QUICK LOGIC QL4016-0CF100C, QL4016-0CF100I, QL4016-0PF100C, QL4016-0PF100I, QL4016-1PF100C Datasheet
...
QL4016 QuickRAM Data Sheet
• • • • • •
16,000 Usable PLD Gate QuickRAM ESP Combining Performance,
Density and Embedded RAM
Device Highlights
High Performance & High Density
• 16,000 Usable PLD Gates with 118 I/Os
• 300 MHz 16-bit Counters, 400 MHz
Datapaths, 160+ MHz FIFOs
• 0.35 µm four-layer metal non-volatile
CMOS process for smallest die sizes
High Speed Embedded SRAM
• 10 dual-port RAM modules, organized in
user-configurable 1,152 bit blocks
• 5 ns access times, each port independently
accessible
• Fast and efficient for FIFO, RAM, and ROM
functions
Advanced I/O Capabilities
• Interfaces with both 3.3 V and 5.0 V devices
• PCI compliant with 3.3 V and 5.0 V busses
for -1/-2/-3/-4 speed grades
• Full JTAG boundary scan
• I/O Cells with individually controlled
Registered Input Path and Output Enables
10
RA M
Blocks
Hi gh Sp eed
Logic Cells
320
Easy to Use / Fast Developm ent
Cycles
• 100% routable with 100% utilization and
complete pin-out stability
• Variable-grain logic cells provide high
performance and 100% utilization
• Comprehensive design tools include high
quality Verilog/VHDL synthesis
© 2002 QuickLogic Corporati on
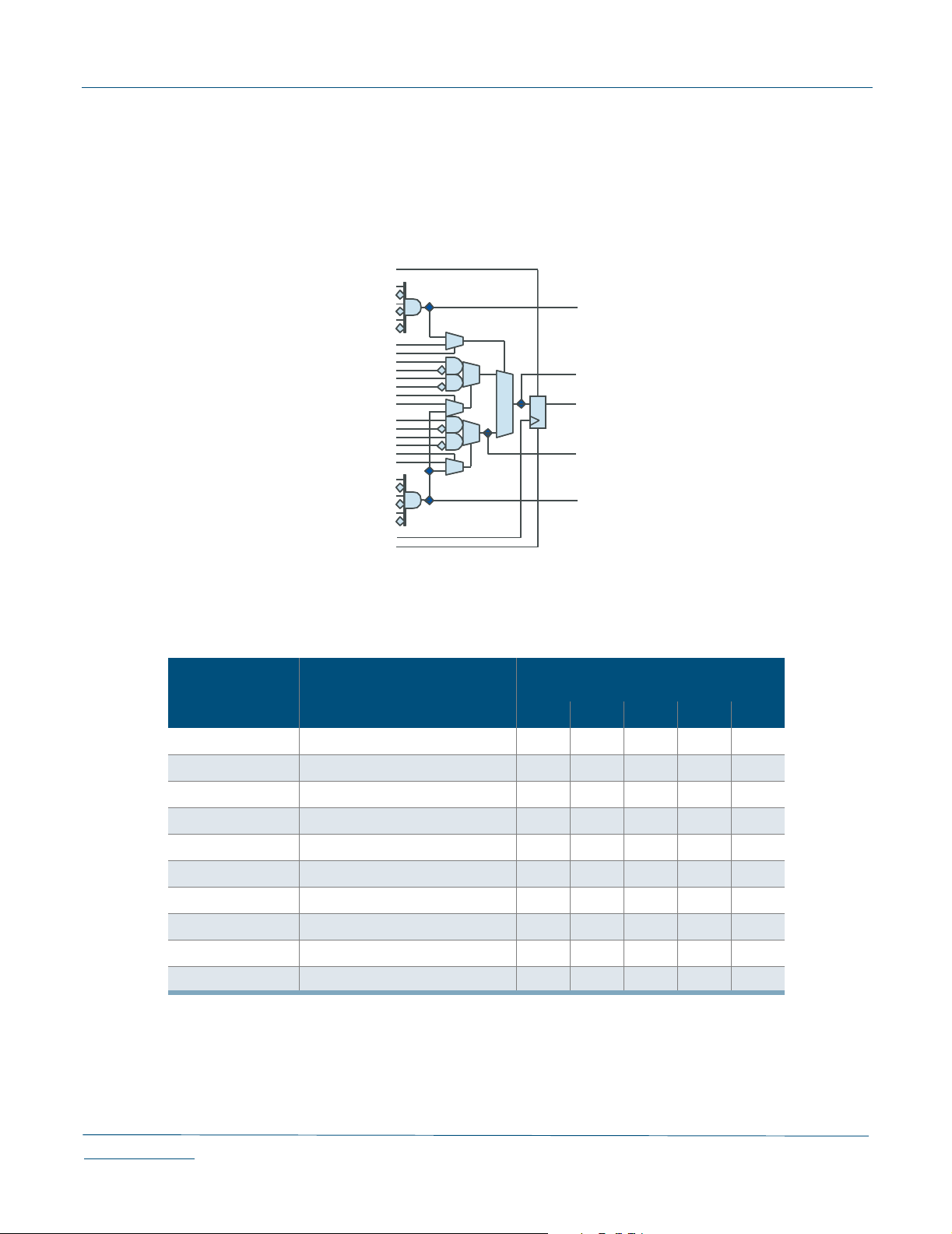
Figure 1: QuickRAM Block Diagram
www.quicklogic.com
Interface
•
•
•
1
•
•
•

