Page 1

Page 2
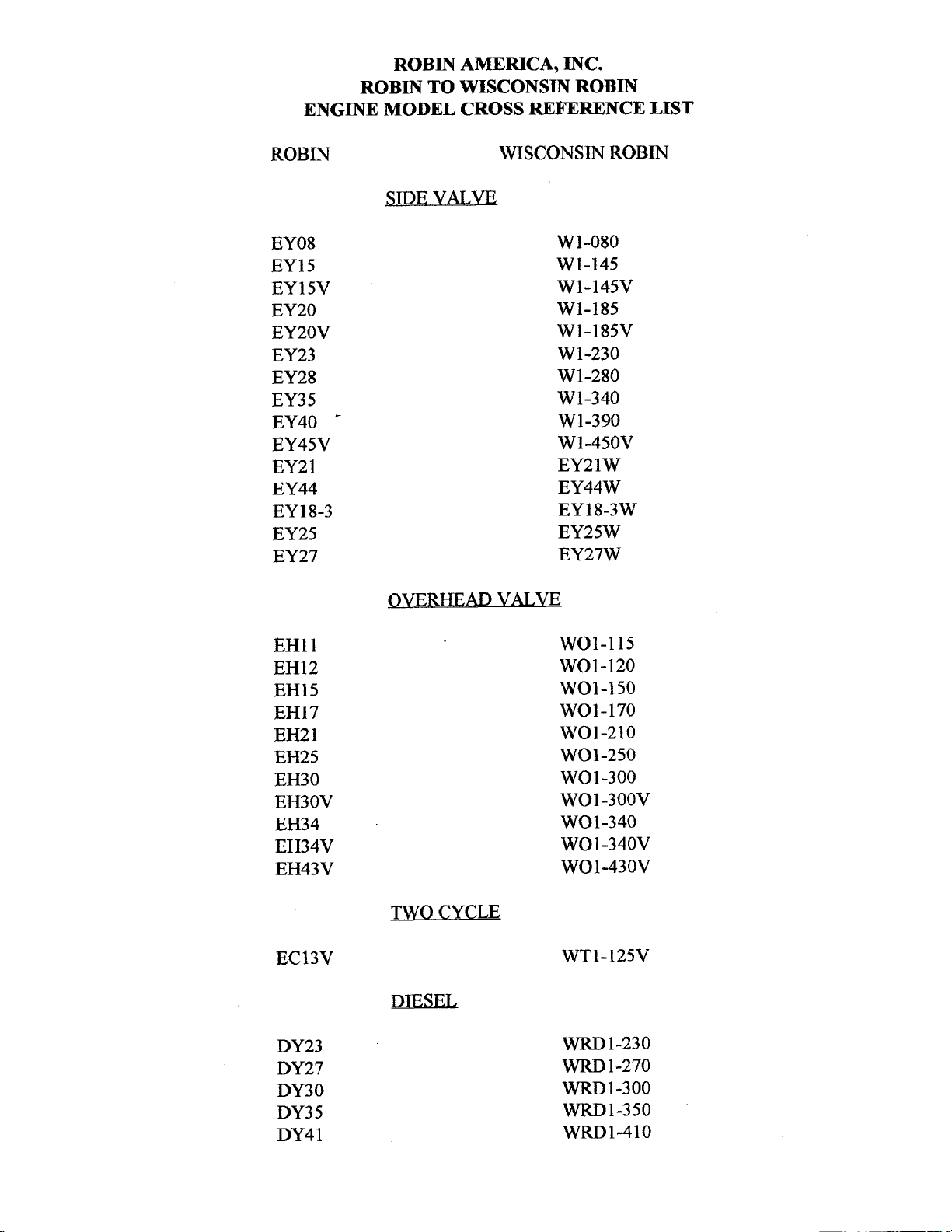
ROBIN
AMERICA, INC.
ROBIN
TO
WISCONSIN
ROBIN
ENGINE
MODEL
CROSS REFERENCE
LIST
ROBIN
EY08
EY15
EY 15V
EY20
EY2OV
EY23
EY28
EY3
5
EY40
-
EY45V
EY2
1
EY44
EY 18-3
EY25
EY27
EH11
EH12
EH15
EH17
EH21
EH25
EH30
EH30V
EH34
EH34V
EH43V
EC13V
DY23
DY27
DY30
DY3
5
DY4 1
WISCONSIN
ROBIN
SIDE
VALVE
W
1-080
W1-145
W1-145V
W1-185
W1-185V
W1-230
W 1-280
W
1-340
W 1-390
Wl-45OV
EY21W
EY44W
EY18-3W
EY25W
EY27W
OVERHEAD
VALVE
WO1-115
wo1-120
WO1-150
WO1-170
wo1-210
WOl-250
WO 1-300
WO1-300V
WO1-340
WO
1
-340V
WO 1-43 OV
TWO CYCLE
WT1-125V
DIESEL
WRD
1-230
WRD
1-270
-1-300
WRD1-350
WRD1-410
0
0
0
Page 3

CONTENTS
Section
Title
Page
1
.
SPECIFICATIONS
...........................................
1
2 .
PERFORMANCE
............................................
2
2.1
.
Maximum Output
.......................................
2
2.2
.
Continuous Rated Output
..................................
2
2.3
.
Maximum Torque and Fuel Consumption Ratio
at
Max
.
Output
........
2
3
.
FEATURES
................................................ 5
4
.
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
of
ENGINE CONSTRUCTION
................
6
4.1
.
4.2
.
4.3
.
4.4
.
.
4.5
.
4.6
.
4.7
.
4.a
.
4.9
.
4-1
0
.
4-1 1
.
4- 1
2
.
4-1 3
.
4.14
.
4-1 5
.
Sectional View of Engine
..................................
6
Crankcase
.............................................
14
Baseplate
.............................................
14
Crankshaft and Connecting
Rod
Assy
..........................
14
Piston
...............................................
14
Driving Shaft (for Model B only)
.............................
15
Cylinder
..............................................
15
Cylinder Head (Model EC10.17.2
5.2
only)
......................
15
Governor
..............................,...............
15
Cool'ing
..............................................
15
Ignition
..............................................
15
Carburetor
............................................
16
Air Cleaner
............................................
16
Reduction Equipment
(for
Model B only)
.......................
16
Starting Pulley or Recoil Starter
.............................
16
5
.
INSTALLATION
.............................................
17
5.1
.
Mounting
.............................................
17
5.2
.
Ventilation
............................................
17
5.3
.
Exhaust
Gas
Evacuation
...................................
17
5.4
.
Fuel System
...........................................
17
5.5
.
Power Transmission to Drive Machines
.........................
17
5.6
.
Wiring
...............................................
18
6
.
DISASSEMBLY
and
REASSEMBLY.
...............................
20
6.1
.
Preparations and Suggestions
................................
20
6.2
.
Special Tools
..........................................
22
6.3
.
Disassembly
and
Reassembly Procedure
........................
24
Page 4

7 . MAGNETO
7.1
.
Magneto.
7.2
.
Breaker Point Adjustment
7.3
.
Timing Adjustment
7.4
.
Magneto Trouble Shooting
8
.
GOVERNOR
8.1
.
Construction and Operation
8.2
.
Governor Adjustment
8.3
.
High Speed Adjustment
9
.
CARBURETOR
9.1
.
Construction and Operation
9.2
.
Disassembly and Reassembly
9.3 .
10
.
RUN-IN
I1
.
TROUBLE SHOOTING
11.1
11.2
11.3
11.4
11
11.6
11.7
Adjustments
OPERATION
.
Starting Difficulties
.
Slow-Speed
.
Overheating and Knocking
.
Power Drop
.5
.
Excessive Fuel Consumption
.
Engine Hunting
.
Other Complaints
................................................
..............
;
..............................
..................................
......................................
.................................
...............................................
................................
....................................
...................................
.............................................
................................
................................
...........................................
of
REASSEMBLED ENGINE
....................
........................................
......................................
out
of
order
...................................
.................................
...........................................
................................
.........................................
.......................................
29
29
29
30
31
32
32
34
36
38
39
39
41
42
43
43
44
44
45
45
45
45
0
12
.
CHECKS and CORRECTIONS
13
.
MAINTENANCE and STORING
13.1
.
Daily Checks and Maintenance
13.2
.
Every 50 Hours
13.3
.
Every
100-200
13.4
.
Every
500-600
13.5
.
Every
1000
Hours
13.6
.
Preparation for Long Abeyance
...................................
..................................
..............................
(10
Day) Checks and Maintenance
Hours (Monthly) Checks and Maintenance
Hours (Semiannual) Checks and Maintenance
(Yearly) Checks and Maintenance
.................
...............
..............................
...........
.........
46
53
53
53
53
53
54
54
Page 5
.-
1.
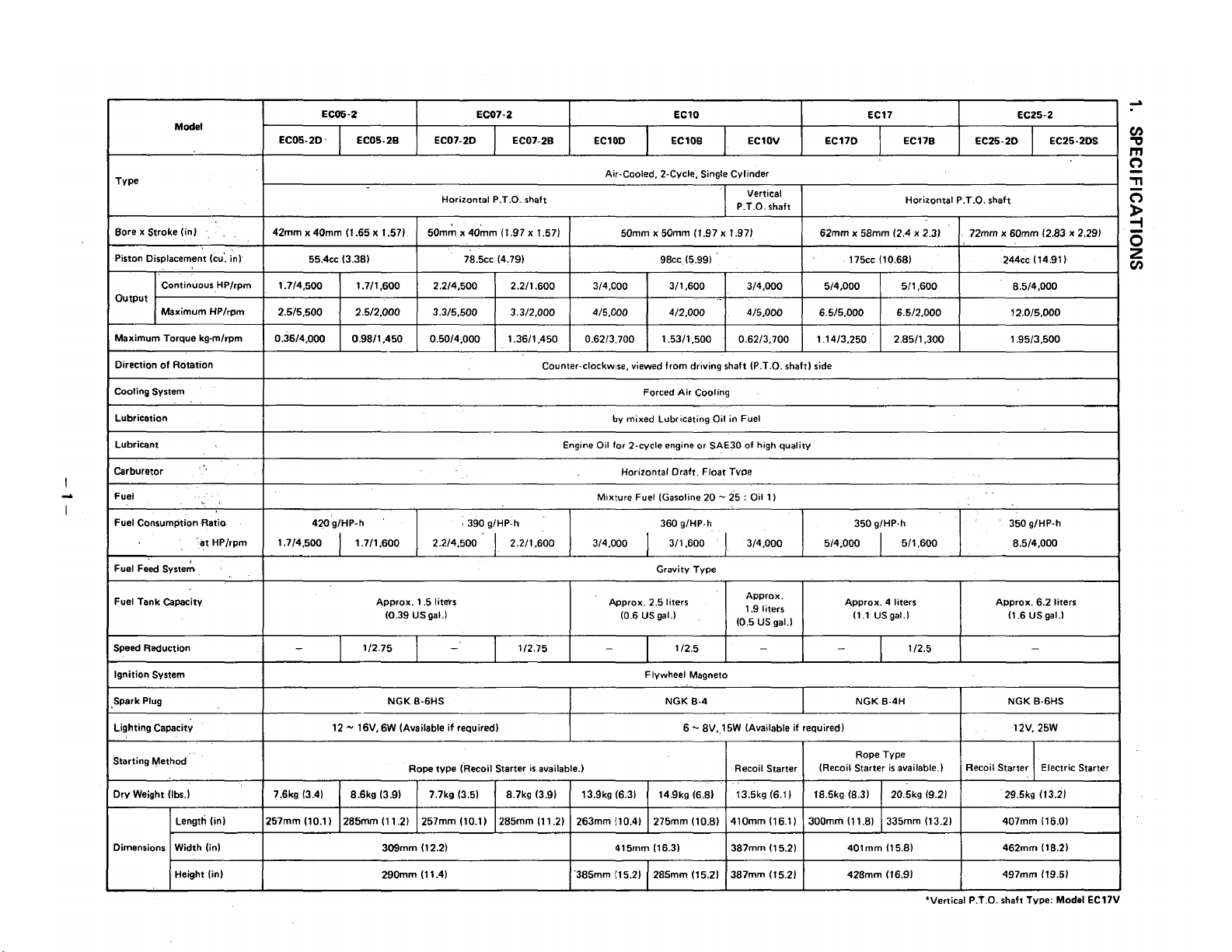
SPECIFICATIONS
1
0
0
'4
c
.
f
Lo
5-
0
m
00
Lo
0
9
.
ln
T
c
a
P
a
-1-
Page 6
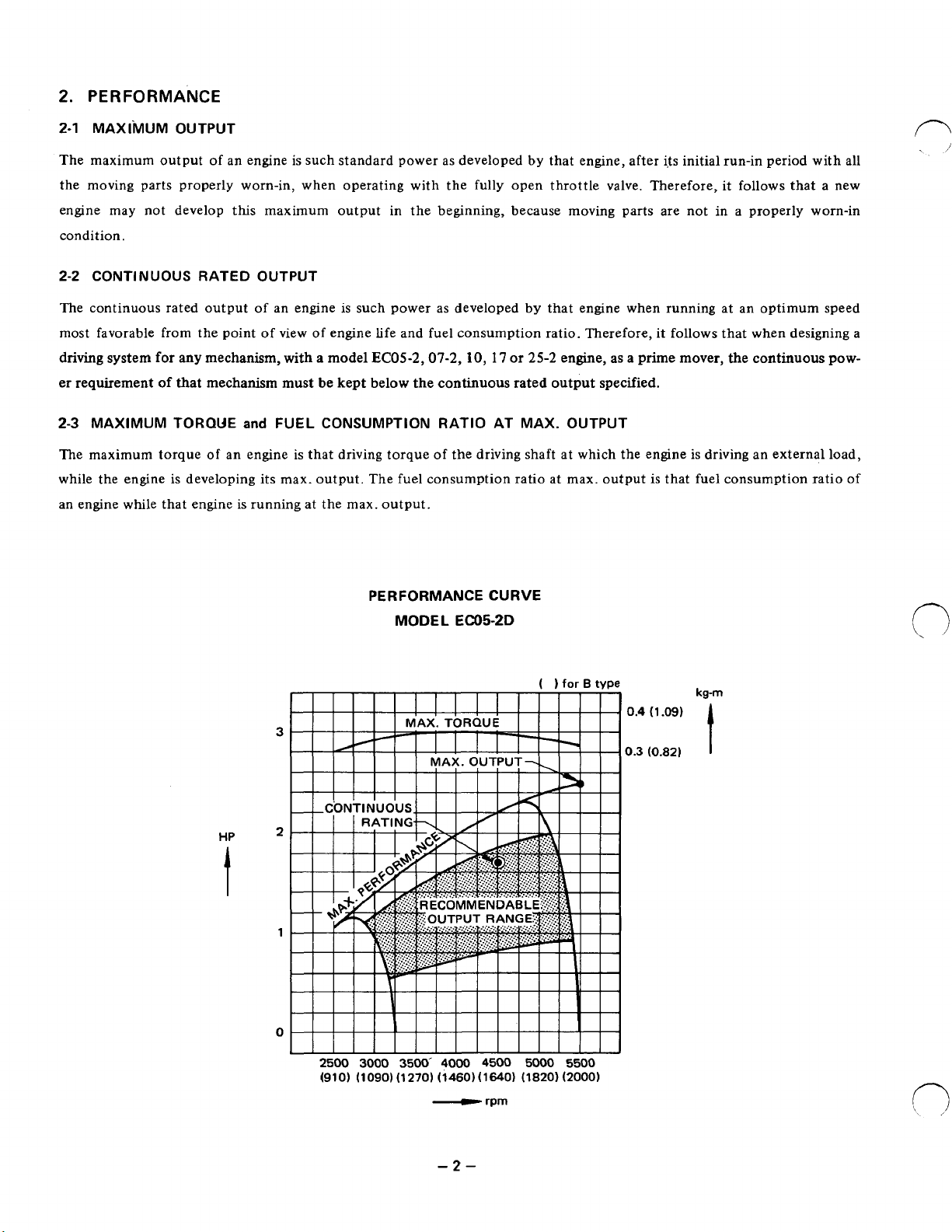
2.
PERFORMANCE
2-1
MAXIMUM OUTPUT
The maximum output
the moving parts properly worn-in, when operating with the fully open throttle valve. Therefore, it follows that a new
engine may not develop this maximum output in the beginning, because moving parts are not in a properly worn-in
condition.
2-2
CONTINUOUS RATED OUTPUT
The continuous rated output
most favorable from the point
driving
er requirement
2-3
The maximum torque of an engine is that driving torque
while the engine is developing its max. output. The fuel consumption ratio at max. output is that fuel consumption ratio
an engine while that engine is running at the max. output.
system
MAXIMUM TORQUE
for
of
of
an
engine is such standard power as developed by that engine, after its initial run-in period with all
of
an engine
of
view of engine life and fuel consumption ratio. Therefore, it follows that when designing a
any mechanism, with a model
that mechanism must
and
FUEL CONSUMPTION RATIO AT MAX. OUTPUT
is
such power as developed by that engine when running at an optimum speed
be
kept below the continuous rated output specified.
EC05-2,07-2,
PERFORMANCE CURVE
MODEL
IO,
17
or
25-2
of
the driving shaft at which the engine is driving an external load,
EC05-2D
engine, as a prime mover, the continuous pow-
of
HP
I
for
B
tvoe
2500 3000 3500'
(910) (1090) (1270) (1460)(1640) (1820) (2000)
4000
4500
5000 5500
0.4
0.3
(1.09)
(0.82)
t
-2-
Page 7
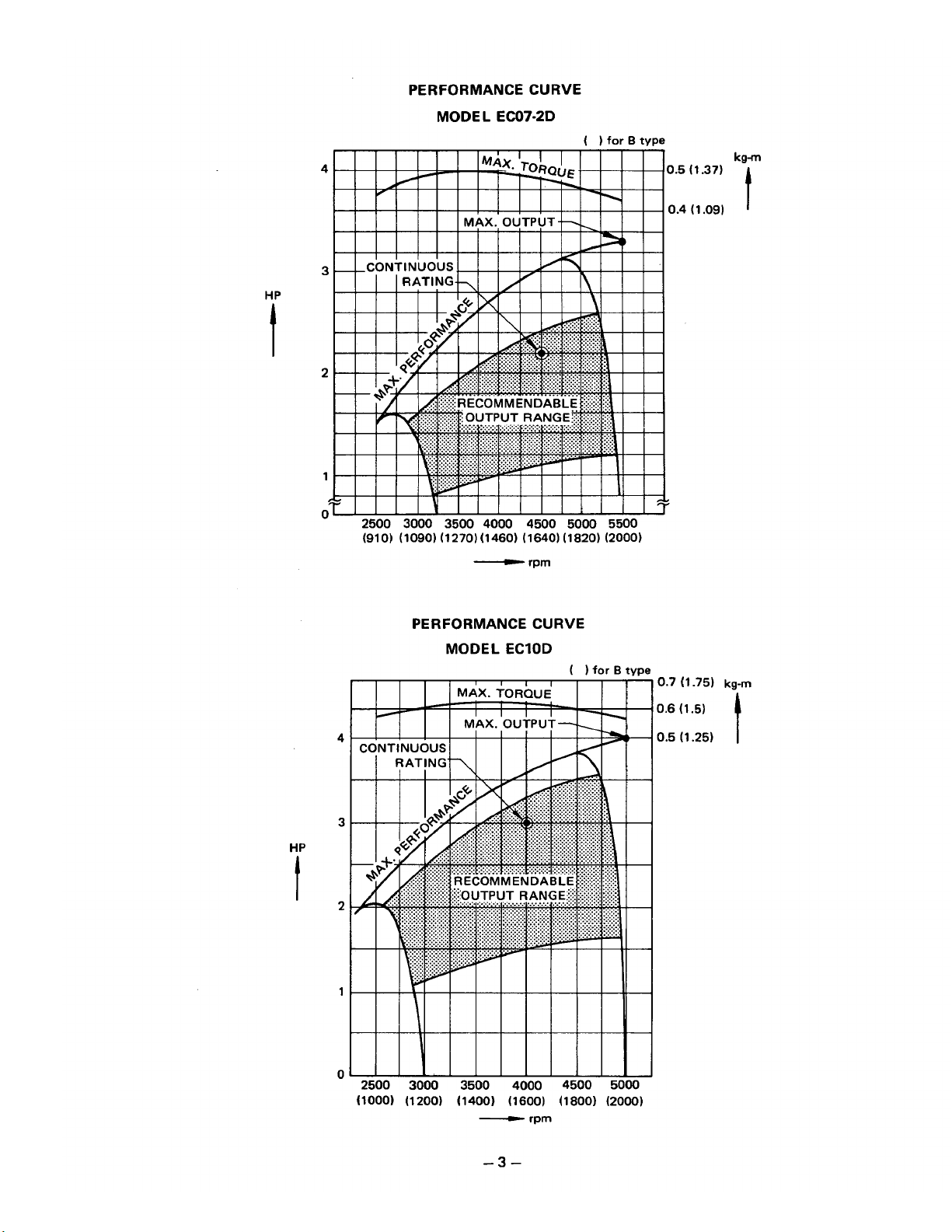
PERFORMANCE CURVE
MODEL EC07-2D
( )
for
B
type
HP
t
4
3
HP
t
2
1
0
PERFORMANCE CURVE
MODEL ECIOD
(
)for
B
tj
(1000) (1200) (1400) (1600)
(1800)
(2000)
-
rpm
-3-
Page 8
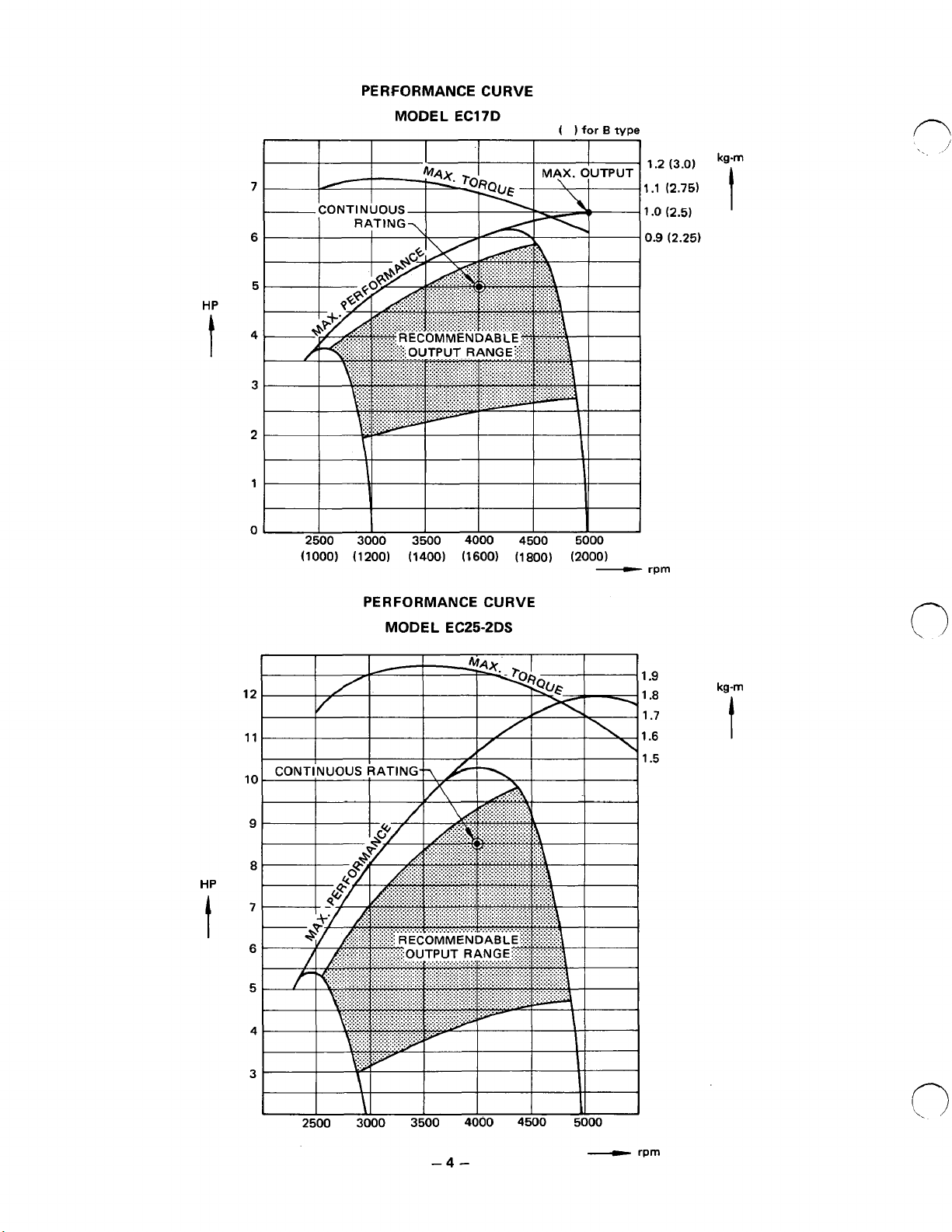
HP
PERFORMANCE CURVE
kg-m
HP
t
PERFORMANCE CURVE
MODEL EC25-2DS
kg-m
-4
-
__c
rpm
Page 9

