Ricoh NC305 Service Manual

RICOH NC305
SERVICE MANUAL

IMPORTANT SAFETY NOTICES
PREVENTION OF PHYS ICAL INJURY
1. Before disassembling or asse mblin g pa rts of the copie r and perip herals,
make sure that the copier power cord is unplu gg ed.
2. The wall outlet should be near the copier an d easily accessible.
3. Note that some compo ne nt s of th e copier and the paper tray unit are
supplied with electrical voltage even if the main switch is turned off.
4. If any adjustment or operat ion check has to be made with exterior covers
off or open while the main switch is turned on, keep hands away from
electrified or mechanically drive n comp on ents.
5. The inside and the met al parts of the fusing unit become extre mely ho t
while the copier is operat ing . Be ca ref ul to avoid touching those
components with your bare hands.
HEALTH SAFETY CONDITIONS
1. Never operate the copier without the ozone filters installed.
2. Always replace the ozone filters with the specified ones at the specifie d
intervals.
3. Toner and developer are non-toxic, but if you get either of them in your
eyes by accident, it may cause temp ora ry e ye disco mfo rt. Try to remove
with eye drops or flush with wat er as first aid. If un succe ssfu l, ge t med ical
attention.
OBSERVANCE OF ELECTRICAL SAFETY STANDARDS
1. The copier and its peripherals must be insta lled and maintained by a
customer service represen tative who has completed the training course
on those models.
2. The RAM board on the main control board has a lithium battery which can
explode if replaced incorre ctly. Re pla ce th e ba tt ery on ly with an iden tica l
one. The manufacturer reco mmen ds replacing the entire RAM board. Do
not recharge or burn this battery. Used batteries must be handled in
accordance with local regula tio ns.

SAFETY AND ECOLOGICAL NOTES FOR DISP OS AL
1. Do not incinerate the toner cartridge or the used toner. Toner dust may
ignite suddenly when exposed to open flame.
2. Dispose of used tone r, developer, and organic photoconductors
according to local regulations. (These are non-toxic supplies.)
3. Dispose of replaced parts in acco rda nce with local regulations.
4. When keeping used lithiu m bat te ries in ord er to dispo se of them later, do
not put more than 100 batteries per seale d box. Storing larger numbers or
not sealing them apart may lead to che mical rea ctions and heat build-up.

RICOH NC305
SECTION 1
OVERALL INFORMATION
20 December 1991 SPECIFICATIONS
1. SPECIFICATIONS
Configuration: Desktop
Copy Process: Electrostatic transfer system
Originals: Book/sheet, fixed plate n
Original Alignment: Left side centered against side scale
Maximum Original Size: A3, 11" x 17"
Copy Paper Size: Maximum: A3, 11" x 17"
Minimum: A6R, 81/2" x 51/2 " lengthwise
Copy Paper Weight: Black or single color copies: 52 to 104 g
14 to 28 lb
Full color copies: 64 to 104 g
17 to 28 lb
Copying Speed:
A4 sideways,
1/2" x 11"
8
sideways, or
smaller sizes.
Black 30 cpm 12 cpm
Single Color
(1C and 2C)
Full Color (3C) 5 cpm 4 cpm
Full Color (6C) 2.5 cpm 2 cpm
7.5 cpm 6 cpm
A4 lengthwise,
1/2" x 11"
8
lengthwise, or
larger sizes.
First Copy
(A4, 81/2" x 11" sideways):
Warm-up Time:
Black: 6 seconds (9.0 s for ID
sensor check cycle)
Single Color (Y, M, C): 12 seconds
Single Color (B, G, R): 16 seconds
Full Color: 20 seconds
Photo Mode: 32 seconds
Within 3.5 minutes (Room temperature 20 °C)
1-1

SPECIFICATIONS 20 December 1991
Automatic Reset: After 60 seconds (Adju sta ble from 0 to 180
minutes by SP mode)
– Black/Color Copy: Black mode
– Copy Counter : 1
– Reproduction Ratio: Full size
– Interrupt Mode: OFF
– Sort/Stack OFF
– Image Density Auto ID
– Program Mode OFF
– All application modes: OFF
Photoconductor: Organic photoconductor drum, 120 mm in
diameter
Drum Charge: Double-wire with grid wires (Neg at ive Cha rge )
Erase Lamp: 128 LEDs (2.5 mm)
Fixed Reproduction Ratio s:4 enlargeme nt ratios and 5 reduction ratios, plus
4 programmable ratios betwe en 50% and 200%
Zoom Range: Zoom from 50% to 200% in 1% increments
(Partial enlargemen t for ra tio s abo ve 142%.)
Scanning System: One directional scanning with mirrors an d len s
Scanner Light Source: Seven halogen bulbs in series (320 W/ 80 V)
Exposure System: Slit expo sure , moving optics
Lens: Through lens, f = 215 mm, F = 4.6
Development: Dual-component dry toner system (Black: 1.0 kg,
color: 0.7 kg)
Toner Replenishment: Black: 390 gram cartridge
Color: 100 gram cartridge
Toner Consumption:
(A4 or 81/2" x 11",
Black: 6,800 copies/cartridge
Color: 1,800 copies/cartridge
7% Originals)
Development Bias: Negative variable bias
Toner Density Control: Primary: Toner density sensor in dev. unit
Secondary: Pattern density detection by
photosenso r
Image Transfer: Single wire DC corona (variable nega tive charg e
through transfer drum sheet)
1-2

20 December 1991 SPECIFICATIONS
Paper Separation: Clamp mechanism, single wire AC corona, and
pick-off pawls
OPC Drum Cleaning: Magnetic brush (250 grams of clea nin g carrier)
with bias roller and pre-cleaning corona (single
wire AC corona)
Quenching: Photo quenching by LEDs
Paper Feeding: Double universal cassett es (25 0 she et capacity)
Paper Feed System: Feed and reverse roller (FRR) system
Image Fusing: Heat and pressure type, silicone rubber rollers
and silicone oil
Fusing Lamp: Two halogen lamps, 650 W and 550 W/115 V,or
230 V
Copy Tray Capacity: 100 sheets for A3 (11" x 17")
250 sheets for all other p ape r sizes
Self-diagnostic Codes: 38 codes, indicated in the copy counter
Power Source: 115 V 60 Hz 12 A
110 V 60 Hz 13 A
220/230/240 V 50 Hz 7 A
Power Consumption: Maximum: 1.4 kW (110/115 V)
1.5 kW (220/230/240 V)
Warm-up: 0.9 kW (average)
Ready: 0.15 kW (fusing lamp off)
0.22 kW (fusing lamp on)
Copy cycle: 1.0 kW (average)
Dimensions (W x D x H): Machine body: 835 x 700 x 507 millimeters
32.87 x 27.56 x 19.9 6 inch es
Weight: Approximately 136 kg (299.8 lb)
Optional Equipment: — ARDF (automatic reverse document feeder)
— 20 bin sorter
— 3rd paper feed table
— Editor
— Large capacity tray
— Multi by-pass tray
— Key counter (locally procured )
1-3
BASIC CONCEPTS OF COLOR COPYING 20 December 1991
2. BASIC CONCEPTS OF COLOR COPYING
2.1 COLOR REPRODUCTION P ROCE SS
2.1.1 Light and Color
1) White Light
When sunlight passes thro ugh a prism, it separates into various colors.
This is because sunlight is compo sed of light of different wavelengths. It
is called "white light" since sunlig ht is sensed as "white" by the eyes.
