Page 1

Operating Instructions and Parts Manual
This .pdf document is bookmarked
15-inch Woodworking Band Saw
Model PM1500
Powermatic
427 New Sanford Road
LaVergne, Tennessee 37086 Part No. M-1791500
Ph.: 800-274-6848 Revision B 08/2014
www.powermati c.c om Copyright © 2014 Powerm atic
Page 2

1.0 Warranty and Service
Powermatic warrants every product it sells against manufacturers’ defects. If one of our tools needs service or repair,
please contact Technical Service by calling 1-800-274-6846, 8AM to 5PM CST, Monday through Friday.
Warranty Period
The general warranty lasts for the time period specified in the literature included with your product or on the official
Powermatic branded website.
• Powermatic products carry a limited warranty which varies in duration based upon the product. (See chart
below)
• Accessories carry a limited warranty of one year from the date of receipt.
• Consumable items are defined as expendable parts or accessories expected to become inoperable within a
reasonable amount of use and are covered by a 90 day limited warranty against manufacturer’s defects.
Who is Covered
This warranty covers only the initial purchaser of the product from the date of delivery.
What is Co vered
This warranty covers any defects in workmanship or materials subject to the limitations stated below. This warranty
does not cover failures due directly or indirectly to misuse, abuse, negligence or accidents, normal wear-and-tear,
improper repair, alterations or lack of maintenance. Powermatic woodworking machinery is designed to be used with
Woo d. Us e of th ese ma chines in the pr oces sing o f metal, plast ics, or other materia ls may void the warranty. The
exceptions are acrylics and other natural items that are made specifically for wood turning.
Warranty Limitations
Woodworking products with a Five Year Warranty that are used for commercial or industrial purposes default to a
Two Year Warranty. Please contact Technical Service at 1-800-274-6846 for further clarification.
How to Get Technical Support
Please contact Technical Service by calling 1-800-274-6846. Please note that you will be asked to provide proof
of initia l p u rch a s e whe n calling. If a product requires further inspection, the Technical Service representative will
explain and assist with any additional action needed. Powermatic has Authorized Service Centers located throughout
the United States. For the name of an Authorized Service Center in your area call 1-800-274-6846 or use the Service
Center Locator on the Powermatic website.
More Informat io n
Powermatic is constantly adding new products. For complete, up-to-date product information, check with your local
distributor or visit the Powermatic website.
How S tat e Law A pplies
This warranty gives you specific legal rights, subject to applicable state law.
Limitations on This Warranty
POWERMATIC LIMITS ALL IMPLIED WARRANTIES TO THE PERIOD OF THE LIMITED WARRANTY FOR EACH
PRODUCT. EXCEPT AS STATED HEREIN, ANY IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS
FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE EXCLUDED. SOME STATES DO NOT ALLOW LIMITATIONS ON HOW
LONG AN IMPLIED WARRANTY LASTS, SO THE ABOVE LIMITATION MAY NOT APPLY TO YOU.
POWERMATIC SHALL IN NO EVENT BE LIABLE FOR DEATH, INJURIES TO PERSONS OR PROPERTY, OR
FOR INCIDENTAL, CONTINGENT, SPECIAL, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES ARISING FROM THE USE OF
OUR PRODUCTS. SOME STATES DO NOT ALLOW THE EXCLUSION OR LIMITATION OF INCIDENTAL O R
CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES, SO THE ABOVE LIMITATION OR EXCLUSION MAY NOT APPLY TO YOU.
Powermatic sells through distributors only. The specifications listed in Powermatic printed materials and on the official
Powermatic website are given as general information and are not binding. Powermatic reserves the right to effect at
any time, without prior notice, those alterations to parts, fittings, and accessory equipment which they may deem
necessary for any reason whatsoever.
Product Listing with Warranty Period
90 Days – Parts; Consumable items
1 Year – Motors, Machine Accessories
2 Year – Woodworking Machinery used for industrial or commercial purposes
5 Year – Woodworking Machinery
NOTE: Powermatic is a division of JPW Industries, Inc. References in this document to Powermatic also apply to
JPW Industries, Inc., or any of its successors in interest to the Powermatic brand.
2
Page 3

2.0 Table of contents
Section Page
1.0 Warranty and Service ..................................................................................................................................... 2
2.0 Table of contents ............................................................................................................................................ 3
3.0 Safety warnings .............................................................................................................................................. 5
4.0 About this manual .......................................................................................................................................... 6
5.0 Features and Terminology ............................................................................................................................. 7
6.0 Specifications ................................................................................................................................................. 8
6.1 Base Hole Centers (PM1500 Band Saw) ................................................................................................... 9
7.0 Setup and assembly ..................................................................................................................................... 10
7.1 Unpacking ................................................................................................................................................ 10
7.2 Shipping contents ..................................................................................................................................... 10
7.3 Location .................................................................................................................................................... 10
7.4 Dust Collection ......................................................................................................................................... 10
7.5 Electrical Connections .............................................................................................................................. 10
7.6 Grounding Instructions ............................................................................................................................. 10
7.7 Extension Cords ....................................................................................................................................... 11
8.0 Adjustments ................................................................................................................................................. 11
8.1 Fence assembly ....................................................................................................................................... 11
8.2 Fence plate ............................................................................................................................................... 11
8.3 Fence to Table Clearance ........................................................................................................................ 12
8.4 Setting Cursor (Zero) Position .................................................................................................................. 12
8.5 Setting Table Parallel to Blade ................................................................................................................. 12
8.6 Setting Fence Parallel to Blade ................................................................................................................ 13
8.7 Fence Locking Tigh tn ess ......................................................................................................................... 13
8.8 Table Tilt ................................................................................................................................................... 14
8.9 90° Table Stop .......................................................................................................................................... 14
8.10 Installing/Changing Blades ..................................................................................................................... 14
8.11 Blade Tension ........................................................................................................................................ 15
8.12 Blade Tracking ....................................................................................................................................... 16
8.13 Upper Blade Guides ............................................................................................................................... 16
8.14 Upper Thrust Bearing .................................................................................................... ......................... 17
8.15 Lower Blade Guides ............................................................................................................................... 17
8.16 Guide Post .............................................................................................................................................. 18
8.17 Guide Post Parallelism ........................................................................................................................... 18
8.18 Resaw Pin .............................................................................................................................................. 18
8.19 Miter Gauge ............................................................................................................................................ 19
8.20 Drive Belt Replacement and Tensioning ................................................................................................ 19
8.21 Brushes .................................................................................................................................................. 20
9.0 Operating Controls ....................................................................................................................................... 20
9.1 Start/Stop ................................................................................................................................................. 20
9.2 Safety Key ................................................................................................................................................ 21
9.3 Brake Pedal .............................................................................................................................................. 21
10.0 Operation ................................................................................................................................................... 21
10.1 General Procedure ................................................................................................................................. 21
10.2 Ripping ................................................................................................................................................... 22
10.3 Crosscutting ........................................................................................................................................... 22
10.4 Resawing ................................................................................................................................................ 22
10.5 Blade Lead ............................................................................................................................................. 22
11.0 Maintenance ............................................................................................................................................... 23
11.1 Lubrication Points ................................................................................................................................... 23
12.0 Blade Selection .......................................................................................................................................... 24
13.0 Blade Selection Guide ................................................................................................................................ 26
14.0 Troubleshooting the PM1500 Band Saw .................................................................................................... 27
14.1 Operational Problems ............................................................................................................................. 27
14.2 Mechanical and Electrical Problems ...................................................................................................... 29
15.0 Replacement Parts ..................................................................................................................................... 30
15.1.1 Complete Machine with Accessories – Ex ploded View ....................................................................... 31
15.1.2 Complete Machine with Accessories – Parts List ................................................................................ 33
15.2.1 Upper Wheel Sliding Bracket & Tension Mech anism Assembly – Exploded View ........................................... 36
15.2.2 Upper Wheel Sliding Bracket & Tension Mechanism Assembly – Parts List ...................................... 36
3
Page 4

15.3.1 Upper Wheel Assembly – Exploded View ........................................................................................... 37
15.3.2 Upper Wheel Assembly – Parts List .................................................................................................... 37
15.4.1 Lower Wheel Assembly – Exploded View ........................................................................................... 37
15.4.2 Lower Wheel Assembly – Parts List .................................................................................................... 37
15.5.1 Trunnion Support Bracket Assembly – Exploded View .................................................................... 38
15.5.2 Trunnion Support Bracket Assembly – Parts List ............................................................................. 38
15.6.1 Guide Bar Bracket Assembly – Exploded View ................................................................................... 39
15.6.2 Guide Bar Bracket Assembly – Parts List ........................................................................................... 39
15.7.1 Upper Blade Guide Assembly – Exploded View ................................................................................. 40
15.7.2 Upper Blade Guide Assembly – Parts List .......................................................................................... 40
15.8.1 Lower Blade Guide Assembly – Exploded View ................................................................................. 41
15.8.2 Lower Blade Guide Assembly – Parts List .......................................................................................... 41
15.9.1 Fence Assembly – Exploded View ...................................................................................................... 42
15.9.2 Fence Assembly – Parts List ............................................................................................................... 42
15.10.1 Miter Gauge Assembly – Exploded View .......................................................................................... 44
15.10.2 Miter Gauge Assembly – Parts Lis t ................................................................................................... 44
16.0 Electrical Connections – 3HP 1PH 230V ................................................................................................... 45
4
Page 5

3.0 Safety warnings
WARNING: For your own safety read instruction
manual before operating Band Saw.
- Wear eye prote cti o n.
- Do not remove jammed cutoff pieces until blade
has stopped.
- Maintain proper adjustment of blade tension,
blade guides, and thrust bearings.
- Adjust upper guide to just clear workpiece.
- Hold workpiece f irmly against table.
1. Read and understand entire owner's manual
before attempting assembly or operation.
2. Read and understand the warnings posted on
the machine and in this manual. Failure to
comply with all of these warnings may cause
serious injury.
3. Replace warning labels if they become
obscur e d or rem ov e d.
4. This band saw is designed and intended for
use by properly trained and experienced
personnel only. If you are not familiar with the
proper and safe operation of a band saw, do
not use until proper training and knowledge
have been obtained.
5. Do not use this band saw for other than its
intended use. If used for other purposes,
Powermatic disclaims any real or implied
warranty and holds itself harmless from any
injury that may result f rom that use.
6. Always wear approved safety glasses/face
shield while using this machine. (Everyday
eyeglasses only have impact resistant lenses;
they are not safety glasses.)
7. Before operating band saw, remove tie, rings,
watches and other jewelry, and roll sleeves up
past the elbows. Remove all loose clothing and
confin e lo n g hair . N on- sl i p f o otw e ar or a nt i- ski d
floor strips are recommended. Do not wear
gloves.
8. Keep work area clean. Cluttered areas and
benches invite accidents.
9. Use proper extension cord. Make sure your
extension cord is in good condition. When
using an extension cord, be sure to use one
heavy enough to carry the current your product
will draw. An undersized cord will cause a drop
in line voltage resulting in loss of power and
over heating. T able 1 shows th e correct size to
use depending on cord length and nameplate
ampere rating. If in doubt, use the next heavier
gage. The smaller the gage number, the
heavier the cord.
10. Secure work. Use clamps or a vise to hold work
when practical. It’s safer than using your hand
and it frees both hands to operate tool.
11. Disconnect tools before servicing; when
changing accessories, such as blade, bits,
cutter s an d the li ke.
12. Direction of feed: Feed work into a blade or
cutter against the direction of rotation of the
blade or cutter only.
13. Adjust upper blade guides to approximately
1/8” ab ov e wor k pi ec e.
14. Make sure blade tension, tracking and blade
guid es are all properly adjusted.
15. Make relief cuts where possible, when cutting
curved stock.
16. When feeding small work pieces into blade,
alway s us e pus h sti ck, fixt ur e, or si mi lar devic e
to ke ep hands at a safe distance.
17. Hold st ock fi rml y an d flat ag ai n st ta ble.
18. Wear ear protectors (plugs or muffs) during
extend e d periods of op er ati o n.
19. Some dust created by power sanding, sawing,
grinding, drilling and other construction
activities contain chemicals known to cause
cancer, birth defects or other reproductive
harm. Som e exa m ples of these chemicals are:
•
Lead from lead based paint.
•
Crystalline silica from bricks, cement and
other ma s o nry pr od u cts .
•
Arsenic and chromium from chemically
treated lumber.
Your risk of exposure varies, depending on
how oft en yo u do this t ype of w ork. To r educe
your exposure to these chemicals, work in a
well-ventilated area and work with approved
safety equipment, such as face or dust masks
that are specifically designed to filter out
microscopic parti cles.
20. Do not operate this machine while tired or
under the influence of drugs, alcohol or any
medication.
21. Make certain switch is in OFF position before
connecting machine to power supply.
22. Make cer t ai n ma c hin e is pro p erl y gr ou n d ed.
23. Do not back stock out of blade while blade is
running.
24. Remove adjusting keys and wrenches. Form a
habit of ch ecking to s ee that key s an d a dju sti n g
5
Page 6

