Page 1

QXP Server 9.2 Web
Integration Guide
Page 2

CONTENTS
Contents
Overview.........................................................................................10
Supported interfaces............................................................................................10
The Dynamic Publishing Process (DPP).................................................................10
The WIG and the XTensions Developer Kit (XDK)................................................11
Changes in this version...................................................................12
Getting started...............................................................................14
Getting started: HTTP and HTTPS........................................................................14
Dissecting a QXP Server URL........................................................................................14
Interpreting the QXP Server Manager response...........................................................15
HTTP GET and POST Requests.....................................................................................15
Getting started: Web services..............................................................................19
QRequestContext..........................................................................................................20
RequestService..............................................................................................................21
QRequest......................................................................................................................25
RequestParameters.......................................................................................................25
NameValueParam..........................................................................................................26
QContentData...............................................................................................................26
QException...................................................................................................................27
QXP Server Manager............................................................................................27
Using the Web interface.................................................................29
Understanding rendering......................................................................................29
Understanding logging.........................................................................................30
Understanding render types.................................................................................31
ave.................................................................................................................................31
eps.................................................................................................................................33
epub..............................................................................................................................35
jpeg...............................................................................................................................36
literal..............................................................................................................................37
pdf.................................................................................................................................38
png................................................................................................................................42
postscript.......................................................................................................................43
qcddoc..........................................................................................................................45
ii | QXP SERVER 9.2 WEB INTEGRATION GUIDE
Page 3

CONTENTS
qxpdoc..........................................................................................................................46
screenpdf.......................................................................................................................47
swf.................................................................................................................................51
Understanding render modifiers...........................................................................53
Box................................................................................................................................53
Boxes.............................................................................................................................54
Compositionzone..........................................................................................................55
Layer..............................................................................................................................55
Layout............................................................................................................................57
Movepages....................................................................................................................57
Page..............................................................................................................................58
Pages.............................................................................................................................59
Scale..............................................................................................................................60
Spread...........................................................................................................................60
Spreads.........................................................................................................................60
Using content modifiers........................................................................................61
Inserting text.................................................................................................................61
Applying a font at import..............................................................................................62
Inserting a picture.........................................................................................................63
Saving a projects with a new name...............................................................................64
Importing XML with placeholders.................................................................................65
Using XML modify................................................................................................67
Modifying box properties and content.........................................................................67
Creating boxes..............................................................................................................71
Deleting boxes..............................................................................................................73
Grouping and ungrouping items...................................................................................74
Creating tables..............................................................................................................75
Using inline tables.........................................................................................................76
Modifying text attributes...............................................................................................79
Modifying picture properties.........................................................................................82
Importing data...............................................................................................................85
Exporting Job Jackets files during deconstruction.......................................................88
Using interactivity..........................................................................................................88
Using XML deconstruct and construct..................................................................88
Deconstructing a project...............................................................................................89
Constructing a project...................................................................................................92
Working with pages and spreads..................................................................................95
Working with layers.......................................................................................................96
Working with boxes.......................................................................................................96
Working with groups.....................................................................................................98
Working with pictures....................................................................................................99
Working with text........................................................................................................100
Working with tables.....................................................................................................102
QXP SERVER 9.2 WEB INTEGRATION GUIDE | iii
Page 4

CONTENTS
Working with sections.................................................................................................104
Working with Composition Zones...............................................................................105
Using XSL transformation............................................................................................105
Working with lists........................................................................................................106
Working with anchored boxes.....................................................................................106
Working with placeholders..........................................................................................107
Working with metadata...............................................................................................109
Working with hidden text............................................................................................110
Creating and using hyperlinks.............................................................................111
Web hyperlinks............................................................................................................111
Anchor hyperlinks........................................................................................................111
Page hyperlinks...........................................................................................................111
Using the Streaming Document Provider...........................................................112
Using administrative request handlers...............................................................112
Addfile.........................................................................................................................113
Delete..........................................................................................................................116
Evaluate.......................................................................................................................117
Exportprefsasjj.............................................................................................................118
Fileinfo.........................................................................................................................119
Flush............................................................................................................................120
Flushall........................................................................................................................120
Getdocinfo..................................................................................................................121
Getdocpoollist.............................................................................................................122
Getlogs........................................................................................................................123
Getprefs......................................................................................................................123
Getprocessid...............................................................................................................124
Getprojinfo..................................................................................................................124
Getrendererprefs.........................................................................................................125
Getserverinfo...............................................................................................................126
Jobjacket.....................................................................................................................127
Preflight.......................................................................................................................127
Setprefs.......................................................................................................................128
Setrendererprefs..........................................................................................................129
Updateprefsfromjj.......................................................................................................134
Using the QXPSM SDK.................................................................135
Writing a Java QXPSM client..............................................................................135
Java sample: Deconstructing a project.......................................................................136
Java sample: Rendering a PDF....................................................................................136
Java sample: Chained request....................................................................................136
Java sample: AddFile request.....................................................................................137
Writing a .NET QXPSM client.............................................................................137
iv | QXP SERVER 9.2 WEB INTEGRATION GUIDE
Page 5

CONTENTS
.NET sample: Deconstructing a project......................................................................138
.NET sample: Rendering a PDF...................................................................................139
.NET sample: Chained request...................................................................................139
Writing an Objective-C client for Mac OS or iOS................................................139
Objective-C sample: Deconstructing a project...........................................................141
Objective-C sample: Rendering a PDF.......................................................................141
Objective-C sample: Chained request........................................................................142
Extending QuarkXPress Server Manager...........................................................142
Writing special request handlers.................................................................................143
Implementing a custom load balancer........................................................................143
Keep document open (sessions).................................................................................144
Using the Extensibility tool..........................................................................................144
Understanding ManagerSDK.xml................................................................................146
Using the RequestParameters class.............................................................................147
Modifier DTD (annotated).............................................................149
Entities (Modifier DTD).......................................................................................149
ADDCELLS (Modifier DTD).................................................................................151
ALIGNHORSETTINGS (Modifier DTD).................................................................152
ALIGNVERSETTINGS (Modifier DTD).................................................................153
ALLOWBOXOFFPAGE (Modifier DTD)...............................................................153
ALLOWBOXONTOPASTEBOARD (Modifier DTD)..............................................154
ANCHOREDBOXREF (Modifier DTD)..................................................................154
ARTICLE (Modifier DTD).....................................................................................155
AUTHOR (Modifier DTD).....................................................................................155
BNSTYLE (Modifier DTD)....................................................................................156
BOTTOM (Modifier DTD)....................................................................................156
BOTTOMGRID (Modifier DTD)............................................................................156
BOX (Modifier DTD)............................................................................................157
BOXREF (Modifier DTD).....................................................................................159
CALLOUTANCHOR (Modifier DTD)....................................................................160
CALLOUTBOXREF (Modifier DTD)......................................................................161
CELL (Modifier DTD)...........................................................................................161
CHILDID (Modifier DTD).....................................................................................163
CLIPPING (Modifier DTD)...................................................................................163
COLGROUP (Modifier DTD)................................................................................165
COLSPEC (Modifier DTD)....................................................................................166
COLUMN (Modifier DTD)....................................................................................166
COMPONENT (Modifier DTD)............................................................................167
COMPOSITIONZONE (Modifier DTD).................................................................168
CONTENT (Modifier DTD)..................................................................................170
CONTENTPH (Modifier DTD)..............................................................................172
QXP SERVER 9.2 WEB INTEGRATION GUIDE | v
Page 6

CONTENTS
CONTINUEDHEADER (Modifier DTD)................................................................172
CONTINUEDTROWSTYLE (Modifier DTD)..........................................................173
CONTOUR (Modifier DTD)..................................................................................173
CONTOURS (Modifier DTD)................................................................................174
COPYFIT (Modifier DTD).....................................................................................174
COPYRIGHT (Modifier DTD)...............................................................................175
DATAPROVIDER (Modifier DTD)........................................................................175
DELETECELLS (Modifier DTD)............................................................................175
DESCRIPTION (Modifier DTD)............................................................................176
DROPCAP (Modifier DTD)..................................................................................176
EBOOKMETADATA (Modifier DTD)...................................................................176
ENTRY (Modifier DTD)........................................................................................177
EVENTCOLSTYLE (Modifier DTD).......................................................................177
EVENTROWSTYLE (Modifier DTD).....................................................................177
FIRSTTCOLSTYLE (Modifier DTD).......................................................................178
FIT (Modifier DTD)..............................................................................................178
FITTEXT (Modifier DTD)......................................................................................179
FOOTER (Modifier DTD).....................................................................................180
FOOTERTROWSTYLE (Modifier DTD).................................................................181
FORMAT (Modifier DTD)....................................................................................181
FRAME (Modifier DTD).......................................................................................183
GEOMETRY (Modifier DTD)................................................................................184
GRID (Modifier DTD)...........................................................................................186
GRIDLINE (Modifier DTD)...................................................................................186
GROUP (Modifier DTD).......................................................................................187
GROUPCHARACTERS (Modifier DTD)................................................................188
GROWACROSS (Modifier DTD)..........................................................................188
GROWDOWN (Modifier DTD).............................................................................189
HEADER (Modifier DTD).....................................................................................189
HEADTROWSTYLE (Modifier DTD).....................................................................189
HEIGHT(Modifier DTD).......................................................................................190
HIDDEN (Modifier DTD)......................................................................................190
HYPERLINK (Modifier DTD)................................................................................191
ID (Modifier DTD)................................................................................................192
INLINETABLE (Modifier DTD).............................................................................192
INSET (Modifier DTD).........................................................................................193
INTERACTIVITY (Modifier DTD)..........................................................................193
ISBN (Modifier DTD)...........................................................................................194
KEEPLINESTOGETHER (Modifier DTD)..............................................................194
KEYWORDS (Modifier DTD)...............................................................................195
LASTTCOLSTYLE (Modifier DTD)........................................................................195
LAYER (Modifier DTD)........................................................................................195
LAYOUT (Modifier DTD).....................................................................................196
vi | QXP SERVER 9.2 WEB INTEGRATION GUIDE
Page 7

CONTENTS
LAYOUTREF (Modifier DTD)...............................................................................197
LEFT (Modifier DTD)...........................................................................................198
LEFTCONTROLPOINT (Modifier DTD)................................................................198
LEFTGRID (Modifier DTD)...................................................................................198
LINESTYLE (Modifier DTD).................................................................................199
LINKEDBOX (Modifier DTD)...............................................................................200
LIST (Modifier DTD)............................................................................................201
LOCATION (Modifier DTD).................................................................................201
LOCKTOGRID (Modifier DTD).............................................................................201
MAX (Modifier DTD)...........................................................................................202
METADATA (Modifier DTD)................................................................................202
MIN (Modifier DTD)............................................................................................202
MOVEDOWN (Modifier DTD).............................................................................202
MOVELEFT (Modifier DTD).................................................................................203
MOVERIGHT (Modifier DTD)..............................................................................203
MOVEUP (Modifier DTD)....................................................................................203
ODDTROWSTYLE (Modifier DTD).......................................................................203
ODDTCOLSTYLE (Modifier DTD)........................................................................204
ORIGIN (Modifier DTD).......................................................................................204
OVERMATTER (Modifier DTD)............................................................................205
PAGE (Modifier DTD)..........................................................................................205
PAGEREF (Modifier DTD)...................................................................................206
PARAGRAPH (Modifier DTD)..............................................................................207
PARENTTABLE (Modifier DTD)...........................................................................208
PICTURE (Modifier DTD).....................................................................................208
PLACEHOLDER (Modifier DTD)..........................................................................211
POSITION (Modifier DTD)...................................................................................211
PROJECT (Modifier DTD)....................................................................................211
PUBLICATION (Modifier DTD)............................................................................212
PUBLICATIONCHANNEL (Modifier DTD)...........................................................213
PUBLISHER (Modifier DTD).................................................................................213
RELPOSITION (Modifier DTD).............................................................................213
RGBCOLOR (Modifier DTD)................................................................................213
RICHTEXT (Modifier DTD)...................................................................................214
RIGHT (Modifier DTD).........................................................................................222
RIGHTCONTROLPOINT (Modifier DTD)..............................................................223
RIGHTGRID (Modifier DTD)................................................................................223
ROW (Modifier DTD)...........................................................................................224
RUBI (Modifier DTD)...........................................................................................226
RUBITEXT (Modifier DTD)...................................................................................226
RULE (Modifier DTD)..........................................................................................227
RUNAROUND (Modifier DTD)............................................................................229
SAVEAS (Modifier DTD)......................................................................................231
QXP SERVER 9.2 WEB INTEGRATION GUIDE | vii
Page 8

CONTENTS
SCALETO (Modifier DTD)....................................................................................232
SECTION (Modifier DTD)....................................................................................233
SHADOW (Modifier DTD)...................................................................................233
SHRINKACROSS (Modifier DTD).........................................................................235
SHRINKDOWN (Modifier DTD)...........................................................................236
SIZE (Modifier DTD)............................................................................................236
SPINEIMAGE (Modifier DTD)..............................................................................236
SPLINESHAPE (Modifier DTD)............................................................................237
SPREAD (Modifier DTD)......................................................................................238
STACKINGORDER (Modifier DTD)......................................................................238
STORY (Modifier DTD)........................................................................................238
SUPPRESSOUTPUT (Modifier DTD)....................................................................239
TAB (Modifier DTD)............................................................................................239
TABLE (Modifier DTD).........................................................................................240
TABLEBREAK (Modifier DTD).............................................................................242
TABLESTYLE (Modifier DTD)...............................................................................243
TABSPEC (Modifier DTD)....................................................................................243
TBODY (Modifier DTD).......................................................................................244
TCOL (Modifier DTD)..........................................................................................244
TCOLSTYLE (Modifier DTD)................................................................................244
TCONTINUED (Modifier DTD)............................................................................245
TEXT (Modifier DTD)...........................................................................................245
TEXTNODEPH (Modifier DTD)............................................................................247
TEXTPH (Modifier DTD)......................................................................................247
TFOOT (Modifier DTD)........................................................................................248
THEAD (Modifier DTD).......................................................................................248
TITLE (Modifier DTD)..........................................................................................248
TOP (Modifier DTD)............................................................................................248
TOPGRID (Modifier DTD)....................................................................................248
TROW (Modifier DTD).........................................................................................249
TROWSTYLE (Modifier DTD)...............................................................................250
VALUE (Modifier DTD)........................................................................................250
VERTEX (Modifier DTD)......................................................................................251
VERTEXPOINT (Modifier DTD)...........................................................................251
VERTICES (Modifier DTD)...................................................................................252
WIDTH (Modifier DTD)........................................................................................252
Sample applications.......................................................................253
Sample applications: QXP Server Manager........................................................253
ASP.NET samples........................................................................................................253
C# samples..................................................................................................................253
Java samples...............................................................................................................254
viii | QXP SERVER 9.2 WEB INTEGRATION GUIDE
Page 9

CONTENTS
JSP samples.................................................................................................................254
Objective-C samples...................................................................................................254
Sample applications legal notice.........................................................................254
Contacting Quark..........................................................................263
Legal notices.................................................................................264
QXP SERVER 9.2 WEB INTEGRATION GUIDE | ix
Page 10

OVERVIEW
Overview
Welcome to the QuarkXPress® Server Web Integration Guide (WIG). The WIG describes the
QuarkXPress Server interface and includes sample applications that demonstrate how to
build a solution that integrates with QuarkXPress Server or QuarkXPress Server Manager.
Supported interfaces
The WIG describes the interfaces available in QuarkXPress Server:
• HTTP: Lets you interact with the server using URLs that contain calls or point to XML
files that contain calls. You can write client applications in any language that supports
HTTP requests. For more information, see "Getting started: HTTP and HTTPS".
• HTTPS: Provides secure HTTP access.
• Web services: Lets you interact with the server via Web services using the
QuarkXPress Server Manager object model. You can write client applications in Java, .NET,
or any other programming language that can consume SOAP-based Web services. For more
information, see "Getting started: Web services".
To develop a custom load balancer or a custom application in Java, you must have
version 1.5 or 1.6 of the JDK.
The Dynamic Publishing Process (DPP)
The Dynamic Publishing Process (DPP) has several stages. You may not need to use all of
these stages every time, but this the order in which they occur:
• Pre-Processing Stage: During this stage, QuarkXPress Server performs any necessary initial
steps, such as creating style sheets, colors, and H&J rules for a new QuarkXPress project.
• Content Loading Stage: During this stage, QuarkXPress Server loads dynamic content into
boxes in the project.
• Layout Modification Stage: During this stage, QuarkXPress Server modifies the layout of the
project.
10 | QXP SERVER 9.2 WEB INTEGRATION GUIDE
Page 11

• Post-Processing Stage: During this stage, QuarkXPress Server examines the project and
performs maintenance tasks.
The WIG and the XTensions Developer Kit (XDK)
The WIG lets Web developers build client applications that use the features available in
QuarkXPress Server. The XDK lets software developers implement features that are not
available in QuarkXPress Server, such as server-side processing and application-specific
services.
The QuarkXPress Server XDK requires knowledge of C or C++.
OVERVIEW
QXP SERVER 9.2 WEB INTEGRATION GUIDE | 11
Page 12

CHANGES IN THIS VERSION
Changes in this version
This version of the QuarkXPress Server WIG includes the following changes.
New features
The following new features have been added:
• Inline tables: For more information, see "Using inline tables."
• Streaming document providers: For more information, see "Using the Streaming Document
Provider."
• App Studio enrichments: You can now create and modify App Studio assets in Modifier
XML. For more information, see "Using interactivity."
• The ability to create ePUB output with ePUB output styles. For more information, see
"epub."
• The ability to create hyperlinks. For more information, see "Creating and using hyperlinks."
Changes to the Modifier DTD
The following element types have been updated:
• PROJECT (Modifier DTD)
• STORY (Modifier DTD)
The following new element types have been added:
• BOTTOMGRID (Modifier DTD)
• COLGROUP (Modifier DTD)
• CONTINUEDTROWSTYLE (Modifier DTD)
• ENTRY (Modifier DTD)
• EVENTCOLSTYLE (Modifier DTD)
• EVENTROWSTYLE (Modifier DTD)
• FIRSTTCOLSTYLE (Modifier DTD)
• FOOTERTROWSTYLE (Modifier DTD)
12 | QXP SERVER 9.2 WEB INTEGRATION GUIDE
Page 13

• HEADTROWSTYLE (Modifier DTD)
• INLINETABLE (Modifier DTD)
• LASTTCOLSTYLE (Modifier DTD)
• LEFTGRID (Modifier DTD)
• ODDTCOLSTYLE (Modifier DTD)
• ODDTROWSTYLE (Modifier DTD)
• RIGHTGRID (Modifier DTD)
• TABLESTYLE (Modifier DTD)
• TBODY (Modifier DTD)
• TCOL (Modifier DTD)
• TCOLSTYLE (Modifier DTD)
• TCONTINUED (Modifier DTD)
• TFOOT (Modifier DTD)
• THEAD (Modifier DTD)
CHANGES IN THIS VERSION
• TOPGRID (Modifier DTD)
• TROW (Modifier DTD)
• TROWSTYLE (Modifier DTD)
QXP SERVER 9.2 WEB INTEGRATION GUIDE | 13
Page 14

GETTING STARTED
Getting started
Getting started: HTTP and HTTPS
The topics below describe how to create requests for the QuarkXPress Server Web interface.
For information about the options available in such requests, see "Using the Web interface."
You can submit HTTP and HTTPS requests to QuarkXPress Server as URLs, either manually
from a browser or automatically from an HTTP client application. QuarkXPress Server
processes such requests and returns rendered content in the HTTP or HTTP responses.
Depending on the type of request, the QuarkXPress Server preferences, and the type of
content returned, the rendered content may be downloaded by the end user, displayed in
the end-user's browser, or saved to a file system location accessible to QuarkXPress Server.
You can write a QuarkXPress Server client application in almost any language that can
generate HTTP GET/POST requests. A QuarkXPress Server HTTP-based solution typically
consists of QuarkXPress Server (running on a server computer connected to a network)
plus a front-end application (usually Web-based) that provides a graphical user interface
(GUI) for end users. The front-end application translates end users' input into HTTP or
HTTPS requests and sends the requests to QuarkXPress Server or QuarkXPress Server
Manager, which processes the requests and returns rendered content.
Dissecting a QXP Server URL
To interact with QuarkXPress Server from a Web browser, use a URL like the following:
http://[server]:[port]/[namespace]/[directory]/[DocumentName]?[parameter]=Value
•
[server]: The name or IP address of the computer for QuarkXPress Server or
QuarkXPress Server Manager.
•
[port]: The port number on which to contact QuarkXPress Server or QuarkXPress Server
Manager. The default port is 8080 for QuarkXPress Server and 8090 for QuarkXPress Server
Manager.
•
[namespace]: Defines what the URL action will be and any parameters and conditions
available to that namespace.
•
[directory]: The path in the document pool where the project is stored, relative to the
QuarkXPress Server document pool. To access the root level, no directory path is necessary.
14 | QXP SERVER 9.2 WEB INTEGRATION GUIDE
Page 15
GETTING STARTED
(Note that you can also supply assets as part of a multipart HTTP request. For more
information, see "Using HTTP POST with QXP Server.")
•
[DocumentName]: The name of the QuarkXPress project to be processed.
•
[parameter]: Further defines the URL action with attributes and values allowed for the
namespace or general call. Pass parameters in the form attribute=value, with parameters
separated by the "&" character.
For QuarkXPress Server Manager, use a URL like the following:
http://[server]:[port]/qxpsm/request/[namespace]/[directory]/
[DocumentName]?[parameter]=Value
Prior to QuarkXPress Server 9.0, you had to use different URL constructions when sending
requests to an instance of QuarkXPress Server Manager in a QPS installation than you did
when sending requests to a free-standing instance of QuarkXPress Server Manager. In
versions 9.0 and later, both can use /qxpsm/request/ after [port]/ .
You can now use both absolute and relative paths when you modify a project with SDK
objects or classes. Relative paths are almost always relative to the document pool. If you
use multiple QuarkXPress Server instances, you should use a common document pool.
Interpreting the QXP Server Manager response
When QuarkXPress Server Manager successfully processes a request through the HTTP
interface, the response is the same as QuarkXPress Server's response unless the user has
supplied additional parameters to QuarkXPress Manager. For more information, see
"Working with QuarkXPress Server Manager" in A Guide to QuarkXPress Server.
If an error occurs, QuarkXPress Server Manager retries the request, either on the same
QuarkXPress server instance or a different one (depending on the error and global settings
established in the QuarkXPress Server Manager client). If QuarkXPress Server Manager
cannot process the request, it returns an XML response describing the error, plus any
header error codes returned by QuarkXPress Server. For example:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<error>
<httpresponsecode>500</httpresponsecode>
<xpressservererrorcode>-43</xpressservererrorcode>
<xpressservererrormessage>File not found.</xpressservererrormessage>
<xpressserverextendedmessage> <![CDATA[ Error #-43 - File not found. ]]>
</xpressserverextendedmessage>
<xpressservermanagererrorcode>M8000001</xpressservermanagererrorcode>
<xpressservermanagererrormessage>The server could not locate the specified
file.
</xpressservermanagererrormessage>
</error>
HTTP GET and POST Requests
The topics below describe how you can use HTML to interact with QuarkXPress Server.
QuarkXPress Server supports both the GET and POST HTML methods. When you use the
GET method, the browser encodes form data into a URL. When you use the POST method,
form data is passed within the message body. Use the GET method only when the form
QXP SERVER 9.2 WEB INTEGRATION GUIDE | 15
Page 16

GETTING STARTED
processing is idempotent. In short: GET is for retrieving data, whereas POST can involve
storing or updating data, ordering a product, or sending an e-mail.
Using HTTP GET with QXP Server
Use HTML like the following to specify a server and port where you want to send a request.
You can specify the name of the target project, the output type, and a scaling value. You
can specify the name of a box and the path of a text or picture files to import into that
box, as long as the file's path is on the server's file system. You can also use HTML like the
following to specify the page number and layout number of the project.
The form section of the HTML should begin with the following line of code:
<form id = form1 method="GET" enctype="application/x-www-form-urlencoded">
For both GET and POST, the browser constructs a form data set and encodes it according
to the ENCTYPE attribute (you can use multipart/form-data for POST and
application/x-www-form-urlencoded (the default) for both POST and GET).
To create fields that let the user specify the server IP address, the port, and the project
name, use HTML like the following:
<TABLE cellSpacing=1 cellPadding=1 border=1 id=TABLE1 >
<TBODY>
<TR>
<TD>
<INPUT id=ServerTxt name=ServerTxt value="Server ID"
readOnly size=13 style="WIDTH: 107px; HEIGHT: 22px">
</TD>
<TD>
<INPUT id=Server maxLength=50 size=16 value=localhost name=Server
style="WIDTH: 170px; HEIGHT: 22px">
</TD>
</TR>
<TR>
<TD>
<INPUT id=PortTxt name=PortTxt value="Port Number"
readOnly size=13 style="WIDTH: 107px; HEIGHT: 22px">
</TD>
<TD>
<INPUT id=Port maxLength=50 size=17 value=8080 name=Port
style="WIDTH: 170px; HEIGHT: 22px">
</TD>
</TR>
<TR>
<TBODY>
</TABLE>
<TR>
<p></p>
<TD>
<INPUT id=DocTxt name=DocTxt value="Document Name"
readOnly size=13 style="WIDTH: 107px; HEIGHT: 22px">
</TD>
<TD>
<INPUT id=Doc maxLength=50 size=18 name=Doc style=
"WIDTH: 170px; HEIGHT: 22px">
</TD>
</TR>
To create a drop-down menu that lets the end user specify a render format, use HTML like
the following:
<SELECT id="select1" name="returntype">
<OPTION value="jpeg">JPEG</OPTION>
<OPTION value="pdf">PDF</OPTION>
<OPTION value="qxpdoc">QuarkXPress document</OPTION>
<OPTION value="eps">EPS Document</OPTION>
16 | QXP SERVER 9.2 WEB INTEGRATION GUIDE
Page 17

GETTING STARTED
<OPTION value="postscript">POSTSCRIPT</OPTION>
<OPTION value="png">PNG</OPTION>
</SELECT><td/>
To create a drop-down menu that lets the end user specify a rendering scale, use HTML
like the following:
<SELECT id="select2" name="scale">
<OPTION value="1">100%</OPTION>
<OPTION value="2">200%</OPTION>
<OPTION value="3">300%</OPTION>
<OPTION value="5">500%</OPTION>
<OPTION value=".5">50%</OPTION>
</SELECT><p/>
To create input fields that let the end user specify a box name and the name of a file to
be imported into that box, use HTML like the following:
<TD>
<INPUT id=box1Txt value="Box Name"
readOnly style="WIDTH: 181px; HEIGHT: 22px" size=16>
</TD>
<TD>
<INPUT id=box1 maxLength=256 size=43 style="
WIDTH: 293px; HEIGHT: 22px"></TD>
</TR>
<TR>
<TR>
<TD>
<INPUT id=box1FileTxt value="File on Server"
readOnly style="WIDTH: 181px; HEIGHT: 22px" >
</TD>
<TD>
<INPUT id=box1File maxLength=256 size=43 style="
WIDTH: 293px; HEIGHT: 22px">
</TD>
</TR>
To create fields that let the end user enter a page number a layout number, use HTML like
the following:
<TABLE cellSpacing=1 cellPadding=1 border=1 style="WIDTH: 188px; HEIGHT: 61px">
<TR>
<TD>
<INPUT id=PageTxt value = "Page"
readOnly style="WIDTH: 50px; HEIGHT: 22px" size=3>
</TD>
<TD>
<input id=Page size="16" maxlength="256"
style="WIDTH: 147px; HEIGHT: 22px">
</TD>
</TR>
<TR>
<TD>
<INPUT id=LayoutTxt value = "Layout"
readOnly style ="WIDTH: 50px; HEIGHT: 22px" size=4>
</TD>
<TD>
<input id=Layout size="16" maxlength="256"
style="WIDTH: 147px; HEIGHT: 22px">
</TD>
</TR>
</TABLE>
To create a button that lets the end user submit the request, use HTML like the following:
<input type="submit" value="Render document"
name="Submit" LANGUAGE="javascript"
onclick="return Submit_onclick()"/>
QXP SERVER 9.2 WEB INTEGRATION GUIDE | 17
Page 18
GETTING STARTED
The above HTML calls a function named Submit_onclick(). You can add such a function
to the <HEAD> section of the HTML. For example:
<head>
<TITLE>Quark Stream</TITLE>
<script ID="clientEventHandlersJS" LANGUAGE="javascript">
function Submit_onclick() {
var prefix;
var renderer;
var file;
var url;
var box1Name;
var dataImportStamp = "@dataimport";
prefix = "http://" + document.getElementById("Server").value + ":";
port = document.getElementById("Port").value + "/";
renderer = document.getElementById("select1").value + "/";
file = document.getElementById("Doc").value;
box1Name = document.getElementById("box1").value;
if (box1Name != "") {
document.getElementById("box1File").name = box1Name + dataImportStamp;
} else {
document.getElementById("box1File").name = "";
}
document.getElementById("Page").name = "Page";
document.getElementById("Layout").name = "Layout";
url = prefix + port + renderer + file;
document.getElementById("form1").action = url;
}
</script>
</head>
The Submit_onclick() function reads the values from the formand builds a request URL
using the server, port, and render type.
If the end user specifies a file name in the "File on Server" text box, he or she must add
file: to the beginning of the file path (for example, file:C:\data.txt).
The code above adds @dataimport to the end of the box name to accommodate data
import.
The action of the form is defined by this line:
document.getElementById("form1").action = url;
This form's method is GET. The user agent gets the value (the URL) of the action, appends
a ? to it, adds the form data set, and submits the URL.
In this scenario, form data must be in ASCII.
Using HTTP GET with QXP Server Manager
HTTP GET with QuarkXPress Server Manager works the same way as HTTP GET with
QuarkXPress Server (see "Using HTTP GET with QXP Server"), except that Quark does not
recommend using GET if you are working with non-ASCII characters. The behavior of GET
requests with characters is highly browser-dependent, and there is no standard that all
browsers follow. Instead, use POST.
18 | QXP SERVER 9.2 WEB INTEGRATION GUIDE
Page 19

