Page 1
Features
• Dual ADC with 8-bit Resolution
• 1 Gsps Sampling Rate per Channel, 2 Gsps in Interlaced Mode
• Single or 1:2 Demultiplexed Output
• LVDS Output Format (100Ω)
• 500 mVpp Analog Input (Differential Only)
• Differential or Single-ended 50Ω PECL/LVDS Compatible Clock Inputs
• Power Supply: 3.3V (Analog), 3.3V (Digital), 2.25V (Output)
• LQFP144 Package
• Temperature Range:
– 0°C < TA < 70°C (Commercial Grade)
– -40°C < TA < 85°C (Industrial Grade)
• 3-wire Serial Interface
– 16-bit Data, 3-bit Address
– 1:2 or 1:1 Output Demultiplexer Ratio Selection
– Full or Partial Standby Mode
– Analog Gain (±1.5 dB) Digital Control
– Input Clock Selection
– Analog Input Switch Selection
– Binary or Gray Logical Outputs
– Synchronous Data Ready Reset
– Data Ready Delay Adjustable on Both Channels
– Interlacing Functions:
Offset and Gain (Channel to Channel) Calibration
Digital Fine SDA (Fine Sampling Delay Adjust) on One Channel
– Internal Static or Dynamic Built-In Test (BIT)
Dual 8-bit
1 Gsps ADC
AT84AD001B
Smart ADC
™
Performance
• Low Power Consumption: 0.7W Per Channel
• Power Consumption in Standby Mode: 120 mW
• 1.5 GHz Full Power Input Bandwidth (-3 dB)
• SNR = 42 dB Typ (6.8 ENOB), THD = -51 dBc, SFDR = -54 dBc at Fs = 1 Gsps
Fin = 500 MHz
• 2-tone IMD3: -54 dBc (499 MHz, 501 MHz) at 1 Gsps
• DNL = 0.25 LSB, INL = 0.5 LSB
• Channel to Channel Input Offset Error: 0.5 LSB Max (After Calibration)
• Gain Matching (Channel to Channel): 0.5 LSB Max (After Calibration)
• Low Bit Error Rate (10
-13
) at 1 Gsps
Application
• Instrumentation
• Satellite Receivers
• Direct RF Down Conversion
• WLAN
2153C–BDC–04/04
1
Page 2

