Page 1

ASM-60
10 Mbps VDSL-Based Modem
Installation and Operation Manual
Notice
This manual contains information that is proprietary to RAD Data Communications. No part of this
publication may be reproduced in any form whatsoever without prior written approval by RAD Data
Communications.
No representation or warranties for fitness for any purpose other than what is specifically mentioned in
this manual is made either by RAD Data Communications or its agents.
For further information contact RAD Data Communications at the address below or contact your local
distributor.
International Headquarters
RAD Data Communications Ltd.
24 Raoul Wallenberg St.
Tel Aviv 69719 Israel
Tel: 972-3-6458181
Fax: 972-3-6498250
E-mail: rad@rad.co.il
© 2001 RAD Data Communications Publication No. 145-200-11/01
U.S. Headquarters
RAD Data Communications Inc.
900 Corporate Drive
Mahwah, NJ 07430 USA
Tel: (201) 529-1100
Toll free: 1-800-444-7234
Fax: (201) 529-5777
E-mail: market@radusa.com
Page 2

Page 3

Warranty
This RAD product is warranted against defects in material and workmanship for a period of one year
from date of shipment. During the warranty period, RAD will, at its option, either repair or replace
products which prove to be defective. For warranty service or repair, this product must be returned to
a service facility designated by RAD. Buyer shall prepay shipping charges to RAD and RAD shall pay
shipping charges to return the product to Buyer. However, Buyer shall pay all shipping charges, duties
and taxes for products returned to RAD from another country.
Limitation of Warranty
The foregoing warranty shall not apply to defects resulting from improper or inadequate maintenance
by Buyer, Buyer-supplied firmware or interfacing, unauthorized modification or misuse, operation
outside of the environmental specifications for the product, or improper site preparation or
maintenance.
Exclusive Remedies
The remedies provided herein are the Buyer’s sole and exclusive remedies. RAD shall not be liable for
any direct, indirect special, incidental, or consequential damages, whether based on contract, tort, or
any legal theory.
Page 4
Safety Warnings
The exclamation point within a triangle is intended to warn the operator or
service personnel of operation and maintenance factors relating to the
product and its operating environment which could pose a safety hazard.
Always observe standard safety precautions during installation, operation and maintenance of this
product. Only a qualified and authorized service personnel should carry out adjustment, maintenance
or repairs to this instrument. No adjustment, maintenance or repairs should be performed by either the
operator or the user.
Telecommunication Safety
The safety status of each of the ports on ASM-60 is declared according to EN 41003 and is detailed in
the table below:
Ports
DTE, Ethernet SELV Circuit operating with Safety Extra-Low Voltage
Line TNV-1 Circuit whose normal operating voltage is within
Safety Status
the limits of SELV, on which overvoltages from
Telecommunications Networks are possible.
Regulatory Information
FCC-15 User Information
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits of the Class A digital device,
pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against
harmful interference when the equipment is operated in a commercial environment. This equipment
generates, uses and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance
with the instruction manual, may cause harmful interference to the radio communications. Operation
of this equipment in a residential area is likely to cause harmful interference in which case the user will
be required to correct the interference at his own expense.
Warning per EN 55022
This is a Class A product. In a domestic environment, this product may cause radio interference, in
which case the user may be required to take adequate measures.
Page 5

Quick Start Guide
Installation of ASM-60 should be carried out only by an experienced technician. If
you are familiar with ASM-60, use this guide to prepare the units for operation.
1. Installing ASM-60
Setting the Internal Switches
Perform the internal settings as follows:
1. Disconnect the power cord from the power source.
2. Slide the blue side panel forward to detach it from the case.
3. Unscrew the two screws located on the bottom panel at the rear end of the
unit.
4. Separate the two halves of the ASM-60 case by lifting the top cover at the end
of the unit and sliding it forward.
5. Set the internal switches of the Ethernet interface board (IR-ETH, IR-ETH/QH
or IR-IP).
Connecting the Interfaces
1. Connect the line to the RJ-45 rear panel connector.
2. Connect the DTE to the appropriate rear panel connector.
3. Connect the control terminal to the front CONTROL DCE connector.
Connecting the Power
• Connect the AC power to the ASM-60 modem.
The PWR indicator turns on.
Installing ASM-60 1
Page 6

Quick Start Guide ASM-60 Installation and Operation Manual
2. Operating ASM-60
Normal Indications
The table below shows the correct status of the indicators a few seconds after
power-up.
Indicator Status
PWR ON
TD Depends on DTE data transmission.
RD Depends on DTE data transmission.
RTS Depends on DTE RTS signal status.
DCD Depends on remote modem data transmission.
TEST OFF
ALM OFF
SYNC A/SYNC B Green or red, depending on remote modem data
transmission.
3. Configuring ASM-60
Configure ASM-60 to the desired operation mode via an ASCII terminal using the
embedded management software. Configuration of the ASM-60 modem includes
selection of a data rate.
Selecting the Data Rate
Main Menu
↓↓↓↓ 1
Configuration
↓↓↓↓ 1
Data Rate
➤ To select the data rate:
1. From the Configuration menu, type 1.
The Data Rate menu appears.
2. Select the data rate by typing the number corresponding to the desired value
and then type 2 to save the changes.
2 Configuring ASM-60
Page 7

Contents
Chapter 1. Introduction
1.1 Overview .......................................................................................................... 1-1
General ...................................................................................................................1-1
Versions...................................................................................................................1-1
Application..............................................................................................................1-1
Features...................................................................................................................1-1
1.2 Physical Description.......................................................................................... 1-3
1.3 Functional Description ...................................................................................... 1-4
1.4 Technical Specifications .................................................................................... 1-5
Chapter 2. Installation and Setup
2.1 Site Requirements and Prerequisites.................................................................. 2-1
2.2 Package Contents.............................................................................................. 2-2
2.3 Installation and Setup........................................................................................ 2-2
Performing the Internal Settings................................................................................2-2
Connecting the Interfaces ........................................................................................2-3
Connecting the Power .............................................................................................2-5
Chapter 3. Operation
3.1 Front Panel Indicators ....................................................................................... 3-1
3.2 Operating ASM-60............................................................................................ 3-2
Turning On ASM-60 ................................................................................................3-2
Normal Indications ..................................................................................................3-2
Turning Off ASM-60 ................................................................................................3-2
Chapter 4. Management from a Terminal
4.1 Preparing for the Control Session ...................................................................... 4-1
Control Port Interface Characteristics........................................................................4-1
Preparing Terminal ..................................................................................................4-1
4.2 Navigating the Management Menus ..................................................................4-2
Terminal Management Menus..................................................................................4-3
4.3 Starting the Control Session............................................................................... 4-3
4.4 Configuring ASM-60.......................................................................................... 4-4
Selecting the Data Rate............................................................................................4-4
4.5 Displaying the ASM-60 System Information....................................................... 4-5
Displaying the ASM-60 Status ..................................................................................4-6
4.6 Resetting ASM-60.............................................................................................. 4-7
Chapter 5. Diagnostics
5.1 Error Detection .................................................................................................5-1
Power-Up Self-Test..................................................................................................5-1
Front-Panel LEDs .....................................................................................................5-1
Alarms.....................................................................................................................5-1
5.2 Displaying the VDSL Performance Diagnostics .................................................. 5-3
5.3 Running the Diagnostic Tests............................................................................. 5-5
Running the LEDs Test .............................................................................................5-5
ASM-60 Installation and Operation Manual i
Page 8

Table of Contents
Appendix A. IR-ETH Interface Module
Appendix B. IR-ETH/QH Interface Module
Appendix C. IR-IP Interface Module
List of Figures
1-1. Typical ASM-60 Application ...................................................................................... 1-1
1-2. 3D View of ASM-60 .................................................................................................. 1-3
1-3. ASM-60 Block Diagram ............................................................................................. 1-4
2-1 Rear Panel of ASM-60 with HSSI Interface.................................................................. 2-3
3-1 ASM-60 Front Panel ................................................................................................... 3-1
4-1. ASM-60 Management Software ................................................................................. 4-3
4-2. Main Menu ...............................................................................................................4-4
4-3. Configuration Menu .................................................................................................. 4-4
4-4. Data Rate Menu ........................................................................................................ 4-5
4-5. Display Menu............................................................................................................ 4-5
4-6. Status Screen.............................................................................................................4-6
4-7. Reset Menu............................................................................................................... 4-7
5-1. Alarms Screen ........................................................................................................... 5-2
5-2. Log File Screen .......................................................................................................... 5-2
5-3. VDSL Performance Screen......................................................................................... 5-4
List of Tables
1-1. Typical ASM-60 Ranges ............................................................................................. 1-2
2-1 Line Connector Pinout ............................................................................................... 2-3
2-2. HSSI Interface Connector Pinout ............................................................................... 2-4
3-1. ASM-60 LED Indicators ............................................................................................. 3-1
3-2. ASM-60 Indicator Status ............................................................................................ 3-2
4-1. Control Port Control Signals....................................................................................... 4-2
5-1. ASM-60 Alarms .........................................................................................................5-3
5-2. ASM-60 Performance Monitoring Parameters ............................................................ 5-4
ii ASM-60 Installation and Operation Manual
Page 9
General
Versions
Chapter 1
Introduction
1.1 Overview
ASM-60 is a VDSL (Very High-bitrate Digital Subscriber Line) modem handling
high data rates. ASM-60 supports HSSI DTE interface, and several Ethernet
interface modules, which allow LAN-to-LAN connectivity using VDSL technology.
Working in full duplex over 4-wire link, the modem can be configured to operate
at the data rates up to 10.240 Mbps.
ASM-60 is available in the two following versions:
• ASM-60/CO, for the central office deployment
Application
Features
• ASM-60/CPE, for customer premises deployment.
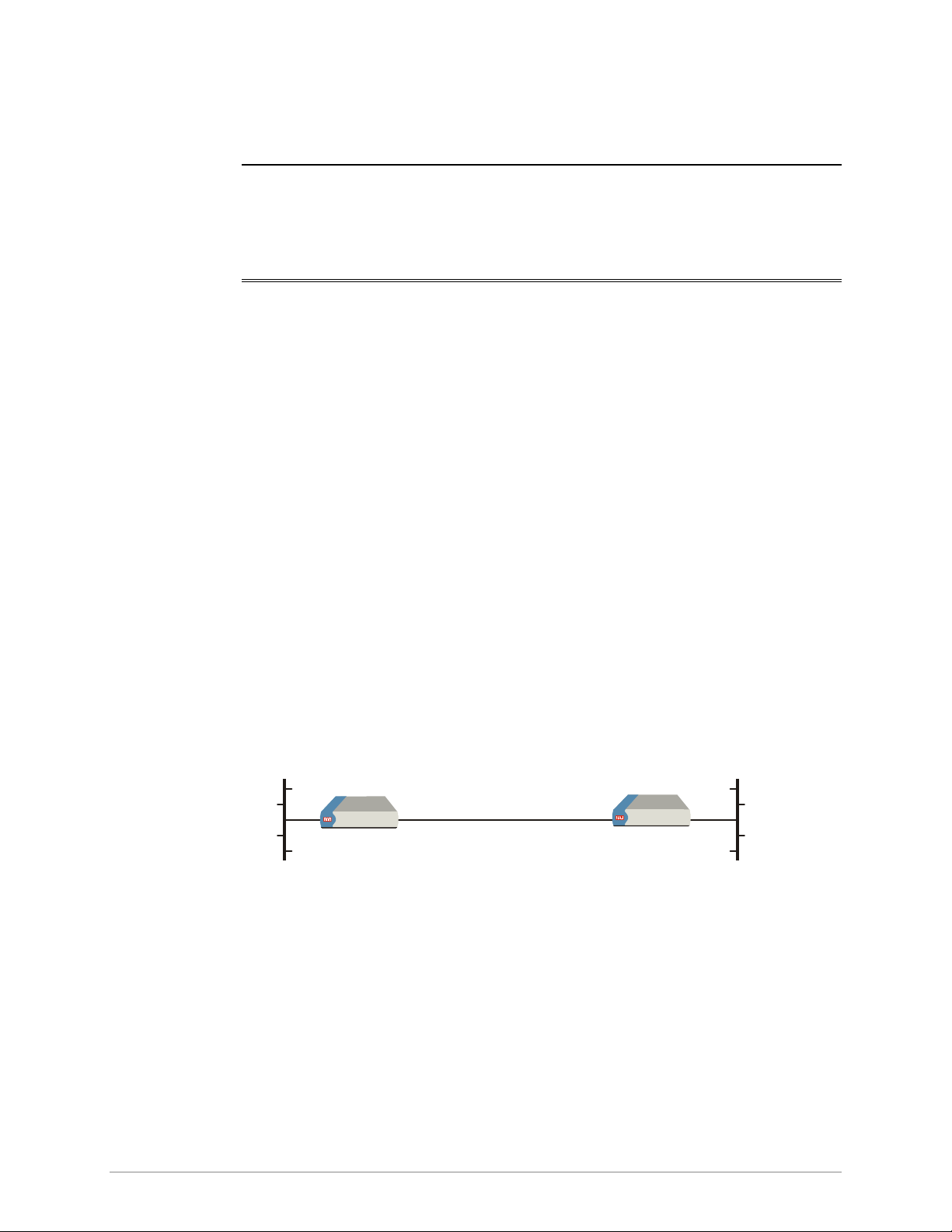
Figure 1-1 shows a typical application for ASM-60, connecting the LANs over an
4-wire line.
Central Office Customer Premises
4-wire
ASM-60/CO ASM-60/CPE
LAN LAN
Figure 1-1. Typical ASM-60 Application
ASM-60 utilizes the QAM VDSL technology to extend the range of data
transmission over 4-wire 24 AWG line up to 1.8 km (1.1 miles). ASM-60 operates
at the following data rates: 4.096 Mbps, 6.144 Mbps and 10.24 Mbps. Table 1-1
lists typical ASM-60 ranges over 24 AWG STP Cat. 5 wire.
2.0 km (1.2 miles)
Overview 1-1
Page 10

