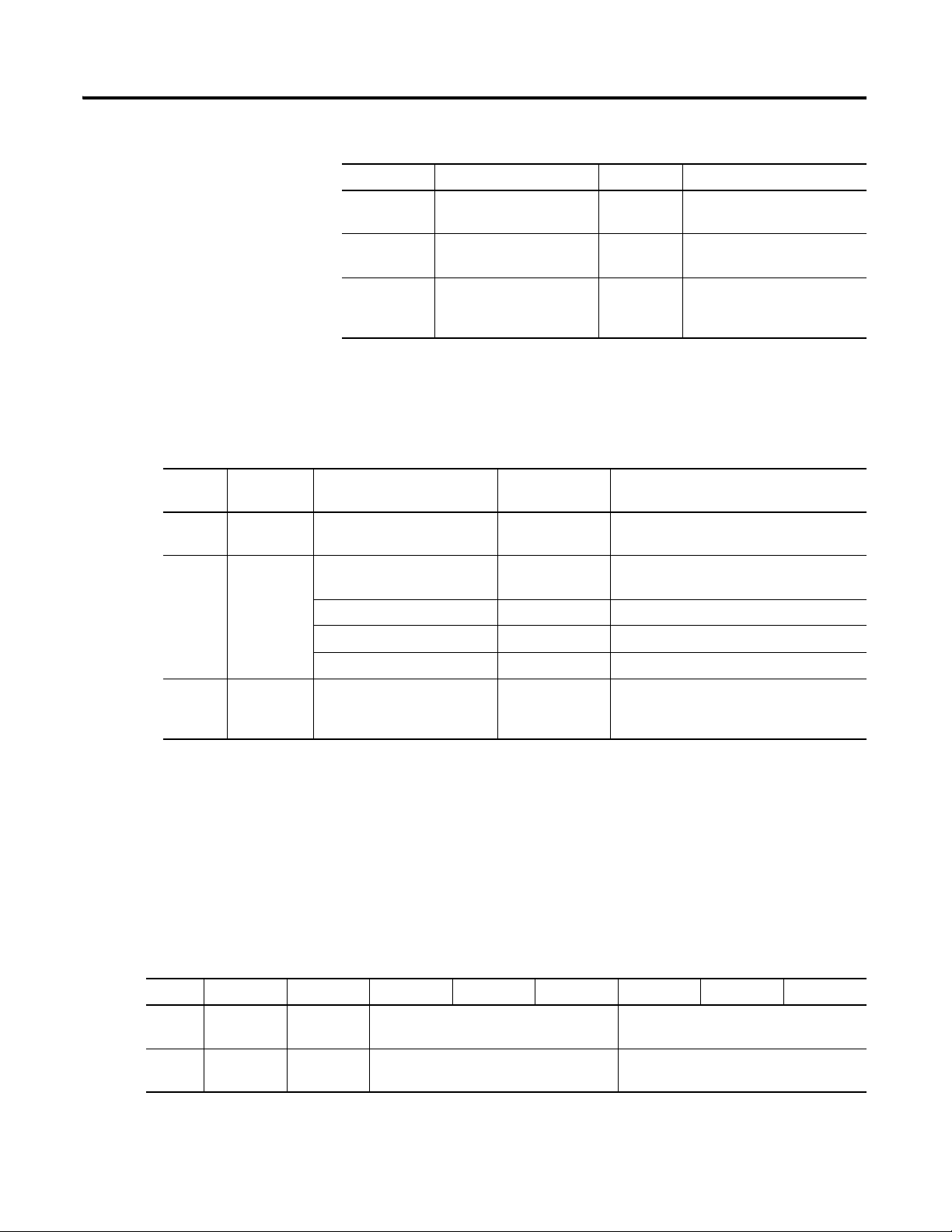
82 DeviceNet Objects
Table C.8 Assembly Object Instances
Instance Name Type Description
101 Default Poll Response
Message
102 - 106 Alternate Poll Response
Message
Input Measurement values
Input Measurement values
199 Alternate Dynamic Poll
Response Message
Input User configurable
measurement values and
configuration parameters
Instance Attributes
Table C.9 Assembly Object Instance Attributes
Access
Attr ID
1 Get Number of Members in list UINT Only supported for Dynamic Assembly
2 Set Member List Array of STRUCT: Only supported for Dynamic Assembly
3 Get Data Defined in tables
Rule Name Data Type Value
instance
instance
Member Data Description UINT Size of member data value in bits
Member Path Size UINT
Member Path Packed EPATH
on the following
pages.
