Preliminary
RT9182
Dual, Low-Noise, 200mA LDO Regulator
General Description
The RT9182 is a dual-channel, low noise, and low
dropout regulator supplying up to 200mA current at
each channel. The output voltage ranges from 1.5V
to 3.3V in 100mV increments and 2% accuracy by
operating from a +2.7V to +6.5V input.
The RT9182 uses an internal PMOS as the pass
device, which consumes 165µA supply current (both
LDOs on) independent of load current and dropout
conditions. The SHDN pin controls both outputs
simultaneously and consumes nearly zero operation
current in the disable mode making the IC suitable
for battery-power devices. Other features include a
reference voltage bypass pin to improve low noise
performance, current limiting, and over temperature
protection.
Ordering Information
RT9182
Package type
E : SOT-26
Operating temperature range
C : Commercial standard
Features
•
Up to 200mA Output Current (Each LDO)
•
Shutdown Function
•
29µµµµV
•
Current Limiting and Thermal Protection
•
Short Circuit Protection
•
120mV Dropout at 100mA Load
•
Two LDOs in SOT-26 Package
Low Noise Output
RMS
Applications
Cellular Phones
z
Laptop, Notebook, and Palmtop Computers
z
Battery-powered Equipment
z
Hand-held Equipment
z
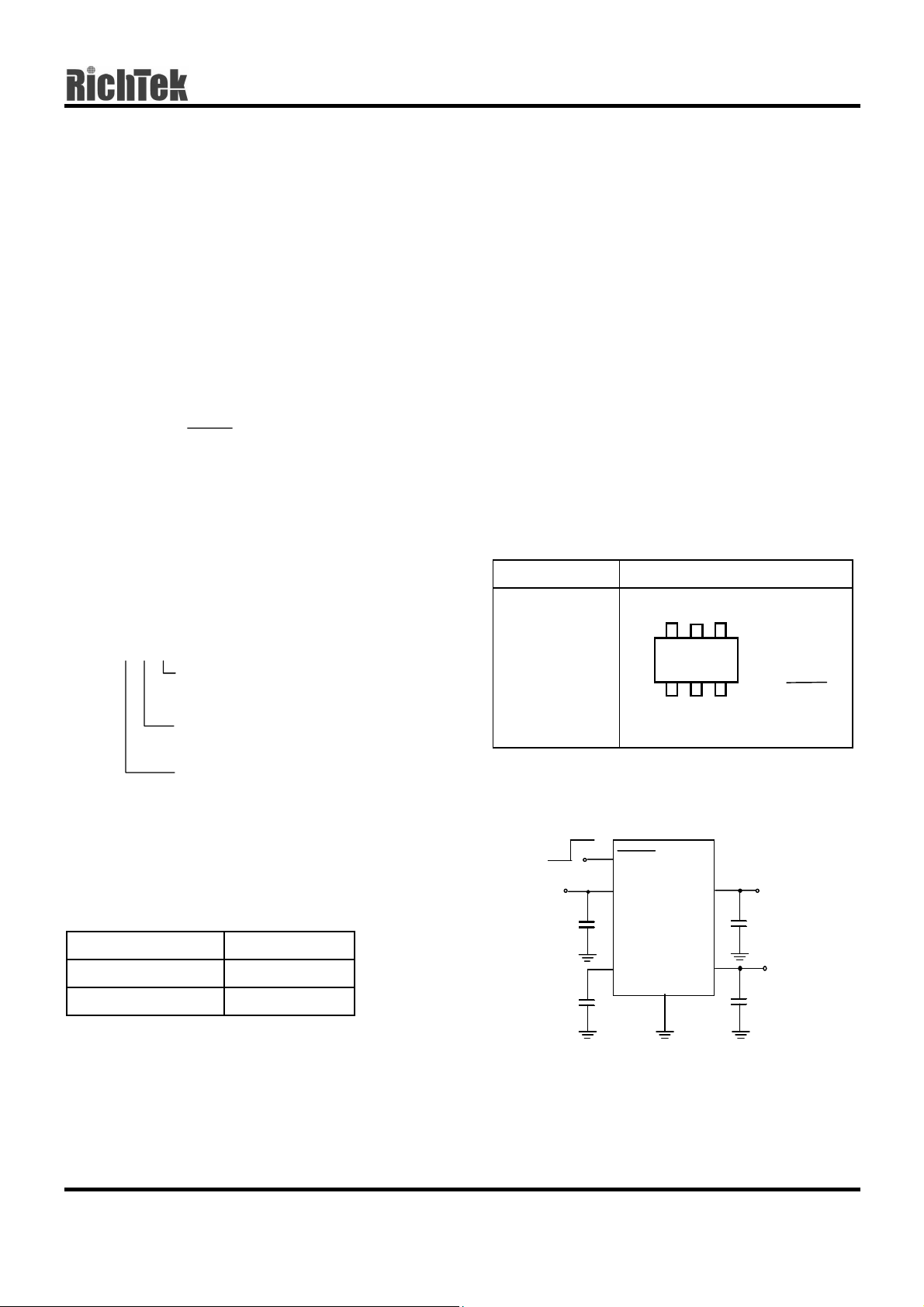
Pin Configurations
Part Number Pin Configurations