Chapter 1 Introduction ASM-60 Installation and Operation Manual
Table 1-1. Typical ASM-60 Ranges
Data Rate 24 AWG
(Mbps) km miles
4.096 2.0 1.2
6.144 2.0 1.2
10.24 1.8 1.1
DTE Interface
The ASM-60 DTE interface supports the following interfaces:
• HSSI
• IR-ETH module with built-in Ethernet bridge
• IR-ETH/QH module with built-in Fast Ethernet bridge and VLAN support
• IR-IP module with built-in IP router.
Management
Setup, control, monitoring of status and diagnostics can be performed using an
ASCII terminal connected to the ASM-60 async DCE control port.
Test Capabilities
ASM-60 performs an extensive self-test at start-up. During the self-test, ASM-60
checks its CPU, internal framer, DTE and interfaces and power supplies. The
self-test results are displayed on the supervisory terminal.
Real Time Alarms
Real time alarms provide real time information on system status indicating loss of
synchronization on line A and line B, DCD status etc.
ASM-60 also features a log file that stores all alarms and events that occurred in the
unit. These alarms can be displayed and cleared.
Statistics Collection
ASM-60 stores the VDSL statistics for the line performance monitoring.
1-2 Overview
Page 11

ASM-60 Installation and Operation Manual Chapter 1 Introduction
1.2 Physical Description
Figure 1-2 shows a 3D view of the ASM-60 standalone modem.
Figure 1-2. 3D View of ASM-60
The front panel includes nine LEDs, which display the status of power, data flow,
control signals and provide diagnostics. The front panel also features a 9-pin
D-type (CONTROL DCE) connector for terminal connection for configuration,
control and monitoring. For detailed description of the front panel, see Chapter 3.
The rear panel includes the AC power connector, a DTE interface connectors and
a line connector. The ASM-60 rear panel is described in greater detail in
Chapter 2.
Physical Description 1-3
Page 12
Chapter 1 Introduction ASM-60 Installation and Operation Manual
y
1.3 Functional Description
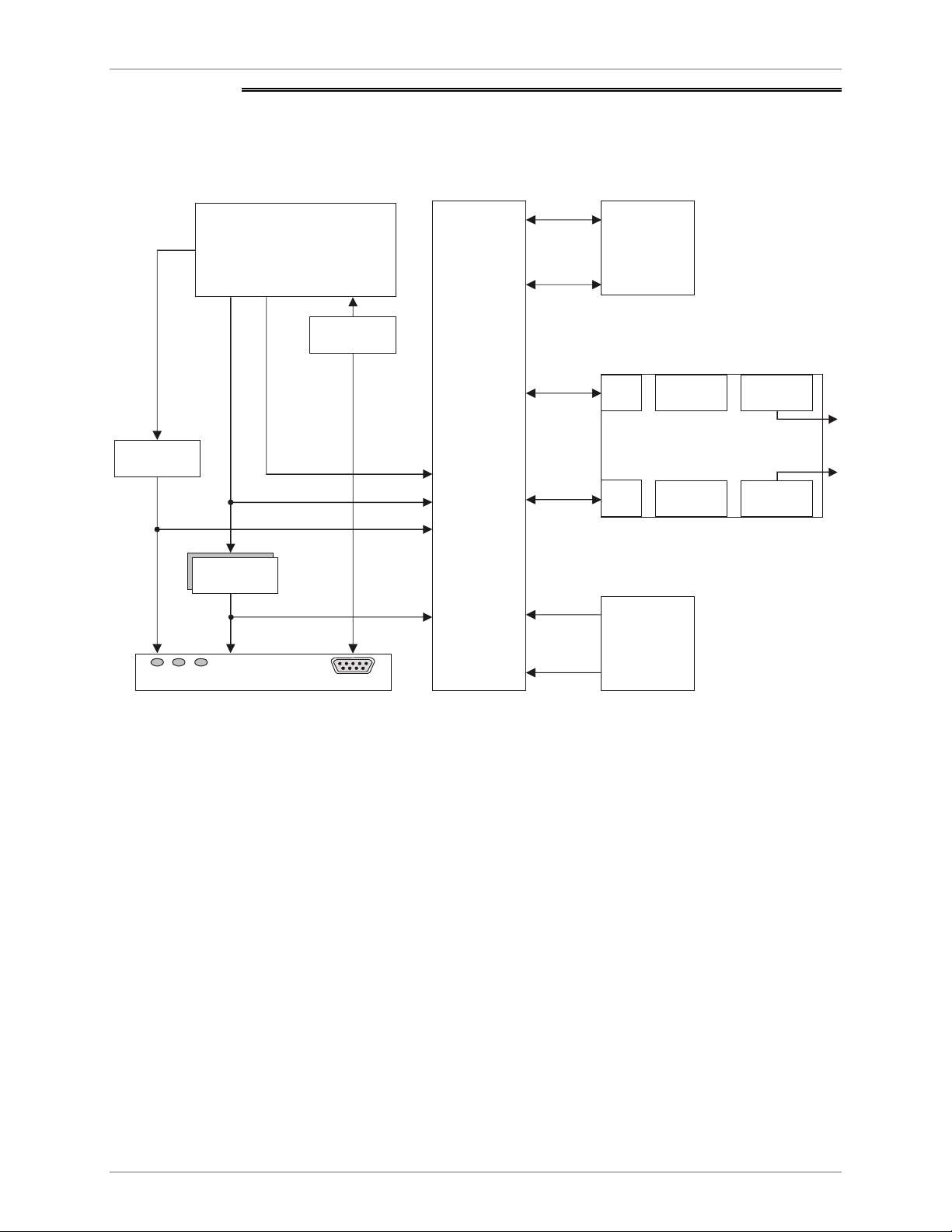
This section provides a functional description (Figure 1-3) of ASM-60 in the form of
block diagrams.
TxD, RxD
A11-A15
Additional
Decoder
Latch/Buffer
LEDs Control
CPU
A0-A7, A14
D8-D15
RS-232
INT, EXT
Clock
Data,
Clock
VDSL
Framer
Data,
Clock
3.3V
5.0V
DTE Interface
EVM1 HYBRID1
EVM2
Power
Suppl
Figure 1-3. ASM-60 Block Diagram
TRANSF.1
VDSL
Line Interface
HYBRID2 TRANSF.2
AC
Line A
Line B
The ASM-60 modem consists of the following major modules:
• CPU and Peripherals – This module, based on a microprocessor, includes
Flash (1 Mb), RAM (0.5 Mb) and EEPROM (8 kb) memory and controls the
ASM-60 operation.
• VDSL Framer – This module encapsulates data bit stream coming from DTE
and transmits it over two different analog lines. At the other end, it reverses the
process by converting the two line data into one bit stream for the DTE. In
addition, the VDSL framer supplies clock to the DTE.
• VDSL Line Interface – Consists of two identical DSP modules. Each module
transmits and receives signals over 2-wire at half of the data rate that running
into the DTE interface.
1-4 Functional Description
Page 13

ASM-60 Installation and Operation Manual Chapter 1 Introduction
1.4 Technical Specifications
Line Interface
DTE Interface
Protocol
Type
Line Coding
Range
Levels
Impedance
Return Loss
Carrier
Data Rate
Type
Very High-bit-rate Digital Subscriber Line (VDSL)
4-wire, unconditioned dedicated lines (twisted pair),
Cat.3 and Cat.5, 19 AWG to 26 AWG
QAM
See Table 1-1
11 dBm
110Ω
More than 15 dB
Constantly On
User-selectable: 4.096 Mbps, 6.144 Mbps or
10.24 Mbps
• HSSI via SCSI 50, female connector
• IR-ETH (Ethernet bridge) via RJ-45 or BNC coax
connectors
• IR-ETH/QH (Ethernet/Fast Ethernet bridge with VLAN
support) via RJ-45 connector
Control Port
Diagnostics
Interface
Type
Format
Baud Rate
Connector
Performance
Monitoring
Self-Test
• IR-IP (IP router) via RJ-45 connector
V.24/RS-232
DCE
8 bits; no parity, 1 stop bit
19.2 kbps
9-pin, D-type, female
VDSL statistics collection
Self-test at start-up
Technical Specifications 1-5
Page 14

Chapter 1 Introduction ASM-60 Installation and Operation Manual
Indicators
Physical
Power
PWR (green)
RTS (yellow)
TD (yellow)
RD (yellow)
DCD (yellow)
TST (red)
ALM (red)
SYNC A (green/red)
SYNC B (green/red)
Height
Width
Depth
Weight
AC Voltage
Protection
Power
Request to Send
Transmit Data
Receive Data
Data Carrier Detect
Test
Alarm
Synchronization line A
Synchronization line B
44 mm / 1.7 in (1U)
215 mm / 8.5 in
243 mm / 9.6 in
1 kg / 3.1 lb
100 to 240 VAC (±10%), 50 to 60 Hz, 6W
AC/DC overvoltage protection circuits are connected via
transformers to the transmit and receive lines
Environment
Fuse
Temperature
Humidity
0.250A, slow-blow
0–50°C / 32–122°F
Up to 90%, non–condensing
1-6 Technical Specifications
Page 15
Warning
Chapter 2
Installation and Setup
This chapter describes installation and setup procedures for the standalone
ASM-60 modem.
ASM-60 is delivered completely assembled. It is designed for tabletop or 19-inch
rack installation.
After installing the unit:
• Refer to Chapter 3 for the operating instructions.
• Refer to Chapter 4 for the detailed system configuration procedures using
ASCII terminal connected to the ASM-60 control port.
If a problem is encountered, refer to Chapter 5 for test and diagnostic instructions.
Internal settings, adjustment, maintenance, and repairs may be performed
only by a skilled technician who is aware of the hazards involved.
Always observe standard safety precautions during installation, operation, and
maintenance of this product.
Caution
2.1 Site Requirements and Prerequisites
ASMi-60 is designed for installation as a desktop unit. A rack mount kit, K-28, for
installation of ASM-60 in a 19-inch rack, is available upon special order.
AC-powered ASM-60 units should be installed within 1.5m (5 ft) of an
easily-accessible grounded AC outlet capable of furnishing the voltage in
accordance with ASM-60 nominal supply voltage.
Allow at least 90 cm (36 in) of frontal clearance for operating and maintenance
accessibility. Allow at least 10 cm (4 in) clearance at the rear of the unit for signal
lines and interface cables.
Do not stack units on top of another.
The ambient operating temperature of ASM-60 should be 0 to 50°C
(32 to 122°F), at a relative humidity of up to 90%, non-condensing.
Site Requirements and Prerequisites 2-1
Page 16
Chapter 2 Installation and Setup ASM-60 Installation and Operation Manual
2.2 Package Contents
The ASM-60 package includes the following items:
• One ASM-60 unit
• ASM-60 Installation and Operation Manual
• AC power cord.
2.3 Installation and Setup
The ASM-60 standalone unit is designed for desktop or bench installation and is
delivered as a fully assembled unit. No provisions are made for bolting the unit to
a tabletop.
➤ To install ASM-60:
1. Determine the required configuration of ASM-60, in accordance with your
application.
2. Set the DIP switches of the Ethernet interface module accordingly.
3. Connect the line (see Connecting the Line below).
4. Connect the DTE (see Connecting the DTE below).
5. Connect power to the unit (see Connecting the Power below).
Performing the Internal Settings
ASM-60 with HSSI interface does not contain any jumpers or switches for user
settings. For instructions on configuring ASM-60 units with an Ethernet interface
module, refer to the respective appendix of this manual.
Access to the inside of the equipment is permitted only to the authorized and
qualified personnel.
To avoid accidental electric shock, always disconnect the interface cables and
Warning
the power cord before removing the unit from its casing.
Line voltages are present inside ASM-60 when it is connected to power and/or
the lines. Moreover, under certain fault conditions, dangerous voltages may
appear on the lines connected to the unit.
Any adjustment, maintenance and repair of the opened instrument under
voltage must be avoided as much as possible and, when inevitable, should be
carried out only by a skilled technician who is aware of the hazard involved.
Capacitors inside the unit may still be charged even after the unit has been
disconnected from its source of power.
Caution
ASM-60 contains components sensitive to electrostatic discharge (ESD). To prevent
ESD damage, avoid touching the internal components. Before moving the jumper,
touch the ASM-60 frame.
2-2 Installation and Setup
Page 17

ASM-60 Installation and Operation Manual Chapter 2 Installation and Setup
Opening the ASM-60 Case
➤ To open the ASM-60 case:
1. Disconnect the power cord from the power source.
2. Slide the blue side panel forward to detach it from the case.
3. Unscrew the two screws located on the bottom panel at the rear end of the
unit.
4. Separate the two halves of the ASM-60 case by lifting the top cover at the end
of the unit and sliding it forward.
Closing the ASM-60 Case
After completing the internal settings, close the unit case.
➤ To close the ASM-60 case:
1. Position the lower half of the ASM-60 case on the flat surface.
2. Return the top cover. Make sure that the front board CONTROL DCE
connector fits the front panel opening correctly, and the top cover guides enter
the corresponding recesses at the end of the unit.
3. Secure the two screws located at the end of the unit.
4. Fit the inside tabs of the blue side panel into the unit case grooves, and slide
the side panel until it snaps into place.
Connecting the Interfaces
Figure 2-1 shows the rear panel of a typical ASM-60 unit with HSSI interface.
:
FOR CONTINUED
CAUTION
PROTECTION AGAINST RISK O F
FIRE, REPLACE ONLY WITH SAME
TYPE AND RATING OF FUSE.
Figure 2-1 Rear Panel of ASM-60 with HSSI Interface
Connecting the Line
The ASM-60 line interface terminates in an 8-pin RJ-45 connector (see Table 2-1).
➤ To connect the RJ-45 connector:
• Connect the line cable to the RJ-45 connector designated LINE.
HSSI
LINE
A-1 2 4 5-B
Table 2-1 Line Connector Pinout
Pin Function
1, 2 Line A
4, 5 Line B
11, 12 Chassis
Installation and Setup 2-3
Page 18

Chapter 2 Installation and Setup ASM-60 Installation and Operation Manual
Connecting the DTE
The ASM-60 DTE interface provides interface for input/output data, clock
reference and control signals between the modem and the DTE. The ASM-60 DTE
interface can be either HSSI interface module, terminating in SCSI 50 female
connector (see Table 2-2), or one of the Ethernet interface modules, described in
greater detail in Appendix A, Appendix B and Appendix C.
➤ To connect the HSSI interface:
• Attach the HSSI cable, terminated by SCSI 50 male connector to the SCSI 50
socket on the rear panel of ASM-60.
Table 2-2. HSSI Interface Connector Pinout
Signal Name Function ASM-60 Signal Direction Pin (+Side) Pin (-Side)
SG Signal Ground 1 26
RT Receive Timing IR-DXC From ASM-60 2 27
CA DCE Available DSR From ASM-60 3 28
RD Receive Data IR-RXD From ASM-60 4 29
LC Loopback Circuit C – From ASM-60 5 30
ST Send Timing IR-TXC From ASM-60 6 31
SG Signal Ground – – 7 32
TA DTE Available DTR – 8 33
TT Terminal Timing IR-EXTC To ASM-60 9 34
LA Loopback Circuit A – – 10 35
SD Send Data IR-TXD To ASM-60 11 36
LB Loopback Circuit B – – 12 37
SG Signal Ground – – 13 38
5 Ancillary to DCE – – 14–18 39–43
SG Signal Ground – – 19 44
4 Ancillary from DCE – – 20–23 45–48
TM Test Mode – – 24 49
SG Signal Ground – – 25 50
2-4 Installation and Setup
Page 19