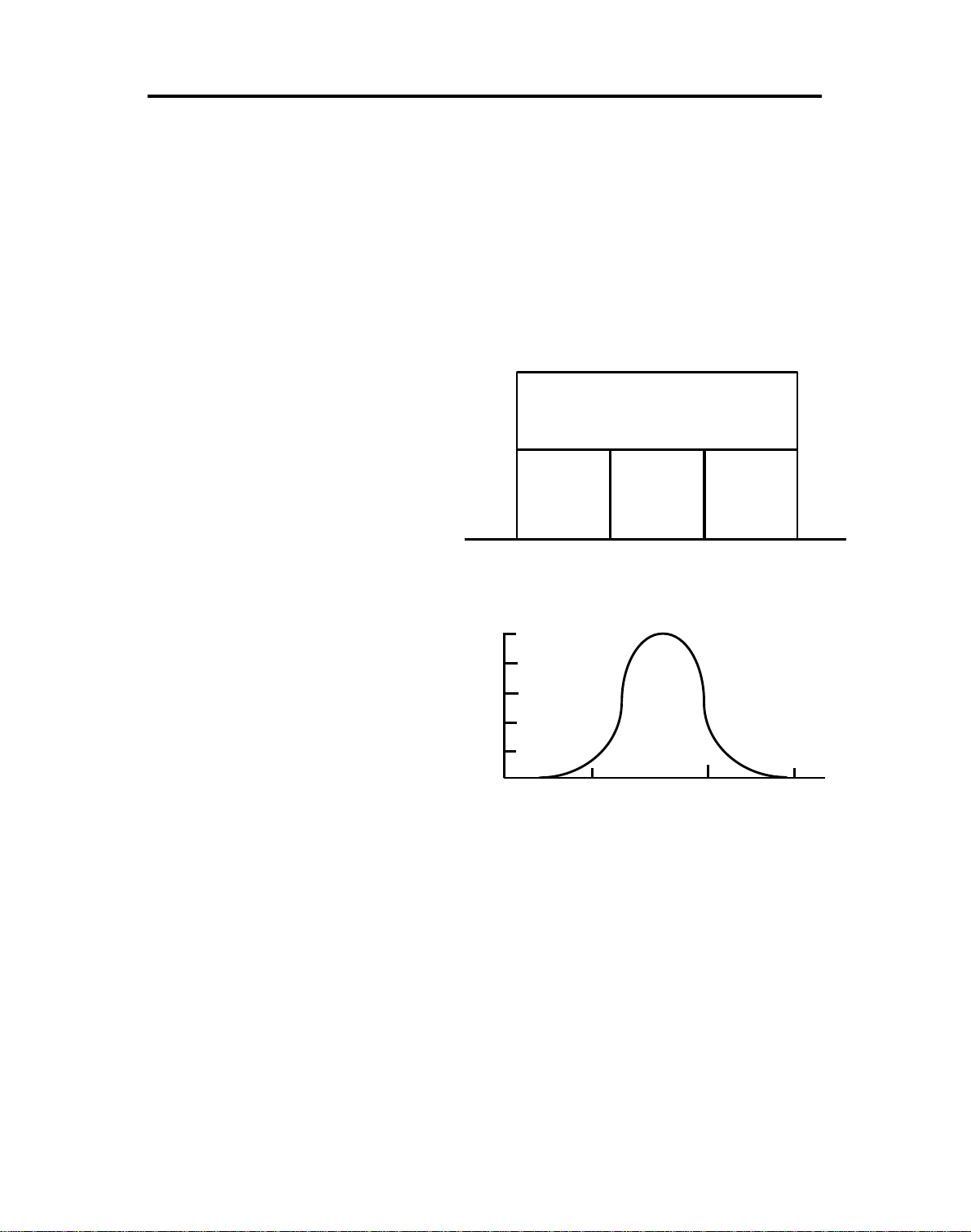
2) Wavelength and Color
The eye senses a different
color when light with a differe nt
wavelength reaches the eye.
• Light with a 580 nm
wavelength is recognized
as "Yellow".
• Light with a 610 nm
wavelength is recognized
as "Orange".
Ultraviolet
light
Violet Blue Green Yellow Orange Red
Blue (B)
400
Green (G)
500 600 700
Red (R)
Infrared
light
When light rays with
wavelengths bet ween 400 and
100
500 nm reach the eye,
violet-blue (in this manual, it is
called "Blue") is recognized.
Also, "Green" is recognized fo r
80
60
40
20
light with wavelengths between
500 and 600 nm, and "Red" is
400
500
600
700 nm
recognized for light with
wavelengths from 600 to 700 nm.
The sensitivity range for the eye is 400 to 700 nm, and the peak
sensitivity is at 556 nm.
Infrared rays have a wavelen gth of more than 700 nm and ultra viole t rays
have a wavelength of less th an 400 nm. Neit he r are visible to the eye.
1-4
20 December 1991 BASIC CONCEPTS OF COLOR COPYING
3) Color of objects
When an object is exposed by th e white light, it absorbs some rays and
reflects other rays.
a. When light rays around 610 nm
are reflected, and other ra ys are
Blue
Green
Red
absorbed, this object is said to be
"Orange".
(B)
(G)
(R)
b. When all light rays are reflecte d,
the object is recognized as
400 500 600
"White".
c. When all rays are absorbed, the
object is recognized as "Black" .
When a white object is seen through a red filter, it is seen to be "red".
Although it reflects all light rays, only red can pass through a red filter.
4) The three basic colors
The eye contains thre e kind s of colo r sensitive cells. These cells are
called B cones, G cones, and R cones an d they are sensitive to "blue",
"green", and "red" light. The pe rception of color depends on th e rela tive
level of excitation of these cells. Blue, green and red are called the "Three
Basic Colors".
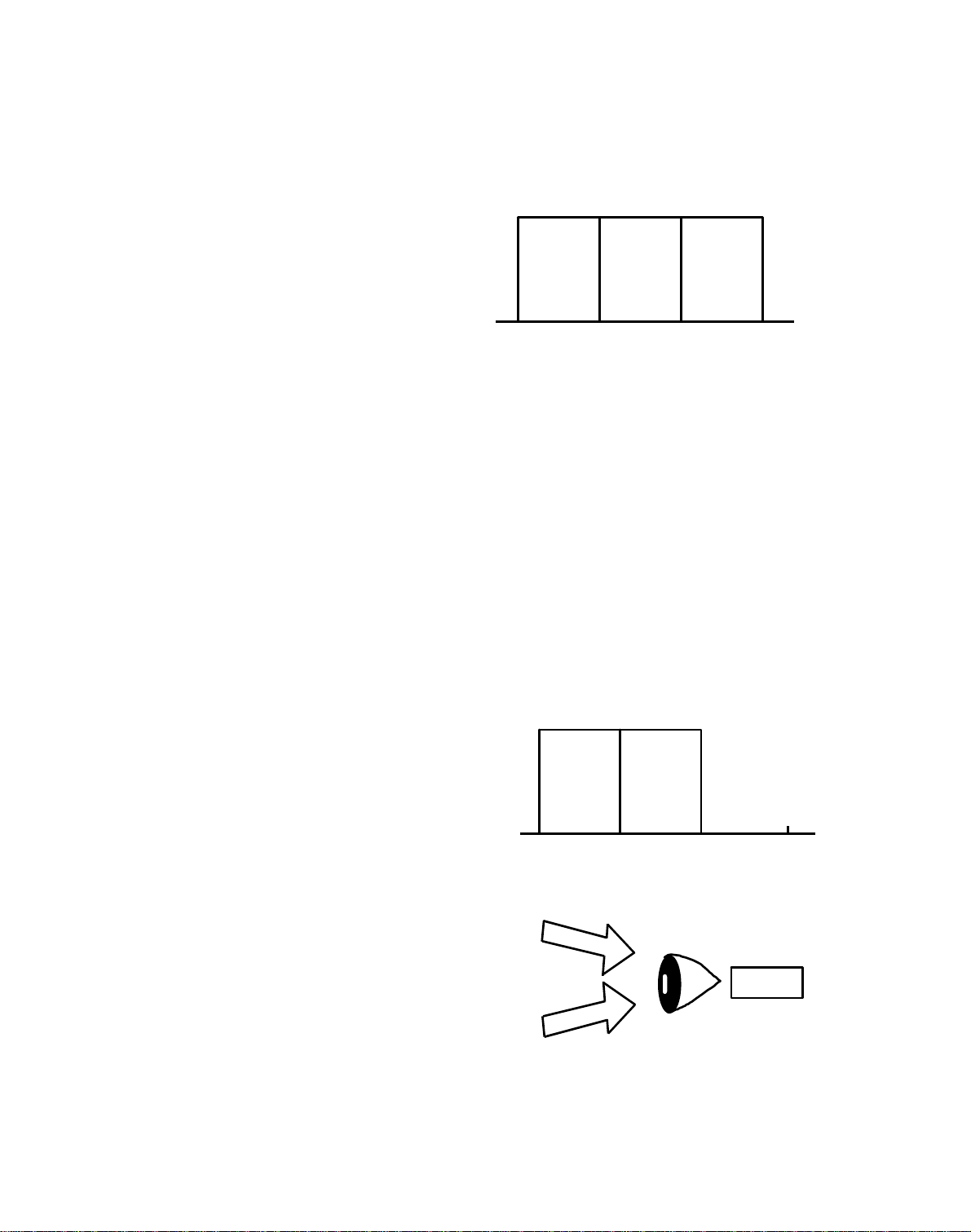
2.1.2 Light Mixture
1) Blue + Green
Blue
Green
When both "Blue" and "Gree n"
light reach the eyes, the eyes
sense a clear light blue, which is
called "Cyan". Since white ligh t
(B)
400 500 600 700nm
(G)
is composed of "Blue" , "Green",
and "Red" light, "Cyan" means
that the red component has been
eliminated from white light.
"Cyan" and "Red" are called
"Complimentary Colors".
