Page 1
INSTALLATION AND OPERATING
INSTRUCTIONS
CATALOG NO. 3400.52E Effective: 02-22-07 Replaces: 04-01-03 P/N 241079 Rev. 6
WARNING: Improper installation, adjustment, alteration, service or maintenance can cause property
damage, personal injury or loss of life. Refer to the user’s information manual provided with this boiler.
FOR YOUR SAFETY: Do not store or use gasoline or other flammable vapors and liquids or other
combustible materials in the vicinity of this or any other appliance. To do so may result in an explosion or fire.
WHAT TO DO IF YOU SMELL GAS:
• Do not try to light any appliance.
• Do not touch any electrical switch; do not use any phone in your building.
• Immediately call your gas supplier from a neighbor's phone. Follow the gas supplier's instructions.
• If you cannot reach your gas supplier, call the fire department.
Installation and service must be performed by a qualified installer, service agency or the gas supplier.
This manual should be maintained in legible condition and kept adjacent to the heater or in a safe place for future
reference.
Models 751, 1001 &
1501 – Types H, WH & P
Advanced
Design
Boiler
L
W
Page 2

2
Page 3

WARNINGS 4
BEFORE INSTALLATION 5
Product Receipt 5
Model Identification 5
Ratings and Certifications 5
Installations at Elevation 5
Component Locations 6
GENERAL SAFETY 7
Time/Temperature Relationships in
Scalds 7
INSTALLATION 8
Installation Codes 8
Equipment Base 8
Clearances 8
Combustion and Ventilation Air 9
Conventional Combustion Air Supply 11
Water Piping 12
Hydronic Heating 13
Gas Supply Connections 21
Electrical Power Connections 23
Venting Connections 25
Venting Installation Tips 27
Venting Configurations 27
Condensate Drain 40
Controls 41
WIRING DIAGRAM 44
PRE START-UP 46
ADB Initial Start-Up 48
OPERATION 51
Lighting Instructions 51
To Turn Off Gas to Appliance 51
MAINTENANCE 51
Suggested Minimum
Maintenance Schedule 51
CONNECTING THE CHX 52
APPENDIX 54
Inside Combustion Air Contamination 54
START-UP CHECKLIST 55
WARRANTY 56
CONTENTS
3
Page 4
4
DANGER:
Indicates the presence of immediate hazards which will cause severe
personal injury, death or substantial property damage if ignored.
WARNING:
Indicates the presence of hazards or unsafe practices which could cause
severe personal injury, death or substantial property damage if ignored.
CAUTION:
Indicates the presence of hazards or unsafe practices which could cause
minor personal injury or product or property damage if ignored.
NOTE:
Indicates special instructions on installation, operation, or maintenance which
are important but not related to personal injury hazards.
DANGER: Make sure the gas on which the heater
will operate is the same type as that specified on the
heater rating plate.
WARNING: Should overheating occur or the gas
supply valve fail to shut, do not turn off or disconnect
the electrical supply to the heater. Instead, shut off
the gas supply at a location external to the heater.
WARNING: Do not use this heater if any part has
been under water. Immediately call a qualified
service technician to inspect the heater and to
replace any part of the control system and any gas
control which has been under water.
WARNING: To minimize the possibility of improper
operation, serious personal injury, fire, or damage to
the heater:
• Always keep the area around the heater free of
combustible materials, gasoline, and other
flammable liquids and vapors.
• Heater should never be covered or have any
blockage to the flow of fresh air to the heater.
WARNING - CALIFORNIA PROPOSITION
65: This product contains chemicals known to the
State of California to cause cancer, birth defects or
other reproductive harm.
WARNING: Risk of electrical shock. More than one
disconnect switch may be required to de-energize
the equipment before servicing.
CAUTION: This heater requires forced water
circulation when the burner is operating. See
minimum and maximum flow rates. Severe damage
will occur if the heater is operated without proper
water flow circulation.
CAUTION: Operation of this heater in low
temperature systems requires special piping to
ensure correct operation.
CAUTION: If this heater is to be installed above
radiation level, it must be provided with a low water
cut-off device at the time of heater installation.
WARNINGS
Pay Attention to These Terms
Page 5
5
BEFORE INSTALLATION
Raypak strongly recommends that this manual be reviewed thoroughly before installing your ADB heater.
Please review the General Safety information before
installing the heater. Factory warranty does not apply
to heaters that have been improperly installed or operated. (Refer to the warranty at the back of this
manual.) Installation and service must be performed
by a qualified installer, service agency or gas supplier.
If, after reviewing this manual, you still have questions
which this manual does not answer, please contact the
manufacturer or your local Raypak representative.
Thank you for purchasing a Raypak product. We hope
you will be satisfied with the high quality and durability
of our equipment.
Product Receipt
On receipt of your heater it is suggested that you visually check for external damage to the shipping crate. If
the crate is damaged, make a note to that effect on the
Bill of Lading when signing for the shipment. Remove
the heater from the shipping packaging. Report any
damage to the carrier immediately.
On occasion, items are shipped loose. Be sure that
you receive the correct number of packages as indicated on the Bill of Lading.
Claims for shortages and damages must be filed with
the carrier by consignee. Permission to return goods
must be received from the factory prior to shipping.
Goods returned to the factory without an authorized
Returned Goods Receipt number will not be accepted.
All returned goods are subject to a restocking charge.
When ordering parts, you must specify the model and
serial number of the heater. When ordering under warranty conditions, you must also specify the date of
installation.
Purchased parts are subject to replacement only
under the manufacturer’s warranty. Debits for defective replacement parts will not be accepted and will be
replaced in kind only per Raypak’s standard warranties.
Model Identification
The model identification number and heater serial
number are found on the heater rating plate located on
the left inside jacket of the heater. The model number
will have the form H4-0751A ADB or similar depending
on the heater size and configuration. The first character of the model number identifies application (H =
Hydronic Heating System, W = Hot Water Supply
System, P = Pool Application). The second character
identifies the firing mode (4 = On-Off firing). The next
four places identify the input of the heater in 1,000s of
BTUH 0751 = 750,000 BTUH). The remaining suffix
identifies the control, ignition, and construction configuration. The last three characters of the model number
identifies the model type (ADB = Advanced Design
Boiler).
Ratings and Certifications
Standards:
• ANSI Z21.13 · CSA 4.9 - latest edition, Gas-Fired
Hot Water Boilers
• CAN 3.1 - latest edition, Industrial and
Commercial Gas-Fired Package Boilers
• ANSI Z21.10.3 · CSA 4.3 - latest edition, Gas Water Heaters
• SCAQMD Rule 1146.2
All Raypak heaters are National Board Approved, and
design-certified and tested by the Canadian Standards
Association (CSA) for the U.S. and Canada. Each
heater is constructed in accordance with Section IV of
the American Society of Mechanical Engineers
(ASME) Heater Pressure Vessel Code and bears the
ASME stamp. The heater also complies with the latest
edition of ASHRAE 90.1 Standard.
Installations at Elevation
No de-rating is required for altitudes up to 7000 feet.
Rated inputs, at sea level settings, are suitable for up
to 5000 feet elevation. At altitudes between 5000 and
7000 feet, rated inputs are achieved with pressure settings adjustment. Consult the factory for installations at
altitudes in excess of 7000 feet.
WARNING: Altering any RAYPAK pressure vessel
by installing replacement heat-exchangers, tube
bundle headers, or any other ASME part not
manufactured and/or approved by RAYPAK will
instantly void the ASME, and agency listings and any
RAYPAK warranty on the vessel. Altering the ASME,
agency ratings of the vessel also violates national,
state, and local approval codes. The terms "boiler"
and "heater" are used interchangeably in this
manual.
Page 6
6
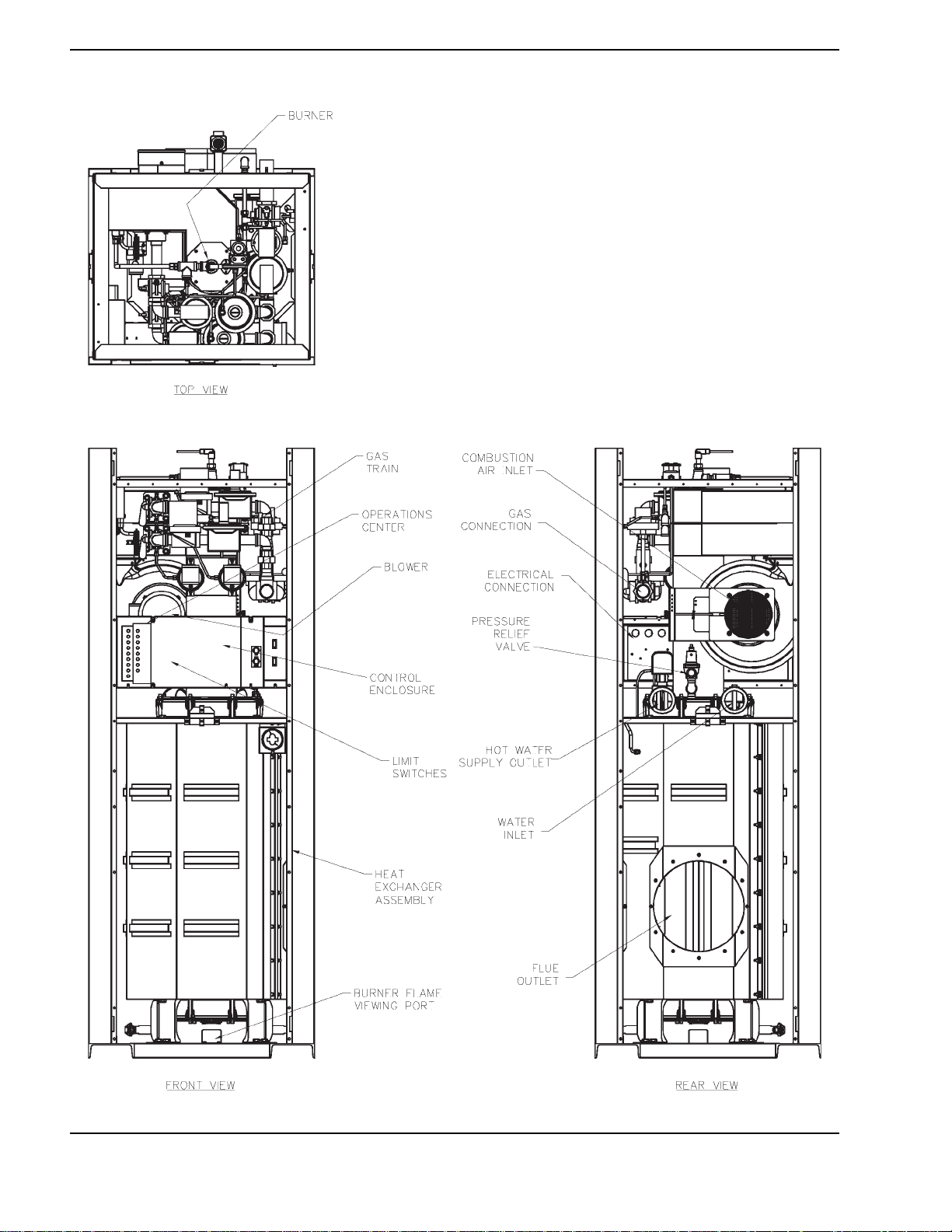
Component Locations
Fig. 1: Component Locations
Page 7
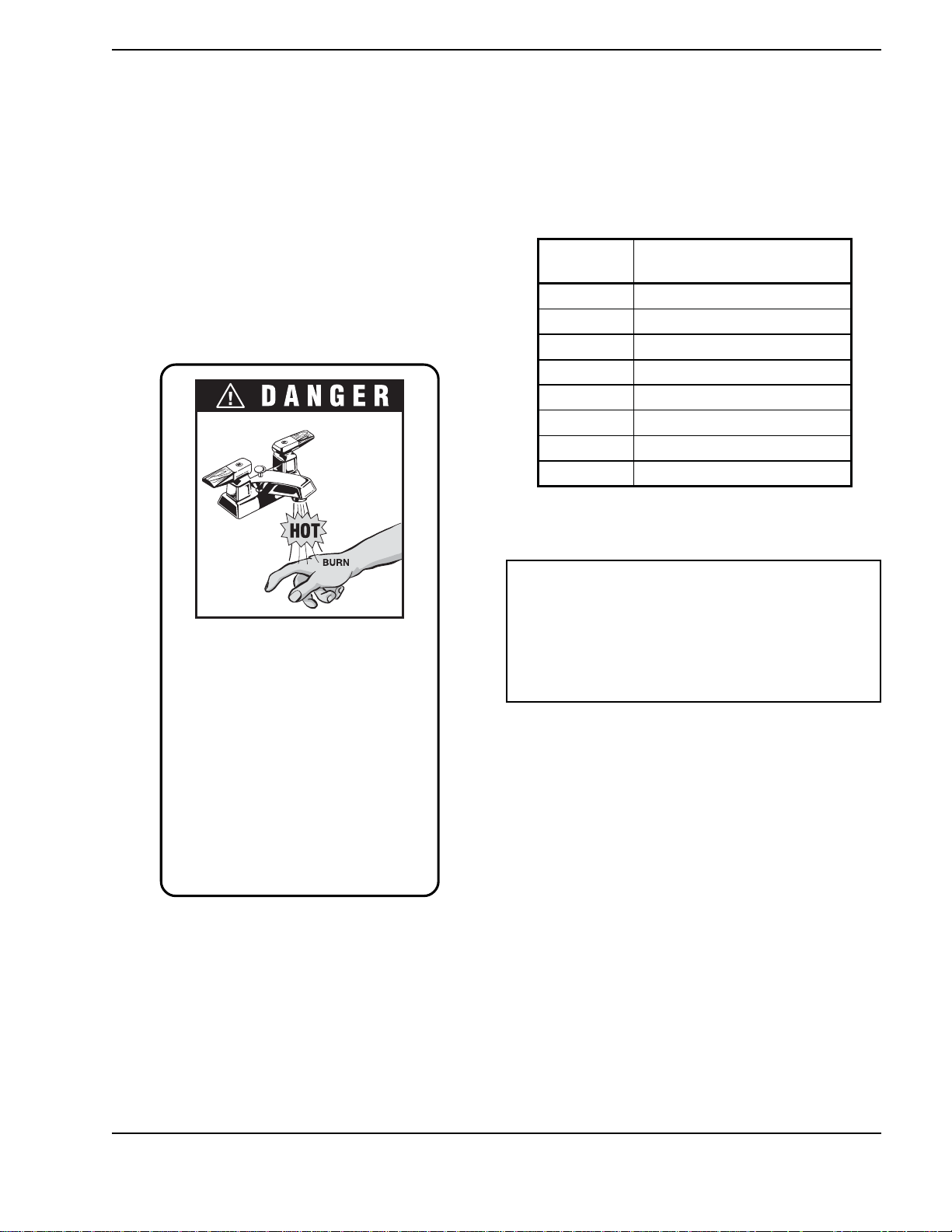
7
GENERAL SAFETY
To meet commercial water use needs, an external
operating control for this hot water boiler is adjustable
up to 210°F. However, water temperatures over 125°F
can cause instant severe burns or death from scalds.
The preferred starting point for setting the control for
supplying general purpose hot water is 125°F.
Safety and energy conservation are factors to be considered when setting the water temperature on the
thermostat. The most energy efficient operation will
result when the temperature setting is the lowest that
satisfies the needs consistent with the application.
Maximum water temperatures occur just after the boiler’s burner has shut off. To determine the water
temperature being delivered, turn on a hot water
faucet and place a thermometer in the hot water
stream.
NOTE: When this water heater is supplying general
purpose hot water for use by individuals, a
thermostatically controlled mixing valve for reducing
point of use water temperature is recommended to
reduce the risk of scald injury. Contact a licensed
plumber or the local plumbing authority for further
information.
Time/Temperature
Relationships in Scalds
The following chart details the relationship of water
temperature and time with regard to scald injury and
may be used as a guide in determining the safest
water temperature for your applications.
Table A: Time to Produce Serious Burn
Water
Temp.
120°F More than 5 minutes
125°F 1-1/2 to 2 minutes
130°F About 30 seconds
135°F About 10 seconds
140°F Less than 5 seconds
145°F Less than 3 seconds
150°F About 1-1/2 seconds
155°F About 1 second
Table courtesy of The Shriners Burn Institute
Time to Produce Serious
Burn
Water temperature over 125°F can
cause instant severe burns or death
from scalds.
Children, disabled, and elderly are
at highest risk of being scalded.
See instruction manual before setting temperature at water heater.
Feel water before bathing or showering.
Temperature limiting valves are
available, see manual.
Page 8
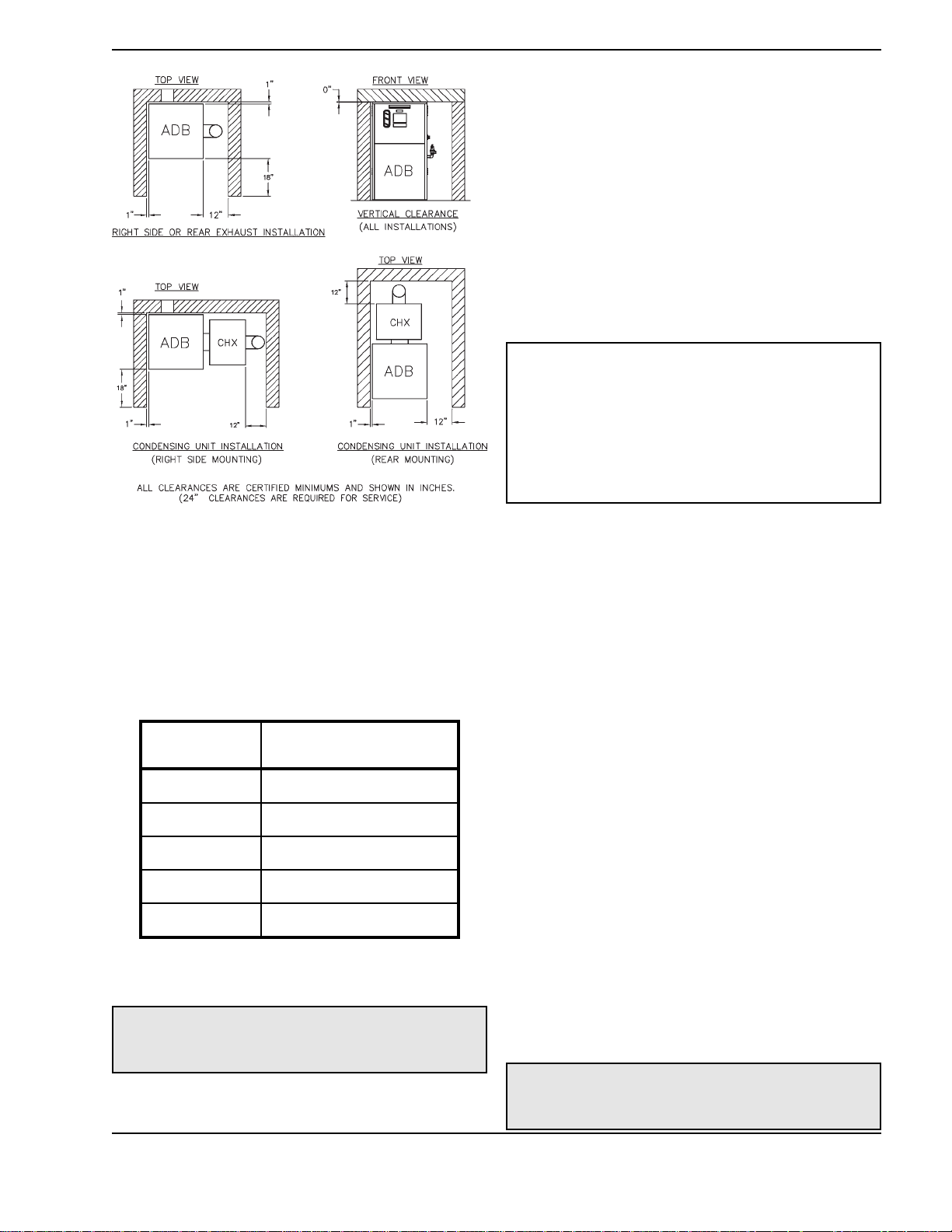
Equipment Base
The boiler should be mounted on a level, structurally
sound surface. The boiler is approved for and can be
installed on a combustible surface but must NEVER
be installed on carpeting. Gas fueled equipment
installed in enclosed parking garages must be located
at least 18 inches above the floor.
In addition, the boiler shall be installed such that the
gas ignition system components are protected from
water (dripping, spraying, rain, etc.) during appliance
operation and service (circulator replacement, control
replacement, etc.).
Clearances
Indoor Installations
8
Table B: Clearances – Indoor Installations
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION
Installation Codes
Installations must follow these codes:
• Local, state, provincial, and national codes, laws,
regulations and ordinances
• National Fuel Gas Code, ANSI Z223.1/NFPA 54 –
latest edition (NFGC)
• National Electrical Code, ANSI/NFPA 70 - latest
edition (NEC)
• Standard for Controls and Safety Devices for
Automatically Fired Boilers, ANSI/ASME CSD-1,
(CSD-1) when required
• For Canada only: CAN/CSA B149 Installation
Code and CSA C22.1 C.E.C. Part 1 (C22.1)
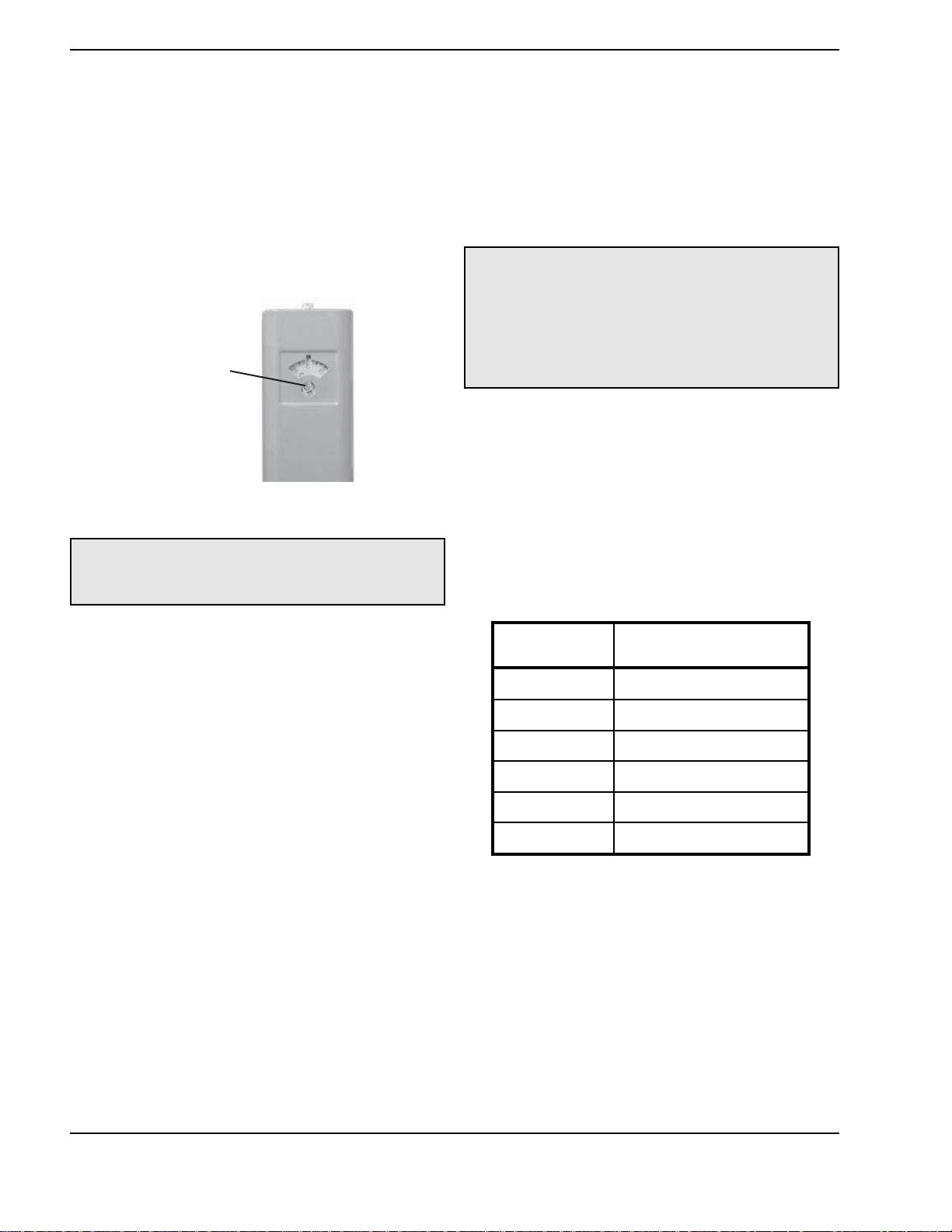
The temperature of the water in the hot water boiler
can be regulated by setting the temperature dial on
front of the thermostat. To comply with safety regulations the thermostat was set at its lowest setting before
the hot water boiler was shipped from the factory. The
illustration below shows the thermostat and how to
adjust the water temperature.
To adjust the water temperature, insert a small straight
screwdriver into slotted screw in hole in front of thermostat and turn wheel to desired setting.
CAUTION: Hotter water increases the risk of
scalding! There is a hot water scald potential if the
thermostat is set too high.
Auto Limit
*DO NOT install on carpeting.
CAUTION: The boiler should be located in an area
where water leakage will not result in damage to the
area adjacent to the appliance or to the structure.
When such locations cannot be avoided, it is
recommended that a suitable catch pan, adequately
drained, be installed under the appliance. The pan
must not restrict air flow.
Heater Side
Min. Clearance from
Combustible Surfaces
Floor *
Rear 12” (water side)
Right 1”
Left 1”
To p 0”
Vent 1”
Adjustment
Screw
Page 9
9
Outdoor Installations
Raypak Advanced Design Boilers are design certified
by CSA for outdoor installation. Roof water drainage
must be diverted away from boilers installed under
overhangs.
Combustion and Ventilation Air
Indoor Units
The boiler must be supplied with sufficient quantities of
non-contaminated air to support proper combustion
and equipment ventilation. Combustion air can be supplied via conventional venting, where combustion air is
drawn from the area immediately surrounding the boiler, or via direct vent, where combustion air is drawn
directly from outside. All installations must comply with
the requirements of NFGC for U.S., CSA B149 for
Canada, and all local codes.
Direct Vent
If outside air is drawn through a vent pipe directly to
the unit for combustion:
1. Install combustion air direct vent in accordance
with the Venting section of this manual.
2. Provide for adequate ventilation of the space
occupied by the boiler(s) by an opening(s) for ventilation air at the highest practical point
communicating with the outdoors. The total cross
sectional area shall be at least one (1) square inch
of free area per 20,000 BTUH of total input rating
of all equipment in the room when the opening is
communicating directly with the outdoors or
through vertical duct(s). The total cross sectional
area shall be at least one (1) square inch of free
area per 10,000 BTUH of total input rating of all
equipment in the room when the opening is communicating with the outdoors through horizontal
duct(s).
3. In cold climates, and to mitigate potential freezeup, Raypak highly recommends the installation of
a motorized sealed damper to prevent the circulation of cold air through the boiler during the
non-operating hours.
NOTE: In calculating free area, the required size of
openings for combustion, ventilation, and dilution air
shall be based on net free area of each opening. If
the free area through a design of louver or grill is
known, it shall be used in calculating the size
opening required to provide the free area specified.
For additional information, refer to the latest NFGC
code requirements.
Fig. 2: Minimum Clearances from Combustible
Surfaces
Heater Side
Min. Clearance from
Combustible Surfaces
Rear 12” (water side)
Right 36”
Left 36”
To p 0”
Vent 1”
Table C: Clearances – Outdoor Installations
WARNING: Combustion air inlet (blower air inlet)
should have 6" minimum clearance from any
obstruction, i.e. walls or other appliances.
CAUTION: Remove the screen off the blower inlet
and install a screen (1/2"-3/4" mesh) on the inlet
elbow.
Page 10
10
U.S. Installations
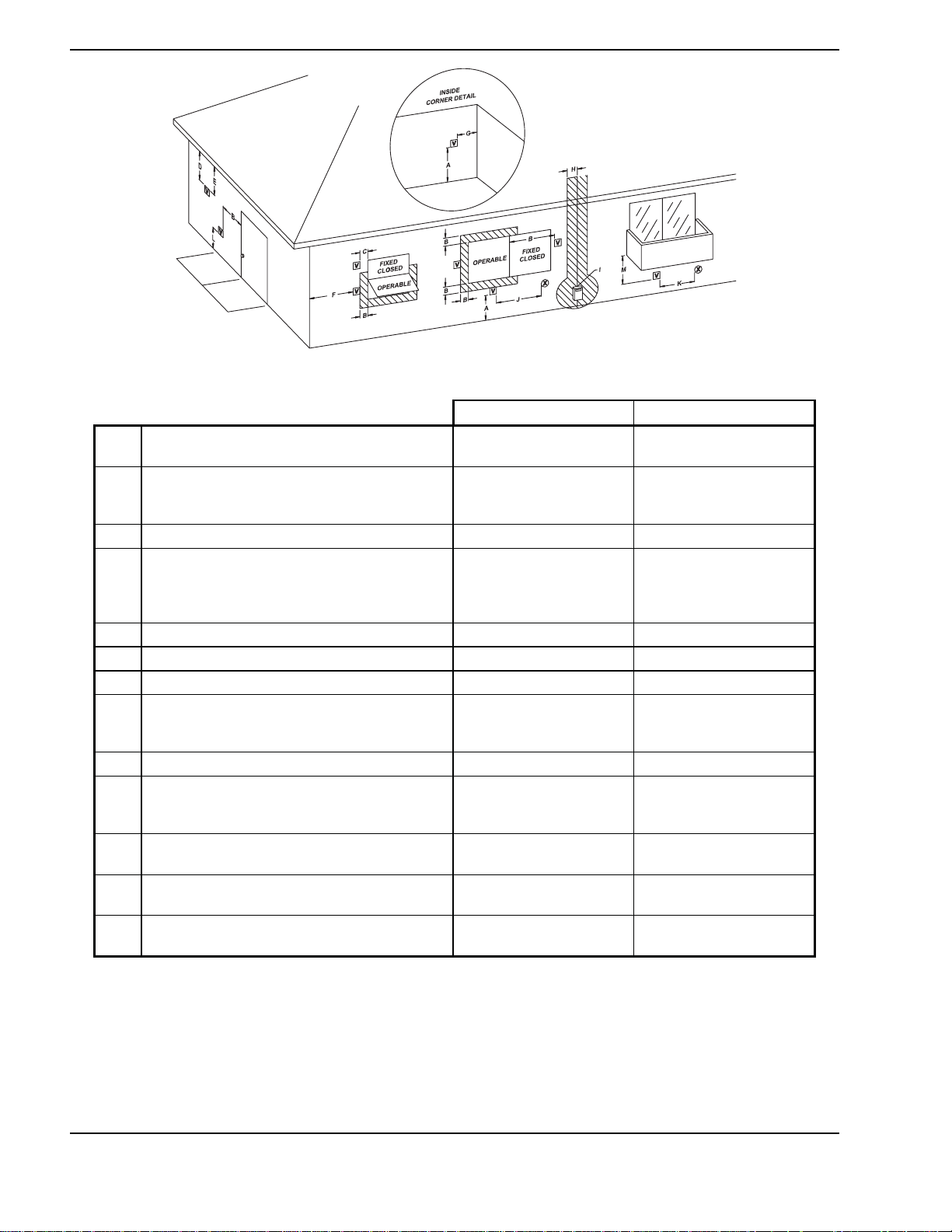
Fig. 3: Minimum Clearances from Vent/Air Inlet Terminations – Indoor and Outdoor Installations
Table D: Vent/Air Inlet Termination Clearances
Clearance above grade, veranda, porch,
A
deck, or balcony
Clearance to window or door that may be
B
opened
4 ft (1.2m) below or to side
of opening; 1 foot (30 cm)
1 ft (30 cm) 1 ft (30 cm)
above opening
1
Canadian Installations
3 ft (91 cm)
2
C Clearance to permanently closed window **
Vertical clearance to ventilated soffit located
above the terminal within a horizontal dis-
D
tance of 2 ft (61cm) from the centerline of the
5 ft (1.5m) *
terminal
E Clearance to unventilated soffit **
F Clearance to outside corner **
G Clearance to inside corner 6 ft (1.83m) *
Clearance to each side of center line ex-
H
tended above meter/regulator assembly
*
3 ft (91 cm) within a height
15 ft above the me-
ter/regulator assembly
I Clearance to service regulator vent outlet * 6 ft (1.83m)
Clearance to non-mechanical air supply inlet
to building or the combustion air inlet to any
J
other appliance
K Clearance to mechanical air supply inlet
Clearance above paved sidewalk or paved
L
driveway located on public property
Clearance under veranda, porch, deck or
M
balcony
1
In accordance with the current ANSI Z223.1/NFPA 54 National Fuel Gas Code
2
In accordance with the current CAN/CG A-B149 Installation C odes
t Vent terminal shall not terminate directly above sidewalk or paved driveway located between 2 single family dwellings that s erves
both dwellings
TT Permitted only if veranda, porch, deck, or balc ony is fully open on a minimum of two sides beneath the floor and top of terminal and
underside of ver anda, porch, deck or balcony is greater than 1 ft (30cm)
* Clearances in accordance with local installation codes and the requirements of the gas supplier
4 ft (1.2m) below or to side
of opening; 1 ft (30 cm)
above opening
3 ft (91 cm) above if within
10 ft (3m) horizontally
7 ft (2.13m) 7 ft (2.13m) t
* 12 in. (30 cm) TT
3 ft (91 cm)
6 ft (1.83m)
Page 11