ASM-60 Installation and Operation Manual Chapter 2 Installation and Setup
Connecting the Power
Before switching on this unit and connecting any other cable, the protective
earth terminals of this unit must be connected to the protective ground
conductor of the power cord. If you are using an extension cord (power cable)
Warning
make sure it is grounded as well.
Any interruption of the protective (grounding) conductor (inside or outside the
instrument) or disconnecting of the protective earth terminal can make this
unit dangerous. Intentional interruption is prohibited.
The line fuse is located in an integral-type fuse holder located on the rear
panel. Make sure that only fuses of the required rating, as marked on the rear
panel, are used for replacement. Do not use repaired fuses or short-circuit the
fuse holder. Always disconnect the mains cable before removing or replacing
the fuse. Whenever it is likely that the fuse protection has been damaged,
make the unit inoperative and secure it against unintended operation.
AC power is supplied to the ASM-60 modem through a standard 3-prong plug
with an integral fuse holder (see Figure 2-1).
AC power should be supplied through the 5 ft (1.5m) standard power cable
terminated by a standard 3-prong plug. The cable is provided with the unit.
➤ To connect the AC power:
1. Connect the power cable to the power connector on the ASM-60 rear panel.
2. Connect the power cable to the mains outlet.
The unit will be turned on automatically upon connection to the mains.
Installation and Setup 2-5
Page 20

Chapter 2 Installation and Setup ASM-60 Installation and Operation Manual
2-6 Installation and Setup
Page 21
Chapter 3
Operation
This chapter provides the description of the ASM-60 front-panel indicators, and
details the modem's operating procedures (turn-on, front-panel indications,
performance monitoring and turn-off).
Installation procedures given in Chapter 2 must be completed and checked before
attempting to operate ASM-60.
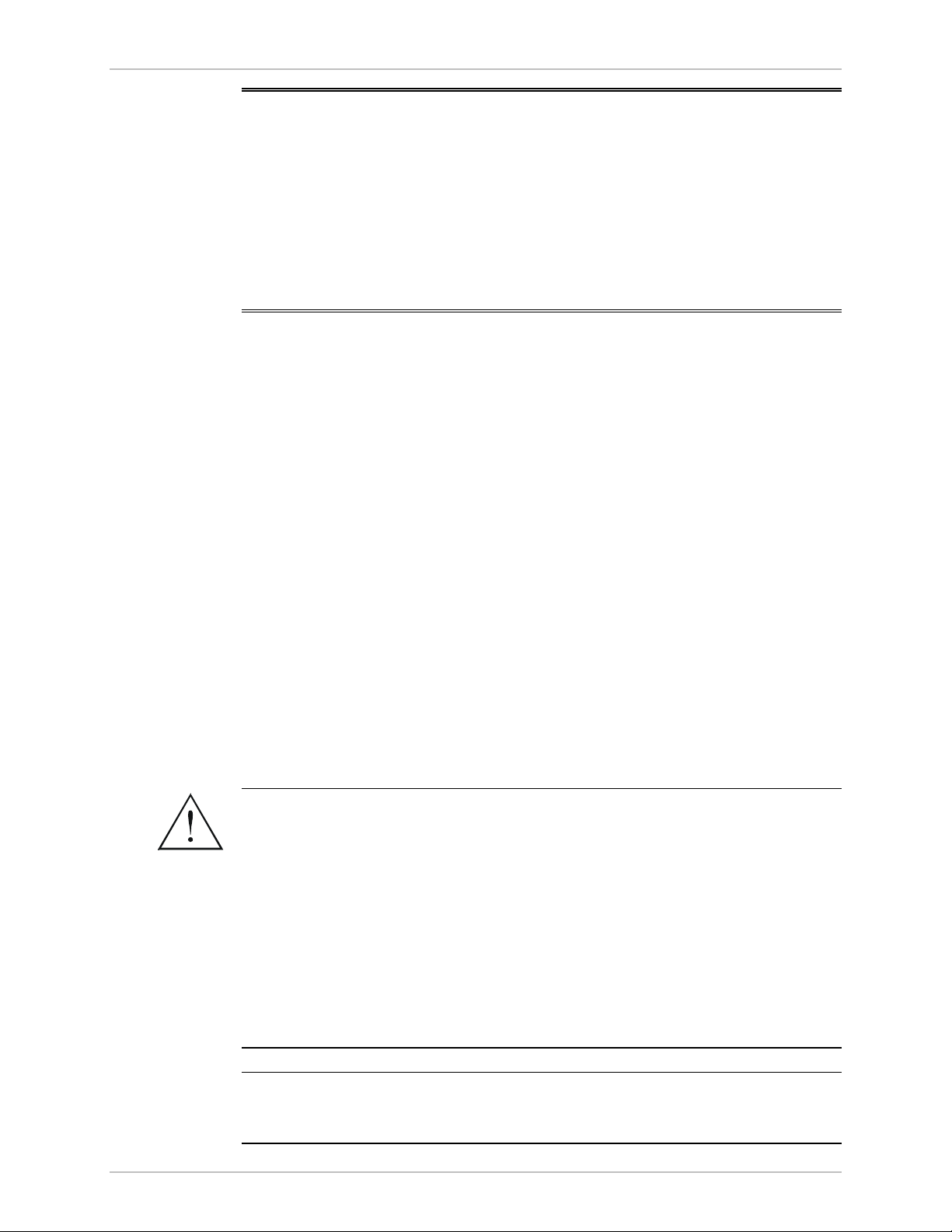
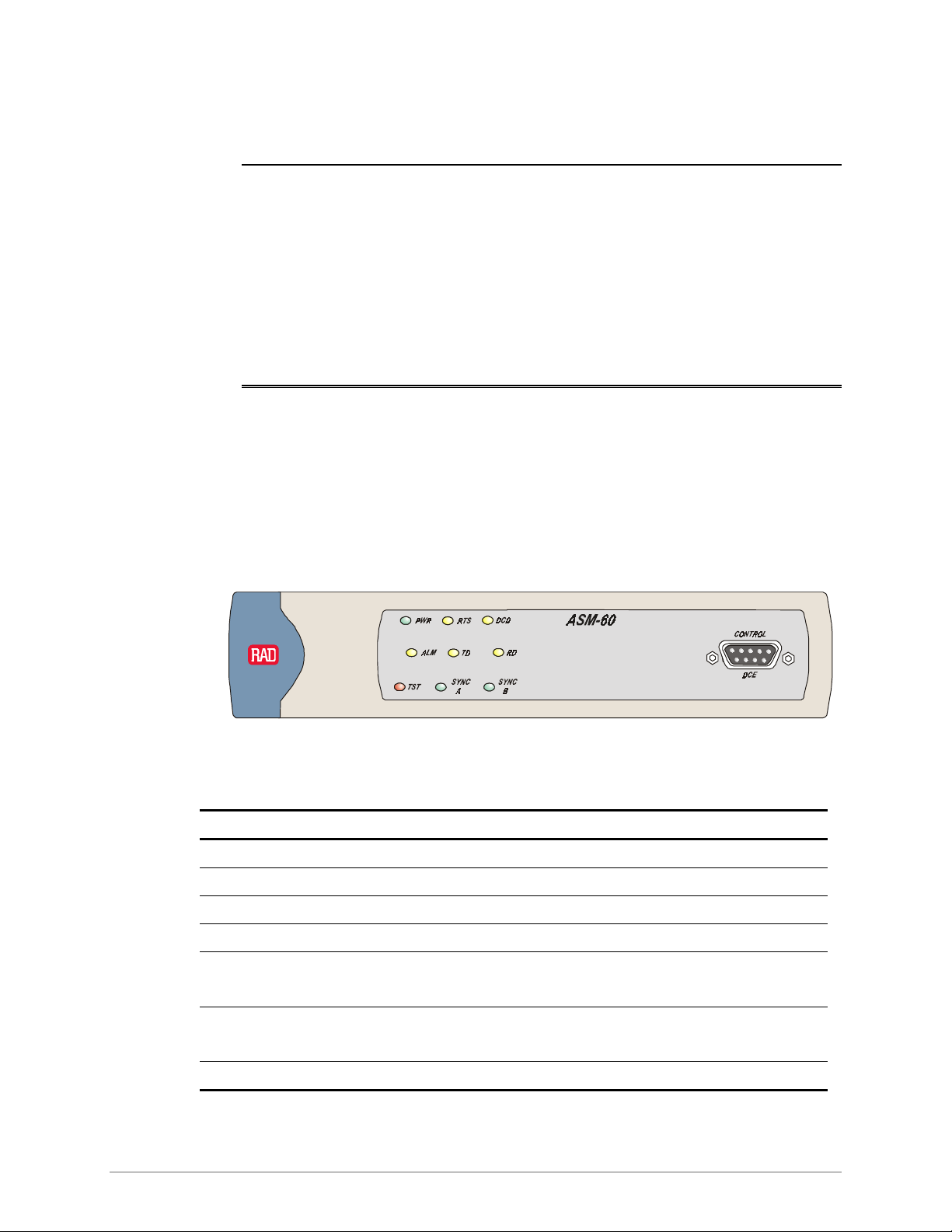
3.1 Front Panel Indicators
The front panel of ASM-60 includes nine LED indicators that show the current
operating status of the unit.
ASM-60 also includes a proprietary 9-pin connector (CONTROL DCE) on its front
panel for connection to a terminal.
Figure 3-1 shows the ASM-60 front panel. Table 3-1 lists and describes the ASM-60
indicators.
Figure 3-1 ASM-60 Front Panel
Table 3-1. ASM-60 LED Indicators
Name Function
PWR (green) ON – Power is ON.
RTS (yellow) ON – DTE activates Request To Send.
DCD (yellow) ON– Link A, link B and internal IMUX are synchronized.
ALM (red) ON – An alarm enters the alarm buffer.
TD (yellow) ON – Data is being transmitted to the DTE.
OFF – Steady mark is being transmitted.
RD (yellow) ON – Data is being received from the DTE.
OFF – Steady mark is being received.
TST (red) Reserved for future use
Front Panel Indicators 3-1
Page 22
Chapter 3 Operation ASM-60 Installation and Operation Manual
Table 3-1. ASM-60 LED Indicators (Cont.)
Name Function
SYNC A (red/green) ON (red) – Data link A is not synchronized with the remote modem.
ON (green) – Data link A is synchronized with the remote modem.
SYNC B (red/green) ON (red) – Data link B is not synchronized with the remote modem.
ON (green) – Data link B is synchronized with the remote modem.
3.2 Operating ASM-60
Turning On ASM-60
ASM-60 is turned on as soon as the power is connected to the unit. The PWR
indicator lights up and remains lit as long as ASM-60 receives power.
ASM-60 requires no operator attention once installed, with the exception of
occasional monitoring of front panel indicators. Intervention is only required for
the ASM-60 configuration events monitoring.
Normal Indications
Table 3-2 shows the status of the ASM-60 indicators, a few seconds after
power-up.
Indicator Status
PWR ON
TD Depends on DTE data transmission.
RD Depends on DTE data transmission.
RTS Depends on DTE RTS signal status.
DCD Depends on remote modem data transmission.
TST OFF
ALM OFF
SYNC A/SYNC B Green or red, depending on remote modem data
If the above LED indications are not obtained following initial power turn-on, refer
to Chapter 5 for the diagnostic test instructions.
Table 3-2. ASM-60 Indicator Status
transmission.
Turning Off ASM-60
To turn off ASM-60, remove the power cord from the power source.
3-2 Operating ASM-60
Page 23

Chapter 4
Management from a
Terminal
The configuration of ASM-60 is performed via menu-driven embedded software
using a standard ASCII terminal or a PC running a terminal emulation application
connected to the front panel CONTROL DCE port. This terminal can be used for
performing the following management activities supported by ASM-60:
• Modifying setup configuration
• Monitoring of device status and settings
• Collect performance statistics
• Restarting ASM-60.
4.1 Preparing for the Control Session
This section describes how to prepare ASM-60 and supervisory terminal for the
control session.
Control Port Interface Characteristics
ASM-60 includes a V.24/RS-232 asynchronous DCE port, designated CONTROL
DCE and terminated in a 9-pin D-type female connector. The control port
continuously monitors the incoming data stream and will immediately respond to
any input string received through this port.
The terminal can be connected either directly to the ASM-60 control port, or
through a modem or any other type of full-duplex data link. The ASM-60 control
port interface type must be set in accordance with the connection method, as
follows:
Preparing Terminal
Any standard ASCII terminal (a “dumb” terminal or a personal computer running
terminal emulation application) equipped with a V.24/RS-232 communication
interface can be used to configure ASM-60.
Control Port Handshaking Protocol
The control lines used in each DCE and DTE mode and the direction of the control
signals are detailed in the following table.
13-Nov-01 18:46 Preparing for the Control Session 4-1
Page 24

Chapter 4 Management from a Terminal ASM-60 Installation and Operation Manual
Table 4-1. Control Port Control Signals
Control Line Interface Type
CTS Out Not Used
DCD Out Out
DSR Out Out
DTR In In
RI Not Used In
RTS In In
DCE DTE
Data Terminal Ready (DTR)
When connected and turned on, the terminal sets the DTR line ON (active) to gain
control over ASM-60 and starts a configuration or monitoring session.
Initiating a Control Session
➤ To initiate a control session:
1. Connect the terminal cable to the CONTROL DCE connector of ASM-60.
2. Turn the control terminal on.
3. Configure the terminal to the default communication parameters: 19.2 kbps,
one start bit, eight data bits, no parity, one stop bit, VT100.
4. Select the full-duplex mode.
5. Turn the terminal echo off
You are now ready to start a control session.
4.2 Navigating the Management Menus
This section provides a general description of the software menu operation and
conventions for navigating the menus.
Figure 4-1 shows a map of the management menus in the ASM-60 embedded
software.
➤ To choose an option:
• Type the number corresponding to the option, and press <Enter>.
The screen for the selected option is displayed.
➤ To correct an erroneous entry:
• Press <Backspace> to clear the error, then enter the correct characters.
or
Press <Esc> to exit the current menu, and then return to the menu to
re-enter the required value.
4-2 Navigating the Management Menus
Page 25

