Page 1

QSC(LP)-200/300
Four Channel RS-422/485 Asynchronous
Communications Adapter
for PCI bus
User's Manual
QUATECH, INC. TEL: (330) 655-9000
5675 Hudson Industrial Parkway FAX: (330) 655-9010
Hudson, Ohio 44236 http://www.quatech.com
Page 2

WARRANTY INFORMATION
Quatech, Inc. warrants the QSC(LP)-200/300 to be free of defects for five (5) years
from the date of purchase. Quatech, Inc. will repair or replace any board that fails to perform
under normal operating conditions and in accordance with the procedures outlined in this
document during the warranty period. Any damage that results from improper installation,
operation, or general misuse voids all warranty rights.
Please complete the following information and retain for your records. Have this
information available when requesting warranty service.
DATE OF PURCHASE:
MODEL NUMBER: QSC(LP)-200/300
PRODUCT DESCRIPTION: Four Channel RS-422/485 Asynchronous
PCI Bus Communications Adapter
SERIAL NUMBER:
Page 3

1998 - 2006, Quatech, Inc.
NOTICE
The information contained in this document cannot be reproduced in any form without
the written consent of Quatech, Inc. Likewise, any software programs that might accompany this
document can be used only in accordance with any license agreement(s) between the purchaser
and Quatech, Inc. Quatech Inc. reserves the right to change this documentation or the product to
which it refers at any time and without notice.
The authors have taken due care in the preparation of this document and every attempt
has been made to ensure its accuracy and completeness. In no event will Quatech, Inc. be liable
for damages of any kind, incidental or consequential, in regard to or arising out of the
performance or form of the materials presented in this document or any software programs that
might accompany this document.
Quatech, Inc. encourages feedback about this document. Please send any written
comments to the Technical Support department at the address listed on the cover page of this
document.
DOS, Windows ME, Windows 2000, Windows 98, Windows 95, Windows NT are trademarks or registered
trademarks of Microsoft Corporation. OS/2 is a registered trademark of IBM Corporation. All other trademarks or
registered trademarks are property of their respective owners.
Page 4

Declaration of Conformity
Manufacturer's Name: Quatech Inc.
Manufacturer's Address: 5675 Hudson Industrial Parkway
Hudson, Ohio 44236 (USA)
Application of Council Directive: 89/336/EEC
Standards to which
Conformity is Declared: * EN50081-1 (EN55022,
EN60555-2, EN60555-3)
* EN50082-1 (IEC 801-2,
IEC 801-3, & IEC 801-4)
Type of Equipment: Information Technology
Equipment
Equipment Class: Commercial, Residential, & Light
Industrial
Product Name: PCI Quad Serial Communications
Card
Model Number : QSC(LP)-200/300 (IND)
Page 5
......................................................................
1
1 General Information
1.1 Features
1.1.1 "IND" Option --- Surge Suppression Upgrade
.........................................................
2 Hardware Configuration
2.1 Signal Connections
..........................................
.................
.....................................
..............................................
2.1.1 AUX(1,2,3,4) (pins 3 and 4, 7 and 8, 11 and 12, 15 and 16)
2.1.2 TGL(1,2,3,4) (pins 1 and 2, 5 and 6, 9 and 10, 13 and 14)
2.1.3 Force High-Speed UART Clock (X8, pins 17 and 18)
3 Hardware Installation
Windows Configuration
4.1 Windows Millennium
4.2 Windows 2000
4.3 Windows 98
4.4 Windows 1995
4.5 Windows NT
4.6 Viewing Resources with Device Manager
..................................................
....................................................
..................................................
...................................................
........................................
........................................
............................................
........................
4.6.1 Changing Resource Settings with Device Manager
......
.......
...........
.............
5
5
5
6
6
6
6
7
8
9
9
10
11
13
14
15
17
5 Other Operating Systems
5.1 Windows NT
5.2 OS/2
...........................................................
5.3 DOS and other operating systems
5.3.1 QTPCI.EXE
6 External Connections
6.1 DTR/DSR or RTS/CTS Operation
6.2 RTS/cts Handshake
6.3 RCLK
6.4 TCLK
6.5 AUXIN/AUXOUT Loopback
..........................................................
..........................................................
...................................................
.................................................
........................................
.............................................
...................................
...............................
...............................
....................................
6.6 Half-Duplex/Full-Duplex/Auto-Toggle Selection
Termination Resistors
6.8 RS-422/485 Peripheral Connection
6.9 RS-422/485 Peripheral Connection
7 PCI Resource Map
.............................................
..............................
..............................
...........................................
.................
21
21
21
21
22
24
24
24
24
24
25
25
26
27
28
29
Page 6

