Page 1

APPLICATION NOTE
SH7145F
Asynchronous Serial Data Transmission/Reception
Summary
The SH7144 series is a single-chip microprocessor based on the SH-2 RISC (Reduced Instruction
Set Computer) CPU core and integrating a number of peripheral functions.
This application note describes asynchronous serial data transmission/reception using the SCI
(Serial Communication Interface) module of the SH7145F. It is intended to be used as reference
by users designing software applications.
The program examples contained in this application note have b een tested. However, operation
should be confirmed before using them in an actual application.
Device for Which Operation Has Been Confirmed
SH7145F
Contents
1. Specifications................................................................................................ 2
2 Functions Used ............................................................................................. 3
3. Operation....................................................................................................... 6
4. Software........................................................................................................ 8
5. Flowcharts..................................................................................................... 11
6. Program Listing............................................................................................. 14
REJ06B0357-0100O/Rev.1.00 March 2004 Page 1 of 17
Page 2
SH7145F
Asynchronous Serial Data Transmission/Reception
1. Specifications
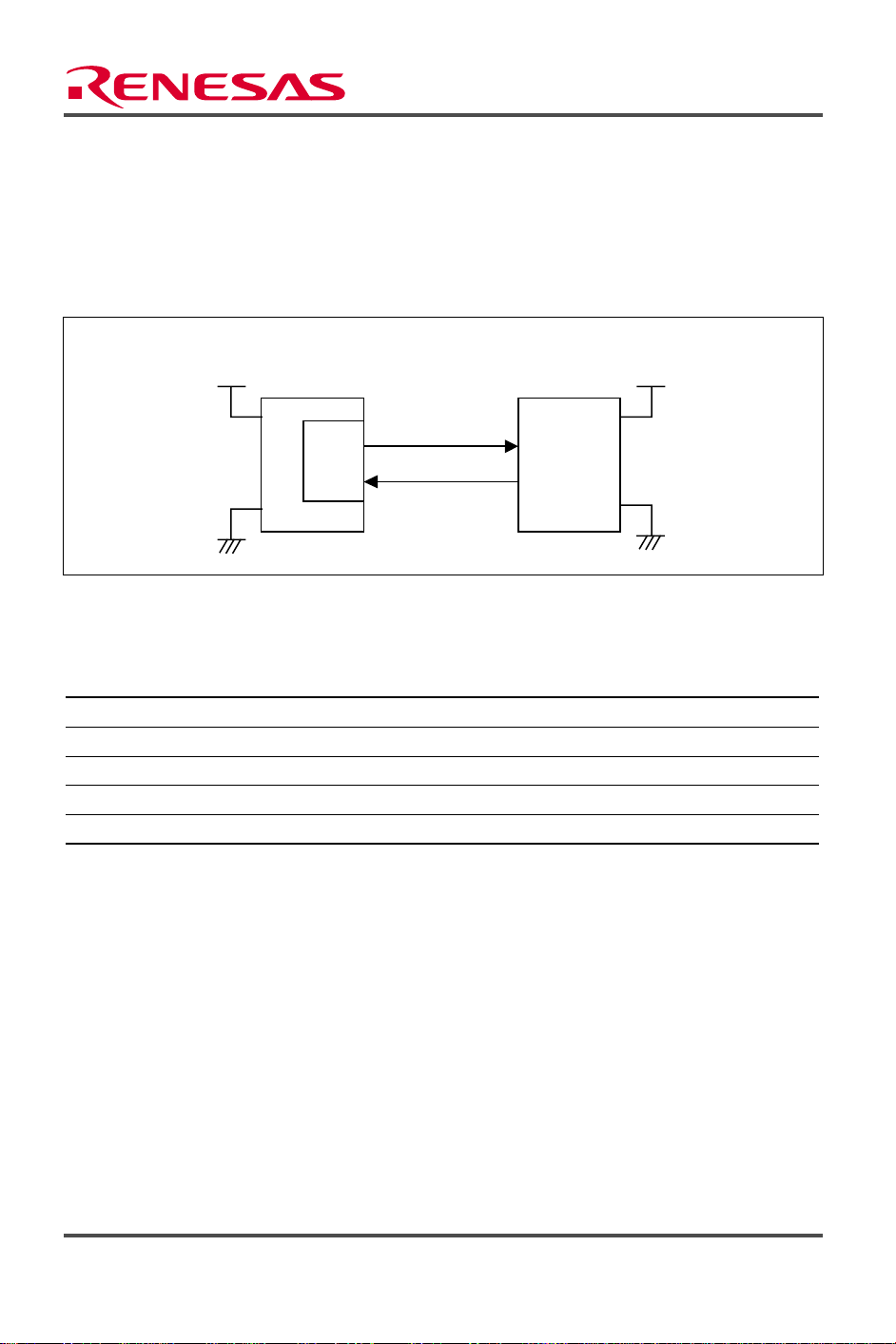
As shown in figure 1, asynchronous serial data transmission is performed using channel 1 (ch1) of
the SCI module of the SH7145F. In this task example 3 bytes of serial data are received by
SH7145,
and the receive data is then transmitted. The communication format is 192,000 bps, 8-
bit, one stop bit, and no parity.