ASM-60 Installation and Operation Manual Chapter 4 Management from a Terminal
Terminal Management Menus
Figure 4-1 shows a map of the management menus in the ASM-60 embedded
software. The second level menus (Configuration, Display, Reset) are described in
its own section in this chapter. The Alarms, Log File, VDSL Performance and Test
menus are described in Chapter 5.
Main Menu
Note
1. Configuration
1. Data Rate
1. 4096 kbps
2. 6144 kbps
3. 10240 kbps
2. Display
1. Status
2. Alarms
3. Log File
4. VDSL Performance
1. Start LEDs Test 1. Factory Setting
4. Reset 5. Debug3. Test
2. Reset Device
3. Reset Device
4. Reset FPGA
Figure 4-1. ASM-60 Management Software
The Debug option is reserved for the use only by the authorized personnel.
4.3 Starting the Control Session
Once you have installed the ASM-60 modems at the central and remote locations,
and completed the installation and operation procedures described in Chapter 2
and Chapter 3, you can start the control session.
When the communication link between the modems is established, the ASM-60
software identifies the unit type (ASM-60/CO or ASM-60/CPE), and runs the
start-up self-test.
During the initialization, the following message is displayed:
Initializing ASM-60/CO or Initializing ASM-60/CPE
If errors were detected during the self-test, ASM-displays the following message:
Initialization Failed
If the self-test is successful, ASM-60 displays the Main menu (see Figure 4-2).
Starting the Control Session 4-3
Page 26

Chapter 4 Management from a Terminal ASM-60 Installation and Operation Manual
ASM-60/CO Main Menu
1. Configuration
2. Display
3. Test
4. Reset
5. Debug
>
ESC - previous menu ; ! - main menu ; & - exit terminal
-------------------------------------------------------
Figure 4-2. Main Menu
Note
At the bottom of the terminal screen, ASM-60 displays the latest alarms as they
enter the alarm log.
4.4 Configuring ASM-60
This section describes the configuration procedures for the ASM-60 modem.
➤ To display the Configuration menu:
• From the Main menu, type 1, and then press <Enter>.
The Configuration menu appears (see Figure 4-3).
ASM-60/CO Configuration
1. Data Rate (current value)
>
ESC - previous menu ; ! - main menu ; & - exit terminal
-------------------------------------------------------
Figure 4-3. Configuration Menu
Selecting the Data Rate
The Data Rate menu allows you to select the ASM-60 transmission rate.
Main Menu
↓↓↓↓ 1
Configuration
↓↓↓↓ 1
Data Rate
➤ To select the data rate:
1. From the Configuration menu, type 1.
The Data Rate menu appears (see Figure 4-3).
2. Select the data rate by typing the number corresponding to the desired value
and then type 2 to save the changes.
4-4 Configuring ASM-60
Page 27

ASM-60 Installation and Operation Manual Chapter 4 Management from a Terminal
Data Rate (current value)
Enter the Devise Bit Rate
1. 4096 kbps
2. 6144 kbps
3. 10240 kbps
>
ESC - previous menu ; ! - main menu ; & - exit terminal
-------------------------------------------------------
Figure 4-4. Data Rate Menu
4.5 Displaying the ASM-60 System Information
The ASM-60 software allows to display the modem system information.
➤ To access the Display menu:
• From the Main menu, type 2.
The Display menu appears (see Figure 4-5).
Display
1. Status
2. Alarms
3. Log File
4. VDSL Performance
>
ESC - previous menu ; ! - main menu ; & - exit terminal
-------------------------------------------------------
Figure 4-5. Display Menu
Note
Refer to Chapter 5 for the description of the ASM-60 alarms, log file and VDSL
performance monitoring.
Displaying the ASM-60 System Information 4-5
Page 28

Chapter 4 Management from a Terminal ASM-60 Installation and Operation Manual
Displaying the ASM-60 Status
Main Menu
↓↓↓↓ 2
Display
↓↓↓↓ 1
Status
Status
Device Rate: 6144 kbps
Remote Status: ASM60/SA CO
Active Software Version: 01.00
Hardware Version (PCB): 00
AFE Version: 00.00
DTE Interface Type: ETH_UTP
DCD Status: FAILED
Line A Lock Status: SYNC LOSS
Line B Lock Status: SYNC LOSS
Test Mode: NO TEST
Press any key to return to previous menu...
You can display the current status of the local and remote ASM-60 modems.
➤ To display the ASM-60 status:
• From the Display menu, type 1.
The Status screen is displayed (see Figure 4-6).
0. Sync Line A is COMPLETE
1. Sync Line B is COMPLETE
>
ESC - previous menu ; ! - main menu ; & - exit terminal
-------------------------------------------------------
Figure 4-6. Status Screen
The Status screen provides the following information on ASM-60:
• Device Rate – The current date rate of ASM-60
• Device Type – ASM-60 type (ASM-60/CO or ASM-60/CPE)
• Active Software Version – Revision the software currently being used by
ASM-60
• Hardware Version (PCB) – The H/W revision of the ASM-60 main board
• AFE Version – The Analog Front End revision
• DTE Interface Type – The ASM-60 DTE interface and its connector type
• DCD Status – Data Carrier Detect status, indicating if the line A, line B and the
IMUX are synchronized
• Line A Lock Status – The synchronization status of the 2-wire line A
• Line B Lock Status – The synchronization status of the 2-wire line B
• Test Mode – The current status of the diagnostic test (active or not active).
4-6 Displaying the ASM-60 System Information
Page 29

ASM-60 Installation and Operation Manual Chapter 4 Management from a Terminal
4.6 Resetting ASM-60
You can perform reset of the main components of ASM-60, or reset the modem to
its factory settings.
➤ To reset ASM-60:
1. From the Main menu, type 4.
The Reset menu appears (Figure 4-7).
2. From the Reset menu, choose one of the following:
1 – To reset ASM-60 to the default data rate – 10.240 kbps.
2 – To reset the ASM-60 CPU (if the Watchdog jumper on the V-Agent
board is set to ON).
3 – To reset the DSP1 and DSP2.
4 – To reset the framer.
Reset
1. Factory Settings
2. Reset Device
3. Log Reset Chipset
4. Reset FPGA
>
ESC - previous menu ; ! - main menu ; & - exit terminal
-------------------------------------------------------
Figure 4-7. Reset Menu
Resetting ASM-60 4-7
Page 30

Chapter 4 Management from a Terminal ASM-60 Installation and Operation Manual
4-8 Resetting ASM-60
Page 31

Chapter 5
Diagnostics
This chapter describes the ASM-60 diagnostic functions, which include:
• Status indications, alarms, power-up self-test
• VDSL performance diagnostics
• LED testing.
5.1 Error Detection
This section explains how to detect and fix errors and other problematic conditions
in ASM-60.
Power-Up Self-Test
ASM-60 performs a hardware self-test upon turn-on. The self-test sequence checks
the critical circuit functions of the modem.
Front-Panel LEDs
The status of ASM-60 is indicated by the ALM, TST, SYNC A and SYNC B
indicators located on the front panel. For the description of LEDs and their
functions, refer to Chapter 3.
Alarms
ASM-60 maintains two alarm buffers: temporary (up to 20 alarms) and permanent
(up to 100 alarms). The temporary alarm buffer is displayed by the ASM-60
management software as Alarms screen (see Figure 5-1), and the permanent alarm
buffer as Log File (see Figure 5-2).
An alarm enters simultaneously both Alarms display and log file, and the ALM LED
turns on to indicate the condition. But once the event that caused the alarm is
cleared, the alarm is removed from the temporary buffer, but it remains in the log
file, enabling you to view the alarm history.
Working with the Temporary Alarms Buffer
Main Menu
↓↓↓↓ 2
Display
↓↓↓↓ 2
Alarms
➤ To access the Alarms screen:
1. From the Main menu, type 2.
2. From the Display menu, type 2.
The Display menu appears.
The Alarms screen appears (Figure 5-1).
Error Detection 5-1
Page 32

Chapter 5 Diagnostics ASM-60 Installation and Operation Manual
Alarms
DCD Failed
>
ESC - previous menu ; ! - main menu ; & - exit terminal
-------------------------------------------------------
Figure 5-1. Alarms Screen
The display of the Alarms screen includes only the name of the alarm.
Once the event that caused the alarm is cleared, the ALM indicator turns off. You
have to exit the Alarms screen to refresh its display and access the screen again to
assure that the alarm was removed from the temporary buffer.
Working with the Log File
Main Menu
↓↓↓↓ 2
Display
↓↓↓↓ 3
Log File
➤ To access the log file:
1. From the Main menu, type 2, and press <Enter>.
The Display menu appears.
2. From the Display menu, type 3, and press <Enter>.
The Log File screen appears (see Figure 5-2). Up to 12 alarms can be
displayed at a time.
3. Follow the instructions at the bottom of display and type C to clear the log file,
type N to display the next page, type P to display the previous page, or press
<Esc> to exit the log file.
Log File
No. 1 SYNC LOSS LINE A Status ON T=0:0:0
No. 2 SYNC LOSS LINE A Status ON T=0:0:20
ESC - Previous Menu, C-Clear, N-Next Page
Figure 5-2. Log File Screen
The display of the Log File screen includes the serial number of an alarm event, its
name, and time elapsed since the last ASM-60 reset. Table 5-1 lists the ASM-60
alarms.
5-2 Error Detection
Page 33

ASM-60 Installation and Operation Manual Chapter 5 Diagnostics
Table 5-1. ASM-60 Alarms
Number Terminal Message Description Severity
1 FPGA DOWNLOAD
FAILED
2 SELF TEST ERROR A problem has been detected during the
3 DSP1 NOT
RESPONDING
4 DSP2 NOT
RESPONDING
5 DCD FAILED Data Carrier Detect failure indicating
6 SYNC LOSS LINE A Loss of synchronization on the 2-wire
7 SYNC LOSS LINE B Loss of synchronization on the 2-wire
8 NO INTERFACE No DTE interface is connected Minor
9 LAN NOT
CONNECTED
Failure to download programming to the
ASM-60 FPGA microprocessor
device self-test
No response from the ASM-60 Digital
Signal Processor 1
No response from the ASM-60 Digital
Signal Processor 2
that ASM-60 cannot receive a carrier
signal from the other unit
line A
line B
The Ethernet interface module is not
connected to the LAN
Major
Major
Major
Major
Major
Major
Major
Minor
Main Menu
↓↓↓↓ 2
Display
↓↓↓↓ 4
VDSL Performance
5.2 Displaying the VDSL Performance Diagnostics
ASM-60 has capabilities for collection of the VDSL performance diagnostics.
➤ To display the VDSL diagnostics:
1. From the Main menu, type 2.
The Display menu appears.
2. From the Display menu, type 4.
The VDSL Performance screen appears (see Figure 5-3). Table 5-2 lists the
ASM-60 performance monitoring parameters.
3. Type C to reset the performance registers, type R to monitor the VDSL
performance, type S to stop monitoring or press <Esc> to exit.
Displaying the VDSL Performance Diagnostics 5-3
Page 34

Chapter 5 Diagnostics ASM-60 Installation and Operation Manual
VDSL Performance
Line A Lock Status: SYNC
Line A Avg. Snr.: 34
Line A BER pre FEC: 0.000E+00
Line A BER after FEC: 0.000E+00
Line B Lock Status: SYNC
Line B Avg. Snr.: 34
Line B BER pre FEC: 0.000E+00
Line B BER after FEC: 0.000E+00
>
ESC - previous menu ; ! - main menu ; & - exit terminal
-------------------------------------------------------
Figure 5-3. VDSL Performance Screen
Note
Figure 5-3 shows VDSL Performance Monitoring screen, as it appears 15 seconds
after the ASM-60 power-up.
Table 5-2. ASM-60 Performance Monitoring Parameters
Display Description
Line A/B Lock Status This parameter provides the information on the status of the
connection between the ASM-60 units (synchronized or not
synchronized). This value is updated every second.
Line A/B Avg. Snr. This parameter provides the avarage signal-to-noise ratio in the line.
Line A/B BER pre FEC This parameter provides the bit error rate before the Forward Error
Correction is performed.
Line A/B BER after FEC This parameter provides the bit error rate after the Forward Error
Correction is performed.
5-4 Displaying the VDSL Performance Diagnostics
Page 35

ASM-60 Installation and Operation Manual Chapter 5 Diagnostics
5.3 Running the Diagnostic Tests
Running the LEDs Test
The ASM-60 modem can perform the front-panel indicators test to verify that the
unit LEDs are functioning properly.
Main Menu
↓↓↓↓ 3
Test
↓↓↓↓ 2
Start LEDs Test
➤ To run the LEDs test:
1. From the Main menu, type 3.
The Test menu appears.
2. From the Test menu, type 2 to run the LEDs test on ASM-60.
All the front-panel LED indicators light up for 3 seconds.
Running the Diagnostic Tests 5-5
Page 36

Chapter 5 Diagnostics ASM-60 Installation and Operation Manual
5-6 Running the Diagnostic Tests
Page 37

Appendix A
IR-ETH Interface Module
IR-ETH is an interface module for RAD modems, used for converting the Ethernet
(10BaseT or 10Base2) electrical levels to the modem TTL levels. It also converts the
Ethernet protocol to HDLC to enable long-distance transmission and avoid the
Ethernet collision limitation.
IR-ETH includes an internal, self-learning Ethernet bridge, which enables a high
performance link between two Ethernet segments at a low transmission rate. The
low-speed HDLC transmission is sent over the link using the modem modulation
technique. It is converted back to an Ethernet signal at the remote modem.
Figure A-1 shows a typical application using an Ethernet interface bridge. Each
modem is connected to an Ethernet network via the Ethernet interface bridge.
ASM-60 ASM-60
100-230 VAC 0.250A T 250V
:
CAUTION
FOR CONTINUED
PROTEC TION AG AINST R ISK OF
FIRE, REPLACE ONLY WITH SAME
TYPE AND RATING OF FUSE.
Figure A-1. Typical Application of ASM-60 with IR-ETH Module
A.1 IR-ETH Connector Options
Figure A-2 and Figure A-3 show the rear panel of ASM-60 with the IR-ETH
connector options. Table A-1 lists the RJ-45 connector pinout.
LINE
RXLINK
TXCOLL
A-1 2 4 5-B
Figure A-2. Rear Panel of ASM-60 with IR-ETH Module (RJ-45 Connector)
10BASE-T
IR-ETH Connector Options A-1
Page 38