Table C.10 Instance 100 Data Format (Alarm and Relay Status Values Assembly)
Byte Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
0 Relay 1
Status
1 Relay 2
Status
Publication GMSI10-UM010C-EN-P - May 2010
0 Alarm 2 Status Alarm 1 Status
00 0
Assembly Instance Attribute Data Format
Instance 100 - Eccentricity Module Alarms
This assembly is sent using COS messaging when any of the Alarm or Relay
Status values change.
Page 91

DeviceNet Objects 83
Table C.10 Instance 100 Data Format (Alarm and Relay Status Values Assembly)
Byte Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
2 Relay 3
Status
3 Relay 4
Status
00 0
00 0
4 Relay 5
Status
00 0
Instance 101 - Eccentricity Module Measurements
This is the default assembly that is sent within the I/O Poll Response message
when an I/O Poll Request is received from a DeviceNet master.
Table C.11 Instance 101 Data Format (Measurement Values Assembly)
Byte Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
0 - 3 Speed
4 - 7 Channel 1 Eccentricity value
8 - 11 Channel 2 Eccentricity value
12 - 15 Channel 1 Gap value
16 - 19 Channel 2 Gap value
20 - 23 Channel 1 Max Gap value
24 - 27 Channel 2 Max Gap value
28 - 31 Channel 1 Min Gap value
32 - 35 Channel 2 Min Gap value
Instance 102 - Eccentricity Module Measurements
This is an alternate assembly for the I/O Poll Response message.
Table C.12 Instance 102 Data Format (Measurement Values Assembly)
Byte Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
0 - 3 Channel 1 Gap value
4 - 7 Channel 2 Gap value
8 - 11 Channel 1 Max Gap value
12 - 15 Channel 2 Max Gap value
16 - 19 Channel 1 Min Gap value
20 - 23 Channel 2 Min Gap value
24 - 27 Channel 1 Eccentricity value
28 - 31 Channel 2 Eccentricity value
32 - 35 Speed
Publication GMSI10-UM010C-EN-P - May 2010
Page 92

84 DeviceNet Objects
Table C.13 Instance 103 Data Format (Measurement Values Assembly)
Byte Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
0 - 3 Channel 1 Eccentricity value
4 - 7 Channel 2 Eccentricity value
8 - 11 Channel 1 Min Gap value
12 - 15 Channel 2 Min Gap value
16 - 19 Speed
20 - 23 Channel 1 Gap value
24 - 27 Channel 2 Gap value
28 - 31 Channel 1 Max Gap value
32 - 35 Channel 2 Max Gap value
Instance 103 - Eccentricity Module Measurements
This is an alternate assembly for the I/O Poll Response message.
Instance 104 - Eccentricity Module Measurements
This is an alternate assembly for the I/O Poll Response message.
Table C.14 Instance 103 Data Format (Measurement Values Assembly)
Byte Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
0 - 3 Channel 1 Eccentricity value
4 - 7 Channel 1 Gap value
8 - 11 Channel 1 Min Gap value
12 - 15 Channel 1 Max Gap value
16 - 19 Speed
20 - 23 Channel 2 Eccentricity value
24 - 27 Channel 2 Gap value
28 - 31 Channel 2 Min Gap value
32 - 35 Channel 2 Max Gap value
Instance 199 - Dynamic Assembly
This Assembly instance can be created and configured with the XM Serial
Configuration Utility or RSMACC Enterprise Online Configuration Utility.
Using the configuration software, you determine the format of the data. This
assembly instance can be selected to be sent in response to an I/O Poll request
from a Master.
Publication GMSI10-UM010C-EN-P - May 2010
Page 93
The dynamic Assembly can include all of the measurement values included in
Assembly instance 101. In addition, the dynamic Assembly can include the
following configuration parameters.
