Page 1
MPA-200/300
RS-422/485 SYNCHRONOUS
ADAPTER CARD
for ISA compatible machines
INTERFACE CARDS FOR IBM PC/AT AND PS/2
User's Manual
QUATECH, INC. TEL: (330) 655-9000
5675 Hudson Industrial Parkway FAX: (330) 655-9010
Hudson, Ohio 44236 http://www.quatech.com
Page 2

Page 3

Warranty Information
Quatech Inc. warrants the MPA-200/300 to be free of defects for
one (1) year
adapter that fails to perform under normal operating conditions and in accordance
with the procedures outlined in this document during the warranty period. Any
damage that results from improper installation, operation, or general misuse voids
all warranty rights.
The authors have taken due care in the preparation of this document and any
associated software program(s). In no event will Quatech Inc. be liable for
damages of any kind, incidental or consequential, in regard to or arising out of the
performance or form of the materials presented herein and in the program(s)
accompanying this document. No representation is made regarding the suitability
of this product for any particular purpose.
Quatech Inc. reserves the right to edit or append to this document or the product(s)
to which it refers at any time and without notice.
Please complete the following information and retain for your records. Have this
information available when requesting warranty service.
from the date of purchase. Quatech Inc. will repair or replace any
Date of purchase:
Model Number:
Serial Number:
MPA-200/300
Single Channel RS-232 SynchronousProduct Description:
Communication ISA Adapter
Quatech Inc., MPA-200/300 Manual
Page 4

The information contained in this document cannot be reproduced in any form
without the written consent of Quatech, Inc. Likewise, any software programs
that might accompany this document can be used only in accordance with any
license agreement(s) between the purchaser and Quatech, Inc. Quatech, Inc.
reserves the right to change this documentation or the product to which it refers at
any time and without notice.
The authors have taken due care in the preparation of this document and every
attempt has been made to ensure its accuracy and completeness. In no event will
Quatech, Inc. be liable for damages of any kind, incidental or consequential, in
regard to or arising out of the performance or form of the materials presented in
this document or any software programs that might accompany this document.
Quatech, Inc. encourages feedback about this document. Please send any written
comments to the Technical Support department at the address listed on the cover
page of this document.
Copyright ©2004 by
Quatech Inc.
5675 Hudson Industrial Parkway
Hudson, Ohio 44236
All rights reserved. Printed in the U.S.A.
Quatech Inc, MPA-200/300 Manual
Page 5

Compliances - Electromagnetic Emissions
EC - Council Directive 89/336/EEC
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits of the
following standards for a digital device:
EN50081-1 (EN55022, EN60555-2, EN60555-3)
EN50082-1 (IEC 801-2, IEC 801-3, IEC 801-4)
Type of Equipment: Information Technology Equipment
Equipment Class: Commercial, Residential, & Light Industrial
FCC - Class B
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B
digital device, pursuant to part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to
provide reasonable protection against harmful interference in a residential
installation. This equipment generates, uses and can radiate radio frequency
energy and if not installed and used in accordance with the instructions, may cause
harmful interference to radio communications. However, there is no guarantee
that interference will not occur in a particular installation, If this equipment does
cause harmful interference to radio or television reception, which can be
determined by turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to
correct the interference by one or more of the following measures:
Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to
which the receiver is connected.
Consult the dealer or an or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
This equipment has been certified to comply with the limits for a Class B
computing device, pursuant to FCC Rules. In order to maintain compliance with
FCC regulations, shielded cables must be used with this equipment. Operation
with non-approved equipment or unshielded cables is likely to result in
interference to radio and TV reception. The user is cautioned that changes and
modifications made to the equipment without the approval of the manufacturer
could void the user's authority to operate this equipment.
Quatech Inc., MPA-200/300 Manual
Page 6

TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
2 HARDWARE INSTALLATION
3 SCC GENERAL INFORMATION
3.1 Accessing the registers ...................................
3.2 Baud Rate Generator Programming .....................
3.3 SCC Data Encoding Methods ............................
4 JUMPER BLOCK CONFIGURATIONS
4.1 J4 - Interrupt Configuration .............................
4.2 J5 & J6 - Interrupt Level Selection .......................
4.3 J10 - Transmit DMA Channel Selection ....................
4.4 J11 - Receive DMA Channel Selection .....................
4.5 J7 - Line Driver Control Selection ........................
4.6 J8 - SYNCA to RLEN control ............................
5 ADDRESSING
6 INTERRUPTS
7 DIRECT MEMORY ACCESS
7.1 Using Terminal Count to Generate an Interrupt .............
8 CONFIGURATION REGISTER
9 COMMUNICATIONS REGISTER
10 DTE / DCE Configuration
10.1 DTE Configuration ...................................
10.2 DCE Configuration ...................................
11 EXTERNAL CONNECTIONS
11.1 MPA-200 and EIA-530 Compatibility ....................
11.2 Null-Modem Cables ...................................
12 DEFINITION OF INTERFACE SIGNALS
13 SPECIFICATIONS
.......................................
.........................
......................
................
.........................................
.........................................
..........................
.......................
.....................
.............................
........................
...........
...................................
2
4
5
6
9
10
11
11
11
12
13
13
14
15
17
18
20
21
23
25
26
27
29
32
32
33
37
Quatech Inc., MPA-200/300 Manual
Page 7