Description The AT84AD001B is a monolithic dual 8-bit analog-to-digital converter, offering low
1.4W power consumption and excellent digitizing accuracy. It integrates dual on-chip
track/holds that provide an enhanced dynamic performance with a sampling rate of up to
1 Gsps and an input frequency bandwidth of over 1.5 GHz. The dual concept, the integrated demultiplexer and the easy interleaving mode make this device user-friendly for
all dual channel applications, such as direct RF conversion or data acquisition. The
smart function of the 3-wire serial interface eliminates the need for external components, which are usually necessary for gain and offset tuning and setting of other
parameters, leading to space and power reduction as well as system flexibility.
Functional Description
The AT84AD001B is a dual 8-bit 1 Gsps ADC based on advanced high-speed
BiCMOS technology.
Each ADC includes a front-end analog multiplexer followed by a Sample and Hold (S/H),
and an 8-bit flash-like architecture core analog-to-digital converter. The output data is
followed by a switchable 1:1 or 1:2 demultiplexer and LVDS output buffers (100Ω).
Two over-range bits are provided for adjustment of the external gain control on each
channel.
A 3-wire serial interface (3-bit address and 16-bit data) is included to provide several
adjustments:
• Analog input range adjustment (±1.5 dB) with 8-bit data control using a 3-wire bus
interface (steps of 0.18 dB)
• Analog input switch: both ADCs can convert the same analog input signal I or Q
• Gray or binary encoder output. Output format: DMUX 1:1 or 1:2 with control of the
output frequency on the data ready output signal
• Partial or full standby on channel I or channel Q
• Clock selection:
– Two independent clocks: CLKI and CLKQ
– One master clock (CLKI) with the same phase for channel I and channel Q
– One master clock but with two phases (CLKI for channel I and CLKIB for
channel Q)
• ISA: Internal Settling Adjustment on channel I and channel Q
• FiSDA: Fine Sampling Delay Adjustment on channel Q
• Adjustable Data Ready Output Delay on both channels
• Test mode: decimation mode (by 16), Built-In Test.
A calibration phase is provided to set the two DC offsets of channel I and channel Q
close to code 127.5 and calibrate the two gains to achieve a maximum difference of
0.5 LSB. The offset and gain error can also be set externally via the 3-wire serial
interface.
The AD84AD001B operates in fully differential mode from the analog inputs up to the
digital outputs. The AD84AD001B features a full-power input bandwidth of 1.5 GHz.
2
AT84AD001B
2153C–BDC–04/04
Page 3
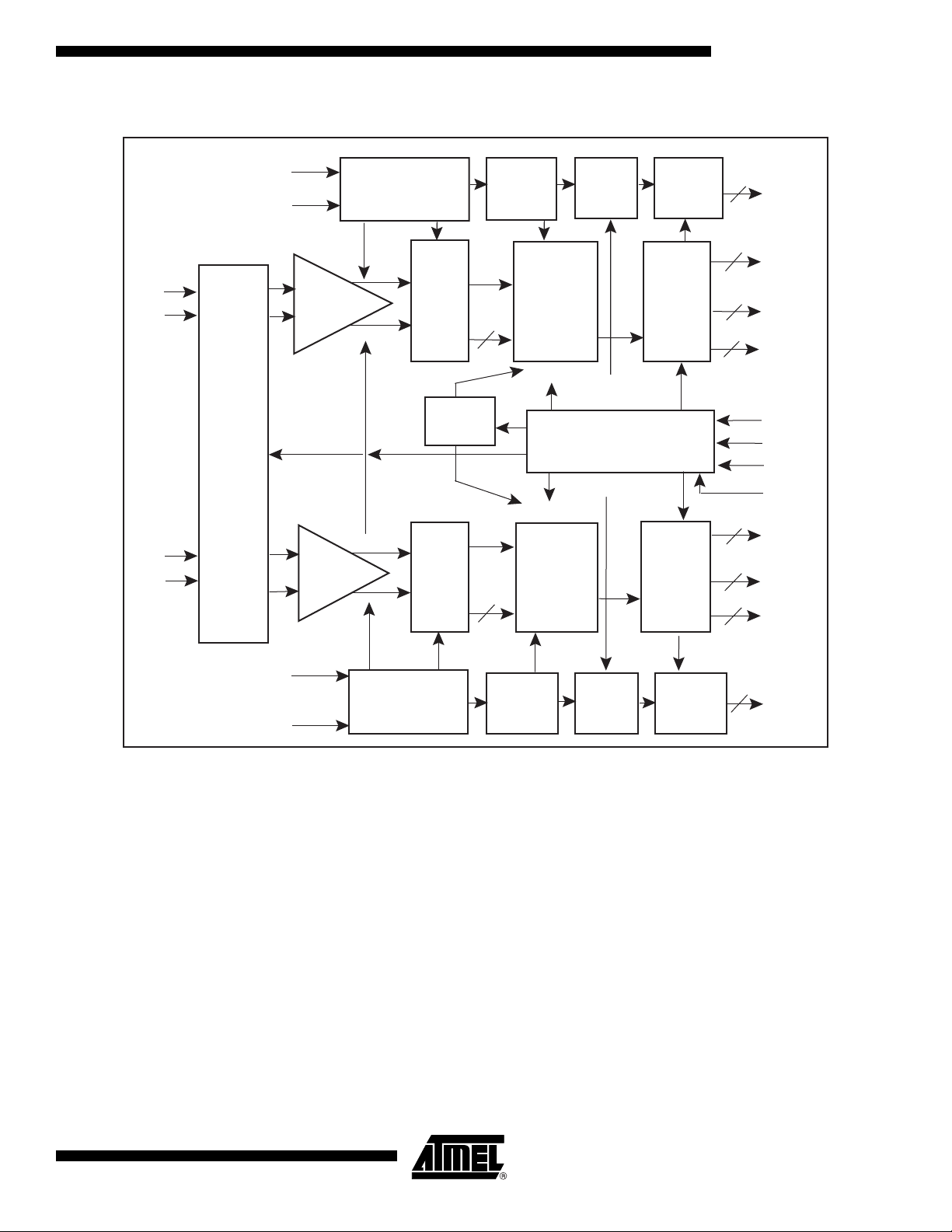
Figure 1. Simplified Block Diagram
AT84AD001B
Vini
Vinib
Vinq
Vinqb
INPUT
MUX
CLKI
DDRB
Gain control I
Calibration
Gain/offset
ISA I
Gain control Q
Calibration
Gain/offset
ISA Q & FiSDA
+
S/H
-
Input switch
+
S/H
-
Clock Buffer
ADC
ADC
8bit
8bit
Q
Divider
2 to16
DoirI
I
8
BIT
DoirQ
8
DMUX
DMUX
DRDA
I
1:2
or
1:1
I
DMUX control
3-wire Serial Interface
3WSI
DMUX control
1: 2
or
1: 1
Q
LVDS
Clock
Buffer
LVDS
Buffer
I
LVDS
buffer
Q
16
16
16
16
2
CLKIO
DOAI
DOAIN
DOBI
DOBIN
2
DOIRI
DOIRIN
Data
Clock
Ldn
Mode
2
DOIRQ
DOIRQN
DOAQ
DOAQN
DOBQ
DOBQN
CLKQ
DDRB
Clock Buffer
Divider
2 to 16
DRDA
Q
LVDS
Clock
Buffer
2
CLKQO
2153C–BDC–04/04
3
Page 4
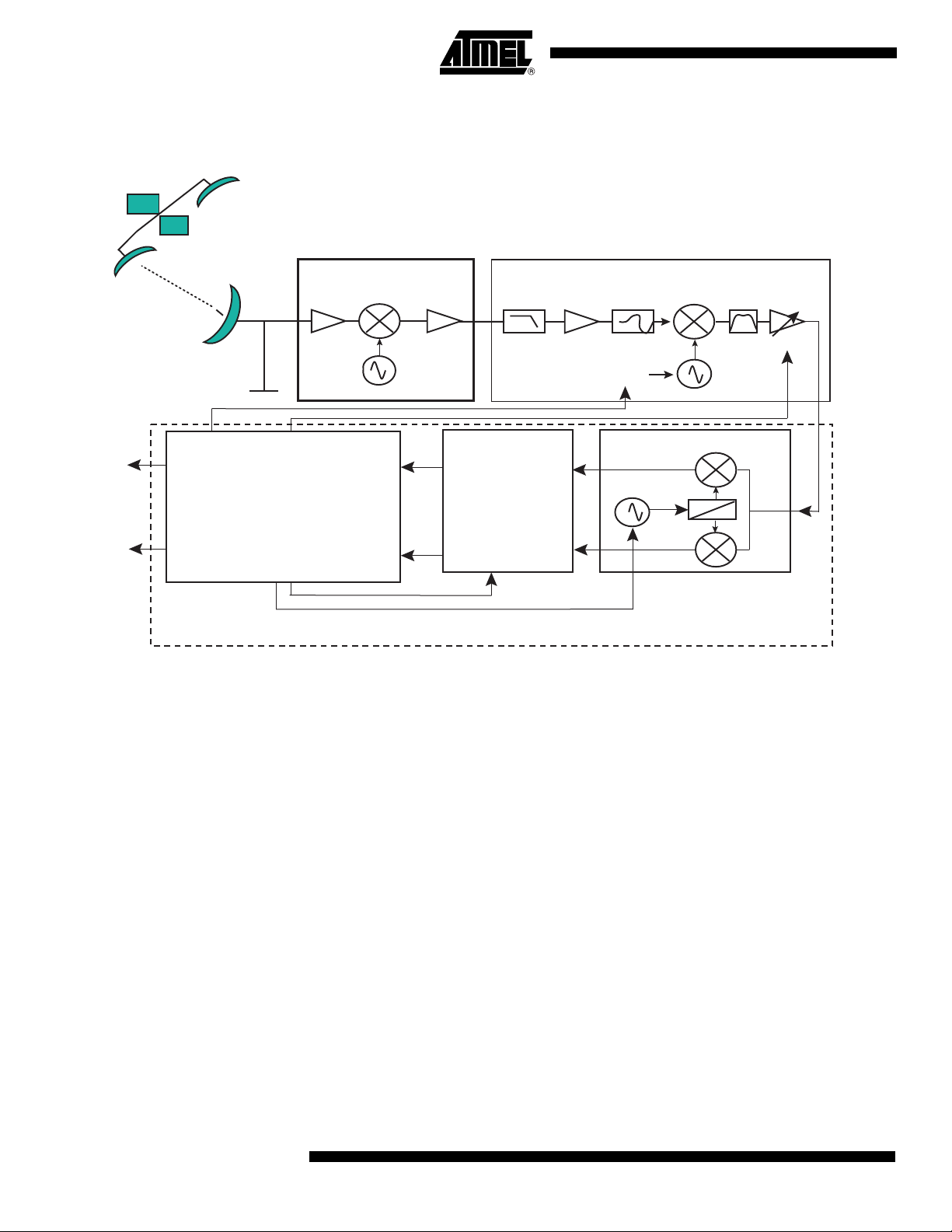
Typical Applications
Figure 2. Satellite Receiver Application
Satellite
Dish
I
Control Functions:
Clock and Carrier
Recovery...
Q
Low Noise Converter
(Connected to the Dish)
Bandpass
Amplifier
11..12 GHz
Local oscillator
Bandpass
Amplifier
I
Q
Demodulation
1..2 GHz
Low Pass
Filter
AT84AD001B
Clock
Satellite Tuner
Tunable
Band Filter
Synthesizer
1.5 … 2.5 GHz
I
Local Oscillator
Q
Q
Band Filter
0
90
Quadrature
IF
AGC
4
AT84AD001B
2153C–BDC–04/04
Page 5
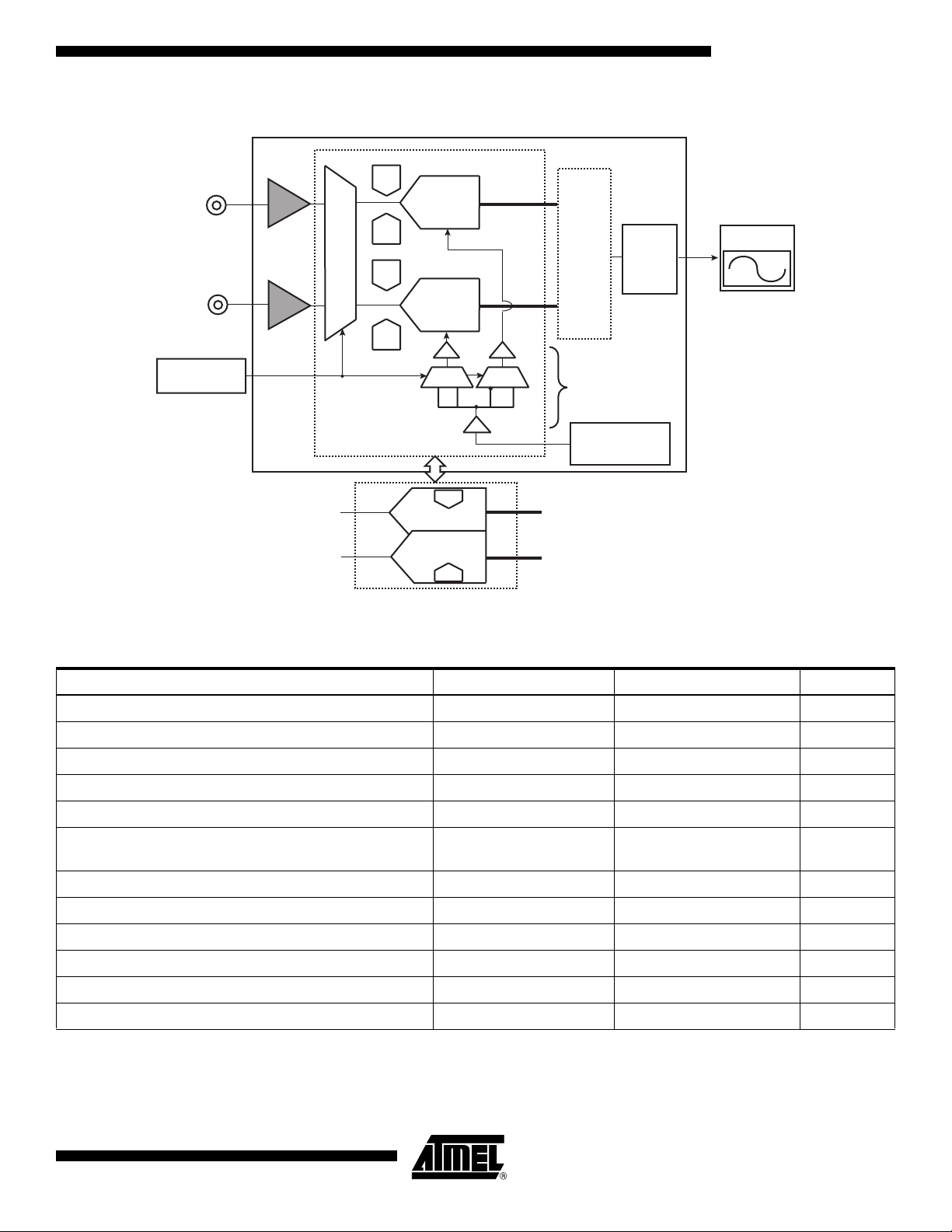
Figure 3. Dual Channel Digital Oscilloscope Application
DAC
Channel B
A
Channel A
A
Gain
ADC B
DAC
Offset
DAC
Offset
Analog switch
DAC
Gain
ADC A
FISO
RAM
AT84AD001B
Display
µP
Channel Mode
Selection
Clock
selection
Timing
circuit
DACs
Smart dual
ADC
DACs
Table 1. Absolute Maximum Ratings
Parameter Symbol Value Unit
Analog positive supply voltage V
Digital positive supply voltage V
Output supply voltage V
Maximum difference between V
Minimum V
CCO
Analog input voltage
CCA
and V
CCD
V
CCA
V
V
or V
INI
V
or V
INQ
Digital input voltage V
Clock input voltage V
Maximum difference between V
CLK
and V
CLKB
CLK
V
or VC
CLK
Maximum junction temperature T
Storage temperature T
Lead temperature (soldering 10s) T
CCA
CCD
CCO
to V
CCO
D
- V
J
stg
leads
CCD
INIB
INQB
LKB
CLKB
3.6 V
3.6 V
3.6 V
± 0.8 V
1.6 V
1/-1 V
-0.3 to V
-0.3 to V
+ 0.3 V
CCD
+ 0.3 V
CCD
-2 to 2 V
125 °C
-65 to 150 °C
300 °C
Note: Absolute maximum ratings are limiting values (referenced to GND = 0V), to be applied individually, while other parameters are
within specified operating conditions. Long exposure to maximum ratings may affect device reliability.
5
2153C–BDC–04/04
Page 6
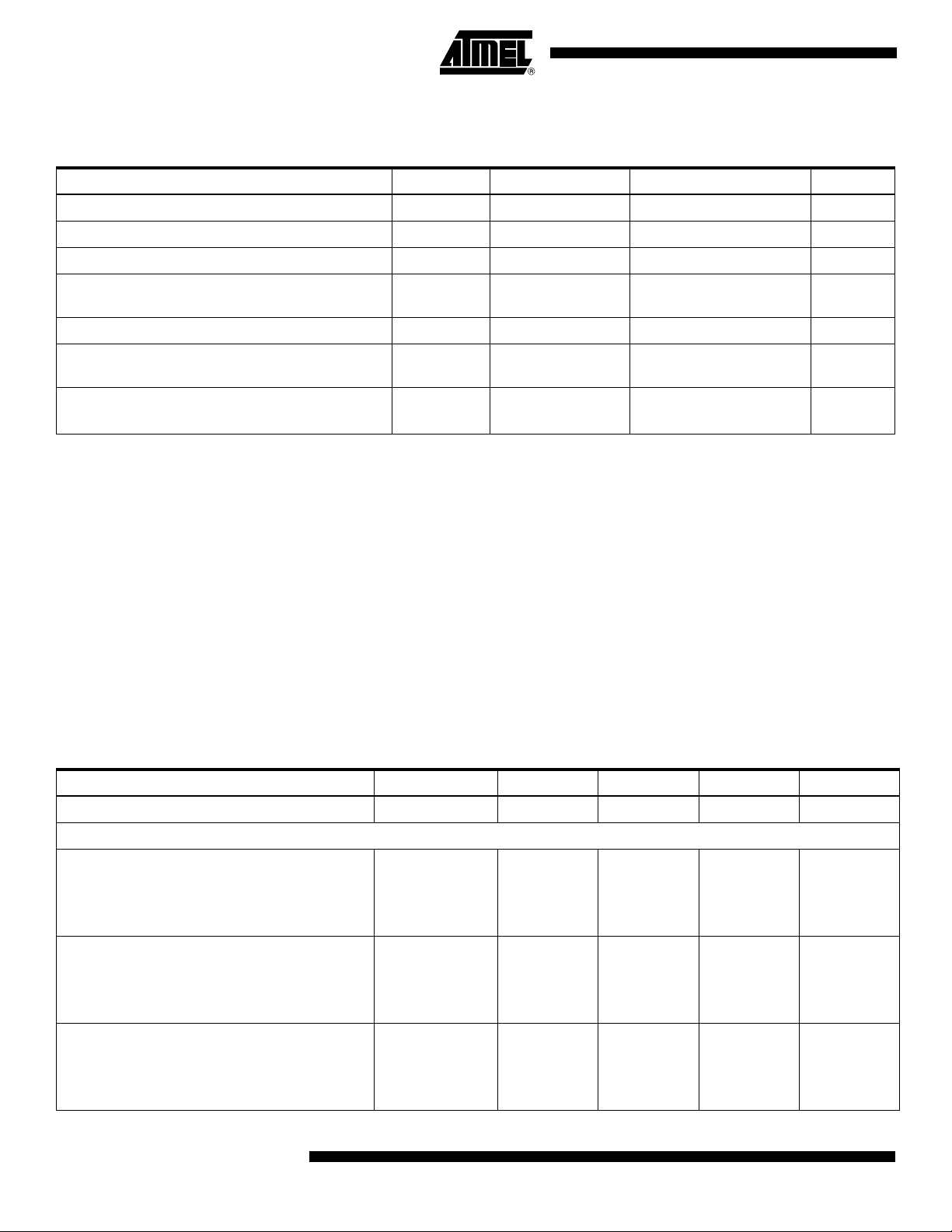
Table 2. Recommended Conditions of Use
Parameter Symbol Comments Recommended Value Unit
Analog supply voltage V
Digital supply voltage V
Output supply voltage V
V
Differential analog input voltage (full-scale)
INi
V
INQ
-V
CCA
CCD
CCO
-V
IniB
or
INQB
3.3 V
3.3 V
2.25 V
500 mVpp
Differential clock input level Vinclk 600 mVpp
Internal Settling Adjustment (ISA) with a 3-wire
serial interface for channel I and channel Q
Operating temperature range T
ISA -50 ps
Ambient
Commercial grade
Industrial grade
< 70
0 < T
A
-40 < TA < 85
Electrical Operating Characteristics
Unless otherwise specified:
•V
•V
• LVDS digital outputs (100Ω)
•T
• Full temperature range: 0° C < T
= 3.3V; V
CCA
- V
INI
INB
(typical) = 25° C
A
or V
CCD
INQ
(industrial grade)
= 3.3V; V
- V
INQB
= 2.25V
CCO
= 500 mVpp full-scale differential input
< 70° C (commercial grade) or -40°C < TA < 85° C
A
°C
Table 3. Electrical Operating Characteristics in Nominal Conditions
Parameter Symbol Min Typ Max Unit
Resolution 8Bits
Power Requirements
Positive supply voltage
- Analog
- Digital
Output digital (LVDS) and serial interface
Supply current (typical conditions)
- Analog
- Digital
- Output
Supply current (1:2 DMUX mode)
- Analog
- Digital
- Output
6
AT84AD001B
V
V
V
I
CCA
I
CCD
I
CCO
I
CCA
I
CCD
I
CCO
CCA
CCD
CCO
3.15
3.15
2.0
3.3
3.3
2.25
150
230
100
150
260
175
3.45
3.45
2.5
180
275
120
180
310
210
V
V
V
mA
mA
mA
mA
mA
2153C–BDC–04/04
Page 7
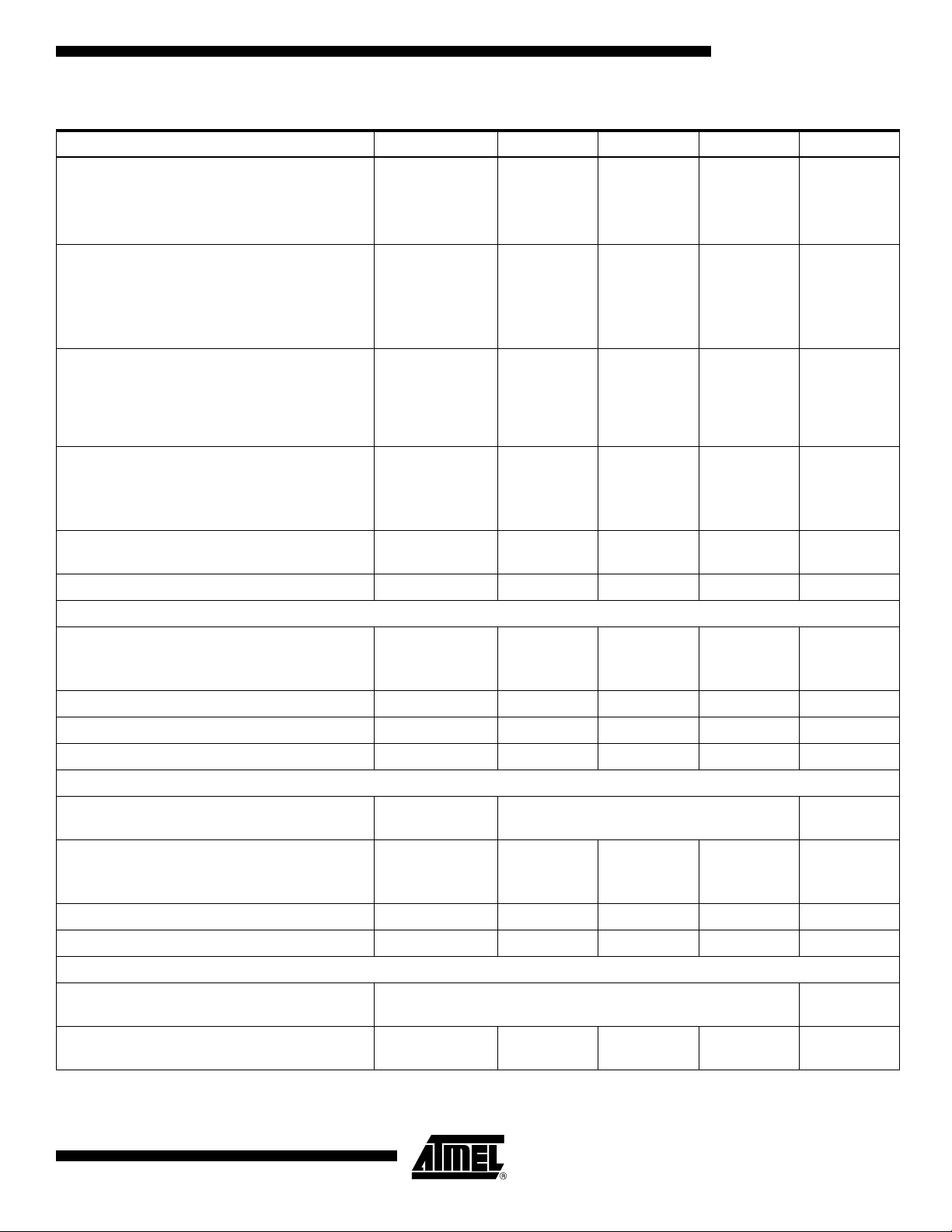
AT84AD001B
Table 3. Electrical Operating Characteristics in Nominal Conditions (Continued)
Parameter Symbol Min Typ Max Unit
Supply current (2 input clocks, 1:2 DMUX mode)
- Analog
- Digital
- Output
Supply current
(1 channel only, 1:1 DMUX mode)
- Analog
- Digital
- Output
Supply current
(1 channel only, 1:2 DMUX mode)
- Analog
- Digital
- Output
I
CCA
I
CCD
I
CCO
I
CCA
I
CCD
I
CCO
I
CCA
I
CCD
I
CCO
150
290
180
80
160
55
80
170
90
180
350
215
95
190
65
95
205
110
mA
mA
mA
mA
mA
mA
mA
Supply current (full standby mode)
- Analog
- Digital
- Output
Nominal dissipation
(1 clock, 1:1 DMUX mode, 2 channels)
I
CCA
I
CCD
I
CCO
P
12
24
3
D
1.4 1.7 W
17
34
5
mA
mA
mA
Nominal dissipation (full standby mode) stbpd 120 mW
Analog Inputs
- V
or
- V
IN
IniB
INQB
mV
450 500 550
mV
2pF
V
INi
Full-scale differential analog input voltage
V
INQ
Analog input capacitance I and Q C
Full power input bandwidth (-3 dB) FPBW 1.5 GHz
Gain flatness (-0.5 dB) 500 MHz
Clock Input
Logic compatibility for clock inputs and DDRB
Reset (pins 124,125,126,127,128,129)
PECL/ECL/LVDS
PECL/LVDS clock inputs voltages
(V
CLKI/IN
or V
CLKQ/QN
)
- V
V
IL
IH
600 mV
Differential logical level
Clock input power level -9 0 6 dBm
Clock input capacitance 2 pF
Digital Outputs
Logic compatibility for digital outputs
(depending on the value of V
CCO
)
Differential output voltage swings
(assuming V
2153C–BDC–04/04
= 2.25V)
CCO
V
OD
LV DS
220 270 350 mV
7
Page 8
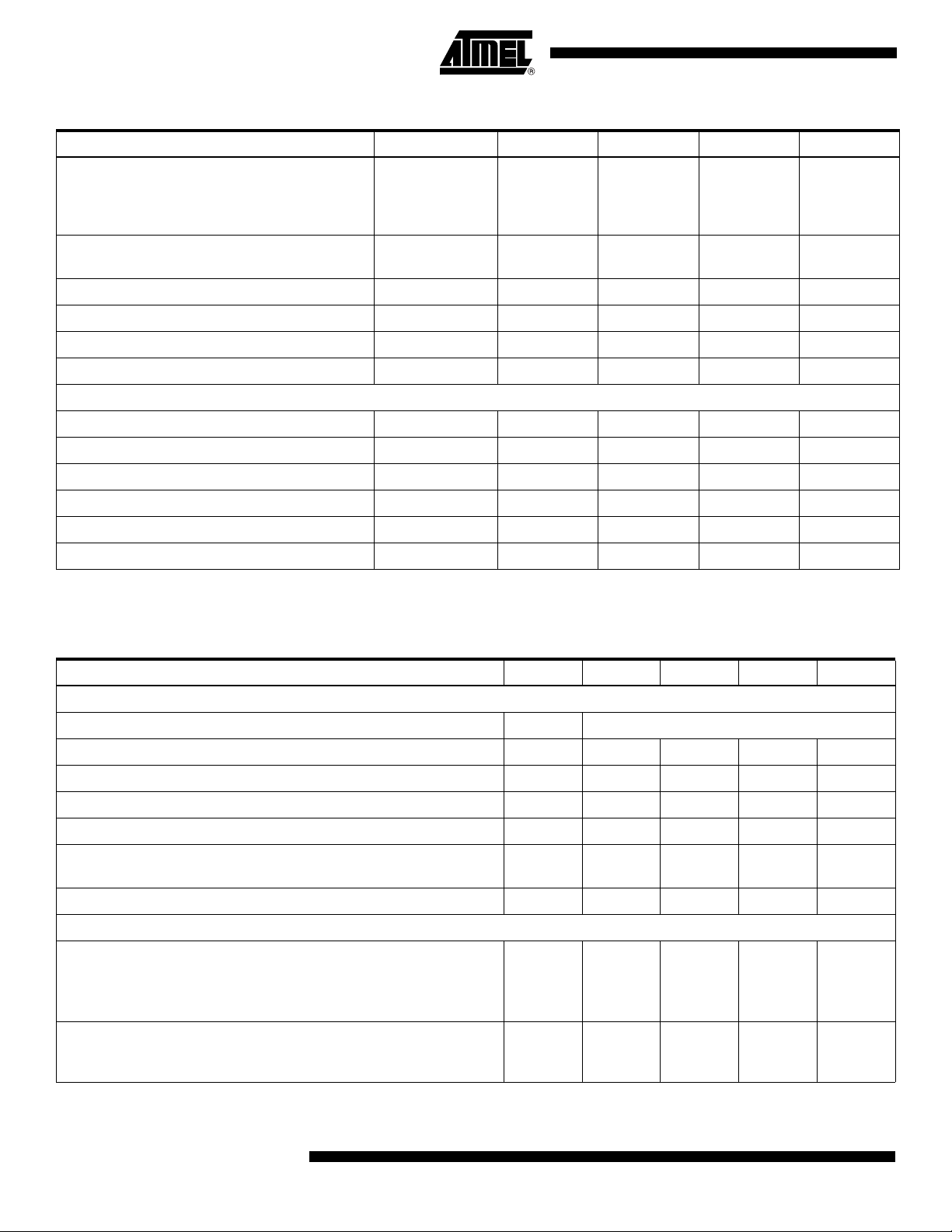
Table 3. Electrical Operating Characteristics in Nominal Conditions (Continued)
Parameter Symbol Min Typ Max Unit
Output levels (assuming V
100Ω differentially terminated
Logic 0 voltage
Logic 1 voltage
Output offset voltage (assuming V
100Ω differentially terminated
Output impedance R
Output current (shorted output) 12 mA
Output current (grounded output) 30 mA
Output level drift with temperature 1.3 mV/°C
Digital Input (Serial Interface)
Maximum clock frequency (input clk) Fclk 50 MHz
Input logical level 0 (clk, mode, data, ldn) -0.4 0 0.4 V
= 2.25V)
CCO
= 2.25V)
CCO
V
OL
V
OH
V
OS
O
1.0
1.25
1125 1250 1325 mV
1.1
1.35
1.2
1.45
50 W
V
V
Input logical level 1 (clk, mode, data, ldn) V
- 0.4 V
CCO
- 0.4 V
CCO
+ 0.4 V
CCO
Output logical level 0 (cal) -0.4 0 0.4 V
Output logical level 1 (cal) V
- 0.4 V
CCO
CCO
V
+ 0.4 V
CCO
Maximum output load (cal) 15 pF
Note: The gain setting is 0 dB, one clock input, no standby mode [full power mode], 1:1 DMUX, calibration off.
Table 4. Electrical Operating Characteristics
Parameter Symbol Min Typ Max Unit
DC Accuracy
No missing code Guaranteed over specified temperature range
Differential non-linearity DNL 0.25 0.6 LSB
Integral non-linearity INL 0.5 1 LSB
Gain error (single channel I or Q) with calibration -0.5 0 0.5 LSB
Input offset matching (single channel I or Q) with calibration -0.5 0 0.5 LSB
Gain error drift against temperature
Gain error drift against V
CCA
0.062
0.064
Mean output offset code with calibration 127 127.5 128 LSB
Transient Performance
LSB/°C
LSB/mV
Bit Error Rate
Fs = 1 Gsps
BER 10
-13
Fin = 250 MHz
ADC settling time channel I or Q
(between 10% - 90% of output response)
V
-V
= 500 mVpp
Ini
iniB
TS 170 ps
Note: Gain setting is 0 dB, two clock inputs, no standby mode [full power mode], 1:2 DMUX, calibration on.
8
AT84AD001B
-10
10
2153C–BDC–04/04
Error/
sample
Page 9
AT84AD001B
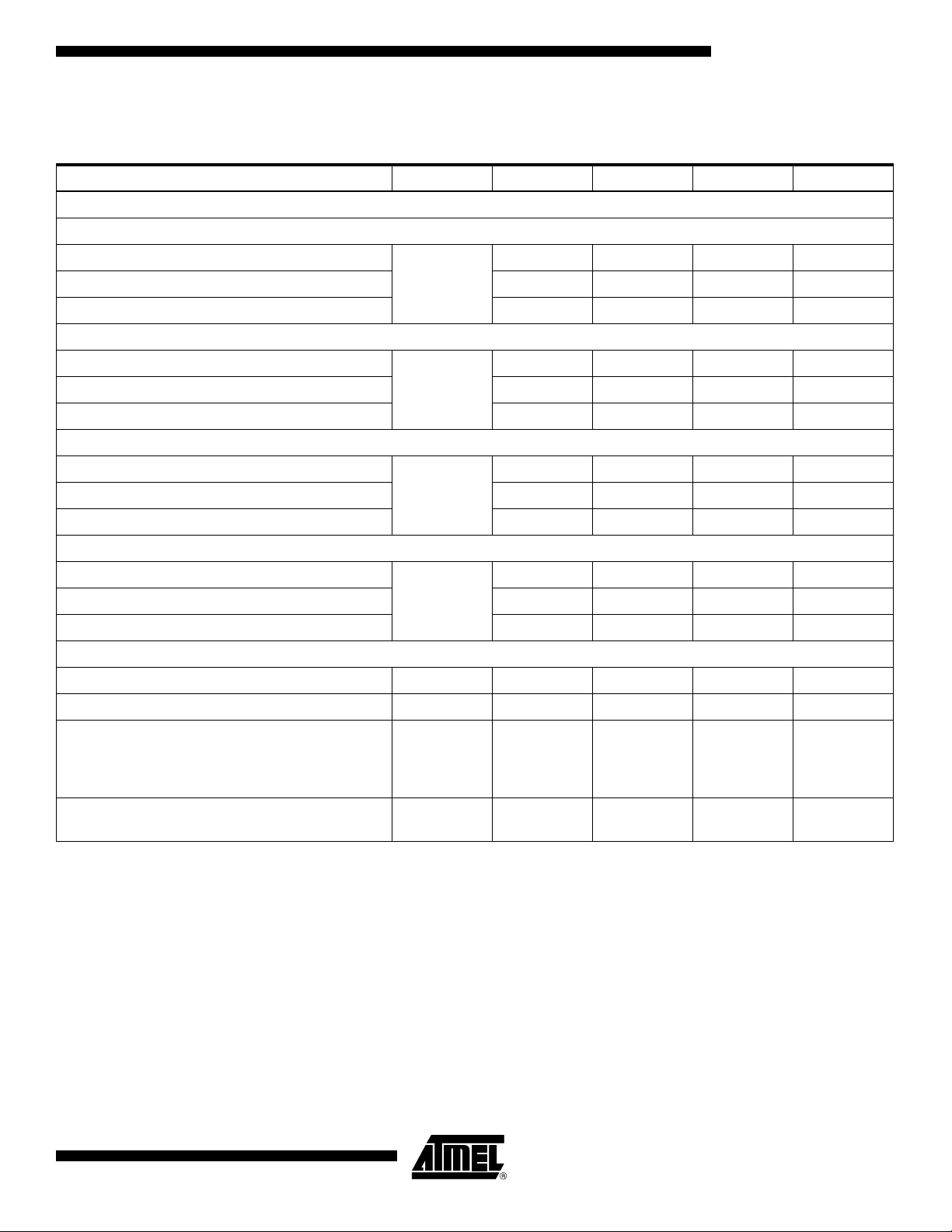
Table 5. AC Performances
Parameter Symbol Min Typ Max Unit
AC Performance
Signal-to-noise Ratio
Fs = 1 Gsps Fin = 20 MHz
Fs = 1 Gsps Fin = 500 MHz 40 42 dBc
Fs = 1 Gsps Fin = 1 GHz 41 dBc
Effective Number of Bits
Fs = 1 Gsps Fin = 20 MHz
Fs = 1 Gsps Fin = 500 MHz 6.5 6.8 Bits
Fs = 1 Gsps Fin = 1 GHz 6.2 Bits
Total Harmonic Distortion (First 9 Harmonics)
Fs = 1 Gsps Fin = 20 MHz
Fs = 1 Gsps Fin = 500 MHz 45 51 dBc
Fs = 1 Gsps Fin = 1 GHz 42 dBc
Spurious Free Dynamic Range
Fs = 1 Gsps Fin = 20 MHz
Fs = 1 Gsps Fin = 500 MHz 48 54 dBc
Fs = 1 Gsps Fin = 1 GHz 43 dBc
Two-tone Inter-modulation Distortion (Single Channel)
= 499 MHz , F
F
IN1
Band flatness from DC up to 600 MHz ±0.5 dB
= 501 MHz at Fs = 1 Gsps IMD -54 dBc
IN2
SNR
ENOB
|THD|
|SFDR|
42 44 dBc
77.2 Bits
48 54 dBc
50 56 dBc
Phase matching using auto-calibration and FiSDA
in interlace mode (channel I and Q)
Fin = 250 MHz
Fs = 1 Gsps
Crosstalk channel I versus channel Q
Fin = 250 MHz, Fs = 1 Gsps
Notes: 1. Differential input [-1 dBFS analog input level], gain setting is 0 dB, two input clock signals, no standby mode,
1:1 DMUX, ISA = -50 ps.
2. Measured on the AT84AD001TD-EB Evaluation Board.
2153C–BDC–04/04
(2)
dϕ -0.7 0 0.7 °
Cr -55 dB
9
Page 10
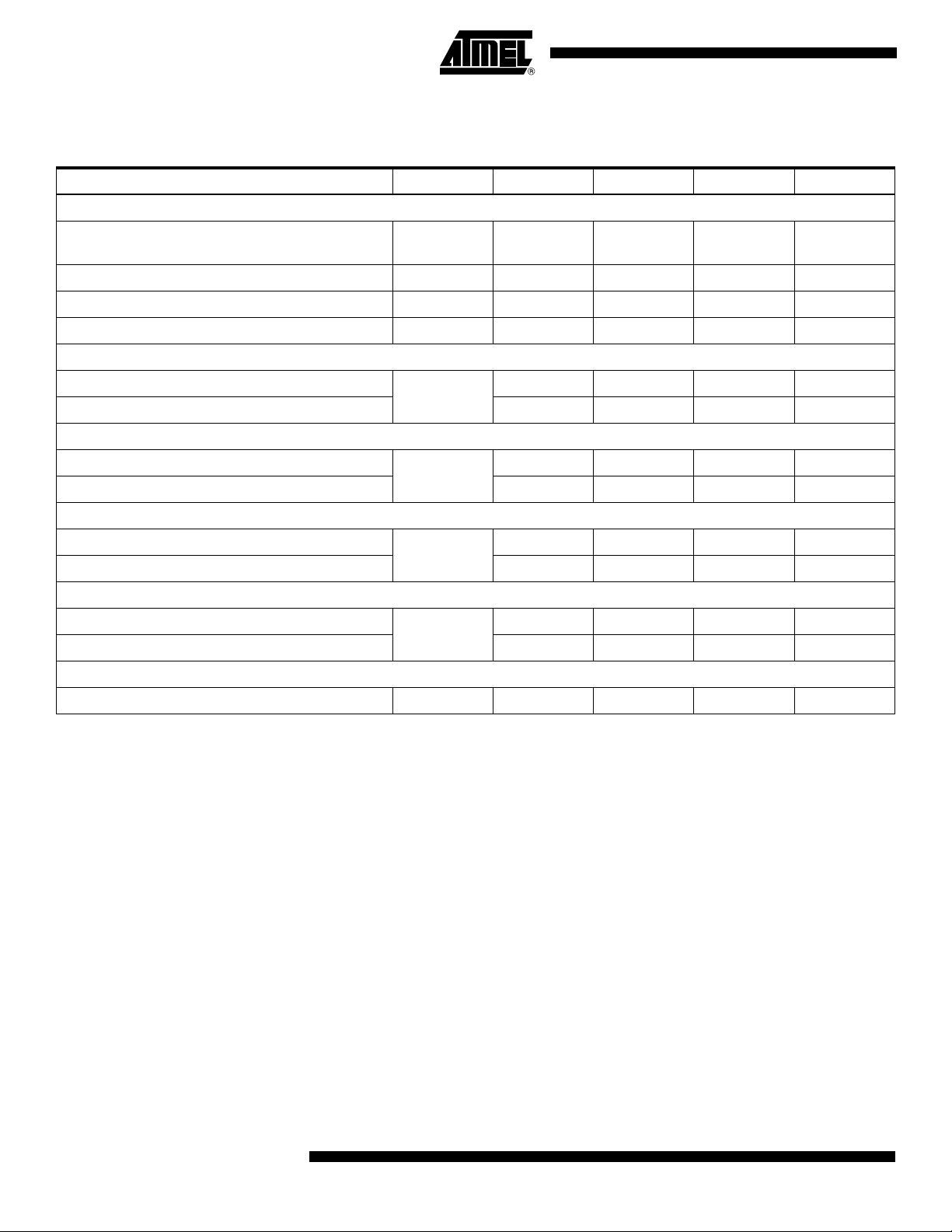
Table 6. AC Performances in Interlace Mode
Parameter Symbol Min Typ Max Unit
Interlace Mode
Maximum equivalent clock frequency Fint = 2 x Fs
Where Fs = external clock frequency
Minimum clock frequency F
F
int
int
2Gsps
20 Msps
Differential non-linearity in interlace mode intDNL 0.25 LSB
Integral non-linearity in interlace mode intINL 0.5 LSB
Signal-to-noise Ratio in Interlace Mode
Fint = 2 Gsps Fin = 20 MHz
42 dBc
iSNR
Fint = 2 Gsps Fin = 250 MHz 40 dBc
Effective Number of Bits in Interlace Mode
Fint = 2 Gsps Fin = 20 MHz
7.1 Bits
iENOB
Fint = 2 Gsps Fin = 250 MHz 6.8 Bits
Total Harmonic Distortion in Interlace Mode
Fint = 2 Gsps Fin = 20 MHz
52 dBc
|iTHD|
Fint = 2 Gsps Fin = 250 MHz 49 dBc
Spurious Free Dynamic Range in Interlace Mode
Fint = 2 Gsps Fin = 20 MHz
|iSFDR|
54 dBc
Fint = 2 Gsps Fin = 250 MHz 52 dBc
Two-tone Inter-modulation Distortion (Single Channel) in Interlace Mode
= 249 MHz , F
F
IN1
= 251 MHz at F
IN2
= 2 Gsps iIMD -54 dBc
int
Note: One analog input on both cores, clock I samples the analog input on the rising and falling edges. The calibration
phase is necessary. The gain setting is 0 dB, one input clock I, no standby mode, 1:1 DMUX, FiSDA adjustment.
10
AT84AD001B
2153C–BDC–04/04
Page 11
AT84AD001B
Table 7. Switching Performances
Parameter Symbol Min Typ Max Unit
Switching Performance and Characteristics - See “Timing Diagrams” on page 12.
Maximum operating clock frequency F
Maximum operating clock frequency in BIT and
decimation modes
(BIT, DEC)
S
F
S
1 Gsps
750 Msps
Minimum clock frequency (no transparent mode)
Minimum clock frequency (with transparent mode) 1 Ksps
Minimum clock pulse width [high]
(No transparent mode)
Minimum clock pulse width [low]
(No transparent mode)
Aperture delay: nominal mode with ISA & FiSDA TA 1 ns
Aperture uncertainty Jitter 0.4 ps (rms)
Data output delay between input clock and data TDO 3.8 ns
Data Ready Output Delay TDR 3 ns
Data Ready Reset to Data Ready TRDR 2 ns
Data Output Delay with Data Ready TD2
Data Ready (CLKO) Delay Adjust (140 ps steps) Tdrda range -560 to 420 ps
Output skew 50 100 ps
Output rise/fall time for DATA (20% - 80%) TR/TF 300 350 500 ps
Output rise/fall time for DATA READY (20% - 80%) TR/TF 300 350 500 ps
Data pipeline delay (nominal mode)
Data pipeline delay (nominal mode) in S/H
transparent mode
F
S
TC1 0.4 0.5 50 ns
TC2 0.4 0.5 50 ns
3.5 (port A, 1:1 DMUX mode)
TPD
4 (port A, 1:2 DMUX mode)
3 (port A, 1:1 DMUX mode)
3.5 (port A, 1:2 DMUX mode)
10 Msps
1/2 Fs
+Tdrda
3 (port B)
2.5 (port B)
ps
Clock cycles
DDRB recommended pulse width 1 ns
2153C–BDC–04/04
11
Page 12
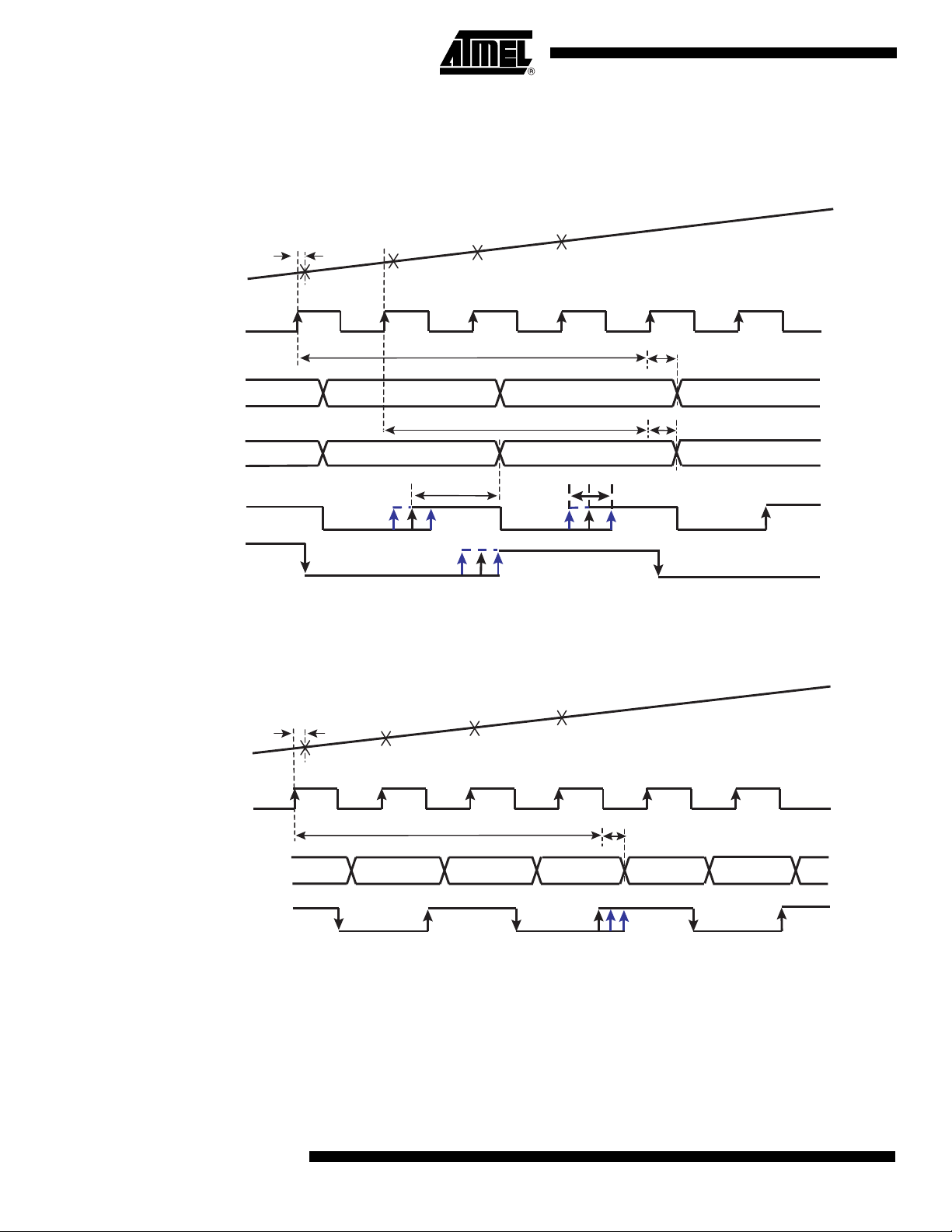
Timing Diagrams
Figure 4. Timing Diagram, ADC I or ADC Q, 1:2 DMUX Mode, Clock I for ADC I, Clock Q for ADC Q
Address: D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
1 1 X X 1 X 0 0
TA
VIN
N + 1
N
N + 2
CLKI or CLKQ
Pipeline delay = 4 clock cycles
DOIA[0:7]
or DOQA[0:7]
DOIB[0:7]
or DOQB[0:7]
N - 4
Pipeline delay = 3 clock cycles
N - 3 N - 1 N +1
TD2
CLKOI or CLKOQ
(= CLKI/2)
CLKOI or CLKOQ
(= CLKI/4)
Figure 5. 1:1 DMUX Mode, Clock I = ADC I, Clock Q = ADC Q
Address: D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
1 1 X X 0 X 0 0
N + 3
N - 2
Programmable delay
TDO
N
TDO
12
TA
VIN
N
N + 1
CLKI or CLKQ
Pipeline delay = 3.5 clock cycles
DOIA[0:7]
or DOQA[0:7]
N - 3
CLKOI or CLKOQ
DOIB[0:7] and DOQB[0:7] are high impedance
AT84AD001B
N + 2
N - 2
N + 3
N - 1
TDO
N
N + 1
2153C–BDC–04/04
Page 13
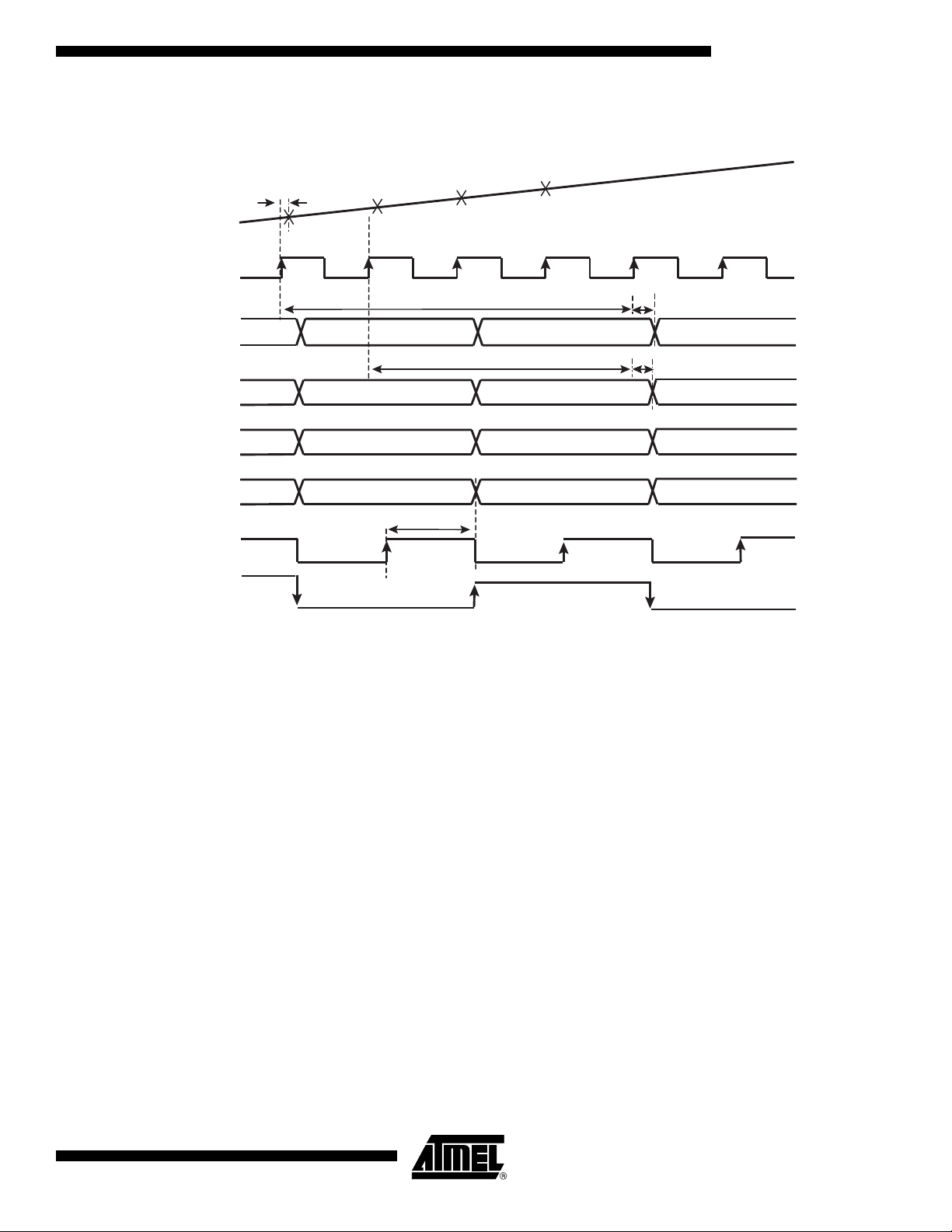
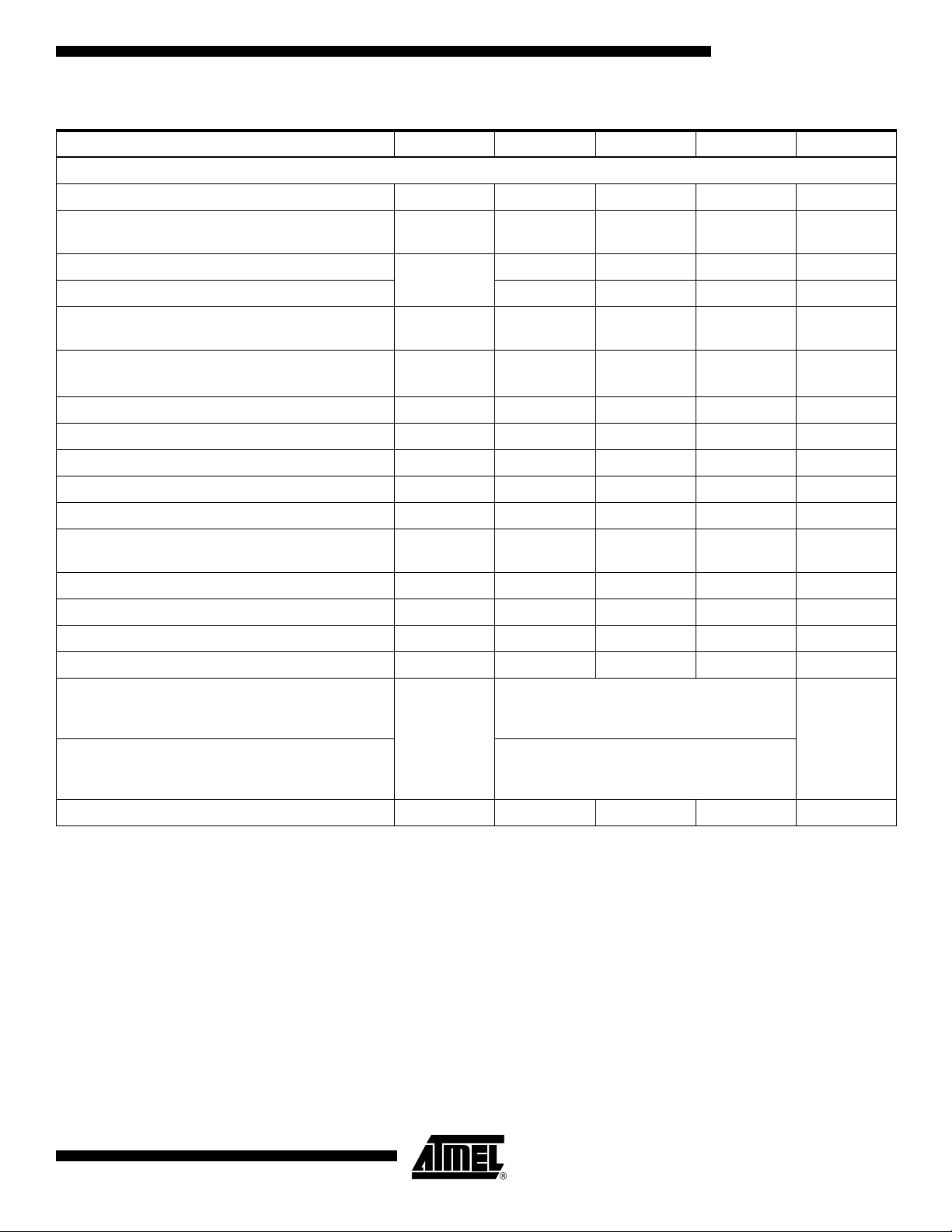
Figure 6. 1:2 DMUX Mode, Clock I = ADC I, Clock I = ADC Q
Address: D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
1 0 X X 1 X 0 0
AT84AD001B
TA
VIN
N
CLKI
DOIA[0:7]
DOIB[0:7]
DOQA[0:7]
DOQB[0:7]
CLKOI
(= CLKI/2)
CLKOI
(= CLKI/4)
CLKOQ is high impedance
N + 1
Pipeline delay = 4 clock cycles
NI - 4
Pipeline delay = 3 clock cycles
NI - 3 NI - 1 NI +1
NQ - 4 NQ - 2 NQ
NQ - 3 NQ - 1 NQ +1
N + 2
TD2
N + 3
NI - 2
TDO
NI
TDO
2153C–BDC–04/04
13
Page 14
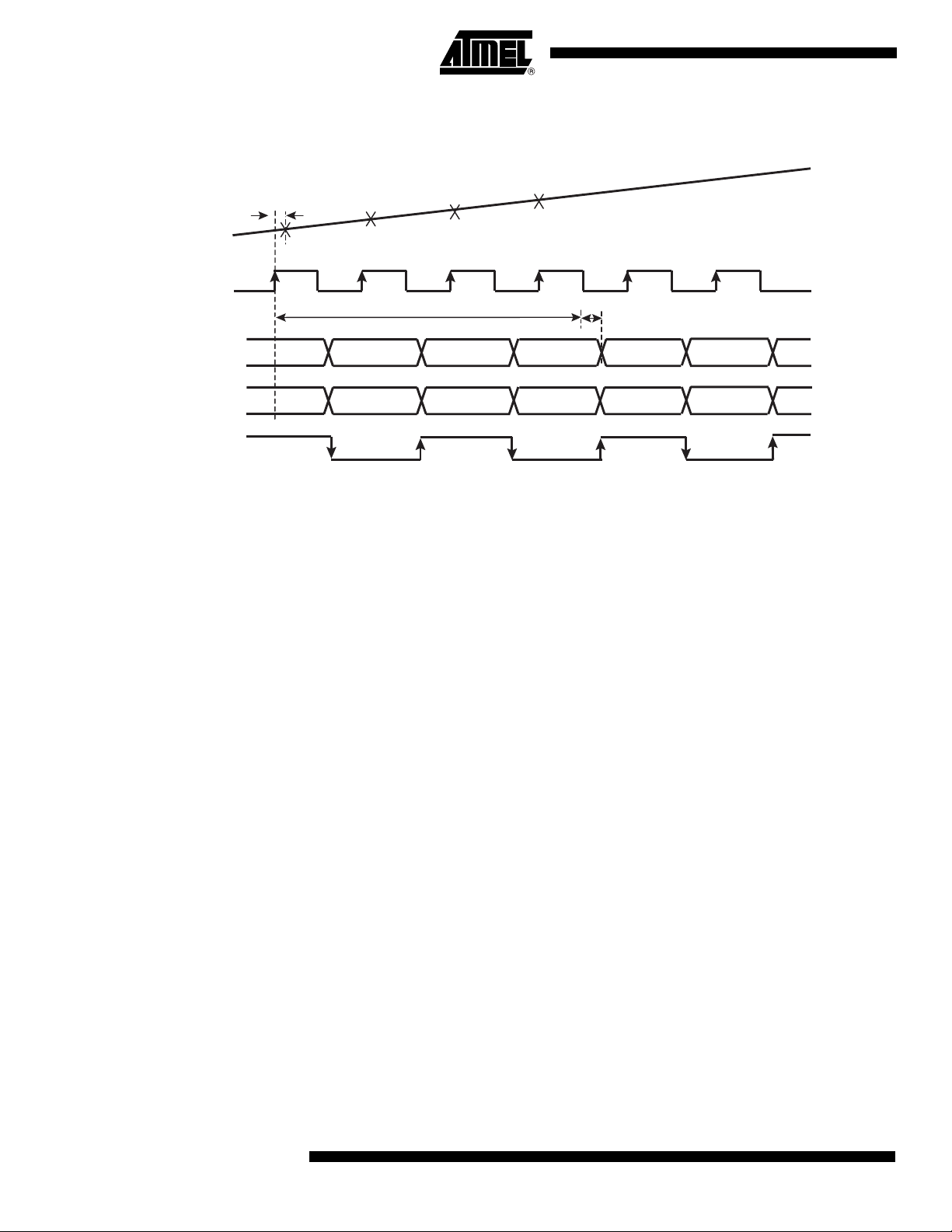
Figure 7. 1:1 DMUX Mode, Clock I = ADC I, Clock I = ADC Q
Address: D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
1 0 X X 0 X 0 0
TA
VIN
N
N + 1
CLKI
Pipeline delay = 3.5 clock cycles
DOIA[0:7]
DOQA[0:7]
N - 3
N - 3
CLKOI
DOIB[0:7] and DOQB[0:7] are high impedance
CLKOQ is high impedance
N + 2
N - 2
N - 2
N + 3
N - 1
N - 1
TDO
N
N
N + 1
N + 1
14
AT84AD001B
2153C–BDC–04/04
Page 15
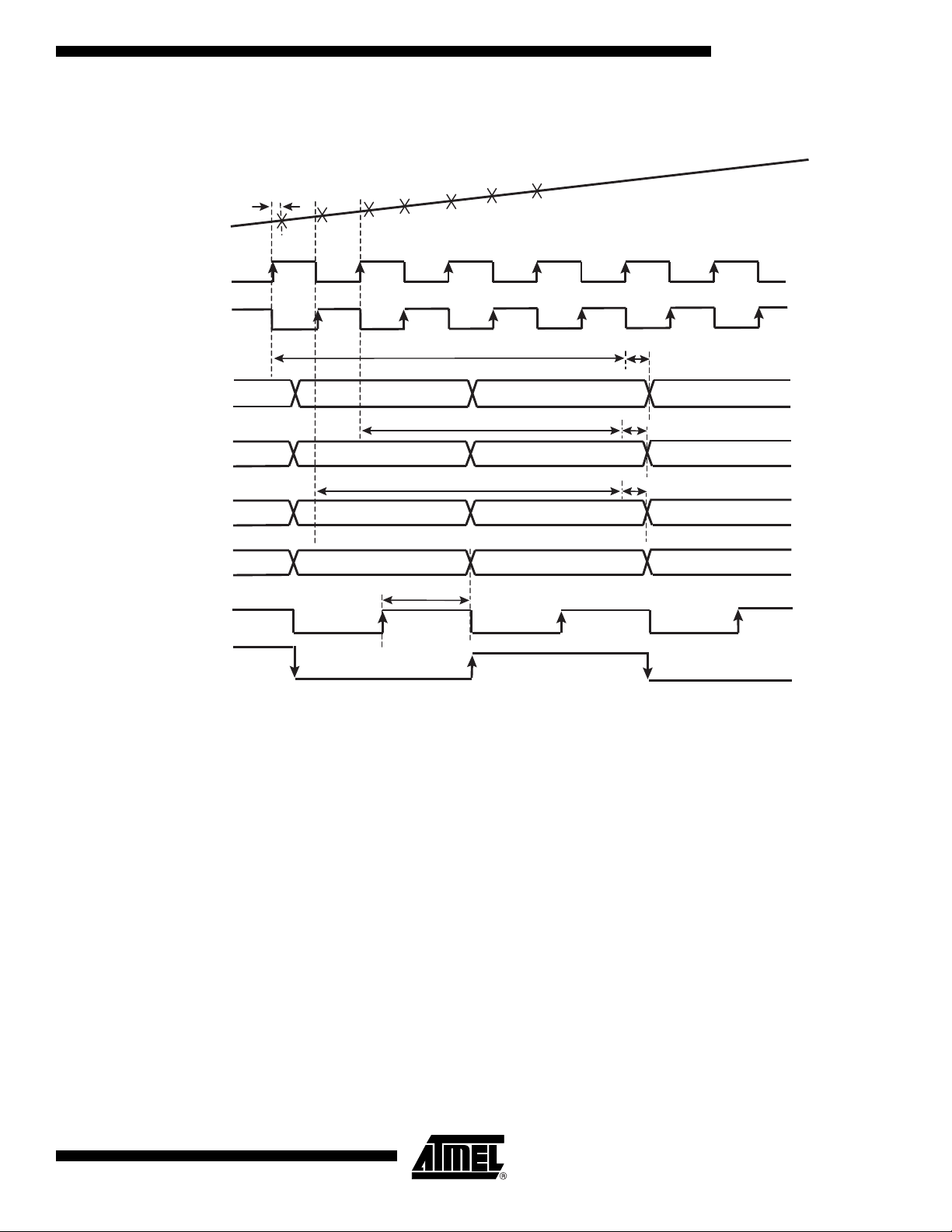
Figure 8. 1:2 DMUX Mode, Clock I = ADC I, Clock IN = ADC Q
Address: D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
0 X X X 1 X 0 0
N + 4
N + 5
VIN
CLKI
CLKIN
TA
N + 2
N + 1
N
N + 3
AT84AD001B
N + 6
DOQA[0:7]
DOQB[0:7]
DOIA[0:7]
DOIB[0:7]
CLKOI
(= CLKI/2)
CLKOI
(= CLKI/4)
CLKOQ is high impedance
Pipeline delay = 4 clock cycles
N - 8
Pipeline delay = 3 clock cycles
N - 6 N - 2 N + 2
Pipeline delay = 3.5 clock cycles
N - 7 N - 3 N + 1
N - 5 N - 1 N + 3
TD2
N - 4
TDO
N
TDO
TDO
2153C–BDC–04/04
15
Page 16
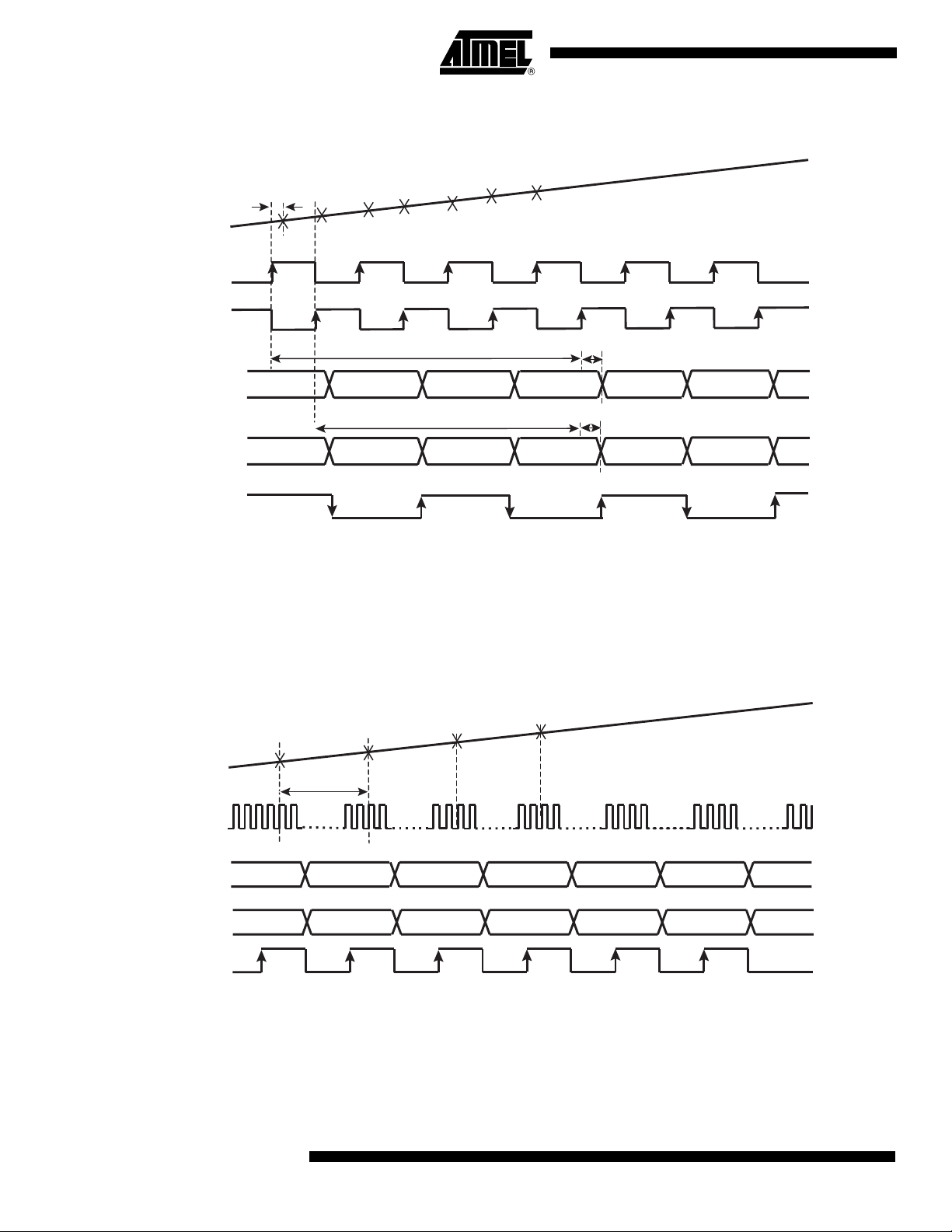
Figure 9. 1:1 DMUX Mode, Clock I = ADC I, Clock IN = ADC Q
Address: D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
0 X X X 0 X 0 0
N + 4
N + 5
VIN
CLKI
CLKIN
TA
N + 2
N + 1
N
N + 3
N + 6
Pipeline delay = 3.5 clock cycles
DOQA[0:7]
DOIA[0:7]
N - 6
Pipeline delay = 3 clock cycles
N - 5
N - 4
N - 3
CLKOI
(= CLKI/2)
DOIB[0:7] and DOQB[0:7] are high impedance
CLKOQ is high impedance
Figure 10. 1:1 DMUX Mode, Decimation Mode Test (1:16 Factor)
Address: D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
1 0 X X 0 X 0 0
N + 16
VIN
N - 16
16 clock cycles
N
N - 2
N - 1
N + 32
TDO
TDO
N
N + 1
N + 2
N + 3
CLKI
DOIA[0:7]
DOQA[0:7]
N - 16
N - 16
N
N
N + 16 N + 32 N + 48
N + 16 N + 32 N + 48
CLKOI
DOIB[0:7] and DOQB[0:7] are high impedance
CLKOQ is high impedance
Notes: 1. The maximum clock input frequency in decimation mode is 750 Msps.
2. Frequency(CLKOI) = Frequency(Data) = Frequency(CLKI)/16.
16
AT84AD001B
2153C–BDC–04/04
Page 17
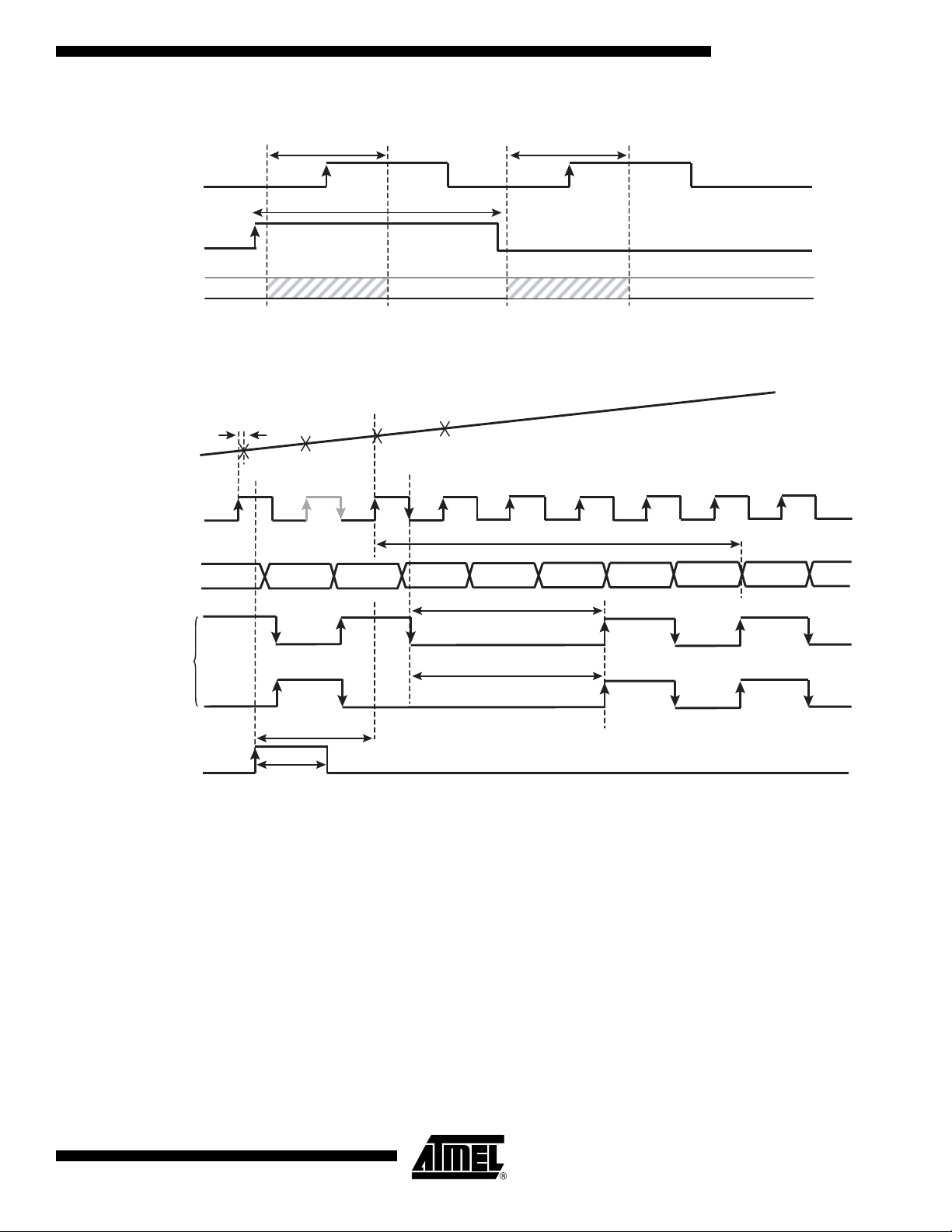
Figure 11. Data Ready Reset
AT84AD001B
500 ps
CLKI or
CLKQ
1 ns min
DDRB
Figure 12. Data Ready Reset 1:1 DMUX Mode
TA
VIN
Clock in
Reset
CLKI or
CLKQ
DOIA[0:7] or
DOQA[0:7]
N
ALLOWED
N + 1
500 ps
FORBIDDENFORBIDDEN
ALLOWED
Pipeline Delay + TDO
N
TDR
CLKOI or
CLKOQ
2 ns
TDR
DDRB
1 ns min
Note: The Data Ready Reset is taken into account only 2 ns after it is asserted. The output clock first completes its cycle (if the reset
occurs when it is high, it goes low only when its half cycle is complete; if the reset occurs when it is low, it remains low) and then
only, remains in reset state (frozen to a low level in 1:1 DMUX mode). The next falling edge of the input clock after reset makes
the output clock return to normal mode (after TDR).
2153C–BDC–04/04
17
Page 18
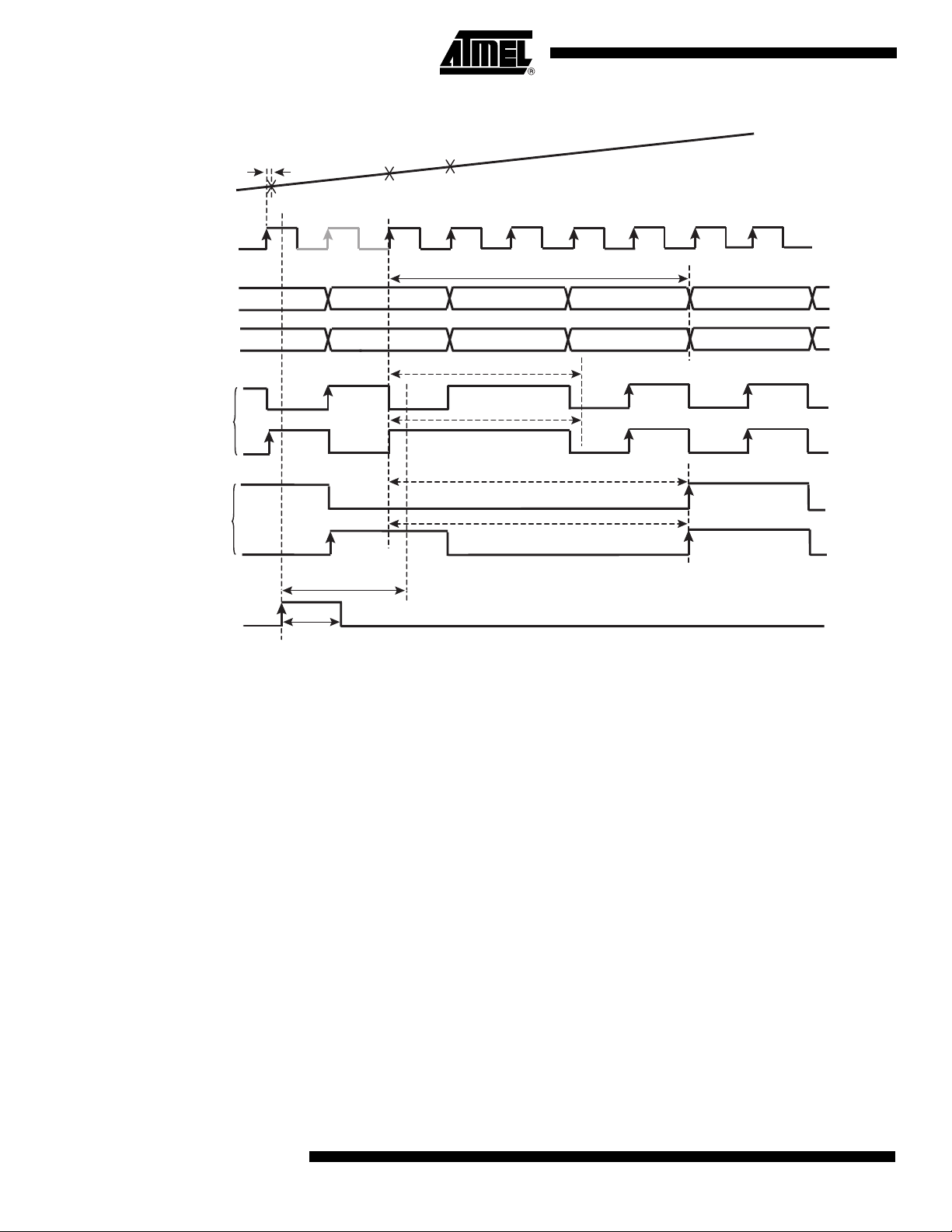
Figure 13. Data Ready Reset 1:2 DMUX Mode
TA
VIN
CLKI or
CLKQ
DOIA[0:7] or
DOQA[0:7]
Clock in
Reset
N
N + 1
Pipeline Delay + TDO
N
DOIB[0:7] or
DOQB[0:7]
CLKOI or CLKOQ
(= CLKI/2)
CLKOI or CLKOQ
(= CLKI/4)
DDRB
Notes: 1. In 1:2 DMUX, Fs/2 mode:
The Data Ready Reset is taken into account only 2 ns after it is asserted. The output clock first completes its cycle (if the
reset occurs when it is low, it goes high only when its half cycle is complete; if the reset occurs when it is high, it remains
high) and then only, remains in reset state (frozen to a high level in 1:2 DMUX Fs/2 mode). The next rising edge of the input
clock after reset makes the output clock return to normal mode (after TDR).
2. In 1:2 DMUX, Fs/4 mode:
The Data Ready Reset is taken into account only 2 ns after it is asserted. The output clock first completes its cycle (if the
reset occurs when it is high, it goes low only when its half cycle is complete; if the reset occurs when it is low, it remains low)
and then only, remains in reset state (frozen to a low level in 1:2 DMUX Fs/4 mode). The next rising edge of the input clock
after reset makes the output clock return to normal mode (after TDR).
N + 1
TDR
TDR
TDR + 2 cycles
TDR + 2 cycles
2 ns
1 ns min
18
AT84AD001B
2153C–BDC–04/04
Page 19