3.
5.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
FEATURES
COMPACT, LIGHT WEIGHT, HIGH PERFORMANCE
and
LOW
FUEL CONSUMPTION.
TROUBLE FREE
because of simple design and easy
to
handle.
HIGH DURABILITY
engine withstand long severe operation.
TILTED OPERATION
available.
As
a
special feature
of
2-cycle engine, can operate at up
to
about
30'
tilted position just before the
fuel
flooding out
from the air-bent
of
carburetor.
EASY STARTING
Recoil type starter
is
available at option.
LIGHTING
for night operation.
Optional lighting is available by installing special lighting coil.
Lighting
Capacity:
EC05-2,07-2
(1
2V - 16V,
6W)
..
EC10, 17 (6
-
8V,
15W)
EC25-2 (1'2V,
18 - 25W)
VERSATILE APPLICATION
Direct,or reduction type engine with horizontal shaft or vertical shaft are available.
Wide selection
of
driving shaft size and shapes are also available beside standard specification.
Further, consult with dealer for smaller fuel tank, heavy-duty filter element for air cleaner and high-performance
muffler.
The engine can control
to
the desired speed with a
ALL-SPEED GOVERNOR.
It can. be set
for
any desired speed
by
simply moving the control lever.
The
setting speed
is
maintained even under vary-
ing
load.
-
Engine withstand
AGAINST HIGH VIBRATION
environment.
Page 10
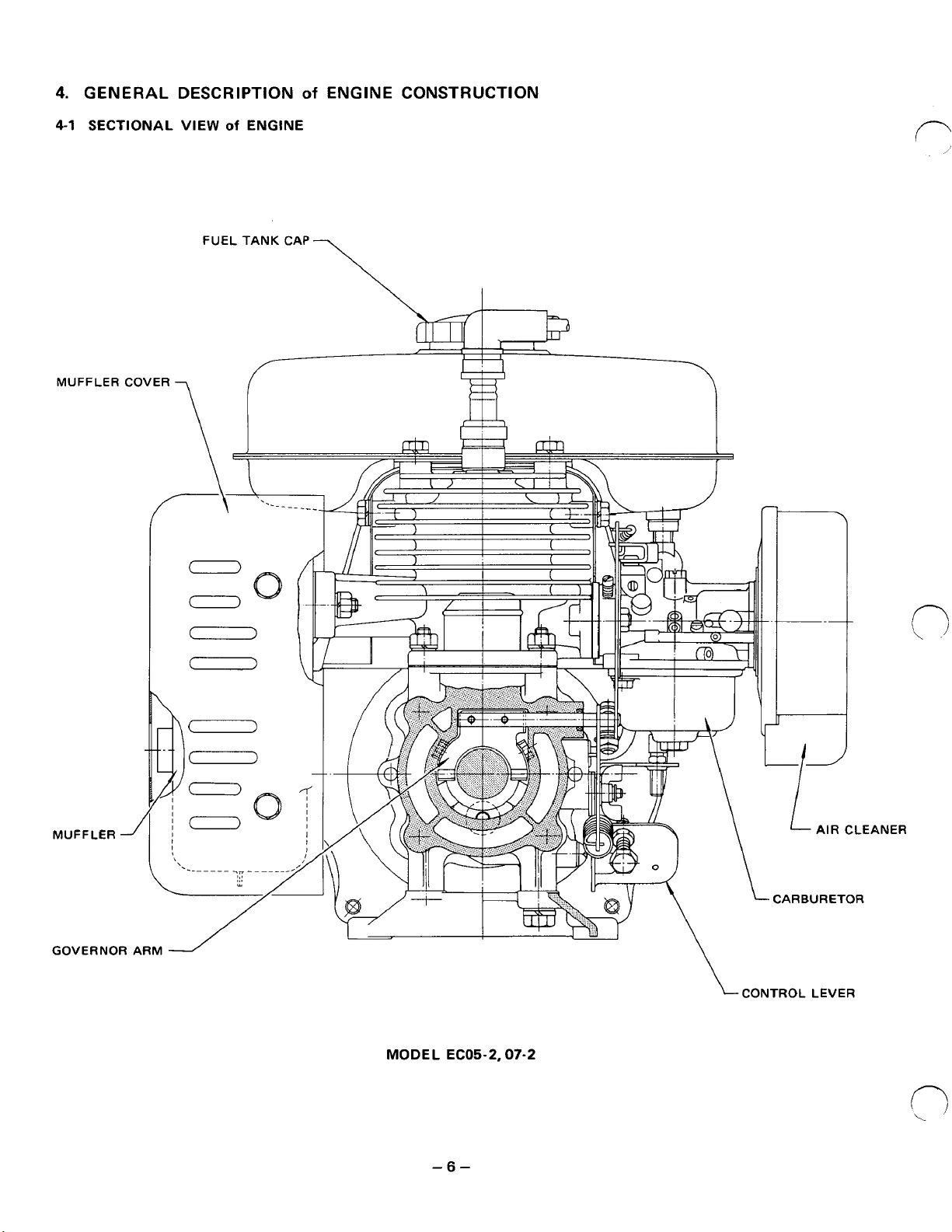
4.
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
4-1
SECTIONAL
VIEW
FUEL TANK CAP
of
ENGINE
of
ENGINE CONSTRUCTION
\
MUFFLER COVER
7
\I
MUFFLER
GOVERNOR
CONTROL LEVER
MODEL EC05-2,07-2
-6-
Page 11
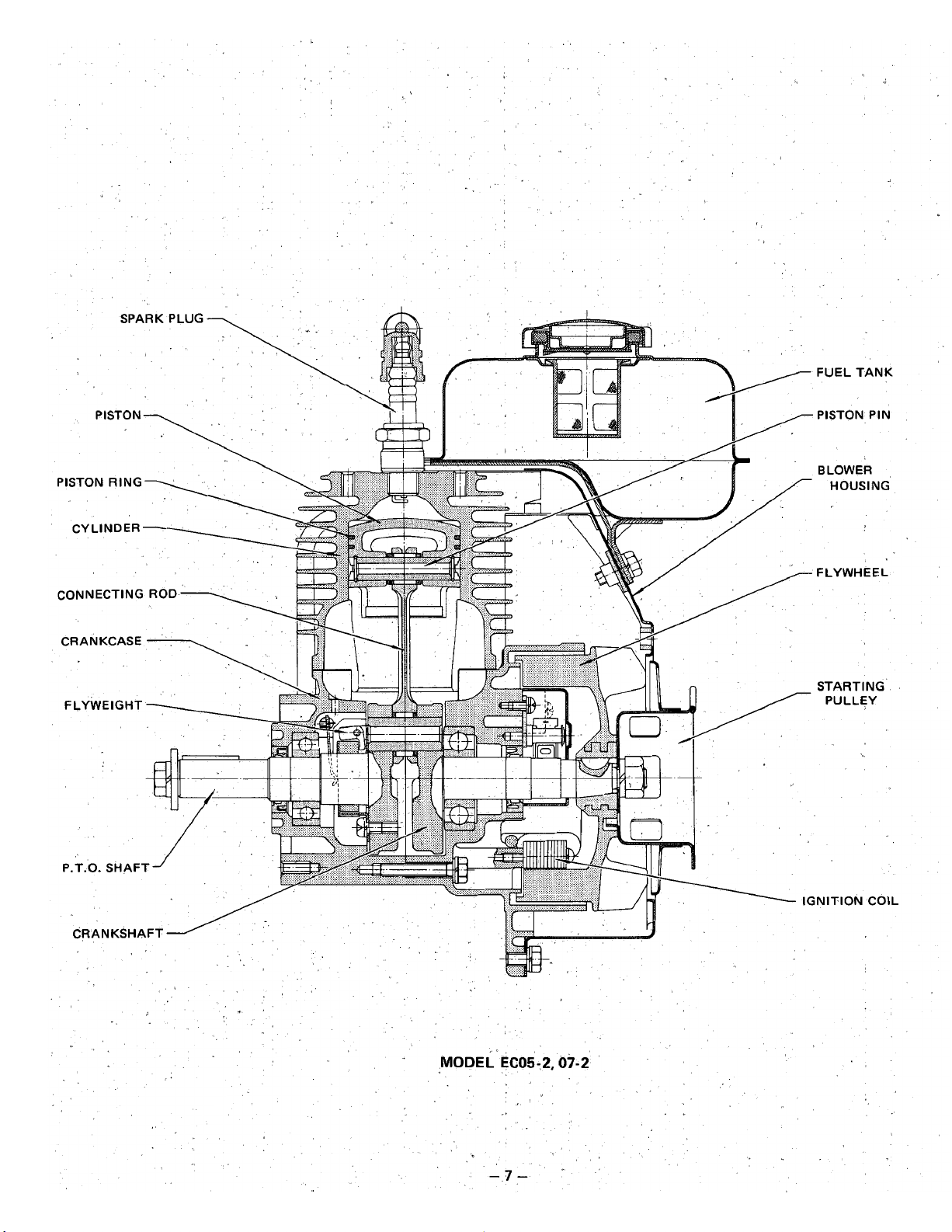
FUEL
TANK
PISTON PIN
BLOWER
HOUSING
FLYWHEEL
STARTING
PULLEY
NlTlON
COIL
MODEL'EC05-2.07-2
I.
Page 12
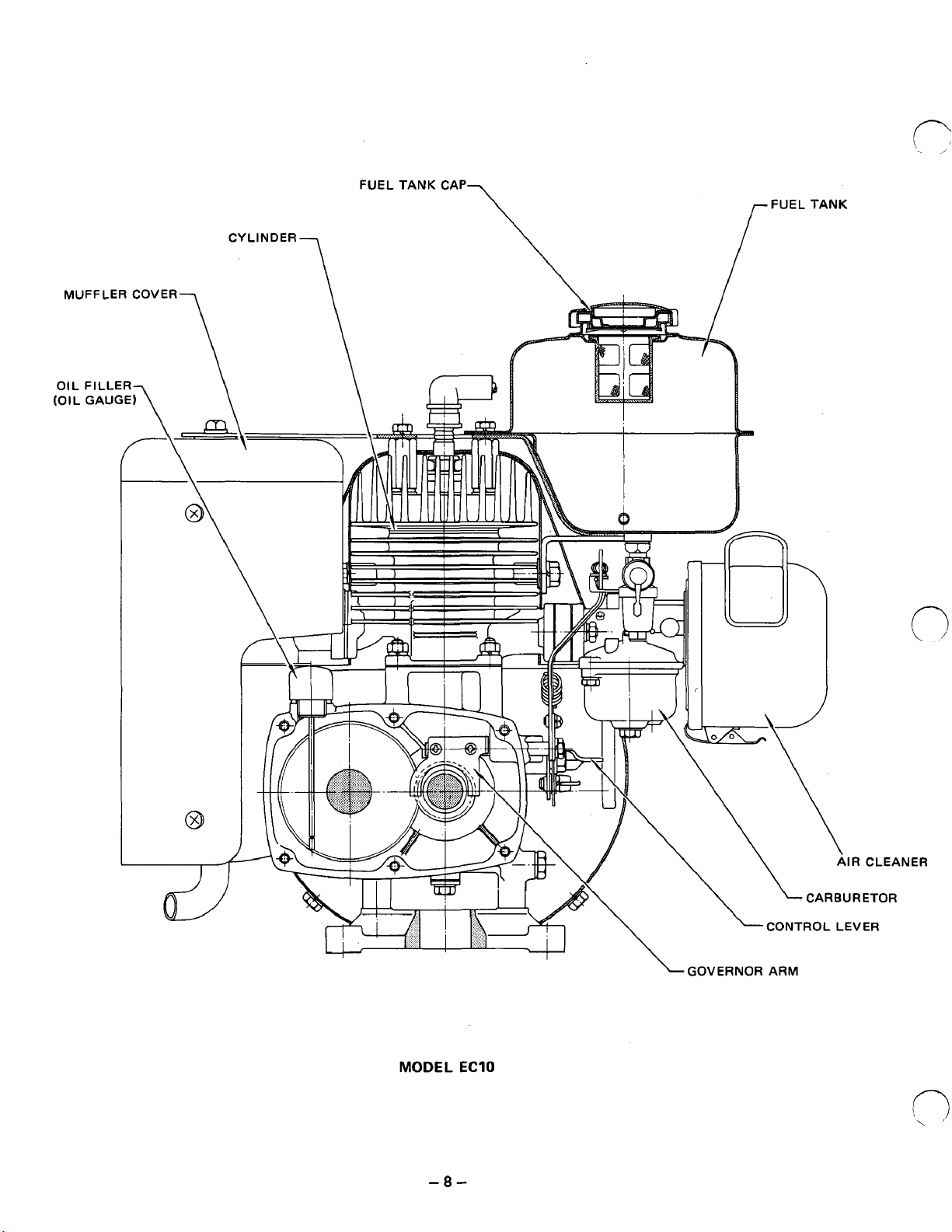
FUEL TANK CAP
r
FUEL TANK
MUFFLER COVER-
CYLINDER
7
\
\
MODEL
-8-
CLEANER
ETOR
'ER
GOVERNOR ARM
ECIO
Page 13
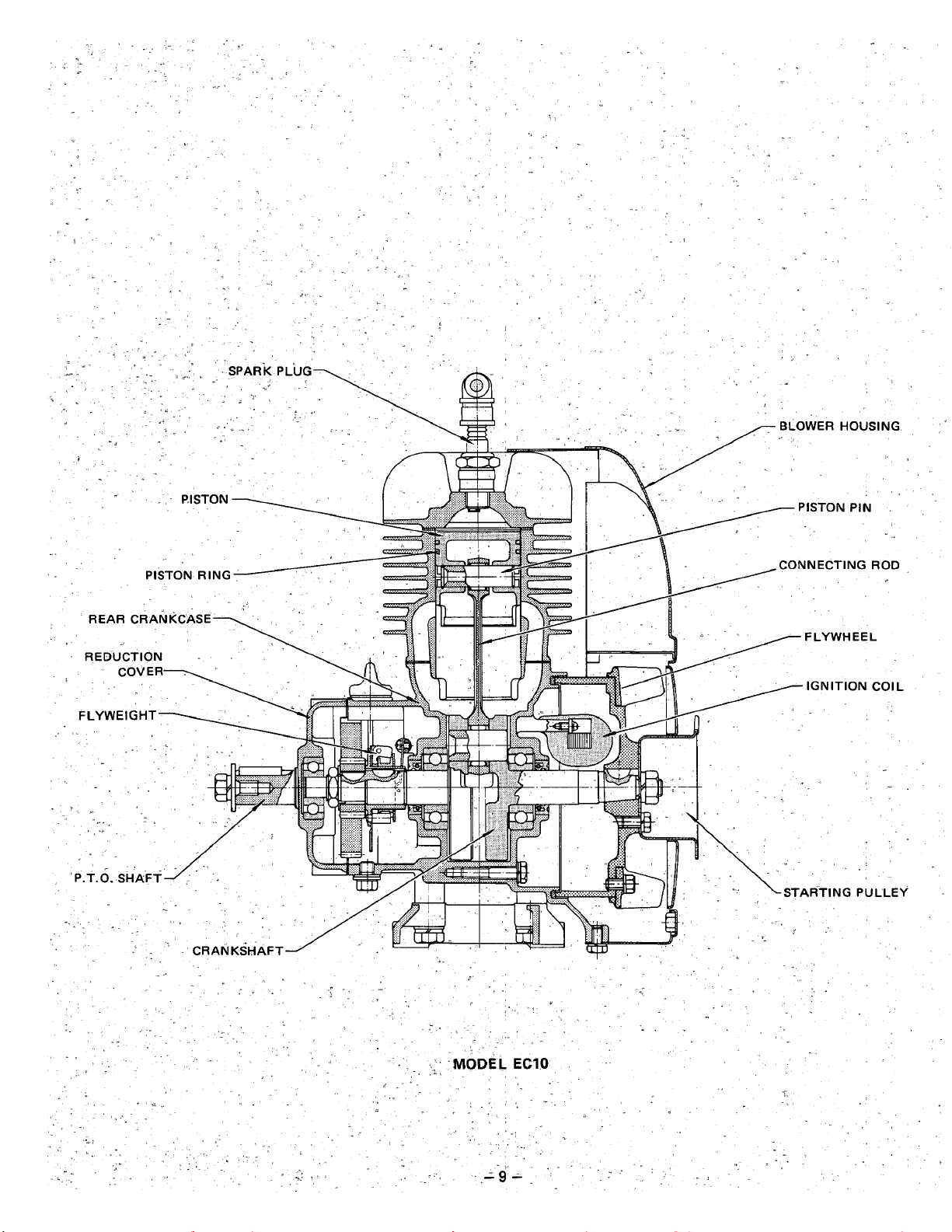
Page 14
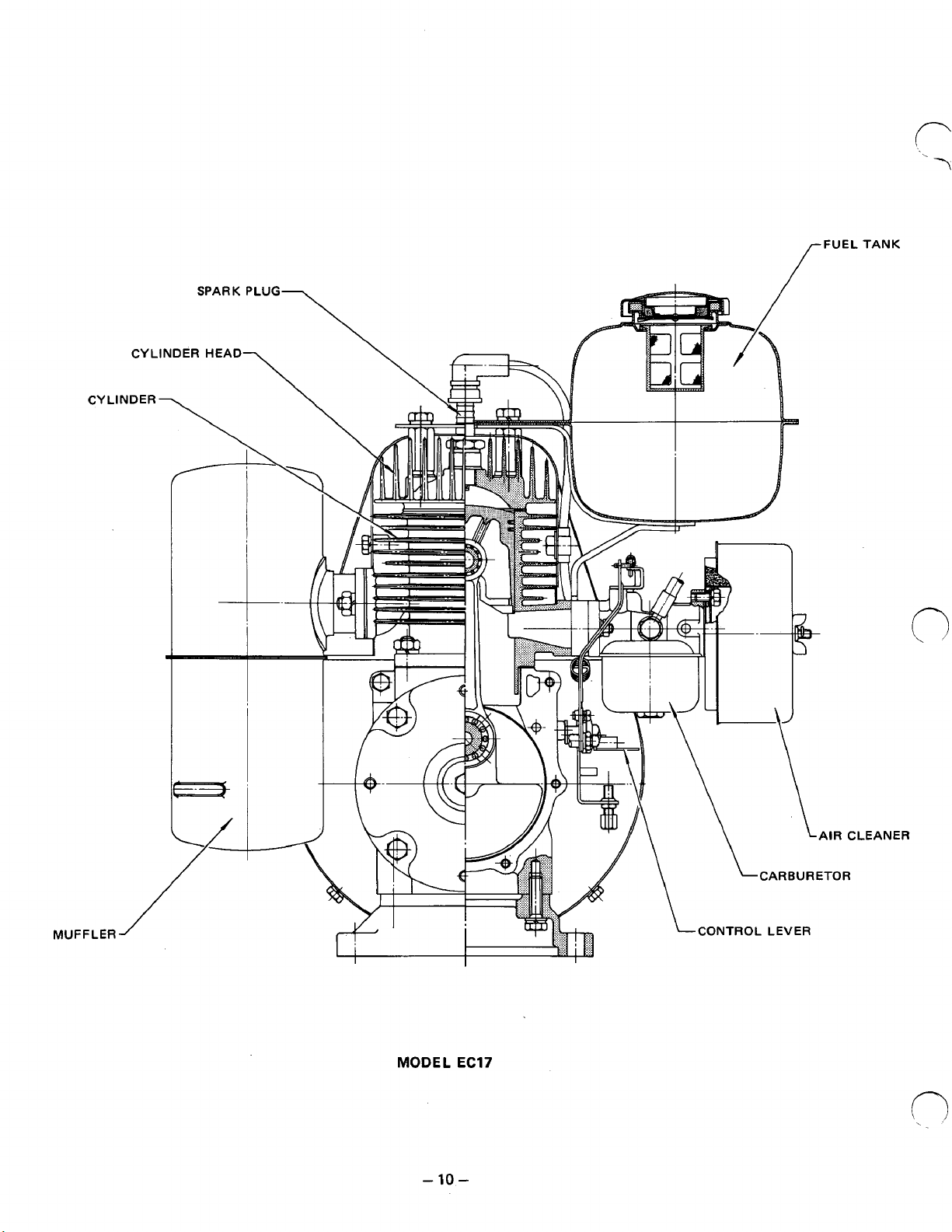
CYLINDE
CYLINDER
\
f
FUELTANK
MUFFLER
MODEL
-10-
:LEANER
EC17
Page 15
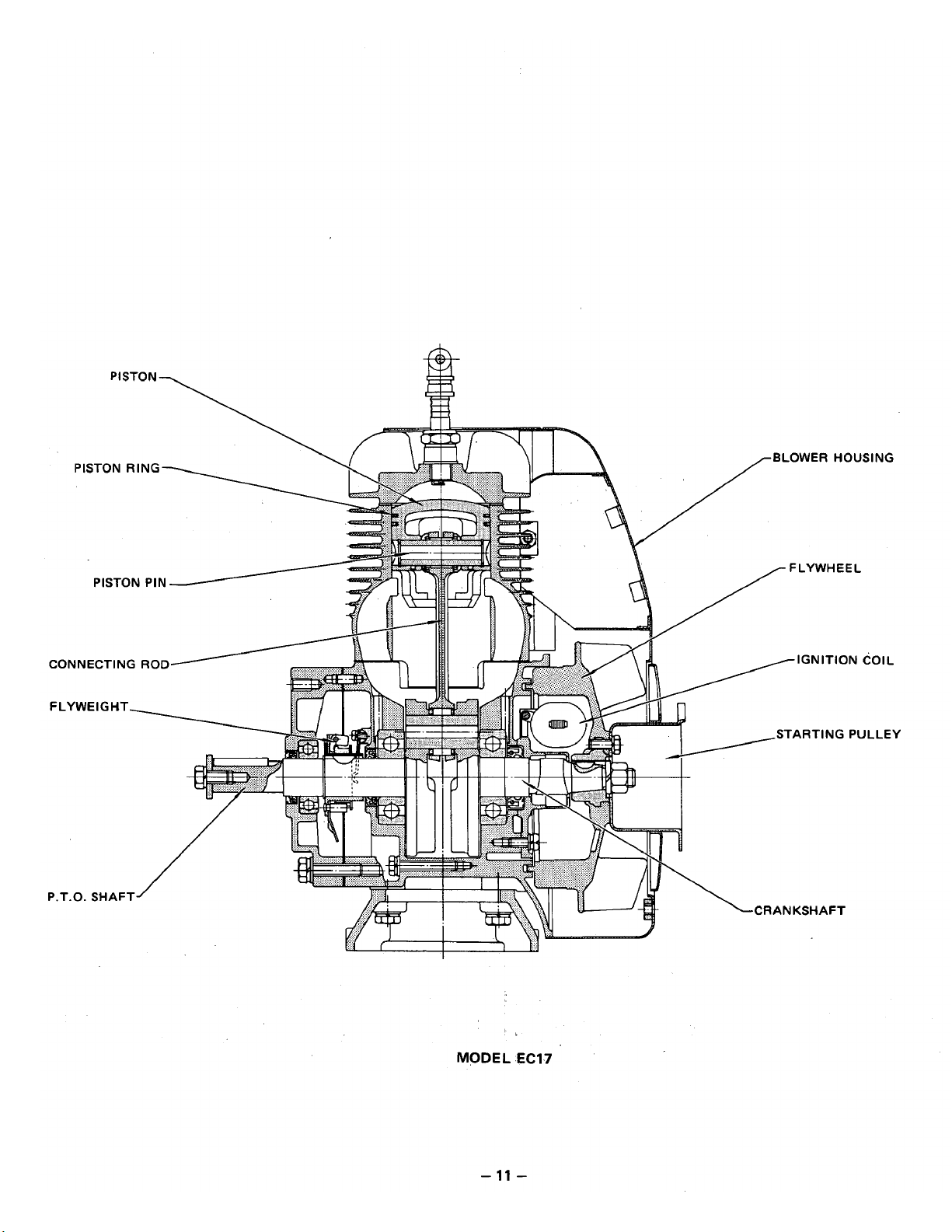
1
1,
MODEL
EC17
-
11
-
Page 16
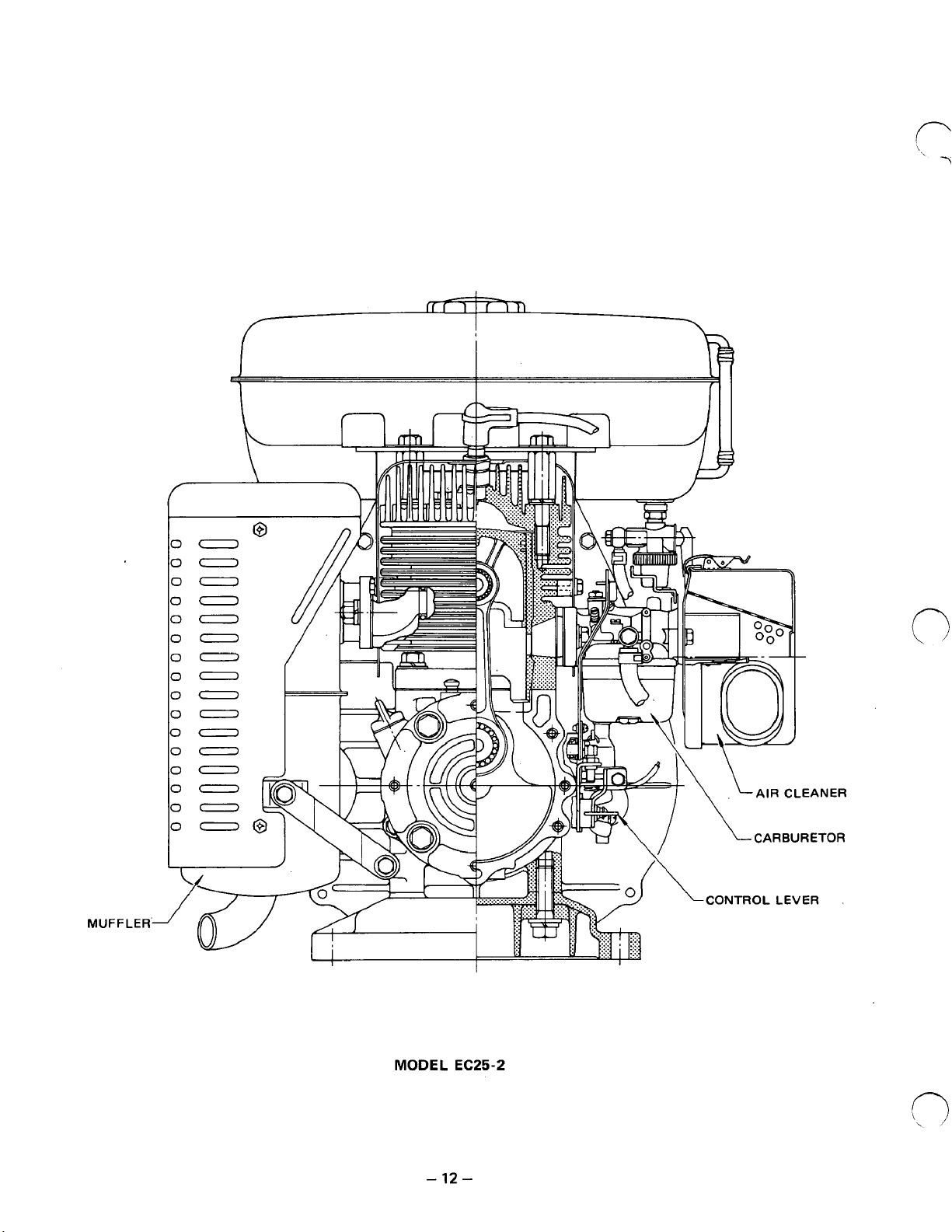
MUFFLER-
00
00
00
00
00
00
00
00
00
00
00
00
00
00
00
MODEL EC25-2
-
12-
Page 17
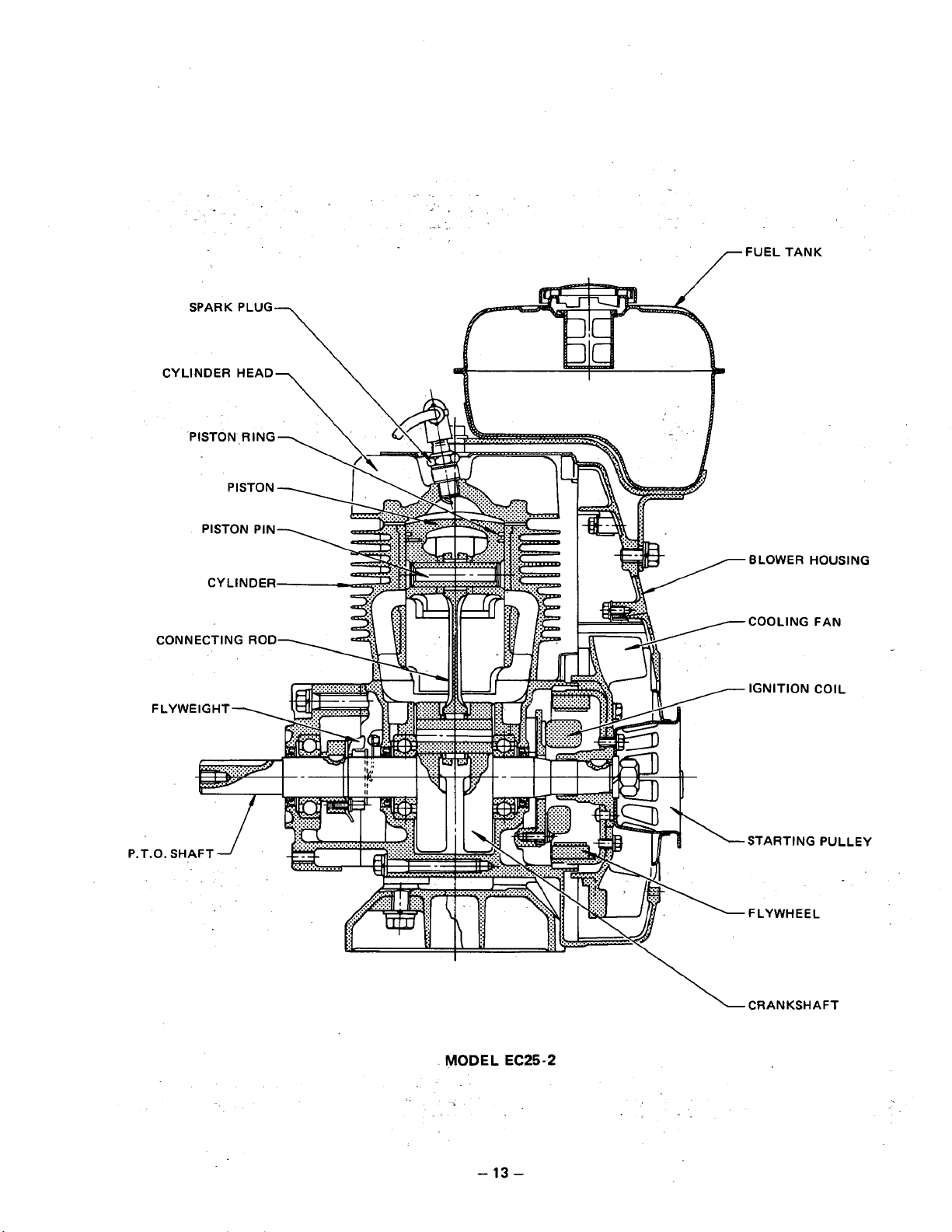
P.
T
7
FUEL
TANK
SPARK PLUG
CYLINDER HEAD7
.BLOWER HOUSING
-COOLING FAN
. IGNITION COIL
.STARTING PULLEY
,FLYWHEEL
-CRANKSHAFT
MODEL
EC25-2
-13-
Page 18
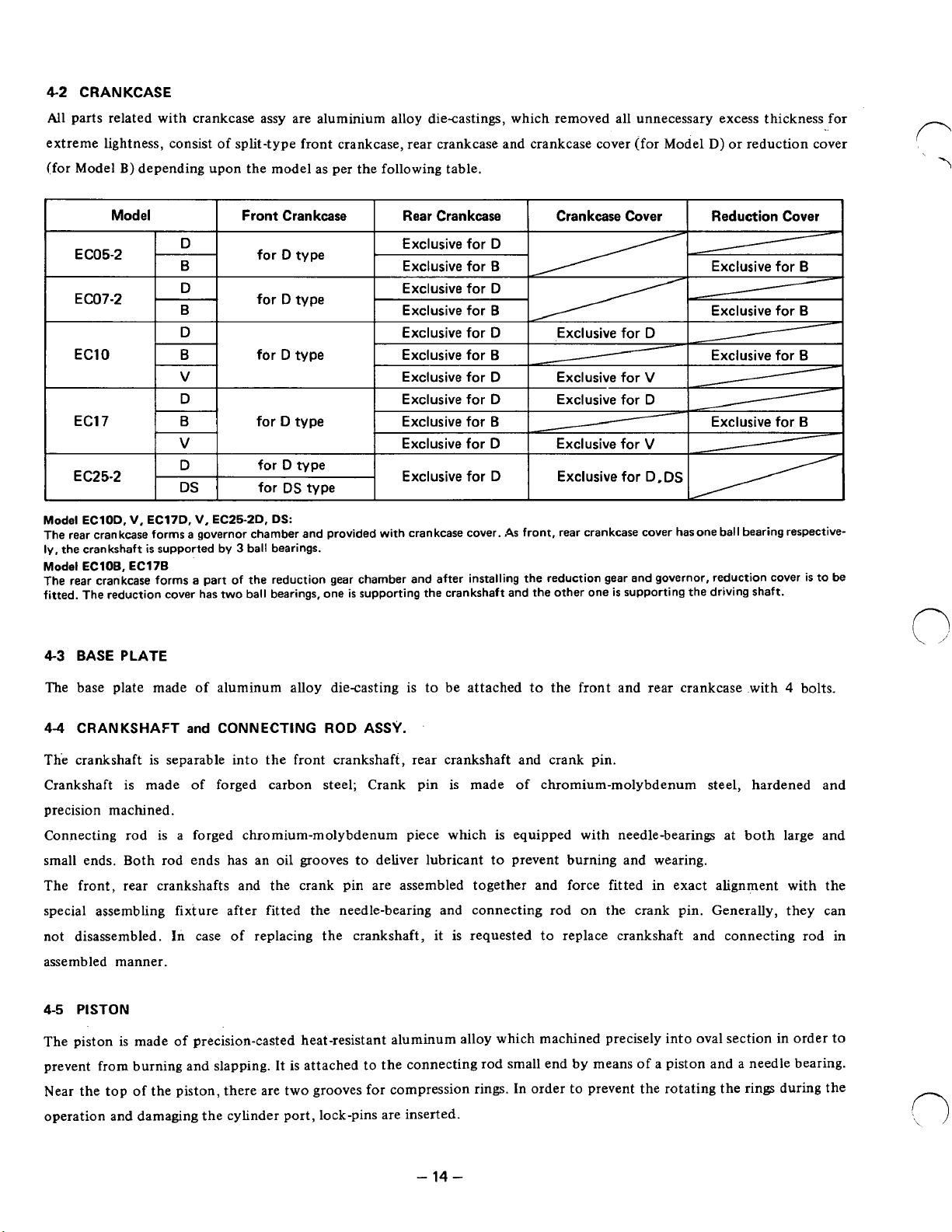
4-2
CRANKCASE
All parts related with crankcase assy are aluminium alloy diecastings, which removed all unnecessary excess thickness for
extreme lightness, consist
split-type front crankcase, rear crankcase and crankcase cover (for Model
D)
or reduction cover
of
(for Model B) depending upon the model as per the following table,
Model
-
D
B
D
B
D
B
EC05-2
EC07-2
EC10 for D type Exclusive for
v
D
EC17
B
v
I
EC25-2
Model EClOD,
The rear crankcase forms a governor chamber and provided with crankcase cover. As front, rear crankcase cover hasone ball bearing respective-
ly,
the crankshaft
Model
The rear crankcase forms
fitted.
The
4-3
BASE PLATE
V.
EClOB,
EC17B
reduction cover has two ball bearings, one
D
DS
EC17D,
is
V.
supported by 3 ball bearings.
a
Front Crankcase
for D type
for
D
type
for
D
type Exclusive for
for D type
for
DS
type
EC25-2D.
part of the reduction gear chamber and after installing the reduction gear and governor, reduction cover
DS:
is
Exclusive for
~
Exclusive for
Exclusive for
Exclusive for
~
Exclusive for
Exclusive for
B
D
B
D
B
D
D
B
Exclusive for
Exclusive for
supporting the crankshaft and the other one
D
D
Crankcase Cover Rear Crankcase
Exclusive for
Exclusive for
~-
Exclusive for
D
V
D
/
Exclusive for
Exclusive for
V
D.DS
is
supporting the driving shaft.
Reduction
Exclusive for
Exclusive for
Exclusive for
Cover
B
B
B
is
to
be
The base plate made
4-4
CRANKSHAFT
of
aluminum alloy diecasting is to be attached
and
CONNECTING ROD ASSY.
to
the front and rear crankcase .with
4
bolts.
The crankshaft is separable into the front crankshaft, rear crankshaft and crank pin.
Crankshaft is made
of
forged carbon steel; Crank pin is made
of
chromium-molybdenum steel, hardened and
precision machined.
Connecting rod is a forged chromium-molybdenum piece which is equipped with needle-bearings at both large and
small ends. Both rod ends has an oil grooves
to
deliver lubricant to prevent burning and wearing.
The front, rear crankshafts and the crank pin are assembled together and force fitted in exact alignment with the
special assembling fixture after fitted the needle-bearing and connecting rod on the crank pin. Generally, they can
not disassembled. In case
of
replacing the crankshaft, it is requested
to
replace crankshaft and connecting rod in
assembled manner.
4-5
PISTON
The piston is made of precision-casted heat-resistant aluminum alloy which machined precisely into oval section in order to
prevent from burning and slapping. It is attached to the connecting rod small end by means
of
a piston and a needle bearing.
Near the top of the piston, there are two grooves for compression rings. In order to prevent the rotating the rings during the
operation and damaging the cylinder port, lock-pins are inserted.
-
14-
Page 19