Serial data
3.3 V 3.3 V
SH7145
transfer
target MCU
the
SCI
(ch1)
TXD
RXD
RXD
TXD
Figure 1 Asynchronous Serial Data Transmission/Reception by SH7145
Table 1 Asynchronous Serial Data Transmission Format
Format Item Setting
Bit rate 19200 bps
Data length 8 bits
Parity bit No
Stop bit 1 bit
Serial/parallel conversion format LSB first
REJ06B0357-0100O/Rev.1.00 March 2004 Page 2 of 17
Page 3
SH7145F
k
Asynchronous Serial Data Transmission/Reception
2 Functions Used
In this task example the SCI (Serial Communication Interface) is used to perform asynchronous
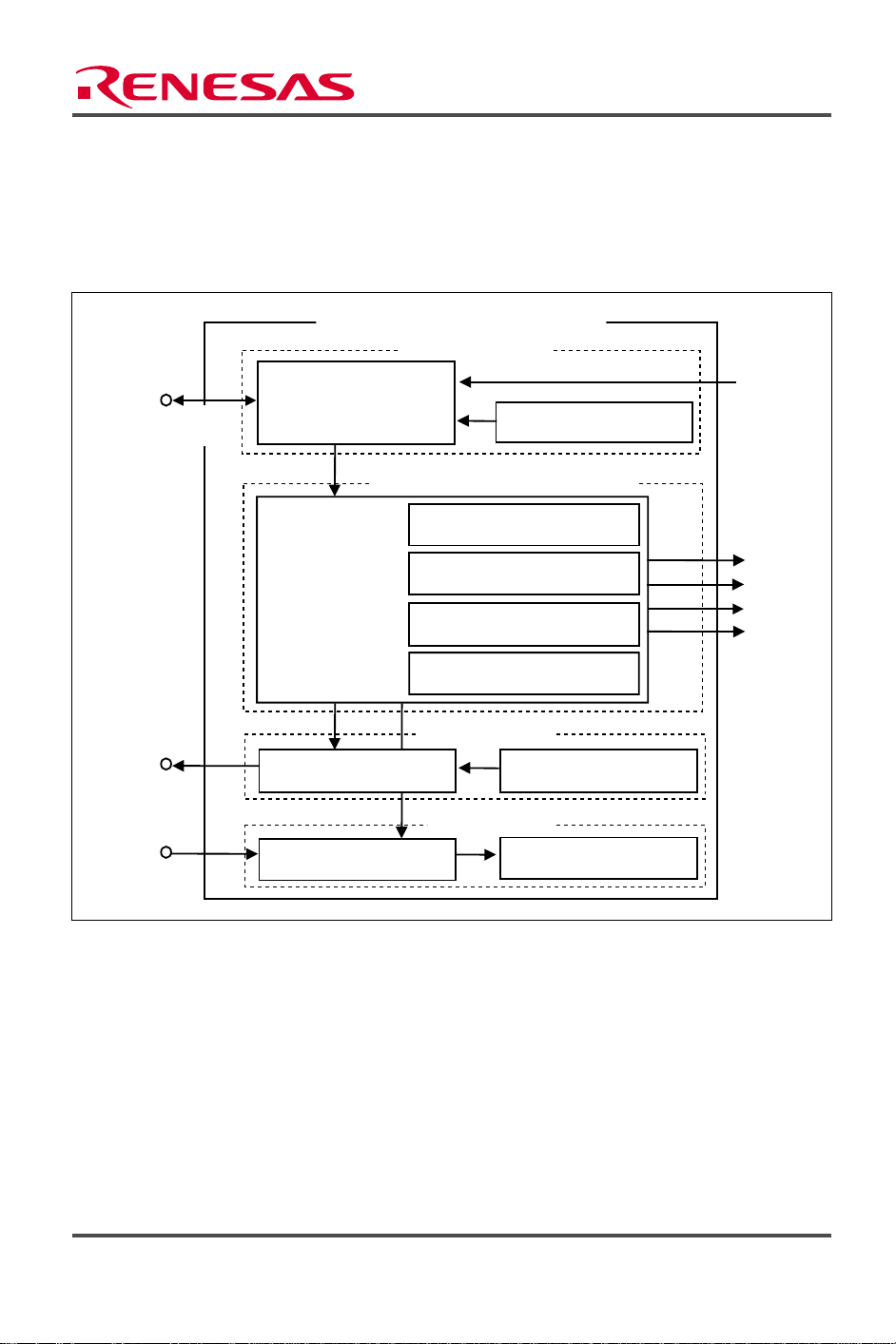
serial data transmission/reception. Figure 2 shows a block diagram of channel 1 (ch1) of the SCI
module. The functions of the elements shown in figure 2 are described below.