3 Quatech Inc., MPA-200/300 Manual
Page 8

1 INTRODUCTION
The Quatech MPA-200/300 is a single channel, synchronous serial communication port for systems utilizing the architecture of the IBM AT personal or compatible computers. The MPA-200 is RS-422 compatible.
The MPA-300 has RS-485 data line drivers and receivers in place of the
MPA-200's RS-422 drivers and receivers. The MPA-300's RS-485 interface will
allow multiple systems to be connected in a multi-drop configuration. Hereafter,
the MPA-200 and MPA-300 will be collectively referred to as the MPA-200
except where noted.
The ports of the MPA-200 occupy an 8 byte block of I/O address space. The base
address of this block may be located anywhere within the available I/O address
space of the system.
The MPA-200 is available with a variety of serial communications controlers
(SCC). All of the available SCC's can support asynchronous formats, byteoriented protocols such as IBM Bisync, and bit-oriented protocols such as HDLC
and IBM SDLC. The SCC's also offer internal functions such as on-chip baud rate
generators, and digital phase-lock loops (DPLL).
The MPA-200 also supports Direct Memory Access (DMA) and interrupts. DMA
channels 1 - 3 can be used for high data transfer rates, while interrupt levels 2 - 7,
10 - 12, and 14 - 15 are available for several interrupt sources.
On the MPA-200, communications is controlled by the SCC labeled U17. There
are seven jumper blocks on the MPA-200 that allow the user to select such
options as DMA channels, interrupt levels and driver control. If the MPA-200 is
configured for data terminal equipment (DTE), external connections are made
through a male D-25 connector CN2. If the MPA-200 is configured for data
communications equipment (DCE), external connections are made through a a
female D-25 connector CN1. These configurations are determined when the board
is manufactured, prior to shipment.
On the MPA-200, the driver circuit consists of one RS-422 driver (U18), one
RS-422 receiver (U26), four RS-422/485 transceivers (U19, U20, U22, U23), two
RS-423 drivers (U24, U25). Each differential pair that is received by the
MPA-200 has a 100 ohm termination resistor.
On the MPA-300, the driver circuit consists of one RS-485 driver (U19), one
RS-485 receiver (U26), four RS-422/485 transceivers (U19, U20, U22, U23), two
RS-423 drivers (U24, U25). Each differential pair that is received by the
MPA-300 has a 150 ohm termination resistor.
Quatech Inc., MPA-200/300 Manual 2
Page 9
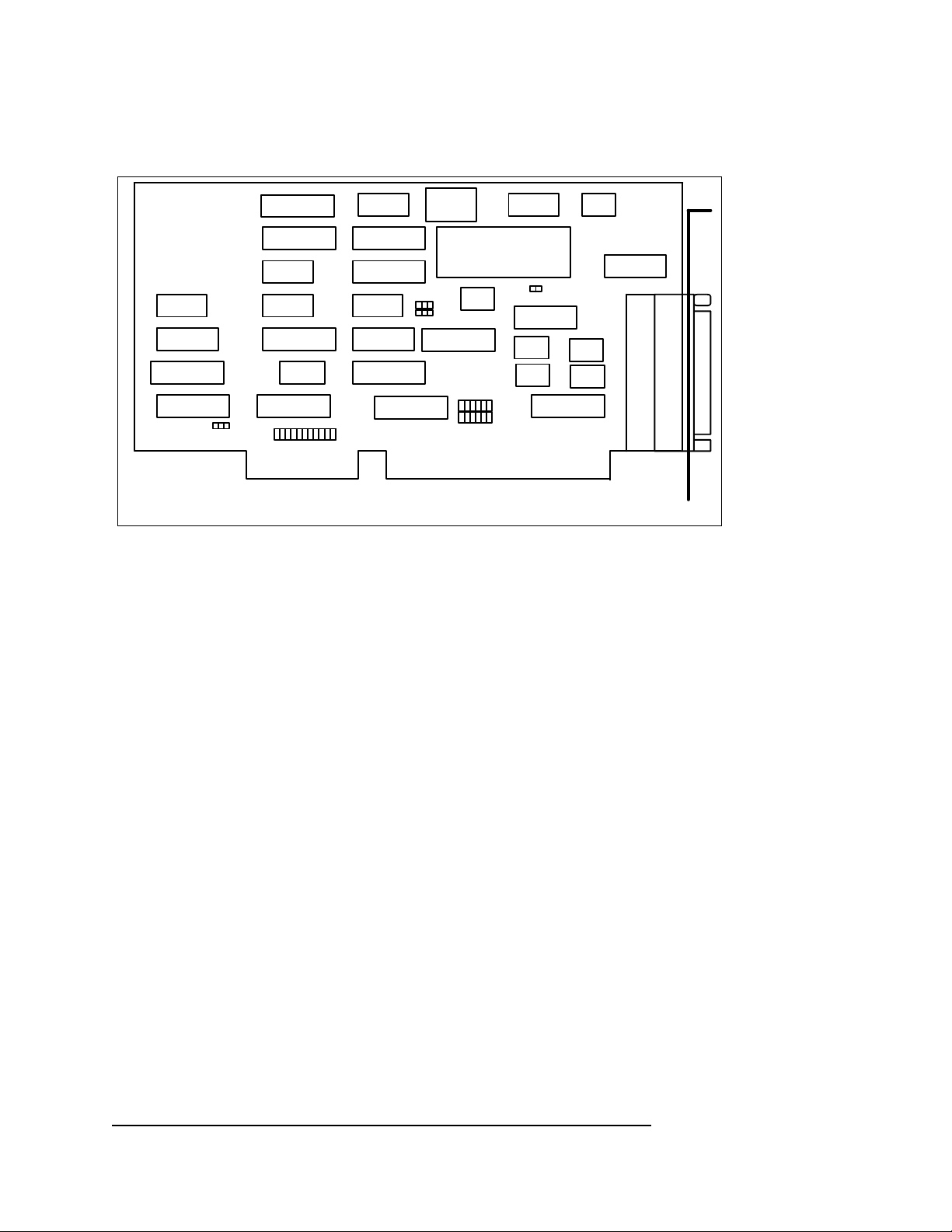
Figure 1 MPA-200 board drawing
Quatech, Inc.
U29
MPA-200
U4
U5
U1
U2
SW1 SW2
U3
J4
U6
U7
U8
J5 J6
U9
U10
U11
U12
U13
U14
U15
J7
X1
U28
U17
U23
J10
J11
U16
J8
U18
U19
U20
U22
U26
CN2CN1
U24
U25
U21
3 Quatech Inc., MPA-200/300 Manual
Page 10
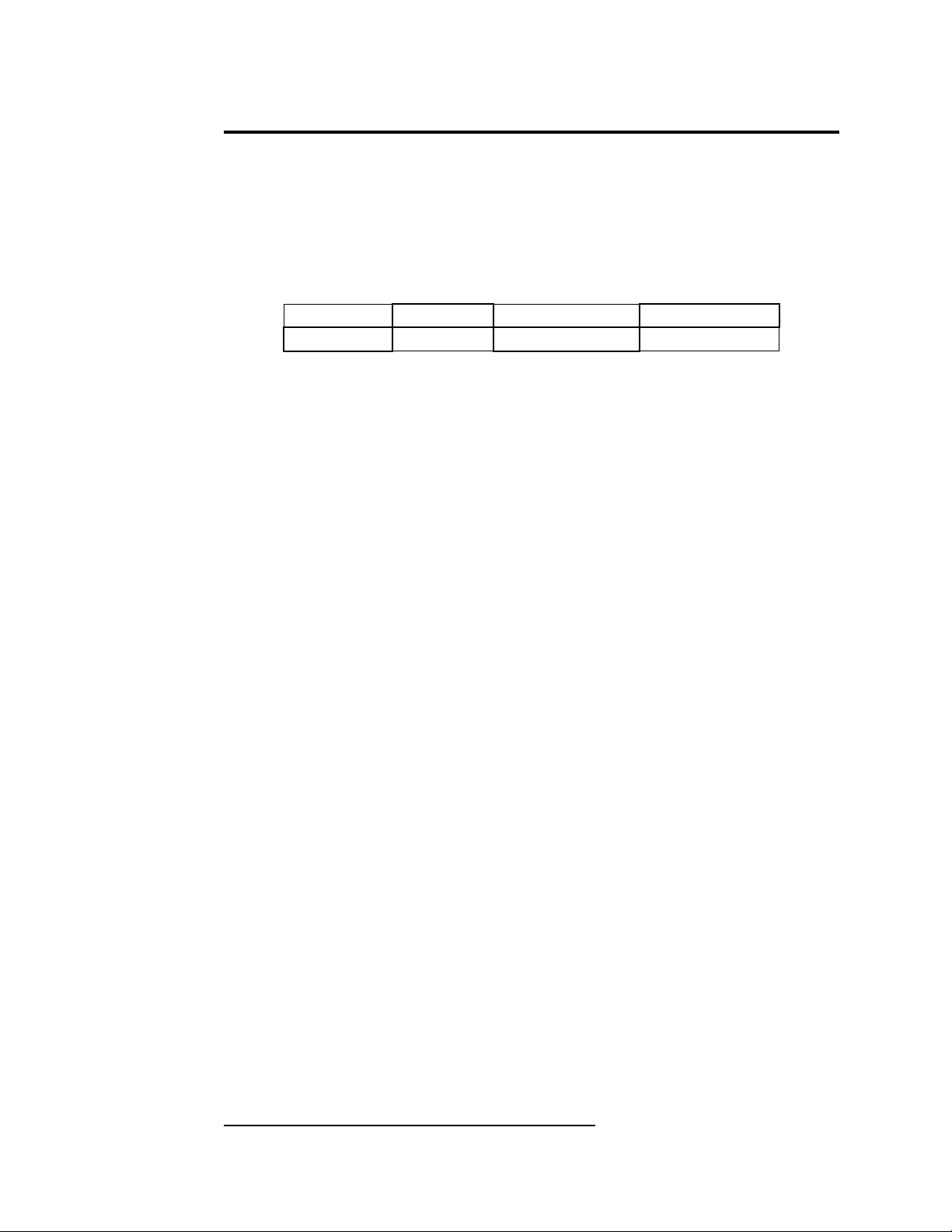
2 HARDWARE INSTALLATION
If the default address and interrupt settings are sufficient, the MPA-200 can be
quickly installed and put to use. The factory default settings are listed below in
Table 1.
Table 1 Default Board Configuration
RxDMATxDMAInterruptAddress
DMA/DRQ 1DMA/DRQ 3IRQ 5300 hex
1. If the default settings are correct, skip to step 2, otherwise refer to the
chapters ADDRESSING on page 15, INTERRUPTS on page 17, and
DIRECT MEMORY ACCESS on page 18 for detailed information on
how to set the address, IRQ, and DMA levels.
2. Turn off the power of the computer system in which the MPA-200 is
to be installed.
3. Remove the system cover according to the instructions provided by the
computer manufacturer.
4. Install the MPA-200 in any vacant expansion slot. The board should
be secured by installing the Option Retaining Bracket (ORB) screw.
5. Replace the system cover according to the instructions provided by the
computer manufacturer.
6. Attach and secure the cable connectors to the desired equipment.
Quatech Inc., MPA-200/300 Manual 4
Page 11