11
Conventional Combustion Air
Supply
U.S. Installations
All Air from Inside the Building
If all combustion air is drawn from the air inside the
building (the mechanical equipment room does not
receive air from outside):
1. The mechanical equipment room must be provided with two permanent openings communicating
directly with additional room(s) of sufficient volume
so that the combined volume of all spaces meets
the criteria for an unconfined space. (An unconfined space is defined as a space whose volume
is more than 50 cubic feet per 1,000 BTUH of the
aggregate input rating of all appliances installed in
that space.)
2. Each opening must have a minimum free area of
one (1) square inch per 1,000 BTUH of the total
input rating of all gas utilization equipment in the
mechanical equipment room.
3. One opening must commence within twelve (12)
inches of the top, and one opening must commence within twelve (12) inches of the bottom of
the room.
4. Refer to NFGC, Part 5, for additional information.
All Air from Outdoors
If all combustion air is drawn from the air outside the
building (the mechanical equipment room directly
communicates with the outdoors), either of the following two methods can be used:
Method 1:
1. The mechanical equipment room must be provided with two permanent openings, one
commencing within (twelve) 12 inches of the top,
and one commencing within twelve (12) inches of
the bottom of the room.
2. The openings must communicate directly, or by
ducts, with the outdoors.
3. Each opening must have a minimum free area of
one (1) square inch per 4,000 BTUH of total input
rating of all equipment in the room when the opening is communicating directly with the outdoors or
through vertical ducts. The minimum free area
required for horizontal ducts is one (1) square inch
per 2,000 BTUH of total input rating to all the
equipment in the room.
4. Refer to NFGC, Part 5, for additional information.
Refer to Appendix A for additional information
about combustion air quality.
Method 2 (normally applied in cold climate regions):
1. The mechanical equipment room must be provided with at least one permanent opening,
commencing within 12 inches of the top of the
enclosure.
2. The opening must communicate directly or by
ducts with outdoors.
3. The opening must have a minimum free area of 1
sq. in per 3000 BTUH of the total input rating of all
equipment in the room, or no less than the sum of
the areas of all vent connectors in the confined
space. Refer to the latest version of NFGC, part 5
for additional information.
1. Ventilation of the space occupied by the boiler
shall be provided by an opening(s) for ventilation
air at the highest practical point communicating
with outdoors. The total cross-sectional area of
such an opening(s) shall be at least 10% of the
area required in (2) and (3), but in no case shall
the cross-sectional area be less than 10 square
inches (6500 square mm).
2. When air supply is provided by natural air flow
from the outdoors for natural draft, partial fan
assisted, fan-assisted or power draft-assisted
burners, there shall be a permanent air supply
opening(s) having a cross section area of not less
than 1 sq. in. per 7000 BTUH (310 sq. mm per kW)
up to and including 1 million BTUH, plus 1 sq. in.
per 14000 BTUH (155 sq. mm per kW) in excess
WARNING: Do not use one permanent opening
method (Method 2) if the equipment room is under
negative pressure condition or the equipment is
common vented with other gas-fired appliances.
Canadian Installations
CAUTION: All combustion air has to be drawn from
the air outside the building (the mechanical
equipment room directly communicates with the
outdoors).
Page 12
of 1 million BTUH. This opening(s) shall be either
located at or ducted to a point neither more than
18 inches (450 mm) nor less than 6 inches (150
mm) above the floor level. The duct can also
"Goose Neck" through the roof. The duct is preferred straight down 18 inches from floor, but do
not place near piping. This air supply opening
requirement shall be in addition to the air opening
for ventilation air required in (1).
3. When air supply is provided by natural air flow
from outdoors for a power burner and there is no
draft regulator, draft hood or similar flue gas dilution device installed in the same space, in addition
to the opening for ventilation air required in (1),
there shall be a permanent air supply opening(s)
having a total cross-sectional area of not less than
1 sq. in. for each 30,000 BTUH (70 sq. mm per
kW) of total rated input of the burner(s), and the
location of the opening(s) shall not interfere with
the intended purpose of the opening(s) for ventilation air referred to (1). This opening(s) can be
ducted to a point neither more than 18 inches (450
mm) nor less than 6 inches (150 mm) above the
floor level. The duct can also "Goose Neck"
through the roof. The duct is preferred to be
straight down 18 inches from floor, but do not
place near piping.
4. Refer to the latest version of CSA B149 for additional information.
WATER PIPING
General
The boiler should be located so that any water leaks
will not cause damage to the adjacent area or structures.
All units should be plumbed in accordance with the
appropriate diagram from the following sections or per
a suitable engineered piping arrangement.
12
Relief Valve Piping
Hydrostatic Test
Unlike many other types of boilers, Raypak boilers do
not require hydrostatic testing prior to being placed in
operation. The heat exchanger has already been factory-tested and is rated for 160 PSI operating
pressure. However, Raypak does recommend hydrostatically testing the piping connections to the boiler
and the rest of the system prior to operation. This is
particularly true for hydronic systems using expensive
glycol-based antifreeze. Raypak recommends conducting the hydrostatic test before connecting gas
piping or electrical supply.
Leaks must be repaired at once to prevent damage to
the boiler. NEVER use petroleum-based stop-leak
compounds.
1. Connect fill water supply. Fill boiler with water (be
sure bleed valve is open). When water flows from
bleed valve, shut off water. Close bleed valve.
Carefully fill the rest of the system, being sure to
eliminate any entrapped air by using high point
vents. Close feed valve. TEST AT standard operating pressure for at least 24 hours.
2. Make sure constant gauge pressure has been
maintained throughout test.
3. Check for leaks. Repair if found.
Low Temperature System
Boiler requires minimum inlet temperature of 105°F.
Consult the following sections for piping details. (For
Pool temperature requirements, See the Pool Heating
Section).
Temperature & Pressure
Gauge
The temperature and pressure gauge is factorymounted in the inlet/outlet header.
WARNING: Pressure relief valve discharge piping
must be piped near the floor close to a floor drain to
eliminate the potential of severe burns. Do not pipe
to any area where freezing could occur. Refer to
local codes.
CAUTION: This boiler requires forced water
circulation when the burner is operating. See Table E
for minimum and maximum flow rates and water
pump selection. The pump must be interlocked with
the boiler to prevent boiler operation without water
circulation.
Page 13
HYDRONIC HEATING
Pump Selection
In order to ensure proper performance of your boiler
system, you must install a properly sized pump.
Raypak recommends using a 20°F ΔT as design ΔT.
(ΔT is the temperature difference between the inlet
and outlet water when the boiler is firing at full rate). If
a ΔT larger than 20°F is necessary, the bypass must
be installed and adjusted to ensure proper hydraulics
through the boiler while still allowing minimum flow to
satisfy the safety flow switch. See Table E for flow rate
requirements.
Pressure Drop in Feet of Head
Feedwater Regulator
Raypak recommends that a feedwater regulator be installed and set at 12 psi minimum pressure at the
highest point of the system. Install a check valve or
back flow device upstream of the regulator, with a
manual shut-off valve as required by local codes.
Piping — Heating Boilers
All high points should be vented. Purge valves and a
bypass valve should be installed. A boiler installed
above radiation level must be provided with a low
water cutoff device. The boiler, when used in connection with a refrigeration system, must be installed so
the chilled medium is piped in parallel with the boiler
with appropriate valves to prevent the chilled medium
from entering the boiler.
13
The boiler piping system of a hot water heating boiler
connected to heating coils located in air handling units
where they may be exposed to circulating refrigerated
air, must be equipped with flow control valves or other
automatic means to prevent gravity circulation of the
boiler water during the cooling cycle. It is highly recommended that the piping be insulated.
Air-Separation/Expansion Tank
All boilers should be equipped with a properly sized
expansion tank with an air separation fitting as shown
in the following diagrams.
Three-Way Valves
Valves designed to blend water temperatures or
reduce water circulation through the boiler should not
be used. Raypak heaters are high recovery low mass
heaters not subject to thermal shock. Raypak offers a
full line of electric sequencers that produce direct reset
of boiler water temperature. Refer to the Controls
Section in our Complete Catalog.
Table D-1
ΔP Should include typical piping To/From a single tank as well as bypass piping.
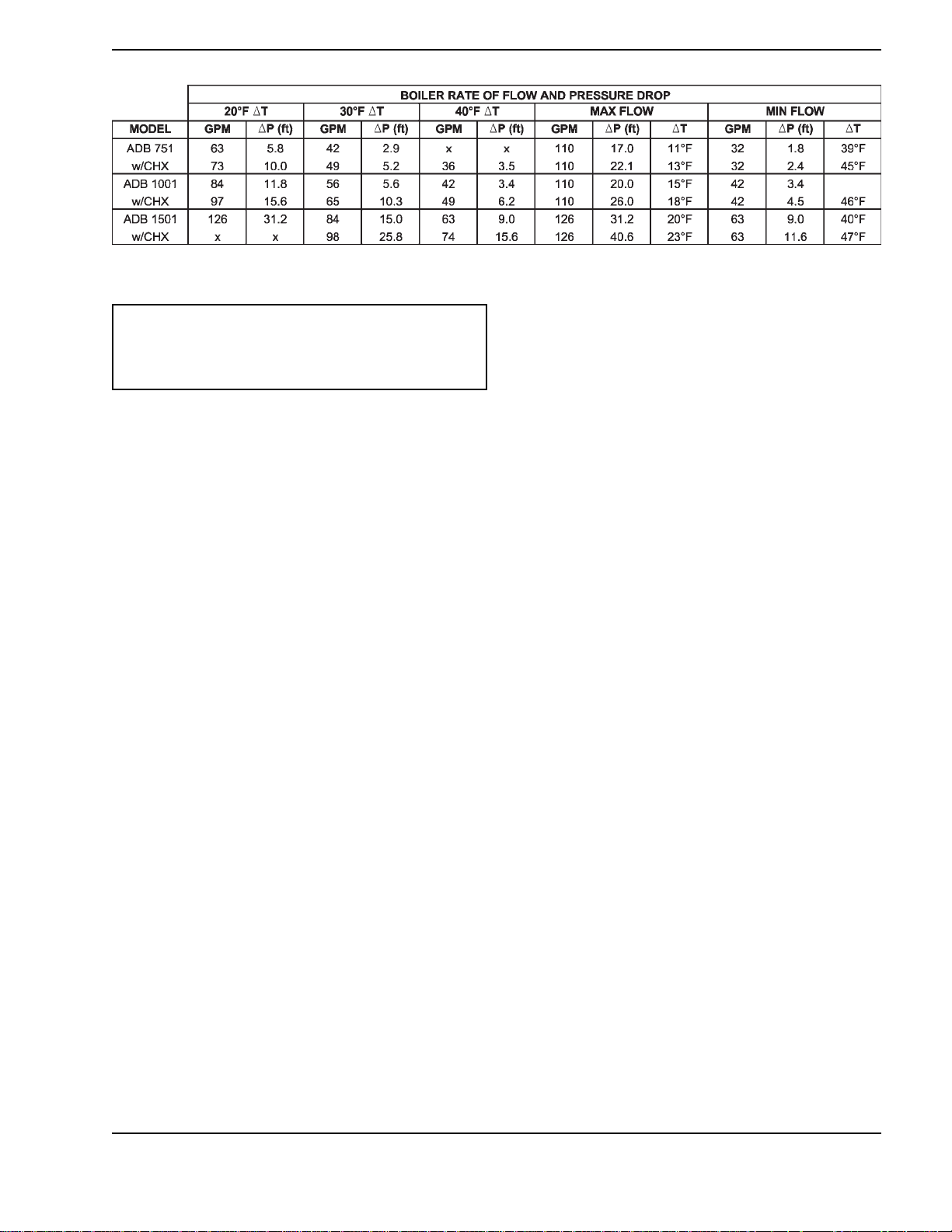
Table E: Rate of Flow and Pressure Drop
NOTE: gpm flow rates limited by maximum
acceptable velocity through heat exchanger tubes.
May be increased by 10% for closed heating
systems. Pressure drop would increase by 21%.
40°F
Page 14
14
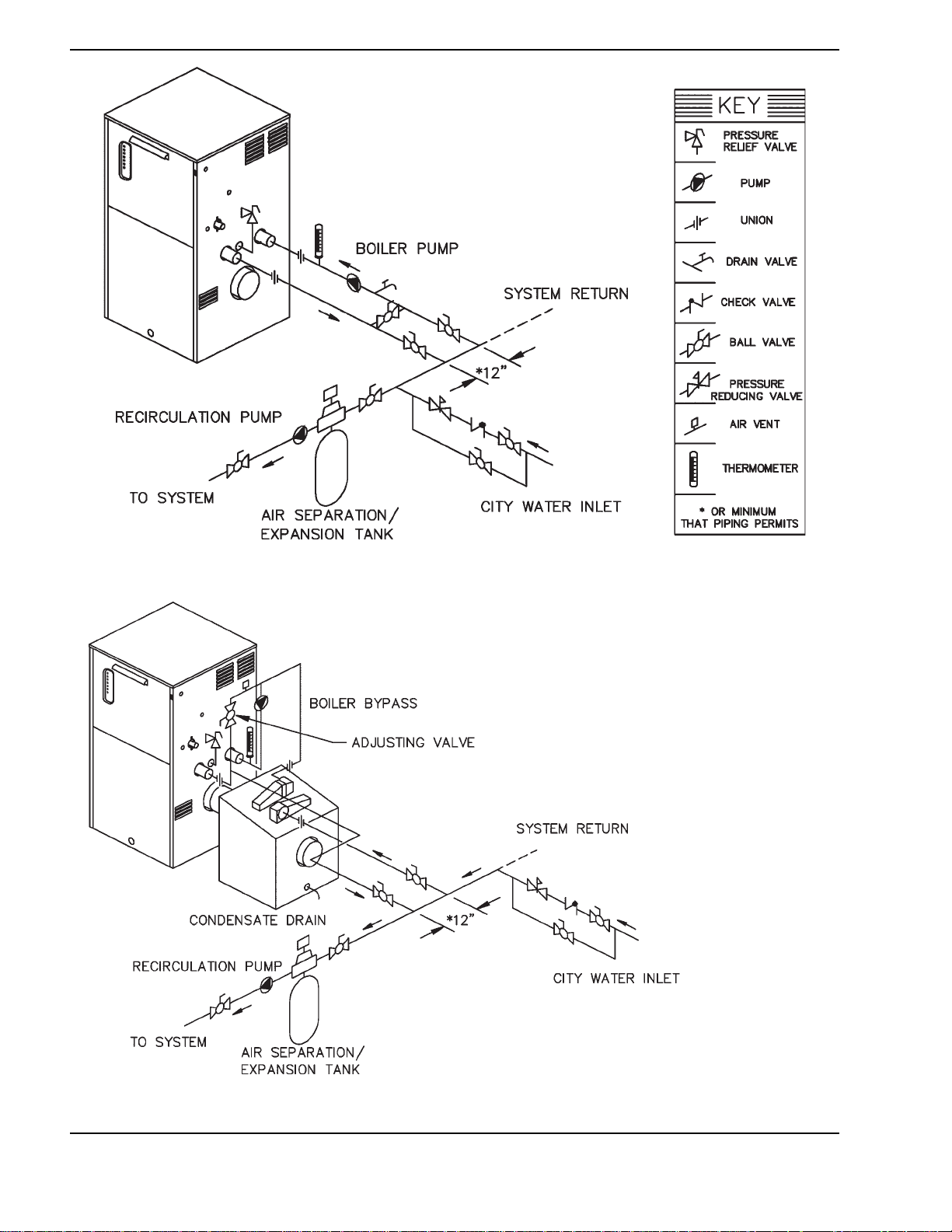
Fig. 4: Single Boiler - Primary/Secondary Piping
Fig. 5: Single Boiler - Primary/Secondary Piping with CHX
Page 15
15
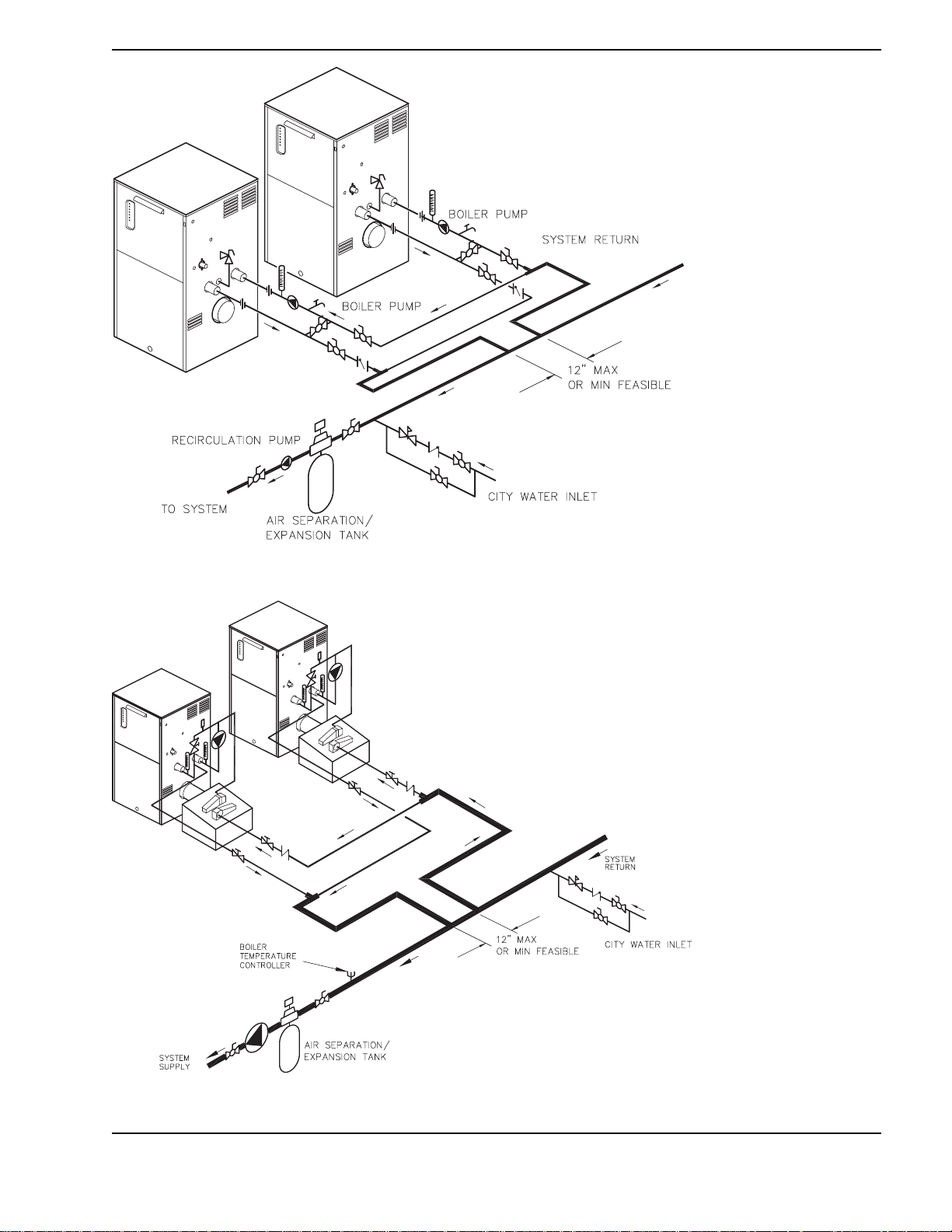
Fig. 6: Dual Boiler Piping
Fig. 7: Dual Boiler - Piping with CHX
Page 16
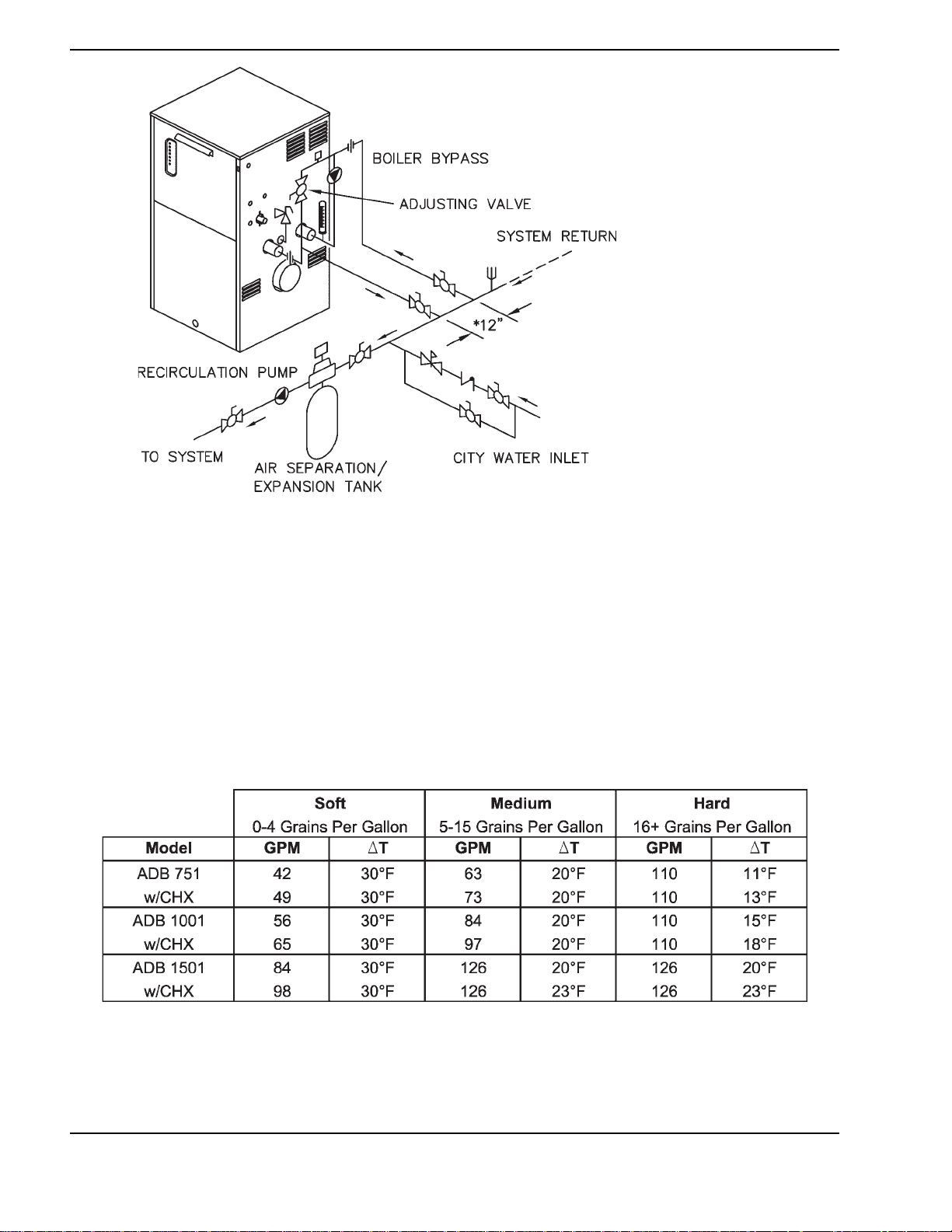
16
Fig. 8: Single Boiler - Low Temperature Application (Heat Pump) Primary/Secondary Piping
DOMESTIC HOT WATER
PIPING
When designing the water piping system for domestic
water applications, water hardness should be considered. Table F indicates the suggested flow rates for
Table F: Domestic Water Heating Boiler Flow Rate Requirements
ΔT=Temperature rise in °F
GPM=Gallons per minute
See Table D for Pressure Drop
soft, medium and hard water. Hardness is specified as
grains per gallon.
Page 17
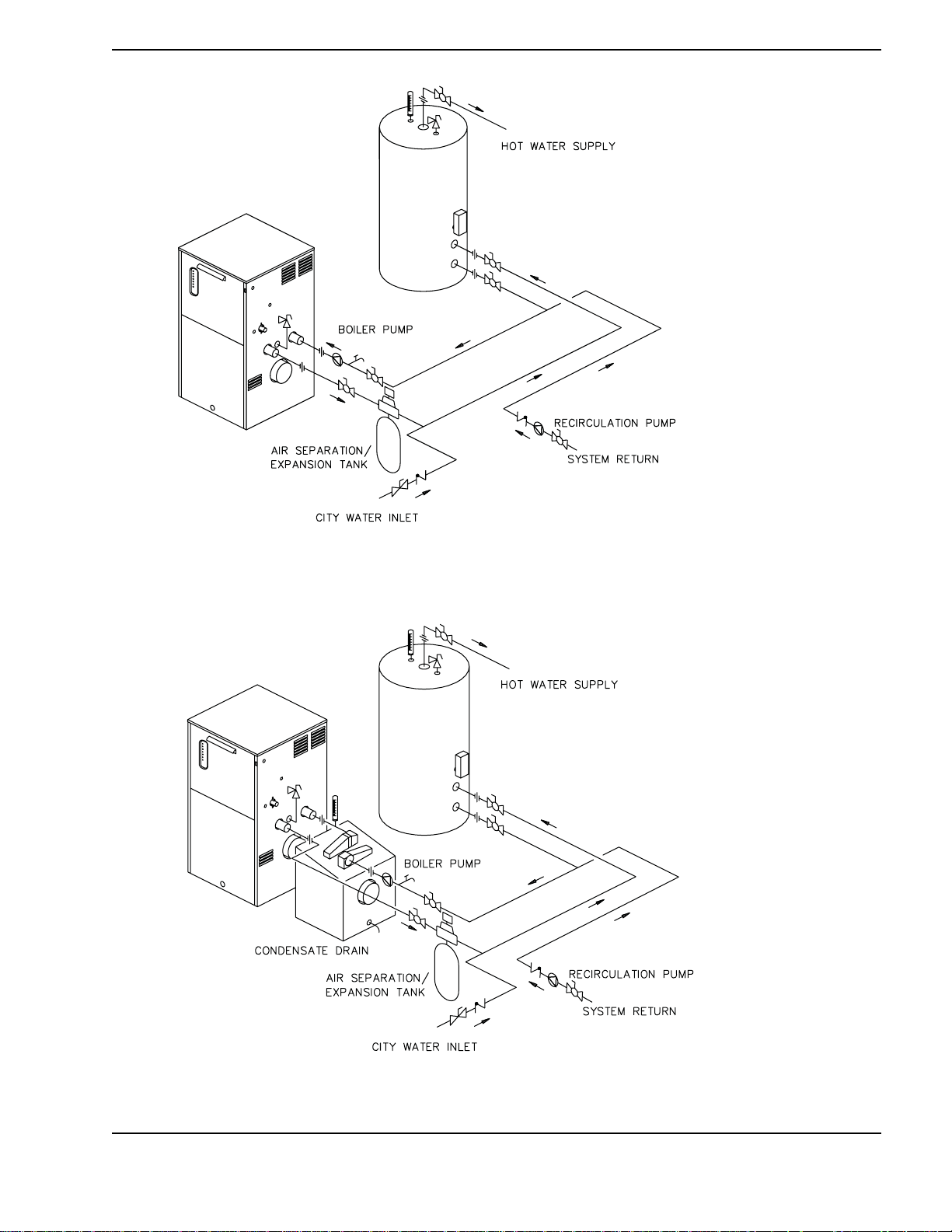
17
Fig. 9: Single Boiler - Domestic Hot Water with One Storage Tank
Fig. 10: Single Boiler - Domestic Hot Water with One Storage Tank and CHX
Page 18
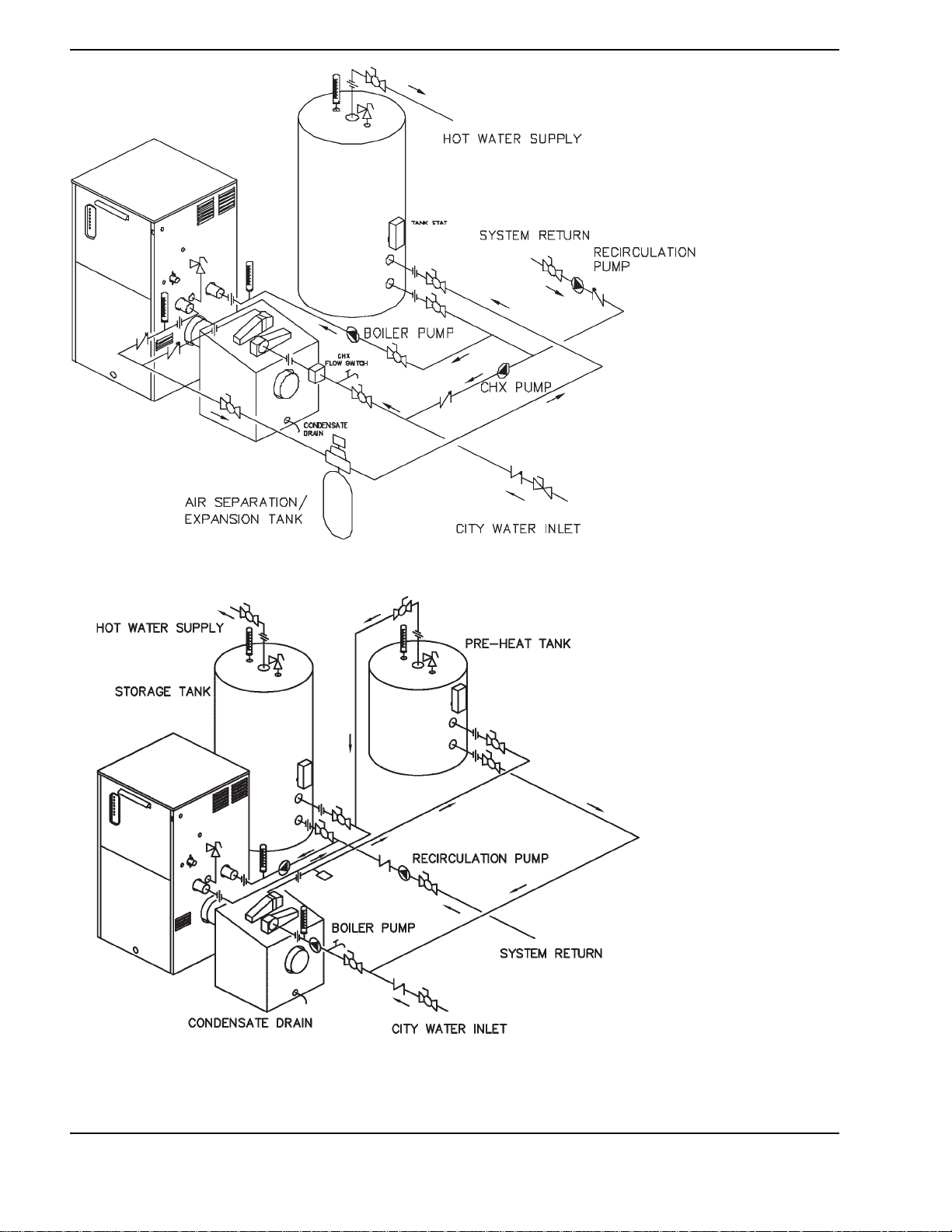
18
Fig. 11: Single Boiler - Domestic Hot Water with One Storage Tank and CHX (2 pump system)
Fig. 12: Single Boiler - Domestic Hot Water with One Storage Tank, One Pre-Heat Tank and CHX
Page 19