4-6
DRIVING
SHAFT
(P.T.O.
shaft)
(for
Model B
only)
The driving shaft is made
of
forged carbon steel and reduction gear
is
force-fitted.
4-7 CYLINDER
‘Model
EC05-2, EC07-2
Monoblock cylinder and cylinder head .is made
of
aluminum alloy diecasting and-inside the cylinder is treated with
hard-chromium plating
to
withstand against the wear by reciprocal motion
of
the piston.
Outside fins
of
cylinder-head are arranged to get efficient heat dispersion and provided with threaded hole for mounting a
spark plug on the top.
Inside the cylinder, one each of intake port, exhaust port and two scavenging ports are positioned to get the maximum
engine performance.
-.
Model
ECIO, EC17
The cylinder is made
of
precision-casted wear-resistant cast iron provided with fins for perfect heat dispersion.
Inside the cylinder, one each
of
intake
port,
exhaust port and two scavenging ports are positioned to get the maximum
engine performance.
The cylinder is attached
to
the crankcase with the flange, which positioned lower part of cylinder, by stud-bolts.
*Model
EC25-2
The cylinder
with
the cylinder liner
is
made of aluminium alloy. The cylinder liner
is
made of special cast iron and are
im-
bedded
in
the
aluminium casting as inserts. Inside the cylinder, one each
of
intake port, exhaust port and four scavenging
ports are positioned
to
the maximum engine performance.
4-8
CYLINDER HEAD
(Model
ECIO,
17,25-2
only)
The cylinder head is made
of
heat-conductive aluminum alloy and is provided with the fins, arranged in the direction
of
cooling air to achieve the efficient cooling.
The combusion chamber forms semi- spherical and is provided with threaded hole for mounting a spark-plug on the top.
4-9 GOVERNOR
The centrifugal flyweight type governor assures constantspeed operation at selected speed, irrespective
of
load fluctuations.
(The governor is built-in the crankcase for Model
EC05-2,07-2)
As
to the detail, refer to section
“8.
GOVERNOR”.
4-10 COOLING
The cooling fan which also serves as a flywheel forcily feeds cooling air to the cylinder and cylinder head with the aid
of
blower housing and air buffle.
4-11 IGNITION
The ignition system
is
of
flywheel magneto type with ignition timing set at
23”
before TDC
for
EC05-2, 07-2, 25-2, 18” be-
fore TDC for EC10 and
22”
before TDC for EC 17 respectively.
The flywheel with steel magnet piece revolves outside the coil and generates the electric power
in
the coil. The flywheel
also
equalize the engine revolution and at the same time,
it
serves as a blower, with its impellers on the circumstance, for cooling
the
engine. The igntition coil and the breaker are mounted
in
the crankcase.
As
to
the detail, refer to “Section
7.
MAGNETO”.
-15-
Page 20

