Page 1
REG10J0121-0200
Renesas Starter Kit for SH7201
User's Manual
RENESAS SINGLE-CHIP MICROCOMPUTER
TM
SuperH
RISC engine
Rev.2.00 Renesas Technology Europe Ltd.
Revision date:11.Mar.2008 www.renesas.com
Page 2

Table of Contents
Chapter 1. Preface..................................................................................................................................................1
Chapter 2. Purpose.................................................................................................................................................2
Chapter 3. Power Supply........................................................................................................................................3
3.1. Requirements...............................................................................................................................................3
3.2. Power – Up Behaviour .................................................................................................................................3
Chapter 4. Board Layout.........................................................................................................................................4
4.1. Component Layout.......................................................................................................................................4
4.2. Board Dimensions........................................................................................................................................5
Chapter 5. Block Diagram.......................................................................................................................................6
Chapter 6. User Circuitry.........................................................................................................................................7
6.1. Switches.......................................................................................................................................................7
6.2. LEDs.............................................................................................................................................................7
6.3. Potentiometer...............................................................................................................................................7
6.4. Serial port.....................................................................................................................................................8
6.5. LCD Module..................................................................................................................................................8
6.6. Option Links..................................................................................................................................................9
6.7. Oscillator Sources ......................................................................................................................................12
6.8. Reset Circuit...............................................................................................................................................12
Chapter 7. Programming Methods........................................................................................................................13
Chapter 8. Headers...............................................................................................................................................14
8.1. Microcontroller Headers.............................................................................................................................14
8.2. Application Headers ...................................................................................................................................18
Chapter 9. Code Development .............................................................................................................................22
9.1. Overview.....................................................................................................................................................22
9.2. Compiler Restrictions .................................................................................................................................22
9.3. Breakpoint Support.....................................................................................................................................22
9.4. Memory Map...............................................................................................................................................22
Chapter 10. Component Placement......................................................................................................................23
Chapter 11. Additional Information........................................................................................................................25
ii
Page 3

Chapter 1. Preface
Cautions
This document may be, wholly or partially, subject to change without notice.
All rights reserved. No one is permitted to reproduce or duplicate, in any form, a part or this entire document without the written
permission of Renesas Technology Europe Limited.
Trademarks
All brand or product names used in this manual are trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective companies or
organisations.
Copyright
© Renesas Technology Europe Ltd. 2008. All rights reserved.
© Renesas Technology Corporation. 2008. All rights reserved.
© Renesas Solutions Corporation. 2008. All rights reserved.
Website:
Glossary
ADC Analog to Digital Converter USB Universal Serial Bus
CPU Central Processing Unit DAC Digital to Analog Converter
DMA Direct Memory Access E10A “E10A for Starter Kit” debugger
FDT Flash Development Tool RSK Renesas Starter Kit
LED Light Emitting Diode LCD Liquid Crystal Display
http://www.renesas.com/
1
Page 4

Chapter 2. Purpose
This RSK is an evaluation tool for Renesas microcontrollers.
Features include:
• Renesas Microcontroller Programming.
• User Code Debugging.
• User Circuitry such as switches, LEDs and potentiometer(s).
• Sample Application.
• Sample peripheral device initialisation code.
The CPU board contains all the circuitry required for microcontroller operation.
This manual describes the technical details of the RSK hardware. The Quick Start Guide and Tutorial Manual provide details of the
software installation and debugging environment.
2
Page 5

