Page 1
Network Guide
Functions Available over a Network
1
Connecting the Network Cable to the Network
2
Setting Up the Machine on a Network
3
Windows Configuration
4
Using the Printer Function
5
Configuring the Network Interface Board Using a Web Browser
6
Appendix
7
Read this manual carefully before you use this machine and keep it handy for future reference. For safe and correct use, be sure to read the
Safety Information in the "Copy Reference" before using the machine.
Page 2

Introduction
This manual contains detailed instructions and notes on the operation and use of this machine. For your
safety and benefit, read this manual carefully before using the machine. Keep this manual in a handy
place for quick reference.
Important
Contents of this manual are subject to change without prior notice. In no event will the company be liable for direct, indirect, special, incidental, or consequential damages as a result of handling or operating the machine.
Two kinds of size notation are employed in this manual. With this machine refer to the metric version.
Trademarks
Microsoft
®
, Windows® and Windows NT® are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation in the
United States and/or other countries.
Other product names used herein are for identification purposes only and might be trademarks of their
respective companies. We disclaim any and all rights to those marks.
The proper names of the Windows operating systems are as follows:
• The product name of Windows
• The product name of Windows
®
98 is Microsoft® Windows 98.
®
Me is Microsoft® Windows Millennium Edition (Windows Me).
• The product names of Windows® 2000 are as follows:
Microsoft® Windows® 2000 Advanced Server
Microsoft® Windows® 2000 Server
Microsoft
• The product names of Windows
Microsoft® Windows® XP Professional
Microsoft
• The product names of Windows
Microsoft® WindowsTM Server 2003 Standard Edition
Microsoft
®
Windows® 2000 Professional
®
XP are as follows:
®
Windows® XP Home Edition
TM
Server 2003 are as follows:
®
WindowsTM Server 2003 Enterprise Edition
Microsoft® WindowsTM Server 2003 Web Edition
Note:
Some illustrations in this manual might be slightly different from the machine.
Page 3
Manuals for This Machine
The following manuals describe the operational procedures of this machine. For
particular functions, see the relevant parts of the manual.
Note
❒ Manuals provided are specific to machine type.
❒ Adobe Acrobat Reader is necessary to view the manuals as a PDF file.
❖ General Settings Guide
Explains User Tools settings, and Address Book procedures such as registering fax numbers, e-mail addresses, and user codes. Also refer to this manual
for explanations on how to connect the machine.
❖ Network Guide (this manual)
Describes procedures for configuring the machine and computers in a network environment.
❖ Copy Reference
Explains Copier functions and operations. Also refer to this manual for explanations on how to place originals.
❖ Printer/Scanner Reference
Describes system settings, functions, troubleshooting and operations for the
machine's printer and scanner function.
❖ Other Manuals
• Manuals for This Machine
•Safety Information
• Quick Reference Copy Guide
• Quick Reference Printer / Scanner Guide
i
Page 4
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Manuals for This Machine ......................................................................................i
How to Read This Manual .....................................................................................1
1. Functions Available over a Network
Using the Printer....................................................................................................3
Network TWAIN Scanner.......................................................................................4
2. Connecting the Network Cable to the Network
Confirming Connection .........................................................................................5
Connecting to the Ethernet Interface .........................................................................6
3. Setting Up the Machine on a Network
User Tools Menu (Interface Settings) ..................................................................7
Printer.........................................................................................................................7
Network TWAIN Scanner ...........................................................................................7
Network Configuration................................................................................................8
Settings You Can Change with User Tools ................................................................9
4. Windows Configuration
Configuring TCP/IP ..............................................................................................11
Configuring a Windows 98SE / Me Computer..........................................................11
Configuring a Windows 2000 Computer ..................................................................11
Configuring a Windows XP Computer......................................................................12
Configuring a Windows Server 2003 computer........................................................12
Configuring a Windows NT 4.0 Computer................................................................13
5. Using the Printer Function
Printing with a Print Server................................................................................. 15
Printing without a Print Server ...........................................................................16
Using TCP/IP Port Type P10001 .............................................................................16
Using Standard TCP/IP Port ....................................................................................17
Using LPR Port ........................................................................................................17
Using the IPP Port....................................................................................................18
6. Configuring the Network Interface Board Using a Web Browser
Features ................................................................................................................19
Settings You Can Change Using a Web Browser .............................................20
Configuring the Network Interface Board Using...............................................21
ii
Page 5

