Page 1

User’s Guide RIGOL
Publication number UGA04107-1210
July 2008
DS1000B Series Digital Oscilloscopes
DS1062/4B,DS1102/4B,DS1202/4B
© 2008 RIGOL Technologies, Inc.
All Rights Reserved
Page 2

Page 3

RIGOL
I
© 2008 RIGOL Technologies, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
RIGOL products are protected by patent law in and outside of P.R. China.
Information in this publication replaces all previously corresponding material.
RIGOL Technologies, Inc. reserves the right to modify or change part of or all
the specifications and pricing policies at company‟s sole decision.
NOTE: RIGOL is registered trademark of RIGOL Technologies, Inc.
© 2008 RIGOL Technologies, Inc.
User‟s Guide for DS1000B Series
Page 4

RIGOL
II
Safety Notices
Review the following safety precautions carefully to avoid any personal injuries or
damages to the instrument and any products connected to it. To avoid potential
hazards, please use the instrument as specified by this manual only.
The instrument should be serviced by Authorized personnel only.
To Avoid Fire or Personal Injury.
Use Proper Power Cord. Use the power cord designed for the instrument and
authorized in your country only.
Ground The Instrument. The oscilloscope is grounded through the grounding
conductor of the power cord. To avoid electric shock the instrument, grounding
conductor(s) must be grounded properly, before making connections to the input or
output terminals of the instrument.
Connect The Probe. The probes‟ ground terminals are at the same voltage level of
the instrument ground. Do not connect the ground terminals to a high voltage.
Observe All Terminal Ratings. To avoid fire or shock hazard, observe all ratings
and marks on the instrument. Follow the user‟s guide for further ratings information
before making connections to the instrument.
Do Not Operate Without Covers. Do not operate the instrument with covers or
panels removed.
Use Proper Fuse. Use the fuse of the type, voltage and current ratings as specified
for the instrument.
Avoid Circuit or Wire Exposure. Do not touch exposed connections and
components when power is on.
Do Not Operate With Suspected Failures. If suspected damage occurs with the
instrument, have it inspected by qualified service personnel before further
operations.
Provide Proper Ventilation. Refer to the installation instructions for proper
ventilation of the instrument.
Do not Operate in Wet/Damp Conditions.
© 2008 RIGOL Technologies, Inc.
User‟s Guide for DS1000B Series
Page 5

RIGOL
III
Do not Operate in an Explosive Atmosphere.
Keep Product Surfaces Clean and Dry.
The disturbance test of all the models meet the limit values of A in the
standard of EN 61326: 1997+A1+A2+A3, but can’t meet the limit values
of B.
Measurement Category
The DS1000B series Digital Oscilloscope is intended to be used for measurements in
Measurement Category I.
Measurement Category Definitions
Measurement Category I is for measurements performed on circuits not directly
connected to MAINS. Examples are measurements on circuits not derived from
MAINS, and specially protected (internal) MAINS derived circuits. In the latter case,
transient stresses are variable; for that reason, the transient withstand capability of
the equipment is made known to the user.
WARNING
IEC Measurement Category I. The input terminals may be connected to circuit
terminal in IEC Category I installations for voltages up to 300 VAC. To avoid the
danger of electric shock, do not connect the inputs to circuit‟s voltages above 300
VAC.
Transient overvoltage is also present on circuits that are isolated from mains. The
DS1000B series Digital Oscilloscopes is designed to safely withstand occasional
transient overvoltage up to 1000 Vpk. Do not use this equipment to measure circuits
where transient overvoltage could exceed this level.
© 2008 RIGOL Technologies, Inc.
User‟s Guide for DS1000B Series
Page 6

RIGOL
IV
!
Hazardous
Voltage
Refer to
Instructions
Protective
Earth Terminal
Earth
Ground
Chassis
Ground
!
!
Safety Terms and Symbols
Terms in This Guide. These terms may appear in this guide:
WARNING: Warning statements identify conditions or practices that could
result in injury or loss of life.
CAUTION: Caution statements identify conditions or practices that could
result in damage to this product or other property.
Terms on the Product: These terms may appear on the product.
DANGER indicates an injury hazard may be immediately accessible.
WARNING indicates an injury hazard may be not immediately accessible.
CAUTION indicates that a potential damage to the instrument or other property
might occur.
Symbols on the Product: These symbols may appear on the Instrument:
© 2008 RIGOL Technologies, Inc.
User‟s Guide for DS1000B Series
Page 7

V
RIGOL
General-Purpose Oscilloscopes
RIGOL DS1000B series digital oscilloscopes offer exceptional waveform viewing
and measurements in a compact, lightweight package. The DS1000B series is ideal
for production test, field service, research, design, education and training involving
applications of analog circuit tests and troubleshooting.
Product features:
Dual Channel or Four Channels, Bandwidth of per channel:
200MHz (DS1202/4B)
100MHz (DS1102/4B)
60MHz (DS1062/4B)
2GSa/s real-time sampling rate and 50GSa/s equivalent sampling rate.
Color TFT 5.7 inch LCD, 320× 240 pixels resolution.
USB storage and direct printing, software upgrade via USB interface.
Adjustable waveform intensity, more effective waveform viewing.
One-touch automatic setup, ease of use (AUTO).
Storage and recurrence of Waveforms and setups, supports CSV, 8 or 24 bits
bitmap and PNG format.
Delayed Scan Function, easy to give attention to both details and overview of a
waveform.
22 Automatic measurements.
Automatic cursor tracking measurements.
Waveform recorder, record and replay dynamic waveforms.
Supports fast offset calibration of an oscilloscope.
Built-in FFT function.
Digital filters, includes LPF, HPF, BPF, BRF.
Pass/Fail detection Function, optically isolated Pass/Fail output.
Add, Subtract and Multiply Mathematic Functions of waveforms.
Advanced trigger types include: Edge, Video, Pulse width, Pattern, Alternative.
Adjustable trigger sensitivity.
Multiple Language User Interface.
Pop-up menu makes it easy to read and easy to use.
Built-in help systems with multinational languages.
Easy-to-use file system supports Chinese & English characters file name input.
Conform to LXI consortium instrument standard class C.
© 2008 RIGOL Technologies, Inc.
User‟s Guide for DS1000B Series
Page 8

RIGOL
VI
Contents
Safety Notices ...........................................................................................II
General-Purpose Oscilloscopes ................................................................... V
Chapter 1 : Getting Started ................................................................. 1-1
The Front Panel and User Interface ......................................................... 1-2
To Inspect the Instrument ...................................................................... 1-5
To Perform a Functional Check ................................................................ 1-6
To Compensate the Probes ..................................................................... 1-8
To Display a Signal Automatically ............................................................ 1-9
To Understand the Vertical System ........................................................ 1-10
To Understand the Horizontal System .................................................... 1-12
To Trigger the Oscilloscope ................................................................... 1-14
To Understand the Quick Function ......................................................... 1-17
Chapter 2 : Operating Your Oscilloscope ............................................ 2-1
To Set up the Vertical System ................................................................. 2-2
To Set the Channels ......................................................................... 2-2
To Use Math Functions ................................................................... 2-13
To Use REF Function ...................................................................... 2-18
Turn on or off Channels .................................................................. 2-26
To Apply the Vertical Knobs ............................................................ 2-27
To Set up the Horizontal System ........................................................... 2-28
To Set up the Trigger System ................................................................ 2-34
Trigger Modes ............................................................................... 2-35
Edge Trigger.................................................................................. 2-36
Pulse Width Trigger ........................................................................ 2-37
Video Trigger ................................................................................. 2-38
Pattern Trigger .............................................................................. 2-41
Alternative Trigger ......................................................................... 2-43
Trigger Settings ............................................................................. 2-46
To Set up the Sampling System ............................................................. 2-52
To Set up the Display System ................................................................ 2-56
To Store and Recall .............................................................................. 2-59
To Set up the Utility ............................................................................. 2-69
The I/O Setup ............................................................................... 2-71
Preference .................................................................................... 2-74
Self-Calibration .............................................................................. 2-75
© 2008 RIGOL Technologies, Inc.
User‟s Guide for DS1000B Series
Page 9

RIGOL
VII
Pass/Fail ........................................................................................ 2-76
Print Setting ................................................................................... 2-80
Waveform Recorder ........................................................................ 2-82
System information ........................................................................ 2-86
Language ...................................................................................... 2-87
Date and Time ............................................................................... 2-88
To Measure Automatically ...................................................................... 2-89
Quick Measurement Setup .............................................................. 2-91
Delay/Phase Setup ......................................................................... 2-92
Voltage Measurements .................................................................... 2-93
Time Measurements ....................................................................... 2-95
To Measure with Cursors ....................................................................... 2-99
Manual Mode ............................................................................... 2-100
Track Mode .................................................................................. 2-102
Auto mode ................................................................................... 2-104
To Use Run Control Buttons ................................................................. 2-105
Chapter 3 : Application & Examples .................................................... 3-1
Example 1: Taking Simple Measurements ................................................. 3-1
Example 2: View a Signal Delay Caused by a Circuit .................................. 3-2
Example 3: Capture a Single-Shot Signal .................................................. 3-3
Example 4: To Reduce the Random Noise on a Signal ............................... 3-4
Example 5: Making Cursor Measurements ................................................. 3-6
Example 6: The Application of the X-Y operation ....................................... 3-8
Example 7: Triggering on a Video Signal ................................................. 3-10
Example 8: FFT Cursor Measurement ..................................................... 3-12
Example 9: Pass/Fail Test ...................................................................... 3-14
Chapter 4 : Troubleshooting ............................................................... 4-1
Chapter 5 : Specifications ................................................................... 5-1
Specifications ......................................................................................... 5-2
General Specifications ............................................................................. 5-6
Chapter 6 : Appendixes ....................................................................... 6-1
Appendix A: Accessories .......................................................................... 6-1
Appendix B: Warranty ............................................................................. 6-2
Appendix C: Maintenance ........................................................................ 6-3
Appendix D: Contact RIGOL ................................................................... 6-4
Index ......................................................................................................... i
© 2008 RIGOL Technologies, Inc.
User‟s Guide for DS1000B Series
Page 10