QL4016 QuickRAM Data Sheet Rev I
Architecture Overview
The QuickRAM family of ESPs (Embedded Standard Products) offers FPGA logic in
combination with Dual-Port SRAM modules. The QL4016 is a 16,000 usable PLD gate
member of the QuickRAM family of ESPs. QuickRAM ESPs are fabricated on a 0.35 µm
four-layer metal process using QuickLogic's patented ViaLink
unique combination of high performance, high density, low cost, and extreme ease-of-use.
The QL4016 contains 320 logic cells and 10 Dual Port RAM modules (see Figure 1). Each
RAM module has 1,152 RAM bits, for a total of 11,520 bits. RAM Modules are Dual Port
(one read port, one write port) and can be configured into one of four modes:
64 (deep) × 18 (wide), 128 × 9, 256 × 4, or 512 × 2 (see
I/Os, the QL4016 is available in 84-pin PLCC, 100-pin TQFP, 100-pin CQFP and 144-pin
TQFP packages.
Designers can cascade multiple RAM modules to increase the depth or width allowed in
single modules by connecting corresponding address lines together and dividing the words
between modules (see
large as 16 bits wide in the smallest QuickRAM device and 44 bits wide in the largest device.
TM
technology to provide a
Figure 4). With a maximum of 82
Figure 2). This approach allows up to 512-deep configurations as
Software support for the complete QuickRAM family, including the QL4016, is available
through two basic packages. The turnkey QuickWorks
TM
package provides the most
complete ESP software solution from design entry to logic synthesis, to place and route, to
simulation. The QuickTools package provides a solution for designers who use Cadence,
Exemplar, Mentor, Synopsys, Synplicity, Viewlogic, Aldec, or other third-party tools for
design entry, synthesis, or simulation.
The QuickLogic
TM
variable grain logic cell features up to 16 simultaneous inputs and five
outputs within a cell that can be fragmented into five independent cells. Each cell has a fanin of 29 including register and control lines (see
RAM
Module
(1,152 bits)
WADDR
RAM
Module
(1,152 bits)
WDATA
Figure 3).
RDATAWDATA
RADDR
RDATA
•
•
www.quicklogic.com
•
2
•
•
•
Figure 2: QuickRAM Module Bits
© 2002 QuickLogic Corporation

