Page 1

SERVICE
MANUAL
Models
EC06,EC08
1193s1 20
Page 2

ROBIN
AMERICA, INC.
ROBIN
TO
WISCONSIN
ROBIN
ENGINE
MODEL
CROSS REFERENCE
LIST
ROBIN
EY08
EY15
EY 15V
EY20
EY2OV
EY23
EY28
EY3
5
EY40
-
EY45V
EY2
1
EY44
EY 18-3
EY25
EY27
EH11
EH12
EH15
EH17
EH21
EH25
EH30
EH30V
EH34
EH34V
EH43V
EC13V
DY23
DY27
DY30
DY3
5
DY4 1
WISCONSIN
ROBIN
SIDE
VALVE
W
1-080
W1-145
W1-145V
W1-185
W1-185V
W1-230
W 1-280
W
1-340
W 1-390
Wl-45OV
EY21W
EY44W
EY18-3W
EY25W
EY27W
OVERHEAD
VALVE
WO1-115
wo1-120
WO1-150
WO1-170
wo1-210
WOl-250
WO 1-300
WO1-300V
WO1-340
WO
1
-340V
WO 1-43 OV
TWO CYCLE
WT1-125V
DIESEL
WRD
1-230
WRD
1-270
-1-300
WRD1-350
WRD1-410
0
0
0
Page 3

CONTENTS
Section
1 . SPECIFICATIONS
2
.
PERFORMANCE
2-1
2-2
2-3
3
.
FEATURES
4
.
DISASSEMBLY and REASSEMBLY
44-2
4-3
4-4
5
.
CONTACT BREAKER ADJUSTING PROCEDURE (EC06)
6
.
CARBURETOR ADJUSTMENT
7
.
GOVERNOR ADJUSTMENT
Maximum Output
Rated Continuous Output
Maximum Torque and Fuel Consumption Ratio
1
Preparations and Suggestions
Special Tools
.
Disassembly Procedure
Reassembly Procedure
Title
..............................................
................................................
........
:
.................................
..................................
at
Maximum Output
........
....................................................
..................................
..................................
.............................................
......................................
.......................................
..................
.....................................
.......................................
;
Page
.
1
2
2
2
2
4
5
5
5
6
9
13
14
15
8
.
TROUBLE-SHOOTING
8-1
8-2
8-3
8-4
8-5
8-6
8-7
9
.
CHECKS and CORRECTIONS
9-
9-2
10
.
MAINTENANCE and STORING
10-
10-2
10-3
10-4
10-5
Starting Trouble
Idling Improper
Overheating and Engine Knocking
Power Drop
Excessive Fuel Consumption
Hunt.ing
Other Troubles
1
Engine Standard Correction Table
Table of Tightening Torque
1
Daily Checks and Maintenance
Every
Every
Yearly Checks and Maintenance
Preparation for Long Abeyance
................................................
50
Hours Checks and Maintenance
150
Hours Checks and Maintenance
...........................................
...........................................
...........................................
...............................
:
.............................................
...................................
..............................................
......................................
...............................
...................................
.....................................
..................................
:
.........................
..........................
................................
.................................
16
16
19
19
19
20
20
20
21
22
24
25
25
25
25
25
25
Page 4

ECOGD
Fuel
Tank
Cap
Recoil Starter
Muffler Cover
Base
Engine
(optional)
Spark
Plug
overnor Lever
Governor Chamber
(Engine base
is
opti
n
onal.)
ECOGB
Page 5