RT9182CE
64
(Plastic SOT-26)
5
321
TOP VIEW
1. VOUT2
2. GND
3. BP
4. SHDN
5. VIN
6. VOUT1
Output voltage
Typical Application Circuit
A : 2.8V (Output1), 2.8V (Output2)
B : 3.0V (Output1), 3.0V (Output2)
ON
Marking Information
V
OFF
OU T2
2. 2
F
µ
SHDN
RT9182
VOUT1VOUT2
V
2. 2µF
OU T1
Part Number Marking
2. 2µF
V
IN
RT9182ACE 2M
RT9182BCE 2Q
DS9182-02 April 2002 www.richtek-ic.com.tw
10nF
BP
VIN
GND
1
RT9182
Pin Description
Pin Name Pin Function
VOUT2 Output2 Voltage
GND Ground
BP Reference Noise Bypass
SHDN Active Low Shutdown Input
VIN Power Input
VOUT1 Output1 Voltage
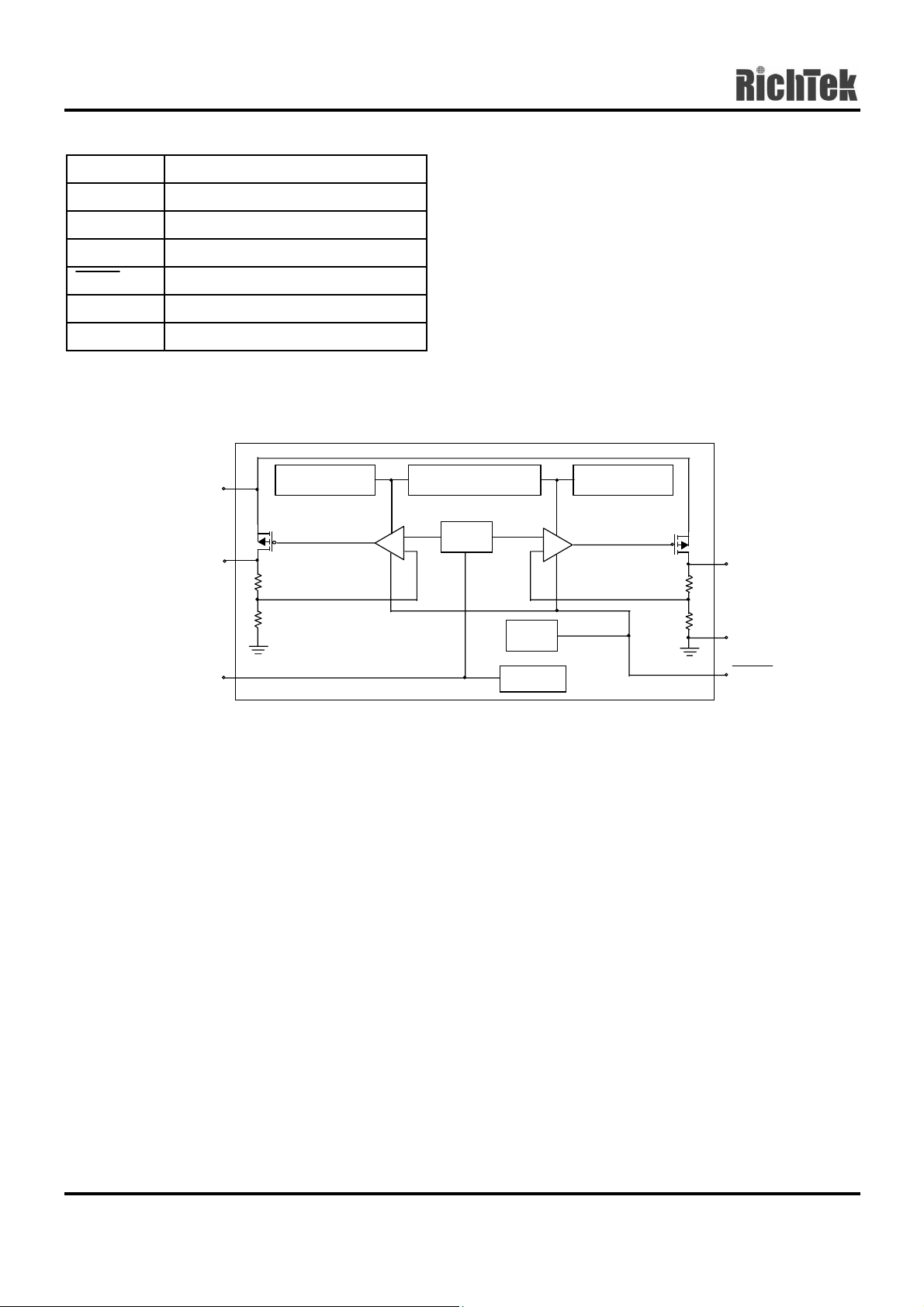
Function Block Diagram
Preliminary
VIN
VOUT1
BP
Thermal ProtectionCurrent Limit Current Limit
_
+
Vref
+
Bias
Start-Up
_
VOUT2
GND
SHDN
www.richtek-ic.com.tw DS9182-02 April 2002
2
Preliminary
RT9182
Absolute Maximum Ratings
z Input Voltage 7V
z Power Dissipation, P
@ TA = 25°C
D
SOT-26 748mW
z Junction Temperature Range -40°C ~ 125°C
z Storage Temperature Range -65°C ~ 150°C
z Operating Temperature Range -40°C ~ 85°C
z Lead Temperature (Soldering, 10 sec.) 260°C
Electrical Characteristics
(V
= 3.6V, CIN = C
IN
Parameter Symbol Test Conditions Min Typ Max Units
= 2.2µF, SHDN = VIN, typical values at TA = 25°C, for each LDO unless otherwise specified.)
OUT
