Page 1
Network Guide
Getting Started
Connecting and Setting Up
Using a Printer Server
Monitoring and Configuring the Printer
Special Operations under Windows
Appendix
Read this manual carefully before you use this machine and keep it handy for future reference. For safe and correct use, be sure to read the Safety
Information in the "General Settings Guide" before using the machine.
Page 2

Introduction
This manual contains detailed instructions and notes on the operation and use of this machine. For your
safety and benefit, read this manual carefully before using the machine. Keep this manual in a handy
place for quick reference.
Important
Contents of this manual are subject to change without prior notice. In no event will the company be liable for direct, indirect, special, incidental, or consequential damages as a result of handling or operating the machine.
Software Version Conventions Used in This Manual
• NetWare 3.x means NetWare 3.12 and 3.2.
• NetWare 4.x means NetWare 4.1, 4.11, 4.2 and IntranetWare.
Trademarks
Microsoft
®
, Windows® and Windows NT® are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation in the
United States and/or other countries.
Apple, AppleTalk, EtherTalk, Macintosh, Mac OS and TrueType are trademarks of Apple Computer,
Inc, registered in the United States and other countries.
Netscape and Netscape Navigator are registered trademarks of Netscape Communications Corpora-
tion.
Novell, NetWare, NDS and NDPS are registered trademarks of Novell, Inc.
PostScript® and Acrobat® are registered trademarks of Adobe Systems, Incorporated.
UNIX is a registered trademark in the United States and other countries, licensed exclusively through
X/Open Company Limited.
®
Citrix
and MetaFrame® are registered trademarks of Citrix Systems, Inc.
Bluetooth is a registered trademark of Bluetooth-SIG Inc. worldwide.
UPnP is a trademark of the UPnP Implementers Corporation.
Other product names used herein are for identification purposes only and might be trademarks of their
respective companies. We disclaim any and all rights to those marks.
The proper names of the Windows operating systems are as follows:
®
• The product name of Windows
• The product name of Windows
• The product name of Windows
• The product names of Windows
Microsoft
Microsoft® Windows® 2000 Server
Microsoft
®
Windows® 2000 Professional
®
Windows® 2000 Advanced Server
• The product names of Windows
Microsoft® Windows® XP Home Edition
Microsoft
• The product names of Windows Server™ 2003 are as follows:
Microsoft
Microsoft
Microsoft
• The product names of Windows NT
Microsoft
Microsoft
• RSA Data Security, Inc. MD5 Message-Digest Algorithm
Copyright
®
Windows® XP Professional
®
Windows Server™ 2003 Standard Edition
®
Windows Server™ 2003 Enterprise Edition
®
Windows Server™ 2003 Web Edition
®
Windows NT® Workstation 4.0
®
Windows NT® Server 4.0
©
1991-2, RSA Data Security, Inc. Created 1991. All rights reserved.
95 is Microsoft® Windows 95.
®
98 is Microsoft® Windows 98.
®
Me is Microsoft® Windows Millennium Edition (Windows Me).
®
2000 are as follows:
®
XP are as follows:
®
4.0 are as follows:
License to copy and use this software is granted provided that it is identified as the “RSA Data Security, Inc. MD5 Message-Digest Algorithm” in all material mentioning or referencing this software
or this function.
License is also granted to make and use derivative works provided that such works are identified
as “derived from the RSA Data Security, Inc. MD5 Message-Digest Algorithm” in all material mentioning or referencing the derived work.
RSA Data Security, Inc. makes no representations concerning either the merchantability of this software or the suitability of this software for any particular purpose. It is provided “as is” without express or implied warranty of any kind.
These notices must be retained in any copies of any part of this documentation and/or software.
Page 3

TABLE OF CONTENTS
Manuals for This Machine.....................................................................................1
How to Read This Manual .....................................................................................3
1. Getting Started
Functions Available over a Network ....................................................................5
Printer.........................................................................................................................5
Internet Fax ................................................................................................................ 5
LAN-Fax .....................................................................................................................6
IP-Fax......................................................................................................................... 6
E-mail .........................................................................................................................6
Scan to Folder ............................................................................................................ 6
Network Delivery Scanner..........................................................................................7
Network TWAIN Scanner ........................................................................................... 7
Document Server ....................................................................................................... 7
2. Connecting and Setting Up
Confirming the Connection...................................................................................9
Connecting to the Ethernet Interface ......................................................................... 9
Connecting to the IEEE 1394 Interface .................................................................... 10
Using the IEEE 802.11b (Wireless LAN)..................................................................11
Setting Up the Machine on a Network................................................................14
Printer/LAN-Fax ....................................................................................................... 14
Internet Fax .............................................................................................................. 16
IP-Fax....................................................................................................................... 19
E-mail .......................................................................................................................21
Scan to Folder ..........................................................................................................24
Network Delivery Scanner........................................................................................26
Network TWAIN Scanner .........................................................................................28
Document Server ..................................................................................................... 30
Network Configuration..............................................................................................32
Interface Settings ..................................................................................................... 37
File Transfer .............................................................................................................42
LDAP Server Settings..........................................................................................50
Before using this function.........................................................................................50
Program/Change/Delete LDAP Server ....................................................................50
Programming the LDAP Server................................................................................51
i
Page 4

3. Using a Printer Server
Preparing Printer Server .....................................................................................57
Printing notification via SmartDeviceMonitor for Client ............................................ 57
Using NetWare ..................................................................................................... 59
Setting Up as a Print Server (NetWare 3.x) ............................................................. 59
Setting Up as a Print Server (NetWare 4.x, 5/5.1, 6/6.5) .........................................60
Using Pure IP in the NetWare 5/5.1 or 6/6.5 Environment....................................... 62
Setting Up as a Remote Printer (NetWare 3.x) ........................................................ 64
Setting Up as a Remote Printer (NetWare 4.x, 5/5.1, 6/6.5) ....................................66
4. Monitoring and Configuring the Printer
Using Web Image Monitor ................................................................................... 69
Displaying Top Page ................................................................................................ 70
When user authentication is set ............................................................................... 71
About Menu and Mode ............................................................................................. 72
Access in the Administrator Mode............................................................................ 74
Displaying Web Image Monitor Help ........................................................................ 74
Using SmartDeviceMonitor for Admin ............................................................... 76
Installing SmartDeviceMonitor for Admin .................................................................77
Changing the Network Interface Board Configuration..............................................77
Locking the Menus on the Machine's Control Panel ................................................ 78
Changing the Paper Type ........................................................................................ 78
Managing User Information ...................................................................................... 79
Configuring the Energy Saver Mode ........................................................................ 81
Setting a Password .................................................................................................. 82
Checking the Machine Status .................................................................................. 83
Changing Names and Comments ............................................................................ 83
Load Fax Journal .....................................................................................................84
Viewing and Deleting Spool Print Jobs ....................................................................85
Managing Address Information ................................................................................ 85
Using SmartDeviceMonitor for Client ................................................................ 86
Monitoring Printers ...................................................................................................86
Checking the Machine Status .................................................................................. 86
When Using IPP with SmartDeviceMonitor for Client .............................................. 87
ii
Page 5

Remote Maintenance by telnet ...........................................................................88
Using telnet .............................................................................................................. 88
access ......................................................................................................................89
appletalk ...................................................................................................................89
autonet .....................................................................................................................90
btconfig.....................................................................................................................90
devicename ..............................................................................................................90
dhcp .........................................................................................................................91
diprint .......................................................................................................................92
dns ...........................................................................................................................92
domainname ............................................................................................................ 93
help ..........................................................................................................................94
hostname ................................................................................................................. 94
ifconfig ...................................................................................................................... 95
info ...........................................................................................................................96
ipp ............................................................................................................................96
netware .................................................................................................................... 96
passwd .....................................................................................................................97
prnlog .......................................................................................................................97
rendezvous............................................................................................................... 98
route .........................................................................................................................99
set ..........................................................................................................................100
show....................................................................................................................... 101
slp........................................................................................................................... 101
smb ........................................................................................................................ 102
snmp ...................................................................................................................... 102
sntp ........................................................................................................................ 105
spoolsw .................................................................................................................. 105
sprint ......................................................................................................................106
status...................................................................................................................... 106
syslog .....................................................................................................................106
upnp .......................................................................................................................106
web......................................................................................................................... 107
wiconfig .................................................................................................................. 107
wins ........................................................................................................................ 110
SNMP................................................................................................................... 111
Getting Printer Information over the Network................................................. 112
Current Printer Status ............................................................................................ 112
Printer configuration ............................................................................................... 119
Understanding the Displayed Information ......................................................120
Print Job Information .............................................................................................. 120
Print Log Information..............................................................................................121
Configuring the Network Interface Board ...............................................................122
Message List ......................................................................................................127
System Log Information .........................................................................................127
iii
Page 6

5. Special Operations under Windows
Printing Files Directly from Windows ..............................................................133
Setup...................................................................................................................... 133
Using a Host Name Instead of an IP Address........................................................ 133
Printing Commands................................................................................................134
6. Appendix
When Using Windows Terminal Service/MetaFrame...................................... 137
Operating Environment .......................................................................................... 137
Supported Printer Drivers....................................................................................... 137
Limitations .............................................................................................................. 137
Using DHCP........................................................................................................139
Using AutoNet ........................................................................................................ 140
Precautions ........................................................................................................141
Connecting a Dial-Up Router to a Network ............................................................ 141
NetWare Printing....................................................................................................143
When the optional IEEE 802.11b interface unit Is Installed ...................................144
Information about Installed Applications ........................................................145
Samba(Ver 2.2.2-1.1).............................................................................................145
®
BSAFE™ .....................................................................................................145
RSA
Specifications.....................................................................................................146
INDEX....................................................................................................... 148
iv
Page 7
Manuals for This Machine
The following manuals describe the operational procedures of this machine. For
particular functions, see the relevant parts of the manual.
Note
❒ Manuals provided are specific to machine type.
❒ Adobe Acrobat Reader is necessary to view the manuals as a PDF file.
❒ Two CD-ROMs are provided:
• CD-ROM 1 “Operating Instructions for Printer/Scanner”
CD-ROM 2 “Scanner Driver & Document Management Utilities”
❖ General Settings Guide
Provides an overview of the machine and describes System Settings (such as
Tray Paper Settings), Document Server functions, and troubleshooting.
Refer to this manual for Address Book procedures such as registering fax
numbers, e-mail addresses, and user codes.
❖ Security Reference
This manual is for administrators of this machine. It describes security functions that the administrators can use to protect data from being tampered, or
prevent the machine from unauthorized use. Also refer to this manual for the
procedures for registering administrators, as well as setting user and administrator authentication.
❖ Network Guide (this manual)
Provides information about configuring and operating the printer in a network environment or using software. This manual covers all models, and
therefore contains functions and settings that may not be available for your
model.
Images, illustrations, functions, and supported operating systems may differ
from those of your model.
❖ Copy Reference
Describes operations, functions, and troubleshooting for the machine’s copier
function.
❖ Facsimile Reference <Basic Features>
Describes operations, functions, and troubleshooting for the machine's facsimile function.
❖ Facsimile Reference <Advanced Features>
Describes advanced facsimile functions such as line settings and procedures
for registering IDs.
❖ Printer Reference
Describes system settings, operations, functions, and troubleshooting for the
machine’s printer function.
1
Page 8

❖ Scanner Reference (PDF file - CD-ROM1)
Describes operations, functions, and troubleshooting for the machine’s scanner function.
❖ Manuals for DeskTopBinder
DeskTopBinder is a utility included on the CD-ROM labeled “Scanner Driver
& Document Management Utilities”.
• DeskTopBinder Lite Setup Guide (PDF file - CD-ROM2)
Describes installation of, and the operating environment for DeskTopBinder Lite in detail. This guide can be displayed from the [Setup] dialog
box when DeskTopBinder Lite is installed.
• DeskTopBinder Introduction Guide (PDF file - CD-ROM2)
Describes operations of DeskTopBinder Lite and provides an overview of
its functions. This guide is added to the [Start] menu when DeskTopBinder
Lite is installed.
• Auto Document Link Guide (PDF file - CD-ROM2)
Describes operations and functions of Auto Document Link installed with
DeskTopBinder Lite. This guide is added to the [Start] menu when DeskTopBinder Lite is installed.
❖ Other manuals
• PS3 Supplement (PDF file - CD-ROM1)
• UNIX Supplement (available from an authorized dealer, or as a PDF file on
our Web site)
2
Page 9

How to Read This Manual
Symbols
In this manual, the following symbols are used:
* The statements above are notes for your safety.
Important
If this instruction is not followed, paper might be misfed, originals might be
damaged, or data might be lost. Be sure to read this.
Preparation
This symbol indicates prior knowledge or preparation is required before operation.
Note
This symbol indicates precautions for operation, or actions to take after mal-operation.
Limitation
This symbol indicates numerical limits, functions that cannot be used together,
or conditions in which a particular function cannot be used.
Reference
This symbol indicates a reference.
[]
Keys that appear on the machine's display panel.
Keys and buttons that appear on the computer's display.
{}
Keys built into the machine's control panel.
Keys on the computer's keyboard.
3
Page 10

4
Page 11

1. Getting Started
Functions Available over a Network
This machine provides printer, LANFax, Internet Fax, and scanner functions over a network. Using the Document Server function, you can
combine copied documents and print
jobs into a single document. Not only
can you print this document straight
away, but you can also store it so it can
be printed again whenever needed.
Printer
The network interface board is compatible with NetWare
TCP/IP), Windows NT 4.0 (TCP/IP,
NetBEUI
*2
, IPP
(TCP/IP, NetBEUI
dows XP, Windows Server 2003
(TCP/IP, IPP
*3
), Windows 95/98/Me
(TCP/IP, NetBEUI
(TCP/IP), and Mac OS (AppleTalk)
protocols. This allows you to operate
the machine in a network that uses different protocols and operating systems.
*1
If the optional 802.11b interface unit is
installed, you can use only infrastructure mode.
*2
For NetBEUI, use the SmartDeviceMonitor for Client port.
*3
IPP (Internet Printing Protocol) is a
protocol for printing via the Internet.
*1
(IPX/SPX,
*3
), Windows 2000
*2
*2
, IPP
, IPP
*3
), Win-
*3
), UNIX
Internet Fax
This machine converts scanned document images to e-mail format and
transmits the data over the Internet.
Specify the e-mail address instead of
the fax number, and then send the
document.
E-mail can be received on a fax machine that supports Internet Fax, or
on a computer that can receive normal e-mail.
You can also receive e-mails or Internet faxes, and then print or forward
them.
Note
❒ To use this function, optional fax
unit is required.
Reference
For details about what settings to
make, see p.14 “Setting Up the Machine on a Network”.
For details about using this function, see “Using Internet Fax Functions”, Facsimile Reference <Basic
Features>.
Reference
For details about what settings to
make, see p.14 “Setting Up the Machine on a Network”.
For details about using this function, see p.57 “Preparing Printer
Server”, or PostScript 3 Supplement.
5
Page 12

Getting Started
1
LAN-Fax
You can fax documents over phone
lines from any computer connected to
the machine via Ethernet, IEEE 1394
(IP over 1394), or wireless LAN.
To send a fax, print from the Windows application you are working
with, select LAN-Fax as the printer,
and then specify the destination.
You can also check the sent image data.
Note
❒ To use this function, optional fax
unit is required.
Reference
For details about what settings to
make, see p.14 “Setting Up the Machine on a Network”.
For details about using this function, see "Sending Fax Documents
from Computers", Facsimile Refer-
ence <Advanced Features>.
Reference
For details about what settings to
make, see p.14 “Setting Up the Machine on a Network”.
For details about using this function, see “Internet Fax Functions
(by Specifying an IP Address)”,
Facsimile Reference <Basic Features>.
Scan file attached to an e-mail can be
sent using the e-mail system through
a LAN or the Internet.
Reference
For details about what settings to
make, see p.14 “Setting Up the Machine on a Network”.
For details about using this function, see "Sending Scan Files by Email", Scanner Reference.
Scan to Folder
IP-Fax
You can send and receive fax documents through fax machines connected directly to the same network using
the TCP/IP protocol. Specify the IP
address or host name instead of the
fax number and then send the document. If Gatekeeper is used, enter the
alias telephone number to send the
document.
No e-mail server is required, and
transmission between IP-fax machine
is faster than between G3 fax machine.
You can also check the sent image data.
Note
❒ To use this function, optional fax
unit is required.
6
You can send scan file directly to
shared folders on computers running
Windows or to FTP servers.
Reference
For details about what settings to
make, see p.14 “Setting Up the Machine on a Network”.
For details about using this function, see “Sending Scan Files by
Scan to Folder”, Scanner Reference.
Page 13

Functions Available over a Network
Network Delivery Scanner
You can use the machine as a delivery
scanner for the ScanRouter delivery
software.
Scan file or document received by fax
can be stored in the delivery server, or
delivered via the network to specified
folders on client computers.
Reference
For details about what settings to
make, see p.14 “Setting Up the Machine on a Network”.
For details about using this function, see "Delivering Scan Files",
Scanner Reference.
Network TWAIN Scanner
You can use the scanning function of
this machine from a computer connected via a network (Ethernet, IEEE
1394(IP over 1394), or IEEE 802.11b
(wireless LAN)).
You can scan documents the same
way you would if you were using a
scanner connected directly to your
computer.
Reference
For details about what settings to
make, see p.14 “Setting Up the Machine on a Network”.
Document Server
You can store copy, fax, printer, and
scanner documents on the hard disk.
Using DeskTopBinder Lite or a Web
browser, you can browse, print, delete, or copy these documents over a
network.
Reference
For details about what settings to
make, see p.14 “Setting Up the Machine on a Network”.
For more information about Document Server operation from the
printer, see "Using the Document
Server", Printer Reference.
For more information about Document Server operation from the
facsimile, see "Using the Document Server", Facsimile Reference
<Advanced Features>.
For more information about Document Server operation from the
scanner, see "Using the Document
Server", Scanner Reference.
For all information about Document Server operation, see "Using
the Document Server", General Set-
tings Guide.
For more information about DeskTopBinder Lite, see the manuals
for DeskTopBinder Lite.
1
For details about using this function, see "Using the Network
TWAIN Scanner Function", Scan-
ner Reference.
7
Page 14