Blue (B)
Green (G)
Cyan (C)
700nm
1-5
BASIC CONCEPTS OF COLOR COPYING 20 December 1991
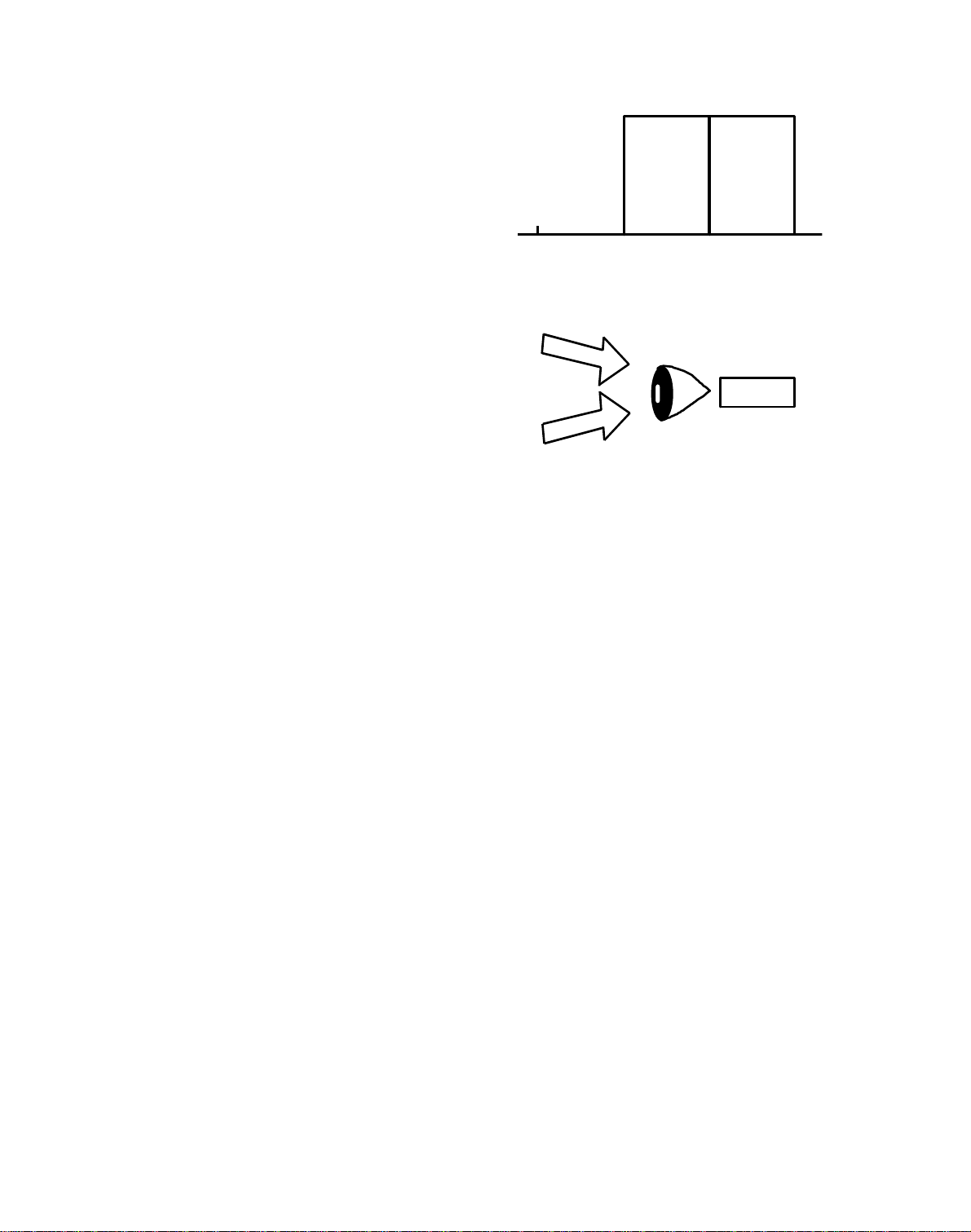
2) Green + Red
When both "Green" and "Red"
Green
Red
light reach the eyes, they sense
"Yellow". Since "Yellow" means
that "Blue" is eliminated from
white light, "Yello w" an d "B lue "
are called "Complimentary
400 500 600 700nm
(G)
(R)
Colors".
Green (G)
Red (R)
Yellow (Y)
1-6
20 December 1991 BASIC CONCEPTS OF COLOR COPYING
3) Blue + Red
When both "Blue" and "Red" light
Blue
Red
reach the eyes, they sense
purple-red color, which is called
"Magenta". "Magenta" and
"Green" are "Complimentary
(B)
400 500 600 700nm
(R)
Colors".
4) Summary
Light
White
B
C
M
Y
R
G
Black
Toner
Y
G
B
R
2.1.3 Color Toner
1) Light Reflective Characteristics
a. Cyan Toner
"Cyan" toner absorbs "Red" ra ys and reflects "Blue" and "Green" rays.
Reflected "B" and "G" rays are seen as "Cyan".
Blue
Green
Blue (B)
Red (R)
Light
MC
Toner
RB
G
B
B
Y
Complimentary Colors
B
C
M
Y
R
G
M
White
G
Magenta (M)
R
C
G
(B)
400 500 600 700nm
(G)
C
White paper
b. Magenta Toner
"Magenta" toner abso rbs "G reen" rays and reflects "Blue" and "Red"
rays. Reflected "B" and "R" rays are seen as "Mag en ta ".
RB
G
Blue
(B)
400 500 600 700nm
Red
(R)
1-7
B
White paper
Toner
R
Toner
M
R
BASIC CONCEPTS OF COLOR COPYING 20 December 1991
c. Yellow Toner
"Yellow" toner absorbs "Blue" rays and reflects "Green" and "Red"
rays. Reflected "green" and "red " ligh t rays are seen as "Yellow".
Red
(R)
400 500 600 700nm
Green
(G)
2) Color Toner Mixtures
a. Cyan + Magenta
When cyan and magenta ton e r ar e
combined on white paper, the magenta
layer absorbs green and the cyan layer
absorbs red. As a result, blue is
reflected.
b. Magenta + Yellow
When magenta and yello w ton er are
combined on white paper, the magenta
layer absorbs green, and the yellow
layer absorbs blue. As a result, red is
reflected.
R
G
B
Y
G
Toner
White paper
Y
G
R
B
C
RB
G
B
White paper
R
G
B
White paper
Black
M
M Toner
Toner
C
R
Y Toner
Toner
M
c. Cyan + Yellow
When "Cyan" and "Yellow" to ne r a re
combined on white paper the "C" laye r
absorbs "Red", and the "Y" layer
absorbs "Blue". As a result, "Gre en" is
reflected.
d. Cyan + Magenta + Yellow
When all three color toners are combined,
the cyan layer absorbs red , th e magenta
layer absorbs green, and the yellow layer
absorbs blue. As a result, no visible lig ht is
reflected, and we see black.
1-8
R
G
B
White paper
R
G
B
White paper
G
Y
Toner
C
Toner
Black
Y Toner
M Toner
Toner
C
20 December 1991 BASIC CONCEPTS OF COLOR COPYING
2.1.4 The Characteristics of Filters
1) Red Filter
The "Red" filter allows "Re d" lig ht to pa ss through and absorbs "Blue" and
"Green".
B
Red
(R)
400 500 600 700nm
G
R
2) Green Filter
The "Green" filter allows "G reen" light to pass through and ab sorbs "Blue"
and "Red".
B
Green
(G)
400 500 600 700nm
G
R
R Filter
G Filter
3) Blue Filter
The "Blue" filter allows "Blu e" light to pass through and absorbs "Green"
and "Red" rays.
B
Blue
(B)
400 500 600 700nm
1-9
G
R
B Filter
BASIC CONCEPTS OF COLOR COPYING 20 December 1991
2.1.5 Full Color Copy Process
Three filters (red, green, blue) and three color toners (cyan, magenta, yellow)
are used to make full color copies as follows.