Base Address and Interrupt Level (IRQ)
............................
29
8 Specifications
..................................................
9 Troubleshooting
...............................................
30
31
Quatech QSC(LP)-200/300 User's Manual 4
Page 7
1 General Information
The Quatech, Inc. QSC(LP)-200/300 provides four RS-422 or RS-485 asynchronous
serial communication interfaces for IBM-compatible personal computer systems using the PCI
expansion bus. The QSC(LP)-200/300 uses Quatech's new Enhanced Serial Adapter design.
Legacy serial port data rates are limited to a maximum of 115,200 bits per second. Quatech
Enhanced Serial Adapters can achieve data rates as high as 921,600 bits per second.
As a PCI device, the QSC(LP)-200/300 requires no hardware configuration. The card is
automatically configured by the computer's BIOS or operating system. The four serial ports share
a single interrupt line and are addressed in a contiguous block of 32 bytes. A special interrupt
status register is provided to help software to manage the shared interrupt.
The QSC(LP)-200/300's serial ports use 16750 Universal Asynchronous
Receiver/Transmitters (UARTs). These UARTs contain hardware buffers (FIFOs) which reduce
processing overhead and allow higher data rates to be achieved. The 16750 contains a 16-byte
FIFO and can transmit and receive data at a rate of up to 921,600 bits per second. The 16750 is
recommended for heavy multitasking environments and for applications involving high data
rates.
The QSC(LP)-200/300 is supported under several popular operating systems and
environments. Contact the sales department for details on current software offerings. Most device
drivers are available for download from the Quatech world wide web site at
http://www.quatech.com.
1.1 Features
The standard QSC(LP)-200/300 implements each of its communication channels with a
16750 UART and uses standard line driver and receiver components. For improved performance
and industrial-grade reliability, Quatech offers the following board upgrades:
1.1.1 "IND" Option --- Surge Suppression Upgrade
The "IND" option provides the protection essential for reliable use in an industrial
environment. Each communication line has a surge suppressor capable of sustaining up to 40A
20us peak transient surges, a clamping voltage of 30V and a peak energy dissipation of 0.1
Joules.
IND OptionPart Number
noQSC(LP)-200/300
yesQSC(LP)-200/300IND
Figure 1 --- QSC(LP)-200/300 Product Series Summary
Quatech QSC(LP)-200/300 User's Manual 5
Page 8
2 Hardware Configuration
The QSC(LP)-200/300 is automatically configured at boot time by the computer's BIOS
or operating system. There are no required switches or jumpers to set for installation.
This chapter lists a number of optional
features. These jumpers, located in a row along the top of the board , control how signals are
routed from the UARTs to the connector, as well as special options.
Any changes from the factory default should be made before installing the
QSC(LP)-200/300 in the computer. These settings can also be changed in Device Manager
under Windows operating systems.
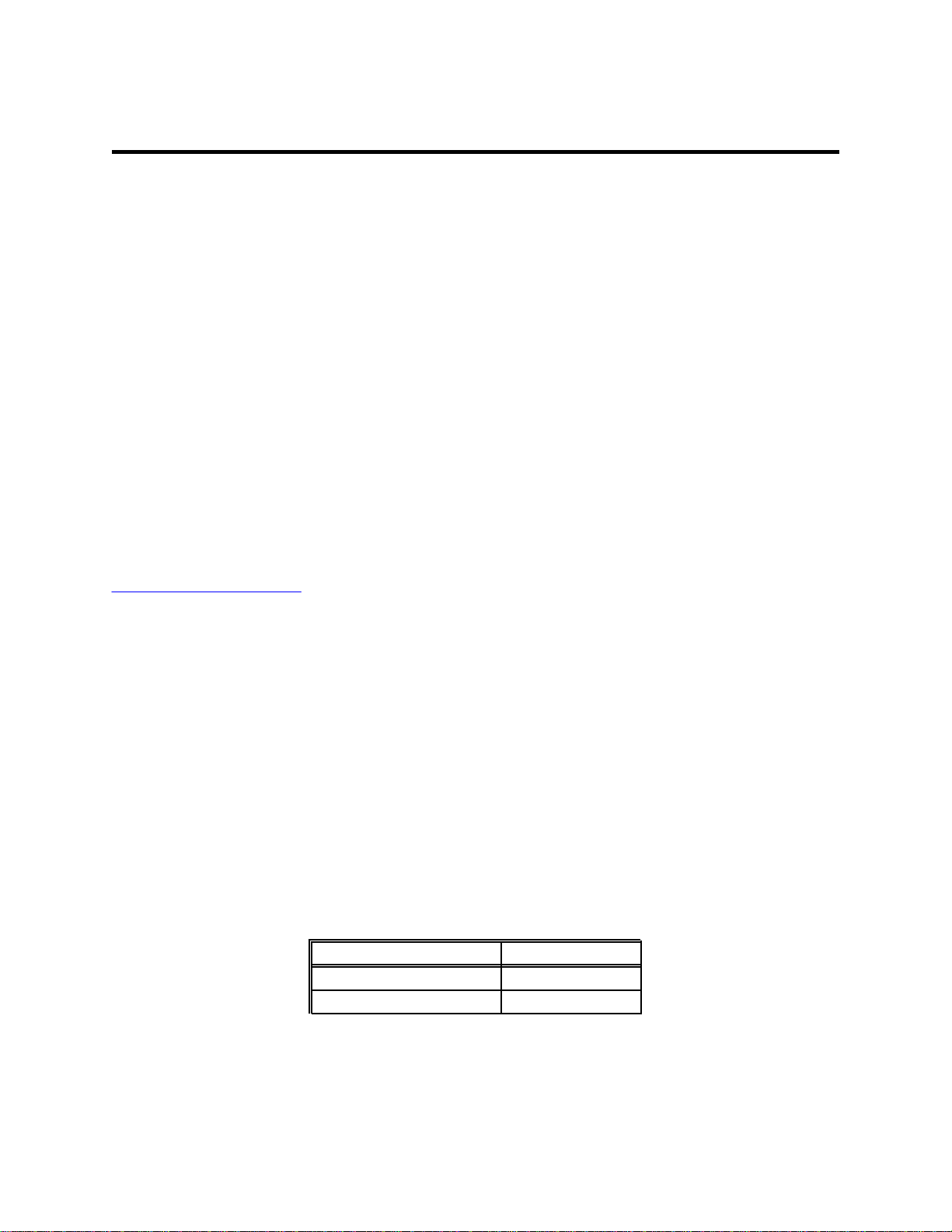
2.1 Signal Connections
The QSC(LP)-200/300 provides each of four serial ports with four differential signal
pairs: TxD, RxD, AUXOUT, and AUXIN. TxD and RxD are always present at the connector.
The AUXOUT and AUXIN signals can be used to support RTS/CTS handshaking, external
clocking, or external signal loopback. The factory default configuration, as shown in Figure 2
with no jumpers across any of the pins, is a loopback of AUXOUT to AUXIN at the connector,
with RTS and CTS looped back on the board. There is an extensive discussion of this topic in
section 6.
jumper settings that control various hardware
Jumper J1 defines the options for this card:
J1
TGL1
AUX1
TGL2
AUX2
TGL3
AUX3
TGL4
AUX4
X8
4
6
8
10
12
14
16
15
18
17
21
3
51719
11
13
Figure 2 - Top Card Edge Jumpers
2.1.1 AUX(1,2,3,4) (pins 3 and 4, 7 and 8, 11 and 12, 15 and 16)
The 1, 2, 3, or 4 will designate which port the settings will be applied to. With NO
jumpers across the “AUX” pins, CTS = RTS and AUXIN = AUXOUT. With a jumper on any
of the “AUX” pins, CTS = AUXIN and AUXOUT = RTS for the given port.
2.1.2 TGL(1,2,3,4) (pins 1 and 2, 5 and 6, 9 and 10, 13 and 14)
The 1, 2, 3, or 4 will designate which port the settings will be applied to. With NO
jumpers across the “TGL” pins, TXEN = 1. With a jumper on any of the “TGL” pins, TXEN
will be set to “Auto-Toggle” for the given port.
Quatech QSC(LP)-200/300 User's Manual 6
Page 9