Table C.15 Instance 199 Component Mapping
DeviceNet Objects 85
EPATH (where ii =
instance number)
Class
Name
Class
Number
21 1D 03 24 ii 30 04 Alarm 31D
21 1D 03 24 ii 30 07 Alarm 31D
21 1D 03 24 ii 30 08 Alarm 31D
21 1D 03 24 ii 30 09 Alarm 31D
21 1D 03 24 ii 30 0A Alarm 31D
21 1D 03 24 ii 30 0B Alarm 31D
21 1D 03 24 ii 30 0C Alarm 31D
21 1D 03 24 ii 30 0F Alarm 31D
21 1D 03 24 ii 30 10 Alarm 31D
21 1D 03 24 ii 30 11 Alarm 31D
21 23 03 24 ii 30 04 Relay 323
21 23 03 24 ii 30 05 Relay 323
21 23 03 24 ii 30 06 Relay 323
21 23 03 24 ii 30 07 Relay 323
21 23 03 24 ii 30 09 Relay 323
21 0F 00 24 ii 30 01 Param 0F
21 0F 00 24 ii 30 01 Param 0F
21 23 03 24 ii 30 0C Relay 323
21 23 03 24 ii 30 0E Relay 323
Instance
Number
h
h
h
h
1 - 2 Alarm Enable 4 BOOL
1 - 2 Condition 7 USINT
1 - 2 Alert Threshold (High) 8 REAL
1 - 2 Danger Threshold
Attribute
Name
Attribute
Number
9REAL
(High)
h
h
1 - 2 Hysteresis 12 REAL
h
h
h
h
h
h
1 - 5 Failsafe Enable 6 BOOL
h
h
h
h
1 - 2 Alert Threshold Low 10 REAL
1 - 2 Danger Threshold Low 11 REAL
1 - 2 Speed Range Enable 15 BOOL
1 - 2 Speed Range High 16 REAL
1 - 2 Speed Range Low 17 REAL
1 - 5 Relay Enable 4 BOOL
1 - 5 Latch Enable 5 BOOL
1 - 5 Delay 7 UINT
1 - 5 Alarm Level 9 BYTE
7 - 11 Parameter Value
1USINT
(Alarm Identifier A)
h
12 - 16 Parameter Value
1USINT
(Alarm Identifier B)
h
h
1 - 5 Logic 12 USINT
1 - 5 Relay Installed 14 BOOL
Data
Ty pe
The dynamic Assembly instance must be instantiated with a call to the class
level Create service. Then the structure can be defined with the
Set_Attribute_Single service for the Member List attribute. Only one dynamic
Attribute instance is supported so subsequent calls to the Create service will
return a Resource Unavailable (0x02) error. The Delete service can be used to
destroy the dynamic Assembly instance so that it can be re-created.
Publication GMSI10-UM010C-EN-P - May 2010
Page 94
86 DeviceNet Objects
Services
Table C.16 Assembly Object Services
Service
Code Class/Instance Usage Name
0E
10
08
09
h
h
h
h
Class/Instance Get_Attribute_Single
Instance Set_Attribute_Single
Class Create
Instance Delete
Connection Object
(Class ID 05
)
H
The Connection Object allocates and manages the internal resources
associated with both I/O and Explicit Messaging Connections.
Class Attributes
The Connection Object provides no class attributes.
Instances
Table C.17 Connection Object Instances
Instance Description
1 Explicit Message Connection for pre-defined connection set
2 I/O Poll Connection
4 I/O COS (change of state) Connection
11 - 17 Explicit Message Connection
Table C.18 Connection Object Instance Attributes
Access
Attr ID
1 Get State USINT State of the object.
2 Get Instance Type USINT Indicates either I/O or Messaging
3 Get Transport Class Trigger BYTE Defines behavior of the Connection.
Publication GMSI10-UM010C-EN-P - May 2010
Rule Name Data Type Description
Instance Attributes
Connection.
Page 95
DeviceNet Objects 87
Table C.18 Connection Object Instance Attributes
Access
Attr ID
Rule Name Data Type Description
4 Get Produced Connection ID UINT Placed in CAN Identifier Field when the
Connection transmits.
5 Get Consumed Connection IDUINT CAN Identifier Field value that denotes
message to be received.
6 Get Initial Comm
Characteristics
BYTE Defines the Message Group(s) across
which productions and consumptions
associated with this Connection occur.
7 Get Produced Connection
Size
UINT Maximum number of bytes transmitted
across this Connection.
8 Get Consumed Connection
Size
UINT Maximum number of bytes received across
this Connection.
9 Get/Set Expected Packet Rate UINT Defines timing associated with this
Connection.