wrenches are removed from the machine
before tur ning it on.
25. Keep safety guards in place at all times when
machine is in use. If removed for maintenance
purposes, use extreme caution and replace the
guards immediately after completion of
maintenance.
26. Check damaged parts. Before further use of
machine, a guard or other part that is damaged
should be carefully checked to determine that it
will operate properly and perform its intended
function. Check for alignment of moving parts,
binding of moving parts, breakage of parts,
mounting and any other conditions that may
affect it s o per ation. A gu ar d or oth er p art th at is
damaged should be properly repaired or
replaced.
27. Keep floor around machine clean and free of
scrap material, oil and grease.
28. Keep visitors a safe di stance from wor k area.
Keep c hil dr en aw a y.
29. Make your workshop child proof with padlocks,
master switc hes or by removing start er keys.
30. Give your work undivided attention. Looking
aroun d, c arryi n g on a c onv ers atio n an d “ho rs eplay” are careless acts that can result in
serious injury.
31. Maintain a bala nced st ance at all tim es so th at
you do not fal l int o blade or ot her m ovin g part s.
Do not overreach or use excessive force to
perform any machine operation.
32. Use the right tool at the correct speed and feed
rate. Do not forc e a tool or at tachm ent to do a
job for which it was not designed. The right tool
will do the job better and more safely.
33. Use recommended accessories; improper
accessories may be hazardous.
34. Maintain tools with care. Keep blades sharp
and clean for best and safest performance.
Follow instructions for lubricating and changing
accessories.
35. Turn off m achine befor e cle aning. Use a br ush
or com pres sed air to re mov e chi ps or de bris —
not your hands.
36. Do not stand on machine. Serious injury could
occur if machine tips over.
37. Never leave machine running unattended. Turn
power off and do not leave band saw until
blade comes t o a complete stop.
38. Remove loose items and unnecessary work
piec es fr om ar ea b efo r e star ting mac hine.
39. Keep h and s out of li ne of s aw bl ad e.
40. Don’t use in dangerous environment. Do not
expos e machi ne to rai n or use in w et or dam p
locations. Keep work area well lighted.
41. Remove safety key from switch whenever band
saw is turned “OFF”, and keep safety key out of
reac h of unauthorized persons or children.
Familiarize yourself with the following safety notices used in this manual:
This means that if precautions are not heeded, it may result in minor injury and/or
possible machine damage.
This means that if precautions are not heeded, it may result in serious injury or
possibly even death.
4.0 About this manual
This manual is provided by Powermatic covering the safe operation and maintenance procedures for a
Powermatic model PM1500 Band Saw. This manual contains instructions on installation, saf ety precautions,
general operating procedures, maintenance instructions and parts breakdown. Your machine has been
designed and constructed to provide years of trouble-free operation if used in accordance with the instructions
as set forth in this document.
This manual is not intended to be an exhaustive guide to band saw operational methods, use of j igs or aftermarket accessories, choice of stock, etc. Additional knowledge can be obtained from e xperienced users or
trade articles. Whatever accepted methods are used, always make personal safety a priority.
Retain this manual for future reference. If the machine transfers own ership, the manu al should accompan y it.
Read and understand the entire contents of this manual before attem pting assembly
or operation! Failure to comply may cause serious injury!
6
Page 7
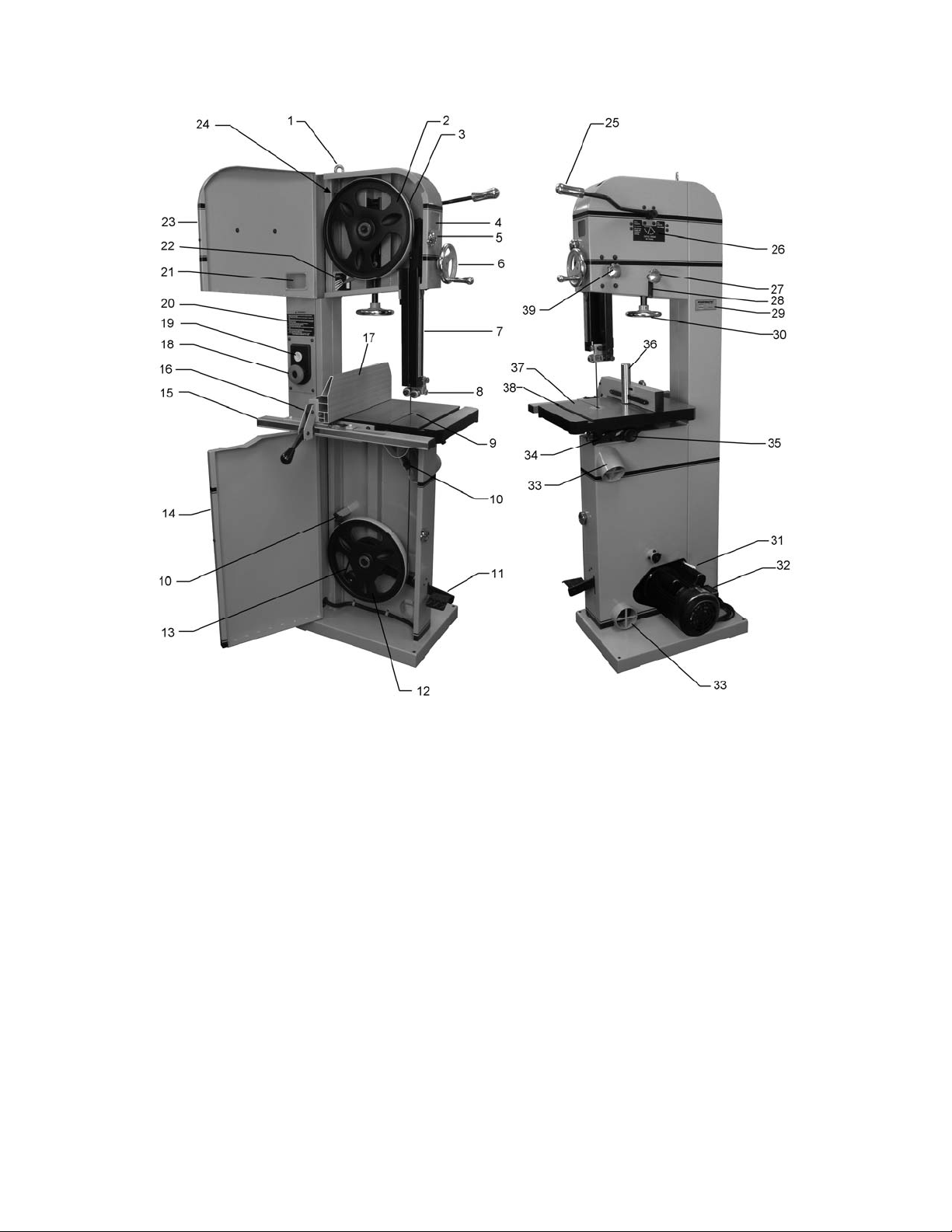
5.0 Features and Terminology
Figure 1
1. Lifting ring
2. Upper wheel
3. Tire
4. Tracking window
5. Door catch
6. Guide post handwheel
7. Guide post
8. Upper bearing blade guides
9. Table insert
10. Blade and wheel brushes
11. Brake pedal
12. Lower wheel
13. Drive belt and pulley
14. Lower door
15. Guide rail
16. Rip fence
17. Aluminum f ence plat e
18. Magnetic switch with power indicator light
19. Safety key
20. Warning label
21. Blade tension window
22. Blade tension scale
23. Upper door
24. Interlock switch
25. Blade tension lever
26. Tension lever position label
27. Tracking knob
28. Tracking knob lock lever
29. Serial number/machin e identificati on plate
30. Blade tension handwheel
31. Motor lift handle
32. 3 horsepower TEFC motor
33. Dust port
34. Trunnion lock handle
35. Trunnion fine adjust knob
36. Resaw pin
37. Cast iron table
38. Miter slot
39. Guide post locking knob
The specifications in this manual were current at time of publication, but because of our policy of continuous
improvement, Powermatic reserves the right to change specifications at any time and without prior notice,
without incurring obligations.
7
Page 8

6.0 Specifications
Model number ............................................................................................................................................ PM1500
Stock number ............................................................................................................................................ 1791500
Motor and electricals:
Motor type ....................................................................... totally enclosed fan cooled, induction, capacitor start
Horsepower ................................................................................................................................................ 3 HP
Phase ........................................................................................................................................................ single
Voltage ....................................................................................................................................................... 230V
Cycle .......................................................................................................................................................... 60Hz
Listed FLA (full load amps) .......................................................................................................................... 12A
Starting amps ............................................................................................................................................... 55A
Running amps (no load) .............................................................................................................................. 3.3A
Start capacitor ....................................................................................................................... 200MFD, 250VAC
Run capacitor ............................................................................................................................. 60µF, 300VAC
Power transfer ........................................................................................................... Poly-V 9 groove belt drive
On/off switch ..................................................................... Magnetic, with power indicator lamp and safety key
Motor speed ...................................................................................................................................... 1720 RPM
Blade speed .................................................................................................................................... 3100 SFPM
Power cord length ....................................................................................................................... 6.6 ft. (200cm)
Power plug installed ..................................................................................................................................... yes
Recommended circuit size 1 ......................................................................................................................... 20A
Sound emission...................................................................... 72 dB at 39” (1000mm) from blade, without load
1
subject to local and national electrical codes.
Capacities:
Maximum cutting height/resaw capacity ....................................................................................... 14” (355mm)
Throat capacity........................................................................................................................ 14-1/2” (368mm)
Minimum blade width .................................................................................................................... 1/8” (3.2mm)
Maximum blade width .................................................................................................................... 1” (25.4mm)
Blade length 2 .................................................................................................................. 153 +/-1/2” (3886mm)
Blade provided ................................................................................................. hook type, 3/8” x 0.065” x 6 TPI
Wheel diameter ............................................................................................................................. 15” (381mm)
2
blade length range is 152-1/2” to 153” for band saws with serial no. 12100002 to 12100052.
Miscellaneous:
Fence plate .................................................................................................. 19-3/4”L x 6-1/2”H (502 x 165mm)
Resaw pin .................................................................................................... 1-1/2” dia x 6-1/2”H (38 x 165mm)
Stand footprint ........................................................................................... 17-3/4”L x 25-1/4”W (450 x 641mm)
Overall dimensions, assembled .................................. 30-1/4”L x 34-3/8”W x 80-1/4”H (768 x 873 x 2038mm)
Miter gauge positive stops .................................................................................................................... 45°, 90°
Materials:
Table ........................................................................................................................................ ground cast iron
Trunnion ............................................................................................................................................... cast iron
Enclosed cabinet ........................................................................................................................................ steel
Band wheels......................................................................................................................................... cast iron
Tires .............................................................................................................................................. polyurethane
Blade guides ................................................................................................................................... ball bearing
Resaw fence ....................................................................................................................... extruded aluminum
Handwheels .................................................................................................................. cast iron, chrome finish
Paint finish...................................................................................................................................... powder coat
Table:
Table dimensions ....................................................................... 21-1/2”L x 16”W x 2”Thk (546 x 406 x 51mm)
Table tilt................................................................................................................................... 10° left, 45° right
Table height from floor at 90-degrees ......................................................................................... 40” (1016mm)
Miter T-slot ............................................................................. 7/8”W x 3/8”D; opening 3/4"W (22 x 9.5; 19mm)
Edge bevel .................................................................................................................................................. front
8
Page 9
Dust coll ection:
Dust port outside diameter .................................................................................................... two at 4” (100mm)
Minimum extraction volume required .................................................................................................. 600 CFM
Weights:
Net weight (fully assembled) ...................................................................................................... 394 lb (179 kg)
Shipping weight .......................................................................................................................... 502 lb (228 kg)
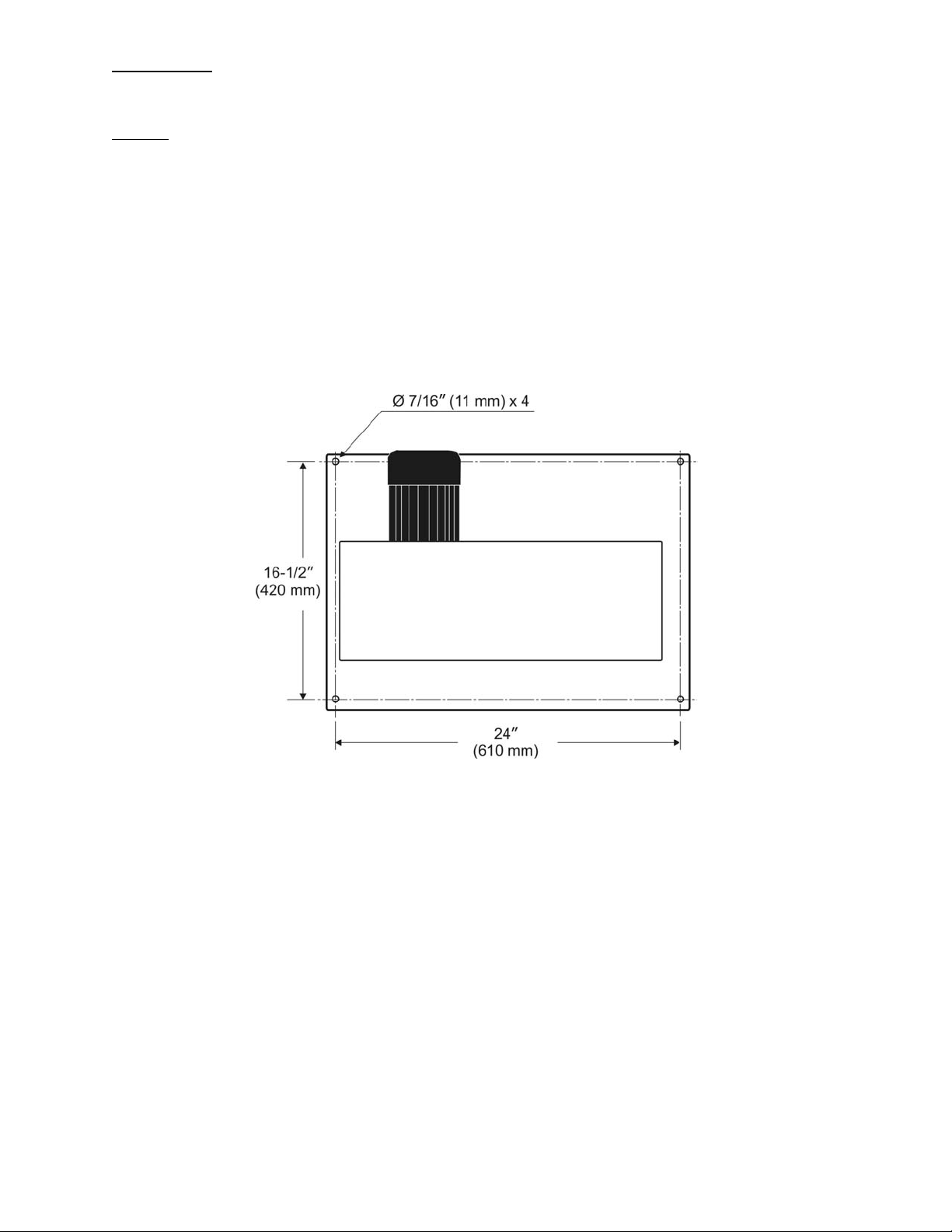
6.1 Base Hole Centers (PM1500 Band Saw)
Figure 2
9
Page 10

