Page 1
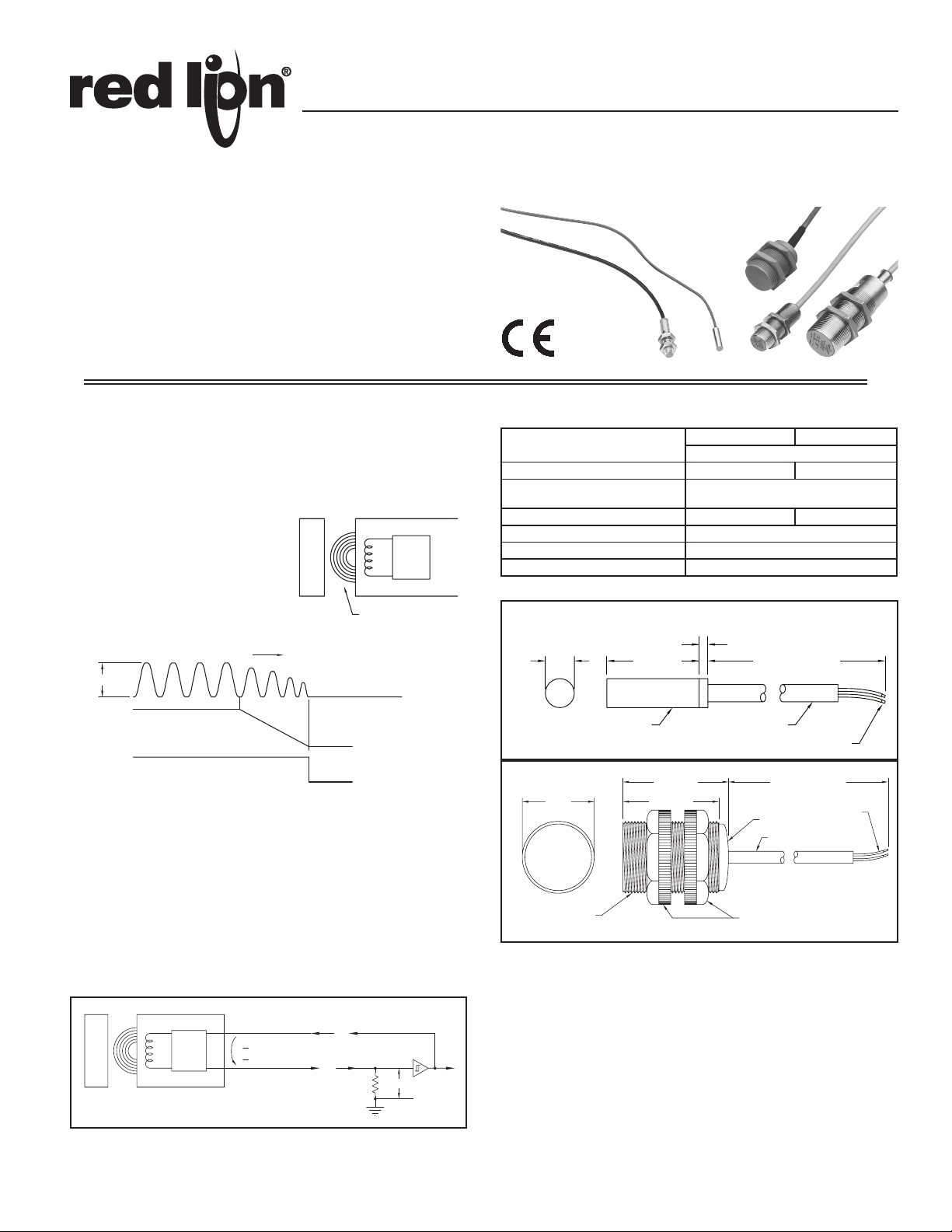
INDUCTIVE PROXIMITY SENSORS
METAL
TARGET
CIRCUIT
OSC.