12 Get/Set Watchdog Time-out
Action
13 Get Produced Connection
Path Length
14 Get Produced Connection
Path
USINT Defines how to handle Inactivity/Watchdog
timeouts.
UINT Number of bytes in the
production_connection_path attribute.
Array of
USINT
Specifies the Application Object(s) whose
data is to be produced by this Connection
Object. See DeviceNet Specification
Volume 1 Appendix I.
15 Get Consumed Connection
Path Length
16 Get Consumed Connection
Path
UINT Number of bytes in the
consumed_connection_path attribute.
Array of
USINT
Specifies the Application Object(s) that are
to receive the data consumed by this
Connection Object. See DeviceNet
Specification Volume 1 Appendix I.
17 Get Production Inhibit Time UINT Defines minimum time between new data
production.
Publication GMSI10-UM010C-EN-P - May 2010
Page 96

88 DeviceNet Objects
Services
Table C.19 Connection Object Services
Service
Code Class/Instance Usage Name
05
0E
10
h
h
h
Instance Reset
Instance Get_Attribute_Single
Instance Set_Attribute_Single
Analog Input Point Object
(Class ID 0A
)
H
Table C.20 Analog Input Point Object Class Attributes
Access
Attr ID
1 Get Revision UINT Revision of the
Rule Name Data Type Description Semantics
The Analog Input Point Object is used to model the Eccentricity
measurements made by the Eccentricity module.
Class Attributes
2
implemented object.
Instances
Table C.21 Analog Input Point Object Instances
Instance Name Description
1 Eccentricity 1 Eccentricity measurement for Channel 1
2 Eccentricity 2 Eccentricity measurement for Channel 2
3 Min Gap 1 Min Gap for Channel 1
Publication GMSI10-UM010C-EN-P - May 2010
4 Min Gap 2 Min Gap for Channel 2
5 Max Gap 1 Max Gap for Channel 1
6 Max Gap 2 Max Gap for Channel 2
Page 97

DeviceNet Objects 89
Instance Attributes
Table C.22 Analog Input Point Object Class Attributes
Access
Attr ID
3 Get Value REAL Measurement value The measured vale in units
4 Get Status BOOL Indicates if a fault or
8 Get Value Data Type USINT Determines the data type
147 Get Data Units ENGUNIT The units context of the
Rule Name Data Type Description Semantics
specified by the Data Units
attribute.
0 = Operating without alarms or
alarm has occurred.
faults
1 = Alarm or fault condition
exists. The Value attribute may
not represent the actual field
value.
1 = REAL
of the Value.
See DeviceNet Specification
Value attribute.
Volume 1 Appendix K.
Valid values for eccentricity:
mils = 0800 hex
µm = 2204 hex
Fixed for Min/Max Gap
Volt = 2D00 hex
Services
Table C.23 Analog Input Point Object Services
Service
Code Class/Instance Usage Name Description
0E
10
h
h
Class/Instance Get_Attribute_Single Returns the contents of the
specified attribute.
Instance Set_Attribute_Single Sets the contents of the
specified attribute.
1 Attributes can only be set while the device is in Program Mode. See the description of the Device Mode Object
for more information.
1
Publication GMSI10-UM010C-EN-P - May 2010
Page 98

90 DeviceNet Objects
Parameter Object
(Class ID 0F
)
H
Table C.24 Parameter Object Class Attributes
Attr ID
2 Get Max Instance UINT Maximum instance
8 Get Parameter Class
9 Get Config.
The Parameter Object provides the interface to the Eccentricity configuration
data. There are 18 Parameter Object instances implemented in the Eccentricity
module.
Instances 1-4 and 7-16 are implemented to provide an alternate method of
setting the configuration parameters with ENGUNIT or EPATH data type.
And Parameter Object instances 17 and 18 provide an alternate method for
setting the Produced Connection Size and Produced Connection Path
attributes for the Poll Connection because these attributes can be difficult to
get/set directly through the Connection Object.
Parameter Object instances 5 and 6 are for setting the update rate of the
eccentricity measurements. The eccentricity update rate is used in place of the
tachometer when no tachometer is available.
Access
Rule Name Data Type Description Semantics
Total number of parameter
Descriptor
Assembly
Instance
number of an object in
this class.
WORD Bits that describe the
parameter.
UINT Set to 0
object instances.
Bit 0 Supports Parameter
Instances
Bit 1 Supports Full Attrib.