Chapter 3. Power Supply
3.1. Requirements
This CPU board operates from a 5V power supply.
A diode provides reverse polarity protection only if a current limiting power supply is used.
All CPU boards are supplied with an E10A debug module and a PSU. When the CPU board is connected to another system that system
should supply power to the CPU board.
All CPU boards have an optional centre positive supply connector using a 2.0mm barrel power jack.
Warning
The CPU board is neither under not over voltage protected. Use a centre positive supply for this board. Weher
possible use the supplied PSU.
3.2. Power – Up Behaviour
When the RSK is purchased the CPU board has the ‘Release’ or stand alone code from the example tutorial code pre-programmed into the
Renesas microcontroller. On powering up the board the user LEDs will start to flash. Pressing any switch will cause the LEDs to flash at a
rate controlled by the potentiometer.
3
Page 6
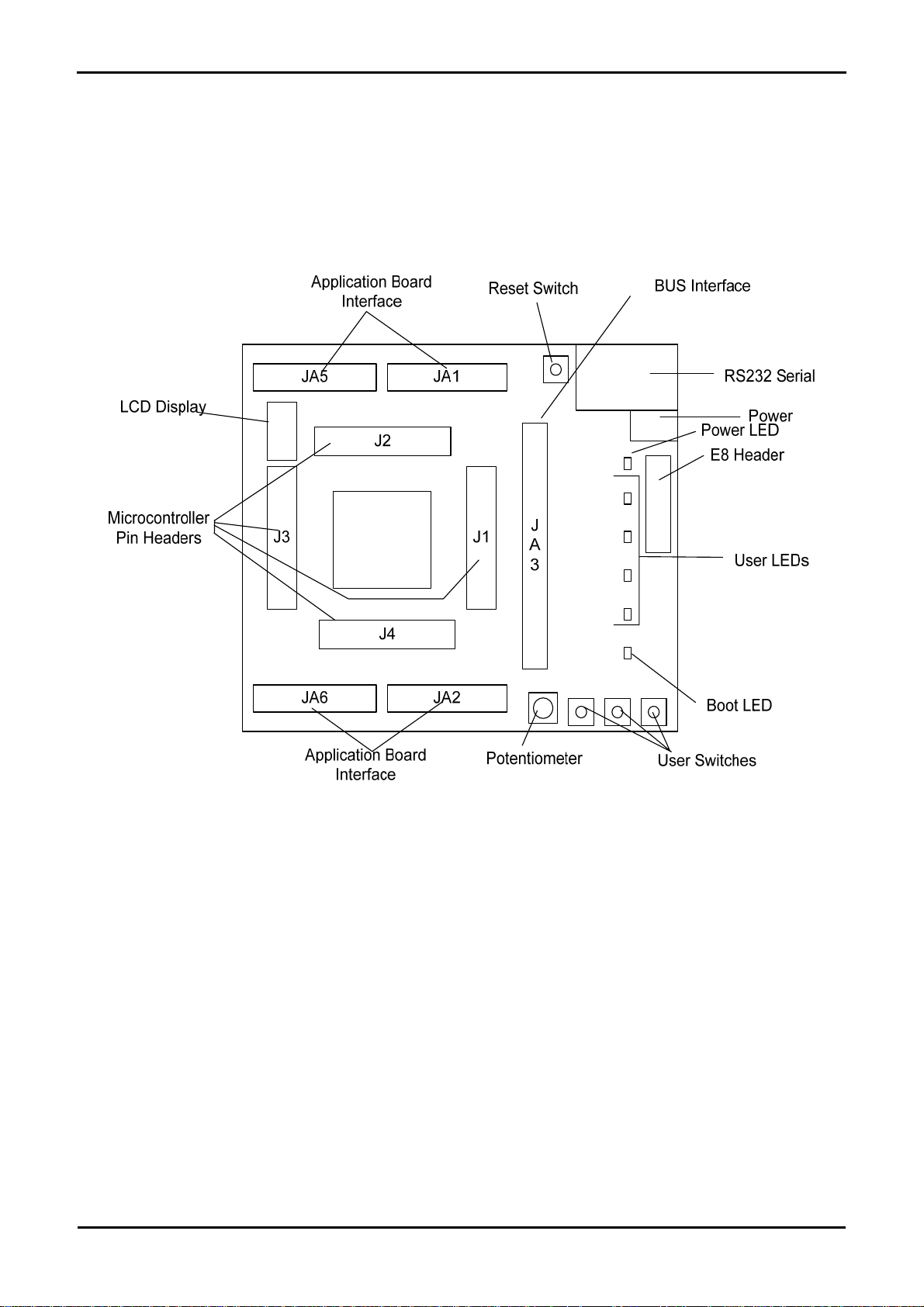
Chapter 4. Board Layout
4.1. Component Layout
The following diagram shows top layer component layout of the board.
Figure 4-1: Board Layout
4
Page 7
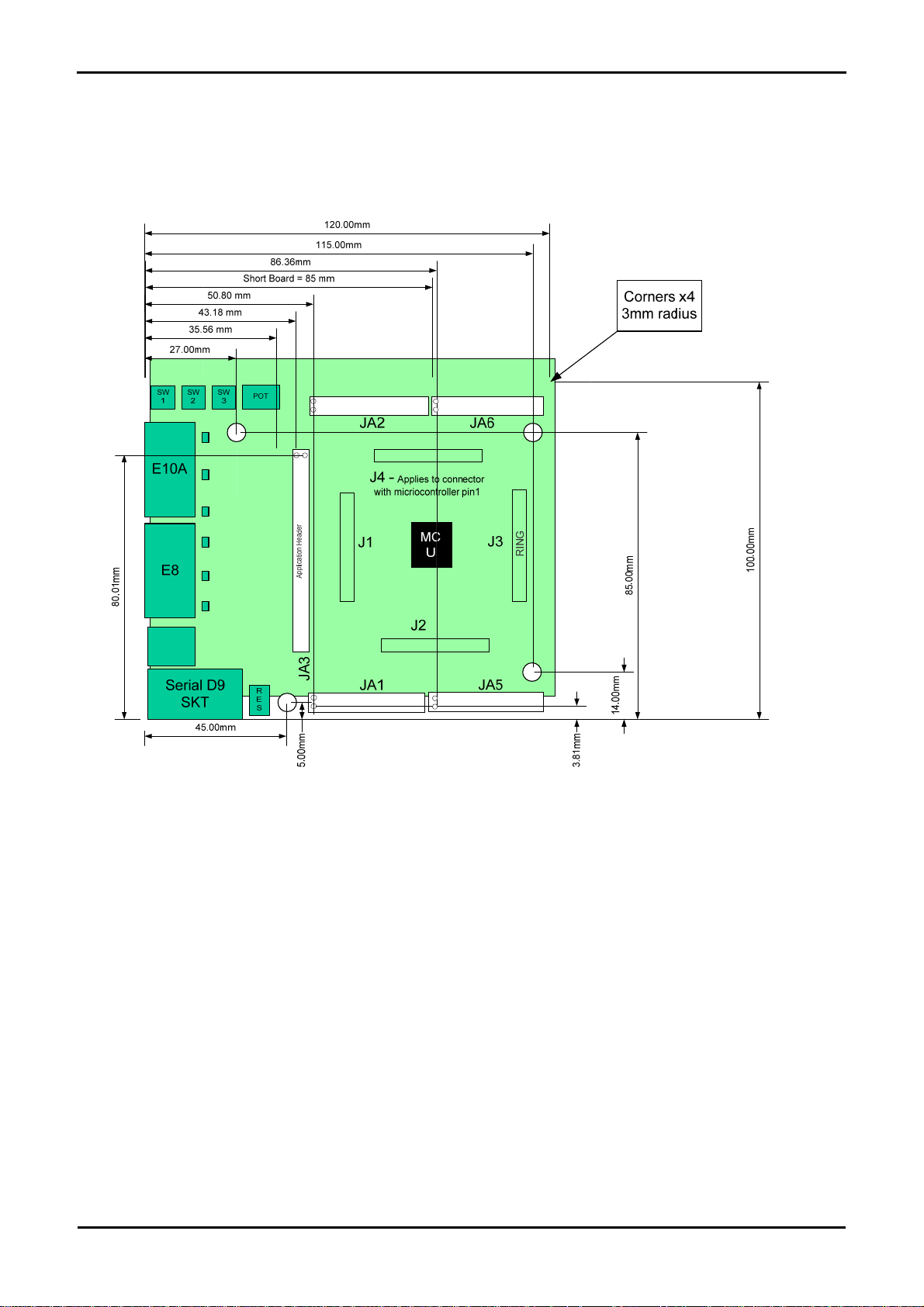
4.2.Board Dimensions
The following diagram gives the board dimensions and connector positions. All through hole connectors are on a common 0.1” grid for easy
interfacing.
Figure 4-2 : Board Dimensions
5
Page 8
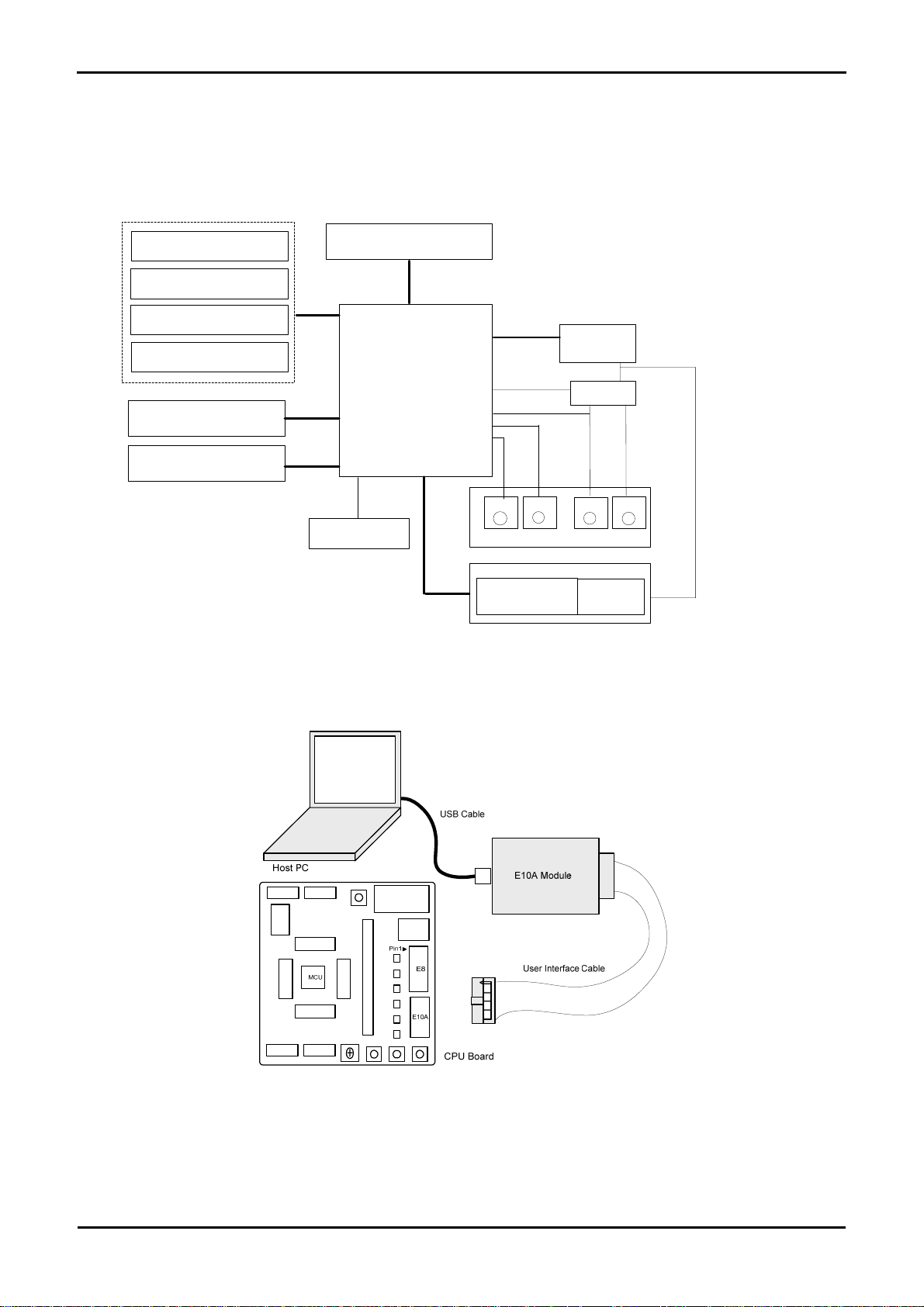
Chapter 5. Block Diagram
Figure 5-5-1 shows the CPU board components and their connectivity.
Application Board
Headers
Microcontroller Pin
Headers
Debug Header Option
Serial Connector Option
External Flash ROM
(4MB)
External SDRAM
(16MB)
Power Jack Option
Microcontroller
ADC Input
Potentiometer
Figure 5-5-1: Block Diagram
Boot mode pins
RESET pin
IRQ pin
IRQ pin
IRQ pin
RESn
SW3SW2
SWITCHES
User: 4 LEDS
1Green, 1Orange, 2Red
LEDs
Boot Circuitry
D-type latch
BOOT
Power: Green
Boot: Orange
BOOT & BOOTn signals
RES
Figure 5-5-2 shows the connections to the RSK.
Figure 5-5-2 : RSK Connections
6
Page 9
Chapter 6. User Circuitry
6.1. Switches
There are four switches located on the CPU board. The function of each switch and its connection are shown in Table 6-1.
Switch Function Microcontroller
RES When pressed; the CPU board microcontroller is reset. RESn, Pin 2
SW1/BOOT* Connects to an IRQ input for user controls.
The switch is also used in conjunction with the RES switch to place
the device in BOOT mode.
SW2* Connects to an IRQ line for user controls. IRQ1 , Pin 58
SW3* Connects to an IRQ line for user controls. Also connects to the ADC
trigger input. The option is a pair of 0R links. For more details on
option links, please refer to
*Refer to schematic for detailed connectivity information.
Sec 6.6.
Table 6-1: Switch Functions
IRQ0, Pin 59
(Port C, bit 22 )
(Port C, bit 23)
IRQ2, Pin 57
(Port C, bit 24)
6.2. LEDs
There are six LEDs on the CPU board. The green ‘POWER’ LED lights when the board is powered. The orange BOOT LED indicates the
device is in BOOT mode when lit. The four user LEDs are connected to an IO port and will light when their corresponding port pin is set low.
Table 6-2, below, shows the LED pin references and their corresponding microcontroller port pin connections.
LED Reference (As
shown on silkscreen)
LED0 Port D bit 13 108 Active Low
LED1 Port C bit 13 68 Active Low
LED2 Port C bit 20 61 Active Low
LED3 Port C bit 21 60 Active Low
Microcontroller Port Pin
function
Table 6-2: LED Port
Microcontroller Pin
Number
Polarity
6.3. Potentiometer
A single turn potentiometer is connected to AN0 of the microcontroller. This may be used to vary the input analog voltage value to this pin
between AVCC and Ground.
7
Page 10