Input Voltage Range
Output Voltage Accuracy
(Load Regulation)
Maximum Output Current
Current Limit
V
IN
∆V
OUTIL
I
MAX
I
LIMIT
= 1mA to 200mA
Continuous 200 -- -- mA
R
= 1Ω
LOAD
2.7 -- 6.5 V
-2 -- +2 %
200 -- 550 mA
No Load -- 165 260
GND Pin Current
Dropout Voltage
(Note)
Line Regulation
SHDN Input High Threshold
SHDN Input Low Threshold
SHDN Input Bias Current
Shutdown Supply Current
I
G
V
DROP
∆V
V
IH
V
IL
I
SD
I
GSD
I
OUT
I
OUT
I
OUT
I
OUT
VIN = (V
LINE
I
OUT
VIN = 2.7V to 6.5V
VIN = 2.7V to 6.5V
SHDN = GND or V
= 100mA (Both LDOs)
= 1mA
= 100mA
= 200mA
+0.4V or 2.7V) to 6.5V
OUT
= 1mA
IN
-- 165 260
-- 1.2 -- mV
-- 120 -- mV
-- 255 -- mV
-0.2 -- +0.2 %/V
1.6 -- --
-- -- 0.4
-- -- 100
SHDN = GND -- 0.01 1
Thermal Shutdown Temperature -- 140 --
µA
µA
V
V
nA
µA
°C
Thermal Shutdown Hysteresis
Output Voltage Noise
Output Voltage AC PSRR
Note : Dropout voltage definition: VIN – V
DS9182-02 April 2002 www.richtek-ic.com.tw
T
SD
e
NO
10Hz to 100kHz, CBP = 10nF
C
= 4.7µF, I
OUT
OUT
100Hz, C
I
= 100mA
LOAD
when V
OUT
LOAD
= 10nF, C
BP
is 50mV below the value of V
= 1mA
OUT
= 4.7µF
-- 10 --
-- 29 --
-- 62 --
(normal)
OUT
µV
°C
RMS
dB
3

RT9182
PSRR
(dB)
Typical Operating Characteristics
V
OUT
= 2.8V, I
= 100mA, VIN = 3.6V, C
LOAD
= 4.7µF, CBP = 10nF, and CIN = 2.2µF, unless otherwise noted.