2.1.3 Force High-Speed UART Clock (X8, pins 17 and 18)
This jumper forces an increase of the UART input clock frequency by a factor of eight.
This feature can allow legacy software to use baud rates above 115,200 bits per second. It is also
useful if the serial port device driver does not directly support setting the higher baud rates
through the Options Register.
If this jumper is applied, it overrides any value written to the Options Register to set the
clock multiplier by software. The effective baud rate will be eight times the value for which the
UART itself is programmed. If selected, the clock multiplier will be applied to all ports on the
card, it is not possible to selectively apply the clock multiplier to a specific port.
The factory default is no jumper applied, which allows for software control of the clock
multiplier via the Options Register. The Options Register powerup default is for a standard
times-1 clock of 1.8432 MHz for compatibility with standard serial ports.
Quatech QSC(LP)-200/300 User's Manual 7
Page 10
3 Hardware Installation
1. Turn off the power of the computer system in which the QSC(LP)-200/300 is to be
installed.
2. Remove the system cover according to the instructions provided by the computer
manufacturer.
3. Make any desired optional jumper setting changes.
4. Install the QSC(LP)-200/300 in any empty PCI expansion slot. The board should be
secured by installing the Option Retaining Bracket (ORB) screw.
5. Replace the system cover according to the instructions provided by the computer
manufacturer.
6. Attach and secure the cable connectors to the desired equipment.
7. Turn on the power of the computer system.
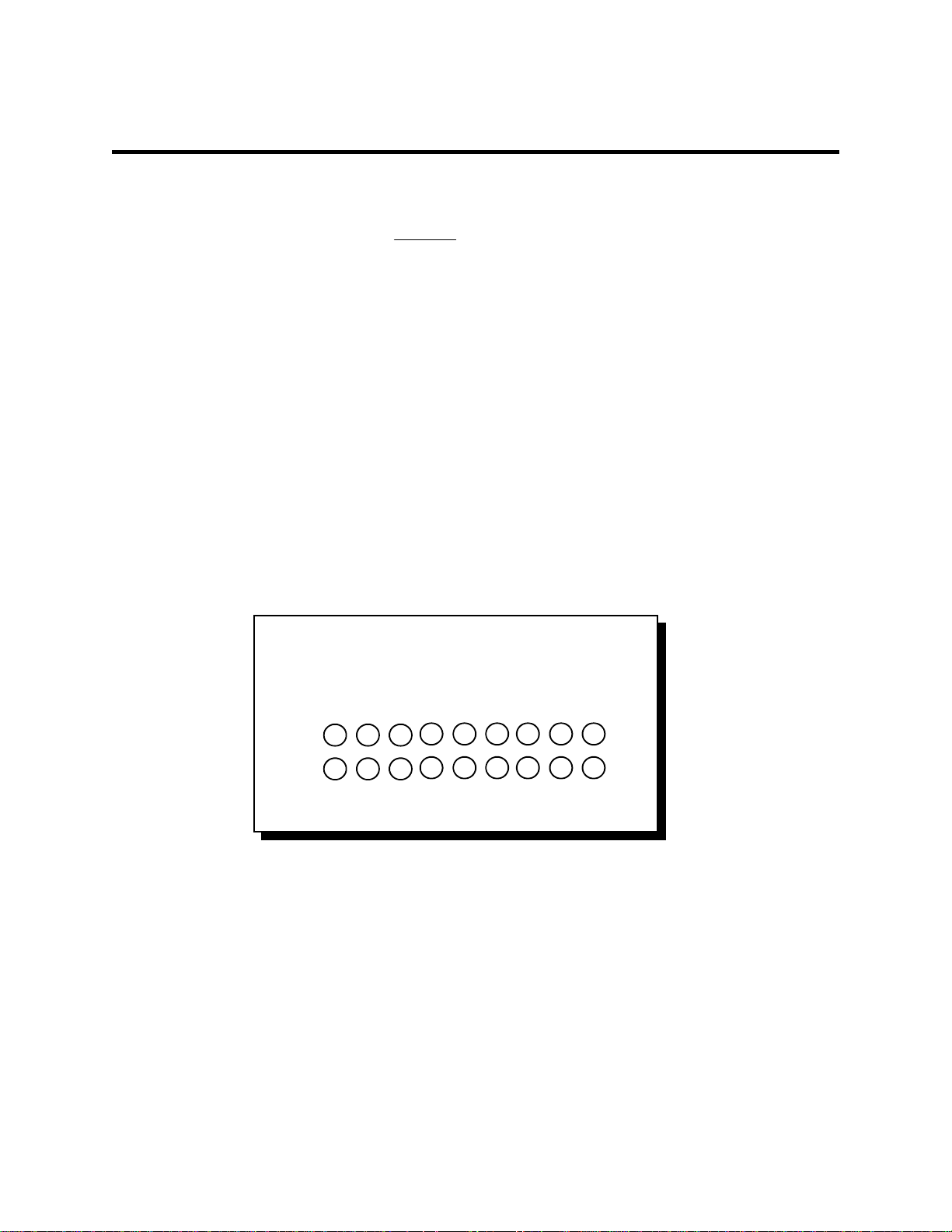
The output of the QSC(LP)-200/300 is a 44-pin custom connector,
which is brought out to four 9-pin D-connectors via a custom cable.
J1
Figure 3 --- Jumper/connector locations
Quatech QSC(LP)-200/300 User's Manual 8
Page 11
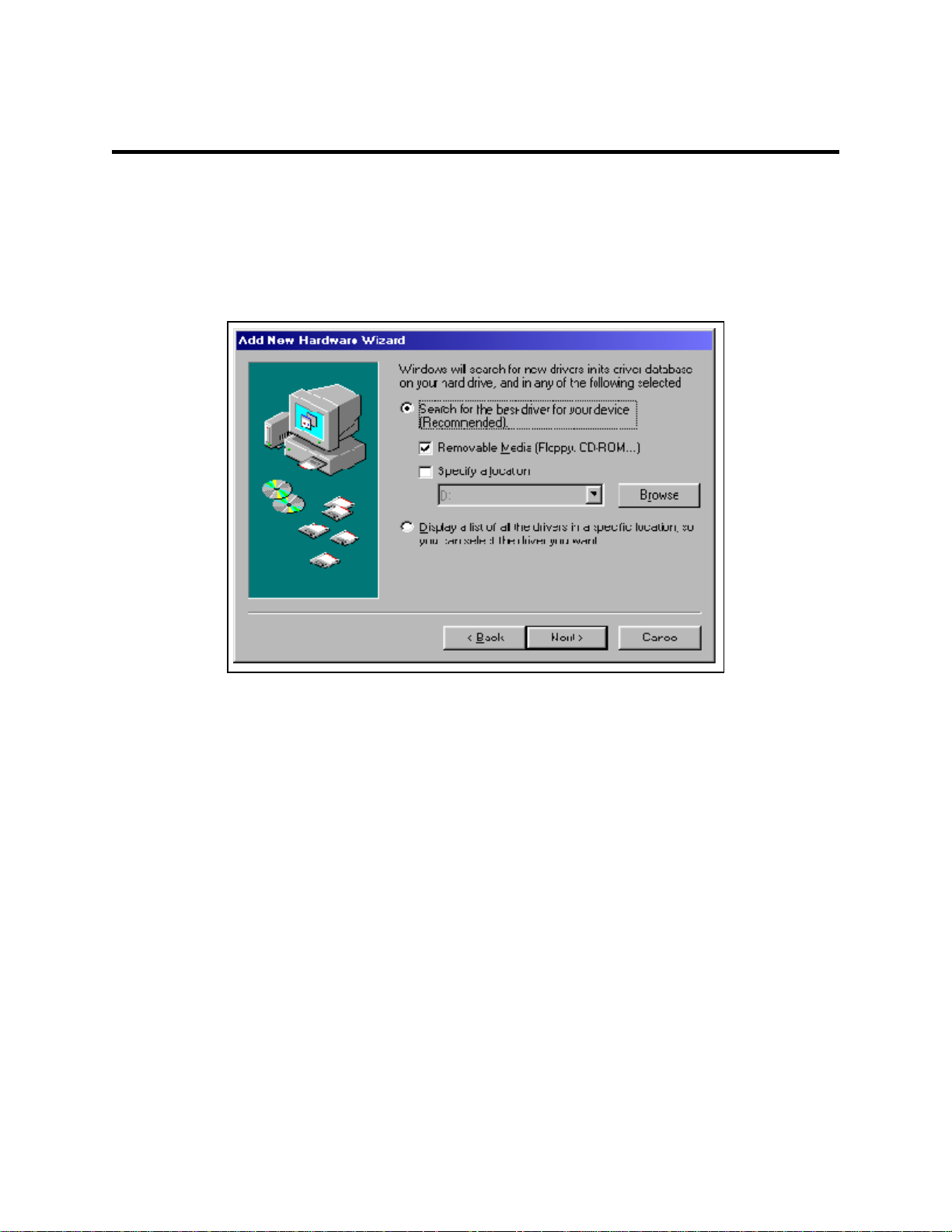
4 Windows Configuration
4.1 Windows Millennium
1. After inserting the QSC(LP)-200/300 for the first time the "Add New Hardware Wizard"
will begin. Select "Search for the best driver for your device.". Check the
"Removable media" and "Specify location" box. Click the "Next" button.
2. Window will locate the proper INF file and copy the file from the CD. Click
the "Next" button.
3. The final dialog screen will verify the file copy from the CD. Click the
"Finish" button.
Quatech QSC(LP)-200/300 User's Manual 9
Page 12

