Page 1

Web Application Developer’s Guide
for the Polycom
®
SoundPoint® IP/SoundStation® IP
Family
SIP 3.1
August, 2008 Edition
1725-17693-310 Rev. A
SIP 3.1
Page 2

Trademark Information
Polycom®, the Polycom logo design, SoundPoint® IP, SoundStation®, SoundStation VTX 1000®, ViaVideo®,
ViewStation®, and Vortex® are registered trademarks of Polycom, Inc. Conference Composer™, Global Management
System™, ImageShare™, Instructor RP™, iPower™, MGC™, PathNavigator™, People+Content™, PowerCam™,
2
Pro-Motion™, QSX™, ReadiManager™, Siren™, StereoSurround™, V
IU™, Visual Concert™, VS4000™, VSX™, and
the industrial design of SoundStation are trademarks of Polycom, Inc. in the United States and various other countries.
All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
Patent Information
The accompanying product is protected by one or more U.S. and foreign patents and/or pending patent applications
held by Polycom, Inc.
© 2008 Polycom, Inc. All rights reserved.
Polycom Inc.
4750 Willow Road
Pleasanton, CA 94588-2708
USA
No part of this document may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical, for
any purpose, without the express written permission of Polycom, Inc. Under the law, reproducing includes translating
into another language or format.
As between the parties, Polycom, Inc. retains title to, and ownership of, all proprietary rights with respect to the software
contained within its products. The software is protected by United States copyright laws and international treaty
provision. Therefore, you must treat the software like any other copyrighted material (e.g. a book or sound recording).
Every effort has been made to ensure that the information in this manual is accurate. Polycom, Inc. is not responsible
for printing or clerical errors. Information in this document is subject to change without notice.
Page 3

About This Guide
The Developer’s Guide for the SoundPoint IP / SoundStation IP family is for
developers of applications which use the Web Server and the Microbrowser on
SoundPoint IP / SoundStation IP phones.
The following related documents for SoundPoint IP / SoundStation IP family
are available:
• Quick Start Guides, which describe how to assemble the phones
• Quick User Guides, which describe the most basic features available on
the phones
• User Guides, which describe the basic and advanced features available on
the phones
• Administrator’s Guide, which describes how to configure, customize,
manage, and troubleshoot SoundPoint IP / SoundStation IP phone
systems
• Technical Bulletins, which describe workarounds to existing issues
• Release Notes, which describe the new and changed features and fixed
problems in the latest version of the software
For support or service, please go to Polycom Technical Support at
http://www.polycom.com/support/voip/.
Polycom recommends that you record the phone model numbers, software
(both the bootROM and SIP), and partner platform for future reference.
SoundPoint IP / SoundStation IP models: ___________________________
BootROM version: ________________________________________________
SIP Application version: ___________________________________________
Partner Platform: _________________________________________________
iii
Page 4

Developer’s Guide SoundPoint IP / SoundStation IP
iv
Page 5

Contents
About This Guide . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . iii
1 Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1–1
2 Application Development . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–1
What is the Microbrowser . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1–1
What is XHTML . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1–2
How to Create Applications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1–3
New Features in SIP 3.1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1–5
Supported XHTML Elements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–1
Basic Tags . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–2
Link Tags . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–3
Input Tags . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–3
Image Tags . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–6
Table Tags . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–7
Meta Information Tags . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–13
SoundPoint IP/SoundStation IP XML API Application Interface . . . . . 2–13
Programmable Soft Keys . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–14
Telephone Integration URIs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–16
Push Requests . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–19
Telephony Notification Events . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–22
Phone State Polling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–27
API Security . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–32
HTTP Support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–33
Microbrowser User Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–33
Launching the Microbrowser . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–34
Navigation and Form Editing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–35
Idle Display Microbrowser . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–35
Developing an XHTML Application . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–36
Changing Configuration Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–36
Sample Applications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–38
v
Page 6

Developer’s Guide SoundPoint IP / SoundStation IP
3 Troubleshooting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3–1
XML Errors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–1
A Appendix . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .A–1
Unsupported XHTML Elements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A–1
Index . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Index–1
vi
Page 7

Overview
1
This chapter provides an overview of the Web Server and the Microbrowser
available on SoundPoint IP 330/320, 430, 501, 550, 560, 600, 601, 650, and 670
desktop phones and SoundStation IP 4000, 6000, and 7000 conference phones.
It also provides an introduction to XHTML and guidelines for the application
development.
This chapter contains information on:
• What is the Microbrowser
• What is XHTML
• How to Create Applications
• New Features in SIP 3.1
To develop an application that can run on the Web Server and the
Microbrowser, refer to Application Development on page 2-1. To troubleshoot
any problems with your applications, refer to Troubleshooting on page 3-1.
What is the Microbrowser
The Microbrowser is like any Web browser—Microsoft Internet Explorer and
Firefox, for example—but supports only a subset of XHTML features. It can
connect to Web servers hosted in the Internet or intranet and download
XHTML pages. The Microbrowser supports a limited number of XHTML 1.0
features—it does not have full Web browser functionality.
The Microbrowser downloads XHTML content from a Web server into the
phone’s memory, then parses the content to identify XHTML tags and renders
these tags onto the phone’s graphic display. The appearance of the rendered
page depends on the graphical capabilities and display size of the device on
which the browser is running. Complicated pages should be avoided on
devices with very small displays.
The Microbrowser does not support scripting (such as JavaScript). All actions
on data entered into forms is processed by the server using POST or GET
methods.
1 - 1
Page 8