SENSING FIELD
] PSA1B, or 2B OUTPUT
] PSA6B, 7B, or 8B OUTPUT
OUTPUT ON
<1mA
OSCILLATOR STALLED
A
MPLITUDE
ABSENT
TARGET
>2.2mA
OUTPUT OFF
SENSOR
TARGET APPROACHING
TARGET PRESENT
TARGET ABSENT
SENSE FERROUS & NON-FERROUS METAL OBJECTS TO
“ZERO SPEED”
2-WIRE CURRENT SOURCE (NAMUR) & 3-WIRE NPN TRUE
OPEN COLLECTOR OUTPUTS
5 SIZES & 3 SENSING DISTANCES FOR APPLICATION
VERSATILITY
L.E.D. TARGET INDICATOR (PSA 2B, 6B, 7B, & 8B)
Bulletin No. PSAB-D
Drawing No. LP0443
Released 05/13
DESCRIPTION & OPERATION
Inductive Proximity Sensors detect the presence of metal objects which come
within range of their oscillating field and provide target detection to “zero
speed”. Internally, an oscillator creates a high frequency electromagnetic field
(RF) which is radiated from the coil and out from the sensor face (See Figure
1). When a metal object enters this field, eddy currents are induced into
the object.
As the metal moves closer to
the sensor, these eddy currents
increase and result in an absorption
of energy from the coil which
dampens the oscillator amplitude
until it finally stops.
Figure 1
MODELS PSA-1B & 2B
The 2-wire Models PSA-1B and 2B contain only the coil and oscillator
circuit (See Figure 2). With no metal object being sensed, the circuit oscillates
and draws greater than 2.2 mA of supply current. As a metal object of sufficient
size is brought into the sensing field, the oscillator amplitude dampens and
finally stops, resulting in less than 1 mA of circuit current being drawn. This
greater than 2.2 mA to less than 1 mA change in circuit current between
oscillating and non-oscillating conditions is converted into a usable voltage
signal (V
) by placing a resistor (RS) in series with the sensor leads.
S
PSA 1B, 2B
METAL
TARGET
OSC.
COIL
CIRCUIT
BRN
> 2.2mA-NO METAL
1mA-METAL SENSED
<
BLUE
Figure 2
+VDC
CNT.
VsRs
PSA-1B & PSA-2B SPECIFICATIONS
1. Power Supply:
2. Maximum Switching Frequency: 5 KHz 500 Hz
3. Output:
4. Maximum Sensing Distance: 0.059" (1.5 mm) 0.394" (10 mm)
5. Wire Color Code: Brown = +VDC; Blue = Count
6. Operating Temperature: -25°C to +70°C (-13°F to +158°F)
7. Construction: NEMA 1, 3, 4, 6, 13, and IEC IP 67.
PSA-1B PSA-2B
+5 to +30 VDC
Less than 1 mA Target Sensed; Greater
than 2.2 mA No Target.
DIMENSIONS In inches (mm)
PSA-1B
.256
(6.5)
DIA.
PSA-2B
(ISO 68 METRIC
TRAIGHT THREADING)
1
1.18
(30)
M30 X 1.5
1.181 (30)
CHROMED
BRASS CASE
1.74 (44)
1.57 (40)
PLASTIC CASE & JAM NUTS
.118 (3.0)
6.56′ (2 METERS)
PVC JACKET
2-CONDUCTORS
6.56' (2 METERS)
2 CONDUCTORS
LED
PVC JACKET
1.42 (32) ACROSS FLATS
.39 (10) THICKNESS
#24 AWG
#20 AWG
Page 2
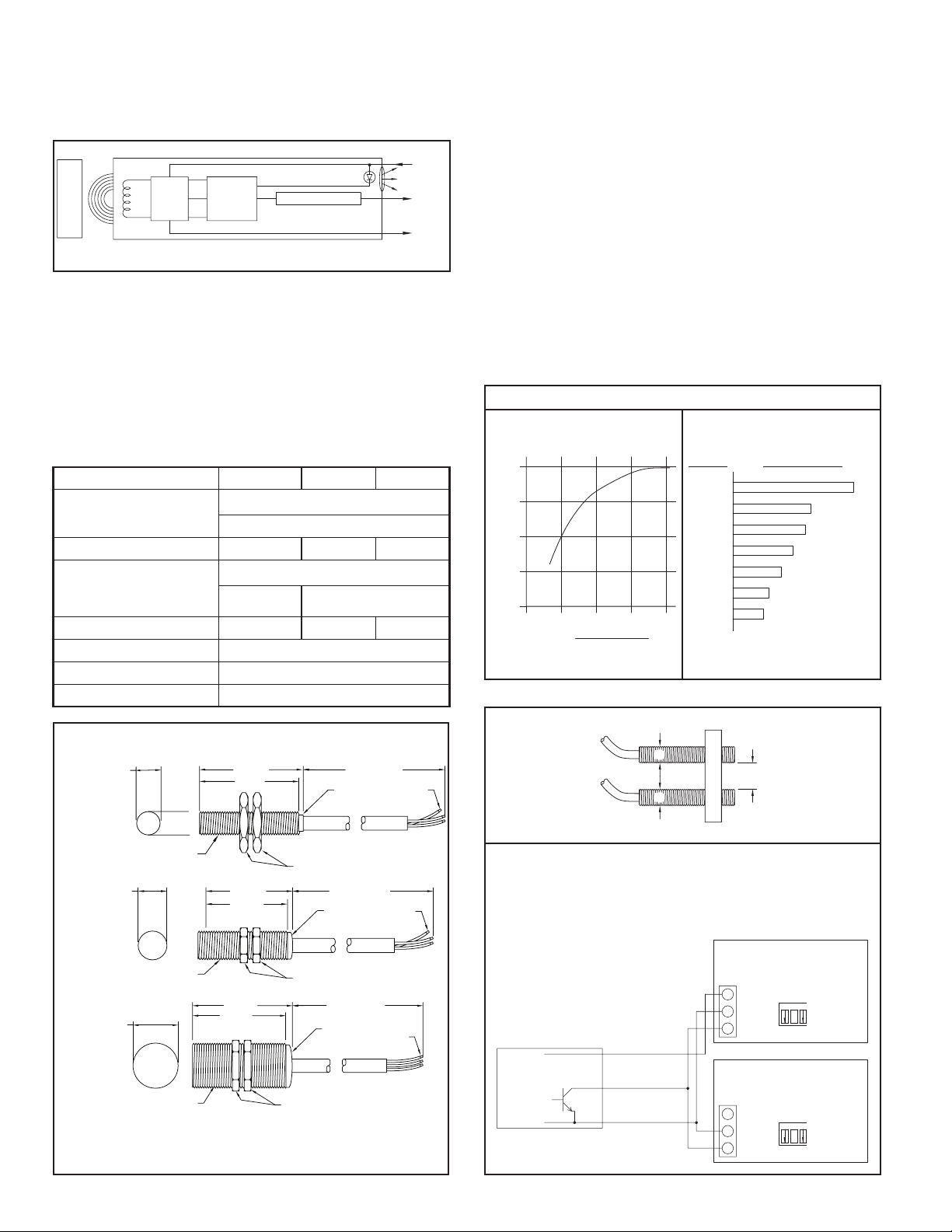
In addition to the coil and oscillator circuit, the 3-wire Models PSA-6B, 7B,
and 8B each contain a Detector Circuit and NPN Transistor Output (See Figure
3). In these units, the Detector Circuit senses when the oscillator stops, and
turns on the Output Transistor which controls the load. The Detector Circuit
also turns on an integrally case mounted L.E.D., visually indicating when a
metal object is sensed.
METAL
TARGET
PSA 6B, 7B, or 8B
COIL
CIRCUIT
OSC.
LED
OUTPUT TRANSISTOR OUTPUTDETECTOR
Figure 3
+VDC
COMMON
PSA-6B, 7B, & 8B
These Inductive Proximity Sensors have a maximum sensing distance of
0.059" (1.5 mm), 0.197" (5 mm) and 0.394" (10 mm) respectively, and operate
over a wide power supply range (See Specifications Below). They are each
housed in threaded metal cases and are supplied with 2 metal jam nuts for
mounting. The NPN transistor outputs are true open collector and are
compatible with most RLC counter and rate input circuits. Maximum sensing
frequencies are ≤ 3 KHz, 1 KHz, and 500 Hz respectively. In addition, the
outputs are overload and short circuit protected. These sensors are shielded for
flush mounting in metal applications.
PSA-6B, 7B, & 8B SPECIFICATIONS
PSA-6B PSA-7B
+10 to +30 VDC
1. Power Supply:
+10 to +30 VDC
@ 10 mA max.