Bit 2 Must do non-volatile store
Bit 3 Params in non-volatile
Instances
There are 18 instances of this object.
Table C.25 Parameter Object Instances
Read
Instance
1 No Transducer 1 Sensitivity Units USINT 0 = mils
2 No Transducer 2 Sensitivity Units USINT 0 = mils
3 No Eccentricity Measurement 1
4 No Eccentricity Measurement 2
Publication GMSI10-UM010C-EN-P - May 2010
Only Name Data Type Valid Values Default Value
USINT 0 = mils
Units
USINT 0 = mils
Units
0
1 = µm
0
1 = µm
0
1 = µm
0
1 = µm
Page 99

DeviceNet Objects 91
Table C.25 Parameter Object Instances
Read
Instance
Only Name Data Type Valid Values Default Value
5 No Eccentricity 1 Update Rate USINT 1-255 seconds 60
6 No Eccentricity 2 Update Rate USINT 1-255 seconds 60
7 No Relay 1 Alarm Identifier A USINT 0 = Alarm 1
0
1 = Alarm 2
8 No Relay 2 Alarm Identifier A USINT 0 = Alarm 1
0
1 = Alarm 2
9 No Relay 3 Alarm Identifier A USINT 0 = Alarm 1
1 = Alarm 2
10 No Relay 4 Alarm Identifier A USINT 0 = Alarm 1
1 = Alarm 2
11 No Relay 5 Alarm Identifier A USINT 0 = Alarm 1
1 = Alarm 2
12 No Relay 1 Alarm Identifier B USINT 0 = Alarm 1
1 = Alarm 2
13 No Relay 2 Alarm Identifier B USINT 0 = Alarm 1
1 = Alarm 2
14 No Relay 3 Alarm Identifier B USINT 0 = Alarm 1
1 = Alarm 2
15 No Relay 4 Alarm Identifier B USINT 0 = Alarm 1
1 = Alarm 2
16 No Relay 5 Alarm Identifier B USINT 0 = Alarm 1
1 = Alarm 2
17 No Poll Connection Produced
Connection Path
1
18 No Poll Connection Produced
Connection Size
1
USINT 101-104 (Assembly Object
instance number)
UINT 4 - 124 36
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
101
1 The Poll Connection Produced Connection Path and Size parameters cannot be set while the Poll connection is
already established with a master/scanner. Attempting to do so will result in an “Object State Conflict” error
(error code 0xC). These Parameter instances are a little more flexible than the actual Connection Object
attributes because they can be set while the connection is in the NON=EXISTENT state (before the master/
scanner allocated the connection).
Publication GMSI10-UM010C-EN-P - May 2010
Page 100

92 DeviceNet Objects
Table C.26 Parameter Object Instance Attributes
Attr ID
1 Set Parameter
2 Get Link Path Size USINT Size of Link Path 0 (These Parameter instances do
3
4 Get Descriptor WORD Description of Parameter Bit 0 = Settable Path support
5 Get Data Type EPATH Data Type Code See DeviceNet Specification
6 Get Data Size USINT Number of Bytes in
Instance Attributes
Access
Rule Name Data Type Description Semantics
Actual value of parameter See Table C.25 for a list of valid
Get
Value
Link Path ARRAY of
DeviceNet
path
Segment Type/
BYTE See DeviceNet
Port
Segment
Address
DeviceNet path to the
object for the Parameter
value.
Specification Volume 1
Appendix I for format.
See DeviceNet
Specification Volume 1
Appendix I for format.
Parameter value.
values for each instance.
not link directly to another
object attribute.)
Bit 1 = Enum Strings support
Bit 2 = Scaling support
Bit 3 = Scaling Links support
Bit 4 = Read Only
Bit 5 = Monitor
Bit 6 = Ext. Prec. scaling
Volume 1 Appendix J, Section
J-6.
Table C.27 Parameter Object Services
Service
Code Class/Instance Usage Name Description
0E
h
10
h
Publication GMSI10-UM010C-EN-P - May 2010
Services
Class/Instance Get_Attribute_Single Returns the contents of the
specified attribute.
Class Set_Attribute_Single Sets the contents of the
specified attribute.
1 Attributes can only be set while the device is in Program Mode. See the description of the Device Mode Object
for more information.
1
 Loading...
Loading...