Developer’s Guide SoundPoint IP / SoundStation IP
The XHTML pages displayed on the Microbrowser can contain static or
dynamic information.
Static XHTML. These pages are created using XHTML editors and hosted by
the Web server. These pages are accessed from the Microbrowser (using HTTP
protocol) by entering the URL to access the page. These XHTML pages are
called static, because the information that is displayed is already coded into
the XHTML pages. These pages do not include information that keep changing
or contact other services for update.
Dynamic XHTML. These pages involves dynamic information updates of
XHTML pages by an application hosted on the Web server. The application
residing on the Web server will get information from an intranet or through
the Internet—data service providers like Yahoo, Exchange Server, Call Control
Servers and other enterprise servers.
Users can launch the Microbrowser on a SoundPoint IP or SoundStation IP
phone by pressing the Applications key, or if there isn’t one on the phone, it
can be accessed through the Menu key by selecting Applications.
Note
What is XHTML
As of SIP 2.2, the Services key and menu entry were renamed Applications,
however the functionality remains the same.
The Microbrowser is supported on:
• SoundPoint IP 330/320 — screen resolution - 102*22 pixels (3” by 1”)
• SoundPoint IP 430 — screen resolution – 132*46 pixels (3.5”*1.5”)
• SoundPoint IP 501 — screen resolution – 160*80 pixels (4” by 2”)
• SoundPoint IP 550/560/601/650 — screen resolution – 320*160 pixels (4”
by 2”)
• SoundPoint IP 670 — screen resolution – 320*160 pixels (4” by 2”)
• SoundStation IP 4000/6000 — screen resolution – 240*68 pixels (2.4” by
0.8”)
• SoundStation IP 7000 — screen resolution – 255*128 pixels (3” by 1.5”)
XHTML is the abbreviation of eXtensible HyperText Markup Language.
1 - 2
XHTML 1.0 is a transformation of HTML 4.01 into valid XML. The use of the
stricter XML syntax makes parsing of XHTML much easier for small clients,
but XHTML 1.0 was also the first step towards making HTML easily
extensible. Moving to XML allowed the methods used to create XML
extensions to apply to HTML as well. Step two occurred with XHTML 1.1,
where XHTML was divided up into ‘modules’, where any features above and
Page 9

Overview
beyond a skeleton set were grouped into individual modules. User agent (UA)
developers could then decide which extensions to support. A simple user
agent can be considered a fully compliant user agent by supporting only the
Basic module, whereas a more powerful browser can support all the official
modules, as well as those developed by third parties.
Modularization is also intended to help content creators. As more and more
devices become web-enabled, the number of platforms a content creator will
be asked to support will become unreasonable. By dividing HTML up into
different ‘building blocks’ content creators can supply a minimal version of
their site for user agents that only support the Basic module, a moderate
version of their site for user agents who support the additional modules, and
a full version of their site for user agents that support the full range of the
XHTML specification.
Finally the X in XHTML was intended to help people who wish to extend
HTML. The use of XML brought a standard grammar with which they could
define their extension, and the modularization meant that their extension
would be just another module that a user agent developer or content creator
could choose to support. Additionally, since XHTML pages should state what
modules are required to accurately render them, the user agent software could
dynamically load a ‘plug-in’ that it could use to render a module that was
defined after the user agent had been originally released.
For more information, go to:
• HTML 4.0—http://www.w3.org/TR/1999/REC-html401-19991224
• XHTML™ 1.0—http://www.w3.org/TR/2002/REC-xhtml1-20020801
• XHTML™
Basic—http://www.w3.org/TR/2000/REC-xhtml-basic-20001219/
• XHTML™ 1.1—http://www.w3.org/TR/2001/REC-xhtml11-20010531/
• XHTML Tables Module -
XHTML™2.0—http://www.w3.org/TR/2004/WD-xhtml2-20040722/m
od-tables.html
For the purposes of this guide, it is assumed that you have experience in
HTML and XHTML programming or access to someone who has such
experience.
How to Create Applications
You can design the following examples of applications:
• Web browser
1 - 3
Page 10

Developer’s Guide SoundPoint IP / SoundStation IP
• Company directory
• Stock ticker
Depending on the type and complexity of the application, you might use one
of the following tools for creation:
• Text editor
• XML editor
• Microsoft Word
When designing applications, you might want to consider the following
guidelines:
Note
These guidelines are for your information only. You are solely responsible for
determining the suitability and applicability of this information to your needs.
1. Spend sufficient time designing the application by:
— Developing a conceptual design
— Describe all user-application interactions
— Plan for all user types
2. Create standardized applications to assist in:
— Lowering design time
— Speed up debugging
— Increasing usability
3. Promote consistent output and predictable user input.
4. Create a prototype application to test on sample users.
5. Thoroughly test your application before releasing to:
— Identify all user interface issues
— Verify that all error conditions are caught cleanly
For step-by-step instructions on how to develop an XHTML application that
can be run on the Microbrowser of all SoundPoint IP and SoundStation IP
phones, refer to Application Development on page 2-1.
1 - 4
Note
Polycom is not responsible for troubleshooting any programming that you create for
the Microbrowser.
Page 11