1) 1st Cycle: Cyan Development wit h "Re d" filte r expo sure
Original
Red
Filter
OPC
Drum
Cyan
Development
White
BGR BGRBRG
BGRYCM
B
GR
Toner
C
C
OPC Drum
C
Black
C
C C
Paper
Image
Transfer
2) 2nd Cycle: Magenta Develop men t with "Gre en " filter exposure
Original
Green
Filter
OPC
Drum
Magenta
Development
White Black
BGRYCM
BGR BGRBRG
BGR
M MM
Toner
M
OPC Drum
Image
Transfer
M
C
C C
M M
C C
M
C
Paper
3) 3rd Cycle: Yellow Development with "Blue" filter exposure
Original
Blue
Filter
OPC
Drum
Yellow
Development
White Black
BGRYCM
BGR
BGR
Y
Y
OPC Drum
Toner
Y
BGRBRG
Y
1-10
Image
Transfer
YM
White
BGRYCM
Y
Y C M CCC
M
Paper
Image Fusing
Paper
Y
M
Black
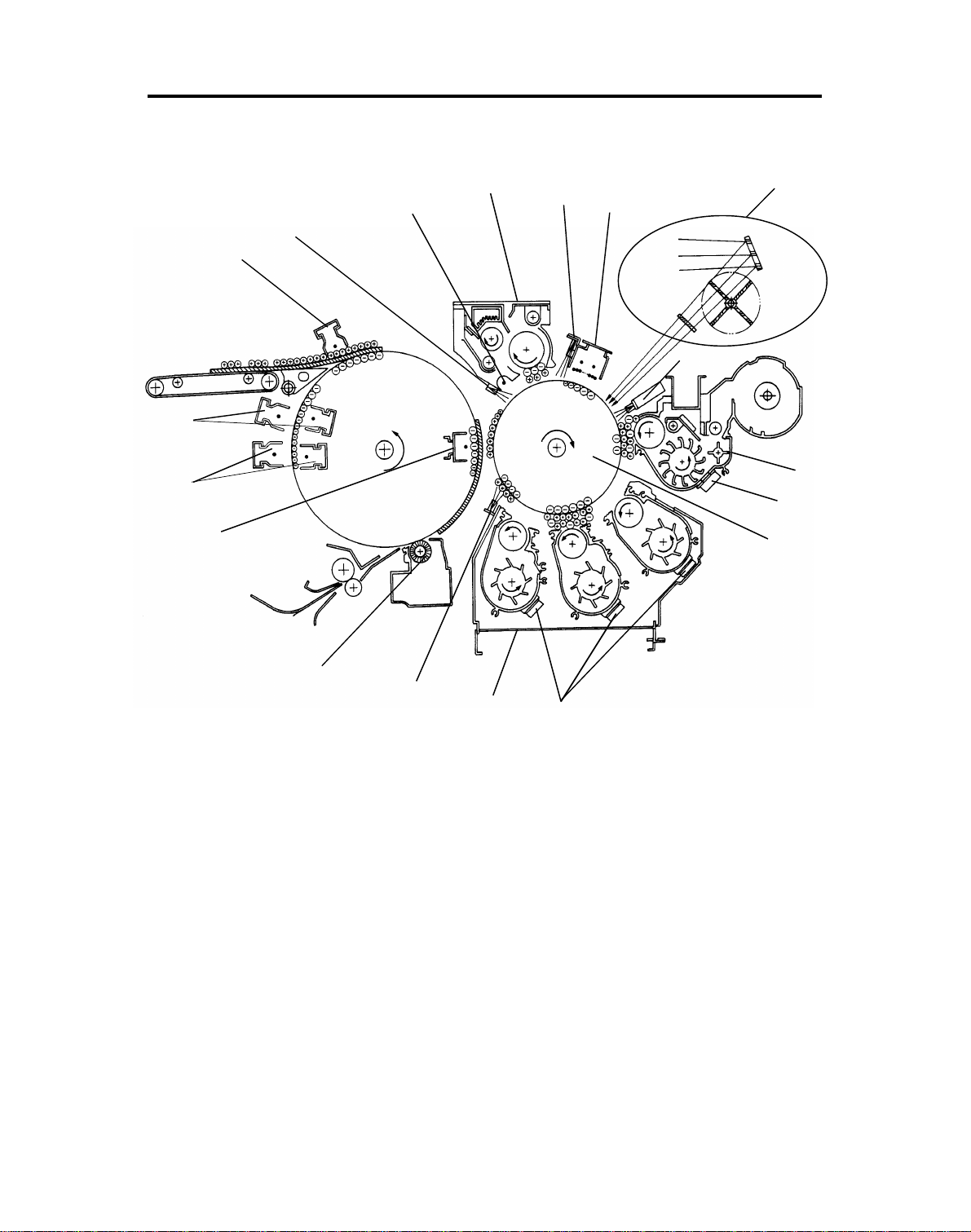
12
2
14
20 December 1991 COPY PROCESS AROUND THE DRUM
3. COPY PROCESS AROUND THE DRUM
15
11
10
9
13
4
8
3
5
6
1
16
7
1) OPC Drum
A unique OPC drum (120 mm diameter) ha s high resistance in the dark
and low resistance under light.
The drum speed is 226 mm/sec. in black development mode and 113
mm/sec. in color development mode.
2) Drum Charge
In the dark, the charge corona unit applies a negative charge to the drum.
The grid plate ensures tha t the charge is applied uniformly. The charge
remains on the drum surfa ce be cause the photoconduct ive drum has high
electrical resistance in the dark.
5
6
1-11

COPY PROCESS AROUND THE DRUM 20 December 1991
3) Exposure
An image of the original is reflected to the OPC drum via mirrors, a len s,
and a light separation filter. The charge on the drum surface is dissipated
in direct proportion to the intensity of the light exposing the OPC drum,
thus producing an electrical lat ent image.
The neutral density filter is used in bla ck and sin gle color cop y mo des.
The color filters are used in fu ll co lor cop y mode and single color erase
mode.
In full color mode, the original is scanned three times with a diffe ren t filt er
being used each time (red filt er fo r cya n development, green filter for
magenta developme nt, blue filter for yellow develo pme nt).
4) Erase
The erase lamp (red LED with 2.5 mm steps) illuminates the areas of the
charged drum surface that will not be used fo r the copy imag e. The
resistance of the drum in the illuminated areas drops and the charge
dissipates.
5) Development
Each time a scan is made, the development roller moves negatively
charged black, cyan, magenta, or yellow developer to the OPC drum. The
toner is attracted to the nega tive ly charged areas on the drum surface,
thus developing the latent image. The other colo r developers remain
inside the development unit.
6) Toner Density Detection
The toner density sensor on the bot to m of ea ch de velo pment unit detects
the magnetic permeability of deve loper each time a scan is made. If the
voltage output by the toner den sity sen sor is lower th an the st anda rd
output voltage, additio nal t oner is su pplied. (The standard output volta ge
is stored in memory when develope r is replace d, and it is updated by ID
sensor data.) The tone r density sensor also detects when toner is about
to run out.
7) Pre-transfer Lamp (PTL)
The pre-transfer lamp LEDs illuminat e the OPC drum to lower the dru m
potential for image transfer and OPC drum cleanin g.
1-12

20 December 1991 COPY PROCESS AROUND THE DRUM
8) Image Transfer
Copy paper is fed to the transfer drum and th e leading edge is clamped.
A negative charge is applie d to the backsid e of paper through the tran sfe r
drum sheet. This charge pulls the tone r particles on the OPC drum
surface onto the copy paper.
When the transfer corona current is applie d, the copy pa per is electrica lly
attracted to the transfer dru m sheet. In full color mode, the copy paper
makes three passes thro ug h the image transfer area. Since the tran sfer
drum sheet has already been charge d during the first transfer cycle, the
second transfer charge must be high er th an the first cha rge for image
transfer to take place. The same is true for the third transfer cycle.
To increase copy speed whe n cop y p aper of A4/11" x 81/2"
( LT sideways) sideways or smaller sizes is fed, the transfe r drum turns in
high speed while a later half of the transfer drum shee t is passing through
image transfer section.
9) Drum Image Control
a. ID Sensor
The sensor pattern is made by charging a strip of the drum and then
erasing all but a small section of th e charged area. This section is
developed with a higher develop ment bias than normal. (There is no
sensor pattern in th e optics.) The ID sensor (photosenso r) d et ect s t he
reflectivity of the pattern and the erased drum surface and outputs two
voltages. The ratio of the one output voltage to the other changes
whenever the toner de nsit y of the sensor pattern change s. The ton er
supply level voltage of the toner de nsit y sensor is then shifted to
increase or decrease the toner concentration in the deve loper and
maintain the correct amount of each color of toner on the OPC drum.
This keeps the colors in balance.
b. VL Sensor
To prevent dirty background on copies due to drum residual charge
and exposure decay of th e dru m surface, the exposure lamp voltag e is
shifted up based on the comparison of VL sensor data with initial set
data. The VL pattern is located in th e op tics, and it is developed during
the copier warm-up cycle if the main switch is turned on and the fusing
temperature is lower than 50°C.
10) Pre-cleaning Corona
The pre-cleaning corona (PCC) a pplies an AC corona with a positive DC
bias to the drum. This reduces the ele ctrica l a tt ract ion of to ne r to th e
drum so that it will be easier to clea n th e drum.
1-13

COPY PROCESS AROUND THE DRUM 20 December 1991
11) Drum Cleaning
Negatively charged cleaning carrier attracts positively charged toner from
the drum surface.
The cleaning bias roller has a negat ive bia s t hat ele ctrically separates
toner from the cleaning carrier. The bia s blade then peels toner off the
roller, and the cleaning coil carries toner to the collectio n bott le.
12) Quenching
After toner is removed from the OPC drum surface, the qu en chin g lamp
(LEDs) turns on to electrically neutralize the drum .
13) Paper Separation
The clamper opens and pushes the paper u p. The pick-o ff pawls then
peel the paper off th e tra nsfer drum. An AC separation coron a breaks the
electrical attraction betwe en the copy pa per and the drum so that the
paper separates easily from the drum.
14) DC Discharge
The inner DC discharge corona applies a positive potent ial to the
negatively charged inner surf ace of th e transfer drum sheet. The outer
DC discharge corona applies a nega tive potential to the oute r surface of
the transfer drum sheet. This discharges the transfer drum sheet.
15) AC Discharge
An AC discharge with differe nt frequency is applied to both the inner and
outer sides of the transf er dru m shee t. This n eutralizes the transfer drum
sheet.