3 SCC GENERAL INFORMATION
The Serial Communications Controller (SCC) is a dual channel, multi-protocol
data communications peripheral. The MPA-200 provides a single channel for
communications, however, to provide full DMA capabilities, both channels of the
SCC can be utilized. The SCC can be software configured to satisfy a wide
variety of serial communications applications. Some of its protocol capabilities
include:
1) Asynchronous Communications
5, 6, 7, or 8 bits per character
1, 1-1/2, or 2 stop bits
Odd, even, or no parity
Times 1, 16, 32, or 64 clock modes
Break generation and detection
Parity, overrun and framing error detection
2) Byte-oriented Synchronous Communications
Internal/external character synchronization
1 or 2 sync characters in separate registers
Automatic Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC) generation/detection
3) SDLC/HDLC (Bit Synchronous) Communications
Abort sequence generation and checking
Automatic zero insertion and deletion
Automatic flag insertion between messages
Address field recognition
I-field residue handling
CRC generation and detection
SDLC loop mode with EOP recognition/loop entry and exit
4) NRZ, NRZI, or FM encoding/decoding
5 Quatech Inc., MPA-200/300 Manual
Page 12

3.1 Accessing the registers
The mode of communication desired is established and monitored through the bit
values of the internal read and write registers. The register set of the SCC includes
16 write registers and 9 read registers. These registers only occupy four address
locations, which start at the MPA-200's physical base address that is configured
via the on board switches. This and all other addresses are referenced from this
base address in the form Base + Offset. An example of this is Base + 1 for the
SCC Control Port, Channel A.
There are two register locations per SCC channel, a data port and a control port .
Accessing the internal SCC registers is a two step process that requires loading a
register pointer to perform the addressing to the correct data register. The first
step is to write to the control port the operation and address for the appropriate
channel. The second step is to either read data from or write data to the control
port. The only exception to this rule is when accessing the transmit and receive
data buffers. These registers can be accessed with the two step process described
or with a single read or write to the data port. The following examples illustrate
how to access the internal registers of the SCC. Also, Table 2 SCC read register
description describes the read registers and Table 3 SCC write register description describes the write registers for each channel.
The MPA-200 has been designed to assure that all back to back access timing
requirements of the SCC are met without the need for any software timing
control. The standard of adding jmp $+2 between IO port accesses is not required
when accessing the MPA-200.
Example 1: Enabling the transmitter on channel A.
mov dx,base ; load base address
add dx,ContA ; add control reg A offset
mov al,05h ; write the register number
out dx,al ;
mov al,08h ; write the data to the register
out dx,al
Example 2: Monitoring the status of the transmit and receive buffers in RR0
of Channel A. Register 0 is addressed by default if no register
number is written to WR0
mov dx,base ; load base address
add dx,ContA ; add control reg A offset
in al,dx ; read the status
Quatech Inc., MPA-200/300 Manual 6
Page 13
Example 3: Write data into the transmit buffer of channel A.
mov dx,base ; load base address
out dx,al ; write data in ax to buffer
Example 4: Read data from the receive buffer of channel A.
mov dx,base ; load base address
in al,dx ; write data in ax to buffer
Table 2 SCC read register description.
Transmit, Receive buffer statuses and external status RR0
Special Receive Condition status, residue codes, error conditions RR1
RR2
The SCC can perform three basic forms of I/O operations: polling, interrupts, and
block transfer. Polling transfers data, without interrupts, by reading the status of
RR0 and then reading or writing data to the SCC buffers via CPU port accesses.
Interrupts on the SCC can be sourced from the receiver, the transmitter, or
External/Status conditions. At the event of an interrupt, Status can be determined,
then data can be written to or read from the SCC via CPU port accesses. For
block transfer mode, DMA transfers accomplish data transfers from the SCC to
memory or from memory to the SCC, interrupting the CPU only when the Block
is finished. Further information on these subjects are found in the chapters titled
INTERRUPTS, and DIRECT MEMORY ACCESS.
Modified Channel B interrupt vector and Unmodified Channel A
interrupt vector
Interrupt Pending bits RR3
LSB of frame byte count register RR6
MSB of frame byte count and FIFO status registerRR7
Receive buffer RR8
Miscellaneous status parameters RR10
Lower byte of baud rate time constantRR12
Upper byte of baud rate time constantRR13
External/Status interrupt information RR15
The SCC incorporates additional circuitry supporting serial communications. This
circuitry includes clocking options, baud rate generator (BRG), data encoding, and
internal loopback. The SCC may be programmed to select one of several sources
to provide the transmit and receive clocks. These clocks can be programmed in
WR11 to come from the RTXC pin, the TRXC pin, the output of the BRG, or the
transmit output of the DPLL. The MPA-200 uses the TRXC pin for its transmit
7 Quatech Inc., MPA-200/300 Manual
Page 14
clock (TCLK) and the RTXC pin for its receive clock (RCLK). Programming of
the clocks should be done before enabling the receiver, transmitter, BRG, or
DPLL.
Table 3 SCC write register description.
WR0
WR4
WR10
Command Register, Register Pointer, CRC initialization, resets for
various modes
Interrupt control, Wait/DMA request controlWR1
Interrupt vectorWR2
Receiver initialization and control WR3
Transmit/Receive miscellaneous parameters and codes, clock rate,
stop bits, parity
Transmitter initialization and control WR5
Sync character (1st byte) or SDLC address field WR6
Sync character (2nd byte) or SDLC FlagWR7
HDLC enhancement registerWR7'
Transmit bufferWR8
Master interrupt control and reset WR9
Miscellaneous transmitter/receiver control bits, NRZI, NRZ, FM
coding, CRC reset
Clock mode and source controlWR11
Lower byte of baud rate time constant WR12
Lower byte of baud rate time constant WR13
WR14
Quatech Inc., MPA-200/300 Manual 8
Miscellaneous control bits: baud rate generator, DPLL control, auto
echo
External/Status interrupt control WR15
Page 15

3.2 Baud Rate Generator Programming
The baud rate generator (hereafter referred to as the BRG) of the SCC consists of
a 16-bit down counter, two 8-bit time constant registers, and an output divide-bytwo. The time constant for the BRG is programmed into WR12 (least significant
byte) and WR13 (most significant byte). The equation relating the baud rate to the
time constant is given below while Table 4 shows the time constants associated
with a number of popular baud rates when using the standard MPA-200 9.8304
MHz clock.
Clock_Frequency
Time_Const =
2&Baud_Rate&Clock_Mode
- 2
Where:
Clock_Frequency = crystal frequency of 9.8304 MHz
Clock_Mode = value programmed in WR4
Baud_Rate = desired baud rate
Table 4 Time constants for common baud rates
Baud Constant (Hex)Baud Rate
38400
-----------------------
19200 -----------------------
9600 ------------------------
4800 ------------------------
2400 ------------------------
1200 ------------------------
600 -------------------------
300 -------------------------
007EH
00FEH
01FEH
03FEH
07FEH
0FFEH
1FFEH
3FFEH
(for 9.8304 Mhz Clock)
9 Quatech Inc., MPA-200/300 Manual
Page 16

3.3 SCC Data Encoding Methods
The SCC provides four different data encoding methods, selected by bits D6 and
D5 in WR10. These four include NRZ, NRZI, FM1 and FM0. The SCC also
features a digital phase-locked loop (DPLL) that can be programmed to operate in
NRZI or FM mode. Also, the SCC contains two features for diagnostic purposes,
controlled by bits in WR14. They are local loopback and auto echo.
For further information on these subjects or any others involving the SCC, contact
the manufacturer of the SCC being used for a complete technical manual.
Quatech Inc., MPA-200/300 Manual 10
Page 17