New Features in SIP 3.1
The following new features were introduced in SIP 3.1:
• SoundPoint IP/SoundStation IP XML API Application
Interface—Expanded support in the Microbrowser for applications on the
SoundPoint IP 320/330, 430, 501, 550, 560, 650, and 670 desktop phones,
and SoundStation IP 4000, 6000, and 7000 conference phones. The
SoundPoint IP/SoundStation IP XML API is intended to provide
developers with flexibility in developing applications on SoundPoint IP
and SoundStation IP phones, while tightly integrating into the phone’s
telephony capabilities and functions.
Overview
1 - 5
Page 12

Developer’s Guide SoundPoint IP / SoundStation IP
1 - 6
Page 13

Application Development
This chapter presents step-by-step instructions on how to develop an XHTML
application that can be run on the Web Server and Microbrowser of certain
SoundPoint IP and SoundStation IP phones. It also describes the configuration
parameters that can be found in the sip.cfg configuration file.
This chapter contains information on:
• Supported XHTML Elements
• SoundPoint IP/SoundStation IP XML API Application Interface
• HTTP Support
• Microbrowser User Interface
2
• Developing an XHTML Application
To troubleshoot any problems with your applications, refer to
Troubleshooting on page 3-1.
Note
Polycom is not responsible for troubleshooting any programming that you create for
the Microbrowser.
Supported XHTML Elements
The Microbrowser supports a subset of XHTML elements. Most are derived
from HTML 4.01.
The supported elements and attributes are:
• Basic Tags
• Link Tags
• Input Tags
• Image Tags
• Table Tags
2 - 1
Page 14

Developer’s Guide SoundPoint IP / SoundStation IP
• Meta Information Tags
Unsupported elements and attributes are described in Unsupported XHTML
Elements on page A-1.
Basic Tags
The following basic tags are supported:
• <!DOCTYPE>—Defines the document type
• <!--...-->—Defines a comment
<!DOCTYPE>
The <!DOCTYPE> declaration is the very first thing in your document, before
the <html> tag. This tag tells the browser which XHTML specification the
document uses. XHTML 1.0 specifies three XML document types: Strict,
Transitional, and Frameset.
• XHTML Strict
— Use this DTD when you want clean markup, free of presentational
clutter.
For example,
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Strict//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-strict.dtd">
• XHTML Transitional
— Use this DTD when you need to use XHTML's presentational features.
For example,
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0
Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd">
• XHTML Frameset
— Use this DTD when you want to use frames.
For example,
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0
Frameset//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-frameset.dtd">
XHTML 1.1 specifies one XML document type: Strict. For example,
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.1//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml11/DTD/xhtml11.dtd">
2 - 2
This tag does not have any attributes.
Page 15