Using HTTP POST with QXP Server
Use HTML like the HTML in "Using HTTP GET with QXP Server" to specify a server and port
where you want to send a request. You can specify the name of the target project, the
output type, and a scaling value. You can specify the name of a box and the path of a text
or picture files to import into that box, as long as the file's path is on the server's file system.
You can also use HTML like the HTML in "Using HTTP GET with QXP Server" to specify the
page number and layout number of the project. Differences between the GET method and
the POST method are described below.
The form section of the HTML should begin with the following line of code:
<form id = form1 method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data">
The following HTML creates a input fields that let the end user specify the name of a file
to be imported into a box:
<TD><INPUT id=box1FileTxt value="File on Client"
readOnly style="WIDTH: 180px; HEIGHT: 22px" ></TD>
<TD><input id=box1File type="file"
size="32" maxlength="256" style="WIDTH: 293px;
HEIGHT: 22px">
</TD></TR>
The action of the form is defined by this line:
GETTING STARTED
document.getElementById("form1").action = url;
The form's method is POST. The user agent conducts an HTTP post transaction using the
value of the action attribute (the URL), and a message is created according to the content
type specified by the enctype attribute.
When you use a multipart HTTP post request, you can include in the request any files
which are required by the rendering process, including QuarkXPress templates, picture
files, modifier XML, and digital publishing assets. For more information, see "Using the
Streaming Document Provider."
Using HTTP POST with QXP Server Manager
HTTP POST with QuarkXPress Server Manager works the same way as HTTP POST with
QuarkXPress Server (see "Using HTTP POST with QXP Server"), except that with
QuarkXPress Server Manager, you must use UTF-8.
Getting started: Web services
The Web services interface is a collection of request classes. You can download the SDK
WSDL class definitions from
http://[server]:[port]/qxpsm/services/RequestService?wsdl (replace [server]
with the QuarkXPress Server Manager computer's IP address and [port] with the
QuarkXPress Server Manager port number.
These classes can be chained together to form compound QuarkXPress Server requests.
The sample applications (see "Sample applications") show how to use these classes to invoke
a QuarkXPress Server command and manipulate the response.
QXP SERVER 9.2 WEB INTEGRATION GUIDE | 19
Page 20
GETTING STARTED
For more information, see "Using the Web interface." In addition to the classes listed there,
the Web services interface includes the following:
•
RequestService processes QuarkXPress Server requests. This object's generic
processRequest() method takes a QRequestContext argument and returns a
QContentData object containing the response. For more information, see the sample
applications and "Using the Web interface."
•
QRequestContext is the argument you pass to RequestService's generic
processRequest() method.This object contains settings which must be set once per
request. Set all chained requests inside the request context.
•
QRequest is the base class for all request objects (such as PDFRenderRequest).
Consequently, all request objects share some common data members.
•
RequestParameters is a generic class for executing any request and for adding dynamic
properties to a request.
•
NameValueParam is a generic class for adding dynamic properties to a request. This class
is specifically for requests that take a box's name and/or ID as the parameter name and
the box's content as the value.
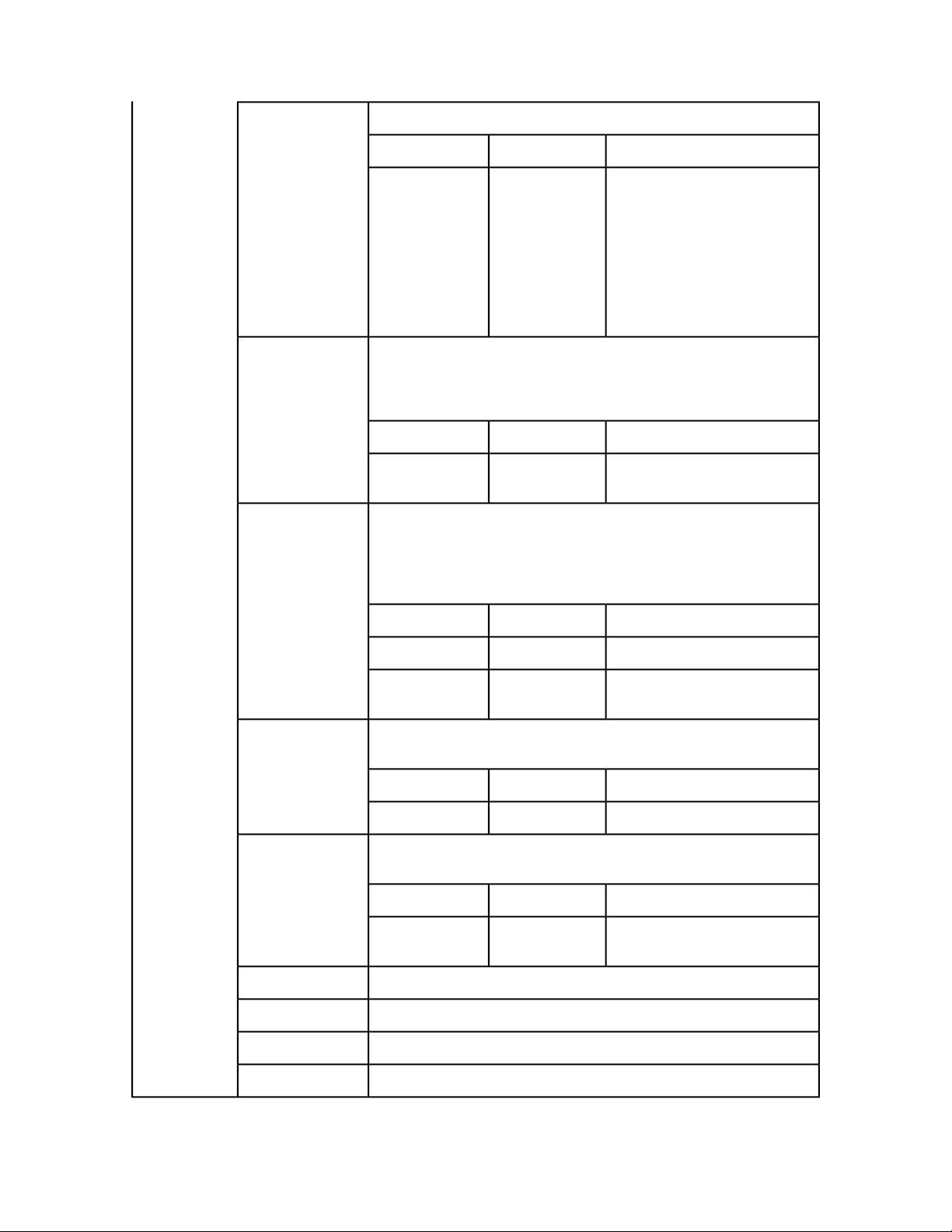
QRequestContext
Description
•
QContentData is the response returned when a request is executed. QContentData is a
hyperlink that follows the same pattern as the classes above.
•
QException is the exception class for QuarkXPress Server Manager. Web services returns
a QException object if an error occurs with any Web service method. You can use try/catch
blocks to handle QException objects.
If you've written a Server XTensions module, you can extend the WIG to include any
changes it makes to the Modifier DTD by simply modifying an XML file and regenerating
the stubs.
To exclude empty tags in the request HTML, set the value of the appropriate variable to
null.
For Javadocs, WSDL schemas, and JSP samples, see the Welcome page that displays when
you launch QuarkXPress Server Manager.
The following topics describe the general Web services classes.
An argument passed to RequestService. Contains settings that must be set once per request. All
chained requests must be set inside the request context.
Web service data objectType
NameMembers
documentName
20 | QXP SERVER 9.2 WEB INTEGRATION GUIDE
DescriptionTypes
File or object name on which the command will be rendered.String
Page 21
GETTING STARTED
serverName
serverPort
userName
userPassword
maxRetries
requestTimeout
useCache
responseAsURL
bypassFileInfo
context
String
Integer
Boolean
Boolean
Boolean
Server name. Default is NULL. Load balancer searches for the host
itself in this case.
Port at which the desired server is listening.Integer
Server admin username.String
Server admin password.String
Max number of times to try executing the command before
returning failure.
Max time out in milliseconds.Integer
Indicates whether the cache should be checked for an existing
result or if the command should be executed again.
This value indicates whether the server should send the response
as-is (text or binary) or store the response on the server and return
its location as a URL. Because the object model works on SOAP,
which can be slow when transferring large binary files, you might
choose to set this value to "true" if you suspect that the response
is going to be several megabytes or larger.
Indicates whether file info should be fetched before executing the
command.
Context in which the command is being executed.String
Example, object
model
RequestService
Description
Methods
QRequestrequest
com.quark.qxpsm.QRequestContext rc = new com.quark.qxpsm.QRequestContext();
rc.documentName = this.DocumentSettings1.documentName.Text;
rc.responseAsURL = this.DocumentSettings1.responseAsURL.Checked;
rc.useCache = this.DocumentSettings1.useCache.Checked;
rc.bypassFileInfo = this.DocumentSettings1.bypassFileInfo.Checked;
//Create the service and call it QRequestContext object
RequestService svc = new RequestService();
com.quark.qxpsm.QContentData qc = svc.processRequest(rc);
Web service called to process the QuarkXPress Server request. RequestService has a generic method
named processRequest() that takes QRequestContext as an argument and returns QContentData
as the QuarkXPress Server response.
Web serviceType
processRequest
Processes the request context and returns the result.
QuarkXPress Server request is instances of request objects chained
together.
DescriptionTypeParameter
QRequestContextrequestCmd
Argument passed to
RequestService. Contains settings
that must be set once per request.
All chained requests are set inside
the request context.
QXP SERVER 9.2 WEB INTEGRATION GUIDE | 21
Page 22
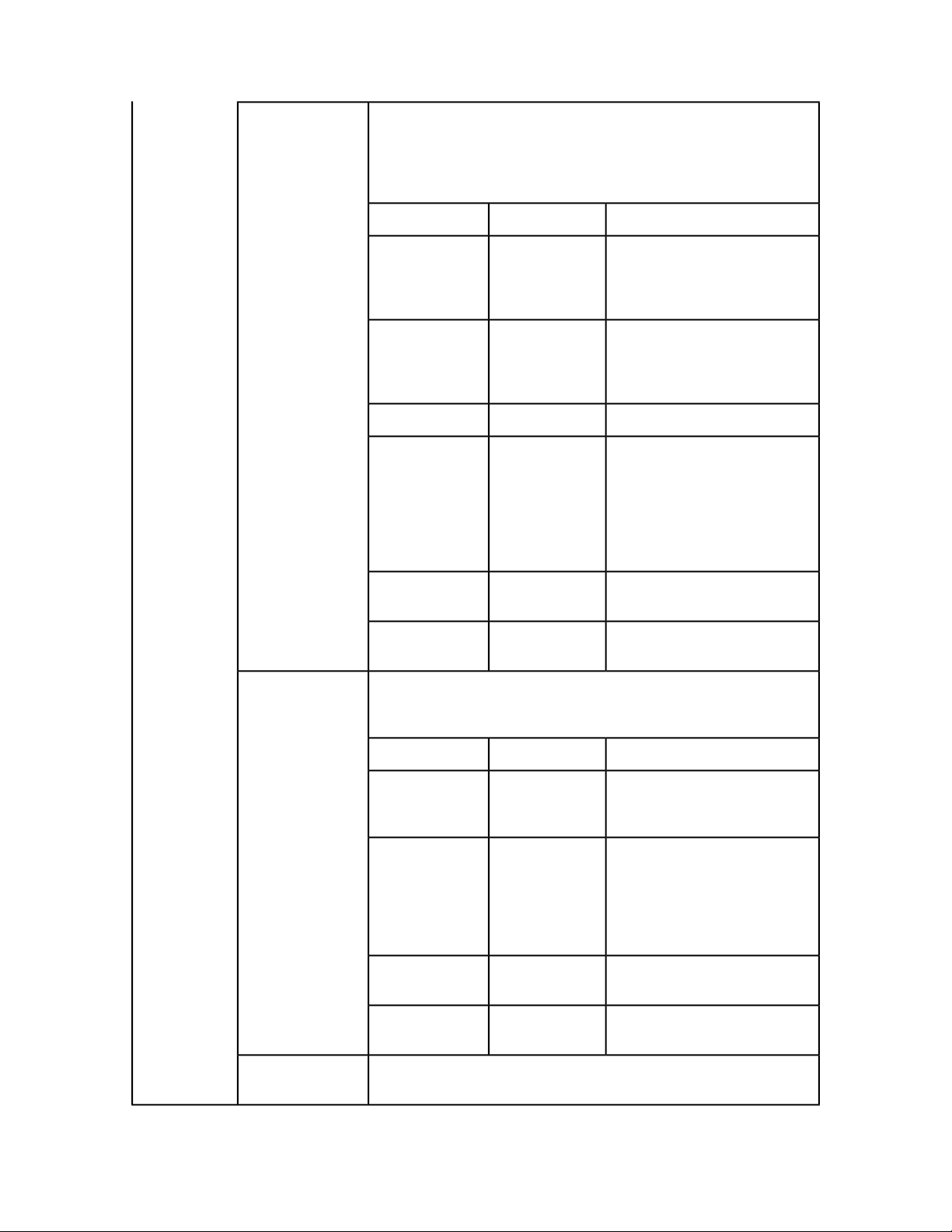
GETTING STARTED
createSession
closeAlldocs
closeDoc
Creates a new session and returns a session ID.
DescriptionTypeParameter
timeout
Closes all open documents in the session without saving them. If the session
does not exist, an error is returned. If an error occurs while closing the
document, it is logged and the document is marked closed in the internal
cache. No error is returned.
sessionId
Closes the specified document without saving it. If the session does not exist,
an error is returned. If the document is not open, and error is returned. If the
document is open in another session, an error is returned. If an error occurs
while closing the document, it is logged and the document is marked closed
in the internal cache. No error is returned.
Long
String
Timeout for the session in
milliseconds. If no call is executed
in that time, session is expired and
all the open documents in that
session are closed without saving. If
0 is passed as value of timeout,
default timeout is used. If a negative
value is passed as timeout, the
session never expires.
DescriptionTypeParameter
Session whose documents are to be
closed.
closeSession
getOpenDocs
getOpenSessions
getPreferences
setPreferences
DescriptionTypeParameter
docName
sessionId
Closes the specified session. If the session does not exist, an error is returned.
If any documents are still open in the session, an error is returned.
sessionId
Gets all the open documents in the session. If the session does not exist, an
error is returned.
sessionId
Gets all open sessions.
Gets QuarkXPress Server preferences.
Sets QuarkXPress Server preferences.
String
String
Document to be closed.String
Session in which document was
opened.
DescriptionTypeParameter
Session to be closed.String
DescriptionTypeParameter
Session whose open documents are
sought.
getXPressDOM
Creates a DOM for the specified document.
22 | QXP SERVER 9.2 WEB INTEGRATION GUIDE
Page 23
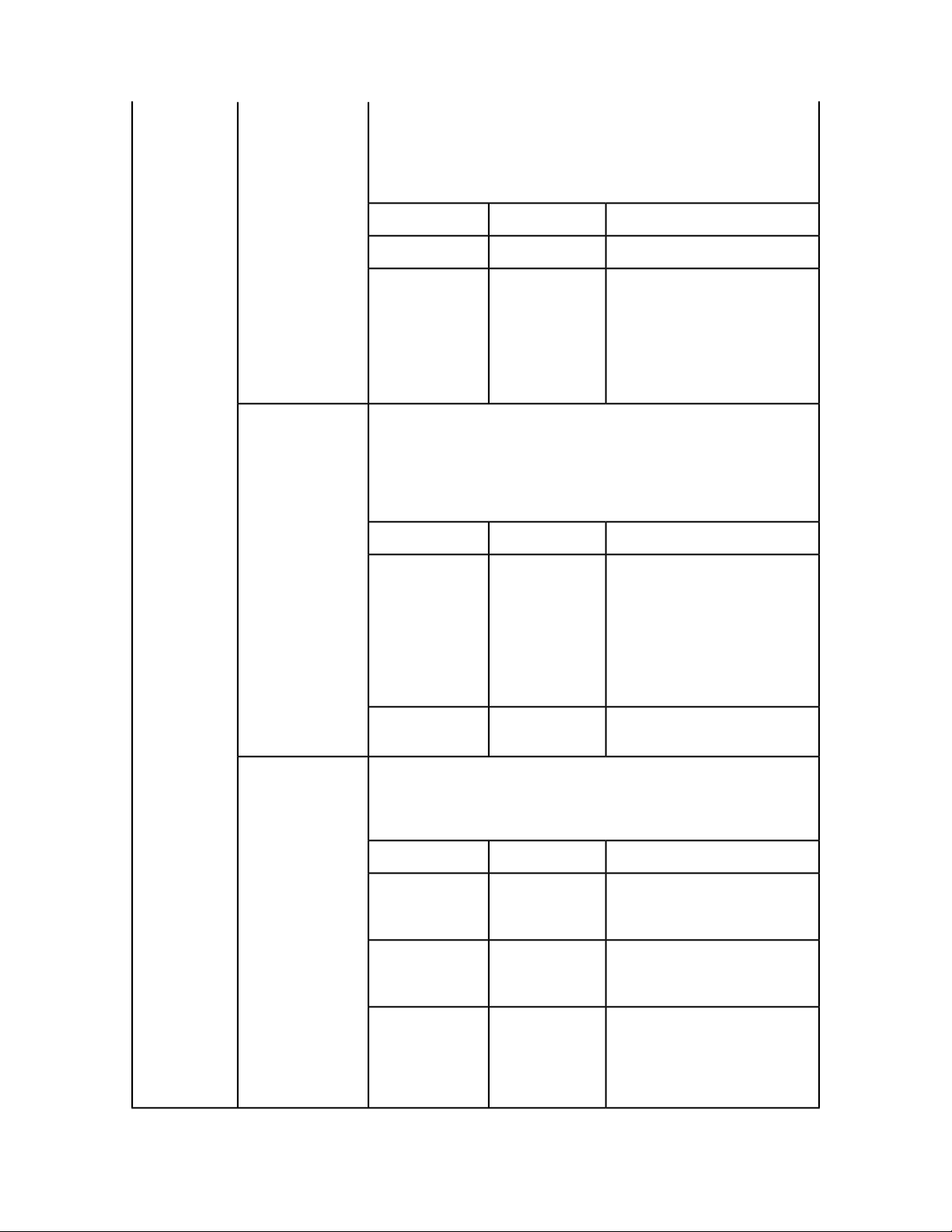
GETTING STARTED
newDoc
Creates a new document for modification and keeps it open until further
notice. The document is created with a single layout. To create a more complex
document, use the processRequestEx API. If a document with the same name
is already open, an error is returned. If the session does not exist, an error is
returned.
DescriptionTypeParameter
docName
jobJacketName
jobTicketName
host
String
String
String
Document to be opened for
modification. Provide the name
only. You can proivde a relative
path when you save the document.
Name of the Job Jackets file to be
used. The Job Jackets file is assumed
to be already available on the
QuarkXPress server computer.
Name of the Job Ticket to be used.String
The QuarkXPress Server instance
that should be used for this
document modification. If null, this
value is supplied by the load
balancer. If the indicated server is
not an active registered server, an
error is thrown.
openDoc
port
sessionId
Opens the specified document and keeps it open until further notice. If the
document is already open, an error is returned. If the session does not exist,
an error is returned.
docName
host
port
sessionId
Integer
String
String
String
Integer
String
The port for the server specified in
the host parameter.
Session in which the document
should be opened.
DescriptionTypeParameter
Document (along with relative path
if required) to be opened for
modification.
QuarkXPress Server instance which
should be used for this document
modification. If null, this value is
supplied by the load balancer. If the
indicated server is not an active
registered server, an error is thrown.
The port for the server specified in
the host parameter.
Session in which the document
should be opened.
processRequestEx
Executes the request context. If a session ID is specified, the document is kept
open after the request is executed. If no session ID is specified, the request is
QXP SERVER 9.2 WEB INTEGRATION GUIDE | 23
Page 24
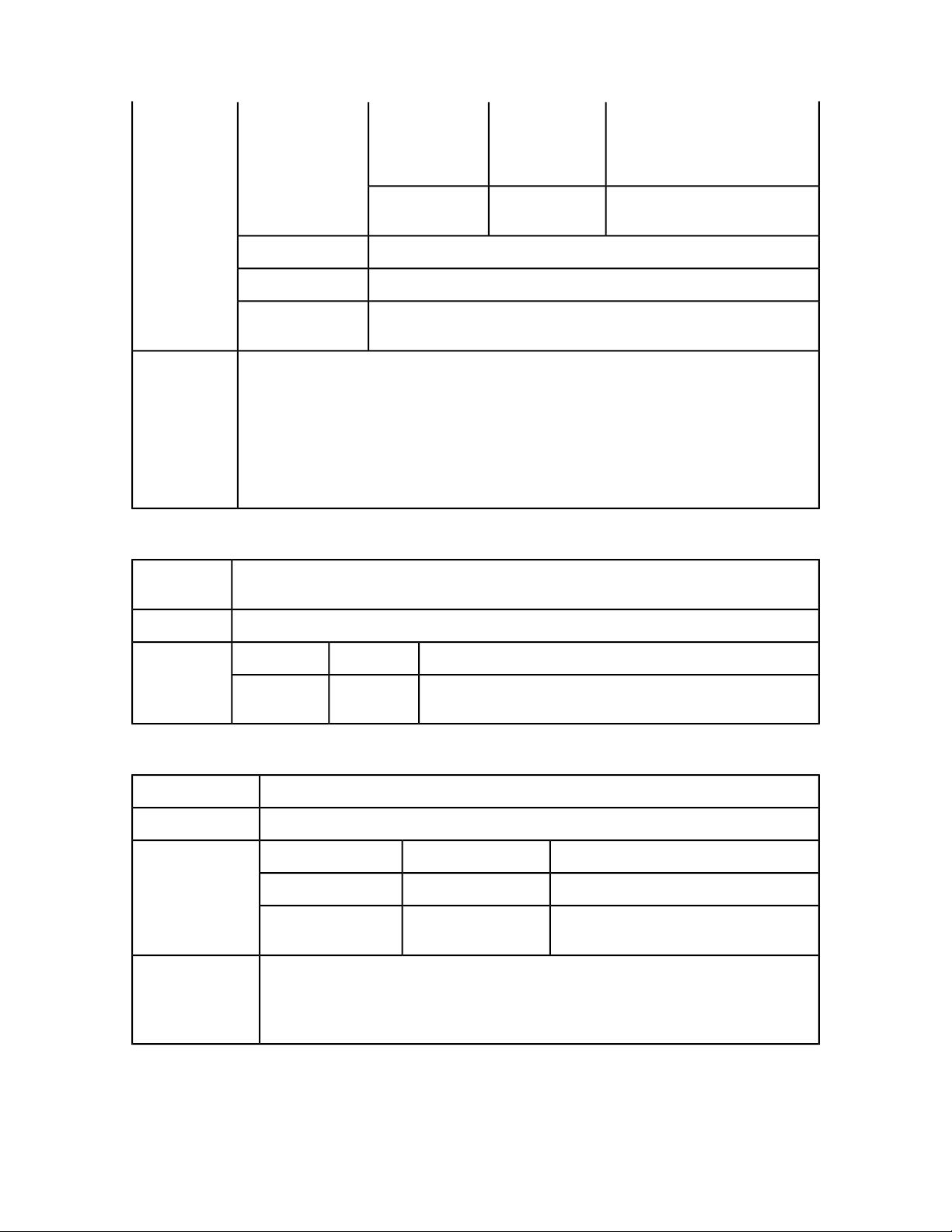
GETTING STARTED
executed normally without keeping the document open. If the document is
open in another session, an error is returned. If the document is marked dirty,
an error is returned (a document is marked dirty when the server that opened
the document has become inactive; in such a case, the document must be
closed and opened again).
DescriptionTypeParameter
saveAllDocs
QRequestContextreqContextObj
sessionId
Saves all open documents in the session. The documents are saved one by
one. If error occurs while saving a document, an error is returned immediately
and the rest of the documents remain unsaved. If a document is marked dirty,
an error is returned (a document is marked dirty when the server that opened
the document has become inactive; in such a case, the document must be
closed and opened again).
relativePath
String
String
Request to be executed.
Session in which the request should
be executed. This value may be null.
If a session ID is provided, the
document is kept open. If no session
ID is provided, the request is
executed normally, as if
processRequest had been called.
DescriptionTypeParameter
Relative path where open
documents should be saved. If this
value is provided, copies of open
documents with changes made so
far are saved in the new location.
The open documents are not saved
but have all of the changes made so
far.
saveDoc
sessionId
Saves the open document. If a document is marked dirty, an error is returned
(a document is marked dirty when the server that opened the document has
become inactive; in such a case, the document must be closed and opened
again).
docName
newName
relativePath
String
String
String
String
Session in which the document
exists.
DescriptionTypeParameter
Document to be saved. Must be the
same name that was used when
opening or creating the document.
New name of the document. If null,
the document is saved with the old
name.
Relative path where the document
should be saved. The relative path
can also contain the new name of
the document. If this is provided, a
copy of the open document with
24 | QXP SERVER 9.2 WEB INTEGRATION GUIDE
Page 25
GETTING STARTED
changes made so far is saved in the
new location. The open document
is not saved but has all of the
changes made so far.
Example, object
model
QRequest
Description
sessionId
getXPressDOMEx
getXMLFromXPressDOM
getXPressDOMFromXML
QRequestContext rc = new QRequestContext();
rc.documentName = "test.qxp";
rc.responseAsURL = false;
JPEGRenderRequest jpegRequest = new JPEGRenderRequest();
rc.request = jpegRequest;
RequestService svc = new RequestService();
QContextData response = svc.processRequest(rc);
Base class for all request objects (such as PDFRenderRequest). All request objects share some common
data members, which are described below.
Web service data objectType
Lets you create a DOM of a particular layout or portion of a layout.
Creates an XML string out of the DOM.
Takes a raw XML representation of a project as a string and returns an object
model representing that project, with Project as the root class.
String
Session in which the document
exists.
Additional
comments
NameMembers
RequestParameters
Generic class for executing any request and for adding dynamic properties to a request.Description
Web service data objectType
NameMembers
requestNamespace
You can use this class to send any request for which a specific class does not exist. When this
request exists in the chain, its namespace is concatenated with the namespaces of other requests.
That means the namespace provided here can be null.
The parameters of this class can be used to parameterize a request being sent to the server.
DescriptionTypes
QRequestrequest
QuarkXPress Server request that includes instances of request objects
chained together.
DescriptionType
Namespace of the request (for example, jpeg).String
NameValueParam[]params
Parameter array for the specified request (for
example, jpegquality).
QXP SERVER 9.2 WEB INTEGRATION GUIDE | 25
Page 26
GETTING STARTED
Example, object
model
NameValueParam
Description
QRequestContext rc = new QRequestContext();
RequestParameters request = new RequestParameters();
request.setRequestNamespace("jpeg");
rc.setRequest = request;
NameValueParam p1 = new NameValueParam();
p1.setParamName = "jpegquality";
p1.setTextValue = "4";
request.setParams(new NameValueParam[]{p1});
Generic class for adding dynamic properties to a request. This class is specifically for requests that take
a box name/id as the parameter name and the box content as the parameter value.
Web service data objectType
NameMembers
paramName
textValue
streamValue
String
String
byte[]
DescriptionType
Name of the parameter. In most cases this will be the name/ID of
the box.
Text value of the box. (You can set either textValue or
streamValue.)
Stream value of the box. (You can set either textValue or
streamValue.)
contentType
QContentData
A response to a Web Services call to QuarkXPress Server.Description
Web service data objectType
NameMembers
contentType
textData
responseURL
streamValue
encodingType
actualServerPortUsed
The MIME content type of the parameter.String
String
String
String
binary
String
DescriptionTypes
The type of the response. For example, "text/xml" or
"text/plain."
If the response type is text, this contains the text.
Otherwise, this value is null.
If the responseAsURL parameter was set to "true" in the
request, this contains the URL of the response.
Otherwise, this value is null.
If the response type is binary, this contains the byte
array. Otherwise, this value is null.
If the response type is text, this value indicates the
encoding of the text (for example, UTF-8 or ANSI).
Identifies the server port.String
actualServerUsed
26 | QXP SERVER 9.2 WEB INTEGRATION GUIDE
Identifies the server.String
Page 27
GETTING STARTED
Example, object
model
QException
Type
headers
multipartResponse
QRequestContext context = new QRequestContext();
context.setDocumentName("sample.qxp");
context.setResponseAsURL(true);
JPEGRenderRequest request = new JPEGRenderRequest();
request.setJPEGQuality("4");
context.setRequest(request);
RequestService requestService = new RequestServiceStub();
QContentData response = requestService.processRequest(context);
System.out.println(response.getResponseURL());
Exception class for QuarkXPress Manager.Description
Exception
NameMembers
httpResponseCode
managerErrorCode
String
String
If the response returned by the server is a set of headers,
this array contains the header response.
If the response returned by the server is multipart, this
array contains the multipart response parts.
DescriptionTypes
HTTP response code.String
QuarkXPress Server Manager error code.String
Example,
object model
QXP Server Manager
managerErrorMessage
serverErrorCode
serverErrorMessage
serverExtendedMessage
String docName = "notexisting.qxp";
try {
QRequestContext ctx = getRequestContext(docName);
QRequest request = getJPEGRequest();
ctx.setRequest(ctx);
QContentData response = getService().processRequest(ctx);
System.out.println(response.getResponseURL());
} catch (QException ex) {
// QuarkXPress Manager threw an QException and it is not
// a runtime exception. QException object will be returned.
System.out.println(ex.getServerErrorCode());
}
QuarkXPress Server Manager localized error message.String
QuarkXPress Server error code.String
QuarkXPress Server response message.String
QuarkXPress Server extended error message.String
The following topics are for people who want to enhance QuarkXPress Server Manager or
integrate it with other software.
Please refer to http://localhost:8090/qxpsmdocs/apidocs/index.html for manager
API documentation. (Note that the port number used to retrieve the API documentation
QXP SERVER 9.2 WEB INTEGRATION GUIDE | 27
Page 28