4-12
CARBURETOR
A
horizontal draft float type carburetor is employed. Its setting has been carefuily determined after thorough testing to
achieve best starting, accelerating, fuel consumption, output and performances.
As
to the detail such as construction, refer
4-13
AIR CLEANER
Air
cleaner used in this model is a semi-wet type cleaner, which contains oil soaked filtering element that traps all
dust particles floating in the intake air
4-14
REDUCTION EQUIPMENT
(For
to
section
so
that clean air is supplied to the carburetor.
Model
B
“9.
CARBURETOR”.
only)
With the Model B engine, rear crankcase and reduction cover forms the reduction chamber, and the revolution
reduced to 1/2.7 for Model EC05-2, 07-2, to 1/25 for Model EClO and EC17 by reduction-gear and pinion, and then its
P.T.O.
transmitted to
Use SAE
4-15
Optional recoil starter is available for Model D and
Starting pulley
By removing the recoil starter, starting the engine can be made by starting pulley.
30
lubricant.
STARTING PULLEY
shaft. Governer is also equipped with reduction chamber and lubricated by same lubricant.
(for
EClO,
17)
or
RECOIL STARTER
of
Model D and B are identified according
B.
Model V is equipped with recoil starter.
to
the direction
of
engine rotation.
of
crankshaft
-
16-
Page 21