1
Getting Started
8
Page 15
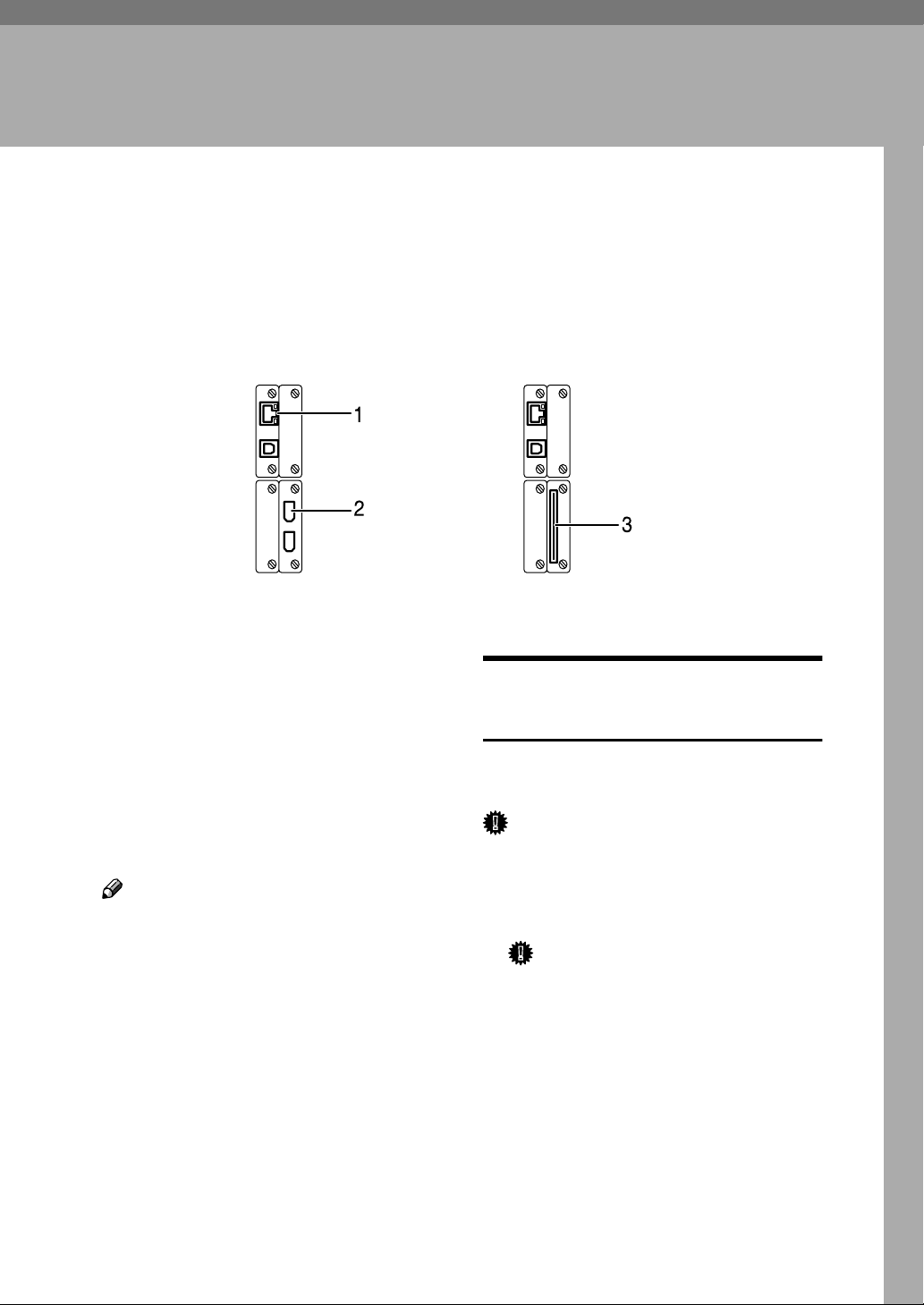
2. Connecting and Setting Up
Confirming the Connection
When the IEEE 1394
interface board (optional)
is installed.
1. 10BASE-T/100BASE-TX port
Port for connecting the 10BASE-T or
100BASE-TX cable
2. IEEE 1394 ports (optional)
Ports for connecting the IEEE 1394 interface cable
When the
wireless LAN board (optional)
is installed.
ZZZ018S
Connecting to the Ethernet Interface
The network interface board supports
10BASE-T or 100BASE-TX connections.
3. Wireless LAN port (optional)
Port for using the wireless LAN
Note
❒ The optional IEEE 1394 interface board
and the IEEE 802.11b interface unit
cannot be installed at the same time.
❒ The position of the port differ depend-
ing on the machine type.
Important
❒ Before making the connection, touch
the metallic part to ground yourself.
Turn off the main power switch.
AAAA
Important
❒ Make sure the main power is
off. See “Turning On the Power”, General Settings Guide.
9
Page 16
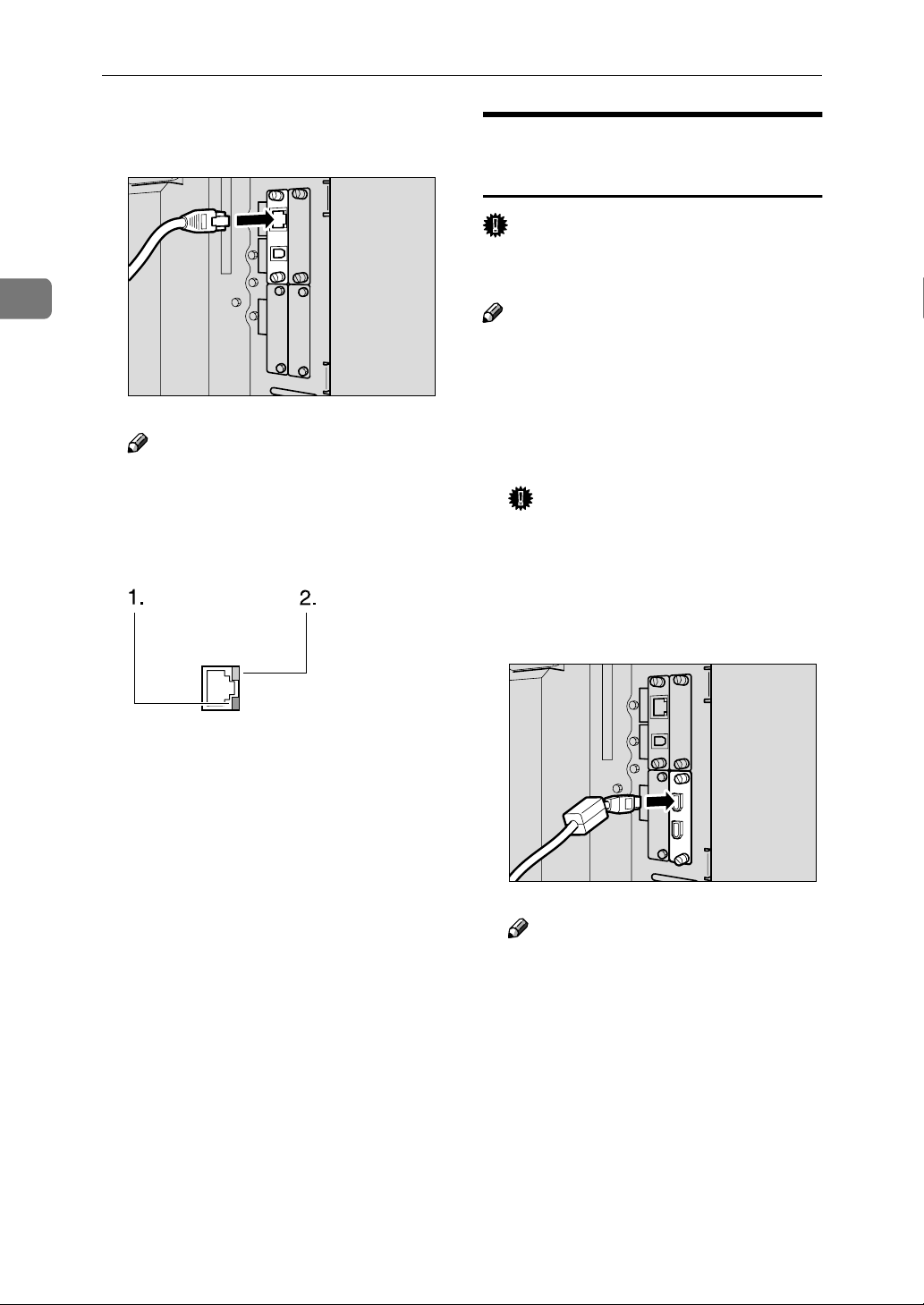
2
Connecting and Setting Up
Connect the Ethernet interface cable
B
to the 10BASE-T/100BASE-TX port.
Note
❒ The position of the port differ
depending on the machine type.
Turn on the main power switch.
C
ZZZ019S
Connecting to the IEEE 1394 Interface
Important
❒ Before making the connection, touch
the metallic part to ground yourself.
Note
❒ Use the interface cable supplied with
the optional IEEE 1394 interface board.
❒ Make sure the interface cable is not
looped.
Turn off the main power switch.
AAAA
Important
❒ Make sure the main power is
off. See “Turning On the Power”, General Settings Guide.
ZZZ023S
1. Indicator (green)
Remains green when the machine is
properly connected to the network.
2. Indicator (yellow)
Turns yellow when 100 BASE-TX is
operating. Turns off when 10 BASE-T
is operating.
Connect the IEEE 1394 interface
BBBB
cable to the IEEE 1394 ports.
Note
❒ Two interface ports are available
for connecting the IEEE 1394 interface cable. Either is suitable.
❒ If you have an interface cable
with a ferrite core, connect the
end nearest to the ferrite core to
the machine.
❒ The position of the port differ
depending on the machine type.
ZZZ020S
10
Turn on the main power switch.
CCCC
Page 17
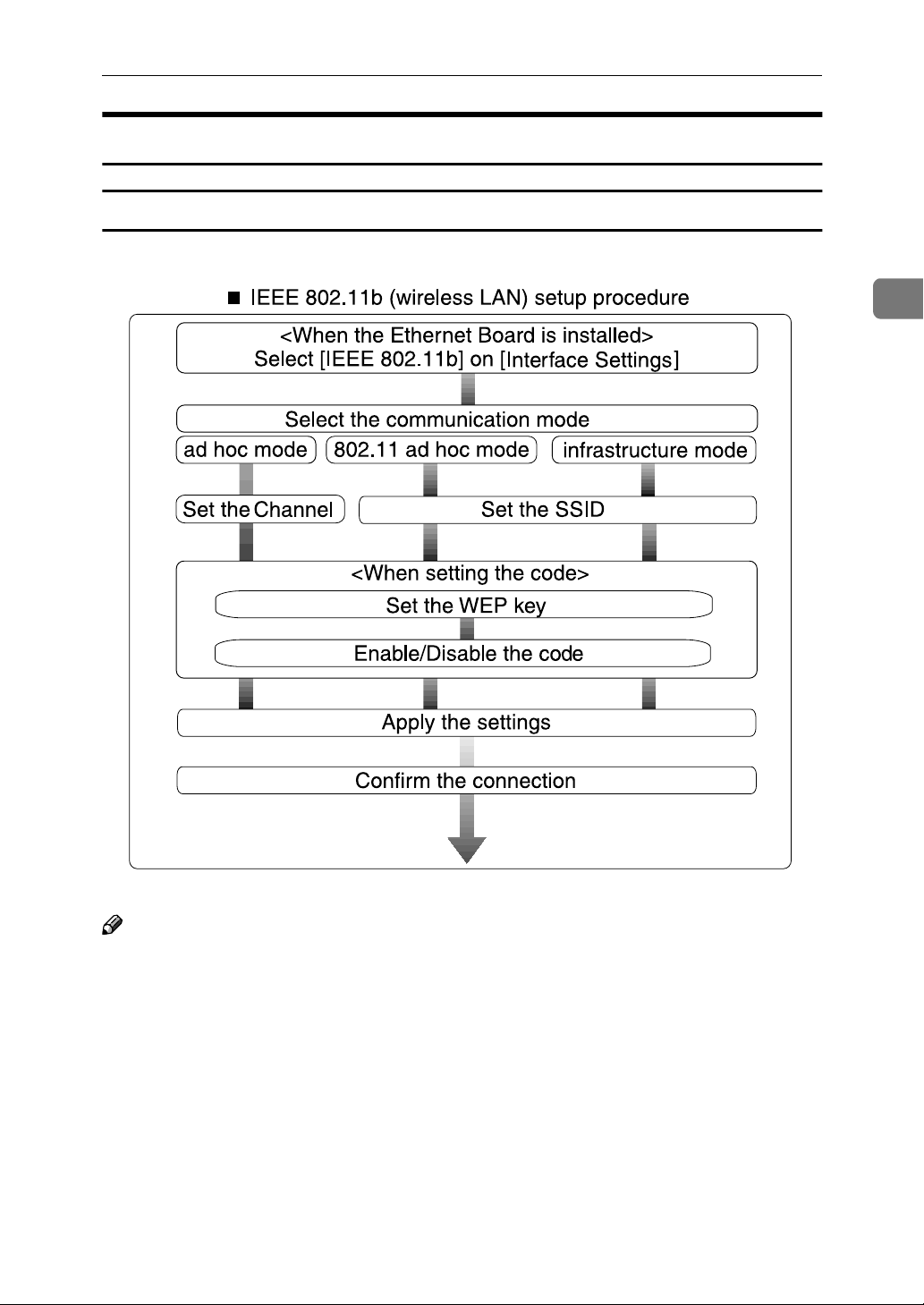
Using the IEEE 802.11b (Wireless LAN)
Setting IEEE 802.11b (Wireless LAN)
Confirming the Connection
2
Note
❒ Select [802.11 Ad hoc] mode when connecting Windows XP as a wireless LAN
client using Windows XP standard driver or utilities, or when not using the
infrastructure mode.
11
Page 18
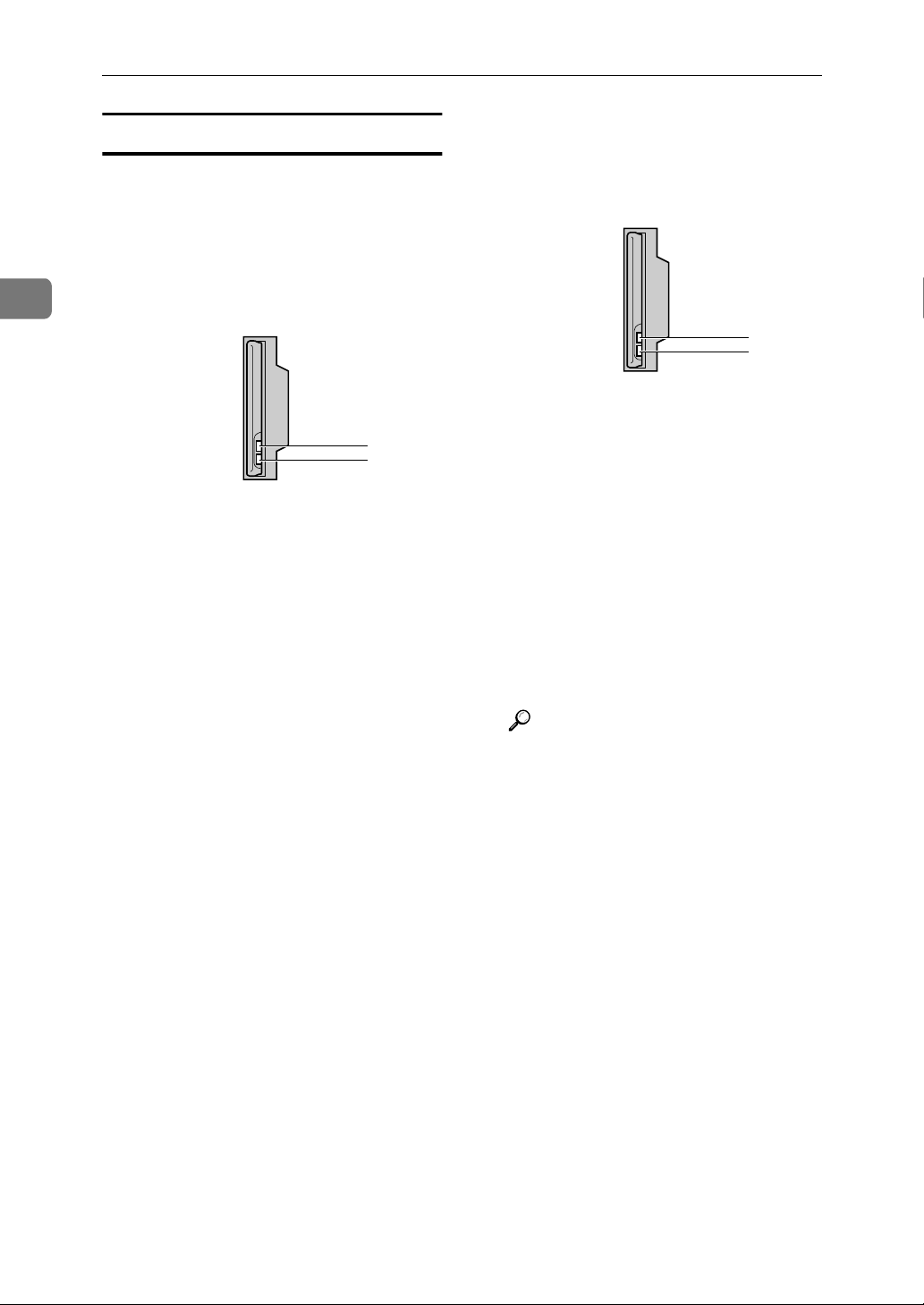
Connecting and Setting Up
2
Confirming the Connection
Make sure the LED of the IEEE
AAAA
802.11b interface unit is lit.
❖ When using in infrastructure mode
1
2
ZZZ024S
1. If [LAN Type] on the [Interface Set-
tings]/[Network] screen is not set to
[IEEE 802.11b], it does not light, even
if the main power is on.
❖ When using in ad hoc mode/802.11
ad hoc mode
1
2
ZZZ024S
1. If the IEEE 802.11b interface unit
is working, it is lit in orange.
2. If it is connected properly to the
network, the LED is green when in
ad hoc mode or 802.11 ad hoc mode.
If the LED is blinking, the machine
is searching for devices. The LED
will light after a few seconds.
2. If it is connected properly to the
network, the LED is green when in
infrastructure mode. If the LED is
blinking, the machine is searching
for devices.
Print the configuration page to
BBBB
verify settings.
Reference
For more information about
printing a configuration page,
see Printer Reference.
12
Page 19

Checking the machine's radio wave status
When using in infrastructure mode,
you can check the machine's radio
wave status using the control panel.
Confirming the Connection
Note
❒ To check the radio wave status,
press [IEEE 802.11b] under [LAN
Type] on the [Network] screen.
Press the {User Tools/Counter/Inquiry}
AAAA
key.
Press [System Settings].
BBBB
Press [Interface Settings].
CCCC
Press [IEEE 802.11b].
DDDD
Press [Wireless LAN Signal].
EEEE
The machine's radio wave status
appears.
After checking radio wave status,
FFFF
press [Exit].
Press the {User Tools/Counter/Inquiry}
GGGG
key to return to the User Tools /
Counter / Inquiry menu.
2
13
Page 20