Functions Description
Table 8. Description of Functions
Name Function
V
CCA
V
CCD
V
CCO
GNDA Analog ground
GNDD Digital ground
GNDO Output ground
V
, V
INI
INIB
V
, V
INQ
INQB
CLKOI, CLKOIN, CLKOQ,
CLKOQN
CLKI, CLKIN, CLKQ, CLKQN Differential clock inputs I and Q
DDRB, DDRBN
Mode
Clk
Data Input data for 3-wire bus
Ldn
<D0AI0:DOAI7>
<D0AI0N:DOAI7N>
<D0BI0:DOBI7>
<D0BI0N:DOBI7N>
Positive analog power supply
Positive digital power supply
Positive output power supply
Differential analog inputs I
Differential analog inputs Q
Differential output data ready I
and Q
Synchronous data ready reset
I and Q
Bit selection for 3-wire bus or
nominal setting
Input clock for 3-wire bus
interface
Beginning and end of register
line for 3-wire bus interface
Differential output data port
channel I
VCCA = 3.3V
VINI
VINIB
VINQ
VINQB
CLKI
CLKIB
CLKQ
CLKQB
GNDA
VCCD = 3.3V VCCO = 2.25V
AT84AD001B
GNDD
GNDO
DOIRI, DOIRIN DOIRQ,
DOIRQN
VtestQ
VtestI
mode dataclk ldn
AT84AD001B
D0AI0 DOAI7
D0AI0N DOAI7N
32
D0BI0
DOBI7
D0BI0N
DOBI7N
D0AQ0 DOAQ7
32
D0AQ0 DOAQ7
DOBQ0
DOQBQ7
DOBQ0N
DOQBQ7N
4
DOIRI, DOIRIN
DOIRQ, DOIRQN
4
CLOCKOI, CLOCKOIB
CLOCKOQ, CLOCKOQB
2
VtestI
VtestQ
Vdiode
Differential output IN range
data I and Q
Test voltage output for ADC Q
(to be left open)
Test voltage output for ADC I
(to be left open)
<D0AQ0:DOAQ7>
<D0AQ0N:DOAQ7N>
<D0BQ0:DOBQ7>
<D0BQ0N:DOBQ7N>
2153C–BDC–04/04
Differential output data port
channel Q
Vdiode
Cal
Output bit status internal
calibration
Test diode voltage for Tj
measurement
19
Page 20