-
5.
INSTALLATION
Since the installation method affects the service life, easy
of
maintenance, frequency
of
check and repair, and operating cost
of
engine,
the following contents
shall
be carefully examined before installing
your
engine.
5-1
MOUNTING
When installing the engine, its mounting position, coupling condition with operating machines, and anchoring or supporting
m&o& must be carefully examined. Particularly when determining its mounting position, due care should be taken
to
assure the convenience
of
such routines as replenishment and checking
of
fuel and oil, checking
of
oil
gauge, spark-plug and
contact breaker point, maintenance
of
oil draining. For details, refer
to
the installation drawing.
Install the engine as much closer as possible to the level. The tilt limit for normal operation should be not more than
30°
from the level.
5-2
VENT1 LATION
The fresh air must be supplied
to
the engine
for
cooling and fuel combustion.
If
the engine
is
operated with a cover or in a
small compartment,' it is required
to
provide a cooling air duct and a baffle plate.for the purpose
of
preventing insufficient
circulation
of
heated air after cooling the engine and/or temperature rise
of
related equipment. High temperature
environment will cause engine vapor-lock, deterioration
of
oil, power reduction,
loss
of
engine life, it is requested to keep
the temperature
of
compartment not to exceed
50°C.
5-3
EXHAUST GAS EVACUATION
As
the exhaust gas is toxic, it must be exhausted outside in case engine is operated indoor.
Output power of 2-cycle engine is considerably influenced by the length
of
exhaust duct,
so
ask for consultation in case any
modification
of
exhaust system is required.
54
FUEL SYSTEM
In case the standard fuel tank can not be used due to space limitation or any other reason, take the following notes into
consideration:-
1) When connecting the fuel pipe, carefully examine heat conductivity, pipe diameter, bend and leakage from fittings to
eliminate air-blocking and vapor-lock.
2)
Men
the
fuel
is
to
be fed by gravity, position of fuel tank bottom should fie
within
the
height
of
5
-
50
cm from
the
fuel
joint
of
the
carburetor.
3)
Fuel must be filtered before it
is
fed to carburetor, by means
of
fuel strainer or filter.
4)
The standard inner diameter
of
fuel pipe is
4
-
5
mm.
.
5)
It is recommended to minimize the length
of
fuel pipe.
5-5
POWER
TRANSMISSION
to
DRIVE
MACHINES
5-5-1
BELT-DRIVE
Be careful with the following items.
Use a V-belt rather thana flat-belt.
Set the driving shaft and the driven shaft of machine in parallel for each other.
Align the driving pulleys
of
engine and machine correctly.
-
17
-
Page 22

*
Mount the driving pulley as close to the engine as possible.
*
Span the driving belt horizontally, if possible.
*
When starting the engine, disconnect the load.
If
a
clutch is not available, a tension pulley or other means must be employed.
5-5-2
FLEXIBLE
When a flexible coupling is used, the run out and mis-alignment between the driven shaft and the engine shaft must be made
as small as possible.
The tolerance on the run
COUPLING
out
and mis-alignment are specified by each coupling manufacturer.
"c3
JIS
CB104 female terminal
JIS
CA104 male terminal
4
LA104 or LA108 plate terminal
p"
SPARK PLUG
CONDENSER
ONTACTBREAKER
IGNITION
LIGHTING SWITCH LAMP
"""
COIL
STOP BUTTON
(6V
-
8V.
r'
\'
15W)
-
18-
Page 23

5-6-2
ENGINE
with STARTING
MOTOR
(for
EC25-2DS
only)
1
START BWTTON
I
R
ECTl
F I
ER
YELLOW^
+
I
PINK
I
I-
-
MAGNETO
LIGHT BLUE
WITH
BLACK TUBE
I
I
I
BATTERY
SPARK PLUG
-
19-
Page 24

6.
DISASSEMBLY
6-1
PREPARATIONS and SUGGESTIONS
and
REASSEMBLY
6-1-1
6-1-2
6-1-3
After disassembing and cleaning the engine parts, check them and, if necessary, correct them according to the
CORRECTION TABLE
Gaskets and fuel pipe shall be replaced to new one.
DISASSEMBLY
When disassembling the engine, memorize where and how each part is assembled
correctly. Tag parts if there is a possibility of confusion.
Take care not to damage packings and gaskets, which are fragile.
In order to prevent missing and misplacing, group related parts together, tentatively assembling them, immediately after disassembled each sub-assemb!y.
Handle the disassembled parts carefully, and wash them in Kerosene.
Use the correct tools in the correct way.
Standard tools required for disassembly and reassembly.
a> Work table
b) Washing pan
c) Disassembling tools
d) Washing
e)
Emery paper, Cloth
Before starting to disassemble the engine, drain fuel and lubricant. (To prevent from danger and stain.)
CLEANING before reassembly
1
)
Check all sliding and rotating parts, such as piston, cylinder, valve, camshaft, crankshaft, gears and bearings for defect.
2) Wash the disassembled parts in Kerosene to remove dust, dirt and contaminated oil thoroughly. Wash them twice, first
time remove visible dirt roughly, and second time using fresh Kerosene.
3)
After washing, blow them thoroughly with compressed air.
4)
Do
not wash electric parts. Wipe them with clean cloth and dry them.
5)
Accumulated carbon
wrap the piston with
6)
Parts
of
7)
Check the cable for any damage.
8)
Clean contact breaker with dry cloth. Check the breaker-point
pitting
9)
Air-cleaner element shall be soaked
1
engine oil, and assemble it after squeezed well.
10) Take special care not to contaminate the parts with dust and apply mobile oil
rust.
CHECKS
oil
(Kerosene or gasoline), Mobile
on
the cylinder-head, gasket, piston, cylinder and inside the muffler to be carefully planed and
oil
stone
to
get smooth surface.
carburetor
or
pyramidding, this should be corrected with
to
be washed carefully with gasoline and blow them thoroughly with compressed
in
the liquid soap and dry
and
CORRECTIONS before reassembly
of
section
''
12.CHECKS and CORRECTIONS".
oil,
Brush
MOO
if
it contact surface is flat. If there
wrapping paper.
thoroughly.
Then put
in
order to be able to reassemble it
air.
is
an evidence of
it
to
mixture
on
the surface in order to prevent from
of
2 - 4
kerosene and
r"
-
20
-
Page 25

'
6-1-4
REASSEMBLY
1)
Before reassembly, wash parts in gasoline.and blow them with compressed'air.
2)
Apply mobile oil on the rotating and sliding surface.
3)
Take care not to contaminate the parts with dust during reassembly.
4)
Be sure to assemble those parts provided with alignment marks by bringing the marks
in
alignment.
5)
Tighten'bolts, nuts and' screws to the correct torque specified. When there
is
no torque specification, tighten them
to torque readings appropriate to the size
Standard Fastening Torque for screws are
as
fallows:
..
6mm-
.
90
kg-cm
(6.5
ft-lbs)
8mm-
250
kgcm
(18
ft-lbs)
10 mm
-
370
kg-cm
(26.7
ft-lbs)
If.small screws are tightened too hard, they may get broken. Tighten the large size screws such as ones for the
magneto flywheel, enough by giving hammer blows
on
the socket wrench handle.
When tightening the several screws fastening the single part, tighten them all evenly, by alternately tightening diagonally
located pairs.
6) Do
not apply
oil
to the part to which packings or sealend to be fitted.
7)
When engine is completely reassembled, make sure that there
is
no
parts remained.
8)
During
the assembly, turn the moving part by hand to check
for
friction and noise.
9)
After the completion of reassembly, turn the engine by hand and check
if
there
is
any disorder or
loose
members.
-
21
-
Page 26

5-2
SPECIAL TOOLS
For
your
reference, the
following'shows
special tools
of
Robin
Engine
for
Disassembly, Meauring
and
Inspection instruments.
f-
Part
No.
2099500407
207 95003.07
Tool
Flywheel Puller
(with bolt)
Valve Spring
Retainer
USe
For
pulling off
Flywheel
For mounting and
dismounting Valvc
Spring Retainer
and Retainer
Lock
Applicable
Model
EY10,13,14
EYl8,25,27
EY33,44
EC05,07,10
EC
17,37
EY10,13,14
EY18,25,27
EY21,80
EY33,44
Shape
20595001 07
2069500107
2079500107
rlalve Guide Puller
For pulling
Valve guide
off
EY13,14
EY18
EY25,27
f
\
-
22
-
Page 27

Part
No.
214 91301
00
1067990100
"20248
PF-2L
~~
-
Tool'
C.
D.
1.
Unit
Checker
T.
C.
1.
Unit
Checker
Timing Tester
Coil
Tester
Uu,
For checking
C.
D.
1.
Unit
For checking
T.C.
1.
Unit
.For adjusting
Timing
For checking
Ignition Coil
Applicable
Model
EY10,13,14
EY18,25,27
EY33,44,21
EY80
EC03,04
EC05,07
EC10,17
EYlO, 13,14
EY 18,25,27
EY33,44,21
EY80
EC03,04,05
EC07,10,17
EC37
EY10,13,14
EY 18,25,27
EY33,44,21
EY80
EC03,04,05
EC07,10,17
EC37
-23
-
Page 28

6-3
DISASSEMBLY
and
REASSEMBLY PROCEDURE
6-3-3 FUEL TANK and FUEL TANK BRACKET
1) Disconnect fuel pipe between strainer and carburetor at carburetor side.
2)
Remove mounting bolts, and detach fuel tank from cylinder head or cylinder.
3)
For Model ECl OV
Unscrew
CAUTION: REPLACE FUEL PIPE ONCE A YEAR
DANGER CAUSED
6-3-2 AIR CLEANER
“Model
1)
Remove air cleaner cover and element.
2)
Unscrew two or three bolts which clamped
Model ECIOV
1) Remove cover and take out outer element and inner element.
2)
Loosen three bolts which clamped base plate to carburetor, and remove base plate.
In reassembly:
Wash element based
‘Model
After washed element with gasoline, soak
drip the oil off.
”
Model EClOV
After washed outer and inner elements with gasoline, soak them into the mixed
6-3-3 CARBURETOR
1)
Remove governor rod and rod spring from carburetor..
2)
Remove carburetor from cylinder block.
In reassembly:
Refer to section
6-3-4 GOVERNOR LEVER
1)
Remove governor lever from governor shaft.
2)
Remove governor spring from control lever.
3)
Control lever and stop plate can be removed by loosing wing-nut
NOTE: When control lever device are disassembled, tentatively assemble them together with governor lever.
In reassembly:
Refer to section
6-3-5
6
x
EC05-2D & 6,07-2D
EC05-2D
“8.
“8.
MUFFLER
’
M8
bolts, then remove fuel tank from blower
BY
THE FUEL LEAKAGE.
&
B,
10D
&
B,
17D
air
on
following procedure before reassembly;
&B,
07-2D
&
6,
1
OD & 6,170
it
into the mixed
GOVERNOR” and section
GOVERNOR”. Assembly shall be made securely including rotation adjustment.
“9.
’
housing.
IN
ORDER
&
B,
25-2D & DS
cleaner base plate to carburetor and remove base plate.
&
B,
and
25-2D
&
oil
of
CARBURETOR”.
TO
PREVENT
FROM
THE
DS
2 - 4
kerosene and 1 engine
oil
of
2
-
or
bolt but do not disassemble unless it necessary.
oil,
then reassemble it after
4
kerosene and 1 engine
OCCURANCE OF
oil.
\
f
\
Unscrew nuts and remove it from cylinder.
6-3-6 BLOWER
1
)
Disconnect stop button wires from Connector.
2)
Unscrew bolts and remove blower housing from crankcase.
HOUSING
-
24
-
Page 29

6-3-7
RECOIL
STARTER
Standard configuration on Model EClOV, 17V.
Optional equipment for other models.
1)
Remove recoil starter from blower housing by unscrew
3
X
M6
bolts
(4
X
M6
bolts for Model EC17)
2)
Remove starting pulley from flywheel by loosing bolts clamped.
NOTE:
Unless it is necessary, do not disassemble recoil starter
as
special tools are required
for
reassembly.
6-3-8
STARTING
PULLEY
and
MAGNETO
(Fig.
6-3-1)
Remove’ starting pulley from flywheel.
Remove flywheel from crankshaft.
Apply a socket wrench over the nut at end of
crankshaft and give the wrench a sharp blow with
a
soft.
hammer.
Remove nut and spring washer. Attach flywheel
puller to flywheel as illustrated in Fig. 6-3-1, turn
center bolt clockwise until flywheel -becomes loose
enough to be removed.
Remove spark plug cap from high tension cable
of
igniton coil and remove ignition coil from crankcase.
Take
off
the point cover and remove contact breaker
and” condenser, from crankcase.
In reassembly:
Fig.
6-3-
1
Refer to “7-2 BREAKER POINT ADJUSTMENT”, “7-3 TIMING ADJUSTMENT” sections.
6-3-9
CYLINDER HEAD
(Model
EC10,
17
only)
1)
Remove spark plug from cylinder head.
2)
Unscrew mounting special bolts and remove cylinder head from cylinder.
3)
Remove cylinder head gasket from cylinder.
In reassembly
:
1)
Clean carbon from combustion chamber and dirt from between the cooling fins of cylinder head.
Check its mounting face for distortion.
2)
Use
new -cylinder head gasket.
NOTE:
Cylinder head gasket must
be
placed folded
edge
upside
(To
the cylinder head).
3)
Cylinder head fin must be placed in paralle with crankshaft.
Fastening torque
of
cylinder head
is
as shown below:
EClO
-
180
-
220
kg-cm
(13
-
16
ft-lbs)
EC17
-
370
-
420
kg-cm (26
-
30
ft-lbs)
EC25-2-
200
-
250
kg-cm (15
-.
18
ft-lbs)
4)
Fastening torque of spark-plug is as shown below:
250
-
300 kg-cm
(18
-
22
ft-lbs)
..
-
25
-
Page 30