6.4. Serial port
The microcontroller programming serial port (SCIF5) is connected to the E8 connector. This serial port can optionally be connected to the
RS232 transceiver by fitting option resistors and the D connector in position J7. The connections to be fitted are listed in the following table.
Description Function Fit for RS232 Remove for E8a Fit for Rs232 Remove for
RS232
TxD5 Programming Serial Port R90 R71 R71 R90
RxD5 Programming Serial Port R92 R77 R77 R92
Table 6-3: Serial Options Links
The board is designed to accept a straight through RS232 cable.
6.5. LCD Module
The LCD module supplied with the RSK can be connected to the connector J6 for use with the tutorial code. Any module that conforms to
the pin connections and has a KS0066u compatible controller can be used. The LCD module uses a 4bit interface to reduce the pin
allocation. No contrast control is provided; this must be set on the display module.
Table 6-4 shows the pin allocation and signal names used on this connector.
The module supplied with the CPU board only supports 5V operation.
J13
Pin Circuit Net Name Device
Pin
1 Ground - 2 5V Only 3 No Connection - 4 DLCDRS 70
5 R/W (Wired to Write only) - 6 DLCDE 69
7 No Connection - 8 No connection 9 No Connection - 10 No connection 11 DLCD4 121 12 DLCD5 120
13 DLCD6 119 14 DLCD7 118
Table 6-4 LCD Module Connections
Pin Circuit Net Name Device
Pin
8
Page 11
6.6. Option Links
Table 6-5 below describes the function of the option links contained on this CPU board. The default configuration is indicated by BOLD
text.
Option Link Settings
Reference Function Fitted Alternative ( Removed ) Related To
R7 FLASH memory Write protects Flash Memory Does not write protect Flash Memory
R8 A-D/D-A Connects microcontroller pin 92 to
AN6
R9 A-D/D-A
R10 A-D/D-A
R11 A-D/D-A Connects microcontroller pin 93 to
R16 Operating mode Connects MD1 = 0
R17 Operating mode Connects MD0 = 1
R18 Operating mode
R19 Potentiometer
R20 SDRAM chip
select
R21 Analog Input Connects microcontroller pin 86 to
Connects microcontroller pin
92 to DA0
Connects microcontroller pin
93 to DA1
AN7
Connects MD0 = 0
Connects potentiometer to
microcontroller pin 86
Enables SDRAM Chip Select
Disconnects microcontroller pin 92
from AN6
Disconnects microcontroller pin 92 from
DA0
Disconnects microcontroller pin 93 from
DA1
Disconnects microcontroller pin 93
from AN7
Does not connect MD1 = 0
Does not connect MD0 = 1
Does not connect MD0 = 0 R17
Disconnects potentiometer from
microcontroller pin 86
Disables SDRAM Chip Select
Disconnects microcontroller pin 86
R9
R8
R11
R10
R15
R18
R21
R19
AN0
R23 Chip Select Connects microcontroller pin 81 to
CS2n
R24 FLASH chip
select
R25 ADTRGn
R26 Transceiver
R28 Motor Control Connects microcontroller pin 80 to
R29 Chip Select
R30 Write Signal Connects microcontroller pin 72 to
R31 CAN
Enables FLASH Chip Select
Connects microcontroller pin
81 to ADTRGn
Enables read from Expansion
Connector
TRISTn
Connects microcontroller pin
80 to CS3n
WRn
Connects microcontroller pin
from AN0
Disconnects microcontroller pin 81
from CS2n
Disables FLASH Chip Select
Disconnects microcontroller pin 81 from
ADTRGn
Disables read from Expansion Connector
Disconnects microcontroller pin 80
from TRISTn
Disconnects microcontroller pin 80 from
CS3n
Disconnects microcontroller pin 72
from WRn
Disconnects microcontroller pin 170 from
R25
R23, R59
R29
R28
R33
R32, R127
170 to CAN1_STBn
CAN1_STBn
9
Page 12