4 JUMPER BLOCK CONFIGURATIONS
The MPA-200 utilizes seven user-selectable jumper blocks , that allow the user
more flexibility when configuring the board. The following section explains the
function of each of the jumper blocks on the MPA-200.
4.1 J4 - Interrupt Configuration
J4 is a three pin jumper which determines whether or not a board’s interrupt is
sharable. By selecting pins 1 & 2, the user has the ability to share an interrupt with
other Quatech expansion cards. The MPA-200 will drive the interrupt onto the bus
only when an interrupt occurs. Otherwise, the output is high impedance. If pins 2
& 3 of J4 are selected, then interrupts abide by the IBM specification and cannot
be shared. Table 5 summarizes the jumper block selections for J4. To maintain
100% ISA bus compatibility J7 should be set in No Interrupt Sharing mode.
Table 5 Jumper Block J4 Selections
PinsInterrupt Function
1&2Interrupt Sharing
2&3No Interrupt Sharing
4.2 J5 & J6 - Interrupt Level Selection
Jumper blocks J5 and J6 select the interrupt level that the MPA-200 utilizes. Interrupt levels IRQ2 - IRQ7 reside on J5, while interrupt levels IRQ10 - IRQ12 and
IRQ14 - IRQ15 reside on J6. Table 6, and Table 7 summarize the jumper block
selections for J5 and J6. The IRQ levels are also marked on the MPA-200 silkscreen for easy identification.
Table 6 Jumper block J5 selections.
PinsInterrupt Level
1&7IRQ2(9)
2&8IRQ3
3&9IRQ4
4&10IRQ5
5&11IRQ6
6&12IRQ7
Table 7 Jumper block J6 selections.
PinsInterrupt Level
11 Quatech Inc., MPA-200/300 Manual
Page 18

1&6IRQ10
2&7IRQ11
3&8IRQ12
4&9IRQ14
5&10IRQ15
4.3 J10 - Transmit DMA Channel Selection
J10 selects the DMA channel to be used for transmit DMA. Three channels (1 - 3)
are available on the MPA-200 for DMA. When selecting a DMA channel, both
the DMA acknowledge (DACK) and the DMA request (DRQ) for the appropriate
channel need to be selected. Table 8 summarizes the jumper block selections for
J10
Table 8 Jumper block J10 selections.
PinsDMA Channel
1&7Channel 1
2&8
3&9Channel 2
4&10
5&11Channel 3
6&12
Quatech Inc., MPA-200/300 Manual 12
Page 19

4.4 J11 - Receive DMA Channel Selection
J11 selects the DMA channel to be used for receive DMA. Three channels (1 - 3)
are available on the MPA-200 for DMA. When selecting a DMA channel, both
the DMA acknowledge (DACK) and the DMA request (DRQ) for the appropriate
channel need to be selected. Table 9 summarizes the jumper block selections for
J11.
Table 9 Jumper block J11 selections.
PinsDMA Channel
1&7Channel 1
2&8
3&9Channel 2
4&10
5&11Channel 3
6&12
NOTE:
Since it is illegal to perform transmit DMA and receive DMA on the
same DMA channel, jumper blocks J10 and J11 should never have the
same pins connected. This condition could result in damage to the
system.
4.5 J7 - Line Driver Control Selection
J7 controls the source for enabling and disabling the driver circuitry on the
MPA-200. By selecting pins 1 & 2, the transmitters on the MPA-200 will always
be enabled. If the user wants the ability to enable and disable the transmitters, pins
2 & 3 should be selected. By doing this, the transmitters are controlled by bit D0
of the communications register. Similarly, by selecting pins 4 & 5, the receivers
on the MPA-200 will always be enabled. If pins 5 & 6 are selected, the receivers
are controlled by bit D1 of the communications register. Table 10 summarizes the
jumper block selections for J7.
13 Quatech Inc., MPA-200/300 Manual
Page 20

Table 10 Jumper block J7 connections
PinsDriver Control Function
1&2Transmitter Always Enabled
2&3Transmitter controlled by Comm. Register
4&5Receiver Always Enabled
5&6Receiver controlled by Comm. Register
4.6 J8 - SYNCA to RLEN control
J8 controls the signal path from the RLEN bit in the Communications register to
the SYNCA input to the SCC. If J8 is installed the RLEN bit may be used to
control the SYNCA pin when the SCC is in external SYNC mode. Note: the
RLEN output is still effected when used to control the SYNCA pin.
Table 11 Jumper J8 Selections
Jumper J8Function
INSYNCA
OUTRLEN
Quatech Inc., MPA-200/300 Manual 14
Page 21

5 ADDRESSING
The MPA-200 occupies a continuous 8 byte block of I/O addresses. For example,
if the base address is set to 300H, then the MPA-200 will occupy address
locations 300H-307H. The base address of the MPA-200 may be set to any of the
first 64 Kbytes (0 - FFFFH) of available I/O address space through the settings of
dip switches SW1 and SW2. SW1 allows the user to select the higher address
signals A15 - A8. SW2 allows the user to select the lower address signals A7 A3. The sixth position of SW2 is not used and can be ignored. Figure 2 shows
some examples of different base addresses.
Figure 1 Address switch selection examples.
A12
A13
A14
A15
ON
1
SW1
3344556
2
Base Address = 300H
A15
A14
A13
A12
ON
1
SW1
2
Base Address = 3F8H
A11
A11
A10
A10
6
7
7
A9
A9
A8
A7
A6
A5
A4
A3
NOT USED
ON
8
A8
8
SW2
ON
SW2
112
A7
3
A4
A6
2
3445566
A5
A3
NOT USED
15 Quatech Inc., MPA-200/300 Manual
Page 22

The first four bytes, Base+0 through Base+3, of address space on the MPA-200
contain the internal registers of the SCC. The next two locations Base+4 and
Base+5 contain the communications register and the configuration register. The
last two address port locations are reserved for future use. The entire address
range of the MPA-200 is shown in Table 12.
Table 12 MPA-200 Address Assignments
Register DescriptionAddress
SCC Data Port, Channel ABase + 0
SCC Control Port, Channel ABase + 1
SCC Data Port, Channel BBase + 2
SCC Control Port, Channel BBase + 3
Communications RegisterBase + 4
Configuration RegisterBase + 5
ReservedBase + 6
ReservedBase + 7
Information on the internal registers of the SCC can be found in the chapter titled
SCC GENERAL INFORMATION starting on page 4. The two onboard registers
give the user additional options pertaining to DMA, and Interrupts. Information on
the configuration register and the communications register can be found in the
chapters CONFIGURATION REGISTER on page 21, and COMMUNICATIONS
REGISTER on page 23.
Quatech Inc., MPA-200/300 Manual 16
Page 23

6 INTERRUPTS
The MPA-200 supports eleven interrupt levels: IRQ2 -7, IRQ10 - 12, and IRQ14
- 15. The interrupt level is selected through jumper blocks J5 and J6 ( see
JUMPER BLOCK CONFIGURATIONS on page 11). The interrupt source is
selected by bits D4 and D5 of the configuration register. The MPA-200 has three
interrupt sources: interrupt on terminal count, interrupt on test mode, and interrupt
from the SCC. Interrupts from the SCC can occur on a number of conditions,
depending on which is programmed. These include interrupt on first character
received, interrupt on all characters received, interrupt on special condition
received, interrupt on character transmitted, and interrupt on External/Status
(see manufacturers data sheets for more details). Also, jumper block J4 can be
selected to provide for interrupt sharing on the MPA-200.
When using interrupts with the MPA-200, it is required that the applications
program have an interrupt service routine (ISR). There are several things that an
ISR must do to allow proper system operation:
1. Do a software interrupt acknowledge to the SCC. This is accomplished by reading the interrupt vector register, status register 2, in
channel B of the SCC. The value supplied by this read can also be
used to vector to the appropriate part of the ISR.
2. Service the interrupt by reading the receiver buffer, writing to the
transmit buffer, etc.
3. Write a Reset Highest Interrupt Under Service (IUS) to the SCC. This
is done by writing a 0x38 to the SCC command register.
4. Check for any additional interrupts pending in the SCC and service
them.
5. For applications running under DOS, a nonspecific End of Interrupt
must be submitted to the interrupt controller. For Interrupts 2-7 this is
done by writing a 0x20 to port 0x20. For Interrupts 10-12,14 and 15
this is done by writing a 0x20 to 0x60, then a 0x20 to 0x20 (Due to the
interrupt controllers being cascaded). Note that this should only be
done if it is a requirement of the operating system being used.
For further information on these subjects or any others involving the SCC contact
the manufacturer of the SCC being used for a complete technical manual.
17 Quatech Inc., MPA-200/300 Manual
Page 24