2
Connecting and Setting Up
Setting Up the Machine on a Network
This section describes the network settings you can change with User Tools (System Settings). Make settings according to functions you want to use and the interface to be connected.
Important
❒ These settings should be made by the systems administrator, or after consult-
ing with the systems administrator.
Reference
For details about settings, see p.37 “Interface Settings”
❖ Viewing the Information Displayed in the List
$ These items must be set to use the function. Be sure to set them before attempting to use the corresponding function.
❍ These items must be set if required.
Printer/LAN-Fax
Interface Settings
Ethernet Interface Settings/
Network
See p.37 “Network”.
IP Address $
Gateway Address ❍
DNS Configuration ❍
DDNS Configuration ❍
Domain Name ❍
WINS Configuration ❍
NW Frame Type ❍
LAN Type
Ethernet Speed ❍
Effective Protocol
SMB Computer Name ❍
SMB Work Group ❍
Permit SNMP V3 Communication
Permit SSL / TLS Communication
Host Name ❍
Machine Name ❍
*2
*3
$
$
❍
❍
14
Page 21
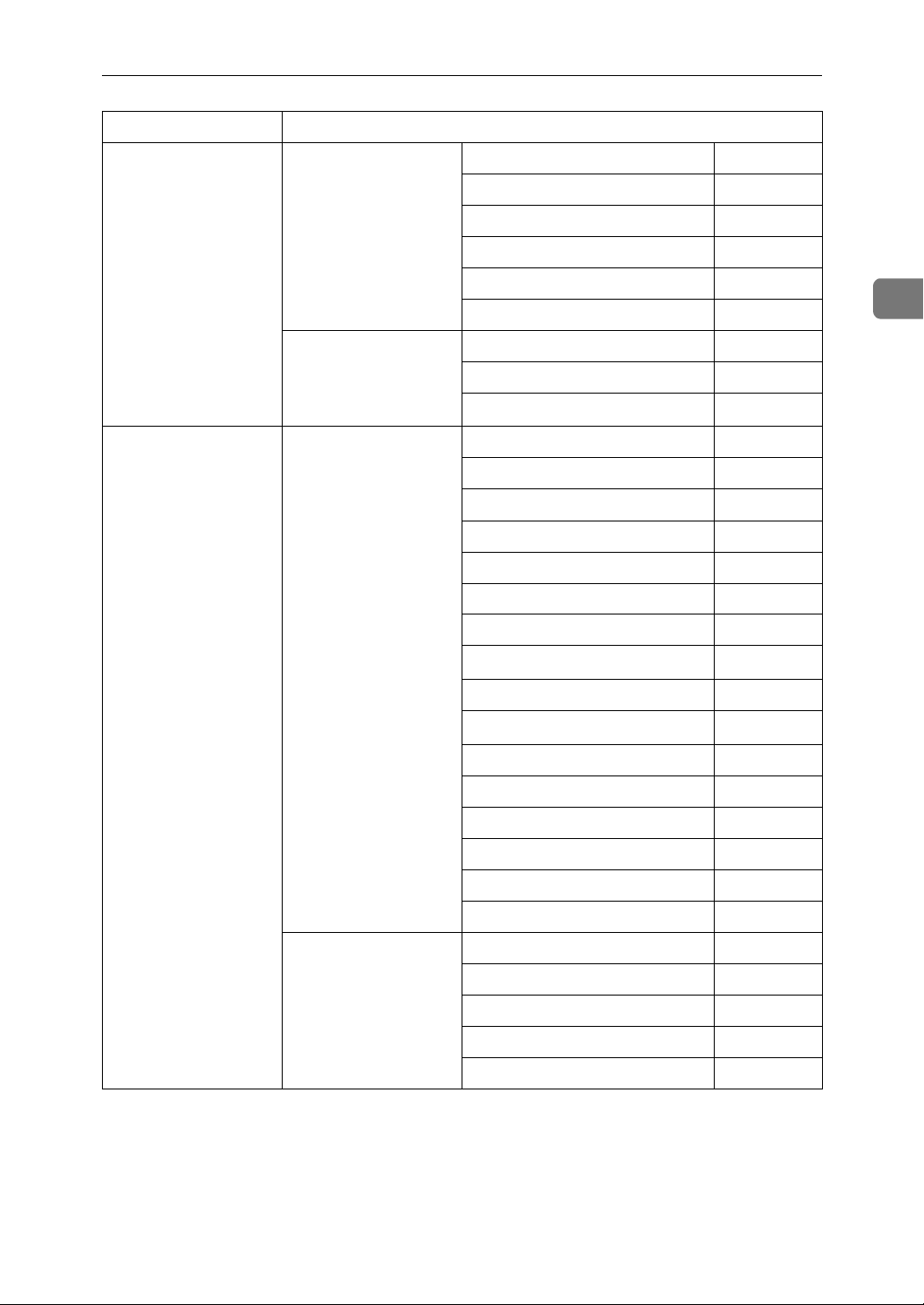
Interface Settings
Setting Up the Machine on a Network
IEEE 1394
(IP over 1394)
IEEE 802.11b
(wireless LAN)
Interface Settings/
IEEE 1394
*1
See p.39 “IEEE 1394”.
Interface Settings/
Network
See p.37 “Network”.
Interface Settings/
Network
See p.37 “Network”.
IP Address $
IP over 1394 $
WINS Configuration ❍
DDNS Configuration ❍
Host Name ❍
Domain Name ❍
Gateway Address ❍
DNS Configuration ❍
Effective Protocol
*3
$
IP Address $
Gateway Address ❍
DNS Configuration ❍
DDNS Configuration ❍
Domain Name ❍
WINS Configuration ❍
NW Frame Type ❍
LAN Type
*2
$
2
Ethernet Speed ❍
Effective Protocol
*3
SMB Computer Name ❍
SMB Work Group ❍
Permit SNMP V3 Communication
Permit SSL / TLS Communication
Host Name ❍
Machine Name ❍
Interface Settings/
IEEE 802.11b
*2
See p.41 “IEEE
802.11b”.
Communication Mode $
SSID Setting ❍
Channel ❍
WEP (Encryption) Setting ❍
Transmission Speed ❍
*1
Appears when the optional IEEE 1394 interface board is installed.
*2
Appears when the optional IEEE 802.11b interface unit is installed.
If Ethernet and IEEE 802.11b (wireless LAN) are both connected to the machine, the
selected interface has priority.
*3
Check [
Effective
] is selected for TCP/IP.
$
❍
❍
15
Page 22
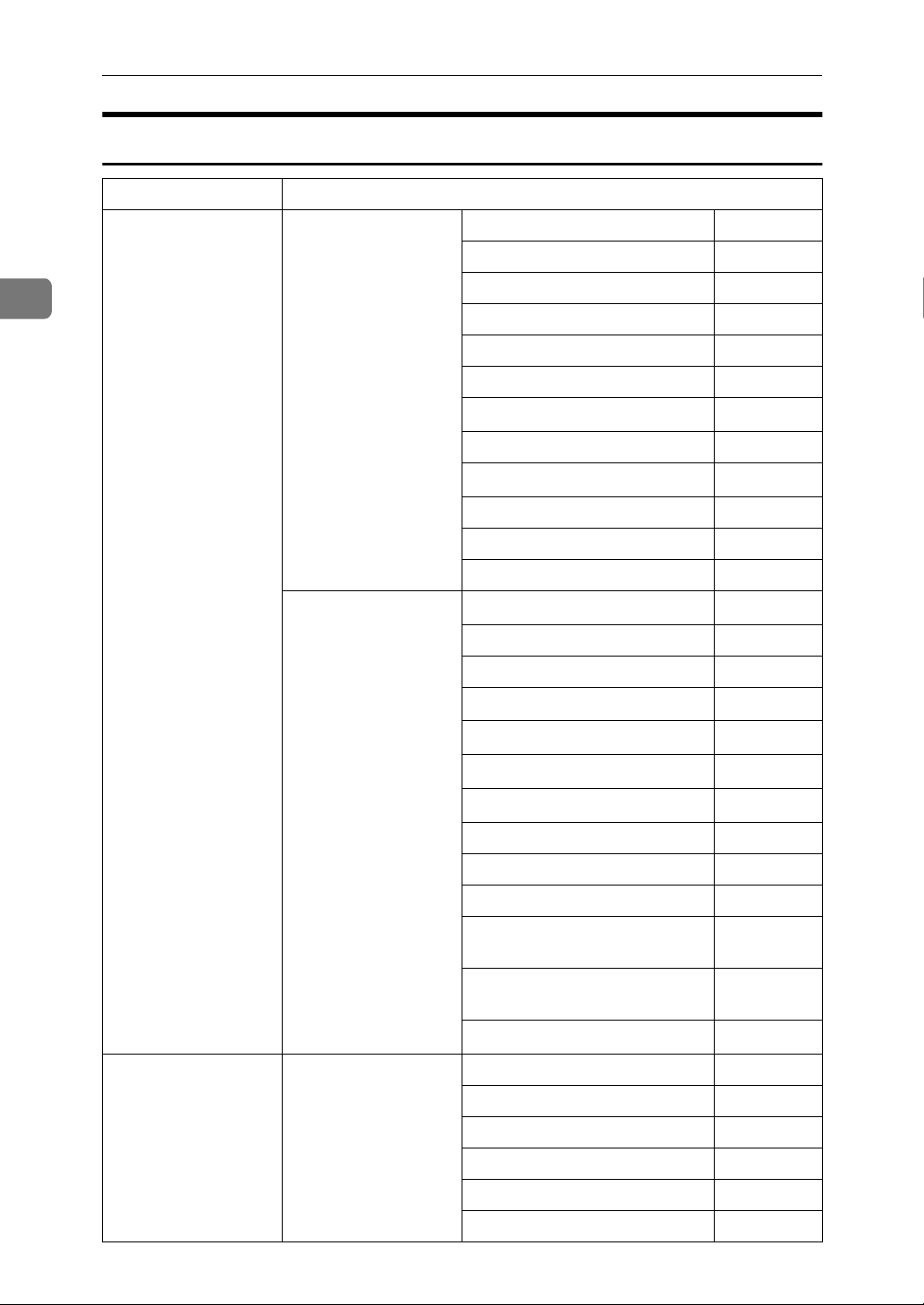
Connecting and Setting Up
Internet Fax
Interface Settings
2
Ethernet Interface Settings/
Network
See p.37 “Network”.
File Transfer
See p.42 “File Transfer”.
IP Address $
Gateway Address $
DNS Configuration ❍
DDNS Configuration ❍
Domain Name ❍
WINS Configuration ❍
LAN Type
*2
$
Ethernet Speed ❍
Effective Protocol
*5
Permit SNMP V3 Communication
Permit SSL / TLS Communication
$
❍
❍
Host Name ❍
SMTP Server
*3
$
SMTP Authentication ❍
POP before SMTP ❍
Reception Protocol
POP3 Setting
*4
*6
Administrator's E-mail Address
E-mail Communication Port
*4 *7
*8
$
❍
❍
$
16
IEEE 1394
(IP over 1394)
Interface Settings/
IEEE 1394
*1
See p.39 “IEEE 1394”.
E-mail Reception Interval ❍
Max. Reception E-mail Size ❍
E-mail Storage in Server ❍
Program / Change / Delete E-
❍
mail Message
Program / Change / Delete
❍
Subject
E-mail Account
*3 *4
$
IP Address $
IP over 1394 $
DDNS Configuration ❍
WINS Configuration ❍
Host Name ❍
Domain Name ❍
Page 23
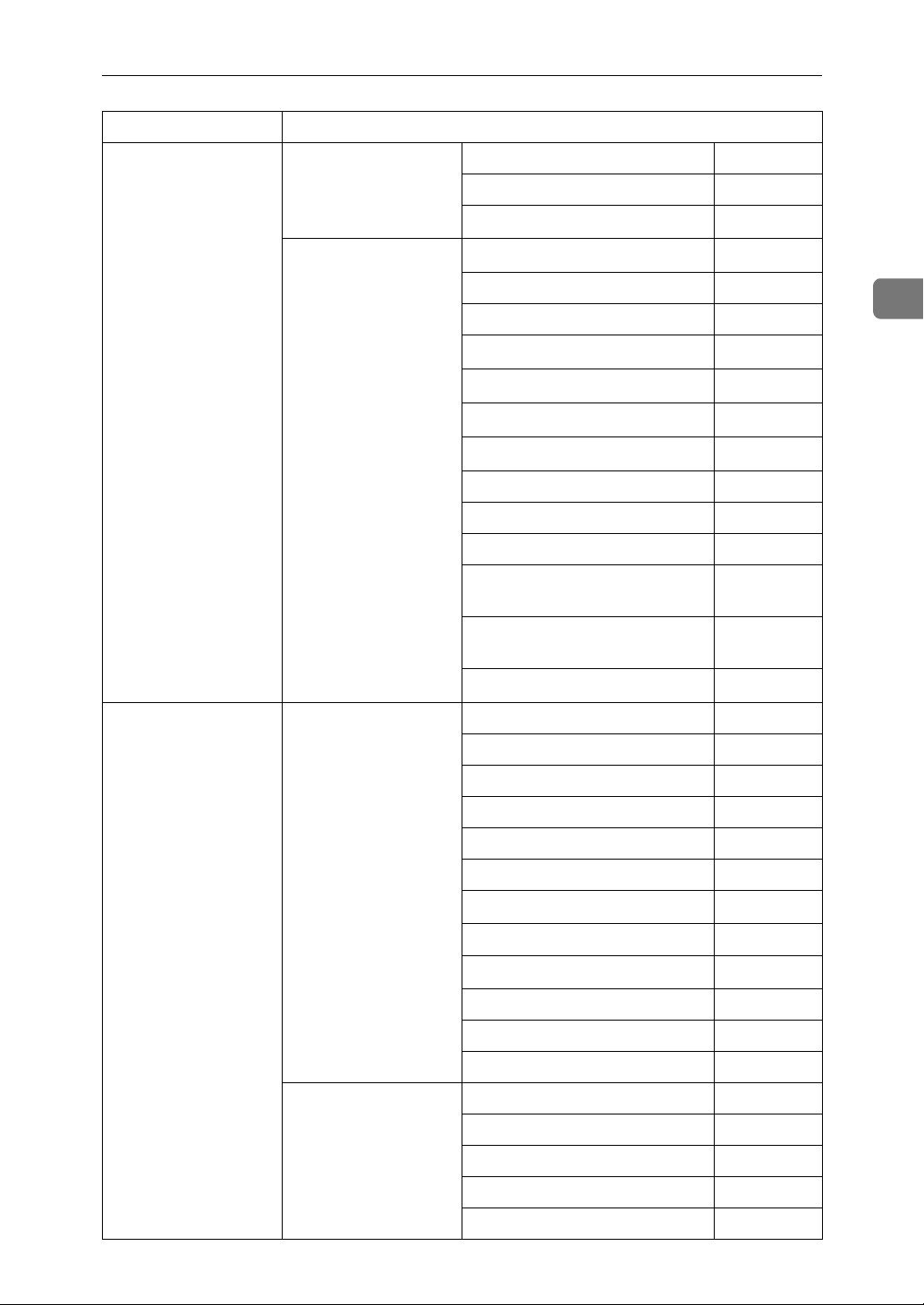
Interface Settings
Setting Up the Machine on a Network
IEEE 1394
(IP over 1394)
Interface Settings/
Network
See p.37 “Network”.
File Transfer
See p.42 “File Transfer”.
Gateway Address $
DNS Configuration ❍
Effective Protocol
SMTP Server
*3
*5
$
$
SMTP Authentication ❍
POP before SMTP ❍
Reception Protocol
POP3 Setting
*4
*6
Administrator's E-mail Address
E-mail Communication Port
*4 *7
*8
$
❍
❍
$
E-mail Reception Interval ❍
Max. Reception E-mail Size ❍
E-mail Storage in Server ❍
Program / Change / Delete E-
❍
mail Message
Program / Change / Delete
❍
Subject
E-mail Account
*3 *4
$
2
IEEE 802.11b
(wireless LAN)
Interface Settings/
Network
See p.37 “Network”.
Interface Settings/
IEEE
802.11bDocument
*2
Server
See p.41 “IEEE
802.11b”.
IP Address $
Gateway Address $
DNS Configuration ❍
WINS Configuration ❍
DDNS Configuration ❍
Domain Name ❍
LAN Type
*2
$
Ethernet Speed ❍
Effective Protocol
*5
Permit SNMP V3 Communication
Permit SSL / TLS Communication
$
❍
❍
Host Name ❍
Communication Mode $
SSID Setting ❍
Channel ❍
WEP (Encryption) Setting ❍
Transmission Speed ❍
17
Page 24
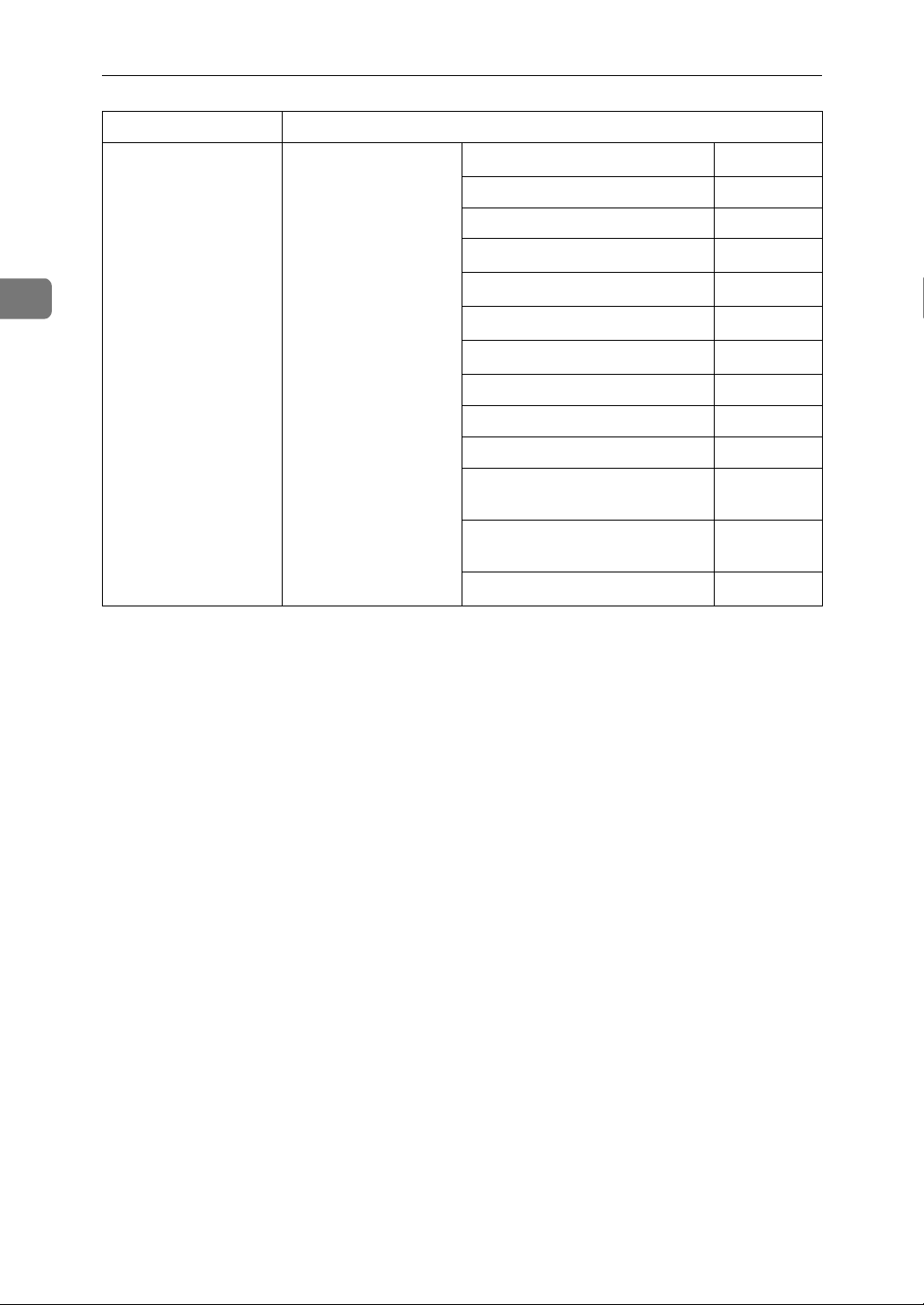
2
Connecting and Setting Up
Interface Settings
IEEE 802.11b
(wireless LAN)
File Transfer
See p.42 “File Transfer”.
SMTP Server
*3
$
SMTP Authentication ❍
POP before SMTP ❍
Reception Protocol
POP3 Setting
*4
*6
Administrator's E-mail Address
E-mail Communication Port
*4 *7
*8
$
❍
❍
$
E-mail Reception Interval ❍
Max. Reception E-mail Size ❍
E-mail Storage in Server ❍
Program / Change / Delete Email Message
Program / Change / Delete
Subject
E-mail Account
*1
Appears when the optional IEEE 1394 interface board is installed.
*2
Appears when the optional IEEE 802.11b interface unit is installed.
*3 *4
If Ethernet and 802.11b (wireless LAN) are both connected to the machine, the selected interface has priority.
*3
Minimum settings required to use transmission.
*4
Minimum settings required to use reception.
*5
Check[Effective] is selected for TCP/IP.
*6
If you select [On] for [POP before SMTP], select this function also.
*7
If you select [On] for [
*8
If you select [On] for [
POP before SMTP
SMTP Authentication
], check the port number for [
], select this function also.
POP3
].
❍
❍
$
18
Page 25
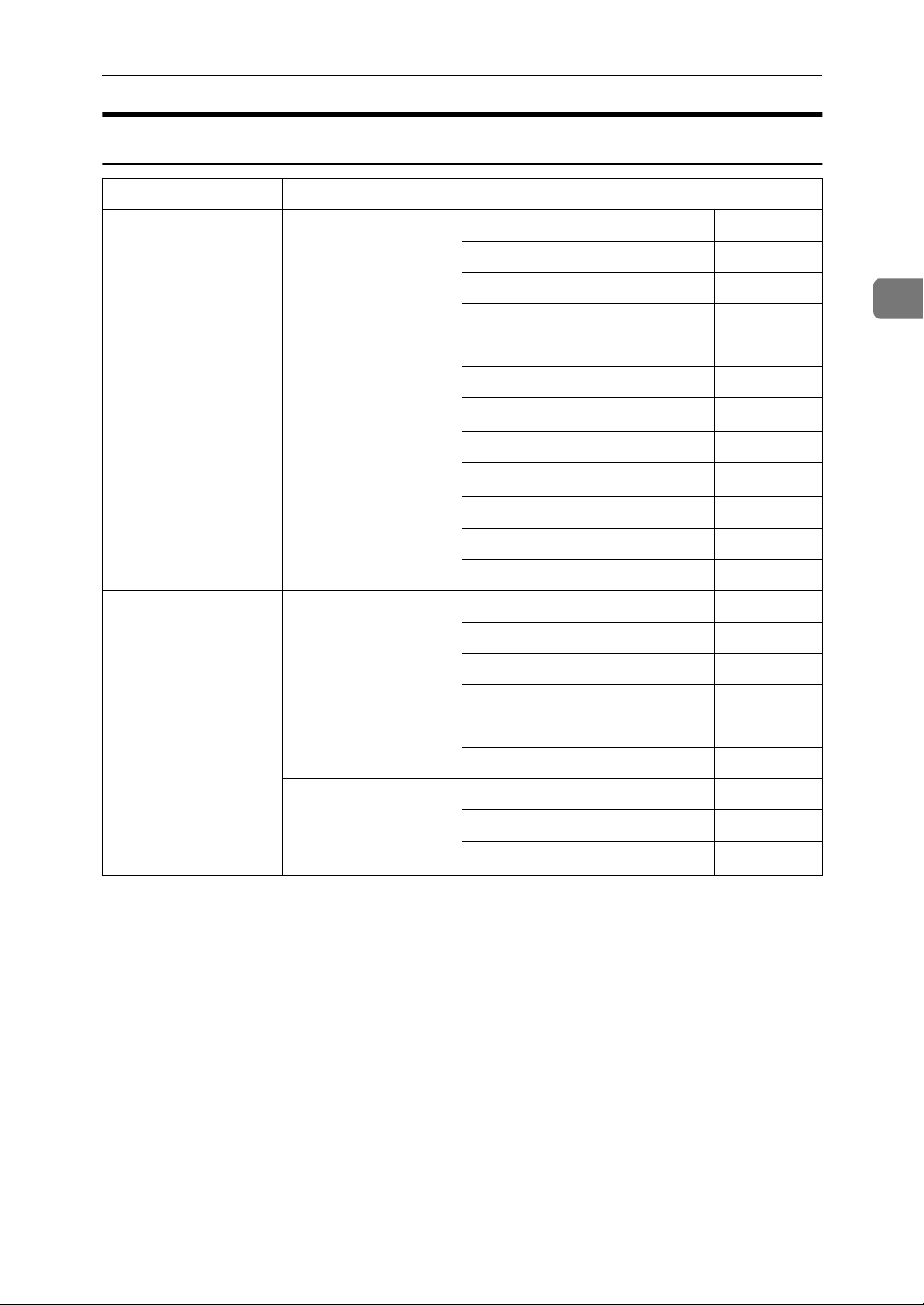
IP-Fax
Interface Settings
Setting Up the Machine on a Network
Ethernet Interface Settings/
Network
See p.37 “Network”.
IEEE 1394
(IP over 1394)
Interface Settings/
IEEE 1394
See p.39 “IEEE 1394”.
*1
IP Address $
Gateway Address $
DNS Configuration $
DDNS Configuration ❍
Domain Name ❍
WINS Configuration ❍
LAN Type
Ethernet Speed ❍
Effective Protocol
Permit SNMP V3 Communication
Permit SSL / TLS Communication
Host Name ❍
IP Address $
IP over 1394 $
DDNS Configuration $
WINS Configuration ❍
Host Name ❍
*2
*3
$
$
❍
❍
2
Interface Settings/
Network
See p.37 “Network”.
Domain Name ❍
Gateway Address $
DNS Configuration ❍
Effective Protocol
*3
$
19
Page 26
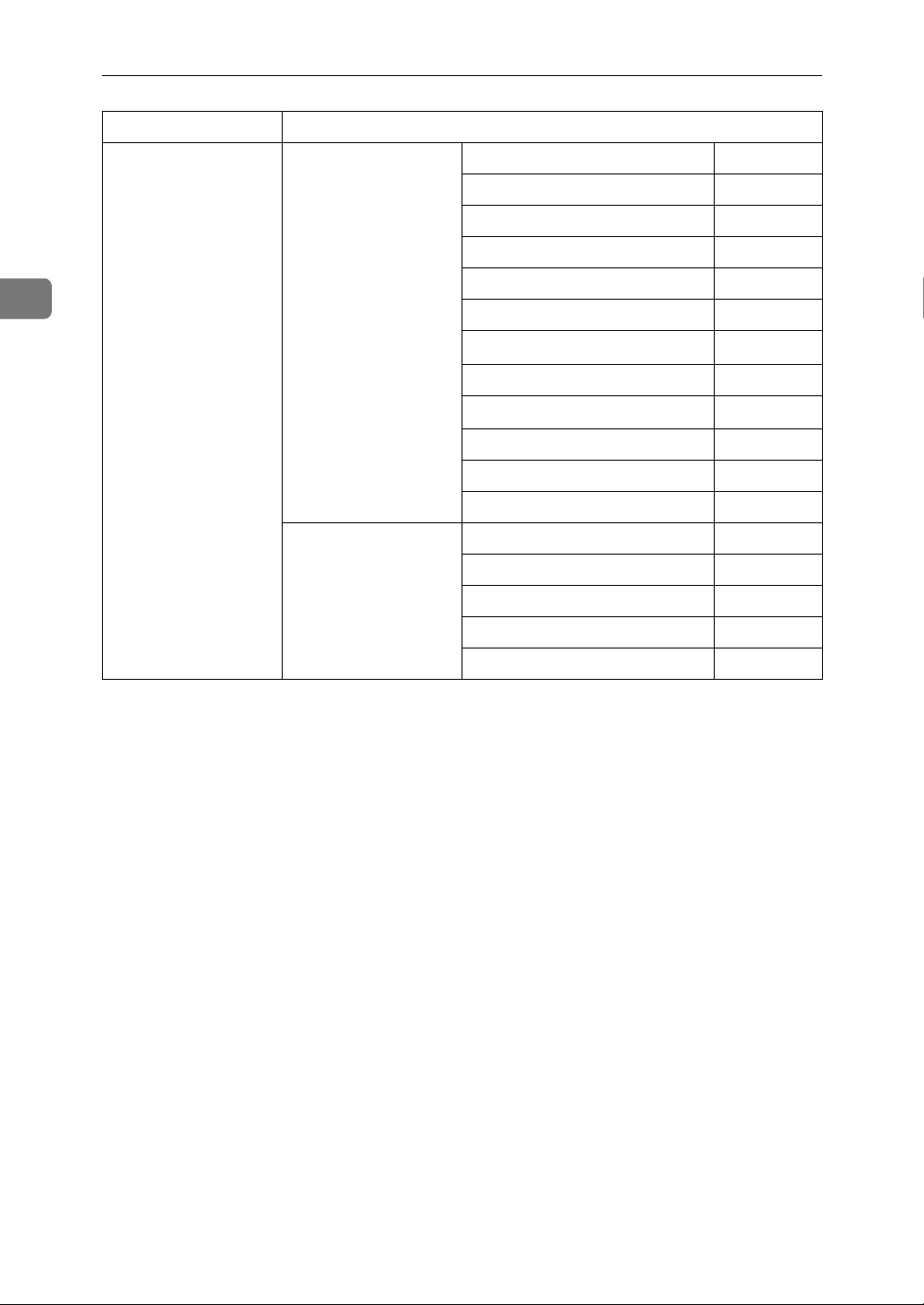
Connecting and Setting Up
Interface Settings
2
IEEE 802.11b
(wireless LAN)
*1
Appears when the optional IEEE 1394 interface board is installed.
*2
Appears when the optional IEEE 802.11b interface unit is installed.
Interface Settings/
Network
See p.37 “Network”.
Interface Settings/
IEEE 802.11b
See p.41 “IEEE
802.11b”.
*3
IP Address $
Gateway Address $
DNS Configuration $
WINS Configuration ❍
DDNS Configuration ❍
Domain Name ❍
LAN Type
Ethernet Speed ❍
Effective Protocol
Permit SNMP V3 Communication
Permit SSL / TLS Communication
Host Name ❍
Communication Mode $
SSID Setting ❍
Channel ❍
WEP (Encryption) Setting ❍
Transmission Speed ❍
*2
*3
If Ethernet and 802.11b (wireless LAN) are both connected to the machine, the selected interface has priority.
*3
Check[Effective] is selected for TCP/IP.
$
$
❍
❍
20
Page 27
Interface Settings
Setting Up the Machine on a Network
Ethernet Interface Settings/
Network
See p.37 “Network”.
File Transfer
See p.42 “File Transfer”.
IP Address $
Gateway Address $
DNS Configuration ❍
DDNS Configuration ❍
Domain Name ❍
WINS Configuration ❍
LAN Type
Ethernet Speed ❍
Effective Protocol
Permit SNMP V3 Communication
Permit SSL / TLS Communication
Host Name ❍
SMTP Server $
SMTP Authentication ❍
POP before SMTP ❍
POP3 Setting
Administrator's E-mail Address ❍
E-mail Communication Port
*2
*3
*4
*5
$
$
❍
❍
❍
❍
2
Program / Change / Delete Email Message
Program / Change / Delete
Subject
Scanner Recall Interval Time ❍
Number of Scanner Recalls ❍
❍
❍
21
Page 28
Connecting and Setting Up
Interface Settings
2
IEEE 1394
(IP over 1394)
Interface Settings/
IEEE 1394
See p.39 “IEEE 1394”.
Interface Settings/
Network
See p.37 “Network”.
File Transfer
See p.42 “File Transfer”.
*1
IP Address $
IP over 1394 $
DDNS Configuration ❍
WINS Configuration ❍
Host Name ❍
Domain Name ❍
Gateway Address $
DNS Configuration ❍
Effective Protocol
SMTP Server $
SMTP Authentication ❍
POP before SMTP ❍
POP3 Setting
Administrator's E-mail Address ❍
E-mail Communication Port
Program / Change / Delete Email Message
*3
*4
*5
$
❍
❍
❍
Program / Change / Delete
Subject
Scanner Recall Interval Time ❍
Number of Scanner Recalls ❍
❍
22
Page 29
Interface Settings
Setting Up the Machine on a Network
IEEE 802.11b
(wireless LAN)
Interface Settings/
Network
See p.37 “Network”.
Interface Settings/
IEEE 802.11b
See p.41 “IEEE
802.11b”.
*2
IP Address $
Gateway Address $
DNS Configuration ❍
DDNS Configuration ❍
Domain Name ❍
WINS Configuration ❍
LAN Type
Ethernet Speed ❍
Effective Protocol
Permit SNMP V3 Communication
Permit SSL / TLS Communication
Host Name ❍
Communication Mode $
SSID Setting ❍
Channel ❍
WEP (Encryption) Setting ❍
Transmission Speed ❍
*2
*3
$
$
❍
❍
2
File Transfer
See p.42 “File Transfer”.
*1
Appears when the optional IEEE 1394 interface board is installed.
*2
Appears when the optional IEEE 802.11b interface unit is installed.
SMTP Server $
SMTP Authentication ❍
POP before SMTP ❍
POP3 Setting
Administrator's Address ❍
E-mail Communication Port
Program / Change / Delete Email Message
Program / Change / Delete
Subject
Scanner Recall Interval Time ❍
Number of Scanner Recalls ❍
*4
*5
If Ethernet and 802.11b (wireless LAN) are both connected to the machine, the selected interface has priority.
*3
Check [
*4
If you select [On] for [POP before SMTP], select this function as well.
*5
If you select [On] for [
Effective
] is selected for TCP/IP.
POP before SMTP
], check the port number for [
POP3
].
❍
❍
❍
❍
23
Page 30
Connecting and Setting Up
Scan to Folder
Interface Settings
2
Ethernet Interface Settings/
Network
See p.37 “Network”.
File Transfer
See p.42 “File Transfer”.
IEEE 1394
(IP over 1394)
Interface Settings/
IEEE 1394
See p.39 “IEEE 1394”.
*1
IP Address $
Gateway Address $
DNS Configuration ❍
DDNS Configuration ❍
Domain Name ❍
WINS Configuration ❍
LAN Type
Ethernet Speed ❍
Effective Protocol
Host Name ❍
Permit SNMP V3 Communication
Permit SSL / TLS Communication
Default User Name / Password
(Send)
Scanner Recall Interval Time ❍
Number of Scanner Recalls ❍
IP Address $
IP over 1394 $
DDNS Configuration ❍
*2
*3
$
$
❍
❍
❍
24
Interface Settings
/Network
See p.37 “Network”.
File Transfer
See p.42 “File Transfer”.
WINS Configuration ❍
Host Name ❍
Domain Name ❍
Gateway Address $
DNS Configuration ❍
Effective Protocol
Default User Name / Password
(Send)
Scanner Recall Interval Time ❍
Number of Scanner Recalls ❍
*3
$
❍
Page 31