R32 Motor Connects microcontroller pin 170
to UD
R33 Write Signal Connects microcontroller pin 72 to
WR0n
R34 Operating mode Connects MD_CLK1 = 1
R35 Operating mode Connects MD_CLK0 = 1
R36 Operating mode
R37 Operating mode
Connects MD_CLK1= 0
Connects MD_CLK0= 0
R39 Power supply Connects AVREF to CON_VREF
R44 Oscillator X1 Connects external clock source to
microcontroller via CON_EXTAL
R45 Oscillator X1 Feedback resistor across X1
R46 Oscillator X1
Connects X1 to microcontroller
R47 Oscillator X1 Connects external clock source to
microcontroller via CON_XTAL
R48 Oscillator X2 Connects external clock source to
Disconnects microcontroller pin 170
R31
from UD
Disconnects microcontroller pin 72
R30
from WR0n
Does not connect MD_CLK1 = 1
Does not connect MD_CLK0 = 1
R36
R37
Does not connect MD_CLK1 = 0 R34
Does not connect MD_CLK0 = 0 R35
Disconnects AVREF from CON_VREF
Disconnects external clock source
R72
R47
from microcontroller
No feedback
-
Disconnects X1 from microcontroller -
Disconnects external clock source
R44
from microcontroller
Disconnects external clock source
R50
microcontroller via CON_RTC_X1
R49 Oscillator X2
Connects X2 to microcontroller
R50 Oscillator X2 Connects external clock source to
microcontroller via CON_RTC_X2
R51 Oscillator X2
Connects X2 to microcontroller
R52 Oscillator X2 Feedback resistor across X2
R54 Serial port
R55 Serial port
R56 Power supply
Connects RXD1 to J10
Connects TXD1 to J10
Connects AVCC to Board_VCC
R57 Power supply Connects AVCC to CON_AVCC
R59 Switches Connects SW3 to ADTRGn
R60 Serial port Connects RS323TX to U9
R62 Power supply
R63 Switches
Connects GROUND to AVSS
Connects SW3 to IRQ2n
R64 Serial port Connects TxD1 to U9
R66 Serial port
Connects TxD0 to U9
from microcontroller
Disconnects X2 from microcontroller R51
Disconnects external clock source
R48
from microcontroller
Disconnects X2 from microcontroller R49
No feedback
Disconnects RXD1 from J10 R55
Disconnects TXD1 from J10 R54
Disconnects AVCC from Board_VCC R57, R72
Disconnects AVCC from CON_AVCC
Disconnects SW3 from ADTRGn
Disconnects RS232TX from U9
R56
R25, R63
R66, R71,
Disconnects GROUND from AVSS Disconnects SW3 from IRQ2n R59
Disconnects TxD1 from U9
R81
Disconnects TxD0 from U9 R60, R71,
R90, R92
R68 Power supply
Connects UC_VCC to
Disconnects UC_VCC from Board_VCC R80, R83
Board_VCC
R69 Power Supply
R70 Serial port Connects RS232RX to U9
Connects CON_5V to Supply
regulator input
Disconnects CON_5V from Supply
regulator input
Disconnects RS323RX from U9
R102
R73, R77,
R92
10
Page 13