Link Tags
Application Development
<!--...-->
The comment tag is used to insert a comment in the source code. A comment
will be ignored by the browser. You can use comments to explain your code,
which can help you when you edit the source code at a later date.
This tag does not have any attributes.
The following link tag is supported:
• <a>—Defines an anchor
Note
The Microbrowser supports both
internal URIs. When a tel:// URL is selected, the phone switches to the telephony
application and dials the number specified in the URL. Currently the number is
dialed as-is, however, full support for tel:// URL parsing as specified in RFC 2806
will be available in a future release.
sip://
URLs are not supported at this time.
http://
and
tel://
URL schemes as well as
<a>
The <a> tag defines an anchor. An anchor can be used to create a link to
another document by using the
href
attribute.
The following attributes are supported:
Attribute Value/s Description
href URL (Ex:” www.polycom.com”) The target URL of the link
name section_name Names an anchor. Use this
attribute to create a bookmark in a
document.
In future versions of XHTML the
name attribute will be replaced by
the id attribute.
Note: This attribute is parsed, but
not used.
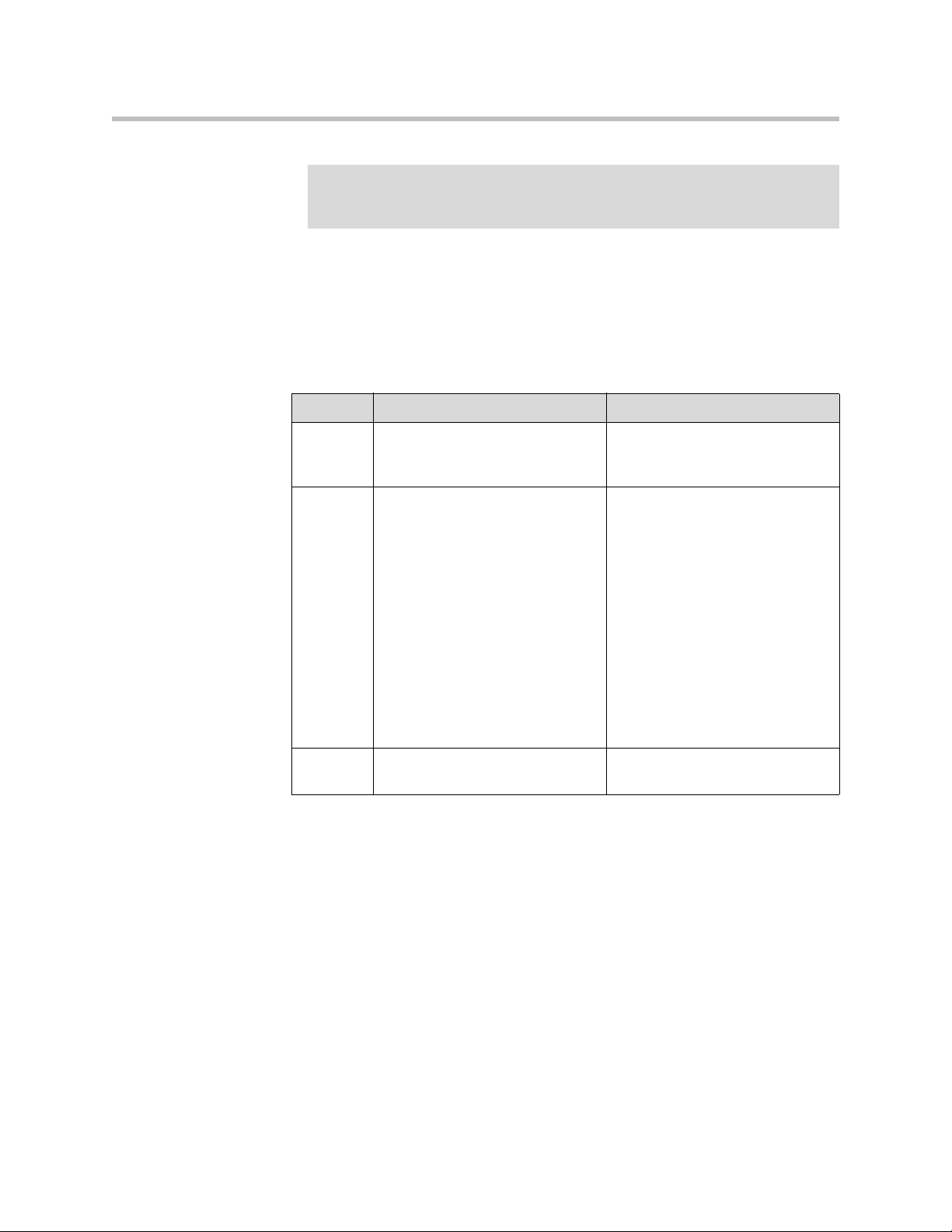
Input Tags
The following input tags are supported:
• <form>—Defines a form
• <input>—Defines an input field
2 - 3
Page 16
Developer’s Guide SoundPoint IP / SoundStation IP
Note
The Microbrowser supports both the GET and POST methods for submitting forms.
Nesting forms within tables is supported. However, nesting of one form tag within
another is not supported and may lead to unexpected results.
<form>
The form element creates a form for user input. A form can contain text fields,
check boxes, radio buttons and more. Forms are used to pass user data to a
specified URL.