Product Summary
Total of 118 I/O Pins
• 110 bi-directional input/output pins, PCI-compliant for 5.0 V and 3.3 V buses for
-1/-2/-3/-4 speed grades
• 8 high-drive input/distributed network pins
Eight Low-Skew Distributed Networks
• Two array clock/control networks available to the logic cell flip-flop clock, set and reset
inputs—each driven by an input-only pin
• Six global clock/control networks available to the logic cell F1, clock, set and reset inputs
and the input and I/O register clock, reset and enable inputs as well as the output enable
contro—each driven by an input-only or I/O pin, or any logic cell output or I/O cell
feedback
High Performance Silicon
• Input + logic cell + output total delays = under 6 ns
• Data path speeds over 400 MHz
• Counter speeds over 300 MHz
• FIFO speeds over 160+ MHz
QL4016 QuickRAM Data Sheet Rev I
© 2002 QuickLogic Corporati on
www.quicklogic.com
•
•
3
•
•
•
•
QL4016 QuickRAM Data Sheet Rev I
Electrical Specifications
AC Characteristic s at VCC = 3.3 V, TA = 25°C (K = 1.00)
To calculate delays, multiply the appropriate K factor from Table 10: Operating Range by the
following numbers in the tables provided.
QS
A1
A2
A3
A4
A5
A6
QS
OP
B1
B2
C1
C2
MP
MS
D1
D2
E1
E2
NP
NS
F1
F2
F3
F4
F5
F6
QC
QR
AZ
OZ
QZ
NZ
FZ
Figure 3: QuickRAM Logic Cell
Table 1: Logic Cell
Symbol Parameter
t
PD
t
SU
t
H
t
CLK
t
CWHI
t
CWLO
t
SET
t
RESET
t
SW
t
RW
Combinatorial Delay
Setup Time
a
Hold Time 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
Clock to Q Delay 0.7 1.0 1.2 1.5 2.5
Clock High Time 1.2 1.2 1.2 1.2 1.2
Clock Low Time 1.2 1.2 1.2 1.2 1.2
Set Delay 1.0 1.3 1.5 1.8 2.8
Reset Delay 0.8 1.1 1.3 1.6 2.6
Set Width 1.9 1.9 1.9 1.9 1.9
Reset Width 1.8 1.8 1.8 1.8 1.8
a
a. These limits are derived from a representative selection of the slowest paths through the Quick-
RAM logic cell including typical net delays. Worst case delay values for specific paths should be
determined from timing analysis of your particular design.
Propagation Delays (ns)
Fanout (5)
1 2 3 4 5
1.4 1.7 1.9 2.2 3.2
1.7 1.7 1.7 1.7 1.7
•
•
www.quicklogic.com
•
4
•
•
•
© 2002 QuickLogic Corporation