Model
Bore
x
Stroke 44mmx40mm
Piston Displacement .60.8 cc 78.5 cc
ECOGD
Air-Cooled, 2-Cycle, Vertical, Piston Valve Type, Single Cylinder Gasoline Engine
ECOGB
I
I.
ECOID
50
mm
ECO~B
x
40
mm
Continuous Rated Output (HP/rpm)
Maximum Output (HP/rpm)
~~
Maximum Torque (kg-m/rpm)
.
Lubrication
~~
Lubricant
I
Carburetor'
Fuel Gasoline-lubricant Mixture (20- 25: 1)
Fuel Consumption Ratio (gr/HP-h)
Fuel Feed Gravity Type
Fuel Tank Capacity 1.5 iitres
Ignition System
Spark Plug
'Starting System
.
_-
.-
~ ~~~
1.6/3600,1.9/4500 11.6/1440, 1.9/1800
2.5/5000
I
0.38/3700
..
I
2.5/2000
.
0.95/1480. 0.51/3600 1.27li440
.'
Counterclockwise
~
Fuel-lubricant Mixture Type
I
390
at
Rated Continuous Output 380
Flywheel Magneto Type
(Contactless Magneto Type
also available.)
NGKB6HS
I
2-Cycle Engine Oil
I
I
as
viewed from
Float Type
is
I
Recoil Starter
2.2/4500
3.3/5500
P.T.O.
~~
Shaft Side Direction of Rotation
at
Rated Continuous Output
L.
Contactless Magneto Type
NGKB7HS
1
1
2.2/1800
3-3/2200
..
..
~ ~~
Speed Governor
Speed Reduction System
Reduction Chamber Oil
.Air Cleaner Semi-wet Type
Dry Weight
I
"
Dimensions
Length
Width 307
Height
..
-
-
mm
256
mm
287 mm 287
Centrifugal Flyweight Type
1/2.5 Reduction 1/2.5 Reduction
Gear Gear
SAE #30
285
mm
307
mm
.
mm
-.
-
256
mm
307
mm
287
mm
-
SAE#30.
285
307
287
mm
mm'
mrn
Page 6
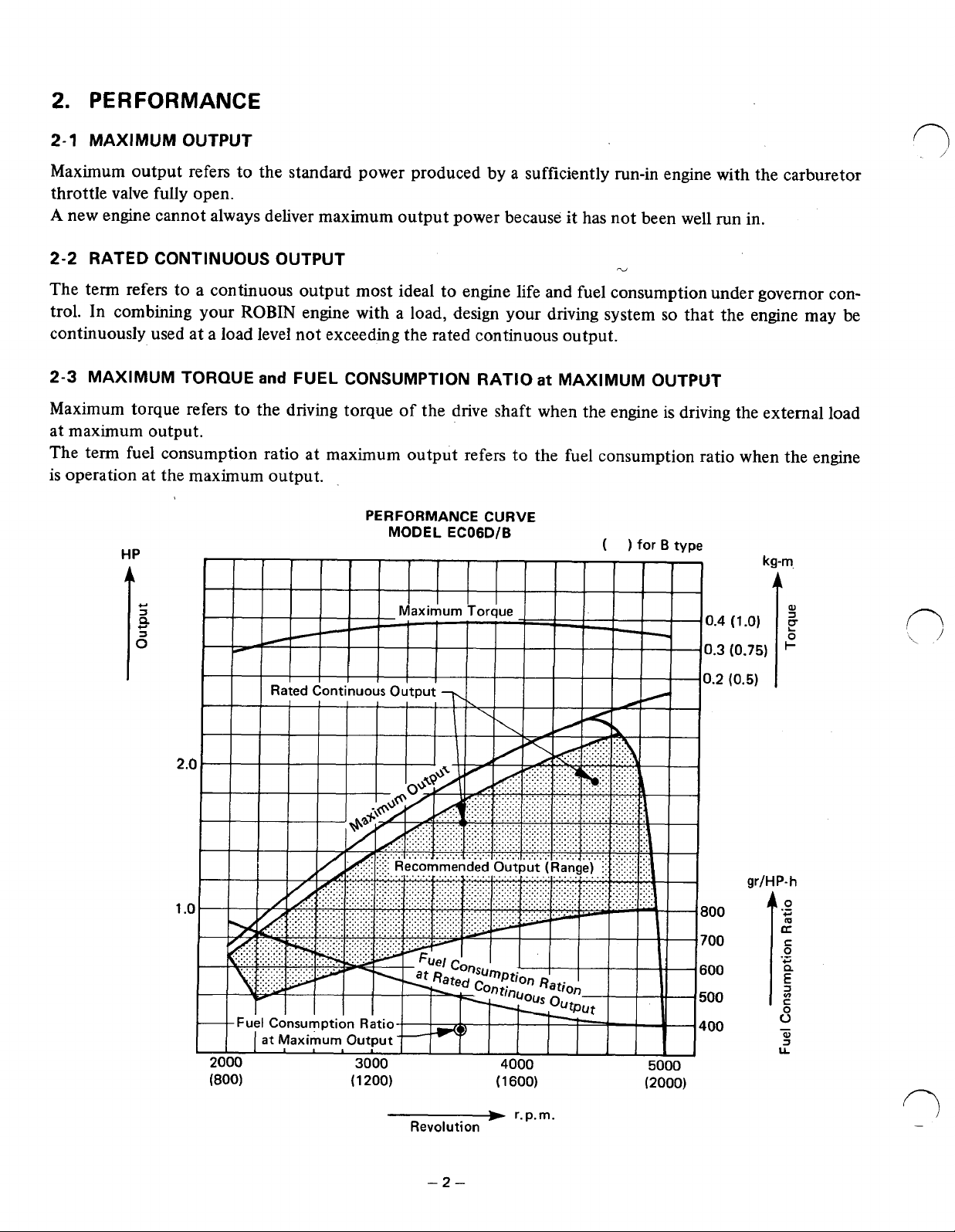
2.
PERFORMANCE
2-1
MAXIMUM OUTPUT
Maximum output refers
throttle valve fully open.
A
new engine cannot always deliver maximum output power because it has not been well run in.
2-2
RATED CONTINUOUS OUTPUT
The term refers to a continuous output most ideal to engine life and fuel consumption under governor con-
In
trol.
continuously used at a load level not exceeding the rated continuous output.
combining your
to
the standard power produced by a sufficiently run-in engine with the carburetor
ri/
ROBIN
engine with a load, design your driving system
so
that the engine may be
0
1
2-3 MAXIMUM TORQUE
Maximum torque refers to the driving torque of the drive shaft when the engine
at maximum output.
The term fuel consumption ratio at maximum output refers
is operation at the maximum output.
HP
w
2
P
+
and
FUEL CONSUMPTION RATIO
PERFORMANCE
MODEL ECOGD/B
to
CURVE
at
MAXIMUM OUTPUT
the fuel consumption ratio when the engine
(
1
for B type
6
I
is
driving the external load
(1
200)
--W
Revolution
-2-
(1
600)
(2000)
r.p.m.
Page 7
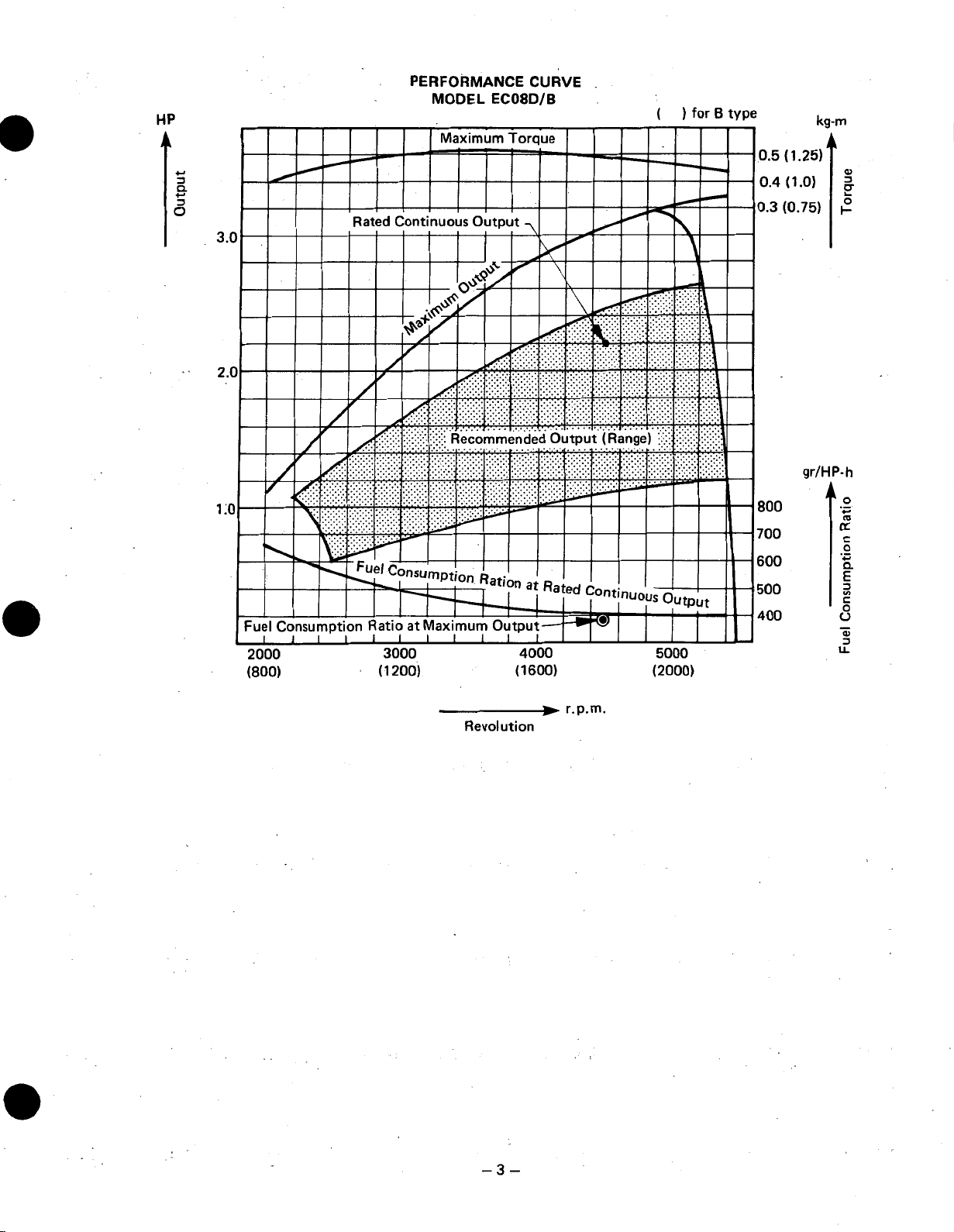
HP
PERFORMANCE
MODEL
EC08D/B
CURVE
.
( )
for
B
type
(
1.25)
kg-m
W
(0.75)
gr/H
P-
h
(1
200)
--*
Revolution
(1
600)
(2000)
r.p.m.
-3-
Page 8