7. Appendix
Using DHCP..........................................................................................................23
SNMP.....................................................................................................................24
Error Messages on the Display ..........................................................................25
Messages without Code Numbers ...........................................................................25
Messages with Code Numbers ................................................................................26
Specifications.......................................................................................................27
INDEX......................................................................................................... 28
iii
Page 6

iv
Page 7

How to Read This Manual
R
R
Symbols
In this manual, the following symbols are used:
WARNING:
This symbol indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if instructions
are not followed, could result in death or serious injury.
CAUTION:
This symbol indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if instructions
are not followed, may result in minor or moderate injury, or damage to property.
* The statements above are notes for your safety.
Important
If this instruction is not followed, paper might be misfed, originals might be
damaged, or data might be lost. Be sure to read this.
Preparation
This symbol indicates prior knowledge or preparation is required before operation.
Note
This symbol indicates precautions for operation, or actions to take after mal-operation.
Limitation
This symbol indicates numerical limits, functions that cannot be used together,
or conditions in which a particular function cannot be used.
Reference
This symbol indicates a reference.
[]
Keys that appear on the machine's display.
[]
Keys and buttons that appear on the computer's display.
{}
Keys built into the machine's control panel.
{}
Keys on the computer's keyboard.
1
Page 8

2
Page 9

1. Functions Available over a Network
This machine provides printer and scanner functions over a network.
Using the Printer
The network interface board is compatible with Windows NT4.0 / 2000
(TCP/IP, IPP
*1
IPP
), and Windows 98SE / Me operating systems and protocols. This flexibility allows you to operate the machine in networks that use different protocols
and operating systems.
*1
IPP (Internet Printing Protocol) is a protocol for printing via the Internet.
*1
), Windows XP (TCP/IP, IPP
*1
), Windows Server 2003 (TCP/IP,
ARL001S
Reference
For details about network settings you need to make, see p.7 “Setting Up the
Machine on a Network”.
For details about network printing, see p.15 “Using the Printer Function”.
3
Page 10
1
Functions Available over a Network
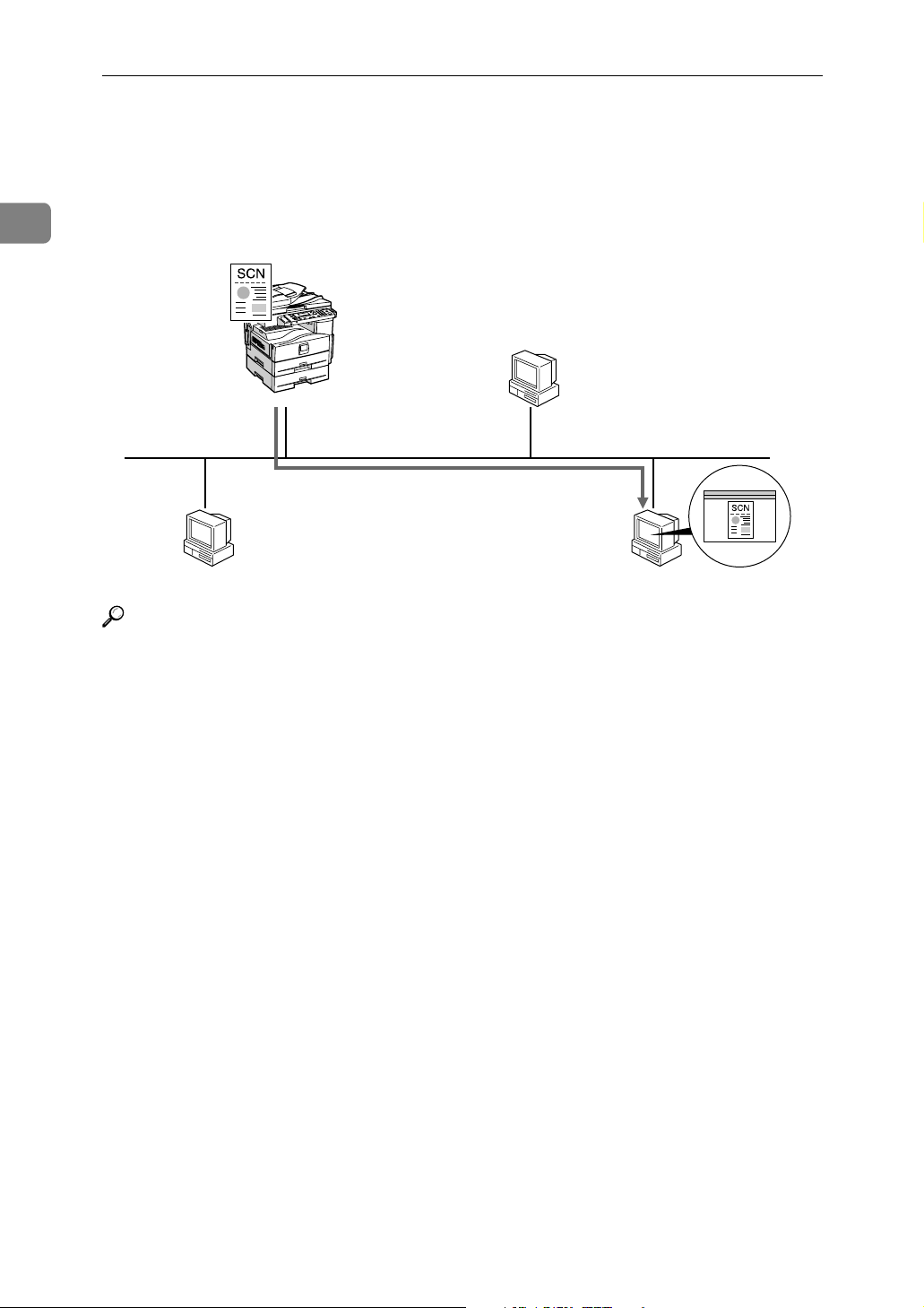
Network TWAIN Scanner
You can use the scanning function of this machine from a computer connected
via a network. You can scan documents the same way you would if you were
using a scanner connected directly to your computer.
ARL002S
Reference
For details about network settings you need to make, see p.7 “Setting Up the
Machine on a Network”.
For details about TWAIN scanning over a network, see "Using the TWAIN
Scanner Function", Printer / Scanner Reference.
4
Page 11
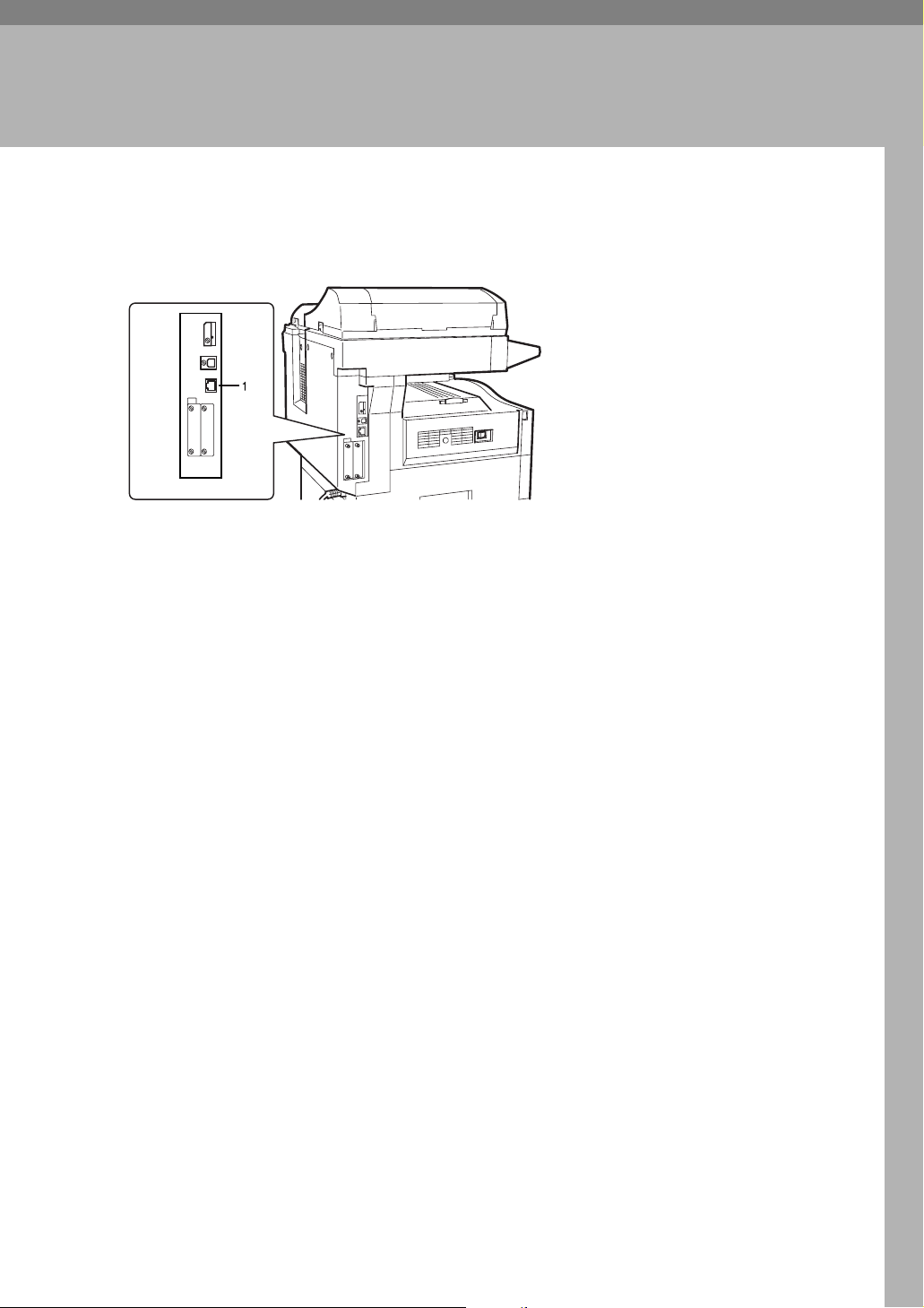
2. Connecting the Network Cable to the Network
Confirming Connection
1. 10BASE-T/100BASE-TX port
Port for connecting the network interface
cable.
ARL003S
5
Page 12