Interface Settings
Setting Up the Machine on a Network
IEEE 802.11b
(wireless LAN)
Interface Settings/
Network
See p.37 “Network”.
Interface Settings/
IEEE 802.11b
See p.41 “IEEE
802.11b”.
*2
IP Address $
Gateway Address $
DNS Configuration ❍
DDNS Configuration ❍
Domain Name ❍
WINS Configuration ❍
LAN Type
Ethernet Speed ❍
Effective Protocol
Permit SNMP V3 Communication
Permit SSL / TLS Communication
Host Name ❍
Communication Mode $
SSID Setting ❍
Channel ❍
WEP (Encryption) Setting ❍
Transmission Speed ❍
*2
*3
$
$
❍
❍
2
File Transfer
See p.42 “File Transfer”.
*1
Appears when the optional IEEE 1394 interface board is installed.
*2
Appears when the optional IEEE 802.11b interface unit is installed.
Default User Name / Password
(Send)
Scanner Recall Interval Time ❍
Number of Scanner Recalls ❍
If Ethernet and IEEE 802.11b (wireless LAN) are both connected to the machine, the
selected interface has priority.
*3
Check [Effective] is selected for TCP/IP.
❍
25
Page 32

Connecting and Setting Up
Network Delivery Scanner
Interface Settings
2
Ethernet Interface Settings/
Network
See p.37 “Network”.
File Transfer
See p.42 “File Transfer”.
IEEE 1394
(IP over 1394)
Interface Settings/
IEEE 1394
See p.39 “IEEE 1394”.
*1
IP Address $
Gateway Address ❍
DNS Configuration ❍
DDNS Configuration ❍
Domain Name ❍
WINS Configuration ❍
LAN Type
Ethernet Speed ❍
Effective Protocol
Permit SNMP V3 Communication
Permit SSL / TLS Communication
Host Name ❍
Delivery Option
Fax RX File Transmission ❍
Scanner Recall Interval Time ❍
Number of Scanner Recalls ❍
IP Address $
IP over 1394 $
DDNS Configuration ❍
*2
*4
*3
$
$
❍
❍
❍
26
Interface Settings/
Network
See p.37 “Network”.
File Transfer
See p.42 “File Transfer”.
WINS Configuration ❍
Host Name ❍
Domain Name ❍
Gateway Address ❍
DNS Configuration ❍
Effective Protocol
Delivery Option
Fax RX File Transmission ❍
Scanner Recall Interval Time ❍
Number of Scanner Recalls ❍
*4
*3
$
❍
Page 33

Interface Settings
Setting Up the Machine on a Network
IEEE 802.11b
(wireless LAN)
Interface Settings/
Network
See p.37 “Network”.
Interface Settings/
IEEE 802.11b
*2
See p.41 “IEEE
802.11b”.
File Transfer
See p.42 “File Transfer”.
IP Address $
Gateway Address ❍
DNS Configuration ❍
DDNS Configuration ❍
Domain Name ❍
WINS Configuration ❍
LAN Type
*2
$
Ethernet Speed ❍
Effective Protocol
*4
Permit SNMP V3 Communication
Permit SSL / TLS Communication
$
❍
❍
Host Name ❍
Communication Mode $
SSID Setting ❍
Channel ❍
WEP (Encryption) Setting ❍
Transmission Speed ❍
Delivery Option
*3
❍
Fax RX File Transmission ❍
Scanner Recall Interval Time ❍
2
Number of Scanner Recalls ❍
*1
Appears when the optional IEEE 1394 interface board is installed.
*2
Appears when the optional IEEE 802.11b interface unit is installed.
If Ethernet and IEEE 802.11b (wireless LAN) are both connected to the machine, the
selected interface has priority.
*3
When delivery option is set to [On], make sure the IP address is set.
*4
Check [Effective] is selected for TCP/IP.
27
Page 34

Connecting and Setting Up
Network TWAIN Scanner
Interface Settings
2
Ethernet Interface Settings/
Network
See p.37 “Network”.
IEEE 1394
(IP over 1394)
Interface Settings/
IEEE 1394
See p.39 “IEEE 1394”.
*1
IP Address $
Gateway Address ❍
DNS Configuration ❍
DDNS Configuration ❍
Domain Name ❍
WINS Configuration ❍
LAN Type
Ethernet Speed ❍
Effective Protocol
Permit SNMP V3 Communication
Permit SSL / TLS Communication
Host Name ❍
IP Address $
IP over 1394 $
DDNS Configuration ❍
WINS Configuration ❍
Host Name ❍
*2
*3
$
$
❍
❍
28
Interface Settings/
Network
See p.37 “Network”.
Domain Name ❍
Gateway Address ❍
DNS Configuration ❍
Effective Protocol
*3
$
Page 35

Interface Settings
Setting Up the Machine on a Network
IEEE 802.11b
(wireless LAN)
*1
Appears when the optional IEEE 1394 interface board is installed.
*2
Appears when the optional IEEE 802.11b interface unit is installed.
Interface Settings/
Network
See p.37 “Network”.
Interface Settings/
IEEE 802.11b
See p.41 “IEEE
802.11b”.
*2
IP Address $
Gateway Address ❍
DNS Configuration ❍
DDNS Configuration ❍
Domain Name ❍
WINS Configuration ❍
LAN Type
Ethernet Speed ❍
Effective Protocol
Permit SNMP V3 Communication
Permit SSL / TLS Communication
Host Name ❍
Communication Mode $
SSID Setting ❍
Channel ❍
WEP (Encryption) Setting ❍
Transmission Speed ❍
*2
*3
If Ethernet and 802.11b (wireless LAN) are both connected to the machine, the selected interface has priority.
*3
Check [Effective] is selected for TCP/IP.
2
$
$
❍
❍
29
Page 36

Connecting and Setting Up
Document Server
Interface Settings
2
Ethernet Interface Settings/
Network
See p.37 “Network”.
IEEE 1394
(IP over 1394)
Interface Settings/
IEEE 1394
See p.39 “IEEE 1394”.
*1
IP Address $
Gateway Address ❍
DNS Configuration ❍
DDNS Configuration ❍
Domain Name ❍
WINS Configuration ❍
LAN Type
Ethernet Speed ❍
Effective Protocol
Permit SNMP V3 Communication
Permit SSL / TLS Communication
Host Name ❍
IP Address $
IP over 1394 $
DDNS Configuration ❍
WINS Configuration ❍
Host Name ❍
*2
*3
$
$
❍
❍
30
Interface Settings/
Network
See p.37 “Network”.
Domain Name ❍
Gateway Address ❍
DNS Configuration ❍
Effective Protocol
*3
$
Page 37

Interface Settings
Setting Up the Machine on a Network
IEEE 802.11b
(wireless LAN)
*1
Appears when the optional IEEE 1394 interface board is installed.
*2
Appears when the optional IEEE 802.11b interface unit is installed.
Interface Settings/
Network
See p.37 “Network”.
Interface Settings/
IEEE 802.11b
See p.41 “IEEE
802.11b”.
*2
IP Address $
Gateway Address ❍
DNS Configuration ❍
DDNS Configuration ❍
Domain Name ❍
WINS Configuration ❍
LAN Type
Ethernet Speed ❍
Effective Protocol
Permit SNMP V3 Communication
Permit SSL / TLS Communication
Host Name ❍
Communication Mode $
SSID Setting ❍
Channel ❍
WEP (Encryption) Setting ❍
Transmission Speed ❍
*2
*3
If Ethernet and IEEE 802.11b (wireless LAN) are both connected to the machine, the
selected interface has priority.
*3
Check [Effective] is selected for TCP/IP.
2
$
$
❍
❍
31
Page 38

2
Connecting and Setting Up
Network Configuration
Any change you make with User
Tools remains in effect even if the
main power switch or operation
switch is turned off, or the {Energy
Saver} or {Clear Modes} key is pressed.
Configuring the network using the control panel
Note
❒ Operations for System Settings are
different from normal operations.
After using User Tools, press the
{User Tools/Counter/Inquiry} key to
exit.
❒ When [User Authentication Manage-
ment] is set, operations are not pos-
sible with the machine unless a
valid user name and password is
entered. For details about user authentication, consult administrator.
Change settings by following the
E
instructions on the display panel,
and then press [OK].
Note
❒ To cancel changes made to set-
tings and return to theSystem
Settings menu, press [Cancel].
Press [Exit].
FFFF
Press the {User Tools/Counter/Inquiry}
GGGG
key.
Note
❒ You can also exit by pressing
[Exit] on the User Tools main
menu.
Press the {User Tools/Counter/Inquiry}
AAAA
key.
Note
❒ The machine will be offline dur-
ing setting.
Press [System Settings].
BBBB
Press [Interface Settings] or [File
CCCC
Transfer].
Select the required menu, and
DDDD
then press the desired key.
32
Page 39

Setting Up the Machine on a Network
Configuring the network using other utilities
As well as using the control panel to make network settings, utilities such as a
Web Image Monitor and SmartDeviceMonitor for Admin can also be used. The
following table shows available settings:
Note
❒❍ Indicates machine settings can be changed.
❒ - Indicates the setting cannot be changed from that device.
SmartDe-
Name on the control panel
Web Image
Monitor
viceMon-
itor for
Admin
telnet
2
Interface
Settings
Network
IP Address
Gateway Address ❍❍❍
DNS
Configuration
DDNS Configuration ❍ - ❍
Domain
Name
WINS
Configuration
Auto-Obtain (DHCP) ❍❍❍
Specify
Auto-Obtain (DHCP) ❍ - ❍
Specify VDNS
Auto-Obtain (DHCP) ❍ - ❍
Specify V Do-
On VPrima-
IP Address
Sub-net
Mask
Server 1
VDNS
Server 2
VDNS
Server 3
main
Name
ry WINS
Server
❍❍❍
❍❍❍
❍ - ❍
❍ - ❍
❍ - ❍
❍ - ❍
❍ - ❍
VSecondary WINS
Server
Scope ID ❍ - ❍
Off ❍ - ❍
❍ - ❍
33
Page 40

2
Connecting and Setting Up
Name on the control panel
Interface
Settings
Network Effective
Protocol
SmartDe-
Web Image
Monitor
TCP/IP -
NetWare ❍
SMB ❍❍❍
AppleTalk ❍❍❍
viceMon-
itor for
Admin
*1
❍
*2
❍
telnet
❍
❍
NW
Frame
Type
SMB Computer Name ❍ - ❍
SMB Work Group ❍ - ❍
Ethernet Speed - - -
LAN
Type
Ping Command - - -
Permit
SNMP V3
Communication
Permit
SSL / TLS
Communication
Auto Select ❍ - ❍
Ethernet II ❍ - ❍
Ethernet 802.2 ❍ - ❍
Ethernet 802.3 ❍ - ❍
Ethernet SNAP ❍ - ❍
Ethernet ❍ - ❍
IEEE 802.11b ❍ - ❍
Encryption Only - - ❍
Encryption / Clear
Text
Ciphertext Only ---
Ciphertext Priority - - -
Ciphertext / Clear
Text
---
---
34
IEEE 1394
Host Name ❍❍❍
Machine Name ❍ - ❍
IP Address
DDNS Configuration ❍ - ❍
Host Name ❍ - ❍
Auto-Obtain (DHCP) ❍ - ❍
Specify
IP Address
Sub-net
Mask
❍ - ❍
❍ - ❍
Page 41

Name on the control panel
Setting Up the Machine on a Network
SmartDe-
Web Image
Monitor
viceMon-
itor for
Admin
telnet
Interface
Settings
IEEE 1394 Domain
Name
WINS
Configuration
IP over
1394
SCSI
print
(SBP-2)
Bidirectional
SCSI
print
IEEE
802.11b
Communication
Mode
Auto-Obtain (DHCP) ❍ --
Specify Domain
Name
On Primary
WINS
Server
Secondary WINS
Server
Scope ID ❍ - ❍
Off ❍ - ❍
Active ❍ - ❍
Inactive ❍ - ❍
Active ❍ - ❍
Inactive ❍ - ❍
Active ❍ - ❍
Inactive ❍ - ❍
802.11 Ad hoc ❍ - ❍
Ad hoc ❍ - ❍
Infrastructure ❍ - ❍
❍ - ❍
❍ - ❍
❍ - ❍
2
SSID Setting ❍ - ❍
Channel ❍ - ❍
WEP (Encryption)
Setting
Wireless LAN Signal ---
Transmission
Speed
Return to Defaults - - -
Print List ---
WEP Active ❍ - ❍
Inactive ❍ - ❍
Encryption ❍ - ❍
Auto - - ❍
11Mbps Fixed - - ❍
5.5Mbps Fixed - - ❍
2Mbps Fixed - - ❍
1Mbps Fixed - - ❍
35
Page 42

Connecting and Setting Up
Name on the control panel
Web Image
Monitor
SmartDeviceMon-
itor for
Admin
telnet
2
File
Transfer
Delivery Option - - -
Capture Server IP Address - - -
Fax RX File Transmission - - -
SMTP Server ❍ --
SMTP Authentication ❍ --
POP before SMTP ❍ --
Reception Protocol ❍ --
POP3 Setting ❍ --
Administrator's E-mail Address ❍ --
E-mail Communication Port ❍ --
E-mail Reception Interval ❍ --
Max. Reception E-mail Size ❍ --
E-mail Storage in Server ❍ --
Default User Name / Password (Send) ❍ --
Program / Change / Delete E-mail Message - - -
Program / Change / Delete Subject - - -
Scanner Recall Interval Time - - -
36
Number of Scanner Recalls - - -
E-mail Account - - -
Auto Specify Sender Name - - -
*1
You can make the TCP/IP settings if SmartDeviceMonitor for Admin is communicating with the machine using IPX/SPX.
*2
You can make the IPX/SPX settings if SmartDeviceMonitor for Admin is communicating with the machine using TCP/IP.
Page 43

Interface Settings
Network
❖ IP Address
Before using this machine in the
network environment, you must
configure the IP address and subnet mask.
• Auto-Obtain (DHCP)
• Specify
When you select [Specify], enter
the [IP Address]and [Sub-net
Mask] as “xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx”(“x”
indicates a number).
• IP Address: 011.022.033.044
• Sub-net Mask: 000.000.000.000
Note
❒ Default: Auto-Obtain (DHCP)
❒ If you use the interface for Eth-
ernet and IEEE 1394 (IP over
1394) at the same time, settings
must be made carefully. See
p.139 “Using DHCP”.
❒ If you install the optional IEEE
1394 interface board and use the
IEEE 1394 interface, you must
set the address of the domain,
different from the [IP Address] of
[IEEE 1394]. If you intend to set
the address for the same domain, set a different value for
the [Sub-net Mask].
❒ When you select [Specify], be
sure not to set the same [IP Ad-
dress] as that of another ma-
chines on the network.
Setting Up the Machine on a Network
❖ Gateway Address
A gateway is a connection or interchange point between two networks. Configure the gateway
address for the router or host computer used as a gateway.
• Gateway Address:000.000.000.000
Note
❒ Default: 000.000.000.000
❖ DNS Configuration
Make settings for the DNS server.
• Auto-Obtain (DHCP)
• Specify
When you select [Specify], enter
the [DNS Server] IP address as
“xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx”(“x ” indi-
cates a number).
• VDNS Server 1:000.000.000.000
• VDNS Server 2:000.000.000.000
• VDNS Server 3:000.000.000.000
Note
❒ Default: Auto-Obtain (DHCP)
❖ DDNS Configuration
You can specify the DDNS settings.
• Active
• Inactive
❖ Domain Name
You can specify the domain name.
• Auto-Obtain (DHCP)
• Specify
• Domain Name
2
❒ The physical address (MAC ad-
dress) also appears.
37
Page 44