Appendix A IR-ETH Interface Module ASM-60 Installation and Operation Manual
:
CAUTION
FOR CONTINUED
PROTEC TION AG AINST R ISK OF
FIRE, REPLACE ONLY WITH SAME
TYPE AND RATING OF FUSE.
100-230 VAC 0.250A T 250V
LINE
A-1 2 4 5-B
RX
10BASE-2
TXCOLL
Figure A-3. Rear Panel of ASM-60 with IR-ETH Module (BNC Connector)
Table A-1. RJ-45 Pinout
Pin Function
3 RCV (+)
6 RCV (-)
1 XMT (+)
2 XMT (-)
– GND
General
LAN
WAN
A.2 Technical Specifications
LAN Table
Filtering and Forwarding
Buffer
Delay
Standard
Data Rate
Connectors
Protocol
Data Rate
10,000 addresses
15,000 pps
256 frames
1 frame
Conforms to IEEE 802.3/Ethernet
10 Mbps (20 Mbps 10BaseT FDX)
• 10BaseT (UTP): Shielded RJ-45
• 10Base2: BNC connector
HDLC
According to the modem transmission rate
A-2 Technical Specifications
Page 39

ASM-60 Installation and Operation Manual Appendix A IR-ETH Interface Module
A.3 Installation and Operation
Figure A-4 and Figure A-5 show the Ethernet bridge layout, the locations of the DIP
switches, and the rear panel components for the UTP and the BNC versions,
respectively.
Figure A-4. IR-ETH Layout (UTP Option)
Figure A-5. IR-ETH Layout (BNC Option)
Installation and Operation A-3
Page 40

Appendix A IR-ETH Interface Module ASM-60 Installation and Operation Manual
DIP Switch Settings
Table A-2 describes functions and default settings of the DIP switch SW-1 sections.
Table A-2. DIP Switch Settings
Section
Number
1 SQ/FD ON – Full-duplex operation
2 CMP ON – Strips padding bits inserted in 64-byte frame
3 FIL ON – Passes only frames destined for another LAN
4
Name Description Default
OFF – Half-duplex operation
OFF – Transmits frames over WAN as is
OFF – Disables LAN filter; passes all frames transparently
(nc)
LED Indicators
Table A-3 lists the IR-ETH LED indicators and describes their functions.
Table A-3. IR-ETH Bridge LED Indicators
LED
Name
LINK ON indicates good link integrity Rear panel Green
Description Location Color
Setting
OFF
OFF
OFF
COLL ON indicates collision on the attached Ethernet
segment
RX ON when data is received from the Ethernet
attached segment
TX ON when data is transmitted from the modem
to the Ethernet segment
ERR D4 Bridge buffer overrun On the
Connecting to LAN
When connecting an IR-ETH interface module with the UTP option, use either a
straight cable or a cross cable for the LAN connection. Use a cross cable when
connecting to a port that does not implement the crossover function internally.
Otherwise, use a straight cable.
Note
Hubs usually do implement the crossover function internally, while network
interface cards and other devices do not.
Rear panel Yellow
Rear panel Yellow
Rear panel Yellow
Red
IR-ETH board
A-4 Installation and Operation
Page 41

Appendix B
IR-ETH/QH Interface Module
B.1 Introduction
The IR-ETH/QH interface module includes a high performance self-learning Fast
Ethernet bridge, which is connected to the LAN via a single 10BaseT or 100BaseT
port, operating in full duplex and providing offer simple and cost-effective
interconnection between 10/100BaseT LANs via VDSL links. The IR-ETH/QH
interface module also supports IEEE 802.1/Q frames, enabling VLAN applications.
The module automatically learns MAC addresses of the LAN to which it is
connected. Its LAN table stores up to 1,000 addresses with 5-minute automatic
aging.
Filtering and forwarding is performed at the maximum theoretical rate of
150,000 packets per second (wire speed). The buffer with 1 Mb DRAM can hold
170 frames with a throughput latency of one frame. The forwarding of the
broadcast and multicast messages from LAN to WAN can be disabled.
Figure B-1 shows a typical application using ASM-60 with IR-ETH/QH module.
ASM-60 ASM-60
Figure B-1. Typical Application of ASM-60 with IR-ETH/QH Module
B.2 IR-ETH/QH Connector
Figure B-2 shows the rear panel of ASM-60, equipped with IR-ETH/QH module.
Table B-1 lists the module's RJ-45 connector pinout.
:
FOR CONTINUED
CAUTION
PROTECTION AGAINST RISK O F
FIRE, REPLACE ONLY WITH SAME
TYPE AND RATING OF FUSE.
LINE
A-1 2 4 5-B
100
ACT
LINK
Figure B-2. Rear Panel of ASM-60 with IR-ETH/QH Module
IR-ETH/QH Connector B-1
Page 42

Appendix B IR-ETH/QH Interface Module ASM-60 Installation and Operation Manual
Table B-1. RJ-45 Connector Pinout
Pin Signal Function
1 RD (+) Receive Data (positive)
2 RD (-) Receive Data (negative)
3 TD (+) Transmit Data (positive)
6 TD (-) Transmit Data (negative)
B.3 Technical Specifications
Bridge
LAN
WAN
LAN Table
Aging
Filtering and
Forwarding Rate
Buffer Size
Delay
Standard
Data Rate
Transmission Line
Line Code
Connector
Protocol
Data Rate
1,000 MAC addresses
5 minute, automatic
150,000 packets per second
170 frames
1 frame
IEEE 802.3/Ethernet V.2, IEEE 802.1/Q
• 10BaseT: 10 Mbps (20 Mbps in full duplex)
• 100BaseT: 100 Mbps (200 Mbps in full duplex)
4-wire, Category 5 UTP, 19 AWG to 26 AWG
• 10BaseT: Manchester
• 100BaseT: MLT3
RJ-45
Point-to-point
512 kbps to 45 Mbps
B-2 Technical Specifications
Page 43

ASM-60 Installation and Operation Manual Appendix B IR-ETH/QH Interface Module
B.4 Installation and Operation
Figure B-3 shows location of the configuration DIP switch on the module’s board.
87654321
S1
ON
Figure B-3. DIP Switch Location
Setting the DIP Switch
Configure the IR-ETH/QH module by setting the DIP switch in accordance with
Table B-2. The DIP switch is located on the reverse side of the IR-ETH/QH
module. To change the switch settings, you must undo three screws on the board
and detach the module from the main unit.
Table B-2. DIP Switch Settings
Section Name Description Possible Settings Factory Setting
1 NC OFF
2 NC OFF
3 10/100 Selects the LAN speed
4 AN1 Controls the LAN
autonegotiation
5 HF1 Selects the LAN mode ON – LAN full duplex mode
6 BPR Controls the backpressure ON – Backpressure is enabled
7 MUL Controls LAN to WAN
multicasting
8 BRD Controls LAN to WAN
broadcasting
ON – LAN speed is set to 100 Mbps
OFF – LAN speed is set to 10 Mbps
ON – LAN autonegotiation is disabled
OFF – LAN autonegotiation is enabled OFF
OFF – LAN half duplex mode
OFF – Backpressure is disabled
ON – Multicast messages from LAN to
WAN are blocked
OFF – Multicast messages from LAN to
WAN are not blocked
ON – Broadcast messages from LAN
to WAN are blocked
OFF – Broadcast messages from LAN
to WAN are not blocked
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
Installation and Operation B-3
Page 44

Appendix B IR-ETH/QH Interface Module ASM-60 Installation and Operation Manual
LED Indicators
Table B-3 lists the IR-ETH/QH rear-panel LED indicators and describes their
functions.
Table B-3. IR-ETH/QH LED Indicators
LED Name Color Description Location
LINK Green ON – LAN is connected to the IR-ETH/QH
Connector
module
ACT Yellow ON – LAN is receiving/transmitting data Connector
100 Green ON – LAN is operating at 100 Mbps
Panel
OFF – LAN is operating at 10 Mbps
Connecting the LAN
Use either a straight cable or a cross cable for the LAN connection.
Use a cross cable when connecting to a port that does not implement the
crossover function internally. Otherwise, use a straight cable.
Note
Hubs usually implement the crossover function internally, while NICs and other
devices do not.
B-4 Installation and Operation
Page 45

Overview
Appendix C
IR-IP Interface Module
C.1 Introduction
IR-IP is a high-performance, miniature IP router based on RAD's unique IP router
chip, the ChipRouter.
IR-IP works by taking each Ethernet frame from the LAN and determining whether
the IP packet is destined for the IP net on the Ethernet LAN. If not, IR-IP forwards
the packet to the WAN (VDSL) link. IP packets received from the WAN link are
automatically forwarded to the LAN if the IP net matches.
IR-IP includes hardware filters which handle all filtering operations at wire speed
from both LAN-to-WAN and WAN-to-LAN, without dropping a single packet.
Filtering and forwarding are performed at the maximum rate of 35,000 and
30,000 frames per second (wire speed), respectively. The buffer can hold
256 frames of maximum size of 1534 bytes and a throughput latency of one
frame.
IR-IP is available with 10BaseT (UTP) interface and is fully
IEEE 802.3/Ethernet v2 compliant. The IR-IP interface can also operate in full
duplex Ethernet applications.
ASM-60 equipped with IR-IP interface module can be used as a Frame Relay
Access Device (FRAD) with an integral IP router. RFC 1490 is supported for a
single DLCI on the WAN link. Detection of the DLCI and the maintenance
protocol is performed automatically. This allows the IR-IP to be used as the
termination unit of IP services over Frame Relay at the customer premises,
opposite a Frame Relay switch in the backbone.
Alternatively, Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) can be run on the WAN link with
automatic negotiation on power-up, as well as support for PAP and CHAP
authentication. With this feature, IR-IP can operate opposite any PPP compliant
access server or backbone router.
IR-IP supports HDLC, which is especially important for broadcast and multicast
applications where bandwidth overhead is critical.
IR-IP supports IP multicast at wire speed, making it suitable for any multicast
environment including high speed downstream environments, such as satellite and
xDSL. Users on the LAN who register with IR-IP for an IP multicast group using the
IGMP protocol filter IP multicast packets at wire speed.
Management and advanced configuration are performed via Telnet.
Introduction C-1
Page 46

Appendix C IR-IP Interface Module ASM-60 Installation and Operation Manual
Application
Figure C-1 shows a typical application of the ASM-60 modem equipped with the
IR-IP interface module.
Router
LAN
WAN
ASM-60
with IR-IP
Figure C-1. Typical Application of ASM-60 with IR-IP
C.2 Technical Specifications
LAN IP Net
Filtering and
Forwarding
Buffer
Delay
Standard
Data Rate
Connector
Protocols
Up to 256 hosts on LAN IP net
30 kbps/35 kbps
256 frames (maximum size – 1534 bytes)
1 frame
Conforms to IEEE 802.3/Ethernet v2
10 Mbps (20 Mbps 10BaseT in full duplex
topology)
10BaseT (UTP): Shielded RJ-45
• PPP (PAP/CHAP)
ASM-60
with HSSI Interface
Router
:
CAUTION
FOR CONTINUED
PROTECTI ON AGAIN ST RISK OF
FIRE, REPLACE ONLY WITH SAME
TYPE AND RATING OF FUSE.
• Frame Relay (RFC 1490)
• HDLC
C.3 Physical Description
Figure C-2 shows the rear panel of ASM-60 with the IR-IP interface module.
LINE
A-1 2 4 5-B
Figure C-2. Rear Panel of ASM-60 with the IR-IP Module
10BASE-T
IR-IP
ACT
ERR
INT
C-2 Physical Description
Page 47

ASM-60 Installation and Operation Manual Appendix C IR-IP Interface Module
IR-IP LEDs
IR-IP contains three LEDs, which indicate the module activity. Table C-1 lists the
LEDs functions.
Table C-1. IR-IP LEDs Functions
Name Type Function
INT Green LED ON – LAN integrity is established.
ACT Yellow LED Blinks – Transmit/receive activity is detected on the
Ethernet link.
ERR Red LED ON – Buffer overflow occurred (during normal operation).
During power-up, provides additional indications,
described below.
IR-IP DIP Switch
IR-IP interface module contains a four-section DIP switch, as seen in Figure C-3.
Table C-2 lists the DIP switch functions.
Figure C-3. IR-IP DIP Switch
Table C-2. IR-IP DIP Switch Functions
No Function Values Default Setting
1 Enables IR-IP to learn its IP ON – IP address learning is enabled
OFF – IP address learning is disabled
2 Selects the WAN protocol ON – PPP protocol
OFF – Frame Relay protocol
3 Selects the LAN mode ON – Full duplex operation
OFF – Half duplex operation
4 Controls the remote WAN test
loopback, which returns packets
received from the WAN back
toward the WAN
ON – The test loopback is activated
OFF – The test loopback is disabled
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
Table C-3 provides the pinout of the IR-IP RJ-45 connector.
Table C-3. RJ-45 Pinout
Pin Name Function
1 TD (+) Transmit data positive
2 TD (-) Transmit data negative
3 RD (+) Receive data positive
6 RD (-) Receive data negative
Physical Description C-3
Page 48

Appendix C IR-IP Interface Module ASM-60 Installation and Operation Manual
C.4 IR-IP Management Subsystem, General
Introduction
The IR-IP interface module management subsystem supports the following
functions:
• Preliminary configuration
• Configuration of management access parameters
• Advanced configuration of IR-IP parameters
• Collection and display of statistical performance data
• Maintenance functions, which include:
Software downloading
Resetting of various subsystems
Display of error log
Ping utility, for checking IP connectivity.
The management subsystem of the IR-IP interface module is a separate,
independent entity, and therefore it cannot be managed through the ASM-60
management subsystem.
The communication with the IR-IP management subsystem is made through the
local LAN interface connector of the IR-IP module, designated 10BASE-T, using
the Telnet protocol. Passwords can be used to prevent unauthorized access.
Accessing the IR-IP Management Subsystem
The IR-IP interface module must be configured in accordance with the specific
requirements of the user’s application before it can be used in the user’s network.
As a result, it is not possible to supply default parameters to enable IR-IP to start
service without any preliminary configuration.
Therefore, to enable the user to establish Telnet communication and configure
IR-IP, IR-IP is delivered with a default set of parameters. The default parameters
are automatically used:
• Before the IP router is configured by the user, e.g., when a new ASM-60 with
IR-IP interface module is put into operation
• After the user’s configuration parameters have been erased.
When the factory-default parameters are used, the ERR indicator located on the
ASM-60 rear panel, near the IR-IP Ethernet interface connector flashes rapidly
(about three times per second).
Note
The flashing of the ERR indicator also serves as a warning to the user that the IR-IP
WAN (VDSL) interface does not send, nor does it receive packets, and therefore IRIP can be accessed only from the LAN.
After configuring IR-IP, it starts normal operation and routes the traffic in
accordance with the user-selected configuration parameters.
To change the parameters of an already-configured IR-IP, establish communication
from a Telnet host using the assigned IP address.
C-4 IR-IP Management Subsystem, General
Page 49