7 DIRECT MEMORY ACCESS
Direct Memory Access (DMA) is a way of directly transferring data to and from
memory, resulting in high data transfer rates with very low CPU overhead. The
MPA-200 allows the user to perform DMA transfers when data is received
(DMARRQ) or when data is transmitted (DMATRQ). Three different DMA
channels are available(DMA1 - DMA3). Which channels are selected is determined by setting jumper blocks J10 and J11 (See Table 8, and Table 9). The
sources of MPA-200’s requests originate from the SCC and can be programmed
for a variety of DMA modes. These modes include DMA request on transmit,
DMA request on receive, and DMA request on both transmit and receive.
For DMA request on transmit, the DMA controller should be programmed first
for an 8 bit read transfer on the desired channel, but not yet enabled. Then the
SCC should be programmed for DMA request on transmit on the desired DMA
source. The sources DMA request on transmit are either the W/REQA pin (pin 10)
of channel A or the DTR/REQA pin (pin 16) of channel A. The source is then
determined by bit D0 of the configuration register.
Note:
The DTR/REQA pin should only be used for DMA transfers if the user
does not require a valid DTR signal at the connector. This is due to the fact
that when DTR/REQA is used for DMA transfer it is not a valid handshake
signal.
After programming the SCC for DMA, one should enable the DMA on the
MPA-200 by setting bit D2 of the configuration register. Next, the DMA on the
SCC should be enabled, and finally, the DMA channel should be unmasked. The
DMA controller will write the data in memory to the SCC. When the transmit
buffer of the SCC becomes empty, a DMA request will be generated and the data
will be transferred.
For DMA request on receive, the DMA controller should be programmed first for
an 8 bit write transfer on the desired channel, but not yet enabled. Next, the SCC
should be programmed for DMA request on receive on the desired DMA source.
The two sources for DMA request on receive are either the W/REQA pin (pin 10)
of channel A or the W/REQB pin (pin 30) of channel B. The source is then determined by bit D1 on the configuration register. After programming the SCC for
DMA, one should enable the DMA on the MPA-200 by setting bit D3 of the
configuration register. Then, the DMA on the SCC should be enabled, and finally
the DMA controller should be enabled. When a character enters the receive buffer
Quatech Inc., MPA-200/300 Manual 18
Page 25

of the SCC, a DMA request is generated. The DMA controller then writes the data
from the SCC into memory.
Programming for DMA request on both transmit and receive is simply a combination of the two. There are three possible configurations that can be used, depending on the sources selected. The first configuration available uses the W/REQA
pin of channel A for DMA request on receive, and the DTR/REQA pin of channel
A for DMA request on transmit. This is done by setting bit D0 and clearing bit
D1 of the configuration register. The second configuration uses the DTR/REQA
pin for DMA request on transmit, and the W/REQB pin for DMA request on
receive. This is done by setting both D0 and D1 of the configuration register.
These two configurations give users an optional way of performing DMA requests
on both transmit and receive. Otherwise, the third configuration should be used.
This configuration uses the W/REQA pin of channel A for DMA request on transmit, and the W/REQB pin of channel B for DMA request on receive. This is done
by clearing bit D0 and setting bit D1 of the configuration register. Figure 3 shows
a block diagram of the DMA circuitry on the MPA-200.
When using the channel A DTR/REQ pin for transmit DMA the SCC must be
programmed so that the request release timing of this pin is identical to the
WAIT/REQ timing. This is done by setting bit D4 of write register 7 prime.
NOTE:
Even though the W/REQA pin can be used for both DMA request on
transmit and receive, obviously it cannot be used for both simultaneously.
Therefore, bits D0 and D1 of the configuration register should never be
cleared at the same time while bits D2 and D3 are both set. This situation
may result in damage to the system.
19 Quatech Inc., MPA-200/300 Manual
Page 26
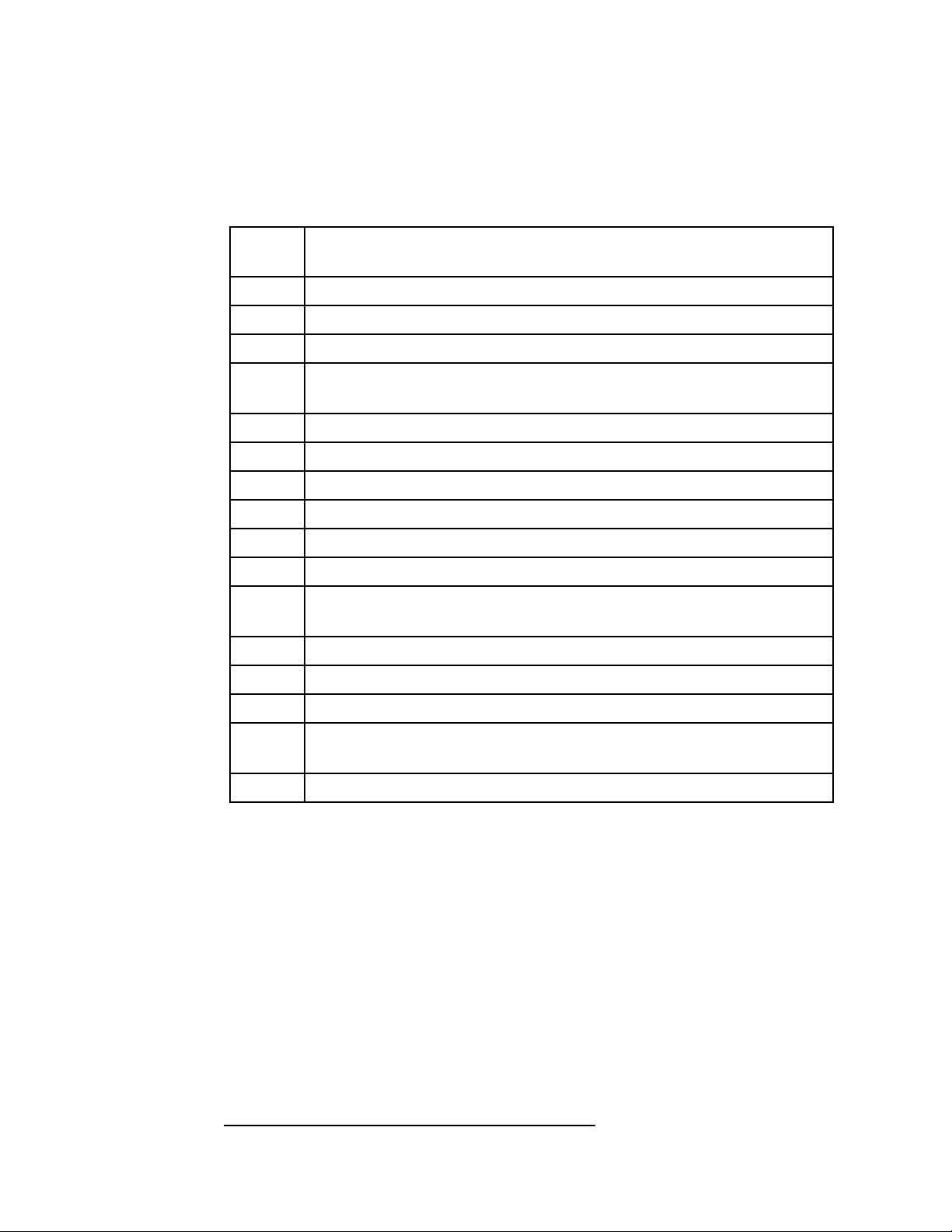
Figure 3 Block diagram of DMA on MPA-200.
W/REQA
DMATRQ
DTR/REQA
DRMRRQ
W/REQB
SCC
7.1 Using Terminal Count to Generate an Interrupt
The MPA-200 allows the option of generating an interrupt whenever the Terminal
Count (TC) signal is asserted. Terminal Count is an indicator generated by the
system’s DMA controller, which signals that the number of transfers programed
into the DMA controller’s transfer register have occurred. This board feature only
works when theinterrupt sharing feature is selected on jumper J4.
PAL
J10
J11
Quatech Inc., MPA-200/300 Manual 20
Page 27
8 CONFIGURATION REGISTER
The MPA-200 is equipped with an onboard register used for configuring information such as DMA enables, DMA sources, interrupt enables, and interrupt sources.
Below is a detailed description of the configuration register. The address of this
register is Base+5. Table 13 details the bit definitions of the configuration
register.
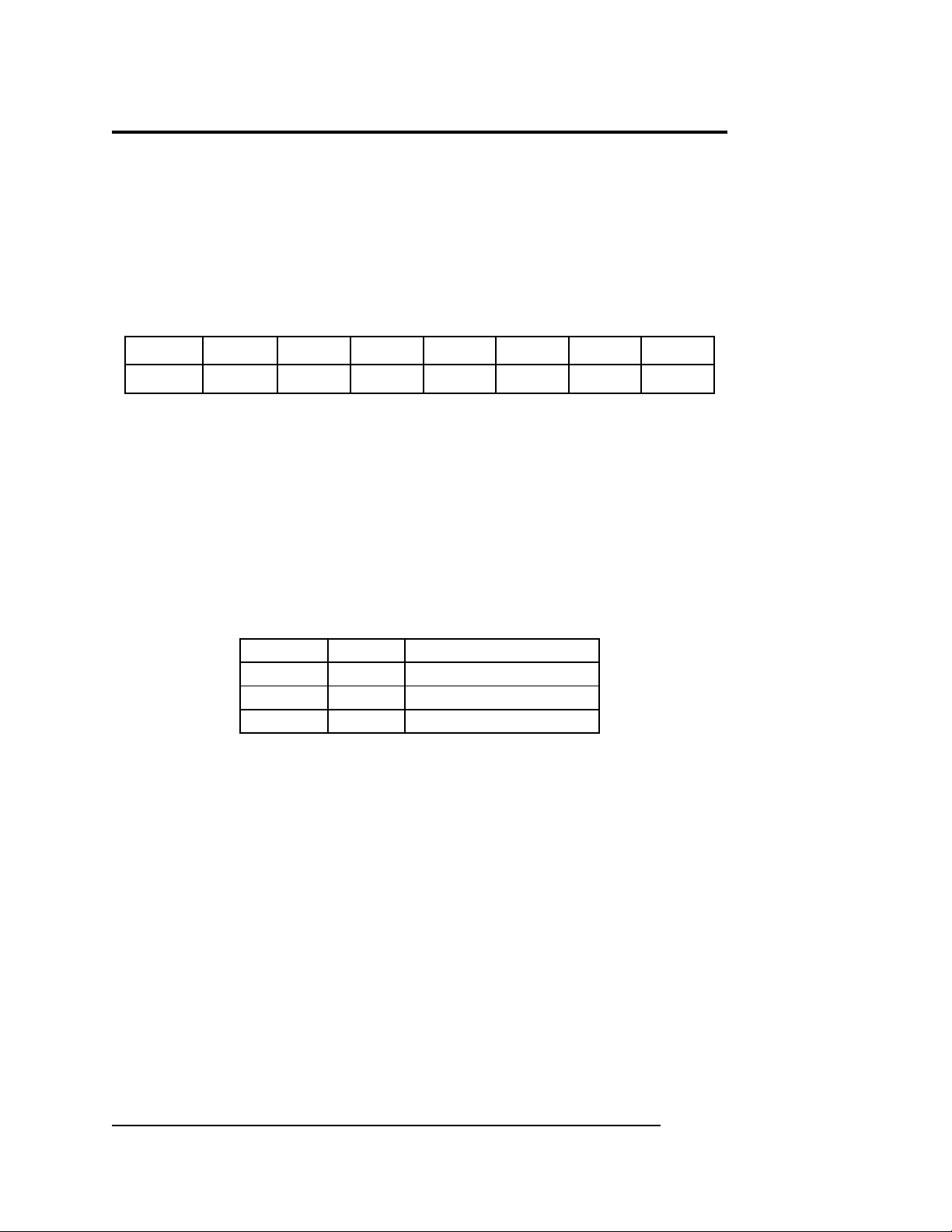
Table 13 Configuration Register - Read/Write
D0D1D2D3D4D5D6D7
TXSRCRXSRCDMTENDMRENINTS0INTS100
D7-D6 Reserved, always 0.
D5-D4 - INTS1, INTS0, INTERRUPT SOURCE AND ENABLE BITS:
These two bits determine the source of the interrupt. The three
sources are interrupt on terminal count (INTTC), interrupt from the
SCC (INTSCC), and interrupt on Test Mode (INTTM). When the
source is set, that interrupt becomes enabled. Below is the mapping
for these bits.
InterruptINTS0INTS1
Interrupts Disabled00
INTTC10
INTSCC01
INTTM11
D3 -DMREN, DMA ON RECEIVE ENABLE:
When set (logic 1), the signal from the SCC’s receive DMA
source is passed on to the selected ISA bus DRQ. When cleared
(logic 0), the SCC cannot drive the receive request signal onto the
ISA bus DRQ.
D2 -DMTEN, DMA ON TRANSMIT ENABLE:
When set (logic 1), the signal from the SCC’s transmit DMA
source is passed on to the selected ISA bus DRQ. When cleared
(logic 0), the SCC cannot drive the transmit request signal onto the
ISA bus DRQ.
21 Quatech Inc., MPA-200/300 Manual
Page 28