19
POOL HEATING
The ADB unit is equipped with an external pump and
bypass arrangement that blends outlet water with the
inlet to increase the inlet water temperature, thereby
reducing the likelihood of condensation forming on the
heat exchanger. The pump also serves to circulate
water through the heater form the main system piping.
To complete the installation of the pool heater, the pool
thermostat needs to be installed in the main return
water line. This will ensure that the heater will be energized at the right time. If the main water line is too far
away from the heater and the capillary bulb will not
reach it, locate the pool thermostat adjacent to the
main line and run wires back to the heater. See Figure
13 and 14.
Adjustment of the bypass valve is critical to proper
operation of the heater. The bypass valve should be
adjusted to achieve a minimum inlet water temperature of 105°F and an outlet water temperature of
125°F. When starting with a cold pool, make initial
adjustments. Make final adjustments when pool water
approaches desired temperature. Refer to Table G for
flow rates.
CAUTION: Power to the heater should be
interlocked with the main system pump to make sure
the heater does not fire without the main system
pump in operation. Improper flow control can
damage the heater. Uncontrolled flow (too high) or
restricted flow (too low) can seriously affect heater
operation. Follow these instructions to make sure
your heater is properly installed.
Table G: Flow Rates
*Loop is secondary piping to heater from main system
CAUTION: ADB bypass piping should be copper
and/or CPVC. PVC piping should NOT be used.
Automatic Chlorinators and
Chemical Feeders
All chemicals must be introduced and completely diluted into the pool or spa water before being circulated
through the heater. Do not place chlorine tablets or
bromine sticks in the skimmer. High chemical concentrations will result when the pump is not running (i.e.
overnight).
Chlorinators must feed downstream of the heater and
have an anti-siphoning device to prevent chemical
backup into the heater when the pump is shut off.
Winterizing Your Heater
When heaters installed outdoors in freezing climate
areas are to be shut down for the winter, please
observe the following procedure:
1. Turn off manual main gas and main gas shut off.
Remove the drain plug or open the drain valves
located on the bottom header.
Pool and Spa Water Chemistry
NOTE: High chemical concentrates from feeders
and chlorinators that are out of adjustment will cause
very rapid corrosion to the heat exchanger in the
heater. Such damage is not covered under the
warranty.
NOTE: Chemical imbalance can cause severe
damage to your heater and associated equipment.
Maintain your water pH between 7.4 and 7.8 and
total alkalinity between 100 and 150 p.p.m. If the
mineral content and dissolved solids in the water
become too high, scale forms inside the heat
exchanger tubes, reducing heater efficiency and also
damaging the heater (max TDS at 3000 ppm). If the
pH drops below 7.2, the heater will be severely
damaged.
NOTE: Heat exchanger damage resulting from
chemical imbalance is not covered under the
warranty.
Page 20