3.
FEATURES
Compact, lightweight, high-powered engine with reliable operation also in the low speed range
1.
2.
Extremely simple in construction, trouble-free, and very easy
Quiet running engine using a lined aluminium cylinder
3.
4.
Equipped with T.C.I. (Transistor Circuit Ignition)
5.
So
durable that the engine can stand hours of tough work.
Needle bearings are used for the crank pins and piston bearings to enable the engine to withstand high-
speed operation under heavy load.
The carburetor works at inclinations of up to aboaut
6.
overflows from its air vent.
The recoil starter permits easy starting.
7.
Useful in a wide range of applications
8.
A
direct-coupled, reduction type engine, and other types that differ from the standard models in drive
shaft dimensions and shape are also available.
The all-speed governor operates at any engine speed.
9.
The desired rpm. can be obtained by simply moving the control lever, and it remains constant even if
the load changes.
Resistant to vibration (EC08)
IO.
Manufacturers of rammers and plates (machines
are using these ROBIN engines.
(EC06)
30"
for
compacting earth by vibration) around the world
to
use
so
that the engine can operate until the fuel
-4-
Page 9

m
4.
DISASSEMBLY
4-1
PRE-PARATIONS
.Disassembly
-1)
In"disassembling, remember the location
in the right way. Attach tags to those parts which might be mistaken for others.
and
REASSEMBLY
and
SUGGESTIONS
of
each part
so
that the disassembled partsEcan be reassembled
...
..
,.
2) Carefully handle the gaskets because they can easily break.
3)
Temporarily fasten disassembled parts in their original positions to prevent them from missing and wrong
reassembly.
4)
Carefully handle disassembled parts and clean them with kerosene.
5)
Use thecorrect tools in the correct way.
6)
Items necessary for disassembly and reassembly
pan
oil
before disassembling.
7)
a. 'Work bench b. Kerosene
e.
Be sure
sandpaper,
to
discharge the'fuel and
spatula, waste cloth
I
c. Disassembly tools d. Kerosene or gasoline
1
-
1.
..
..
.Reassembly
1)
Use new packing and gaskets in reassembling the engine.
2) Clean the parts with fresh gasoline, and blow them dry with compressed air before reassembling.
3)
Apply 2-cycle oil to the rotary and sliding parts.
4)
Keep the.parts free
of
dust during reassembly.
Tighten.the bolts, nuts, and screws.with the specified torques.
5)
Each'time a set
6)
After reassembling the engine, turn
of
main parts is installed, manually'turn it and check for smoothness and noise.'
it
manually and check
for
abnormalities and looseness.
.
.
I
4-2
SPECIAL TOOLS
.
.%
"
..
..
..
Flywheel
Fig.
Pulley
1
Page 10
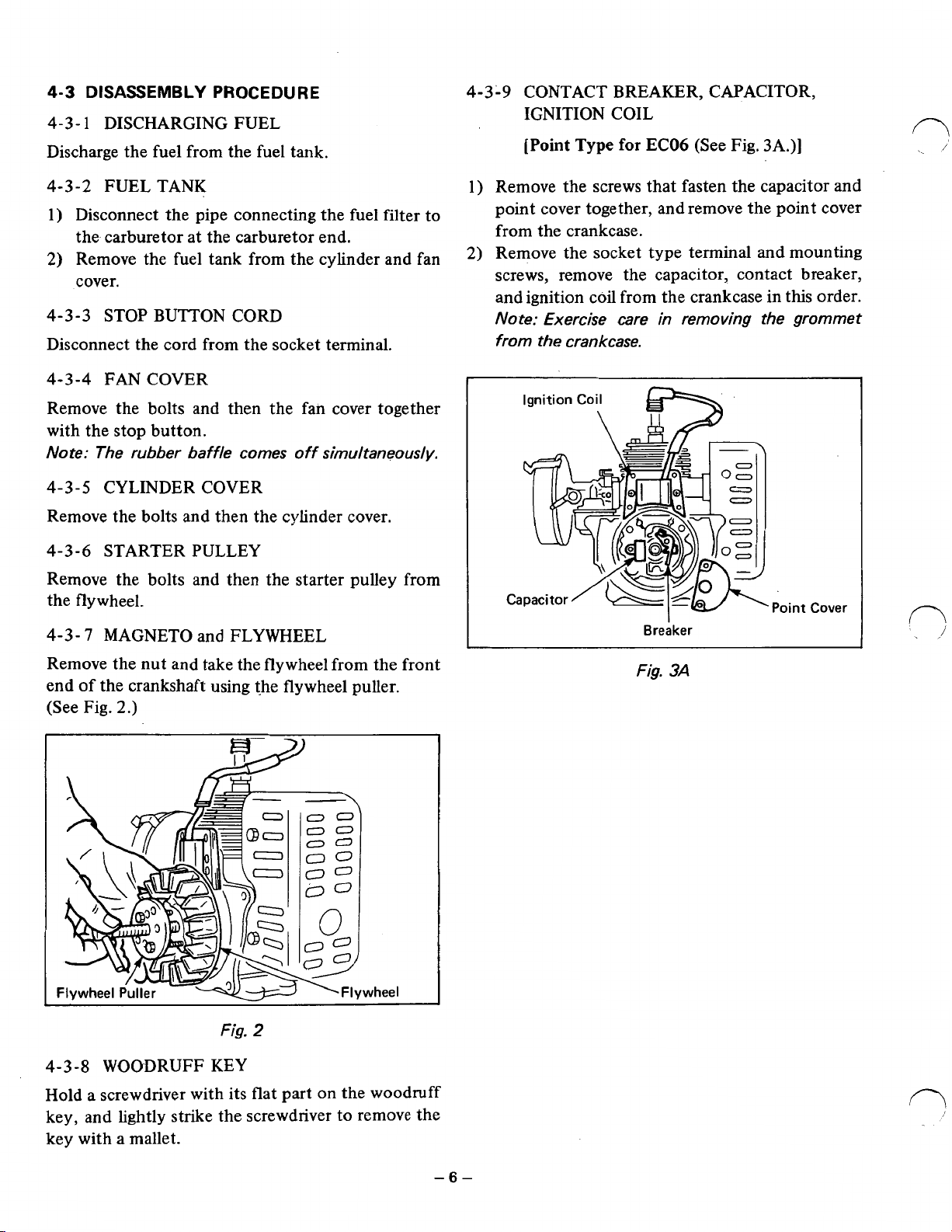
4-3
DISASSEMBLY
4-3-
1
DISCHARGING FUEL
PROCEDURE
Discharge the fuel from the fuel tank.
4-3-9
CONTACT BREAKER, CAPACITOR,
IGNITION COIL
[Point
Type
for
EC06
(See Fig.
3A.)]
n
\/
4-3-2
FUEL TANK
1) Disconnect the pipe connecting the fuel filter to
the carburetor at the carburetor end.
2)
Remove the fuel tank from the cylinder and fan
cover.
4-3-3
STOP BUTTON CORD
Disconnect the cord from the socket terminal.
4-3-4
FAN COVER
Remove the bolts and then the fan cover together
with the stop button.
Note: The rubber baffle comes off simultaneously.
4-3-5
CYLINDER COVER
Remove the bolts and then the cylinder cover.
4-3-6
STARTER PULLEY
Remove the bolts and then the starter pulley from
the flywheel.
4-3-
7
MAGNETO and FLYWHEEL
1) Remove the screws that fasten the capacitor and
point cover together, and remove the point cover
from the crankcase.
2)
Remove the socket type terminal and mounting
screws, remove the capacitor, contact breaker,
and ignition coil from the crankcase in this order.
Note: Exercise care in removing the grommet
from the crankcase.
Ignition
Coil
Breaker
Point
Cover
Remove the nut and take the flywheel from the front
end of the crankshaft using the flywheel puller.
(See Fig.
4-3-8
2.)
Fig.
WOODRUFF KEY
2
Hold a screwdriver with its flat part on the woodruff
key, and lightly strike the screwdriver to remove the
key with a mallet.
Fig.
3A
-6-
Page 11