Digital Output Coding (Nominal Settings)
Table 9. Digital Output Coding (Nominal Setting)
Differential
Analog Input
Volt a g e Leve l
Digital Output
I or Q (Binary Coding)
Out-of-range Bit
> 250 mV > Positive full-scale + 1/2 LSB 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
250 mV
248 mV
1 mV
-1 mV
-248 mV
-250 mV
Positive full-scale + 1/2 LSB
Positive full-scale - 1/2 LSB
Bipolar zero + 1/2 LSB
Bipolar zero - 1/2 LSB
Negative full-scale + 1/2 LSB
Negative full-scale - 1/2 LSB
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0
1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
< -250 mV < Negative full-scale - 1/2 LSB 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1
Pin Description
Table 10. AT84AD001B LQFP 144 Pin Description
Symbol Pin number Function
GNDA, GNDD, GNDO
V
CCA
V
CCD
V
CCO
V
INI
V
INIB
V
INQ
10, 12, 22, 24, 36, 38, 40, 42, 44, 46, 51,
54, 59, 61, 63, 65, 67, 69, 85, 87, 97, 99,
109, 111, 130, 142, 144
41, 43, 45, 60, 62, 64 Analog positive supply: 3.3V typical
9, 21, 37, 39, 66, 68, 88, 100, 112, 123,
141
11, 23, 86, 98, 110, 143
57, 58
55, 56
47, 48
Ground pins. To be connected to external
ground plane
3.3V digital supply
2.25V output and 3-wire serial interface
supply
In-phase (+) analog input signal of the
sample & hold differential preamplifier
channel I
Inverted phase (-) of analog input signal
)
(V
INI
In-phase (+) analog input signal of the
sample & hold differential preamplifier
channel Q
0
0
0
0
0
0
V
INQB
49, 50
Inverted phase (-) of analog input signal
(V
)
INQ
CLKI 124 In-phase (+) clock input signal
CLKIN 125
Inverted phase (-) clock input signal
(CLKI)
CLKQ 129 In-phase (+) clock input signal
20
AT84AD001B
2153C–BDC–04/04
Page 21