Page 11

1-1
Chapter 1 : Getting Started
This chapter covers the following topics:
The front panel and user interface
To inspect the instrument
To perform a functional check
To compensate the probes
To display a signal automatically
To understand the vertical system
To understand the horizontal system
To trigger the oscilloscope
To understand the quick function
RIGOL
© 2008 RIGOL Technologies, Inc.
User‟s Guide for DS1000B Series
Page 12
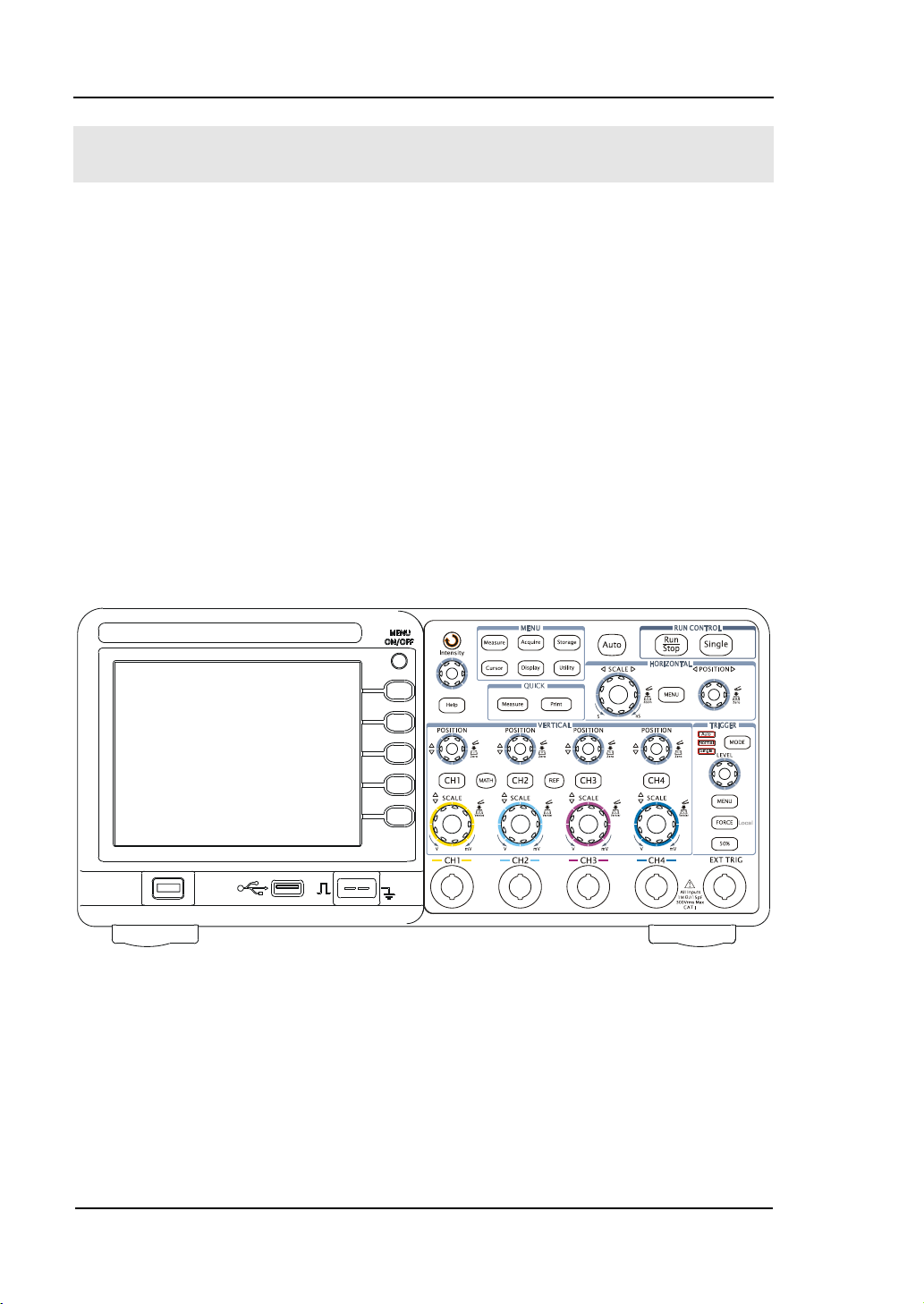
RIGOL
1-2
The Front Panel and User Interface
Being familiar with the front panel of an oscilloscope is the first priority when you get
a new type digital oscilloscope. This chapter will bring you a brief introduction and
description of the front panel operations of DS1000B series digital oscilloscopes. It is
a great help for your understanding to the layout of the knobs and keys and how to
use them. Read the chapter carefully before further operations.
Figure 1-1, the front Panel; the knobs are used most often and are similar to the
knobs on other oscilloscopes. There are five gray buttons defined as No.1 to No.5
from up to bottom on the right side of the display which are menu operating buttons.
The buttons not only allow you to use some of the functions directly but also bring up
soft button menus on the screen, which enable the access to many measurement
features associated with the advanced functions, mathematics, and reference or to
run control features.
Figure 1-1
DS1000B Series Oscilloscope‟s Front Panel
© 2008 RIGOL Technologies, Inc.
User‟s Guide for DS1000B series
Page 13
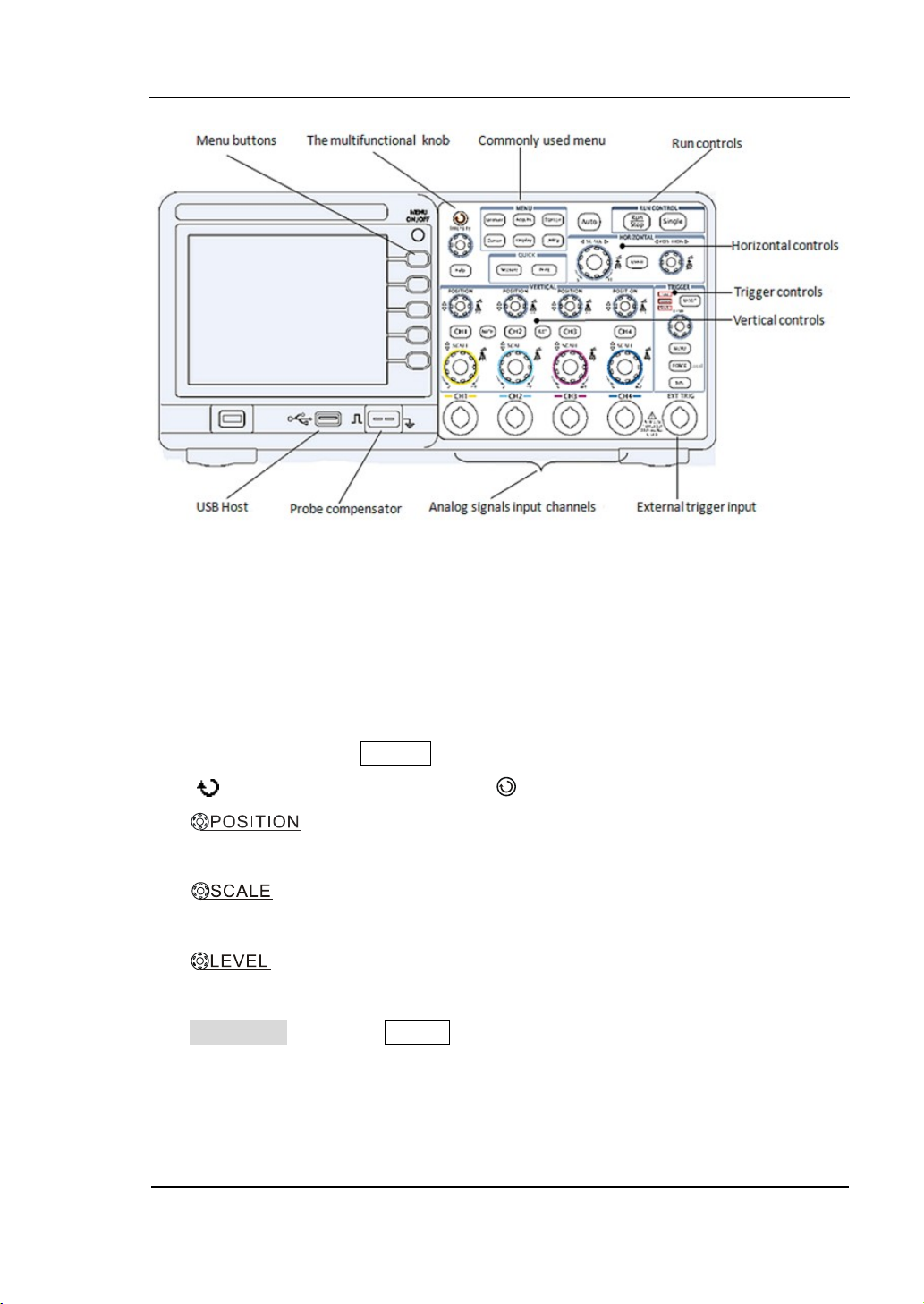
RIGOL
1-3
Figure 1-2
Front Panel Controls
Notation definitions in this User’s Guide:
Throughout this guide, notation symbols of buttons and knobs are the same of those
on front-panel.
A box around the name of the key denotes MENU function buttons on
front-panel, such as Measure.
( ) denotes the multi-function knob .
denotes the three POSITION knobs (two channels) or five
POSITION knobs (four channels)
denotes the three or five SCALE knobs according to the quantities of
the channels of different types of oscilloscopes.
denotes the LEVEL knob.
The name with a drop shadow denotes the menu operating key, such as
Waveform soft key in Storage menu.
© 2008 RIGOL Technologies, Inc.
User‟s Guide for DS1000B Series
Page 14
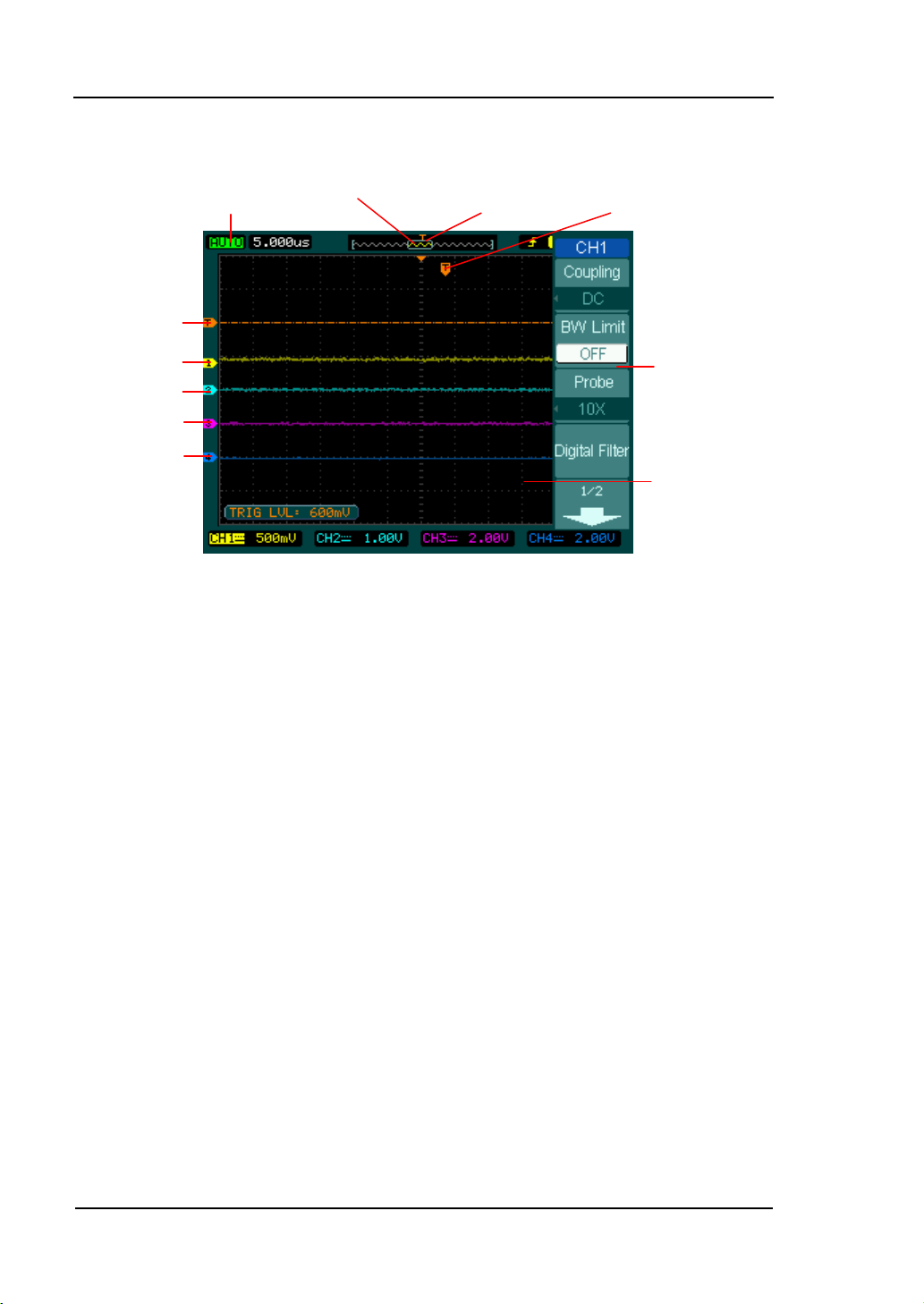
RIGOL
1-4
Waveform display
windows
Mark of channel1
Mark of channel2
Mark of channel3
Mark of channel4
Trigger symbol
Running status
Location of the current
waveform in the memory
Trigger position
in the memory
Trigger position in
current waveform
windows
Menu
Display screen
Figure 1-3
© 2008 RIGOL Technologies, Inc.
User‟s Guide for DS1000B series
Page 15

1-5
RIGOL
To Inspect the Instrument
After receiving a new DS1000B series oscilloscope, please inspect the instrument as
follows:
1. Inspect the shipping container for damage.
Keep the damaged shipping container or cushioning material until the contents
of the shipment have been checked for completeness and the instrument has
been checked mechanically and electrically.
2. Check the accessories.
Accessories supplied with the instrument are listed in "Accessories" in this guide.
If the contents are incomplete or damaged notify the RIGOL Sales
Representative.
3. Inspect the instrument.
In case there is any mechanical damage or defect, or the instrument does not
operate properly or fails performance tests, notify the RIGOL Sales
Representative.
If the shipping container is damaged, or the cushioning materials show signs of
stress, notify the carrier as well as the RIGOL sales office. Keep the shipping
materials for the carrier‟s inspection.
RIGOL offices will arrange for repair or replacement at RIGOL‟s option without
waiting for claim settlement.
© 2008 RIGOL Technologies, Inc.
User‟s Guide for DS1000B Series
Page 16
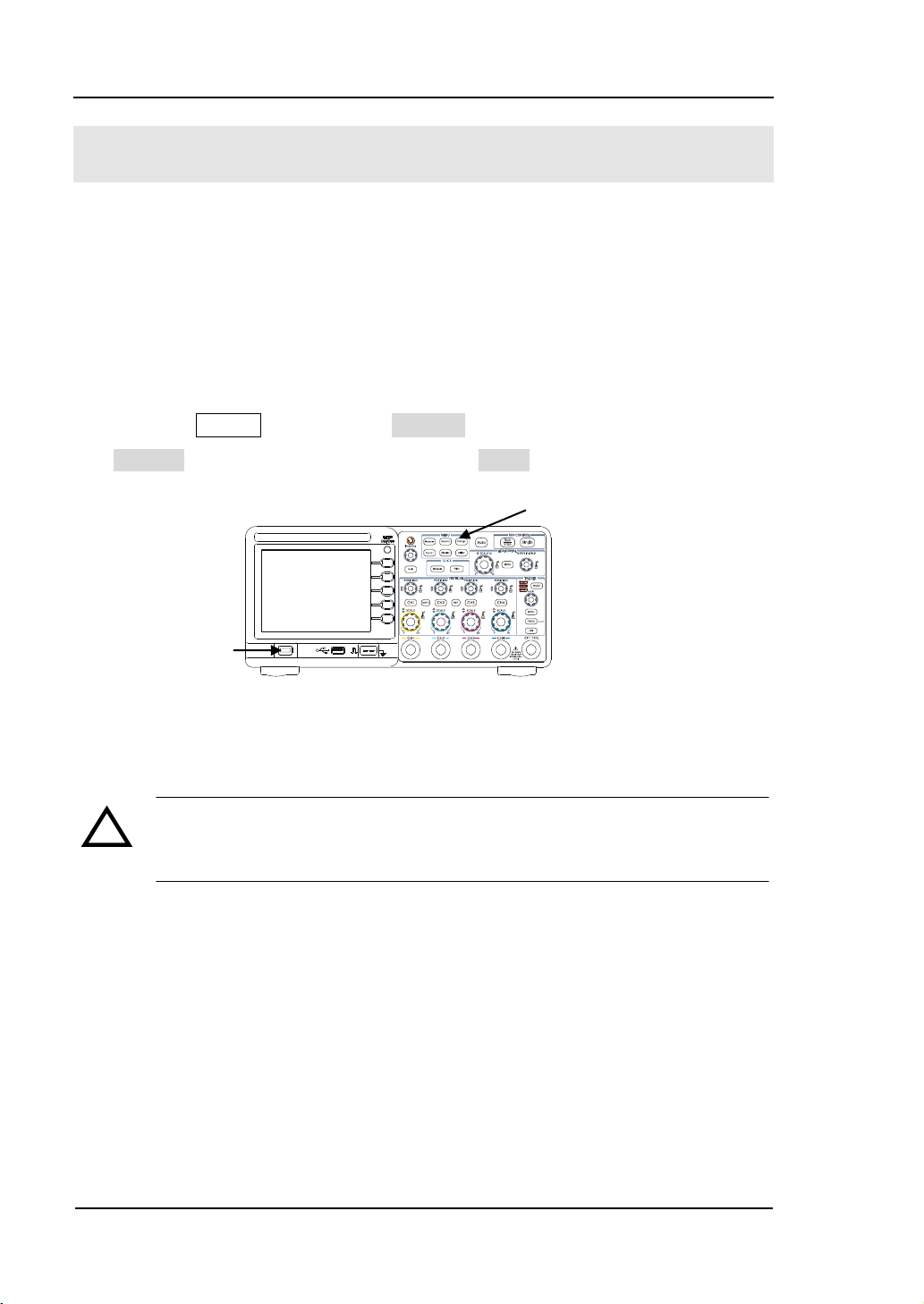
RIGOL
1-6
!
Storage button
Power
To Perform a Functional Check
Perform this quick functional check to verify that the instrument is operating
correctly.
1. Turn on the instrument.
Use the power cord designed for the oscilloscope only.
Use a power source that delivers 100 to 240 V, 45Hz to 440Hz.
Turn on the instruments, and wait until the display shows the waveform window.
Push the Storage button, select Storage in the top menu box and push the
Factory menu box, then continue pressing Load.
Figure 1-4
Turn on the instrument
WARNNING:
To avoid electric shock, be sure the oscilloscope is properly grounded.
2. Input a signal to a channel of the oscilloscope
① Set the attenuation switch on the probe to 10X and connect the probe to Channel
1 on the oscilloscope.
To do this:
Align the slot in the probe connector with the socket on the Bayonet Nut
Push to connect, and twist to the right to lock the probe in place.
Attach the probe tip and ground lead to the PROBE COMP connector.
Connector (BNC) connector of CH1 or CH2.
© 2008 RIGOL Technologies, Inc.
User‟s Guide for DS1000B series
Page 17
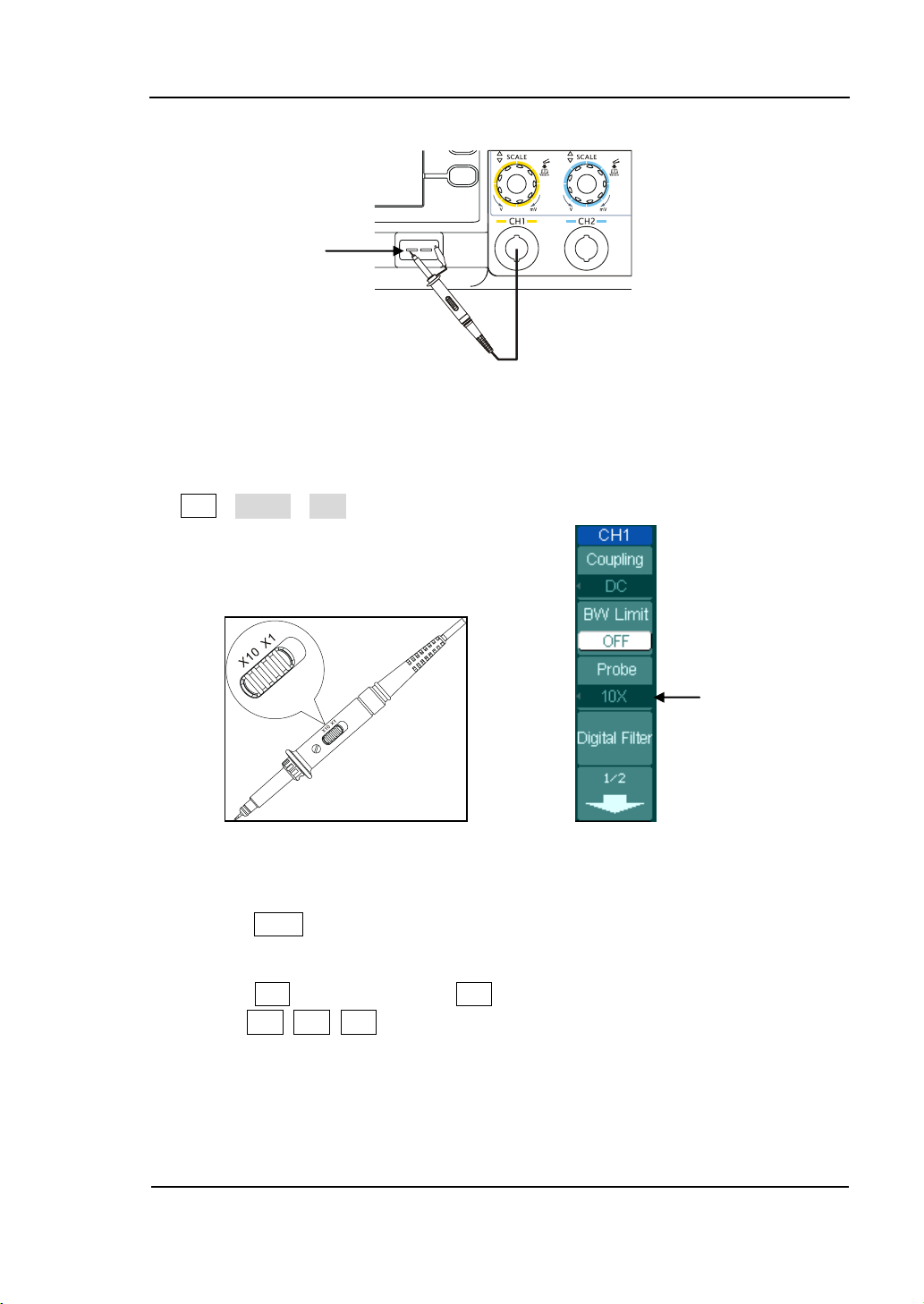
RIGOL
1-7
Probe scale
Probe compensator
Figure 1-5
Attach the probe
② Set the probe attenuation of the oscilloscope to 10X. To do this, push
CH1→Probe→10X.
Figure 1-6 Figure 1-7
Set the probe The CH1 menu
③ Push the AUTO button. Within a few seconds, a square wave will be displayed on
the screen.
④ Push the OFF button or push the CH1 button again to turn off Channel 1.
Push the CH2, CH3, CH4 buttons to turn on channel 2, channel3, channel4, repeat
steps 2 and 3.
NOTE: The signal output from Probe compensator should only be used for probe
compensation, not for calibration.
© 2008 RIGOL Technologies, Inc.
User‟s Guide for DS1000B Series
Page 18
RIGOL
1-8
!
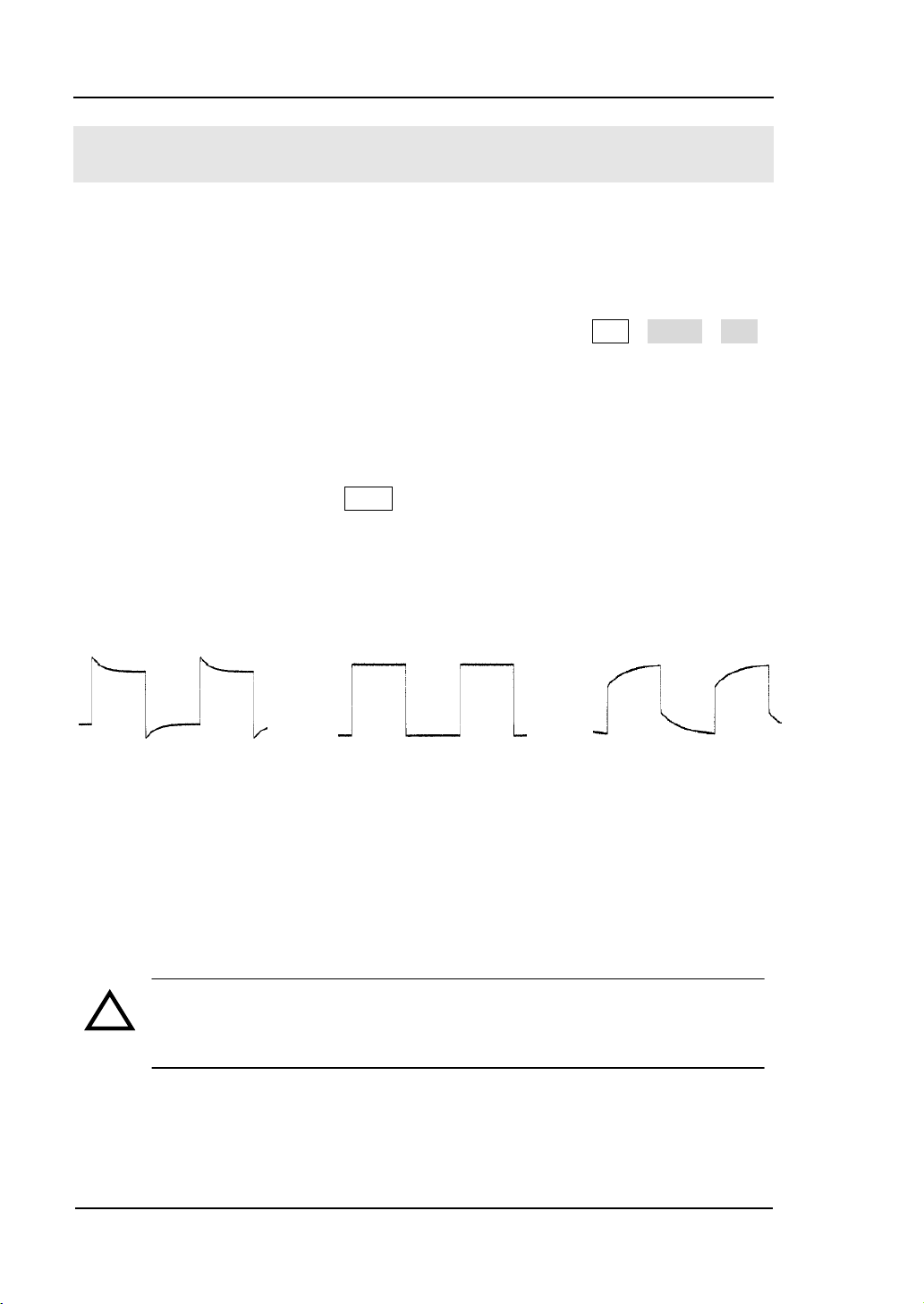
To Compensate the Probes
Perform this adjustment to match the characteristics of the probe and the channel
input. This should be performed whenever attaching a probe to any input channel at
the first time.
1. From CH1 menu, set the Probe attenuation to 10X (press CH1→Probe→10X).
Set the switch to 10X on the probe and connect it to CH1 of the oscilloscope.
When using the probe hook-tip, inserting the tip into the hook-tip firmly to
ensure a tight connection.
Attach the probe tip to the connector of the Probe compensator and link the
reference wire cramp with the ground connector of the probe compensator,
Select CH1, and then press AUTO.
2. Check the shape of the displayed waveform.
Over Compensated Correctly Compensated Under Compensated
Figure 1-9
Figure 1-8
Check the shape
3. If necessary, use a non-metallic tool to adjust the variable capacitor of the probe
for the flattest square wave being displayed on the oscilloscope.
4. Repeat if necessary.
WARNNING: To avoid electric shock while using the probe, be sure the
perfection of the insulated cable, and do not touch the metallic portions of
the probe head while it is connected with a voltage source.
© 2008 RIGOL Technologies, Inc.
User‟s Guide for DS1000B series
Page 19