SCI0 synchronous serial transfer function block
On-chip
peripheral cloc
Pφ/128
Pφ/32
Pφ/8
Pφ1
SCI1 clock I/O pin
(SCK1)
External
clock
Baud rate generator
Clock
Transmit/receive operation control settings
Transfer rate generator
Bit rate register 1
(BRR_1)
SCI1 transmit data
output pin
(TXD1)
SCI1 receive data
input pin
(RXD1)
Transmit/receive
control circuit
Transmit shift register 1
(TSR_1)
Receive shift register 1
(RSR_1)
Serial mode register 1
(SMR_1)
Serial control register 1
(SCR_1)
Serial status register 1
(SSR_1)
Serial direction control register 1
(SDCR_1)
Transmit data control
Transmit data register 1
(TDR_1)
Receive data control
Receive data register 1
(RDR_1)
Interrupt
requests
Figure 2 SCI (ch1) Block Diagram
• Asynchronous Mode
Serial data communication is performed using synchronization by character unit. This allows
serial communication with a standard dedicated asynchronous communication chip such as a
Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter (UART) or Asynchronous Communication
Interface Adapter (ACIA). In addition, the asynchronous mode supports serial communication
among multiple processors (multiprocessor communication function).
TEI_1
TXI_1
RXI_1
ERI_1
REJ06B0357-0100O/Rev.1.00 March 2004 Page 3 of 17
Page 4

Asynchronous Serial Data Transmission/Reception
• On-Chip Peripheral Clock Pφ
This is the reference clock for operation of on-chip peripheral functions. The clock signal is
generated by a clock oscillator.
• Receive Shift Register (RSR_1)
This register is used to receive serial data. Serial data is i nput to RSR_1 from the RxD_1 pin.
When one frame of data has been received, it is automatically tra nsferred to the receive data
register (RDR_1). RSR_1 cannot be accessed by the CPU.
• Receive Data Register (RDR_1)
Received data is stored in this 8-bit register. When one frame of data has been received, it is
automatically transferred from RSR_1. RSR_1 and RDR_1 are in a double-buffer
configuration, allowing continuous reception of data. RDR_1 is a receive-only register, so it
can only be read b y the CPU.
• Transmit Shift Register (TSR_1)
This register is used to transmit serial data. In order to transmit data, the data is first
transferred from the transmit data register (TDR_1) to TSR_1. Then the transmit data is
output from the TxD_1 pin. TSR_1 cannot be accessed directly by the CPU.
• Transmit Data Register (TDR_1)
SH7145F
Data to be transmitted is stored in this 8-bit register. When it is detected that TDR_1 is empty,
data that has been written to TDR_1 is automatically transferred to TSR_1. TDR_1 and
TSR_1 are in a double-buffer configuration. This allows data to be transferred to TSR_1 after
one frame of data has been transmitted and the next frame of data is still being written to
TDR_1, making possible continuous transmission of data. It is always possible to read or
write to the TDR from the CPU, but before writing to the TDR it should be confirmed that the
value of the TDRE bit in the serial status register (SSR_1) is 1.
• Serial Mode Register (SMR_1)
This 8-bit register is used to select the serial data communication format and the clock source
for the on-chip baud rate generator.
• Serial Control Register (SCR_1)
This register is used for transmit and receive control, interrupt control, and to select the
transmit and receive clock source.
• Serial Status Register (SSR_1)
This register comprises the SCI1 stat us flag and the transmit and receive multiprocessor bits.
TDRE, RDRF, ORER, PER, and FER can be cleared only.