ASM-60 Installation and Operation Manual Appendix C IR-IP Interface Module
Default IP Communication Parameters
The default IP communication parameters of the interface module are:
• The default IP address of the IR-IP Ethernet port is 192.168.205.1, and the
default IP subnet mask is 255.255.255.252.
• The port will accept IP communication only from the IP address
192.168.205.2. Therefore, as long as the factory defaults are in effect, you
must assign this address to the Telnet host used to configure IR-IP.
Using the IP learning mechanism, as explained below you can change the default
parameters.
Note
In the default configuration, the IR-IP WAN interface is disabled. In order to enable
the WAN interface, you have to modify the Ethernet port address or the IP subnet
mask.
C.5 Performing Preliminary Configuration
General
The software necessary for performing all the management and configuration
functions is stored in the IR-IP interface module, and therefore you only need a
regular Telnet host to perform all the activities described in this appendix.
A Telnet host is any computer, e.g., an IBM PC or compatible that fulfills the
following minimum requirements:
• A standard 10BaseT Ethernet interface
• A TCP/IP protocol stack, and therefore is capable of supporting IP
communication through the Ethernet interface
• Telnet client software
• A ping utility.
Outline of Preliminary Configuration
➤ To perform the preliminary configuration procedure:
1. Connect the Telnet host to the IR-IP interface module.
2. Configure the Telnet host to enable communication with the IR-IP interface
module using the default IP parameters.
3. Establish communication with IR-IP and assign the prescribed IP address to its
LAN interface.
4. Establish again communication with IR-IP and continue the preliminary
configuration in accordance with the Quick Setup Menu section below.
Performing Preliminary Configuration C-5
Page 50

Appendix C IR-IP Interface Module ASM-60 Installation and Operation Manual
Connecting the Telnet Host
Before starting the management and configuration activities, it is necessary to
establish IP communication between your Telnet host and the IR-IP interface
module. For this purpose, it is necessary to provide a communication path.
Because of the method used to assign an IP address to IR-IP Ethernet port, it is
recommended to connect the Telnet host directly to the IP router 10BASE-T
connector. This is made by connecting an Ethernet cross cable between the
Ethernet connector of the Telnet host and the IR-IP connector.
However, you may also connect through a common LAN: in this case, connect
your Telnet host and IR-IP to Ethernet hub ports using straight cables.
Preliminary Telnet Host Configuration
You can use the IP learning mechanism to configure the IP communication
parameters of the IR-IP LAN interface. In this case, skip to the Assigning the Router
LAN Interface Address section below.
If you prefer to use the factory-default parameters to establish IP communication
between your Telnet host and IR-IP, configure the Telnet host as follows:
1. Temporarily configure the host IP address as 192.168.205.2.
2. The initial destination IP address to be used by the host is 192.168.205.1.
Note
The first step in the preliminary configuration process is to assign the desired IP
address to the LAN interface of the IR-IP interface module.
After an IP address is assigned and saved, you must change the destination IP
address of the Telnet host to the new address, otherwise it is not possible to
continue the configuration process. At the same time, you can also change the
temporary IP address assigned to the host (192.168.205.2) back to its permanent
address.
Assigning the Router LAN Interface Address
The IP address of the IR-IP LAN interface must be configured as part of the
preliminary configuration process. To simplify this process, IR-IP includes a simple
and convenient IP address learning mechanism.
The IP address can be configured and changed at any time, even after the
complete IR-IP configuration process has been performed, because it does not
affect other configuration parameters. Moreover, the IP subnet mask is
automatically adapted to the new IP address.
IP Learning Mechanism
To simplify the configuration process, IR-IP has a special mechanism for
configuring the IP address of its LAN interface. Setting section 1, called IP address
learning, of the IR-IP DIP switch (Figure C-3) to ON enables this mechanism.
The IP learning mechanism enables IR-IP to learn its LAN interface IP address by
receiving frames sent by a ping utility to the prescribed LAN IP address.
Note
C-6 Performing Preliminary Configuration
To use the IP learning mechanism, you do not need to know the current address of
IR-IP LAN interface, but only the prescribed IP address.
Page 51

ASM-60 Installation and Operation Manual Appendix C IR-IP Interface Module
The IP address is actually retrieved from the ARP frames sent during pinging to
locate the ping destination, not from the ping frames.
To ensure that the process is correctly performed, it is recommended to check the
contents of the ARP table before starting the ping utility, to make sure that it does
not contain the address to be assigned to the IP router LAN interface.
➤ To view and edit the ARP table contents:
If the Telnet host you are using runs under Microsoft Inc. Windows ™ 95, 98 or
NT, use the following procedure to view and edit the ARP table contents:
1. Display the table using the
arp -a
command.
2. If the table includes the intended IP address, remove it from the table using
the
arp -d
command.
If for some reason the IP learning process does not succeed, before repeating it
make sure to remove the IP address from the table.
Assigning a LAN IP Address to a New IR-IP
The following procedure enables you to configure the LAN IP address of a new
IR-IP router, i.e., a router using the default parameters (see the Accessing the IR-IP
Management Subsystem section above).
If ASM-60 is already operating, skip Step 2 in the following procedure.
➤ To configure the IP router LAN address:
1. Make sure the preparations described above have been completed, including
the configuration of the ping utility.
2. Turn ASM-60on and monitor the IP router indicators:
The INT indicator turns on
The ERR indicator lights steadily for approx. 15 seconds, and then starts
flashing at a rapid rate (about three times per second).
If the ERR indicator turns off, skip to the What to Do If ... section below.
3. Set section 1 of IR-IP DIP switch to ON.
The ERR indicator starts flashing faster (approximately four times a second).
4. Send a ping to the new address to be used by IR-IP. A confirmation should be
received after the third ping: after the confirmation, the flashing will slow
down to approximately twice a second.
If your host does not begin to receive ping replies after three unsuccessful
attempts, skip to the What to Do If ... section below.
5. Return section 1 of the IR-IP DIP switch to the OFF position.
The ERR indicator must turn off.
At this stage, the communication with IR-IP router is lost, because its IP address
has been changed. Therefore, you must reconfigure the destination IP address of
the Telnet host. If you wish, you may also change the temporary IP address
assigned to the host (192.168.205.2) back to its permanent address.
Performing Preliminary Configuration C-7
Page 52

Appendix C IR-IP Interface Module ASM-60 Installation and Operation Manual
After changing the destination IP address of the Telnet host, it is recommended to
turn ASM-60 off for a few seconds and then back on, before continuing the
configuration of the IP router in accordance with the Quick Setup Menu section
below. At this time, in Step 2 the ERR indicator turns off after the 15-second
interval.
Changing the LAN IP Address of a Configured IR-IP
The LAN IP address of an already-configured IR-IP can be changed while it
operates, this means it is not necessary to turn ASM-60off before starting the
configuration procedure. Note however that the IP traffic flow through IR-IP will
be disrupted until the other stations in the IP network learn the new address.
To change the LAN IP address of an already-configured IR-IP, use the procedure
described above for a new IR-IP with the following differences:
1. Configure the destination address of the ping utility to the new LAN interface
IP address. It is not necessary to change the Telnet host source address.
2. When ready, set section 1 of the IR-IP DIP switch to ON.
The ERR indicator starts flashing faster (approximately four times a second).
3. Perform Steps 4, 5 of the procedure used for a new IR-IP.
What to Do If ...
➤ The INT indicator does not light immediately after ASM-60 is turned on
The IR-IP interface module does not receive power from the ASM-60 power
supply. Service is required.
Note
After the power-up process ends, the INT indicator shows LAN integrity. It may stay
turned off without indicating power supply failure.
➤ The ERR indicator does not light immediately after ASM-60 is turned on
IR-IP is faulty and must be replaced.
➤ After turn-on, the ERR indicator lights for 15 seconds and then turns off. ACT
does not light, and there is no response from IR-IP
No software loaded into IR-IP. Download software using the procedure described
in the New Software Download Menu section below.
➤ After turn-on, the ERR indicator lights for 15 seconds, and then turns off. ACT
lights from time to time, but there is no response from IR-IP
IR-IP has been configured. If you do not know the current IP address of the LAN
interface, erase IR-IP router configuration using the procedure given in the Erasing
User’s Configuration section below.
➤ No ping replies from IR-IP
If your host does not begin to receive ping replies after three unsuccessful
attempts, check the physical connection path between the Telnet host Ethernet
interface and the IR-IP 10BASE-T connector.
➤ The IP learning process is not successful
Check that the prescribed IP address does not appear in the ARP table.
C-8 Performing Preliminary Configuration
Page 53

ASM-60 Installation and Operation Manual Appendix C IR-IP Interface Module
C.6 IR-IP Management Utility
General Operating Procedures
The IR-IP interface module is managed via a simple, menu-driven utility that uses a
basic terminal user interface. A typical screen is shown in Figure C-4.
As seen in Figure C-4, each screen has a header that identifies the device being
configured and its logical name, assigned by the user, followed by the running
software revision and date. The bottom line of the screen displays prompts that
guide you in the execution of the various activities.
Use the following general procedures to perform the desired activity:
• To change a parameter or to select a menu item, type the corresponding line
number.
• For a parameter, which has a discrete set of values, the parameter values are
enclosed in brackets [ ]. To select a new value, press the spacebar to scroll
among the available values until the desired value is displayed, and then press
<Enter> to select the displayed value.
• To enter a value which requires free text entry, type in the desired string and
then press <Enter>. Use backspace to erase the current string.
• After all the parameters have been selected, a prompt appears, requesting that
you confirm the changes.
Note
For proper display of the screens, you must:
• Select a fixed-pitch system font for the display. Use your operating system
documentation to find how to select a proper font.
• Configure the Telnet utility to use VT-100 terminal emulation.
Starting a Management Utility
The management utility is started automatically when Telnet communication is
established. If password protection is enabled (see the Management Access Menu
section below), you will be prompted to enter the Telnet password. The opening
screen, which appears after the Telnet session activation, is the IR-IP Main menu
(see Figure C-4).
IR_IP <IR-IP> S/W Ver. 1.00 31/IR (date)
1. Quick Setup
2. Management Access
3. Advanced Setup
4. Device Control
5. View
6. Diagnostic Tool (PING terminal)
Press one of the numbers to select or ESC:
Figure C-4. IR-IP Main Menu
IR-IP Management Utility C-9
Page 54

Appendix C IR-IP Interface Module ASM-60 Installation and Operation Manual
To end the utility, press <Esc> when the Main menu is displayed. This will also
end the Telnet session.
Menu Structure of Management Utility
Figure C-5 shows the menu structure of the IR-IP management utility.
Main Menu
1. Quick Setup
1. LAN IP Address
2. LAN IP Mask
3. WAN IP Address
4. WAN IP Mask
5. Default Gateway
6. Read Protocol From DIP Switches
7. Protocol
2. Management
Access
1.Telenet Password
2. Telenet Activity Timeout
3. SNMP Access
4. SNMP Read Community
5. SNMP Write Community
6. SNMP Trap Community
7. SNMP Management Table
3. Advanced Setup 4. Device Control
1. Device Identification
1. Device Name
2. Contact Person
3. System Location
2. Interface Parameters
1. LAN Status
2. WAN Status
3. WAN Throttle
4. Aging Timeout
3. Protocol P arameters (FR)
1. Self Learn
2. Maintenance Protocol
3. DLCI
4. CIR
5. EIR
3. Protocol Parameters ( PPP)
1. Header and Control Field Compression
2. Protocol Field Compression
3. Authentication Protocol
4. Security Host/Guest
5. User Name To Send
6. Password To Send
7. User Name To Accept
8. Password To Accept
4. Multicast
1. Multicast Forwarding
2. Static Groups
1. New Soft ware Download
1. Server IP Address
2. File Name
3. Total Timeout
4. Start Operation
2. View Error Log
3. Resets
1. Reset Device
2. Reset LAN
3. Reset WAN
Figure C-5. Management Utility, Menu Structure
5. View
1. Configuration and Connection
2. ARP Tables
3. Multicast Groups Table
4. Statistics
6. Diagnostic Tool
PING Terminal
1. Ping IP Address
2. Start Pinging
3. Stop Pinging
C.7 Quick Setup Menu
The Quick Setup menu is used to select the main parameters’ values that must be
defined before you start using IR-IP.
Use the Advanced Setup menu (see the Advanced Setup Menu section below) to
specify values for other IR-IP configuration parameters not included in this menu.
➤ To access the Quick Setup menu:
• From the Main menu, type 1.
The Quick Setup menu appears (Figure C-6).
C-10 Quick Setup Menu
Page 55

ASM-60 Installation and Operation Manual Appendix C IR-IP Interface Module
IR_IP <IR-IP> S/W Ver. 1.00 31/IR (date)
Quick Setup
=====================================================================
1. LAN IP Address :192.168.100.001
2. LAN IP Mask :255.255.255.000
3. WAN IP Address (empty for unnumbered) :...............
4. WAN IP Mask (empty for unnumbered) :...............
5. Default Gateway (empty - WAN interface) :...............
6. Read Protocol From DIP Switches :[ Yes ]
7. Protocol :[ Frame Relay ]
Press one of the numbers to select or ESC:
Figure C-6. Quick Setup Menu
LAN IP Address
Used to enter the IP address for the IP router LAN interface. This is the address to
which nodes connected to the local LAN send packets addressed to the WAN.
LAN IP Mask
Used to enter the IP subnet mask. The IP router supports a maximum of 254 hosts
on the LAN, therefore you must use Class C subnet masks. The basic subnet IP
mask for Class C addresses, which supports the maximum possible number of
hosts, 254, is 255.255.255.0. To help you understand the selection of IP subnet
masks, Figure C-7 provides a configuration example for a LAN with 6 nodes: the IP
subnet mask for a 6-node IP network is 255.255.255.248.
IP Address
Mask
WAN IP Address
Used to enter the IP address for the IR-IP WAN interface, i.e., the IP address to be
used by IP hosts on the WAN to reach this IR-IP interface module.
LAN IP Address: 192.168.1.2
Mask: 255.255.255.248
Figure C-7. Selecting the IP Subnet Mask
ASM-60 with IR-IP
192.168.1.1192.168.1.1192.168.1.1192.168.1.1192.168.1.1Default Gateway
.6.5.4.3192.168.1.2
.248.248.248.248255.255.255.248
If the WAN IP Address field remain blank, IR-IP operates in the Unnumbered
Router Mode.
WAN IP Mask
Used to enter the IP subnet mask for the WAN interface.
Quick Setup Menu C-11
Page 56