1-9
RIGOL
To Display a Signal Automatically
The DS1000B series oscilloscope has an automated feature to display the input
signal in best-fit status. The input signal should be 50 Hz or higher and a duty cycle is
greater than 1%.
Press the AUTO button, the oscilloscope automatically sets up VERTICAL,
HORIZONTAL and TRIGGER controls to display the input signal. Adjust the controls
manually to get the best results if necessary.
Using the automatic setting:
1. Connect a signal to the oscilloscope (such as channel 1) as described above.
2. Press AUTO.
The oscilloscope may change the current settings to display the signal; adjusts
the vertical and horizontal scaling, the trigger coupling, type, position, level, and
mode.
© 2008 RIGOL Technologies, Inc.
User‟s Guide for DS1000B Series
Page 20
RIGOL
1-10
Measurement hints
If the channel is DC coupled, measuring the DC and AC components of the
signal by simply noting its distance from the ground symbol.
If the channel is AC coupled, the DC component of the signal is blocked, allow
you to use greater sensitivity to display the AC component of the signal.
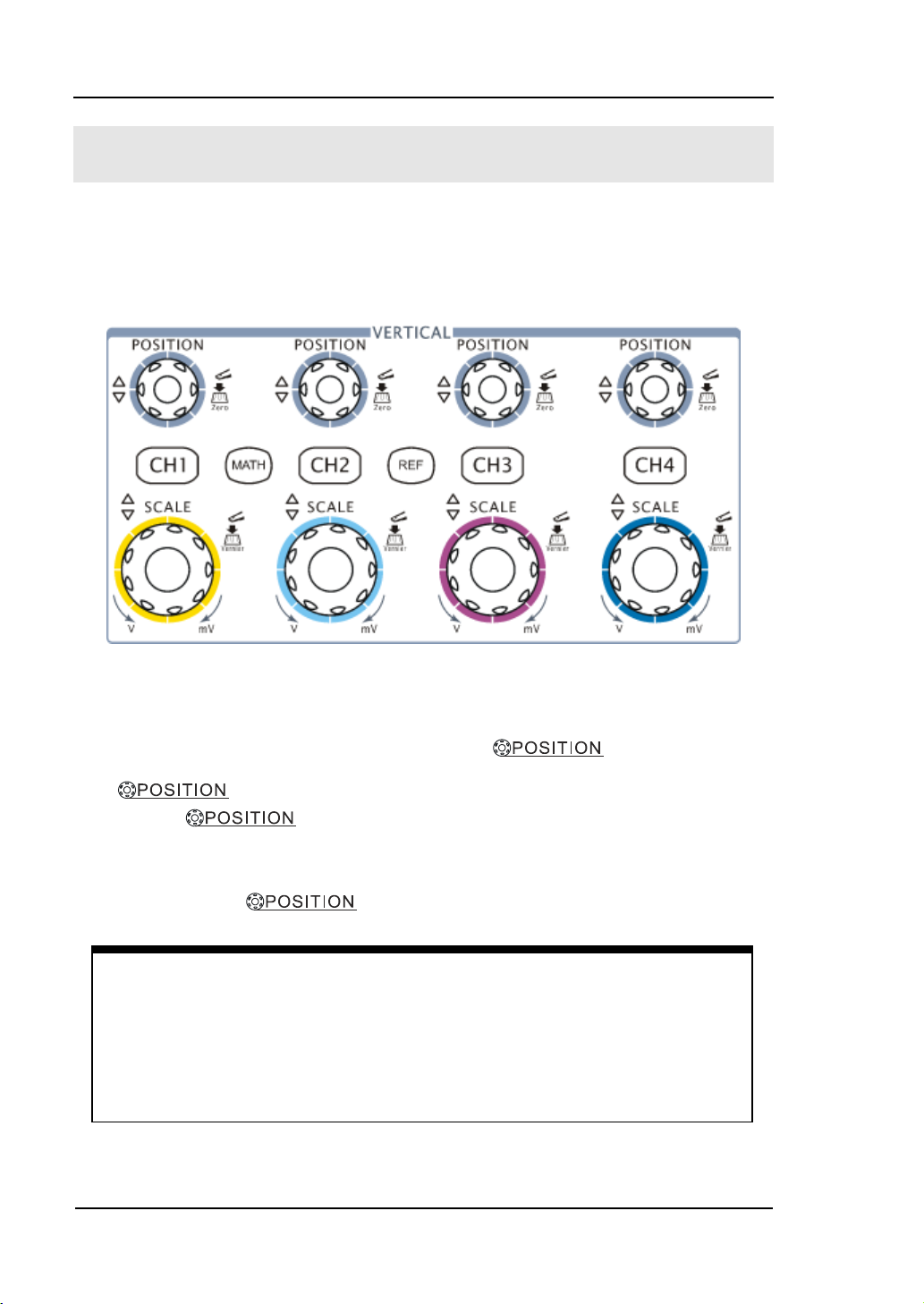
To Understand the Vertical System
As shown in Figure 1-9, there are several series buttons and knobs in the VERTICAL
control area. The following exercises will gradually conduct you to be familiar with
the using of the vertical parameters settings.
1. Center the signal on the display with the knob.
The knob moves the signal vertically, and it is calibrated. Note that
turning the knob, a voltage value is displayed for a short time
indicating its value with respect to the ground reference located at the center of the
screen. Also notice that the ground symbol on the left side of the display moves in
conjunction with the knob.
Figure 1-9
The vertical control window
User‟s Guide for DS1000B series
© 2008 RIGOL Technologies, Inc.
Page 21
RIGOL
1-11
Vertical offset back to 0 shortcut key
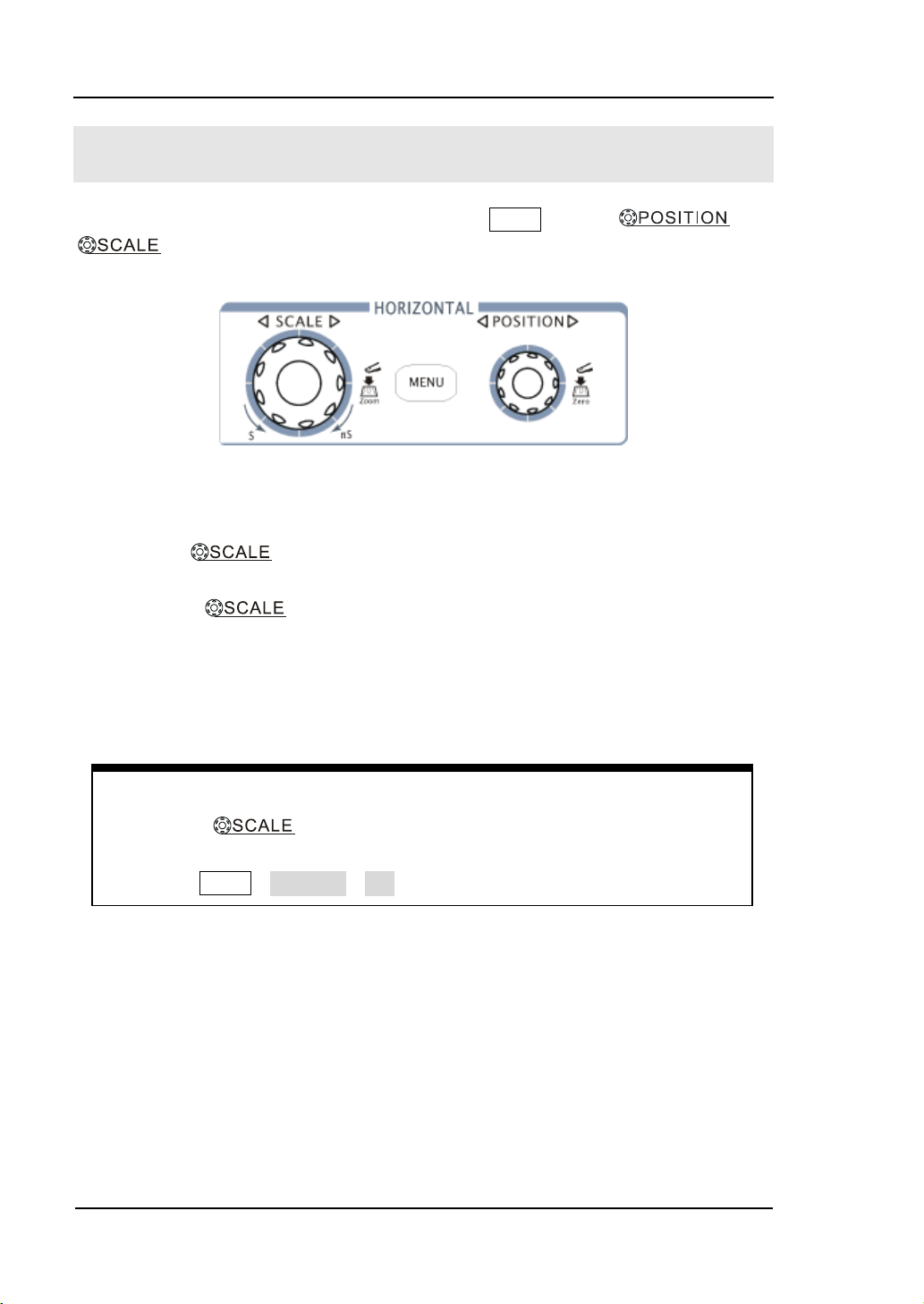
Turn the knob to change the vertical display position of
channel and press the knob to set the vertical display position
back to 0 as a shortcut key, this is especially helpful when the trace position is
far out of the screen and want it to get back to the screen center immediately.
Coarse/Fine Shortcut key
The Coarse/Fine vertical control can be set by simply pressing the vertical
knob.
2. Change the vertical setup and notice that each change affects the
status bar differently.
Change the vertical sensitivity with the knob and notice the change
in the status bar at the bottom of the display.
When you Press CH1, CH2, CH3, CH4, MATH, REF, the operating menus,
symbols, waveforms and status information of corresponding channel and
settings will be displayed on the screen. The current selected channel will be
shut down when you press the key associated with the channel one more time.
© 2008 RIGOL Technologies, Inc.
User‟s Guide for DS1000B Series
Page 22
RIGOL
1-12
Delayed Scan Shortcut key
To press the knob in the horizontal control area on the front-panel
is another way to enter or exit Delayed Scan mode and it is equal to the menu
operations, MENU→Delayed→ON.
To Understand the Horizontal System
Figure 1-10 shows the HORIZONTAL controls: MENU button, and
knobs of horizontal system. Following the exercise to familiarize with the
buttons, knobs, and status bar.
Figure 1-10
The horizontal system
1. Turn the knob and notice the change in the status bar.
The horizontal knob changes the sweep speed in a 1-2-5 step sequence,
and displays the value at the upper-left of the display. The time base ranges of the
DS1000B series is from 5 ns/div* to 50 s/div.
* NOTE: The speed of horizontal scan varies by different models.
User‟s Guide for DS1000B series
© 2008 RIGOL Technologies, Inc.
Page 23
RIGOL
1-13
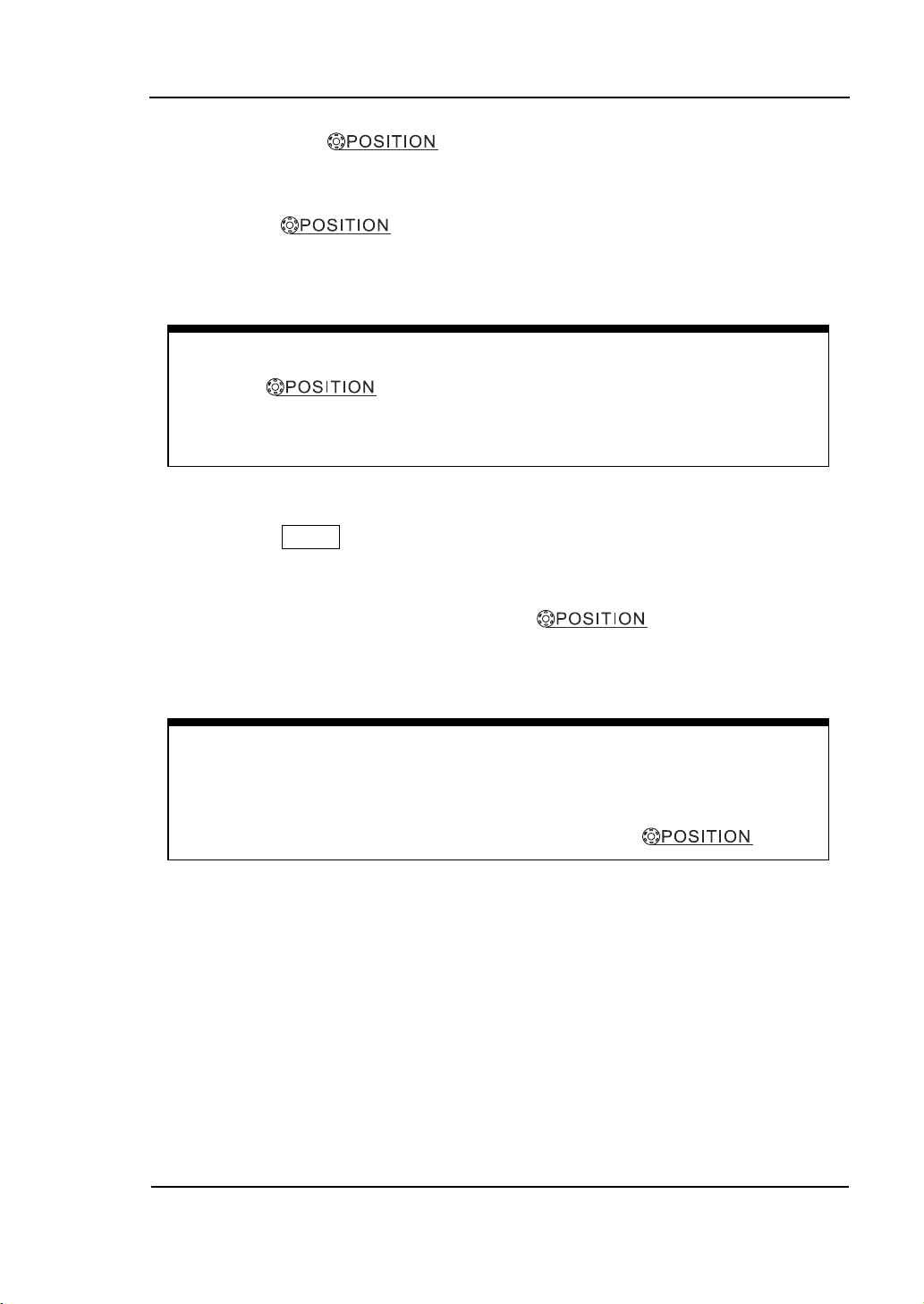
Horizontal offset back to 0 shortcut key
Press the knob to set the horizontal offset to 0 as a shortcut
key, this is especially helpful when the trigger point is far out of the screen and
want it to get back to the screen center immediately.
Horizontal position control
Trig-Offset: Denotes the real position of the trigger point relative to the
midpoint of the memory. In this setting, the trigger position will be
changed horizontally when you turning the knob.
2. The horizontal knob moves displayed signal horizontally
on the waveform window.
The horizontal knob adjusts the trigger offset of signal, when turning
the knob; you can note that the waveform moves horizontally in conjunction with the
knob.
3. Press the MENU key to display the Time menu.
You can enter or exit the Delayed Scan mode, toggle the display mode among Y-T,
X-Y or ROLL mode, and turn the horizontal knob to adjust trigger
offset.
© 2008 RIGOL Technologies, Inc.
User‟s Guide for DS1000B Series
Page 24
RIGOL
1-14
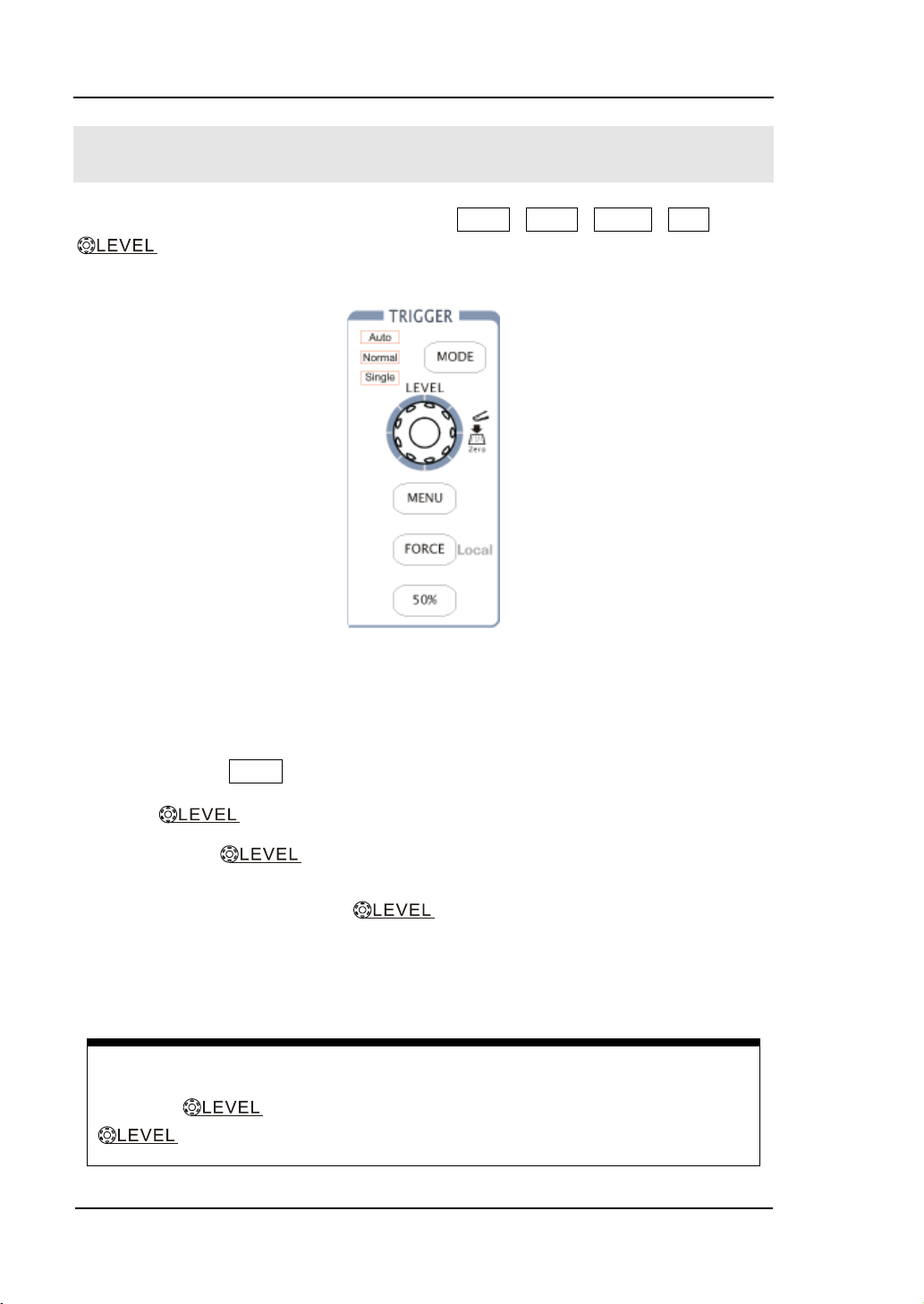
Turn the knob to change the trigger level value and press the
knob to set trigger level back to 0 as a shortcut key.
To Trigger the Oscilloscope
Figure 1-11 shows the TRIGGER control: MODE, MENU, FORCE, 50% and a
knob. Following the exercises to familiarize with the buttons, trigger level
knob and status bar.
Figure 1-11
The trigger control window
Three kinds of trigger modes can be switched among Auto, Normal and Single
with pressing MODE button.
1. Use knob to change the settings of trigger level.
Turning the knob, you will observe a nacarat trigger line, a trigger
sign and a trigger level value displaying pane on the screen moving up and down.
When you stop turning the knob, the trigger line, trigger sign and
trigger value pane will disappear in five seconds. During the same time of
moving the trigger line, you will notice that the displayed value of trigger level
has been changed on the screen.
© 2008 RIGOL Technologies, Inc.
User‟s Guide for DS1000B series
Page 25