• Serial Direction Control Register (SDCR_1)
This register is used to select whether the LSB or MSB is first. For 8-bit communication
either LSB-first or MSB-first may be selected, but LSB-first should be used for 7-bit
communication.
REJ06B0357-0100O/Rev.1.00 March 2004 Page 4 of 17
Page 5

Asynchronous Serial Data Transmission/Reception
• Bit Rate Register (BRR_1)
This 8-bit register is used to adjust the bit rate. The SCI has independent baud rate generators
for the individual channels, allowing different bit rates to be set for each. See the hardware
manual for details on sett ing values, execution rate relationship s, etc.
Table 2 shows the function allocations for the task example.
Table 2 Function Allocations
Function Classification Function Allocation
TXD1 Pin Channel 1 transmit data output pin
RXD1 Pin Channel 1 transmit data input pin
SMR_1 SCI1 Sets communication format to asynchronous mode
SCR_1 SCI1 Enables transmit operation
SSR_1 SCI1 Status flag showing SCI1 operation status
SDCR_1 SCI1 Specifies LSB-first
BRR_1 SCI1 Sets communication bit rate
TSR_1 SCI1 Register for transmitting serial data
TDR_1 SCI1 Register for storing transmit data
RSR_1 SCI1 Register for receiving serial data
RDR_1 SCI1 Register for storing receive data
SH7145F
REJ06B0357-0100O/Rev.1.00 March 2004 Page 5 of 17
Page 6
SH7145F
Asynchronous Serial Data Transmission/Reception
3. Operation
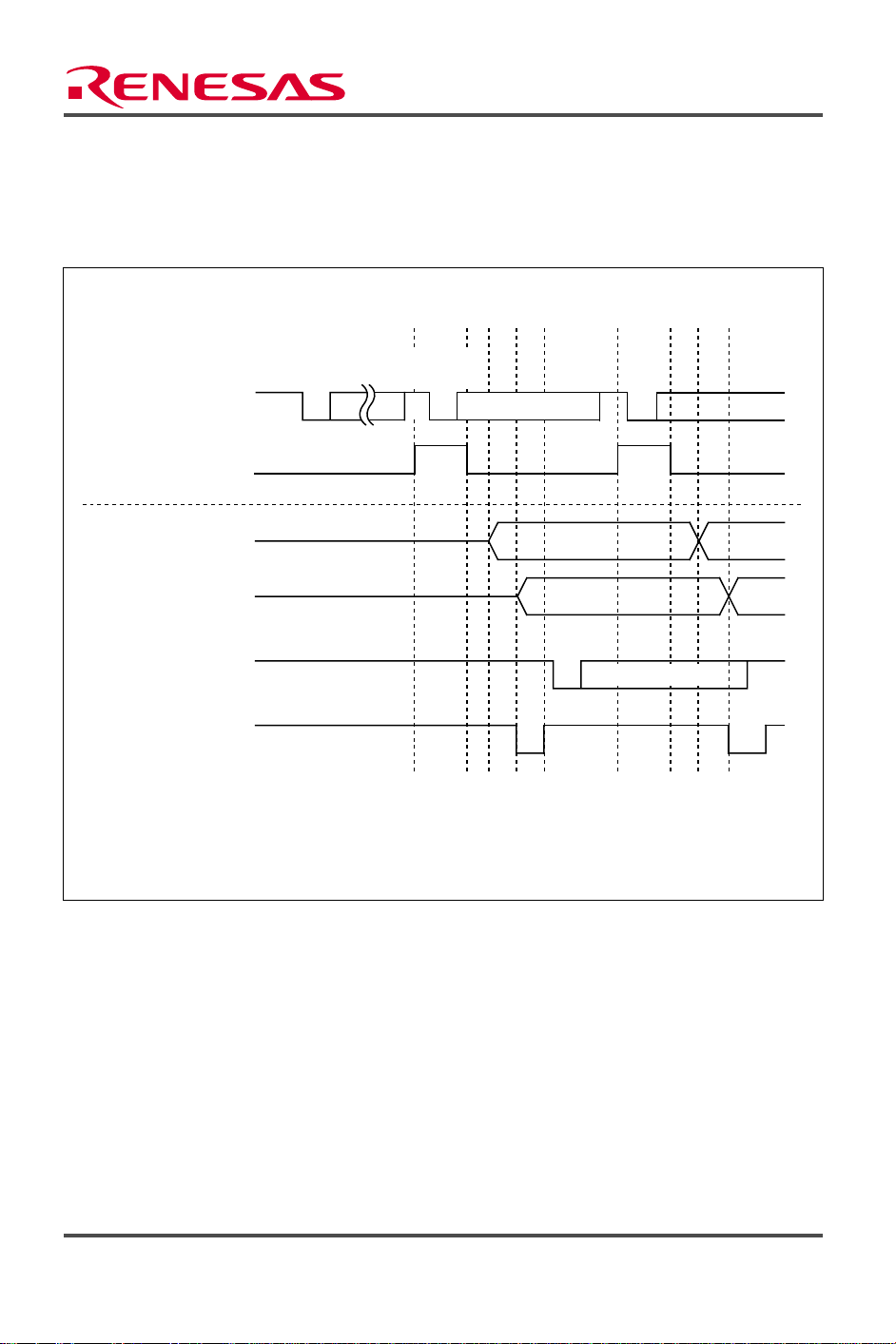
Figure 3 shows the operation of asynchronous mode data transmission in the task example. To
help explain figure 3, table 3 lists the software and hardware processing that is performed.