GETTING STARTED
is 8090 by default, but you should use whatever port number you specified when installing
QuarkXPress Server Manager.)
QuarkXPress Server Manager was developed using interface-based programming and uses
the Spring Framework to instantiate pluggable objects. When QuarkXPress Server Manager
starts up, it reads the contents of a Spring context definition file named
"ManagerContainerConfig.xml" and instantiates all of the beans listed in the file.
QuarkXPress Server Manager then initializes by reading various configuration options
from a file named "ManagerConfig.xml."
You can deploy QuarkXPress Server Manager in its own Tomcat container, in an external
Tomcat container, or in a shared Spring context. For more information, see "Deploying
QuarkXPress Server Manager" in the QuarkXPress Server ReadMe.
28 | QXP SERVER 9.2 WEB INTEGRATION GUIDE
Page 29
Using the Web interface
The topics below describe the features available via the QuarkXPress Server Web interface.
The topics covered here include the following:
• Render types are namespaces you can use to return a QuarkXPress project in a specified file
format.
• Render modifiers let you control which parts of a project are rendered and set the scale of
the returned renderings.
USING THE WEB INTERFACE
• Content modifiers let you alter the content and formatting of boxes in layouts without using
the XML modify parameter.
• XML modify lets you modify QuarkXPress projects using XML.
•
The xml namespace deconstructs a project according to the Modifier DTD. The construct
namespace lets you turn an XML representation of a QuarkXPress project back into a
QuarkXPress project.
• Administrative request handlers let you change the behavior of QuarkXPress Server.
QuarkXPress Server uses case-sensitive XML.
Understanding rendering
Rendering is the process in which QuarkXPress Server opens a QuarkXPress project,
transforms it into a different format (the render type), and then sends a response to the
requestor. Depending on the type of rendering operation, the response may be a message
or a rendered file.
For information on how to submit a render request, see "Getting started: HTTP and HTTPS."
Alerts
document type.
Please select a
QuarkXPress
document or
template.
HTTP Error #500Cannot open this
This alert displays if you try to render a file that is not a QuarkXPress project.
QXP SERVER 9.2 WEB INTEGRATION GUIDE | 29
Page 30
USING THE WEB INTERFACE
read or write to disk.
required volume or
folder.
HTTP Error #404File not found
QuarkXPress Server Error #–43
This alert displays if you try to render a project that does not exist.
HTTP Error #500I/O error trying to
QuarkXPress Server Error #–36
This alert displays if QuarkXPress Server is running on Windows and a shared
network folder was selected as the document pool, but the folder is no longer
shared.
What to do: In the QuarkXPress Server administration interface, choose
Administration > Preferences > General and set Document Root Folder
to a shared folder.
HTTP Error #404Cannot find
QuarkXPress Server Error #–35
This alert displays if QuarkXPress Server is running on Mac OS and a shared
network volume was selected as the document pool, but the volume is no
longer shared.
What to do: In the QuarkXPress Server administration interface, choose
Administration > Preferences > General and set Document Root Folder
to a shared folder.
Example, GET
URL
Understanding logging
If a request succeeds, a transaction success message is written to the QuarkXPress Server
transaction log file. This message includes the transaction ID, date, time, request type,
project name, response type, response size in bytes, and client IP address. For example:
07/03/2011 14:37:47 - RequestURI = /xml/sample.qxp TransactionUUID =
afb6f457-80ae-4d5d-a434-ce9f3e089761 Client = 10.91.30.216 Type = text/xml
Size = 4846
If an alert is displayed, an error message is written to the QuarkXPress Server transaction
log file. The transaction entry contains the date and time of the request, the error code,
and the error message. The following is a sample of an error log transaction entry:
See Understanding loggingLogs
http://localhost:8080/sample.qxp
There are two ways to specify a render format:Notes
1. Enter the render type directly in the browser address
field:http://localhost:8080/pdf/project.qxp.
2. In the QuarkXPress Server administration interface, choose Administration > Preferences >
General and choose the default render type from the Default Renderer Type drop-down menu.
09/03/2011 13:54:33 - RequestURI = /sample.qcd TransactionUUID =
dffc3a7e-11fd-4d97-b3fe-8f2129353d58 Client = 10.91.30.216 Error #10120 Cannot open this document type. Please select a QuarkXPress document or template.
30 | QXP SERVER 9.2 WEB INTEGRATION GUIDE
Page 31
The "QuarkXPress Server Log.log" file also contains system-level log information. For
example, if a request makes a renderer stop working, you can figure out which request it
was using the transaction ID and the transaction log.
09/03/2011 014:00:07 ERROR
[com.quark.qxps.core.server.ServerRendererMonitor][pool-1-thread-1] - The
QuarkXPress Server Renderer with processId 2620 had quit while processing the
transaction 87212dae-6ba3-4b3f-97bb-ea8f0c255bf9.
To download all logs to a non-server computer, click Show Transaction Log in the
QuarkXPress Server Web interface, then click Download Logs on the upper right.
Understanding render types
Render types are namespaces you can use to return a QuarkXPress project in a specified file
format. The topics covered here include the following:
USING THE WEB INTERFACE
QuarkXPress Server Manager object model classesDescriptionFunction
ave
raw
Returns a .zip file containing an App Studio
AVE issue file and its corresponding manifest.
Returns an EPS file.eps
Returns an ePUB file.epub
Returns a JPEG image.jpeg
Returns a PDF file.pdf
Returns a PNG image.png
Returns a PostScript file.postscript
Returns a QuarkCopyDesk article.qcddoc
Returns a QuarkXPress project file.qxpdoc
Returns an RLE Raw Custom format image.qxpr
Returns a project in a QuarkXPress internal
format.
Returns a low-resolution PDF file.screenpdf
Returns a SWF file.swf
AVERenderRequest
EPSRenderRequest
EPubRenderRequest
JPEGRenderRequest
PDFRenderRequest
PNGRenderRequest
PostScriptRenderRequest
CopyDeskDocRequest
QuarkXPressRenderRequest
RLERawCustomRenderRequest
RawCustomRenderRequest
ScreenPDFRenderRequest
SWFRenderRequest
The default render type is JPEG.
Developers can implement additional rendering formats through server XTensions software.
ave
The ave render type returns a .zip file containing an App Studio AVE issue file and its
corresponding manifest.
QXP SERVER 9.2 WEB INTEGRATION GUIDE | 31
Page 32

USING THE WEB INTERFACE
Namespace
Parameters
Render modifier
parameters
AVE
outputstyle
format
layout
page
pages
stylename
String
String
range)
Lets you specify an output style. To
use a named output style, use the
name of that output style. For
example:
http://localhost:8080/ave/
sample.qxp?outputstyle=stylename
To use settings that have been
captured with the Capture Settings
in the QuarkXPress Export AVE for
iPad dialog box, use document. For
example:
http://localhost:8080/ave/
sample.qxp?outputstyle=document
Lets you specify an output format.
Use avemag for AVE-Mag or avedoc
for AVE-Doc. The default is avemag.
Lets you specify a layout by name
or ID. The first layout is Layout 1.
Lets you specify a page.Integer
Lets you specify a range of pages.String (page
Alerts
Example, GET URL
Example, object
model
A .zip file containing an App Studio AVE issue file and its corresponding manifest.Response
HTTP Error #406The renderer for this image type has no
way of rendering the desired objects.
This Output Style does not exist.
This Output Style cannot be used with
this render type.
select a QuarkXPress document or
template.
supported
See Understanding loggingLogs
http://localhost:8080/ave/sample.qxp?
format=avemag&layout=2
Request object name: AVERenderRequest
//STEP1: Create the QuarkXPress Server Request
//Context and set the necessary properties
com.quark.qxpsm.QRequestContext requestCtx =
new com.quark.qxpsm.QRequestContext();
This alert displays if you submit a render request with
the box parameter.
This alert displays if you specify a nonexistent output
style.
This alert displays if you specify an output style that
is incompatible with this render type.
HTTP Error #10120Cannot open this document type. Please
This alert displays if you submit an ave request for a
QuarkCopyDesk article.
HTTP Error #10545AVE-Doc for an App Studio layout is not
This alert displays if you submit an ave request with
format=avedoc for an App Studio layout.
32 | QXP SERVER 9.2 WEB INTEGRATION GUIDE
Page 33

eps
USING THE WEB INTERFACE
Boolean responseAsURL = false;
requestCtx.setDocumentName(docName);
//STEP 2(SPECIFIC TO REQUESTS):
//Create the AVE renderer
//request and embed it in the request context.
AVERenderRequest avereq = new AVERenderRequest();
avereq.setAVEData(request.getParameter("AVEData"));
avereq.setFormat(request.getParameter(
"Format"));
avereq.setLayout(request.getParameter(
"Layout"));
requestCtx.setRequest(avereq);
//STEP3: Create the WIG service and call the
//processRequest() API
RequestService service = new RequestServiceStub();
com.quark.qxpsm.QContentData data =
service.processRequest(requestCtx);
The default AVE output style is used.Notes
The eps render type returns an EPS rendering of a page or spread.
Namespace
Parameters
EPS
outputstyle
epsformat
epspreview
epsdata
epstransparent
stylename
color
tiff | none
ascii | binary |
clean8bit
1 | 0 | true | false
| yes | no
Lets you specify an output style. To
use a named output style, use the
name of that output style. For
example:
http://localhost:8080/pdf/
sample.qxp?outputstyle=stylename
To use settings that have been
captured with the Capture Settings
in the QuarkXPress Print dialog
box, use document. For example:
http://localhost:8080/pdf/
sample.qxp?outputstyle=document
Lets you specify an EPS format. The
default value is color.
Lets you include or omit a TIFF
preview. The default value is tiff.
Lets you specify a data type for the
EPS file. The default value is
clean8bit.
Lets you specify whether the EPS
can include transparent areas.
updateimage
true | false
Lets you specify whether to update
imported pictures.
QXP SERVER 9.2 WEB INTEGRATION GUIDE | 33
Page 34

USING THE WEB INTERFACE
Render modifier
parameters
updateflow
page
produceblankpages
scale
spread
layout
downloadlayoutFonts
true | false
1 | 0 | true | false
| yes | no
Float .1 to 6.92
for Windows .1
to 8 on Mac OS
Integer
String
1 | 0 | true | false
| yes | no
Lets you specify whether to update
the text flow version of a project to
the current version.
Lets you specify a page.Integer
Lets you specify whether to render
blank pages.
Lets you specify a scaling
percentage. The valid values are
from .1 (10%) to 8 (800%) on
Mac OS or 6.92 (692%) on
Windows.
Lets you specify a spread. The first
spread is spread 1. In a facing-page
document, spread 1 consists of the
first page.
Lets you specify a layout by name
or ID. The first layout is Layout 1.
Lets you specify whether to
download all fonts used in the
layout and all system fonts.
Alerts
Example, GET URL
Example, object
model
downloadImportedPdfEpsFonts
An EPS file.Response
way of rendering the desired objects.
This Output Style does not exist.
This Output Style cannot be used with
this render type.
See Understanding loggingLogs
http://localhost:8080/eps/sample.qxp?epsformat=
color&epsdata=clean8bit&epspreview=tiff&epsbleed=
0&epstransparent=0
Request object name: EPSRenderRequest
//STEP1: Create the QuarkXPress Server Request
//Context and set the necessary properties
com.quark.qxpsm.QRequestContext requestCtx =
new com.quark.qxpsm.QRequestContext();
Boolean responseAsURL = false;
requestCtx.setDocumentName(docName);
1 | 0 | true | false
| yes | no
HTTP Error #406The renderer for this image type has no
This alert displays if you submit a render request with
the pages or box parameter.
This alert displays if you specify a nonexistent output
style.
This alert displays if you specify an output style that
is incompatible with this render type.
Lets you specify whether to
download all fonts required by
imported PDF and EPS files.
//STEP 2(SPECIFIC TO REQUESTS):
//Create the EPS renderer
//request and embed it in the request context.
34 | QXP SERVER 9.2 WEB INTEGRATION GUIDE
Page 35

EPSRenderRequest epsreq = new EPSRenderRequest();
epsreq.setEPSData(request.getParameter("EPSData"));
epsreq.setEPSFormat(request.getParameter(
"EPSFormat"));
epsreq.setEPSPreview(request.getParameter(
"EPSPreview"));
requestCtx.setRequest(epsreq);
//STEP3: Create the WIG service and call the
//processRequest() API
RequestService service = new RequestServiceStub();
com.quark.qxpsm.QContentData data =
service.processRequest(requestCtx);
USING THE WEB INTERFACE
Notes
epub
Namespace
Render modifier
parameters
Alerts
You can specify an output style and set additional local parameters of that output style. For
example, if no bleed setting is specified in the output style named "mystylename", you can
specify a bleed setting with a URL like the following:
http://localhost:8080/eps/sample.qxp?
outputstyle=mystylename?bleed=symmetric
You can override settings in an output style. For example, if an asymmetric bleed is specified
in the output style named "mystylename," you could override it with the same URL.
If you do not specify an EPS output style, the default EPS output style is used.
The epub render type returns an ePUB rendering of a layout or layout family.
ePUB
layout
outputstyle
An ePUB (.epub) file.Response
way of rendering the desired objects.
String
String
HTTP Error #406The renderer for this image type has no
This alert displays if you submit a render request with
the pages or box parameter.
Lets you specify a layout by name
or ID. The first layout is Layout 1.
Lets you specify an ePUB output
style by name or ID.
Example, GET URL
Example, object
model
HTTP Error #10543ePub not created. There is no reflow
layout in the document.
See Understanding loggingLogs
http://localhost:8080/epub/sample.qxp?
outputstyle=epub1&layout=2
Request object name: EPubRenderRequest
//STEP1: Create the QuarkXPress Server Request
//Context and set the necessary properties
com.quark.qxpsm.QRequestContext requestCtx =
new com.quark.qxpsm.QRequestContext();
Boolean responseAsURL = false;
requestCtx.setDocumentName(docName);
//STEP 2(SPECIFIC TO REQUESTS):
This error appears if there is no reflow layout.
QXP SERVER 9.2 WEB INTEGRATION GUIDE | 35
Page 36

USING THE WEB INTERFACE
jpeg
The jpeg render type returns a JPEG rendering of a page or spread.
//Create the ePUB renderer
//request and embed it in the request context.
EPubRenderRequest epubreq = new EPubRenderRequest();
epubreq.setEPubData(request.getParameter("EPubData"));
epubreq.setCreateTOC(request.getParameter(
"CreateTOC"));
epubreq.setLayout(request.getParameter(
"Layout"));
requestCtx.setRequest(epubreq);
//STEP3: Create the WIG service and call the
//processRequest() API
RequestService service = new RequestServiceStub();
com.quark.qxpsm.QContentData data =
service.processRequest(requestCtx);
You can only create an ePUB file from a project that includes a reflow article.Notes
Namespace
Parameters
Render
modifier
parameters
JPEG
jpegquality
upadateimage
updateflow
pasteboard
showboxoutline
boxes
page
scale
1 | 2 | 3 | 4
true | false
true | false
true | false
Float .1 to 6.92 for
Windows .1 to 8
on Mac OS)
Lets you specify the image quality of a rendered JPEG
image. The valid values are: 1 (highest quality), 2 (high
quality), 3 (medium quality), and 4 (lowest quality). The
default value is 1.
Lets you specify whether to update imported pictures.true | false
Lets you specify whether to update the text flow version
of a project to the current version.
Lets you specify whether to display pasteboard items.
Works only with spread parameter. The default value is
true. For example:
http://localhost:8080/jpeg/document.qxp?
spread=1&pasteboard=true
Lets you specify whether to include bounding box outlines
in the response JPEG image even if the boxes have no
content.. The default value is false.
Lets you request multiple boxes.String
Lets you request a single page.Integer
Lets you specify a scaling percentage. The valid values are
from .1 (10%) to 8 (800%) on Mac OS or 6.92 (692%) on
Windows.
box
spread
layout
Integer
String
36 | QXP SERVER 9.2 WEB INTEGRATION GUIDE
Lets you request a single box.String
Lets you specify a spread. The first spread is spread 1. In a
facing-page document, spread 1 consists of the first page.
Lets you specify a layout by name or ID. The first layout
is Layout 1.
Page 37

USING THE WEB INTERFACE
A JPEG file.Response
See Understanding loggingLogs
Example, GET
URL
Example,
object model
literal
http://localhost:8080/jpeg/sample.qxp?jpegquality=1
Request object name: JPEGRenderRequest
// STEP1: Create the QuarkXPress Server Request
// Context and set the necessary properties
com.quark.qxpsm.QRequestContext requestCtx =
new com.quark.qxpsm.QRequestContext();
Boolean responseAsURL = false;
requestCtx.setDocumentName(docName);
// STEP2: Create the JPEG renderer request and attach it
// to the request context.
JPEGRenderRequest jpreq = new JPEGRenderRequest();
jpreq.setJPEGQuality(request.getParameter("jpegQuality"));
jpreq.setLayout(request.getParameter("Layout"));
requestCtx.setRequest(jpreq);
// STEP3: Create the WIG service and call the processRequest() API
RequestService service = new RequestServiceStub();
com.quark.qxpsm.QContentData data = service.processRequest(requestCtx);
The literal render type returns the contents of a file without any attempt to process it
as a template. Depending on the file's MIME type, the requested project can be displayed
within the browser (for example, if the response is a JPEG file) or saved to disk (for example,
if the response is a Microsoft Word document).
Namespace
Alerts
Example, GET URL
Example, object
model
literal
The requested file returned in the HTTP response.Response
Incorrect
administration
realm username
and password.
See Understanding loggingLogs
http://localhost:8080/literal/Story.doc
Request object name: LiteralRequest
com.quark.qxpsm.QRequestContext rc =
new com.quark.qxpsm.QRequestContext();
if(!this.DocumentSettings1.documentName.Text.Equals(""))
rc.documentName = this.DocumentSettings1.documentName.Text;
rc.request = new LiteralRequest();
//Create the service and call it with QRequestContext object
RequestService svc = new RequestService();
com.quark.qxpsm.QContentData qc = svc.processRequest(rc);
HTTP Error #401
This alert displays if you specify an invalid administrator user name and
password.
What to do: Use the user name and password set in the Authentication pane
of the General Preferences dialog box (Administration > Preferences >
General) in the QuarkXPress Server Web interface.
QXP SERVER 9.2 WEB INTEGRATION GUIDE | 37
Page 38

USING THE WEB INTERFACE
pdf
The pdf render type returns a PDF rendering of a project.
Namespace
Parameters
PDF
outputstyle
title
subject
author
keywords
includehyperlinks
exportlistsashyperlinks
stylename,
document
1 | 0 | true |
false | yes | no
1 | 0 | true |
false | yes | no
Lets you specify an output style. To use a named
output style, use the name of that output style.
For example:
http://localhost:8080/pdf/
sample.qxp?outputstyle=stylename
To use settings that have been captured with the
Capture Settings in the QuarkXPress Export as
PDF dialog box, use document. For example:
http://localhost:8080/pdf/
sample.qxp?outputstyle=document
Lets you specify the title of the PDF file.String
Lets you specify the subject of the PDF file.String
Lets you specify the author of the PDF file.String
Lets you specify keywords for the PDF file.String
Lets you specify whether to include hyperlinks
in the PDF file.
Lets you specify whether to export lists as
hyperlinks. To use this parameter, you must set
includehyperlinks to true.
exportindexesashyperlinks
exportlistsasbookmarks
mode
printcolors
plates
produceblankpages
useopi
1 | 0 | true |
false | yes | no
1 | 0 | true |
false | yes | no
composite or
separations
cmyk, rgb,
grayscale,
cmykandspot,
asis
inripseps
1 | 0 | true |
false | yes | no
false | yes | no
Lets you specify whether to export the index as
hyperlinks. To use this parameter, you must set
includehyperlinks to true.
Lets you specify whether to export lists as
bookmarks. To use this parameter, you must set
includehyperlinks to true.
Lets you specify whether the PDF file is a
composite or includes separations.
Lets you specify the color space of the PDF file.
This option is available only when mode is set to
composite.
Lets you specify a separation method. This option
is available only when mode is set to
separations.
Lets you specify whether to include blank pages.
This option is available only when mode is set to
composite.
Lets you specify whether to use OPI.1 | 0 | true |
38 | QXP SERVER 9.2 WEB INTEGRATION GUIDE
Page 39

USING THE WEB INTERFACE
images
registration
offset
bleed
offsetbleed
spreads
lowresolution
colorimagedownsample
grayscaleimagedownsample
includeimages,
omittiff,
omittiffandeps
off, centered,
offcenter
points)
symmetric
0–6 (in inches)
false | yes | no
false | yes | no
9–2400
Lets you specify whether to include TIFF and EPS
images from an OPI server.
Lets you include, omit, and configure registration
marks.
Lets you specify the offset of registration marks.0–30 (in
Lets you specify a bleed type.pageitemsonly,
Lets you specify a bleed offset to use. This option
is available only when bleed is set to
symmetric.
Lets you specify whether to output spreads.1 | 0 | true |
Lets you request a low-resolution (36 dpi) PDF.1 | 0 | true |
Lets you specify the resolution of color images.9–2400
Lets you specify the resolution of grayscale
images.
monochromeimagedownsample
colorcompression
grayscalecompression
monochromecompression
pdffile
psfile
thumbnail
mode
9–2400
true | false
true | false
true | false
String
String
separations
Lets you specify the resolution of monochrome
images.
Lets you specify whether medium-quality manual
JPEG compression should be applied to color
images.
Lets you specify whether medium-quality manual
JPEG compression should be applied to grayscale
images.
Lets you specify whether ZIP compression should
be applied to monochrome images.
Lets you specify the PDF name. This option is
available only when PDF to Folder is selected in
QuarkXPress Server PDF preferences.
Lets you specify the PostScript file name. This
option is available only when PostScript for later
Distilling is selected in QuarkXPress Server PDF
preferences.
Lets you embed a thumbnail in the PDF file.bw | color
Lets you specify the PDF file's color mode.composite |
fontdownload
yes | no
Lets you turn font download on or off. You
cannot specify which fonts are downloaded.
QXP SERVER 9.2 WEB INTEGRATION GUIDE | 39
Page 40

USING THE WEB INTERFACE
layers
verification
separate
produceblankplates
download
layoutstart
String
yes | no
1 | 0 | true |
false
1 | 0 | true |
false | yes | no
Lets you specify which layers should be included,
as a comma-separated list.
Lets you use PDF/X–1a or PDF/X–3 verification.pdfx1a | pdfx3
Lets you specify whether to output each page as
a separate file.
Lets you specify whether to include blank plates.yes | no
When download is true, the browser always
displays a dialog box that lets the end user save
the returned file, even if the browser can display
it.
When download is false, the browser attempts
to display the returned file. If the browser cannot
display the file, it lets the end user save the
returned file.
The default value is false.
Lets you specify the number of the first layout
to render when you render multiple layouts as
separate PDF files. PDF files are saved at the
location specified in QuarkXPress Server
preferences (Administration > Preference >
General > Server > Document Root Folder). The
first layout in a project is layout 0. For example:
http://localhost:8080/pdf/multilayout.qxp?
layoutstart=0&layoutend=3
Render modifier
parameters
layoutend
updateimage
updateflow
page
pages
spread
layout
Integer
true | false
true | false
range)
Integer
String
Lets you specify the number of the last layout to
render when you render multiple layouts as
separate PDF files. PDF files are saved at the
location specified in QuarkXPress Server
preferences (Administration > Preference >
General > Server > Document Root Folder). The
first layout in a project is layout 0. For example:
http://localhost:8080/pdf/multilayout.qxp?
layoutstart=0&layoutend=3
Lets you specify whether to update imported
pictures.
Lets you specify whether to update the text flow
version of a project to the current version.
Lets you specify a single page.Integer
Lets you specify a range of pages.String (page
Lets you specify a spread. The first spread is
spread 1. In a facing-page document, spread 1
consists of the first page.
Lets you specify a layout by name or ID. The first
layout is Layout 1.
40 | QXP SERVER 9.2 WEB INTEGRATION GUIDE
Page 41