RIGOL
1-15
2. Change the trigger setup and notice these changes in the status bar.
Press MENU button in the Trigger control area.
A soft button menu appears on the display showing the trigger setting choices as
shown in Figure 1-12.
· Press No.1 menu operating button to choose trigger mode as Edge.
· Press No.2 menu operating button to choose trigger source as CH1.
· Press No.3 menu operating button to choose slope type as .
· Press No.4 menu operating button to choose sweep mode as Auto.
· Press No.5 menu operating button to enter secondary menu of
Trigger Set Up, so as to perform a further configuration about
Trigger Coupling modes, trigger sensitivities, and trigger holdoff
Figure 1-12 time.
NOTE: The change of trigger mode, source selection and slope type will lead to the
change of the status bar on the upper-right of the screen.
3. Press 50%
Press the 50% button to set the trigger level to the center of the signal‟s amplitude.
4. Press FORCE
Start an acquisition even if no valid trigger signal has been found, usually used in
“Normal” or “Single” trigger mode. This button has no effect if the acquisition is
already stopped.
© 2008 RIGOL Technologies, Inc.
User‟s Guide for DS1000B Series
Page 26
RIGOL
1-16
Key point:
Holdoff: A time interval before the oscilloscope responses to next trigger
signal. During this Holdoff period, the trigger system becomes “blind” to
trigger signals. This function helps to view complex signals such as an AM
waveform. Press Holdoff button to activate ( ) knob, then turn it to adjust
Holdoff time.
User‟s Guide for DS1000B series
© 2008 RIGOL Technologies, Inc.
Page 27
RIGOL
1-17
To Understand the Quick Function
The following figure shows that there are two buttons in the QUICK function area.
The exercise below will gradually conduct you to familiarize the settings of the
buttons.
Figure 1-13
The quick function menu
1. Firstly, you need to press the button Measure form the main MENU, then press
the button associated with QuickMea, you will navigate into the quick
measurement setting menu. Three measuring items can be pre-set from the 22
measurements. Now, Press Measure button from the quick control area to enter
quick measurement, three measuring parameters pre-defined will be displayed
on the screen.
2. Use Print button to perform a quick print, you can set screen quantities need to
be printed or store datum to the USB disk.
© 2008 RIGOL Technologies, Inc.
User‟s Guide for DS1000B Series
Page 28

Page 29
RIGOL
2-1
Chapter 2 : Operating Your Oscilloscope
By now, a user should understand the VERTICAL, HORIZONTAL and TRIGGER
control systems and know how to determine the system setup from the status bar of
a DS1000B series digital oscilloscope. This chapter will go through all groups of
front-panel buttons, knobs and menus; and further the knowledge of the operation
by hints in this guide. It is strongly recommended to perform all of the following
exercises to get the most of the powerful measurement capabilities of the
oscilloscope.
The following topics will be elaborated in this chapter:
To set up the vertical system ( CH1, CH2, CH3, CH4, MATH, REF ,
Vertical , Vertical )
To set up the horizontal system (MENU, Horizontal ,
Horizontal )
To set up the trigger system (MODE, , MENU, FORCE, 50%)
To set up the sampling system (Acquire)
To set up the display system (Display)
To save and recall waveforms or setups
(Storage)
To set up utility (Utility)
To measure automatically (Measure)
To measure with cursors (Cursor)
To use run control buttons (Auto, Run/Stop, Single)
© 2008 RIGOL Technologies, Inc.
User‟s Guide for DS1000B Series
Page 30