20
Fig. 13: Single Boiler - Pool Application
Fig. 14: Single Boiler - Pool Application with CHX
Page 21

21
Fig. 15: Double Boiler - Pool Application
This based on average pool depth of 4’ 6” (4.5 ft)
Table H: ADB Pool Sizing; Indoor or Outdoor
GAS SUPPLY
CONNECTIONS
Gas piping must have a sediment trap ahead of the
boiler gas controls, and a manual shut-off valve located outside the heater jacket. A pounds to inches
regulator must be installed to reduce to gas supply
pressure to under 14 in. WC. The regulator should be
placed a minimum distance of 10 times the pipe diameter upstream of the boiler gas controls. All gas piping
must be tested after installation in accordance with
local codes. The boiler and its gas connection must be
leak-tested before placing it in operation.
DANGER: Make sure the gas on which the boiler
will operate is the same type as specified on the
boiler model and rating plate.
Page 22

22
Fig. 16: Connections
Gas Supply Connection
The boiler must be isolated from the gas supply piping
system by closing the manual shutoff valve during any
pressure testing of the gas supply piping system at
test pressures equal to or less than 1/2 PSIG. Relieve
test pressure in the gas supply line before reconnecting the boiler and its manual shut off valve to the gas
supply line. FAILURE TO FOLLOW THIS PROCE-
DURE MAY DAMAGE THE GAS VALVES. Over
pressurized gas valves are not covered by warranty.
The boiler and its gas connections shall be leak tested
before placing the appliance in operation. Use soapy
water for leak test: DO NOT use open flame.
Gas Supply Pressure
A minimum of 7 in. WC and a maximum of 10.5 in. WC
upstream gas pressure is required under load and no
load conditions for natural gas. A minimum of 12 in.
WC and a maximum of 13 in. WC is required for
propane gas. The gas pressure regulator supplied is
for low pressure service. If upstream pressure
exceeds 14 in. WC, an intermediate gas pressure regulator, of the dead lockup type, must be installed.
When connecting additional gas utilization equipment
to the gas piping system, the existing piping must be
checked to determine if it has adequate capacity.
CAUTION: The boiler and its manual shutoff valve
must be disconnected from the gas supply during
any pressure testing of the gas supply system at test
pressures in excess of 1/2 PSIG (3.45 kPa).
CAUTION: Do not use Teflon tape on gas line pipe
thread. A pipe compound rated for use with Propane
gas systems is recommended. Apply sparingly only
on male pipe ends, leaving the 2 end threads bare.
CAUTION: Support gas supply piping with
hangers, not by the boiler or its accessories. Ensure
the gas piping is protected from physical damage
and freezing where required.
Model
1-1/2”
NPT
2” NPT
2-1/2”
NPT
3” NPT
751 65 200 N/A N/A
1001 35 125 200 N/A
1501 15 60 125 225
NOTE: The supply gas pressure must not fluctuate
by more than +/- 1.0 in. WC. For fluctuating gas supply contact the factory.
Maximum equivalent pipe length.
Natural gas 100 BTU/FT
3
.60 specific gravity @.5 in. WC pressure
drop.
Table I: Gas Pipe Sizing
Page 23

23
Gas Pressure Regulator
The gas pressure regulator is nominally preset to the
outlet values shown in Tables T and U, within +.1 in.
WC. If an adjustment is needed, turn the adjustment
screw clockwise to increase pressure or counterclockwise to lower pressure.
Venting of Diaphragm Gas
Components
Boilers have gas train components that have
diaphragms in their construction that are supplied with
a bleed line connection that must be connected to the
outside atmosphere as required by NFGC or (for
Canada) the B149 Installation code and applicable
provisions of local codes. Under NO circumstances
shall bleed lines terminate in the gas utilization equipment flue or exhaust system.
ELECTRICAL POWER
CONNECTIONS
Installations must follow these codes:
· National Electrical Code and any other national,
state, provincial or local codes or regulations having
jurisdiction.
· Safety wiring must be N.E.C. Class 1.
· Boiler must be electrically grounded as required by
N.E.C. ANSI/NFPA 70-latest edition.
· In Canada, C.S.A. C22. 1 C.E.C. Part 1.
The boiler is wired for 120 VAC. The voltage is indicated on the tie-in leads. Consult the wiring diagram
shipped with the boiler in the instruction packet. The
“TH” leads are connected to the remote tank control
stat, thermostat, or electronic boiler control as applicable. 24 Volts are supplied to this connection through
the boiler transformer. DO NOT attach line voltage to
the “TH” leads. Before starting the boiler check to
insure proper voltage to the boiler and pump.
Install a separate disconnect means for each load.
Use appropriate-sized wire as defined by NEC, CSA
and/or local code. All primary wiring should be 125% of
minimum rating.
It is strongly recommended that all individually-powered control modules and the boiler should be
supplied from the same power source.
Surge Protection
Microprocessor-based and solid state controls are vulnerable to damage from voltage and amperage
fluctuations in the power supply. All sensitive control
components should be protected by a suitable commercial-grade surge protection device.
If any of the original wire as supplied with the boiler
must be replaced, it must be replaced with 105°C wire
or its equivalent.
Check the Power Source
Using a volt-ohm meter (VOM), check the following
voltages at the circuit breaker panel prior to connecting any equipment: Make sure proper polarity is
followed and house ground is proven.
AC = 108 Volts AC Minimum, 132 Volts MAX
AB = 108 Volts AC Minimum, 132 Volts MAX
BC = Must be less than 1.0 Volts AC
Making the Electrical Connections
Refer to Fig. 18 and the wiring diagram.
1. Verify circuit breaker is properly sized by referring
to boiler rating plate. Adedicated motor duty circuit
breaker should be provided.
2. Turn off all power to the boiler. Verify that power
has been turned off by testing with a volt-ohm
meter prior to working with any electrical connections or components.
3. Observe proper wire colors while making electrical
connections. Many electronic controls are polarity
sensitive. Components damaged by improper
electrical installation are not covered by warranty.
Fig. 17: Check Power Source
Page 24