4.2 Windows 2000
1. After inserting a QSC(LP)-200/300 for the first time, the "Add New Hardware Wizard
will appear at start up. Click the "OK" button.
2. When the following dialog box appears, insert the Communications Driver CD (shipped
with the device). Click the "OK" button.
3. The following dialog box will display the appropriate INF file on the CD in
drive. Click the "OK" button.
4. Window will copy the INF file from the cd and display a final dialog
indication that the process is complete. Click the "Finish" button.
Quatech QSC(LP)-200/300 User's Manual 10
Page 13

4.3 Windows 98
1. After inserting a QSC(LP)-200/300 for the first time, the "Add New Hardware Wizard
will appear at start up. Click the "Next" button.
2. Select "Search for the best driver for you device". Click the "Next" button.
3. On the next dialog, select the "CD - ROM drive" check box. Insert the
Communication Drivers CD (shipped with the device) into the CD - ROM drive.
Click the "Next" button.
Quatech QSC(LP)-200/300 User's Manual 11
Page 14

4. The following dialog box will display the appropriate INF file on the cd in
drive. Click the "Next" button.
5. Window will copy the INF file from the cd and display a final dialog
indication that the process is complete. Click the "Finish" button.
Quatech QSC(LP)-200/300 User's Manual 12
Page 15

4.4 Windows 1995
Windows 95 maintains a registry of all known hardware installed in your computer.
Inside this hardware registry Windows 95 keeps track of all of your system resources, such as I/O
locations, IRQ levels, and DMA channels. The "Add New Hardware Wizard" utility in Windows
95 was designed to add new hardware and update this registry.
An "INF" configuration file is included with the QSC(LP)-200/300 to allow easy
configuration in the Windows 95 environment. Also a custom Windows 95 serial device driver is
included with the QSC(LP)-200/300 to support the use of the 16750 UART's 64 byte FIFO.
Windows 95 uses the "INF" file to determine the system resources required by the
QSC(LP)-200/300, searches for available resources to fill the boards requirements, and then
updates the hardware registry with an entry that allocates these resources
The following instructions provide step-by-step instructions on installing the
QSC(LP)-200/300 in Windows 95 using the "New Hardware Found" wizard.
1. After booting the computer with a newly-installed QSC(LP)-200/300, the "New
Hardware Found" dialog box will appear. If you have never installed a Quatech PCI
communications adapter before, the dialog box may simply indicate that it has found a
"PCI Card."
2. Select the radio button for "Driver from disk provided by hardware manufacturer." Click
the "OK" button to continue.
3. An "Install From Disk" dialog box should pop up. Insert the cd with the Quatech INF files
on it, select the correct drive letter, and click the "OK" button. Windows 95 automatically
browses the root directory for an INF file that defines configurations for Multi-function
Adapters. If no INF files are found, click the "Browse" button and search the Win95 sub
directory on the installation cd. You are not required to select the file name. After finding
the directory containing the INF files, Windows 95 will choose the correct file.
4. The "New Hardware Found" dialog box will appear again, this time for an "Unknown
Device."
5. Again select the radio button for "Driver from CD provided by hardware manufacturer."
Click the "OK" button to continue.
6. Another "Install From CD" dialog box will pop up. The path should already be pointing
to the Quatech CD. Click the "OK" button to continue.
7. You should now see the "Copying Files" dialog box as Windows 95 copies the driver
files from the CD.
8. The installation utility will ask for your Windows 95 installation disks. Serial
communication ports require two drivers supplied by Microsoft to function:
SERIAL.VXD and SERIALUI.DLL. Insert the disk or CD and click "OK".
Quatech QSC(LP)-200/300 User's Manual 13
Page 16