USING THE WEB INTERFACE
Example, GET
URL
spreads
true | false | yes
| no
A PDF file.Response
HTTP Error #500This page range is invalidAlerts
QuarkXPress Server Error #147
Lets you specify that the output use spreads.Boolean 1 | 0 |
This alert displays if you try to render an invalid page
range.
HTTP Error #500No file produced. The project
requested contains only blank
pages.
This Output Style cannot be
used with this render type.
See Understanding loggingLogs
This URL renders "sample.qxp" as a PDF with a symmetric bleed:
http://localhost:8080/pdf/sample.qxp?
bleed=symmetric&offsetbleed=2
This URL renders a PDF in which color images are downsampled to a resolution of 300 dpi and
manual medium-quality JPEG compression is applied:
http://localhost:8080/pdf/sample.qxp?
colorimagedownsample=300&colorcompression=true
This alert displays if you try to render a a project that
contains only blank pages.
This alert displays if you specify a nonexistent output style.This Output Style does not exist.
This alert displays if you specify an output style that is
incompatible with this render type.
Example, object
model
Request object name: PDFRenderRequest
// STEP1: Create the QuarkXPress Server Request Context
// and set the nescessary properties
com.quark.qxpsm.QRequestContext requestCtx =
new com.quark.qxpsm.QRequestContext();
Boolean responseAsURL = false;
requestCtx.setDocumentName(docName);
// STEP 2(SPECIFIC TO REQUESTS):
// Create the PDF renderer request
// and embed it in the request context.
PDFRenderRequest pdfreq = new PDFRenderRequest();
pdfreq.setAuthor(request.getParameter("Author"));
pdfreq.setTitle(request.getParameter("Title"));
pdfreq.setLayout(request.getParameter("Layout"));
pdfreq.setSpread(request.getParameter("Spread"));
pdfreq.setPage(request.getParameter("mPage"));
pdfreq.setPages(request.getParameter("Pages"));
if( strLowResolution !=null &&
strLowResolution.equals("True"))
pdfreq.setLowResolution("true");
requestCtx.setRequest(pdfreq);
// STEP3: Create the WIG service and
// call the processRequest() API
RequestService service = new RequestServiceStub();
com.quark.qxpsm.QContentData data =
service.processRequest(requestCtx);
For more information about the object model, see the samples.
QXP SERVER 9.2 WEB INTEGRATION GUIDE | 41
Page 42
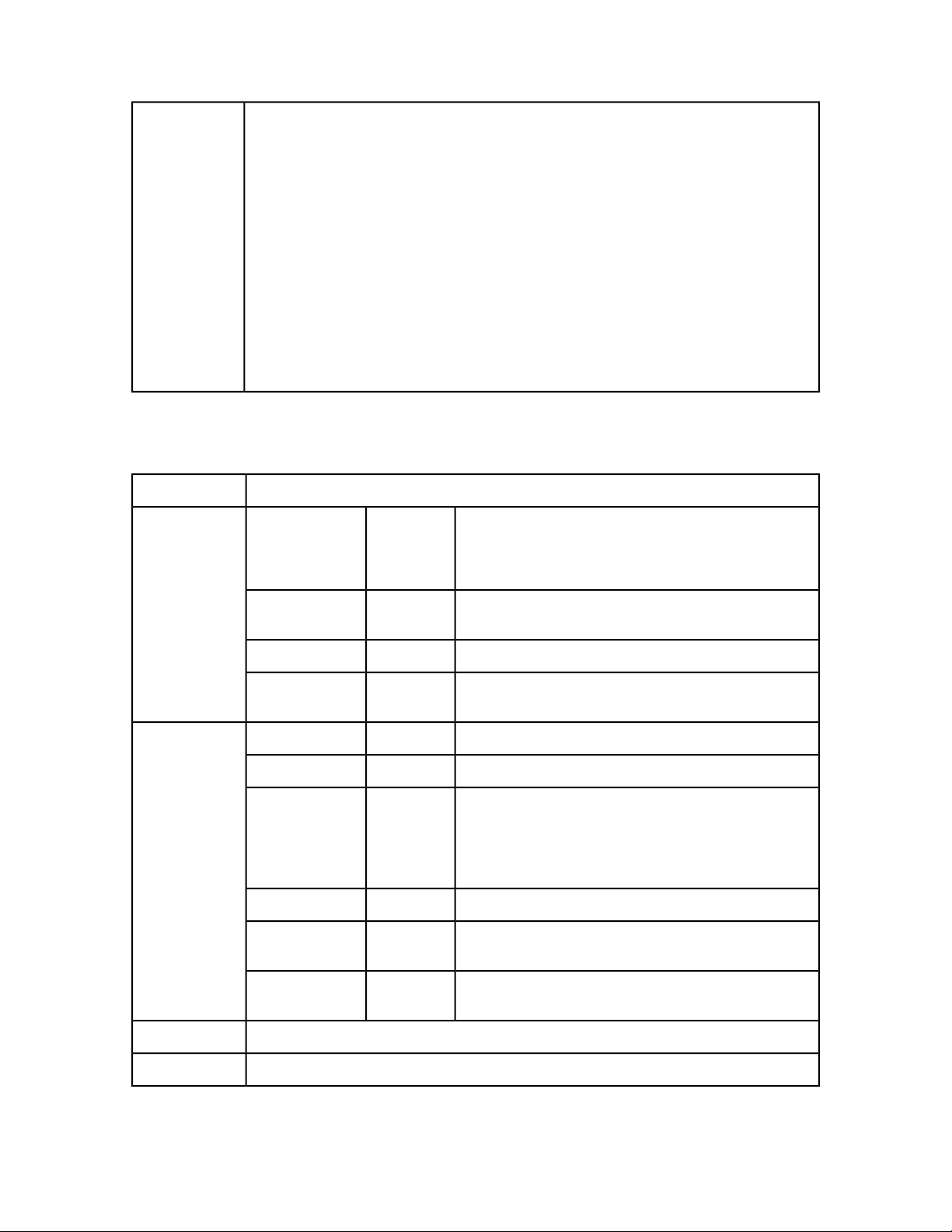
USING THE WEB INTERFACE
Notes
Namespace
Parameters
png
There are three ways to generate PDF files with QuarkXPress Server. You can generate a PDF file in
QuarkXPress Server and return it to the end user, generate the PDF in QuarkXPress server and save
it to a folder on the server computer, or generate a PostScript file for later distilling and save it to
a folder on the server computer. To choose one of these output methods in QuarkXPress Server,
choose Administration > Preferences > Renderer > PDF) and then click DirectPDF, PDFtoFolder,
or PS4D (PostScript for Later Distilling). If you choose either of the last two options, click Browse
and navigate to the target folder, then choose an option from the Default Name drop-down menu.
You can specify an output style and set additional local parameters of that output style. For example,
if no bleed setting is specified in the output style named "mystylename", you can specify a bleed
setting with a URL like the following:
http://localhost:8080/pdf/sample.qxp?
outputstyle=mystylename&bleed=symmetric
You can override settings in an output style. For example, if an asymmetric bleed is specified in
the output style named "mystylename," you could override it with the same URL.
If you do not specify a PDF output style, the default PDF output style is used.
The png render type returns a PNG rendering of a page or spread.
PNG
pngcompression
1 | 2 | 3 | 4
Lets you specify the compression of a PNG response. The valid
values are: 1 (lowest compression), 2 (medium compression),
3 (high compression), and 4 (highest compression). The default
value is 1.
Render modifier
parameters
transparentpng
upadateimage
updateflow
boxes
page
scale
box
spread
layout
A PNG file.Response
true | false
true | false
Float .1 to
6.92 for
Windows .1
to 8 on
Mac OS
Integer
String
Lets you specify whether to generate a PNG file that uses
transparency.
Lets you specify whether to update imported pictures.true | false
Lets you specify whether to update the text flow version of a
project to the current version.
Lets you request multiple boxes.String
Lets you specify a single page.Integer
Lets you specify a scaling percentage. The valid values are
from .1 (10%) to 8 (800%) on Mac OS or 6.92 (692%) on
Windows.
Lets you request a single box.String
Lets you specify a spread. The first spread is spread 1. In a
facing-page document, spread 1 consists of the first page.
Lets you specify a layout by name or ID. The first layout is
Layout 1.
See Understanding loggingLogs
42 | QXP SERVER 9.2 WEB INTEGRATION GUIDE
Page 43

USING THE WEB INTERFACE
Example, GET
URL
Example, object
model
postscript
http://localhost:8080/png/sample.qxp?pngcompression=1
Request object name: PNGRenderRequest
// STEP1: Create the QuarkXPress Server Request
// Context and set the nescessary properties
com.quark.qxpsm.QRequestContext rc =
new com.quark.qxpsm.QRequestContext();
Boolean responseAsURL = false;
rc.setDocumentName(docName);
// STEP 2(SPECIFIC TO REQUESTS):Create the PNG renderer
// request and embed it in the request context.
PNGRenderRequest pngreq = new PNGRenderRequest();
pngreq.setPNGCompression(request.getParameter(
"PNGCompression"));
pngreq.setLayout(request.getParameter("Layout"));
pngreq.setSpread(request.getParameter("Spread"));
pngreq.setPage(request.getParameter("mPage"));
rc.setRequest(pngreq);
// STEP3: Create the WIG service and call the processRequest() API
RequestService service = new RequestServiceStub();
com.quark.qxpsm.QContentData data = service.processRequest(rc);
The postscript render type returns a PostScript rendering of a project.
Namespace
Parameters
PostScript
prntbleed
outputstyle
clip<Boolean>,
top<float>,
bottom<float>,
left<float>,
right<float> | sym,
clip<Boolean>,
amount<float>
stylename,
document
Lets you specify bleed values for a page.Page | asym,
To specify an asymmetric bleed, use the following format:
prntbleed=asym,clip,top,bottom,
left, right
The clip value is Boolean (yes/no). The top, bottom, left,
and right values are float values. For example:
http://localhost:8080/
postscript/Sample.qxp?
prntbleed=asym,true,1,2,2,1
The above example results in an asymmetric bleed of 1 on
the top, 2 on the bottom, 2 on the left, and 1 on the right.
To specify a symmetric bleed, use the following format:
prntbleed=sym,clip,amount
The clip value is Boolean (yes/no). The amount value is a
float value. For example:
http://localhost:8080/
postscript/Sample.qxp?
prntbleed=sym,true,1
The above example results in a symmetric bleed of 1 on all
sides. Default: prntbleed=sym,yes,0
Lets you specify an output style. To use a named output
style, use the name of that output style. For example:
http://localhost:8080/
postscript/
sample.qxp?outputstyle=stylename
QXP SERVER 9.2 WEB INTEGRATION GUIDE | 43
Page 44

USING THE WEB INTERFACE
To use settings that have been captured with the Capture
Settings in the QuarkXPress Print dialog box, use
document. For example:
http://localhost:8080/
postscript/
sample.qxp?outputstyle=document
Render modifier
parameters
Alerts
updateimage
updateflow
page
pages
spread
layout
A PostScript file.Response
invalid.
The document
requested contains
only blank pages.
Lets you specify whether to update imported pictures.true | false
true | false
range)
Integer
String
HTTP Error #500This page range is
QuarkXPress Server Error #147
This alert displays if you try to render an invalid page range.
HTTP Error #500No file produced.
This alert displays if you try to render a a project that contains only blank pages.
Lets you specify whether to update the text flow version of
a project to the current version.
Lets you specify a single page.Integer
Lets you specify a range of pages.String (page
Lets you specify a spread. The first spread is spread 1. In a
facing-page document, spread 1 consists of the first page.
Lets you specify a layout by name or ID. The first layout is
Layout 1.
Example, GET
URL
Example, object
model
HTTP Error #500PostScript printer
mapped to file not
found
does not exist.
This Output Style
cannot be used
with this render
type.
See Understanding loggingLogs
http://localhost:8080/postscript/Sample.qxp
Request object name: PostScriptRenderRequest
// STEP1: Create the QuarkXPress Server Request
// Context and set the nescessary properties
com.quark.qxpsm.QRequestContext requestCtx =
new com.quark.qxpsm.QRequestContext();
Boolean responseAsURL = false;
requestCtx.setDocumentName(docName);
This alert displays if the PostScript printer or driver is not set to Print to File.
This alert displays if you specify a nonexistent output style.This Output Style
This alert displays if you specify an output style that is incompatible with this
render type.
44 | QXP SERVER 9.2 WEB INTEGRATION GUIDE
Page 45
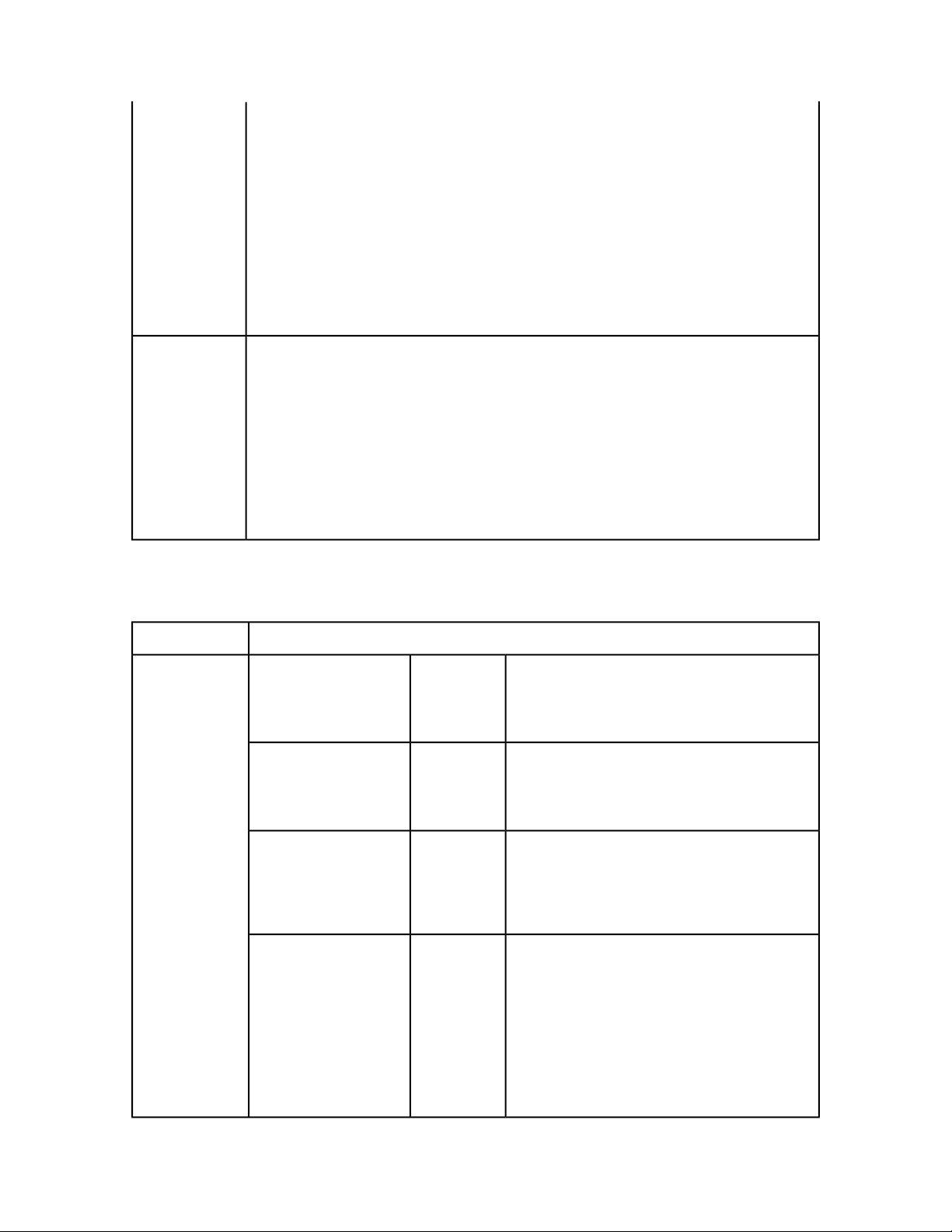
USING THE WEB INTERFACE
// STEP 2(SPECIFIC TO REQUESTS):
// Create the Post Script renderer
// request and embed it in the request context.
PostScriptRenderRequest pscreq =
new PostScriptRenderRequest();
pscreq.setPrintBleed(request.getParameter("PrintBleed"));
pscreq.setPrintPPD(request.getParameter("PrintPPD"));
pscreq.setPages(request.getParameter("Pages"));
requestCtx.setRequest(pscreq);
// STEP3: Create the WIG service and call the
// processRequest() API
RequestService service = new RequestServiceStub();
com.quark.qxpsm.QContentData data = service.processRequest(requestCtx);
To create a PostScript file, you must have a PostScript driver on the server computer.Notes
You can specify an output style and set additional local parameters of that output style. For example,
if no bleed setting is specified in the output style named "mystylename", you can specify a bleed
setting with a URL like the following:
http://localhost:8080/eps/sample.qxp?
outputstyle=mystylename&bleed=symmetric
You can override settings in an output style. For example, if an asymmetric bleed is specified in
the output style named "mystylename," you could override it with the same URL.
If you do not specify a PostScript-compatible output style, the default PostScript-compatible output
style is used.
Namespace
Parameters
qcddoc
The qcddoc render type returns a QuarkCopyDesk article.
qcddoc
article
component
format
saveastemplate
String
String
lightweight |
fullfeatured
true | false
Lets you specify which article in a project to render.
For example:
http://localhost:8080/qcddoc/
abc.qxp?article=article1
Lets you specify which component in an article to
render. For example:
http://localhost:8080/copydesk/
abc.qcd?component=comp1
Lets you render an article in lightweight or
full-featured format. For example:
http://localhost:8080/qcddoc/
abc.qxp?article=article1&
format=fullfeatured
Lets you save a copy of an article that was created in
QuarkCopyDesk as a template. The default value is
true. For example:
http://QXPServer8:8080/saveas/
qcddoc/article.qcd?saveastemplate=true
You can also use this parameter to save a copy of a
template as an article. For example:
http://QXPServer8:8080/saveas/
qcddoc/template.qct?saveastemplate=false
QXP SERVER 9.2 WEB INTEGRATION GUIDE | 45
Page 46
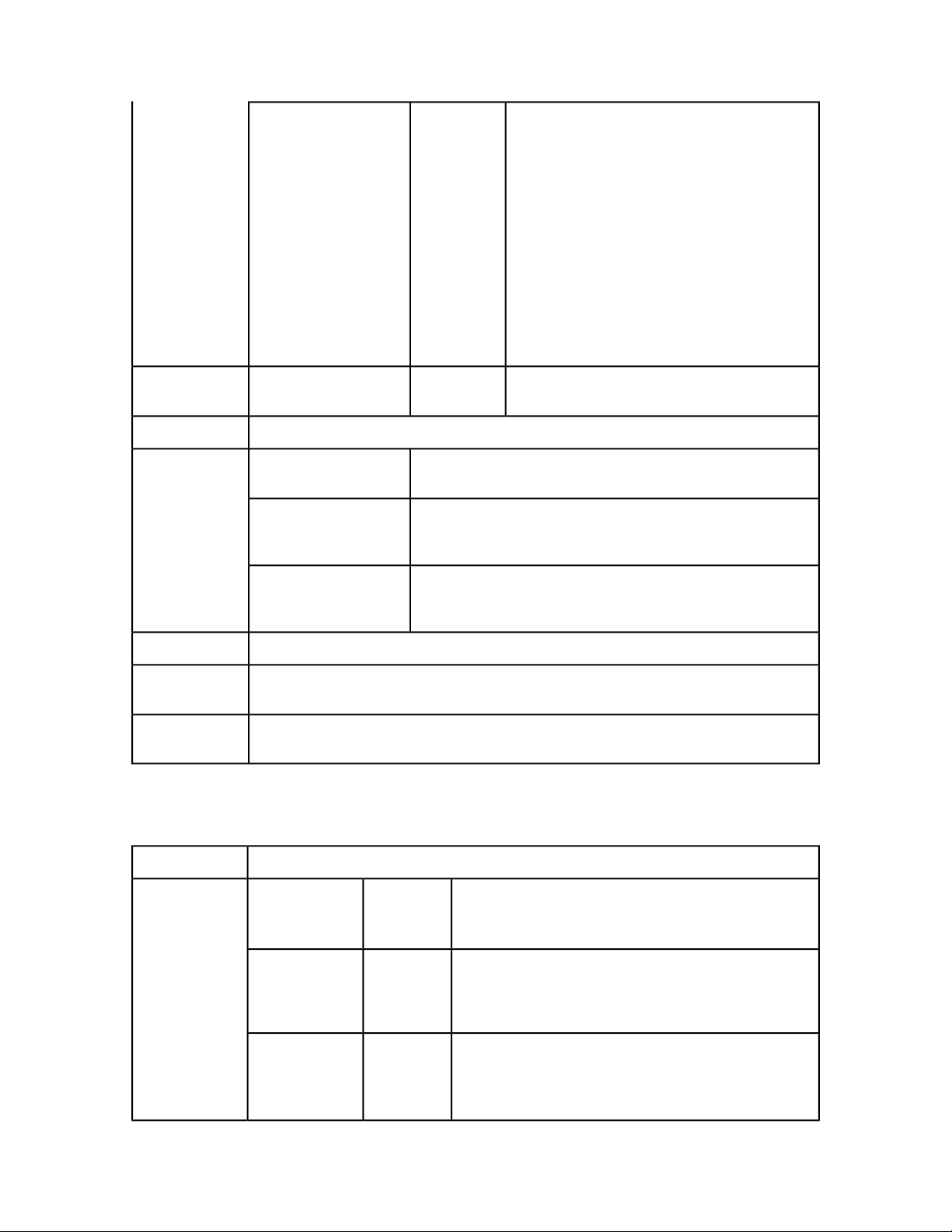
USING THE WEB INTERFACE
Render modifier
parameters
Alerts
includepagepicture
A QuarkCopyDesk article.Response
There is no box with the
specified identifier.
in the article name can't be
greater than max limit.
true | false | 1 |
0
XMLmodify
This alert displays if the box corresoponding to a referenced component
does not exist.
This alert displays if an article name is longer than 32 characters.The number of characters
Lets you include a page picture when you export an
article from a QuarkXPress layout. Valid options are:
picformat (embedded or separate)
quality (blackandwhite or color)
picdpi (72, 144, or 200)
spreadrange (all or first)
For example:
http://localhost:8080/saveas/qcddoc/
4.qxp?includepagepicture=1&
quality=blackandwhite&picdpi=144&
spreadrange=first
http://localhost:8080/saveas/qcddoc/
PagePicture.qxp?includepagepicture=true
Lets you modify the article with XML. For more
information, see "Using XML modify."
Example, GET
URL
Example, object
model
qxpdoc
Namespace
Parameters
The article/component
name is not unique.
See Understanding loggingLogs
http://localhost:8080/qcddoc/copydesk/sample.qcd
Request object name: CopyDeskDocRequest
This alert displays if you create or change the name of an article or
component so that it is the same as the name of an existing article or
component.
The qxpdoc render type returns a QuarkXPress project.
qxpdoc
qxpdocver
upadateimage
8 | 9
true | false
Indicates the QuarkXPress version format to use. For example:
http://localhost:8080/qxpdoc/
construct/project1.qxp?qxpdocver=8
Lets you specify whether to return modified pictures in the
response or not. If set to false, modified pictures are not
returned. If set to true, modified pictures are returned. The
default value is true.
saveastemplate
true | false
46 | QXP SERVER 9.2 WEB INTEGRATION GUIDE
Lets you save a copy of a project as a template. The default
value is true. For example:
http://localhost:8080/saveas/
qxpdoc/project.qxp?saveastemplate=true
Page 47
USING THE WEB INTERFACE
You can also use this parameter to save a copy of a template as
a project. For example:
http://localhost:8080/saveas/
qxpdoc/template.qpt?saveastemplate=false
Render modifier
parameters
Alerts
Example, GET
URL
Example, object
model
layout
A QuarkXPress project.Response
document return
is disabled.
this image type
has no way of
rendering the
desired objects.
QuarkXPress
Project down to an
earlier version.
See Understanding loggingLogs
http://localhost:8080/qxpdoc/sample.qxp
Request object name: QuarkXPressRenderRequest
// STEP1: Create the QuarkXPress Server Request
// Context and set the nescessary properties
com.quark.qxpsm.QRequestContext requestCtx =
new com.quark.qxpsm.QRequestContext();
Boolean responseAsURL = false;
requestCtx.setDocumentName(docName);
String
HTTP Error #500QuarkXPress
This alert displays if Disable QXD Return is checked in the QuarkXPress Server
administration interface (Administration > Preferences > General > Server).
HTTP Error #406The renderer for
This alert displays if you submit a qxpdoc render request with the page, pages,
box, or spread parameter.
HTTP Error #500Cannot save a
This alert displays if you attempt to save a QuarkXPress 6.x project to an earlier
version of QuarkXPress with the qxpdocver parameter.
Lets you specify a layout by name or ID. The first layout is
Layout 1.
// STEP 2(SPECIFIC TO REQUESTS):Create the QuarkXPress
// renderer request and embed it in the request context.
QuarkXPressRenderRequest qxpreq = new
QuarkXPressRenderRequest();
qxpreq.setDocumentVersion(request.getParameter(
"XpressDocVersion"));
qxpreq.setLayout(request.getParameter("Layout"));
requestCtx.setRequest(qxpreq);
// STEP3: Create the WIG service and call the processRequest() API
RequestService service = new RequestServiceStub();
com.quark.qxpsm.QContentData data = service.processRequest(requestCtx);
screenpdf
The screenpdf render type returns a low-resolution PDF rendering of a project. This
render type overrides the PDF Workflow setting in the QuarkXPress Server administration
interface (Administration > Preferences > Renderer > PDF) and always sends the PDF
file to the browser.
QXP SERVER 9.2 WEB INTEGRATION GUIDE | 47
Page 48

USING THE WEB INTERFACE
Namespace
Parameters
Screenpdf
outputstyle
title
subject
author
keywords
includehyperlinks
exportlistsashyperlinks
stylename
1 | 0 | true | false |
yes | no
1 | 0 | true | false |
yes | no
Lets you specify an output style. To use a named
output style, use the name of that output style.
For example:
http://localhost:8080/screenpdf/
sample.qxp?outputstyle=stylename
To use settings that have been captured with the
Capture Settings in the QuarkXPress Print dialog
box, use document. For example:
http://localhost:8080/screenpdf/
sample.qxp?outputstyle=document
Lets you specify the title of the PDF file.String
Lets you specify the subject of the PDF file.String
Lets you specify the author of the PDF file.String
Lets you specify keywords of the PDF file.String
Lets you specify whether to include hyperlinks
in the PDF file.
Lets you specify whether to export lists as
hyperlinks. To use this parameter, you must set
includehyperlinks to true.
exportindexesashyperlinks
exportlistsasbookmarks
mode
printcolors
plates
produceblankpages
useopi
images
1 | 0 | true | false |
yes | no
1 | 0 | true | false |
yes | no
composite or
separations
cmyk, rgb,
grayscale,
cmykandspot, asis
inripseps
1 | 0 | true | false |
yes | no
yes | no
includeimages,
omittiff,
omittiffandeps
Lets you specify whether to export the index as
hyperlinks. To use this parameter, you must set
includehyperlinks to true.
Lets you specify whether to export lists as
bookmarks. To use this parameter, you must set
includehyperlinks to true.
Lets you specify whether the PDF file is a
composite or includes separations.
Lets you specify the color space of the PDF file.
This option is available only when mode is set to
composite.
Lets you specify a separation method. This option
is available only when mode is set to
separations.
Lets you specify whether to include blank pages.
This option is available only when mode is set to
composite.
Lets you specify whether to use OPI.1 | 0 | true | false |
Lets you specify whether to include TIFF and EPS
images from an OPI server.
48 | QXP SERVER 9.2 WEB INTEGRATION GUIDE
Page 49

USING THE WEB INTERFACE
registration
offset
bleed
offsetbleed
spreads
lowresolution
colorimagedownsample
grayscaleimagedownsample
monochromeimagedownsample
colorcompression
off, centered,
offcenter
symmetric
0–6 (in inches)
yes | no
yes | no
9–2400
9–2400
true | false
Lets you include, omit, and configure registration
marks.
Lets you specify the offset of registration marks.0–30 (in points)
Lets you specify a bleed type.pageitemsonly,
Lets you specify a bleed offset to use. This option
is available only when bleed is set to symmetric.
Lets you specify whether to output spreads.1 | 0 | true | false |
Lets you request a low-resolution (36 dpi) PDF.1 | 0 | true | false |
Lets you specify the resolution of color images.9–2400
Lets you specify the resolution of grayscale
images.
Lets you specify the resolution of monochrome
images.
Lets you specify whether medium-quality manual
JPEG compression should be applied to color
images.
grayscalecompression
monochromecompression
pdffile
psfile
thumbnail
mode
fontdownload
layers
transparencyres
true | false
true | false
String
String
separations
yes | no
String
Integer value from
36 to 3600
Lets you specify whether medium-quality manual
JPEG compression should be applied to grayscale
images.
Lets you specify whether ZIP compression should
be applied to monochrome images.
Lets you specify the PDF name. This option is
available only when PDF to Folder is selected in
QuarkXPress Server PDF preferences.
Lets you specify the PostScript file name. This
option is available only when PostScript for later
Distilling is selected in QuarkXPress Server PDF
preferences.
Lets you embed a thumbnail in the PDF file.bw | color
Lets you specify the PDF file's color mode.composite |
Lets you turn font download on or off. You
cannot specify which fonts are downloaded.
Lets you specify which layers should be included,
as a comma-separated list.
Lets you specify the resolution for flattened
content.
verification
Lets you use PDF/X–1a or PDF/X–3 verification.pdfx1a | pdfx3
QXP SERVER 9.2 WEB INTEGRATION GUIDE | 49
Page 50