QL4016 QuickRAM Data Sheet Rev I
[8:0]
[17:0]
[1:0]
Table 2: RAM Cell Synchronous Write Timing
Symbol Parameter
t
SWA
t
HWA
t
SWD
t
HWD
t
SWE
t
HWE
t
WCRD
WA Setup Time to WCLK 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0
WA Hold Time to WCLK 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
WD Setup Time to WCLK 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0
WD Hold Time to WCLK 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
WE Setup Time to WCLK 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0
WE Hold Time to WCLK 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
WCLK to RD (WA=RA)
WA
WD
WE
WCLK
RE
RCLK
RA
RD
MODE ASYNCRD
Figure 4: QuickRAM Module
1 2 3 4 5
a
5.0 5.3 5.6 5.9 7.1
[8:0]
[17:0 ]
Propagation Delays (ns)
Fanout
a. Stated timing for worst case Propagation Delay over process variation at VCC = 3.3 V and
TA = 25
settings as specified in the Operating Range.
Symbol Parameter
Logic Cells 1 2 3 4 5
t
SRA
t
HRA
t
SRE
t
HRE
t
RCRD
a. Stated timing for worst case Propagation Delay over process variation at VCC = 3.3 V and
TA = 25
settings as specified in the Operating Range.
© 2002 QuickLogic Corporati on
° C. Multiply by the approp riate Dela y Factor, K, f or speed gra de, voltag e and tempe rature
Table 3: RAM Cell Synchronous Read Timing
Propagation Delays (ns)
Fanout
RA Setup Time to RCLK 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0
RA Hold Time to RCLK 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
RE Setup Time to RCLK 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0
RE Hold Time to RCLK 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
RCLK to RD
a
4.0 4.3 4.6 4.9 6.1
× C. Multiply by the approp riate Delay Factor , K, for speed grade, volta ge and temperature
www.quicklogic.com
•
•
5
•
•
•
•
QL4016 QuickRAM Data Sheet Rev I
Table 4: RAM Cell Asynchronous Read Timing
Symbol Parameter
Propagation Delays (ns)
Fanout
1 2 3 4 5
RPDRD RA to RD
a
3.0 3.3 3.6 3.9 5.1
a. Stated timing for worst case Propagation Delay over process variation at V
TA = 25
°C. Multiply by the appropr iate Delay Factor, K, for speed gra de, volta ge and tempe ratu re
settings as specified in the Operating Range.
Table 5: Input-Only / Clock Cells
Symbol Parameter
Propagation Delays (ns)
1 2 3 4 8 12 24
t
IN
t
INI
t
ISU
t
IH
t
ICLK
t
IRST
t
IESU
t
IEH
High Drive Input Delay 1.5 1.6 1.8 1.9 2.4 2.9 4.4
High Drive Input, Inverting Delay 1.6 1.7 .19 2.0 2.5 3.0 4.5
Input Register Set-Up Time 3.1 3.1 3.1 3.1 3.1 3.1 3.1
Input Register Hold Time 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
Input Register Clock To Q 0.7 0.8 1.0 1.1 1.6 2.1 3.6
Input Register Reset Delay 0.6 0.7 0.9 1.0 1.5 2.0 3.5
Input Register Clock Enable Setup Time 2.3 2.3 2.3 2.3 2.3 2.3 2.3
Input Register Clock Enable Hold Time 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
= 3.3 V and
CC
Fanout
•
•
www.quicklogic.com
•
6
•
•
•
Table 6: Clock Cells
Symbol Parameter
Propagation Delays (ns)
Fanout
a
1 2 3 4 8 10 11
t
ACK
t
GCKP
t
GCKB
Array Clock Delay 1.2 1.2 1.3 1.3 1.5 1.6 1.7
Global Clock Pin Delay 0.7 0.7 0.7 0.7 0.7 0.7 0.7
Global Clock Buffer Delay 0.8 0.8 0.9 0.9 1.1 1.2 1.3
a. The array dist ribu ted ne tw ork s co nsi st of 40 ha lf columns and the glo bal d is tributed networks con-
sist of 44 half columns, each driven by an independent buffer. The number of half columns used
does not affect clo ck buffer delay . The arra y clock has up to eight loads per ha lf column. The global
clock has up to 11 loads per half column.
© 2002 QuickLogic Corporation

Table 7: I/O Cell Input Delays
QL4016 QuickRAM Data Sheet Rev I
Symbol Parameter
Propagation Delays (ns)
1 2 3 4 8 10
t
I/O
t
ISU
t
IH
t
IOCLK
t
IORST
t
IESU
t
IEH
Input Delay (bidirectional pad) 1.3 1.6 1.8 2.1 3.1 3.6
Input Register Set-Up Time 3.1 3.1 3.1 3.1 3.1 3.1
Input Register Hold Time 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
Input Register Clock to Q 0.7 1.0 1.2 1.5 2.5 3.0
Input Register Reset Delay 0.6 0.9 1.1 1.4 2.4 2.9
Input Register Clock Enable Set-Up Time 2.3 2.3 2.3 2.3 2.3 2.3
Input Register Clock Enable Hold Time 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
a. Stated timing for worst case Propagation Delay over process variation at V
TA = 25
° C. Multiply by the approp riate Dela y Factor, K, f or speed gra de, voltag e and tempe rature
settings as specified in the Operating Range.
Table 8: I/O Cell Output Delays
Symbol Parameter
Propagation Delays (ns)
Output Load Capacitance (pF)
3 50 75 100 150
t
OUTLH
t
OUTHL
t
PZH
t
PZL
t
PHZ
t
PLZ
Output Delay Low to High 2.1 2.5 3.1 3.6 4.7
Output Delay High to Low 2.2 2.6 3.2 3.7 4.8
Output Delay Tri-state to High 1.2 1.7 2.2 2.8 3.9
Output Delay Tri-state to Low 1.6 2.0 2.6 3.1 4.2
Output Delay High to Tri-state
Output Delay High to Tri-state
a
a
2.0 - - - -
1.2 - - - -
Fanout
= 3.3 V and
CC
a
a. These loads are used for t
© 2002 QuickLogic Corporati on
1ΚΩ
(see Figure 5)
PXZ
tPHZ
5 pF
Figure 5: Loads Used for t
1ΚΩ
PXZ
tPLZ
5 pF
www.quicklogic.com
•
•
7
•
•
•
•