@ 10 mA max.
REVERSE POLARITY PROTECTION
2. Maximum Switching Frequency:
3. Output:
≤ 3 KHz 1 KHz 500 Hz
NPN Open Collector Output,
Overload and Short Circuit protected.
V
= 1.8 V @
SAT
150 mA max. load
V
200 mA max. load
4. Maximum Sensing Distance: 0.059" (1.5 mm) 0.197" (5 mm) 0.394" (10 mm)
5. Wire Color Code: Brown = +VDC; Blue = Common; Black = Output
6. Operating Temperature: -25°C to +70°C (-13°F to +158°F)
7. Construction: NEMA 1, 3, 4, 6, 13 and IEC IP 67
DIMENSIONS In inches (mm)
PSA-6B
.315
(8)
1.64 (41.6) 6.56' (2 METERS)
1.57 (40)
LED
= 1.8 V @
SAT
3-CONDUCTORS
PSA-8B
#24 AWG
SELECTION & APPLICATION OF PROXIMITY
SENSORS
Selection of the proper proximity sensor depends on the size, material, and
spacing of the target being sensed and the sensing distance that can be
maintained. The maximum sensing distance is defined as the distance in which
the sensor is just close enough to detect a ferrous target whose diameter is equal
to or greater than the sensor diameter. In actual application, the sensing distance
should be between 50 to 80% of the maximum sensing range to assure reliable
detection. For target sizes smaller than the sensor diameter, the maximum
sensing distance can be estimated from the curve (See Figure 4). A further
reduction factor must also be applied if the target material is non-ferrous metal
(See Figure 5). Ideally, spacing between adjacent targets should be at least one
sensor diameter so that the first target completely leaves the sensors field before
the next target appears. Individual targets can still be resolved as separate
objects if this spacing is reduced to 70 or 75% of the sensor diameter, however,
this can introduce a minimum limit on sensing distance that makes adjustment
more critical. All Proximity sensors are internally shielded which allows the
sensor face to be flush mounted in metal applications without reducing sensing
distance. In applications where proximity sensors must be placed next to each
other, a distance of at least 1 sensor diameter should separate sensors to
eliminate any frequency interference (See Figure 6).
MAXIMUM SENSING DISTANCE REDUCTION FACTORS
Reduction in the max. sensing distance
due to decrease in diameter of ferrous
targets.
100
50
% OF MAX. SENSING DISTANCE
0
0 .25 .5 .75 1
RATIO,
TARGET DIAMETER
SENSOR DIAMETER
Figure 4
MINIMUM SENSOR SPACING
Typical reduction factors for various nonferrous targets with diameters equal to or
greater than sensor diameter.
MATERIAL
MILD STEEL
STAINLESS
STEEL
MERCURY
LEAD
BRASS
ALUMINUM
COPPER
Nominal sensing range x % sensing
distance = actual sensing range
% SENSING DISTANCE
APPROX. 40%
APPROX. 30%
APPROX. 25%
Figure 5
D
1 x D
D
100%
APPROX. 65%
APPROX. 60%
APPROX. 50%
M8 X 1
PSA-7B
PSA-8B
NOTES:
(ISO 68 METRIC
STRAIGHT THREADING)
.708
(18)
(ISO 68 METRIC
STRAIGHT THREADING)
1.181
(30)
(ISO 68 METRIC
STRAIGHT THREADING)
M18 X 1
M30 X 1.5
2.13 (54) 6.56' (2 METERS)
1.97 (50)
2.52 (64) 6.56' (2 METERS)
2.37 (60)
.51 (13) ACROSS FLATS
.16 (4) THICKNESS
.94 (24) ACROSS FLATS
.16 (4) THICKNESS
1.42 (36) ACROSS FLATS
.19 (5) THICKNESS
1. PSA 6B case material = #303 stainless steel.
2. PSA 7B & 8B case = chromed brass.
3. PVC Cable Jacket.
LED
LED
#20 AWG
3-CONDUCTORS
#20 AWG
3-CONDUCTORS
Figure 6
Note: PSA-6B, 7B, and 8B outputs are NPN open collector outputs. A
PSA-6B, 7B, or 8B may be used as an input to more than 1 indicator or
control only if the respective power supplies of each unit are
“unregulated” and can load share. It is recommended to use only one
power supply for sensor power. An indicator or control with a regulated
power supply may not be paralleled.