USING THE WEB INTERFACE
Render
modifier
parameters
separate
produceblankplates
updateimage
updateflow
page
pages
spread
layout
spreads
A screen-resolution PDF fileResponse
yes | no
true | false
true | false
Integer
String
| false | yes | no)
HTTP Error #500This page range is invalid.Alerts
QuarkXPress Server Error #147
This alert displays if you try to render an invalid page range.
Lets you specify whether to output each page as
a separate file.
Lets you specify whether to include blank plates.yes | no
Lets you specify whether to update imported
pictures.
Lets you specify whether to update the text flow
version of a project to the current version.
Lets you specify a single page.Integer
Lets you specify a range of pages.String (page range)
Lets you specify a spread. The first spread is spread
1. In a facing-page document, spread 1 consists
of the first page.
Lets you specify a layout by name or ID. The first
layout is Layout 1.
Lets you specify that the output use spreads.Boolean (1 | 0 | true
Example, GET
URL
Example,
object model
HTTP Error #500No file produced. The
document requested contains
only blank pages.
See Understanding loggingLogs
http://localhost:8080/screenpdf/sample.qxp?
colorimagedownsample=72&colorcompression=0
Request object name: ScreenPDFRenderRequest
// STEP1: Create the QuarkXPress Server Request Context
// and set the nescessary properties
com.quark.qxpsm.QRequestContext requestCtx =
new com.quark.qxpsm.QRequestContext();
String docName = request.getParameter("documentName") ;
requestCtx.setDocumentName(docName);
// STEP 2(SPECIFIC TO REQUESTS):
// Create the QuarkXPress renderer
// request and embed it in the request context.
ScreenPDFRenderRequest screenpdfRequest = new
ScreenPDFRenderRequest();
screenpdfRequest.setColorImageDownSample(
request.getParameter("ColorImageDownSample"));
screenpdfRequest.setCompression(request.getParameter(
"Compression"));
requestCtx.setRequest(screenpdfRequest);
This alert displays if you try to render a a project that contains only
blank pages.
// STEP3: Create the WIG service and
50 | QXP SERVER 9.2 WEB INTEGRATION GUIDE
Page 51

// call the processRequest() API
RequestService service = new RequestServiceStub();
com.quark.qxpsm.QContentData data =
service.processRequest(requestCtx);
swf
The swf render type returns a SWF (Flash) rendering of a Print layout or an Interactive
layout.
SWFNamespace
USING THE WEB INTERFACE
Parameters
version
layout
page
pages
fullscreen
embedallfonts
compressswf
compressaudio
jpegquality
download
swf6 | swf7
string
true | false
true | false
true | false
true | false
1–100
true | false
Lets you specify the minimum compatible
version of Flash Player.
Lets you specify a layout by name or ID. The first
layout is Layout 1.
Lets you specify a single page.string
Lets you specify a range of pagesstring
Lets you specify whether the SWF file should run
in full-screen mode by default.
Lets you indicate whether to include any fonts
that are necessary to correctly render text in Text
Box objects within the exported SWF file
Lets you specify whether to compress the
exported file.
Lets you specify whether to compress audio in
the exported file.
Lets you specify the quality of JPEG images in
the exported file, with 100 being highest quality.
When download is true, the browser always
displays a dialog box that lets the end user save
the returned file, even if the browser can display
it.
When download is false, the browser attempts
to display the returned file. If the browser cannot
display the file, it lets the end user save the
returned file.
The default value is false.
spreads
updateimage
Boolean 1 | 0 |
true | false | yes
| no
true | false
Lets you specify that the output use spreads.
Applicable only to Print layouts.
Lets you specify whether to update imported
pictures.
QXP SERVER 9.2 WEB INTEGRATION GUIDE | 51
Page 52

USING THE WEB INTERFACE
Alerts
Example, GET
URL
updateflow
A single SWF file or a multipart reply containing an SWF file and a set of support files.Response
A multipart reply can result if you render an Interactive layout that uses external assets -- for
example, if the layout includes a Video object containing a video file that has been specified by
choosing Choose from a drop-down menu. In this case, the reply includes a "RelativePath" parameter
for each file, and each file is saved in the directory indicated by this "RelativePath" parameter
You can use the saveas request handler to save the files that are included in a multipart reply in
a particular directory, using the relative folder hierarchy that was specified in the multipart reply.
exist.
exist.
Unknown swf player version.
Value of jpegquality is outside
range, valid values are 1 - 100.
See Understanding loggingLogs
This URL renders the Interactive layout named "Presentation" in the "sample.qxp" file as a
free-standing SWF file set to display in full-screen mode:
http://localhost:8080/swf/sample.qxp?
layout=Presentation&fullscreen=true
true | false
This alert displays if you try to render a nonexistent page.The requested page does not
This alert displays if you try to render an invalid page range.This page range is invalid.
This alert displays if you try to render a nonexistent leyout.The requested layout does not
This alert displays if you specify an invalid version parameter.
This alert displays if you specify an invalid jpegquality
parameter.
Lets you specify whether to update the text flow
version of a project to the current version.
Example, object
model
Request object name: SWFRenderRequest
// STEP1: Create the QuarkXPress Server Request Context
// and set the nescessary properties
com.quark.qxpsm.QRequestContext requestCtx =
new com.quark.qxpsm.QRequestContext();
Boolean responseAsURL = false;
requestCtx.setDocumentName(docName);
// STEP 2(SPECIFIC TO REQUESTS):Create the SWF renderer request
// and embed it in the request context.
SWFRenderRequest swfreq = new SWFRenderRequest();
swfreq.setVersion(request.getParameter("Version"));
swfreq.setLayout(request.getParameter("Layout"));
swfreq.setPage(request.getParameter("Page"));
swfreq.setFullscreen(request.getParameter("Fullscreen"));
swfreq.setEmbedallfonts(request.getParameter(
"Embedallfonts"));
swfreq.setCompressswf(request.getParameter("Compressswf"));
swfreq.setCompressaudio(request.getParameter(
"Compressaudio"));
swfreq.setJpegquality(request.getParameter("Jpegquality"));
swfreq.setDownload(request.getParameter("Download"));
requestCtx.setRequest(swfreq);
// STEP3: Create the WIG service and call the processRequest() API
RequestService service = new RequestServiceStub();
com.quark.qxpsm.QContentData data = service.processRequest(requestCtx);
52 | QXP SERVER 9.2 WEB INTEGRATION GUIDE
Page 53
Understanding render modifiers
Render modifiers let you control which parts of a project are rendered and set the scale of
the returned renderings. The topics covered here include the following:
DescriptionProperty
USING THE WEB INTERFACE
Box
Boxes
Layer
Layout
Movepages
Page
Pages
Scale
Spread
Spreads
The box render modifier lets you render a single box.
The boxes render modifier lets you render multiple boxes.
The layer render modifier lets you show and hide layers prior to rendering. This render modifier also
lets you add and remove layers from a project on the server.
The layout render modifier lets you render a particular layout.
The movepages render modifier lets you move pages prior to rendering.
The page render modifier lets you render a single page.
The pages render modifier lets you render multiple pages.
The scale render modifier lets you specify the scale at which content is rendered.
The spread render modifier lets you render a single spread.
The spreads render modifier lets you render multiple spreads.
Additional render-type-specific parameters are listed on each render type's page.
In the QuarkXPress Server Manager API, render modifiers are properties of render request
classes.
Box
Parameters
Compatible with
Alerts
Render modifier names are not case-sensitive.
The box render modifier lets you render a single box.
box
overlap
jpeg, png, raw
the specified
identifier.
The box must be
within the page
boundaries.
String
HTTP Error #500There is no box with
This alert displays if you request a box that does not exist.
HTTP Error #500Cannot render box.
This alert displays if you request a box that is outside the page boundary.
Lets you specify which box to render.String
Lets you specify whether to show the area overlapped by
the specified box.
QXP SERVER 9.2 WEB INTEGRATION GUIDE | 53
Page 54

USING THE WEB INTERFACE
image type has no
way of rendering the
desired objects.
See Understanding loggingLogs
HTTP Error #406The renderer for this
This alert displays if you try to use the box parameter with the eps, pdf,
or qxpdoc render types.
Example GET
URL
Notes
Boxes
Parameters
Compatible with
Alerts
http://localhost:8080/png/sample.qxp?box=pictbox
To render a box in a particular layout, use a URL like the following:
http://localhost:8080/png/sample.qxp?
layout=2&page=3&box=textbox
When you render using the box parameter, the box ID has a higher priority than the
box name.
The boxes render modifier lets you render multiple boxes.
boxes
overlap
jpeg, png, raw
the specified
identifier.
String
HTTP Error #500There is no box with
This alert displays if you request a box that does not exist.
Lets you specify which boxes to render.String
Lets you specify whether to show the area overlapped by the
specified boxes.
Example GET
URL
Notes
HTTP Error #500Cannot render box.
The box must be
within the page
boundaries.
image type has no
way of rendering the
desired objects.
See Understanding loggingLogs
http://server:port/jpeg/doc.qxp?boxes=box1,box2
To render boxes in a particular layout, use a URL like the following:
http://localhost:8080/png/sample.qxp?
layout=2&page=3&box=textbox
This alert displays if you request a box that is outside the page boundary. .
HTTP Error #406The renderer for this
This alert displays if you try to use the boxes parameter with the eps, pdf,
or qxpdoc render types.
When you render using the box parameter, the box ID has a higher priority than the
box name.
54 | QXP SERVER 9.2 WEB INTEGRATION GUIDE
Page 55

Compositionzone
The compositionzone parameter lets you return an XML representation of one or more
Composition Zones items.
USING THE WEB INTERFACE
Parameters
Compatible with
Alerts
Layer
Parameters
compositionzone
compositionzones
xml
Param.
See Understanding loggingLogs
String
String
Error #10401Invalid box given in Box
This alert displays if you request a box that is not a Composition Zones
item.
Lets you specify which Composition Zones item to
return. For example:
http://localhost:8080/xml/sample.qxp?
compositionzone=czbox
Lets you specify which Composition Zones items to
return. For example:
http://localhost:8080/xml/sample.qxp?
compoxitionzones=czbox1, czbox2
The layer render modifier lets you show and hide layers prior to rendering. This render
modifier also lets you add and remove layers from a project on the server.
layer
String
Lets you specify which layer to render. You can specify
multiple layer names in one request.
addlayer
deletelayer
alllayers
layerattribute
name
visible
suppressoutput
String
String
Boolean (1 | 0 | true
| false | yes | no)
String
String
Boolean (1 | 0 | true
| false | yes | no)
Boolean (1 | 0 | true
| false | yes | no)
Lets you add a new layer. You can add one layer per
request.
Lets you delete a layer and the items on that layer. You
can delete one layer per request.
Lets you render every layer in the project, including
hidden and suppressed layers.
Lets you modify the attributes of a layer. You can
modify one layer per request.
Lets you specify a new name for a layer. You must use
this parameter in conjunction with the
layerattribute parameter.
Lets you make a layer visible or invisible. You can use
this parameter in conjunction with the addlayer and
layerattribute parameters. This parameter overrides
QuarkXPress layer visibility preferences.
Lets you suppress or allow the output of a layer. You
can use this parameter in conjunction with the
addlayer and layerattribute parameters. This
parameter overrides QuarkXPress suppress output
preferences.
QXP SERVER 9.2 WEB INTEGRATION GUIDE | 55
Page 56

USING THE WEB INTERFACE
Compatible with
Alerts
locked
keeprunaround
eps, jpeg, png, postscript, qcddoc, qxpdoc, raw, pdf, screenpdf, swf, xml
exist. Please verify
the layer name.
same name already
exists.
name of the default
layer.
Boolean (1 | 0 | true
| false | yes | no)
Boolean (1 | 0 | true
| false | yes | no)
HTTP Error #500This layer does not
This alert displays if you specify an invalid layer name with the layer,
layerattribute, or deletelayer parameter.
HTTP Error #500Specify a layer name.
This alert displays if you do not specify a layer name with the layer,
layerattribute, addlayer, or deletelayer parameter.
HTTP Error #500A layer with the
This alert displays if you try to add a layer that already exists or change the
name of a layer to a name is already used in the project.
HTTP Error #500Cannot change the
This alert displays if you try to change the name of the default layer.
Lets you lock or unlock a layer. You can use this
parameter in conjunction with the addlayer and
layerattribute parameters. This parameter overrides
QuarkXPress layer locking preferences.
Lets you set or change a layer's Keep Runaround
setting. You can use this parameter in conjunction
with the addlayer and layerattribute parameters.
This parameter overrides QuarkXPress Keep Runaround
preferences.
Example GET
URL
HTTP Error #500Cannot delete the
default layer.
value.
locked and cannot be
modified.
See Understanding loggingLogs
To render a single layer, use a URL like the following:
http://localhost:8080/doc.qxp?layer=layer1
To add a layer, use a URL like the following:
http://localhost:8080/qxpdoc/doc.qxp?addlayer=
NewLayer&visible=yes&suppressoutput=yes&locked=no
To delete a layer, use a URL like the following:
http://localhost:8080/qxpdoc/doc.qxp?deletelayer=Layer1
To render all layers in a project, use a URL like the following:
http://localhost:8080/qxpdoc/doc.qxp?alllayers=true
To set layer attributes, use a URL like the following:
http://localhost:8080/qxpdoc/doc.qxp?layerattribute=
Layer1&name=Layer2&visible=true&keeprunaround=true
This alert displays if you try to delete the default layer.
HTTP Error #500Invalid parameter
This alert displays if you do not specify additional attributes or specify
attributes with invalid values in an addlayer or layerattribute request.
HTTP Error #500This layer has been
This alert displays if you try to add or modify an item on a locked layer.
56 | QXP SERVER 9.2 WEB INTEGRATION GUIDE
Page 57

USING THE WEB INTERFACE
Example, object
model
Layout
To add a new layer to a project, use code like the following:
Layer layer = new Layer();
layer.name = "New Layer";
layer.operation = "CREATE";
RGBColor rgbcolor = new RGBColor();
layer.RGBColor = rgbcolor;
layout.layer = new Layer[]{layer};
To edit the properties of an existing layer, use the following object hierarchy:
ModifierRequest < Project < Layout < Layer
To delete a layer, set its operation attribute to "DELETE".
You cannot add, modify, or delete multiple layers in a single request.Notes
You cannot print layers whose visible and suppressoutput properties are set to false.
You can render a hidden or suppressed layer by referencing it with the layer parameter.
Suppressed layers are rendered for the jpeg, png, and qxpdoc render types, but not for the pdf,
postscript, and eps render types.
You can use the deconstruct and getdocinfo request handlers to view information about the
layers in a project.
When you add a layer using addlayer, any unspecified attributes use the settings in the
QuarkXPress Server layer preferences (Administration > Preferences > Renderer > Layers).
If the visible property is set to false, the suppressoutput property is automatically set to
true.
The layout render modifier lets you render a specific layout.
Parameters
Compatible with
Alerts
Example GET
URL
Movepages
Parameters
layout
eps, jpeg, png, postscript, raw, pdf, screenpdf, swf
layout does not
exist.
See Understanding loggingLogs
To render a layout by its layer ID, use a URL like the following:
http://localhost:8080/png/sample.qxp?layout=2
To render a layout by its name, use a URL like the following:
http://localhost:8080/png/sample.qxp?layout=Layout 2
String
HTTP Error #500The requested
This alert displays if you supply an invalid layout value.
Lets you specify which layout to render. The first layout is layout
1.
The movepages render modifier lets you move pages prior to rendering.
movepages
afterpage
String
String
Lets you specify which pages to move. You can use a single
page number (for example, 2) or a range of pages with the
starting and ending page numbers separated by a hyphen
(for example, 2–5).
Lets you specify the page after which the page or pages
should be moved. To move pages to the beginning of a
QXP SERVER 9.2 WEB INTEGRATION GUIDE | 57
Page 58

USING THE WEB INTERFACE
layout, use afterpage=start. To move pages to the end
of a layout, use afterpage=end.
Compatible with
Alerts
Example GET
URL
Example, object
model
eps, jpeg, png, postscript, qcddoc, qxpdoc, raw, pdf, screenpdf, swf, xml
QuarkXPress Server Error #61This page does not
exist.
QuarkXPress Server Error #62Invalid page range.
QuarkXPress Server Error #51The specified page
range cannot be
moved there.
QuarkXPress Server Error #146This page range is
invalid.
QuarkXPress Server Error #10108Invalid parameter
value.
See Understanding loggingLogs
To move pages 2–3 to after page 5, use a URL like the following:
http://localhost:8080/abc.qxp?movepages=2–3&afterpage=5
To move page 7 to the beginning of a layout, use a URL like the following:
http://localhost:8080/abc.qxp?movepages=7&afterpage=
start
To move pages before rendering a layout, use code like the following:
// STEP1: Create the QuarkXPress Server Request Context
// and set the nescessary properties
com.quark.qxpsm.QRequestContext requestCtx =
new com.quark.qxpsm.QRequestContext();
Boolean responseAsURL = false;
requestCtx.setDocumentName(docName);
// STEP 2(SPECIFIC TO REQUESTS):Create the PDF
// renderer request and embed it in the request context. the request context.
PDFRenderRequest pdfreq = new PDFRenderRequest();
pdfreq.setMovePages("2-4");
pdfreq.setAfterPage("7");
requestCtx.setRequest(pdfreq);
// STEP3: Create the WIG service and call the
// processRequest() API
RequestService service = new RequestServiceStub();
com.quark.qxpsm.QContentData data = service.processRequest(
requestCtx);
Notes
The movepages operation executes only after all other modifications are complete. For example,
if you use movepages in a modify request, the pages are moved only after the modify request is
complete.
Page
The page render modifier lets you render a single page.
Parameters
page
58 | QXP SERVER 9.2 WEB INTEGRATION GUIDE
Lets you specify which page to render.Integer
Page 59

USING THE WEB INTERFACE
Compatible with
Alerts
Example GET
URL
Example, object
model
Notes
eps, jpeg, png, postscript, qcddoc, raw, pdf, screenpdf, swf
HTTP Error #500The requested page does
not exist.
image type has no way
of rendering the desired
objects.
See Understanding loggingLogs
http://localhost:8080/png/sample.qxp?page=2
To add a new page to an existing spread in a project, use code like the following:
Spread spread = new Spread();
Page page = new Page();
page.UID = "5";
page.operation = "CREATE";
spread.page = new Page[]{page};
To edit the properties of an existing page, use the following object hierarchy:
ModifierRequest < Project < Layout < Spread < Page
To delete a page, set its operation attribute to "DELETE".
To render a page in a particular layout, use a URL like the following:
http://localhost:8080/png/sample.qxp?layout=2&page=3
This alert displays if you attempt to render a page that does not exist.
HTTP Error #406The renderer for this
This alert displays if you use a page parameter with the qxpdoc render
type.
Pages
Parameters
Compatible with
Alerts
Example, GET
URL
Notes
The pages render modifier lets you render multiple pages. The pdf and postscript
namespaces support this parameter.
pages
eps, jpeg, png, postscript, raw, pdf, screenpdf, swf
HTTP Error #500This page range is
invalid.
this image type has
no way of
rendering the
desired objects.
See Understanding loggingLogs
http://localhost:8080/pdf/sample.qxp?pages=2–4
To render pages in a particular layout, use a URL like the following:
http://localhost:8080/pdf/sample.qxp?layout=2&pages=2,3
QuarkXPress Server Error #147
This alert displays if you try to render a page range that exceeds the number
of pages in the project.
HTTP Error #406The renderer for
This alert displays if you use the pages parameter with the jpeg, eps, png,
or qxpdoc render type.
Lets you specify which pages to render.String (page range)
QXP SERVER 9.2 WEB INTEGRATION GUIDE | 59
Page 60
USING THE WEB INTERFACE
Scale
The scale render modifier lets you specify the scale at which content is rendered.
Parameters
Compatible with
Alerts
Example, GET
URL
Spread
Parameters
Compatible with
Alerts
scale
eps, jpeg, png, raw
parameter.
See Understanding loggingLogs
http://localhost:8080/png/sample.qxp?scale=2
Float
HTTP Error #500Invalid scale
This alert displays if an invalid scale value is provided.
What to do: Enter a valid scale value.
Lets you specify a scaling percentage. The valid values are
from .1 (10%) to 8 (800%) on Mac OS or 6.92 (692%) on
Windows.
The spread render modifier lets you render a single spread.
spread
eps, jpeg, png, postscript, raw, pdf, screenpdf, swf
spread does not
exist.
Integer
HTTP Error #500The requested
This alert displays if you specify an invalid spread.
Lets you specify which spread to render. Spread numbers
start with 1. The first spread is spread 1. In a facing-page
document, spread 1 consists of the first page.
Example, GET
URL
Example, Object
Model
Spreads
Parameters
Compatible with
See Understanding loggingLogs
http://localhost:8080/png/sample.qxp?spread=2
To add a spread to a project, use code like the following:
Spread spread = new Spread();
spread.UID = "5";
spread.operation = "CREATE";
layout.spread = new Spread[]{spread};
Spread is located at the following place in the object hierarchy:
ModifierRequest < Project < Layout < Spread
To delete a spread, set its operation attribute to "DELETE".
The spreads render modifier lets you render layouts in spreads mode, so that pages in
spreads are rendered side-by-side rather than as individual pages.
spreads
eps, jpeg, png, postscript, raw, pdf, screenpdf, swf
Boolean (1 | 0 | true | false | yes |
no)
Lets you specify whether to render spreads
(true) or individual pages (false).
60 | QXP SERVER 9.2 WEB INTEGRATION GUIDE
Page 61
USING THE WEB INTERFACE
See Understanding loggingLogs
Example, GET
URL
http://localhost:8080/pdf/sample.qxp?spreads=true
Using content modifiers
Content modifiers let you alter the content and formatting of boxes in layouts without using
the XML modify parameter.
Inserting text
This topic explains how to import text into a box. Any existing text in the box is replaced.
A preview of the project with the imported text.Response
The name of the target box.String[box name]Parameters
Specify the name and location of the imported file with the file:
prefix. The imported file must be available to QuarkXPress Server.
To import a file that is in a subfolder of the document pool on
Mac OS, use a path like the following:
file:subfolder:MyFile.ext
To import a file that is in a subfolder of the document pool on
Windows, use a path like the following:
file:subfolder\MyFile.ext
Logs
Example, GET
URL
Example, object
model
HTTP Error #404File not found.Alerts
QuarkXPress Server Error #–43
This alert displays if the imported file is not available to QuarkXPress Server.
If the request succeeds, a transaction success message is written to the QuarkXPress Server transaction
log file. For example:
8/3/2005 11:27:42 — jpeg/sample.qxp — Type: image/jpeg — Size: 31715 — Client: 127.0.0.1
If an alert displays, an error message is written to the QuarkXPress Server error log file. For example:
8/10/2005 10:32:57 — Error — Error Code: –43 — File not found.
http://localhost:8080/sample.qxp?Author=NewText
http://localhost:8080/sample.qxp?TopStory=file:TopStory.doc
Request object name: RequestParameters
com.quark.qxpsm.QRequestContext rc =
new com.quark.qxpsm.QRequestContext();;
if(!this.DocumentSettings1.documentName.Text.Equals(""))
rc.documentName =
this.DocumentSettings1.documentName.Text;
// STEP 2 (SPECIFIC TO REQUESTS):Create the Box Param
// renderer request and embed it in
RequestParameters request = new RequestParameters();
NameValueParam nameValue1 = new NameValueParam();
nameValue1.paramName = this.boxname1.Text;
if(!this.boxvalue1.Text.Equals(""))
nameValue1.textValue = this.boxvalue1.Text;
QXP SERVER 9.2 WEB INTEGRATION GUIDE | 61
Page 62

USING THE WEB INTERFACE
request.params = new NameValueParam[]{nameValue1};
rc.request = request;
// Create the service and
// call it with QRequestContext object
RequestService svc = new RequestService();
com.quark.qxpsm.QContentData qc = svc.processRequest(rc);
Box names are case-sensitive.Notes
Use "&" to change the contents of multiple boxes in one request. The general URL for the
multiple-box request is:http://localhost:8080/sample.qxp?text1=
NewText1&text2=NewText2 where text1 and text2 are the names of the two different boxes.
You can use "&" to change the contents of multiple boxes in one request. For example:
http://localhost:8080/sample.qxp?
Headline=headline.txt&Story=file:Story.doc
You can import an XTags file generated by QuarkXPress.
Applying a font at import
This topic explains how to apply a font to a new text flow. When you use this method,
QuarkXPress Server ignores the original font of the target text box and inserts the new
text with the font specified by the parameter.
Parameters
Alerts
Logs
Example, GET
URL
Example, object
model
fontname
A preview of the project with the font applied to the imported text.Response
This alert displays if you specify a font that is unavailable.The specified font is not
available.
If the request succeeds, a transaction success message is written to the QuarkXPress Server transaction
log file. For example:
12/2/2005 16:24:13 — project2.qxp — Type: image/jpeg — Size: 11380 — Client: 127.0.0.1
If an error occurs, the error message is written to the QuarkXPress Server Error Log. The transaction
entry in the error log contains the date and time of the request, the error code, and the error
message. The following is a sample of an error transaction log entry:
12/2/2005 16:16:26 — Error — Error Code: –43 — File not found.
To apply Comic Sans MS to text in the box named "HeadBox," use a URL like the following:
http://localhost:8080/png/sample.qxp?HeadBox=Headline&fontname=Comic Sans MS
Request object name: RequestParameters
com.quark.qxpsm.QRequestContext rc =
new com.quark.qxpsm.QRequestContext();
if(!this.DocumentSettings1.documentName.Text.Equals(""))
rc.documentName =
this.DocumentSettings1.documentName.Text;
The name of the font to be applied.String
// STEP 2(SPECIFIC TO REQUESTS):Create the fontname
// renderer request and embed it in
RequestParameters request = new RequestParameters();
NameValueParam nameValue1 = new NameValueParam();
nameValue1.paramName = this.boxname.Text;
if(!this.boxvalue1.Text.Equals(""))
nameValue1.textValue = this.fontname.Text;
request.params = new NameValueParam[]{nameValue1};
rc.request = request;
62 | QXP SERVER 9.2 WEB INTEGRATION GUIDE
Page 63
// Create the service and
// call it with QRequestContext object
RequestService svc = new RequestService();
com.quark.qxpsm.QContentData qc = svc.processRequest(rc);
Inserting a picture
This topic explains how to import a picture into an empty box or replace an existing
picture with a new one.
USING THE WEB INTERFACE
Parameters
Logs
[box name[
A preview of the project with the imported picture.Response
HTTP Error #404File not found.Alerts
QuarkXPress Server Error #–43
This alert displays if the imported file is not available to QuarkXPress Server.
HTTP Error #500The specified file
failed to load in
the picture box.
If the request succeeds, a transaction success message is written to the QuarkXPress Server transaction
log file. For example:
8/3/2005 11:27:42 — jpeg/sample.qxp — Type: image/jpeg — Size: 31715 — Client: 127.0.0.1
If an alert is displayed, an error message is written to the QuarkXPress Server error log. The following
is a sample of the error log entry:
8/10/2005 10:39:07 — Error — Error Code: 10339 — The specified file failed to load in the picture
box.
This alert displays if you attempt to import an invalid picture file.
The name of the target box.String
Specify the name and location of the imported file with the file:
prefix. The imported file must be available to QuarkXPress Server.
To import a file that is in a subfolder of the document pool on
Mac OS, use a path like the following:
file:subfolder:MyFile.ext
To import a file that is in a subfolder of the document pool on
Windows, use a path like the following:
file:subfolder\MyFile.ext
Example, GET
URL
Example, object
model
http://localhost:8080/sample.qxp?
PictureBox=file:FrenchOpen.pdf
Request object name: RequestParameters
com.quark.qxpsm.QRequestContext rc = new com.quark.qxpsm.QRequestContext();
if(!this.DocumentSettings1.documentName.Text.Equals(""))
rc.documentName = this.DocumentSettings1.documentName.Text;
//STEP 2(SPECIFIC TO REQUESTS):Create the Box Param
//renderer request and embed it in
RequestParameters request = new RequestParameters();
NameValueParam nameValue1 = new NameValueParam();
nameValue1.paramName = this.boxname1.Text;
if(!this.boxvalue1.Text.Equals(""))
nameValue1.textValue = this.boxvalue1.Text;
request.params = new NameValueParam[]{nameValue1};
rc.request = request;
QXP SERVER 9.2 WEB INTEGRATION GUIDE | 63
Page 64