[
T.
C.
I.
(Transistor Control Ignition) magneto]
1
)
Features
The T.C.I. magneto completely solves the prob-
lems with the conventional point type magneto,
is,
that
ignition timing deviation due to mechanical wear,
etc.
2)
Construction
The components
shown in Fig.
are explained.
stains, burns, rusting during long storage,
of
the magneto assembly are as
3B.
T.C.I.
The main parts
Unit
Generating Assembly
of
the magneto
Flywheel Complete
./
FLYWHEEL COMPLETE
The FLYWHEEL COMPLETE has perma-
so
nent- magnets
magnets generates an AC electromotive force
in the primary coil
bly.
GENERATING ASSEMBLY
The GENERATING ASSEMBLY consists
the primary coil and secondary coil. The rotation
erates a voltage in the primary coil and feeds
a current. At the same time a high voltage
induced in the secondary coil. This high voltage causes the spark plug
T.C.I. UNIT
The T.C.I.
and
primary current waveform generated in the
GENERATING ASSEMBLY,
the transistor
rent.
This abrupt current change causes a high voltage to be induced in the secondary coil.
of
the FLYWHEEL COMPLETE gen-
other semi-conductor parts. It senses the
that the rotation of these
of
the generating assem-
to
spark.
UNIT
consists maily
to
cut
off
and
the primary coil cur-
of
an SCR
switches
of
is
~
Fig.
3B
3)
Wiring diagram
Prim r Wir
r
Plug
Spark
-
T.C.I.
Unit
-7-
*
Assembly
Fig.
3C
Page 12

4-3-
10
CARBURETOR, GOVERNOR LEVER
4-
3 - 13
REDUCTION GEAR (Type B only)
1) Remove the nut and then the carburetor from
the cylinder.
2)
Loosen the nut, and remove the governor lever
from the governor shaft.
3)
Remove the governor spring from the governor
lever.
c
Carburetor
Governor Lever
L
1) Remove the drain plug from the reduction chamber to discharge the
2)
Remove the reduction chamber cover from the
oil.
engine.
3)
Remove the nuts, and pull the reduction pinion
out from the crankshaft.
(See Fig.
4)
Remove the woodruff key.
Reduction Cover
6.)
%@"
Reduction Pinion
eduction Chamber
'Drain Plug
%
Woodruff Key
Fig.
4
4-3-
1
1
SPARK PLUG
Remove the spark plug using a box wrench.
4-3
-
12
MUFFLER (MUFFLER
COVER)
Remove the nuts, and then the muffler from the cyl-
Nut
5.)
p/
Muffler Cover
inder. (See Fig.
Note: Keep the muffler cover on.
Fig.
6
4-3-14
CYLINDER
Remove the nuts, and carefully lift the cylinder off,
exercising care not to damage the contact surfaces
of
the piston and cylinder. (See Fig.
Note: Hold the piston when the cylinder
a
certain height from the crankcase,
cylinder off the piston. Damage to them can be prevented this way.
Cylinder
7.)
and
is
lifted
raise the
rankcase
to
n
\
fig.
5
-8-
Fig.
7
Page 13

4-3-
15 DIVIDING CRANKCASE
4-4
REASSEMBLY
PROCEDURE
Remove the bolts, and carefully strike the crankcase
with a mallet to part it. (See Fig.
8.)
Clean the divided crankcase with gasoline, and apply
engine oil to the bearing, and grease to the oil seal
lips.
Note: Be careful not to damage the crankcase joint.
\
Rear Crankcase
I
Crankshaft
Fig.
8
Fro"; Crankcase
4-4-1 CRANKSHAFT COMPLETE and PISTON
Apply engine oil to the needle bearing, and fit
it
onto
the small end of the connecting rod. With the mark
M
on the piston head on the flywheel (magneto) side,
fit
the piston head on the piston. Apply engine
oil
to
the piston, and lightly strike the pin into the piston
with a mallet (until the pin
is
poisitoned inward
of
the clip grooves). Then fit two clips into the clip
10
grooves. (See Fig.
Note: Be careful not to damage the piston pin hole
in the piston. Be sure to use new clips. The mark
must be in the direction of the front
crankshaft.
.)
M
end
of the
4-3- 16 PISTON, PISTON PIN, NEEDLE BEAR-
ING, and CLIPS (See Fig.
Remove the clips. With a iron rod
9.)
10
to 1 1 mm in
diameter on the piston pin, lightly strike it with a
plastic Hammer to remove the piston pin. Pull out
the iron rod, and remove the piston and needle bearing.
Note: Be careful not to damage the.piston pin hole
in
the piston.
Fig.
-10
.
I
4-4-2 INSERTING CRANKSHAFT INTO
CRANKCASE
Place the rear half
of
the crankcase
on
the work
bench securely, and insert the crankshaft into the
crankcase bearing by hand.
Note: See that the front and rear halves of the crank-
case can
4-4-3
Wipe the joint surfaces
of
from them, apply a sealant
be
reassembled properly.
CRANKCASE REASSEMBLY (See Fig.
of
the front and rear halves
1
the crankcase until oil is completely removed
to
them, and with the
1.)
dowels in line with their matching holes, reassemble
the crankcase.
Note: Exercisegood care not to damage the governor
sleeve, yoke assembly, and oil seals. Keep the joint
surfaces of the front and rear halves of the crankcase
parallel to each other
the original assembly.
in
pressing them together into
-9-
Page 14