(1)
(3)
TxD1
(pin)
RDRF
(SSR_1 bit)
Receive operation
Transmit operation
TDR_1
(register)
TSR_1
(register)
TXD1
(pin)
Start
bit
0
Data
bits
(2)
Stop
bit
1
(6)
(4)
(7) (8)
(5)
Start
bit
Data bits D0 to D7
0
(9)
(10)
Start
bit
Data bits D0 to D7
0
(11)
(12)(13)
(14)
(15)
TDRE
(SSR_1 bit)
Notes: 1. The start bit, transmit data, parity bit, and stop bit are output, in that order, from the TxD1 pin.
2. To perform continuous reception, read data transferred to RDR until reception of next data is
complete.
Figure 3 Data Transmission Operation
REJ06B0357-0100O/Rev.1.00 March 2004 Page 6 of 17
Page 7

SH7145F
Asynchronous Serial Data Transmission/Reception
Table 3 Processing
Software Processing Hardware Processing
(1) — RSR_1 receives serial data and transfers it
to RDR_1
(2) — Set RDRF flagin SSR_1 to 1
(3) Read data from RDR_1
(4) Clear RDRF flag in SSR_1 to 0
(5) WritereceivedatatoTDR_1 —
(6) Clear TDRE flag in SSR_1 to 1 —
(7) — TransferdatafromTDR_1toTSR_1
(8) — Set TDRE flag in SSR_1 to 1 and output
transmit data from pin TXD1
(9) — RSR_1 receives serial data and transfers it
to RDR_1
(10) — Set RDRF flag in SSR_1 to 1
(11) Read data from RDR_1
(12) Clear RDRF flag in SSR_1 to 0
(13) Write receive data to TDR_1 —
(14) Clear TDRE flag in SSR_1 to 1 —
(15) — Transfer data from TDR_1 to TSR_1
(16) Repeat Repeat
REJ06B0357-0100O/Rev.1.00 March 2004 Page 7 of 17
Page 8

Asynchronous Serial Data Transmission/Reception
4. Software
(1) Module Descriptions
Table 4 lists the modules used in the task example.
Table 4 Module Descriptions
Module Label Function
Main routine main Calls modules
SCI routine init_sci Initial settings of SCI1
Receive routine rcv_sci Receives serial data
Transmit routine trans_sci Transmits serial data
Error handling err_int Handles receive errors
(2) Argument Descriptions
Table 5 lists the arguments used in the task example.
SH7145F
Table 5 Argument Descriptions
Argument Function Module
Rev_data[0–2] Stores SCI_1 receive data Receive routine
trans_data Transmits data from SCI_1 Transmit routine
(3) On-Chip Register Descriptions
Table 6 lists the on-chip registers used in the task example. The set values shown are the values
used in the task exam ple and differ from the initial settings.