QL4016 QuickRAM Data Sheet Rev I
DC Characteristics
The DC specifications are provided in the tables below.
Parameter Value Parameter Value
VCC Voltage -0.5 V to 4.6 V DC Input Current ±20 mA
V
Voltage -0.5 V to 7.0 V ESD Pad Protection ±2000 V
CCIO
Input Voltage -0.5 V to V
Latch-up Immunity ±200 mA Lead Temperature 300°C
Symbol Parameter Military Industrial Commercial Unit
V
CC
V
CCIO
TA Ambient Temperature -55 - -40 85 0 70 °C
TC Case Temperature - 125 - - - - °C
Supply Voltage 3.0 3.6 3.0 3.6 3.0 3.6 V
I/O Input Tolerance Voltage 3.0 5.5 3.0 5.5 3.0 5.25 V
Table 9: Absolute Maximum Ratings
+0.5 V Storage Temperat ure -65°C to +150°C
CCIO
Table 10: Operating Range
Min Max Min Max Min Max
K Delay Factor
-0 Speed Grade 0.42 2.03 0.43 1.90 0.46 1.85 n/a
-1 Speed Grade 0.42 1.64 0.43 1.54 0.46 1.50 n/a
-2 Speed Grade 0.42 1.37 0.43 1.28 0.46 1.25 n/a
-3 Speed Grade 0.43 0.90 0.46 0.88 n/a
-4 Speed Grade 0.43 0.82 0.46 0.80 n/a
•
•
www.quicklogic.com
•
8
•
•
•
© 2002 QuickLogic Corporation

QL4016 QuickRAM Data Sheet Rev I
Table 11: DC Characteristics
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min Max Units
VIH Input HIGH Voltage 0.5VCC VCCIO+0.5 V
VIL Input LOW Voltage -0.5 0.3 V
CC
V
IOH = -12 mA 2.4 V
VOH Output HIGH Voltage
IOH = -500 µA 0.9VCC V
IOL = 16 mA
a
0.45 V
VOL Output LOW Voltage
IOL = 1.5 mA 0.1 V
II I or I/O Input Leakage Current VI = V
IOZ 3-State Output Leakage Current VI = V
CI Input Capacitance
IOS Output Short Circuit Current
ICC D.C. Supply Current
b
c
d
VO = GND -15 -180 mA
VI, VIO = V
or GND -10 10 µA
CCIO
or GND -10 10 µA
CCIO
VO = V
CCIO
CC
or GND 0.50 (typ) 2 mA
40 210 mA
CC
10 pF
V
ICCIO D.C. Supply Current on VCCIO 0 100 µA
a. Applies only to -1/-2/-3/-4 com mercial grade devices . These s peed gra des are also PCI-com plia nt. All
other devices have 8mA IOL specifications.
b. Capacitance is sample tested only. Clock pins are 12 pF maximum.
c. Only one output at a time. Duration should not exceed 30 seconds.
d. For -1/-2/-3/-4 commerc ial gra de devices only. Ma xi mu m I CC is 3 m A for -0 commercial grade a nd all
industrial grade devices and 5 mA for all military grade devices. For AC conditions, contact
QuickLogic customer applications group (see Contact Information) .
© 2002 QuickLogic Corporati on
www.quicklogic.com
•
•
9
•
•
•
•

QL4016 QuickRAM Data Sheet Rev I
Kv and Kt Graphs
1.1000
1.0800
1.0600
1.0400
1.0200
Kv
1.0000
0.9800
0.9600
0.9400
0.9200
3 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 3.6
Figure 6: Voltage Factor vs. Supply Voltage
Voltage Factor vs. Supply Voltage
Supply Voltage (V)
Temper ature Factor vs. Ope ra ting Te mpe ratur e
1.15
1.10
1.05
Kt
-60 -40 -20 0 20 40 60 80
1.00
0.95
0.90
0.85
Junction Tem per ature C
Figure 7: Temperature Factor vs. Operating Temperature
•
•
www.quicklogic.com
•
10
•
•
•
© 2002 QuickLogic Corporation