16) Transfer Drum Cleaning
After the copy cycle, th e clea ning brush contacts the tra nsfer drum sheet
and removes toner on the transfe r drum. The transfer drum may become
dirty if there is a paper jam or if a large original is copied onto a small
sheet of copy paper. This is to avo id to ne r st ain s on th e reverse side of
the next copy.
1-14
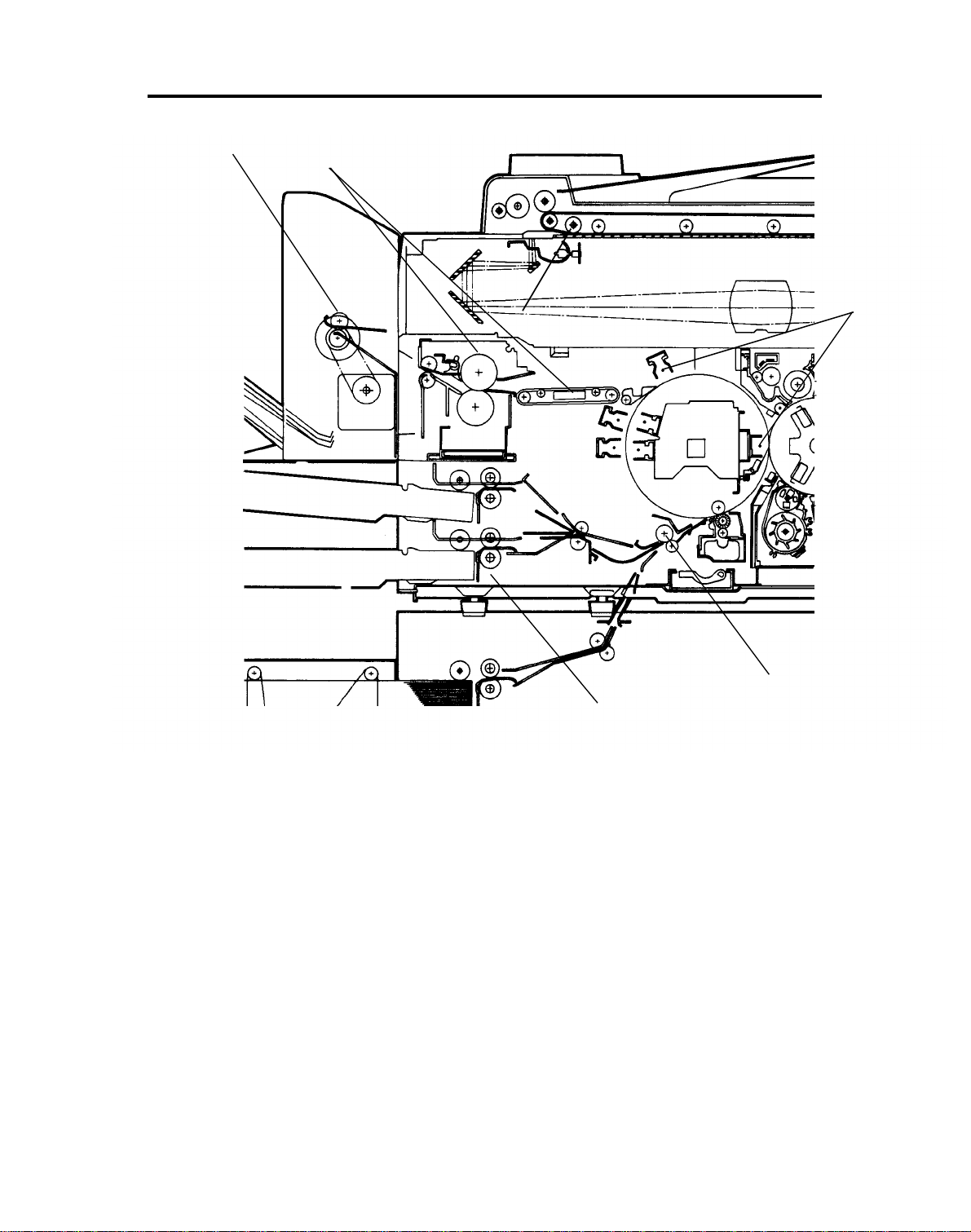
20 December 1991 PAPER PATH
4. PAPER PATH
(5)
(4)
(6)
(3)
(1)
1) Paper Feed
This copier uses the feed and reverse roller (FRR) system. The FRR
mechanism takes a sheet off the pap er sta ck a nd feeds it to the
registration rollers.
The standard version of th is copier has two paper feed station s. An
additional paper feed station is available when the copier is installed with
the optional table .
The optional multi by-pass tray can be used only in the fist paper fe ed
station.
The copy paper capacity is as follows:
Cassette: 250 she ets
Large capacity tray: 1000 sheets
Multi by-pass tray: 50 sheets
(2)
1-15

PAPER PATH 20 December 1991
2 ) Registration
When the copy paper reaches the registratio n rolle rs (not turning at this
time), it buckles slightly to correct skew an d sea t be twe en the ro llers.
The registration rollers start turn ing to feed paper to the paper clamp. The
rollers turn quicker than normal at this time so that the paper buckles
slightly when the leading edge con ta cts the clamp. This ensures that
there will be no skewing when the paper is clamped.
3) Image Transfer and Paper Separation
See the Drum Processes section.
4) Paper Transport/Image Fusing
After paper separation , th e pa per is tra nsp ort ed to th e fu sing ro llers by
the transport belt. The tra nsp ort vacuum fan pulls the paper onto the belt
to ensure smooth transport.
The paper passes betwee n the fusing rollers, which bond the ton er to the
paper with heat and pressure.
In both OHP mode an d glo ss copy mode (only for copy paper in A4/1 1" x
81/2" (LT sideways) or smaller sizes), turning spe ed of th e fu sing rollers is
lowered to supply more heat to the paper.
5) Copy Tray/Sorter
The copy is fed out to the copy tray by the exit rollers or to the to p bin of
the 20 bin sorter.
The sort and stack functions of the sorter can only be used wit h
black/white copies.
6) Auto Reverse Document Feeder
The optional document fe eder ha s thre e mod es: ADF, SADF, ARDF.
The bottom sheet is separate d fro m t he origin al stack by the separation
belt and is fed to the exposure glass.
1-16
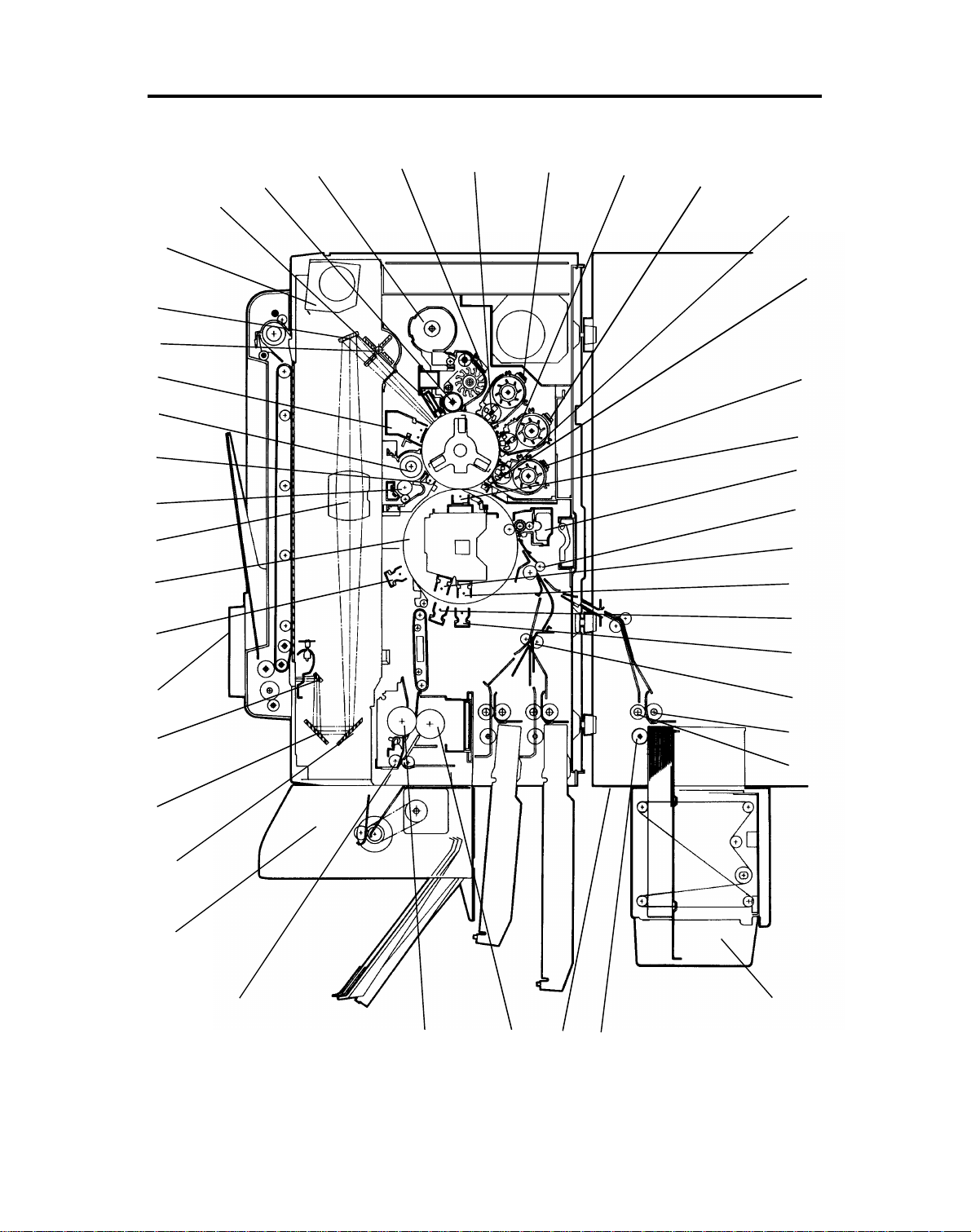
9
12
13
20
21
20 December 1991 MECHANICAL COMPONENT LAYOUT
5. MECHANICAL COMPONENT LAYOUT
11
8
7
6
5
10
14
15
16
17
18
19
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
4
3
2
11
11
41
40
39
38
37
36
33
34
35
42
1-17

MECHANICAL COMPONENT LAYOUT 20 December 1991
1. 3rd Mirror
2. 2nd Mirror
3. 1st Mirror
4. ARDF
5. Separation Corona Unit
6. Transfer Drum