RIGOL
2-2
Menu
Settings
Comments
Coupling
AC
DC
GND
Restraint the DC component of the
input signal and passes the AC
component with frequency higher
than 5Hz.
Passes both AC and DC
components of the input signal
Disconnect the input signal.
BW Limit
ON
OFF
Limit the channel‟s bandwidth to
20MHz to reduce display noise.
Get full bandwidth.
Probe
0.001X
.
.
1000X
Set up the oscilloscope‟s probe
attenuation factor to make the
vertical scale readout correct.
Digital filter
Set up digital filter (See table 2-4).
1/2
Go to the next menu page (The
followings are the same, no more
explanation).
To Set up the Vertical System
To Set the Channels
Each channel of DS1000B series digital oscilloscope has an independent operation
menu and it will pop-up after pressing any button among CH1, CH2, CH3, CH4. The
settings of all items in the menu are shown in the table below.
Figure 2-1 Table 2-1 The Channel menu (Page 1/2)
© 2008 RIGOL Technologies, Inc.
User‟s Guide for DS1000B series
Page 31

2-3
Menu
Settings
Comments
2/2
Back to the previous menu page
(The followings are the same, no
more explanation).
Volts/Div
Coarse
Fine
To change the Volts/Dive settings in
a 1-2-5 sequence from 2mv/div to
10v/div with knob.
To change the Volts/Dive settings in
small steps between the coarse
settings.
Invert
ON
OFF
Turn on the invert function.
Restore to original display of the
waveform.
Unit
V/ A/ W/ U
Set “V”, “A”, “W” or “U” as the unit of
vertical channel.
Figure 2-2 Table 2-2 The Channel menu (Page 2/2)
RIGOL
© 2008 RIGOL Technologies, Inc.
User‟s Guide for DS1000B Series
Page 32

RIGOL
2-4
DC coupling
Setup
DC coupling
Status symbol
To set up channel coupling
To use Channel 1 as an example, input a square wave signal with DC shift.
Press CH1→Coupling→DC to set “DC” coupling. Both the AC component and the
DC component of the input signal will pass.
The waveform is displayed as Figure 2-3:
Figure 2-3
Waveform display
Press CH1→Coupling→AC, to set “AC” coupling. It will pass AC component of the
input signal with frequency higher than 5 Hz and restraint DC component of the input
signal.
The waveform is displayed as Figure 2-4:
© 2008 RIGOL Technologies, Inc.
User‟s Guide for DS1000B series
Page 33

RIGOL
2-5
GND coupling
Status symbol
GND coupling
Setup
AC coupling
Setup
AC coupling
Status symbol
Figure 2-4
Waveform display
Press CH1→Coupling→GND, to set “GND” coupling, it disconnects the input signal.
The screen displays as Figure 2-5:
Figure 2-5
Screen display
© 2008 RIGOL Technologies, Inc.
User‟s Guide for DS1000B Series
Page 34

RIGOL
2-6
Turn off the
BW limit
To set up the channel bandwidth limit
Take Channel 1 for an example, input a signal containing high frequency component.
Press CH1→BW Limit→OFF, to set up bandwidth limit to “OFF” status. The
oscilloscope is set to full bandwidth and passing the high frequency component in
the signal.
The waveform is displayed as Figure 2-6:
Figure 2-6
Turn off the BW limit
Press CH1→BW Limit→ON, to set up bandwidth limit to “ON” status. It will
restraint the frequency component higher than 20MHz.
The waveform is displayed as Figure 2-7:
© 2008 RIGOL Technologies, Inc.
User‟s Guide for DS1000B series
Page 35

RIGOL
2-7
20MHz BW limit
Mark of
BW limit
Figure 2-7
Turn on the BW limit
© 2008 RIGOL Technologies, Inc.
User‟s Guide for DS1000B Series
Page 36

RIGOL
2-8
Probe attenuation factors
Corresponding settings
1:1000,1:100,1:10
0.001X,0.01X,0.1X
1:1,2:1,5:1
1X,2X,5X
10:1,20:1,50:1
10X,20X,50X
100:1,200:1,500:1
100X,200X,500X
1000:1
1000X
Vertical volt/div.
Probe attenuation
To set up Probe Attenuation
The oscilloscope allows selecting the attenuation factor for the probe. The
attenuation factor changes the vertical scaling of the oscilloscope so that the
measurement results reflect the actual voltage levels at the probe tip.
To change (or check) the probe attenuation setting, press the CH1, CH2, CH3 or
CH4 button (according to which channel is in using). Toggle the Probe soft button to
match the attenuation factor of the probe.
This setting remains in effect until changed again.
Figure 2-8 shows an example for using a 1000:1 probe and its attenuation factor.
Table 2-3 Probe setting
Figure 2-8
Using a 1000:1 probe
© 2008 RIGOL Technologies, Inc.
User‟s Guide for DS1000B series
Page 37

RIGOL
2-9
Coarse/Fine Shortcut key:
To change Coarse/Fine setting, not only by menu operation but also by
pressing vertical knob.
Fine adjustment data
Fine adjustment
To change the Volts/Div settings
The Volts/Div control has Coarse or Fine configuration. The Vertical Sensitivity is
2mv/div - 10V/div.
Coarse: It is the default setting of Volts/Div in a 1-2-5-step sequence from 2mV/div,
5mV/div, 10mV/div, to 10 V/div.
Fine: This setting changes the vertical scale to small steps between the coarse
settings. It will be helpful to adjust the waveform in smooth steps.
© 2008 RIGOL Technologies, Inc.
Figure 2-9
Fine configurations
User‟s Guide for DS1000B Series
Page 38

RIGOL
2-10
Invert off
Invert on
To invert a waveform
Invert turns the displayed waveform 180 degrees with respect to the ground level.
When the oscilloscope is triggered on the inverted signal, the trigger is also inverted.
Figure 2-10 and Figure 2-11 show the changes before and after the inversion
respectively.
Figure 2-10
The waveform before inversion
Figure 2-11
The waveform after inversion
© 2008 RIGOL Technologies, Inc.
User‟s Guide for DS1000B series
Page 39

RIGOL
2-11
Turn off digital
filter
Turn on digital
filter
To configure the Digital Filter
Press CH1→ Digital filter, it will display the digital filter menu. Turn the digital filter
on or off as shown in the following figure. Turn ( ) knob to adjust the upper and
lower limit of frequency after turning on the digital filter.
Figure 2-12
Turn off digital filter
Figure 2-13
Turn on digital filter
© 2008 RIGOL Technologies, Inc.
User‟s Guide for DS1000B Series
Page 40

RIGOL
2-12
Menu
Settings
Comments
Digital Filter
On
Off
Turn on the digital filter.
Turn off the digital filter.
Filter Type
Setup as LPF (Low Pass Filter).
Setup as HPF (High Pass Filter).
Setup as BPF (Band Pass Filter).
Setup as BRF (Band Reject Filter).
Upper limit
<frequency>
Turn ( ) knob to set upper limit
high limit.
Lower limit
<frequency>
Turn ( ) knob to set lower limit.
Back to higher level menu (The
followings are the same, no more
explanation).
Figure 2-14 Table 2-4 The Filter menu
© 2008 RIGOL Technologies, Inc.
User‟s Guide for DS1000B series
Page 41

RIGOL
2-13
Menu
Settings
Comments
Operate
A+B
A-B
A× B
FFT
Add source A and source B.
Subtract source B from source A.
Multiply source B by source A.
Fast Fourier Transform.
Source A
CH1, CH2,
CH3, CH4
Define CH1, CH2, CH3 or CH4 as
source A.
Source B
CH1, CH2,
CH3, CH4
Define CH1, CH2, CH3 or CH4 as
source B.
Invert
ON
OFF
Invert the MATH waveform.
Restore to original waveform display.
Math Scale
To Use Math Functions
The mathematic functions include “add”, “subtract”, “multiply” and “FFT” for Channel
1, Channel 2, Channel3 and Channel4. The mathematic result can be measured by
the grid and the cursor.
Figure 2-15
The Math function
Figure 2-16 Table 2-5 The Math menu (Page 1/2)
© 2008 RIGOL Technologies, Inc.
User‟s Guide for DS1000B Series
Page 42

RIGOL
2-14
Menu
Settings
Comments
The multifunctional knob ( )
adjusts the vertical position of the
Math waveform.
The multifunctional knob ( )
adjusts the vertical amplitude of
the Math waveform.
Figure 2-17 Table 2-6 The Math menu (Page 2/2)
© 2008 RIGOL Technologies, Inc.
User‟s Guide for DS1000B series
Page 43

RIGOL
2-15
Menu
Settings
Comments
Operate
A+B
A-B
A× B
FFT
Add source A to source B.
Subtract source B from source A.
Multiply source B by source A.
Fast Fourier Transform.
Source
CH1, CH2,
CH3, CH4
Define CH1, CH2, CH3 or CH4 as
FFT source.
Window
Rectangle
Hanning
Hamming
Blackman
Select window for FFT.
Display
Split
Full screen
Display FFT waveform on half screen.
Display FFT waveform on full screen.
Using FFT function
The FFT (Fast Fourier Transform) process converts a time-domain signal into its
frequency components mathematically. FFT waveforms are useful in the following
applications:
Measuring harmonic content and distortion in systems
Characterizing noise in DC power supplies
Analyzing vibration
Figure 2-18 Table 2-7 The FFT menu (Page 1/2)
© 2008 RIGOL Technologies, Inc.
User‟s Guide for DS1000B Series
Page 44

RIGOL
2-16
Key points for FFT
1. Signals that have a DC component or offset can cause incorrect FFT waveform
component magnitude values. To minimize the DC component, choose AC
Coupling on the source signal.
2. To reduce random noise and aliases components in repetitive or single-shot
events, set the oscilloscope acquisition mode to Average.
3. To display FFT waveforms with a large dynamic range, use the dBVrms scale.
The dBVrms scale displays component magnitudes using a log scale.
Menu
Settings
comments
The multifunctional knob( )
adjusts the vertical position of
Math
The multifunctional knob( )
adjusts the vertical amplitude
of Math
Vertical
scale
Vrms
dBVrms
Set Vrms as vertical scale unit
Set dBVrms as vertical scale
unit
Figure 2-19 Table 2-8 The FFT menu (Page 2/2)
User‟s Guide for DS1000B series
© 2008 RIGOL Technologies, Inc.
Page 45

RIGOL
2-17
Window
Features
Best for measuring
Rectangle
Best frequency resolution
and worst amplitude
accuracy.
This is essentially the same
as no window.
Transients or bursts, the signal
levels before and after the event
are nearly equal.
Equal-amplitude sine waves with
fixed frequencies.
Broadband random noise with a
relatively slow varying spectrum.
Hanning
Hamming
Better frequency resolution,
poorer amplitude accuracy
than Rectangular.
Hamming has slightly better
frequency resolution than
Hanning.
Sine, periodic, and narrow-band
random noise.
Transients or bursts where the
signal levels before and after the
events are significantly different.
Blackman
Best amplitude accuracy,
worst frequency resolution.
Single frequency waveforms, to
find higher order harmonics.
Key points:
FFT Resolution: The FFT resolution is the quotient between sampling rate and
the number of FFT points. With a fixed FFT points, the lower sampling rate, the
better the resolution.
Nyquist Frequency
The highest frequency that any real-time digitizing oscilloscope can acquire
without aliasing. It‟s normally half of the sample rate. This frequency is called
the Nyquist frequency. Frequency above the Nyquist frequency will be under
sampled, causing a situation known as aliasing.
Selecting an FFT Window
DS1000B series oscilloscope provides four FFT windows. Each window is a trade-off
between frequency resolution and amplitude accuracy. It depends on the desired
measurement and the source signals characteristics to determine the window to use.
Use the following guidelines to select the best window.
Table 2-9 FFT Windows
© 2008 RIGOL Technologies, Inc.
User‟s Guide for DS1000B Series
Page 46

RIGOL
2-18
Menu
Settings
Comments
Channel
REF 1
REF 2
REF 3
REF 4
Turn on or turn off one to four REF
channels
Current
REF 1
REF 2
REF 3
REF 4
Select the current REF channel
which is optional from REF1 to
REF4. (According to the available
channel, for example, if only REF1
is turned on, then only REF1 can be
chosen as the current channel.)
Source
CH1, CH2,
CH3, CH4,
MATH
Select CH1, CH2, CH3,CH4,MATH
as the source channel whose input
waveforms will be compared with
the reference waveforms.
location
Internal
external
Select memory location in scope.
Select memory location out scope.
To Use REF Function
Reference Waveforms are saved waveforms to be selected for display. The reference
function will be available after saving the selected waveform to non-volatile memory.
During the actual measurement process, you can use DS1000B series digital
oscilloscope to observe the waveforms of correlative components. It will help you to
determine the cause of malfunction when you compare the measured waveform with
the reference waveform. The method is particularly useful under the circumstance of
having reference waveforms.
Press REF button to display the Reference waveform menu.
Figure 2-20 Table 2-10 REF menu when using internal memory (Page 1/3)
© 2008 RIGOL Technologies, Inc.
User‟s Guide for DS1000B series
Page 47

RIGOL
2-19
Menu
Settings
Comments
Save
Save REF waveform to outer memory
location.
The multifunctional knob ( )
adjusts the vertical position of REF
The multifunctional knob ( )
adjusts the vertical amplitude of REF
Menu
settings
comments
Reset
Reset REF waveform.
Imp./Exp.
Go to import menu (see table 2-14).
Menu
settings
comments
Reset
Reset REF waveform.
Import
Go to import menu (see table 2-18).
Figure 2-21 Table 2-11 REF menu when using internal/external memory (Page 2/3)
Figure 2-22 Table 2-12 REF menu when using internal memory (Page 3/3)
Figure 2-23 Table 2-13 REF menu when using external memory (Page 3/3)
© 2008 RIGOL Technologies, Inc.
User‟s Guide for DS1000B Series
Page 48

RIGOL
2-20
Menu
Settings
Comments
Explorer
Path
Directory
File
Switch to Path, directory or file.
Export
Export the REF file from internal
memory to external memory (see table
2-15).
Import
Import the REF file to internal memory.
Delete
File
Delete file.
To Import and Export
Press REF →Imp./Exp. and go to the following menu.
Figure 2-24 Table 2-14 The Imp./Exp. Menu
The screen of Import and Export as follows
User‟s Guide for DS1000B series
Figure 2-25
Import of export the figure
© 2008 RIGOL Technologies, Inc.
Page 49

2-21
Menu
Settings
Comments
Move the input focus
point of files‟ name up
and down.
Move the focus point to
next location.
To delete chosen letter.
Save
Execute the operation.
Export
Press REF→Imp./Exp.→ Export and go to the following menu.
Figure 2-26 Table 2-15 The Export menu
The screen of Export is as follows.
RIGOL
© 2008 RIGOL Technologies, Inc.
Figure 2-27
Figure export
User‟s Guide for DS1000B Series
Page 50