Connecting the Network Cable to the Network
2
Connecting to the Ethernet Interface
The network interface board supports
10BASE-T or 100BASE-TX connections.
A Turn off the main power switch.
Important
❒ Make sure the main power is
off. See “Turning On the Power”, Copy Reference.
B Loop the network interface cable
and attach the ferrite core.
Note
❒ The network interface cable
loop should be about 10 cm
(4”)(A) from the end of the cable (closest end to the printer).
The ferrite core at the end of the
cable should be a ring type.
C Connect the network interface ca-
ble to the 10BASE-T/100BASE-TX
port.
ARL008S
D Turn on the main power switch.
1.
2.
AAW022S1
1. Indicator (green)
Remains green when the machine is
properly connected to the network.
AAW026S1
2. Indicator (yellow)
Turns yellow when 100 BASE-TX is
operating. Turns off when 10 BASE-T
is operating.
6
Page 13

3. Setting Up the Machine on a Network
User Tools Menu (Interface Settings)
This section describes the network settings you can change with User Tools (Interface Settings). Make settings according to the functions you want to use and
the interface to be connected.
Important
❒ These settings should be made by the systems administrator, or after consult-
ing with the systems administrator.
Reference
For details about settings, see p.9 “Settings You Can Change with User Tools”
❖ Viewing the Information Displayed in the List
$ These items must be set to use the function. Be sure to set them before attempting to use the corresponding function.
❍ These items must be set if required.
Printer
Interface Settings/Network
See p.9 “Interface Settings”.
IP Address $
Gateway Address ❍
Ethernet Speed ❍
Network TWAIN Scanner
Interface Settings/Network
See p.9 “Interface Settings”.
IP Address $
Gateway Address ❍
Ethernet Speed ❍
Settings
Settings
7
Page 14

Setting Up the Machine on a Network
3
Network Configuration
Changes made with User Tools remain in effect after the main power
switch or operation switch is turned
off, or the {Clear Modes} key is
pressed.
Configuring the network using the control panel
Note
❒ Operations for Interface Settings
are different from normal operations. To exit User Tools, press the
{User Tools/Counter} key.
❒ If a key operator code has been set,
the key operator code entry screen
appears. Enter the code, and then
press the {OK} key. For details
about the key operator code, see
General Settings Guide.
A Press the {User Tools/Counter} key.
B Select [Interface Settings] using the
{U} or {T} key, and then press
the {OK} key.
C Select the setting you want to
change, and then press the {OK}
key.
D
Change the setting, and then press
the {OK} key.
Note
❒ Press the {Escape} key to cancel
the setting.
E Press the {User Tools/Counter} key.
Configuring the network using other utilities
Network settings can be made not only from the control panel, but by Web
browser also. The following table shows the settings you can make using a Web
browser:
Note
❒❍ Indicates machine settings that can be changed.
❒ - Indicates the setting cannot be changed from that device.
Name on the control panel Web browser
Interface Settings
Network IP Address Auto-Obtain (DHCP) ❍
Specify IP Add. ❍
Subnet M ❍
Mac Add. -
Gateway Address ❍
Ethernet Speed -
8
Page 15