Read and understand all
instructions before attempting assembly or
operation of band saw. Failure to comply may
cause serious injury.
7.0 Setup and assembly
7.1 Unpacking
1. Remove all contents from shipping carton. Do
not discard any shipping material until band
saw is assembled and running satisfactorily.
2. Inspect contents for shipping damage. Report
any damage immediately to your distributor
and shipping agent.
3. Compare contents of shipping carton with the
contents list in this manual. Report shortages,
if any, to your distributor.
Note: Some parts may have come pre-assembled
to the saw.
7.2 Shipping contents
Carton contents (see Figure 3):
1 Band saw (not shown)
1 Fence assembly with aluminum fence plate
1 Miter gauge
1 Resaw pin and handle
1 Owner’s manual (not shown)
1 Warranty card (not shown)
Tools required for set up and assembly:
Hoist or forklift, with straps
Machinist square
Use a hoist or forklift with straps to remove band
saw from pallet. The straps used should have a
minimum 500-lb. lifting capacity. Do NOT place
forks or straps directly beneath table or against
handles or levers – use the lifting eye atop the
band saw.
Move band saw to its permanent location, which
should be dry and well lit, with a level floor and
enough space on all sides to handle long stock or
perform routine maintenance on the machine.
Make sure floor is able to support weight of
machine. If desired, band saw can be secured to
floor using lag screws (not provided) through the
four holes in base. See Figure 2 for hole spacing.
Exposed metal surfaces, such as table surface and
blade guides, have been given a protective coating
at the factory. This coating should be removed with
a soft cloth moistened with solvent. Do not get
solvents near plastic or rubber parts; and do not
use an abrasive pad as it may scratch exposed
surfaces.
The handle on the front handwheel may be in
rever se posit ion for shipping. Reinst all it i n proper
position on the handwheel. Use a wrench on the
flat to tighten it to the handwheel.
7.4 Dust Collection
The use of a dust collection system is strongly
recommended for this band saw. It will help keep
the shop clean, as well as red uce potential health
hazards caused by inhalation of wood dust. The
collector should have a capacity sufficient for this
size machine – 400 CFM is recommended.
Powermatic has a line of dust collection systems
available; see your dealer or visit our website listed
on the cover.
Connect the hoses of your dust collection system
to the saw’s dust ports (4” outside diameter).
Secure tightly with hose clamps (not provided).
Figure 3
7.3 Location
Remove all crating and plastic from around
machine. Remove any screws or straps holding
band saw to shipping pallet.
Exercise care when removing
machine from shipping pallet.
7.5 Electrical Connections
Electrical connections must be
made by a qualified electrician in compliance
with all relevant codes. This machine must be
properly grounded to help prevent electrical
shock and possible fatal in j ury.
The band saw is factory wired for 230 volts. It is
recommended that the band saw be co nnected to
a grounded and dedicated 20 amp c ircuit wit h a 20
amp circuit breaker or time delay fuse. Local codes
take precedence over recommendations.
7.6 Grounding Instructions
1. All grounded, cord-connected tools:
In the event of a malfunction or breakdown,
grounding provides a path of least resistance for
electric current to reduce t he risk of electr ic shock.
This tool is equipped with an electric cord having
10
Page 11
an equipment-grounding conductor and a
grounding plug. The plug must be plugged into a
matching outlet that is properly installed and
grounded in accordance with all local codes and
ordinances. Do not modify the pl ug provided - if it
will not fit the outlet, have the proper outlet installed
by a qualified electrician.
Improper connection of the equipment-grounding
conductor can result in a risk of electric shock. The
cond uctor with insulatio n having an outer surface
that is green with or without yellow stripes is the
equipment-grounding conductor. If repair or
replacement of the electric cord or plug is
necessary, do not connect the equipmentgrounding conductor to a live terminal.
Check with a qualified electrician or service
personnel if the grounding instructions are not
completely understood, or if in doubt as to whether
the tool is properly grounded. Use only 3-wire
extension cords that have 3-pro ng gro unding pl ugs
and 3 pole receptacles that accept the tool's plug.
Repair or replace damaged or worn cord
immediately.
2. Grounded, cord-connected tools intended for
use on a supply circuit having a nominal rating
between 150 – 250 volts, inclusive:
This tool is intended for use on a circuit that has an
outlet that looks like the one illustrated in Figure 4.
The tool has a grounding plug that looks like the
plug illustrated in Figure 4. Make sure the tool is
connected to an outlet having the same
configuration as the plug. No adapter is available
or should be used with this tool. If the tool must be
reconnected for use on a diff erent type of electric
circuit, the reconnection should be made by
qualified service personnel; and after reconnection,
the tool should comply with all local codes and
ordinances.
Make sure the voltage of your power supply
matches the specifications on the motor plate of
the Band Saw.
on the machine’s motor plate. An undersized cord
will cause a drop in line voltage resulting in loss of
power and overheating.
Use Table 1 as a general guide in choosing the
correct size cord. The smaller the gauge number,
the heavier the cord. If in doubt, use the next
heavier gauge.
Recommended G auges (A WG ) of E x tension Cords
Volts Total length of cord
in feet
120 25 50 100 150
Ampere rating
More
than
0 6
6 10
10 12
12 16
Not more
than
NR: Not Recommended.
240 50 100 200 300
Table 1
Minimum gauge cord
18 16 16 14
18 16 14 12
16 16 14 12
14 12 NR NR
8.0 Adjustments
Tools required for adjustments:
Machinist square
Cross point (Phillips) screwdriver
Hex keys, 4mm/5mm/6mm
13mm wrench
Straight edge and gauge
8.1 Fence assembly
Refer to Figure 5.
Place fence body onto guide tube (as shown in
Figure 9). Raise fence lever all the way up to install
or remove fence from guide rail. Midway lever
position allows fence to slide along guide rail.
Lowest lever position locks fence in place.
Figure 4
7.7 Extension Cords
The use of extension cords is discouraged; try to
position machines within reach of power source. If
an extension cord becomes necessary, make sure
the cord rating is suitable for the amperage listed
Figure 5
8.2 Fence plate
Refer to Figures 6 and 7.
Loosen lock bar (A) using knobs (B). Pull out on
lock b ar unt i l it pr ot rud es e no ug h o n w hic h to s lid e
the aluminum fence plate from one end, as shown
in Figure 6. Retighten knobs.
11
Page 12
Figure 8
8.4 Setting Cursor (Zero) Position
Figure 6 – vertical position
The aluminum fence plate can be installed in one
of two positions; vertically (resaw position), as
shown in Figure 6; or horizontally as shown in
Figure 7.
Horizontal position is useful for smaller workpieces.
(The zero setting of the cursor cannot be used with
horizontal fence position.)
Figure 7 – horizontal position
8.3 Fence to Table Clearance
1. Check clearance between table and bottom of
fence (Figure 8). The fence plate should not
rub against table surface but be slightly above
it. This gap should be the same at both front
and back of table.
2. If clearance is not equal, use a 5mm hex key
to rotate the two nylon adjustment screws (C,
Figure 6) the same amount to raise or lower
fence body on guide tube. Clockwise raises
fence body, counterclockwise lowers.
Refer to Figure 9.
1. The fence must be set so that cursor reads
zero at line of blade. The fence plate must be
installed on fence body in vertical position, and
blade must be installed and fully tensioned.
2. Slide fence flush against flat of blade, as
shown. (Do not force fence into blade so that
blade deflects.)
3. If cursor is not at zero, loosen two screws (D,
Figure 9) and shift cursor as needed.
Retighten screws.
Figure 9
8.5 Setting Table Parallel to Blade
Refer to Figures 10 and 11.
1. The table has been aligned by the
manufacturer so that the miter slot is parallel to
the blade; it should not require adjustment.
However, in the future you may wish to confirm
the setting is still accurate. A wide blade is
recommended for the procedure.
2. Disconnect band saw from power source.
3. Blade should be fully tensioned (see section
8.11).
4. Place a long straightedge fl ush against blade,
making sure it contacts both front a nd back of
blade. (Do not deflect blade by pushing into it.)
See Figure 10.
12
Page 13
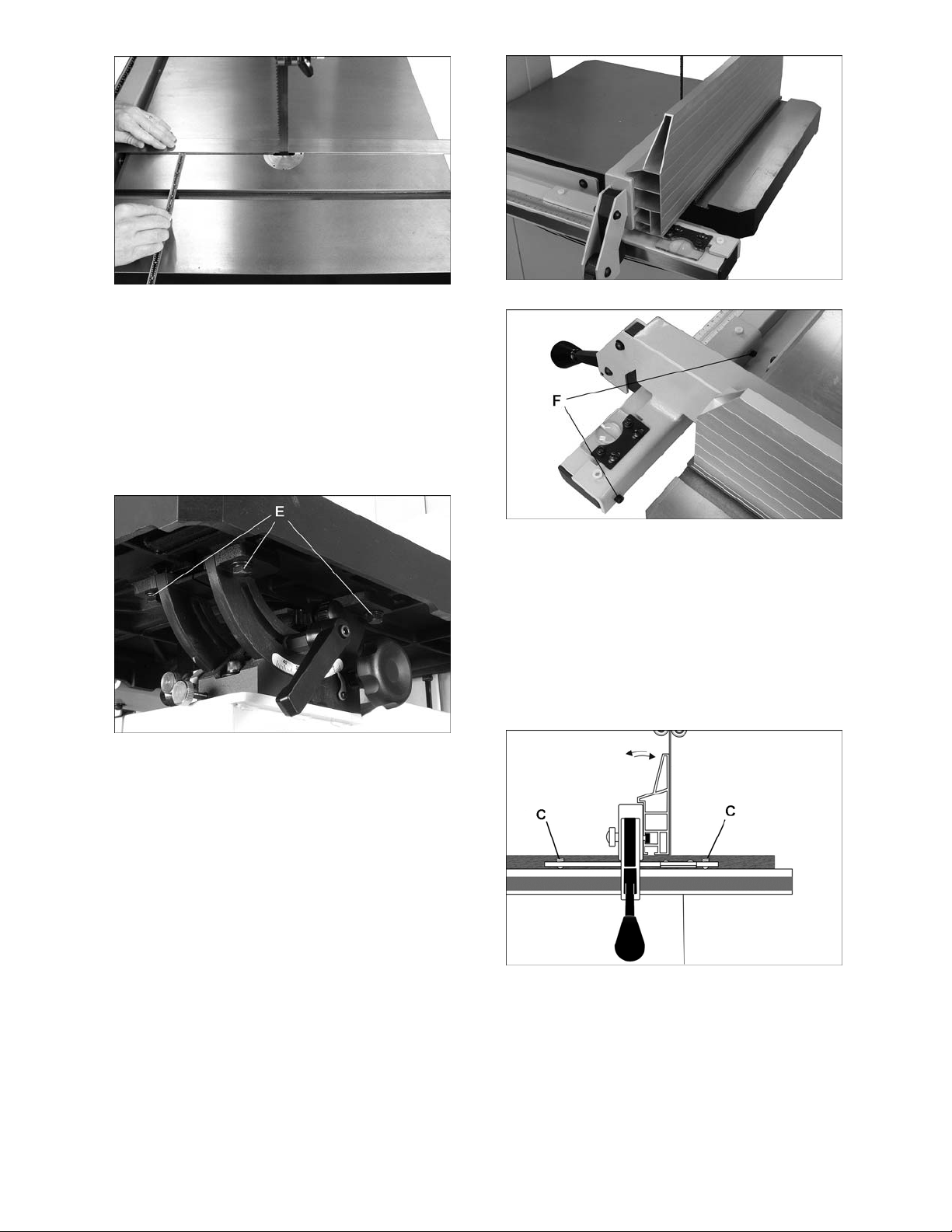
Figure 10
5. Use a gauge to carefully measure distance
from miter slot to straight edge. Take
measurements at both front and back of table
– these should be identical.
6. If m iter slot is not parallel to blade, loosen four
screws (E, Figure 11) that secure table to
trunnion, and shift table as needed until miter
slot is parallel to blade.
7. Tighten the four scre ws.
Figure 11
Figure 12
Figure 13
The fence must also be vertically parallel to blade.
Refer to Figure 14:
3. Make sure table has been set 90° to blade
(see section 8.9).
4. Slide fence (with aluminum plate securely
fastened) against blade; do not push into
blade. Turn either of the nylon adjustment
screws (C) until fence is parallel to blade along
vertical leng th of fenc e.
8.6 Setting Fence Parallel to Blade
Refer to Figures 12 through 14.
Fence must be parallel to flat of blade f or accurate
cutting. Since miter slot has been set parallel to
blade from the manufacturer (and confirmed by
user, as described in section 8.5), the miter slot
can be used to set fence parallelism.
1. Slide fence to edge of miter slot, as shown in
Figure 12. The fence should align with miter
slot along its entire length.
2. If adjustment is needed, use one of the back
adjustment screws (F, Figure 13) to t urn fence
in line with miter slot (5mm hex key).
Figure 14
8.7 Fence Locking Tightness
The tightness of fence against guide rail tube can
be adjusted by rotating back adjustment screws (F,
Figure 13). Rotate the two screws equally
(clockwise to tighten).
Because these screws are also used to align fence
to blade, after adjusting fence locking tightness,
13
Page 14
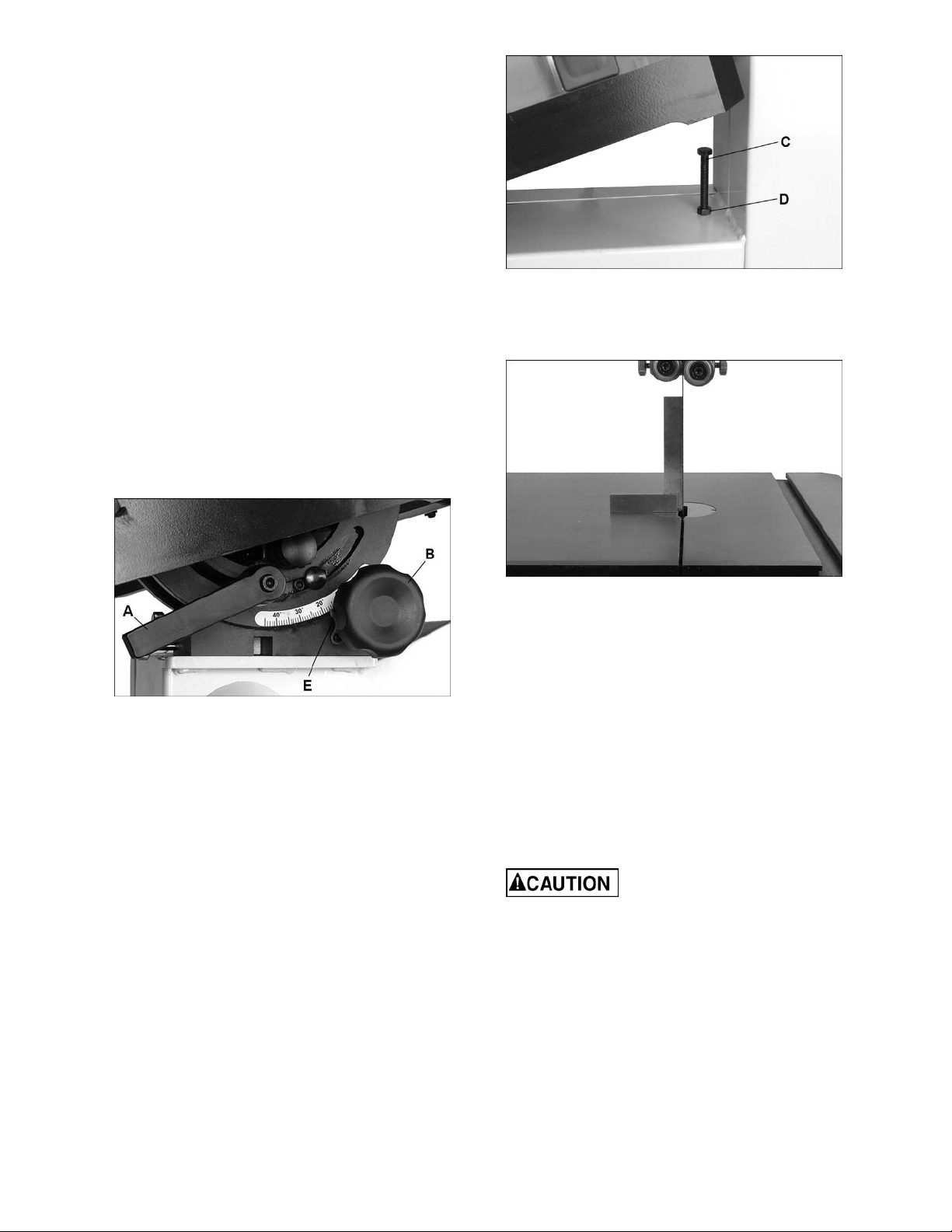
you should inspect fence-to-blade relationship, as
explained in section 8.6.
8.8 Table Tilt
Refer to Figure 15.
1. Loosen lock handle (A).
2. For right tilt (as viewed from front or operator’s
side of saw), push on table while rotating knob
(B) clockwise to tilt table up to 45°. Use knob
(B) for fine adjustment.
3. For left tilt (as viewed from front or operator’s
side of saw), loosen lock lever (A) and rotate
knob (B) clockwise a turn or two to release
pressure on the 90° stop bolt (shown in Figure
16). Remove stop bolt, then rotate k nob to tilt
table up to 15°.
4. Tighten lock handle (A) to secure setting.
NOTE: The lock handle (A) can be pivoted to
more convenient posit ions. Simply lift straight
out on handle and rotate it on the pin, then
release handle making sure it seats itself on
the pin.
Figure 16
4. Place a square on table and against blade to
check that table is 90° to blade. See Figure 17.
Do not push square into blade.
Figure 15
8.9 90° Table Stop
Refer to Figures 16 and 17.
The 90° positive stop ensures that table will always
be perpendicular to blade after table is returned to
horizontal position. Check and adj ust this 90° stop
as follows:
1. Disconnect machine from power source.
2. Make sure blade is under full tension.
3. Tilt table until it rests on stop bolt (C).
Figure 17
5. If table and blade are not square, use a 13mm
wrenc h to loo sen lo ck nut (D, F igure 1 6) t hen
rotate stop bolt. Turn stop bolt as needed until
there is no longer light showing between
square and blade.
6. Tighten lock nut (D) to secure table stop in
position.
7. Tighten lock handle (A, Figure 15).
8. Check that scale pointer (E, Figure 15) is at
zero. If necessary, loosen screw on pointer
and shift pointer to zero. Re-tighten screw.
8.10 Installing/Changing Blades
Always wear gloves when
handling blades. New blades are usually
packaged in coiled position; to prevent injury
uncoil them slowly and carefully, while wearing
work gloves and safety glasses.
The PM1800 band saw is designed for blades from
1/8” to 1” wide.
Refer to Figure 18.
1. Disconnect machine from power source.
2. Remove table insert (F, Figure 18).
3. Pull out table pi n (G).
14
Page 15