R71 Serial port Connects serial port PTTX to
RS232 Serial
R72 Power supply
R73 Serial port
R76 Power supply
Connects VREF to Board_VCC
Connects RS232 Serial to RxD0
Connects LCD power to internal
5V
R77 Serial port Connects serial port PTRX to
RS232 Serial
R78 Serial port Shuts down RS232 transceiver
R80 Power supply
Connects Board_VCC to
CON_3V3
R81 Serial port Connects RxD1 to U9
R82 Serial port
R83 Power supply
Enables RS232 transceiver
Connects 3.3V supply from U8
to Board_VCC
Disconnects serial port PTTX from
RS232 Serial
R60, R66,
R90
Disconnects VREF from Board_VCC R56, R39
Disconnects RS232 Serial from RxD0 R70, R77,
R92
Disconnects LCD power from internal 5V R102
Disconnects serial port PTRX from
RS232 Serial
Enables RS232 transceiver
R70, R73,
R92
R82
Disconnects Board_VCC from CON_3V3 R68, R83
Disconnects RxD1 from U9
R64
Shuts down RS232 transceiver R78
Disconnects 3.3V supply from U8 R68, R80
R90 E8 connector
R92 E8 connector
R102 Power Supply
R104 CAN transceiver
0
R106 CAN transceiver
0
R107 CAN transceiver
0
R108 CAN transceiver
0
R109 CAN transceiver
1
R111 CAN transceiver
Connects PTTX to E8_TXD on
E8 connector
Connects PTRX to E8_RXD on
E8 connector
Connects J11 to Board_VCC
Connects CAN0_EN to CAN
transceiver 0
Connects CRx0 to CAN
transceiver 0
Connects 5V to CAN
transceiver 0 VBAT
Connects CTx0 to CAN
transceiver 0
Connects CAN1_EN to CAN
transceiver 1
Connects CRx1 to CAN
Disconnects PTTX from E8_TXD R60, R71
Disconnects PTRX from E8_RXD R70, R77
J11 disconnected from Board_VCC Disconnects CAN0_EN from CAN
R105
transceiver
Disconnects CRx0 from CAN transceiver -
Disconnects 5V from CAN transceiver -
Disconnects CTx0 from CAN transceiver -
Disconnects CAN1_EN from CAN
R110
transceiver
Disconnects CRx1 from CAN transceiver -
1
R112 CAN transceiver
1
R118 CAN transceiver
1
R120 CAN transceiver
1
transceiver 1
Connects CTx1 to CAN
transceiver 1
Connects 5V to CAN
transceiver 1 VBAT
Connects CAN0_ERRn to
microcontroller pin 173
11
Disconnects CTx1 from CAN transceiver -
Disconnects 5V from CAN transceiver -
Disconnects CAN0_ERRn from
microcontroller pin 173
-
Page 14

R123 CAN transceiver
0
R124 CAN transceiver
0
R127 CAN transceiver
0
R130 Power supply
R134 Interrupt Connects BUSYn from FLASH
Connects CAN0_STBn to
microcontroller pin 166
Connects CAN1_ERRn to
microcontroller pin 174
Connects CAN1_STBn to R31
Connects E8_VCC to the
regulator input
memory chip U3 to microcontroller
IRQ3n
Table 6-5 Option Links
Disconnects CAN0_STBn from
microcontroller pin 166
Disconnects CAN1_ERRn from
microcontroller pin 174
Disconnects CAN0_STBn from R31 R31
Disconnects E8_VCC from the regulator
input
Disconnects BUSYn from FLASH
memory chip U3 from microcontroller
IRQ3n
-
-
R102
-
6.7. Oscillator Sources
A crystal oscillator is fitted on the CPU board and used to supply the main clock input to the Renesas microcontroller. details the
oscillators that are fitted and alternative footprints provided on this CPU board:
Table 6-
Component
Crystal (X1) Fitted 10MHz (HC49/4H package)
Crystal (X2) Fitted 32.768kHz (90SMX package)
Table 6-6: Oscillators / Resonators
Warning: When replacing the default oscillator with that of another frequency, the debugging monitor will not function unless the following
are corrected:
• FDT programming kernels supplied are rebuilt for the new frequency
6.8. Reset Circuit
The CPU Board includes a simple latch circuit that links the mode selection and reset circuit. This circuit is not required on customers’
boards as it is intended for providing easy evaluation of the operating modes of the device on the RSK. Please refer to the hardware
manual for more information on the requirements of the reset circuit.
The reset circuit operates by latching the state of the boot switch (SW1) on pressing the reset button. This control is subsequently used to
modify a port pin state to select which code is executed.
The reset is held in the active state for a fixed period by a pair of resistors and a capacitor. Please check the reset requirements carefully to
ensure the reset circuit on the user’s board meets all the reset timing requirements.
12
Page 15