Settings You Can Change with User Tools
Interface Settings
❖ IP Address
To use this machine in a network
environment, you must first configure its IP address and subnet
mask.
•Auto-Obtain (DHCP)
•Specify
When you select [Specify], enter
[IP Address:] and [Sub-net Mask:]
as “xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx”(“x” indicates a number).
• IP Address: 011.022.033.044
User Tools Menu (Interface Settings)
❖ Ethernet Speed
Set the network access speed.
Select a speed that is suitable for
your network environment. [Auto
Select] should usually be selected.
•Auto Select
• 100Mbps Fixed
•10Mbps Fixed
Note
❒ Default: Auto Select
3
•
Sub-net Mask: 000.000.000.000
Note
❒ Default: Auto-Obtain (DHCP)
❒ When you select [Specify], be
sure not to set the same [IP Ad-
dress:] as that of another ma-
chine on the network.
❒ The physical address (MAC ad-
dress) also appears.
❖ Gateway Address
A gateway is a connection or interchange point between two networks. Configure the gateway
address for the router or host computer used as a gateway.
•
Gateway Address: 000.000.000.000
Note
❒ Default: 000.000.000.000
9
Page 16

3
Setting Up the Machine on a Network
10
Page 17

4. Windows Configuration
Configuring TCP/IP
This section explains configuring
Windows for TCP/IP and IPP.
Configuring a Windows 2000
Computer
Configuring a Windows 98SE /
Me Computer
Follow the procedure below to configure a Windows 98SE / Me computer to use TCP/IP.
A Open [Control Panel], and then
double-click the Network icon.
Make sure [TCP/IP] is selected in
the [The following network compo-
nents are installed] box on the [Con-
figuration] tab.
Note
❒ Select TCP/IP if it is not already
selected.
❒ If TCP/IP is not installed, click
[Add] on the [Configuration] tab to
install it. For details about installing TCP/IP, see Windows
98SE / Me Help.
B Click [Properties].
C Configure TCP/IP using the ap-
propriate IP address, subnet
mask, and other settings.
Check with the network administrator that the settings are correct.
Follow the procedure below to con-
figure a Windows 2000 computer to
use TCP/IP.
A On the [Start] menu, point to [Set-
tings], and then click [Network and
Dial-up Connections].
B Double-click [Local Area Connec-
tion]. On the [General] tab, click
[Properties].
C
Make sure [Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)
is selected in the [Components
checked are used by this connection]
box on the [General] tab.
Note
❒ Select TCP/IP if it is not already
selected.
❒ If TCP/IP is not installed, click
[Install] on the [General] tab to install it. For details about installing TCP/IP, see Windows 2000
Help.
D Click [Properties].
E Configure TCP/IP using the ap-
propriate IP address, subnet
mask, and other settings.
]
Check with the network administrator that the settings are correct.
11
Page 18

Windows Configuration
4
Configuring a Windows XP Computer
Follow the procedure below to configure a Windows XP computer to use
TCP/IP.
A On the [Start] menu, click [Control
Panel], and then click [Network Connections].
B Click [Network Connections], and
then double-click [Local Area Con-
nection].
C On the [General] tab, click [Proper-
ties].
D
Make sure [Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)
is selected in the [This connection
uses the following items] box on the
[General] tab.
Note
❒ Select TCP/IP if it is not already
selected.
❒ If TCP/IP is not installed, click
[Install] on the [General] tab to install it. For details about installing TCP/IP, see Windows XP
Help.
E Click [Properties].
F Configure TCP/IP using the ap-
propriate IP address, subnet
mask, and other settings.
Check with the network administrator that the settings are correct.
Configuring a Windows Server
2003 computer
Follow the procedure below to con-
figure a Windows Server 2003 com-
puter to use TCP/IP.
A On the [Start] menu, point to [Con-
trol Panel], point to [Network Connections], and then click [Local Area
Connection].
B On the [General] tab, click [Proper-
ties].
C
Make sure [Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)
is selected in the [This connection
]
uses the following items] box on the
[General] tab.
Note
❒ Select TCP/IP if it is not already
selected.
❒ If TCP/IP is not installed, click
[Install] on the [General] tab to install it. For details about installing TCP/IP, see Windows
Server 2003 Help.
D Click [Properties].
E Configure TCP/IP using the ap-
propriate IP address, subnet
mask, and other settings.
Check with the network administrator that the settings are correct.
]
12
Page 19