4. Adjust upper and lower blade guides away
from blade (see sections 8.13 and 8.15).
Figure 18
5. Move quick tension lever to “Full Release
(Blade Change)” position.
6. Open upper and lower doors by rotating door
catches.
7. Carefully remove blade from top wheel, then
from between upper and lower blade guides
and lower wheel. Slide blade out t hrough slot
in table.
8. Guide new blade through table slot. Place
blade loosely in upper and lower blade guides.
Make sure blade teeth point down toward
table, and toward front of saw. (If the teeth will
not point down, no matter how you orient
blade, then blade is twisted inside-out. Twist it
into correct position and re-install it.)
9. Position blade at center of upper and lower
wheels.
10. Reinstall table insert (F) and table pin ( G).
11. Before operating band saw, the new blade
must be tensioned and tracked, in that order.
Find instructions for tensioning and tracking
the blade in sections 8.11 and 8.12. The blade
guides must also be set properly according to
instructions in sections 8.13 through 8.16.
4. Open upper door.
5. Rotate tension handwheel (A, Figure 20) until
scale pointer (B) indicates width of installed
blade.
TIP: Use the band saw’s gauge setting initially.
As yo u becom e fam iliar wit h the m achi ne and
with different properties of band saw blades,
you may find it necessary to change blade
tension from initial setting. Keep in mind that
not only changes in blade width, but also type
of material being cut will have an effect on
blade tension. Too little or too much blade
tension can cause blade breakage a nd/or poor
cutting performance.
Figure 19
8.11 Blade Tension
Refer to Figure 19.
1. Disconnect machine from power source.
2. Back off upper and lower guide bearings to
eliminate any contact with blade.
3. With blade centered on wheels, move quick
tension lever to “Full Tension” position, as
shown in Figure 19. NOTE: You should feel
tension lever settle into each of its three
positions.
Figure 20
6. Make a note of the specific tension setting for
a particular blade. Tension can then be re-set
quickly when that blade is reinstalled.
IMPORTANT: When band saw is not being
used, move quick tension lever to “Partial
Tension-Idle/Tracking” position. This will
prolong the life of bla de and tires, and reduce
load on wheels, bearings and other
components.
15
Page 16

8.12 Blade Tracking
Refer to Figures 21 and 22.
After proper tensioning, the blade must be tracked.
“Tracking” refers to position of blade on the wheels
while machine is in operation. Tracking should be
checked periodically, and is mandatory af ter every
blade change. Blade tracking is done by hand wit h
machine disconnected from power.
1. Disconnect machine from power source.
2. Blade must be correctly tensioned (section
8.11).
3. Make sure blade guides and other parts of
machine will not interfere with blade
movement. Lower guide post until you can see
blade through tracking window (C).
7. If blade tends to move toward edge of wheel,
set lever to “Partial Tension-Idle/T racking.”
8. Loosen lock handle (D, Figure 21) and slightly
rotate tracking knob (E) with your right hand
while continuing to rotate wheel with your left.
Observe blade through tracking window.
Rotating knob clockwise will cause blade to
move toward rear edge of wheel. Rotating
knob counterclockwise will cause blade to
move toward front edge of wheel.
IMPORTANT: This adjustment is sensitive;
perform in small increments and give blade
time to react to changes.
9. When blade is tracking in center of wheel, retighten lock handle (D), and close upper door.
10. Move tension lever to “Full Tension” position,
and connect band saw to power. Turn it on for
a brief time to observe the blade in action
through tracking window.
11. If further adjustments are needed, disconnect
from power and repeat above procedure.
NOTE: An interlock switch in the upper housing
prevents operation of saw unless tension lever is in
ful l tensi o n position.
Figure 21
4. Set quick tension lever initially to “Partial
Tension-Idle/Tracking” position, as shown in
Figure 21.
5. Open upper door to expose wheel.
6. Rotate wheel by hand, observing position of
blade through tracking window. As you rotate
wheel, move lever to “Full Tension” position.
The blade should continue to ride upon center
of tire (Figure 22).
8.13 Upper Blade Guides
The bearing guides should be set so that contact
between blade and guides will occur only when
blade is under pressure from a workpiece. To
adjust upper bearing guides for proper blade
control, proceed as follows.
Refer to Figures 23 through 24.
1. Disconnect machine from power source.
2. Blade must already be tensioned and tracking
correctly. Place quick tension lever in “Full
Tension” position.
3. Lower guide post until upper guide bearings
are a few inches off the table. (The reason for
this will be evident la ter in section 8.17)
4. Loosen lock knob (F, Figure 23).
Figure 22
Figure 23
5. Slide entire guide bracket until front of guide
bearings are about 0.015” (1/64”) behind the
16
Page 17

blade’s gullet (curved area at base of tooth).
See Figure 24.
Figure 24
6. Tighten lock knob (F) to secure this position.
7. Loosen lock knob (G) for one of the guide
bearings.
8. The guide bearing rotates on an eccentric
shaft. Adjust guide bearing by rotating the
knurled knob (H) with a 5mm hex key, until
guide bearing is approximately 0.004” from
blade. A quick way to achie ve this spac ing is
by placing a single t hickness of a c risp dollar
bill (a dollar bill is approximate ly 0.004” thick)
between blade and guide bearing. See Figure
25. Adjust guide bearing until it just lightly grips
the dollar bill.
8.14 Upper Thrust Bearing
Refer to Figures 23 and 26:
1. The thrust bearing prevents backward
deflection of blade during cutting. A groove
provided in the bearing surface helps stabilize
the moving blade.
2. Loosen lock knob (I) and push thrust bearing
(J) up to back of blade.
3. Adjust thrust bearing until space between
groove bottom and back edge of blade is
approximately 0.015” (1/64”). Tighten lock
knob (I).
4. If lateral adjustment of bearing is needed to
align groove with blade, loosen set screw (K)
at front of bearing assembly, and shift bearing
as needed. Retighten set screw.
5. Make sure all lock knobs on upper guide
bearing assembly are tightened when
adjustments are finished.
Figure 25
NOTE: Do not force guide bearing against side
of blade. It should generally only make contact
with blade when there is pressure from the
cutting operation.
9. Tighten lock knob (G).
10. Repeat process for opposite guide bearing.
Figure 26
8.15 Lower Blade Guides
Refer to Figures 27 and 28.
1. Disconnect band saw from power source.
2. Adjust lower guide bearings and lower thrust
bearing below table, using same procedure
and measurements as for upper guide
bearings and thrust bearing described above.
Movement summary: Loosen lock knob (L) to
move guide bracket. Loosen lock knob (M) to
rotate side bearing, using knurled knob (N).
Loosen lock ring (O, Figure 27) and rotate
knob (P) to adjust thrust beari ng in relation to
blade.
3. Make sure all knobs are tightened after
adjustments are complete.
17
Page 18

8.17 Guide Post Parallelism
The guide post should be parallel to blade
throughout vertical travel of the guide post; thus the
guide bearings will maintain their relationship to
blade at any height from the table and won’t
require re-setting each time guide post is moved.
This setting has been accurately made by the
manufacturer and should not require immediate
attention, but may be checked in future as follows:
1. Disconnect band saw from power source.
Figure 27
Figure 28
8.16 Guide Post
Refer to Figure 29.
1. Disconnect band saw from power sour ce.
2. Loosen lock k nob (A) a nd raise or lower guide
post (B) using handwheel (C).
3. Position blade guide assembly so that bottom
of guide bearings are about 1/8” above
material to be cut. Or, simply lower guide post
until scale pointer (D) indicates the height of
your workpiece. This provides minimal
clearance between workpiece and bottom of
guide bearings, which will minimize blade
deflection as well as enhance operator safety.
4. Tighten lock knob (A).
2. Move blade tension lever to “Full Tension”
position.
3. The guide bearings in low position should
already be set in relation to blade (see section
8.13). Also, the table must be square with
blade (see section 8.5)
4. Loosen lock knob (A, Figure 28) and raise
guide post to a high position.
5. Confirm that guide po st travels straight up and
down, and guide bearings maintain their
relationship to blade.
6. If guide post doe s not go stra ight up and down
(blade begins deflecting when guide post is
raised), slightly loosen the four screws (E,
Figure 29) and adjust guide post assembly as
needed.
7. When finished adjusting, securely tighten the
four screws (E).
8. Verify the setting by raising and lowering guide
post.
8.18 Resaw Pin
Refer to Figure 30.
The resaw pin provides a single contact point while
ripping a workpiece into thinner boards.
Remove aluminum plate and mount resaw pin to
slot in fence body, securing it with knob, as shown.
The resaw pin is usually positioned so that its
center is approximately even with the front edge of
the blade.
Figure 29
Figure 30
18
Page 19