REJ06B0357-0100O/Rev.1.00 March 2004 Page 8 of 17
Page 9

Asynchronous Serial Data Transmission/Reception
Table 6 On-Chip Register Descriptions
SH7145F
Register
Bit
MSTCR1 MSTP17 0 Module standbycontrol register 1
SCR_1 H'70 Serial control register 1 (SCI_1)
TIE 0 Transmit interrupt enable
RIE 1 Receive interrupt enable
TE 1 Transmit enable
RE 1 Receive enable
MPIE 0 Multiprocessor interrupt enable
TEIE 0 Transmit end interrupt enable
CKE1
CKE2
SMR_1 H'00 Serial mode register 1
C/A 0 Communicationmode
CHR 0 Characterlength (enabled in asynchronous mode only)
PE 0 Parity enable (enabled in asynchronous mode only)
O/E 0 Parity mode (enabled in asynchronous mode when PE = 1)
STOP 0 Stop bit length (enabled in asynchronous mode only)
Set Value Function
SCI1 standby control bit
Standby cancelled when MSTP17 = 0
Transmit and receive control, interrupt control, transmit and receive
clock source control
TXI interrupt requests enabled when set to 1
RXI and ERI interrupt requests enabled when set to 1
Transmit operations enabled when set to 1
Receive operations enabled when set to 1
(In asynchronous mode, enabled when MP = 1 in SMR)
In the task example, disabled because MP = 0
TEI interrupt requests enabled when set to 1
0
Clock enable 1, 0
0
Selects clock source and SCK pin function
In the task example, clock source is on-chip clock and SCK pin is not
used
Selects communication format and the clock source for on-chip baud
rate generator
Asynchronous mode when cleared to 0
8-bit transmission and reception when 0
No-parity transmission and reception when 0
(In this example PE = 0 and this bit is disabled)
1-stop-bit transmission and reception when 0
REJ06B0357-0100O/Rev.1.00 March 2004 Page 9 of 17
Page 10

SH7145F
Asynchronous Serial Data Transmission/Reception
Register
Bit
SMR_1 MP 0 Multiprocessor mode (enabled in asynchronous mode only)
CKS1
CKS2
BRR_1 H'40 Bit rate register 1
SDCR_1 H'F2 Serial direction control register 1
SSR_1 H'xx Serial sta tusregister 1
TDRE * Transmit data register empty (status flag)
RDRF * Receive data register full (status flag)
ORER * Overrun error (status flag)
FER * Framing error (status flag)
PER * Parity error (status flag)
TEND * Transmit end (status flag)
MPB 0 Multiprocessor bit
MPBT 0 Multiprocessor bit transfer
PACRL2
PA4MD1
PA4MD0
PA3MD1
PA3MD0
Set Value Function
Multiprocessor communication disabled when 0
0
Clock select 1, 0
0
When value is 00, Pφ clock selected using on-chip baud rate generator
as clock source
8-bit register for adjusting bit rate
DIR bit (bit 3) selects LSB-first or MSB-first
In task example, DIR = 0 (LSB-first)
Comprises SCI1 status flag and transmit and receive multiprocessor bits
Only 0 may be written to the status flag, to clear it
0
Port A control register L2
1
Function setting for port A multiplex pin (TXD1)
0
Port A control register L2
1
Function setting for port A multiplex pin (RXD1)
*: Can only be cleared to 0. Setting to 1 is performed by hardware.
REJ06B0357-0100O/Rev.1.00 March 2004 Page10 of 17
Page 11

5. Flowcharts
(1) Main Routine
SH7145F
Asynchronous Serial Data Transmission/Reception
main()
init_sci()
rcv_sci()
rcv_sci()
rcv_sci()
Initialize SCI module
Receive 1st byte of data
Receive 2nd byte of data
Receive 3rd byte of data
REJ06B0357-0100O/Rev.1.00 March 2004 Page11 of 17
Page 12

(2) SCI1 Initialize Routine
SH7145F
Asynchronous Serial Data Transmission/Reception
init_sci()
Cancel SCI1 module standby status
Clear to 0 bits TIE, RIE, TE, RE, MPIE,
and TEIE in SCR_0
Select on-chip clock as clock source
using CKE1 and CKE0 in SCR_0
Using SMR_1, select asynchronous
mode, 8 data bits, no parity, 1 stop bit,
and Pφ as baud rate generator clock
source
Using BRR_1, set communication
speed to 19,200 bps
Using DIR bit in SDCR_1, select
LSB-first communication
Wait minimum
1-bit transfer time
Yes
Using SCR_1, enable ERI interrupt
Using PACRL2, set PA3 (pin 133) to
RXD function and PA4 (pin 134)
to RXD function
Set bits TE and RE in SCR_1 to 1 to
enable transmit operation and receive
operation
RTE
No
REJ06B0357-0100O/Rev.1.00 March 2004 Page12 of 17
Page 13

(3) Data Receive Routine
SH7145F
Asynchronous Serial Data Transmission/Reception
rcv_sci()
(4) Data Transfer Routine
Wait until
RDR_1 finishes receiving
data
Yes
Read receive data from RDR_1 and
store it in on-chip RAM