Configuring a Windows NT 4.0 Computer
Follow the procedure below to configure a Windows NT 4.0 computer to
use TCP/IP.
A Open [Control Panel], and then
double-click the Network icon.
Make sure [TCP/IP Protocol] is selected in the [Network protocols]
box on the [Protocols] tab.
Configuring TCP/IP
Note
❒ Select TCP/IP if it is not already
selected.
❒ If TCP/IP is not installed, click
[Add] on the [Protocols] tab to install it. For more information
about installing TCP/IP, see
Windows NT 4.0 Help.
B Click [Properties].
C Configure TCP/IP using the ap-
propriate IP address, subnet
mask, and other settings.
Check with the network administrator that the settings are correct.
4
13
Page 20

4
Windows Configuration
14
Page 21

5. Using the Printer Function
Printing with a Print Server
This section explains configuring a
network client computer when using
Windows 2000 / XP or Windows
Server 2003 as a print server.
When using a Windows 2000 / XP or
Windows Server 2003 print server, select a shared printer.
This section describes running [Add
Printer Wizard] on each client compu-
ter, and adding the Windows 2000 /
XP, or Windows Server 2003 print
server as the network printer.
These instructions are for Windows
98SE.
Limitation
❒ If you are using a Windows XP
print server, client computers cannot receive notification of print job
completion.
A Right-click [Network Neighborhood],
and then click [Explore] in the context menu.
B On the network tree, double-click
the name of the computer used as
the print server. The printers connected to the network are displayed.
C Double-click the name of the
printer you want to use, and then
click [Yes].
The printer icon appears in the
[Printers] window.
ARL005S
This section assumes the client is already configured to communicate
with a Windows 2000 / XP, or Windows Server 2003 print server. Do not
begin the following procedure until
the client computer is set up and configured correctly.
15
Page 22

5
Using the Printer Function
Printing without a Print Server
You can use this machine as a network printer without connecting to a
print server.
You can configure the following
ports:
❖ TCP/IP Port Type P10001
Print via TCP/IP using TCP/IP
Port Type P10001.
Note
❒ TCP/IP Port Type P10001 can
be used with Windows 98SE /
Me.
❖ Standard TCP/IP port
Print via TCP/IP using a standard
TCP/IP port.
Note
❒ A standard TCP/IP port can be
used with Windows 2000 / XP
or Windows Server 2003.
❖ LPR port
Print via TCP/IP using an LPR
port.
Using TCP/IP Port Type
P10001
TCP/IP Port Type P10001 can be used
with Windows 98SE / Me if the nec-
essary printer driver has been in-
stalled.
A In the [Printers] window, click the
icon of the printer you want to
use. On the [File] menu, click
[Properties].
B Click the [Details] tab, and then
click [Add Port].
C Click the [Other] radio button,
click [TCP/IP Port Type P10001], and
then click [OK].
Add TCP/IP Port Type P10001
Wizard will start.
D Click [Next >].
E Enter the IP address, and then
click [Next >].
16
Note
❒ An LPR port can be used with
Windows 2000 / XP, or Windows Server 2003.
❖ IPP port
Print via ipp or http using an IPP
port.
Note
❒ An IPP port can be used with
Windows XP, or Windows
Server 2003.
Note
❒ Enter [Port Name:] if necessary.
F Click [Finish].
Page 23