Power-up Sequencing
V
CC
V
CCIO
Internal Logic
Cells, RAM
blocks, etc
IO Cells
V
CCIO
V
CC
Voltage
(V
CCIO
-VCC)
MAX
400 us
Time
QL4016 QuickRAM Data Sheet Rev I
V
CC
Figure 8: Power-up Requirements
The following requirements must be met when powering up the device (refer to Figure 8):
• When ramping up the power supplies keep (V
CCIO
-VCC)
≤ 500 mV. Deviation from
MAX
this recommendation can cause permanent damage to the device.
• V
• The power supply must take greater than or equal to 400 µs to reach VCC. Ramping
An internal diode is present in-between VCC and V
must lead VCC when ramping the device.
CCIO
to VCC/V
earlier than 400 µs can cause the device to behave improperly.
CCIO
, as shown in Figure 9.
CCIO
© 2002 QuickLogic Corporati on
Figure 9: Internal Diode Between VCC and VCCIO
www.quicklogic.com
•
•
11
•
•
•
•

QL4016 QuickRAM Data Sheet Rev I
JTAG
TCK
TMS
TRSTB
RDI
TAp Controller
State Machine
(16 States)
Mux
Instruction Decode
&
Control Logic
Instruction Register
Boundary-Scan Register
(Data Register)
Internal
Register
User Defined Data Register
I/O Registers
Figure 10: JTAG Block Diagram
Bypass
Register
Mux
TDO
Microprocessors and Application Specific Integrated Circuits (ASICs) pose many design
challenges. One of these challenges concerns the accessibility of test points. The Joint Test
Access Group (JTAG) formed in response to this challenge, resulting in IEEE standard
1149.1, the Standard Test Access Port and Boundary Scan Architecture.
The JTAG boundary scan test methodology allows complete observation and control of the
boundary pins of a JTAG-compatible device through JTAG software. A Test Access Port
(TAP) controller works in concert with the Instruction Register (IR); these allow users to run
three required tests, along with several user-defined tests.
JTAG tests allow users to reduce system debug time, reuse test platforms and tools, and reuse
subsystem tests for fuller verification of higher level system elements.
•
•
www.quicklogic.com
•
12
•
•
•
© 2002 QuickLogic Corporation

QL4016 QuickRAM Data Sheet Rev I
The 1149.1 JTAG standard requires the following three tests:
• Extest Instruction. The Extest instruction performs a PCB interconnect test. This test
places a device into an external boundary test mode, selecting the boundary scan
register to be connected between the TAP's Test Data In (TDI) and Test Data Out (TDO)
pins. Boundary scan cells are preloaded with test patterns (via the Sample/Preload
Instruction), and input boundary cells capture the input data for analysis.
• Sample/Preload Instruction. This instruction allows a device to remain in its
functional mode, while selecting the boundary scan register to be connected between
the TDI and TDO pins. For this test, the boundary scan register can be accessed via a
data scan operation, allowing users to sample the functional data entering and leaving
the device.
• Bypass Instruction. The Bypass instruction allows data to skip a device's boundary
scan entirely, so the data passes through the bypass register. The Bypass instruction
allows users to test a device without passing through other devices. The bypass register
connects the TDI and TDO pins, allowing serial data to be transferred through a device
without affecting the operation of the device.
© 2002 QuickLogic Corporati on
www.quicklogic.com
•
•
13
•
•
•
•