The following attributes are supported:
Attribute Value/s Description
action URL
Ex: http://www.google.com
method get
post
A URL that defines where to send
the data when the subm it butt on is
pushed
The HTTP method for sending
data to the action URL. Default is
get.
method="get": This method
sends the form contents in the
URL:
URL?name=value&name=value.
Note: If the form values contains
non-ASCII characters or exceeds
100 characters you MUST use
method="post".
method="post": This method
sends the form contents in the
body of the request.
2 - 4
name form_name Defines a unique name for the
form
Page 17
Application Development
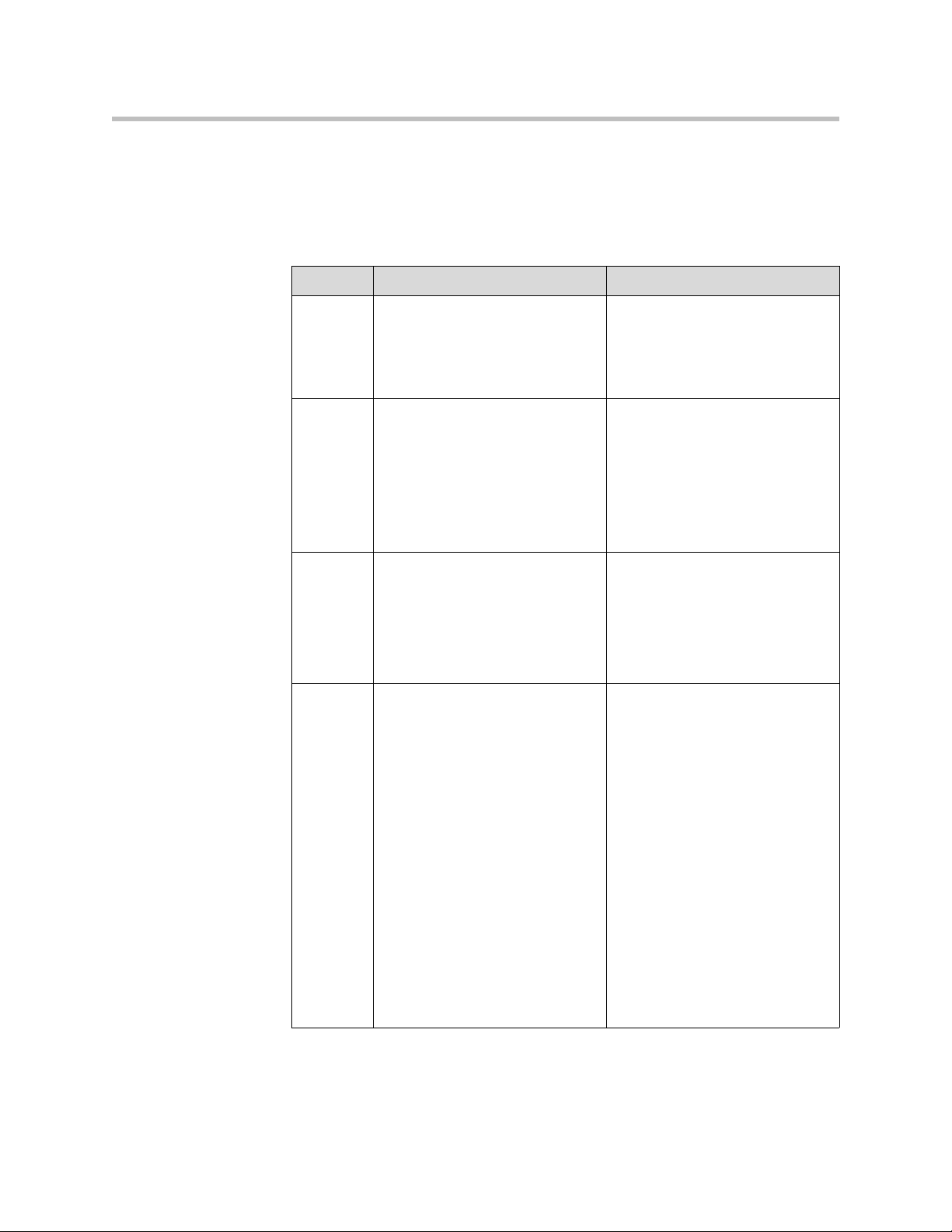
<input>
The <input> tag defines the start of an input field where the user can enter
data. In XHTML the <input> tag must be properly closed.
The following attributes are supported:
Attribute Value/s Description
checked checked Indicates that the input element
should be checked when it first
loads.
Note: Used with type="checkbox"
and type="radio"
name field_name Defines a unique name for the
input element.
Note: This attribute is required
with type="button",
type="checkbox", type="file",
type="hidden", type="image",
type="password", type="text", and
type="radio"
type checkbox
hidden
password
radio
reset
submit
text
value value For buttons, reset buttons and
Indicates the type of the input
element. The default value is
"text".
submit buttons: Defines the text on
the button.
For image buttons: Defines the
symbolic result of the field passed
to a script.
For checkboxes and radio buttons:
Defines the result of the input
element when clicked. The result
is sent to the form's action URL.
For hidden, password, and text
fields: Defines the default valu e of
the element.
Note: Cannot be used with
type="file"
Note: This attribute is required
with type="checkbox" and
type="radio"
2 - 5
Page 18