7. Lens
8. Cleaning Bias Roller
9. PCC
10. Cleaning Roller
11. Charge Corona Unit
12. Color Filters
13. 4th Mirror
23. Cyan Development Rolle r
24. Pre-transfer Lamp (PTL)
25. Cyan Toner Density Sensor
26. Transfer Corona Unit
27. Transfer Drum Cleaning Unit
28. Registration Roller
29. Inner Discharge DC Corona
30. Inner Discharge AC Corona
31. Outer Discharge DC Corona
32. Outer Discharge AC Corona
33. Relay Roller
34. Reverse Roller
35. Paper Feed Roller
14. Optics Cooling Fan
15. Erase Lamp
16. Black Development Roller
17. Black Toner Supply Unit
18. Black Toner Density Sensor
19. Yellow Development Roller
20. Yellow Toner Density Sensor
21. Magenta Develop ment Roller
22. Magenta Toner Density Sensor
36. Pick-up Roller
37. Table with 3rd Paper Feed Unit
38. Pressure Roller
39. Hot Roller
40. Exit Roller
41. Sorter
42. Large Capacity Tray
1-18
20 December 1991 ELECTRICAL COMPONENT DESCRIPTIONS
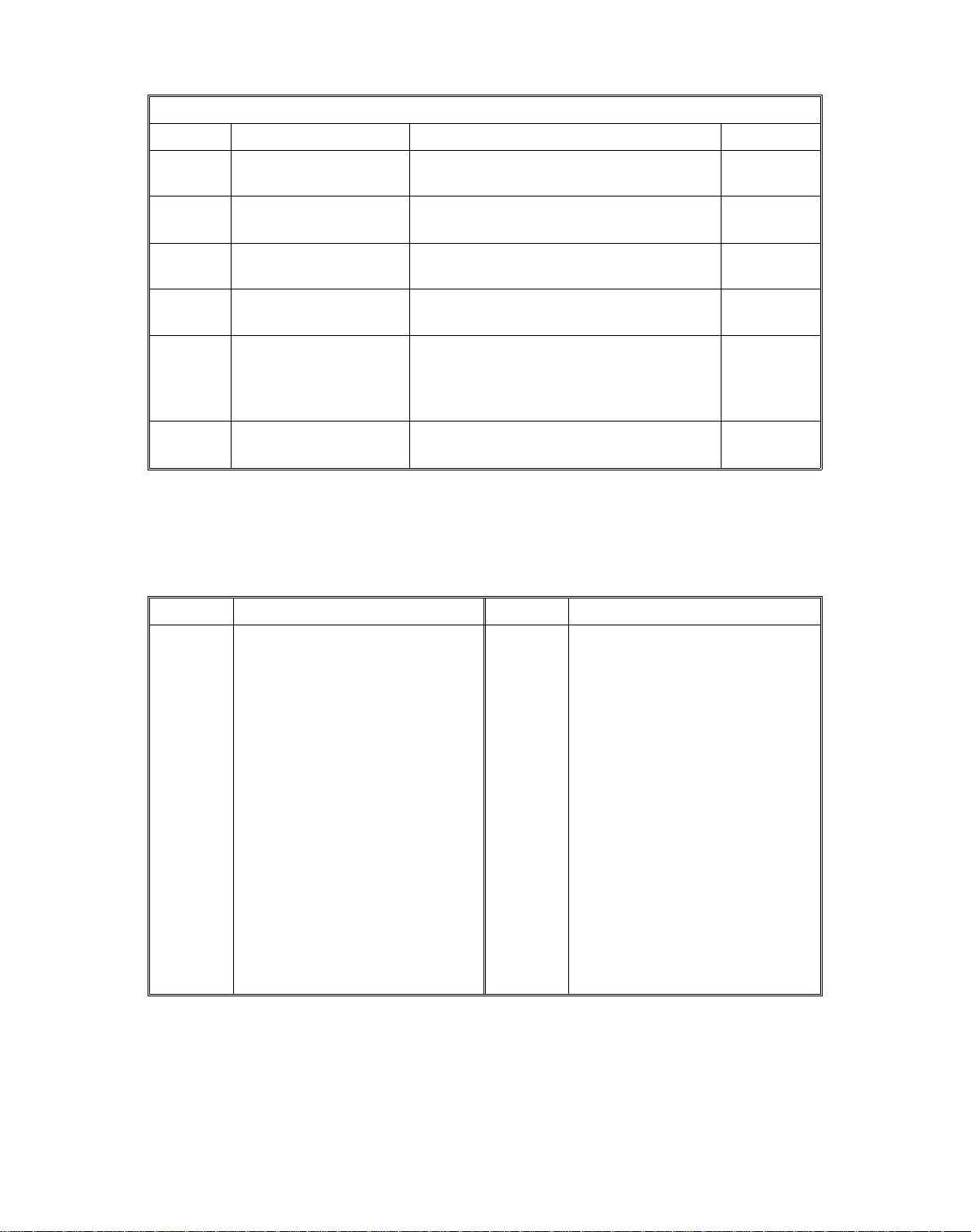
6. ELECTRICAL COMPONENT DESCRIPTIONS
SYMBOL NAME FUNCTION LOCATION
MOTORS
M1 Scanner Motor Drives the scanner. (servomotor) 56
M2 2nd Scanner Position
Motor
M3 Lens Motor Positions the lens based on the
M5 Filter Motor Rotates the filter assembly to position the
M6 Optics Cooling Fan Cools the optics cavity. 57
M7 Paper Feed Motor Drives the paper feed rollers, relay
M8 Registration Motor Turns the registration rollers. 72
M9 1st Lift Motor Lifts the first cassette’s bottom plate. 51
M10 2nd Lift Motor Lifts the second cassette’s bottom plate. 73
M11 Transport Vacuum Fan Provides suction so paper is held firmly
M13 OPC Drum Motor Turns the OPC drum. (servomotor) 77
M14 Transfer Drum Motor Turns the transfer drum. (servomotor) 84
M15 Transfer Drum
Cleaning Motor
M17 Transfer Exhaust Fan Removes the air around the transport
M18 Development Drive
Motor
M19 Cyan Development
Motor
M20 Magenta
Development Motor
M21 Yellow Development
Motor
M24 OPC Drum Cleaning
Motor
M25 Power Supply Cooling
Fan
M26 Charge Fan Provides a flow of air to the charge
M27 3rd Lift Motor Lifts the 3rd cassette’s bottom plate. 112
Positions the 2nd scanner based on the
reproduction ratio. (stepper)
reproduction ratio. (stepper)
proper filter in the light path. (stepper)
rollers, transport belt, fusing rollers, and
exit rollers. (encoder speed controlled)
on the transport belt.
Turns the transfer drum cleaning brush. 82
and the transfer drum sections.
Drives the black development unit. In
reverse rotation, drives the color
development units except the
development roller sleeves.(encoder
speed controlled)
Turns the cyan development roller
sleeve. (encoder speed controlled)
Turns the magenta development roller
sleeve. (encoder speed controlled)
Turns the yellow development roller
sleeve. (encoder speed controlled)
Drives the OPC drum cleaning unit.
(encoder speed controlled)
Cools the power supply unit. 62
corona unit to prevent uneven charge.