See section 10.4 for further information about using
resaw pin.
8.19 Miter Gauge
Refer to Figures 31 and 32.
A miter gauge is provided for crosscutting
operations. Install miter gauge by sliding end of
miter gauge bar into table T-slot.
The miter gauge should fit snugly within miter slot
while still sliding easily. The miter gauge bar has
two slots, each with a set screw (Figure 31). Rotate
one or both of these set screws with a 4mm hex
key as needed, to eliminate any play between miter
gauge bar and miter slot.
3. Flip stop plate (C) back dow n, and loosen 90°
stop he x nut. Adj ust sc rew u nti l it cont act s 90°
stop plate.
4. Re- t ight en he x nut .
5. Loosen set screw at base of pointer (B) and
shift pointer so that it lines up with 90° mark on
scale.
6. Re-tighten set screw.
7. The 45° stops can be checked in similar
fashion, using an angle gauge similar to that
shown in Figure 32.
To adjust miter gauge angle for operations:
1. Loosen handle (A).
2. Rotate gauge body until pointer (B) lines up
with desired angle on scale. You may have to
pivot 90° stop plate (C) out of the way to allow
the body to rotate.
3. Tighten handle (A).
4. There are t hree stops: at 90°, a nd 45° left and
right. Each of these can be adjusted by
loosening hex nut (D) and turni ng screw (E) as
needed. Re-tighten hex nut (D) when
adjustment is finished.
Figure 31
If table/miter slot is square to blade (see section
8.5) the miter gauge will also be square to blade.
Before operating, however, t he 90° setting of m iter
gauge should be checked in relation to b lade, as
follows.
1. Place a square against miter gauge face, and
against flat of blade, as shown in Figure 32.
(Place square against flat of blade, not against
the teeth which are set wider than the blade
body). A wide blade is preferred for this
procedure.
8.20 Drive Belt Replacement and
Tensioning
The drive belt and pulleys are properly adjusted at
the factory. However, belt tension should be
occasionally checked when the band saw is new,
as a new belt may stretch slightly during the
breaking-in process.
If belt becomes worn, cracked, frayed or glazed, it
should be replaced as follows:
Refer to Figures 33 and 34.
1. Disconnect machine from power source.
2. Open upper and lower doors and remove
blade.
3. Remove screw (F, Figure 33) from lower wheel
shaft with a 6mm hex key, and remove lower
wheel.
Figure 32
2. Flip 90° stop plate (C) out of the way, and
loosen handle (A). Shift miter gauge body until
it is flush with square, then re-tighten hand le
(A).
19
Page 20

Figure 33
4. Loosen motor lock h andle (G, Figure 34).
5. Raise motor lift handle (H) and retighten motor
lock handle to hold motor in raised position.
6. Remove old belt and install new one, making
sure it seats properly in pulley grooves.
7. Loosen motor lock handle (G) and allow motor
to lower.
8.21 Brushes
Refer to Figure 35.
Two adjustable brushes are located in lower wheel
housing. They should remain in constant contact
with blade or wheel to prevent buildup of gum and
debris.
Figure 35
9.0 Operating Controls
9.1 Start/Stop
Figure 34
8. The weight of the motor itself should produce
proper tension for the belt. Check tension by
pushing with moderate pressure on the belt
halfway between the pulleys. An adequately
tensioned belt will deflect about 1/2”. If tension
isn’t s trong enough, push down on motor.
9. Tighten motor lock handle (G).
10. Reinstall lower wheel, and tighten screw (F)
securely.
11. Install blade, and verify blade tension and
tracking before operating (sections 8.11 and
8.12).
Refer to Figure 36.
Power Indicator Light – The start switch (A) has
a power indicator lamp which is on whenever
there is power connected to the band saw, not
just when the band saw is running. Do not
assume that no light means there is no power
to the machine. If the bulb is bad, t here will be
no indication. Always check before use.
Do not rely that no lig ht means
no power to the machine. Always check for power
first. Failure to comply may cause serious injury!
Start – Press green start switch (A).
When power is connected to machine, the green
light is always on regardless of whether band saw
is running or not.
Stop – Press red switch (B) to stop.
Reset – If band saw stops witho ut pressing the
stop button (as result of tripped fuse or circuit
breaker, etc.) proceed as follows:
1. Press red switch to reset.
2. Press green switch to restart machine.
20
Page 21

Figure 36
before opening guards/doors, making adj ustments,
or leaving the area.
10.0 Operation
The following section contains basic information,
and is not intended to cover all possible
applications or techniques using the band saw.
Consult pub lished sources of inform ation, acquire
formal training, and/or talk to experienced band
saw users to gain proficiency and knowledge of
band saw operations.
(The following figures may or may not show your
specific model, but procedures are the same.)
9.2 Safety Key
The start/stop switch on the Band Saw comes
equipped with a magnetic safety key (C, Figure
36). When in place on the switch, the magnetic
safety key trips a relay which will allow the machine
to start and stop when the respective switches are
pressed. Being magnetic, the lock can be removed
to make the machine inoperable and can be
hidden for safe storage by attaching it to another
magnetic surface.
When using the band saw, place the key on the
switch cover, lining up arrow on key with REMOVE
arrow on cover. Then rotate key so that arrow li nes
up with LOCK arrow on cover. This will prevent the
safety key coming loose from vibration when
machine is in use.
9.3 Brake Pedal
When the stop button is used to shut off the band
saw, the blade will coast slowly to a stop. An
alternate method of stopping the machine is to
press and hold the brake pedal, shown in Figure
37. The blade will stop moving in approximately
three to four seconds after pedal is pressed.
Restart saw by pressing start switch on column.
NOTE: Unnecessary and excessive use of brake
pedal may shorten life of brake pad.
10.1 General Procedure
1. Make sure blade is adjusted correctly for
tension and tracking, and that upper and lower
guide bearings and thrust bearings are set in
proper relation to blade.
2. Adjust guide post so that guide bearings are
just above workpiece (about 1/8”) allowing
minimum exposure to blade.
3. If using the fence, move it into position and
lock it to guide rail. If using miter gauge for a
crosscut, the fence should be moved safely
out of the way.
4. Turn on band saw and allow a few seconds for
machine to reach full speed.
Whenever possible, use a push
stick, hold-down, power feeder, jig, or similar
device while feeding stock, to prevent your hands
getting too close to the blade.
5. Place the straightest edge of the workpiece
against the fence for a rip cut; or against the
miter gauge for a crosscut. Push workpiece
slowly into blade, while also keeping it pressed
against fence or held against miter gauge. Do
not force workpiece into blade.
Additional operating tips:
Make relief cuts whenever possible. A relief cut is
an extra cut made through the waste port ion of a
workpiece up to the layout line. When that
intersection is reached by the blade while following
the layout line, the waste portion comes free. This
helps prevent pinching of the back edge of the
blade in the cut.
Figure 37
After machine is shut off, allow
wheels and blade to come to a complete stop
When cutting, do not overfeed
blade; overfeeding will reduce blade life, and may
cause blade to break.
When cutting long stock, the operator should use
roller stands, support tables, or an assistant to help
stabilize the workpiece.
21
Page 22

10.2 Ripping
Ripping is cutting lengthwise down the workpiece,
along the grain of wood. See Figure 38. Always
use a push stick or similar device when ripping
narrow pieces.
Figure 38 (ripping)
10.3 Crosscutting
Crosscutting is cutting across the grain of the
workpiece, while using the m iter gauge to feed t he
workpiece into the blade.
The right hand should hold workpiece steady
against miter gauge, while left hand pushes miter
gauge past blade, as shown in Figure 39.
Do not use fence in conjunction wit h miter gauge.
The offcut of the workpiece must not be
constrained during or after the cutting process.
The ideal blade for resawing is the widest one the
machine can handle, as the wider the blade the
better it can hold a straight line.
Resawing can be performed using the aluminum
fence plate or the resaw pin. When using the plate,
use a push block, push stick, or similar device to
keep your hands away from the blade. The resaw
pin o ff ers a pivo t po int b y w hic h you c an c aref ull y
follow your layout line; it is especially useful for
sawing curves, when the fence cannot be used
and it is difficult to control the cut freehand.
Figure 40 demonstrates resawing with the
aluminum plate; Figure 41, with the resaw pin.
Figure 40 (resawing)
Using the fence in conjunction
with miter gauge can cause binding and possible
damage to blade.
Figure 39 (crosscut)
10.4 Resawing
Resawing is the process of slic ing stock to reduce
its thickness, or to prod uce boards t hat are thinner
than the original workpiece, such as veneers.
Figure 41 (resaw pin)
10.5 Blade Lead
Blade lead, or drift, is when the blade begins to
wander off the cutting line even when the band
saw fence is being used. Figure 42 shows an
example of blade lead. It is more common with
small, narrow blades, and is almost always
attributable to poor blade quality, or lack of proper
adjustments. Inspect the band saw for the
following:
• Fence not parallel to miter slot and blade.
• Blade not tensioned correctly.
• Blade is dull.
• Teeth have excessive “set” on one side of
blade.
• Workpiece being fed too quickly.
22
Page 23

Figure 42
If the blade is suspect, but replacing it is not
currently an option, the blade lead can be
temporarily compensated for by skewing the fence:
1. Cut a scrap piece of wood about the same
length as the band saw table, and joint one
edge along its length, or rip it on a table saw to
give it a straight edge.
2. Draw a line on the board parallel with the
jointed, or straight edge of the board.
3. Move the band saw fence out of the way, and
carefully make a freehand cut along your
drawn line on the board. Stop about midway
on the board, and shut off the band saw (allow
blade to come to a complete stop) but do not
allow the board to move.
4. Clamp the board to the table.
5. Slide the band saw fence over against the
board until it contacts t he straight edge of the
board at some point. Lock the fence down.
6. Use the back adjustment screws (F, Figure 13)
to line up fence against board.
NOTE: Skewing the fence to correct b lade lead is
effective for that particular blade; when a new
blade is installed, the fence will need re-adjustment
and re-squaring to miter slot. See appropriate
sections in this manual.
11.0 Maintenance
Before doing maintenance on
the machine, disconnect it from electrical supply by
pulling out plug or switching off main switch!
Failure to comply may cause serious injury.
Clean band saw regularly to rem ove any resinous
deposits and sawdust.
Keep miter slot, and guide bearings, clean and free
of resin.
Keep blade clean and sharp. Check it periodically
for cracks or other signs of wear.
The drive belt should be c hecked periodically. If it
looks worn, frayed, glazed or otherw ise damaged,
replace it.
Remove any deposits from band wheels to avoid
vibration and potential blade breakage.
Vacuum or blow out dust from inside cabinet. (Use
proper dust mask equipment).
The table surface must be kept clean and free of
rust for best results. If rust appears, it can often be
removed with a mixture of household ammonia,
good commercial detergent and #000 steel wool.
Alternatively, commercial rust removers can be
found at many hardware stores.
Apply a light coat of paste wax to table. There are
also products in aerosol form available in major
hardware stores and supply catalogs. Whatever
method is chosen, the coating should protect the
metal and provide a smooth surface, without
staining workpieces.
If the power cord is worn, c ut, or damaged in any
way, have it replaced immediately.
11.1 Lubrication Points
1. Periodically apply a light, non-hardening
grease to rack and pinion system of guide post
(Figure 43).
Figure 43
2. Grease the sliding surfaces of the table
trunnions (Figure 44).
23
Page 24

Figure 44
3. Grease blade tension screw (Figure 45).
Figure 45
4. Oil any pins, shafts, and j oints. (Do not get oil
on pulleys or belts.)
Note: Bearings on the band saw are pre-lubricated
and sealed, and do not require attention.
Width
Band saw blades come in different standard
widths, measured from back edge of blade to tip of
tooth. Generally, wider blades are used for ripping
or making straight cuts, such as resawing.
Narrower blades are often used when the part
being cut has curves with small radii. When cutting
straight lines with a narrow blade, the blade may
have a tendency to drift (see section 10.5).
Pitch
Pitch is measured in “teeth per inch” (TPI) and can
be constant or variable. Figure 46 shows blades
with different pitches.
A fine pitch (more teeth per inch) will cut slowly but
more smoothly. A coarse pitch (fewer teeth per
inch) will cut faster but more roughly.
As a rule of thumb, the thicker the workpiece, the
coarser will be the blade pitch. If you have to cut a
hard or very brittle materia l, you will probab ly want
to use a blade with a finer pitch in order to get
clean cu ts .
Using a blade with too few teeth may cause
vibration and a rough cut, while too many teeth
may cause the gullets to fill with sawdust and
overheat the blade.
As a general rule, use a blade that will have from 6
to 12 teeth in the workpiece at any given time.
12.0 Blade Selection
Using the proper blade for t he job will increase t he
operating efficiency of your band saw, help reduce
necessary saw maintenance, and improve your
productivity. Thus, it is important to follow certain
guidelines when selecting a saw blade.
Here are factors to consider during selection:
• Type of material you will be cutting.
• Thickness of workpiece.
• Features of workpiece, such as bends or
curves with small radii.
These factors are important because they involve
basic concepts of saw blade desig n. There are f ive
(5) blade features that are normally changed to
meet certain kinds of sawing requirements. They
are:
1. width
2. pitch (number of teeth per inch)
3. tooth form (or shape)
4. “set” of the teeth
5. the blade material itself
Figure 46 – Blade Pitch
Shape
Figure 47 shows common types of tooth shape, or
form. Tooth shape has an effect on cutting rate.
The Regular, or standard blade, has evenly spaced
teeth that are the same size as the gullets, and a
zero-degree rake (i.e. cutting angle). These offer
precise, clean cuts at slower rates. It is usually a
good choice for cutting curves and making
crosscuts.
The Skip type has fewer teeth and larger gullets
with a zero rake. It allow s faster cutting rates t han
the Regular type, with a s lightly coarser fi nish. It is
useful for resawing and ripping thick stock, as well
as cutting softwoods.
24
Page 25