Developer’s Guide SoundPoint IP / SoundStation IP
Image Tags
The following image tag is supported:
• <img>—Defines an image
The Microbrowser supports images stored in uncompressed .bmp format.
While all BMP bit depths will be displayed to the best of the phone’s ability, it
is recommended that the image format most suitable for the target platform be
chosen. For example:
• The SoundPoint IP 601 LCD supports four levels of grey, so a 16-color
BMP format would be most appropriate.
• The SoundPoint IP 670 LCD supports 12-bit color.
Images can be scrolled up and down, however images that are too wide will
be truncated.
Various platforms have differing limits due to memory. There are also
differing pixel limits for devices of differing pixel depth. A 1 bit per pixel
image 160x80 requires only 1600 bytes. For a 24 bit picture, the memory
requirement is 38400 bytes.
There are several limits depending on the source data (this involves the cache
limits in configuration) and the display converted data, which is dependant on
available RAM (and is limited in the code depending on platform).
Note
<img>
The img element defines an image.
The "align", "border", "hspace", and "vspace" attributes of the image element are
not supported in XHTML 1.0 Strict DTD.
The following attributes are supported:
Attribute Value/s Description
src URL
(Ex:
“http://www.topxml.com/images/to
pxml_site.gif”
or ”c:\images\img1.jpg” )
height Pixels (number, EX: “30” )
%
width Pixels (number, EX: “30” )
%
The URL of the image to display
Specifies the height of the image
in pixel or percent.
Specifies the width of the image in
pixel or percent.
2 - 6
Page 19
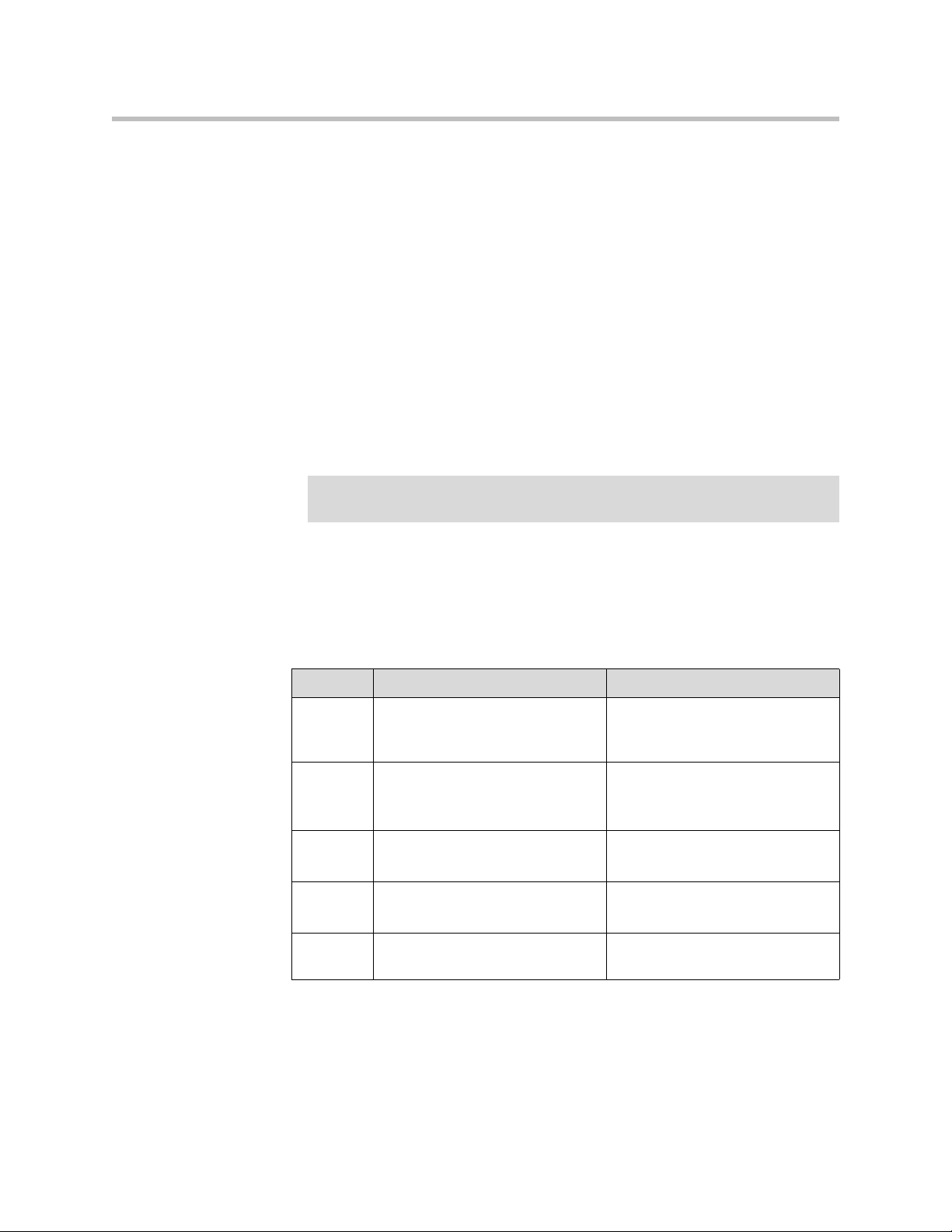
Tab le Tags
Application Development
The following table tags are supported:
• <table>—Defines a table
• <caption>—Defines a table caption
• <th>—Defines a table header
• <tr>—Defines a table row
• <td>—Defines a table cell
• <thead>—Defines a table header
• <tbody>—Defines a table body