Crankshaft
Rear Crankcase
\
Governor
Yo
1
ke
4-4-7
I
Tighten the spark plug into the cylinder.
Note: Tightening torque.
4-4-8
Tighten the governor lever to the governor shaft with
the nut. (For the adjusting procedure, refer to the
section on governor adjustments.)
SPARK PLUG
.
. .
GOVERNOR LEVER
. .
.
275
+25
kg-crn
E
I
Front Crankcase
4-4-4
Tighten the bolts with spring washers and plain washers.
Note: Tightening torque
4-4-5
Replace the old cylinder gasket with a new one, apply oil to the cylinder and piston, make sure that the
piston
and install the cylinder.
Note: Be careful not to let the gasket slide
place.
Governors'
Fig.
CRANKCASE
CYLINDER REASSEMBLY
rings
and
cylinder are positioned correctly,
Cylinder
I
1
1
.
. . . . .
1
10
(See
'I
f
20
kg-cm
Fig. 12.)
out
of
4-4-9
Hook the governor spring to the governor lever and
governor. (See Fig.
Note: Be careful of the hooking positions.
4-4-
GOVERNOR SPRING
13.)
/
Governor Lever
Fig.
10 CARBURETOR
Governor Spring
(attached
13
to
bottom)
n
Fig.
12
4-4-6
Tighten the nuts with spring washers and plain washers.
Note: Tigtening torque.
CYLINDER TIGHTENING
.
. . . . . .
Tighten all the four nuts evenly.
1
10
k
IO
kg-crn
-
a
Replace the old gasket with
the carburetor.
Note: Tightening torque
4-4-
11 MUFFLER (MUFFLER COVER)
Replace the old gasket with a new one, and tighten
the muffler to the cylinder.
Note: Tightening torque
4-4-
12 WOODRUFF
Drive the woodruff key into the keyway in the crankshaft using a mallet.
Note: Drive it parallel
4-4-
13
IGNITION
TIGHTENING
With the high-tension cord (to be connected
spark plug) up, temporarily tighten the ignition
10
-
.
. .
KEY
to
the shaft axis.
COIL
new one, and install
.
.
.
. . . .
80
2
.
. . . .
.
80
f
TEMPORARY
IO
IO
kg-cm
kg-cm
to
n
the
coil.
Page 15

4-4-
14
CONTACT BREAKER (POINT)
CAPACITOR (EC06)
Install the contact breaker by inserting'its shaft into
the matching hole in the rcrankcase. Pass the cord
under the capacitor into the cord hole in the crankcase.
Temporarily tighten the capacitor.
4-4- 15 IGNITION TIMING CHECK (EC06)
Temporarily install the flywheel, and check and ad-
just the ignition timing.
(For ignition timing adjustment, refer to the section
on contact breaker adjusting procedure.)
Note: Ignition timing
...............
23"
k2'
4-4-
17
FLYWHEEL (MAGNETO)'
Install the flywheel on the crankshaft by tightening
the nut'with plain and spring washers.
Note: Completely remove oil from the tapered por-
tion.
Tightening torque
.......
400
k
20
kg-cm
4-4- 18 IGNITION COIL
Adjust the air gap with a searcher, and tighten the
ignition coil with plain and spring washers. (See Fig.
15.)
Note: Air gap.
Tightening torque
....
.0.5
foe.
..........
mm
50
f5
kg-cm
4-4- 16 POINT COVER (EC06)
,
,'
Remove the flywheel, fit the point-to-capacitor lead
into the crankcase groove, and install the.point cover. (See Fig. 14.)
Tighten the temporarily tightened capacitor securely.
Note: Tightening torque
Lead
Capacitor Lead
Primary Wire
Turn primary wire once and
pull
it in direction
A.
.........
Wiring Method
Crankcase Groove
II
-./
I
w
I
25
f
2
kg-cm
//
I
Capacitor lead
primary wire here.
Fig.
14
is
above
15
Fig.
4-4-,19 STARTER PULLEY
to
Tighten the starter pulley
the flywheel with the
bolt. (Use plain and spring washers.)
Note: Tightening torque
........
90
f
IO
kg-cm
4-4-20 FAN COVER, STOP BUTTON,
GROMMET (See Figs. 16 and
Install the stop button with lockwasher
17.)
on
the fan
cover. Insert the high-tension cord into the grommet, and install baffle rubber on the fan cover. Fit
the grommet into the fan cover groove and, with the
tip
of
the rubber baffle at the round boss
in
the
crankcase, fasten the fan cover on the crankcase
with the bolt.
Note: Be careful not to pinch the stop button cord
fan
between the crankcase and
care not to drop the rubber baffle during fan cover
reassembly.
Tightening torque
.L
........
cover.
90
Also
2
10
exercise
kg-cm
-11
-
Page 16

4-4-21
CYLINDER COVER
Insert the cylinder cover tips into the matching slots
in the crankcase, and tighten the cylinder cover on
the cylinder. (See
Note: Insert the cylinder cover tips in
both sides.
Tightening torque
Fig.
18.)
.
. . .
. . .
.
80
to
f
the
10
slots
kg-cm
on
(Position
Fig.
16
Buffle
Whichever type, D or
the
punched marks on the crankcase in reassembing.
Flat surface inside
Note:
Rubber
Type
Install
right
installing Method
B,
your engine
Punched Mark (case)
Baffle Rubber
D
of
is,
Wider end up
the magneto.
in
Model
be careful of
Dl
4-4-22
Cylinder Cover
FUEL
TANK
Installing Method
Crankcase
Fig.
18
Insert the fuel pipe into the carburetor, clamp it,
fan
10
cover.
kg-cm
and mount the fuel tank on the cylinder
Note: Tightening torque
. . . .
. . . .
90
f
f7
,’
Wider end up
Punched Mark (case)
Flat surface inside
Baffle Rubber
Type
,
.Note:
Install left
fig.
of
the magneto.
17
-
12
-
Page 17