,
6-3-10
1) Remove cylinder from crankcase by removing nut and spring washer.
NOTE: For
2)
3)
In reassembly:
1) Clean carbon deposit from cylinder head and combustion chamber.
CAUTION: WITHOUT CLEANING THE CARBON DEPOSIT, IT MAY DAMAGE THE PISTON AND INNER
CYLINDER
Model
EC05:2,07-2 Remove spark plug prior
Remove cylinder gasket.
For Model EClOV remove intake pipe from cylinder.
SURFACE
Replace cylinder gasket
Intake
walls, then after assembled the cylinder securely, make sure
Fastening torque
EC05-2 90-100 kg-cm
EC07-2 90-100 kg-cm
EClO
EC17 180-220 kg-cm (13-1
EC25-2
OF CYLINDER WHEN REASSEMBLY.
to
new one.
of
cylinder should be positioned
of
cylinder
is
as
shown below: Fastening torque
90-100 kgcm
340-400
to
kgcm (25-29 ft-lbs)
the left against view from blower side, Apply
(6.59
(6.5-7
(6.5-7
ft-lbs) E05-2 250-300 kg-cm (18-22 ft-lbs)
ft-lbs) E07-2 250-300 kg-cm (18-22 ft-lbs)
ft-lbs)
6
ft-lbs)
to
removing cylinder.
if
the crankshaft rotate smoothly.
of
spark plug for EC05-2,
oil
to
piston ring and cylinder
07-2:
CAUTIONS:
r)
WHEN
2)
BEFORE REASSEMBLE CYLINDER, APPLY OIL ON NEEDLE BEARING LOCATED TO END OF
CONNECTING
6-3-1
1
PISTON
1) Remove both side piston pin clips
2) Pull out piston pin and disconnect the needle bearing from small end
CAUTION: IN ORDER NOT TO DAMAGE PISTON, PULL OUT PISTON PIN BY FIRMLY HOLD PISTON. ALSO
TAKE A SPECIAL CAUTION WHEN DISASSEMBLE NEEDLE BEARING.
3)
Remove piston rings from piston by expanding the open ends
In'reassembly
PISTON RINGS
If
an expanding tool is not available, install rings by placing the open end
far enough
CAUTIONS:
1)
BE EXTREMELY CAREFUL NOT
2)
STRIKE THE KNOCK PIN TO THE GROOVE LOCATED ON OPEN END OF RINGS (THIS
PREVENT FROM THE ROTATION OF RINGS WHILE OPERATING THE ENGINE.)
31
ASSEMBLE RINGS IN THE ORDER OF 2ND RING AND IST RING.
1ST RING
2ND RING- PERKARIZED SURFACE (2ND RING FOR MODEL EC25-2
FASTENING
:
(Fig.
to
slip over the piston and carry it into correct groove,
-
CYLINDER,
ROD.
TIGHTEN
FOUR
6-3-2, 6-3-3)
TO
DISTORT AND BRAKE THE RING.
CHROMIUM PLATED SURFACE
FACE.)
(RING FOR MODELS EC05-2,07-2
NUTS
UNIFORMLY.
of
of
rings.
of
connecting rod.
the ring
on
(Fig.
IS
NOT CHROMIUM PLATED.)
first land of piston, spread ring only
IS
TO
6-3-3)
IS
CHROMIUM PLATED
SUR-
-
26
-
Page 31

TOP
RING
SECOND
RING
..........
ISTON
RING
Fig.
6-3-2
Fig.
6-3-3
PISTON
1) Position the
“F”
mark
of
piston to blower side and reassemble the piston and connecting rod by firmly striking the
piston pin, and needle bearing.
CAUTION: APPLY
OIL
TO THE NEEDLE BEARING BEFORE REASSEMBLE IT
TO
PISTON-PIN.
2)
Assemble piston pin clip.
CAUTION: REPLACE PISTON PIN CLIP
IF
THERE
IS
ANY LOOSENESS AFTER REASSEMBLE IT.
3)
Be sure that piston and connecting rod moves smoothly after reassembled.
6-3-12
CRANKCASE COVER (Model
D
and
V
only)
(
Fig.
6-3-4)
1) Discharge oil by opening oil drain plug.
(No
discharg-
ing the
oil
is required for Model
EC05-2
and
07-2)
2)
Remove bolt and washer
from
crankshaft end.
3)
Remove bolts on crankcase.
4)
Detach cover gasket.
In reassembly:
1) Replace cover gasket to new one.
2)
Check bail bearing and
oil
seal
if
there is any damage.
And replace it if necessary.
3)
Apply oil on bearing and oil seal, and coat oil-seal
guide to the contact surface
of
crankcase cover.
Fig.
6-34
Attach
oil
seal guide on end
of
crankshaft and mount crankshaft in crankcase with extra care not to damage
lips
of
oil seal. Then fasten the bolts uniformly.
Fastening torque
is:
EClO
180
-
220
kg-cm
(13
-
16
ft-lbs)
EC17
180
-
220
kg-cm
(13
-
16
ft-lbs)
EC25-2
200
-
250
kg-cm
(1
5
-
18
ft-lbs)
6-3-13
GOVERNER PLATE
(Model
D
and
V)
1) Pull out governer plate, governer sleeve, washer and clip from crankshaft.
2)
Remove woodruff key
In reassembly: Reassembly with reverse sequence correctly.
-
27
-
Page 32

6-3-14 REDUCTION COVER
1
)
Discharge
2)
Remove reduction cover by loosen the bolts on crankcase.
3)
Remove washer and bolt on driving shaft end.
4)
PUn
5)
Open tab of lock-washer and pull out pinion, governer platp, governer sleeve, washer and clip from crankshaft, and
detach
In reassembly:
Reassemble with reverse sequences. After tighten the nut, bend the tab of lock-washer without fail.
6-3-15 GOVERNOR SHAFT
1)
Unscrew 2 screws and remove governor arm.
2)
Pull out governor shaft with governor lever from’crankcase.
oil
by opening oil drain plug.
out driving shaft with reduction gear from reduction cover.
2
woodruff keys.
(Model
B)
f
“.
NOTE: Do
In reassembly: Refer to section
6-3-16 CONTROL
Unless it is required, do not remove control lever from crankcase.
In disassembly and reassembly, refer to section
6-3-17 BASE PLATE
Base plate can be removed by loosening 4 bolts on crankcase.
In reassembly
After reassembled base-plate
rod.
6-3-
18
Unscrew 4 bolts which fastening front crankcase and rear crankcase and separate both crankcase by tapping them with soft
hammer, and detach crankshaft connecting rod assy.
In reassembly
Before reassemble the front and rear crankcase, check bearings and oil seals if there is any damage and replace them in
case any damage found.
Apply oil onto the bearings of both crankcase and ascertain there is no warp on the lip of oil seal.
Clean the joint of both crankcases and apply seal end. Assemble the crankshaft and joint both crankcases with press (or
tap them with soft hammer) having extra care not to damage the oil seal.
Fastening torque is:-
not
disassemble if
LEVER
:
C RAN KCASE
:
EC05-2
EC07-2
not
necessary.
“8.
GOVERNOR”.
to
the crankcase, be sure that crankshaft moves smoothly by holding small end of connecting
-
90-100 kg-cm (6.5-7.0 ft-lbs)
-
90-100
kg-cm
(6.5-7.0
“8.
GOVERNOR”.
ft-lbs)
EClO
EC17
EC25-2
-
-
-200-250
90-100 kg-cm (6.5-7.0 ft-lbs)
90-100 kg-cm (6.5-7.0 ft-lbs)
kg-cm (1 5-1 8 ft-lbs)
i
\
CATUION:
BY
NOTE: After reassemble the crankshaft to the crankcase, be sure that crankshaft moves smoothly.
6-3-19 CRANKSHAFT
Reassembly of crankshaft requires special tools.
Sub-assembly of crankshaft and connecting rod assembly
WHEN
TIGHTENING DIAGONALLY LOCATED PAIRS AT SUGGESTED FASTENING
TIGHTEN
and
CONNECTING ROD
THE
SEVERAL
BOLTS
ASSY.
FASTENING
is
available as a spare parts.
-
28
-
CRANKCASE,
,TIGHTEN
TORQUE.
THEM
ALL
EVENL
y
Page 33

..
7.
MAGNETO
.
,
.
7-1
'
MAGNETO
._
.
.'
".
,
r
The spark for ignition is furnished by a magneto assembly. The magneto consists of a flywheel, ignition coil and breaker
'
assembly .(.including condenser),
of
which flywheel is 'mounted on. crankshaft and ignition coil and breaker assembly are
mounted
.-
in crankcase directly.
7-2
BREAKER
POINT
ADJUSTMENT
(Fig.
7-2)
The breaker points, which are mounted
in
the crankcase in-
side the flywheel should be checked twice a season
or
when-
ever the ignition, spark becomes weak. If there is,evidence
of
pitting or pyramidding, the breaker points must be corrected, and then it becomes necessary to readjust the gap to
its proper clearance.
(0.4
mm
for Model EC10)
The normal breaker point opening is
0.4
mm at full separa-
tion. Since the spark timing
of
18"
is
regulated by the
point
opening, use a timihg light to obtain
an
accurate spark ad-
vance. (Refer to
"7-3
TIMING
ADJUSTMENT.")
NOTEI The point gap
of
other engines.than model EC70 is
as
follows:
EC05
:
0.35
mm
EC07-2
:
0.35mm'
ECl7
:
0.30
mm
EC25-2
:
0.35mm
I.
Ftg.
7-2
i'
To adjust breaker poixit opening, remove starting pulley, blower houshg and flywheel from the eingine and proceed as follows:
1-
(See
Fig.
7-2.)
1)
Remove breaker cover from contact breaker.
2)
Turn
crankshaft .over until. breaker arm comes in contact with. the high point
of
the breaker cam. (maximum point
',
.
opening of
0.4
mm)
3)
Loosen contact suppoit plate lock screw just enough
so
that bracket can be moved.
4)
Insert
a
0.4
mm feeler gauge between the points.
CAUTION:
ADJUS?
BREAKER POINT GAP WITHOUT OPENING
IT
MORE THAN
2
mm,
OTHERWISE RATED
,-
HEEL-PRESSING FORCE MAY
NOT
BE: OBTAINED 'DUE
TO
THE BENDING
Of
CONTACT BREAKER
ARM.
5)
Apply a screw driver to.adjusting tab and move the contact support plate just enough
so
that a slight drag is felt while
sliding the feeler gauge from between the points.
6)
kghten lock screw and recheck breaker point gap.
..
7)
Pull a strip of
8 - 10
mm wide white paper through the closed points
to
remove
oil
and dust on the point surfaces.
I.
.
'
CAUTION: WHEN INSERTING A SHEET
OF
PAPER;, NEVER OPEN THE BREAKER POINT GAP MORE THAN:2mm.'
8)
Mount flywheel, blower housing and starting pulley on engine after adjustment.
-. .
..
~
...
,.
..
..
VI
..
Page 34

With the Model
TDC
on
the compression stroke.
vance
is
obtained when the breaker point opening
proper point opening. However, the advance timing
timing
light
NOTE:
Spark advance
EC05, EC07-2, EC25-2
EClO
EC17
EC05-2,07:2,
as shown
in
Fig.
of
each model
10,
This
7-3-3.
23"
:
18
.-
22"
17
and
25-2
spark advance of
is
as
follows:
engines, the spark
is
timed to occur
18"
-
23"
is
controlled
is
adjusted according to the
is
more accurately adjusted through the following procedures using
18" - 23"
by
the breaker point opening and this ad-
BREAKER POINT ADJUSTMENT
before the position reaches
to its
a
NOTE:
7-3-1 ALIGNMENT MARK
For timing adjustment, the following alignment marks are provided as
7-3-2
Refer
to
section
*Line mark
*Line mark
DEFERENCE
D
type and V type: Clockwise
B
type: Counter-clockwise arrow
on
on
"4-1
I
IGNITION.
for
TIMING ADJUSTMENT
crankcase
flywheel circumference and cooling
among
MAGNETO
arrow
"and
"12.
CHECKSand
(See
fan
for
D
TYPE, V TYPE
is
embossed on cooling fan.
is
embossed
CORRECTIONS."
Fig. 7-3-1.)
and
B
on
cooling fan.
shown
TYPE
on
Fig.
(See
Fig. 7-3-2.)
7-3-1.
TIMING
MARKS
Fig.
7-3-
7
Fig.
7-3-2
-
30
-
Page 35

7-3-3
FOR
TIMING ADJUSTMENT, THE FOLLOWING PROCEDURES USING A TIMING,TESTER:
Disconnect the stop button lead wires and the coil primary wire.
Remove blower housing from engine.
Connect the timing tester lead with red rubber cap to
the coil primary wire and ground the lead with black
rubber cap to crankcase. (See
Fig.
7-3-3.)
While the
points are open, the buzzer within tester remains ringing and when the points are closed, the tester remains
silent.
Turn flywheel slowly counter-clockwise (D type and
V
type engines) or clockwise
(B
type engines) until the
buzzer within tester becomes silent.
Then, turn flywheel very slowly clockwise
(D
type and
V
type engines) or counter-clockwise (B type engines)
and stop immediately the moment the buzzer within
TIMI
\
GROUND
WIRE
tester begins ringing.
Fig.
7-3-3
Check
if
line mark
on
the flywheel
is
in
the line with line mark on the crankcase. When the line marks are in alignment,
the timing
is
correct.
If the timing mark lines are not
in
alignment, then readjust the point opening according to the BREAKER POINT
AD-
JUSTMENT, by-removing the flywheel and repeat the checking procedures
3)
through
S).
Afer completing the timing adjustment re-mount the blower housing and connect the coil primary lead to the stop button.
MAGNETO’
TROUBLE
SHOOTING
When the engine does not start or starts with difficulty, or when its operation is unstable, the following tests will clarify
if
they are caused by a defect in the magneto.
1) Check ignition cable for possible corrosion, broken, worn insulator or loose connection.
2)
Check the sparking as described later
in
this section.
3)
Check if the breaker points require cleaning, or adjusting
or
not.
If
the points are badly corroded or pitted. Condenser
may have to be replaced.
Refer to “BREAKER P0IN.T ADJUSTMENT”
4)
If no spark takes place, replace ignition coil.
SPARK
TESTING
Remove spark plug from cylinder head and place it on blower
housing,
with the ignition cable connected to it.
Crank the’ engine several times by starting pulley and observe the spark in the spark gap of spark plug. If the spark is strong,
the ignition system can be eliminated as the source of trouble.
If the spark is weak or there is no spark at all, repeat the checks according
to
the procedures
1)
through
3)
above. The
The correct electrode gap is
0.5
-
0.7
mm.‘ (Refer to section
12.
CHECKS and CORRECTION.”)
-31
-
Page 36

8.
GOVERNOR
8-1
CONSTRUCTION
and
OPERATION
In the model EC05-2,
plete, governor sleeve and governor arm are installed
case (EC05-2D, 07-2D) or
07-2,
EC05-2,
As
the engine speed fluctuates, flyweight on the governor plate complete, rotating together with the crankshaft, changes its
by the mixture fuel).
07-2,
10,
17
and
25-2
engines, a centrifugal flyweight type governor
in
the governor chamber (EClOD,
in
the reduction chamber (type B and
V),
and lubricated
is
used. The governor plate com-
lev,
17D and
by
the lubricating
25-2D),
oil
(in the model
in
the crank-
opening angle and moves the governor sleeve, which in turn rotates the governor shaft through the governor arm. The governor lever
tle lever through
is
connected to the extending
the
governor rod at the other end; thus the throttle valve
part
of the governor shaft and this governor lever
is
opened
is
connected to the carburetor throt-
or
closed and engine speed and output
are controled.
When the crankshaft rotation increases, all the relevant members move
in
the direction indicated by-marks and the car-
buretor throttle valve closes, reducing the fuel supply and consequently reducing the speed and output. When the crankshaft
rotation decreases, the same members
moie
in
the direction indicated by-- --marks and the carburetor throttle valve open,
increasing the fuel supply and consequently recovering the failing speed and output.
GOVERNOR
THROTTLE LEVER
ROD
SPRING GOVERNOR
ROD
THROTTLE VALVE
GOVERNOR LEVER
FLYWEIGHT
GOVERNOR
CRANKSHAFT
GOVERNOR SLEEVE
GOVERNOR SPRING
ARM
CONTROL
LEVER-
CARBURETOR
STOPPER
HIGH SPEED STOPPER
PLATE
BOLT
Fig.
8-
1-
1
Model
-
32
ECO5-2,
-
07-2
Page 37

I.
..,
\-SPACER
\“SET
PIN
GOVERNOR SLEEVE
..
..
..
Fig.
8-1-2
Model
ECIO,
17,25-2
-33-
’
Page 38

8-2
GOVERNOR
The governor linkage should be adjusted, after reassemble it according to the following procedures.
1)
Connect governor rod and rod spring to carburetor throttle lever and governor lever, then install these to governor
shaft.
NOTE: Never tighten adjusting plate set screw at
shaft
2)
Connect governor lever and control lever with governor spring, and install control lever on crankcase.
ADJUSTMENT
this
time, and do not fixed adjusting plate, governor lever and governor
8-2-1
IN
CASE
OF
MODELS
As
shown by arrow mark
er to
high
speed side (clockwise) until stop fully, and
fasten the control lever
Loosen lock nut at the end
screw on adjusting plate.
As
shown
plate
Tighten both lock nut at the end
shown on
by
the
arrow
all
the way until it will not travel
Fig.
8-2-3
EC10,
EC17
(See
Figs.
8-2-1,8-2-2
on
Fig.
8-2-1
turn control lev-
by
tightening wing bolt.
of
governor shaft and set
on
Fig.
8-2-2,
move adjusting
any
more.
of
governor shaft as
and set screw on adjusting plate.
and
8-2-3.)
Fig.
8-2-1
Fig, 8-2-2
-34-
Fig.
8-2-3
Page 39