"TH" leads. Before starting the boiler, ensure that there
is proper voltage to the boiler and pump.
The boiler must be electrically grounded in accordance
with National Electrical Code ANSI/NFPA No. 70 and
CSA C22.1 C.E.C. Part 1 in Canada.
Notes:
1. Field installed ground to inside of junction box.
2. If any of the original wire as supplied with the boiler must be replaced, it must be replaced with
105°C wire or its equivalent.
24
4. Provide an external surge suppressor capable of
maintaining system integrity.
5. Provide overload protection and a disconnect
means for equipment serviceability as required by
local and state code.
6. Install boiler controls, thermostats, or building
management systems in accordance with the
applicable manufacturer’s instructions.
7. Conduit should not be used as the ground. There
must be a solid wired ground.
Electrical Connections — Domestic
Hot Water
The ADB is wired for 120 VAC. The voltage is indicated on the tie-in leads. Consult the wiring diagram
shipped with the boiler in the instruction packet. The
"TH" leads are for the remote tank control through the
boiler transformer. DO NOT attach line voltage to the
NOTE: A grounding electrode conductor shall be
used to connect the equipment grounding
conductors, the equipment enclosures, and the
grounded service conductor to the grounding
electrode.
Fig. 18: Field Wiring Connections
CAUTION: When servicing controls, label all wires
prior to disconnection. Wiring errors can cause
improper and dangerous operation. Verify proper
operation after servicing.
DANGER — SHOCK HAZARD — Make sure
electrical power to the heater is disconnected to
avoid potential serious injury or damage to
components.
Fig. 19: Single Stage Tankstat
Fig. 20: 2-Stage Tankstat
BREAK THE WIRE NUT AT THE
BOILER "TH" CONNECTIONS AND
ATTACH TO THE SINGLE TANKSTAT
PER ILLUSTRATION
BREAK THE WIRE NUT AT THE
BOILER "TH" CONNECTIONS AND
ATTACH TO THE DUAL TANKSTAT
PER ILLUSTRATION
Page 25

25
VENTING
CONNECTIONS
General
Definition of Appliance Categories
Boilers are divided into four categories based on the
pressure produced in the exhaust and the likelihood of
condensate production in the vent.
Category I: A boiler which operates with a non-positive vent static pressure and with a vent gas
temperature that avoids excessive condensate production in the vent.
Category II: A boiler which operates with a non-positive vent static pressure and with a vent gas
temperature that may cause excessive condensate
production in the vent.
Category III: A boiler which operates with a positive
vent pressure and with a vent gas temperature that
avoids excessive condensate production in the vent.
Category IV: A boiler which operates with a positive
vent pressure and with a vent gas temperature that
may cause excessive condensate production in the
vent.
See Table J for vent category requirements for the
Advanced Design Boiler.
CAUTION: Proper installation of flue exhaust
venting is critical for the safe and efficient operation
of the boiler. For vent systems not shown in this
section please contact your local authorized
representative.
CAUTION: Stable vent pressure is critical to the
safe and proper operation of the heater. A
combination of barometric dampers, balancing
dampers, extractors, or draft inducers may be
required to stabilize the vent pressure.
NOTE: For additional information on appliance
categorization, see appropriate ANSI Z21 Standard
and the latest edition Standard of National Fuel Gas
Code or in Canada, the latest edition of CSA
Standard B149 Installation Code for Gas Burning
Appliances and Equipment, or applicable provisions
of local building codes.
Table J: ADB Category Determination for Venting Purpose and Venting Arrangement
NOTE: PVC or CPVC vent may be used in conjunction with CHX, special piping arrangement has to be made. Contact manufacturer for details.
A
D
B
V
E
N
T
I
N
G
A
R
R
A
N
G
E
M
E
N
T
S
Tight
Tight
Page 26

26
Determination of Appliance
Category for Venting Purposes and
Venting Arrangements
Support of Vent Stack
The weight of the vent stack or chimney must not rest
on the boiler vent connection. Support must be provided in compliance with applicable codes. The vent
should also be supported to maintain proper clearances from combustible materials.
Use insulated vent pipe spacers where the vent passes through combustible roofs and walls.
Vent Terminal Location
Give special attention to the location of the vent termination to avoid possibility of property damage or
personal injury.
a) Gases may form a white vapor plume in winter.
The plume could obstruct a window view if the termination is installed in close proximity to windows.
b) Prevailing winds could cause freezing of conden-
sate and water/ice buildup on building, plants or
roof.
c) The bottom of the vent terminal and the air intake
shall be located at least 12 inches above grade,
including normal snow line.
d) Un-insulated single-wall metal vent pipe shall not
be used outdoors on cold climates for venting gas
utilization equipment.
e) Through-the-wall vents for Category II and IV
appliances and non-categorized condensing appliances shall not terminate over public walkways or
WARNING: Contact the manufacturer of the vent
material if there is any question about the appliance
categorization and suitability of a vent material for
application on a Category III or IV vent system.
Using improper venting materials can result in
personal injury, death or property damage.
over an area where condensate or vapor could
create a nuisance or hazard or could be detrimental to the operation of regulators, relief valves, or
other equipment. Where local experience indicates that condensate is a problem with Category
I and III appliances, this provision shall also apply.
f) Locate and guard vent termination to prevent acci-
dental contact by people and pets.
g) DO NOT terminate vent in window well, stairwell,
alcove, courtyard or other recessed area, unless
previously approved by local authority.
h) DO NOT terminate above any door, window, or
gravity air intake. Condensate can freeze causing
ice formations.
i) Locate or guard vent to prevent condensate from
damaging exterior finishes. Use a 2' x 2' rust
resistant sheet metal backing plate against brick
or masonry surfaces.
j) DO NOT extend exposed vent pipe outside of
building. Condensate could freeze and block vent
pipe.
k) Multiple direct vent caps, when installed in the
same horizontal plane, should have a three (3)
foot clearance from the side of one vent cap to the
side of the adjacent vent cap(s).
U.S. Installations
Refer to latest edition of the National Fuel Gas Code.
Vent termination requirements are as follows:
a) Vent must terminate at least four (4) feet below,
four (4) feet horizontally, or one (1) foot above any
door, window or gravity air inlet to the building.
b) The vent must not be less than seven (7) feet
above grade when located adjacent to public walkways.
c) Terminate vent at least three (3) feet above any
forced air inlet located within ten (10) feet.
d) Vent must terminate at least four (4) feet horizon-
tally, and in no case above or below unless four (4)
feet horizontal distance is maintained, from electric meters, gas meters, regulators, and relief
equipment.
NOTE: During winter months check the vent cap
and make sure no blockage occurs from build up of
snow. Condensate can freeze on the vent cap.
Frozen condensate on the vent cap can result in a
blocked flue condition.
Page 27

27
e) Terminate vent at least six (6) feet away from adja-
cent walls.
f) DO NOT terminate vent closer than five (5) feet
below roof overhang.
Canadian Installations
Refer to the latest edition of CSA B149 Installation
Code.
A vent shall not terminate:
a) Directly above a paved sidewalk or driveway
which is located between two single family
dwellings and serves both dwellings.
b) Less than 7 ft. (2.13m) above a paved sidewalk or
paved driveway located on public property.
c) Within 6 ft. (1.8m) of a mechanical air supply inlet
to any building.
d) Above a meter/regulator assembly within 3 ft.
(900mm) horizontally of the vertical center-line of
the regulator.
e) Within 6 ft. (1.8m) if any gas service regulator vent
outlet.
f) Less than 1 ft. (300mm) above grade level.
g) Within 3 ft (1m) of a window or door which can be
opened in any building, any non-mechanical air
supply inlet to any building to the combustion air
inlet of any other appliance.
h) Underneath a verandah, porch or deck, unless:
(i) the verandah, porch or deck is fully open on a
minimum of two sides beneath the floor, and
(ii) the distance between the top of the vent termi-
nation and the underside of the verandah,
porch or deck is greater than 1 ft (30cm).
Venting Installation Tips
Support piping:
· horizontal runs- at least every five (5) feet.
· vertical runs - use braces:
· under or near elbows
Follow items listed below to avoid personal injury or
property damage.
· Cut nonmetallic vent pipe with fine-toothed hacksaw
(34 teeth per inch).
· Do not use nonmetallic vent pipe or fittings that are
cracked or damaged.
· Do not use nonmetallic vent fittings if they are cut or
altered.
· Do not drill holes, or use screws or rivets, in nonmetallic vent pipe or fittings.
To make metallic vent joints:
· Do not install seams of vent pipe on bottom of runs.
· Completely seal all joints and seams with silicone
sealant.
Venting Configurations
The following is a detailed explanation of each venting
system WITHOUT and WITH add-on condensing heat
exchanger (CHX), its installation requirements, the
components used, and part numbers for each.
For boilers connected to gas vents or chimneys, vent
installations shall be in accordance with Part 7,
Venting of Equipment, of the latest edition of National
Fuel Gas Code, or in Canada, the latest edition of CSA
B149 Installation Code for Gas Burning Appliances
and Equipment, or applicable provisions of local building codes.
NOTE: For direct vent installations where the air is
piped in from outside, the protective screen on the
combustion air blower may be relocated to the air
inlet termination elbow to act as an inlet screen.
NOTE: The words "Flue Exhaust", "Flue" and
"Exhaust Vent" are used interchangeably.
WARNING: Examine the venting system at least
once a year. Check all joints and vent pipe
connections for tightness, corrosion or deterioration.
Page 28

28
Natural Draft Vertical Venting without Add-on Condensing Heat
Exchanger (Category I)
Fig. 21: Natural Draft Vertical Venting without Add-on Condensing Heat Exchanger (Category I)
NOTE:
*Rear venting is recommended to minimize interference with water piping
**Vent lengths are based on a lateral length of 2 feet. Refer to the latest edition of the National Fuel Gas Code for further details (ANSI Z223.1), or in Canada, the latest edition of CSA B149.
Table K: Natural Draft Vertical Vent without Add-on Condensing Heat Exchanger
ADB-1501
Page 29

29
Natural Draft Vertical Venting
System Installation
Natural draft venting uses the natural buoyancy of the
heated flue products to create a thermal driving head
that expels the exhaust gases from the flue. The negative draft must be within the range of 0.01 in. to 0.08
in. WC negative to ensure proper operation. The vent
material must be in accordance with the above instructions for vent materials. Vent material must be listed by
a nationally recognized test agency.
The maximum and minimum venting length for
Category I appliance shall be determined per the latest edition of the National Fuel Gas Code (U.S.) or
B149 Installation Code (Canada).
The diameter of vent flue pipe should be sized according to Part 11 of the latest edition of the National Fuel
Gas Code (U.S.) and part 7 and appendix B of the
CSA B149 Installation Code (Canada). The flue pipe
diameter for conventional negative draft venting using
double-wall B type vent is 8” for the ADB 751, 10” for
the 1001, and 12” for the ADB 1501.
The connection from the appliance vent to the stack
must be as direct as possible and shall be the same
diameter as, or larger than the vent outlet. The vent
must be installed to prevent accumulation of
condensate and, where necessary, have means
provided for drainage of condensate. The horizontal
breaching of a vent must have an upward slope of not
less than 1/4 inch per linear foot from the boiler to the
vent terminal. The horizontal portions of the vent shall
also be supported for the design and weight of the
material employed to maintain clearances and to
prevent physical damage or separation of joints.
Natural Draft Vertical Vent
Termination
The vent terminal should be vertical and should terminate outside the building at least two (2) feet above the
highest point of the roof that is within 10 feet. The vent
cap should have a minimum clearance of four (4) feet
horizontally from and in no case above or below
(unless a four (4) foot horizontal distance is maintained) electric meters, gas meters, regulators and
relief equipment.
The distance of the vent terminal from adjacent public
walkways, adjacent buildings, open windows and
building openings must be consistent with the National
Fuel Gas Code, or in Canada, the latest edition of the
CSA B149 Installation Code for Gas Burning
Appliances and Equipment. Gas vents supported only
by flashing and extended above the roof more than
five feet should be securely guyed or braced to withstand snow and wind loads.
Natural Draft Vertical Venting with
Common Venting System, Category
I Appliance Only
(NOT to be Utilized with Add-on
Condensing Heat Exchanger)
Manifolds that connect more than one boiler to a common chimney must be sized to handle the combined
load. Consult available guides for proper sizing of the
manifold and the chimney. At no time should the area
of the vent be less than the area of the largest boiler
exhaust outlet.
Common venting systems may be too large when an
existing unit is removed. At the time of removal of an
existing appliance, the following steps must be followed with each appliance remaining connected to the
common venting system placed in operation, while the
other appliances remaining connected to the common
venting system are not in operation.
a) Seal any unused opening in the common venting
system.
b) Visually inspect the venting system for proper size
and horizontal pitch and determine there is no
blockage or restriction, leakage, corrosion or other
unsafe condition.
c) Insofar as is practical, close all building doors and
windows and all doors between the space in which
the appliances remaining connected to the common venting system are located and other spaces
of the building. Turn on clothes dryers and any
NOTE: Vent Adapter will have to be used to connect
B vent to the unit.
CAUTION: Listed vent cap terminal must be used
and sized adequately to evacuate the flue products
from the boilers.
WARNING: Vent connectors serving appliances
vented by natural draft shall not be connected into
any portion of mechanical draft systems operating
under a positive pressure.
CAUTION: Vent connectors for natural draft
venting systems must be type “B” vent or better.
Page 30

30
appliance not connected to the common vent system. Turn on any exhaust fans, such as range
hoods and bathroom exhausts, so they will operate at maximum speed. Do not operate summer
exhaust fan. Close fireplace dampers.
d) Place in operation the appliances being inspected.
Follow the manufacturers instructions for lighting
each appliance. Adjust thermostat so appliance
will operate continuously.
e) Test for natural draft (negative pressure) 12"
above the outlet elbow after 5 minutes of main
burner operation. Use the flame of a match or candle, or smoke from a cigarette, cigar or pipe, toilet
paper trick.
f) After it has been determined that each appliance
remaining connected to the common venting system properly vents when tested as outlined above,
return doors, windows, exhaust fans, fireplace
dampers and other gas burning appliances to their
previous conditions of use.
g) Any improper operation of the common venting
system should be corrected so that the installation
conforms with the latest edition of the National
Fuel Gas Code, ANSI Z223.1, in Canada, the latest edition of CSA B149 Installation Code for Gas
Burning Appliances and Equipment.
When re-sizing any portion of the common venting
system, the common venting system should be resized to approach the minimum size as
determined using the appropriate tables in
Appendix G in the latest edition of the National
Fuel Gas Code, ANSI Z223.1, in Canada,
Appendix B of the latest edition of the Installation
Code for Gas Burning Appliances and Equipment.
Fig. 22: Horizontal Thru-Wall Venting without Add-on
Condensing Heat Exchanger (Category III)
Table L: Horizontal Thru-wall Venting without Add-on
Condensing Heat Exchanger (Category III)
ADB-1501
Page 31

31
Horizontal Thru-wall Direct Venting
System (Category III) Installation
These installations utilize the boiler-mounted blower to
vent the combustion products to the outdoors.
Combustion air is taken from inside the room and the
vent is installed horizontally through the wall to the outdoors. Adequate combustion and ventilation air must
be supplied to the boiler room in accordance with the
National Fuel Gas Code or, in Canada, the latest edition of CSA B149 Installation Code for Gas Burning
Appliances and Equipment.
The total length of the thru-wall exhaust vent system
cannot exceed sixty-five (65) feet in length for the flue
outlet. Each elbow used is equal to ten (10) feet of
straight pipe. This will allow installation in one of the
four following combinations:
· 65′ of straight flue pipe.
· 55′ of straight flue pipe and one elbow.
· 45′ of straight flue pipe and two elbows.
· 35′ of straight pipe and three elbows.
The direct vent cap is not considered in the overall
length of the venting system. The vent must be
installed to prevent the flue gas leakage. Care must be
taken during assembly to ensure that all joints are
sealed properly and are airtight.
The vent must be installed to prevent the potential
accumulation of condensate in the vent pipes. It is recommended that:
a) The vent be installed with a slight downward slope
of not more than 1/4" per foot of horizontal run to
the vent terminal.
b) The vent be insulated through the length of the
horizontal run.
For appliances installed in extreme cold climate, it is
recommended that:
a) The vent be installed with a slight upward slope of
not more than 1/4" per foot of horizontal run to the
vent terminal. In this case, an approved condensate trap must be installed per applicable codes.
b) The vent be insulated through the length of the
horizontal run.
Horizontal Thru-wall Direct Vent
Termination
The direct vent cap MUST be mounted on the exterior
of the building. The direct vent cap cannot be installed
in a well or below grade. The direct vent cap must be
installed at least one (1) foot above ground level and
above normal snow levels. The Raypak supplied direct
vent cap must be used.
The Stainless Steel direct vent cap must be furnished by the boiler manufacturer in accordance
with its listing.
WARNING: No substitutions of flue pipe or vent
cap material are allowed. Such substitutions would
jeopardize the safety and health of inhabitants.
WARNING: For common vent installations, contact
the factory.
Fig. 23: Horizontal Thru-Wall Direct
Venting/Combustion Air
(Category III)
Page 32