5.
CONTACT
1)
Remove the fan cover.
2)
Remove the starter pulley.
3)
Remove the flywheel.
4)
Loosen the capacitor screws.
5)
Remove the point cover.
6)
Remove carbon and other foreign particles from the point, polish-the contact surface with sandpaper
No.400
7)
Temporarily fasten the flywheel, bring the mark F in line with the matching mark on the crank case, and
remove the flywheel, exercising care not to turn it.
8)
Now, in this state, adjust the contact breaker
or equivalent, and wipe dirt off with a cloth.
BREAKER
ADJUSTING PROCEDURE (EC06)
as
shown below. (See Fig. 19.)
Mark
Fig.
19
Note: If the points are open in the sate illustrated above, ignition timing goes wrong
Be careful not to move the points especially when tigtenirig the breaker mount screw.
.
Ignition timing
a). Loosen the breaker mounting screw.
b) Push the breaker in the arrow direction
timing tester, for example), and tighten'the breaker mounting screw.
c) After the point adjustment, install the point cover, capacitor, magneto, and fan cover in this order.
. . . . .
. . . . . .
.
. . . .
. .
.
.I.
. .
.
.
.
. .
23"
*2''
to a position just before the points begin
to
a serious extent.
to
open (using a
-
13
-
Page 18

6.
CARBURETOR ADJUSTMENT
The carburetor is carefuuly adjusted in the factory before shipment. Never attempt to adjust it except when
necessary.
n
I
1) Idling Adjustment (See Fig.
20.)
Move the governor lever to the lowest speed position
(so
that the carburetor throttle valve fully
closes), and check that the engine idles quiet and
smooth. This is the ideal idling condition. Normally, the engine is set to an idling speed of 1600
k
100
rpm, for which the following two methods
may be used.
a) Low-speed stopper screw
Engine speed increases if the low-speed stopper screw
on
the carburetor is turned clockwise, or decreases if it is turned counterclockwise.
b)
Pilot screw (Do not turn it except
when necessary.)
When the pilot screw
is
turned clockwise,
the fuel-air mixture decreases and the engine
slows down. If the pilot screw is turned counterclockwise, the fuel-air mixture increases
to raise engine speed. The normal position
the pilot screw
is
one turn and a quarter back
from the clockwise extremity.
of
Fig.
20
2)
Maximum Speed Adjustment (See Fig.
The standard maximum speed
EC06,
or
5500
rpm for EC08.
is
2
5000
Move the governor lever to the highest speed
position, adjust the crankshaft rpm to
(EC06) or
5500
(EC08) with the high-speed
stopper bolt, and lock the bolt with the nut.
1.)
rpm for
5000
Low Speed
Fig.
21
Governor
Lever
-
14
-
Page 19

7.
GOVERNOR ADJUSTMENT
Fully open the carburetor butterfly valve, fasten the
governor lever, turn the governor shaft fully counterclockwise, and fasten the governor lever on the
ernor shaft with the nut. (See
Figs.
22
and,23.)
gov-
Fig.
22
Governor Rod Spri
Throttle Lever
Governor Lever
Crankshaft
Governor Rod
Carburetor
eed
Stopper
Bolt
Governor
Sleev
Control Lever
Fig.
-
15
23
-
Page 20

8.
TROUBLE-SHOOTING
The following three conditions must be satisfied for satisfactory engine start:
1)
The cylinder filled with a proper fuel-air mixture
2)
An appropriate compression in the cylinder
3)
Good
spark at correct time to ignite mixture
The engine cannot be started unless these three conditions are met. There are also other factors which make
engine start difficult, e.g., a heavy load on the engine when it
is
about
to
start at low speed, and a high back
pressure due to a long exhaust pipe, just to say a few,
The most common causes of engine troubles are given below:
8-1
STARTING
Trouble
No
or little
spark
TROUBLE
Cause
Spark plug defective
High-tension cable
defective
Contact breaker
defective
I
I
(1)
If spark plug is dirty, clean it well with gasoline
or polish it with sand-paper. Remove foreign
matter if any.
(2)
Adjust spark gap to
(3)
If spark plug hasfaulty instulation due to
breakage, replay it with a new one.
If defective, replace the cable and ignition coil
together.
(1)
If points are rough, polish them with sand-
No.
paper
(2)
If point gap is wrong, loosen contact mount
screw, and adjust it to
Also
adjust ignition timing if possible.
(3)
If ignition timing is wrong, adjust it to
23' f 2'
(4)
If breaker has faulty insulation, replace
the breaker with
(5)
If capacitor is defective, replace
a new one.
Remedy
0.6 - 0.7
400.
before top dead center.
a
new one.
mm.
0.35 ? 0.05
it
mm.
with
Preventive hints
(1)
Use a spark plug of the speci-
Do
fied heat value.
low-quality oil. Clean the air
cleaner to prevent dust from
entering.
(2)
Be carefid not to strike the
center pole or forcibly twist
it in adjusting spark gap.
Otherwise, insulation breaks
down.
not use
-
16
-
Page 21

rrouble
Vo
or little
;park
No
or
little compression
Cause
Magneto defective
Electrical system
defective
Fuel leaks from
gaskets
or
other
Piston defective
Remedy
(1)
If coil is broken or its insulation defective,
replace magneto with a new one.
(2)
If magnetism
has
decreased, have it remagnetized at magneto manufacturer's or
replace magneto.with
~~ ~ ~~
(1)
If stop button is defective (grounded),
a
new one.
repair or replace it.
(2)
If primary wire is grounded to the engine
body, insulate it with tape.
(1)
If head gasket is defective, replace it
with a new one.
(2) If spark plug is loose, retighten it securely.
(3)
If spark plug is defective, replace
it
with
a new one.
(1)
If piston is worn, replace it with a new one.
(2) If piston rings are worn, replace them
with new ones.
Preventive
[l)
Keep air cleaner clean.
:2)
Do
not use lowquality oil.
(3)
Change
oil
periodically.
hints
No
fuel
feed
Excessive
fuel
suction
Fuel tank defective
Carburetor
defective
Carburetor
defective
(1)
Clean tank outlet if clogged up.
(2)
Clean fuel strainer if clogged up.
(3)
If wrong fuel is used or if water is in fuel
tank, change fuel.
(4)
If air is trapped in fuel pipe, discharge air.
(1) Clean carburetor if clogged up.
(2) Replace carburetor with a new one if
defective.
if
Clean jets and orifices
(1)
Fully open choke, half open throttle valve,
clogged up.
'
and start engine.
(2j Remove crankcase drain plug, close fuel cock,
actuate starter a few times to discharge
excess fuel.
(1)
If carburetor overflows, check needle
valve seat for wear, and replace if
necessary.
(1)
Pour fuel into the fuel tank
through filter.
(2)
Use gasoline-oil
(25
mixture.
(1)
Never close choke if engine
is warm.
(2)
Be sure to idle engine for
some time before stopping it.
This'not only
makes
starting easy but helps extend
engine life.
(3)
Completely clean air cleaner
because a clogged up
cleaner thickness
fuel.
to
next
air
1)
.
Excessive
resistance
to starting
Excessive load
Piston or
connecting rod
sticky
(1
j
Adjust power transmission belt tension
if
too high.
(2)
If it is still hard to start, install a clutch.
(1)
If
piston
is
sticky, replace it with a new one.
If
connecting rod is sticky at large or
(2)
small end, replace it with a new one.
-
17
-
(1)
Do
not use lowquality oil.
(2) Use-fuel of correct gasoline-
oil
ratio.
Page 22