Connecting and Setting Up
2
❖ WINS Configuration
You can specify the WINS server
settings.
• On
If [On] is selected, enter the
[VWINS Server] IP address as
“xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx”(“x ” indi-
cates a number).
If DHCP is in use, specify the
[Scope ID].
• Primary WINS Server
• Secondary WINS Server
• Scope ID
• Off
Limitation
❒ Enter a [Scope ID] using up to 31
alphanumeric characters.
Note
❒ Default: Off
❖ Effective Protocol
Select the protocol to use in the
network.
• TCP/IP:Effective/Invalid
• NetWare:Effective/Invalid
❖ SMB Computer Name
Specify the SMB computer name.
❖ SMB Work Group
Specify the SMB work group.
❖ Ethernet Speed
Set the access speed for networks.
Select a speed that matches your
network environment. [Auto Select]
should usually be selected.
• Auto Select
• 100Mbps Full Duplex
• 100Mbps Half Duplex
• 10Mbps Full Duplex
• 10Mbps Half Duplex
Note
❒ Default: Auto Select
❖ LAN Type
When you have installed the optional IEEE 802.11b interface unit,
select interface, IEEE 802.11b
(wireless LAN) or Ethernet.
• Ethernet
• IEEE 802.11b
• SMB:Effective/Invalid
• AppleTalk:Effective/Invalid
❒ Default: TCP/IP: Effective, Net-
❖ NW Frame Type
Select the frame type when you
use NetWare.
• Auto Select
• Ethernet II
• Ethernet 802.2
• Ethernet 802.3
• Ethernet SNAP
❒ Default: Auto Select
38
Note
Ware: Effective, SMB: Effective,
AppleTalk: Effective
Note
Note
❒ Default: Ethernet
❒ Appears when the optional IEEE
802.11b interface unit is installed.
❒ If Ethernet and IEEE 802.11b (wire-
less LAN) are both connected to
the machine, the selected interface
takes precedence.
Page 45

Setting Up the Machine on a Network
❖ Ping Command
Check the network connection
with ping command using given
IP address.
Note
❒ If you fail to connect to the net-
work, check the following, and
then retry the ping command.
• Check TCP/IP of the printer
is active.
• Check that the machine with
assigned IP address is connected to the network.
• There is a possibility that same
IP address is used for the specified equipment .
❖ Permit SNMP V3 Communication
Set the encrypted communication
of SNMP v3.
• Encryption Only
• Encryption / Clear Text
Note
❒ If you set to [Encryption Only],
you need to set password for
the machine.
❖ Permit SSL / TLS Communication
Set the encrypted communication
of SSL/TLS.
• Ciphertext Only
• Ciphertext Priority
• Ciphertext / Clear Text
Note
❒ Default: Ciphertext Priority
❒ If you set to [Encryption Only], you
need to install the server authentification for the machine.
❖ Host Name
Specify the host name.
IEEE 1394
Preparation
You must install the optional IEEE
1394 interface board in the machine.
❖ IP Address
When you connect the machine to
a network using the IEEE 1394 interface, you must configure the IP
address and subnet mask.
• Auto-Obtain (DHCP)
• Specify
When you select [Specify], enter
the [IP Address] and [Sub-net
Mask] as “xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx”(“x”
indicates a number).
• IP Address: 011.022.033.044
• Sub-net Mask: 000.000.000.000
Note
❒ Default: Auto-Obtain (DHCP)
❒ If you use the interface for Eth-
ernet and IEEE 1394 (IP over
1394) at the same time, settings
must be made carefully. See
p.139 “Using DHCP”
❒ When you use the IEEE 1394 in-
terface on a network, you cannot use the Ethernet interface in
the same domain. To use both
interfaces in the same domain,
set different values for the [Sub-
net Mask].
❒ The physical address (EUI-64)
also appears.
❖ DDNS Configuration
You can specify the DDNS settings.
• Active
• Inactive
2
❖ Machine Name
Specify the machine name.
❖ Host Name
Specify the host name.
39
Page 46

Connecting and Setting Up
2
❖ Domain Name
Make settings for the domain name.
• Auto-Obtain (DHCP)
• Specify
• Domain Name
Note
❒ Default: Auto-Obtain (DHCP)
❖ WINS Configuration
You can specify the WINS server
settings.
• On
If [On] is selected, specify the
[VWINS Server] IP address as
“xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx” (“xxx” indicates a number).
If DHCP is in use, specify the
[Scope ID].
• Primary WINS Server
• Secondary WINS Server
• Scope ID
• Off
Limitation
❒ Enter [Scope ID] using up to 31
alphanumeric characters.
Note
❒ Default: Off
❖ IP over 1394
When you use the IP over 1394 function of the IEEE 1394 interface to
connect the machine to the network,
or you print from computer with the
IP over 1394 driver, you must specify [Active]for [IP over 1394].
❖ SCSI print (SBP-2)
When you print using the SCSI
print client function supported by
Windows 2000/XP, or Windows
Server 2003, you must set [SCSI
print (SBP-2)].
• Active
• Inactive
Limitation
❒ The IEEE 1394 interface can be
used when Windows 2000 Service Pack 1 or later is installed. If
the Service Pack is not installed,
only one SCSI print device is
connectable via 1394 bus.
Note
❒ Default: Active
❖ Bidirectional SCSI print
Specifies the printer's response
mode etc. for status requests when
using the IEEE 1394 interface.
• On
• Off
Note
❒ Default: On
❒ If this is set to [Off], bidirectional
communication will not work.
40
• Active
• Inactive
Limitation
❒ Printing with IP over 1394 is pos-
sible under Windows Me/XP and
Windows Server 2003
Note
❒ Default: Active
Page 47

Setting Up the Machine on a Network
IEEE 802.11b
Preparation
You must install the optional IEEE
802.11b interface unit into the machine.
Note
❒ Be sure to make all settings simul-
taneously.
❖ Communication Mode
Specifies the communication mode
of the wireless LAN.
• 802.11 Ad hoc
• Ad hoc
• Infrastructure
Note
❒ Default: 802.11 Ad hoc
❖ SSID Setting
Specifies SSID to distinguish the
access point in infrastructure
mode or 802.11 ad hoc mode.
Limitation
❒ The characters that can be used
are ASCII 0x20-0x7e (32 bytes).
Note
❒ Default: blank (ASSID)
❒ If blank is specified in 802.11b
ad hoc mode or ad hoc mode,
“ASSID” appears.
❖ Channel
Specifies a channel when you select 802.11b ad hoc mode or ad hoc
mode.
Note
❒ Default: 11
❒ The following channels are avail-
able:
• Metric version: 1-13
❖ WEP (Encryption) Setting
Specifies the encryption of the
IEEE 802.11b (wireless LAN). If
this is set to [Active], you must enter the WEP key.
• VWEP
• Active
• Inactive
• VEncryption
10 alphanumeric characters
must be entered for 64 bit, 26
characters for 128 bit.
Note
❒ Default: Inactive
❖ Wireless LAN Signal
Shows the radio wave conditions
of the access point connected in infrastructure mode.
Note
❒ Radio wave status is displayed
when you press [Wireless LAN
Signal].
❖ Transmission Speed
Specifies the communication
speed of the IEEE 802.11b (wireless
LAN).
• Auto
• 11Mbps Fixed
• 5.5Mbps Fixed
• 2Mbps Fixed
• 1Mbps Fixed
Note
❒ Default: Auto
❖ Return to Defaults
You can return the IEEE 802.11b
(wireless LAN) settings to their defaults.
• No
• Yes
2
• Inch version: 1-11
41
Page 48

Connecting and Setting Up
2
Print List
You can check items related to the
network in use.
Reference
For details about printing, see p.42
“Printing the Interface Settings”.
Printing the Interface Settings
The configuration page shows the
current network settings and network
information.
Press the {User Tools/Counter/Inquiry}
AAAA
key.
Press [System Settings].
BBBB
Press [Interface Settings].
CCCC
Press [Print List].
DDDD
Press the {Start} key.
EEEE
The configuration page is printed.
Press [Exit].
FFFF
Press the {User Tools/Counter/Inquiry}
GGGG
key.
Note
❒ You can also exit by pressing
[Exit] on the User Tools main
menu.
File Transfer
❖ Delivery Option
Enables or disables sending stored
or scanned documents via the
ScanRouter delivery software delivery server.
• On
• Main Delivery Server IP Ad-
dress
• Sub Delivery Server IP Address
• Off
Note
❒ Default: Off
❒ Set this option when specifying
whether or not to use the ScanRouter delivery software. If you
do, you will have to re-register
I/O devices in the ScanRouter
delivery software.
❖ Capture Server IP Address
Specify the capture server IP address.
Note
❒ This setting appears when the
media link board is installed,
and that the capture function is
being used by the ScanRouter
delivery software.Set this option using the I/O device settings in the ScanRouter delivery
software.
42
Page 49

Setting Up the Machine on a Network
❖ Fax RX File Transmission
• VSetting per Line
Specifies whether or not received fax documents are sent
to the ScanRouter delivery software for each fax line.
• Line 1: Deliver to Server/Do
not Deliver
• Line 2: Deliver to Server/Do
not Deliver
• E-mail: Deliver to Server/Do
not Deliver
• IP-Fax: Deliver to Server/Do
not Deliver
Note
❒ Default: Do not Deliver
• Print at Delivery
Specifies whether or not received fax documents sent to
the ScanRouter delivery software should also be printed at
the same time.
• Print
• Do not Print
Note
❒ Default: Do not Print
• File to Deliver
Specifies whether all received
fax documents or only received
fax documents that include delivery codes (documents with
an ID and SUB/SEP code) are
sent to the ScanRouter delivery
software.
• File with Delivery Code
• All Files
• VDelivery Failure File
• Print File
• Delete File
If a received fax document cannot be sent to the ScanRouter
delivery software, it is stored in
memory. To print a stored file,
select [Print File]; to delete, select
[Delete File].
Note
❒ If the machine can send the
data to the ScanRouter delivery software, it does so automatically.
❒ If you delete the data, you
will not be able to distribute
or print it.
❖ SMTP Server
Specify the SMTP server name.
If DNS is in use, enter the host
name.
If DNS is not in use, enter the
SMTP server IP address.
• Server Name
• Port No.:25
Limitation
❒ Enter the [Server Name] using up
to 127 alphanumeric characters.
Spaces cannot be used.
Note
❒ Enter[Port No.] between 1 and
65535 using the number keys,
and then press the [#]key.
❒ The SMTP server shares its port
number with direct SMTP.
2
Note
❒ Default: All Files
43
Page 50

Connecting and Setting Up
2
❖ SMTP Authentication
You can configure SMTP authentication (PLAIN, LOGIN, CRAMMD5, DIGEST-MD5).
Authentication prevents unauthorized access, by making users enter a
user name and password when
sending e-mail to the SMTP server.
• On
If the SMTP server requires authentication, set [SMTP Authenti-
cation] to [On], and then specify
[User Name], [Password], and
[VEncryption].
• User Name
• E-mail Address
• Password
• VEncryption
Auto/On/Off
• Off
Limitation
❒ Enter [User Name] using up to
191 alphanumeric characters.
Spaces cannot be used.
❒ Depending on the SMTP server
type, "realm" must be specified.
Add "@" after the user name, as
in "user name@realm".
❒ Enter [Password] using up to 63
alphanumeric characters. Spaces cannot be used.
❒ Enter the user name and pass-
word to be set for [Administra-
tor's E-mail Address] when using
Internet Fax.
Note
❒ Default: Off
❒ [VEncryption]-[Auto]: If the authen-
tication method is PLAIN,
LOGIN, CRAM-MD5, or DIGEST-MD5.
❒ [VEncryption]-[On]: If the authenti-
cation method is CRAM-MD5 or
DIGEST-MD5.
❒ [VEncryption]-[Off]: If the authenti-
cation method is PLAIN, or
LOGIN.
❖ POP before SMTP
You can configure POP authentication (POP before SMTP).
Authentication prevents unauthorized access, by authenticating
with the POP server before sending e-mail to the SMTP server.
• On
To enable POP server authentication before sending e-mail via
the SMTP server, set [POP before
SMTP] to [On].
E-mail is sent to the SMTP server after the time specified for
[VWait Time after Auth.] has
elapsed.
•VWait Time after Auth.: 300msec
• User Name
• E-mail Address
• Password
• Off
44
Page 51

Setting Up the Machine on a Network
Limitation
❒ Enter [User Name] using up to 63
alphanumeric characters. Spaces cannot be used.
❒ Enter [Password] using up to 63
alphanumeric characters. Spaces cannot be used.
Note
❒ Default: Off
❒ Using the number keys, you can
set [VWait Time after Auth.] from
zero to 10,000 milliseconds, in
increments of one millisecond.
❒ If you select [On], enter [Server
Name] in [POP3 Setting]. Also,
check the port number for
[POP3] in [E-mail Communication
Port].
❖ Reception Protocol
Specify Reception Protocol for receiving Internet faxes.
• Off
• POP3
• SMTP
Note
❒ Default: Off
❖ POP3 Setting
Specify the POP3 [Server Name] for
receiving Internet faxes.
The specified POP3 server name is
used for [POP before SMTP].
If DNS is in use, enter the host
name.
If DNS is not in use, enter the POP3
or server IP address.
• Server Name
• VEncryption
• Auto
• On
• Off
Limitation
❒ Enter POP3 [Server Name] using
up to 127 alphanumeric characters. Spaces cannot be used.
Note
❒ VEncryption-[Auto]: Password
encryption is automatically set
according to the POP server settings.
❒ VEncryption-[On]: Encrypt pass-
word.
❒ VEncryption-[Off]: Do not encrypt
password.
❖ Administrator's E-mail Address
On e-mailed scanned documents,
if the sender is not specified this
appears as the sender’s address.
This can be used as the sender with
SMTP authentication for Internet
Fax. If [On] is selected for [SMTP Au-
thentication] be sure to enter the ad-
ministrator's e-mail address here.
This can be used as the destination
for data transmission result cc emails, as well as the destination for
data communication management
e-mail.
Limitation
❒ Enter up to 128 alphanumeric
characters.
❖ E-mail Communication Port
Specify the [POP3] port numbers
for receiving Internet faxes.
The specified POP3 port number is
used for [POP before SMTP].
• POP3: 110
Note
❒ Default: POP3/110
❒ Enter a port number between 1
and 65535 using the number
keys, and then press the [#]
key.
2
45
Page 52

Connecting and Setting Up
2
❖ E-mail Reception Interval
Specify, in minutes, the time limit
for receiving Internet faxes via
POP3 or IMAP4 server.
• On: 15 minute(s)
• Off
Note
❒ Default: On/15 minute(s)
❒ If [On] is selected, the number of
times can be set from 1 to 1440
in increments of one minute, using the number keys.
❖❖❖❖ Max. Reception E-mail Size
Specify the [Max. Reception E-mail
Size] for receiving Internet faxes.
Note
❒ Default: 2MB
❒ Using the number keys, enter a
size from one to 50 MB in increments of one megabyte.
❖ Program / Change / Delete E-mail Mes-
sage
You can program, change, or delete the e-mail message used when
sending an Internet fax or scan file
as an attachment.
• Program / Change
• Delete
Note
❒ Enter a name using up to 20 al-
phanumeric characters.
❒ Enter up to five lines of text.
Each line can consist of up to 80
alphanumeric characters.
❖ Program / Change / Delete Subject
You can program, change, or delete the subject used when sending
an Internet fax or scan file as an attachment.
• Program / Change
❖❖❖❖ E-mail Storage in Server
You can specify whether or not to
store received Internet fax e-mails
on the POP3 or IMAP4 server.
• Off
• All
• Errors Only
Note
❒ Default: Off
❖❖❖❖ Default User Name / Password (Send)
You can specify the user name and
password required when sending
scan file directly to a shared folder
on a computer running Windows,
or to an FTP server.
• SMB User Name
• SMB Password
• FTP User Name
• FTP Password
Limitation
❒ Enter up to 128 alphanumeric
characters.
46
• Delete
Note
❒ Enter a subject using up to 20 al-
phanumeric characters.
❖ Scanner Recall Interval Time
Specifies the interval the machine
waits before resending scan file, if
they cannot be sent to the delivery
server or mail server.
Note
❒ Default: 300 seconds
❒ The interval time can be set
from 60 to 999 seconds in one
second increments, using the
number keys.
❒ This setting is for the scanner
function.
❖ Number of Scanner Recalls
Sets a maximum number of times
scan file is resent to the delivery
server or mail server.
• On: 3 time(s)
Page 53

Setting Up the Machine on a Network
• Off
Note
❒ Default: On/3 time(s)
❒ If [On] is selected, the number of
times can be set from 1 to 99 using the number keys.
❒ This setting is for the scanner
function.
❖ E-mail Account
Specify [E-mail Address], [User
Name], and [Password] for receiving
Internet faxes.
• VFax Mail Reception
• E-mail Address
• User Name
• Password
Limitation
❒ Enter an e-mail address using up
to 128 alphanumeric characters.
❒ Enter a user name using up to
64 alphanumeric characters.
❒ Enter a password using up to 64
alphanumeric characters.
❖ Auto Specify Sender Name
Set name of the sender when sending an e-mail.
• On
• Scanner: If the sender is not
specified, the administrator's
e-mail address is entered in
the [From:] box. If the sender
is specified, the specified email address is entered in the
[From:] box.
• Fax: If the sender is not spec-
ified, the machine's e-mail
address is entered in the
[From:] box. If the machine's
e-mail address is not set, or
the e-mail address is not registered, the administrator's email address is entered in the
[From:] box.
• Off
• Scanner: If the sender is not
specified, the e-mail cannot be
sent. If the sender is specified,
the specified e-mail address is
entered in the [From:] box.
• Fax: If the sender is not speci-
fied, the e-mail cannot be sent.
If the sender is specified, the
specified e-mail address is entered in the [From:] box.
2
47
Page 54

Connecting and Setting Up
2
Programming, changing, or deleting an e-mail message
Limitation
❒ Enter a name using up to 20 alpha-
numeric characters.
❒ Enter up to five lines of text. Each
line can consist of up to 80 alphanumeric characters.
Press the {User Tools/Counter/In-
AAAA
quiry} key.
Press [System Settings].
BBBB
Press [File Transfer].
CCCC
Press [T Next].
DDDD
The next screen appears.
Press [Program / Change / Delete E-
EEEE
mail Message].
Programming an e-mail message
A Press [*Not programed].
B Press [Change], and then enter
the name.
Changing an e-mail message
A Select the e-mail message to
change.
B If you want to change the sub-
ject, press [Change].
C Change the subject, and then
press [OK].
D If you want to change the text,
press [Edit].
E Press [U] or [T] to select the
line to change.
F Change the text, and then press
[OK].
G Press [OK].
Deleting an e-mail message
A Press [Delete].
B Select the e-mail message to
delete.
The confirmation message
about deleting appears.
C To delete the data, press [Yes].
Press [Exit].
FFFF
48
Reference
For more information about
entering text, see “Entering
Text”, General Settings Guide.
C Press [OK].
D Press [Edit], and then enter the
text.
To start a new line, press [OK] to
return to the e-mail message
screen, and then press [T] in [Se-
lect Line to Edit:].
E Press [OK].
The e-mail message screen appears.
F Press [OK].
Press [Exit].
GGGG
Press the {User Tools/Counter/In-
HHHH
quiry} key.
Note
❒ You can also exit by pressing
[Exit] on the User Tools main
menu.
Page 55

Setting Up the Machine on a Network
Programming, changing, or deleting a subject
Limitation
❒ Enter a subject using up to 20 al-
phanumeric characters.
Note
❒ [Urgent] and [High] are programmed
as the e-mail subjects.
Press the {User Tools/Counter/In-
AAAA
quiry} key.
Press [System Settings].
BBBB
Press [File Transfer].
CCCC
Press [TNext]. The next screen ap-
DDDD
pears.
Press [Program / Change / Delete Sub-
EEEE
ject].
Deleting a subject
A Press [Delete].
B Select the subject to delete.
The confirmation message
about deleting appears.
C To delete the subject, press [Yes].
Press [Exit].
FFFF
Press [Exit].
GGGG
Press the {User Tools/Counter/Inquiry}
HHHH
key.
You can also exit by pressing [Exit]
on the User Tools main menu.
2
Programming a subject
A Press [*Not programed], and then
enter the text.
Reference
For more information about
entering text, see “Entering
Text”, General Settings Guide.
B Press [OK].
Changing a subject
A Select the subject to change.
B Enter the text.
C Press [OK].
49
Page 56

2
Connecting and Setting Up
LDAP Server Settings
Program the LDAP server to find up
e-mail destinations in the LDAP server Address Book directly. This function is possible when sending scan
files by e-mail using the scanner or
fax function, or when entering authentication information.
Before using this function
To start an LDAP search, make sure
that the items listed below are set. For
other items, check your environment
and make any necessary changes.
• Server Name
• Search Base
Program/Change/Delete LDAP Server
To enter Program/Change/Delete
LDAP Server
Press the {User Tools/Counter/Inquiry}
A
key.
Press [System Settings].
BBBB
• Port No.
• Search Conditions
• Authentication method selection
Note
❒ For authentication method, se-
lect from [High Security], [On], or
[Off].
• User Name/Password
The settings above differ depending on server environment. Check
your environment and make any
necessary changes.
Note
❒ To use the LDAP server in Admin-
istrator Tools, select [On] under
[LDAP Server].
❒ This function supports LDAP Ver-
sion 2.0 and 3.0. Ver 2.0 does not
support High Security authentication.
Press [Administrator Tools], and then
C
press [TNext] twice.
Press [Program / Change / Delete LDAP
DDDD
Server].
To program/change the LDAP
server
Select the LDAP server you want
AAAA
to program or change.
When programming the server, select [*Not Programmed].
Set each item as necessary.
BBBB
50
Page 57