RIGOL
2-22
Menu
Settings
Comments
Explorer
Path
Directory
File
Switch among Path, Directory
and File.
New File
(Folder)
Set up new file in Path and File.
Set up new folder in directory.
Delete File
(Folder)
Delete chosen file (Folder).
Save to External Memory
Press REF→Save and navigate to the following menu.
Figure 2-28 Table 2-16 The Save menu
The screen of Save is as follows:
Figure 2-29
The figure of save
© 2008 RIGOL Technologies, Inc.
User‟s Guide for DS1000B series
Page 51
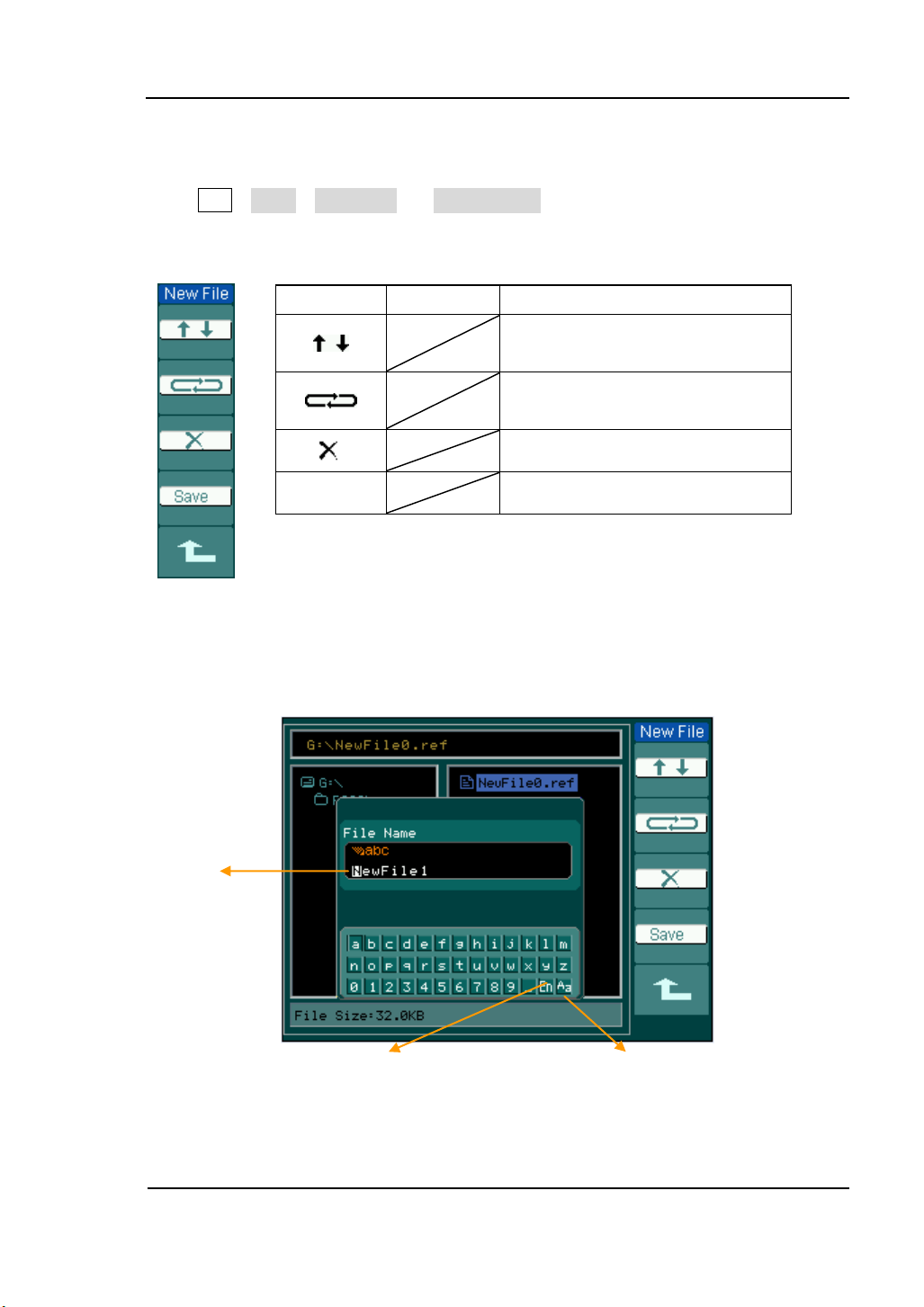
RIGOL
2-23
Menu
Settings
Comments
Move the focus point of file
name up and down.
Move the focus point to the next
location.
To delete chosen letter.
Save
Execute the saving operation.
Switch Capital on/off
Switch Chinese/English
The File name
key in pane
New File (or New Folder)
Press REF→Save→New File (or New Folder) and go to the following menu.
Figure 2-30 Table 2-17 The New File menu
The screen of File Name input is as follows:
© 2008 RIGOL Technologies, Inc.
Figure 2-31
File Name inputting interface
User‟s Guide for DS1000B Series
Page 52

RIGOL
2-24
Menu
Settings
Comments
Explorer
Path
Directory
File
Switch among Path, Directory and
File.
Import
Import the REF file into internal
memory.
Import
Press REF→Import and go to the following menu.
Figure 2-32 Table 2-18 The Import menu
The screen of Import is as follows:
Figure 2-33
The figure of import
© 2008 RIGOL Technologies, Inc.
User‟s Guide for DS1000B series
Page 53

RIGOL
2-25
To Display a Reference Waveform
Figure 2-34
Reference waveform display
Push REF button to show the reference waveform menu.
Continue Pressing button No.1 to turn on or turn off one to four reference
channels.
Select a REF channel as the current reference channel from the channels
activated by step 2.
Continue pressing button No.3 to select a signal source channel from CH1, CH2,
CH3, CH4 and MATH.(If the MATH is not available ,press MATH button to
activate MATH)
Turn vertical knob , multifunctional knob , vertical knob
to adjust the waveform (derived from step 4) to a suitable position
and expand or express the waveform horizontally to a proper situation.
Access page 1 of REF menu, Press button No.4 to select the saving location of
REF waveform.
Access page 2 of REF menu, and then press button No.2 to save the current
waveform on the screen to internal or external memory as a reference
waveform.
NOTE:
The Reference function is not available in X-Y mode.
© 2008 RIGOL Technologies, Inc.
User‟s Guide for DS1000B Series
Page 54

RIGOL
2-26
Channel Mode
Settings
Status Indicator
Channel 1 (CH1)
ON
Selected
OFF
CH1 (yellow letters with black background)
CH1 (black letters with yellow background)
No indicator
Channel 2 (CH2)
ON
Selected
OFF
CH2 (sky blue letters with black background)
CH2 (black letters with blue background)
No indicator
Channel 3(CH3)
ON
Selected
OFF
CH3(pink letters with black background)
CH3(black letters with pink background)
No indicator
Channel4(CH4)
ON
Selected
OFF
CH4(black letter with navy blue background)
CH4(navy blue letter with black background)
No indicator
MATH
ON
Selected
OFF
Math (black letter)
Math (purple letter)
No indicator
Turn on or off Channels
CH1, CH2, CH3, CH4 and Ext. trigger channels are input channels. All functions
applied will base on operating the instrument with channels, so MATH and REF can
be regarded as relatively isolated channels.
Press the corresponding button (for example: CH1, CH2, CH3, CH4, MATH, REF) on
the front panel to turn the channels on. The backlight indicates the channel is
currently active. When a channel is currently selected, press the button with respect
to the channel again will turn it off and the backlight goes off. When a channel is not
currently selected, press the button associated with the channel will select the
channel as the current channel.
Table 2-19 The Channels menu
User‟s Guide for DS1000B series
© 2008 RIGOL Technologies, Inc.
Page 55

RIGOL
2-27
To Apply the Vertical Knobs
Use the vertical controls to display signal waveforms by adjusting the vertical
knob, and the knob, and setting the input parameters.
1. Using vertical knob.
The vertical control changes the vertical position of signal
waveforms in all channels (excluding MATH and REF). The resolution changes
according to the vertical level set. Pressing this knob will clear the channel‟s
vertical offset to zero.
2. Using vertical knob.
The vertical control changes the vertical sensitivity of signal
waveforms in all channels (excluding MATH and REF). If the Volts/Div is set to
“Coarse”, the waveform scales in a 1-2-5 step sequence from 2
mV ,5mv,10mv…to 10 V. If the Volts/Div is set to “Fine”, it scales to small steps
between the coarse settings. Turn the knob clockwise to decrease the vertical
scale, turn the knob counter-clockwise to increase the vertical Volts/Div setting.
You can toggle between “coarse” and “Fine” setting through pressing the
knob.
3. Channels(excluding Math and REF ) would be adjustable by the
vertical and only when they are selected.
4. During the vertical positioning, a position message is displayed on the left
bottom of the screen, in the same color along with the corresponding channel.
The unit is V (Volts).
© 2008 RIGOL Technologies, Inc.
User‟s Guide for DS1000B Series
Page 56

RIGOL
2-28
To Set up the Horizontal System
The oscilloscope shows the time per division in the scale readout. With the horizontal
control buttons and knobs, you can change the horizontal time base and trigger
offset which indicates the horizontal location of trigger in the memory.
The horizontal controls change the horizontal scale and position of waveforms. The
horizontal center of the screen is the time reference for waveforms. Changing the
horizontal scale causes the waveform to be expanded or compressed with respect to
the screen center.
Horizontal position changes the displayed waveform position, relative to the trigger
point.
The Horizontal Knobs
: The horizontal knob adjusts the horizontal position of
all channel (including Math) waveforms. The resolution of this control
varies with the time base. Pressing this button clears the trigger
offset and moves the trigger point to the horizontal center of the
screen.
: Use to select the horizontal time/div (scale factor) for the
main or the Delayed Scan time base. When Delayed Scan is enabled, it
changes the width of the window zone by changing the Delayed Scan
time base.
Horizontal Menu.
Press the horizontal MENU button to display the horizontal menu. The settings of this
menu are listed in the following table.
© 2008 RIGOL Technologies, Inc.
User‟s Guide for DS1000B series
Page 57

2-29
⑤
Menu
Settings
Comments
Delayed
ON
OFF
Turn on the Delayed Scan mode.
Turn off the Delayed Scan mode.
Time Base
Y-T
X-Y
Roll
Show the relative relation
between vertical voltage and
horizontal time.
Show CH1 amplitude value at X
axis; show CH2 amplitude value
at Y axis.
In Roll Mode, the waveform
display updates from right to left.
Trig-offset Reset
Adjust the trigger position to the
center of the memory.
Figure 2-35 Table 2-20 The Horizontal menu
① ② ③ ④
RIGOL
© 2008 RIGOL Technologies, Inc.
Figure 2-36
Status bar and mark for Horizontal control
User‟s Guide for DS1000B Series
Page 58

RIGOL
2-30
Key Points
Y-T: The conventional oscilloscope display format. It shows that the voltage of a
waveform record (on the vertical axis) varies along with time (on the
horizontal axis).
X-Y: XY format displays channel 1 in the horizontal axis and channel 2 in the
vertical axis.
Roll Mode: In this mode, the waveform display rolls from right to left. No trigger
or horizontal offset control of waveforms is available during Roll Mode, and
it‟s only available when set to 500ms/div or slower.
Slow Scan Mode: This mode is available when the horizontal time base is set to
50ms or slower. In this mode, the oscilloscope acquires sufficient data for
the left part to the trigger point, then wait for trigger, when trigger occurs, it
continue to draw the rest part from the trigger point to the end of the right
side. When choosing this mode to view low frequency signals, it is
recommended that the channel coupling be set as DC.
Time/Div: Horizontal scale. If the waveform acquisition is stopped (using the
Run/Stop button), the Time/Div control expands or compresses the
waveform.
Marks Indicator
① The horizontal time base (main time base).
② The position of the current waveform window in the memory.
③ The trigger position in the memory.
④ The trigger position in the current waveform windows.
⑤ The trigger‟s horizontal offset with respect to the center of the window.
User‟s Guide for DS1000B series
© 2008 RIGOL Technologies, Inc.
Page 59

RIGOL
2-31
Waveform to be horizontally expanded
Expanded waveform in horizontal
Time base of
Delayed Scan
Delayed Scan:
The Delayed Scan is a magnified portion of the main waveform window. Use Delayed
Scan to locate and horizontally expand part of the main waveform window for a more
detailed (higher horizontal resolution) analysis of signal. The Delayed Scan time base
setting cannot be set slower than the Main time base setting.
Figure 2-37
Delayed Scan windows
The following steps show you how to use Delayed Scan.
1. Connect a signal to the oscilloscope and obtain a stable display.
2. Press horizontal MENU→Delayed→ON or press horizontal knob to
enter Delayed Scan mode.
The screen will be split into two parts. The upper half displays the main waveform
window and the lower half displays an expanded portion of the main waveform
window. This expanded portion of the main window is called the Delayed Scan
window. Two blocks shaded at the upper half; the un-shaded portion is expanded in
the lower half. The horizontal and knobs control the size
and position of the Delayed Scan. The value at top of the screen is the main time
base and the value on the center bottom means the Delayed Scan time base.
© 2008 RIGOL Technologies, Inc.
User‟s Guide for DS1000B Series
Page 60

RIGOL
2-32
Delayed Scan Shortcut Key:
Delayed Scan function can be activated not only by menu but also by pressing
horizontal knob.
Use the horizontal knob to change the position of the expanded
portion.
Turn the horizontal knob to adjust the Delayed Scan resolution.
To change the main time base, turn off the Delayed Scan mode.
Since both the main and Delayed Scan waveform windows are displayed, each
waveform window occupies a half of the original waveform window. They are
both compressed vertically to a half size, the same as the vertical divisions.
© 2008 RIGOL Technologies, Inc.
User‟s Guide for DS1000B series
Page 61

RIGOL
2-33
X-Y Format
This format is useful for studying phase relationships between two signals.
Channel 1 in the horizontal axis(X) and channel 2 in the vertical axis(Y), the
oscilloscope uses a none-trigger acquisition mode, data is displayed as dots.
Figure 2-38
X-Y display format
NOTE: The X-Y display format is only suitable for CH1, CH2, CH3; CH4.In the normal
condition, the oscilloscope can acquire waveforms with any sampling rate. You can
also adjust the sampling rate and the vertical scaling of the channel when you use
the X-Y display format. You can reduce the sampling rate so as to display a better
Lissajous figure.
The following modes or functions will not work in X-Y format.
Cursor Measurements(excluding manual mode )
REF and MATH Operations
Delayed Scan Mode
Vector Display Mode
Horizontal knob
Trigger Controls(excluding MODE button)
© 2008 RIGOL Technologies, Inc.
User‟s Guide for DS1000B Series
Page 62

RIGOL
2-34
To Set up the Trigger System
The trigger determines when the oscilloscope starts to acquire data and display a
waveform. When a trigger is set up properly, it can convert unstable displays or blank
screens into meaningful waveforms.
When the oscilloscope starts to acquire a waveform, it collects enough data so that it
can draw the waveform to the left of the trigger point. The oscilloscope continues to
acquire data while waiting for the trigger condition to occur. After it detects a trigger,
the oscilloscope continues to acquire enough data so that it can draw the waveform
to the right of the trigger point.
The trigger control area on the front panel includes a knob and four buttons:
MODE : With the button, three kinds of trigger mode can be toggled among Auto,
Normal, and Single.
: Use the knob to adjust the trigger level; press the knob to reset the
trigger level to zero.
50%: Specify the trigger level to the vertical midpoint between the peaks of
the trigger signal by pressing the instant execute button.
FORCE: Force to create a trigger signal and the function is mainly used in
Normal and Single mode
MENU: The button that activates the trigger controls menu.
Figure 2-39
Trigger controls
© 2008 RIGOL Technologies, Inc.
User‟s Guide for DS1000B series
Page 63

RIGOL
2-35
Trigger Modes
The oscilloscope provides five trigger modes: Edge, Pulse, Video, Pattern and
Alternative.
Edge: An edge trigger occurs when the trigger input passes through a specified
voltage level in the specified slope direction.
Pulse: Use this trigger mode to catch pulses with certain pulse width.
Video: Use video trigger mode on fields or lines for standard video signals.
Pattern: Recognising trigger by searching specified code.
Alternative: Trigger on non-synchronized signals.
© 2008 RIGOL Technologies, Inc.
User‟s Guide for DS1000B Series
Page 64