• <tfoot>—Defines a table footer
Note
XHTML tables must be properly formatted (should include <tbody> and </tbody>
tags).
<table>
The <table> tag defines a table. Inside a <table> tag you can put table headers,
table rows, table cells, and other tables.
The following attributes are supported:
Attribute Value/s Description
align Left
center
right
border Pixels (number, EX: “30” ) Specifies the border width.
cellpaddingPixels (number, EX: “30” )
%
cellspacing Pixels (number, EX: “30” )
%
Aligns the table. Deprecated. Use
styles instead.
Tip: Set border="0" to display
tables with no borders!
Specifies the space between the
cell walls and contents
Specifies the space between cells.
width %
Specifies the width of the table
Pixels (number, EX: “30” )
2 - 7
Page 20
Developer’s Guide SoundPoint IP / SoundStation IP
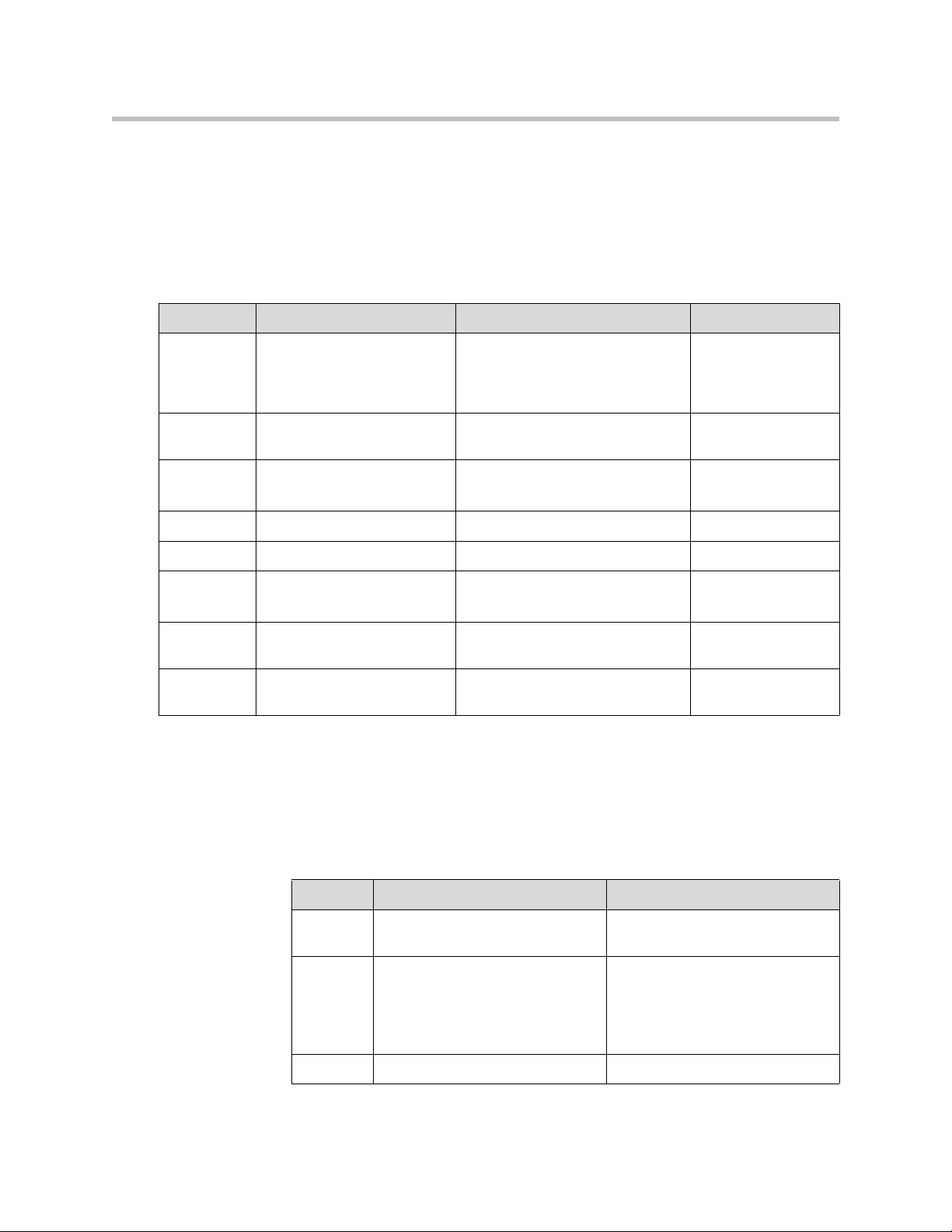
<caption>
This element defines a table caption. The <caption> tag must be inserted
immediately after the <table> tag. You can specify only one caption per table.
Usually the caption will be centered above the table. The “align” attribute of
the caption element is not supported in XHTML 1.0 Strict DTD.
The following attributes are supported:
Attribute Value/s Description MB Support
align Left
right
top
bottom
id unique_name Defines a unique name for the map
class class_rule
style_rule
title tooltip_text A text to display in a tool tip Need to verify
style style_definition An inline style definition Need to verify
dir ltr (left to right)
rtl (left to right)
lang language_code (Ex: EN,
deu/ger, hin)
xml:lang language_code (Ex: EN,
deu/ger, hin)
How to align the caption.
Deprecated. Use styles instead.
tag.
The class of the element Need to verify
Sets the text direction Need to verify
Sets the language code Need to verify
Sets the language code Need to verify
Need to verify
Need to verify
<th>
This tag defines a table header cell in a table. The text within the th element