Appendix C IR-IP Interface Module ASM-60 Installation and Operation Manual
Default Gateway
Operation without Default Gateway
The IP interface module is intended to enable the extension of LANs through the
ASM-60 VDSL link. Therefore, its default routing operation is different from the
default routing operation of standard IP routers:
• IR-IP forwards packets with destinations not located on the local LAN through
the WAN interface
• Packets received from the WAN interface and destined to hosts located on the
local LAN are forwarded to the LAN; other packets are discarded.
The default operation is used when the Default Gateway field is blank.
Operation with Default Gateway
You can instruct IR-IP to send packets with destinations not located on the local
LAN to a specific router, which is called the default gateway. The default gateway
must be connected to the local LAN.
To use this option, enter the IP address of another router attached to the local LAN
in the Default Gateway field.
Note
It is very important to obtain the correct parameters from the system administrator
or ISP. The most common problem when establishing an IP connection is incorrect
configuration of IP parameters and default gateway. Do not try to guess these
parameters.
Read Protocol from DIP Switches
Selecting YES for this parameter forces IR-IP router card to use the WAN protocol
selected by section 2 of its DIP switch: PPP or Frame Relay.
If you want to be able to select the WAN protocol by means of the Protocol field
(parameter 7) of the Quick Setup menu, select NO.
Protocol
Used to select the WAN protocol to be used by the IP router card: PPP, HDLC or
Frame Relay.
This parameter is available only if the Read Protocol from DIP Switches parameter
is set to NO.
C.8 Management Access Menu
The Management Access menu is used to enable the use of passwords to protect
the access to IR-IP management utility, and control the inactivity time-out interval.
When password protection is enabled, a Telnet management session can start only
after the correct password is entered.
C-12 Management Access Menu
Page 57

ASM-60 Installation and Operation Manual Appendix C IR-IP Interface Module
➤ To access the Management Access menu:
• From the Main menu, type 2.
The Management Access menu appears (Figure C-8).
IR_IP <IR-IP> S/W Ver. 1.00 31/IR (date)
Quick Setup
Management Access
=====================================================================
1. Telnet Password :..........
2. Telnet Inactivity Timeout (min) :300..
3. SNMP Access :Disabled
4. SNMP Read Community :public....
5. SNMP Write Community :public....
6. SNMP Trap Community :public....
7. SNMP Management Table :>>>
Press one of the numbers to select or ESC:
Note
Since the IP router card does not support SNMP management, the SNMP Read
Community, SNMP Write Community, SNMP Trap Community, and SNMP
Management Table parameters are not used.
Telnet Password
By default, management access to IR-IP via Telnet is unrestricted. To restrict
access, enter a Telnet password by selecting 1 in the Management Access menu.
The password can include up to 10 characters, and is case-sensitive. The next time
a Telnet session is opened, a password must be entered to enable you to access
the IR-IP menus.
At any time, only one Telnet connection to IR-IP is permitted. Any attempt to
open an additional connection while the current session is open is rejected.
Telnet Inactivity Timeout
This parameter specifies the time a Telnet session is kept open when there is no
keyboard activity. When the specified time-out expires, the Telnet session is closed
and another user can access IR-IP.
Figure C-8. Management Access Menu
C.9 Advanced Setup Menu
The Advanced Setup menu is used to select the desired group of IR-IP
configuration parameters.
The parameters accessed through Advanced Setup menu supplement the
parameters available on the Quick Setup screen, by providing control over all the
other IR-IP parameters.
Advanced Setup Menu C-13
Page 58

Appendix C IR-IP Interface Module ASM-60 Installation and Operation Manual
➤ To access the Advanced Setup menu:
• From the Main menu, press 3.
The Advanced Setup menu appears (Figure C-9).
IR_IP <IR-IP> S/W Ver. 1.00 31/IR (date)
Quick Setup
Management Access
Advanced Setup
=====================================================================
1. Device identification
2. Interface Parameters
3. Protocol Parameters
4. Multicast IP
Press one of the numbers to select or ESC:
Figure C-9. Advanced Setup Menu
Device Identification Menu
The Device Identification menu is used to define and store in the IR-IP logistic
information: the logical name of IR-IP, information on the contact person and
device location.
➤ To access the Device Identification menu:
• From the Advanced Setup menu, type 1.
The Device Identification menu appears (Figure C-10).
IR_IP <IR-IP> S/W Ver. 1.00 31/IR (date)
Quick Setup
Management Access
Advanced Setup
.....................................................................
Device identification
=====================================================================
1. Device Name :IR-IP..
2. Contact Person :Name of contact Person
3. System Location :The location of this device
Press one of the numbers to select or ESC:
Figure C-10. Device Identification Menu
Device Name
Select this parameter to assign an arbitrary name to IR-IP for identification by the
system manager (up to eight characters). The assigned name is displayed in the
screen header.
C-14 Advanced Setup Menu
Page 59

ASM-60 Installation and Operation Manual Appendix C IR-IP Interface Module
Contact Person
Select this parameter to enter the name of the person to be contacted with matters
pertaining to this equipment unit.
System Location
Select this parameter to enter the physical location of the device.
Interface Parameters Menu
The Interface Parameters menu is used to control the operation of IR-IP interfaces.
➤ To access the Interface Parameters menu:
• From the Advanced Setup menu, type 2.
The Interface Parameters menu appears (Figure C-11).
IR_IP <IR-IP> S/W Ver. 1.00 31/IR (date)
Quick Setup
Management Access
Advanced Setup
.................................................................
Device identification
Interface Parameters
=================================================================
1. LAN Status :[ Open ]
2. WAN Status :[ Open ]
3. WAN Throttle :[ Full ]
4. Aging Timeout (min) :5.
Press one of the numbers to select or ESC:
Figure C-11. Interface Parameters Menu
LAN Status
Used to enable/disable the flow of packets through LAN interface:
• Open – the flow of packets is enabled.
• Closed – the flow of packets is disabled. As a result, IR-IP does not accept, nor
sends packets to the LAN, but its WAN interface may still be active, and can
interact with other IP hosts on the WAN.
WAN Status
Used to enable/disable the flow of packets through the WAN interface:
• Open – the flow of packets is enabled.
• Closed – the flow of packets through the WAN interface is disabled. As a
result, IR-IP does not accept from, nor sends packets to the WAN. However,
the LAN interface of the IP router is still active.
WAN Throttle
This parameter specifies the maximum data rate at which frames are sent to the
WAN (i.e., to the ASM-60 VDSL link).
Advanced Setup Menu C-15
Page 60

Appendix C IR-IP Interface Module ASM-60 Installation and Operation Manual
The available selections are:
• 64 kbps
• 128 kbps
• 256 kbps
• 512 kbps
• 1024 kbps
• Full (no restriction on the rate).
Since the IP router buffers have a limited capacity (256 frames), it is recommended
to select the WAN Throttle parameter in accordance with the line rate.
Aging Timeout
Used to specify the time after which inactive LAN stations are removed from the
IR-IP ARP table.
A station is defined as inactive when no IP traffic is received from it by the IR-IP
LAN interface.
WAN Protocol Parameters – Frame Relay Protocol Menu
The Frame Relay Protocol Parameters menu is used to configure the parameters
Frame Relay WAN for protocol (the WAN protocol is selected by means of the
Quick Setup Menu) in Figure C-6.
➤ To access the Protocol Parameters menu:
• From the Advanced Setup menu, type 3.
Self Learn
Used to specify whether the Frame Relay DLCI and maintenance protocol is
learned automatically (ENABLED), or is manually entered (DISABLED).
Maintenance Protocol
When the Self Learn parameter is DISABLED, use this parameter to specify the
desired maintenance protocol.
DLCI
When the Self Learn parameter is DISABLED, use this parameter to specify the
DLCI used for exchanging maintenance protocol messages.
CIR
Used to specify the maximum amount of data, in bits, which the Frame Relay
network guarantees to transfer during the measurement interval (the measurement
interval is usually one second).
The value of this parameter is obtained from your Frame Relay service provider.
C-16 Advanced Setup Menu
Page 61

ASM-60 Installation and Operation Manual Appendix C IR-IP Interface Module
EIR
Used to specify the maximum amount of data, in bits, that the Frame Relay
network will attempt to deliver during the measurement interval. The value of this
parameter is obtained from the Frame Relay service provider.
A typical Frame Relay Protocol Parameters menu is shown in Figure C-12.
IR_IP <IR-IP> S/W Ver. 1.00 31/IR (date)
Quick Setup
Management Access
Advanced Setup
.....................................................................
Device identification
Interface Parameters
Protocol Parameters
=====================================================================
1. Self Learn :[ Enabled ]
2. Maintenance Protocol :[ ANSI T1.617 ANNEX D ]
3. DLCI (0-None) :0..
4. CIR :0.......
5. EIR :64000...
Press one of the numbers to select or ESC:
Figure C-12. Frame Relay Protocol Parameters Menu
WAN Protocol Parameters – PPP Protocol Menu
The PPP Protocol Parameters menu is used to configure the parameters PPP WAN
for protocol (the WAN protocol is selected by means of the (the WAN protocol is
selected by means of the Quick Setup Menu) in Figure C-6.
➤ To access the Protocol Parameters menu:
• From the Advanced Setup menu, type 3.
Header and Control Field Compression
Used to control the use of header and control field compression type according to
RFC 1661. It is strongly recommended that this compression be used for
troubleshooting only.
Protocol Field Compression
Used to control the use of protocol field compression type according to RFC 1661.
It is strongly recommended that this compression be used for troubleshooting only.
Authentication Protocol
Used to select the authentication protocol used by an IP router configured as host
to validate incoming connections.
Advanced Setup Menu C-17
Page 62

Appendix C IR-IP Interface Module ASM-60 Installation and Operation Manual
Security Host/Guest
This option can be used to configure the IP router either as a guest unit, to be
authenticated by another router, or as a host unit, that authenticates other routers.
User Name To Send
The name by which an IP router card configured as guest identifies itself.
Password To Send
The password by which an IP router card configured as guest identifies itself.
User Name To Accept
The user name to be accepted by an IP router configured as host, when an
incoming connection request is received.
Password To Accept
The user password to be accepted by an IP router configured as host, when an
incoming connection request is received.
A typical PPP Protocol Parameters menu is shown in Figure C-13.
IR_IP <IR-IP> S/W Ver. 1.00 31/IR (date)
Quick Setup
Management Access
Advanced Setup
.....................................................................
Device identification
Interface Parameters
Protocol Parameters
=====================================================================
1. Header and Control Field Compression :[ No ]
2. Protocol Field Compression: :[ No ]
3. Authentication Protocol :[ NONE/NONE ]
4. Security Host / Guest :[ Guest ]
5. User Name To Send :.................
6. Password To Send :.................
7. User Name To Accept :.................
8. Password To Accept :.................
Press one of the numbers to select or ESC:
Figure C-13. PPP Protocol Parameters Menu
C-18 Advanced Setup Menu
Page 63

ASM-60 Installation and Operation Manual Appendix C IR-IP Interface Module
Multicast IP Menu
The Multicast IP menu is used to specify the IP multicast frame forwarding
parameters, and to access the static multicast groups’ table.
➤ To access the Multicast IP menu:
• From the Advanced Setup menu, press 4.
The Multicast IP menu appears (Figure C-14).
IR_IP <IR-IP> S/W Ver. 1.00 31/IR (date)
Quick Setup
Management Access
Advanced Setup
.....................................................................
Device identification
Interface Parameters
Protocol Parameters
Multicast IP
=====================================================================
1. Multicast forwarding :[ Disable ]
2. Static groups :>>>
Press one of the numbers to select or ESC:
Figure C-14. Multicast IP Menu
Multicast Forwarding
Used to control the forwarding of IP multicast frames. The following selections are
available:
• DISABLED – Disables multicast forwarding in both directions.
• LAN to WAN – Enables forwarding of IP multicast frames addressed to groups
appearing in the Static Multicast Groups table, from the LAN to the WAN.
• WAN to LAN – Enables forwarding of IP multicast frames addressed to groups
appearing in the Static Multicast Groups table, from the WAN to the LAN.
• BIDIRECTIONAL – Enables forwarding of IP multicast frames addressed to
groups appearing in the Static Multicast Groups table, in both directions.
• WAN to LAN + IGMP – Enables forwarding of IP multicast frames addressed to
groups appearing in the Static Multicast Groups table, from the WAN to the LAN.
In addition, more groups can be added dynamically (the additional can be viewed
using the View menu – Figure C-19).
• TRANSPARENT – All the IP multicast frames are forwarded, irrespective of the
Static Multicast Groups table.
Advanced Setup Menu C-19
Page 64

Appendix C IR-IP Interface Module ASM-60 Installation and Operation Manual
Static Groups
Select this parameter to access the static multicast groups table. The table is used
to specify the IP addresses for up to 10 IP multicast groups. You can add, change,
or delete each entry in the table (see the prompt line).
➤ To access the Static Groups menu:
• From the Multicast IP menu, type 2.
The following screen appears:
IR_IP <IR-IP> S/W Ver. 1.00 31/IR (date)
Static Multicast Groups Table
-----------------------------
Group IP Address
1. ................
2. ................
3. ................
4. ................
5. ................
6. ................
7. ................
8. ................
9. ................
10. ...............
Press 'A'-add, 'E'-edit, 'D'-delete, 'C'-clear all, 'ESC'-exit:
Figure C-15. Static Multicast Groups Table
C.10 Device Control Menu
The Device Control menu is used to download software from TFTP servers and
perform interface and device resets.
➤ To access the Device Control menu:
• From the Main menu, type 4.
The Device Control menu appears (Figure C-16).
IR_IP <IR-IP> S/W Ver. 1.00 31/IR (date)
Quick Setup
Management Access
Advanced Setup
Device Control
----------------------------------------------------------
1. New Software Download
2. View error LOG
3. Resets
Press one of the numbers to select or ESC:
Figure C-16. Device Control Menu
C-20 Device Control Menu
Page 65