Spark plugs won't spark.
w
OK
-
Wire connector loose
L
Connect connector securely.
Not
~
on engine
-
OK
T.C.I. unit faulty
Generating assembly faulty
1)
Continuity test on T.C.I. unit
Conduct this test using the T.C.I. unit checker (Part
No.106
Select either
79902
AC
or
00).
DC.
(Battery
stalled inside.)
Connect the unit's primary lead (black
for
type
D,
or yellow for type
E
(black) and the unit casing (or the
B)
crankcase if the unit is mounted on the
engine) to jack
C
(red) with the supplied
cable.
Turn the select dial to the position cor-
respoilding to the,engine type.
Keep the check switch
in
the
ON
tion, and wait until the pilot lamp
lights.
Wire damaged
securely mounted
is
in-
to jack
Check Switch Select
posi-
(LED)
Mount it on engine securely.
Conduct continuity test on
T.C.I.
Conduct continuity test on
coil. [See
Robin Checker
Fig.
Replace damaged parts.
for
Dial
24
T.C.I.
Spark
unit. [See
5.2).]
Gap
5.
I).]
Unit
Check Window
wer
Select
Switch
i
r"\
\I
-
la
-
Page 23

e) When the pilot lamp turns on, return the check switch to the
OFF
position. The
normal if a spark is observed at that instant.
If the T.C.I. unit checker is not available, use
"i) Connect the positive
Connect the negative
Resistance:
80
*ii) Connect the negative
Connect the positive
7
Resistance:
If
the
T.C.I.
2)
Continuity test on generating assembly
unit is found not normal by the above test, replace the unit.
to
(+)
terminal
(-)
terminal of the tester to the unit casing.
to 150 ohms (Tester range
(-)
terminal
(+)
terminal
10 k oiims
(Tester range
of
of
a
circuit tester as described below.
the tester to the primary lead.
x
1
ohm)
of
the tester to the p$mary lead.
the tester to the unit casing.
x
100
ohms)
Measure the resistance with a circuit tester.
a) Resistance between primary lead and core:
b) Resistance between secondary lead and core:
1.1
to 1.5 ohms
10
to
13
k ohms
'
If the generating assembly is found not normal by the above test, replace the assembly.
Note: A circuit tester is not
pending on the type
so
accurate that the resistance values measured by the tester may vary de-
of
tester, or the condition
of
battery, or the skill of operator.
T.C.I.
-
unit is
-
0
8-2
IDLING
1)
If the carburetor's pilot screw is not correctly adjusted, adjust it. (Refer
IMPROPER
adjustments.)
2)
Any
of
starting trouble causes leads to improper idling.
8-3
OVERHEATING
1)
If
ignition timing is advanced, adjust it to
2)
If
the cmbustion chamber has excessive carbon deposits, clean it.
3)
If a spark plug
for EC06,
4)
If the gasoline air-mixture is
NGK
and
ENGINE KNOCKING
23"
*
2".
(EC06)
'
of
a heat value too low is used, use one of the specified heat value. Example:
B7HS
for
EC08
too
lean, clean the jets and orifices
of
the carburetor.
cleaner.
5)
If
overload is the case, reduce it to normal level or below.
8-4
POWER
1)
Replace the cylinder, piston, and/or piston rings if worn.
2)
If
the carburetor is faulty, adjust or clean it.
3)
If the spark plug is faulty (dirty, leaky, or not properly insulated), clean or replace it.
4)
Retighten the cylinder if gas leaks.
5)
Replace or adjust if the magneto
6)
Clean the air cleaner if clogged up.
7)
Replace the crankshaft oil seals
DROP'
or
contact breaker is faulty.
if
compressed gas leaks due to seal wear.
to
the section on carburetor
NGK
Also
clean the air-
B6HS
-19-
Page 24

8-5
EXCESSIVE FUEL CONSUMPTION
1)
If the gasoline-air mixture fuel is too rich, clean the carburetor jets and orifices.
2)
Replace the carburetor if its throttle shaft is worn.
3)
Retighten or replace parts if fuel leaks.
4)
Take the steps against power drop described in Paragraph
also results from power drop.
8-6
HUNTING
1)
If the governor lever, governor shaft, or governor spring is not properly set or adjusted, readjust or correct it.
2)
If the mixture fuel is too lean, clean the carburetor.
3)
If the carburetor pilot screw is the cause, readjust it.
4)
If the governor spring is worn, replace it.
5)
If the governor sleeve does not work properly, correct it.
6)
Replace the flyweight or governor sleeve if
7)
If
the governor shaft does not work properly, correct it.
8-7
OTHER TROUBLES
worn.
8-4
above because excessive fuel consumption
1)
Carburetor overflow
If
the fuel overflows the carburetor to the air cleaner, or collects excessively in the crankcase during
stoppage, either the float valve or float is faulty. Replace or correct the faulty one.
2)
If the engine abruptly stops with an abnormal noise, it is due to a sticky piston, crankshaft, or connecting rod. Adjust or replace the faulty parts.
3)
If
any abnormal noise
start the engine again until the cause is determined.
If you cannot find the cause, contact your nearest dealer or service shop, and observe their advice.
is
heard during engine operation, be sure to stop the engine immediately.
Do
not
f"\
/
-
20
-
Page 25

..
..
. .
':
0.
-.
._
.
.
.
..
..
..
..
..
..
.I
'9.
CHECKS
~-
-.
.
.
After disassembiing and cleaning the'engine, check and adjust the parts according to the Standard Correction
.
;Table, .-which provides important information to be referred to in adjusting
'
.
;.fWiliar-with the table and conform to the.standards specified in servicing the engine.
"
.
..
I.
.
...
.-
,%
and
..
.
.j
.
CORRECTIONS
.."
...
I
.
,.
,
.I
8
...
.,
,,
-.,
or
repairing the engine. Be
The terms used in the table are defined as follows:
.
1)
-
Correction
Repair, adjustment, or replacement of any engine part
2)
Correction limit
'
-
The limit
.
of
wear, damage,
.-
or
function degradation beyond which an engine part can hardly serve its
purpose unless if is corrected.
.
:
3)
Standard dimensions
Design dimensions less tolerance
..
-21
-
Page 26