Chapter 7. Programming Methods
The board is intended for use with HEW and the supplied E10A debugger only. Please refer to the datasheet of the Flash memory used on
this RSK to learn programming methods of the Flash programming.
13
Page 16

Chapter 8.Headers
8.1. Microcontroller Headers
Table 8-1 to show theTable 8-4 microcontroller pin headers and their corresponding microcontroller connections. The header pins
connect directly to the microcontroller pin unless otherwise stated.
* marks pins where a the link to the microcontroller pin is open circuit due to unfitted link (link ID in brackets)
J1
Pin Circuit Net Name Device Pin Pin Circuit Net Name Device Pin
1 GND - 23 A(5) 23
2 RESn 2 24 A(6) 24
3 UC_VCC - 25 A(7) 25
4 NMI 4 26 A(8) 26
5 GND - 27 A(9) 27
6 CON_RTC_X1* 7 28 A(10) 28
7 CON_RTC_X2* 6 29 A(11) 29
8 GND - 30 A(12) 30
9 CON_XTAL* 9 31 A(13) 31
10 COM_EXTAL* 10 32 A(14) 32
11 GND - 33 A(15) 33
12 CKIO* 12 34 A(16) 34
13 UC_VCC - 35 A(17) 35
14 MD_CLK0 14 36 A(18) 36
15 MD_CLK1 15 37 A(19) 37
16 GND - 38 GND 17 A(0) 17 39 A(20) 39
18 UC_VCC - 40 UC_VCC 19 A(1) 19 41 A(21) 41
20 A(2) 20 42 A(22) 42
21 A(3) 21 43 A(23) 43
22 A(4) 22 44 Not connected -
Table 8-1: J1 microcontroller header
14
Page 17

J2
Pin Circuit Net Name Device
Pin
Pin Circuit Net Name Device
Pin
1 GND - 23 SDCKE 67
2 DREQ3 46 24 LED1 68
3 DACK3 47 25 DLCDE 69
4 DACT3 48 26 DLCDRS 70
5 DTEND3 49 27 WR1n 71
6 CTx0 50 28 WR0n_WRn 72
7 CRx0 51 29 RDn 73
8 CTx1 52 30 GND -
9 UC_VCC - 31 SDCS0n 75
10 CRx1 54 32 UC_VCC 11 GND - 33 PTCK 77
12 IRQ3n 56 34 PTRX 78
13 IRQ2n 57 35 PTTX 79
14 IRQ1n 58 36 CS3n_TRISTn 80
15 IRQ0n 59 37 CS2n_ADTRGn 81
16 LED3 60 38 CS1n 82
17 LED2 61 39 CS0n 83
18 DQM1 62 40 AVCC 19 DQM0 63 41 VREF 20 SDWEn 64 42 ADPOT_AN0 86
21 SDCASn 65 43 AN1 87
22 SDRASn 66 44 AN2 88
Table 8-2: J2 microcontroller header
15
Page 18

J3
Pin Circuit Net Name Device Pin Pin Circuit Net Name Device Pin
1 AN3 89 23 TxD1 111
2 AN4 90 24 SCK0 112
3 AN5 91 25 RxD0 113
4 AN6_DA0 92 26 TxD0 114
5 AN7_DA1 93 27 SCK4 115
6 AVSS - 28 RxD4 116
7 IO0 95 29 TxD4 117
8 IO1 96 30 DLCD7 118
9 IO2 97 31 DLCD6 119
10 IO3 98 32 DLCD5 120
11 IO4 99 33 DLCD4 121
12 IO5 100 34 GND 13 UC_VCC - 35 PIN123 123
14 IO6 102 36 PIN124 124
15 GND - 37 GND 16 IO7 104 38 UDTRSTn 126
17 SCL2 105 39 UC_VCC 18 SDA2 106 40 UDTMS 128
19 LED0 108 41 UDTDO 129
20 BOOTn 107 42 UDTDI 130
21 SCK1 109 43 UDTCK 131
22 RxD1 110 44 ASEBRKn 132
Table 8-3: J3 microcontroller header
16
Page 19

J4
Pin Circuit Net Name Device Pin Pin Circuit Net Name Device Pin
1 ASEMDn 133 23 GND -
2 MD1 134 24 TIOC3A 154
3 MD0 135 25 UC_VCC -
4 WDT_OVFn 136 26 Up 158
5 GND - 27 TIOC3C 159
6 D(0) 138 28 Un 160
7 UC_VCC - 29 Vp 161
8 D(1 140 30 Wp 162
9 D(2) 141 31 Vn 163
10 D(3) 142 32 Wn 164
11 D(4) 143 33 CAN0_EN 165
12 D(5) 144 34 CAN0_STBn 166
13 D(6) 145 35 UC_VCC 14 D(7) 146 36 CAN1_EN 168
15 D(8) 147 37 GND 16 D(9) 148 38 UD_CAN1_STBn 170
17 D(10) 149 39 TMO0 171
18 D(11) 150 40 TMRI0 172
19 D(12) 151 41 CAN1_ERRn* 174
20 D(13) 152 42 CAN0_ERRn* 173
21 D(14) 153 43 UC_VCC 22 D(15) 154 44 MRESn 176
Table 8-4: J4 microcontroller header
17
Page 20