8-2-2
'
IN
CASE
OF
MODELS EC05-2, EC07-2
(See
Figs.
8-2-4
and
8-2-5.)
1)
As
shown by arrow mark on Fig.
8-2-
5
turn control lever to high speed side (counter-clockwise)
until
stop fully, and
fasten the control lever
by
tightening wing nut.
2)
With a screw driver inserted in the groove of governor shaft, turn it counter-clockwise fully (until it
will
not turn any
more) and then lock governor. lever to governor shaft by tightening clamp nut. (See Figs.
8
-24
and
8
-2-5.)
GOVERNORSHAFT
\I
GOVERNOR
Fig.
8-2-
4
Fig.
8-2-5
8-2-3
IN
CASE
OF
MODEL EC25-2
(See
Fig.
8-2-6.)
Governor adjustment procedure
is
exactly same as that for
model
EC10.
LCLAMP
NUT
Fig.
8
-2-
6
-
35
-
Page 40

8-3
HIGH
SPEED ADJUSTMENT
*
Maximum speed for standard engine:
...............
...............
................
NO
TACHOMETER
8-3-1
EC05-2
EC07-2
EClO
WHEN
(Fig.
8-31
5,500
5,500
5,000
IS
AVAILABLE
r.p.m. EC17
r.p.m. EC2 5-2
r.p.m.
................
...............
5,000
5,000
r.p.m.
r.p.m.
Unless required in the process
crankcase. If it is necessary to remove them,
case, control lever must be turned clockwise
per bolt on control lever (Fig. 8-3-1).
When reassembling, re-establish the recorded dimension
WHEN A TACHOMETER
8-3-2
1)
Install stopper plate, control lever and other related parts.
2) By turning control lever with governer spring on it, increase gradually the engine speed up to specified engine speed.
3)
Then follow the below:
In case of models EC05-2,07-2 and 25-2, locate high speed stopper bolt on the control lever and lock it
as
work
In case
will
Make sure that the governor spring
2 holes (EC05-2),4 holes (EC17) or
Normally, hook governor spring in the second hole from the top (ECl
stopper of control lever against the stopper plate.
of
models EClO and EC17, locate stopper plate and fasten
work as stopper of control lever.
of
disassembling, do not remove control lever stopper plate and/or other related
in
models EClO and EC17 record the dimension
all
the way.) In models EC05-2, EC07-2 and EC25-2, never
"L"
in
models EClO and ECl7.
IS
AVAILABLE
is
put back
3
holes (EC25-2) on the governor lever.
in
the same hole
on
the governor lever as before. There are 5 holes (EC10) or
it
to crankcase
0,
17) or in the lower hole (EC05-2,07-2 and 25-2).
ADJUSTING
"L"
prior to removeing. (This
turn
so
that wing bolt on stopper plate
SCREW
parts
high
speed stop
so
that it will
(THROTTLE
from
WIRE)
GOVERNOR LEVER
GOVERNOR
SPRING
Fig.
8-3-
1
Model
-
36
EC05-2,
-
07-2
CONTROL LEVER
HIGH
SPEED STOPPER BOLT
Page 41

/-
GOVERNOR SPRING
'
ADJUSTING
SCREW
(THROTTLE
WIRE)
Fig.
8-3-2
Model
EClO,
17
SPRING
Page 42

9.
CARBURETOR
PILOT AIR JET
CHOKE LEVER
PILOT SCREW
PILOT OUTLET
BANJO BOLT
STRAINER
BLEED
AIR
JET
CHOKE VALVE
PILOT JET
MAIN AIR JET
MAIN
NOZZLE FLOAT CHAMBER
MAIN JET
/
FUEL
DRAIN
PLUG
NEEDLE VALVE
THROTTLE VALVE
BASIC FUEL LEVEL
““““C
FUEL
-I
Fig-
-38
9
7
-
Page 43

9-1
CONSTRUCTION
and
OPERATION
9-1-1 FLOAT
SYSTEM
The float chamber is located just below carburetor main body and serves to maintain the fuel level at a constant height by a
joint action of float
(F)
and needle valve
(NV)
incorporated. The fuel flows from the fuel tank into float chamber via needle
valve, which is kept open while the fuel level is low, but closed when the fuel level reaches a predetermined level causing the
float to move up.
9-1-2
THROTTLE VALVE
The throttle valve is operated by the control lever and controls the amount
of
air-fuel mixture and controls engine output
power.
The richness
of
mixture or the air-fuel ratio is automatically regulated at the optimum valve regardless
of
the throttle valve
position.
9-1-3
CHOKE VALVE
The choke valve is operated by the choke lever and when it is closed, the air-fuel mixture becomes rich, and as it is opened
the more, the leaner will be the mixture. The choke system serves to facilitate start-up in cold season. When engine is
cranked with choke closed, the negative pressure to main nozzle increases to introduce fuel in large quantities to make
start-up easy.
9-1-4
PILOT SYSTEM
and
MAIN SYSTEM
This pilot system feeds fuel to engine during idle and slow speed operation.
The fuel fed through main jet
(MJ)
is measured by pilot jet
(PJ),
mixed with air measured by pilot air jet
(PAJ),
regulated
by pilot screw, and then fed to engine through pilot outlet
(PO)
and bypass
(BP).
The fuel
is
mainly fed from pilot outlet
(PO)
during idling.
This main system feeds fuel
to
engine during medium and high-speed operation.
The air measured
by
main air jet (MAJ) is mixed into fuel through bleed holes
of
main nozzle
(MN)
and discharged
to
main
bore
(MB)
as
atomized fuel where it is mixed with intake air through air cleaner to become an optimum air-fuel mixture to
be supplied to engine.
9-2
DISASSEMBLY
and
REASSEMBLY
(Fig.
9-2)
Besides mechanical failures, most trouble are caused. by incorrect mixing ratio. The most common causes
of
such incorrect
fuel-air mixtures are clogged jets, restricted air and fuel passages, and variations in fuel level, In order to obtain the full
performance of carburetor, it is necessary
to
keep air cleaner and carburetor clean
so
that air and fuel flow without any
restriction.
Observe following disassembly and reassembly procedures. (see Fig.
9-2)
CAUTION: AFTER DISASSEMBLY, CLEAN ALL PARTS
IN
A SUITABLE SOLVENT, ALL JETS AND VALVES
SHOULD BE BLOWN OUT WITH FRESH COMPRESSED AIR, NEV€R USE A DRILL OR WIRE TO CLEAN OUT
JETS OR IDLE HOLES.
-
39
-
Page 44

31
22
\
25."-3&
9-2-1 THROTTLE SYSTEM
1)
Remove guide screw
CAUTION: TAKE CARE
2)
Remove spring
9-2-2 CHOKE SYSTEM
1)
Take out Philips-screw
2)
When choke shaft
In
reassembly:
1)
Insert spring
2)
When assembling choke, the flat
(24)
is
(32)
and steel ball (31)
Fig.
92
(22),
Philips-screw (171, remove throttle valve (16), and then pull out throttle shaft
NOT
TO
DAMAGE'ENDS
by unscrewing throttle stop screw
(20),
remove choke valve (1
pull out, choke spring
on
(32)
in
the hole and install choke shaft (18).
choke valve must be toward the main air jet side.
OF
THROTTLE
(23).
9),
pull
out
and steel ball
-
40
-
VALVE.
choke shaft
(31)
should be removed, lest they be lost.
(18).
(1
5).
Page 45

9-2-3 PILOT SYSTEM.
..
1) Remove pilot jet (21) using a suitable tool while taking care not to damage it.
2)
Remove pilot screw
(25)
and spring
(26)
In reassembly:
.I
-.
.11
1) Tighten pilot jet and pilot plug firmly to prevent fuel leakage.
2)
Replace pilot screw if tapered end
is
damaged.
*
.
CAUTION:
DO
IQOT
OVERTIGHTEN.
9-2-4 FLOAT
SYSTEM
1) Remove guide holder
(5)
and float chamber (1 1).
2) Remove screw (14) and float arm
(8)
by taking out!float pin
(9).
CAUTION: TAKE CARE NOT TO DAMAGE FLOAT AND FLOAT ARM.
3)
Remove needle valve (7) and packing
(6).
CAUTION: WHEN REPLACING NEEDLE VALVE, REPLACE
IT
TOGETHER WITH VALVE SEAT WITHOUT FAIL.
In assembly:
Wash inside
of
float chamber with gasoline.
9-2-5 MAIN
SYSTEM
1)
Remove main jet
(4)
from guide holder
(5)
using a suitable tool.
CAUTION: TAKE CARE NOT TO DAMAGE
IT.
2)
Remove main nozzle
(3).
NOTE: In case
of
ECIO,
no need to remove main nozzle because
of
main nozzle being incorporated into carburetor body.
In reassembly:
1)
Tighten main jet securely to guide holder and tighten guide holder to carburetor body.
2) Tighten guide holder to
70
-
80
kg-cm
(5.5
lbs-ft).
A
too rich fuel mixture will result
if
not tightened securely.
9-3
ADJUSTMENTS
When the control lever is set at slow speed side, the engine should be operated on idling speed.
*The idling speed
of
engine is adjusted
in
the following sequence.
Specified idling speed:
EC05-2.
.............
1300 r.p.m.
*
100
..
EC25-2.
..............
1500r.p.m. * 100
EC07-2
..............
1300 r.p.m. k 100
EClO 1300 r.p.m.
f
100
.
EC17
.................
1300
r.p.m. k 100
.-
...............
,
1) Adjust pilot screw by turning
it
counterclockwise by 1 turn (1 % turn for Model EC17) after fully, closing
it
once.
CAUTION:
DO
NOT OVERTIGHTEN PILOT SCREW WHEN CLOSING IT FULLY. THE NEEDLE POINTMIGHTBE
DAMAGED
BY
OVERTIGHTENING.
2) THROTTLE STOP SCREW
Turn throttle stop screw clockwise until the specified idling speed is obtained.
If this speed exceeds specified idling speed, turn throttle stop screw counterclockwise.
..
-41
-
Page 46

10.
RUN
IN
OPERATION
An
overhauled engine must
Especially when cylinder, piston or
of
REASSEMBLED ENGINE
be
carefully run-in to get proper surface condition
piston
rings are replaced, a thorough run-in operation
The recommended run-in schedule is as follows:
LOAD
EC05-2
EC17 EClO EC07-2
EC25-2
on
newly installed parts.
is
indispensable.
SPEED TIME
I
1.5 HP
1.8
HP
2.0 HP
2.3 HP
No load
No
load
No
load
3.0
HP
5.0
5.5
HP
HP 3.5 HP
8.0
9.5
HP
HP
I
2,000
rprn
3,000
rprn
4.000 rprn
4,000 rprn
4,500 rprn
I
10
10
10
30
60
rnin.
rnin.
rnin.
min.
rnin.
I
~
-
42
-
Page 47

.I
11.
TROUBLE
SHOOTING
For a gasoline engine
to
start and run satisfactorily, the following three reyuirements must be met:
1)
The cylinder filled with a proper fuel-air mixture.
2)
An
appropriate compression in the cylinder.
3)
Good spark at correct time
to
ignite the mixture.
If
all
the three requirements are
not
met simultaneously, an engine can not be started. There are also other factors such as
heavy load at starting and too long an exhaust pipe causing a high back pressure, which contribute to hard starting.
The most
common
causes
of engine troubles are given below.
11-1
STARTING
DIFFICULTIES
Cause
~
Defects in spark plug
Defects
in
high-tension
cable
Defects
in
contact
breaker
Defects
in
magneto
Other defects
in
electric system
Gas leak through head
gasket'or other parts
Defects in piston
assembly
Remedy
1) If contaminated, wash in gasoline, remove
2)
If
spark plug
is
broken and lost insulation,
3)
Adjust spark gap to
0.5
-
0.6mm. (for Model
foreign material and dry.
replace
plug.
EC10)
If cable
is
burnt, replace cable along with coil.
1)
If breaker points are rough, smooth out
surface with emery paper
(#400).
2)
If
breaker point gap
is
incorrect, adjust
it
to
specified
0.4
*
0.05mm (for Model EC10) by
loosening contact support plate lock screws.
3)
If
spark timing is incorrect, adjust
it
to
18"-23" before TDC. (refer to
4-1 1
)
4)
If
breaker
is
defective in insulation, replace
breaker.
5)
If
condenser
is
defective, replace.
1)
If
wire or insulation
is
broken, replace
2)
If
magnetism
is
weak, re-magnetize (at
the
magneto.
magneto maker) or replace.
'
1)
If
stop-button
is
faulty, (short circuiting)
replace or repair.
2)
If
primary wire
is
grounded to the engine
body, insulate
it
with insulating adhesive
tape.
1)
If
head gasket
is
defective, replace.
2)
If
head bolts are loose, tighten.
3)
If
spark plugs are loose, tighten.
4)
If
spark plugs are defective, replace.
1)
If piston
is
worn, replace.
2)
If
cylinder is worn, re-bore and use oversize
piston and piston ring.
(No
oversize for
EC052 and
07-2.)
3)
If
piston rings are worn, replace.
4)
If
piston rings are stuck, clean or replace
rings.
Preventive measure
1)
Use spark plugs of specified heat range.
Do
not
use
poor grade oil. Clean air cleaner and
avoid dust entry.
2)
When spark gap
is
adjusted, if center
el-
trode
is
hit or bent, insulator may get
damaged.
1) Keep air cleaner always clean.
2)
Do
not use poor grade oil. Change oil
regularly.
-43
-
Page 48

Cause
in
Defects
system
Defects in carburetor
Defects in carburetor
Excess load
fuel tank
Remedy
1)
Clean clogged tank outlet.
2)
Clean clogged fuel strainer.
3)
If incorrect fuel is poured into tank or
water is mixed, drain tank completely and
fill
it
4)
1
2)
1)
2)
If
wear. Replace, if necessary.
1)
2)
with correct fuel.
When fuel pipe is locked with air, expel1 air.
)
If clogged with
If defective, replace.
Clean jets and other orifices,
clogged.
Start engine with fully open choke vatve and
half open throttle valve.
Remove drain plug from crankcase, and
close fuel cock, repeat starting operation
several times to evacuate excess fuel.
fuel overflows, check needle valve seat for
If power transmission
correct tension.
If
load
dust,
clean.
if
belt
is
too tight,
is
still too heavy, install a clutch.
they are
Preventive measure
11
Be sure to use a filter when adding fuel.
2)
Use
mixture (gasoline
1)
Never
close
warm.
2)
When stopping the engine, run it at
speed for a while. This practice not only
favourably affects next starting, but
improves engine life.
3)
Clogged air-cleaner results in
fuel mixture.
C\ean
it
throughly.
Be careful clogged carburetor.
25
:
oil
1
choke valve when engine
)
as fuel.
too
slow
rich air-
is
also
p
\.
'
1)
If piston seizes, correct or replace.
2)
If
connecting rod large end
seize, replace.
or
small end
11-2
SLOW-SPEED
1)
If
the pilot screw in the carburetor is not correctly adjusted, correct it. Refer to section
Piston or Connecting
Rod
seized
out of
order
of CARBURETOR".
2)
Most defects listed as causes
11-3
OVERHEATING
1)
If the ignition timing is
and
Model EC05-2,07-2,25-2
2) If
if
3)
Model EClO
Model EC17
too
much carbon deposits in the combustion chamber,
the heat
...............
..............
range
of
the spark plug is
Model EC05-2,07-2,25-2
Model EClO
Model EC17
4)
If the air-fuel mixture is too lean, clean jets and other holes in .the carburetor.
...............
...............
for
starting difficulty are also causes for faulty slow-speed operating.
KNOCKING
too
far advanced, correct it.
.....
23"
18"
.22"
too
NGK
.....
NGK
NGK
cool, replace
B6HS
B-4
B-4H
remove
it
with correct one.
it.
Clean the aircleaner also.
5)
If the load is in excess, reduce it below the specified continuous load.
1
)
Do not use poor grade oil.
2)
Use
fuel
of
proper mixing ratio.
"9-3.
ADJUSTMENTS
-
44
-
Page 49