The Hook type blade has larger teeth and gullets
and a positive rake angle for more aggressive,
faster cutting when resawing or rippi ng thick stock,
especially hardwoods.
Variable-tooth blades combine features of the other
shapes, with tooth style and spacing varying on the
same blade. This produces smooth cuts while
dampening vibration.
Figure 47 – Blade Tooth Shape
Set
The term “set” refers to the way in which the saw
teeth are bent or positioned. Bending the teeth
creates a kerf that is wider than the back of the
blade. This helps the operator m ore easily pivot a
workpiece through curve cuts, and decreases
friction between blade and workpiece on straight
cuts.
Set patterns are usually selected depending upon
the type of material that needs to be cut. Three
common set patterns are shown in Figure 48.
Generally, the Raker set is used for cutting metal
workpieces; the Wavy set, when the thickness of
the workpiece changes, such as cutting hollow
tub ing or s tr uc t ur a ls. The Straight, or Alternate, set
is the one most used f or woodworking b lades, and
is also used to cut plastics.
Material
Band saw blades can be made from different types
of metals. The most common include spring steel,
carbon steel, bimetal (alloy steel equipped with a
high speed cobalt steel edge welded to it), or
carbide tips .
Because of the importance of blade selection, it is
recommended that you use the blade selection
guide (section 13.0). Also, listening to experienced
band saw users will produce valuable information
as to blade types currently on the market along
with their pros and cons.
Blade Breakage
Band sa w blad es are subje ct to hig h stre sses a nd
breakage may sometimes be unavoidable.
However, many factors can be controlled to help
prevent most blade breakage. Here are some
common causes for breakage:
1. Misalignment of blade guides.
2. Feeding workpiece too quickly.
3. Using a wide bl ade to cut a tight radius curve.
4. Excessive tension.
5. Teeth are dull or improperly set.
6. Upper guides set too high off workpiece.
7. Faulty weld on blade.
Although not essential, some users round or
“stone” the back edge of their blade. This is done
by placing a sharpening stone on the table and in
light contact with the back corners of the blade as
the blade is running. Rounding can help the back
blade edge move more smoothly through the kerf,
smooths the weld, and helps prevent cracks from
starting at the back corners.
Figure 48 – Blade Set
25
Page 26

13.0 Blade Selection Guide
Identify the material and thick ness of your workpiece. T he chart will show recommended PITCH, blade TYPE ,
and FEED RATE.
Key: H – Hook L – Low
S – Skip M – Medium
R – Regular H – High
Example: 10/H/M means 10 teeth per inch / Hook Type Blade / Medium Feed
Tables 3 and 4
For Radius Cutting
Study the part drawing or prototype, or actually measure the smallest
cutting radius required, and locate this radi us (in inches) on the chart
at the right. Follow the curve to where the approximate blade width is
specified. If a radius falls between two of the curves, select the widest
blade that will saw this radius.
This procedure should be used for making initial blade selections.
These recommendations can, of course, be adj usted to meet specific
requirements of a cutting job. Compromises may be necessary if you
cannot find all needed specifications in a single blade.
26
Page 27

14.0 Troubleshooting the PM1500 Band Saw
14.1 Operational Problems
Table 5
Trouble Probable Cause Remedy
Table tilt does not hold
position under load.
Table will not tilt. Trunnion not lubricated. Lubricate trunnion.
Table vibration while
sawing.
Surface finish on
workpiece is rough.
Blade cutting
inaccurately. Cuts not
straight.
Lock handle not tight. Tighten lock handle.
Trunnion locking mechanism is broken
or worn.
Trunnion jammed. Disassemble and replace jammed
Drive belt too slack. Increase tension on drive belt (sect.
Incorrect choice of saw blade pitch. Check blade selection chart and use
Saw dust or debris on band wheel. Or
tire is worn/damaged.
Blade pitch too coarse. Change to finer pitch blade.
Workpiece being fed too strongly. Reduce feed force.
Gum or pitch on blade. Clean blade.
Worn blade teeth or damaged blade. Replace blade.
Fence not parallel to blade. Align fence properly (sect. 8.6).
Replace trunnion locking mechanism.
parts.
8.20). Replace belt if worn.
correct blade (sect. 13.0).
Keep band wheels clean. Replace tires
if necessa ry.
Blade cannot be
tensioned properly.
Blade binds in
workpiece.
Blade forms cracks at
base of teeth.
Incorrect adjustment of blade guides. Adjust blade guides properly (sect. 8.13
thru 8.15).
Workpiece being fed too strongly. Reduce feed force.
Upper blade guides not located close
enough to workpiece.
Incorrect choice of saw blade for that
particular operation.
Blade tension too light. Increase tension (sect. 8.11).
Tension spring is fatigued. Replace tension spring (contact Walter
Incorrect blade tension or damaged
blade.
Blade too wide for desired radius. Select narrower blade (sect. 13.0).
Teeth not suitable for operation, or
incorrectly set.
Blade thickness not suitable for band
wheel diameter.
Position guides about 1/8” above
workpiece.
Install correct blade.
Meier service representative).
Correct accordingly.
Replace with proper blade.
Replace with proper thickness blade.
27
Page 28

Trouble Probable Cause Remedy
Cracks on back edge
of blade.
Blade breaks
prematurely.
Blade sharpened incorrectly, becomes
overheated.
Band wheels have become misaligned. Contact service representative.
Workpiece being fed too quickly.
Welding on blade not perfectly aligned.
Thrust bearing is worn; caused by
constant contact with back of blade.
Feed force too great. Reduce feed force.
Blade pitch too coarse.
Guide bearings not properly supporting
blade.
Sharpen blade properly or replace.
Reduce feed speed to lessen strain on
blade.
Eliminate welded part, and re-weld
properly; or acquire a new blade. Round
the back edge of a new blade.
Replace thrust bearing. Adjust new
bearing according to instructions (sect.
8.14).
Refer to blade selection chart; use finer
pitch blade.
Check guide bearings for correct
position and signs of wear. Adjust or
replace as needed.
Blade breaks close to
weld.
Premature dulling of
saw teeth.
Blade tensioned too tightly. Reduce tension.
Blade overheated during welding.
Blade cooled too rapidly after welding.
Blade pitch too fine.
Feed pressure too light. Increase feed pressure.
Cutting rate too low. Increase feed pressure and cutting rate.
Incorrect choice of blade.
Chipped tooth or foreign object lodged
in cut.
Have blade annealed, or eliminate
brittle part and weld correctly.
Have blade annealed, or eliminate
brittle part and weld correctly.
Refer to blade selection chart (sect.
13.0). Use blade with coarser pitch.
Re-examine material. Select proper
blade from chart (sect. 13.0).
Stop saw and remove lodged particle.
Replace blade if damaged.
28
Page 29

14.2 Mechanical and Electrical Problems
Table 6
Trouble Probable Cause Remedy
Machine will not
start/restart or
repeatedly trips circuit
breaker or blows
fuses.
Verify machine is connected to power
No incoming power.
Cord damaged. Replace cord.
Overload automatic reset has not been
reset.
Band Saw frequently trips.
Building circuit breaker trips or fuse
blows.
Switch or motor failure (how to
distinguish).
Motor overheated.
Motor failure.
Miswiring of unit.
source, and safety key is installed on
switch.
Reset overload by pushing in
completely the OFF (red) button on the
magnetic switch. Allow a few minutes
for machine to cool. If problem persists,
check amp setting on motor star ter.
One cause of overloading trips which
are not electrical in nature is too heavy
a cut. The solution is to reduce feed
pressure into the blade. If too heavy a
cut is not the problem, then check the
amp setting on the overload relay.
Match the full load amps on the motor
as noted on the motor plate. If amp
setting is correct, there is probably a
loose electrical lead.
Verify that band saw is on a circuit of
correct size. If circuit size is correct,
there is probably a loose electrical lead.
Check amp setting on motor starter.
If yo u have acce ss to a volt meter, you
can separate a starter failure from a
motor failure by first, verifying incoming
voltage at 230+/-10% and second,
checking the voltage between starter
and motor at 230+/-10%. If incoming
voltage is incorrect, you have a power
supply problem. If voltage between
starter and motor is incorrect, you have
a starter problem. If voltage between
starter and motor is correct, you have a
motor problem.
Clean motor of dust or debris to allow
proper air circulation. Allow motor to
cool down before restarting.
If electric motor is suspect, you have
two options: Have a qualified electrician
test the motor for function or remove the
motor and take it to a q ualified electric
motor repair shop for testing.
Double check to confirm all electrical
connections are correct. Refer to wiring
diagram to make any needed
corrections.
29
Page 30

Trouble Probable Cause Remedy
Machine will not
start/restart or
repeatedly trips circuit
breaker or blows
fuses.
(continued)
Switch failure.
If the start/stop switch is suspect, you
have two options: Have a qualified
electrician test the switch for function, or
purchase a new start/stop switch and
establish if that was the problem on
change-out.
Band Saw does not
attain full speed.
Extension cord too light or too long.
Low current. Contact a qualified electrician.
Replace with adequate size and length
cord.
15.0 Replacement Parts
Replacement parts are listed on the followi ng pages. To order parts or reach our service departm ent, call 1800-274-6848 Monday through Friday (see our website for business hours, www.powermatic.com). Having the
Model Number and Serial Number of your machine available when you call will allow us to serve you quickly
and accurately.
30
Page 31

15.1.1 Complete Machine with Accessories – Exploded View
31
Page 32

32
Page 33

15.1.2 Complete Machine with Accessories – Parts List
Index No Part No Description Size Qty
1 ................ PM2000-105.............. Powermatic Nameplate, Large ................................ . ..................................... 1
2 ................ TS-0254011 .............. Socket Head Button Screw ...................................... 1/4"-20UNCx3/8"L......... 2
3 ................ TS-1550041 .............. Flat Washer ............................................................. M6 x Ø16 ...................... 2
4 ................ PM1500-004.............. Lifting Eye ................................................................ M10 ............................... 1
5 ................ PM1500-005.............. Machine Main Body Frame ...................................... ...................................... 1
6 ................ PM1500-006.............. Switch Bracket ......................................................... ...................................... 1
7 ................ TS-2246082 .............. Socket Head Button Screw ...................................... M6x8 ............................. 6
8 ................ TS-1550041 .............. Flat Washer ............................................................. M6 x Ø13 ...................... 2
9 ................ PM1500-009.............. Power Cord .............................................................. 14AWGx3Cx3.4M ......... 1
10 .............. PM1500-010.............. Upper Wheel Sliding Bracket Assembly .................. ...................................... 1
11 .............. PM1500-011.............. Tension Pointer........................................................ ...................................... 1
12 .............. PM1500-012.............. Step Screw .............................................................. ...................................... 1
13 .............. TS-2248202 .............. Socket Head Button Screw ...................................... M8x20 ........................... 4
14 .............. TS-2361081 .............. Lock Washer ............................................................ M8 ................................. 4
15 .............. PM1500-015.............. Motor Bracket Lock Handle ..................................... M10x33 ......................... 1
16 .............. PM1500-016.............. Motor Mount Plate ................................................... . ..................................... 1
17 .............. TS-1524011 .............. Set Screw ................................................................ M8x8 ............................. 2
18 .............. TS-2248202 .............. Socket Head Button Screw ...................................... M8x20 ........................... 4
19 .............. PM1500-019.............. Upper Wheel Assembly ........................................... Ø15” .............................. 1
20 .............. PM1500-020.............. Lower Wheel Assembly ........................................... Ø15” .............................. 1
21 .............. PM1500-021.............. Saw Blade…………………… …………...153"L / 3/8"W / 0.65mm Thk ........... 1
22 .............. TS-1504041 .............. Hex Socket Screw ................................................... M8x20 ...................... 2
23 .............. TS-2361081 .............. Lock Washer ............................................................ M8 ................................. 2
24 .............. TS-1550061 .............. Flat Washer ............................................................. M8 x Ø30 ...................... 2
25 .............. PM1500-025.............. Motor Pulley ............................................................. ...................................... 1
26 .............. PM1500-026.............. Poly-V Belt ............................................................... 290J9 ............................ 1
27 .............. PM1500-027.............. Upper Cabinet Door ................................................. ...................................... 1
28 .............. TS-1505031 .............. Socket Head Cap Screw ......................................... M10x25 ......................... 1
29 .............. TS-2361101 .............. Lock Washer ............................................................ M10 ............................... 3
30 .............. TS-1550071 .............. Flat Washer ............................................................. M10 x Ø20 .................... 2
31 .............. PM1500-031.............. Motor Cord ............................................................... 14AWGx3Cx1.7M ......... 1
32 .............. TS-2246082 .............. Socket Head Button Screw ...................................... M6x8 ............................. 2
33 .............. TS-2361061 .............. Lock Washer ............................................................ M6 ................................. 1
34 .............. TS-1550041 .............. Flat Washer ............................................................. M6 x Ø16 ...................... 2
35 .............. PM1500-035.............. Support Plate .......................................................... ...................................... 1
36 .............. PM1500-036.............. Magnetic Switch Assembly ...................................... 230V/60Hz/1PH ............ 1
............... PM2000-298.............. Safety Key for Magnetic Switch ............................... ...................................... 1
37 .............. PM1500-037.............. Handwheel ............................................................... 6” ................................... 1
38 .............. PM1500-038.............. Locating Block ......................................................... ...................................... 1
39 .............. PM1500-039.............. Tapping Screw ......................................................... M4x8 ............................. 2
40 .............. PM1500-040.............. Wire Connector ........................................................ 224-201 ......................... 1
41 .............. TS-1523041 .............. Socket Set Screw .................................................... M6x12 ........................... 2
42 .............. TS-1523051 .............. Socket Set Screw .................................................... M6x16 ........................... 4
43 .............. PM1500-043.............. Face Plate................................................................ ...................................... 1
44 .............. TS-1504041 .............. Socket Head Cap Screw.......................................... M8x20 ........................... 1
45 .............. PM1500-045.............. Table Insert (Aluminum) .......................................... ...................................... 1
46 .............. PM1500-046.............. Roll Pin .................................................................... Ø4x8 ............................. 2
47 .............. PM1500-047.............. Table Pin Assembly ................................................. ...................................... 1
48 .............. TS-1534032 .............. Pan Head Bolt w/Flange .......................................... M6x10 ........................... 1
49 .............. TS-1503021 .............. Socket Head Cap Screw.......................................... M6x10 ........................... 2
50 .............. PM1500-050.............. Viewing Window ...................................................... ...................................... 2
51 .............. PM1500-051.............. Limit Switch.............................................................. AZD-1112...................... 1
52 .............. TS-2284302 .............. Phillips Pan Head Machine Screw ........................... M4x30 ........................... 2
53 .............. TS-1521031 .............. Socket Set Screw .................................................... M4x8 ............................. 8
54 .............. PM1500-054.............. Switch Cord ............................................................. 18AWGx2Cx1.2M ......... 1
55 .............. PM1500-055.............. Lock Knob ................................................................ M10x30 ......................... 1
56 .............. TS-1482051 .............. Hex Cap Screw ........................................................ M6x25 ........................... 2
57 .............. TS-1550041 .............. Flat Washer ............................................................. M6 x Ø13 ...................... 4
58 .............. PM1500-058.............. Brush ....................................................................... ...................................... 2
59 .............. TS-1503061 .............. Socket Head Cap Screw.......................................... M6x25 ........................... 1
33
Page 34