AT84AD001B
Table 10. AT84AD001B LQFP 144 Pin Description (Continued)
Symbol Pin number Function
CLKQN 128
DDRB 126 Synchronous data ready reset I and Q
DDRBN 127 Inverted phase (-) of input signal (DDRB)
Inverted phase (-) clock input signal
(CLKQ)
DOAI0, DOAI1, DOAI2, DOAI3, DOAI4,
DOAI5, DOAI6, DOAI7
DOAI0N, DOAI1N, DOAI2N, DOAI3N,
DOAI4N, DOAI5N, DOAI6N, DOAI7N,
DOBI0, DOBI1, DOBI2, DOBI3, DOBI4,
DOBI5, DOBI6, DOBI7
DOBI0N, DOBI1N, DOBI2N, DOBI3N,
DOBI4N, DOBI5N, DOBI6N, DOBI7N
DOAQ0, DOAQ1, DOAQ2, DOAQ3,
DOAQ4, DOAQ5, DOAQ6, DOAQ7
DOAQ0N, DOAQ1N, DOAQ2N, DOAQ3N,
DOAQ4N, DOAQ5N, DOAQ6N, DOAQ7N
DOBQ0, DOBQ1, DOBQ2, DOBQ3,
DOBQ4, DOBQ5, DOBQ6, DOBQ7
DOBQ0N, DOBQ1N, DOBQ2N,
DOBQ3N, DOBQ4N, DOBQ5N,
DOBQ6N, DOBQ7N
117, 113, 105, 101, 93, 89, 81, 77
118, 114, 106, 102, 94, 90, 82, 78
119, 115, 107, 103, 95, 91, 83, 79
120, 116, 108, 104, 96, 92, 84, 80
136, 140, 4, 8, 16, 20, 28, 32
135, 139, 3, 7, 15, 19, 27, 31
134, 138, 2, 6, 14, 18, 26, 30
133, 137, 1 ,5, 13, 17, 25, 29
In-phase (+) digital outputs first phase
demultiplexer (channel I) DOAI0 is the
LSB. D0AI7 is the MSB
Inverted phase (-) digital outputs first
phase demultiplexer (channel I) DOAI0N
is the LSB. D0AI7N is the MSB
In-phase (+) digital outputs second phase
demultiplexer (channel I) DOBI0 is the
LSB. D0BI7 is the MSB
Inverted phase (-) digital outputs second
phase demultiplexer (channel I) DOBI0N
is the LSB. D0BI7N is the MSB
In-phase (+) digital outputs first phase
demultiplexer (channel Q) DOAI0 is the
LSB. D0AQ7 is the MSB
Inverted phase (-) digital outputs first
phase demultiplexer (channel Q) DOAI0N
is the LSB. D0AQ7N is the MSB
In-phase (+) digital outputs second phase
demultiplexer (channel Q) DOBQ0 is the
LSB. D0BQ7 is the MSB
Inverted phase (-) digital outputs second
phase demultiplexer (channel Q)
DOBQ0N is the LSB. D0BQ7N is the MSB
In-phase (+) out-of-range bit input
DOIRI 75
DOIRIN 76 Inverted phase of output signal DOIRI
DOIRQ 34
DOIRQN 33 Inverted phase of output signal DOIRQ
MODE 74
CLK 73 Input clock for 3-wire bus interface
DATA 72 Input data for 3-wire bus
LND 71
CLKOI 121 Output clock in-phase (+) channel I
2153C–BDC–04/04
(I phase) combined demultiplexer
out-of-range is high on the leading edge of
code 0 and code 256
In-phase (+) out-of-range bit input
(Q phase) combined demultiplexer
out-of-range is high on the leading edge of
code 0 and code 256
Bit selection for 3-wire bus interface or
nominal setting
Beginning and end of register line for
3- wire bus interface
21
Page 22