RIGOL
2-36
Menu
Settings
Comments
Source
CH1
CH2
CH3
CH4
EXT
EXT/5
AC Line
Select CH1 as trigger source.
Select CH2 as trigger source.
Select CH3 as trigger source.
Select CH4 as trigger source.
Select EXT TRIG as trigger source.
Select attenuated EXT TRIG/5 as
trigger source.
Select power line as trigger source.
Slope
Rising edge
Falling edge
Rising &
Falling edges
Trigger on rising edge.
Trigger on falling edge.
Trigger on both ring & falling edge.
Sweep
Auto
Normal
Single
Acquire waveform even no trigger
occurred.
Acquire waveform when trigger
occurred.
When trigger occurs, acquire one
waveform then stop.
Set up
To go to Set Up menu, see table 2-36
Edge Trigger
An edge trigger determines whether the oscilloscope finds the trigger point on the
rising or the falling edge of a signal. Select Edge trigger Mode to trigger on Rising
edge, falling edge or rising & falling edge.
Figure 2-40 Table 2-21 The Trigger menu
© 2008 RIGOL Technologies, Inc.
User‟s Guide for DS1000B series
Page 65

RIGOL
2-37
Menu
Settings
Comments
Source
CH1
CH2
CH3
CH4
EXT
EXT/5
Select CH1 as trigger source.
Select CH2 as trigger source.
Select CH3 as trigger source
Select CH4 as trigger source l
Select EXT TRIG as trigger
source
Select attenuated EXT TRIG/5
as trigger source.
When
(+Pulse width more than)
(+Pulse width less than)
(+Pulse width equal to)
(-Pulse width less than)
(-Pulse width more than)
(-Pulse width equal to)
To select pulse condition.
Settings
<Width>
To set required pulse width.
Menu
Settings
Comments
Sweep
Auto
Normal
Single
Acquire waveform even no trigger occurred.
Acquire waveform when trigger occurred.
When trigger occurs, acquire one waveform
and then stop.
Set Up
To go to Set Up menu, see table 2-36.
Pulse Width Trigger
Pulse trigger occurs according to the width of pulse. The abnormal signals can be
detected through setting up the pulse width condition.
Figure 2-41 Table 2-22 The Trigger menu (Page 1/2)
Figure 2-42 Table 2-23 The Trigger menu (Page 2/2)
Note: The Pulse width adjust range is 20ns ~ 10s. When the condition is met, it will
trigger and acquire the waveform.
© 2008 RIGOL Technologies, Inc.
User‟s Guide for DS1000B Series
Page 66

RIGOL
2-38
Menu
Settings
Comments
Source
CH1
CH2
CH3
CH4
EXT
EXT/5
Selects CH1 as trigger source.
Selects CH2 as trigger source.
Selects CH3 as trigger source.
Selects CH4 as trigger source.
Select EXT TRIG as trigger source.
Select EXT TRIG/5 as trigger
source.
Polarity
Normal polarity
Inverted polarity
Triggers on positive going sync
pulses.
Triggers on negative going sync
pulses.
Sync
All Lines
Line Num
Odd field
Even field
Trigger on all lines.
Trigger on a specified line.
Select to trigger on odd field.
Select to trigger on even field.
Video Trigger
Choose video trigger to trigger on fields or lines of NTSC, PAL, or SECAM standard
video signals. Trigger coupling preset to DC.
Figure 2-43 Table 2-24 The Video Trigger menu (Page 1/2)
© 2008 RIGOL Technologies, Inc.
User‟s Guide for DS1000B series
Page 67

RIGOL
2-39
Menu
Settings
Comments
Line Num
< Line sync >
Select the specified line number for sync.
Standard
PAL/SECM
NTSC
Select Video standard.
Sweep
Auto
Normal
Single
Force the oscilloscope to trigger in the
absence of trigger condition.
Lets oscilloscope to trigger in the
suitable trigger condition.
Lets oscilloscope to trigger one time in
the suitable trigger condition, and then
stop.
Set Up
To go to set up menu, see Table 2-36.
Menu
Settings
Comments
Standard
PAL/SECAM
NTSC
Select Video standard.
Sweep
Auto
Normal
Single
Force the oscilloscope to trigger in the
absence of trigger condition.
Lets oscilloscope to trigger in the
suitable trigger condition.
Lets oscilloscope to trigger one time in
the suitable trigger condition, and then
stop.
Set Up
To go to set up menu, see Table 2-36.
Figure 2-44 Table 2-25 The Video Trigger menu (Page 2/2 when Sync is set as the
specified line)
Figure 2-45 Table 2-26 The Video Trigger menu (Page 2/2 When the Sync is set as
© 2008 RIGOL Technologies, Inc.
All lines, Odd field and Even field)
User‟s Guide for DS1000B Series
Page 68

RIGOL
2-40
Key points:
Sync Pulses: When Normal Polarity is selected, the trigger always occurs on
negative-going sync pulses. If the video signal has positive-going
sync pulses, use the inverted Polarity.
Figure 2-46
Video Trigger: Line Synchronization
Figure 2-47
Video Trigger: Field Synchronization
© 2008 RIGOL Technologies, Inc.
User‟s Guide for DS1000B series
Page 69

RIGOL
2-41
Menu
Settings
Comments
Channel
CH1
CH2
CH3
CH4
EXT
EXT/5
To select CH1 as trigger source
To select CH2 as trigger source
To select CH3 as trigger source
To select CH4 as trigger source
To set EXT as trigger source
To set EXT/5 as trigger source to expand
trigger level range.
Code
H
L
X
To set the code of the selected channel
as logic high value.
To set the code of the selected channel
as logic low value.
To set the code of the selected channel
as neglect value.
To specify trigger to the rising edge of
signal
To specify trigger to the falling edge of
signal
Sweep
Auto
Normal
Single
Acquire waveform even no trigger
occurred.
Acquire waveform when trigger occurred.
When trigger occurs, acquire one
waveform then stop.
Set up
To go to set up menu, see Table 2-36.
Pattern Trigger
Pattern trigger recognises the trigger condition through inspecting the code preset
which means the logic values or the logic combination.Every channel has its own
logic value,such as,logic high value,logic low value,and the neglect value.
Figure 2-48 Table 2-27 The Pattern Trigger menu
© 2008 RIGOL Technologies, Inc.
User‟s Guide for DS1000B Series
Page 70

RIGOL
2-42
Figure 2-49
Pattern trigger: set code as falling edge
© 2008 RIGOL Technologies, Inc.
User‟s Guide for DS1000B series
Page 71

RIGOL
2-43
Menu
Settings
Comments
Alt Channel
CH1-CH2
CH1-CH3
CH1-CH4
CH2-CH3
CH2-CH4
CH3-CH4
To specify the current alternative trigger
channels as any two channels selected
form CH1, CH2, CH3, CH4.
select
CH1, CH2
CH3, CH4
To select vertical channel among CH1,
CH2, CH3, CH4 in alternative trigger
mode so as to configure further settings.
Type
Edge
Pulse
Video
Choose trigger type for the current
channel.
Menu
settings
comments
Edge type
( rising
edge)
( falling
edge)
( both
rising edge
and falling
edge)
Trigger on rising edge.
Trigger on falling edge.
Trigger on both ring & falling edge.
Set up
To go to set up menu. See Table 2-36
Alternative Trigger
When alternative trigger is on, the trigger sources come from two vertical channels.
This mode can be used to observe two non-related signals. You can choose two
different trigger modes for the two vertical channels. The options are as follows:
Edge, Pulse and video. The info of the trigger level of the two channels will be
displayed on the upper-right of the screen.
Figure 2-50 Table 2-28 The Alternative trigger menu (Page 1/2 Trigger Type: Edge)
Figure 2-51 Table 2-29 The Alternative trigger menu (Page 2/2 Trigger Type: Edge)
© 2008 RIGOL Technologies, Inc.
User‟s Guide for DS1000B Series
Page 72

RIGOL
2-44
Menu
Settings
Comments
Alt Channel
CH1-CH2
CH1-CH3
CH1-CH4
CH2-CH3
CH2-CH4
CH3-CH4
To specify the current alternative
trigger channels as any two channels
selected form CH1, CH2, CH3, CH4.
select
CH1, CH2,
CH3, CH4
To select vertical channel among CH1,
CH2, CH3, CH4 in alternative trigger
mode so as to configure further
settings.
type
Edge trigger
Pulse trigger
Video trigger
Select trigger type for current
channel.
Menu
Settings
Comments
When
(+Pulse width less than)
(+Pulse width more than)
(+Pulse width equal to)
(-Pulse width less than)
(-Pulse width more
than)
(-Pulse width equal to)
To set trigger conditions.
Settings
<Pulse width >
To set up width value of
the pulse.
Set Up
To go to set up menu. See
Table 2-36.
Figure 2-52 Table 2-30 The Alternative trigger menu (Page 1/2 Trigger Type: Pulse)
Figure 2-53 Ta ble 2-31 The Alternative trigger menu (Page 2/2 Trigger Type: Pulse)
User‟s Guide for DS1000B series
© 2008 RIGOL Technologies, Inc.
Page 73

2-45
Menu
Settings
Comments
Alt
Channel
CH1-CH2
CH1-CH3
CH1-CH4
CH2-CH3
CH2-CH4
CH3-CH4
To specify the current
alternative trigger channels as
any two channels selected form
CH1, CH2, CH3, CH4.
select
CH1, CH2,
CH3, CH4
To select vertical channel
among CH1, CH2, CH3, CH4 in
alternative trigger mode so as
to configure further settings.
Type
Edge trigger
Pulse trigger
Video trigger
To select trigger type for
current channel.
Menu
Settings
Comments
Polarity
Normal polarity
Inverted polarity
Trigger on negative going
sync pulses.
Trigger on positive going sync
pulses.
Sync
ALL lines
Line Num
Trigger on all lines.
Trigger on a specified line.
Odd field
Even field
Select to trigger on odd field
or even field.
Standard
PAL/SECM
NTSC
Select Video standard.
Set Up
To go to set up menu, see
Table 2-36.
Figure 2-54 Table 2-32 The Alternative trigger menu
(Page 1/2 Trigger Type: Video)
RIGOL
Figure 2-55 Table 2-33 The Alternative trigger menu
© 2008 RIGOL Technologies, Inc.
(Page 2/2 Trigger Mode: Video)
User‟s Guide for DS1000B Series
Page 74

RIGOL
2-46
Menu
Settings
Comments
Coupling
DC
AC
LF Reject
Allow all signals pass.
Block DC signals.
Reject DC and low frequency
signals.
HF reject
On
off
Passes high frequency
component.
Blocks high frequency
component, passes low
frequency component.
Sensitivity
<Sensitivity Setting>
Set trigger sensitivity.
Holdoff
<Holdoff Setting>
Set time slot before another
trigger event.
Trigger Settings
Set up different trigger settings according to different trigger modes. When in the
mode of Video and Alternative, only trigger sensitivity, trigger holdoff time, holdoff
reset is adjustable.
Figure 2-56 Table 2-34 The Trigger Set Up menu
(Page 1/2 Settings for trigger coupling, trigger sensitivity and Holdoff)
© 2008 RIGOL Technologies, Inc.
User‟s Guide for DS1000B series
Page 75

RIGOL
2-47
Menu
Settings
comments
Holdoff
Reset Holdoff time to 100ns.
Menu
Settings
Comments
Sensitivity
<Sensitivity Setting>
Set trigger sensitivity.
Holdoff
<Holdoff Setting>
Set time slot before another
trigger event.
Holdoff
Reset
Reset Holdoff time to 100ns.
Figure 2-57 Table 2-35 Restore the trigger holdoff time to default (page 2/2)
When Settings for “sensitivity” and “Hold off” in the Video and Alternative trigger
mode, the menu is shown below.
Figure 2-58 Table 2-36 The Trigger Set Up menu
© 2008 RIGOL Technologies, Inc.
User‟s Guide for DS1000B Series
Page 76

RIGOL
2-48
Trigger site
Trigger holdoff
Time of holdoff
Trigger Holdoff
You can use trigger Holdoff to stabilize a complex waveform, such as a pulse
sequence. Holdoff time is the oscilloscope‟s waiting period before starting a new
trigger. During Holdoff, oscilloscope will not trigger until Holdoff ends. For instance:
To trigger on the first pulse on a group of them, users can set the holdoff time to
Pulse cluster width.
Figure 2-59
Trigger Holdoff
To use trigger Holdoff:
1. Press the MENU button of the trigger control system to display the Menu.
2. Press Set Up key to display trigger set up menu.
3. Turn the multi function knob ( ) to change Holdoff time until waveform is stable.
4. Press Trigger Hold off reset to reset the Holdoff time to its default value.
© 2008 RIGOL Technologies, Inc.
User‟s Guide for DS1000B series
Page 77

2-49
Trigger Key points
1. Trigger Source:
Trigger occurs from several sources: Input channels (CH1, CH2, CH3, CH4), AC
Line, Ext, Ext/5.
CH1, CH2, CH3, CH4:
It is the most commonly used trigger source. The channel works when it is
selected as a trigger source whatever displayed.
Ext Trig:
The instrument can be triggered from an external source while acquiring data
from CH1, CH2, CH3, and CH4. For example, be a trigger source with an
external clock or a signal from another part of the test circuit. The Ext, Ext/5
trigger sources use an external trigger signal connected to the EXT TRIG
connector. Ext uses the signal directly; it has a trigger level range of -0.6 V to
+0.6 V. The EXT/5 trigger source attenuates the signal by 5X, which extends the
trigger level range to -3V to +3 V allowing the oscilloscope to trigger on a larger
signal.
RIGOL
AC Line:
AC power can be used to display signals related to the power line frequency,
such as lighting equipment and power supply devices. The oscilloscope gets
triggered on its AC power input, but an AC trigger signal is not required. When
AC Line is selected as a trigger source, the oscilloscope automatically set
coupling to DC, set trigger level to 0V.
2. Sweep Mode:
The sweep mode determines how the oscilloscope behaves in the absence of a
trigger event. The oscilloscope provides three trigger modes: Auto, Normal, and
Single.
Auto:
This sweep mode allows the oscilloscope to acquire waveforms even when it
does not detect a trigger condition. If no trigger condition occurs while the
oscilloscope is waiting for a specific period (as determined by the time-base
© 2008 RIGOL Technologies, Inc.
User‟s Guide for DS1000B Series
Page 78

RIGOL
2-50
setting), it will force itself to trigger.
When forcing invalid triggers, the oscilloscope cannot synchronize the waveform,
and the waveform seems to roll across the display. If valid triggers occur, the
display becomes stable on the screen.
Any factor results in the instability of waveforms can be detected by Auto Trigger,
such as the output of Power supply.
NOTE: When horizontal control is set under 50 ms/div, Auto mode allows the
oscilloscope not to capture trigger signal.
Normal:
The Normal mode allows the oscilloscope to acquire a waveform only when it is
triggered. If no trigger occurs, the oscilloscope keeps waiting, and the previous
waveform will remain on the display.
Single:
In Single mode, after pressing the RUN/STOP key, the oscilloscope waits for
trigger. While the trigger occurs, the oscilloscope acquires one waveform then
stop.
3. Coupling:
Trigger coupling determines which signal component passing to the trigger circuit.
Coupling types include AC, DC, LF Reject and HF Reject.
AC: AC coupling blocks DC components and attenuate signal lower than
10 Hz.
DC: DC coupling passes both AC and DC components.
LF Reject: LF Reject coupling blocks DC component, and attenuates all
signal with a frequency lower than 10 kHz.
HF Reject: HF Reject coupling attenuates all signals with a frequency
higher than 100 kHz.
4. Pre-trigger/delayed trigger:
The data is collected before and after trigger.
The trigger position is typically set at the horizontal center of the screen. In the
full-screen display the 6div data of pre-trigger and delayed trigger can be
© 2008 RIGOL Technologies, Inc.
User‟s Guide for DS1000B series
Page 79