32
Table M: Horizontal Thru-wall Direct Venting without Add-on
Secondary Condensing Heat Exchanger
Horizontal Thru-wall Direct Venting
System (Category III) Installation
These installations utilize the boiler mounted blower to
draw combustion air from outdoors and vent combustion products to the outdoors.
The total length of the thru-wall exhaust vent cannot
exceed forty-five (45) feet in length for the flue outlet.
Each elbow used is equal to ten (10) feet of straight
pipe. This will allow installation in one of the three following combinations:
· 45′ of straight flue pipe.
· 35′ of straight flue pipe and one elbow.
· 25′ of straight flue pipe and two elbows.
The total length air supply pipe cannot exceed fortyfive (45) feet in length for the combustion air inlet.
Each elbow used is equal to ten (10) feet of straight
pipe. This will allow installation in one of the three following combinations:
· 45′ of straight combustion air pipe
· 35′ of straight combustion air pipe and one elbow.
· 25′ of straight combustion air pipe and two elbows.
The direct vent cap is not considered in the overall
length of the venting system.
Care must be taken during assembly that all joints are
sealed properly and are airtight.
The vent must be installed to prevent the potential
accumulation of condensate in the vent pipes. It is recommended that:
a) The vent be installed with a slight downward slope
of not more than 1/4" per foot of horizontal run to
the vent terminal.
b) The vent be insulated through the length of the
horizontal run.
For appliances installed in extreme cold climate, it is
recommended that:
a) The vent be installed with a slight upward slope of
not more than 1/4" per foot of horizontal run to the
vent terminal. In this case, an approved condensate trap must be installed per applicable codes.
b) The vent be insulated through the length of the
horizontal run.
Horizontal Thru-wall Direct Vent
Termination
The direct vent cap MUST be mounted on the exterior
of the building. The direct vent cap cannot be installed
in a well or below grade. The direct vent cap must be
installed at least one (1) foot above ground level and
above normal snow levels.
Multiple direct vent caps MUST NOT be installed with
one combustion air inlet directly above a direct vent
cap. This vertical spacing would allow the flue products from the direct vent cap to be pulled into the
combustion air intake installed above.
ÁDB-1501
Page 33

33
This type of installation can cause non warrantable
problems with components and poor operation of the
unit due to the recirculation of flue products. Multiple
direct vent caps, when installed in the same horizontal
plane, should have three (3) foot clearance from the
side of one vent cap to the side of the adjacent vent
cap(s).
Combustion air supplied from outdoors must be free of
particulate and chemical contaminants. To avoid a
blocked flue condition, keep the vent cap clear of
snow, ice, leaves, debris, etc.
The Stainless Steel direct vent cap must be furnished by the boiler manufacturer in accordance
with its listing.
WARNING: For common vent installations call
factory.
WARNING: No substitutions of flue pipe or vent
cap material are allowed. Such substitutions would
jeopardize the safety and health of inhabitants.
Fig. 24: Vertical Direct Venting/Combustion Air
(Category I)
*Vent lengths are based on a lateral length of 2 feet. Refer to the latest edition of National Fuel Gas Code for further details
(ANSI Z223.1) or in Canada, the latest edition of CSA B149 Installation Code.
Table N: Vertical Direct Venting without Add-on Condensing Heat Exchanger
ADB-1501
Page 34

34
Vertical Direct Venting System
Installation
These installations utilize the boiler mounted blower to
draw combustion air from outdoors and uses the natural buoyancy of the heated flue products to create a
thermal driving head that expels the exhaust gases
from the flue. The negative draft must be within the
range of -0.01 in. to -0.08 in. WC to ensure proper
operation.
The vent material must be in accordance with the
above instructions for vent materials. Vent material
must be listed by a nationally recognized test agency.
The maximum and minimum venting length for
Category I appliance shall be determined per the latest edition of the National Fuel Gas Code (U.S.) and
CSA B149 Installation Code (Canada).
The diameter of vent flue pipe should be sized according to part 11 of the latest edition of the National Fuel
Gas Code (U.S.) and part 7 and Appendix B of CSA
B149 Installation Code (Canada). The flue pipe diam
eter for conventional negative draft venting using
double-wall B type vent is 12” for the ADB 1501.
The connection from the appliance vent to the stack
must be as direct as possible and should be the same
as or larger than the vent outlet. The vent must be
installed to prevent accumulation of condensate and,
where necessary, have means provided for drainage
of condensate. The horizontal breaching of a vent
must have an upward slope of not less than 1/4 inch
per linear foot from the boiler to the vent terminal.
The horizontal portions of the vent shall also be supported for the design and weight of the material
employed to maintain clearances and to prevent physical damage or separation of joints.
Vertical Direct Vent Termination
The vent terminal should be vertical and should terminate outside the building at least two (2) feet above the
highest point of the roof within 10 feet. The vent cap
should have a minimum clearance of four (4) feet horizontally from and in no case above or below (unless a
four (4) foot horizontal distance is maintained) electric
meters, gas meters, regulators and relief equipment.
The distance of the vent terminal from adjacent public
walkways, adjacent buildings, open windows and
building openings must be consistent with the National
Fuel Gas Code, or in Canada, the latest edition of CSA
B149 Installation Code for Gas Burning Appliances
and Equipment. Gas vents supported only by flashing
and extended above the roof more than five feet
should be securely guyed or braced to withstand snow
and wind loads.
The vertical direct vent cap is designed for roof top
mounting only. The air inlet opening MUST be installed
one (1) foot above the roof line or above normal snow
levels that might obstruct combustion air flow. This
dimension is critical to the correct operation of the boiler and venting system and reduces the chance of
blockage from snow. The vent cap must have a minimum 3 foot vertical clearance above the air inlet
opening.
Fig. 25: Vertical Venting with Add-on Condensing Heat
Exchanger (Category IV) Domestic Water
Page 35

35
Table O: Vertical Vent (CATEGORY IV) with Add-on Condensing Heat Exchanger
Model Venting Category
Certified Venting
Material
Vent Size (inches)
Maximum Vent
Length (feet)
ADB-751 w/CHX IV
UL 1738 Certified
Venting Material e.g.
AL29-4C Stainless
Steel PVC*, CPVC*
8
55 Subtract 10 ft per
elbow, Max. 3
elbows
ADB-1001 w/CHX IV
UL 1738 Certified
Venting Material e.g.
AL29-4C Stainless
Steel PVC*, CPVC*
10
55 Subtract 10 ft per
elbow, Max. 3
elbows
ADB-1501 w/CHX IV
UL 1738 Certified
Venting Material e.g.
AL29-4C Stainless
Steel PVC*, CPVC*
12
55 Subtract 10 ft per
elbow, Max. 3
elbows
Vertical Vent (Category IV) with
Add-on Condensing Heat Exchanger
Installation
These installations utilize the boiler mounted blower to
vent the combustion products to the outdoors.
Combustion air is taken from inside the room and the
vent is installed vertically through the roof to the outdoors. Adequate combustion and ventilation air must
be supplied to the boiler room in accordance with the
National Fuel Gas Code or, in Canada, the latest edition of CSA B149 Installation Code for Gas Burning
Appliances and Equipment.
UL 1738 Certified Venting Material (e.g. AL29-4C)
MUST be used. The vent must be installed to prevent
the flue gas leakage. Care must be taken during
assembly to ensure that all joints are sealed properly
and are airtight.
For certain installations, i.e. pool, heat-pump domestic
hot water with pre-heat tank, PVC or CPVC may be
used. Contact the manufacturer for details.
To prevent the condensation accumulation in the vent,
it is required to install the horizontal portion of vent with
a slight upward slope of not more than 1/4" per foot of
horizontal run and an approved condensate trap must
be installed per applicable codes.
The Stainless Steel non-restricted direct vent cap
must be furnished by the boiler manufacturer in
accordance with its listing.
WARNING: No substitutions of flue pipe or vent
cap material are allowed. Such substitutions would
jeopardize the safety and health of inhabitants.
Fig. 26: Horizontal Thru-wall Venting with Add-on Condensing Heat Exchanger (CHX)
*Contact the manufacturer for details.
Page 36

36
Model Venting Category
Certified Venting
Material
Vent Size (inches)
Maximum Vent
Length (feet)
ADB-751 w/CHX IV
UL 1738 Certified
Venting Material e.g.
AL29-4C Stainless
Steel PVC*, CPVC*
8
55 Subtract 10 ft per
elbow, Max. 3
elbows
ADB-1001 w/CHX IV
UL 1738 Certified
Venting Material e.g.
AL29-4C Stainless
Steel PVC*, CPVC*
10
55 Subtract 10 ft per
elbow, Max. 3
elbows
ADB-1501 w/CHX IV
UL 1738 Certified
Venting Material e.g.
AL29-4C Stainless
Steel PVC*, CPVC*
12
55 Subtract 10 ft per
elbow, Max. 3
elbows
*Contact the manufacturer for details.
Table P: Horizontal Thru-wall Venting with Add-on Condensing Heat Exchanger
Horizontal Thru-wall Venting
System (Category IV) Installation
This installation utilize the boiler mounted blower to
vent the combustion products to the outdoors.
Combustion air is taken from inside the room and the
vent is installed horizontally through the wall to the outdoors. Adequate combustion and ventilation air must
be supplied to the boiler room in accordance with the
National Fuel Gas Code or, in Canada, the latest edition of CSA B149 Installation Code for Gas Burning
Appliances and Equipment.
UL 1738 Certified Venting Material (e.g. AL29-4C)
MUST be used. The vent must be installed to prevent
flue gas leakage. Care must be taken during assembly
to ensure that all joints are sealed properly and are airtight.
For certain installations, i.e. pool, heat pump, domestic hot water supply with pre-heat tank, PVC or CPVC
may be used. Contact manufacturer for details.
To prevent condensate accumulation in the vent, it is
required to install the horizontal portion of vent with a
slight upward slope of not more than 1/4" per foot of
horizontal run and an approved condensate trap must
be installed per applicable codes, so the condensation
in the vent pipe drains back to the boiler.
The Stainless Steel non-restrictive direct vent cap
must be furnished by the boiler manufacturer in
accordance with its listing.
WARNING: For common vent installations contact
factory.
WARNING: No substitutions of flue pipe or vent
cap material are allowed. Such substitutions would
jeopardize the safety and health of inhabitants.
Page 37

37
Model
Venting
Category
Certified Venting
Material
Vent Size
(inches)
Maximum Vent
Length (feet)
Combustion Air
Intake Pipe
Material
Air Inlet
Size
(inches)
Max. Air
Intake Length
(feet)
ADB-751
w/CHX
IV
UL 1738 Certified
Venting Material e.g.
AL29-4C Stainless
Steel PVC*, CPVC*
8
35
Subtract 10 ft per
elbow, Max. 3
elbows
Galvanized
Steel
PVC, ABS
CPVC
6
35
Subtract 10 ft
per elbow,
Max. 3 elbows
ADB-1001
w/CHX
IV
UL 1738 Certified
Venting Material e.g.
AL29-4C Stainless
Steel PVC*, CPVC*
10
35
Subtract 10 ft per
elbow, Max. 3
elbows
Galvanized
Steel
PVC, ABS
CPVC
6
35
Subtract 10 ft
per elbow,
Max. 3 elbows
ADB-1501
w/CHX
IV
UL 1738 Certified
Venting Material e.g.
AL29-4C Stainless
Steel PVC*, CPVC*
12
35
Subtract 10 ft per
elbow, Max. 3
elbows
Galvanized
Steel
PVC, ABS
CPVC
8**
35
Subtract 10 ft
per elbow,
Max. 3 elbows
*Contact the manufacturer for details.
**If the boiler is direct vented, a 6 to 8 in. adapter must be installed at the blower inlet.
Fig. 27: Horizontal Thru-Wall Direct Venting/Combustion Air with Add-on
Condensing Heat Exchanger (Category IV)
Table Q: Horizontal Thru-wall Direct Venting with Add-on
Condensing Heat Exchanger
Page 38

38
Horizontal Thru-wall Direct Venting
System with Add-on Condensing
Heat Exchanger (Category IV)
Installation
These installations utilize the boiler mounted blower to
draw combustion air from outdoors and vent combustion products to the outdoors.
UL 1738 Certified Venting Material (e.g. AL29-4C)
MUST be used. The vent must be installed to prevent
the flue gas leakage. Care must be taken during
assembly to ensure that all joints are sealed properly
and are airtight.
For certain installations, i.e. pool, heat-pump, domestic hot water supply with pre-heat tank, PVC or CPVC
may be used. Contact manufacturer for details.
To prevent condensate accumulation in the vent, it is
required to install the horizontal portion of vent with a
slight upward slope of not more than 1/4" per foot of
horizontal run and an approved condensate trap must
be installed per applicable codes.
The Stainless Steel non-restricted direct vent cap
must be furnished by the boiler manufacturer in
accordance with its listing.
WARNING: For common vent installations, contact
the factory.
WARNING: No substitutions of flue pipe or vent
cap material are allowed. Such substitutions would
jeopardize the safety and health of inhabitants.
Fig. 28: Vertical Direct Venting/Combustion Air with Add-on Condensing
Heat Exchanger (Category IV)
Page 39

39
Model
Venting
Category
Certified Venting
Material
Vent Size
(inches)
Maximum Vent
Length (feet)
Combustion Air
Intake Pipe
Material
Air Inlet
Size
(inches)
Max. Air
Intake Length
(feet)
ADB-751
w/CHX
IV
UL 1738 Certified
Venting Material e.g.
AL29-4C Stainless
Steel PVC*, CPVC*
8
35
Subtract 10 ft per
elbow, Max. 3
elbows
Galvanized
Steel
PVC, ABS
CPVC
6
35
Subtract 10 ft
per elbow,
Max. 3 elbows
ADB-1001
w/CHX
IV
UL 1738 Certified
Venting Material e.g.
AL29-4C Stainless
Steel PVC*, CPVC*
10
35
Subtract 10 ft per
elbow, Max. 3
elbows
Galvanized
Steel
PVC, ABS
CPVC
6
35
Subtract 10 ft
per elbow,
Max. 3 elbows
ADB-1501
w/CHX
IV
UL 1738 Certified
Venting Material e.g.
AL29-4C Stainless
Steel PVC*, CPVC*
12
35
Subtract 10 ft per
elbow, Max. 3
elbows
Galvanized
Steel
PVC, ABS
CPVC
8**
35
Subtract 10 ft
per elbow,
Max. 3 elbows
*Contact the manufacturer for details.
**If the boiler is direct vented, a 6 to 8 in. adapter must be installed at the blower inlet.
Table R: Vertical Direct Venting with Add-on
Secondary Condensing Heat Exchanger
Vertical Direct Venting System With
Add-on Condensing Heat Exchanger
(Category IV) Installation
These installations utilize the boiler mounted blower to
draw combustion air from outdoors and vent combustion products to the outdoors.
UL 1738 Certified Venting Material (e.g. AL29-4C)
MUST be used. The vent must be installed to prevent
flue gas leakage. Care must be taken during assembly
to ensure that all joints are sealed properly and are airtight.
For certain installations, i.e. pool, heat-pump, domestic hot water supply with pre-heat tank, PVC or CPVC
may be used. Contact manufacturer for details.
To prevent the condensation accumulation in the vent,
it is required to install the horizontal portion of vent with
a slight upward slope of not more than 1/4" per foot of
horizontal run and an approved condensate trap must
be installed per applicable codes.
The Stainless Steel non-restricted direct vent cap
must be furnished by the boiler manufacturer in
accordance with its listing.
Outdoor Installation with Add-On
Condensing Heat Exchanger
Outdoor models are self-venting when installed with
the factory-supplied non-restricted direct vent cap and
require no additional vent piping. This special vent cap
is provided with the boiler in accordance with CSA
requirements. It must be installed directly on the boiler
in a horizontal position. Notching of the vent cap
mounting flange may be necessary to clear outlet piping on some models.
Care must be taken when locating the outdoor unit
because the flue gases discharged from the vent cap
can condense as they leave the cap. Improper location
can result in damage to adjacent structures or building
finish. For maximum efficiency and safety, the following precautions must be observed:
a) Outdoor models must be installed outdoors and
must use the non-restricted direct vent cap supplied by the manufacturer.
b) Periodically check venting system. The boiler’s
venting areas must never be obstructed in any
way and minimum clearances must be observed to
prevent restriction of combustion and ventilation
air. Keep area clear and free of combustible and
flammable materials.
c) Do not locate adjacent to any window, door walk-
way, or gravity air intake. The vent should be
located four (4) feet horizontally from such areas.
d) Install above grade level and above normal snow
levels.
WARNING: For common vent installations, contact
the factory.
WARNING: No substitutions of flue pipe or vent
cap material are allowed. Such substitutions would
jeopardize the safety and health of inhabitants.
Page 40

40
e) A venting system shall terminate at least 3 feet
above any forced air inlet located within 10 feet.
f) Adjacent brick or masonry surfaces must be pro-
tected with a rust-resistant sheet metal plate.
g) Multiple Outdoor Vent installations require a four
(4) feet clearance between vent caps.
The Stainless Steel non-restricted vent cap must
be furnished by the boiler manufacturer in accordance with its listing.
The outdoor vent terminal must be installed in a horizontal position to prevent recirculation of flue products.
The vent cap must be mounted directly on the vent
pipe of the boiler.
NOTE: Condensate can freeze on the vent cap.
Frozen condensate on the vent cap can result in a
blocked flue condition.
CONDENSATE DRAIN
The Condensing Heat Exchanger (CHX) can generate
up to 1 (one) gallon per hour (gph) of condensate for
every 100,000 BTUH. The maximum condensation
rate for the ADB 751 is 7.5 gph, the ADB 1001 is 10
gph, and the ADB 1501 is 15 gph.
NOTE: In areas of high winds (alleyways, air
handlers, etc.), a downward 90° - elbow must be
mounted on the combustion air inlet to prevent any
air flow fluctuation.
WARNING: All condensation should be disposed of
according to local, county, state, and federal laws.
Refer to NFGC, section 7.9, for additional
information.
Fig. 29: Condensate Trap Alignment
Page 41