Table 10. AT84AD001B LQFP 144 Pin Description (Continued)
Symbol Pin number Function
CLKOIN 122 Inverted phase (-) output clock channel I
CLKOQ 132
CLKOQN 131 Inverted phase (-) output clock channel Q
VtestQ, VtestI 52, 53 Pins for internal test (to be left open)
Cal 70 Calibration output bit status
Vdiode 35
Figure 14. AT84AD001B Pinout (Top View)
Output clock in-phase (+) channel Q,
1/2 input clock frequency
Positive node of diode used for die
junction temperature measurements
LQFP 144
20 by 20 by 1.4 mm
Atmel - Dual 8-bit
22
AT84AD001B
2153C–BDC–04/04
Page 23

Typical Characterization Results
Nominal conditions (unless otherwise specified):
•V
•V
• LVDS digital outputs (100Ω)
• TA (typical) = 25° C
• Full temperature range: 0
= 3.3V; V
CCA
- V
INI
INB
< TA < 85° C (industrial grade)
or V
= 3.3V; V
CCD
to V
INQ
AT84AD001B
= 2.25V
CCO
= 500 mVpp full-scale differential input
INQB
°C < TA < 70°C (commercial grade) or -40°C
Typical Full Power Input Bandwidth
• Fs = 500 Msps
• Pclock = 0 dBm
•Pin = -1 dBFS
• Gain flatness (±0.5 dB) from DC to > 500 MHz
• Full power input bandwidth at -3 dB > 1.5 GHz
Figure 15. Full Power Input Bandwidth
0
-1
-2
-3
-4
-5
dBFS
-6
-7
-8
-9
-10
-11
100 300 500 700 900 1100 1300 1500 1700 1900 2100 2300 2500 2700 2900
Fin (MHz)
-3 dB Bandwidth
2153C–BDC–04/04
23
Page 24

Typical Crosstalk Figure 16. Crosstalk (Fs = 500 Msps)
80
70
60
50
40
dBc
30
20
10
0
0 100 200 300 400 500 600 700 800 900 1000
Note: Measured on the AT84AD001TD-EB Evaluation Board.
Fin (MHz)
Typical DC, INL and DNL Patterns
1:2 DMUX mode, Fs/4 DR type
Figure 17. Typical INL (Fs = 50 Msps, Fin = 1 MHz, Saturated Input)
0,6
0,4
0,2
0
INL (Lsb )
-0,2
-0,4
-0,6
1 16 31 46 61 76 91 106 121 136 151 166 181 196 211 226 241 256
Codes
24
AT84AD001B
2153C–BDC–04/04
Page 25

Figure 18. Typical DNL (Fs = 50 Msps, Fin = 1 MHz, Saturated Input)
0,3
0,2
0,1
0
DNL (Lsb)
-0,1
-0,2
-0,3
1 16 31 46 61 76 91 106 121 136 151 166 181 196 211 226 241 256
Typical Step Response Figure 19. Step Response
250
200
AT84AD001B
Codes
150
Codes
100
50
0
2.4E-12 1.3E-09 2.5E-09 3.8E-09 5.0E-09 6.3E-09 7.5E-09 8.8E-09
• Fs = 1 Gsps
• Pclock = 0 dBm
• Fin = 100 MHz
•Pin = -1 dBFS
Channel IA Channel QA
Time (s)
2153C–BDC–04/04
25
Page 26

Figure 20. Step Response (Zoom)
250
200
150
Codes
100
50
0
4.9E-09 6.1E-09 7.4E-09
• Fs = 1 Gsps
• Pclock = 0 dBm
• Fin = 500 MHz
•Pin = -1 dBFS
Figure 21. Step Response
250
200
90%
Tr = 160 ps
10%
Channel IA Channel QA
Time (s)
150
Codes
100
50
0
4.9E-13 2.5E-10 5.0E-10 7.5E-10 1.0E-09 1.3E-09 1.5E-09 1.8E-09
Channel IA Channel QA
Time (s)
26
AT84AD001B
2153C–BDC–04/04
Page 27

Figure 22. Step Response (Zoom)
)
250
AT84AD001B
Typical Dynamic Performances Versus Sampling Frequency
200
150
odes
100
50
9.8E-10
10%
0
1.2E-09 1.5E-09
Channel IA Channel QA
90%
Tr = 170 ps
ime (s
Figure 23. ENOB Versus Sampling Frequency in Nyquist Conditions (Fin = Fs/2)
7.6
7.4
7.2
7.0
6.8
ENOB (Bit)
6.6
6.4
6.2
6.0
100 200 300 400 500 600 700 800 900 1000 1100
Fs (Msps)
Figure 24. SFDR Versus Sampling Frequency in Nyquist Conditions (Fin = Fs/2)
-50
-53
-56
-59
SFDR (dBc)
-62
-65
100 300 500 700 900 1100
Fs (Msps)
2153C–BDC–04/04
27
Page 28

Figure 25. THD Versus Sampling Frequency in Nyquist Conditions (Fin = Fs/2)
-48
-50
-52
-54
THD (dBc)
-56
-58
-60
100 300 500 700 900 1100
Fs (Msps)
Figure 26. SNR Versus Sampling Frequency in Nyquist Conditions (Fin = Fs/2)
45
44
Typical Dynamic Performances Versus Input Frequency
43
SNR (dBc)
42
41
40
100 300 500 700 900 1100
Fs (Msps)
Figure 27. ENOB Versus Input Frequency (Fs = 1 Gsps)
8.0
7.5
7.0
6.5
ENOB (Bit)
6.0
5.5
28
5.0
0 200 400 600 800 1000
Fin (MHz)
AT84AD001B
2153C–BDC–04/04
Page 29

Figure 28. SFDR Versus Input Frequency (Fs = 1 Gsps)
-35
-40
-45
-50
SFDR (dBc)
-55
-60
-65
0 200 400 600 800 1000
Fin (MHz)
Figure 29. THD Versus Input Frequency (Fs = 1 Gsps)
-35
AT84AD001B
-40
-45
-50
THD (dBc)
-55
-60
-65
0 200 400 600 800 1000
Fin (MHz)
Figure 30. SNR Versus Input Frequency (Fs = 1 Gsps)
50
48
46
44
42
40
SNR (dBc)
38
36
34
32
30
0 200 400 600 800 1000
Fin (MHz)
2153C–BDC–04/04
29
Page 30

Typical Reconstructed
0
50
100
150
200
250
1 513 1025 1537 2049 2561 3073 3585
Signals and Signal
Spectrum
Figure 31. Fs = 1 Gsps and Fin = 20 MHz (1:2 DMUX, Fs/2 DR Type, FiSDA = -15 ps, ISA = -50 ps)
250
200
150
Codes
100
50
0
1 513 1025 1537 2049 2561 3073 3585
Samples
Ch IA
Ch QA
20
0
-20
-40
dBc
-60
-80
-100
-120
0 31 62 93 125 156 187 218 249
F (Msps)
Figure 32. Fs = 1 Gsps and Fin = 500 MHz (1:2 DMUX, Fs/2 DR Type, FiSDA = -15 ps, ISA = -50 ps)
20
0
-20
-40
Codes
Ch IA
Ch QA
Samples
dBc
-60
-80
-100
-120
0 31 62 93 125 156 187 218 249
F (Msps)
Ch IA
Ch QA
Ch IA
Ch QA
Figure 33. Fs = 1 Gsps and Fin = 1 GHz (1:2 DMUX, Fs/2 DR Type, FiSDA = -15 ps, ISA = -50 ps)
250
200
150
Codes
100
50
0
1 513 1025 1537 2049 2561 3073 3585
Samples
Ch IA
Ch QA
Note: The spectra are given with respect to the output clock frequency observed by the acquisition system (Figures 31 to 33).
30
AT84AD001B
20
0
-20
-40
dBc
-60
-80
-100
-120
0 31 62 93 125 156 187 218 249
F (Msps)
Ch IA
Ch QA
Fout/2
2153C–BDC–04/04
Page 31

AT84AD001B
Figure 34. Fs = 1 Gsps and Fin = 20 MHz (Interleaving Mode Fint = 2 Gsps, Fs/4 DR Type, FiSDA = -15 ps, ISA = -50 ps)
250
200
150
Codes
100
50
0
1 2048 4095 6142 8189 10236 12283 14330 16377
Samples
20
0
-20
-40
dBc
-60
-80
-100
-120
0 125 250 375 500 624 749 874 999
Fs (MHz)
Fs/2
Figure 35. Fs = 1 Gsps and Fin = 250 MHz (Interleaving Mode Fint = 2 Gsps, Fs/4 DR Type, FiSDA = -15 ps, ISA = -50 ps)
250
200
150
Codes
100
50
0
1 2048 4095 6142 8189 10236 12283 14330 16377
Samples
20
0
-20
-40
dBc
-60
-80
-100
-120
0 125 250 375 500 624 749 874 999
Fs (MHz)
Fs/2
2153C–BDC–04/04
31
Page 32

Typical Performance Sensitivity Versus Power Supplies and Temperature
Figure 36. ENOB Versus V
Fs/4 DR Type, ISA = -50 ps)
7.4
7.2
7.0
6.8
ENOB (Bit)
6.6
6.4
6.2
6.0
3.1 3.15 3.2 3.25 3.3 3.35 3.4 3.45 3.5
CCA
= V
(Fs = 1 Gsps, Fin = 500 MHz, 1:2 DMUX,
CCD
Vcca = Vccd (V)
Figure 37. SFDR Versus V
Fs/4 DR Type, ISA = -50 ps)
-40
-45
-50
SFDR (dBc)
-55
-60
3.1 3.15 3.2 3.25 3.3 3.35 3.4 3.45 3.5
CCA
= V
(Fs = 1 Gsps, Fin = 500 MHz, 1:2 DMUX,
CCD
Vcca = Vccd (V)
32
AT84AD001B
2153C–BDC–04/04
Page 33

AT84AD001B
Figure 38. THD Versus V
Fs/4 DR Type, ISA = -50 ps)
-40
-45
-50
THD (dBc)
-55
-60
3.1 3.15 3.2 3.25 3.3 3.35 3.4 3.45 3.5
Figure 39. SNR Versus V
Fs/4 DR Type, ISA = -50 ps)
45.0
CCA
CCA
= V
= V
(Fs = 1 Gsps, Fin = 500 MHz, 1:2 DMUX,
CCD
Vcca = Vccd (V)
(Fs = 1 Gsps, Fin = 500 MHz, 1:2 DMUX,
CCD
44.0
43.0
SNR (dBc)
42.0
41.0
40.0
3.1 3.15 3.2 3.25 3.3 3.35 3.4 3.45 3.5
Vcca = Vccd (V)
2153C–BDC–04/04
33
Page 34

Figure 40. ENOB Versus Junction Temperature (Fs = 1 Gsps, 1:2 DMUX, Fs/4 DR
Type, ISA = -50 ps)
8.0
7.5
7.0
6.5
ENOB (Bit)
6.0
5.5
5.0
-50 -25 0 25 50 75 100
Tj (˚C)
1 Gsps 20 MHz
1 Gsps 502 MHz
1 Gsps 998 MHz
Figure 41. SFDR Versus Junction Temperature (Fs = 1 Gsps, 1:2 DMUX, Fs/4 DR
Type, ISA = -50 ps)
-35
1 Gsps 998 MHz
-40
-45
-50
SFDR (dBc)
-55
1 Gsps 502 MHz
1 Gsps 20 MHz
34
-60
-65
-50 -25 0 25 50 75 100
Tj (˚C)
AT84AD001B
2153C–BDC–04/04
Page 35

AT84AD001B
Figure 42. THD Versus Junction Temperature (Fs = 1 Gsps, 1:2 DMUX, Fs/4 DR
Type, ISA = -50 ps)
-35
1 Gsps 998 MHz
-40
-45
THD (dBc)
-50
-55
-60
-50 -25 0 25 50 75 100
Tj (˚C)
1 Gsps 502 MHz
1 Gsps 20 MHz
Figure 43. SNR Versus Junction Temperature (Fs = 1 Gsps, 1:2 DMUX, Fs/4 DR
Type, ISA = -50 ps)
45.0
44.0
43.0
SNR (dBc)
42.0
41.0
1 Gsps 20 MHz
1 Gsps 502 MHz
2153C–BDC–04/04
40.0
1 Gsps 998 MHz
-50 -25 0 25 50 75 100
Tj (˚C)
35
Page 36

Test and Control Features
3-wire Serial Interface Control Setting
Table 11. 3-wire Serial Interface Control Settings
Mode Characteristics
Mode = 1 (2.25V) 3-wire serial bus interface activated
3-wire serial bus interface deactivated
Nominal setting:
Dual channel I and Q activated
One clock I
0 dB gain
DMUX mode 1:1
Mode = 0 (0V)
DRDA I & Q = 0 ps
ISA I & Q = 0 ps
FiSDA Q = 0 ps
Binary output
Decimation test mode OFF
Calibration setting OFF
Data Ready = Fs /2
36
AT84AD001B
2153C–BDC–04/04
Page 37

AT84AD001B
3-wire Serial Interface and Data Description
The 3-wire bus is activated with the control bit mode set to 1. The length of the word is
19 bits: 16 for the data and 3 for the address. The maximum clock frequency is
50 MHz.
Table 12. 3-wire Serial Interface Address Setting Description
Address Setting
Standby
Gray/binary mode
1:1 or 1:2 DMUX mode
000
001
010
011
100
Analog input MUX
Clock selection
Auto-calibration
Decimation test mode
Data Ready Delay Adjust
Analog gain adjustment
Data7 to Data0: gain channel I
Data15 to Data8: gain channel Q
Code 00000000: -1.5 dB
Code 10000000: 0 dB
Code 11111111: 1.5 dB
Steps: 0.011 dB
Offset compensation
Data7 to Data0: offset channel I
Data15 to Data8: offset channel Q
Data7 and Data15: sign bits
Code 11111111b: 31.75 LSB
Code 10000000b: 0 LSB
Code 00000000b: 0 LSB
Code 01111111b: -31.75 LSB
Steps: 0.25 LSB
Maximum correction: ±31.75 LSB
Gain compensation
Data6 to Data0: channel I/Q (Q is matched to I)
Code 11111111b: -0.315 dB
Code 10000000b: 0 dB
Code 0000000b: 0 dB
Code 0111111b: 0.315 dB
Steps: 0.005 dB
Data6: sign bit
Internal Settling Adjustment (ISA)
Data2 to Data0: channel I
Data5 to Data3: channel Q
Data15 to Data6: 1000010000
2153C–BDC–04/04
37
Page 38