D1 -RXSRC, RECEIVE DMA SOURCE:
When set (logic 1), this bit allows the source for receive DMA to
come from the W/REQB pin of channel B on the SCC. When
cleared (logic 0), the source for receive DMA comes from the
W/REQA pin of channel A on the SCC.
D0 -TXSRC, TRANSMIT DMA SOURCE:
When set (logic 1), this bit allows the source for transmit DMA to
come from the DTR/REQA pin of channel A on the SCC. When
cleared (logic 0), the source for transmit DMA comes from the
W/REQA pin of channel A on the SCC.
NOTE:
If both D0 and D1 are cleared (logic 0), then the transmit
and receive DMA requests both come from the W/REQA
pin of channel A on the SCC. Proper board function is
not guaranteed under this condition.
Quatech Inc., MPA-200/300 Manual 22
Page 29

9 COMMUNICATIONS REGISTER
The MPA-200 is equipped with an onboard communications register which gives
the user options pertaining to the clocks and testing. The user can specify the
source and type of clock to be transmitted or received. Test mode bits pertain only
to the DTE versions and can be ignored if using a MPA-200 configured DCE.
The address of this register is Base+4. Table 14 and the descriptions that follow
detail the communications register.
NOTE:
The Local Loopback Test and the Remote Loopback Test cannot be
performed simultaneously. Thus, bits D5 and D4 of the communications
register should not be simultaneously set (logic 1) .
Table 14 COMMUNICATIONS Register - Read/Write
D7 -TEST MODE STATUS (DTE only, read only):
This bit can read the status of the Test Mode signal on a DTE,
allowing the user to monitor this signal without generating any
interrupts.
D6 - Reserved, always 0.
D5 -LOCAL LOOPBACK ENABLE (DTE only):
When set (logic 1), this bit allows the DTE to test the functioning
of the DTE/DCE interface and the transmit and receive sections of
the local DCE. When cleared (logic 0), no testing occurs.
D4 -REMOTE LOOPBACK ENABLE (DTE only):
When set (logic 1), this bit allows the DTE to test the transmission
path up to and through the remote DCE to the DTE interface and
the similar return transmission path. When cleared (logic 0), no
testing occurs. If jumper J8 is in place the Remote Loopback is
also used to control the Sync input of the Channel A data receiver.
This is useful in situations where it is desired to receive
unformatted serial data.
D0D1D2D3D4D5D6D7
TXDENRXDENTCKENRCKENRLENLLEN0TM ST
23 Quatech Inc., MPA-200/300 Manual
Page 30

D3 -RECEIVE CLOCK ENABLE (DCE only):
When set (logic 1), this bit allows the DCE to transmit its receive
clock (RCLK). When cleared (logic 0), the DCE receives its
RCLK. Since a DTE can only receive its RCLK, writing to this bit
has no effect on a DTE.
D2 -TRANSMIT CLOCK ENABLE (DTE only):
When set (logic 1), this bit allows the DTE to transmit its transmit
clock (TCLK). When cleared (logic 0), the DTE receives its
TCLK. Since a DCE can only transmit its TCLK, writing to this bit
has no effect on a DCE.
D1 -RECEIVER ENABLE:
If J7 is configured to allow the Communications Register to
control the MPA-200’s receivers (see Table 10 on page 14) then
when D1 is set (logic 1) the receivers are enabled and when D1 is
cleared (logic 0) the receivers are disabled.
D0 -TRANSMITTER ENABLE:
If J7 is configured to allow the Communications Register to
control the MPA-200’s receivers (see Table 10 on page 14) then
when D0 is set (logic 1) the transmitters are enabled and when D0
is cleared (logic 0) the transmitters are disabled.
Quatech Inc., MPA-200/300 Manual 24
Page 31