74
46
64
49
47
52
58
61
60
59
54
53
1-19
ELECTRICAL COMPONENT DESCRIPTIONS 20 December 1991
M28 Black Development
Motor
M29 Front Exhaust Fan Removes the air on the front side. 120
SOLENOIDS
SOL1 Pick-up Solenoid Controls the up-down movement of the
SOL2 Transfer Drum
Cleaning Solenoid
SOL3 Cleaning Support
Solenoid
SOL4 Paper Clamp Solenoid Opens and closes the transfer drum
SOL5 Pick-up Solenoid (3rd
paper feed)
MAGNETIC CLUTCHES
MC1 1st Feed Clutch Starts paper feed from the first feed
MC2 2nd Feed Clutch Starts paper feed from the second feed
MC3 Relay Roller Clutch Turns the relay rollers. 71
MC4 Black Toner Supply
Clutch
MC5 Cyan Toner Supply
Clutch
MC6 Magenta Toner
Supply Clutch
MC7 Yellow Toner Supply
Clutch
MC8 3rd Feed Clutch Starts paper feed from the 3rd feed
MC9 Relay Roller Clutch
(3rd paper feed)
Turns the black development roller
sleeve.
pick-up rollers.
Presses the transfer drum cleaning brush
against the transfer drum sheet during
the transfer drum cleaning cycle.
Presses the cleaning support roller
against the transfer drum sheet during
the transfer drum cleaning cycle.
clamp.
Controls the up-down movement of the
3rd pick-up roller.
station.
station.
Turns the black toner supply roller. 95
Turns the cyan toner supply roller. 94
Turns the magenta toner supply roller. 93
Turns the yellow toner supply roller. 92
station
Turns the 3rd relay roller. 113
116
70
82
84
85
107
69
68
108
SWITCHES
SW1 Main Switch Provides power to the copier. 38
SW2 Front Cover AC
Safety Switch
SW3 Front Cover DC
Safety Switch
Cuts AC power when the front cover is
opened.
Cuts DC power when the front cover is
opened.
1-20
36
37
20 December 1991 ELECTRICAL COMPONENT DESCRIPTIONS
SW4 3rd Paper Feed DC
Switch
SW5 3rd Paper Feed AC
Switch
SW6 Platen cover Closed
Switch
SENSORS
S1 1st Scanner HP
Sensor
S2 2nd Scanner HP
Sensor
S3 Lens HP Sensor Notifies the CPU when the lens is in the
S5 Filter HP Sensor Notifies the CPU when the filter is in the
S6 Auto Image Density
Sensor
S7 1st Paper End Sensor Informs the CPU when the first cassette
S8 2nd Paper End Sensor Informs the CPU when the second
S9 1st Paper Size Sensor Informs the CPU what size paper is in
S10 2nd Paper Size Sensor Informs the CPU what size paper is in
S11 1st Lift Sensor Detects the correct feed height of the first
S12 2nd Lift Sensor Detects the correct feed height of the
S13 Relay Sensor Controls paper feed clutch OFF timing. 29
S14 Registration Sensor Detects misfeeds and controls relay
S15 OHP Sensor Detects the OHP sheet. 25
S16 Transfer Drum HP
Sensor
S18 Black Toner Density
Sensor
S19 Cyan Toner Density
Sensor
S20 Magenta Toner
Density Sensor
Cuts DC power when the 3rd front cover
is opened.
Cuts AC power when the 3rd front cover
is opened.
Detects when the platen cover or the
document feeder is closed, and gives the
signal to perform original size detection
with closed platen cover condition.
Notifies the CPU when the scanner is at
the home position.
Notifies the CPU when the second
scanner is at its home position.
home position.
home position.
Senses the background density of the
original.
runs out of paper.
cassette runs out of paper.
the first cassette.
the second cassette.
cassette.
second cassette.
roller clutch OFF timing.
Informs the CPU when the transfer drum
is in the home position.
Senses the amount of toner in the black
developer.
Senses the amount of toner in the cyan
developer.
Senses the amount of toner in the
magenta developer.
105
105
118
1
2
7
22
28
40
39
35
34
33
32
27
76
96
89
91
1-21
ELECTRICAL COMPONENT DESCRIPTIONS 20 December 1991
S21 Yellow Toner Density
Sensor
S23 ID Sensor Detects the density of the image on the
Senses the amount of toner in the yellow
developer.
90
17
drum.
S24 V
L Sensor Senses the density of the VL pattern on
18
the drum. This data is used to calculate
drum residual voltage and drum
illumination decay.
S26 Toner Overflow Sensor Detects when the used toner bottle is full. 8
S28 Pick-off Sensor Detects misfeeds. 26
S29 Exit Sensor Detects misfeeds. 104
S30 Oil End Sensor Detects when the silicone oil bottle is
103
empty.
S32 Cyan Dev. Motor
Sensor
S33 Magenta Dev. Motor
Sensor
S34 Yellow Dev. Motor
Sensor
S35 3rd Paper Size Sensor Informs the CPU what size paper is in
Monitors the speed and direction of the
motor.
Monitors the speed and direction of the
motor.
Monitors the speed and direction of the
motor.
13
14
15
109
the 3rd cassette.
S36 3rd Paper End Sensor Informs the CPU when the 3rd cassette
111
runs out of paper.
S37 Relay Sensor (3rd
Paper Feed)
S38 3rd Lift Sensor Detects the correct feed height of the 3rd
Controls 3rd paper feed clutch OFF
timing.
110
106
cassette.
S39 Multi By-pass Sensor Informs the CPU of the width of paper
115
which is in the multi by-pass tray.
S40 Original Width Sensor Detects the original width. 117
S41 Original Length Sensor Detects the original length. 119
S42 Platen Cover Position
Sensor
Gives the signal to perform original size
detection with open platen cover
114
condition.
PCBs
PCB1 Main PCB Controls all machine functions. 19
PCB2 Servomotor PCB Controls the scanner motor, the OPC
20
drum motor, and the transfer drum motor.
PCB3 Motor PCB Controls eight DC motors. 12
PCB4 Process PCB Controls all corona and bias power
11
packs, AC drive unit sensors, and
clutches in the development units, etc.
PCB5 DC Power PCB Provides DC power. 21
1-22
20 December 1991 ELECTRICAL COMPONENT DESCRIPTIONS
PCB6 AC Drive PCB Provides AC power to the exposure lamp
bulbs and the fusing lamp.
PCB7 Operation Panel PCB The user controls the machine through
this PCB.
PCB9 Transfer Drum
Interface PCB
LAMPS
L1 Exposure Lamp Unit Applies high intensity light to the original
L2 Erase Lamp Discharges the drum outside of the
L3 Pre-transfer Lamp
(PTL)
L4 Quenching Lamp Neutralizes any charge remaining on the
L5 Fusing Lamp (2 pcs) Provides heat to the hot roller. 102
POWER PACKS
PP1 Charge PP Provides high voltage for the charge
PP2 Separation PP Provides high voltage for the separation
PP3 Transfer PP Provides high voltage for the transfer
PP4 Transfer Drum
Cleaning PP
Interfaces the transfer drum cleaning
motor/solenoid and the wire cleaner
motor with the transfer power pack.
for exposure.
image area.
Reduces the amount of charge on the
drum surface before transfer.
drum surface after cleaning.
corona wires and grill wires, the
pre-cleaning corona, development bias,
and cleaning bias.
corona and the outer AC and DC
discharge coronas.
corona and the inner AC and DC
discharge coronas.
Provides high voltage for the transfer
drum cleaning bias.
45
24
83
4
66
65
67
10
5
87
75
HEATERS
H1 OPC Drum Heater Keeps the OPC drum warm to prevent
condensation on the drum.
H2 Anti-condensation
Heater
COUNTERS
CO1 Black Scan Counter Counts the number of black scans. 31
CO2 Color Scan Counter Counts the number of color scans. 30
CO4 Key Counter Used for control of authorized use.
Prevents moisture from condensing on
the optics.
Copier will not operate until installed.
1-23
79
43
–
ELECTRICAL COMPONENT DESCRIPTIONS 20 December 1991
OTHERS
TH Fusing Thermistor Senses the temperature of the hot roller. 101
TF Fusing Thermofuse Opens the fusing lamp circuit if the fusing
unit overheats.
TS Drum Thermoswitch Activates when the drum temperature
becomes high to turn off the drum heater.
NF Noise Filter Removes electrical noise from the AC
input lines.
CB Circuit Breaker Guards against voltage surges in the AC
input lines.
RA Main Relay Provides AC power to the +24 volt circuit
of the DC power PCB and to the AC
drive PCB after the main switch is turned
on.
TR Transformer Drops the line voltage to 100 volts AC for
the sorter and the exposure lamp unit.
100
78
42
41
44
50
NOTE: Difference with A030 copier.
1. The following electrical compone nt s have been disco nt inu ed or newly
added.
SYMBOL Discontinued components SYMBOL Added components
M 4 Light Shield Motor M28 Black Development Motor
M12 Fusing Exhaust Fan M29 Front Exhaust Fan
M16 Transfer Corona Wire Cleaner
Motor
M22 Development Cooling Fan S39 Multi By-pass Sensor
M23 Magnetic Shield Motor S40 Original Width Sensor
S 4 Light Shield HP Sensor S41 Original Length Sensor
S17 Wire Cleaner HP Sensor S42 Platen Cover Position Sensor
S22 Magnetic Shield HP Sensor
S25 Cleaning Sensor
S27 Cleaning Motor Pulse Sensor
S31 Magnetic Shield Sensor
PCB8 Sorter Interface PCB
CO3 Total Copy Counter
SW6 Platen Cover Closed Switch
2. The second registrat ion sensor in the A030 copier is named as the OHP
sensor (S16) in this A072 copier.