ASM-60 Installation and Operation Manual Appendix C IR-IP Interface Module
New Software Download Menu
IR-IP operates as a TFTP client, and therefore it is possible to update its software
by downloading new software from another computer that operates as a TFTP
server.
The New Software Download menu is used to specify the software downloading
parameters.
➤ To access the New Software Download menu:
• From the Device Control submenu, type 1.
New Software Download menu appears (Figure C-17).
IR_IP <IR-IP> S/W Ver. 1.00 31/IR (date)
Quick Setup
Management Access
Advanced Setup
Device Control
.....................................................................
New Software Download
=====================================================================
1. Server IP Address :...............
2. File Name :...................
3. Total Timeout (sec) :..
4. Start operation :>>>
Press one of the numbers to select or ESC:
Figure C-17. New Software Download Menu
Server IP Address
Used to enter the IP address of the TFTP server.
File Name
Used to enter the name and path of the file to be transferred from the TFTP server.
Total Timeout
Used to enter the time IP router should wait for an acknowledgment from the
TFTP server, for example 60 seconds.
Start Operation
After selecting all the necessary parameters, type 4 on the New Software
Download screen and then press <Enter> to start the downloading.
You can follow the progress of the downloading process (indicated by arrows).
Upon completion of the download process, the unit performs a reset. The Telnet
connection is lost and must be restarted if required.
Device Control Menu C-21
Page 66

Appendix C IR-IP Interface Module ASM-60 Installation and Operation Manual
View Error Log Screen
This item of the Device Control submenu is used to view the error log file. This file
logs errors detected in IR-IP for debug and technical support purposes.
Resets Menu
The Resets menu allows you to perform reset of IR-IP, or its interfaces.
This operation can be used to restore normal operation after service is disrupted
by an abnormal condition. Any data stored in the IR-IP buffers is discarded, and
the flow of traffic is temporarily interrupted.
➤ To access the Resets menu:
• From the Device Control menu, type 3.
The following screen appears:
IR_IP <IR-IP> S/W Ver. 1.00 31/IR (date)
Quick Setup
Management Access
Advanced Setup
Device Control
.....................................................................
New Software Download
View error LOG
Resets
=====================================================================
1. Reset Device
2. Reset LAN
3. Reset WAN
Press one of the numbers to select or ESC:
Figure C-18. Resets Menu
Reset Device
➤ To restart IR-IP:
• From the Resets menu, type 1.
You will be prompted to confirm the reset operation.
Note
Resetting the device will restart the IR-IP interface module, and therefore traffic flow
is temporarily interrupted, and the Telnet connection is lost.
Reset LAN
➤ To reset the LAN interface:
• From the Resets menu, type 2.
You will be prompted to confirm the reset operation.
Note
This operation restarts the IR-IP LAN controller.
To continue your Telnet session, press any key within 15 seconds following the
confirmation of the reset operation.
C-22 Device Control Menu
Page 67

ASM-60 Installation and Operation Manual Appendix C IR-IP Interface Module
Reset WAN
➤ To reset the WAN interface:
• From the Resets menu, type 3.
You will be prompted to confirm the reset operation.
Note
Resetting the WAN interface causes the WAN controller to be restarted. This results
in renegotiation of the WAN protocol parameters.
To continue your Telnet session, press any key within 15 seconds following the
confirmation of the reset operation.
C.11 View Menu
The View menu is used to view the IR-IP configuration data, and display
information on its ARP tables, multicast Groups tables and statistics.
➤ To access the View menu:
• From the Main menu, type 5.
The View menu appears (Figure C-19).
IR_IP <IR-IP> S/W Ver. 1.00 31/IR (date)
Quick Setup
Management Access
Advanced Setup
Device Control
View
----------------------------------------------------------
1. Configuration and Connection
2. ARP Tables
3. Multicast Groups Table
4. Statistics
Press one of the numbers to select or ESC:
Figure C-19. View Menu
Configuration and Connection
This screen is used to view the configuration parameters of IR-IP. In addition, you
can also view the current status of the LAN and WAN interface.
➤ To access the Configuration and Connection screen:
• From the View menu, type 1.
The View Configuration screen appears (Figure C-20).
View Menu C-23
Page 68

Appendix C IR-IP Interface Module ASM-60 Installation and Operation Manual
IR_IP <IR-IP> S/W Ver. 1.00 31/IR (date)
VIEW CONFIGURATION
------------------
BOOT Version :1.06 18.03.1999
Device Name :IP router card
System Location :The location of this device
Contact Person :Name of contact Person
MAC Address : 00-20-D2-16-3F-9B
Default Gateway : WAN
Intrf Type Baud(Kbps) Prot IP Address IP Mask Status
.....................................................................
LAN UTP ------- Ethr 192.168.205.005 255.255.255.000 Connected
WAN V.110 FR Not Conn.
Press any key to continue:
Figure C-20. View Configuration Screen
ARP Tables
This screen is used to display the IR-IP ARP table. This table shows the IP address
assigned to each station on the LAN (the stations are identified by their MAC
addresses).
➤ To access the ARP Tables screen:
• From the View menu, type 2.
The ARP Tables screen appears (Figure C-21).
IR_IP <IR-IP> S/W Ver. 1.00 31/IR (date)
ARP Table
---------
IP Address MAC Address IP Address MAC Address
192.168.205.003 00-40-33-20-C8-3C
Press any key for exit
Figure C-21. ARP Tables Screen
Multicast Groups Table Screen
This screen is used to display information about the multicast group IP addresses
and their status.
➤ To access the Multicast Groups Table screen:
• In the View menu, type 3.
The Multicast Groups Table screen appears (Figure C-22).
C-24 View Menu
Page 69

ASM-60 Installation and Operation Manual Appendix C IR-IP Interface Module
IR_IP <IR-IP> S/W Ver. 1.00 31/IR (date)
Multicast Groups Table
----------------------
Group IP Address Status Group IP Address Status
Press any key for exit
Figure C-22. Multicast Groups Table Screen
Statistics Screen
The Statistics screen is used to display statistical information on the traffic between
the networks connected by IR-IP. The data displayed on this screen enables you to
evaluate the IR-IP performance. Two different Statistics screens are used, one for
the LAN side and the other for the WAN side.
➤ To access the Statistics menu:
• In the View menu, type 4.
The LAN and WAN Statistics screens appear (Figure C-23 and Figure C-24).
IR_IP <IR-IP> S/W Ver. 1.00 31/IR (date)
SYSTEM STATISTICS
-----------------
Counter Name Val Counter Name Val
LAN in Octets 83504 LAN IP Header Errors 0
LAN Unicast Frames In 1 LAN IP Address Errors 0
LAN Non-Unicast Frames In 9 LAN Alignment Errors 0
LAN Out Octets 83504 LAN CRC Errors 0
LAN Unicast Frames Out 3560 LAN Single Collisions 0
LAN Non-Unicast Frames Out 0 LAN Multiple Collisions 0
LAN to WAN Frames Passed 1698 LAN Late Collisions 0
LAN IP Datagram Received 2638 LAN Excessive Collisions 0
LAN to CPU Frames Discarded 0 LAN Frames Too Long Errors 0
LAN to WAN Frames Discarded 0 LAN RX FIFO Overrun Error 0
LAN Out Errors 0 LAN SQE Transmitted 0
LAN RX Frames Errors 0 LAN Deferred Frames 1
LAN MAC Receive Errors 0 LAN Carrier Sense Lost 0
LAN MAC TX Errors 0 LAN FIFO Underrun 0
N - Next Screen. ESC - Back To Previous Menu.
R - Refresh Page. C - Clear The Counters Of This Page.
Figure C-23. LAN Statistics Screen
View Menu C-25
Page 70

Appendix C IR-IP Interface Module ASM-60 Installation and Operation Manual
IR_IP <IR-IP> S/W Ver. 1.00 31/IR (date)
SYSTEM STATISTICS
---------------- Counter Name Val Counter Name Val
WAN in Octets 83504 WAN Alignment Errors 0
WAN Out Octets 1950 WAN Aborted Frames 0
WAN Out Frames 1723 WAN Short Frames 0
WAN to LAN Frames Transfer 1698 WAN RX FIFO Overrun Error 0
WAN IP Datagram Received 1723 WAN to CPU Frames Errors 0
WAN to CPU Discarded 0 WAN Frame Too Long Errors 0
WAN to LAN Discarded 0 WAN IP Header Errors 0
WAN Out Errors 0 WAN IP Addres Errors 0
WAN CRC Errors 0
PPP Address Error 0
PPP Control Error 0
DLCI Unrecognized Error 0
Frame Relay Forward Conge 0
Frame Relay Backward Conge 0
P - Previous Screen. ESC - Back To Previous Menu.
R - Refresh Page. C - Clear The Counters Of This Page.
Figure C-24. WAN Statistics Screen
C.12 Diagnostic Tool (Ping Terminal) Menu
This section provides information on the diagnostic tool provided with IR-IP (the
ping utility).
➤ To access the Diagnostic Tools menu:
• In the Main menu, type 6.
The Diagnostic Tools menu appears (Figure C-25).
IR_IP <IR-IP> S/W Ver. 1.00 31/IR (date)
Quick Setup
Management Access
Advanced Setup
Device Control
View
Diagnostic Tools (PING terminal)
=====================================================================
1. Ping IP Address :192.168.100.011
2. Start Pinging :>>>
3. Stop Pinging :>>>
Press one of the numbers to select or ESC:
Figure C-25. Diagnostic Tools Menu
C-26 Diagnostic Tool (Ping Terminal) Menu
Page 71

ASM-60 Installation and Operation Manual Appendix C IR-IP Interface Module
Using the Ping Function
The Ping option is used to confirm IP connectivity by pinging other IP hosts.
Connectivity is confirmed by receiving a reply from the remote (pinged) IP host.
➤ To ping a host:
1. From the Diagnostic Tools menu, type 1 and enter the desired host IP address.
2. Press <Enter> to confirm the destination IP address.
3. To start pinging, type 2 on the Diagnostic Tools screen.
After pinging starts, you can monitor the ping status. A typical screen is
shown in Figure C-26.
Note
After pinging is started, it continues in the background even if you exit the
Diagnostics Tools screen. In this case, a Ping Running message appears in the top
upper left-hand corner of the screen.
4. To stop pinging, type 3 from the Diagnostic Tools menu.
A Ping Stopped message is displayed.
To clear the message and return to the Diagnostic Tools screen, press any
key.
IR_IP <IR-IP> S/W Ver. 1.00 31/IR (date)
Quick Setup
Management Access
Advanced Setup
Device Control
View
Diagnostic Tools (PING terminal)
=====================================================================
1. Ping IP Address :192.168.100.011
2. Start Pinging :>>>
3. Stop Pinging :>>>
Pinging 192.168.212.001 Sent 27 Recvd 25 Lost 2 Resp.Time 60 ms
Press one of the numbers to select or ESC:
Figure C-26. Diagnostic Tools Menu after Receiving Pinging Response
Diagnostic Tool (Ping Terminal) Menu C-27
Page 72

Appendix C IR-IP Interface Module ASM-60 Installation and Operation Manual
C.13 Erasing User’s Configuration
The user-defined configuration parameters are stored in the IP router card flash
memory. After the user-defined configuration parameters are erased, the IP router
card automatically loads the default parameters.
You may want to erase the current configuration parameters:
1. Before IR-IP is prepared for operation in a new application.
2. When you cannot configure IR-IP because its current LAN-interface IP address
and/or the Telnet password, are not known.
➤ To erase the user’s configuration:
1. Turn ASM-60 off.
2. Set all the four sections of the IR-IP DIP switch (Figure C-3) to ON.
3. Turn ASM-60 on and monitor the ERR indicator: it must turn on and light
steadily.
4. While the ERR indicator is lit (within 15 seconds), set sections 1 and 2 of the
DIP switch to OFF.
The IP router configuration is erased.
Note
If you do not set sections 1 and 2 to OFF within 15 seconds of power-up, the IP
router card ignores the setting of all the four sections to ON and starts normal
operation. In this case, it is recommended to turn ASM-60 off and then back on.
To abort the whole operation, turn ASM-60 off, return all the four-switch section to
the desired positions, and then turn ASM-60 on again.
5. Turn ASM-60 off, and the return all the four sections of the DIP switch to the
desired positions.
C.14 Erasing IR-IP Software
You may erase the IR-IP application software, without erasing the user-defined
parameters.
After the application software is erased, IR-IP starts its TFTP server application, and
waits for the downloading of software by a TFTP client connected to its LAN
interface. The procedure to be used to download the application software in this
case is also described below.
You may want to erase the application software if the downloading of new
software using the Device Control menu (see Figure C-16) fails, and IR-IP does not
function properly.
Erasing Application Software
➤ To erase the application software:
1. Turn ASM-60 off.
C-28 Erasing IR-IP Software
Page 73

ASM-60 Installation and Operation Manual Appendix C IR-IP Interface Module
2. Set all the four sections of IR-IP DIP switch to ON.
3. Turn the ASM-60 on and monitor the IP router ERR indicator: it must turn on
and light steadily.
4. While the ERR indicator is lit (within 15 seconds), set sections 3 and 4 of IR-IP
DIP switch to OFF.
The IP router application software is erased.
Note
If you do not set sections 3 and 4 to OFF within 15 seconds of power-up, IR-IP
ignores the setting of all the four sections to ON and starts normal operation. In this
case, it is recommended to turn ASM-60 off and then back on.
Alternately, to abort the whole operation, turn ASM-60 off, return all the four
switches to the desired positions, and then turn ASM-60 on again.
5. Turn ASM-60 off, and the return all the four sections of the DIP switch to the
desired positions.
Downloading New Software
After erasing the application software, you can download new software from any
computer that can serve as a TFTP client.
To enable the downloading, IR-IP automatically activates its TFTP server
application with the following factory-default IP parameters:
• IP address: 192.168.205.1
• Subnet mask: 255.255.255.252.
Connect the computer serving as a TFTP client to the IR-IP 10BASE-T connector in
the way as a Telnet host used for preliminary configuration (see the Performing
Preliminary Configuration section). The computer IP parameters must be
configured as follows:
• IP address 192.168.205.2
• Subnet mask 255.255.255.252
• Default gateway 192.168.205.1
➤ To download new software:
1. If necessary, turn ASM-60 off.
2. Set all the four sections of the IR-IP DIP switch to OFF.
3. Turn ASM-60 on and monitor the ERR indicator: it must start flashing.
4. Connect the computer to the IP router LAN interface and configure its IP
parameters as explained above.
5. Run a standard TFTP client application on the Telnet host, and download the
appropriate software file.
If the download is successful, IR-IP starts using the new software.
If the downloading fails, repeat the download process.
Erasing IR-IP Software C-29
Page 74

Appendix C IR-IP Interface Module ASM-60 Installation and Operation Manual
C-30 Erasing IR-IP Software
 Loading...
Loading...