114
POWER DROP
1)
If the cylinder, piston or piston rings are worn, replace them or re-finish the cylinder by boring and fit oversize piston
and piston rings. Replace or clean sticking piston rings.
j
NOTE:
No
oversize
for
EC052,
07-2.
, ,
,
2)
If the carburetor is out of order, re-adjust or clean it.
3)
If the spark plug is faulty (contamination, gas leakage or faulty insulation), clean it or replace it.
4)
If combustion gas leaks through the cylinder, and cylinder head. joint, re-tighten the clamping screws.
If the gasket is faulty, replace it.
5)
If the magneto or the contact breaker is faulty, replace them or re-adjust them.,
6)
If the aircleaner is clogged, clean it.
7)
If the fuel system
is
clogged,’ clean it.
8)
If the oil seals at the crankshaft are worn and let the compressed gas through, replace them.
a”
11-5
EXCESSIVE
FUEL CONSUMPTION
..
1) If
too
rich air-fuel mixture, clean jets and small holes in carburetor.
2)
If
the throttle shaft
of
carburetoris worn, replace throttle shaft. (carburetor).
3)
If fuel leakage, re-tighten screws or replace.
4)
If beside these causes, also caused by power drop, perform remedies
for
power drop, according to 114.
POWER
DROP.
11-6
ENGINE HUNTING
1) If the governor lever, governor shaft, governor spring or other members are incorrectly adjusted, re-adjust or correct
them.
2)
If the fuel-air mixture
is
too lean. Clean the carburetor.
3)
If the pilot screw in the carburetor is incorrectly adjusted, re-adjust it.
,
4)
If the governor spring
is
deformed permanently, replace it.
5)
If the governor sleeve is not functioning correctly, correct it.
6)
If
the
flyweight or the governor sleeve
is
worn, replace the worn one.
7)
If the governor shaft is not functioning properly, correct it.
11-7
OTHER COMPLAINTS
1) Fuel overflow from carburetor
If the fuel flows towards the aircleaner or much fuel flows into the crankcase while the engine is standing still (overflowing), the needle vahe or the float is faulty. Correct or replace them.
2)
If the engine suddenly stops with abnormal noise, the piston or the crankshaft and connecting rod assembly is seized.
Correct them or replace them.
3)
If the engine produces abnormal noise during operation, be sure to stop the engine and do not start it again before the
cause is found.
If
the cause for the trouble
is
not found,- contact our distributor and entrust the engine in the hand of our service
engineer.
-
45
-
Page 50

12.
CHECKS
and
CORRECTIONS
After disassembling and cleaning the engine parts, check them, and if necessary, correct them according
table.
The correction table applies whenever engines are repaired. Its contents should be thoroughly understood by those who
undertake the repairing.
Its specifications must be abided by
Below, terms employed in the correction table are explained.
CORRECTION
All operations performed on the engine parts for the' purpose
of
consisting
STANDARD SIZE
The design dimension
CORRECTION TOLERANCE
The tolerance on the re-finished part dimension or on the readjusted dimension.
CORRECTION LIMIT
The limit on the part and adjustment, beyond which any dimensional and functional changes, due to wear, burn, and
other causes will adversely affect the normal engine performance,
USE
LIMIT
The limit, beyond which the part is no longer usable, due to defects
NOTE:
Alldimensions in the
repairs, readjustments, and replacements.
of
to
effect correct maintenance.
the part without the tolerance.
"CORRECTION
TA6LE"are given in millimeter, except where otherwise specified,
of
improving or recovering the engine performance,
in
function or strength.
to
the correction
-46-
Page 51

CORRECTION
TABLE
I
REMARKS
ENGINE
MODEL
EC05-2
EC07-2
EC10
EC17
EC25-2
EC05-2
EC07-2
EC10
EC17
EC25-2
All
.All
ECO5-2
EC07-2
EClO
EC17
EC25-2
'EC05-2
EC07-2
EC10
EC17
EC25-2
EC052
EC10
EC17
EC07-2
EC25-2
EC05-2
EC07-2
EClO
EC17
EC25-2
:ORRECTlOh
-
METHOD
Correct
Boring
USE
LIMIT
ITEM
TOOL
-
Surface
plate,
Feeler
LIMIT
~ ~~~~
Flatness
of
cylinder
head
_c
0.2
0.1 5
I
Oel
40.01
6
S.T.D.
500
OS.
50.259
4-0.02
OS.
62.250
0
O.S.
62.500
O.S.
72.250
OS.
72.500
Bore
0.1 5 0.65
I
Roundness
I
0.01
t"--
Cylindricity
1
0.015
S.T.D.
41.960
1
S.T.D.
49.966
S.T.D.
49.930
Iiameter at
,
P"
8(ECO5,07
5-23(EClO)
3-28(EC17)
?om
bottom,
n transverse
:o
piston pin.
Irnax. dia.)
0-25(EC25-2
Replace
Outside Diameter Micrometer
-0.1
0.03
-0.035
-0.1
0.03
-0.035
0.1 5
62.196
I
O.S.
S.T.D.
61.940
OS.
62.440
S.T.D.
71.920
O.S.
72.170
+
-0.009
-0.020
-0.001
-0.0
12
Cylinder
gauge
Vernier
caliper
Replace Piston pin hole
I
-0.008
+0.005
1.8
N.05
1
a.03
0.1
5
-1
m.02
0
Keystone
Width
of
ring groove
Replace
x
40.02
Keystone
1.59
I
+O.O2
0
-47
-
Page 52

ITEM
Clearance between
piston ring and
piston groove
Clearance between
piston and cylinder
Fit between piston
and piston pin
Ring gap
Ring width
EC05-2
EC07-2
EC17 0.05-0.1
EC25-2
EC05-2
2nd
0.05-0.09
0.08-0.04
u
0.1 1-0.07
0.10-0.06
1-1
EC25-2
EC05-2
EC07-2
EC70
EC17
EC25-2
EC05-2 TOP
EC07-2 2nd
EC17 I 2nd
EC25-2
EC05-2
EC07-2
EC10
EC17
I
TOP
2nd
Top
Top
I
2nd
TOP 2.0 -0.01
2nd
I
10.005T-0.013L
I
1'8
1
2.0
0.10-0.04
0.006L-
0.007L-
0.0
0.1
0.2-0.4
-0.02
-0.04
-0.03
-0.3
-
-
12T
-0.03
-0.05
2ORRECTIOF
0.25
USE
LIMIT
0.15
0.25
REMARKS
Max. cylinder
3ia. and max.
piston dia.
TOOL
-eeler
awe
3ylinder
)awe.
Micrometer
I
Cylinder-
0.06L
0.06
L
gauge.
Micrometer
I
1.5 Replace
1.5
I
-0.1
-0.1
Top ring
keystone
is
Micrometer
METHOD
Replace
Replace
Replace
Replace
I
I
10.5@
20.24
29.68@
EC05-2
EC07-2 -0.008
EC25-2 180
EC05-2
EC07-2
-1
EC25-2
I
I
I
-0.006
-0.014
-0.0
-0.005
-0.0
-0.003
-0.008
N.0
a.004
a.009
a.014
0.025-
0.005
0.035
16
13
17
I
I
1
-0.03
a.020
M.055
-0.03
a.020
M.055
Keystone
Clearance in
radial direc-
t
ion
Micrometer
Cylinderawe
Cylindergauge,
Micrometer
Reolace
Replace
Obtain correc
clearance
replacing part!
by
-
4%
-
Page 53

ITEM
ENGINE STANDARD CORRECTION
(MODEL
I
SIZE
REMARKS
USE
I
TOOL
:ORRECTION
METHOD
EC05-2
M.018
EC07-2
M.011
EC10
a.020
3ylinderlauw
Small end
I.D.
Replace
4.0.020
Clearance in
tion
1
EC17
I I
:m8
1
-0.005
EC25-2
+0.013
kl
I
ri
0.055
EC05-2
Clearance between EC07-2
small end
I.D.
0.03-0.01
and piston pin
needle bearing
0.03-0.004
EC25-2 0.025-0.003
:ylinderJauge,
Micrometer
3btain correct
Aearance
by
replacing parts
I
'
0.6-0.1
I
ECO5-2
Large end side or
small end side
Feelerjaw
0.5-0.1
0.6-0.1
0.8-0.1
,
Replace
Large end side
clearance
Parallelism and Parallelism
Twist between large
end and small end
bores Twist
EC07-2
I
1
1
.
1
1:;
EC10
EC25-2
0.1
Holding large
end as reference, measure
test bar,
(L=
100)
inserted
in small end.
Test bar,
Dialindicator
Replace
0.3
Large and small end I ~~07-2 EC05-2 I Roundness
I
Max.
0.005
I.D.
roundness
&
cylindricity
EC05-2
EC05-2
1
EC07-2
1
75
I
20.05
.
I
Distance between
large end
&
small
end bores
EC17
Mandrels,
Micrometer
Replace
I
EC25-2
I
t0.05
1
20
I
15.26
I
I
EC07-2
I
-0.01
1
I
0
11
21.675@
0--0.007
0--0.008
-0.020
Crankpin
O.D.
Micrometer Replace
I
EC25-2
I
25P
I
-0,010
I
-0.003-
.
EC05-2
Crankpin
O.D.
I
EC07-2
1
Roundness
I
Max. 0.005
Roundness
.
I
EClO
1-1
Replace
Micrometer
&
Cylindricity
EC17
I I
Cylindricity
I
Max. 0.005
I
EC25-2
EC05-2
EC07-2
20b
Crankshaft journal
0
O.D.
-0.01
-0.04
Micrometer
Replace
I
'
EC25-2
3W
-49
-
Page 54

ITEM
Thrust clearance
between crankshaft
&
crankcase
Runout
of
crankshaft
Dia. of small end
needle bearing
needles
Metering needle
unscrew
Pilot screw unscrew
Meteling needle
unscrew
Pilot screw unscrew
Metering needle
unscrew
Pilot screw unscrew
iNGlNE STANDARD
MODEL
EC05-2
EC07-2
+
EClO
EC17
EC25-2
EC05-2
EC07-2
EC10
EC17
EC25-2
EC05-2
EC07-2
-1
EC25-2
EC052 Fixed
EC07-2
EC17
EC25-2
I
I
1.750
20
Fixed
I7
Fixed
I
CORRECTION
0.1-0.84
0.1-0.6
0.05
0
-0.003
0
-0.004
-0.002
-0.004.
0
-0.002
*x
I
0.12
US
E
LIMIT
1
.o
REMARKS
Measure
between
bearing
&
crankshaft
Supporting
assembled
crankshaft
between
centers,
measure
journal
Model BV18
Model BV21
Model BV28
TOOL
Dialindicator
Micrometer Replace
:ORRECTION
METHOD
Replace
Correct
Spark plug
Spark timing
(before T.D.C.)
Spark plug gap
Point opening
~ ~~
Spark gap
I
EC07-2
EClO
EC17
EC25-2
EC07-2
EC25-2
EC05-2
E
CO 7-2
KI
EC25-2
EC07-2
EC17
EC25-2
ECO5-2
EC07-2
EClO
EC17
EC25-2
NGK B-6HS
I
I
NGK
I
NGK B4H
1
NGK B-6HS
I
23" (fixed)'
1
0.6-0.7
0.5-0.6
1
0.6-0.7
I
0.35
Min.
8-4
8
I-
Three needle!
300
test at
(500) r.p.m.
magnet
revolution
Timing.
tester
Feelergauge
Breaker
contact
point
Spanner
Feeler-
gauge
Adjust
Adjust
-
50
-
Page 55

ITEM
REMARKS
CORRECTION LIMIT
HP/rpm
MODEL
EC05-2
3.3/5,500
EC07-2
2.515.500
Max. Output'
6.515,OQO
EC17
415,000
EClO
Below
110%
of
rated output
EC25-2
1215.000
EC05-2
2.215,500
E
CO
7-2
1.715.500
Continuous Rated Output
5.014,OOO
EC17
314,000
EClO
EC25-2
8.514.000
ITEM
REMARKS
CORRECTION LIMIT
Literlhr
MODEL
EC05-2
3.97
EC25-2
2.33
EC17
1.44
1.14
EC07-2
0.95
Fuel Consumption
EC10
up
1
35Qh
rated output
Standard consumption
At continuous
ITEM
REMARKS
MODEL
EC05-2
EC07-2
Engine
Oil
for
2-cycle engine
or
SAEBO
of
high quality
Lubricating oil
EC25-2
EC17
EClO
(Mixture Fuel, gasoline 25
:
oil
11
ITEM
MODEL
STANDARD
CORRECTION
TOLERANCE
REMARKS
EC05-2
EC07-2
EClO
EC17
1,300
*too
Min. Accelerating revolution
EC25-2
*loo
1,500
-
51
-
Page 56

ITEM
I I
Magneto clamp nuts
Spark
plug
QJ
P
G
p
Cylinder clamp nuts
._
C
0)
c
v1
LL
B
Crankcase clamp bolts
v,
I
I
MODEL
I
EC05-2
EC07-2
EClO 400-500
EC17 450-500
1
EC25-2
EC05-2
EC07-2
EC25-2
EC05-2
EC07-2 90-1
EClO
EC17 180-220
EC25-2 340-400 25-29
EC05-2
EC07-2
EC25-2 200-250 15-18
I
I
I
kg-cm
390-420 28-30
800-1000
250-300
00
90-100 6.5-7.3
I
I
I
I
ft-lbs
29-36
33-36
58-72
18-22
6.5-7.3
13-16
TOOL
Toque
wrench
REMARKS
f-7
\
-'
Reduction cover clamp bolts EC10 180-220
Crankcase cover clamp
bolts
EC17 90-100 6.5-7.3
EC17
EClO
EC 25-2 200-250 15-1 8
13-16
180-220 13-16
\
-
52
-
Page 57

13
MAINTENANCE
and
STORING
I
The following .maintenance jobs apply when the engine is operated. correctly under normal conditions. The indicated
maintenance intervals are by no means guarantees for maintenance free operations during these intervals.
For
example, if the engine is operated in extremely dusty conditions, the air cleaner -should be cleaned every day, instead
of every 50,hours.
13-1
DAILY CHECKS
and
MAINTENANCE
Checks and Maintenance Reasons for requiring them
I
Remove dust from whatever parts which accumu-
lated dust.
The governor linkage is especially susceptible
to
dust,
I-
Check external fuel leakage. If any, retighten or
replace.
Not only wasteful but".also dangerous.
Check screw tightening.
If
any loose one
is
found,
accidents.
re-tighten
Loose screws and
nuts
will result in vibration
Check-
oil
level in governor or reduction chamber
will fail.
and add up as necessary.
If
the engine is operated 'without sufficient oil; it
13-2 EVERY
50
HOURS
(IO
DAY) CHECKS
and
MAINTENANCE
Checks and.Maintenance Reasons for requiring them
Clean air cleaner.
Check spark plug. If contaminated, wash in gasoline
Clogged air cleaner harms engine operation.
difficult.
or polish with emery paper.
Output power is reduced and starting
is
made
13-3
EVERY
100-200
HOURS (MONTHLY) CHECKS
and
MAINTENANCE
Checks and Maintenance
e.
Reasons for requiring them
I
.Clean fuel strainer and fuel tank:
I
,
The engine will be out
of
order.
1
Clean contact breaker points.
Contaminated oil accelerates wear,
Change governor or reduction chamber oil.
The engine output drops.
'
13-4 EVERY
500-600
HOURS (SEMIANNUAL) CHECKS
and
MAINTENANCE
Checks and Maintenance Reasons for requiring them
Remove cylinder head and remcve carbon deposit.
'-
Remove carbon deposit from &exhaust port and
The engine will be out of order.
muffler.
'
.
Disassemble'and clean carburetor.
-.53
-
Page 58

13-5
EVERY
1000
HOURS (YEARLY) CHECKS
and
MAINTENANCE
I
Perform overhauls, clean correct
Change piston rings.
Replace fuel pipe once a year.
13-6
PREPARATION
1) Perform the above
2)
Drain fuel from the fuel tank and carburetor float chamber. Drain oil from governor
3)
To
prevent rust in the cylinder bore, apply
hand. Re-install the spark plug.
Turn
the starting pulley by hand and leave it where the resistance is the heaviest.
4)
Clean the engine outside with oiled cloth.
5)
Put a vinyl
or
Checks and Maintenance Reasons for requiring them
or
replace parts.
for
LONG
13-1
other cover over the engine and store the engine in dry place.
ABEYANCE
and 13-2 maintenance jobs.
oil
through the spark plug hole and turn the crankshaft several turns by
The engine output drops and become out of order.
To
prevent from danger caused by the fuel leakage.
or
reduction chamber.
1
-
54
-
Page 59

Page 60

c
Page 61

".
Page 62

c
Page 63

Industrial
Engines
 Loading...
Loading...