8.2.Application Headers
Table 8-5 and belowTable 8-6 show the standard application header connections.
Note: Asterisk indications apply to all tables in this section
* marks pins where a the link to the microcontroller pin is via a 100R resistor and to BOARD VCC via a 4k7 resistor (100R ID & 4k7 ID)
** marks pins where a the link to the microcontroller pin is open circuit due to unfitted link (link ID in brackets)
*** marks pins where a the link to the microcontroller pin is via a fitted 0R link (link ID in brackets)
JA1
Pin Header Name CPU board
Signal Name
1 5V CON_5V - 14 DAC1 DA1 93*** (R10)
2 0V(5V) GROUND - 15 IO_0 IO0 95
3 3V3 CON_3V3 - 16 IO_1 IO1 96
4 0V(3V3) GROUND - 17 IO_2 IO2 97
5 AVcc CON_AVCC 84** (R57) 18 IO_3 IO3 98
6 AVss AVSS 94 19 IO_4 IO4 99
7 AVref CON_VREF 85** (R39) 20 IO_5 IO5 100
8 ADTRG ADTRGn 57** (R59) 21 IO_6 IO6 101
9 AD0 AN0 86** (R21) 22 IO_7 IO7 102
10 AD1 AN1 87 23 IRQ3 IRQ3n 56
11 AD2 AN2 88 24 IIC_EX - 12 AD3 AN3 89 25 IIC_SDA SDA2 106* (R13 & R4)
13 DAC0 DA0 92*** (R9) 26 IIC_SCL SCL2 105* (R12 & R3)
Device Pin Pin Header Name CPU board
Signal Name
Table 8-5: JA1 Standard Generic Header
Device Pin
18
Page 21

JA2
Pin Header Name CPU board
Signal Name
Device Pin Pin Header Name CPU board
Signal Name
Device Pin
1 RESn RESn 2 14 Un Un 160
2 EXTAL CON_EXTAL 10** (R44) 15 Vp Vp 161
3 NMIn NMI 4 16 Vn Vn 163
4 Vss1 GROUND - 17 Wp Wp 162
5 WDT_OVF WDT_OVFn 136 18 Wn Wn 164
6 SCIaTX TxD0 114 19 TMR0 TMO0 171
7 IRQ0 IRQ0n 59 20 TMR1 TIOC3A 156
8 SCIaRX RXD0 113 21 TRIGa TMRI0 172
9 IRQ1 IRQ1n 58 22 TRIGb TIOC3C 159
10 SCIaCK SCK0 112 23 IRQ2 IRQ2n 57
11 UD UD 170** (R32) 24 TRISTn TRISTn 80** (R28)
12 CTSRTS - - 25 Reserved
13 Up Up 158 26 Reserved
Table 8-6: JA2 Standard Generic Header
19
Page 22

JA3
Pin Header Name CPU board
Signal Name
Device Pin Pin Header Name CPU board
Signal Name
Device Pin
1 BA(0) BA(0) - 26 BWRn BWRn -
2 BA(1) BA(1) - 27 BCS1n BCS1n -
3 BA(2) BA(2) - 28 BCS2n BCS2n -
4 BA(3) BA(3) - 29 BD(8) BD(8) -
5 BA(4) BA(4) - 30 BD(9) BD(9) -
6 BA(5) BA(5) - 31 BD(10) BD(10) -
7 BA(6) BA(6) - 32 BD(11) BD(11) -
8 BA(7) BA(7) - 33 BD(12) BD(12) -
9 BA(8) BA(8) - 34 BD(13) BD(13) 10 BA(9) BA(9) - 35 BD(14) BD(14) 11 BA(10) BA(10) - 36 BD(15) BD(15) 12 BA(11) BA(11) - 37 BD(16) BD(16) 13 BA(12) BA(12) - 38 BD(17) BD(17) 14 BA(13) BA(13) - 39 BD(18) BD(18) 15 BA(14) BA(14) - 40 BD(19) BD(19) 16 BA(15) BA(15) - 41 BD(20) BD(20) 17 BD(0) BD(0) - 42 BD(21) BD(21) 18 BD(1) BD(1) - 43 BD(22) BD(22) 19 BD(2) BD(2) - 44 BSDCLK BSDCLK 20 BD(3) BD(3) - 45 BCS3n BCS3n 21 BD(4) BD(4) - 46 Bus Control --- 22 BD(5) BD(5) - 47 BWR1n BWR1n 23 BD(6) BD(6) - 48 BWR0n BWR0n 24 BD(7) BD(7) - 49 Data Bus Strobe --- 25 BRDn BRDn - 50 Reserved --- -
Table 8-7: JA3 Standard Generic Header
20
Page 23

JA5
Pin Header Name CPU board
Signal Name
Device Pin Pin Header Name CPU board
Signal Name
1 AD4 AN4 90 13 Reserved
2 AD5 AN5 91 14 Reserved
3 AD6 AN6 92** (R8) 15 Reserved
4 AD7 AN7 93** (R11) 16 Reserved
5 CAN1TX CTx0 50 17 Reserved
6 CAN1RX CRx0 51 18 Reserved
7 CAN2TX CTx1 52 19 Reserved
8 CAN2TX CTx1 54 20 Reserved
9 Reserved 21 Reserved
10 Reserved 22 Reserved
11 Reserved 23 Reserved
12 Reserved 24 Reserved
Table 8-8: JA5 Standard Generic Header
JA6
Device Pin
Pin Header Name CPU board
Signal Name
Device Pin Pin Header Name CPU board
Signal Name
Device Pin
1 DREQ DREQ3 46 13 Reserved
2 DACK DACK3 47 14 Reserved
3 TEND DTEND3 49 15 Reserved
4 STBYn DACT3 48 16 Reserved
5 RS232TX RS232TX (R60)**** 17 Reserved
6 RS232RX RS232RX (R70)**** 18 Reserved
7 SCIbRX RxD1 110 19 Reserved
8 SCIbTX TxD1 111 20 Reserved
9 SCIcTX TxD4 117 21 Reserved
10 SCIbCX SCK1 109 22 Reserved
11 SCIcCK SCK4 115 23 Reserved
12 SCIcRX RxD4 116 24 Reserved
Table 8-9: JA6 Standard Generic Header
**** This signal is only connected to the named link, which is not fitted to the board. For details refer to the RSKSH7201 circuit schematics
page 5
21
Page 24