NOTE:
You may be able to skip this step if you are certain that your system has the latest
version of these files installed. If you do not have your Windows 95 install disks
immediately available, click "OK" anyway. A dialog box appears with an option
to Skip the files. Click the Skip button and the files will not be installed. This is
all right if the latest version of these drivers are currently in the
\WINDOWS\SYSTEM directory.
9. The "New Hardware Found" dialog will repeat as each serial port is registered with
Windows 95.
10. Installation is complete.
4.5 Windows NT
The Windows NT device driver is installed by running the SETUP program. Up to 256
serial ports are supported. There is a command line-based configuration utility which is used for
adding PCI bus and ISA bus serial ports. Please refer to the documentation included with the
device driver for full installation and configuration details.
Quatech QSC(LP)-200/300 User's Manual 14
Page 17

4.6 Viewing Resources with Device Manager
This discussion applies equally to Windows 95/98/ME and 2000/XP. Windows
maintains a registry of all known hardware installed within the computer. Inside this hardware
registry Windows keeps track of all the computer's resources, such as base I/O addresses, IRQ
levels, and DMA channels. In the case of a PCI plug-in card, Windows configures the new
hardware using free resources it finds within the hardware registry, and updates the registry
automatically.
To view and/or edit hardware devices in Windows use the system Device Manager.
Consult Windows on-line help for details on the use of the Device Manager.
The following instructions provide step-by-step instructions on viewing resources used by
the QSC(LP)-200/300 in Windows using the "Device Manager" utility. Select Start|Help from
within Windows for additional information on this utility.
1. Double click the "System" icon inside the Control Panel folder. This opens up the System
Properties box.
2. Click the "Device Manager" tab located along the top of the System Properties box. This
lists all hardware devices registered inside the Windows registry. Additional information
is available on any of these devices by right-clicking on the device name and then
selecting "Properties" from the pop-up menu.
3. Double click the device group "Multi-function Adapters". The QSC(LP)-200/300
“parent device” belongs to this hardware class. The full device name for the
QSC(LP)-200/300 is Quatech QSC(LP)-200/300 PCI Four-Port RS-422/RS485 Serial
Adapter.
4. Double click the QSC(LP)-200/300 name and a properties dialog should open for the
hardware adapter.
5. Click the "Resources" tab located along the top of the properties box to view the
resources Windows has allocated for Input/Output Range and Interrupt Request.
Because PCI is a true plug-and-play bus, do not attempt to modify the configuration
values listed. Click "Cancel" to exit without making changes.
6. Double click the hardware class Ports (Com and LPT). Each Quatech PCI Serial
Port listed in this class is a “child device” of the QSC(LP)-200/300 “parent device.”
Windows 95 does not assign COM1-COM4 to ports addressed at nonstandard locations.
So in Windows 95, the QSC(LP)-200/300 ports will be enumerated starting with COM5
(or higher) even if lower logical numbers are available.
7. Select any of the Quatech Serial Ports listed under the group Port (COM and LPT) and
click the "Properties" button. This action opens a properties dialog for the specific COM
port on the QSC(LP)-200/300. Then click the Resources tab to view the Input/Output
Quatech QSC(LP)-200/300 User's Manual 15
Page 18

Range and Interrupt Request resource allocations. These will match those of the “parent
device.” Click "Cancel" to exit without making changes.
8. Click the "Port Settings" tab and then click the "Advanced" button. The
QSC(LP)-200/300 driver will display a custom Advanced Port Settings control, which
allows the ports UART compatibility mode and FIFO threshold levels to be configured.
The threshold values of full-scale for the transmit buffer and ¾-scale for the receive
buffer are optimal for most applications. Note that the FIFO option for each of the
QSC(LP)-200/300's four ports is configured independently.
9. Use the Logical COM Port names to access the serial ports on your QSC(LP)-200/300
through your software applications. Note: The Logical COM Port name is assigned to
your ports by Windows. This name is required by Windows applications when accessing
a particular port.
Quatech QSC(LP)-200/300 User's Manual 16
Page 19

4.6.1 Changing Resource Settings with Device Manager
1. Start the Windows 95/98/ME Device Manager.
2. Double click on the hardware class Multi-Port Serial Adapters to list hardware
devices in the class.
3. The QSC(LP)-200/300 “parent device” belongs to this hardware class. The full
device name for the QSC(LP)-200/300 is Quatech QSC(LP)-200/300: Four-Port
RS-422/485 Serial Adapter.
4. Open the Properties dialog for the QSC(LP)-200/300 device, then click the
Resources tab to view the Input/Output Range and Interrupt Request resource
allocations.
5. Open the Properties dialog for the QSC(LP)-200/300 device (Figure 12), then click
the Advanced tab to view the clock rate settings.
Quatech QSC(LP)-200/300 User's Manual 17
Page 20

Data Rate Multiplier
DescriptionMax bpsClock Mode
Auto clock mode enables applications to request any
921,600Auto
baud rate up to 921,600. The hardware drivers will
select the correct clock multiplier based on the baud
rate requested
The X1 clock mode mimics a standard COM port. The
115,200X1
hardware drivers lock the clock to the standard rate.
The port will run at the baud rate requested by the
application.
The X2 clock mode locks the ports hardware clock at
double the standard rate. The baud rate the port runs at
230,400X2
will always be double the rate requested by the
applications. This mode is useful for legacy
applicattions which cannot request baud rates over
115,200
The X4 clock mode locks the ports hardware clock at
four times the standard rate. The baud rate the port
460,800X4
runs at will always be four times the rate requested by
the application. This mode is useful for legacy
applications which cannot request baud rates over
115.200.
The X8 clock mode locks the ports hardware clock at
eight times the standard rate. The baud rate the port
921,600X8
runs at will always be eight times the rate requested by
the application. This mode is useful for legacy
applications which cannot request baud rates over
115.200.
6. Double click the hardware class Ports (Com and LPT). Each Quatech PCI Serial
Port listed in this class is a “child device” of the QSC(LP)-200/300 “parent device.”
7. Open the Properties dialog for a COM port, then click the RS-422/485 tab to view
the settings for that port.
Quatech QSC(LP)-200/300 User's Manual 18
Page 21

RS-422/485 Connector Setup
RTS routed to CTS, AUXIN routed to
Loopback All
AUXOUT, and TCLK routed to RCLK.
Used when external handshaking or
clocking signals are not available.
RTS routed to AUXOUT, AUXIN
Modem Control
routed to CTS, and TCLK routed to
RCLK. Used when RTS/CTS
handshaking is required.
RTS routed to CTS, AUXIN routed to
RCLK, and TCLK routed to AUXOUT.
Clocks
Used to connect ports transmitting at
different baud rates. In order to
function, all ports must have and use
this feature.
Receive Control
Receivers are always enabled. In a Half
Always Receive
Duplex mode, you will receive what you
transmit (sometimes called echo).
Quatech QSC(LP)-200/300 User's Manual 19
Page 22