1-24

RICOH NC305
SECTION 2
DETAILED DESCRIPTIONS

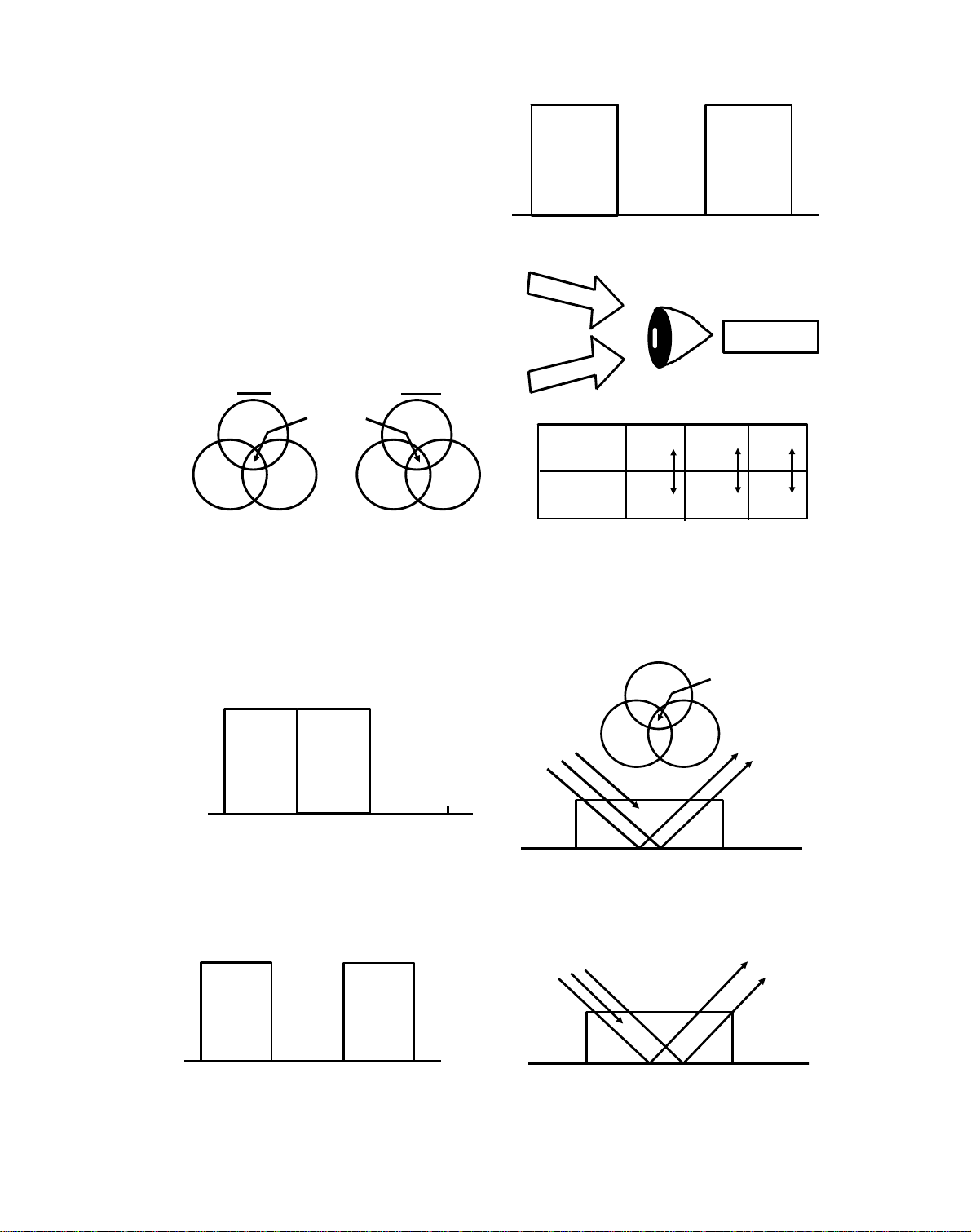
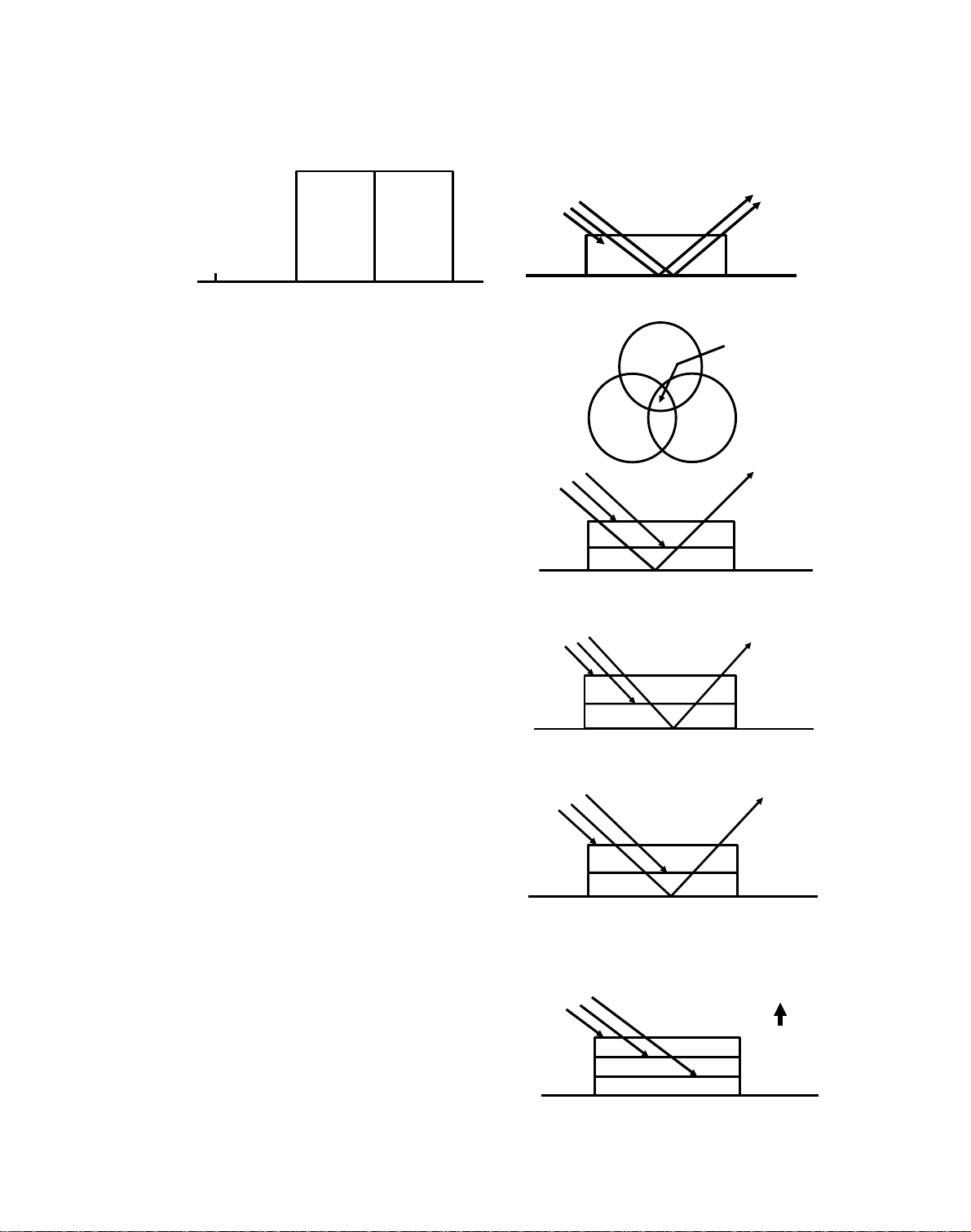
7 November 1991 OPC DRUM
1. OPC DRUM
1.1 OPC DRUM CHARACTERISTICS
An OPC has the following characteristics:
• Able to accept a high negative electrical charg e in the dark. (The
electrical resistance of a photoco nd uct or is high in the absence of
light.)
• Dissipates the electrical charge when exposed to light. (Exp osure to
light greatly increases th e conductivity of a photocond uct or.)
• The amount of charge dissipation is in direct proportion to the
intensity of the light. That is, whe re stro ng er ligh t is directed to the
photoconductor surface , a smalle r voltage remains on the OPC.
• Unlike F type selenium drums, temperature compensation and rest
time compensation are not requ ired . Howe ver, some compensation
for change in the drum’s residual voltage is required.
• Drum conditioning is required to maintain a high negative charge on
the drum surface.
2-1
 Loading...
Loading...