Index No Part No Description Size Qty
60 .............. PM1500-060.............. Door Lock Knob ....................................................... ...................................... 2
61 .............. TS-1541021 .............. Nylon Lock Hex Nut ................................................. M6 ................................. 6
62 .............. PM1500-062.............. Strain Relief ............................................................. PG13.5 .......................... 2
63 .............. PM1500-063.............. Pointer ..................................................................... ...................................... 1
64 .............. TS-2311101 .............. Hex Nut .................................................................... M10 ............................... 1
65 .............. TS-1491151 .............. Hex Cap Screw ........................................................ M10x90 ......................... 1
66 .............. TS-1503061 .............. Socket Head Cap Screw.......................................... M6x25 ........................... 2
67 .............. PM1500-067.............. Blade Tracking Adjustment Knob ............................ M10x50 ......................... 1
68 .............. PM1500-068.............. Lock Handle ............................................................. M10 ............................... 1
69 .............. PM1500-069.............. Cam ......................................................................... ...................................... 1
70 .............. PM1500-070.............. Shaft Fixed Block ..................................................... ...................................... 1
71 .............. PM1500-071.............. Tension Quick release Handle................................. ...................................... 1
72 .............. PM1500-072.............. Tension Quick release Lever ................................... ...................................... 1
73 .............. TS-1540081 .............. Hex Nut .................................................................... M12 ............................... 1
74 .............. PM1500-074.............. Tension Quick release Lever Shaft.......................... ...................................... 1
75 .............. TS-2248202 .............. Socket Head Button Screw ...................................... M8x20 ........................... 4
76 .............. TS-2361081 .............. Lock Washer ............................................................ M8 ................................. 4
77 .............. PM1500-077.............. Washer .................................................................... ...................................... 1
78 .............. TS-1524051 .............. Socket Set Screw .................................................... M8x20 ........................... 4
79 .............. TS-1540061 .............. Hex Nut .................................................................... M8 ................................. 4
80 .............. PM1500-080.............. Lower Wheel Shaft .................................................. ...................................... 1
81 .............. PM1500-081.............. Motor........................................................................ 3HP, 1PH, 230V............ 1
.............. PM1500-081-01 ........ Motor Fan (not shown)............................................. ...................................... 1
.............. PM1500-081-02 ........ Motor Fan Cover (not shown) .................................. ...................................... 1
.............. PM1500-081-03 ........ Start Capacitor (not shown) ..................................... 200MFD, 250VAC ......... 1
.............. PM1500-081-04 ........ Running Capacitor (not shown) ............................... 60µF, 300VAC .............. 1
.............. PM1500-081-05 ........ Junction Box (not shown) ........................................ ...................................... 1
.............. PM1500-081-06 ........ Junction Box Cover (not shown) .............................. ...................................... 1
.............. PM1500-081-07 ........ Centrifugal Switch (not shown) ............................... ...................................... 1
82 .............. PM1500-082.............. Lower Cabinet Door ................................................. ...................................... 1
83 .............. PM1500-083.............. Strain Relief Fixed Plate .......................................... ...................................... 1
84 .............. JMS12SCMS-81 ....... Pan Head Bolt w/Flange .......................................... M5x8 ............................. 1
85 .............. PM1500-085.............. Trunnion Support Bracket Assembly ....................... ...................................... 1
86 .............. TS-1505051 .............. Socket Head Cap Screw ......................................... M10x35 ......................... 2
87 .............. TS-2361101 .............. Lock Washer ............................................................ M10 ............................... 2
88 .............. TS-1550071 .............. Flat Washer ............................................................. M10 x Ø23 .................... 2
89 .............. 3520B-126................. Handle ..................................................................... ...................................... 2
90 .............. PM1500-090.............. Handwheel ............................................................... ...................................... 1
91 .............. PM1500-091.............. Guide Bar Bracket Assembly ................................... ...................................... 1
92 .............. TS-2248202 .............. Socket Head Button Screw ..................................... M8x20 ........................... 4
93 .............. TS-2361081 .............. Lock Washer ............................................................ M8 ................................. 4
94 .............. TS-1550061 .............. Flat Washer ............................................................. M8 x Ø18 ...................... 4
95 .............. PM1500-095.............. Upper Blade Guide Support Assembly .................... ...................................... 1
96 .............. PM1500-096.............. Lower Blade Guide Support Assembly .................... ...................................... 1
97 .............. TS-2246082 .............. Socket Head Button Screw ...................................... M6x8 ............................. 2
98 .............. TS-1550041 .............. Flat Washer ............................................................. M6 x Ø16 ...................... 2
99 .............. PM1500-099.............. Blade Guard Cover ................................................. ...................................... 1
100 ............ PM1500-012.............. Shoulder bolt............................................................ ...................................... 1
101 ............ PM1500-101.............. Plastic Washer ......................................................... M6xØ13, Thk 1.5mm .... 1
102 ............ PM1500-102.............. Sliding Plate ............................................................. ...................................... 1
103 ............ TS-1541011 .............. Nylon Lock Hex Nut ................................................. M5 ................................. 2
104 ............ PM1500-104.............. Protect Cover ........................................................... ...................................... 1
105 ............ PM1500-101.............. Plastic Washer ......................................................... M6xØ13,Thk 1.5mm. .... 2
106 ............ TS-1533032 .............. Phillips Pan Head M achine Screw ........................... M5x10 ........................... 2
107 ............ PM1500-107.............. Fence Assembly ...................................................... ...................................... 1
108 ............ PM1500-108.............. Table ........................................................................ 21½"x16"....................... 1
109 ............ PM1500-109.............. Miter Gauge Assembly ............................................ ...................................... 1
110 ............ PM1500-110.............. Limit Switch.............................................................. KL7141.......................... 1
111 ............ TS-1540021 .............. Hex Nut .................................................................... M4 ................................. 2
112 ............ PM1500-112.............. Limit Switch Cord ..................................................... 18AWGx2Cx2 .2m ......... 1
113 ............ PM1500-113.............. Wire Jacket .............................................................. ½"x1100mm(L) ............. 1
114 ............ PM1500-114.............. Wire Bushing ........................................................... ...................................... 1
34
Page 35

Index No Part No Description Size Qty
115 ............ JWTS10-217 ............. Tapping Screw ......................................................... M4x8 ............................. 2
116 ............ PM1500-116.............. Wire Fixed Clamp .................................................... 5/8” ................................ 2
117 ............ TS-2284302 .............. Phillips Pan Head Machine Screw ........................... M4x30 ........................... 2
118 ............ TS-1550021 .............. Flat Washer ............................................................. M4xØ8 .......................... 2
119 ............ PM1500-119.............. Plastic Bumper......................................................... 9mmx10mm .................. 1
120 ............ PM1500-120.............. Foot Brake Lever ..................................................... ...................................... 1
121 ............ TS-1503041 .............. Socket Head Cap Screw.......................................... M6x16 ........................... 4
122 ............ PM1500-122.............. Spring ...................................................................... ...................................... 1
123 ............ TS-2311061 .............. Hex Nut .................................................................... M6 ................................. 2
124 ............ PM1500-124.............. Nylon Set Screw ...................................................... M7x10 ........................... 1
125 ............ PM1500-125.............. Foot Brake Pedal ..................................................... ...................................... 1
126 ............ TS-2361061 .............. Lock Washer ............................................................ M6 ................................. 4
127 ............ PM1500-127.............. Bushing .................................................................... ...................................... 2
128 ............ PM1500-128.............. Brake Pad ................................................................ ...................................... 1
129 ............ TS-1503061 .............. Socket Head Cap Screw.......................................... M6x25 ........................... 2
130 ............ TS-1504051 .............. Socket Head Cap Screw.......................................... M8x25 ........................... 1
131 ............ TS-2361081 .............. Lock Washer ............................................................ M8 ................................. 1
132 ............ TS-1550061 .............. Flat Washer ............................................................. M8 x Ø30 ...................... 1
133 ............ PM1500-133.............. Bushing .................................................................... ...................................... 1
134 ............ TS-1490041 .............. Hex Cap Screw ........................................................ M8x25 ........................... 4
135 ............ TS-2361081 .............. Lock Washer ............................................................ M8 ................................. 4
136 ............ TS-1550061 .............. Flat Washer ............................................................. M8 x Ø18 ...................... 4
137 ............ PM1500-137.............. Plate......................................................................... ...................................... 1
138 ............ PM1500-138.............. Lower Blade Guard .................................................. ...................................... 1
139 ............ TS-2246082 .............. Socket Head Button Screw ...................................... M6 x 8 ........................... 2
140 ............ TS-2361061 .............. Lock Washer ............................................................ M6 ................................. 2
141 ............ TS-1550041 .............. Flat Washer ............................................................. M6 x Ø13 ...................... 2
.................. 3520B-157................. Upper (Narrow) Stripe, 50”L (not shown)................. ...................................... 4
.................. 3520B-158................. Lower (Wide) Stripe, 50”L (not shown) .................... ...................................... 2
.................. PM1500-WL .............. Warnin g Label (not shown) ...................................... 4”H x 5-1/4”W................ 1
.................. PM1500-ID ................ I.D. Label (not shown).............................................. ...................................... 1
.................. PM1500-GS .............. Guide Post Scale (not shown) ................................. ...................................... 1
.................. PM1500-TLL ............. Tension Lever Label (not shown) ............................ ...................................... 1
.................. PM1500-BTL ............. Blade Tension Label (not shown) ............................ ...................................... 1
35
Page 36

15.2.1 Upper Wh eel Sli ding Brac ket & Tensio n Mech anism A ssembly – E xploded Vi ew
Part Assembly No.: PM1500-010
15.2.2 Upper Wheel Sliding Bracket & Tension Mechanism Assembly – Parts List
Index No Part No Description Size Qty
1 ................ PM1500-010-01 ........ Spring ...................................................................... . ..................................... 1
2 ................ PM1500-010-02 ........ Bushing .................................................................... ...................................... 1
3 ................ PM1500-010-03 ........ Plate......................................................................... ...................................... 1
4 ................ TS-1540021 .............. Hex Nut .................................................................... M4 ................................. 1
5 ................ A077 .......................... Socket Set Screw .................................................... M4x25 ........................... 1
6 ................ BB-51201 .................. Thrust Bearing ......................................................... ...................................... 1
7 ................ PM1500-010-07 ........ Adjustment Screw Rod ............................................ ...................................... 1
8 ................ PM1500-010-08 ........ Adjustment Plate...................................................... ...................................... 1
9 ................ PM1500-010-09 ........ Screw Bushing ......................................................... ...................................... 1
10 .............. TS-1550061 .............. Flat Washer ............................................................. M8 x Ø18 ...................... 4
11 .............. TS-2361081 .............. Lock Washer ............................................................ M8 ................................. 5
12 .............. TS-2248202 .............. Socket Head Button Screw ...................................... M8x20 ........................... 3
13 .............. PM1500-010-13 ........ Limit Switch Plate .................................................... ...................................... 1
14 .............. PM1500-010-14 ........ Fixed Position Block ................................................ ...................................... 1
15 .............. TS-1524011 .............. Hex Socket Screw ................................................... M8x6 ............................. 5
16 .............. PM1500-010-16 ........ Wheel Shaft ............................................................. . ..................................... 1
17 .............. TS-2248302 .............. Socket Head Button Screw ...................................... M8x30 ........................... 2
18 .............. PM1500-010-18 ........ Locating Block ......................................................... ...................................... 1
19 .............. TS-1523031 .............. Socket Set Screw .................................................... M6x10 ........................... 2
20 .............. PM1500-010-20 ........ Fixed Block .............................................................. ...................................... 2
21 .............. PM1500-010-21 ........ Socket Set Screw .................................................... M10x50 ......................... 2
22 .............. TS-1541041 .............. Nylon Lock Hex Nut ................................................. M10 ............................... 2
23 .............. TS-1550071 .............. Flat Washer ............................................................. M10 ............................... 2
24 .............. PM1500-010-24 ........ Guide Post ............................................................... ...................................... 2
25 .............. PM1500-010-25 ........ Collar ....................................................................... ...................................... 2
26 .............. TS-1550061 .............. Flat Washer ............................................................. M8 x Ø30 ...................... 1
27 .............. PM1500-010-27 ........ Upper Wheel Sliding Bracket ................................... ...................................... 1
28 .............. PM1500-010-28 ........ Bushing .................................................................... DU1610 ......................... 4
36
Page 37

15.3.1 Upper Wheel Assembly – Exploded View
Part Assembly No.: PM1500-019
15.3.2 Upper Wheel Assembly – Parts List
Index No Part No Descripti on Size Qt y
1 ................ PM1500-019-01 ........ Upper Wheel ............................................................ Dia.15 inches. ............... 1
2 ................ PM1500-019-02 ........ Spacer ..................................................................... ...................................... 1
3 ................ JWBS20QT-504 ........ Retaining Ring ......................................................... R52 ............................... 2
4 ................ BB-6205LLU.............. Ball Bearing ............................................................. 6205LLU. ...................... 2
5 ................ PM1500-019-05 ........ Tire........................................................................... ...................................... 1
15.4.1 Lower Wheel Assembly – Exploded View
Part Assembly No.: PM1500-020
15.4.2 Lower Wheel Assembly – Parts List
Index No Part No Descripti on Size Qt y
1 ................ PM1500-020-01 ........ Lower Wheel ............................................................ Dia.15 inches. ............... 1
2 ................ PM1500-019-02 ........ Spacer ..................................................................... ...................................... 1
3 ................ JWBS20QT-504 ........ Retaining Ring ......................................................... R52 ............................... 2
4 ................ BB-6205LLU.............. Ball Bearing ............................................................. 6205LLU. ...................... 2
5 ................ PM1500-019-05 ........ Tire........................................................................... ...................................... 1
6 ................ PM1500-020-06 ........ Drive Pulley.............................................................. . ..................................... 1
7 ................ TS-1504031 .............. Socket Head Cap Screw.......................................... M8x16 ........................... 4
37
Page 38