Chapter 9. Code Development
9.1. Overview
Note: For all code debugging using Renesas software tools, the CPU board must be connected to a PC USB port via an E10A. An E10A is
supplied with the RSK product.
Due to the continuous process of improvements undertaken by Renesas the user is recommended to review the information provided on
the Renesas website at
www.renesas.com to check for the latest updates to the Compiler and Debugger manuals.
9.2. Compiler Restrictions
The compiler supplied with this RSK is fully functional for a period of 60 days from first use. After the first 60 days of use have expired, the
compiler will default to a maximum of 256k code and data. To use the compiler with programs greater than this size you will need to
purchase the full tools from your distributor.
9.3.Breakpoint Support
This RSK is supplied with E10A emulator which supports breakpoints in ROM. For more details on breakpoints & E10A functions please
refer to ‘SuperH Family E10A-USB Emulator User’s Manual’.
9.4.Memory Map
The memory map shown in this section visually describes the locations of the each memory areas when operating the RSK in the default
mode.
Figure 9-1: Memory Map
22
Page 25

Chapter 10. Component Placement
Figure 11-1: Component Placement (Top Layer)
23
Page 26
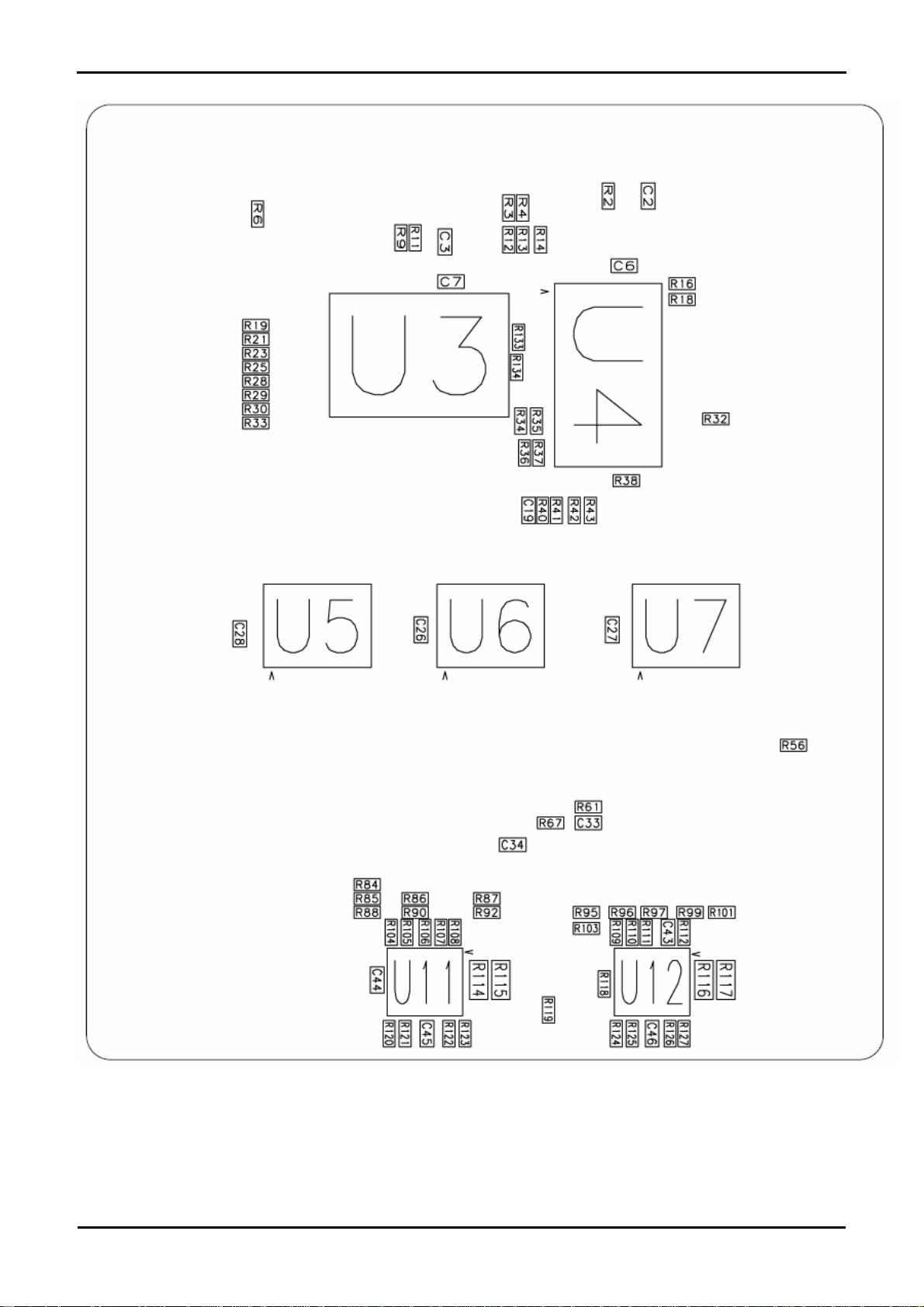
Figure 11-2: Component Placement (Bottom Layer)
24
Page 27

Chapter 11. Additional Information
For details on how to use High-performance Embedded Workshop (HEW), refer to the HEW manual available on the CD or installed in the
Manual Navigator.
For information about the SH7201 microcontrollers refer to the SH7201 Group Hardware Manual
For information about the SH7201 assembly language, refer to the SH Series Programming Manual
For information about the E10A Emulator, please refer to the SH Family E10A-USB Emulator User’s Manual.
Online technical support and information is available at:
Technical Contact Details
America:
Europe:
Japan:
General information on Renesas Microcontrollers can be found on the Renesas website at:
techsupport.rta@renesas.com
tools.support.eu@renesas.com
csc@renesas.com
http://www.renesas.com/renesas_starter_kits
http://www.renesas.com/
25
Page 28

Renesas Starter Kit for SH7201
User's Manual
Publication Date Rev.2.00 11.Mar.2008
Published by:
Renesas Technology Europe Ltd.
Duke’s Meadow, Millboard Road, Bourne End
Buckinghamshire SL8 5FH, United Kingdom
©2008 Renesas T echnology Europe and Renesas Solutions Corp., All Rights Reserved.
Page 29

Renesas Starter Kit for SH7201
User's Manual
Renesas Technology Europe Ltd.
Dukes Meadow, Millboard Road, Bourne End Buckinghamshire SL8 5FH, United Kingdom
 Loading...
Loading...