Table 12. 3-wire Serial Interface Address Setting Description (Continued)
Address Setting
Testability
Data3 to Data0 = 0000
101
110
111
Mode S/H transparent OFF: Data4 = 0 ON: Data4 = 1
Data7 = 0
Data8 = 0
Built-In Test (BIT)
Data0 = 0 BIT Inactive Data0 = 1 BIT Active
Data1 = 0 Static BIT Data1 = 1 Dynamic BIT
If Data1 = 1, then Ports BI & BQ = Rising Ramp
Ports AI & AQ = Decreasing Ramp
If Data1 = 0, then Data2 to Data9 = Static Data for BIT
Ports BI & BQ = Data2 to Data9
Ports AI & AQ = NOT (Data2 to Data9)
Data Ready Delay Adjust (DRDA)
Data2 to Data0: clock I
Data5 to Data3: clock Q
Steps: 140 ps
000: -560 ps
100: 0 ps
111: 420 ps
Fine Sampling Delay Adjustment (FiSDA) on channel Q
Data10 to Data6: channel Q
Steps: 5 ps
Data4: sign bit
Code 11111: -75 ps
Code 10000: 0 ps
Code 00000: 0 ps
Code 01111: 75 ps
Notes: 1. The Internal Settling Adjustment could change independently of the two analog sampling times (TA channels I and Q) of the
sample/hold (with a fixed digital sampling time) with steps of ±50 ps:
Nominal mode will be given by Data2…Data0 = 100 or Data5…Data3 = 100.
Data5…Data3 = 000 or Data2…Data0 = 000: sampling time is -200 ps compared to nominal.
Data2…Data0 = 111 or Data5…Data3 = 111: sampling time is 150 ps compared to nominal.
We recommend setting the ISA to -50 ps to optimize the ADC’s dynamic performances.
2. The Fine Sampling Delay Adjustment enables you to change the sampling time (steps of ±5 ps) on channel Q more precisely, particularly in the interleaved mode.
3. A Built-In Test (BIT) function is available to rapidly test the device’s I/O by either applying a defined static pattern to the dual
ADC or by generating a dynamic ramp at the output of the dual ADC. This function is controlled via the 3-wire bus interface
at the address 110. The maximum clock frequency in dynamic BIT mode is 750 Msps.
Please refer to “Built-In Test (BIT)” on page 43 for more information about this function.
4. The decimation mode enables you to lower the output bit rate (including the output clock rate) by a factor of 16, while the
internal clock frequency remains unchanged. The maximum clock frequency in decimation mode is 750 Msps.
5. The “S/H transparent” mode (address 101, Data4) enables bypassing of the ADC’s track/hold. This function optimizes the
ADC’s performances at very low input frequencies (Fin < 50 MHz).
6. In the Gray mode, when the input signal is overflow (that is, the differential analog input is greater than 250 mV), the output
data must be corrected using the output DOIR:
If DOIR = 1: Data7 unchanged
Data6 = 0, Data5 = 0, Data4 = 0, Data3 = 0, Data2 = 0, Data1 = 0, Data0 = 0.
In 1:2 DMUX mode, only one out-of-range bit is provided for both A and B ports.
38
AT84AD001B
2153C–BDC–04/04
Page 39

Table 13. 3-wire Serial Interface Data Setting Description
AT84AD001B
Setting for Address:
000 D15 D14 D13 D12 D11 D10 D9
Full standby mode XXXXXX 0 XXXXXXX11
Standby channel I
Standby channel Q
No standby mode XXXXXX 0 XXXXXXX00
Binary output mode XXXXXX 0 XXXXXX1XX
Gray output mode XXXXXX 0 XXXXXX0XX
DMUX 1:2 mode XXXXXX 0 XXXXX1XXX
DMUX 1:1 mode XXXXXX 0 XXXXX0XXX
Analog selection mode
→ ADC I
Input I
Input Q → ADC Q
Analog selection mode
Input I
→ ADC I
Input I → ADC Q
Analog selection mode
Input Q
Input Q → ADC Q
→ ADC I
(2)
(3)
XXXXXX 0 XXXXXXX01
XXXXXX 0 XXXXXXX10
XXXXXX 0 XXX11XXXX
XXXXXX 0 XXX10XXXX
XXXXXX 0 XXX0XXXXX
(1)
D8 D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
Clock Selection mode
CLKI
→ ADC I
CLKQ → ADC Q
Clock selection mode
CLKI
→ ADC I
CLKI → ADC Q
Clock selection mode
CLKI
→ ADC I
CLKIN → ADC Q
Decimation OFF modeXXXXXX 0 0XXXXXXXX
Decimation ON mode XXXXXX 0 1XXXXXXXX
Keep last calibration
calculated value
No calibration phase
No calibration phase
No calibration value
Start a new calibration
phase
(4)
(5)
XXXXXX 0 X11XXXXXX
XXXXXX 0 X10XXXXXX
XXXXXX 0 X0XXXXXXX
XXXX0 1 0 XXXXXXXXX
XXXX0 0 0 XXXXXXXXX
XXXX1 1 0 XXXXXXXXX
2153C–BDC–04/04
39
Page 40

Table 13. 3-wire Serial Interface Data Setting Description (Continued)
Setting for Address:
000 D15 D14 D13 D12 D11 D10 D9
Control wait bit
calibration
In 1:2 DMUX
FDataReady
I & Q = Fs/2
In 1:2 DMUX
FDataReady
I & Q = Fs/4
Notes: 1. D9 must be set to “0”
(6)
2. Mode standby channel I: use analog input I Vini, Vinib and Clocki.
3. Mode standby channel Q: use analog input Q Vinq, Vinqb and Clockq.
4. Keep last calibration calculated value - no calibration phase: D11 = 0 and D10 = 1. No new calibration is required. The values taken into account for the gain and offset are either from the last calibration phase or are default values (reset values).
5. No calibration phase - no calibration value: D11 = 0 and D10 = 0. No new calibration phase is required. The gain and offset
compensation functions can be accessed externally by writing in the registers at address 010 for the offset compensation
and at address 011 for the gain compensation.
6. The control wait bit gives the possibility to change the internal setting for the auto-calibration phase:
For high clock rates (> 500 Msps) use a = b = 1.
For clock rates > 250 Msps and < 500 Msps use a = 1 and b = 0.
For clock rates > 125 Msps and < 250 Msps use a = 0 and b = 1.
For low clock rates < 125 Msps use a = 0 and b = 0.
X X a b X X 0 XXXXXXXXX
X 0 X X X X 0 XXXXXXXXX
X 1 X X X X 0 XXXXXXXXX
(1)
D8 D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
3-wire Serial Interface Timing Description
The 3-wire serial interface is a synchronous write-only serial interface made of three
wires:
• sclk: serial clock input
• sldn: serial load enable input
• sdata: serial data input
The 3-wire serial interface gives write-only access to as many as 8 different internal registers of up to 16 bits each. The input format is always fixed with 3 bits of register
address followed by 16 bits of data. The data and address are entered with the Most
Significant Bit (MSB) first.
The write procedure is fully synchronous with the rising clock edge of “sclk” and
described in the write chronogram (Figure 44 on page 41).
• “sldn” and “sdata” are sampled on each rising clock edge of “sclk” (clock cycle).
• “sldn” must be set to 1 when no write procedure is performed.
• A minimum of one rising clock edge (clock cycle) with “sldn” at 1 is required for a
correct start of the write procedure.
• A write starts on the first clock cycle with “sldn” at 0. “sldn” must stay at 0 during the
complete write procedure.
• During the first 3 clock cycles with “sldn” at 0, 3 bits of the register address from
MSB (a[2]) to LSB (a[0]) are entered.
• During the next 16 clock cycles with “sldn” at 0, 16 bits of data from MSB (d[15]) to
LSB (d[0]) are entered.
• An additional clock cycle with “sldn” at 0 is required for parallel transfer of the serial
data d[15:0] into the addressed register with address a[2:0]. This yields 20 clock
cycles with “sldn” at 0 for a normal write procedure.
40
AT84AD001B
2153C–BDC–04/04
Page 41

Figure 44. Write Chronogram
AT84AD001B
• A minimum of one clock cycle with “sldn” returned at 1 is requested to close the
write procedure and make the interface ready for a new write procedure. Any clock
cycle where “sldn” is at 1 before the write procedure is completed interrupts this
procedure and no further data transfer to the internal registers is performed.
• Additional clock cycles with “sldn” at 0 after the parallel data transfer to the register
(done at the 20th consecutive clock cycle with “sldn” at 0) do not affect the write
procedure and are ignored.
It is possible to have only one clock cycle with “sldn” at 1 between two following write
procedures.
• 16 bits of data must always be entered even if the internal addressed register has
less than 16 bits. Unused bits (usually MSBs) are ignored. Bit signification and bit
positions for the internal registers are detailed in Table 12 on page 37.
To reset the registers, the Pin mode can be used as a reset pin for chip initialization,
even when the 3-wire serial interface is used.
Mode
sclk
sldn
sdata
Internal register
value
Reset setting
Reset
12 345 1314151617181920
a[2] a[1]
a[0] d[15]
d[8]
d[7]
d[6]
d[5]
d[4]
d[3]
d[2]
d[1]
d[0]
New d
Write procedure
Figure 45. Timing Definition
Mode
sclk
sldn
Twlmode
Tdmode
Tssldn
Thsldn
Tsclk
Twsclk
Tdmode
2153C–BDC–04/04
sdata
Tssdata
Thsdata
41
Page 42

Table 14. Timing Description
Name Parameter
Tsclk Sclk period 20 ns
Twsclk High or low time of sclk 5 ns
Tssldn Setup time of sldn before rising edge of sclk 4 ns
Thsldn Hold time of sldn after rising edge of sclk 2 ns
Tssdata Setup time of sdata before rising edge of sclk 4 ns
Thsdata Hold time of sdata after rising edge of sclk 2 ns
Twlmode Minimum low pulse width of mode 5 ns
Tdmode
Minimum delay between an edge of mode and the
rising edge of sclk
Min Typ Max
10 ns
Val ue
Unit
Calibration Description The AT84AD001B offers the possibility of reducing offset and gain matching between
the two ADC cores. An internal digital calibration may start right after the 3-wire serial
interface has been loaded (using data D12 of the 3-wire serial interface with address
000).
The beginning of calibration disables the two ADCs and a standard data acquisition is
performed. The output bit CAL goes to a high level during the entire calibration phase.
When this bit returns to a low level, the two ADCs are calibrated with offset and gain and
can be used again for a standard data acquisition.
If only one channel is selected (I or Q) the offset calibration duration is divided by two
and no gain calibration between the two channels is necessary.
Figure 46. Internal Timing Calibration
3-wire Serial Interface
LDN
CAL
Tcal
The Tcal duration is a multiple of the clock frequency ClockI (master clock). Even if a
dual clock scheme is used during calibration, ClockQ will not be used.
The control wait bits (D13 and D14) give the possibility of changing the calibration’s setting depending on the clock’s frequency:
• For high clock rates (> 500 Msps) use a = b = 1, Tcal = 10112 clock I periods.
• For clock rates > 250 Msps and < 500 Msps use a = 1, b = 0, Tcal = 6016 clock I
periods.
• For clock rates > 125 Msps and < 250 Msps use a = 0, b = 1 ,Tcal = 3968 clock I
periods.
• For low clock rates (< 125 Msps) use a = 0, b = 0 , Tcal = 2944 clock I periods.
42
AT84AD001B
2153C–BDC–04/04
Page 43

The calibration phase is necessary when using the AT84AD001B in interlace mode,
where one analog input is sampled at both ADC cores on the common input clock’s ris
ing and falling edges. This operation is equivalent to converting the analog signal at
twice the clock frequency
Table 15. Matching Between Channels
AT84AD001B
-
Parameter
Gain error (single channel I or Q) without calibration 0 LSB
Gain error (single channel I or Q) with calibration -0.5 0 0.5 LSB
Offset error (single channel I or Q) without calibration 0 LSB
Offset error (single channel I or Q) with calibration -0.5 0 0.5 LSB
Mean offset code without calibration (single channel I or Q) 127.5
Mean offset code with calibration (single channel I or Q) 127 127.5 128
Val ue
During the ADC’s auto-calibration phase, the dual ADC is set with the following:
• Decimation mode ON
• 1:1 DMUX mode
• Binary mode
Any external action applied to any signal of the ADC’s registers is inhibited during the
calibration phase.
Gain and Offset Compensation Functions
It is also possible for the user to have external access to the ADC’s gain and offset compensation functions:
• Offset compensation between I and Q channels (at address 010)
• Gain compensation between I and Q channels (at address 011)
UnitMin Typ Max
To obtain manual access to these two functions, which are used to set the offset to middle code 127.5 and to match the gain of channel Q with that of channel I (if only one
channel is used, the gain compensation does not apply), it is necessary to set the ADC
to “manual” mode by writing 0 at bits D11 and D10 of address 000.
Built-In Test (BIT) A Built-In Test (BIT) function is available to allow rapid testing of the device’s I/O by
either applying a defined static pattern to the ADC or by generating a dynamic ramp at
the ADC’s output. The dynamic ramp can be used with a clock frequency of up to
750 Msps. This function is controlled via the 3-wire bus interface at address 101.
• The BIT is active when Data0 = 1 at address 110.
• The BIT is inactive when Data0 = 0 at address 110.
• The Data1 bit allows choosing between static mode (Data1 = 0) and dynamic mode
(Data1 = 1).
When the static BIT is selected (Data1 = 0), it is possible to write any 8-bit pattern by
defining the Data9 to Data2 bits. Port B then outputs an 8-bit pattern equal to Data9 ...
Data2, and Port A outputs an 8-bit pattern equal to NOT (Data9 ... Data2).
43
2153C–BDC–04/04
Page 44

Example:
Address = 110
Data =
D15 D14 D13 D12 D11 D10 D9 D8 D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
XXXXXX0101010101
One should then obtain 01010101 on Port B and 10101010 on Port A.
When the dynamic mode is chosen (Data1 = 1) port B outputs a rising ramp while Port A
outputs a decreasing one.
Note: In dynamic mode, use the DRDA function to align the edges of CLKO with the middle of
the data.
Decimation Mode The decimation mode is provided to enable rapid testing of the ADC at a maximum clock
frequency of 750 Msps. In decimation mode, one data out of 16 is output, thus leading to
a maximum output rate of 46.875 Msps.
Note: Frequency (CLKO) = frequency (Data) = Frequency (CLKI)/16.
Die Junction Temperature Monitoring Function
A die junction temperature measurement setting is included on the board for junction
temperature monitoring.
The measurement method forces a 1 mA current into a diode-mounted transistor.
Caution should be given to respecting the polarity of the current.
In any case, one should make sure the maximum voltage compliance of the current
source is limited to a maximum of 1V or use a resistor serial-mounted with the current
source to avoid damaging the transistor device (this may occur if the current source is
reverse-connected).
The measurement setup is illustrated in Figure 47.
Figure 47. Die Junction Temperature Monitoring Setup
VDiode (Pin 35)
1 mA
GNDD
(Pin 36)
Protection
Diodes
44
AT84AD001B
2153C–BDC–04/04
Page 45

AT84AD001B
The VBE diode’s forward voltage in relation to the junction temperature (in steady-state
conditions) is shown in Figure 48.
Figure 48. Diode Characteristics Versus T
860
840
820
800
780
760
740
720
Diode Voltage (mV)
700
680
660
640
620
-20-100 102030405060708090100110120
J
Junction Temperature (˚C)
VtestI, VtestQ VtestI and VtestQ pins are for internal test use only. These two signals must be left
open.
Equivalent Input/Output Schematics
Figure 49. Simplified Input Clock Model
CLK
CLKB
VCCD/2
50Ω
50Ω
VCCD
GNDD
100Ω
100Ω
2153C–BDC–04/04
45
Page 46

Figure 50. Simplified Data Ready Reset Buffer Model
VCCD
DDRB
100Ω
VCCD/2
50Ω
Figure 51. Analog Input Model
DC Coupling
(Common Mode = Ground = 0V)
50Ω
GND
VinI
50Ω
DDRBN
Vinl Reverse
Termination
VinI Double Pad
VinQ Reverse
Termination
ESD
ESD
Vcca
GND
50Ω
Sel Input I
GND – 0.4V
MAX
GNDD
100Ω
Vcca
GND
46
GND
VinQ
AT84AD001B
VinQ
Double
Pad
Sel Input Q
2153C–BDC–04/04
Page 47

Figure 52. Data Output Buffer Model
VCCO
GNDO
AT84AD001B
DOAIO, DOAI7
DOBIO, DOBI7
DOAION, DOAI7N
DOBION, DOBI7N
Definitions of Terms
Table 16. Definitions of Terms
Abbreviation Definition Description
BER Bit Error Rate
DNL
ENOB
FPBW
IMD
INL
JITTER
NPR Noise Power Ratio
Differential
Non-Linearity
Effective Number of
Bits
Full Power Input
Bandwidth
Inter-Modulation
Distortion
Integral
Non-Linearity
Aperture
uncertainty
The probability to exceed a specified error threshold for a sample at a maximum specified
sampling rate. An error code is a code that differs by more than ±4 LSB from the correct code
The differential non-linearity for an output code i is the difference between the measured step
size of code i and the ideal LSB step size. DNL (i) is expressed in LSBs. DNL is the
maximum value of all DNL (i). A DNL error specification of less than 1 LSB guarantees that
there are no missing output codes and that the transfer function is monotonic
ENOB
The analog input frequency at which the fundamental component in the digitally
reconstructed output waveform has fallen by 3 dB with respect to its low frequency value
(determined by FFT analysis) for input at full-scale -1 dB (-1 dBFS)
The two tones intermodulation distortion (IMD) rejection is the ratio of either of the two input
tones to the worst third order intermodulation products
The integral non-linearity for an output code i is the difference between the measured input
voltage at which the transition occurs and the ideal value of this transition. INL (i) is
expressed in LSBs and is the maximum value of all |INL (i)|
The sample-to-sample variation in aperture delay. The voltage error due to jitters depends on
the slew rate of the signal at the sampling point
The NPR is measured to characterize the ADC’s performance in response to broad
bandwidth signals. When applying a notch-filtered broadband white noise signal as the input
to the ADC under test, the Noise Power Ratio is defined as the ratio of the average out-ofnotch to the average in-notch power spectral density magnitudes for the FFT spectrum of the
ADC output sample test
SINAD 1.76– 20
---------------------------------------------------------------------------- -=
6.02
A
-----------
log+
Fs/2
Where A is the actual input amplitude and Fs is
the full scale range of the ADC under test
2153C–BDC–04/04
47
Page 48