41
CONTROLS
Central Point Wiring (CPW)
Central Point Wiring is an advanced control integration
technique that provides complete boiler diagnostic
capability and greatly simplifies troubleshooting. At the
heart of CPW is the Operations Status Center, which
is comprised of two different circuit boards: the CPW
board and one or more U-2 Diagnostic Boards.
The CPW Board
The Central Point Wiring (CPW) board serves as the
central tie point for connecting all other control components in the boiler. The CPW board provides boiler
operating status and fault indication using eight LEDs
which function as described in Table S.
In addition to monitoring and displaying boiler status,
the CPW board controls the timing of various operating functions including: boiler pump turn-off delay,
blower fan pre-purge, and blower fan post-purge. The
location of each user adjustable timing is shown in
Figure 30.
WARNING: Installation, adjustment and service of
boiler controls including timing of various operating
functions must be performed by a qualified installer
or service agency. Failure to do so may result in
control damage, boiler malfunction, property
damage, personal injury, or death.
WARNING: Turn off the power to the boiler before
installation, adjustment or service of the Central
Point Wiring board or any boiler controls. Failure to
do so may result in board damage, boiler
malfunction, property damage, personal injury, or
death.
CAUTION: This appliance has provisions to be
connected to more than one (1) supply source. To
reduce the risk of electric shock, disconnect all such
connections before servicing.
CAUTION: Risk of electric shock. More than one
(1) disconnect switch may be required to deenergize the equipment before servicing.
Table S: CPW Board LED Indicators
Light noitacidnIroloC
Power CDV 42neerG is applied to the system
Pump Green Boiler Pump is energized.
Pilot Yellow Power applied to the Pilot Gas Valve. (PV signal on.)
Main Gas rewoPne
Call for Heat rehTneerG mostat is closed. Call for heat present.
Service Red (Flashing) One or more of the safeties are open. Refer to U-2 Board
Blower Green Blower is energized.
erG applied to Main Gas Valve. (MV signal on.)
.delbasid si draoB .draob eht no tnerruc daolrevOdeRrorrE metsyS
Page 42

42
Fig. 30: CPW Board
Pump Turn-off Delay
The CPW board has a built-in pump driver with pump
turn-off delay, which allows the operator to set how
long the pump will run after the boiler shuts off. The
delay is factory-set for 7 minutes but can be fieldadjusted from 3 minutes to 10 minutes. The pump
relay can directly power a pump of up to 12.0 amps
draw or 3/4 hp capacity. Pumps with larger amp draws
should be energized through a pump contactor that is
controlled by the CPW board.
By properly setting the pump turn-off delay, the boiler
pump will continue running for a limited period of time
in order to extract any residual heat from the combustion chamber. The pump will then shut off to conserve
energy until the next call for heat.
The pump-off time delay should be set to the minimum
time required to extract all residual heat from the heat
exchanger. If temperature as monitored at the boiler
outlet increases more than 5°F after the pump turns off
following a firing cycle, the pump-off time delay should
be extended by thirty seconds. Increase or decrease
time delay as appropriate until outlet temperature does
not spike more than 5°F after pump shut-off following
a prolonged firing cycle (> 5min.)
Blower Fan Pre-purge
The CPW board has a built-in pre-purge delay which
operates the blower fan for a user-adjustable time
period prior to pilot trial for ignition. The pre-purge period ensures that the combustion chamber is clear of all
excess combustible gases prior to commencing the
pilot ignition cycle. The pre-purge delay is factory set
for 45 seconds and it can be adjusted in the field from
45 seconds to 120 seconds. To optimize boiler
response time on call-for-heat, set the pre-purge delay
to the minimum allowed by local, state or national
code.
Blower Fan Post-purge
The CPW board has a built-in post-purge delay to
exhaust residual combustion products after the main
gas valve closes. The post-purge timing is factory set
at 3 minutes and is not field-adjustable.
Freeze Protection Feature
The CPW board is programmed to turn-off the blower
in case there is a lock-out condition. If there is a call for
heat signal, and the pilot valve signal is removed and
not reactivated within a pre-set time for any reason,
the CPW board will turn off the blower to prevent blowing cold air continuously and freezing the heat
exchanger. The blower drives will open and the system
will lock in the off state.
To restart the system, primary power or the thermostat
signal must be turned off and back on. The pre-set
freeze protection feature time is approximately 5 minutes.
CAUTION: The boiler requires forced water
circulation when the burner is operating and the
pump must be interlocked with the boiler. See the
Water Piping section for minimum and maximum
water flow rates and pump selection.
NOTE: Pump will come on when power is first
applied to the boiler.
Page 43

43
U-2 Diagnostics Board
The U-2 Diagnostics board is a solid-state electronic
fault indicator that has been engineered to enhance
safety, simplify troubleshooting and minimize equipment down time. The U-2 safety board is the central
point for wiring, operations monitoring, and fault indication for the boiler safeties. By having each safety
report directly to the U-2 board, each safety function
can be individually monitored.
The U-2 adds complete diagnostics features that aid in
the rapid diagnosis of irregularities in boiler operation.
A single U-2 Diagnostics Board can monitor a maximum of eight safeties at one time. If, due to code
requirements, more than eight safety devices must be
monitored, two or more boards will be used to provided extended diagnostics capabilities. Advanced
Design Boilers equipped with the standard safety suite
will utilize the configuration shown in Table T.
The U-2 safety board has a series of red LED lights to
indicate a fault occurring at a monitored safety. An
additional light indicates that the diagnostics board is
energized and is currently monitoring for safety faults.
(In order to prevent spurious alarm conditions, the U-2
board monitors safeties only during the actual firing
cycle.)
Once a fault has been detected, the U-2 board will illuminate the corresponding LED lamp, will shut-down
the boiler, and will light the flashing red LED “Service”
lamp on the CPW board. If more than one fault is
detected, the U-2 board will display the priority fault
based on the safety hierarchy as labeled on the U-2
board. Once the first fault is cleared, the second fault
lamp will illuminate until cleared.
WARNING: Only qualified persons shall attempt to
repair the boiler. Improper adjustment, service or
maintenance may damage the equipment, create a
hazard resulting in asphyxiation, explosion, fire,
electric shock, personal injury or property damage,
and will void the warranty.
Table T: U-2 Diagnostic Board LEDs
Light noitacidnIroloC
System Enabled Yellow U-2 Diagnostics safety board is functional.
Manual High Limit Red Water temperature is over the manual high limit setting.
Auto High Limit Red Water temperature is over the auto high limit setting.
Low Water Cut-off (option) Red Insufficient water volume for boiler operation.
High/Low Gas Pressure Red Gas supply pressure is below or above the allowed minimum gas supply
pressure to ensure safe operation.
Burner High Limit Red Mixer or PVC vent pipe, if installed, is over heated.
.wol oot si etar wolf retaWdeRhctiwS wolF
Blower/Ignition Lockout Red Blower failure, not enough combustion air or the equipment has an ignition
lock-out condition.
Blocked Vent Red The vent pressure switch has detected a blocked vent.
Page 44

44
WIRING
DIAGRAM
Figure L-2
WIRING DIAGRAM
Page 45

45
Ignition Control Module
The intermittent ignition device conserves energy by
automatically extinguishing the pilot when the desired
temperature is reached. When additional heat is needed, the combustion air blower starts to purge all air
from the combustion chamber for about 45 seconds.
On proof of air flow, the air proving switch closes and
the pilot reignites electrically, eliminating the fuel costs
of maintaining a constant pilot.
To ensure safe operation, the gas valve cannot open
until the pilot relights and is verified. The 100% pilot
safety is an electronic device which closes the main
gas valve within 8/10 of a second whenever the pilot
flame is interrupted. Pilot flame is automatically lit
when the device is powered and pre-purged. Unit performs its own safety check and opens the main valve
only after the pilot is proven to be lit.
High Limit — Manual Reset
This appliance is equipped with a manual reset, high
limit, safety device. Push the reset button and adjust
the setting to 40°F above the desired operating temperature.
Flow Switch
Dual-purpose control shuts off boiler in case of pump
failure or low water condition. Mounted and wired in
series with the main gas valve. Check with the manufacturer for proper paddle size. Utilize correct paddle
size for proper operation.
High Limit — Auto Reset
This appliance is equipped with an automatic, high
limit, safety device. Set the auto high limit to 30°F
above the desired operating temperature.
Fig. 31: Ignition Module
Fig. 32: High Limit — Manual Reset
NOTE: Flow switch will not operate if flow is less
than 20 gpm.
Fig. 33: Flow Switch
Fig. 34: Auto Reset — High Limit
Page 46

46
Low Water Cut Off (Optional)
The low water cut off automatically shuts down the
burner whenever water level drops below the level of
the sensing probe. A 3 second time delay prevents
premature lockout due to temporary conditions such
as power fluctuations or air pockets.
High and Low Gas Pressure
Switches — Manual Reset
The low gas pressure switch mounts upstream of the
gas pressure regulator to ensure that sufficient gas
pressure is present for proper regulator performance.
The low gas pressure switch automatically shuts down
the boiler if gas supply drops below the factory setting
of 6 in. WC for Natural gas, and 10 in. WC for Propane
gas.
The high gas pressure switch (optional) mounts downstream of the gas pressure regulator. If the gas
pressure regulator fails, the high gas pressure switch
automatically shuts down the burner.
Fig. 35: Low Water Cut Off
Fig. 36: Gas Pressure Switch
PRE-START-UP
Fill the System:
1. Close manual and automatic air vents and drain
cock.
2. Fill to correct system pressure. Correct pressure
will vary with each application.
3. Open automatic air vent two turns.
4. Slowly feed water to boiler.
5. Starting on the lowest floor, open air vents one at
a time until water squirts out. Close vent.
6. Repeat with remaining vents.
7. Close manual water feed valve when correct boiler pressure is reached.
Inspect Venting System:
1. Check all vent pipe connections and flue pipe
material.
2. Ensure vent terminations are installed per code
and are clear of all debris or blockage.
For Your Safety — Read Before
Lighting
1. This appliance has an intermittent pilot. It is
equipped with an ignition device which automatically lights the pilot. DO NOT try to light the pilot or
burner by hand.
2. BEFORE OPERATING, smell all around the appliance area for gas. Be sure to smell next to the
floor because some gas is heavier than air and will
settle on the floor.
3. WHAT TO DO IF YOU SMELL GAS:
• Do not try to light any appliance.
• Do not touch any electrical switch; do not use
any telephone in your building.
• Immediately call your gas supplier from a
neighbor's telephone. Follow the gas supplier's instructions.
• If you cannot reach your gas supplier, call the
fire department.
4. Use only your hand to push in or turn the gas control knob. Never use tools. If the knob will not turn
by hand, do not try to repair it, call a qualified service technician. Forced or attempted repair may
WARNING: If you do not follow these instructions
exactly, a fire or explosion may result causing
property damage, personal injury or loss of life.
Page 47

47
result in a fire or explosion.
5. Do not use this appliance if any part has been
under water, immediately call a qualified service
technician to inspect the appliance and to replace
any part of the control system and any gas control
which has been under water.
Pre-Start-up Check
1. Verify boiler is filled with water.
2. Check system piping for leaks. If found, repair
immediately.
3. Vent air from system. Repeat steps 4 and 5 under
“Fill the System.” Air in system can interfere with
water circulation and cause improper heat distribution.
Fig. 37: Component and Pressure Tap locations
Fig. 38: Blower “T” Fitting Detail
Page 48

48
ADB INITIAL START-UP
Tools Needed
• One 8-0-8 , 16” scale manometer (or larger)
• Four 4-0-4, 8” scale manometers (or larger)
• “T” fitting
• 7/16” and 1/2" open end wrenches
• Small and large flat-head screwdrivers
• Volt meter
• Amp probe
• Elec. Dual reading thermometer with strap on sensors
• 3/16” Allen wrench
• Combustion analyzer
Preparation for Start-up
Check Power Supply
With voltmeter at incoming power check voltage
between:
Hot - Common (»120 VAC)
Hot – Ground (»120 VAC)
Common - Ground (< 1 VAC)
If Common - Ground is > 1 VAC - STOP: Contact electrician to correct ground failure.
Attach Manometers to Measure
Pressures (See Fig. 37)
• Attach 16" scale manometer to the first gas shutoff valve pressure tapping, Location (1)
• Attach one 8" scale manometer to each manual
gas valve pressure tapping, Locations (2) and (3).
• Attach one 8" scale manometer to the outlet side
of pilot gas valve pressure tapping, Location (4).
• Attach one 8" manometer to “T” fitting, air pressure
switch, and aluminum tubing, Location (5).
Turn Off The 1 1/2” Manual Gas Valve;
Turn Off Pilot Gas Valve;
Reset Low Gas Pressure Cut-off Switch;
Bleed Air from Gas Line
• With power off, slightly open union outside the
cabinet to bleed air.
• Close union when you smell gas.
• Wait minimum 5 minutes to clear the gas out of the
boiler room before continuing.
Check the Gas Supply Pressure,
Location (1)
• Leave pilot gas valve and first manual gas valve
closed;
• Slowly turn on main gas shut-off valve (outside the
unit);
• Read the gas supply pressure from the manometer (Location 1);
• If pressure is > 14" W.C., Turn off the valve;
• Check if the service regulator is installed and/or
adjust the service regulator.
START-UP
Blower Adjustment
1. Main gas shut-off valve is still closed;
2. Turn power on;
3. Check blower manometer reading, Location (5).
Compare your reading to the “Pre-Fire” values
shown in tables T and U. If not, adjust the air shutter on the blower to attain the correct value;
4. Turn power off.
Pilot Adjustment
1. Turn on the gas shut-off valve, the main gas manual valve, and the pilot manual valve;
2. Turn off the manual gas valves at Locations (2)
and (3);
3. Turn power on, after 40-45 seconds, ignition control will energize and send spark to ignition,
observe through view port for spark;
4. If you do not see spark, turn off power, check igni-
CAUTION: Verify that the vent system and
combustion air supply have been approved.
WARNING: DO NOT TURN ON GAS AT THIS
TIME.
WARNING: Failure to do this may burn out 120V24V transformer, or may cause other safety control
damage or failure.
CAUTION: Make sure there is no ignition source in
the boiler room.
NOTE: Reference the start-up pressures settings
located on the side of the control box.
Page 49

49
tion wire and proper grounding and wiring. Turn
power back on. Repeat Step 3. If there is still no
spark after several attempts the igniter may be
misaligned;
5. Check to see if igniter is grounded out by pulling
the spark wire and doing a continuity check
between the igniter and burner. If the igniter is
grounded out, it must be realigned. Remove the
burner. Loosen the igniter nut, locate the igniter in
the center of the burner head and tighten igniter
nut. Confirm it is centered and reinstall burner
head;
6. If you have spark, turn off unit;
7. Turn on power. Unit will pre-purge 40-45 seconds
and move onto ignition trial. You will hear a click
from pilot gas valve (you will not hear the sparking);
8. The pilot may not light at first trial; leave the unit
running until you have pilot. If you still do not see
pilot over 90 seconds; turn off the unit; repeat
steps 6-8;
9. Check pilot manifold pressure, Location (4).
Compare the reading to the value listed in the
tables;
10. Check pilot flame; 8 distinct circular blue flames
around the center of the pilot;
11. Replace the cap for pilot manifold adjustment
screw; do not over-tighten.
Note: For different gas control options, call the factory for proper pressure settings.
Note: For different gas control options, call the factory for proper pressure settings.
Table U: Pressure Settings and Emission Guidelines (True Readings) for NAT. GAS
Table V: Pressure Settings and Emission Guidelines (True Readings) for LP GAS
Page 50

50
Main Burner Adjustment
1. Turn on the unit; about 45 seconds later, the pilot
should light. If the pilot fails to light, repeat pilot
adjustment.
2. Turn the top manual valve on, Location (2). The
inner burner will fire.
3. Make sure that the supply gas manometer reads
between 7 – 14 in. WC (dynamic pressure).
4. Check manifold pressure, Location (2); this should
read to within ± 0.1 in. WC of the values shown in
tables U and V.
5. If adjustment is required, remove screw cap off the
top gas pressure regulator, and adjust regulator.
6. Slowly turn the bottom manual valve on, Location
(3). The outer burner will fire.
7. Make sure that the supply gas manometer reads
between 7 – 14 in. WC (dynamic pressure).
8. Check manifold pressure, Location (3); this should
read to within ± 0.1 in. WC of the values shown in
tables U and V.
9. If adjustment is required, remove screw cap off the
bottom gas pressure regulator, and adjust regulator.
10. The blower pressure should increase about 3/10
in. (0.3 in.) WC equaling the “Firing” value in tables
U and V.
11. Lock the blower shutter by tightening the shutter
nut while holding the black knob fixed.
12. Allow minimum 5 minutes of run time; then attach
flue analyzer, check emission and compare the
CO2 reading to that of table U and V.
13. If CO2 is high, reduce bottom manifold gas pressure.
14. If CO2 is low, increase the bottom manifold gas
pressure.
15. All pressure readings especially manifold pressures should be within ±0.1 in. of listed values.
16. Replace the screw caps back on the gas regulators.
Your ADB is tuned in!
Safety Inspection
· Check thermostat and high limit settings.
· Attach thermometers to IN/OUT piping and take
temperature measurement, see Table E and G for
correct flow balance.
· During the following safety checks leave manometers, and analyzer hooked up, check and record.
· If other gas fired equipment in the room and on
same gas main, check gas pressures on ADB with
them running.
Remember, supply gas should always be
between 7 in. and 14 in. WC.
· Check thermostat control for ON/OFF operation;
· Check safety Hi Limits for ON/OFF operation;
· While in operation inspect flow switch;
· Check the low gas pressure switch, it is factory set
at 6 in. WC for natural gas;
· High gas pressure switch (optional) at 1 in. WC
above manifold pressure;
· Insert ignition control lockout test as safety check
Follow-up
• Safety checks must be recorded as performed;
• Turn unit on;
• After main burner ignition. Check Manometers for
proper readings;
• Verify that the blower shutter is locked;
• Cycle unit several times and recheck readings;
• Re-analyze with unit running record or print
results;
• Turn unit off, remove all Manometers and replace
blower switch hose, replace all gas pressure caps
and plugs;
• Check for gas leak one more time;
• Check around unit for debris and remove combustible and flammable products, i.e. paper,
gasoline etc.
POST START-UP CHECK
Check off steps as completed:
1. Boiler and heat distribution units or storage tank
filled with water?
2. Automatic air vent, if used, open two full turns during venting procedure?
3. Air purged from system?
4. Air purged from gas piping? Piping checked for
leaks?
5. Followed start-up procedure for proper start-up?
6. Is burner flame visible?
7. Test safety controls: If boiler is equipped with a low
water cutoff or additional safety controls, test for
operation as outlined by manufacturer. Burner
should be operating and should go off when controls are tested. When safety devices are restored,
NOTE: Emissions will vary with different
applications (hydronic, water heater, or pool),
venting (including direct vent), ambient conditions (T,
P, and humidity), and the condition of the boiler.
NOTE: For high altitude (above 5000 ft), call the
factory for proper pressure settings.
Page 51