QL4016 QuickRAM Data Sheet Rev I
Pin Descriptions
Pin Function Description
Table 12: Pin Descriptions
TDI/RSI
TRSTB/RRO
TMS Test Mode Select for JTAG
TCK Test Clock for JTAG
TDO/RCO
STM Special Test Mode Must be grounded during normal operation.
I/ACLK
I/GCLK
I High-drive input Use for input signals with high fanout.
I/O Input/Output pin Can be configured as an input and/or output.
V
CC
V
CCIO
GND Ground pin Connect to ground.
Test Data In for JTAG /RAM init.
Serial Data In
Active low Reset for JTAG /RAM
init. reset out
Test data out for JTAG /RAM init.
clock out
High-drive input and/or array
network driver
High-drive input and/or global
network driver
Power supply pin Connect to 3.3V supply.
Input voltage tolerance pin
Hold HIGH during normal operation. Connects to serial
PROM data in for RAM initialization. Connect to VCC if
unused.
Hold LOW during normal operation. Connects to serial
PROM reset for RAM initialization. Connect to GND if
unused.
Hold HIGH during normal operation. Connect to VCC if
not used for JTAG.
Hold HIGH or LOW during normal operation. Connect to
VCC or ground if not used for JTAG.
Connect to serial PROM clock for RAM initialization. Must
be left unconnected if not used for JTAG or RAM
initialization.
Can be configured as either or both.
Can be configured as either or both.
Connect to 5.0V supply if 5V input tolerance is required,
otherwise connect to 3.3V supply.
GND/THERM Ground/Thermal pin
Ordering Information
QuickLogic device
QuickRAM device
part number
Speed Grade
0 = Quick
1 = Fast
2 = Faster
3 = Faster
*4 = Wow
•
•
www.quicklogic.com
•
14
•
•
•
Available on 456-PBGA only. Connect to ground plane on
PCB if heat sinking desired. Otherwise may be left
unconnected.
QL 4016 - 1 PF144 C
Operating Range
C = Commercial
I = Industrial
M = Military
Package Code
PL84 = 84-pin PLCC
PF100 = 100-pin TQFP
CF100 = 100-pin CQFP
PF144 = 144-pin TQFP
* Contact QuickLogic regarding availabliity
© 2002 QuickLogic Corporation

84 PLCC Pinout Diagram
11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 84 83 82 81 80 79 78 77 76 75
QL4016 QuickRAM Data Sheet Rev I
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
84 PLCC Pinout Table
84 PLCC Function 84 PLCC Function 84 PLCC Function 84 PLCC Function
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
I/O
I/O
I/O
VCCIO
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
TDO
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
GND
I/O
I
IOIOIOIOIO
TDO
IO
IO
IO
IO
IO
IO
IO
GND
IO
I
ACLK/I
I
GCLK/I
VCC
IO
IO
IO
IO
IO
IO
IO
TDIIOIO
33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53
IO
IOIOIOIOIO
VCCIO
GND
IO
IO
IO
VCC
QuickRAM
QL4016-1PF84C
VCCIOIOIOGNDIOIOIOIOIOVCCIOIOIOIOIOIOTRSTB
Figure 11: Top View of 84 Pin PLCC
Table 13: 84 PLCC Pinout Table
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
ACLK/I
I
GCLK/I
VCC
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
TDI
I/O
I/O
VCC
I/O
I/O
I/O
GND
I/O
I/O
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
I/O
I/O
I/O
VCCIO
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
TRSTB
TMS
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
GND
I/O
I
IO
GCLK/I
ACLK/I
STM
VCC
GND
TCK
IO
IO
IO
IO
IO
IO
IO
IO
IO
IO
IO
IO
IO
IO
IO
TMS
74
73
72
71
70
69
68
67
66
65
I
64
63
I
62
61
60
59
58
57
56
55
54
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
ACLK/I
I
GCLK/I
VCC
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
TCK
STM
I/O
I/O
VCC
I/O
I/O
GND
I/O
I/O
© 2002 QuickLogic Corporati on
www.quicklogic.com
•
•
15
•
•
•
•

QL4016 QuickRAM Data Sheet Rev I
100 TQFP/CQFP Pinout Diagram
Pin 1
Pin 26 Pin 51
Figure 12: Top View of 100 Pin TQFP/CQFP
144 TQFP Pinout Diagram
Pin 76
QuickRAM
QL4016-1PF100C
Pin 1
Pin 109
QuickRAM
QL4016-1PF144C
Pin 37 Pin 73
Figure 13: Top View of 144 Pin TQFP
•
•
www.quicklogic.com
•
16
•
•
•
© 2002 QuickLogic Corporation