USING THE WEB INTERFACE
//Create the service and call it with QRequestContext object
RequestService svc = new RequestService();
com.quark.qxpsm.QContentData qc = svc.processRequest(rc);
Box names are case-sensitive.Notes
You can use "&" to change the contents of multiple boxes in one request. For example:
http://localhost:8080/sample.qxp?
Logo=file:logo.jpeg&TopPicture=file:TopPicture.eps
Saving a projects with a new name
The saveas content modifier lets you save modified QuarkXPress projects in any supported
format to the document pool or to any network location accessible to QuarkXPress Server.
If you send a saveas request to QuarkXPress Server Manager using HTTP or the Web
services interface while the common doc pool switch is set to off in the QuarkXPress Server
Manager client, the file is saved to all registered QuarkXPress Server instances. If the
common doc pool is enabled, the file can be saved to any one registered QuarkXPress
server instance.
Parameters
newname
path
savetopool
replace
The message "Document successfully saved."Response
pathname.
Lets you specify a name for the saved-as project.String
String
true | false
true | false
HTTP Error #404File not found.Alerts
QuarkXPress Server Error #–43
This alert displays if you supply an incorrect file name or the file is not available
to QuarkXPress Server.
HTTP Error #404Bad filename/
QuarkXPress Server Error #–43
This alert displays if you supply an incorrect file name or the file is not available
to QuarkXPress Server.
Lets you specify a location for the saved-as project (other than
the document pool).
Lets you specify whether the project should be saved to the
document pool.
The default value for this paramter is true. However, if you specify
a path value, the default value changes to false, which means if
you want the project saved to the document pool, you must
explicitly set savetopool to true.
Lets you specify whether the saved project should replace a project
with the same name. The default value is true.
HTTP Error #500The file path is
invalid.
folder is
Read-Only.
This alert displays if you supply an invalid path parameter.
What to do: Specify the correct file path with the path parameter.
HTTP Error #500The specified
This alert displays if you try to save a project to a folder with read-only access.
64 | QXP SERVER 9.2 WEB INTEGRATION GUIDE
Page 65
USING THE WEB INTERFACE
Logs
Example, GET
URL
Example, object
model
If the request succeeds, a transaction success message is written to the QuarkXPress Server transaction
log file. For example:
11/16/2005 15:41:42 — saveas/5mb.qxp — Type: — Size: 28 — Client: 127.0.0.1
If an alert displays, an error message is written to the QuarkXPress Server error log file. For example:
11/16/2005 15:42:12 — Error — Error Code: 10371 — The file path is invalid.
To save a PDF file named "Customer1.pdf" in the folder HDD:temp and also in the document pool,
use a URL like the following. Note that this URL will cause the saved-as file to replace any existing
file with the same name.
http://localhost:8080/saveas/pdf/sample.qxp?
newname=Customer1&path=HDD:temp&savetopool=true
Request object name: SaveAsRequest
com.quark.qxpsm.QRequestContext rc = new com.quark.qxpsm.QRequestContext();
if(!this.DocumentSettings1.documentName.Text.Equals(""))
rc.documentName =
this.DocumentSettings1.documentName.Text;
// STEP 2 (SPECIFIC TO REQUESTS):
// Create the Save as request and chain it to the document context
SaveAsRequest saveasreq = new SaveAsRequest();
saveasreq.newName = this.newname.Text;
if((this.path.Text != null) &&
(!this.path.Text.Equals("")))
saveasreq.newFilePath = this.path.Text;
saveasreq.replaceFile = this.replace.Checked.ToString();
saveasreq.saveToPool =
this.savetopool.Checked.ToString();
rc.request = saveasreq;
Parameters
// Create the service and call it with QRequestContext object
RequestService svc = new RequestService();
com.quark.qxpsm.QContentData qc = svc.processRequest(rc);
Importing XML with placeholders
This topic explains how to import XML data into boxes using QuarkXPress placeholders.
To use this feature, you must have a QuarkXPress project that has been set up with
placeholders that correspond to the element types in a source XML file. For more
information, see A Guide to XML Import.
thexmldoc
layout
paginate
XML
String
XML
Lets you specify the XML file containing the data to import. The path
can be absolute or relative to the location of the XML file. You can
also supply XML as a string.
Lets you specify which layout to render. The first layout is layout 1.
You can also specify a layout by name.
Lets you specify the XML file containing the data to import. The
paginate parameter reates enough pages in the target layout to
accommodate the records in the XML.
This parameter works only with the pdf, postscript, and qxp render
types. If you use it with any other render type, the server returns only
the first page of the paginated layout.
QXP SERVER 9.2 WEB INTEGRATION GUIDE | 65
Page 66

USING THE WEB INTERFACE
The layout with the imported XML.Response
If you do not supply an XML string or file (for example:
http://localhost:8080/pdf/Sample.qxp?paginate),
QuarkXPress Server attempts to use the XML file that was associated
with the layout in QuarkXPress.
Alerts
Logs
Example, GET
URL
HTTP Error #500Invalid XML
String
If the project is successfully rendered, a transaction success message is written to the
QuarkXPress Server transaction log file. The transaction entry consists of the date and time of the
request, the render type, the project name, the type of response produced by the server, the size
of the response returned in bytes, and the client IP address. The following is a sample of a transaction
entry:
8/5/2005 18:11:54 — sample.qxp — Type: image/jpeg — Size: 65982 — Client: 127.0.0.1
If an alert displays, an error message is written to the QuarkXPress Server error log file. For example:
8/9/2005 12:38:42 — Error — Error Code: 10396 — Invalid XML String.
This alert displays if you supply an invalid XML string in the thexmldoc parameter.
When QuarkXPress Server is running on Windows, use a URL like the following:
http://localhost:8080/Sample.qxp?thexmldoc=<?xml
version="1.0"?>
<BookReview><Book><Title>C:\Autumn.jpg</Title>
<Author> Brian Kernighan and Dennis Ritchie</Author>
</Book></BookReview>
When QuarkXPress Server is running on Mac OS, use a URL like the following:
http://localhost:8080/Sample.qxp?thexmldoc=<?xml version=
"1.0"?>
<BookReview><Book><Title>/Volumes/MacHD/Pictures/abc.tiff</
Title>
<Author> Brian Kernighan and Dennis Ritchie</Author>
</Book></BookReview>
Alternatively, you can specify a path to a file containing the XML:
http://localhost:8080/Sample.qxp?paginate=
file:MacHD:Sample.xml
Example, object
model
Request object names: XMLImportRequest
com.quark.qxpsm.QRequestContext rc = new com.quark.qxpsm.QRequestContext();
if(!this.DocumentSettings1.
documentName.Text.Equals(""))
rc.documentName =
this.DocumentSettings1.documentName.Text;
// STEP 2 (SPECIFIC TO REQUESTS): Create the XML Import request
XMLImportRequest xmlimportreq = new XMLImportRequest();
xmlimportreq.XMLDocument = this.thexmldoc.Text;
rc.request = xmlimportreq;
// STEP 3(SPECIFIC TO REQUESTS): Create the JPEG renderer request
JPEGRenderRequest jpreq = new JPEGRenderRequest();
xmlimportreq.request = jpreq;
// Create the service and call it with QRequestContext object
RequestService svc = new RequestService();
com.quark.qxpsm.QContentData qc = svc.processRequest(rc);
66 | QXP SERVER 9.2 WEB INTEGRATION GUIDE
Page 67

Using XML modify
The modify parameter lets you modify a QuarkXPress project using XML.
This topic covers the modify parameter when it is used without the construct namespace.
You can also use the modify parameter to specify an XML file to use when constructing
a project; for more information, see "Constructing a project".
The xml namespace takes two arguments: the name of the project to be modified, and a
modify parameter with the string or the path of the XML file that describes how to create
the project:
http://QXPServer8:8080/project1.qxp?modify=
file:path to XML file on server http://QXPServer8:8080/
project1.qxp?modify=XML string
You can also modify QuarkCopyDesk articles. To modify a QuarkCopyDesk article:
http://localhost:8080/copydesk/abc.qcd?modify=
file:XMLfile.xml
Modifier DTDDTD
USING THE WEB INTERFACE
Parameters
Example GET
URL
Example XML
Logs
modify
http://QXPServer8:8080/project1.qxp?modify=file:sample.xml
This XML deletes page 2 of a QuarkXPress layout:
<PROJECT>
<LAYOUT>
<ID NAME="Layout 1" />
<SPREAD>
<ID UID="1" />
<PAGE OPERATION="DELETE">
<ID UID="2" />
</PAGE>
</SPREAD>
</LAYOUT>
</PROJECT>
The updated QuarkXPress project.Response
If the request succeeds, a transaction success message is written to the QuarkXPress Server
transaction log file. For example:
8/3/2005 11:27:42 — jpeg/sample.qxp — Type: image/jpeg — Size: 31715 — Client: 127.0.0.1
If an alert is displayed, an error message is written to the QuarkXPress Server error log. The following
is a sample of the error log entry:
8/10/2005 10:39:07 — Error — Error Code: 10339 — The specified file failed to load in the picture
box.
String
Lets you specify an XML file or string that describes how to create a
project. The path can be absolute or a relative path in the document
pool. Use the file: indicator to specify the path.
Note that you can also include an XML file as part of a multipart HTTP
request.
Modifying box properties and content
To modify box properties and content, use the following parameters in the Modifier DTD:
QXP SERVER 9.2 WEB INTEGRATION GUIDE | 67
Page 68

USING THE WEB INTERFACE
• "BOX (Modifier DTD)"
• "ID (Modifier DTD)"
• "TEXT (Modifier DTD)"
• "PICTURE (Modifier DTD)"
• "GEOMETRY (Modifier DTD)"
• "CONTENT (Modifier DTD)"
• "SHADOW (Modifier DTD)"
• "FRAME (Modifier DTD)"
• "PLACEHOLDER (Modifier DTD)"
• "METADATA (Modifier DTD)"
The following XML shows how some of these parameters work.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<PROJECT>
<LAYOUT>
<ID NAME="Layout 1"/>
<SPREAD>
<ID UID="1"/>
<BOX BOXTYPE="CT_TEXT">
<ID NAME="SERVICES"/>
<GEOMETRY>
<MOVEUP>50</MOVEUP>
<MOVELEFT>30</MOVELEFT>
<ALLOWBOXONTOPASTEBOARD>true</ALLOWBOXONTOPASTEBOARD>
</GEOMETRY>
<CONTENT CONVERTQUOTES="true">
HD:QuarkXPress:DocPool:Services.txt</CONTENT>
</BOX>
<BOX BOXTYPE="CT_TEXT">
<ID NAME="FAMILY"/>
<GEOMETRY>
<MOVERIGHT>20</MOVERIGHT>
<MOVEDOWN>30</MOVEDOWN>
<ALLOWBOXONTOPASTEBOARD>true</ALLOWBOXONTOPASTEBOARD>
<ALLOWBOXOFFPAGE>true</ALLOWBOXOFFPAGE>
</GEOMETRY>
</BOX>
<BOX BOXTYPE="CT_TEXT">
<ID NAME="PRODUCTS"/>
<GEOMETRY>
<GROWACROSS>44</GROWACROSS>
<GROWDOWN>30</GROWDOWN>
<ALLOWBOXONTOPASTEBOARD>false</ALLOWBOXONTOPASTEBOARD>
</GEOMETRY>
</BOX>
<BOX BOXTYPE="CT_PICT">
<ID NAME="MAP"/>
<GEOMETRY>
<SHRINKACROSS>30</SHRINKACROSS>
<SHRINKDOWN>30</SHRINKDOWN>
</GEOMETRY>
</BOX>
<BOX COLOR="Blue" BOXTYPE="CT_PICT">
<ID NAME="CONTACT"/>
<GEOMETRY>
<STACKINGORDER>BRINGTOFRONT</STACKINGORDER>
<RUNAROUND TYPE="ITEM" TOP="4" RIGHT="4"
LEFT="4" BOTTOM="4"/>
<ALLOWBOXOFFPAGE>false</ALLOWBOXOFFPAGE>
</GEOMETRY>
</BOX>
</SPREAD>
68 | QXP SERVER 9.2 WEB INTEGRATION GUIDE
Page 69

</LAYOUT>
</PROJECT>
A preview of the QuarkXPress project with a new box created in the specified position.Response
USING THE WEB INTERFACE
Logs
Example GET
URL
File not found.Alerts
filename/pathname.
document is not
valid or well
formed.
document
contains an
invalid tag value.
If the request succeeds, a transaction success message is written to the QuarkXPress Server transaction
log file. For example:
8/3/2005 11:27:42 — jpeg/sample.qxp — Type: image/jpeg — Size: 31715 — Client: 127.0.0.1
If an alert displays, an error message is written to the QuarkXPress Server error log file. For example:
When QuarkXPress Server is running on Windows, use a URL like the following:
http://localhost:8080/sample.qxp?modify=
file:C:\updateBox.xml
When QuarkXPress Server is running on Mac OS, use a URL like the following:
http://localhost:8080/sample.qxp?modify=
file:MacHD:xml:updateBox.xml
You can also supply a string that consists of valid XML commands. For example:
http://localhost:8080/sample.qxp?modify=
<PROJECT><LAYOUT><ID UID="Layout1"/><SPREAD><ID UID="1"/>
<BOX BOXTYPE="CT_PICT" COLOR="Blue" SHADE="50" OPACITY="50">
<ID NAME="MOUNTAINS"/><CONTENT> file:Services.eps</CONTENT>
</BOX></SPREAD></LAYOUT></PROJECT>
HTTP Error #404
QuarkXPress Server Error #–43
This alert displays if you specify an invalid XML file or request a document
that is not available to QuarkXPress Server.
HTTP Error #404Bad
QuarkXPress Server Error #–37
This alert displays if you specify an invalid file name or path.
HTTP Error #500The XML
This alert displays if the XML you supply is not well-formed or does not adhere
to the Modifier DTD.
HTTP Error #500The XML
This alert displays if you supply an invalid value in the XML.
Example 1, object
model
Request object names:
ModifierRequest
ModifierRequestContents
Layout
ID
Box
Geometry
Runaround
ModifierFileRequest
For ModifierFileRequest, the member contents are used to set the file path or send
the XML itself.
com.quark.qxpsm.QRequestContext rc = new com.quark.qxpsm.QRequestContext();
QXP SERVER 9.2 WEB INTEGRATION GUIDE | 69
Page 70

USING THE WEB INTERFACE
if(!this.DocumentSettings1.documentName.Text.Equals(""))
rc.documentName = this.DocumentSettings1.documentName.Text;
//STEP 2(SPECIFIC TO REQUESTS):
//Create the BOX modifier renderer request and
//embed it in request context
ModifierRequest request = new ModifierRequest();
Project contents = new Project();
Geometry geo = new Geometry();
geo.moveUp = this.moveup.Text;
geo.color = this.color.Text;
geo.growDown = this.growdown.Text;
geo.shrinkAcross = this.shrinkacross.Text;
Box box = new Box();
box.UID = this.Boxid.Text;
box.geometry = geo;
Layout layout1 = new Layout();
layout1.name = this.layout.Text;
layout1.boxes = new Box[]{box};
if(this.runaround.Checked == true)
{
Runaround runaround = new Runaround();
runaround.type = this.runaroundtype.Text;
runaround.top = this.top.Text;
runaround.left = this.left.Text;
runaround.right = this.right.Text;
geo.runaround = runaround;
}
contents.layouts = new Layout[]{layout1};
request.project = contents;
rc.request = request;
Example 2, object
model
//Create the service and call it with QRequestContext object
RequestService svc = new RequestService();
com.quark.qxpsm.QContentData qc = svc.processRequest(rc);
To edit the geometrical properties of an existing box in a QuarkXPress project, use the following
object hierarchy:
ModifierRequest < Project < Layout < Spread < Box < Geometry
The Geometry object has the following properties:
allowBoxOffPage
allowBoxOnToPasteBoard
angle
growAcross
growDown
layer
linestyle (of type 'Linestyle')
moveDown
moveLeft
moveRight
moveUp
page
position (of type 'Position')
runaround (of type 'Runaround')
shape
shrinkAcross
shrinkDown
stackingOrder
suppressOutput
The Runaround object has the following properties:
bottom
edited
70 | QXP SERVER 9.2 WEB INTEGRATION GUIDE
Page 71

invert
left
noise
outset
outsideOnly
pathName
restrictToBox
right
smoothness
threshold
top
type
Creating boxes
To create a new box, use the following parameters in the Modifier DTD:
• "BOX (Modifier DTD)"
• "ID (Modifier DTD)"
• "TEXT (Modifier DTD)"
• "PICTURE (Modifier DTD)"
USING THE WEB INTERFACE
• "GEOMETRY (Modifier DTD)"
• "CONTENT (Modifier DTD)"
• "SHADOW (Modifier DTD)"
• "FRAME (Modifier DTD)"
The following XML shows how some of these parameters work.
<PROJECT>
<LAYOUT>
<ID UID="layout 1"/>
<SPREAD>
<ID UID="1"/>
<ID/>
<BOX OPERATION="CREATE" BOXTYPE="CT_PICT">
<ID NAME="PRODUCTS"/>
<GEOMETRY PAGE="2" SHAPE="SH_RECT">
<POSITION>
<TOP>5</TOP>
<LEFT>5</LEFT>
<BOTTOM>10</BOTTOM>
<RIGHT>10</RIGHT>
</POSITION>
</GEOMETRY>
</BOX>
</SPREAD>
</LAYOUT>
</PROJECT>
A preview of the QuarkXPress project with new box created in specified position.Response
File not found.Alerts
HTTP Error #404
QuarkXPress Server Error #–43
This alert displays if you specify an invalid XML file or request a document
that is not available to QuarkXPress Server.
QXP SERVER 9.2 WEB INTEGRATION GUIDE | 71
Page 72

USING THE WEB INTERFACE
pathname.
is not valid or well
formed.
contains an invalid
tag value.
HTTP Error #404Bad filename/
QuarkXPress Server Error #–37
This alert displays if you specify an invalid file name or path.
HTTP Error #500The XML document
This alert displays if the XML you supply is not well-formed or does not
adhere to the Modifier DTD.
HTTP Error #500The XML document
This alert displays if you supply an invalid value in the XML.
Logs
Example, GET
URL
Example, object
model
If the request succeeds, a transaction success message is written to the QuarkXPress Server transaction
log file. For example:
The following is a sample of a transaction entry: 8/3/2005 11:27:42 — jpeg/sample.qxp — Type:
image/jpeg — Size: 31715 — Client: 127.0.0.1
If an alert displays, an error message is written to the QuarkXPress Server error log file. For example:
4/12/2007 14:51:50 — Error — Error Code: 10207 — The XML document is not valid or well formed.
Project: /table.qxp
When QuarkXPress Server is running on Windows, use a URL like the following:
http://localhost:8080/sample.qxp?modify=
file:C:\createBox.xml
When QuarkXPress Server is running on Mac OS, use a URL like the following:
http://localhost:8080/sample.qxp?modify=
file:MacHD:xml:createBox.xml
You can also supply a string that consists of valid XML commands. For example:
http://localhost:8080/sample.qxp?modify=<PROJECT><LAYOUT>
<ID UID="layout 1"/><SPREAD><ID UID="1"/><ID/>
<BOX OPERATION="CREATE" BOXTYPE="CT_PICT"><ID NAME="PRODUCTS"/>
<GEOMETRY PAGE="2" SHAPE="SH_RECT"><POSITION><TOP>5</TOP>
<LEFT>5</LEFT><BOTTOM>10</BOTTOM><RIGHT>10</RIGHT></POSITION>
</GEOMETRY></BOX></SPREAD></LAYOUT></PROJECT>
To create a new box, use code like the following:
Spread spread = new Spread();
Box box = new Box();
box.name = "textbox1";
Geometry geometry = new Geometry();
Position position = new Position();
position.top = "110";
position.left = "89";
position.bottom = "220";
position.right = "300";
geometry.position = position;
geometry.shape = "SH_RECT";
geometry.page = "1";
geometry.layer = "Default";
box.geometry = geometry;
box.boxType = "CT_TEXT";
box.operation = "CREATE";
spread.box = new Box[]{box};
72 | QXP SERVER 9.2 WEB INTEGRATION GUIDE
Page 73
Use the following object hierarchy:
ModifierRequest < Project < Layout < Spread < Box < Geometry
Deleting boxes
To delete a box, use the following parameters in the Modifier DTD:
• "BOX (Modifier DTD)"
• "ID (Modifier DTD)"
The following XML shows how these parameters work.
<PROJECT>
<LAYOUT>
<ID UID="Layout 1"/>
<SPREAD>
<ID UID="1"/>
<BOX OPERATION="DELETE">
<ID NAME="SERVICES"/>
</BOX>
</SPREAD>
</LAYOUT>
</PROJECT>
USING THE WEB INTERFACE
Logs
A preview of the QuarkXPress project with the box deleted.Response
File not found.Alerts
pathname.
document is not
valid or well
formed.
document
contains an
invalid tag value.
If the request succeeds, a transaction success message is written to the QuarkXPress Server transaction
log file. For example:
8/3/2005 11:27:42 — jpeg/sample.qxp — Type: image/jpeg — Size: 31715 — Client: 127.0.0.1
If an alert displays, an error message is written to the QuarkXPress Server error log file. For example:
HTTP Error #404
QuarkXPress Server Error #–43
This alert displays if you specify an invalid XML file or request a document that
is not available to QuarkXPress Server.
HTTP Error #404Bad filename/
QuarkXPress Server Error #–37
This alert displays if you specify an invalid file name or path.
HTTP Error #500The XML
This alert displays if the XML you supply is not well-formed or does not adhere
to the Modifier DTD.
HTTP Error #500The XML
This alert displays if you supply an invalid value in the XML.
Example GET
URL
When QuarkXPress Server is running on Windows, use a URL like the following:
http://localhost:8080/sample.qxp?modify=
file:C:\deleteBox.xml
When QuarkXPress Server is running on Mac OS, use a URL like the following:
http://localhost:8080/sample.qxp?modify=
file:MacHD:xml:deleteBox.xml
QXP SERVER 9.2 WEB INTEGRATION GUIDE | 73
Page 74
USING THE WEB INTERFACE
You can also supply a string that consists of valid XML commands. For example:
http://localhost:8080/sample.qxp?modify=
<PROJECT><LAYOUT><ID UID="Layout1"/><SPREAD>
<ID UID="1"/><BOX OPERATION="DELETE">
<ID NAME="HISTORY"/></BOX></SPREAD>
</LAYOUT></PROJECT>
Notes
You can use the xml namespace or Telegraph XTensions software to determine the ID or name of
the box you want to delete.
Grouping and ungrouping items
To group boxes using XML modify, use XML like the following:
<BOX BOXTYPE="CT_TEXT" COLOR="White">
<ID NAME="MainStoryText" UID="217"/>
</BOX>
<BOX BOXTYPE="CT_PICT">
<ID NAME="MainStoryPhoto" UID="218"/>
</BOX>
<GROUP>
<ID NAME="MainStoryGroup" UID="300" OPERATION="CREATE"/>
<BOXREF NAME="MainStoryText" UID="217"/>
<BOXREF NAME="MainStoryPhoto" UID="218"/>
</GROUP>
To add a box to an existing group, use XML like the following:
<GROUP>
<ID NAME="MainStoryGroup" UID="300"/>
<BOXREF NAME="MainStoryText" UID="217"/>
<BOXREF NAME="MainStoryPhoto" UID="218" OPERATION="CREATE"/>
</GROUP>
To remove a box from an existing group, use XML like the following:
<GROUP>
<ID NAME="MainStoryGroup" UID="300"/>
<BOXREF NAME="MainStoryHead" UID="216"/>
<BOXREF NAME="MainStoryText" UID="217"/>
<BOXREF NAME="MainStoryPhoto" UID="218" OPERATION="DELETE"/>
</GROUP>
To ungroup an existing group, use XML like the following:
<GROUP>
<ID NAME="MainStoryGroup" UID="300" OPERATION="DELETE"/>
</GROUP>
To proportionally scale all of the items in a group, add a <GEOMETRY> element that indicates
the new size of the group, like so:
<GROUP>
<ID NAME="MainStoryGroup" UID="300"/>
<GEOMETRY>
<POSITION>
<TOP>10.0</TOP>
<LEFT>10.0</LEFT>
<BOTTOM>50.0</BOTTOM>
<RIGHT>70.0</RIGHT>
</POSITION>
</GEOMETRY>
</GROUP>
74 | QXP SERVER 9.2 WEB INTEGRATION GUIDE
Page 75

USING THE WEB INTERFACE
The order of the <BOXREF> elements in a <GROUP> indicates the order in which the boxes
were selected prior to grouping. The z-order of boxes in the layout is determined by the
order of the <BOX> elements in the XML, from rearmost to frontmost.
XML representations of groups created by versions of QuarkXPress Server prior to 8.1 are
ignored during construct and modify calls, as they were in earlier versions of QuarkXPress
Server.
Creating tables
To create a new table, use the following parameters in the Modifier DTD:
• "SPREAD (Modifier DTD)"
• "TABLE (Modifier DTD)"
• "COLSPEC (Modifier DTD)"
• "COLUMN (Modifier DTD)"
• "ROW (Modifier DTD)"
Logs
• "CELL (Modifier DTD)"
The following XML shows how some of these parameters work.
<PROJECT>
<LAYOUT>
<ID UID="Layout 1"/>
<SPREAD>
<ID UID="1"/>
<TABLE OPERATION="CREATE" ROWS="5" COLUMNS="3">
<ID NAME="STATS"/>
<GEOMETRY PAGE="1"/>
<POSITION>
<TOP>5</TOP>
<LEFT>5</LEFT>
<BOTTOM>30</BOTTOM>
<RIGHT>30</RIGHT>
</POSITION>
</GEOMETRY>
<FRAME WIDTH="1" COLOR="Gray"/>
</TABLE>
</SPREAD>
</LAYOUT>
</PROJECT>
Rather than creating tables manually, you can use the Inline Tables feature, which is much
easier to use. For more information see "Using inline tables."
A preview of the QuarkXPress project with new table created in the specified position.Response
If the request succeeds, a transaction success message is written to the QuarkXPress Server transaction
log file. For example:
4/10/2007 17:54:37 — tab.qxp — Type: image/jpeg — Size: 9049 — Client: 127.0.0.1
Example GET
URL
When QuarkXPress Server is running on Windows, use a URL like the following:
http://localhost:8080/sample.qxp?modify=
file:C:\createTable.xml
QXP SERVER 9.2 WEB INTEGRATION GUIDE | 75
Page 76
USING THE WEB INTERFACE
When QuarkXPress Server is running on Mac OS, use a URL like the following:
http://localhost:8080/sample.qxp?modify=
file:MacHD:xml:createTable.xml
You can also supply a string that consists of valid XML commands. For example:
http://localhost:8080/sample.qxp?modify=
<LAYOUT><ID UID="Layout1"/><SPREAD><ID UID="1"/>
<TABLE OPERATION="CREATE" ROWS="5" COLUMNS="3">
<ID NAME="STATS"/><GEOMETRY PAGE="1"/><POSITION>
<TOP>5</TOP><LEFT>5</LEFT><BOTTOM>30</BOTTOM>
<RIGHT>30</RIGHT></POSITION></GEOMETRY>
</TABLE>SPREAD></LAYOUT></PROJECT>
Example, object
model
To add a new table to an existing spread, use code like the following:
Spread spread = new Spread();
Table table = new Table();
table.name = "textbox1";
Geometry geometry = new Geometry();
Position position = new Position();
position.top = "110";
position.left = "89";
position.bottom = "220";
position.right = "300";
geometry.position = position;
geometry.shape = "SH_RECT";
geometry.page = "1";
geometry.layer = "Default";
table.geometry = geometry;
table.rows = "2";
table.columns = "4";
table.maintainGeometry = "true";
table.operation = "CREATE";
spread.tables = new Table []{table};
Use the following object hierarchy:
ModifierRequest < Project < Layout < Spread < Table
To delete a table, provide the table's name or ID and set the operation attribute to "DELETE".
Using inline tables
The Inline Tables feature makes it easy to create an anchored table. Rather than having to
specify every attribute of a table, you can simply specify the content for a table as a series
of <TROW> and <ENTRY> elements in an <INLINETABLE> element, like so:
<STORY>
<INLINETABLE>
<THEAD>
<TROW>
<ENTRY>Year</ENTRY>
<ENTRY>2012</ENTRY>
<ENTRY>2013</ENTRY>
<ENTRY>2014</ENTRY>
<ENTRY>2015</ENTRY>
</TROW>
</THEAD>
<TBODY>
<TROW>
<ENTRY>Revenue</ENTRY>
<ENTRY>000</ENTRY>
<ENTRY>100</ENTRY>
76 | QXP SERVER 9.2 WEB INTEGRATION GUIDE
Page 77