LDAP Server Settings
To finish programming/changing the
LDAP Server
Press [Change] after setting each item.
A
Press [Exit].
BBBB
Press [Exit].
CCCC
Press the {User Tools/Counter/Inquiry}
D
key.
Programming the LDAP Server
To enter an identification name
Register a name for the LDAP server
that will appear on the server selection
screen of the LDAP search operation.
Press [Change] under [Identification
AAAA
Name].
Enter the server’s identification name.
B
Press [OK].
CCCC
To enter a server name
2
To delete the programmed LDAP
server
Press [Delete].
AAAA
Select the LDAP server you want
BBBB
to delete.
Press [Yes].
CCCC
Register the LDAP server’s host name
or IP address.
Press [Change] under [Server Name].
AAAA
Enter the LDAP server name.
BBBB
Press [OK].
CCCC
51
Page 58

Connecting and Setting Up
2
To enter the search base
Select a route folder defined by the
LDAP server to start the search from
e-mail addresses registered in the selected folder are search targets.
Press [Change] under [Search Base].
AAAA
Enter the search base.
BBBB
Note
❒ For example, if the search target
is the sales department of ABC
company, enter “dc=sales department, o=ABC”. (In this example, the description is for an
active directory. “dc” is for the
organization unit, and “o” is for
the company.)
❒ Search base registration may be
required depending on your
server environment. When registration is required, unspecified searches will result in error.
Check you server environment
and enter any required specifications.
Press [OK].
CCCC
To enter a port number
Specify the port number for communicating with the LDAP server. Specify a port that is compliant with your
environment.
Press [Change] under [Port No.].
AAAA
Enter the port number using the
BBBB
number keys, and then press [#].
Note
❒ When SSL is set to [On], the port
number automatically changes
to “689”.
❒ This function supports the TLS
v1, SSL v3 and v2.
To start SSL communication
Use SSL to communicate with the
LDAP server.
Press [On].
AAAA
Note
❒ To use SSL, the LDAP server
must support SSL.
❒ When SSL is set to [On], the port
number automatically changes
to “689”.
52
❒ SSL setting must be enabled on
this machine. For details, consult
your network administrator.
Page 59

LDAP Server Settings
To set authentication
To make a search request to the LDAP
server, use the administrator account
for authentication.
For details about the administrator
account, see “To enter the user name
and password”.
Press [TNext].
AAAA
Press [On] or [High Security] under
B
[Authentication].
To enter the user name and
password
When [On] or [High Security] is selected
for the authentication setting, use the
administrator account name and
password. Do not enter the administrator account name and password
when using authentication for each
individual or each search.
Press [TNext].
AAAA
Press [Change] under [User Name].
BBBB
2
Note
❒ Authentication settings must
comply with your server’s authentication settings. Check
your server settings before setting this machine.
❒ [High Security] is available only
with LDAP Version 3.0.
❒ When [High Security] is selected,
the administrator password is
encrypted before it is sent to the
network. When [On] is selected,
the password is sent without
encryption.
Enter the user name, and then
CCCC
press [OK].
Note
❒ Procedures for the user name
setting differ depending on
server environment. Check
your server environment before
making the setting.
• Example setting procedures:
Domain Name\User Name
User Name@Domain Name
CN=Name, OU=Department
Name, DC=Server Name
Press [Change] under [Password].
DDDD
Enter the password, and then
EEEE
press [OK].
53
Page 60

Connecting and Setting Up
2
Note
❒ The user name and password
are required for administrator
access to the LDAP server.
❒ You can set the user name and
password in this machine’s Address Book to allow individual
authentication access to the
LDAP server. Use Administrator Tools to select the user name
and password you want to use.
For details, see General Settings
Guide.
To test the connection
Access the LDAP server to check the
proper connection is established.
Check authentication works according to the authentication settings.
Press [Connection Test].
AAAA
A connection test is carried out.
Press [Exit].
BBBB
Note
❒ If the connection test fails, check
your settings and try again.
Press [Change] for items you want
BBBB
to use as search conditions from
the following: [Name], [E-mail Ad-
dress], [Fax Number], [Company
Name], and [Department Name].
Enter the attribute you want to use
CCCC
when searching for e-mail addresses, and then press [OK].
Note
❒ The attribute value may change
depending on the server environment. Check the attribute
value complies with your server
environment before setting it.
❒ You can leave items blank, but
you cannot leave attributes
blank when searching for e-mail
addresses from the LDAP server Address Book.
❒ This function does not check search
conditions or the search base.
To set search conditions
You can enter an attribute as a typical
search keyword. Using the entered attribute, the function searches the
LDAP server’s Address Book.
Press [TNext]twice.
AAAA
54
Page 61

LDAP Server Settings
To set search options
To search the LDAP server data using
a keyword other than prepared keywords such as Name, E-mail Address, FAX Number, Company
Name, and Department Name, specify the attribute for the keyword registered in your LDAP server, and the
name to be displayed on the control
panel during the search. For example,
to search e-mail addresses by employee number, enter “employeeNo.”
in the Attribute field, and “Employee
No.” in the key display field.
Press [TNext] three times.
AAAA
• Without key display registration
• With key display registration
2
Note
❒ The key does not appear on the
search screen unless both “At-
tribute” and “Key Display” are
registered. Make sure you register both to use the optional
search.
Press [Change] under [Attribute].
BBBB
Enter the attribute you want to
CCCC
use when searching for e-mail addresses, and then press [OK].
Note
❒ The attribute value may change
depending on the server environment. Check the attribute
complies with your server environment before setting it.
Press [Change] under [Key Display].
DDDD
Enter the key display, and then
EEEE
press [OK].
The registered “key display” appears as a keyword for searching
LDAP.
55
Page 62

2
Connecting and Setting Up
56
Page 63

3. Using a Printer Server
Preparing Printer Server
This section explains how to configure
the machine as a Windows network
printer. The machine is configured to
enabling network clients to use it.
When the network printer is connected via SmartDeviceMonitor for Client,
you can set the printing notification
function to notify clients of the results
of their print jobs.
Printing notification via SmartDeviceMonitor for Client
Follow the procedure below to configure the machine to use the printing
notification function of SmartDeviceMonitor for Client.
Important
❒ Under Windows 2000, Windows
XP Professional, or Windows Server 2003, to change printer properties in the [Printer] folder, you need
Printer Management access authentication; under Windows NT
4.0, Full Control access authentication. Log on to the file server as an
Administrator or member of the
PowerUsers group.
Open the [Printers] window from
A
the [Start] menu.
The [Printers] window appears.
Click the icon of the machine you
B
want to use. On the [File] menu,
click [Properties]. The printer
properties appear.
On the [Sharing] tab, click [Shared as:].
C
To share the machine with users
D
using a different version of Windows, click [Additional Drivers...].
Note
❒ If you have installed an alternative
driver by selecting [Shared as:]
during the printer driver installation, this step can be ignored.
Click [OK]. Close the printer prop-
E
erties.
Setting the print server
Important
❒ Under Windows 2000, Windows
XP Professional, or Windows Server 2003, to change printer properties in the [Printer] folder, you need
Printer Management access authentication; under Windows NT
4.0, Full Control access authentication. Log on to the file server as an
Administrator or member of the
PowerUsers group.
From the [Start] button on the task
A
bar, point to [Program], point to
[SmartDeviceMonitor for Client], and
then click [Print Server Settings].
The print server setting dialog box
appears.
Select the [Notify Client of Printing]
B
check box, and click [OK].
After print server setting is made, a
dialog box appears. Confirm the
dialog box content, and click [OK].
Click [Cancel] to interrupt the procedure.
A dialog box appears for client
C
setting. Click [OK].
57
Page 64

Using a Printer Server
3
The print server setting is complete. Each client must be set to receive print notification.
Note
❒ Current printing jobs restart
from the beginning after the
spooler pauses briefly.
❒ When the expansion function is
not used, the function is automatically set as available.
❒ If you log on using an account
that does not have Administrator privileges, the client may not
be notified.
Setting a Client
From the [Start] button on the task
A
bar, point to [Program], point to
[SmartDeviceMonitor for Client], and
then click [Setting Expansion Func-
tion].
A dialog box for setting the expansion function appears.
Select the [Use the expansion func-
B
tion] check box in [Notify Printing].
Select the [Notify when using the print
C
server] check box.
Click [OK].
D
The dialog box for setting the expansion function closes. The client
setting is completed.
Note
❒ Set the printing notification func-
tion on the printer driver as well
as on SmartDeviceMonitor for
Client.
58
Page 65

Using NetWare
Using NetWare
This section describes the setting procedure for network printers in the
NetWare environment. In the NetWare environment, you can connect
the machine as a “print server” or “re-
mote printer”.
❖ Setting procedure
• When using the machine as a
print server
Installing SmartDeviceMon-
A
itor for Admin
Setting the network interface
B
board.
Turning the machine off and
C
then back on.
• When using the machine as a
remote printer
Installing SmartDeviceMoni-
A
tor for Admin.
Setting the network interface
B
board.
Setting NetWare.
C
Starting the print server.
D
Note
❒ This procedure assumes an envi-
ronment is already prepared for
normal NetWare running the
printing service setting.
❒ The procedure is explained with
the following example settings:
• File server’s name …CAREE
Note
❒ The NetWare Client provided
by Novell is required to set the
printing environment using
SmartDeviceMonitor for Admin under the following environments:
• NDS mode in Windows 95/
98/Me
• NDS or Bindery mode in Windows 2000/XP, Windows NT
4.0
Reference
For details about installing
SmartDeviceMonitor for Admin, see p.77 “Installing SmartDeviceMonitor for Admin”.
❖ Printers listed by SmartDeviceMoni-
tor for Admin
SmartDeviceMonitor for Admin
lists printers connected to the network. If you cannot identify the
machine you want to configure,
print configuration page, and then
check the machine name.
Setting Up as a Print Server (NetWare 3.x)
Follow the procedure below to connect the machine as a print server using NetWare 3.x.
3
• Print server’s name …PSERV
• Printer’s name …R-PRN
• Queue name …R-QUEUE
❖ Using SmartDeviceMonitor for Admin
To use the machine in a NetWare
environment, use SmartDeviceMonitor for Admin to set the NetWare printing environment.
Log on to the file server as a su-
A
pervisor or supervisor equivalent.
Start NIB Setup Tool from the
B
[Start] menu.
Click [Wizard], and then click [OK].
C
Select a machine you want to con-
D
figure.
59
Page 66

Using a Printer Server
3
Enter the printer name in the [De-
E
vice name:] box and a comment in
the [Comment] box, and then click
[Next].
Select the [NetWare] check box,
F
and then click [Next].
Click [Bindery mode], enter the file
G
server name in the [File Server
Name:] box, and then click [Next].
In the [File Server Name:] box, enter
the name of the file server in which
a print server is created. You can
also click [Browse...] to browse
through available file servers.
Enter the print server name in the
H
[Print Server Name:] box, the printer
name in the [Printer Name:] box,
and the print queue name in the
[Print Queue Name] box, and then
click [Next].
• In the [Print Server Name:] box,
enter the name of the NetWare
print server using up to 47 characters.
• In the [Printer Name:] box, enter
the name of the NetWare printer.
• In the [Print Queue Name] box, en-
ter the name of the print queue
to be added to NetWare.
Check the settings, and then click
I
[Next].
The settings are applied, and NIB
Setup Tool quits.
Turn the printer off and then on
J
again.
Note
❒ To check that the configuration
is made correctly, enter the following from the command
prompt.
❒ If the printer works as config-
ured, the name of the print server appears as a connected user.
❒ If you cannot identify the print-
er you want to configure, check
the printer name with the configuration page printed from
the printer. For details about
printing a configuration page,
see Printer Reference.
❒ If no printer names appear in
the list, match the frame types
of IPX/SPXs for the computer
and printer. Use the [Network]
dialog box of Windows to
change the frame type of the
computer.
Setting Up as a Print Server (NetWare 4.x, 5/5.1, 6/6.5)
Follow the procedure below to connect the printer as a print server using
NetWare 4.x, NetWare 5/5.1, or NetWare 6/6.5.
Important
❒ When using the printer as a print
server in NetWare 4.x, NetWare
5/5.1, or NetWare 6/6.5, set it to
the NDS mode.
❒ When using NetWare 5/5.1 or
NetWare 6/6.5, set the printer as a
print server.
Log on to the file server as a su-
A
pervisor or supervisor equivalent.
Start NIB Setup Tool on the [Start]
B
menu.
Click [Wizard], and then click [OK].
C
Select a printer you want to con-
D
figure.
60
F:> USERLIST
Page 67

Using NetWare
Enter the printer name in the [De-
E
vice name:] box and a comment in
the [Comment] box, and then click
[Next].
Select the [NetWare] check box,
F
and then click [Next].
Click [NDS mode], enter the file
G
server name in the [File Server
Name:] box, the NDS tree name in
the [NDS Tree] box, and the context
in the [NDS Context:] box, and then
click [Next].
In the [File Server Name:] box, enter
the name of the file server in which
a print server is created. You can
also click [Browse...] to browse
through available file servers and
NDS context names.
In the [NDS Tree] box, enter the
name of the NDS tree in which a
print server is created using up to
32 alphanumeric characters. Hyphens and underscores can also be
used. You can also click [Browse...]
to browse through available NDS
trees.
For a context, object names are entered from the lowest object with
each object separated by a period.
For example, if you want to create
a print server in NET under DS, enter "NET.DS".
Enter the print server name in the
H
[Print Server Name:] box, the printer
name in the [Printer Name:] box, the
print queue name in the [Print
Queue Name] box, and the print
queue volume in the [Print Queue
Volume] box, and then click [Next].
• In the [Print Server Name:] box,
enter the name of the NetWare
print server using up to 47 characters.
• In the [Printer Name:] box, enter
the name of the NetWare printer.
• In [Print Queue Name] box, enter
the print queue volume.
• In [Print Queue Volume], type the
print queue volume. For a volume, object names are entered
from the lowest object with each
object separated by a period.
You can also click [Browse...] to
browse through available volumes.
Check the settings, and then click
I
[Next].
The settings are applied, and NIB
Setup Tool quits.
Turn the printer off and then on
J
again.
Note
❒ To check that the configuration
is made correctly, enter the following from the command
prompt.
3
F:> NLIST USER /A/B
❒ If the printer works as config-
ured, the name of the print server appears as a connected user.
61
Page 68

Using a Printer Server
3
❒ If you cannot identify the print-
er you want to configure, check
the printer name with the configuration page printed from
the printer. For details about
printing a configuration page,
see Printer Reference.
❒ If no printer names appear in
the list, match the frame types
of IPX/SPXs for the computer
and printer. Use the [Network]
dialog box of Windows to
change the frame type of the
computer.
Reference
When using the printer in a
pure IP environment of NetWare 5/5.1 or NetWare 6.0, see
p.62 “Using Pure IP in the NetWare 5/5.1 or 6/6.5 Environment”.
Using Pure IP in the NetWare 5/5.1 or 6/6.5 Environment
Setting up using NIB Setup Tool
Log on to the file server as an ad-
A
ministrator or administrator
equivalent.
Start NIB Setup Tool on the [Start]
B
menu.
Click [Property Sheet], and then
C
click [OK].
Select a printer you want to con-
D
figure.
On the [NetWare] tab, Select [File
E
Server Mode] or [NDS mode] in the
[Logon Mode] area.
When [File Server Mode] is selected,
the network connection is established based on the string entered
in the [File Server Name(F):] box.
When [NDS mode] is selected, the
network connection is established
based on the string entered in the
[NDS Tree] box.
Follow the procedure below to connect the printer as a print server in a
pure IP environment of NetWare
5/5.1 or NetWare 6/6.5.
Important
❒ When creating a queued print serv-
er in a pure IP environment of NetWare 5/5.1 or NetWare 6/6.5,
create a print queue on the file server using NetWare Administrator.
❒ This printer is not available as a re-
mote printer for use in a pure IP
environment.
❒ To use the printer in a pure IP en-
vironment, set it to TCP/IP.
62
In the [Print Server Name:] box, en-
F
ter the name of the print server.
In the [File Server Name:] box, enter
G
the name of the file server in
which a print server is created.
You can also click [Browse...] to browse
through available file servers.
Enter the NDS tree name in the
H
[NDS Tree] box.
Enter up to 32 alphanumeric characters. Hyphens and underscores
can also be used.
Page 69

Using NetWare
In the [NDS Context:] box, enter the
I
context of the print server.
You can also click [Browse...] to
browse through available NDS
trees and NDS contexts.
For a context, object names are entered from the lowest object with
each object separated by a period.
For example, if you want to create
a print server in Net under DS, enter "NET.DS".
In the [Print Server Operation Mode]
J
area, click [As Print Server].
Click [OK] to close the [NIB Setup
K
Tool] dialog box.
Check the settings, and then click
G
[Create].
Select the object in which the
H
printer is located, and then click
[Create] on the [Object] menu.
In the [Class of new object] box,
I
click [Printer], and then click [OK].
For NetWare 5, click [Printer (Non
NDPS)].
In the [Printer name] box, enter the
J
printer name
Select the [Define additional proper-
K
ties] check box, and then click
[Create].
Click [Assignments], and then click
L
[Add] in the [Assignments] area.
In the [Available objects] box, click
M
the queue you, and then click
[OK].
3
Setting up using NWadmin
From Windows, start NWadmin.
A
For details about NWadmin, see
the NetWare manuals.
Select the object in which the
B
print queue is located in the directory tree, and then click [Create] on
the [Object] menu.
In the [Class of new object] box,
C
click [Print Queue], and then click
[OK].
In the [Print Queue Name] box, enter
D
the name of the print queue.
In the [Print Queue Volume] box,
E
click [Browse].
In the [Available objects] box, click
F
the volume in which the print
queue is created, and then click
[OK].
Click [Configuration], click [Parallel]
N
in the [Printer type] list, and then
click [Communication].
Click [Manual load] in the [Commu-
O
nication type] area, and then click
[OK].
Check the settings, and then click
P
[OK].
Select a context specified using
Q
NIB Setup Tool, and then click
[Create] on the [Object] menu.
In the [Class of new object] box,
R
click [Print Server], and then click
[OK]. For NetWare 5, click [Print
Sever (Non NDPS)].
In the [Print Server Name] box, enter
S
the print server name.
Use the same print server name
specified using NIB Setup Tool.
63
Page 70

Using a Printer Server
3
Select the [Define additional proper-
T
ties] check box, and then click
[Create].
Click [Assignments], and then click
U
[Add] in the [Assignments] area.
In the [Available objects] box, click
V
the queue you created, and then
click [OK].
Check the settings, and then click
W
[OK].
Start the print server by entering
X
the following from the console of
the NetWare server.
If the print server is in operation,
quit and restart it.
❖ To exit
CAREE: unload pserver
❖ To start
On the [NetWare] tab, enter the
E
name of the print server in the
[Print Server Name:] box.
In the [File Server Name:] box, enter
F
the name of the file server in
which a print server is created.
You can also click [Browse...] to
browse through available file servers.
In the [Print Server Operation Mode]
G
area, click [As Remote Printer].
In the [Remote Printer No.] box, en-
H
ter the printer number.
Use the same printer number created in the print server.
A confirmation message appears.
I
Click [OK].
On the [NIB] menu, click [Exit].
J
CAREE: load pserver
print_server_name
Setting Up as a Remote Printer (NetWare 3.x)
Follow the procedure below to use
the printer as a remote printer under
NetWare 3.x.
Setting up using NIB Setup Tool
Log on to the file server as a su-
A
pervisor or supervisor equivalent.
Start NIB Setup Tool from [Start]
B
menu.
Click [Property Sheet], and then
C
click [OK].
Select a printer you want to con-
D
figure.
Setting up using PCONSOLE
Enter “PCONSOLE” from the com-
A
mand prompt.
F:> PCONSOLE
Create a print queue.
B
When using the existing print
queue, go to the procedure for creating a printer.
From the [Available Options] menu,
C
select [Print Queue Information], and
then press the {Enter} key.
Press {Insert} key, and then enter a
D
print queue name.
Press {ESC} key to return to the
E
[Available Options] menu.
Set up the network connection to
F
a printer.
64
Page 71

Using NetWare
On the [Available Options] menu,
G
click [Print Server Information], and
then press the {ENTER} key.
To create a new print server, press
H
the {INSERT} key, and then enter a
print server name.
For a currently defined print server, select a print server in the [Print
Server] list.
Use the same printer name specified using NIB Setup Tool.
From the [Print Server Information]
I
menu, select [Print Server Configura-
tion].
From the [Print Server Configuration]
J
menu, select [Printer Configuration].
Select the printer indicated as [Not
K
Installed].
Use the same printer number specified as the remote printer number
using NIB Setup Tool.
To change the printer name, enter
L
a new name.
A name “Printer x” is assigned to
the printer. The “x” stands for the
number of the selected printer.
As type, select [Remote Parallel, LPT1].
M
The IRQ, Buffer size, Starting form,
and Queue service mode are automatically configured.
Select the printer created.
R
Press the {INSERT} key to select a
S
queue serviced by the printer.
You can select several queues.
Follow the instructions on the
T
screen to make other necessary
settings.
Following these steps, check that
the queues are assigned.
Press the {ESC} key until "Exit?"
U
appears, and then select [Yes] to
exit PCONSOLE.
Start the print server by entering
V
the following from the console of
the NetWare server.
If the print server is in operation,
quit and restart it.
❖ To quit
CAREE: unload pserver
❖ To start
CAREE: load pserver
print_server_name
Note
❒ If the printer works as config-
ured, the message "Waiting for
job" appears.
3
Press the {ESC} key, and then
N
click [Yes] on the confirmation
message.
Press the {ESC} key to return to
O
[Print Server Configuration Menu].
Assign print queues to the created
P
printer.
From [Print Server Configuration Menu],
Q
select [Queues Serviced By Printer].
65
Page 72