15.5.1 Trunnion Support Bracket Assembly – Exploded View
Part Assembly No.: PM1500-085
15.5.2 Trunnion Support Bracket Assembly – Parts List
Index No Part No Descripti on Size Qt y
1 ................ TS-1550061 .............. Flat Washer ............................................................. M8 x Ø18 ...................... 4
2 ................ TS-2361081 .............. Lock Washer ............................................................ M8 ...... ........................... 1
3 ................ TS-1541031 .............. Nylon Lock Hex Nut ................................................. M8 ................................. 2
4 ................ TS-2284062 .............. Phillips Pan Head Machine Screw ........................... M4x6 ............................. 2
5 ................ PM1500-085-05 ........ Gear Rack................................................................ ...................................... 1
6 ................ TS-2284061 .............. Phillips Flat Head Machine Screw ........................... M4x6 ............................. 1
7 ................ PM1500-085-07 ........ Carriage Bolt ............................................................ M8x85 ........................... 1
8 ................ PM1500-085-08 ........ Trunnion Block ......................................................... ...................................... 1
9 ................ PM1500-085-09 ........ Carriage Bolt ............................................................ M8x80 ........................... 1
10 .............. PM1500-085-10 ........ Lock Handle ............................................................. ...................................... 1
11 .............. PM1500-085-11 ........ Tilt Scale .................................................................. ...................................... 1
12 .............. PM1500-085-12 ........ Adjustment Knob Bolt .............................................. ...................................... 1
13 .............. TS-1550021 .............. Flat Washer ............................................................. M4 x Ø8 ........................ 2
14 .............. PM1500-085-14 ........ Angle Pointer ........................................................... ...................................... 1
15 .............. TS-1524011 .............. Adjustment Knob Bolt .............................................. M6 ................................. 1
16 .............. PM1500-085-16 ........ Locking Ring ............................................................ . ..................................... 1
17 .............. TS-1540041 .............. Hex Nut .................................................................... M6 ................................. 2
18 .............. PM1500-085-18 ........ Adjustment Plate...................................................... ...................................... 1
19 .............. TS-1533032 .............. Phillips Pan Head Machine Screw ........................... M5x8 ............................. 2
20 .............. PM1500-085-20 ........ Set Screw ................................................................ ...................................... 1
21 .............. PM1500-085-21 ........ Lock Knob ................................................................ ...................................... 1
22 .............. PM1500-085-22 ........ Trunnion Support Bracket ........................................ ...................................... 1
23 .............. PM1500-085-23 ........ Gear ......................................................................... ...................................... 1
24 .............. TS-2235061 .............. Socket Head Cap Screw.......................................... M5x6 ............................. 6
25 .............. PM1500-085-25 ........ Adjustment Shaft ..................................................... ...................................... 1
26 .............. PM1500-085-26 ........ Retaining Ring ......................................................... R22 ............................... 1
27 .............. BB-608ZZ .................. Ball Bearing ............................................................. 608ZZ............................ 1
28 .............. PM1500-085-28 ........ Thrust Bearing Holder.............................................. ...................................... 1
29 .............. PM1500-085-29 ........ Retaining Ring ......................................................... S8.................................. 1
30 .............. PM1500-085-30 ........ Adjustment Bar ........................................................ ...................................... 1
31 .............. TS-1523011 .............. Socket Set Screw .................................................... M6x 6 ............................. 1
38
Page 39

15.6.1 Guide Bar Bracket Assembly – Exploded View
Part Assembly No.: PM1500-091
15.6.2 Guide Bar Bracket Assembly – Parts List
Index No Part No Description Size Qty
1 ................ PM1500-091-01 ........ Guide Bar................................................................. . ..................................... 1
2 ................ TS-1540031 .............. Hex Nut .................................................................... M5 ................................. 2
3 ................ TS-1533032 .............. Phillips Pan Head Machine Screw ........................... M5x 10 ........................... 2
4 ................ PM1500-091-04 ........ Cover ....................................................................... ...................................... 1
5 ................ TS-2361081 .............. Lock Washer ............................................................ M8 ................................. 4
6 ................ TS-1504031 .............. Hex Socket Screw ................................................... M8x16 ........................... 4
7 ................ 6286927 .................... Phillips Flat Head Machine Screw ........................... M4x10 ........................... 1
8 ................ PM1500-091-08 ........ Guide Bar Rack (short) ............................................ ...................................... 1
9 ................ PM1500-091-09 ........ Cover ....................................................................... ...................................... 1
10 .............. PM1500-091-10 ........ Fixed Pin .................................................................. ...................................... 1
11 .............. PM1500-091-11 ........ Gear ......................................................................... ...................................... 1
12 .............. PM1500-091-12 ........ Fixed Plate ............................................................... ...................................... 1
13 .............. PM1500-091-13 ........ Worm Shaft .............................................................. ...................................... 1
14 .............. TS-154010 ................ Hex Nut .................................................................... M16 ............................... 1
15 .............. PM1500-091-15 ........ Guide Bracket .......................................................... ...................................... 1
18 .............. PM1500-091-18 ........ Bushing .................................................................... ...................................... 1
19 .............. PM1500-091-19 ........ Collar ....................................................................... ...................................... 1
20 .............. PM1500-091-20 ........ Guide Bar Rack (long) ............................................. ...................................... 1
21 .............. TS-1523021 .............. Socket Set Screw .................................................... M6x8 ............................. 2
22 .............. TS-1540021 .............. Hex Nut .................................................................... M4 ................................. 1
23 .............. TS-1532032 .............. Phillips Pan Head Machine Screw ........................... M4x10 ........................... 1
24 .............. TS-1522011 .............. Socket Set Screw .................................................... M5x5 ............................. 1
25 .............. PM1500-091-25 ........ Plastic Washer ......................................................... ...................................... 2
39
Page 40

15.7.1 Upper Blade Guide Assembly – Exploded View
Part Assembly No.: PM1500-095
15.7.2 Upper Blade Guide Assembly – Parts List
Index No Part No Description Size Qty
1 ................ PM1500-095-01 ........ Upper Blade Guide Support..................................... ...................................... 1
2 ................ PM1500-095-02 ........ Eccentric Shaft......................................................... ...................................... 2
3 ................ 6286478 .................... Retaining Ring ......................................................... S12................................ 2
4 ................ BB-6201ZZ ................ Ball Bearing ............................................................. 6201ZZ.......................... 4
5 ................ PM1500-095-05 ........ Knurled Knob ........................................................... ...................................... 2
6 ................ TS-1503081 .............. Socket Head Cap Screw.......................................... M6x35 ........................... 2
7 ................ PM1500-095-07 ........ Upper Spacing Sleeve ............................................. ...................................... 1
8 ................ TS-1523011 .............. Socket Set Screw .................................................... M6x6 ............................. 2
9 ................ PM1500-085-29 ........ Retaining Ring ......................................................... S8.................................. 1
10 .............. PM1500-085-28 ........ Thrust Bearing Holder.............................................. ...................................... 1
11 .............. BB-608ZZ .................. Ball Bearing ............................................................. 608ZZ............................ 1
12 .............. PM1500-085-26 ........ Retaining Ring ......................................................... R22 ............................... 1
13 .............. PM1500-085-25 ........ Adjustment Shaft ..................................................... ...................................... 1
14 .............. PM1500-095-14 ........ Hex Post .................................................................. ...................................... 1
15 .............. PM1500-095-15 ........ Upper Blade Guide Support Block ........................... ...................................... 1
16 .............. PM1500-095-16 ........ Lock Knob ................................................................ . ......... ............................ 4
40
Page 41

15.8.1 Lower Blade Guide Assembly – Exploded View
Part Assembly No.: PM1500-096
15.8.2 Lower Blade Guide Assembly – Parts List
Index No Part No Description Size Qty
1 ................ PM1500-096-01 ........ Lower Blade Guide Support..................................... ...................................... 1
2 ................ PM1500-096-02 ........ Eccentric Shaft......................................................... ...................................... 2
3 ................ PM1500-095-03 ........ Retaining Ring ......................................................... S12................................ 2
4 ................ BB-6201ZZ ................ Ball Bearing ............................................................. 6201ZZ.......................... 4
5 ................ PM1500-095-05 ........ Knurled Knob ........................................................... ...................................... 2
6 ................ TS-1503081 .............. Hex Socket Screw (Black) ....................................... M6x35 ........................... 2
7 ................ PM1500-095-16 ........ Lock Knob ............................................................... ...................................... 1
8 ................ PM1500-096-08 ........ Lock Knob ................................................................ ......... ............................. 2
41
Page 42

15.9.1 Fence Assembly – Exploded View
Part Assembly No.: PM1500-107
15.9.2 Fence Assembly – Parts List
Index No Part No Description Size Qty
1 ................ PM1500-107-01 ........ Fence Body.............................................................. ........... ........................... 1
2 ................ PM1500-107-02 ........ Lock Knob ............................................................... M8x52 ........................... 2
3 ................ PM1500-107-03 ........ Resaw Lock Knob ................................................... M10x 50 ......................... 1
4 ................ PM1500-107-04 ........ Nylon Set Screw ...................................................... M10x12 ......................... 2
5 ................ TS-1541021 .............. Nylon Lock Hex Nut ................................................. M6 ................................. 1
6 ................ TS-1541031 .............. Nylon Hex Nut (Black) ............................................. M8 ................................. 1
7 ................ 992322 ...................... Roll Pin .................................................................... Ø5x26 ........................... 1
8 ................ PM1500-107-08 ........ Resaw Pin................................................................ 1½ “x 6½ “(Dia.xH)........ 1
9 ................ PM1500-107-09 ........ Lock Bar................................................................... ...................................... 1
10 .............. PM1500-107-10 ........ Nylon Pad ................................................................ ...................................... 3
11 .............. PM1500-107-11 ........ Tube Plug ................................................................ 40x80mm ...................... 1
12 .............. TS-1525011 .............. Socket Set Screw .................................................... M10x10 ......................... 2
13 .............. TS-2246352 .............. Socket Head Button Screw ...................................... M6x35 ........................... 1
14 .............. TS-2361061 .............. Lock Washer ............................................................ M6 ................................. 1
15 ............. TS-1550041 .............. Flat Washer ............................................................. M6 x Ø13 ...................... 1
16 .............. 9180-56 ..................... Socket Head Button Screw ...................................... M8x35 ........................... 1
17 .............. PM1500-107-16 ........ Spring ...................................................................... . ..................................... 1
18 .............. PM1500-107-17 ........ Handle Lock Bracket................................................ ...................................... 1
19 .............. PM1500-107-18 ........ Lock Handle ............................................................. ...................................... 1
20 .............. PM1500-107-19 ........ Knob ........................................................................ M8x21 .. ......................... 1
21 .............. PM1500-107-20 ........ Fence Plate.............................................................. 19½ “x 6½ “(Lx W) ......... 1
22 .............. PM1500-107-22 ........ Hex Flange Nut ........................................................ M5 ................................. 2
42
Page 43

Index No Part No Description Size Qty
23 .............. PM1900-108-6 .......... Phillips Pan Head Machine Screw ........................... M5x8 ............................. 2
24 .............. TS-1550031 .............. Flat Washer ............................................................. M5 x Ø12 ...................... 2
25 .............. PM1500-107-25 ........ Cursor Bracket ......................................................... ...................................... 1
26 .............. PM1500-107-26 ........ Convex Cursor ......................................................... ...................................... 1
27 .............. TS-2285121 .............. Phillips Flat Head Machine Screw ........................... M5x12 ........................... 2
28 .............. PM1500-107-28 ........ Scale Label .............................................................. ...................................... 1
29 .............. PM1500-107-29 ........ Guide Rail Tube ....................................................... ...................................... 1
30 .............. PM1500-107-30 ........ Tube Plug ................................................................ 30x60mm ...................... 2
31 .............. PM1500-107-31 ........ Guide Rail ................................................................ ...................................... 1
32 .............. TS-1482031 .............. Hex Cap Screw ........................................................ M6x16 ........................... 5
33 .............. TS-2361061 .............. Lock Washer ............................................................ M6 ................................. 5
34 .............. TS-1550041 .............. Flat Washer ............................................................. M6 x Ø16 ...................... 5
43
Page 44

15.10.1 Miter Gauge Assembly – Exploded View
Part Assembly No.: PM1500-109
15.10.2 Miter Gauge Assembly – Parts List
Index No Part No Description Size Qty
1 ................ 6295167 .................... Miter Gauge Body .................................................... ...................................... 1
2 ................ TS-1533062 .............. Pan Head Screw ..................................................... M5x20 ........................... 3
3 ................ TS-1540031 .............. Hex Nut ................................................................... M5 ................................. 3
4 ................ 6295168 .................... Steel Pin .................................................................. ...................................... 1
5 ................ PM1500-109-05 ........ Guide Bar................................................................. ...................................... 1
6 ................ 6295163 .................... Guide Disc ............................................................... ...................................... 1
7 ................ PM1800-461.............. Flat Head Screw ...................................................... M6x8 ............................. 1
8 ................ 6295171 .................... Stop Tab .................................................................. ...................................... 1
9 ................ PM1800-462.............. Spring Pin ................................................................ 3x6mm .......................... 1
10 .............. 6295169 .................... Pointer ..................................................................... ...................................... 1
11 .............. SS050100 ................. Socket Set Screw .................................................... M5x5 ............................. 1
12 .............. PM1800-451.............. Handle ..................................................................... M8x 20 ........................... 1
13 .............. PM2000-343.............. Socket Set Screw .................................................... M8x6 ............................. 2
14 .............. TS-0680031 .............. Flat Washer ............................................................. M8x Ø18 ....................... 1
44
Page 45

16.0 Electrical Connections – 3HP 1PH 230V
45
Page 46

This page intentionally left blank.
46
Page 47

This page intentionally left blank.
47
Page 48

427 New Sanford Road
LaVergne, Tennessee 37086
Phone: 800-274-6848
www.powermatic.com
48
 Loading...
Loading...