USING THE WEB INTERFACE
<ENTRY>200</ENTRY>
<ENTRY>300</ENTRY>
</TROW>
<TROW>
<ENTRY>Liabilities</ENTRY>
<ENTRY>000</ENTRY>
<ENTRY>100</ENTRY>
<ENTRY>200</ENTRY>
<ENTRY>300</ENTRY>
</TROW>
</TBODY>
</INLINETABLE>
...
</STORY>
The number of rows in such a table is determined by the number of <TROW> elements.
The number of columns is determined by the maximum number of <ENTRY> elements in
a <TROW>.
In the <TBODY> element, each <TROW> contains one or more <ENTRY> elements. If you
don't style the text in an <ENTRY> element, it uses the default styling, which can be defined
in a <TROWSTYLE> or <TCOLSTYLE> element (see below).
The <THEAD> element lets you create a repeating header for the table. The <TCONTINUED>
element lets you create a "continued" row for the table. If you don't supply either of these
elements, you must create the header row manually as a <TROW> in the <TBODY>.
For each row and column, you can specify the following things:
•
COLOR: Cell background color.
•
SHADE: Cell background shade.
•
STORYDIRECTION: Story direction.
An <INLINETABLE> can also include optional <COLGROUP> elements, which allow you to
specify column attrbutes in the form of <TCOL> elements, like so:
<INLINETABLE>
<COLGROUP>
<TCOL INDEX="1" WIDTH="250">
</TCOL>
</COLGROUP>
...
The INDEX value indicates the column number. You can specify the WIDTH of a column
in points by omitting a unit indicator, or as a percentage of the table width by including
a % after the number.
If you deconstruct a table that was created with an <INLINETABLE> element, the resulting
XML describes the table as a <TABLE> element, not an <INLINETABLE> element.
Using table styles
Table styles make it easy to style inline tables. Rather than applying formatting directly,
you can define a table style, then apply the table style to inline tables like so:
<INLINETABLE TABLESTYLEREF="TableStyle1">
For example, assume you want to create a table where alternating rows are shaded, the
grid is a particular color, the insets are a particular amount, and so forth. Instead of
QXP SERVER 9.2 WEB INTEGRATION GUIDE | 77
Page 78

USING THE WEB INTERFACE
specifying the formatting for such a table manually for every row, you can define the
table's qualities in a table style, like so:
<PROJECT>
<TABLESTYLE WIDTH="95">
<ID NAME="tableStyle10"/>
<TROWSTYLE INSET="2">
<TOPGRID COLOR="none"/>
<BOTTOMGRID COLOR="none"/>
</TROWSTYLE>
<HEADTROWSTYLE COLOR="red" SHADE="30">
<TOPGRID COLOR="red" WIDTH="1"/>
<BOTTOMGRID COLOR="black" WIDTH="1"/>
</HEADTROWSTYLE>
<ODDTROWSTYLE COLOR="black" SHADE="20">
<TOPGRID COLOR="none"/>
<BOTTOMGRID COLOR="none"/>
</ODDTROWSTYLE>
<EVENTROWSTYLE COLOR="magenta" SHADE="60">
<TOPGRID COLOR="none"/>
<BOTTOMGRID COLOR="none"/>
</EVENTROWSTYLE>
<TCOLSTYLE>
<LEFTGRID COLOR="none"/>
<RIGHTGRID COLOR="none"/>
</TCOLSTYLE>
<FIRSTTCOLSTYLE COLOR="Cyan" SHADE="90"/>
<LASTTCOLSTYLE COLOR="Cyan" SHADE="50"/>
</TABLESTYLE>
...
</PROJECT>
A <TABLESTYLE> lets you specify the following things:
•
<TROWSTYLE>: A row style to be applied to every row in the table. One of the two
mandatory elements of <TABLESTYLE>. Includes the INSET attribute, which lets you
specify the inset to apply on all four sides.
•
<HEADTROWSTYLE>: A row style to be applied only to the header row.
•
<ODDTROWSTYLE> and <EVENTROWSTYLE>: Row styles that let you format odd and even
rows differently.
•
<TCOLSTYLE>: A column style. One of the two mandatory elements of <TABLESTYLE>.
Note that when the table is created, column styles override row styles.
•
<FIRSTTCOLSTYLE> and <LASTTCOLSTYLE>: Column styles that let you style the first
and last column of a table differently.
•
<TOPGRID> and <BOTTOMGRID>: A grid line at the top or bottom of a row's cells.
•
<LEFTGRID> and <RIGHTGRID>: A grid line at the left or right edge of a column's cells.
To apply a table style to an inline table, add a TABLESTYLEREF attribute to the
<INLINETABLE> element, like so:
<INLINETABLE TABLESTYLEREF="tableStyle10">
You can also override <TABLESTYLE> attributes by specifying them as part of the table,
like so:
<TROW>
<TOPGRID COLOR="black" WIDTH="1"/>
<BOTTOMGRID COLOR="red" WIDTH="1"/>
<ENTRY COLSPAN="5">Statements</ENTRY>
</TROW>
78 | QXP SERVER 9.2 WEB INTEGRATION GUIDE
Page 79

Here, we've created a cell that spans five columns by supplying only one <ENTRY>, and
we've specified a black, one-point top line and a red, one-point bottom line for that row
only.
Modifying text attributes
You can use the modify parameter to change the attributes of text in a QuarkXPress project.
All modifications are done on a text box basis. To modify text properties, use the following
parameters in the Modifier DTD:
• "BOX (Modifier DTD)"
• "ID (Modifier DTD)"
• "TEXT (Modifier DTD)"
• "STORY (Modifier DTD)"
• "PARAGRAPH (Modifier DTD)"
• "FORMAT (Modifier DTD)"
• "DROPCAP (Modifier DTD)"
USING THE WEB INTERFACE
• "TABSPEC (Modifier DTD)"
• "TAB (Modifier DTD)"
• "RULE (Modifier DTD)"
• "RICHTEXT (Modifier DTD)"
The following XML shows how some of these parameters work.
<PROJECT>
<LAYOUT>
<ID UID="Layout 1"/>
<SPREAD>
<ID UID="1"/>
<BOX BOXTYPE="CT_TEXT">
<ID NAME="ABOUT"/>
<TEXT>
<STORY CLEAROLDTEXT="true" FITTEXTTOBOX="true"
CONVERTQUOTES="true">
<RICHTEXT FONT="Castellar" PLAIN="true"/>
</STORY>
</TEXT>
</BOX>
<BOX BOXTYPE="CT_TEXT">
<ID NAME="HISTORY"/>
<TEXT>
<STORY>
<PARAGRAPH>
<FORMAT ALIGNMENT="RIGHT"/>
<RICHTEXT SIZE="12">This text is 12pt and right
justified.</RICHTEXT>
</PARAGRAPH>
</STORY>
</TEXT>
</BOX>
<BOX BOXTYPE="CT_TEXT">
<ID NAME="PRODUCTS"/>
<TEXT>
<STORY>
<RICHTEXT BOLD="true">This is bold text.</RICHTEXT>
<RICHTEXT BOLD="true" COLOR="Red" ITALIC="true"
SIZE="20">This text is bold, red, italic, and 20pt.
QXP SERVER 9.2 WEB INTEGRATION GUIDE | 79
Page 80

USING THE WEB INTERFACE
</RICHTEXT>
</STORY>
</TEXT>
</BOX>
</SPREAD>
</LAYOUT>
</PROJECT>
A preview of a QuarkXPress project with the values in the ModifierXT tags applied on text boxes.Response
File not found.Alerts
pathname.
document is not
valid or well
formed.
with the
specified
identifier.
value is outside
the valid range.
color is not
available to the
document
HTTP Error #404
QuarkXPress Server Error #–43
This alert displays if you specify an invalid XML file or request a document that
is not available to QuarkXPress Server.
HTTP Error #404Bad filename/
QuarkXPress Server Error #–37
This alert displays if you specify an invalid file name or path.
HTTP Error #500The XML
This alert displays if the XML you supply is not well-formed or does not adhere
to the Modifier DTD.
HTTP Error #500There is no box
This alert displays if the box specified by the child text node of an <ID> element
does not exist.
HTTP Error #500The text size
This alert displays if the value specified in a <SIZE> element is invalid.
What to do: Specify a value between 2 and 720 points.
HTTP Error #500The specified
This alert displays if the value specified in a <COLOR> element is invalid.
HTTP Error #500The specified
Logs
font is not
available
document
contains an
invalid tag value.
box cannot be
modified.
If the request succeeds, a transaction success message is written to the QuarkXPress Server transaction
log file. For example:
8/3/2005 11:27:42 — jpeg/sample.qxp — Type: image/jpeg — Size: 31715 — Client: 127.0.0.1
If an alert displays, an error message is written to the QuarkXPress Server error log file. For example:
8/5/2005 13:32:10 — Error — Error Code: 10006 — There is no box with the specified identifier.
This alert displays if the value specified in a <FONT> element is invalid or the
specified font is not present on the server.
HTTP Error #500The XML
This alert displays if you supply an invalid value in the XML.
HTTP Error #500The specified
This alert displays if you try to modify text properties on a box that is not a text
box.
80 | QXP SERVER 9.2 WEB INTEGRATION GUIDE
Page 81

USING THE WEB INTERFACE
Example GET
URL
Example 1,
object model
When QuarkXPress Server is running on Windows, use a URL like the following:
http://localhost:8080/sample.qxp?modify=
file:C:\modifier.xml
When QuarkXPress Server is running on Mac OS, use a URL like the following:
http://localhost:8080/sample.qxp?modify=
file:MacHD:xml:modifier.xml
You can also supply a string that consists of valid XML commands. For example:
http://localhost:8080/sample.qxp?modify=
<PROJECT><LAYOUT><ID UID="1"/><SPREAD><ID UID="1"/>
<BOX BOXTYPE="CT_TEXT"><ID NAME="BACKGROUND"/>
<TEXT><STORY><RICHTEXT FONT="Castella" PLAIN="true">
This is text.</RICHTEXT></STORY></TEXT></BOX>
</SPREAD></LAYOUT></PROJECT>
Request object names:
ModifierRequest
ModifierStreamRequest
Project
RichText
Text
ID
Box
Layout
ModifierFileRequest
For ModifierFileRequest, the member contents are used to set the file path or send
the XML itself.
com.quark.qxpsm.QRequestContext rc = new com.quark.qxpsm.QRequestContext();
if(!this.DocumentSettings1.documentName.Text.Equals(""))
rc.documentName = this.DocumentSettings1.documentName.Text;
// STEP 2 (SPECIFIC TO REQUESTS):Create the Text Modifier
// renderer request and embed it in request context
ModifierRequest textReq = new ModifierRequest();
Project contents = new Project();
RichText richText1 = new RichText();
richText1.value = this.text1.Text;
richText1.color = this.color1.Text;
Text boxText1 = new Text();
Story story = new Story();
story.richText = new RichText[]{richText1};
boxText1.story = story;
if(this.fittextbox1.Checked)
boxText1.fitTextToBox = "true";
if(this.clearoldtext1.Checked)
boxText1.clearOldText = "true";
Box box1 = new Box();
box1.UID = txtBox1;
box1.text = boxText1;
Layout layout1 = new Layout();
layout1.name = layoutText;
layout1.boxes = new Box[]{box1};
contents.layouts = new Layout[]{layout1};
textReq.contents = contents;
rc.request = textReq;
// Create the service and call it with QRequestContext object
QXP SERVER 9.2 WEB INTEGRATION GUIDE | 81
Page 82

USING THE WEB INTERFACE
RequestService svc = new RequestService();
com.quark.qxpsm.QContentData qc = svc.processRequest(rc);
Example 2,
object model
Notes
Modifying picture properties
To edit the properties of an existing text box in a QuarkXPress project, use the following object
hierarchy:
ModifierRequest < Project < Layout < Spread <
Box < Text < Story < Paragraph < RichText
For a list of the RichText object's properties, see the JavaDoc installed with QuarkXPress Manager.
The Story object also contains some text-related properties: fitTextToBox, includeStylesheets,
convertQuotes, and clearOldText.
The <FITTEXTTOBOX> attribute depends on two preferences: Allow Text to Grow and Font Size.
To set these preferences in QuarkXPress Server, choose QuarkXPress > Server > Preferences and
then click Modifier in the list on the left.
You can modify the properties (such as origin, scale, angle, skew, and orientation) of
pictures in a QuarkXPress project with XML. To modify picture properties, use the following
parameters in the Modifier DTD:
• "BOX (Modifier DTD)"
• "ID (Modifier DTD)"
• "PICTURE (Modifier DTD)"
The following XML shows how some of these parameters work.
<PROJECT>
<LAYOUT>
<ID UID="1"/>
<SPREAD>
<ID UID="1"/>
<BOX BOXTYPE="CT_PICT">
<ID NAME="PEOPLE"/>
<PICTURE SCALEACROSS="50" SCALEDOWN="50" OFFSETACROSS="20"
OFFSETDOWN="20"/>
</BOX>
<BOX BOXTYPE="CT_PICT">
<ID NAME="MOUNTAINS"/>
<PICTURE FIT="CENTERPICTURE" ANGLE="30" SKEW="30"
FLIPHORIZONTAL="false"/>
</BOX>
<BOX BOXTYPE="CT_PICT">
<ID NAME="OFFICES"/>
<PICTURE FIT="FITPICTURETOBOX" ANGLE="30" SKEW="30"
FLIPHORIZONTAL="false"/>
</BOX>
<BOX BOXTYPE="CT_PICT">
<ID NAME="PRODUCTS"/>
<PICTURE FIT="FITPICTURETOBOX" ANGLE="30" SKEW="30"
FLIPHORIZONTAL="false"/>
</BOX>
<BOX BOXTYPE="CT_PICT">
<ID NAME="SERVICES"/>
<PICTURE FIT="FITPICTURETOBOXPRO"/>
</BOX>
</SPREAD>
</LAYOUT>
</PROJECT>
A preview of the QuarkXPress project with image modifier tags applied to the picture boxes.Response
82 | QXP SERVER 9.2 WEB INTEGRATION GUIDE
Page 83

USING THE WEB INTERFACE
File not found.Alerts
pathname.
document is not
valid or well
formed.
with the specified
identifier.
Across should be
between 10% and
1000%.
Down should be
between 10% and
1000%.
HTTP Error #404
QuarkXPress Server Error #–43
This alert displays if you specify an invalid XML file or request a document that
is not available to QuarkXPress Server.
HTTP Error #404Bad filename/
QuarkXPress Server Error #–37
This alert displays if you specify an invalid file name or path.
HTTP Error #500The XML
This alert displays if the XML you supply is not well-formed or does not adhere
to the Modifier DTD.
HTTP Error #500There is no box
This alert displays if the box specified by the child text node of the <ID> element
does not exist.
HTTP Error #500The value of Scale
This alert displays if the value of the child text node of a <SCALEACROSS>
element is invalid.
HTTP Error #500The Value of Scale
This alert displays if the value of the child text node of a <SCALEDOWN> element
is invalid.
Offset Across is in
invalid range.
Offset Down is in
invalid range
Picture Angle
must be between
–360 and 360
degrees.
Picture Skew must
be between –75
and 75 degrees.
document
contains an
invalid tag value.
cannot be
modified.
HTTP Error #500The value of
This alert displays if the value of the child text node of the <OFFSETACROSS>
element is invalid.
HTTP Error #500The value of
This alert displays if the value of the child text node of the <OFFSETDOWN>
element is invalid.
HTTP Error #500The value of
This alert displays if the value of the child text node of the <ANGLE> element
is invalid.
HTTP Error #500The value of
This alert displays if the value of the child text node of the <SKEW> element is
invalid.
HTTP Error #500The XML
This alert displays if you supply an invalid value in the XML.
HTTP Error #500The specified box
This alert displays if you try to modify picture properties on a box that is not a
picture box.
QXP SERVER 9.2 WEB INTEGRATION GUIDE | 83
Page 84

USING THE WEB INTERFACE
Logs
Example GET
URL
Example 1,
object model
If the request succeeds, a transaction success message is written to the QuarkXPress Server transaction
log file. For example:
8/3/2005 11:27:42 — jpeg/sample.qxp — Type: image/jpeg — Size: 31715 — Client: 127.0.0.1
If an alert displays, an error message is written to the QuarkXPress Server error log file. For example:
8/10/2005 10:39:07 — Error — Error Code: 10339 — The specified file failed to load in the picture
box.
When QuarkXPress Server is running on Windows, use a URL like the following:
http://localhost:8080/sample.qxp?modify=
file:C:\imageProperties.xml
When QuarkXPress Server is running on Mac OS, use a URL like the following:
http://localhost:8080/sample.qxp?modify=
file:MacHD:xml:imageProperties.xml
You can also supply a string that consists of valid XML commands. For example:
http://localhost:8080/sample.qxp?modify=
<PROJECT><LAYOUT><ID UID="1"/><SPREAD>
<ID UID="1"/><BOX BOXTYPE="CT_PICT">
<ID NAME="EVEREST"/>
<PICTURE SCALEACROSS="50" OFFSETDOWN="20"
ANGLE="30" FIT="CENTERPICTURE" SKEW="30"
FLIPHORIZONTAL="false"/></BOX></SPREAD>
</LAYOUT></PROJECT>
Request object names:
ModifierRequest
ModifierStreamRequest
Project
Box
Picture
Layout
ModifierFileRequest
For ModifierFileRequest, the member contents are used to set the file path or send
the XML itself.
com.quark.qxpsm.QRequestContext rc = new com.quark.qxpsm.QRequestContext();
if(!this.DocumentSettings1.documentName.Text.Equals(""))
rc.documentName = this.DocumentSettings1.documentName.Text;
// STEP 2(SPECIFIC TO REQUESTS):Create the Image
// Modifier renderer request and embed it in
ModifierRequest imgReq = new ModifierRequest();
Project contents = new Project();
Picture picture1 = new Picture();
picture1.scaleAcross = this.scaleacross1.Text;
picture1.scaleDown = this.scaledown1.Text;
if(this.fitpicturebox1.Checked == true)
picture1.fitPictureToBox = "true";
if(this.flipvertical1.Checked == true)
picture1.flipVertical = "true";
if(this.fliphorizontal1.Checked == true)
picture1.flipHorizontal = "true";
Box box1 = new Box();
box1.UID = txtBox1;
box1.picture = picture1;
Layout layout1 = new Layout();
layout1.name = layoutText;
imgReq.contents = contents;
84 | QXP SERVER 9.2 WEB INTEGRATION GUIDE
Page 85

USING THE WEB INTERFACE
contents.layouts = new Layout[]{layout1};
layout1.boxes = new Box[]{box1};
rc.request = imgReq;
// Create the service and call it with QRequestContext object
RequestService svc = new RequestService();
com.quark.qxpsm.QContentData qc = svc.processRequest(rc);
Example 2,
object model
Importing data
To edit the properties of an existing text box in a QuarkXPress project, use the following object
hierarchy:
ModifierRequest < Project < Layout < Spread < Box < Picture
For a list of the Picture object's properties, see the JavaDoc installed with
QuarkXPress Manager.
You cannot replace an image with the Modifier XTensions software.Notes
If you specify <FITPICTURETOBOX>, <FITBOXTOPICTURE>, and <FITPICTURETOBOXPRO> for a
picture, only the first of these elements will be applied.
Imports text or image data into a project. You can use import any text or picture file format
supported by QuarkXPress, including XPress Tags files.
You can import .doc, .docx, .dot, .dotx, and .docm files.
To import text or image data into a project, use the following parameters in the Modifier
DTD:
• "BOX (Modifier DTD) "
• "ID (Modifier DTD)"
• "PICTURE (Modifier DTD)" (this is not a required element when importing data)
• "TEXT (Modifier DTD)"
• "STORY (Modifier DTD)"
• "CONTENT (Modifier DTD)"
The following XML shows how some of these parameters work.
<PROJECT>
<ID NAME="Layout 1"/>
<SPREAD>
<ID UID="1"/>
<BOX BOXTYPE="CT_PICT">
<ID NAME="ABOUT"/>
<PICTURE/>
<CONTENT>C:\docs\file1.jpg</CONTENT>
</BOX>
<BOX BOXTYPE="CT_TEXT">
<ID NAME="PRODUCTS"/>
<CONTENT>file:C:\docs\file2.txt</CONTENT>
</BOX>
<BOX BOXTYPE="CT_TEXT">
<ID NAME="SERVICES"/>
<TEXT>
<STORY FILE="file:C:\docs\file3.doc" CONVERTQUOTES="true"
INCLUDESTYLESHEETS="true"/>
</TEXT>
</BOX>
</SPREAD>
QXP SERVER 9.2 WEB INTEGRATION GUIDE | 85
Page 86
USING THE WEB INTERFACE
</LAYOUT>
</PROJECT>
Response
A preview of a QuarkXPress project with a value in the data import XML tags applied to the text
boxes.
File not found.Alerts
document is not
valid or well
formed.
with the
specified
identifier.
box is not a
picture or text
box.
cannot be
manipulated.
HTTP Error #404
QuarkXPress Server Error #–43
This alert displays if you specify an invalid XML file or request a document that
is not available to QuarkXPress Server.
HTTP Error #500The XML
This alert displays if the XML you supply is not well-formed or does not adhere
to the Modifier DTD.
HTTP Error #500There is no box
This alert displays if the box specified by the child text node of the <ID> element
does not exist.
HTTP Error #500The specified
This alert displays if you request a box that is not a text box or a picture box.
HTTP Error #500A locked layer
This alert displays if you request data from a box on a locked layer.
What to do: Open the project in QuarkXPress, display the Layers palette, and
unlock the box's layer.
Logs
Example GET
URL
HTTP Error #500Unable to read
picture (#106)
pathname
If the request succeeds, a transaction success message is written to the QuarkXPress Server transaction
log file. For example:
8/5/2005 18:11:54 — sample.qxp — Type: image/jpeg — Size: 65982 — Client: 127.0.0.1
If an alert displays, an error message is written to the QuarkXPress Server error log file. For example:
8/5/2005 18:01:59 — Error — Error Code: 10343 — A locked Layer cannot be manipulated.
When QuarkXPress Server is running on Windows, use a URL like the following:
http://localhost:8080/Sample.qxp?modify=
file:c:\file.xml
When QuarkXPress Server is running on Mac OS, use a URL like the following:
http://localhost:8080/Sample.qxp?modify=
file:HDD:file.xml
You can also supply a string that consists of valid XML commands. For example:
http://localhost:8080/sample.qxp?modify=
<PROJECT><LAYOUT><ID UID="Layout1"/><SPREAD><ID UID="1"/>
<BOXBOXTYPE="CT_TEXT"><ID NAME="TREES"/>
QuarkXPress Server Error #–109
This alert displays if you try to import a text file into a picture box.
HTTP Error #404Bad filename/
QuarkXPress Server Error #–37
This alert displays if you try to import an invalid or nonexistent file into a box.
86 | QXP SERVER 9.2 WEB INTEGRATION GUIDE
Page 87

USING THE WEB INTERFACE
<CONTENT>C:\docs\file1.jpg</CONTENT>
</BOX></SPREAD></LAYOUT></PROJECT>
When specifying a path, use URLs like the following:
http://localhost:8080/Sample.qxp?
textboxname@dataimport=file:c:\file.txt
http://localhost:8080/Sample.qxp?
pictureboxname@dataimport=c:\file.jpg
You can import text directly into a box from the URL string. For example:
http://localhost:8080/Sample.qxp?
textboxname@dataimport=Newdata
When you import a file that uses style sheets, you can control how those style sheets are handled.
For example:
http://localhost:8080/Documentname?
textboxname@dataimport=file:c:\file.doc&
textboxnameincludestylesheets@dataimport=yes
You can control how quotation marks are handled at import. For example:
http://localhost:8080/Documentname?
textboxname@dataimport=file:c:\file.doc&
textboxnameconvertquotes@dataimport=yes
Example, object
model
Request object names:
ModifierRequest
ModifierStreamRequest
Project
RichText
Text
ID
Box
Layout
ModifierFileRequest
For ModifierFileRequest, the member contents are used to set the file path or send
the XML itself.
com.quark.qxpsm.QRequestContext rc = new com.quark.qxpsm.QRequestContext();
if(!this.DocumentSettings1.documentName.Text.Equals(""))
rc.documentName = this.DocumentSettings1.documentName.Text;
// STEP 2 (SPECIFIC TO REQUESTS):Create the data import
// request and embed it in request context
ModifierRequest request = new ModifierRequest();
Project requestContents = new Project();
Content boxContent1 = new Content();
Box box1 = new Box();
box1.UID = txtBox1;
box1.content = boxContent1;
Layout layout1 = new Layout();
layout1.name = layoutText;
if(!this.content1.Text.Equals(""))
{
boxContent1.value = this.content1.Text;
Text text1 = new Text();
text1.font = this.fontname1.Text;
box1.text = text1;
if(this.includestylesheets1.Checked == false)
boxContent1.includeStylesheets = "false";
if(this.convertquotes1.Checked == false)
QXP SERVER 9.2 WEB INTEGRATION GUIDE | 87
Page 88

USING THE WEB INTERFACE
boxContent1.convertQuotes = "false";
}
else if (null != uplTheFile.PostedFile)
{
Stream theStream = uplTheFile.PostedFile.InputStream;
StreamReader reader = new StreamReader(theStream);
boxContent1.value = reader.ReadToEnd();
}
layout1.boxes = new Box[]{box1};
requestContents.layouts = new Layout[]{layout1};
request.contents = requestContents;
rc.request = request;
// Create the service and call it with QRequestContext object
RequestService svc = new RequestService();
com.quark.qxpsm.QContentData qc = svc.processRequest(rc);
Notes
BoxParam XTensions software lets you import only files in the document pool. Modifier XTensions
software, however, lets you import files that are located anywhere on the server computer, at any
accessible network location, or supplied as part of a multipart HTTP request.
Exporting Job Jackets files during deconstruction
While using the xml namespace to deconstruct a QuarkXPress project, you can specify the
jjname parameter in the same request to output the Job Jackets file to the document pool.
For example:
http://localhost:8080/xml/project.qxp?jjname=jjfilename.xml
You can then use the construct namespace to create new QuarkXPress projects that are
based on that Job Jackets file's resources and layout specifications.
The jjname parameter exports QuarkXPress project resources and layout specifications to
a Job Ticket. Resources defined at the Job Jackets level are not exported to the Job Ticket.
Using interactivity
The <INTERACTIVITY> element describes an asset used as an interactive element for a
format such as App Studio, ePUB, or Blio.
The specific schema for an interactive element is determined by the XTensions module
that owns that element, so such schemas are not defined here. The best way to create or
modify an <INTERACTIVITY> element is to deconstruct it and then use the deconstructed
XML as a template.
Using XML deconstruct and construct
The xml namespace deconstructs a project according to the Modifier DTD. The construct
namespace lets you turn an XML representation of a QuarkXPress project back into a
QuarkXPress project.
This means you can deconstruct a project into an XML representation, change the XML
in accordance with the Modifier DTD, and then have the server generate an updated
88 | QXP SERVER 9.2 WEB INTEGRATION GUIDE
Page 89