3
Using a Printer Server
Setting Up as a Remote Printer (NetWare 4.x, 5/5.1, 6/6.5)
Follow the procedure below to use
the printer as a remote printer under
NetWare 4.x, 5/5.1 and 6/6.5.
Important
❒ To use the printer as a remote
printer under NetWare 4.x, 5/5.1,
6/6.5, set it to NDS mode.
❒ Do not use the printer as a remote
printer when Pure IP is used.
Setting up using NIB Setup Tool
Log on to the file server as an ad-
A
ministrator or administrator
equivalent.
In the [File Server Name(F):] box, en-
H
ter the name of the file server in
which a print server is created.
You can also click [Browse...] to
browse through available file servers. Enter up to 47 alphanumeric
characters.
In the [NDS Tree(T):] box, enter the
I
NDS tree name and create the file
server.
You can also click [Browse...] to
browse through available NDS
trees and NDS contexts. Enter up
to 32 alphanumeric characters. Hyphens and underscores can also be
used.
In the [NDS Context(C):] box, enter a
J
context in which the print server
is created.
Start NIB Setup Tool from [Start]
B
menu.
Click [Property Sheet], and then
C
click [OK].
Select a printer you want to con-
D
figure.
Click [NetWare].
E
In the [Logon Mode] area, click [File
F
Server Mode] or [NDS mode].
If [File Server Mode] is selected, the
network connection is established
based on the string you entered.
If [NDS mode] is selected, the network connection is established
based on the string you entered.
In the [Print Server Name(P):] box,
G
enter the name of the print server.
Use the same print server name in
NWadmin. Enter up to 47 alphanumeric characters.
Enter up to 127 alphanumeric
characters.
For context, object names from
Root are entered from the lowest
object, with each object separated
by a period. For example, to create
a print server in the NETWORK
object under the organization object DS of Root, enter “NET-
WORK.DS".
In the [Print Server Option Mode] ar-
K
ea, click [As Remote Printer(R)].
In the [Remote Printer No.(N)] box,
L
enter the printer number. Use the
same printer number created.
Click [OK] to close [NIB Setup Tool ].
M
66
Page 73

Setting up using NWadmin
From Windows, start NWadmin.
A
For details about NWadmin, see
the NetWare manuals.
Set up the network connection to
B
a print queue. Select the object in
which the print queue is located
in the directory tree, and then
click [Create] on the [Object] menu.
In the [Class of new object] box,
C
click [Print Queue], and then click
[OK].
In the [Print Queue Name] box, enter
D
the name of the print queue.
In the [Print Queue Volume] box,
E
click [Browse].
In the [Available objects] box, click
F
the volume in which the print
queue is created, and then click
[OK].
Check the settings, and then click
G
[Create].
Set up the network connection to
H
a printer. Select the object in
which the printer is located, and
then click [Create] on the [Object]
menu.
In the [Class of new object] box,
I
click [Printer], and then click [OK].
For NetWare 5, click [Printer (Non
NDPS)].
In the [Printer name] box, enter the
J
printer name
Select the [Define additional proper-
K
ties] check box, and then click
[Create].
Using NetWare
Assign print queues to the created
L
printer. Click [Assignments], and
then click [Add] in the [Assign-
ments] area.
In the [Available objects] box, click
M
the queue you created, and then
click [OK].
Click [Configuration], click [Parallel]
N
in the [Printer type] list, and then
click [Communication].
Click [Manual load] in the [Commu-
O
nication type] area, and then click
[OK]. Check the settings, and then
click [OK].
Set up the network connection to
P
a print server. Select a context
specified using NIB Setup Tool,
and then click [Create] on the [Ob-
ject] menu.
In the [Class of new object] box,
Q
click [Print Server], and then click
[OK]. For NetWare 5, click [Print
Sever (Non NDPS)].
In the [Print Server Name:] box, en-
R
ter the print server name.
Use the same print server name
specified using NIB Setup Tool.
Select the [Define additional proper-
S
ties] check box, and then click
[Create].
Assign the printer to the created
T
print server. Click [Assignments],
and then click [Add] in the [Assign-
ments] area.
In the [Available objects] box, click
U
the queue you created, and then
click [OK].
In the [Printers] area, click the print-
V
er you assigned, and then click
[Printer Number]
3
67
Page 74

Using a Printer Server
Enter the printer number, and
W
then click [OK]. Check the settings, and then click [OK].
Use the same printer number specified as the remote printer number
using NIB Setup Tool.
Start the print server by entering
X
the following from the console of
the NetWare server.
3
If the print server is in operation,
quit and restart it.
❖ To exit
CAREE: unload pserver
❖ To start
CAREE: load pserver
print_server_name
68
Page 75

4. Monitoring and Configuring the Printer
Using Web Image Monitor
Using Web Image Monitor, you can check the machine status and change settings.
❖ Available operations
The following operations can be remotely performed using Web Image Monitor from a client computer.
• Displaying machine status or settings
• Checking the print job status or history
• Checking, modifying, printing, or deleting print jobs stored in the Docu-
ment Server
• Interrupting currently printing jobs
• Resetting the printer
• Managing the Address Book
• Making machine settings
• Making network protocol settings
• Making security settings
❖ Configuring the machine
To perform the operations from Web Image Monitor, TCP/IP is required. After the machine is configured to use TCP/IP, operations from Web Image
Monitor become available.
❖ Recommended Web browser
• Windows:
Internet Explorer 5.5 SP1 or higher
Netscape Navigator 7.0 or higher
• Mac OS:
Netscape Navigator 7.0 or higher
Safari 1.0 or higher
Note
❒ To use Netscape Navigator with Secured Sockets Layer (SSL: an encryption
protocol), use Netscape Navigator 7.0 or higher.
❒ If the previous versions of the Web browser above are used or JavaScript and
cookies are not enabled with the Web browser used, display and operation
problems may occur.
❒ If you are using a proxy server, change the Web browser settings. Contact
your network administrator for information about the settings.
❒ The previous page may not appear even after the back button of a Web
browser is clicked. If this happens, click the refresh button of a Web browser.
❒ Updating the machine information is not automatically performed. Click [Re-
fresh] in the display area to update the machine information.
69
Page 76

4
Monitoring and Configuring the Printer
Displaying Top Page
This section explains the Top Page and how to display Web Image Monitor.
Start your Web browser.
A
Enter “http: //(machine's address)/” in the address bar of a Web browser.
B
Top Page of Web Image Monitor appears.
Note
❒ If the machine's host name has been registered on the DNS or WINS server,
you can enter it. For details, see p.139 “Using DHCP”.
❒ When setting SSL, a protocol for encrypted communication, under envi-
ronment which server authentification is issued , enter "https://(machine's address)/".
Every Web Image Monitor page is divided into the following areas:
1
2
1. Header area
The link to help and dialog box for
keyword search appears.
2. Menu area
The dialog box for switching to the
user mode and administrator mode
appears, and each mode's menu will
be displayed.
If you select menu, it's content will be
shown on the work area, or the sub area.
4
4
3
ZZZ008S
3. Display area
Displays the contents of the item selected in the menu area.
Machine information in the display
area is not automatically updated.
Click [Refresh] at the upper right in the
display area to update the machine information. Click the Web browser's
[Refresh] button to refresh the entire
browser screen.
Machine status, network interface
board names, and comments are displayed.
70
4. Help
Use Help to view or download Help
file contents.
Page 77

When user authentication is set
Login (using Web Image Monitor)
Follow the procedure below to log on
when user authentication is set.
Click [Login].
AAAA
Enter a login user name and pass-
BBBB
word, and then click [OK].
Using Web Image Monitor
For details about the user name
and password, consult your network administrator.
Note
❒ For user code authentication,
enter a user code in [User Name],
and then click [OK].
❒ The procedure may differ de-
pending on the Web browser
used.
Log Off (using Web Image Monitor)
Click [Logout] to log off.
Note
❒ When you log on and made the
setting, always click [Logout].
4
71
Page 78

Monitoring and Configuring the Printer
About Menu and Mode
There are two modes available with Web Image Monitor: user mode and administrator mode.
Displayed Items may differ depending on the machines.
❖ About User Mode
In the user mode, machine status, settings, and print job status can be viewed,
but the machine settings cannot be changed.
4
1
2
3
1. Status
Machine status, including the amount
of remaining paper in paper trays and
the amount of remaining toner, is displayed.
2. Job
Allows you to display list of Spooled
print Job, Job History, Error Log,
Locked Print and Sample Print jobs.
This also perform or delete Locked
Print and Sample print jobs.
ZZZ009S
3. Configuration
Display current machine and network settings, and download help
files.
72
Page 79

Using Web Image Monitor
❖ Administrator Mode
In the administrator mode, you can configure various machine settings.
1
2
3
4
5
6
ZZZ010S
4
1. Status
Machine status, including the amount
of remaining paper in paper trays and
the amount of remaining toner, is displayed.
2. Job
Allows you to display list of Spool
Print Job, Job History, Error Log,
Locked Print and Sample Print jobs.
This also allows you to delete Spooled
Print Job, Locked Print and Sample
Print jobs.
3. Address Book
User information can be registered,
displayed, changed, and deleted.
4. Configuration
Make system settings for the machine,
interface settings, and security.
5. Reset Printer Job
Click to reset current print jobs and
print jobs in queue. This button is located on Top Page.
6. Reset Device
Click to reset the printer. If a print job
is being processed, the printer will be
reset after the print job is completed.
This button is located on Top Page.
73
Page 80

Monitoring and Configuring the Printer
4
Access in the Administrator Mode
Follow the procedure below to access
Web Image Monitor in the administrator mode.
On Top Page, click [Login].
AAAA
The dialog box for entering the
user name and password appears.
Enter your user name and pass-
BBBB
word, and then click [OK].
For details about the user name
and password, consult your network administrator.
Note
❒ For user authentication, enter a
login user name and password,
and then click [OK].
❒ For user code authentication,
enter a user code in [User Name],
and then click [OK].
Displaying Web Image Monitor Help
When using Help for the first time,
clicking either [Help] in the header
area or the icon marked "?" in the display area makes the following screen
appear, in which you can view Help
in two different ways, as shown below:
❖❖❖❖ Viewing Help on our Web site
Downloading Help to your computer
❖❖❖❖ Downloading and Checking Help
You can download Help to your
computer. As the Help URL, you
can specify the path to the local file
to view the Help without connecting to the Internet.
Note
❒ By clicking [Help] in the header ar-
ea, the contents of Help appear.
❒ By clicking "?", the Help icon in the
display area, Help for the setting
items in the display area appears.
74
Page 81

Using Web Image Monitor
Downloading Help
In the [OS] list, select the operat-
AAAA
ing system.
In the [Language] list, select the
BBBB
language.
Click [Download].
CCCC
Download Help by following the
DDDD
instructions on the screen.
Store the downloaded compressed
E
file in a location, and then decompress the file.
To view the downloaded Web Image Monitor Help, set the path to
the location of the decompressed
file.
Linking the URL of the Help File to the [Help] Button.
You can link the URL of the help file
on a computer or Web server to the
[Help] button.
Log on to Web Image Monitor in
AAAA
the administrator mode.
In the menu area, click [Configura-
BBBB
tion].
Click [Webpage].
CCCC
In the [Help URL] box, enter the
DDDD
URL of the help file.
If you saved the help file to
"C:\HELP\EN", enter "file://C:/
HELP/". For example, if you saved
the file to a Web server, and the
URL of the index file is "http://
a.b.c.d/HELP/EN/index.html",
enter "http://a.b.c.d/HELP/".
4
Click [Apply].
EEEE
75
Page 82

Monitoring and Configuring the Printer
Using SmartDeviceMonitor for Admin
4
Using SmartDeviceMonitor for Admin, you can monitor the network
printers. Also, you can change the
configuration of the network interface board using TCP/IP or IPX/SPX.
❖❖❖❖ Protocol stack provided with Operat-
ing System
• Windows 95/98/Me
TCP/IP
IPX/SPX
NetWare
NetWare Client32 for Windows
95
IntraNetWare Client for Windows 95
Novell Client for Windows
95/98/Me
• Windows 2000
TCP/IP
IPX/SPX
NetWare
Novell Client for Windows
NT/2000/XP
❖❖❖❖ Available operations
The following functions are available:
• Limits settings done from the
control panel, and disables
changes made to certain items.
• Enables selection of paper type
loaded in the machine.
• Switches to, and comes out of
Energy Saver mode.
• Checks information about printing, paper quantity, etc.
• Simultaneously monitors multiple printers. When there are
many printers, you can create
groups and classify printers to
facilitate management.
• Checks the machine's network settings and detailed device information.
• Enables you to change the machine's network settings.
• You can check details of print
jobs sent from a computer.
76
• Windows Server 2003
TCP/IP
IPX/SPX
• Windows XP
TCP/IP
IPX/SPX
Novell Client for Windows
NT/2000/XP
• Windows NT 4.0
TCP/IP
IPX/SPX
Client Service for NetWare
NetWare Client32 for Windows
NT
IntraNetWare Client for Windows NT
Novell Client for Windows
NT/2000/XP
• Allows you to check job histories
of printed, faxed (LAN-Fax),
scanned, and photocopied documents identified by user codes.
• Allows selection of functions such as
printing and scanning for each user code.
• Fax numbers and e-mail addresses stored in the machine can be
changed and saved by computer.
• You can check each fax job history entry.
• You can make settings for and
display the status changes of
group devices.
• Using Address Management Tool,
you can manage LAN-Fax numbers, user names for Scan to
Folder, and addresses for sending and receiving Internet faxes.
• The e-mail sender’s name and
folder can be protected.
Page 83

Using SmartDeviceMonitor for Admin
Installing SmartDeviceMonitor for Admin
Follow the procedure below to install
SmartDeviceMonitor for Admin
Quit all applications currently running.
AAAA
Insert the CD-ROM into the CD-
BBBB
ROM drive.
The installer starts.
Note
❒ Auto Run may not work under
certain operating system settings. In this case, launch “Set-
up.exe” located on the CDROM root directory.
Select an interface language, and
CCCC
then click [OK].
The following languages are available: Czech, Danish, German, English,
Spanish, French, Italian, Hungarian,
Dutch, Norwegian, Polish, Portuguese , Finnish, Swedish, Chinese
Simple and Chinese Traditional.
Changing the Network Interface Board Configuration
Follow the procedure below to
change the network interface board
configuration using SmartDeviceMonitor for Admin.
Start SmartDeviceMonitor for Admin.
AAAA
On the [
BBBB
Device
IPX/SPX
[
machines using the selected protocol appears.
❒ Select the protocol of the ma-
❒ If you are using TCP/IP SNMP
In the list, select a machine whose
CCCC
configuration you want to change.
On the [Tools] menu, click [NIB Set-
DDDD
up Tool].
Group
] menu, point to [
], and then click [
] or [
TCP/IP(SNMPv3)
Note
chine whose configuration you
want to change.
v3, enter the user authentication.
Search
TCP/IP
]. A list of
],
4
Click [SmartNetMonitor for Client/Admin]
DDDD
installation, and then click [Next].
The software license agreement appears
EEEE
in the [
After reading through its contents,
click [I accept the agreement] if you
agree, and then click [Next >].
Follow the instructions on the screen.
FFFF
A message appears when the installation is complete.
Click [OK].
GGGG
❒ If you are required to restart the
License Agreement
Note
computer after installing SmartDeviceMonitor for Admin, restart the computer and continue
the configuration.
] dialog box.
A Web browser opens and the dialog box for entering the user name
and password for the Web Image
Monitor administrator appears.
For details about the user name
and password, consult your network administrator.
NIB Setup Tool starts when the network interface board is default. Click
[Web Browser], and then click [OK].
Enter required setting items.
EEEE
Configure settings using Web Image Monitor. For details, see p.69
“Using Web Image Monitor”.
Quit Web Image Monitor.
FFFF
Quit SmartDeviceMonitor for Admin.
GGGG
77
Page 84

Monitoring and Configuring the Printer
4
Locking the Menus on the Machine's Control Panel
Follow the procedure below to lock the
menus on the machine's control panel.
Start SmartDeviceMonitor for Admin.
AAAA
On the [
BBBB
Device
IPX/SPX
[
A list of machines using the selected protocol appears.
❒ Select the protocol of the ma-
❒ If you are using TCP/IP SNMP
Select a machine.
CCCC
Group
] menu, point to [
], and then click [
] or [
TCP/IP(SNMPv3)
Note
chine whose configuration you
want to change.
v3, enter the user authentication.
Search
TCP/IP
].
],
Changing the Paper Type
Follow the procedure below to change
the paper type.
Start SmartDeviceMonitor for Admin.
AAAA
On the [
BBBB
Device
IPX/SPX
[
A list of machines using the selected protocol appears.
❒ Select the protocol of the ma-
❒ If you are using TCP/IP SNMP
In the list, select a machine whose
CCCC
configuration you want to change.
Group
] menu, point to [
], and then click [
] or [
TCP/IP(SNMPv3)
Note
chine whose configuration you
want to change.
v3, enter the user authentication.
Search
TCP/IP
].
],
78
On the [Tools] menu, point to [De-
DDDD
vice Settings], and then click [Lock
Operation Panel Menu].
A Web browser opens and the dialog box for entering the password
for the Web Image Monitor administrator appears.
Enter the user name and pass-
EEEE
word, and then click [OK].
For details about the user name
and password, consult your network administrator.
The [System] page of Web Image
Monitor appears.
Select [Level 1] or [Level 2] in the
FFFF
[Protect Printer Operation Panel] list.
Click [Apply].
GGGG
Quit Web Image Monitor.
HHHH
Reference
For details about setting items,
see Help in the [General Settings]
on [Configuration] page.
On the [Tools] menu, point to [De-
DDDD
vice Settings], and then click [Select
Paper Type].
A Web browser opens and the dialog box for entering the password
for the Web Image Monitor administrator appears.
Enter the user name and pass-
EEEE
word, and then click [OK].
For details about the user name
and password, consult your network administrator.
The [Paper] page appears.
Select a paper type in the [Paper
FFFF
Type] list for each tray.
Click [Apply].
GGGG
Quit Web Image Monitor.
HHHH
Reference
For details about setting items,
see Help in the [General Settings]
on [Configuration] page.
Page 85

Using SmartDeviceMonitor for Admin
Managing User Information
Follow the procedure below to manage the user's information using
SmartDeviceMonitor for Admin.
Prints jobs can be managed and functions restricted by user codes.
Starting User Management Tool
Follow the procedure below to start
User Management Tool.
Start SmartDeviceMonitor for Admin.
AAAA
On the [
BBBB
Device
IPX/SPX
[
A list of machines using the selected protocol appears.
❒ Select the protocol of the ma-
❒ If you are using TCP/IP SNMP
In the list, select a machine you
CCCC
want to manage.
On the [Tools] menu, click [User
DDDD
Management Tool].
The dialog box for entering the
user name and password appears.
Enter the user name and pass-
EEEE
word, and then click [OK].
For details about the user name
and password, consult your network administrator.
Group
] menu, point to [
], and then click [
] or [
TCP/IP(SNMPv3)
Note
chine whose configuration you
want to change.
v3, enter the user authentication.
Search
TCP/IP
].
],
Displaying the Number of Sheets Printed
Follow the procedure below to display the number of sheets printed under each user code.
Start SmartDeviceMonitor for Admin
AAAA
User Information Management Tool.
Click the [User Page Count] tab of
BBBB
User Management Tool.
The number of pages printed under each user code appears.
Click [Finish] on the [File] menu to
CCCC
quit User Management Tool.
Exporting the information about the number of pages printed
Follow the procedure below to export
the information of the number of pages printed under each user code as a
.csv file.
Start SmartDeviceMonitor for Admin
AAAA
User Information Management Tool.
Click the [User Page Count] tab of
BBBB
User Management Tool.
On the [File] menu, click [Export
CCCC
User Statics List].
Specify the save location and file
DDDD
name, and then click [Save].
Click [Finish] on the [File] menu to
EEEE
quit User Management Tool.
4
User Management Tool starts.
Reference
For details about User Management Tool, see SmartDeviceMonitor for Admin Help.
79
Page 86

Monitoring and Configuring the Printer
4
Resetting the number of pages printed to 0.
Follow the procedure below to reset
the number of pages printed under
each user code to 0.
Start SmartDeviceMonitor for Admin
AAAA
User Information Management Tool.
Click the [User Page Count] tab of
BBBB
User Management Tool.
Click the user whose information
CCCC
you want to reset.
On the [Edit] menu, click [Reset
DDDD
User Counters].
Select the check box of the items
EEEE
you want to reset, and then click
[OK].
A confirmation message appears.
Click [Yes].
FFFF
Restricting Functions
Follow the procedure below to restrict use of individual functions.
Start SmartDeviceMonitor for Admin
AAAA
User Information Management Tool.
On the [Edit] menu of User Man-
BBBB
agement Tool, click [Restrict Ac-
cess To Device].
Select the check box of the func-
CCCC
tions you want to restrict.
Click [OK].
DDDD
A confirmation message appears.
Click [Yes].
EEEE
The settings are applied.
The number of pages printed is reset to 0.
On the [Edit] menu, click [Apply
GGGG
Settings].
Changes are applied to information on the [User Page Count] tab.
Click [Finish] on the [File] menu to
HHHH
quit User Management Tool.
80
Page 87