Counter #1 and #2 both contain
unregulated +12 VDC Power
Supplies.
PSA 6B, 7B, or 8B
NPN OPEN
COLLECTOR
+VDC
OUTPUT
COMMON
COUNTER #1
+12V
COMM.
CNT.
COUNTER #2
+12V
COMM.
CNT.
TYPICAL COUNTER
INPUT SWITCH SET-UP
SRC
1 2
*
SNK
TYPICAL COUNTER
INPUT SWITCH SET-UP
SRC
123
*
SNK
2
LO FRQ
LO BIAS
3
HI
HI
LO FRQ
LO BIAS
HI
HI
* APPLICATION
DEPENDENT
* APPLICATION
DEPENDENT
Page 3

TYPICAL HOOK-UPS
PSA 1B or 2B
< 1mA > 2.2mA
CURRENT SOURCE
BRN
BLUE
TYPICAL COUNTER
INPUT SWITCH SET-UP
+12V
COMM.
CNT.
SRC
123
*
SNK
LO FRQ
HI
LO BIAS
* APPLICATION
DEPENDENT
HI
PSA 6B, 7B, or 8B
NPN OPEN
COLLECTOR
APPLICATION SELECTION CHART
PSA-1B PSA-2B PSA-6B PSA-7B PSA-8B
MAX. SENSING DISTANCE 0.059" (1.5 mm) 0.394" (10 mm) 0.059" (1.5 mm) 0.197" (5 mm) 0.394" (10 mm)
MAX. SWITCHING FREQ. 5 KHz 500 Hz ≤ 3 KHz 1 KHz 500 Hz
POWER SUPPLY 5-30 VDC 5-30 VDC 10-30 VDC 10-30 VDC 10-30 VDC
OUTPUT <1 mA> 2.2 mA <1 mA> 2.2 mA NPN Open Collector Transistor
L.E.D. TARGET INDICATOR No Yes Yes Yes Yes
MODELS MB4B & 5B MOUNTING BRACKETS
PSA 6B, 7B, or 8B = BRN
PSA 6B, 7B, or 8B = BLK
PSA 6B, 7B, or 8B = BLU
TYPICAL COUNTER
INPUT SWITCH SET-UP
+12V
COMM.
CNT.
SRC
123
*
SNK
LO FRQ
LO BIAS
HI
HI
* APPLICATION
DEPENDENT
The Models MB4B and 5B are stainless steel right angle
mounting brackets, designed to provide easy mounting and
adjustment of PSA-7B and 8B respectively, using the 2 hex jam
nuts provided with each sensor.
DIMENSIONS In inches (mm)
BRACKET
MODEL NO.
MB4B PSA7B
SENSOR
MODEL
A B C D E F G H J SLOT
1.63
(41.5)
1.00
(25.4)
2.5
(63.5)
1.25
(31.8)
DIMENSIONS
0.62
(15.7)
DIMENSIONS
30°
J
F
0.31
(7.9)
1.88
(47.8)
0.75
(19.1)
H
A
B
C
G
E
D
0.06
(1.5)
0.22 X 0.75
(5.6 X 19.1)
MB5B PSA8B
2.62
(66.5)
1.75
(44.5)
4.25
(108.0)
1.75
(44.5)
0.88
(22.4)
0.37
(9.5)
3.50
(88.9)
ORDERING INFORMATION
MODEL NO. DESCRIPTION PART NUMBER
PSA1B 2-Wire Cylindrical Proximity Sensor PSA1B000
PSA2B 2-Wire, 30 mm Threaded Proximity Sensor PSA2B000
PSA6B 8mm Threaded Proximity Sensor PSA6B000
PSA7B 18mm Threaded Proximity Sensor PSA7B000
PSA8B 30mm Threaded Proximity Sensor PSA8B000
MB4B Mounting Bracket for PSA7B MB4B0000
MB5B Mounting Bracket for PSA8B MB5B0000
Do not dispose of unit in trash - Recycle
3
1.19
(30.2)
0.07
(1.8)
0.28 X 1.25
(7.1 X 31.8)
Page 4

 Loading...
Loading...