USING THE WEB INTERFACE
version of the QuarkXPress project. You can even create new QuarkXPress projects from
scratch using XML.
In addition, you can use the construct namespace to:
• Create a page based on a master page
• Create a project from XML, using a Job Jackets file as the basis for the project
• Modify text font and style, including OpenType styles
• Apply style sheets and local formatting to text
• Create and populate tables
• Import pictures into picture boxes and specify picture attributes
The DTD used for XML construction and deconstruction is completely Unicode-compliant,
making it ideal for use in international publishing. Furthermore, the use of this DTD
ensures that the schema of XML output created by Constructor does not change when
server preferences change. For more information, see "Modifier DTD (annotated)."
Some minor QuarkXPress features are not available through the Modifier DTD. However,
this DTD represents the majority of all user-editable aspects of a QuarkXPress project.
The deconstruct namespace/request no longer exists. If you try to use it in this version of
QuarkXPress Server, an error is returned.
Deconstructing a project
The xml namespace returns an XML representation of the target project. To use this
namespace, use a URL like the following:
http://QXPServer8:8080/xml/project1.qxp
When you use the xml namespace, QuarkXPress Server returns an XML file that represents
the deconstructed project. This XML file adheres to the Modifier DTD (see "Modifier DTD
(annotated)").
An XML file that represents a deconstructed project does not contain all of the information
necessary to reconstruct the project. The definitions of the project's resources (such as style
sheets, colors, and master page definitions) are stored in a Job Jackets file. For example,
you can apply a style sheet to a paragraph by indicating the style sheet’s name, like so:
<PARAGRAPH PARASTYLE="BodyText">
<RICHTEXT>The sun has risen.</RICHTEXT>
</PARAGRAPH>
The above information is included in the deconstructed project’s XML file. The definition
of the “BodyText” style sheet, however, is stored in the Job Jackets file.
The URL of a deconstructed Job Jackets file is indicated by the PROJECT@JOBJACKET
attribute. If you need access to new colors, style sheets, master pages, or other resources,
add them to the Job Jackets file indicated by this URL.
QXP SERVER 9.2 WEB INTEGRATION GUIDE | 89
Page 90

USING THE WEB INTERFACE
Projects can also refer to resources defined with the QuarkXPress Server Document Controls
submenu (Server/QuarkXPress Server menu). QuarkXPress Server looks for resources first
in the Job Jackets file and then in the server-defined resources.
XML
Creates an XML file from a QuarkXPress project. The XML is returned in a fixed format
that adheres to the Modifier DTD. You can use the returned XML to create or modify a
QuarkXPress document using the construct namespace or modify parameter.
Namespace
Parameters
xml
Modifier DTDDTD
box
boxes
XSL
layout
relativegeometry
relativetopage
copyfitinfo
Returns XML only for the box with the given ID or name.
Returns XML only for the boxes with the IDs or names supplied as a
comma -separated list.
Specifies the path of an XSL file for transforming the returned XML. Use
the file: indicator to specify the path.
Specifies the name or number of the layout containing the box to render.
The first layout is layout 1. Note that this parameter works only with the
box parameter.
Tells the xml namespace to describe <GEOMETRY> elements using
<RELPOSITION> rather than <POSITION>. This allows an item's position
to be defined either in relation to the page or in relation to the entire
spread.
Use only with the relativegeometry parameter. Tells the xml
namespace to describe <GEOMETRY> elements using <RELPOSITION>
elements in which ORIGIN@RELATIVETO="page" (as opposed to
"spread").
QuarkXPress Server returns copyfitting information for QuarkCopyDesk
articles by default. To retrieve copyfitting information when
deconstructing a QuarkXPress project, include copyfitinfo=true in
the xml request. For example:
http://localhost:8080/xml/sample.qxp?
copyfitinfo=true
Refer to the Modifier DTD
Response
Sample response:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="no"?>
<PROJECT JOBJACKET="Macintosh HD:QuarkXPress DocPool:
default job jackets:New Job Jacket.xml"
JOBTICKET="Default Job Ticket"
PROJECTNAME="project1.qxp">
<LAYOUT MEDIATYPE="PRINT">
<ID NAME="Layout 1" UID="1"/>
<LAYER KEEPRUNAROUND="false" LOCKED="false"
SUPPRESS="false" VISIBLE="true">
<ID NAME="Default" UID="-1"/>
<RGBCOLOR BLUE="231" GREEN="231" RED="231"/>
</LAYER>
90 | QXP SERVER 9.2 WEB INTEGRATION GUIDE
Page 91

USING THE WEB INTERFACE
<SPREAD>
<ID UID="1"/>
<PAGE MASTER="3" POSITION="RIGHTOFSPINE"
FORMATTEDNAME="1">
<ID UID="1"/>
</PAGE>
<BOX BOXTYPE="CT_TEXT" COLOR="None" OPACITY="100%"
SHADE="100%">
<ID NAME="Introduction" UID="5"/>
<GEOMETRY LAYER="Default" PAGE="1" SHAPE="SH_RECT">
<POSITION>
<TOP>39.064</TOP>
<LEFT>39.026</LEFT>
<BOTTOM>63.951</BOTTOM>
<RIGHT>214.611</RIGHT>
</POSITION>
<SUPPRESSOUTPUT>false</SUPPRESSOUTPUT>
<RUNAROUND TYPE="NONE"/>
</GEOMETRY>pre
<FRAME GAPCOLOR="White" GAPOPACITY="100%"
GAPSHADE="100%"OPACITY="100%" SHADE="100%"
STYLE="Solid" WIDTH="0 pt"/>
<TEXT>
<STORY>
<COPYFIT FITAMOUNT="0.033""
NUMBEROFCHARACTERS="6"
NUMBEROFLINES="1" NUMBEROFWORDS="1"
STATE="underFit"/>
<PARAGRAPH PARASTYLE="launch">
<RICHTEXT CHARSTYLE="launch">LAUNCH</RICHTEXT>
</PARAGRAPH>
</STORY>
</TEXT>
</BOX>
<BOX BOXTYPE="CT_PICT" COLOR="None" OPACITY="100%"
SHADE="100%">
<ID NAME="Sunrise" UID="6"/>
<PICTURE SCALEACROSS="100%" SCALEDOWN="100%"/>
<CONTENT>
Macintosh HD:QuarkXPress Server Documents:sunrise.tif
</CONTENT>
<GEOMETRY LAYER="Default" PAGE="1" SHAPE="SH_RECT">
<POSITION>
<TOP>0</TOP>
<LEFT>0</LEFT>
<BOTTOM>800</BOTTOM>
<RIGHT>600</RIGHT>
</POSITION>
<SUPPRESSOUTPUT>false</SUPPRESSOUTPUT>
<RUNAROUND BOTTOM="0" LEFT="0" RIGHT="0" TOP="0"
TYPE="ITEM"/>
</GEOMETRY>
<FRAME GAPCOLOR="White" GAPOPACITY="100%"
GAPSHADE="100%"
OPACITY="100%" SHADE="100%" STYLE="Solid"
WIDTH="0"/>
<PICTURE/>
</BOX>
</SPREAD>
</LAYOUT>
</PROJECT>
QXP SERVER 9.2 WEB INTEGRATION GUIDE | 91
Page 92
USING THE WEB INTERFACE
Logs
Example GET
URL
Example, Object
Model
Constructing a project
If the request succeeds, a transaction success message is written to the QuarkXPress Server transaction
log file. For example:
8/3/2004 17:16:11 — xml/sample.qxp — Type: text/xml — Size: 2364 — Client: 127.0.0.1
http://localhost:8080/xml/sample.qxp
You can also deconstruct QuarkCopyDesk articles. To deconstruct a QuarkCopyDesk article, use
the following:
http://localhost:8080/xml/copydesk/abc.qcd
Request object name: XMLRequest
XMLRequest xmlRequest = new XMLRequest();
QRequestContext context = new QRequestContext();
context.setDocumentName("SAMPLE_DOCUMENT.qxp");
context.setResponseAsURL(false);
context.setRequest(xmlRequest);
QContentData response = new RequestServiceStub().processRequest(context);
System.out.println(response.getTextData());
The construct namespace takes two arguments: The name of the project to be created,
and a modify parameter that points to the XML file or string that describes how to create
the project. For example:
http://QXPServer8:8080/construct/project1.qxp?
modify=file:path to XML file on server
or:
http://QXPServer8:8080/construct/project1.qxp?modify=XML string
There is a length limitation of 4096 characters on URLs, so you will probably want to use
an XML file rather than an XML string.
If you are using QuarkXPress Server Manager, you can send a similar command with a
QuarkXPress Server Manager URL or through Web services.
Every project created with the construct namespace must be based on a Job Ticket in a
Job Jackets file. Using construct to create a project is roughly equivalent to using the
File > New > Project from Ticket command in QuarkXPress.
When you create a project using the construct namespace, you must supply the path to
the Job Jackets file that will supply the project's resources. To do so, indicate the URL of
the Job Jackets file in the PROJECT@JOBJACKET attribute and the name of the Job Ticket
in the PROJECT@JOBTICKET attribute. (<PROJECT> is the root element of the Modifier
DTD. For more information, see "Modifier DTD (annotated).")
For example, to create a project from a Job Ticket named "Tall US Brochure Ticket" in a
Job Jackets file named "BrochureJJ.xml," use XML like the following:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="no" ?>
<PROJECT JOBJACKET="MacintoshHD:brochures:BrochureJJ.xml"
JOBTICKET="Tall US Brochure Ticket"
PROJECTNAME="project1.qxp">
92 | QXP SERVER 9.2 WEB INTEGRATION GUIDE
Page 93
Construct
The construct namespace lets you create a QuarkXPress project using XML.
USING THE WEB INTERFACE
Namespace
Parameters
Example GET
URL
Example XML
construct
Modifier DTDDTD
modify
qxpdocver
http://QXPServer8:8080/construct/
project1.qxp?modify=file:sample.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<PROJECT JOBJACKET="C:\XML\New Job Jacket 3.xml"
JOBTICKET="Default Job Ticket"
PROJECTNAME="project1.qxp">
<LAYOUT>
<ID NAME="Layout 1"/>
<SPREAD>
<ID UID="1"/>
<PAGE>
<ID UID="1"/>
</PAGE>
</SPREAD>
</LAYOUT>
</PROJECT>
String
8 | 9
The string or the path of the XML file that describes how to
create the project. Use the file: indicator to specify the
path.
Indicates the QuarkXPress version format to use. For example:
http://QXPServer8:8080/construct/
qxpdoc/project1.qxp?qxpdocver=8
Logs
A new QuarkXPress project.Response
HTTP Error #404File not found.Alerts
QuarkXPress Server Error #–43
This alert displays if you specify an invalid XML file or request a document
that is not available to QuarkXPress Server. For example, this error can
occur if an image or text file file mentioned in a <CONTENT> element is
invalid or missing.
HTTP Error #404Bad filename/pathname.
QuarkXPress Server Error #–37
This alert displays if you specify an invalid file name or path.
HTTP Error #500The XML document is
not valid or well formed.
contains an invalid tag
value.
If the request succeeds, a transaction success message is written to the QuarkXPress Server transaction
log file. For example:
8/3/2005 11:27:42 — jpeg/construct/table.qxp — Type: image/jpeg — Size: 31715 — Client: 127.0.0.1
This alert displays if the XML you supply is not well-formed or do not
adhere to the Modifier DTD.
HTTP Error #500The XML document
This alert displays if you supply an invalid value in the XML.
QXP SERVER 9.2 WEB INTEGRATION GUIDE | 93
Page 94

USING THE WEB INTERFACE
If an alert is displayed, an error message is written to the QuarkXPress Server error log. The following
is a sample of the error log entry:
8/10/2005 10:39:07 — Error — Error Code: 10339 — The specified file failed to load in the picture
box.
Example, object
model
Request Object Names:
XMLRequest
ConstructRequest
ConstructFileRequest
ConstructStreamRequest
To construct a new QuarkXPress project by editing an existing document, first deconstruct a
QuarkXPress project using code like the following:
XMLRequest dcnstrq = new XMLRequest();
rc.request = dcnstrq;
Next, alter the project by manipulating the XML. When you're done, pass the modified XML
document to ConstructStreamRequest to create a new QuarkXPress project. For example:
ConstructStreamRequest cnstrq =
new ConstructStreamRequest();
cnstrq.modify = Buffer; // Byte[] for the modified XML
rc.request = cnstrq;
QuarkXPressRenderRequest qxprq =
new QuarkXPressRenderRequest();
cnstrq.request = qxprq;
Alternatively, you can deconstruct a QuarkXPress project using code like the following:
RequestServiceService svc =
new RequestServiceService()
Project proj = svc.getDOM("document.qxp");
Next, alter the project by manipulating the XML. When you're done, pass the modified Project
instance to ConstructRequest to create a new QuarkXPress project. For example:
ConstructRequest cnstrq =
new ConstructRequest();
cnstrq.project = proj;
QRequestContext rc = new QRequestContext();
rc.request = cnstrq;
QuarkXPressRenderRequest qxprq =
new QuarkXPressRenderRequest();
cnstrq.request = qxprq;
Notes
The construct namespace takes two arguments: The name of the project to be created and a
modify parameter with the string or the path of the XML file that describes how to create the
project:
http://localhost:8080/qxpdoc/construct/project1.qxp?
modify=file:path to XML file on server
http://localhost:8080/qxpdoc/construct/project1.qxp?
modify=<xml-string>
Construct and modify
The modify parameter lets you modify existing projects. For example:
http://QXPServer8:8080/project1.qxp?
modify=file:path to XML file on server
or:
http://QXPServer8:8080/project1.qxp?modify=XML string
94 | QXP SERVER 9.2 WEB INTEGRATION GUIDE
Page 95

It's important to understand that although the construct namespace uses the same DTD
that you use when you modify an existing project, the construct namespace uses it
differently. When you use the construct namespace, the XML you pass simply contains
a description of everything in the document you want to create — much as an HTML file
describes a page you want to display in a browser. There is no need to use a command
and create elements such as ADDCELLS, OPERATION, and MOVERIGHT; you simply describe
each item in the layout with elements such as <BOX> and <TABLE>, and specify each item's
position with the <POSITION> element type. When you use the modify attribute without
the construct namespace, however, the XML you pass must contain commands that
show how you want QuarkXPress Server to modify the project.
For more information, see "Modifier DTD (annotated)."
Working with pages and spreads
The root element of a deconstructed QuarkXPress project is <PROJECT>. Within each
<PROJECT> element are one or more <LAYOUT> elements. Each layout contains one or
more <SPREAD> elements, and each <SPREAD> contains one or more <PAGE> elements.
Each layout, spread, and page has a unique name, indicated by its <ID> element.
USING THE WEB INTERFACE
Each layout can have a unique name, indicated by its <ID> element's NAME attribute. You
can use a layout's name when referring to that layout in a non-construct call that uses the
MODIFY attribute. The ID@NAME attribute is ignored for <SPREAD> and <PAGE> elements,
but you can refer to them numerically with their <ID> element's UID attribute, with "1"
being the first, "2" being the second, and so forth.
With most element types, it is best to assign an ID@NAME value to an element and use that
to refer to the element, because ID@UID values are defined by QuarkXPress Server and thus
ignored for construct calls. <PAGE> and <SPREAD> are exceptions to this rule.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="no" ?>
<PROJECT JOBJACKET=" MacintoshHD:brochures:BrochureJJ.xml"
JOBTICKET="Tall US Brochure Ticket"
PROJECTNAME="project1.qxp">
<LAYOUT>
<ID NAME="Layout 1" />
<SPREAD>
<ID UID="1" />
<PAGE POSITION="RIGHTOFSPINE" MASTER="3">
<ID UID="2" />
</PAGE>
...
Each page has a POSITION attribute that indicates which side of the spine it is on. (In
single-sided layouts, every page is given a POSITION of RIGHTOFSPINE).
You can assign items to a page using the GEOMETRY element, which is a child of the BOX
and TABLE elements. For example:
<BOX BOXTYPE="CT_TEXT" COLOR="White">
<ID NAME="Title Box" />
<GEOMETRY LAYER="Default" PAGE="1" SHAPE="SH_RECT">
<POSITION>
<TOP>90</TOP>
<LEFT>95</LEFT>
<BOTTOM>190</BOTTOM>
<RIGHT>195</RIGHT>
</POSITION>
QXP SERVER 9.2 WEB INTEGRATION GUIDE | 95
Page 96

USING THE WEB INTERFACE
</GEOMETRY>
</BOX>
Master pages are stored in a deconstructed project’s Job Jackets file. To create a page from
this master page, insert a MASTER attribute into the PAGE element and indicate the number
of the target master page. Master page numbering is as follows:
1 = blank single page
2 = blank facing-page
3 = the first user-defined master page in the Job Jackets file (by default, the master page
named "A-Master A")
For example, to create a master page based on the first user-defined master page in the
Job Jackets file, you could use XML like the following:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="no" ?>
<PROJECT JOBJACKET=" file://brochures/BrochureJJ.xml"
JOBTICKET="Tall US Brochure Ticket"
PROJECTNAME="project1.qxp">
<LAYOUT>
<ID NAME="Layout 1"/>
<SPREAD>
<ID UID="1" />
<PAGE MASTER="3" POSITION="LEFTOFSPINE">
<ID UID="2" />
</PAGE>
...
Note that each page has a POSITION attribute that indicates where that page falls with
regard to the spine.
Working with layers
To create a layer in XML, use the LAYER element. For example:
<LAYER KEEPRUNAROUND="true" LOCKED="false"
SUPPRESS="false" VISIBLE="true">
<ID NAME="Layer 1" />
</LAYER>
The RGBCOLOR element defines the layer's color as displayed in the Layers palette.
You can assign items to a layer using the GEOMETRY element, which is a child of the BOX
and TABLE elements. For example:
BOX BOXTYPE="CT_TEXT" COLOR="White">
<ID NAME="Main Layer" />
<GEOMETRY LAYER="Default" PAGE="1" SHAPE="SH_RECT">
<POSITION>
<TOP>90</TOP>
<LEFT>95</LEFT>
<BOTTOM>190</BOTTOM>
<RIGHT>195</RIGHT>
</POSITION>
</GEOMETRY>
</BOX>
Working with boxes
To add text and pictures to a project, you must add text boxes and picture boxes to the
project’s <SPREAD> element. Both are represented by <BOX> elements, but text boxes have
a BOXTYPE attribute of CT_TEXT, and picture boxes have a BOXTYPE attribute of CT_PICT.
You can read about how <BOX> elements are put together in the Modifier DTD, but for
96 | QXP SERVER 9.2 WEB INTEGRATION GUIDE
Page 97

USING THE WEB INTERFACE
purposes of illustration, the sample XML below describes a spread that contains a text box
and a picture box.
<SPREAD>
<ID UID="1" />
<!-- TEXT BOX -->
<BOX BOXTYPE="CT_TEXT" COLOR="White">
<ID NAME="Headline Box" />
<GEOMETRY LAYER="Default" PAGE="1" SHAPE="SH_RECT">
<POSITION>
<TOP>200</TOP>
<LEFT>80</LEFT>
<BOTTOM>450</BOTTOM>
<RIGHT>475</RIGHT>
</POSITION>
</GEOMETRY>
<TEXT>
<STORY>
<PARAGRAPH PARASTYLE="Normal">
<RICHTEXT>This is text in a box.</RICHTEXT>
</PARAGRAPH>
</STORY>
</TEXT>
</BOX>
<!-- PICTURE BOX -->
<BOX BOXTYPE="CT_PICT">
<ID NAME="Main Story Photo" />
<GEOMETRY LAYER="Default" PAGE="1" SHAPE="SH_RECT">
<POSITION>
<TOP>90</TOP>
<LEFT>95</LEFT>
<BOTTOM>190</BOTTOM>
<RIGHT>195</RIGHT>
</POSITION>
</GEOMETRY>
<PICTURE ANGLE="0°" FLIPHORIZONTAL="false"
FLIPVERTICAL="false" FULLRES="false" MASK="None"
OFFSETACROSS="0 OFFSETDOWN="0" OPACITY="100%"
SCALEACROSS="100%" SCALEDOWN="100%" SHADE="100%"
SKEW="0°" SUPRESSPICT="false"/>
<CONTENT>Macintosh HD:DocPool:flower1.jpg</CONTENT>
</BOX>
</SPREAD>
This example will work for a construct request. For a modify request, add the attribute
value OPERATION="CREATE" in the BOX element.
All BOX elements can contain a GEOMETRY element that indicates the position and size of
the box, a FRAME element that describes the box's frame (if any), and a SHADOW element
that describes the box's drop shadow. Additional BOX elements are described in the following
sections.
The z-order (stacking order) of boxes in the layout is determined by the order of the <BOX>
elements in the XML, from rearmost to frontmost.
Fitting a box to text or a picture
The <FIT> element type lets you automatically adjust the size of a box to fit the text or
picture in that box.
The default behaivior is to not fix a box to its content. To use this feature, you must supply
<MAX> and <MIN> elements. Each <MAX> or <MIN> element lets you specify a maximum
or minimum size for the box, a maximum or minimum location for the resized box, or a
QXP SERVER 9.2 WEB INTEGRATION GUIDE | 97
Page 98

USING THE WEB INTERFACE
maximum or minimum scale percentage for the box. Note that you can use different types
of <MAX> and <MIN> elements in a <FIT> element, but you can use only one <MAX> element
and one <MIN> element per <FIT> element.
The FIT@POINT attribute lets you indicate the direction in which the box should grow or
shrink. The available options are TOPLEFT, BOTTOMLEFT, TOPRIGHT, and BOTTOMRIGHT.
The FIT@AVOIDBOXESBY attribute lets you specify the distance between the POINT side
or corner of a resized box and any other items around it. A box will expand only until it
is this distance from an adjacent item.
The FIT@PROPORTIONAL attribute lets you specify whether the resized box should have
the same aspect ratio as the original box.
For example:
<BOX>
<ID UID="5"/>
<GEOMETRY>
<POSITION>
<TOP>224.001</TOP>
<LEFT>110.003</LEFT>
<BOTTOM>381</BOTTOM>
<RIGHT>253.253</RIGHT>
</POSITION>
<FIT POINT="BOTTOMLEFT" PROPORTIONAL="true">
<MAX>
<LOCATION X="320" Y="560"/>
</MAX>
<MIN>
<SIZE HEIGHT="100" WIDTH="10"/>
</MIN>
</FIT>
</GEOMETRY>
<BOX/>
To use this feature, you must have FitBoxToContent XTensions software loaded.
For pictures, <FIT> is equivalent to PICTURE@FIT="FITBOXTOPICTURE". <MAX> and
<MIN> have no effect.
Working with groups
To add boxes to a group, create a <GROUP> element and then insert <BOXREF> elements
that refer to the boxes you want in the group. For example, the group described below
includes the two boxes described above it:
<BOX BOXTYPE="CT_TEXT" COLOR="White">
<ID NAME="MainStoryText" UID="217"/>
</BOX>
<BOX BOXTYPE="CT_PICT">
<ID NAME="MainStoryPhoto" UID="218"/>
</BOX>
<GROUP>
<ID NAME="MainStoryGroup" UID="300"/>
<BOXREF NAME="MainStoryText" UID="217"/>
<BOXREF NAME="MainStoryPhoto" UID="218"/>
</GROUP>
98 | QXP SERVER 9.2 WEB INTEGRATION GUIDE
Page 99

USING THE WEB INTERFACE
You can nest one group within another by adding a <BOXREF> that refers to the child
group, like so:
<GROUP>
<ID NAME="MainStoryGroup" UID="300"/>
<BOXREF NAME="MainStoryText" UID="217"/>
<BOXREF NAME="MainStoryPhoto" UID="218"/>
</GROUP>
<BOX BOXTYPE="CT_PICT">
<ID NAME="Masthead" UID="001"/>
</BOX>
<GROUP>
<ID NAME="MainStoryPage" UID="218"/>
<BOXREF NAME="Masthead" UID="001"/>
<BOXREF NAME="MainStoryGroup" UID="300"/>
</GROUP>
To anchor a group in a text box, use XML like the following. Note that you must set
BOX@ANCHOREDGROUPMEMBER="true" for all boxes in the group, and set
GROUP@ANCHOREDIN for the anchored group.
<BOX BOXTYPE="CT_TEXT" COLOR="White" ANCHOREDGROUPMEMBER="true" >
<ID NAME="MainStoryText" UID="217"/>
</BOX>
<BOX BOXTYPE="CT_PICT" ANCHOREDGROUPMEMBER="true" >
<ID NAME="MainStoryPhoto" UID="218"/>
</BOX>
<GROUP ANCHOREDIN="MainStoryText">
<ID NAME="MainStoryGroup" UID="300"/>
<BOXREF NAME="MainStoryText" UID="217"/>
<BOXREF NAME="MainStoryPhoto" UID="218"/>
</GROUP>
<BOX BOXTYPE="CT_TEXT" COLOR="White">
<ID NAME="MainStoryText" UID="217"/>
<TEXT>
<STORY>
<PARAGRAPH>
</ANCHOREDBOXREF>
</PARAGRAPH>
</STORY>
</TEXT>
</BOX>
<ANCHOREDBOXREF OFFSET="0">MainStoryGroup
The order of the <BOXREF> elements in a <GROUP> indicates the order in which the boxes
were selected prior to grouping. The z-order of boxes in the layout is determined by the
order of the <BOX> elements in the XML, from rearmost to frontmost.
Working with pictures
The <PICTURE> element supports a variety of features, including the ability to specify
runaround, opacity, and drop shadow characteristics. For more information, see the
Modifier DTD .
<PROJECT>
<LAYOUT>
<ID NAME="Layout 1"/>
<SPREAD>
<ID UID="1"/>
<BOX COLOR="Magenta" SHADE="50%" OPACITY="100%">
<ID NAME="pict1"/>
<PICTURE MASK="Test Alpha1"/>
<FRAME STYLE="Triple" WIDTH ="5" COLOR="Cyan" SHADE="100%"
OPACITY="100%" GAPCOLOR="Yellow"
QXP SERVER 9.2 WEB INTEGRATION GUIDE | 99
Page 100

USING THE WEB INTERFACE
GAPSHADE="80%" GAPOPACITY="100%"/>
</BOX>
<BOX>
<ID NAME="pict2"/>
<PICTURE SUPRESSPICT="true" FULLRES="true" PICCOLOR="Cyan"
SHADE="90" OPACITY="90"/>
<SHADOW COLOR="Cyan" SHADE="90" ANGLE="130" OPACITY="100"
DISTANCE="5" SKEW="10"
SCALE="90" BLUR="3"/>
</BOX>
<BOX>
<ID NAME="pict3"/>
<GEOMETRY>
<RUNAROUND TYPE="NONWHITEAREAS" OUTSET="10" NOISE="5"
SMOOTHNESS="5"
THRESHOLD="10" INVERT="true" OUTSIDEONLY="true"
RESTRICTTOBOX="true"/>
</GEOMETRY>
</BOX>
<BOX>
<ID NAME="pict4"/>
<PICTURE FIT="FITPICTURETOBOX" SCALEACROSS="40"
SCALEDOWN="50" FLIPVERTICAL="true"
FLIPHORIZONTAL="false" ANGLE="40" SKEW="20"/>
</BOX>
</SPREAD>
</LAYOUT>
</PROJECT>
Working with text
Every <BOX> element for text contains a <TEXT> element, and every <TEXT> element
contains a <STORY> element. A <STORY> element can contain <PARAGRAPH> elements,
each of which contains <RICHTEXT> elements. A <STORY> element can also simply contain
<RICHTEXT> elements.
A text <BOX> element can also contain a <CONTENT> element that indicates the origin of
the text in that box.
A text <BOX> element in a deconstructed project can also contain <PLACEHOLDER> elements,
which allow XML Import XTensions software to insert text from a different XML source.
<PLACEHOLDER> elements are ignored by the construct namespace and the modify
parameter; placeholders must be inserted in QuarkXPress using XML Import XTensions
software.
Applying style sheets
Like other resources, style sheets are defined in a deconstructed project’s Job Jackets file.
To apply a paragraph style sheet to text, use the PARASTYLE attribute of the <PARAGRAPH>
element. For example, to apply the paragraph style sheet named “BodyText” to a paragraph,
use XML like the following:
<PARAGRAPH PARASTYLE="BodyText">
<RICHTEXT MERGE="true">The sun has risen.</RICHTEXT>
</PARAGRAPH>
To apply a character style sheet to text, use the CHARSTYLE attribute of the <RICHTEXT>
element. For example, to apply the character style sheet named “Emphasis” to a word, use
XML like the following:
<PARAGRAPH PARASTYLE="BodyText">
<RICHTEXT>The </RICHTEXT>
<RICHTEXT CHARSTYLE="Emphasis">sun</RICHTEXT>
100 | QXP SERVER 9.2 WEB INTEGRATION GUIDE
 Loading...
Loading...