2-51
surveyed. More data (14div) of pre-trigger and 1s delayed trigger can be
surveyed by adjusting the horizontal knob.
This feature is very useful to study the events that led up to the trigger point.
Everything on the right of the trigger point is called post-trigger information. The
delay range (pre-trigger and post-trigger information) depends on the sweep
speed selected.
3. Adjustable trigger sensitivity
To avoid the influence of noise from the physical world, and get the stable trigger,
the trigger circuit has adopted Stickiness. In DS1000B series, the stickiness is
adjustable from 0.1div-1.0div, which means when it sets to 1.0div; the trigger
circuit will not affect any signal with peak-peak amplitude less than 1.0div, so as
to avoid the influence of the noise.
RIGOL
© 2008 RIGOL Technologies, Inc.
User‟s Guide for DS1000B Series
Page 80

RIGOL
2-52
Menu
Settings
Comments
Acquisition
Normal
Average
Peak Detect
Normal Acquisition mode.
Average Acquisition mode.
Peak Detect Acquisition mode.
Sampling
Real-Time
Equ-Time
Real-time sampling mode.
Equivalent sampling mode.
Sinx/x
ON
OFF
Set the interpolation as Sinx/x.
Set the interpolation as
linearity.
Sa Rate
Display sampling rate.
Acquire setup button
To Set up the Sampling System
Figure 2-60 shows, the Acquire button at the MENU of the front panel.
Figure 2-60
The Acquire setup button
Press the Acquire button, the interface menu shows as follows:
Figure 2-61 Table 2-37 The Acquire menu
© 2008 RIGOL Technologies, Inc.
User‟s Guide for DS1000B series
Page 81

RIGOL
2-53
The waveform displayed on the screen will change in conjunction with the setting of
Acquire menu.
Figure 2-62
Signal that contains noise, and without average sampling
Figure 2-63
Display signal after average 256 times sampling
Note:
Select Real-time acquisition to observe the single-shot or pulse signals.
Select Equ-Time to observe high frequency repetitive signals.
© 2008 RIGOL Technologies, Inc.
User‟s Guide for DS1000B Series
Page 82

RIGOL
2-54
To reduce the displayed random noise, select the Average Acquisition. This
mode would make the screen refresh slower.
To Avoid signal aliasing, select Peak Detect Acquisition.
Figure 2-64
Signal with Peak Detect Acquisition
The Peak Detect effect is shown as the figure above.
Stop Acquisition: When the scope is acquiring waveforms, the waveforms is in a
live status; when acquisition is stopped, frozen waveform will be displayed, the
position and scale can still be adjusted by vertical control and horizontal control.
© 2008 RIGOL Technologies, Inc.
User‟s Guide for DS1000B series
Page 83

RIGOL
2-55
Key Points
Real-time Sampling:
DS1000B has Real-time sampling rate up to 2GSa/s. At the time base 50ns or
faster, the oscilloscopes use the sine(x)/x interpolation to expand the horizontal
time base.
Equivalent sampling:
Known as Repetitive sampling to get up to 20ps of horizontal resolution (equivalent
50Gsa/s). This mode is good for observing repetitive signals, and it is not
recommended for single-shot or pulse.
Normal:
Oscilloscope acquires signal by equal time interval.
Average Acquisition:
Apply averaging to your signal to remove uncorrelated noise and improve
measurement accuracy. Reduces random or uncorrelated noise in the signal
display. The averaged waveform is a running average over a specified number of
acquisitions from 2 to 256.
Peak Detect:
Peak Detect mode captures the maximum and minimum values of a signal, and
finds highest and lowest record points over many acquisitions.
© 2008 RIGOL Technologies, Inc.
User‟s Guide for DS1000B Series
Page 84

RIGOL
2-56
Menu
Setting
Comments
Type
Vectors
Dots
Display waveforms as vectors.
Display waveforms as dots.
Clear
Clear all existing waveforms from
screen.
Persist
Infinite
OFF
The sample points remain displayed
until turn the persistence “OFF”.
Turn off the persistence function.
Intensity
<percentage>
Set up waveform intensity.
Display setup button
To Set up the Display System
The menu button for the display system on the front panel is shown in the following
figure.
Figure 2-65
The display setup button
Press the Display button, the interface menu for settings shows as follows.
Figure 2-66 Table 2-38 The Display menu (Page 1/3)
© 2008 RIGOL Technologies, Inc.
User‟s Guide for DS1000B series
Page 85

2-57
Menu
Settings
Comments
Grading
On
Off
The waveform is displayed in
multiple levels of pixel intensity.
Grid
Display grids and coordinates on the
screen.
Turn off the grids.
Turn off the grids and coordinates.
Menu
Display
1s
2s
5s
10s
20s
Infinite
Set the time before menu fades
away. The menu will be hidden after
the set time of last button pressing.
Menu
Settings
Comments
GridBright
<percentage>
Set up grid brightness.
Screen
Normal
Inverted
Set to normal mode.
Set to invert color display mode.
Screen
persist
To show the last acquired waveform
when the acquisition is stopped.
To show the accumulated acquired
waveforms when the acquisition is
stopped.
Skin
Classical
Modern
Tradition
Succinct
To set the display screen of the
oscilloscope
Figure 2-67 Table 2-39 The Display menu (Page 2/3)
RIGOL
Figure 2-68 Table 2-40 The Display menu (Page 3/3)
© 2008 RIGOL Technologies, Inc.
User‟s Guide for DS1000B Series
Page 86

RIGOL
2-58
Adjusting waveform intensity
Turn the multifunctional knob ( ) to adjust waveform intensity.
Key points:
Display type: Display type includes Vector and Dot. In vectors type, oscilloscope
connects dots through digital interpolation including both linearity and sin(x)/x.
Sin(x)/x interpolation is suitable for Real-time sampling and will be more effective at
50ns or faster time base.
Refresh rate: It is an important performance of digital oscilloscopes. It means the
number of display refreshing per second and it will affect the ability to observe
signal.
User‟s Guide for DS1000B series
© 2008 RIGOL Technologies, Inc.
Page 87

2-59
Storage setup button
RIGOL
To Store and Recall
Figure 2-69 shows the menu button for the storage system on the front panel.
Figure 2-69
The Storage setup button
Press the Storage button to show the menu for the settings of the storage system.
Waveforms and setups can be stored in and recalled from both internal memory and
external memory. The waveform files, setup files, 8 or 24 bits format bitmap files,
CSV format files and PNG (Portable Network Graphics format) files in external
memory can be created and deleted. System supports English/Chinese file name
input.
© 2008 RIGOL Technologies, Inc.
User‟s Guide for DS1000B Series
Page 88

RIGOL
2-60
Menu
Settings
Comments
Storage
Waveform
Setups
8-Bitmap
24-Bitmap
PNG
CSV
Factory
Store or recall waveform.
Store or recall instrument setups.
Create or delete 8bits bitmap files.
Create or delete 24bits bitmap files.
Create or delete PNG format files.
Create or delete CSV files.
Recall factory setups.
Load
Recall factory setups or files.
Disk Mana.
Go to disk manage menu (see Table
2-48).
Menu
Settings
Comments
Storage
Waveform
Setups
8-Bitmap
24-Bitmap
PNG
CSV
Factory
Store or recall waveform.
Store or recall instrument setups.
Create or delete 8bits bitmap files.
Create or delete 24bits bitmap files.
Create or delete PNG format files.
Create or delete CSV files.
Recall factory setups.
Internal
Go to menu for internal memory
operation (see Table 2-46).
External
Go to menu for external memory
operation (see Table 2-47).
Disk Mana.
Go to disk manage menu (see Table
2-48).
Waveform and setup menus are as follows:
Figure 2-70 Table 2-41 The Storage menu
For factory default setups, the menu is as follows:
Figure 2-71 Table 2-42 The Storage menu
© 2008 RIGOL Technologies, Inc.
User‟s Guide for DS1000B series
Page 89

2-61
Menu
Settings
Comments
Storage
Waveform
Setups
8-Bitmap
24-Bitmap
PNG
CSV
Factory
Store or recall waveform.
Store or recall setups.
Create or delete 8bits Bitmap files.
Create or delete 24bits Bitmap files.
Create or delete Portable Network
Graphics format files.
Create or delete CSV files.
Recall factory setups.
Para Save
On
Off
Save the current oscilloscope
settings in different format with the
same file name.
External
Go to menu for external memory
operation (see Table 2-47).
Disk Mana.
Go to disk manage menu (see Table
2-48).
Menu
Settings
Comments
Storage
Waveform
Setups
8-Bitmap
24-Bitmap
PNG
CSV
Factory
Store or recall waveform.
Store or recall instrument setups.
Create or delete 8bits bitmap files.
Create or delete 24bits bitmap files.
Create or delete PNG format files.
Create or delete CSV files.
Recall factory setups.
Data
Depth
Displayed
Maximum
Save currently displayed waveform
data to CSV file.
Save the whole waveform data in
memory to CSV file.
Para Save
On
Off
Save the current oscilloscope
settings in different format with the
same file name.
External
Go to menu for external memory
operation (see Table 2-47).
Disk Mana.
Go to disk manage menu (see Table
2-48).
For bitmap, the menu is as follows:
Figure 2-72 Table 2-43 The Storage menu
RIGOL
For CSV, the menu is as follows.
Figure 2-73 Table 2-44 The Storage menu
© 2008 RIGOL Technologies, Inc.
User‟s Guide for DS1000B Series
Page 90

RIGOL
2-62
Menu
Settings
Comments
Storage
Waveform
Setups
8-Bitmap
24-Bitmap
PNG
CSV
Factory
Store or recall waveform.
Store or recall instrument setups.
Create or delete 8bits bitmap files.
Create or delete 24bits bitmap files.
Create or delete PNG format files.
Create or delete CSV files.
Recall factory setups.
Para Save
On
Off
Save the current oscilloscope
settings in different format with the
same file name.
External
Go to menu for external memory
operation (see Table 2-47).
Disk Mana.
Go to disk manage menu (see Table
2-48).
For PNG, the menu is as follows.
Figure 2-74 Table 2-45 The Storage menu
© 2008 RIGOL Technologies, Inc.
User‟s Guide for DS1000B series
Page 91

2-63
Internal Memory
Menu
Settings
Comments
Internal
Int_00 (N)
.
.
.
Int_09 (N)
Set up the location of files in internal
memory.
Load
Recall waveform files and setup files
from the internal memory location.
Save
Save waveform files and setup files to
the internal memory location.
Delete
Files
Delete selected files.
Press Storage→Internal to go to the following menu.
Figure 2-75 Table 2-46 The Memory menu
RIGOL
© 2008 RIGOL Technologies, Inc.
User‟s Guide for DS1000B Series
Page 92

RIGOL
2-64
Menu
Settings
Comments
Explorer
Path
Directory
File
Switch among Path, Directory
and File.
New File
(Folder)
To create new file or folder.(see
table 2-13)
Delete File
(Folder)
Delete file (Folder).
Load
Recall waveform and setup from
USB storage device.
Files
File info.
Current directory
Back to previous
folder
Path
External Memory
Press Storage→ External to go to the following menu.
Figure 2-76 Table 2-47 The Memory menu
File system is as follows:
Figure 2-77
File system display screen
© 2008 RIGOL Technologies, Inc.
User‟s Guide for DS1000B series
Page 93

RIGOL
2-65
U-disk Selection:
Figure 2-78
U-disk selection
DS1000B series have two USB Host ports on the front and rear panel. When both
ports were inserted USB flash drive, the screen will appear a U-disk selection
interface as Figure 2-78.
Turn the multifunction knob to choose the driver. The front one marked “F:”, the rear
one “G:”.
© 2008 RIGOL Technologies, Inc.
User‟s Guide for DS1000B Series
Page 94

RIGOL
2-66
Menu
Settings
Comments
Explorer
Path
Directory
File
Switch among Path, Directory and
File.
New folder
To create new folder (same as new
files, see table 2-13).
Delete File
Delete selected file.
Load
Recall waveform, setup, recorded
waveform, Pass/Fail file.
Menu
Settings
Comments
Rename
To rename a file (see Table 2-50).
Disk info
Display disk information.
Disk Management
Press Storage→Disk Mana. to go to the following menu.
Figure 2-79 Table 2-48 The Disk Management menu (Page 1/2)
Figure 2-80 Table 2-49 The Disk Management menu (Page 2/2)
© 2008 RIGOL Technologies, Inc.
User‟s Guide for DS1000B series
Page 95

2-67
Menu
Settings
Comments
To move the input focus point
of file name up and down.
To move the focus point to the
next location.
To delete chosen letter.
OK
Rename the file.
Rename
Press Storage→Disk Mana.→Rename to go to the following menu.
Figure 2-81 Table 2-50 The Rename menu
The Rename system screen is as follows:
RIGOL
© 2008 RIGOL Technologies, Inc.
Figure 2-82
Rename the file
User‟s Guide for DS1000B Series
Page 96

RIGOL
2-68
Factory
The oscilloscope has default settings and can be recalled at anytime by user.
Memory location
Specify the memory location to save/recall the waveforms and setups.
Load
Recall saved waveforms, setups and default settings.
Save
Save waveforms and setups.
NOTE:
1. Select Save stores not only the waveforms, but also the current settings of the
oscilloscope
2. To ensure the setups being saved properly, only after the settings are changed
for more than 5 seconds, user could turn off the instrument. The oscilloscope
can store 10 settings permanently and can restore at anytime.
© 2008 RIGOL Technologies, Inc.
User‟s Guide for DS1000B series
Page 97
2-69
Menu
Setting
Comments
I/O setting
Setup I/O configuration.
Sound
(ON)
(OFF)
Turn beeper sound on/off.
Counter
OFF
ON
Turn off Frequency Counter.
Turn on Frequency Counter.
Language
简体中文
繁体中文
English
Japanese
Français
Select languages.
(More languages may be added
in later firmware versions.)
System function setup
button
RIGOL
To Set up the Utility
The following figure shows the menu button for the Utility on the front panel.
Figure 2-83
The Utility setup button
Press the Utility button to show the menu of the settings in the Utility system.
Figure 2-84 Table 2-51 The Utility menu (Page 1/3)
© 2008 RIGOL Technologies, Inc.
User‟s Guide for DS1000B Series
Page 98

RIGOL
2-70
Menu
Settings
Comments
Pass/Fail
Setup Pass/Fail test.
Record
Setup Waveform Recorder.
Print set
Setup printing.
Menu
Settings
Comments
Self-Cal
Execute Self-calibration.
System Info
Show the following information:
Serial number, software version,
installed module.
Preference
Go to preference menu.
Date/Time
Set the real date and time for
system.
Figure 2-85 Table 2-52 The Utility menu (Page 2/3)
Figure 2-86 Table 2-53 The Utility menu (Page 3/3)
Note:
Self-Cal: Oscilloscope will calibrate parameter of vertical system (CH1, CH2, CH3,
CH4 and Ext); horizontal system and trigger system .The oscilloscope can normally
work under different environments.
© 2008 RIGOL Technologies, Inc.
User‟s Guide for DS1000B series
Page 99

2-71
The I/O Setup
Menu
Display
Comments
LAN Set
Set network function, the local area
network interface corresponds with the
LXI standard.
USB
Device
Auto Detect
Computer
PictBridge
Set USB device function, connect USB
interface to the needed device.
GPIB#
<Address>
Set the GPIB address, the address range
is from 0 to 30.
Press Utility→IO Setting to go to the following menu.
Figure 2-87 Table 2-54 The I/O Setup menu
RIGOL
© 2008 RIGOL Technologies, Inc.
User‟s Guide for DS1000B Series
Page 100

RIGOL
2-72
Menu
Display
Comments
LAN Init
Load
Load the LAN initial data
Move up/down the setting focus
Move left/right the setting focus
LAN Setting
Press LAN Set to enter the following interface.
Figure 2-88
LAN Setting interface
The black parts in the setting area are the current items can be set. Turn the
multifunction knob to set the item on the cursor. IP information can be modify by
using the multifunction knob.
Figure 2-89 Table 2-55 LAN Setting menus
© 2008 RIGOL Technologies, Inc.
User‟s Guide for DS1000B series
 Loading...
Loading...