Receivers are only enabled when not
When NOT Tranmitting
transmitting. In a Half Duplex mode,
you will not receive what you transmit.
RS-422/485 Duplex Mode
Transmitters and receivers are always
Full Duplex
enabled; ports can send and receive
simultaneously. Used in four-wire
communication.
Half Duplex using RTS
Half Duplex using DTR
RTS is set to enable the transmitters.
Used in two-wire communication.
DTR is set to enable the transmitters.
Used in two-wire communication
Hardware automatically enables the
transmitters when transmitting.
Auto Toggle
Transmitters will turn off three bit-times
after the last stop bit of the last
character, regardless of baud rate. Used
in two-wire communication.
8. To summarize the RS-422/485 output drivers enable options: The
QSC(LP)-200/300’s ports may be configured for either full duplex or half duplex
operation with this option. The default setting is the RS-422/485 ports are configured
for full duplex operation with the RS-422/485 output drivers always enabled. In half
duplex mode, the RS-422/485 transmitter may be enabled and disabled via the RTS
(request to send) or DTR (data terminal ready) signals, or in auto-toggle mode, set to
enable only when data is being transmitted. Both RTS and DTR are controlled
through the Modem Control Register of the 16750.
9. Click the "Port Settings" tab and then click the "Advanced" button. The
QSC(LP)-200/300 driver will display a custom Advanced Port Settings control, which
allows the ports UART compatibility mode and FIFO threshold levels to be
configured. The threshold values of full-scale for the transmit buffer and ¾-scale for
the receive buffer are optimal for most applications. Note that the FIFO option for
each of the QSC(LP)-200/300's four ports is configured independently.
Quatech QSC(LP)-200/300 User's Manual 20
Page 23

5 Other Operating Systems
Device drivers for Windows NT and OS/2 are also available for the QSC(LP)-200/300.
The board can be used under DOS and other operating systems as well in many circumstances.
The software described below can be obtained from the Quatech web site if it did not come with
the board.
5.1 Windows NT
The Windows NT device driver is installed by running the SETUP program. Up to 256
serial ports are supported. There is a command line-based configuration utility which is used for
adding PCI bus and ISA bus serial ports. Please refer to the documentation included with the
device driver for full installation and configuration details.
5.2 OS/2
The OS/2 device driver supports up to 32 serial ports in a system. Installation is a manual,
but simple, process. Please refer to the documentation included with the device driver for full
installation and configuration details.
5.3 DOS and other operating systems
The QSC(LP)-200/300 is not a direct drop-in replacement for a legacy serial port because
its base address and IRQ cannot be fixed at values such as 3F8 hex, IRQ 4 (COM1) or 2F8 hex,
IRQ 3 (COM2), etc. Rather, the system BIOS assigns the address and the IRQ in a plug-and-play
fashion at boot time. Software which is to use the QSC(LP)-200/300 must be able to
accommodate any valid assignments of these resources.
For Windows 95, Windows NT and OS/2, the Quatech device drivers determine what the
resource assignments are and proceed accordingly. In other cases, however, the user must
intervene. The discussion below will center on DOS, but the concepts can be applied to other
operating systems as well.
Many DOS applications support user configuration of the base address and IRQ of a
serial port. Such applications can generally make use of the QSC(LP)-200/300. Older
applications, as well as some custom software, may use hard-coded standard legacy serial port
addresses. These applications will require modifications to support PCI devices.
Custom applications for which the customer has source code can be modified to make
just a few PCI BIOS function calls to obtain all the necessary configuration information. The PCI
BIOS specification can be obtained from the PCI Special Interest Group. Contact Quatech
technical support for more information.
Quatech QSC(LP)-200/300 User's Manual 21
Page 24

5.3.1 QTPCI.EXE
Quatech's "QTPCI" utility supplies the information required when modifying the serial
port settings of the application. This program should be run from real DOS, not in a Windows
DOS box.
Figure 4 shows the Basic Mode display for the QSC(LP)-200/300 after the "Q" key has
been pressed. In this example, the QSC(LP)-200/300 uses I/O base address FFA0 hex and IRQ 3.
The hardware revision of the QSC(LP)-200/300 is also displayed. Pressing the "N" key will show
similar information for all non-Quatech PCI devices in the system, including those devices
integrated on the motherboard.
The QTPCI program is capable only of displaying the PCI configuration. It cannot be used
to make changes.
Figure 4 --- QTPCI.EXE Basic Mode display
Quatech QSC(LP)-200/300 User's Manual 22
Page 25

Figure 5 shows the Expert Mode display for the QSC(LP)-200/300 after the "Q" key has
been pressed. The information from the Basic Mode display is presented along with more details
such as the Vendor and Device IDs, PCI Class Code, size of memory and I/O regions, etc.
Pressing the "N" key will show similar information for all non-Quatech PCI devices in the
system, including those devices integrated on the motherboard. In this example, the "Base addr
0" resource is reserved.
For users interested in even more details, PCI BIOS information can be displayed by
pressing the "B" key. Pressing the "I" key displays the PCI interrupt routing table.
Figure 5 --- QTPCI.EXE Expert Mode display
Quatech QSC(LP)-200/300 User's Manual 23
Page 26

6 External Connections
The QSC(LP)-200/300 provides four differential communication signals per channel. The
two output signals are Transmit Data (TxD) and Auxiliary Output (AUXOUT). The two input
signals are Receive Data (RxD) and Auxiliary Input (AUXIN). A ground signal is also provided.
The available input signals for AUXIN are Clear To Send (CTS) and the Receive Clock
(RCLK). The available output signals for AUXOUT are Request To Send (RTS), the Transmit
Clock (TCLK), and the AUXIN signal (for loopback). Either half-duplex or full-duplex operation
can be selected for each communications channel. Auto-Toggle is also jumper selectable .If
half-duplex operation is selected, one of the UART's signals (either DTR or RTS) is used to
enable the transmitter drivers. The inverse of the transmitter enable can be used to enable the
receiver drivers.
Configuration is usually done using Soft Select, accessable through Device Manager in
Windows operating systems. Hardware overrides are available via jumper J1 for interface signal
routing.
6.1 DTR/DSR or RTS/CTS Operation
The DTR or RTS modem control output of the UART can be used to enable and disable
the transmit drivers. These options are selectable per channel. The factory default, with no
jumpers across any of the pins in J1, is for both the drivers and receivers of both channels to be
continuously enabled. . These option are not selectable via jumpers, they are only accessable
through Device Manager under Window operating systems.
6.2 RTS/CTS Handshake
Transmission of RTS, combined with reception of CTS, allows for hardware handshaking
(data flow control) between the UART and the external device. RTS is transmitted on AUXOUT
and CTS is received on AUXIN by connecting a jumper across the “AUX” pins for the
appropriate port of the jumper block J1. If RTS/CTS handshaking is not desired, the RTS output
can be looped back to the CTS input by removing the any jumper from “AUX” pins for the
appropriate port of the jumper block J1.
6.3 RCLK
This is the clock signal used by the receiver portion of the UART. It is generally provided
by connecting it to the UART's own transmit clock output (TCLK). This signal can only be
accessed via Soft Select through Device Manager. RCLK is affected by the “Loopback All”,
“Modem Control”, or “Clocks” selections under “RS-422/485 connector set-up” on the
RS-422/485 tab of each port’s property dialog.
6.4 TCLK
This is the output clock signal used by the transmitter portion of the UART. It is generally
connected to the UART's own receive clock input (RCLK). This signal can only be accessed via
Soft Select through Device Manager. TCLK is affected by the “Loopback All”, “Modem
Quatech QSC(LP)-200/300 User's Manual 24
Page 27