51
burners should reignite after pre-purge time delay.
8. Test limit control: While burner is operating, move
indicator on high limit control below actual boiler
water temperature. Burner should go off while
blower circulator continues to operate. Raise setting on limit control above boiler water
temperature and burner should reignite after prepurge time delay.
9. Test ignition system safety device:
• Turn power off.
• Close the pilot manual valve.
• Turn power on; after about 45 seconds of pre-
purge, the pilot comes on. The pilot (and
therefore the burner) should fail to light. The
standard lockout time is 90 seconds; then the
pilot light goes off and the boiler goes into
post-purge. (If the lockout module is attached
to boiler, a lockout light comes on.)
• Turn the power off; open the pilot manual
valve; (reset the lockout module if applicable).
• Wait 30 seconds, then turn power on. The
burner should ignite after pre-purge time
delay.
10. To restart system, follow the lighting instructions.
11. High limit control set to design temperature
requirements of system? For multiple zones: flow
adjusted as required in each zone?
12. Boiler cycled with thermostat? Raise to highest
setting and verify boiler goes through normal startup cycle. Reduce to lowest setting and verify boiler
goes off.
13. Observed several operating cycles for proper
operation?
14. Set room thermostat or tankstat to desired temperature?
15. Reviewed all instructions shipped with this boiler
with owner or maintenance personnel, returned to
envelope and given to owner or placed in pocket
inside front panel on boiler?
OPERATION
Operating Instructions
Lighting Instructions:
1. STOP! Read the safety information first.
2. Set the thermostat to the lowest setting.
3. Turn off all electric power to the appliance.
4. This appliance is equipped with an ignition device
which automatically lights the burner. DO NOT try
to light the burner by hand.
5. Remove upper front panel.
6. Turn on main manual gas valve and pilot manual
gas valve.
7. Wait five (5) minutes to clear out any gas. Then
smell for gas, especially near the floor. If you then
smell gas. STOP! Follow the steps in the safety
information. If you do not smell gas, go to next
step.
8. Turn on all electric power to the appliance.
9. Set thermostat to desired setting. The appliance
will operate. The pilot burner will light after the prepurge time delay (45 seconds). Then the pilot will
light the main burner.
10. If the appliance will not operate, follow the instruction "To Turn Off Gas to Appliance", and contact a
qualified service technician.
11. Replace upper front panel.
To Turn Off Gas to Appliance
1. Set the thermostat to lowest setting.
2. Turn off all electric power to the appliance if service is to be performed.
3. Remove upper front panel.
4. Turn off main manual gas valve and manual pilot
gas valve.
5. Replace access panel.
If boiler fails to start, check for:
• Loose connections, blown fuse or service
switch off?
• High temperature limit switch set below boiler
water temperature?
• Thermostat set below room temperature?
• Gas not turned on at meter or boiler?
• Incoming dynamic gas pressure less than 6 in.
WC for Natural gas, 10 in. WC for Propane?
MAINTENANCE
Suggested Minimum
Maintenance Schedule:
Regular service by a qualified service agency and
maintenance must be performed to ensure maximum
boiler operating efficiency.
Maintenance as outlined below may be performed by
the owner.
Yearly (Beginning of each heating
season):
1. Annual service call by qualified service agency.
2. Visually check top of vent for soot. Call service
person to clean. Some sediment at bottom of vent
is normal.
Page 52

52
3. Visually inspect venting system for proper function, deterioration or leakage.
4. Check that boiler area is free from combustible
materials, gasoline, and other flammable vapors
and liquids.
5. Check for and remove any obstruction to the flow
of combustion or ventilation air to boiler.
6. Follow pre-start-up check in Section N.
7. Visually inspect burner flame. Should see light
blue flame, with some orange at flame edge.
8. Check operation of safety devices. Refer to manufacturer’s instructions.
9. Follow oil-lubricating instructions on circulator.
Over-oiling will damage circulator. Water-lubricated circulators do not need oiling.
10. Visually inspect condensate drain piping for proper operation or deterioration (if appropriate).
Check for plugged condensate trap. Use clean-out
plug to clear trap.
11. To avoid potential of severe burn, DO NOT REST
HANDS ON OR GRASP PIPES. Use a light touch
- return piping will heat up quickly.
12. If mixing valve does not seem to be working, the
spring and thermostat may need to be replaced.
Call a qualified service technician.
13. Check for piping leaks around circulators, mixing
valves, relief valves and other fittings. Repair, if
found. DO NOT use petroleum based stop leak.
Daily:
1. Check that boiler area is free from combustible
materials, gasoline, and other flammable vapors
and liquids.
2. Check for and remove any obstruction to the flow
of combustion or ventilation air to boiler.
Monthly:
1. Check for piping leaks around circulators, mixing
valves, relief valves, and other fittings. If found,
repair at once. DO NOT use petroleum-based stop
leak compounds.
2. Visually inspect burner flame.
3. Visually inspect venting system for proper function, deterioration or leakage.
4. Check air vents for leakage.
5. Check the hose fitting/orifice on the blower. Make
certain that orifice is not blocked by grease, dirt or
any other debris. If necessary, use a thin wire to
clean up the orifice.
Periodically:
1. Check relief valve. Refer to manufacturer’s
instructions on valve.
2. Test low water cutoff, if used. Refer to manufacturer’s instructions.
3. Visually inspect condensate drain hose for proper
operation or deterioration (if appropriate). Check
for plugged condensate trap. Use cleanout plug to
clear trap.
4. Clean screen in vent termination and air intake.
Cleaning Boiler Heating
Surfaces:
The following service procedures must be performed
ONLY by a qualified service agency. Boiler owner
should not attempt these procedures:
1. If you find soot in top of vent elbow (some sediment in bottom of vent is normal) - remove vent
attachment to the ADB and clean flue exhaust baffle inside the boiler. Also check burner, replace if
damaged.
2. If you find rust deposits in vent elbow - check for
high water flow rate or low inlet water temperatures. Clean boiler as above.
CONNECTING THE
CONDENSING HEAT
EXCHANGER (CHX)
Refer to Fig. 39 for the following steps:
1. Remove the shroud.
2. Remove the top cover.
3. Secure the 15° elbows (supplied) as shown one
on each side of the CHX, using the stainless steel
screws (supplied).
4. Seal the connection with high temperature RTV
(supplied).
5. Replace the top cover.
6. Level the CHX with the ADB by adjusting the leveling screws at the base.
7. Place a line of RTV on the crimped end of the flue
outlet from the ADB and slide the CHX to join the
ADB flue outlet to the CHX flue inlet.
8. Connect the CHX water as specified in the piping
diagram. Check for water leak.
9. Secure the flue connection from step 7 above with
the stainless steel screws (supplied).
NOTE: Connect the vent before connecting the
water piping. Install unions on water inlet and outlet
of CHX for ease of maintenance. The CHX requires
cleaning as often as once a year.
Page 53

53
10. Connect the flue vent (Category IV venting, UL
1738 Certified Venting Material) to the 15° elbow
of the CHX flue outlet.
11. Connect the PVC pipe (not supplied) for condensate water disposal (check with local authority
regarding condensate disposal).
12. Replace the shroud.
13. Allow the silicone (RTV) to cure over-night.
Vent Switch Adjustment:
In order to ensure proper operation of the ADB boiler
with a CHX attached to it, the vent switch must be
adjusted to proper setting. The vent switch is located
on the J-box, just outside the ignition module. Use the
following steps:
• Turn power off; disconnect the electrical wiring
and the rubber hose.
• Remove the switch (it has a black plastic orifice at
the hose connection).
• On the backside, remove the (purple) seal from
atop the adjusting screw.
• Turn the plastic hex screw 1-1/2 turn clockwise.
• Seal with silicone.
• Reinstall in reverse order.
Table W: CHX Rate of Flow and Pressure Drop
Fig. 39: Connecting Add-on Condensing Heat Exchanger to ADB
Page 54

54
APPENDIX
Inside Combustion Air
Contamination:
All boilers experience some condensation during startup. The condensate from flue gas is slightly acidic. In
most cases the pH level is not harmful to vents or
drains. When combustion air is contaminated by
vapors from products in areas listed below, the acidic
levels in the condensate increase. Higher acidic levels
attack many materials, including stainless steel commonly used in high efficiency systems.
The ADB can use special corrosion-resistant nonmetallic vent material. You may, however, choose to
use outside combustion air for one or more of these
reasons:
• installation is in an area containing contaminants
listed below which will induce acidic condensation.
• you want to reduce infiltration into your building
through openings around windows and doors.
• you are using AL29-4C stainless steel vent pipe,
which is more corrosion-resistant than standard
metallic vent pipe. In extremely contaminated
area, this may also experience deterioration.
Products causing contaminated combustion air:
• spray cans containing chloro/fluorocarbons
• permanent wave solutions
• chlorinated waxes/cleaners
• chlorine-based swimming pool chemicals
• calcium chloride used for thawing
• sodium chloride used for water softening
• refrigerant leaks
• paint or varnish removers
• hydrochloric acid/muriatic acid
• cements and glues
• anti-static fabric softeners used in clothes dryers
• chloride-type bleaches, detergents, and cleaning
solvents found in household laundry rooms
• adhesives used to fasten building products
• ... and other similar products
Areas causing contaminated combustion air:
• dry cleaning/laundry areas and establishments
• metal fabrication plants
• beauty shops
• refrigeration repair shops
• photo processing plants
• auto body shops
• plastic manufacturing plants
• furniture refinishing areas and establishments
• new building construction
• remodeling areas
Check for areas and products as listed above before
installing boiler. If found:
• remove products permanently, OR
• provide outdoor combustion air
Page 55

55
START-UP CHECKLIST FOR FAN-ASSISTED
RAYPAK PRODUCTS ADB, HI-DELTA & MV B
This start-up checklist is to be completely filled out by the service technician starting up the Raypak Boiler or Heater
for the first time. All information may be used for warranty purposes and to ensure that the installation is correct.
Additionally this form will be used to record all equipment operation functions and required settings.
GAS SUPPLY DATA CLEARANCES
Regulator Model & Size _________ / ______CFH Front Clearance _______________In.
Gas Line Size (in room) ________________In. NPT Right Side Clearance _______________In.
Length of Gas Line ________________Eq Ft Left Side Clearance _______________In.
Low Gas Pressure Setting ________________In. WC Rear Clearance _______________In.
High Gas Pressure Setting ________________In. WC Overhead Clearance _______________In.
Gas Shut-Off Valve Type ________________
( Ball, Lube cock)
Sediment Trap ________________Y/N Voltage Supply (VAC) No Load______ Load_____
Port _______Std______Full Voltage -24 VAC _______________VAC
Voltage Com to Ground _______________VAC
VISUAL INSPECTION OF COMPONENTS
Verify inspection was done and condition of components are in
good working order with a “yes”
Wiring Harness _________________ Y/N Operating Control Setting _______________deg F
Burner/s (flame) _________________ Y/N
Refractory (visual) _________________ Y/N Sketch plumbing on reverse side
Remote flame sense _________________ Y/N
Covers in place for outdoor _________________ Y/N Flow Rate in GPM or Delta T _______________If Avail
VENTING
Vent Size: _____________ Stack Height:_______ Low Water Cutoff _______________Test
Category: _________ sketch vent on reverse side ***
Vent Material: __________________ Plumbing Size _______________
Vent Termination Type: __________________ Pump Size: _________
Combustion Air Openings: Low __________ in2 Impeller trim____________ Pump Model___________
Ventilation air High __________ in2 Louvers __________________ Screens________________
Pump Economaster setting _______________Minutes
EMISSIONS SETTINGS AND TEST INFORMATION
(AT FULL FIRE)
Blower Pressure Setting _________________In. WC See manual or card tag
Supply Gas Pressure
Verify stable pressure static &
Pilot Gas Pressure _________________In. WC See manual or card tag
Manifold Gas Pressure _________________In. WC See manual or card tag
The following measurements must be obtained with a Combustion Analyzer.
NOX _________________PPM Less than 20 PPM (If required by Certifying Agency)
Free Oxygen _________________% See manual
CO _________________PPM Less than 150 PPM
CO2 _________________% See manual
Model Number: ______________________________ Serial Number: _______________________________
*** Note: draw venting with details, such as extractors,
barometric dampers, blast dampers or draft inducers
_________________In. WC
dynamic condition
ELECTRICAL
Hot Surface Igniter
Auto High Limit Setting
Manual Reset High Limit Setting
_______________Ohms
_______________deg F
_______________deg F
WATER SUPPLY
Measure flow rate at full fire
Number of Tanks and Size Qty____ _______Gallons
(boiler) Pump HP: ______
Nominal Factory Recommended Settings
See manual or card tag
Site Altitude Above Sea Level __________________Ft.
Job Name _______________________________________________________________________________________
Address _________________________________________________________________________________________
Physical Location of Boiler: Indoors______; Outdoors______; Ground Level______; Roof______; Below Grade______
Mechanical Contractor / Installer _______________________________________________________________________
Date and Time of Start-up _____________Print Name and Signature of Start-up Technician_________________________
Information must be faxed to: (805) 278-5471 in order to ensure warranty consideration Attn: Service Manager
Page 56

56
LIMITED PARTS WARRANTY
ADVANCED DESIGN BOILER™
SCOPE:
Raypak, Inc. ("Raypak") warrants to the original owner that all parts of this boiler which are actually manufactured by Raypak
will be free from failure under normal use and service for the specified warranty periods and subject to the conditions set forth
in this Warranty. Labor charges and other costs for parts removal or reinstallation, shipping and transportation are not covered by this Warranty but are the owner's responsibility.
HEA
T EXCHANGER W
ARRANTY
:
° Ten (10) Years from date of boiler installation. This includes only cupro-nickel with bronze or cast iron waterways.
° T
wenty (20) Years from date of boiler installation against "Thermal Shock" (excluded, however, if caused by boiler operation at large changes exceeding 150°F between the water temperature at intake and boiler temperature, or operating at boiler
temperatures exceeding 230°F).
BL
UFF HEAD BODY BURNER WARRANTY
:
° T
en (10) Y
ears from date of boiler installation.
ANY O
THER PART MANUFA
CTURED BY RAYPAK:
One (1) Year warranty from date of boiler installation, or eighteen (18) months from date of factory shipment based on
Raypak's records, whichever comes first.
SATISFACTORY PROOF OF INSTALLATION DATE, SUCH AS INSTALLER INVOICE, IS REQUIRED. THIS WARRANTY
WILL BE VOID IF THE BOILER RATING PLATE IS ALTERED OR REMOVED.
ADDITION
AL
WARRANTY EXCLUSIONS:
This warranty does not cover failures or malfunctions resulting from:
1. Failure to properly install, operate or maintain the boiler in accordance with our printed instructions provided;
2. Abuse, alteration, accident, fire, flood and the like;
3. Sediment or lime buildup, freezing, or other conditions causing inadequate water circulation;
4. High velocity flow exceeding boiler design rates;
5. Failure of connected systems devices, such as pump or controller;
6. Use of non-factory authorized accessories or other components in conjunction with the boiler system;
7. Failing to eliminate air from, or replenish water in, the connected water system;
8. Chemical, particulate matter or other airborne contamination of combustion air or use of chemical additives to water.
P
AR
TS REPLACEMENT:
Under this Warranty, Raypak will furnish a replacement for any failed part. The failed part must first be returned to Raypak if
requested, with transportation charges prepaid, and all applicable warranty conditions found satisfied. The replacement part
will be warranted for only the unexpired portion of the original warranty. Raypak makes no warranty whatsoever on parts not
manufactured by it, but Raypak will apply any such warranty as may be provided to it by the parts manufacturer.
T
O MAKE
WARRANTY CLAIM:
Promptly notify the original installer, supplying the model and serial numbers of the unit, date of installation and description
of the problem. The installer must then notify his Raypak distributor for instructions regarding the claim. If either is not available, contact Service Manager, Raypak, Inc., 2151 Eastman Avenue, Oxnard, CA 93030 or call (805) 278-5300. In all cases
proper authorization must first be received from Raypak before replacement of any part.
EX
CLUSIVE WARRANTY - LIMITATION OF LIABILITY:
This is the only warranty given by Raypak. No one is authorized to make any other warranties on Raypak's behalf. THIS
WARRANTY IN LIEU OF ALL OTHER WARRANTIES, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO
IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. RAYPAK'S SOLE LIABILITY AND THE SOLE REMEDY AGAINST RAYPAK WITH RESPECT TO DEFECTIVE PARTS SHALL BE AS PROVIDED
IN THIS WARRANTY. IT IS AGREED THAT RAYPAK SHALL HAVE NO LIABILITY, WHETHER UNDER THIS WARRANTY,
OR IN CONTRACT, TORT, NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE, FOR ANY SPECIAL, CONSEQUENTIAL, OR INCIDENTAL
DAMAGE, INCLUDING DAMAGE FROM WATER LEAKAGE. Some states do not allow limitations on how long an implied
warranty lasts, or for the exclusion of incidental or consequential damages. So the above limitation or exclusion may not
apply to you.
This Limited Warranty gives you specific legal rights. You may also have other rights which may vary from state to state. We
suggest that you complete the information below and retain this certificate in the event warranty service is needed.
Reasonable proof of the effective date of the warranty (date of installation) must be presented, otherwise, the effective date
will be based on the date of manufacture plus thirty (30) days.
Page 57

www.raypak.com
Raypak, Inc., 2151 Eastman Avenue, Oxnard, CA 93030 (805) 278-5300 FAX: (800) 872-9725
Raypak Canada LTD, 2805 Slough Street, Mississauga, Ontario, Canada L4T 1G2 (905) 677-7999 FAX: (905) 677-8036
Litho in U. S. A.
 Loading...
Loading...