OUT
Preliminary
Quiescent Current vs. Supply Voltage
240
200
µ
160
120
80
Quiescent Current ( A)
40
0
2.5 3.5 4.5 5.5 6.5
No Load
= 100mA, both outputs
I
Load
Supply Voltage (V)
Quiescent Current vs. Load Current
180
150
µ
120
Both outputs loaded
Output Voltage Accuracy vs. Temp.
1.0
0.8
0.6
0.4
0.2
0.0
-0.2
-0.4
Output Voltage (%)
-0.6
-0.8
-1.0
-40 -15 10 35 60 85
Temperature ( C)
°
Dropout Voltage vs. Temp.
300
250
200
90
60
Quiescent Current ( A)
30
0
0 40 80 120 160 200
Load Current (mA)
Quiescent Current vs. Temp.
200
175
150
µ
125
100
75
50
Quiescent Current ( A)
25
150
100
Dropout Voltage (mV)
50
I
0
-40 -15 10 35 60 85
Temperature ( C)
LOAD
°
PSRR vs. Frequency
70
60
50
40
30
20
10
I
LOAD
= 200mA
= 1mA
0
-40 -15 10 35 60 85
Temperature ( C)
°
0
10 100 1K 10K 100K 1M
Frequency (Hz)
www.richtek-ic.com.tw DS9182-02 April 2002
4

120
>
>
>
p
g
>
>
>2↓
↓
↓
(
p
)
)
>
>
>
µ
>
>
>2 >
>
>
≈
(
p
)
≈
100
80
60
Channel-to-Channel Isolation
vs. Frequency
Preliminary
RT9182
Noise Density vs. Frequency
10K
Hz
1K
40
Channel Isolation (dB)
20
0
100 1K 10K 100K 1M
R
Frequency (Hz)
Line Transient Response
T
led
1
1
1 >1
AC-Cou
20mV/Div
Output Voltage Deviation
≈
4.5
3.5
2
2↓2
Input Voltage (V)
T
50µS/Div
Time
LOAD
= 100Ω
≈
100
Noise Density (nV/ )
10
10 100 1K 10K 100K
Frequency (Hz
Load Transient Response
Output Voltage Deviation
Load Current
(I
led
1
1
AC-Cou
1 >1
2
2 >2
100mA/Div 50mV/Div
T
Peak value depends on C
T
= 0 to 80mA)
LOAD
10µS/Div
Time
C
OUT
ESR
OUT
= 2.2µF
Shutdown Response
I
= 50mA
e
ut Volta
1V/Div
Out
1 >
1 >
1 >1 >
≈
2
2
2 >2
5V/Div
Shutdown Voltage
DS9182-02 April 2002 www.richtek-ic.com.tw
1mS/Div
Time
LOAD
T
≈
T
Output Voltage (AC-Coupled)
Output Noise (10Hz to 100kHz)
V/Div
1
1
1 >1
100
T
1mS/Div
Time
I
LOAD
= 1mA
5

RT9182
Functional Description
Preliminary
The RT9182 is integrated with two low noise, low
dropout, and low quiescent current linear regulators
designed primarily for battery-powered applications.
Output voltages are optional ranging from 1.5V to
3.3V, and each channel can supply current up to
200mA.