Control”, or “Clocks” selections under “RS-422/485 connector set-up” on the RS-422/485 tab of
each port’s property dialog.
6.5 AUXIN/AUXOUT Loopback
The AUXIN signal is an input from the external device, and connecting it to the
AUXOUT signal provides for a loopback mode of operation. In other words, whatever signal is
transmitted by the external device over the AUXIN line will be fed back to the external device
over the AUXOUT line. This mode is accomplished by default or by removing the jumper from
the “AUX” pins for the appropriate port of the jumper block J1.
6.6 Half-Duplex/Full-Duplex/Auto-Toggle Selection
Using the hardware overrides provided by jumper block J1, the transmitters and receivers
of each channel can be forced into Auto-Toggle mode. Additionally, operation in either
half-duplex or full-duplex modes can be implemented via Soft Select, which is accessable via
Device Manager under the Windows operating system.
The transmit drivers can be controlled by either the Data Terminal Ready (DTR) or the
Request to Send (RTS) output from the UART. When disabled, the transmit drivers enter a
high-impedance state. The receivers can be controlled by the inverse of the transmit enable.
The drivers and receivers are always enabled in full-duplex mode.
WARNING:
When operating in half-duplex mode, the transmitter drivers must
be disabled before receiving any data. Failure to do so may result
in multiple active output drivers being connected together, which
may cause damage to the board, the computer, and the external
device.
Quatech QSC(LP)-200/300 User's Manual 25
Page 28
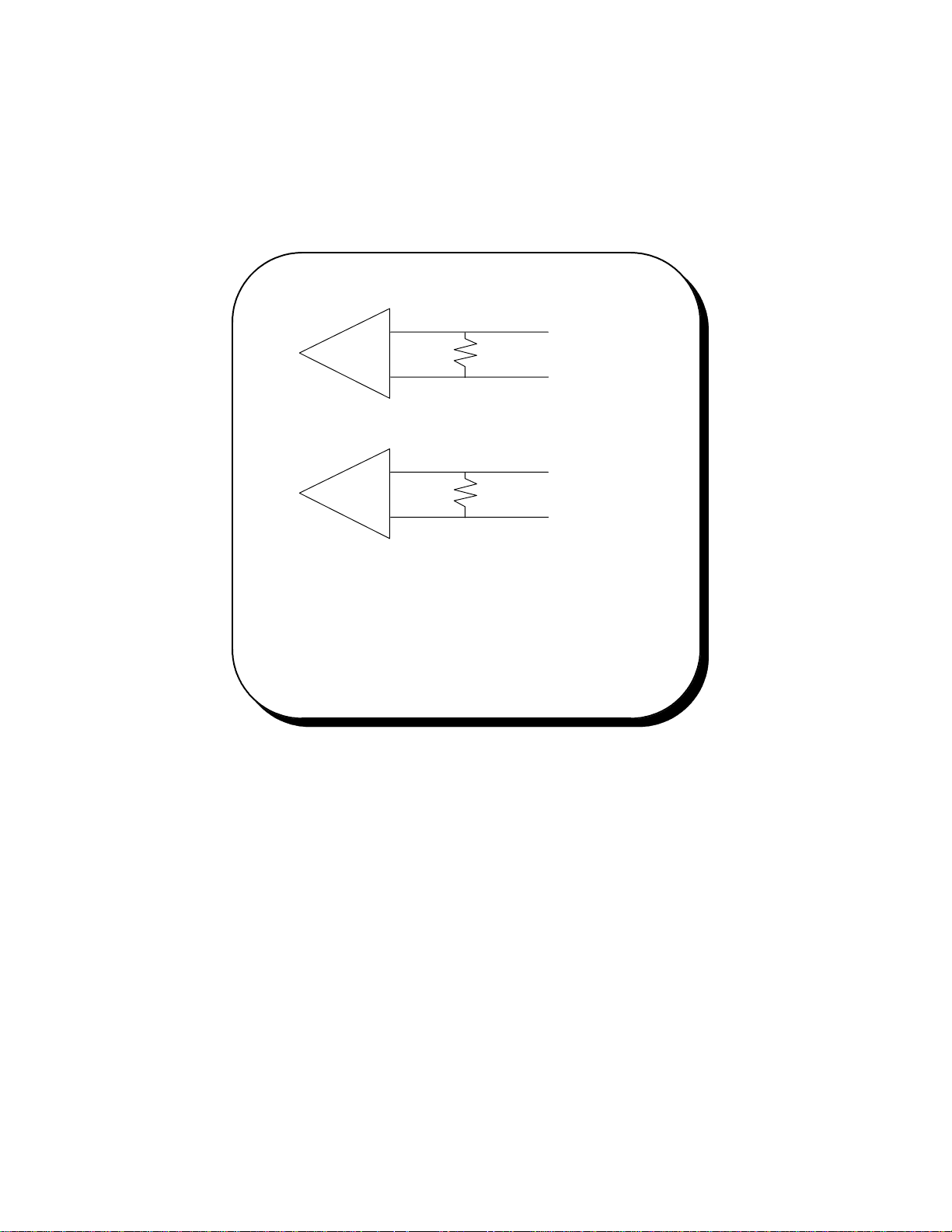
6.7 Termination Resistors
No termination resistors are provided on the ports. Both output and input signals are connected
only to the external connector. Any termination which is required must be added externally.
RS-422/485 Receiver
12
+
Rt
-
RS-422/485 Receiver
+
Rt
-
RXD+
RXD-
AUXIN+
AUXIN-
Recommended Termination Resistor Values
RS-422
100 ohm 1/2W resistor
RS-485
60 ohms total resistance
(120 ohms at each end)
Figure 6. RS-422/485 Termination
Quatech QSC(LP)-200/300 User's Manual 26
Page 29