9-1
ENGINE
STANDARD
CORRECTION
TABLE
Measuring/Correcting
I
Point Model
Clearance between
piston and cylinder
Bore EC06
dia.
Piston ring
side clearance
Correction
T
EC06 0.18L Calculate from parts
EC08
Standard Dimensions
Perpendicular to pin
0.07-0.1
Pin direction
0.09-0.146L
Perpendicular to pin
0.04-0.076
Pin direction
0.07-0.1 26L
06L
L
tO.016
0
44@
EC08
M.016
0
Limit
+0.08
Measuring
measurements.
Average
and minimum
of
maximum
inside diameters
5w
EC06
EC08
EC06
43.930
49.960
First ring
0.05-0.09L
Second ring
0.04-0.08L
-0.05
0.1 5L
Average
and minimum outside
diameters
Measure after
removing carbon.
of
maximum
Instrument
Cylinder gauge
Micrometer
Searcher
Correction
/
Replace
Replace
Replace Piston outside
Replace
EC08
Piston ring
groove width
Piston ring width Em, EC08
Ring
gap
Clearance between
piston and piston
pin
Piston pin
Piston pin
outside diameter
hole
EC06, EC08
EC06, EC08
EC06, EC08
EC06, EC08
EC06, EC08
First ring
0.06-0.1OL
Second ring
0.03-0.07L
1.8
1.8
0.1
-0.3
0.005T-0.014L
4-0.13
-0.10
.o
1
0.03L Calculate from parts
-0.017
Measure maximum
groove width.
Measure minimum
Lvidrh.
Ring in contact with
cylinder wall
measurements
Measure maximum
inside diameter
~~ ~~
Measure minimum
outside diameter.
Block gauge Replace
Replace Micrometer
Searcher Replace
Replace
Cylinder gauge
Micrometer Replace
Replace M.03
-
22
-
Page 27

MeasuringlCorrecting
I
Point
Model Standard Dimensions
Correction
Limit
Measuring instrument
Correction
Connecting rod
large end side
clearance
Crankshaft
deviation
Crankshaft
axial play
Main bearing
outside
diameter
Housing inside
diameter
Bearing outside
diameter
Main bearing
outside diameter
clearance
EC06, EC08 0.1
~
EC06. EC08
EC08
EC06,
EC06,
EC08
EC06, EC08 Front case
EC06, EC08 Measure bearing
EC06, EC08
-0.6L
0.05 or less
0.1 5-0.69
0.050T-0.01.4T
47@
Rear case
Front case 470
Rear case
Front
0.013T-0.006L
Rear
0.01
420
420
T-0.009L
0.8
L
0.1
0.1
0
-0.04
-0.016
0.01
0.01
2L
5L
Measure after
reassembly
in
reassembled state,
support both ends
of
crankshaft, and
measure
7.5
web.
Measure after
reassembly.
Calculate from
parts measurements
Housing
outside diameter
Calculate from parts
measurements.
it
mm
from crank
about
Searcher
Dial gauge
Dial gauge
Cylinder gauge
Micrometer
Replace
Replace
Replace
Replace
Replace
Replace
Bearing inside
diameter
Crankshaft outside
diameter
Connecting rod
small end inside
diameter
Ignition timing
Point gap
Air gap EC06
EC06,
EC06, EC08 Measure crankshaft
EC06, EC08
~
EC06
EC06
EC08
20@
23'
0.35
0.5
0.6-0.7
M.005
-0.02
+0.026
f
2O
*
0.05
0
-0.1
Measure bearing
inside diameter.
outside diameter
Cylinder gauge Replace
Micrometer
Cylinder gauge
Timing tester
Searcher Adjust
Searcher
Searcher Adjust
Replace
Adjust
Adjust
-
23
-
Page 28

9-2
TABLE
of
TIGHTENING TORQUE
No.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
Parts
to tighten
Cylinder Cover, Muffler Cover
Fan Cover, Tank Support Plate,
Starter, Starter Pulley
Crankcase
Air Cleaner
Reduction Cover
Muffler
Cylinder
Carburetor
Governor Yoke
Governor
Ignition coil
Contact Breaker, Condensor
Point Cover
Plate
Tightening torque
kgcm
80*10
90k10
110 -+20
50
+5
110+20
80+10
110+10
80
+lo
18 *2
5025
50 *5
25
+2
.
Screw
diameter
M6 5T
M6 5T
M6 7T
M5 5T
M6
7T
M6
M6 7T
M6 4T
M3 4T
M5 4T
M5 4T
M4 4T
Remarks
Type
B
only
Nut
Nut
Nut
Apply screw lock (FT15 or equivalent)
and install (as in the
case
of
EC05, EC07)
13
14
15
16
17
18
Note:
Reduction Pinion
Spark Plug
Magneto Flywheel
Governor Lever
Stop Button
Rear Half of Crankcase
Be
careful not to apply screw lock more than necessary.
340 220
275 *25
+
20
400
80*10
40 +5
-
MI2 4T
MI4
M10 6T
M6 4T
M4 4T
M6
(Stand)
Nut, Type
Apply screw lock (FT15 or equivalent)
and install
B
only
(as
in the
case
of EC05, EC07)
-
24
-
Page 29

0
10.
,
The following maintenance jobs apply when the engine is operated correctly under normal conditions. The
indicated maintenance intervals are by
MAINTENANCE and STORING
..
no
means guarantees- for maintenance free operations during these
intervals. For example, if the engine is operated in extremely dusty conditions, the air cleaner should be
cleaned every day, instead of every
50
hours.
0
.10-1
2)
3)
4)
10-2
DAILY CHECKS and.MAINTENANCE
1)
Remove just from whatever which accumulated dust.
Check external fuel leakage.
If
any, retighten or replace.
Check screw tightening. If any lose one is found, retighten.
Clean air cleaner.
EVERY
50
HOURS
CHECKS
and
MAINTENANCE
Check spark plug. If contaminated, wash in gasoline or polish with emery paper.
10-3-
1)
2)
3)
10-4
EVERY
150
HOURS CHECKS and MAINTENANCE
Clean fuel straine-r and fuel tank.
Clean contact breaker points.
Clean exhaust
YEARLY CHECKS and MAINTENANCE
port
of cylinder and both inlet and outlet
..
of
muffler.
1) Remove carbon from cylinder head and piston head.
2)
Clean fuel tank inside.
3)
Clean carburetor float chamber inside.
4)
Clean contact breaker and adjust point gap.
5)
Replace fuel pipe once a year.
10-5
1) Perform the above 10- 1 and
2)
3)
PREPARATION
for
LONG ABEYANCE
10-2
maintenance jobs.
Drain fuel from the fuel tank and carburetor float chamber.
Remove spark plug, and apply 5 to
10
cc of lubricating oil through the spark plug hole. Perform idle
operation several times by pulling the recoil starter handle slowly. Re-install the spark plug.
4)
Clean the engine outside with oiled cloth.
5)
Put a vinyl
.'
.
...
or
other cover over the engine and store the engine in dry place.
-.
L.
I
-
25
-
Page 30

Page 31

Industrial
Engines
 Loading...
Loading...