Shutdown
The RT9182 is shutdown by pulling the SHDN input
low, and turned on by driving the input high. If this
feature is not to be used, the SHDN input should be
tied to VIN to keep the regulator on at all times (the
SHDN input must not be left floating).
Internal P-Channel Pass Transistor
The RT9182 features double typical 1.5Ω P-channel
MOSFET pass transistors. It provides several
advantages over similar designs using PNP pass
transistors, including longer battery life. The P-
channel MOSFET requires no base drive, which
reduces quiescent current considerably. PNP-based
regulators waste considerable current in dropout
when the pass transistor saturates. They also use
high base-drive currents under large loads. The
RT9182 does not suffer from these problems and
consume only 165µA of quiescent current whether in
dropout, light-load, or heavy-load applications.
Current Limit and Thermal Protection
The RT9182 includes two independent current limit
structure which monitor and control each pass
transistor’s gate voltage limiting the guaranteed
maximum output current to 200mA minimum.
event of fault conditions. Do not exceed the absolute
maximum junction-temperature rating of T
for continuous operation. The output can be shorted
to ground for an indefinite amount of time without
damaging the part by cooperation of current limit and
thermal protection.
Operating Region and Power Dissipation
The maximum power dissipation of RT9182 depends
on the thermal resistance of the case and circuit
board, the temperature difference between the die
junction and ambient air, and the rate of airflow. The
power dissipation across the device is
P = I
The maximum power dissipation is:
PMAX = (T
where TJ - TA is the temperature difference between
the RT9182 die junction and the surrounding
environment, θ
junction to the surrounding environment. The GND
pin of the RT9182 performs the dual function of
providing an electrical connection to ground and
channeling heat away. Connect the GND pin to
ground using a large pad or ground plane.
Low-Noise Operation
An external 10nF bypass capacitor at BP, in
conjunction with an internal resistor, creates a
lowpass filter. The RT9182 exhibits 29µVRMS of
output voltage noise with C
2.2µF.
OUT
(VIN - V
- TA) / θ
J
JA
).
OUT
JA
is the thermal resistance from the
= 10nF and C
BP
= +150°C
J
OUT
=
Thermal-overload protection limits total power
dissipation in the RT9182. When the junction
temperature exceeds T
sensor signals the shutdown logic turning off the
pass transistor and allowing the IC to cool. The
thermal sensor will turn the pass transistor on again
after the IC’s junction temperature cools by 10°C,
resulting in a pulsed output during continuous
thermal-overload conditions. Thermal-overloaded
protection is designed to protect the RT9182 in the
www.richtek-ic.com.tw DS9182-02 April 2002
= +140°C, the thermal
J
6

Applications Information
Preliminary
RT9182
Capacitor Selection and Regulator Stability
Like any low-dropout regulator, the external
capacitors used with the RT9182 must be carefully
selected for regulator stability and performance.
Using a capacitor whose value is > 1µF on the
RT9182 input and the amount of capacitance can be
increased without limit. The input capacitor must be
located a distance of not more than 0.5" from the
input pin of the IC and returned to a clean analog
ground. Any good quality ceramic or tantalum can be
used for this capacitor. The capacitor with larger
value and lower ESR (equivalent series resistance)
provides better PSRR and line-transient response.
The output capacitor must meet both requirements
for minimum amount of capacitance and ESR in all
LDO applications (see Fig.1). The RT9182 is
designed specifically to work with low ESR ceramic
output capacitor in space-saving and performance
consideration. Using a ceramic capacitor whose
value is at least 1µF with ESR is > 5mΩ on the
RT9182 output ensures stability. The RT9182 still
works well with output capacitor of other types due to
the wide stable ESR range. Output capacitor of larger
capacitance can reduce noise and improve load-
transient response, stability, and PSRR. The output
capacitor should be located not more than 0.5"
from the V
pin of the RT9182 and returned to a
OUT
clean analog ground.
Note that some ceramic dielectrics exhibit large
capacitance and ESR variation with temperature. It
may be necessary to use 2.2µF or more to ensure
stability at temperatures below -10°C in this case.
Also, tantalum capacitors, 2.2µF or more may be
needed to maintain capacitance and ESR in the
stable region for strict application environment.