Clear RDRF flag in SSR_1 to 0
Transmit receive data without
modification
RTE
trans_sci()
No
Wait until
possible to write to
TDR_1
Yes
Write transmit data to TDR_1
Clear TDRE bit in SSR_1 to 0
RTE
No
REJ06B0357-0100O/Rev.1.00 March 2004 Page13 of 17
Page 14

SH7145F
Asynchronous Serial Data Transmission/Reception
6. Program Listing
/**************************************************************/
/* SH7145F Application Note */
/* */
/* Function */
/* :SCI1 */
/* */
/* External input clock : 12.5MHz */
/* Internal CPU clock : 50MHz */
/* Internal peripheral clock : 25MHz */
/* */
/* Written :2003/7 Rev.1.0 */
/**************************************************************/
#include "iodefine.h"
#include <machine.h>
/*------------ Symbol Definition ----------------------------------------------*/
#define COUNT 3
/*------------ Function Definition --------------------------------------------*/
void main(void);
void init_sci(void);
unsigned char rcv_sci(unsigned char);
void trans_sci(char);
void err_int(void);
void dummy_f(void);
/*------------ RAM allocation Definition --------------------------------------*/
volatile unsigned char Rev_data[COUNT];
/**************************************************************/
/* main Program */
/**************************************************************/
void main( void )
{
unsigned chari=0;
init_sci(); /* Initialize SCI */
i = rcv_sci(i); /* Receive 1st byte of serial data */
i = rcv_sci(i); /* Receive 2nd byte of serial data */
i = rcv_sci(i); /* Receive 3rd byte of serial data */
while(1); /* LOOP */
}
/**************************************************************
REJ06B0357-0100O/Rev.1.00 March 2004 Page14 of 17
Page 15

Asynchronous Serial Data Transmission/Reception
Function : init_sci
Operation : Initialize serial (sci1)
Asynchronous receive operation
-Data : 8bit
-Stop bit : 1bit
-Parity bit : No
**************************************************************/
void init_sci(void)
{
unsigned long i;
P_STBY.MSTCR1.BIT.MSTP17 = 0; /* disable SCI1 standby mode */
/* Initialize SCI Asynchronous mode * */
P_SCI1.SCR_1.BYTE &= 0x03 ; /* clear TIE,RIE,TE,RE,MPIE,TEIE */
P_SCI1.SCR_1.BIT.CKE = 0; /* clock:internal,SCK:output */
P_SCI1.SMR_1.BYTE = 0x00; /* 8bit,No parity,1stop bit */
// CA = 0; /* Asynchronous mode */
// CHR = 0; /* data length 8bits */
// PE = 0; /* No parity */
// OE = 0; /* (=0)even parity */
// STOP = 0; /* 1 stop bit */
// CKS = 0; /* clock source=Pφ(25MHz) */
SH7145F
P_SCI1.BRR_1 = 40; /* 19200bps@25MHz(Peripheral) */
P_SCI1.SDCR_1.BIT.DIR = 0; /* LSB first send */
for( i=0; i < 0x0300 ; i++); /* Wait 1bit */
P_SCI1.SCR_1.BIT.TIE = 0; /* TXI1 interrupt disable */
P_SCI1.SCR_1.BIT.RIE = 0; /* RXI1,ERI interrupt disable */
/* Initialize SCI1 PORT */
P_PORTA.PACRL2.BIT.PA4MD = 1; /* set TXD1(PA4:134pin@SH7145) */
P_PORTA.PACRL2.BIT.PA3MD = 1; /* set RXD1(PA3:133pin@SH7145) */
P_SCI1.SCR_1.BYTE |= 0x30; /* TE=RE=1,Transmit and Receive Enable */
}
/******************************************************************************/
/* Function : rcv_sci */
/* Operation : Serial data receive and send function calls */
/* Argument : None */
/* Value returned : None */
/******************************************************************************/
unsigned char rcv_sci(unsigned char rev_count)
{
while(P_SCI1.SSR_1.BIT.RDRF == 0); /* Wait until reception finishes */
Rev_data[rev_count] = P_SCI1.RDR_1; /* get receive data */
REJ06B0357-0100O/Rev.1.00 March 2004 Page15 of 17
Page 16

SH7145F
Asynchronous Serial Data Transmission/Reception
P_SCI1.SSR_1.BIT.RDRF = 0; /* Clear RDRF */
trans_sci(Rev_data[rev_count]); /* Transmit receive data */
rev_count++ ; /* Increment storage address */
return(rev_count);
}
/************************************************************************/
/* Function : trans_sci */
/* Operation : Write 1 character to serial output */
/* Argument : trans_data */
/* Value returned : None */
/************************************************************************/
void trans_sci(char tarans_data) {
while(!(P_SCI1.SSR_1.BYTE & 0x80)){ /* Wait until data can be written to TDR */
; /* (until TDRE is set to 1) */
}
P_SCI1.TDR_1 = (unsigned char)trans_data; /* Write data to TDR */
P_SCI1.SSR_1.BYTE &= 0x7F; /* Clear flag, transmit */
}
/**************************************