144 & 100 TQFP Pinout Table
Table 14: 144 & 100 TQFP Pinout Table
144TQFP 100TQFP Function 144TQFP 100TQFP Function 144TQFP 100TQFP Function 144TQFP 100TQFP Function
1 2
2 3
3 NC
4 4
5 NC
6 5
7 NC
8 6
9 NC
10 7
11 NC
12 NC
13 8
14 NC
15 9
16 10
17 11
18 12
19 13
20 14
21 15
22 16
23 17
24 18
25 NC
26 19
27 NC
28 20
29 21
30 NC
31 NC
32 22
33 23
34 NC
35 NC
36 24
37 25
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
VCC
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
GND
I/O
I
ACLK / I
VCC
I
GCLK / I
VCC
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
GND
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
38 26
39 27
40 28
41 29
42 NC
43 30
44 31
45 NC
46 32
47 33
48 NC
49 34
50 35
51 36
52 NC
53 37
54 38
55 39
56 40
57 41
58 42
59 NC
60 43
61 44
62 45
63 NC
64 NC
65 46
66 NC
67 NC
68 NC
69 47
70 48
71 49
72 50
73 51
74 52
TDI
I/O
I/O
I/O
VCC
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
GND
I/O
I/O
I/O
GND
I/O
I/O
I/O
VCCIO
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
GND
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
TRSTB
TMS
I/O
I/O
75 53
76 54
77 55
78 NC
79 NC
80 NC
81 56
82 NC
83 57
84 NC
85 58
86 NC
87 59
88 60
89 61
90 62
91 63
92 64
93 65
94 66
95 67
96 NC
NC 68
97 NC
98 69
99 NC
100 70
101 71
102 NC
103 NC
104 72
105 NC
106 73
107 74
108 75
109 76
110 77
QL4016 QuickRAM Data Sheet Rev I
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
VCC
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
GND
I/O
I
ACLK / I
VCC
I
GCLK / I
VCC
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
GND
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
TCK
STM
111 78
112 79
113 80
114 NC
115 81
116 82
117 83
118 NC
119 84
120 NC
121 NC
122 85
123 NC
124 86
125 87
126 88
127 89
128 90
129 91
130 92
131 NC
132 93
133 NC
134 94
135 NC
136 NC
NC 95
137 NC
138 NC
139 96
140 97
141 98
142 99
143 100
144 1
I/O
I/O
I/O
VCC
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
GND
I/O
I/O
I/O
GND
I/O
I/O
I/O
VCCIO
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
GND
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
TDO
I/O
© 2002 QuickLogic Corporati on
www.quicklogic.com
•
•
17
•
•
•
•

QL4016 QuickRAM Data Sheet Rev I
Contact Information
Telephone:408 990 4000 (US)
416 497 8884 (Canada)
44 1932 57 9011 (Europe)
49 89 930 86 170 (Germany)
852 8106 9091 (Asia)
81 45 470 5525 (Japan)
E-mail: info@quicklogic.com
Support:support@quicklogic.com
Web site:http://www.quicklogic.com/
Revision History
Revision Date Comments
Table 15: Revision History
A not avail. First release.
B not avail.
C not avail.
D not avail.
E not avail.
F not avail.
G not avail.
H May 2000 Update of AC/DC Specs and reformat
I May 2002
Copyright Information
Copyright © 2002 QuickLogic Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
The information contained in this product brief, and the accompanying software programs are protected by copyright. All rights are reserved by QuickLogic Corporation. QuickLogic Corporation
reserves the right to make periodic modifications of this product without obligation to notify any person or entity of such revision. Copying, duplicating, selling, or otherwise distributing any part of this
product without the prior written consent of an authorized representative of QuickLogic is prohibited.
Added Kfactor, Power-up, JTAG and mechanical
drawing information. Reformatted.
•
•
www.quicklogic.com
•
18
•
•
•
QuickLogic, pASIC, and ViaLink are registered trademarks, and SpDE and QuickWorks are trademarks of QuickLogic Corporation.
Verilog is a registered trademark of Cadence Design Systems, Inc.
© 2002 QuickLogic Corporation
 Loading...
Loading...