Printing without a Print Server
Configuring the port settings
A In the [Printers] window, click the
icon of the printer you want to
use. On the [File] menu, click
[Properties].
B Click the [Details] tab, and then
click [Port Settings…].
The TCP/IP Port Type P10001
Configuration dialog box appears.
• You can select either Raw or
LPR port.
• You can change the IP address
of the port.
Note
❒ If the IP address of the ma-
chine is changed, you must
change the port settings also.
• Both Raw and LPR support
SNMP.
Important
❒ Do not change Port Number,
Timeout, or Queue Name.
E In the [Printer Name or IP Address]
box, enter the printer name or IP
address, and then click [Next >].
F
In the [Add Standard TCP/IP Printer Port
]
Wizard
dialog box, click [Finish].
G Click [Close].
H Check the location of the selected
printer, and then click [Close].
Using LPR Port
This procedure explains changing the
port settings under Windows 2000
when a printer driver has been installed.
A In the [Printers] window, click the
icon of the printer you want to
use. On the [File] menu, click
[Properties].
B Click the [Ports] tab, and then
click [Add Port].
C Click [LPR Port], and then click
[New Port].
5
Using Standard TCP/IP Port
This procedure explains changing the
port settings under Windows 2000
when a printer driver has been installed.
A In the [Printers] window, click the
icon of the printer you want to
use. On the [File] menu, click
[Properties].
B Click the [Ports] tab, and then
click [Add Port].
C Click [Standard TCP/IP], and then
click [New Port].
D
In the [Add Standard TCP/IP Printer Port
Wizard
]
dialog box, click [Next >].
D In the [Name or address of server pro-
viding lpd] box, enter the printer's
IP address.
You must install “Print Services for
Unix” before you can use the LPR
port. If the dialog box does not appear, install the necessary print
service, and then try again.
For details about performing installations, see your operating system’s Help files.
E In the [Name of printer or print queue
on that server] box, enter “lp”, and
then click [OK].
F Click [Close].
G Check the location for the select-
ed printer, and then click [Close].
17
Page 24

Using the Printer Function
5
Using the IPP Port
An IPP port can be used with Windows 2000 / XP or Windows Server
2003.
This procedure explains making the
port settings under Windows XP.
A In the [Printers and Faxes] window,
click [Add printer] on the [File]
menu.
Add Printer Wizard will start.
B Click [Next >].
C Click the [A network printer or a at-
tached to another computer] radio
button, and then click [Next >].
D
Click the [Connect to a printer on the
Internet or on a home or office network:
radio button, and then enter “http://printer's IP address/ipp/port1”
or “ipp://printer's IP address/ipp/port1” in the
[
URL:] box.
G Select the printer driver.
The printer driver paths are as follows:
• Windows 98SE / Me
CD-ROM
drive:DRIVERSDDSTWIN9X_
ME(language)DISK1
• Windows 2000 / XP or Windows Server 2003
CD-ROM
drive:DRIVERSDDSTWIN2K_
XP(language)DISK1
H Click [OK] twice.
I Click [Next >], and then [Finish].
]
(Example: IP address is 192.168.15.16)
http://192.168.15.16/ipp/
port1
ipp://192.168.15.16/ipp/
port1
E Click [Next >].
F Click [Have Disk], and then click
[Browse].
18
Page 25

6.
Configuring the Network Interface
Board Using a Web Browser
Features
You can check the status of the machine and change its settings using a Web
browser.
❖ What can I do?
You can remotely check the status of the machine remotely, and if necessary
change its settings over the network using a Web browser.
The following functions are available using a Web browser:
• Displaying machine status/settings
• Resetting network settings
• Making machine settings
❖ Configuring the machine
This requires TCP/IP to be installed. After the machine has been configured
to use TCP/IP, it will be possible to adjust its settings using a Web browser.
Reference
For details about configuring the machine to use TCP/IP, see p.7 “Setting
Up the Machine on a Network”.
❖ Browser
Note
❒ If you are using a proxy server, change the Web browser settings. Consult
your network administrator about the settings.
❒ The machine's information is not updated automatically. Click [Reload] or
[Refresh] on the Web browser to update it.
❖ Specifying the address
Enter the machine's IP address in the [Address] box, using the following format: http://XXX.XXX.XXX.XXX (Replace XXX with the appropriate numbers.) Alternatively, you can enter the machine's host name if it is already
registered on the DNS or WINS server.
19
Page 26