Interrupt handling
**************************************/
#pragma interrupt(err_int)
void err_int(void)
{
if(P_SCI1.SSR_1.BIT.ORER == 1){ /* Overrun error */
P_SCI1.SSR_1.BIT.ORER = 0; /* ORER flag clear */
}
if(P_SCI1.SSR_1.BIT.FER == 1){ /* Framing error */
P_SCI1.SSR_1.BIT.FER = 0; /* FER flag clear */
}
if(P_SCI1.SSR_1.BIT.PER == 1){ /* Parity error */
P_SCI1.SSR_1.BIT.PER = 0; /* PER flag clear */
}
}
#pragma interrupt(dummy_f)
void dummy_f(void)
{
/* Other Interrupt */
}
REJ06B0357-0100O/Rev.1.00 March 2004 Page16 of 17
Page 17

SH7145F
Asynchronous Serial Data Transmission/Reception
Keep safety first in your circuit designs!
1. Renesas Technology Corp. puts the maximum effort into making semiconductor products better and
more reliable, but there is always the possibility that trouble may occur with them. Trouble with
semiconductors may lead to personal injury, fire or property damage.
Remember to give due consideration to safety when making your circuit designs, with appropriate
measures such as (i) placement of substitutive, auxiliary circuits, (ii) use of nonflammable material or
(iii) prevention against any malfunction or mishap.
Notes regarding these materials
1. These materials are intended as a reference to assist our customers in the selection of the Renesas
Technology Corp. product best suited to the customer's application; they do not convey any license
under any intellectual property rights, or any other rights, belonging to Renesas Technology Corp. or
a third party.
2. Renesas Technology Corp. assumes no responsibility for any damage, or infringement of any thirdparty's rights, originating in the use of any product data, diagrams, charts, programs, algorithms, or
circuit application examples contained in these materials.
3. All information contained in these materials, including product data, diagrams, charts, programs and
algorithms represents information on products at the time of publication of these materials, and are
subject to change by Renesas Technology Corp. without notice due to product improvements or
other reasons. It is therefore recommended that customers contact Renesas Technology Corp. or
an authorized Renesas Technology Corp. product distributor for the latest product information
before purchasing a product listed herein.
The information described here may contain technical inaccuracies or typographical errors.
Renesas Technology Corp. assumes no responsibility for any damage, liability, or other loss rising
from these inaccuracies or errors.
Please also pay attention to information published by Renesas Technology Corp. by various means,
including the Renesas Technology Corp. Semiconductor home page (http://www.renesas.com).
4. When using any or all of the information contained in these materials, including product data,
diagrams, charts, programs, and algorithms, please be sure to evaluate all information as a total
system before making a final decision on the applicability of the information and products. Renesas
Technology Corp. assumes no responsibility for any damage, liability or other loss resulting from the
information contained herein.
5. Renesas Technology Corp. semiconductors are not designed or manufactured for use in a device or
system that is used under circumstances in which human life is potentially at stake. Please contact
Renesas Technology Corp. or an authorized Renesas Technology Corp. product distributor when
considering the use of a product contained herein for any specific purposes, such as apparatus or
systems for transportation, vehicular, medical, aerospace, nuclear, or undersea repeater use.
6. The prior written approval of Renesas Technology Corp. is necessary to reprint or reproduce in
whole or in part these materials.
7. If these products or technologies are subject to the Japanese export control restrictions, they must
be exported under a license from the Japanese government and cannot be imported into a country
other than the approved destination.
Any diversion or reexport contrary to the export control laws and regulations of Japan and/or the
country of destination is prohibited.
8. Please contact Renesas Technology Corp. for further details on these materials or the products
contained therein.
REJ06B0357-0100O/Rev.1.00 March 2004 Page17 of 17
 Loading...
Loading...