10 DTE / DCE Configuration
The MPA-200 can be purchased in either Data Terminal Equipment (DTE) or
Data Communications Equipment (DCE) configuration. The two configurations
share some important features, but have significant differences which need to be
mentioned.
Both the DTE and DCE configurations allow the user to enable and disable the
driver circuitry on the MPA-200 through the settings of jumper block J7. See the
chapter JUMPER BLOCK CONFIGURATIONS on page 11 for further information on the configuration of this jumper block. They both also have the ability to
receive data and receive clock (RCLK) on channel B of the SCC. This allows the
user to transmit and receive on two different channels.
The differences between the MPA-200’s DTE configuration and its DCE configuration include signal definitions, control signals, clocking options and testing. The
following sections describe each configuration individually and in detail.
25 Quatech Inc., MPA-200/300 Manual
Page 32

10.1 DTE Configuration
The control signals that the DTE can generate are the Request To Send (RTS) and
Data Terminal Ready (DTR). It can receive the signals Carrier Detect (CD), Clear
to Send (CTS), and Data Set Ready (DSR). All of the control signals are
controlled through channel A of the SCC, with the exception of the DSR signal,
which is received on channel B.
The DTE’s transmit clock (TCLK from the SCC TRXCA pin) can be transmitted
on TTCLK or received on RTCLK depending on TCKEN (D2 of the communications register). The receive clock (RCLK from the SCC RTxC pins) can be
received on RRCLK or can be generated on the TRxCB pin of the SCC, depending on RCKEN ( D3 of the communications register). The DTE can not transmit
its RCLK. Figure 4 illustrates the clock circuitry of the MPA-200 for it's DTE
configuration.
Figure 2 DTE Clock Configuration
RTXCA
(RCLK)
RTXCB
TRXCB
RCKEN
TCKEN
TRXCA
(TCLK)
RRCLK
RTCLK
TTCLK
The testing signals that the DTE can generate are the Local Loopback Test (LL)
and the Remote Loopback Test (RL). These signals are can be controlled through
the onboard communications register. The DTE can generate an interrupt when a
Test Mode (TM) condition is received. Table 15 summarizes the signals on the
DTE.
Quatech Inc., MPA-200/300 Manual 26
Page 33

10.2 DCE Configuration
On the MPA-200, the difference between the DTE and DCE signals is that, with
the exception of a few control signals, the pins used for signal transmission on the
DTE are used for signal reception on the DCE and vice versa. For example, pin 2
of the DCE connector is received data, yet the corresponding DTE signal is the
transmitted data. This allows the user to connect a DTE device to a DCE device
and perform communication without the use of any customized cable or adapter.
The control signals that the DCE can generate are the Clear to Send (CTS),
Carrier Detect (CD), and Data Set Ready (DSR). It can receive the signals Data
Terminal Ready (DTR) and Ready to Send (RTS). All of the control signals are
controlled through channel A of the SCC, with the exception of the CD signal,
which is generated on channel B.
Depending on the value of TCKEN (D2 of the communications register) the
DCE’s transmit clock (TCLK from the SCC ‘s TRXCA pin) can either be transmitted on TTCLK, or not used at all because the DCE can not receive a TCLK.
Depending on the value of RCKEN (D3 of the communications register), the
DCE’s receive clock (RCLK from the SCC’s RTXC pins) can either be received
on RRCLK or generated on TRXCB of the SCC. In this second case, the signal
from TRXCB is also transmitted on RTCLK. Figure 5 illustrates the clock
circuitry of the MPA-200 for its DCE configuration.
27 Quatech Inc., MPA-200/300 Manual
Page 34

Figure 3 DCE Clock Configuration
RTXCA
(RCLK)
RTXCB
TRXCB
RCKEN
TCKEN
TRXCA
(TCLK)
RRCLK
RTCLK
TTCLK
The Test Mode (TM) signal is always in the OFF condition and cannot be changed
by the user. The Local Loopback (LL) and Remote Loopback (RL) test signals are
not implemented on the DCE. Table 16 summarizes the signals on the DCE.
Quatech Inc., MPA-200/300 Manual 28
Page 35

11 EXTERNAL CONNECTIONS
When configured as a DTE, the MPA-200 uses a D-25 short body male connector
(labeled CN2). When configured as a DCE, the MPA-200 uses a D-25 long body
female connector (labeled CN1). Table 15 and Table 16 describe the pin out
definitions for both connectors and Figure 6 and Figure 7 illustrate the pin-outs
for each of the connectors..
Table 15 DTE Connector Pin Definitions
SCC PinSignalPin
CGND1
TXDA+TXD2
RXDA+RXD3
RTSA+RTS4
CTSA+CTS5
DCDB+DSR6
DGND7
DCDA+CD8
RTXC-RRCLK9
DCDA-CD10
TRXCA-TTCLK11
TRXCB-RTCLK12
CTSA-CTS13
TXDA-TXD14
TRXCB+RTCLK15
RXDA-RXD16
TRXC+RRCLK17
COMM REG D5LLBK18
RTSA-RTS19
DTR/REQA+DTR20
COMM REG D4RLBK21
DCDB-DSR22
DTR/REQA-DTR23
TRXCA+TTCLK24
COMM REG D7TEST MODE25
29 Quatech Inc., MPA-200/300 Manual
Page 36
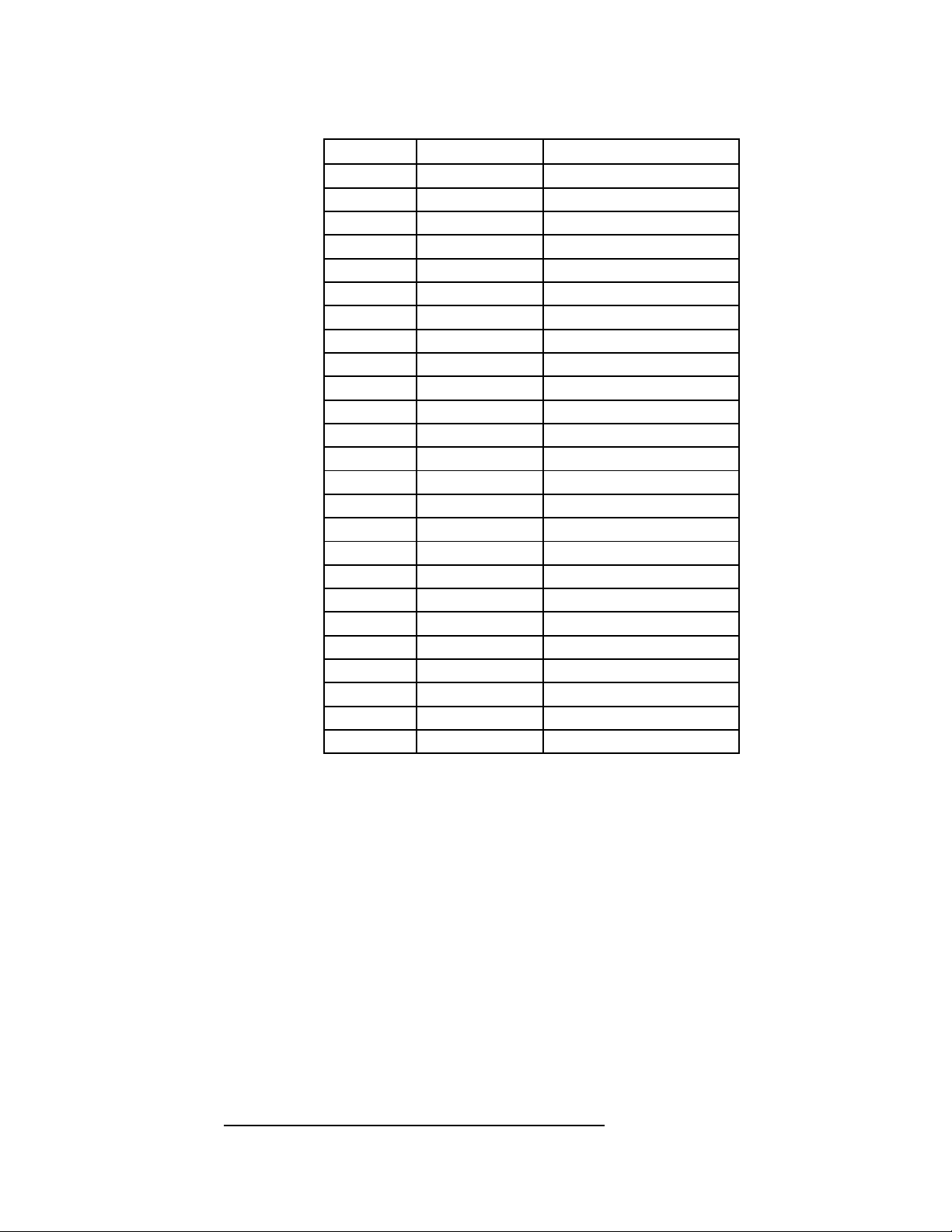
Table 16 DCE Connector Pin Definitions
No Connect1
DGND7
No Connect18
No Connect21
SourceSignalPin
RXDA+RXD2
TXDA+TXD3
CTSA+CTS4
RTSA+RTS5
DTR/REQA+DTR6
DTR/REQB+CD8
TRXCA-TTCLK9
DTR/REQB-CD10
RTXC-RRCLK11
TRXCB-RTCLK12
RTSA-RTS13
RXDA-RXD14
TRXCB+RTCLK15
TXDA-TXD16
TRXCA+TTCLK17
CTSA-CTS19
DCDA+DSR20
DTR/REQA-DTR22
DCDA-DSR23
TRXC+RRCLK24
Always ZeroTEST MODE25
Quatech Inc., MPA-200/300 Manual 30
Page 37