Table 16. Definitions of Terms (Continued)
Abbreviation Definition Description
ORT
Overvoltage
Recovery Time
The time to recover a 0.2% accuracy at the output, after a 150% full-scale step applied on
the input is reduced to midscale
PSRR
SFDR
SINAD
SNR
SSBW
TA Aperture delay
TC
TD1
TD2
TDO
TDR
TF Fall Time
Power Supply
Rejection Ratio
Spurious Free
Dynamic Range
Signal to Noise and
Distortion Ratio
Signal to Noise
Ratio
Small Signal Input
Bandwidth
Encoding Clock
period
Time Delay from
Data Transition to
Data Ready
Time Delay from
Data Ready to
Data
Digital Data Output
Delay
Data Ready Output
Delay
The ratio of input offset variation to a change in power supply voltage
The ratio expressed in dB of the RMS signal amplitude, set at 1 dB below full-scale, to the
RMS value of the highest spectral component (peak spurious spectral component). The peak
spurious component may or may not be a harmonic. It may be reported in dB (related to the
converter -1 dB full-scale) or in dBc (related to the input signal level)
The ratio expressed in dB of the RMS signal amplitude, set to 1 dB below full-scale (-1
dBFS) to the RMS sum of all other spectral components including the harmonics, except DC
The ratio expressed in dB of the RMS signal amplitude, set to 1 dB below full-scale, to the
RMS sum of all other spectral components excluding the first 9 harmonics
The analog input frequency at which the fundamental component in the digitally
reconstructed output waveform has fallen by 3 dB with respect to its low frequency value
(determined by FFT analysis) for input at full-scale -10 dB (-10 dBFS)
The delay between the rising edge of the differential clock inputs (CLK, CLKB) [zero crossing
point] and the time at which VIN and VINB are sampled
TC1 = minimum clock pulse width (high)
TC = TC1 + TC2
TC2 = minimum clock pulse width (low)
The general expression is TD1 = TC1 + TDR - TDO with TC = TC1 + TC2 = 1 encoding clock
period
The general expression is TD2 = TC2 + TDR - TDO with TC = TC1 + TC2 = 1 encoding clock
period
The delay from the rising edge of the differential clock inputs (CLK, CLKB) [zero crossing
point] to the next point of change in the differential output data (zero crossing) with a
specified load
The delay from the falling edge of the differential clock inputs (CLK, CLKB) [zero crossing
point] to the next point of change in the differential output data (zero crossing) with a
specified load
The time delay for the output data signals to fall from 20% to 80% of delta between the low
and high levels
THD
TPD Pipeline Delay
TR Rise Time The time delay for the output data signals to rise from 20% to 80% of delta between the low
48
AT84AD001B
Total Harmonic
Distortion
The ratio expressed in dB of the RMS sum of the first 9 harmonic components to the RMS
input signal amplitude, set at 1 dB below full-scale. It may be reported in dB (related to the
converter -1 dB full-scale) or in dBc (related to the input signal level )
The number of clock cycles between the sampling edge of an input data and the associated
output data made available (not taking into account the TDO)
and high levels
2153C–BDC–04/04
Page 49

AT84AD001B
Table 16. Definitions of Terms (Continued)
Abbreviation Definition Description
TRDR Data Ready Reset
Delay
TS Settling Time The time delay to rise from 10% to 90% of the converter output when a full-scale step
The delay between the falling edge of the Data Ready output asynchronous reset signal
(DDRB) and the reset to digital zero transition of the Data Ready output signal (DR)
function is applied to the differential analog input
VSWR Voltage Standing
Wave Ratio
The VSWR corresponds to the ADC input insertion loss due to input power reflection. For
example, a VSWR of 1.2 corresponds to a 20 dB return loss (99% power transmitted and 1%
reflected)
2153C–BDC–04/04
49
Page 50

Using the AT84AD001B Dual 8-bit 1 Gsps ADC
Decoupling, Bypassing and Grounding of Power Supplies
Figure 53. V
Figure 54. V
PC Board 2.25V
and V
CCD
PC Board 3.3V
PC Board GND
Bypassing and Grounding Scheme
CCO
PC Board GND
Bypassing and Grounding Scheme
CCA
The following figures show the recommended bypassing, decoupling and grounding
schemes for the dual 8-bit 1 Gsps ADC power supplies.
L
VCCD
1µF
100 pF
L
VCCA
C
C
L
VCCO
1µF
100 pF
C
Note: L and C values must be chosen in accordance with the operation frequency of the application.
Figure 55. Power Supplies Decoupling Scheme
10 nF
VCCA
GNDA
VCCO
GNDO
100 pF
VCCO
10 nF
GNDO
VCCA
100 pF
GNDA
VCCD
100 pF 10 nF
GNDD
Note: The bypassing capacitors (1 µF and 100 pF) should be placed as close as possible to the board connectors, whereas the
decoupling capacitors (100 pF and 10 nF) should be placed as close as possible to the device.
50
AT84AD001B
2153C–BDC–04/04
Page 51

AT84AD001B
Analog Input Implementation
Figure 56. Termination Method for the ADC Analog Inputs in DC Coupling Mode
Channel I
Channel Q
The analog inputs of the dual ADC have been designed with a double pad implementation as illustrated in Figure 56. The reverse pad for each input should be tied to ground
via a 50Ω resistor.
The analog inputs must be used in differential mode only.
50Ω
50Ω Source
GND
GND
50Ω Source
GND
50Ω
50Ω
GND
50Ω
VinI
VinI
VinIB
VinIB
VinQ
VinQ
VinQB
VinQB
Dual ADC
2153C–BDC–04/04
51
Page 52

Figure 57. Termination Method for the ADC Analog Inputs in AC Coupling Mode
50Ω
50Ω Source
Channel I
GND
GND
50Ω
50Ω
50Ω Source
Channel Q
GND
GND
50Ω
VinI
VinI
VinIB
VinIB
VinQ
VinQ
VinQB
VinQB
Dual ADC
Clock Implementation The ADC features two different clocks (I or Q) that must be implemented as shown in
Figure 58. Each path must be AC coupled with a 100 nF capacitor.
Figure 58. Differential Termination Method for Clock I or Clock Q
ADC Package
100 nF
CLK
50Ω
100 nF
CLKB
Note: When only clock I is used, it is not necessary to add the capacitors on the CLKQ and
CLKQN signal paths; they may be left floating.
VCCD/2
50Ω
Differential Buffer
52
AT84AD001B
2153C–BDC–04/04
Page 53

Figure 59. Single-ended Termination Method for Clock I or Clock Q
AT84AD001B
VCCD
AC coupling capacitor
50Ω
Source
AC coupling capacitor
50Ω
Output Termination in 1:1 Ratio
R1
CLK
50Ω
50Ω
CLKB
VCCD/2
When using the integrated DMUX in 1:1 ratio, the valid port is port A. Port B remains
unused.
Port A functions in LVDS mode and the corresponding outputs (DOAI or DOAQ) have to
be 100Ω differentially terminated as shown in Figure 60 on page 54.
The pins corresponding to Port B (DOBI or DOBQ pins) must be left floating (in high
impedance state).
R2
Figure 60 shows the example of a 1:1 ratio of the integrated DMUX for channel I (the
same applies to channel Q).
2153C–BDC–04/04
53
Page 54

Figure 60. Example of Termination for Channel I Used in DMUX 1:1 Ratio (Port B Unused)
DOBI0 / DOBI0N
DOBI1 / DOBI1N
DOBI2 / DOBI2N
Port B
Port A
DOBI3 / DOBI3N
DOBI4 / DOBI4N
DOBI5 / DOBI5N
DOBI6 / DOBI6N
DOBI7 / DOBI7N
DOAI0 / DOAI0N
DOAI1 / DOAI1N
DOAI2 / DOAI2N
DOAI3 / DOAI3N
DOAI4 / DOAI4N
DOAI5 / DOAI5N
DOAI6 / DOAI6N
DOAI7 / DOAI7N
Floating (High Z)
Dual ADC Package
VCCO
DOAI0
DOAI0N
Z0 = 50Ω
Z0 = 50Ω
LVDS In
100Ω
LVDS In
Note: If the outputs are to be used in single-ended mode, it is recommended that the true and false signals be terminated with a 50Ω
resistor.
Using the Dual ADC With and ASIC/FPGA Load
54
AT84AD001B
Figure 61 on page 55 illustrates the configuration of the dual ADC (1:2 DMUX mode,
independent I and Q clocks) driving an LVDS system (ASIC/FPGA) with potential additional DMUXes used to halve the speed of the dual ADC outputs.
2153C–BDC–04/04
Page 55

Figure 61. Dual ADC and ASIC/FPGA Load Block Diagram
AT84AD001B
Data rate = FsI/2
CLKI/CLKIN @ FsI
CLKQ/CLKQN @ FsQ
Port A
Channel I
Port A
Channel Q
Dual 8-bit 1 Gsps ADC
Port B
Channel I
DEMUX
8:16
Data rate = FsQ/2
DMUX
8:16
DMUX
8:16
Data rate = FsQ/4
ASIC / FPGA
Port B
Channel Q
Note: The demultiplexers may be internal to the ASIC/FPGA system.
2153C–BDC–04/04
DMUX
8:16
55
Page 56

Thermal Characteristics
Simplified Thermal
Model for LQFP 144
The following model has been extracted from the ANSYS FEM simulations.
Assumptions: no air, no convection and no board.
20 x 20 x 1.4 mm
Figure 62. Simplified Thermal Model for LQFP Package
Silicon Junction
355 µm silicon die
25 mm
λ
40 µm Epoxy/Ag glue
λ
Copper paddle
λ
Aluminium paddle
λ
Resin bottom
λ = 0.007W/cm/
2
= 0.95W/cm/˚C
= 0. 02 W / c m/ ˚C
= 2.5W/cm/˚C
= 0. 75W /c m/ ˚C
˚C
0.6˚C/watt
1.4˚C/watt
0.1˚C/watt
Aluminium paddle Resin
0.1˚C/watt
4.3˚C/watt
6.1˚C/watt
8.3˚C/watt
Resin
λ
= 0.007W/cm/˚C
1.5˚C/watt
λ
= 0.007W/cm/˚C
Package top
5.5˚C/watt
Leads tip
Copper alloy leadframe
λ
= 25W/cm/˚C
Package
bottom
100 µm air gap λ = 0.00027W/cm/
11.4˚C/watt
˚C
Assumptions:
Die 5.0 x 5.0 = 25 mm
2
40 µm thick Epoxy/Ag glue
Package bottom
connected to:
(user dependent)
100 µm thermal grease gap diamater 12 mm
λ = 0.01W/cm/
˚C
Top of user board
1.5˚C/watt
Note: The above are typical values with an assumption of uniform power dissipation over 2.5 x 2.5 mm2 of the top surface of the die.
Thermal Resistance from Junction to Bottom of Leads
Thermal Resistance from Junction to Top of Case
Thermal Resistance from Junction to Bottom of Case
Thermal Resistance from Junction to Bottom of Air Gap
Assumptions: no air, no convection and no board.
The thermal resistance from the junction to the bottom of the leads is 15.2°C/W typical.
Assumptions: no air, no convection and no board.
The thermal resistance from the junction to the top of the case is 8.3° C/W typical.
Assumptions: no air, no convection and no board.
The thermal resistance from the junction to the bottom of the case is 6.4° C/W typical.
The thermal resistance from the junction to the bottom of the air gap (bottom of package) is 17.9° C/W typical.
56
AT84AD001B
2153C–BDC–04/04
Page 57

AT84AD001B
Thermal Resistance from Junction to Ambient
Thermal Resistance from Junction to Board
The thermal resistance from the junction to ambient is 25.2° C/W typical.
Note: In order to keep the ambient temperature of the die within the specified limits of the
device grade (that is TA max = 70°C in commercial grade and 85°C in industrial grade)
and the die junction temperature below the maximum allowed junction temperature of
105°C, it is necessary to operate the dual ADC in air flow conditions (1m/s recommended).
In still air conditions, the junction temperature is indeed greater than the maximum
allowed T
- T
- TJ = 25.2°C/W x 1.4W + TA = 35.28 + 85 = 125.28°C for industrial grade devices
.
J
= 25.2°C/W x 1.4W + TA = 35.28 + 70 = 105.28°C for commercial grade devices
J
The thermal resistance from the junction to the board is 13° C/W typical.
2153C–BDC–04/04
57
Page 58

Ordering Information
Part Number Package Temperature Range Screening Comments
AT84XAD001BTD LQFP 144 Ambient Prototype
Prototype version
Please contact your local Atmel sales office
AT84AD001BCTD LQFP 144
AT84AD001BITD LQFP 144
AT84AD001TD-EB LQFP 144 Ambient Prototype Evaluation Kit
C grade
0°C < TA < 70°C
I grade
-40°C < TA < 85°C
Standard
Standard
58
AT84AD001B
2153C–BDC–04/04
Page 59

Packaging Information
Figure 63. Type of Package
AT84AD001B
N
1
E1
A
B
D
D1
Dims. Tols. Leads 144L
A max. 1.60
A1 0.05 min./0.15 max.
A2 +/- 0.05 1.40
D +/-0.20 22.00
D1 +/-0.10 20.00
E +/-0.20 22.00
E
E1 +/-0.10 20.00
L +0.15/-0.10 0.60
e basic 0.50
b +/-0.05 0.22
ddd 0.08
ccc max. 0.08
o 0 - 5
Notes: 1. All dimensions are in millimeters
2. Dimensions shown are nominal with tolerances as indicated
3. L/F: eftec 64T copper or equivalent
4. Foot length: "L" is measured at gauge plane
at 0.25 mm above the seating plane
Body +2.00 mm footprint
o
o
D
o
TYP.
A2
12
A1
0.20 RAD max.
A
C
0.17 max
0.25
e
0.20 RAD nom.
o
o
+
6
4
-
0
L
ddd e
c
b
A-B e
12
Stand off
A
1
D e
Note: Thermally enhanced package: LQFP 144, 20 x 20 x 1.4 mm.
A
o
TYP.
Seating plane
C
Lead coplanarity
ccc
c
2153C–BDC–04/04
59
Page 60

Atmel Corporation Atmel Operations
2325 Orchard Parkway
San Jose, CA 95131, USA
Tel: 1(408) 441-0311
Fax: 1(408) 487-2600
Regional Headquarters
Europe
Atmel Sarl
Route des Arsenaux 41
Case Postale 80
CH-1705 Fribourg
Switzerland
Tel: (41) 26-426-5555
Fax: (41) 26-426-5500
Asia
Room 1219
Chinachem Golden Plaza
77 Mody Road Tsimshatsui
East Kowloon
Hong Kong
Tel: (852) 2721-9778
Fax: (852) 2722-1369
Japan
9F, Tonetsu Shinkawa Bldg.
1-24-8 Shinkawa
Chuo-ku, Tokyo 104-0033
Japan
Tel: (81) 3-3523-3551
Fax: (81) 3-3523-7581
Memory
2325 Orchard Parkway
San Jose, CA 95131, USA
Tel: 1(408) 441-0311
Fax: 1(408) 436-4314
Microcontrollers
2325 Orchard Parkway
San Jose, CA 95131, USA
Tel: 1(408) 441-0311
Fax: 1(408) 436-4314
La Chantrerie
BP 70602
44306 Nantes Cedex 3, France
Tel: (33) 2-40-18-18-18
Fax: (33) 2-40-18-19-60
ASIC/ASSP/Smart Cards
Zone Industrielle
13106 Rousset Cedex, France
Tel: (33) 4-42-53-60-00
Fax: (33) 4-42-53-60-01
1150 East Cheyenne Mtn. Blvd.
Colorado Springs, CO 80906, USA
Tel: 1(719) 576-3300
Fax: 1(719) 540-1759
Scottish Enterprise Technology Park
Maxwell Building
East Kilbride G75 0QR, Scotland
Tel: (44) 1355-803-000
Fax: (44) 1355-242-743
RF/Automotive
Theresienstrasse 2
Postfach 3535
74025 Heilbronn, Germany
Tel: (49) 71-31-67-0
Fax: (49) 71-31-67-2340
1150 East Cheyenne Mtn. Blvd.
Colorado Springs, CO 80906, USA
Tel: 1(719) 576-3300
Fax: 1(719) 540-1759
Biometrics/Imaging/Hi-Rel MPU/
High Speed Converters/RF Datacom
Avenue de Rochepleine
BP 123
38521 Saint-Egreve Cedex, France
Tel: (33) 4-76-58-30-00
Fax: (33) 4-76-58-34-80
Literature Requests
www.atmel.com/literature
Disclaimer: Atmel Corporation makes no warranty for the use of its products, other than those expressly contained in the Company’s standard
warranty which is detailed in Atmel’s Terms and Conditions located on the Company’s web site. The Company assumes no responsibility for any
errors which may appear in this document, reserves the right to change devices or specifications detailed herein at any time without notice, and
does not make any commitment to update the information contained herein. No licenses to patents or other intellectual property of Atmel are
granted by the Company in connection with the sale of Atmel products, expressly or by implication. Atmel’s products are not authorized for use
as critical components in life support devices or systems.
© Atmel Corporation 2004. All rights reserved. Atmel® and combinations thereof are the registered trademarks and Smart ADC™ is the trade-
mark of Atmel Corporation or its subsidiaries. Other terms and product names may be the trademarks of others.
Printed on recycled paper.
2153C–BDC–04/04
0M
 Loading...
Loading...