6.8 RS-422/485 Peripheral Connection
The QSC(LP)-200/300 is a DTE device which connects to peripheral equipment
through four female D-9 connectors. The onboard connector is a D-44 connector, which is
brought out into four separate D-9 connectors via a custom cable assembly. The pin-out for the
D-44 connector is listed in Figure 7. The serial port connections are listed in Figure 9.
Pin number
description
Pin numberSignal
description
Figure 7. D-44 connector definitions
Pin numberSignal
Signal
description
txd3+31auxout3-16nc1
rxd3-32rxd3+17gnd2
auxout3+33auxin3-18txd3-3
nc34auxin0+19nc4
txd2+35auxout2-20nc5
rxd2-36rxd2+21gnd6
auxout2+37auxin2-22txd2-7
nc38auxout1-23auxin1+8
txd1+39rxd1+24nc9
rxd1-40auxin1-25gnd10
auxout1+41auxin2+26txd1-11
txd0+42auxout0-27nc12
rxd0-43rxd0+28gnd13
auxout0+44auxin0-29txd0-14
Xauxin3+30nc15
1
44
D-44 connector
Figure 8. D-44 pin-out.
Quatech QSC(LP)-200/300 User's Manual 27
Page 30

6.9 RS-422/485 Peripheral Connection
The QSC(LP)-200/300 connects to peripheral equipment through four male D-9
connectors. The serial port connector definitions are listed in Figure 10.
D-9 Connector PinSignalDescription
2TxD+
7TxD4RxD+
8RxD1AUXOUT+
6AUXOUT5AUXIN+
9AUXIN3GND
Figure 9 --- QSC(LP)-200/300 connector definitions
1
6
2
7
3
8
4
9
5
male D-9 connector
Figure 10 --- QSC(LP)-200/300 output connectors
Quatech QSC(LP)-200/300 User's Manual 28
Page 31

7 PCI Resource Map
Listed below are the PCI resources used by the QSC(LP)-200/300. Such information may
be of use to customers writing their own device drivers or other custom software. A detailed
description of the QSC(LP)-200/300's UARTs is available on the Quatech web site.
(all numbers in hex)
PCI Vendor ID: 0x135C Quatech, Inc.
PCI Device ID: 0x01A0 QSC(LP)-200/300
PCI Class Code
Base class: 0x07 Simple communications controller
Subclass: 0x02 Multiport serial controller
Interface: 0x00
IRQ sourced by: INTA#
Base Address and Interrupt Level (IRQ)
The base address and IRQ used by the QSC(LP)-200/300 are determined by the BIOS or
operating system. Each serial port uses 8 consecutive I/O locations. The four ports reside in a
single block of I/O space in eight-byte increments, along with a sixteen-byte reserved region, for
a total of 32 contiguous bytes, as shown in Figure 11.
I/O Address RangePort
Base Address + 00 to Base Address + 07Serial 1
Base Address + 08 to Base Address + 15Serial 2
Base Address + 16 to Base Address + 23Serial 3
Base Address + 24 to Base Address + 31Serial 4
Figure 11. Serial Port I/O addresses
Both serial ports share the same IRQ. The QSC(LP)-200/300 signals a hardware interrupt
when either port requires service. The interrupt signal is maintained until no port requires
service. Interrupts are level-sensitive on the PCI bus.
The base address and IRQ are automatically detected by the device drivers Quatech
supplies for various operating systems. For cases where no device driver is available, such as for
operation under DOS, Quatech supplies the "QTPCI" DOS software utility for manually
determining the resources used. See page 22 for details.
Quatech QSC(LP)-200/300 User's Manual 29
Page 32

8 Specifications
Bus interface: PCI, 32-bit bus, Universal Signalling Voltage
Dimensions: approx. 4.725" x 2.5"
Serial ports
Controller: 16750 with 64-byte FIFOs
Interface: Custom cable to four female D-9 connectors
Transceivers: MAX-3076E or compatible
Differential output: 2V min. with 50-ohm load (RS-422)
Output rise/fall time: 15ns max.
Differential input
threshold: -0.2V min., -0.05V max.
Input resistance: 96k ohm min..
Input current: -100 microAmps min., +125 microAmps.
IBM-compatible computers
1.5V min. with 27-ohm load (RS-485)
Power requirements
+5 volts: approx. 250 mA
Temperature: operating 0° to 70°
storage -50° to 80°
Humidity: 10% to 90%
Quatech QSC(LP)-200/300 User's Manual 30
Page 33

9 Troubleshooting
Listed here are some common problems and frequent causes of those problems. If the
information here does not provide a solution, contact Quatech technical support.
Any unauthorized repairs or modifications will void the
Computer will not boot up.
1. Is the QSC(LP)-200/300 properly inserted? Remove the card and try again. Perhaps try a
different expansion slot.
2. Ensure that an ISA-bus card is not using the same IRQ that the PCI BIOS tries to assign
to the QSC(LP)-200/300. Most computers have BIOS setup options to reserve IRQs for
either ISA or PCI use. Try reserving the IRQ for the ISA card. The BIOS will
automatically choose a different IRQ for the QSC(LP)-200/300. An address conflict is
unlikely because most PCI-based computers will assign I/O addresses in such a way that
they cannot conflict with ISA-bus devices.
3. The QSC(LP)-200/300 may be defective. Contact technical support for instructions.
Cannot communicate with other equipment.
1. Are the cable connections correct? Are the cables securely attached?
2. Is the software configured with the correct base address and IRQ information for the
QSC(LP)-200/300? (This is mainly a DOS issue.)
QSC(LP)-200/300's warranty.
3. Is the device driver installed?
4. If you are trying to communicate with another DTE, a null-modem cable will be required.
5. If possible, use a loopback connector to test the port. This connector needs to connect the
following sets of signals on a D-9 connector:
TxD+ and RxD+ (pins 2 and 4)
TxD- and RxD- (pins 7 and 8)
AuxOut+ and AuxIn+(pins 1 and 5)
AuxOut- and AuxIn- (pins 6 and 9)
Quatech QSC(LP)-200/300 User's Manual 31
Page 34

QSC(LP)-200/300
User's Manual
Revision 1.14
November 2006
940-0146-114
Quatech QSC(LP)-200/300 User's Manual 32
 Loading...
Loading...