Figure 4 MPA-200 DTE Output Connector
-CTS 13
-RTCLK 12
-TTCLK 11
-CD 10
-RRCLK 9
+CD 8
DGND 7
+DSR 6
+CTS 5
+RTS 4
+RXD 3
+TXD 2
CGND 1
Figure 5 MPA-200 DCE Output Connector
25 TEST MODE
24 +TTCLK
23 -DTR
22 -DSR
21 RLBK
20 +DTR
19 -RTS
18 LLBK
17 +RRCLK
16 -RXD
15 +RTCLK
14 -TXD
+RXD 2
+TXD 3
+CTS 4
+RTS 5
+DTR 6
DGND 7
+CD 8
-TTCLK 9
-CD 10
-RRCLK 11
-RTCLK 12
-RTS 13
14 -RXD
15 +RTCLK
16 -TXD
17 +TTCLK
18 N/C
19 -CTS
20 +DSR
21 N/C
22 -DTR
23 -DSR
24 +RRCLK
25 TEST MODE
31 Quatech Inc., MPA-200/300 Manual
Page 38

11.1 MPA-200 and EIA-530 Compatibility
If the MPA-200 is to be connected with an EIA-530 device, it may be necessary to
swap the +/- conductors on the TXD and RXD signals.
11.2 Null-Modem Cables
The MPA-200 does not use a standard asynchronous PC serial port connector pin
out. Typical off-the-shelf null-modem cables cannot be used with this card.
Quatech Inc., MPA-200/300 Manual 32
Page 39

12 DEFINITION OF INTERFACE SIGNALS
CIRCUIT AB - SIGNAL GROUND
CONNECTOR NOTATION: DGND
DIRECTION: Not applicable
This conductor directly connects the DTE circuit ground to the
DCE circuit ground.
CIRCUIT CC - DATA SET READY (DSR)
CONNECTOR NOTATION: +DSR,-DSR
DIRECTION: From DCE
This signal indicates the status of the local DCE by reporting to the
DTE device that a communication channel has been established.
CIRCUIT BA - TRANSMITTED DATA (TxD)
CONNECTOR NOTATION: +TXD,-TXD
DIRECTION: To DCE
This signal transfers the data generated by the DTE through the
communication channel to one or more remote DCE data stations.
CIRCUIT BB - RECEIVED DATA (RxD)
CONNECTOR NOTATION: +RXD,-RXD
DIRECTION: From DCE
This signal transfers the data generated by the DCE through the
communications channel to one or more remote DTE data stations.
CIRCUIT DA - TRANSMIT ELEMENT TIMING (TxcLK- DTE Source)
CONNECTOR NOTATION: +TTCLK,-TTCLK
DIRECTION: To DCE
This signal, generated by the DTE, provides the DCE with element
timing information pertaining to the data transmitted by the DTE.
The DCE can use this information for its received data.
33 Quatech Inc., MPA-200/300 Manual
Page 40

CIRCUIT DB - TRANSMIT ELEMENT TIMING (TxClk - DCE Source)
CONNECTOR NOTATION: +RTCLK,-RTCLK
DIRECTION: From DCE
This signal, generated by the DCE, provides the DTE with element
timing information pertaining to the data transmitted to the DCE.
CIRCUIT DD - RECEIVER ELEMENT TIMING (RxClk - DCE Source)
CONNECTOR NOTATION: +RRCLK,-RRCLK
DIRECTION: From DCE
This signal, generated by the DCE, provides the DTE with element
timing information pertaining to the data transmitted by the DCE.
CIRCUIT CA - REQUEST TO SEND (RTS)
CONNECTOR NOTATION: +RTS,-RTS
DIRECTION: To DCE
This signal controls the data channel transmit function of the local
DCE and, on a half-duplex channel, the direction of the data
transmission of the local DCE.
CIRCUIT CB - CLEAR TO SEND (CTS)
CONNECTOR NOTATION: +CTS,-CTS
DIRECTION: From DCE
This signal indicates to the DTE whether the DCE is conditioned to
transmit data on the communication channel.
CIRCUIT CF - CARRIER DETECT (CD)
CONNECTOR NOTATION: +CD,-CD
DIRECTION: From DCE
This signal indicates to the DTE whether the DCE is conditioned to
receive data from the communication channel, but does not
indicate the relative quality of the data signals being received.
Quatech Inc., MPA-200/300 Manual 34
Page 41

CIRCUIT CD - DTE READY (DTR)
CONNECTOR NOTATION: +DTR,-DTR
DIRECTION: To DCE
This signal controls the switching of the DCE to the
communication channel. The DTE will generate this signal to
prepare the DCE to be connected to or removed from the
communication channel.
CIRCUIT LL - LOCAL LOOPBACK (LL)
CONNECTOR NOTATION: LLBK
DIRECTION: To DCE
This signal provides a means whereby a DTE may check the
functioning of the DTE/DCE interface and the transmit and receive
sections of the local DCE.
Note:
The local loopback and remote loopback signals are optional and are
omitted from the DCE configuration of the MPA-200. Since testing will
never occur for this configuration, the test mode signal will always be in
the OFF condition for the DCE. These three test signals follow the
EIA-423-A standard while the remaining signals follow the EIA-422-A
standard.
CIRCUIT RL - REMOTE LOOPBACK (RL)
CONNECTOR NOTATION: RLBK
DIRECTION: To DCE
This signal provides a means whereby a DTE or a facility test
center may check the transmission path up to and through the
remote DCE to the DTE interface and the similar return
transmission path.
35 Quatech Inc., MPA-200/300 Manual
Page 42

CIRCUIT TM - TEST MODE (TM)
CONNECTOR NOTATION: TEST MODE
DIRECTION: From DCE
This signal indicates to the DTE that the DCE is in a test condition.
The DCE generates this signal when it has received a local
loopback or remote loopback signal from the DTE.
Quatech Inc., MPA-200/300 Manual 36
Page 43

13 SPECIFICATIONS
Bus interface: IBM AT 16-bit bus
Controller: Serial Communications Controller, 6 MHz
(determined by user, typically an Intel 82530).
Physical Dimensions: 7.65” x 4.2”
Interface: DTE: male D-25 connector
DCE: female D-25 connector
Transmit drivers: EIA-422: MC3487 or compatible
EIA-423: MC3488 or compatible
EIA-485: 75174 or compatible
Receive buffers: EIA-422: MC3486 or compatible
EIA-423: 75176 or compatible
EIA485: 75175 or compatible
Transceivers: EIA-422: 75176 or compatible
EIA-485: 75176 or compatible
I/O Address range: 0000H - FFFFH
Interrupt levels: IRQ 2-7, 10-12, 14-15
Power requirements:
Typ
(mA)
Max
(mA)I
Supply Voltage (Volts)I
514021248
123625
-123625
37 Quatech Inc., MPA-200/300 Manual
Page 44

MPA-200/300
User's Manual
Version 5.31
March 2004
Part No. 940-0038-531
 Loading...
Loading...