Using SmartDeviceMonitor for Admin
Setting Applicable Functions to New Users
Follow the procedure below to add
new users and set functions applicable to them.
Start SmartDeviceMonitor for Admin
AAAA
User Information Management Tool.
Click the [Access Control List] tab of
BBBB
User Management Tool.
On the [Edit] menu, click [Add New
CCCC
User].
Enter the user code and user name.
DDDD
Select the check box of the func-
EEEE
tions applicable to the new user.
Note
❒ If the check boxes are unavaila-
ble, there is no restriction to use
that function. For details, see
SmartDeviceMonitor for Admin Help.
Click [OK].
FFFF
The new user is added.
On the [Edit] menu, click [Apply
GGGG
Settings].
The settings are applied.
Click [Finish] on the [File] menu to
HHHH
quit User Management Tool.
Reference
For details about setting restrictions, see SmartDeviceMonitor
for Admin Help.
Configuring the Energy Saver Mode
Follow the procedure below to configure Energy Saver mode.
Start SmartDeviceMonitor for Admin.
AAAA
On the [
BBBB
Device
IPX/SPX
[
A list of machines using the selected protocol appears.
❒ Select the protocol of the ma-
❒ If you are using TCP/IP SNMP
Select the machine whose settings
CCCC
you want to make.
To make settings for all machines in
the selected group, select no machine.
On the [Group] menu, point to [En-
DDDD
ergy Save Mode], point to [Set Individually] to make the settings for
only the selected machine or
point to [Set By Group] to make the
settings for all machines in the selected group, and then click [On]
or [Off].
Quit SmartDeviceMonitor for
EEEE
Admin.
Group
] menu, point to [
], and then click [
] or [
TCP/IP(SNMPv3)
Note
chine whose configuration you
want to change.
v3, enter the user authentication.
Reference
For details about the setting value for Energy Saver mode, see
SmartDeviceMonitor for Admin Help.
Search
TCP/IP
].
],
4
81
Page 88

Monitoring and Configuring the Printer
Setting a Password
On the [New Password], enter a pass-
JJJJ
word.
4
Follow the procedure below to set a
password.
Start SmartDeviceMonitor for Admin.
AAAA
On the [
BBBB
Device
IPX/SPX
[
A list of machines using the selected protocol appears.
❒ Select the protocol of the ma-
❒ If you are using TCP/IP SNMP
In the list, select a machine whose
CCCC
configuration you want to change.
On the [Tools] menu, click [NIB Set-
DDDD
up Tool].
A Web browser opens and the dialog box for entering the password
for the Web Image Monitor administrator appears.
Group
] menu, point to [
], and then click [
] or [
TCP/IP(SNMPv3)
Note
chine whose configuration you
want to change.
v3, enter the user authentication.
Search
TCP/IP
].
],
Enter the same password in [Con-
firm Password] .
Click [OK].
KKKK
Quit Web Image Monitor.
LLLL
Quit SmartDeviceMonitor for Admin.
MMMM
82
NIB Setup Tool starts when the
network interface board is default.
Click [Web Browser], and then click
[OK].
Enter the user name and pass-
EEEE
word, and then click [OK].
For details about the user name
and password, consult your network administrator.
Top Page of Web Image Monitor
appears.
Click [Configuration].
FFFF
Click [Device Settings].
GGGG
Click [Program/Change Administrator].
HHHH
Click [Change].
IIII
Page 89

Using SmartDeviceMonitor for Admin
Checking the Machine Status
Follow the procedure below to check
machine status.
Start SmartDeviceMonitor for Admin.
AAAA
On the [
BBBB
Device
IPX/SPX
[
The status of machines is indicated
by icons in the list.
❒ For details about status icons,
❒ If you are using TCP/IP SNMP
To obtain status details, click the
CCCC
machine in the list, and then click
[Open] on the [Device] menu.
The machine status appears in the
dialog box.
Quit SmartDeviceMonitor for Admin.
DDDD
❒ For details about items in the di-
Group
] menu, point to [
], and then click [
] or [
TCP/IP(SNMPv3)
Note
see SmartDeviceMonitor for
Admin Help.
v3, enter the user authentication.
Note
alog box, see SmartDeviceMonitor for Admin Help.
Search
TCP/IP
].
],
Changing Names and Comments
Follow the procedure below to
change the names and comments of
the machine.
Start SmartDeviceMonitor for Admin.
AAAA
On the [
BBBB
Device
IPX/SPX
[
A list of machines using the selected protocol appears.
❒ Select the protocol of the ma-
❒ If you are using TCP/IP SNMP
Select a machine in the list.
CCCC
On the [Tools] menu, click [NIB Set-
DDDD
up Tool].
A Web browser opens and the dialog box for entering the password
for the Web Image Monitor administrator appears.
NIB Setup Tool starts when the
network interface board is default.
Click [Web Browser], and then click
[OK].
Group
] menu, point to [
], and then click [
] or [
TCP/IP(SNMPv3)
Note
chine whose configuration you
want to change.
v3, enter the user authentication.
Search
TCP/IP
].
],
4
Enter the user name and password,
EEEE
and then click [OK].
Top Page of Web Image Monitor appears.
For details about the user name
and password, consult your network administrator.
Click [Configuration].
FFFF
Click [Device Settings].
GGGG
83
Page 90

Monitoring and Configuring the Printer
On the [System] page, enter the de-
HHHH
vice name in the [Device name:] box
and a comment in the [Comment]
box, and click [Apply].
Load Fax Journal
Start SmartDeviceMonitor for Admin.
AAAA
4
• In the [Device name:] box, enter a
device name on the machine using up to 31 characters.
• In the [Comment] box, enter a
comment on the machine using
up to 31 characters.
Click [OK].
IIII
Quit Web Image Monitor.
JJJJ
Quit SmartDeviceMonitor for Admin.
KKKK
On the [
BBBB
Device
IPX/SPX
[
A list of machines using the selected protocol appears.
❒ Select the protocol of the ma-
❒ If you are using TCP/IP SNMP
Select a machine.
CCCC
On the [Tools] menu, click [Load
DDDD
Fax Journal].
A Web browser opens and the dialog box for entering the user name
and password for the Web Image
Monitor administrator appears.
For details about the user name
and password, consult your network administrator.
Group
] menu, point to [
], and then click [
] or [
TCP/IP(SNMPv3)
Note
chine whose configuration you
want to change.
v3, enter the user authentication.
TCP/IP
].
Search
],
84
Check the Load Fax Journal area
EEEE
that appears in the Web Image
Monitor.
Reference
For details, see Help in Load
Fax Journal area.
Page 91

Using SmartDeviceMonitor for Admin
Viewing and Deleting Spool Print Jobs
Start SmartDeviceMonitor for Admin.
AAAA
On the [
BBBB
Device
IPX/SPX
[
A list of machines using the selected protocol appears.
❒ Select the protocol of the ma-
❒ If you are using TCP/IP SNMP
Select a machine.
CCCC
On the [Tools] menu, click [Spool
DDDD
Printing Job List(Printer)].
Group
] menu, point to [
], and then click [
] or [
TCP/IP(SNMPv3)
Note
chine whose configuration you
want to change.
v3, enter the user authentication.
Search
TCP/IP
].
Managing Address Information
Start SmartDeviceMonitor for Admin.
AAAA
On the [
BBBB
],
Device
IPX/SPX
[
A list of machines using the selected protocol appears.
❒ Select the protocol of the ma-
❒ If you are using TCP/IP SNMP
Select a machine.
CCCC
On the [Tools] menu, click [Address
DDDD
Management Tool].
Group
] menu, point to [
], and then click [
] or [
TCP/IP(SNMPv3)
Note
chine whose configuration you
want to change.
v3, enter the user authentication.
Search
TCP/IP
].
],
4
A Web browser opens and the dialog box for entering the user name
and password for the Web Image
Monitor administrator appears.
For details about the user name
and password, consult your network administrator.
Check the Spool Printing Job List
EEEE
that appears in the Web Image
Monitor.
To delete the Spool Printing Job,
select the document you want to
delete and then click [Delete].
Note
❒ To display Spool Printing Job List,
spool must be set to [Enable] on
Web Image Monitor in advance.
Reference
For details, see Help in Spool
Printing Job List area.
The dialog box for entering the
user name and password appears.
Enter the user name and pass-
EEEE
word, and then click [OK].
Address Management Tool starts.
For details about the user name
and password, consult your network administrator.
Reference
For details, see Address Management Tool Help.
85
Page 92

4
Monitoring and Configuring the Printer
Using SmartDeviceMonitor for Client
To view the status of machines using
SmartDeviceMonitor for Client, configure SmartDeviceMonitor for Client
beforehand.
Monitoring Printers
Follow the procedure below to monitor the machine using SmartDeviceMonitor for Client.
Start SmartDeviceMonitor for Client.
AAAA
The SmartDeviceMonitor for Client icon appears in the task tray.
Right-click the SmartDeviceMon-
BBBB
itor for Client icon, and check that
the machine appears on the popup menu.
Checking the Machine Status
Follow the procedure below to check
machine status using SmartDeviceMonitor for Client.
Start SmartDeviceMonitor for Client.
AAAA
For status details, right-click the
BBBB
SmartDeviceMonitor for Client
icon, and then click the machine.
The machine status appears in the
dialog box.
Note
❒ For details about items in the di-
alog box, see SmartDeviceMonitor for Client Help.
Click [Options...] on the pop-up
CCCC
menu if the machine does not appear on the pop-up menu.
The [SmartDeviceMonitor for Client -
Options] dialog box appears.
Click the machine you want to
DDDD
monitor, and then select the [To Be
Monitored] check box in the [Monitoring Information Settings] area.
Note
❒ To display the machine status in
the task tray using the SmartDeviceMonitor for Client icon, select the [Displayed on Task Bar]
check box.
❒ For details about status icons,
see SmartDeviceMonitor for
Client Help.
Click [OK].
EEEE
The dialog box closes and the configured machine is monitored.
86
Page 93

When Using IPP with SmartDeviceMonitor for Client
When using IPP with SmartDeviceMonitor for Client, note the following:
• The network printer can only receive one print job from SmartDeviceMonitor for Client at a time.
While the network printer is printing, another user cannot access it
until the job is finished. In this
case, SmartDeviceMonitor for Client tries to access the network
printer until the retry interval expires.
• If SmartDeviceMonitor for Client
cannot access the network printer
and times out, it will stop sending
the print job. In this case, you
should cancel the paused status
from the print queue window.
SmartDeviceMonitor for Client
will resume access to the network
printer. You can delete the print
job from the print queue window,
but canceling a print job printed by
the network printer might cause
the next job sent from another user
to be incorrectly printed.
• If a print job sent from SmartDeviceMonitor for Client is interrupted and the network printer cancels
the job because something went
wrong, send the print job again.
• Print jobs sent from another computer do not appear in the print
queue window, regardless of protocol.
Using SmartDeviceMonitor for Client
• If various users send print jobs using SmartDeviceMonitor for Client
to network printers, the printing
order might not be the same as that
in which the jobs were sent.
• An IP address cannot be used for
the IPP port name because the IP
address is used for the SmartDeviceMonitor for Client port name.
• When setting SSL, a protocol for
encrypted communication, under
environment which server authentification is issued, enter "https://(machine's address)/".
Internet Explorer must be installed
on your computer. Use the highest
version. Internet Explorer 6.0 or
higher is recommended.
• If the [Security Alert] dialog box ap-
pears when accessing the machine
using IPP to create or configure an
IPP port, or when printing, install
the certificate. To select the certificate store location when using Certificate Import Wizard, click [Place
all certificates in the following store],
and then click [Local Computer] under [Trusted Root Certification Author-
ities].
Note
❒ For details about SSL settings,
consult your network administrator.
4
87
Page 94

Monitoring and Configuring the Printer
Remote Maintenance by telnet
4
Important
❒ Remote Maintenance should be
password-protected so that access
is allowed to administrators only.
❒ The password is the same as the
one of Web Image Monitor administrator. When the password is
changed using "mshell", other
passwords change also.
❒ Some command cannot be set de-
pending on the model type.
Using telnet
Follow the procedure below to use
telnet.
Important
❒ Only one user at a time can log on
to perform remote maintenance.
Use the IP address or the host name
AAAA
of the machine to start telnet.
% telnet IP_address
Enter your user name and password.
BBBB
For details about the user name
and password, consult your network administrator.
Quit telnet.
DDDD
msh> logout
The configuration message about
saving the changes appears.
Enter "yes" to save the changes,
EEEE
and then press the {# Enter} key.
If you do not want to save the
changes, enter "no", and then press
the {# Enter} key. To make further
changes, enter "return" at the command line, and then press the {# En-
ter} key.
Note
❒ If the message "Can not write
NVRAM information" appears,
the changes are not saved. Repeat the procedure above.
❒ When the changes are saved,
the network interface board is
reset automatically with that
changes.
❒ When the network interface
board resets, the print job in print
process will be printed. However, print jobs in queue will be
canceled.
88
Note
❒ For user authentication, enter a
login user name and password,
and then click [OK].
❒ For user code authentication,
enter a user code in [User Name],
and then click [OK].
Enter a command.
CCCC
Page 95

Remote Maintenance by telnet
access
Use the “access” command to view
and configure access control. You can
also specify two or more access ranges.
❖❖❖❖ View settings
msh> access
❖❖❖❖ Configuration
msh> access ✩ range “startaddress end-address”
• ✩ represents a target number
between 1 and 5. (Up to five access ranges can be registered
and selected.)
Example: to specify accessible IP
addresses between 192.168.0.10
and 192.168.0.20:
msh> access 1 range
192.168.0.10 192.168.0.20
appletalk
Use the “appletalk” command to view
and configure Appletalk parameters.
❖❖❖❖ View settings
msh> appletalk
• [2] means "active" and [0]
means "inactive".
• The default is [2].
❖❖❖❖ Changing PAP timeout configuration
msh> appletalk ptimeout
value > 0
• Timeout value becomes effective.
msh> appletalk ptimeout
value = 0
• Timeout value becomes ineffective.
4
❖❖❖❖ Access control initialization
msh> access flush
• Use the "flush" command to restore the default settings so that
all access ranges become
"0.0.0.0".
Note
❒ The access range restricts comput-
ers from use of the machine by IP
address. If you do not need to restrict printing, make the setting
"0.0.0.0".
❒ Valid ranges must be from lower
(start address) to higher (end address).
❒ Up to five access ranges can be
specified. The entry is invalid if the
target number is omitted.
❒ You cannot access Web Image Mon-
itor from a restricted IP address.
89
Page 96

Monitoring and Configuring the Printer
4
autonet
Use the “autonet” command to configure AutoNet parameters.
❖❖❖❖ View settings
The following command displays
the current AutoNet settings:
msh> autonet
❖❖❖❖ Configuration
You can configure AutoNet settings.
msh> autonet {on|off}
• {on} means "active" and {off}
means "inactive".
❖❖❖❖ Current interface priority configura-
tion display
msh> autonet priority
❖❖❖❖ Interface priority configuration
msh> autonet priority
“interface_name”
• You can give interface's AutoNet parameter priority.
• Priority settings are available
when multiple interfaces are installed.
• ip1394 can be specified only
when the IEEE 1394 interface is
installed.
• wlan can be specified only when
the IEEE 802.11b interface is installed.
Interface name Interface config-
ured
ether Ethernet interface
btconfig
Use the "btconfig" command to make
Bluetooth settings.
❖❖❖❖ View settings
Bluetooth settings are displayed.
msh> btconfig
❖❖❖❖ Mode settings
You can set the Bluetooth operation mode to {private} or {public}.
msh> btconfig {private |
public}
• The default is {public}.
devicename
Use the "devicename" command to
display and change the printer name.
❖❖❖❖ View settings
msh> devicename
❖❖❖❖ Printer name configuration
msh> devicename name
“string”
• Enter a printer name using up
to 31 alphanumeric characters.
• Set single names for each printer.
❖❖❖❖ Printer name initialization
msh> devicename clear name
• Reset the printer name to its default.
ip1394 IEEE 1394 interface
wlan IEEE 802.11b inter-
face
Note
❒ If an interface is not selected, the
current interface connection set-
90
tings remain in effect.
Page 97

dhcp
Use the "dhcp" command to configure DHCP settings.
❖❖❖❖ View settings
The following command displays
the current DHCP settings.
msh> dhcp
❖❖❖❖ Configuration
You can configure DHCP.
msh> dhcp “interface_name”
{on|off}
• Click {on} to enable dhcp. Click
{off} to disable DHCP.
• If the DNS server address and
domain name are obtained from
DHCP, be sure to click {on}.
• ip1394 can be specified only
when the IEEE 1394 interface is
installed.
• wlan can be specified only
when the IEEE 802.11b interface
is installed.
Interface name Interface config-
ured
ether Ethernet interface
ip1394 IEEE 1394 interface
wlan IEEE 802.11b inter-
face
Remote Maintenance by telnet
❖❖❖❖ DNS server address selection
msh> dhcp dnsaddr {dhcp |
static}
• Specify whether to obtain the
DNS server address from the
DHCP server or use the address
set by a user.
• To obtain the DNS server address
from the DHCP server, specify
"dhcp". To use the address set by
a user, specify "static".
❖❖❖❖ Domain name selection
msh> dhcp domainname {dhcp
| static}
• Specify whether to obtain the
domain name from the DNS
server or use the domain name
set by a user.
• To obtain the domain name from
the DHCP server, specify "dhcp".
To use the domain name set by a
user, specify "static".
Reference
For details about DHCP functions,
see p.139 “Using DHCP”.
For details about setting the DNS
server address, see p.92 “dns”.
For details about setting the domain name, see p.93 “domain-
name”.
4
❖❖❖❖ Current interface priority configura-
tion display
msh> dhcp priority
❖❖❖❖ Interface priority configuration
msh> dhcp priority
“interface_name”
• You can select which interface
has DHCP parameter priority.
• Priority settings are available
when multiple interfaces are installed.
91
Page 98

Monitoring and Configuring the Printer
4
diprint
The direct printing port enables direct
printing from a network-connected
computer.
Use the “diprint” command to change
direct printing port settings.
❖❖❖❖ View settings
The following command displays
the current direct printing port settings:
msh> diprint
Example output:
port 9100
timeout=300(sec)
bidirect on
• The “port” specifies the port
number of the direct printing
port.
• The “bidirect” setting indicates
whether the direct printing port
is bidirectional or not.
❖❖❖❖ Setting timeout
msh> diprint timeout {30–
65535}
• You can specify the timeout interval to use when the printer is
expecting data from the network.
• The default is 300 seconds.
❖❖❖❖ Setting bidirect
msh> diprint bidirect { on
| off }
• You can specify whether the direct printing port is bidirectional or not.
dns
Use the “dns” command to configure
or display DNS (Domain Name System) settings.
❖❖❖❖ View settings
The following command displays
current DNS settings:
msh> dns
❖❖❖❖ DNS server configuration
The following command enables or
disables the DNS server address:
msh> dns “number” server
“server address”
The following command displays
a configuration using the IP address 192.168.15.16 on a DNS 1
server:
msh> dns 1 server 192.168.
15.16
• You can register up to three
DNS server numbers.
• You cannot use “255.255.255.255”
as the DNS server address.
❖❖❖❖ Dynamic DNS function setting
msh> dns “interface_name”
ddns {on|off}
• You can set the dynamic DNS
function "active" or "inactive".
• {on} means "active" and {off}
means "inactive".
• ip1394 can be specified only
when the IEEE 1394 interface is
installed.
• wlan can be specified only
when the IEEE 802.11b interface
is installed.
92
Interface name
ether Ethernet interface
ip1394 IEEE 1394 interface
wlan
Interface configured
IEEE 802.11b interface
Page 99

Remote Maintenance by telnet
❖❖❖❖ Specifying the record overlap opera-
tion
msh> dns overlap {update|add}
• You can specify operations performed when records overlap.
• update
To delete old records and register new records.
• add
To add new records and store
the old records.
• When CNAME overlaps, it is always changed, irrespective of
settings.
❖❖❖❖ CNAME registration
msh> dns cname {on|off}
• You can specify whether to register CNAME.
• {on} means "active" and {off}
means "inactive".
• The CNAME registered is the
default name beginning with
rnp. CNAME cannot be
changed.
❖❖❖❖ A records registration
❖❖❖❖ Record updating interval settings
msh> dns interval “time”
• You can specify the interval after which records are updated
when using the dynamic DNS
function.
• The updating interval is specified hourly. It can be entered between 1 and 255 hours.
• The default is 24 hours.
domainname
Use the "domainname" command to
display or configure the domain
name settings.
You can configure the Ethernet interface, IEEE 1394 interface, or IEEE
802.11b interface.
❖❖❖❖ View settings
The following command displays
the current domain name:
msh> domainname
❖❖❖❖ Interface domain configuration
msh> domainname “interface_
name”
4
msh> dns arecord {dhcp|own}
• {dhcp}
You can specify the method of
registering an A record when
the dynamic DNS function is
enabled and DHCP is used.
• {own}
To register an A record using
the printer as the DNS client.
The DNS server address and the
domain name already designated are used for the registration.
93
Page 100

4
Monitoring and Configuring the Printer
❖❖❖❖ Setting the Domain Name
msh> domainname “interface_
name” name “domain name”
• A domain name can be entered
using up to 63 alphanumeric
characters.
• The Ethernet interface and IEEE
802.11b interface will have the
same domain name.
• ip1394 can be specified only
when the IEEE 1394 interface is
installed.
• wlan can be specified only when
the IEEE 802.11b interface is installed.
Interface Interface set
ether Ethernet interface
ip1394 IEEE 1394 interface
wlan IEEE 802.11b inter-
face
❖❖❖❖ Deleting the Domain Name
msh> domainname “interface_
name” clear name
hostname
Use the “hostname” command to
change the printer name.
❖❖❖❖ View settings
msh> hostname
❖❖❖❖ Configuration
msh> hostname “interface_
name ” “printer_name”
• Enter the printer name using
up to 63 alphanumeric characters.
• You cannot use a printer name
starting with "RNP" or "rnp".
• The Ethernet interface and IEEE
802.11b interface will have the
same printer name.
• ip1394 can be specified only
when the IEEE 1394 interface is
installed.
• wlan can be specified only
when the IEEE 802.11b interface
is installed.
help
Use the "help" command to display
the available command list and the
procedures for using those commands.
❖❖❖❖ Command list display
msh> help
❖❖❖❖ Display of procedure for using com-
mands
msh> help “command_name”
94
Interface name Interface config-
ured
ether Ethernet interface
ip1394 IEEE 1394 interface
wlan
IEEE 802.11b interface
❖❖❖❖ Initializing the printer name for each
interface
msh> hostname “interface_
name” clear name
 Loading...
Loading...