Tantalum capacitors maybe suffer failure due to
surge current when it is connected to a low-
impedance source of power (like a battery or very
large capacitor). If a tantalum capacitor is used at the
input, it must be guaranteed to have a surge current
rating sufficient for the application by the
manufacture.
Region of Stable C
100
10
Ω
1
(mΩ)
ESR (Ω)
0.1
OUT
C
0.01
0.001
0 40 80 120 160 200
Load Current (mA)
ESR vs. Load Current
OUT
C
= 4.7µF
OUT
C
= 1µF
OUT
Fig. 1
Use a 10nF bypass capacitor at BP pin for low output
voltage noise. The capacitor, in conjunction with an
internal resistor, which connects bypass pin and the
band-gap reference, creates a low-pass filter for
noise reduction. Increasing the capacitance will
slightly decrease the output noise, and it is almost
independent of the start-up time. The capacitor
connected to the bypass pin for noise reduction must
have very low leakage. This capacitor leakage
current causes the output voltage to decline by a
proportional amount to the current.
Load-Transient Considerations
The RT9182 load-transient response graphs show
two components of the output response: a DC shift
from the output impedance due to the load current
change, and the transient response. The DC shift is
quite small due to the excellent load regulation of the
IC. Typical output voltage transient spike for a step
change in the load current from 0mA to 50mA is tens
mV, depending on the ESR of the output capacitor.
Increasing the output capacitor’s value and
decreasing the ESR attenuates the overshoot.
DS9182-02 April 2002 www.richtek-ic.com.tw
7

RT9182
Preliminary
Input-Output (Dropout) Voltage
A regulator’s minimum input-output voltage
differential (or dropout voltage) determines the lowest
usable supply voltage. In battery-powered systems,
this will determine the useful end-of-life battery
voltage. Because the RT9182 uses a P-channel
MOSFET pass transistor, the dropout voltage is a
function of drain-to-source on-resistance [R
DS(ON)
multiplied by the load current.
Reverse Current Path
The power transistor used in the RT9182 has an
inherent diode connected between each regulator
input and output (see Fig.2). If the output is forced
above the input by more than a diode-drop, this diode
will become forward biased and current will flow from
the V
terminal to VIN. This diode will also be
OUT
turned on by abruptly stepping the input voltage to a
value below the output voltage. To prevent regulator
mis-operation, a Schottky diode could be used in the
applications where input/output voltage conditions
can cause the internal diode to be turned on (see
Fig.3). As shown, the Schottky diode is connected in
parallel with the internal parasitic diode and prevents
it from being turned on by limiting the voltage drop
across it to about 0.3V < 100mA to prevent damage
to the part.
]
V
IN
V
OU T
Fig. 2
V
IN
V
OU T
Fig. 3
www.richtek-ic.com.tw DS9182-02 April 2002
8

Package Information
D
Preliminary
RT9182
C
b
A
e
B
A1
Symbol
A 0.889 1.295 0.035 0.051
A1 -- 0.152 -- 0.006
B 1.397 1.803 0.055 0.071
Dimensions In Millimeters Dimensions In Inches
Min Max Min Max
H
L
b 0.356 0.559 0.014 0.022
C 2.591 2.997 0.102 0.118
D 2.692 3.099 0.106 0.122
e 0.838 1.041 0.033 0.041
H 0.102 0.254 0.004 0.010
L 0.356 0.610 0.014 0.024
SOT- 26 Surface Mount Package
DS9182-02 April 2002 www.richtek-ic.com.tw
9

RT9182
Preliminary
RICHTEK TECHNOLOGY CORP.
Headquarter
6F, No. 35, Hsintai Road, Chupei City
Hsinchu, Taiwan, R.O.C.
Tel: (8863)5510047 Fax: (8863)5537749
www.richtek-ic.com.tw DS9182-02 April 2002
RICHTEK TECHNOLOGY CORP.
Taipei Office (Marketing)
8F-1, No. 137, Lane 235, Paochiao Road, Hsintien City
Taipei County, Taiwan, R.O.C.
Tel: (8862)89191466 Fax: (8862)89191465
Email: marketing@richtek-ic.com.tw
10
 Loading...
Loading...