6
Configuring the Network Interface Board Using a Web Browser
Settings You Can Change Using a Web Browser
❖ System
• Reset
Reset the machine's settings.
•Factory Defaults
Reset the machine's settings to their default values.
•Unit Status
Display the machine's network settings.
• Network Address
Display the machine's serial number and Ethernet address (MAC address).
• Change Password
Change the password.
❖ Protocols
• Setup TCP/IP
Configure the machine's TCP/IP settings.
•Setup IPP
Configure the machine's IPP settings.
❖ Others
Printer Status
Display the machine's printer status.
20
Page 27

Configuring the Network Interface Board Using
Configuring the Network Interface Board
Using
A Start the Web browser.
B
Enter the machine's IP address in the
[
Address] box, using the following
format: http://XXX.XXX.XXX.XXX
(Replace XXX with the appropriate
numbers.)
The Web browser identifies the
machine by its IP address, and
then displays the status of that machine.
C In the menu area, select the set-
ting you want to change, and then
configure it as necessary.
Note
❒ Enter a password if necessary.
❒ Default password is "sysadm".
6
21
Page 28

Configuring the Network Interface Board Using a Web Browser
6
22
Page 29

7. Appendix
Using DHCP
If this machine is configured for DHCP, and the DHCP request fails four times,
BOOTP takes over the request. If the BOOTP request fails three times, the Default IP address is used.
23
Page 30

Appendix
SNMP
The machine is equipped with an SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) agent that operates under UDP and IPX on the Ethernet interface. The
SNMP manager enables you to get information about the machine.
The default community names are “public” and “private”. You can get MIB information using these community names.
❖ Supported MIBs
•MIB-II
•PrinterMIB
•HostResourceMIB
7
24
Page 31

Error Messages on the Display
Error Messages on the Display
This section explains the most common network-related messages that appear
on the display. If a message not shown here appears, follow its instructions.
Messages without Code Numbers
Message Causes Solutions
hCannot connect to network
Check IP Address
hCannot connect to network
Contact key operator
Ethernet Board Error An Ethernet board error has
hServer communicat. failed
Contact key operator
Network connection could
not be established.
Network connection could
not be established.
occurred.
Cannot communicate with the
server.
Check the machine's IP address.
Check the network. If this
message continues to appear,
contact your key operator.
Turn off the main power
switch, wait a few seconds,
and then turn it back on. If this
message continues to appear,
contact your sales or service
representative.
Check the server. If this message continues to appear, contact your key operator.
Reference
Before turning the main power off, see “Turning On the Power”, Copy Reference.
7
25
Page 32

Appendix
Messages with Code Numbers
7
Message Causes Solutions
Cannot
connect
with DHCPserver
The same
IP Address already
exists
Check
network
settings
The same
IP Address exists on
several
interfaces
Cannot
set within the
same subnet range
The DHCP server cannot be
found.
The specified IP address overlaps
another IP address.
An unauthorized value is specified as the IP address or gateway
address.
IP addresses overlap across multiple interfaces.
IP addresses of simultaneously
operating interfaces overlap.
The subnet masks of simultaneously operating interfaces overlap.
Check the DHCP server is running
on the network.
The IP address specified for the
machine overlaps another IP address in use. Check the address of
the device indicated in <MAC address>.
Change the IP address, subnet
mask, or gateway address to the
correct value.
The IP address of the specified interface overlaps the IP address of
another interface. Configure the
IP address so it does not overlap.
The subnet range of the specified
interface overlaps the subnet
range of another interface.
Configure the subnet mask so it
does not overlap.
Code
numbers
101
102
103
004
005
❖ Code Numbers
Displays the problem interface.
•1XX: Ethernet
• 0XX: Independent of interface
26
Page 33

Specifications
Interface 100BASE-TX, 10BASE-T
Protocol • Printer
TCP/IP
LPR
IPP
• Network Scanner
TCP/IP
• Management Function
TCP/IP
SNMP
HTTP
DHCP
SNMP MIB-II, PrinterMIB, HostResourceMIB
Specifications
7
27
Page 34

INDEX
C
configuration
Web Browser
D
DHCP, 23
E
Ethernet Speed, 9
G
Gateway Address, 9
I
Interface Settings, 9
IP Address
M
, 9
, 19
MIB, 24
S
SNMP, 24
specifications
, 27
W
Web Browser, 19
28 GB GB AE AE B280-7905A
Page 35

Copyright © 2006
Page 36

Network Guide
GB GB
AE AE B280-7905A
 Loading...
Loading...