usually renders in bold. The “bgcolor”, “height”, “width”, and “nowrap”
attributes of the th element are not supported in XHTML 1.0 Strict DTD.
2 - 8
The following attributes are supported:
Attribute Value/s Description
abbr abbr_text Specifies an abbreviated version
of the content in a cell
align left
right
center
justify
char
axis category_names Defines a name for a cell
Specifies the horizontal alignment
of cell content
Page 21
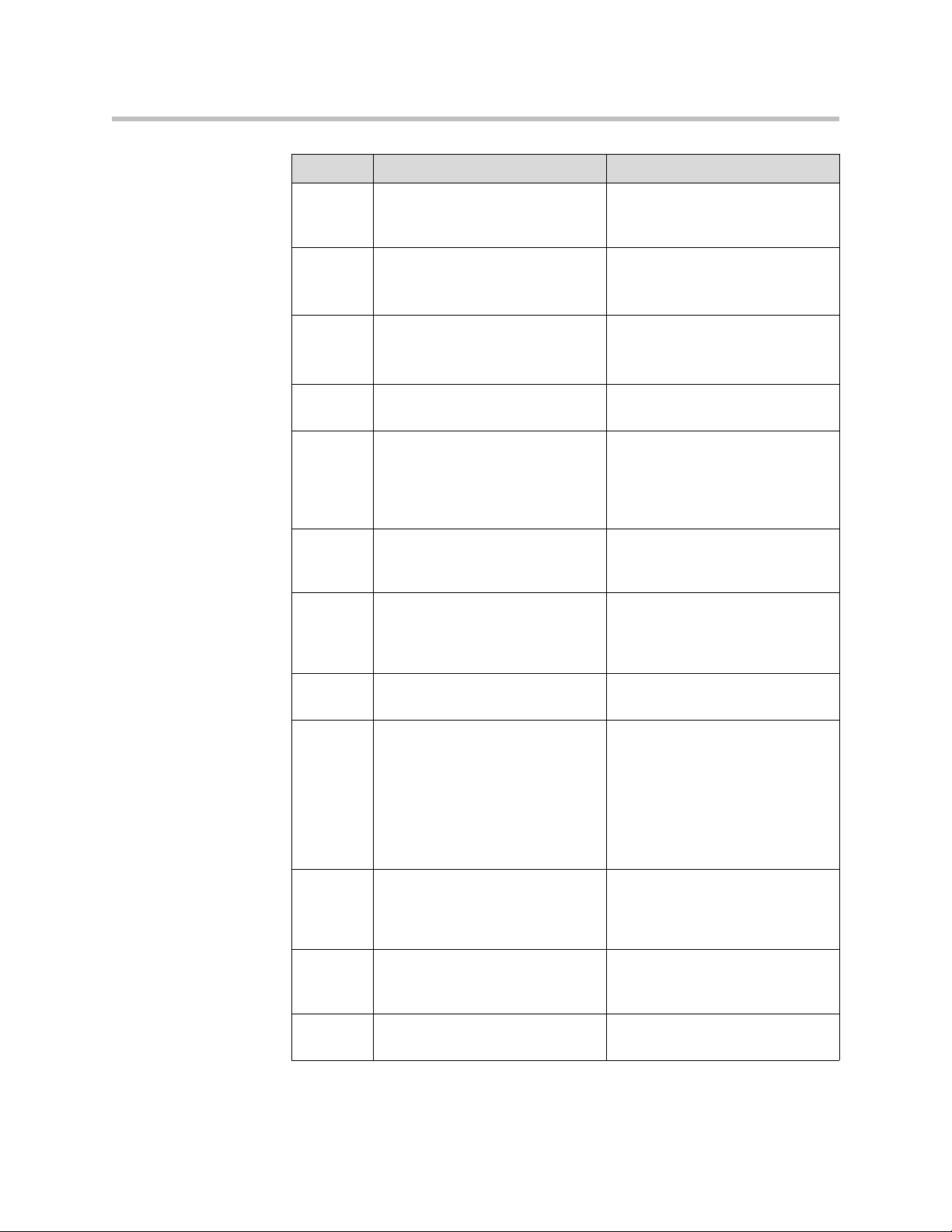
Attribute Value/s Description
Application Development
bgcolor rgb(x,x,x)
#xxxxxx
colorname
Specifies the background color of
the table cell. Deprecated. Use
styles instead.
char character Specifies which character to align
text on.
Note: Only used if align="char"!
charoff Pixels (number, EX: “30” )
%
Specifies the alignment offset to
the first character to align on.
Note: Only used if align="char"!
colspan number Indicates the number of columns
this cell should span.
headers header_cells'_id A space-separated list of cell IDs
that supply header information for
the cell. This attribute allows
text-only browsers to render the
header information for a given cell.
height Pixels (number, EX: “30” ) Specifies the height of the table
cell. Deprecated. Use styles
instead.
nowrap nowrap Whether to disable or enable
automatic text wrapping in this
cell. Deprecated. Use styles
instead.
rowspan number Indicates the number of rows this
cell should span.
scope col
colgroup
row
rowgroup
Specifies if this cell provides
header information for the rest of
the row that contains it (row), or for
the rest of the column (col), or for
the rest of the row group that
contains it (rowgroup), or for the
rest of the column group that
contains it
valign top
middle
Specifies the vertical alignment of
cell content
bottom
baseline
width Pixels (number, EX: “30” )
%
Specifies the width of the table
cell. Deprecated. Use styles
instead.
id unique_name Defines a unique name for the
map tag.
2 - 9
Page 22
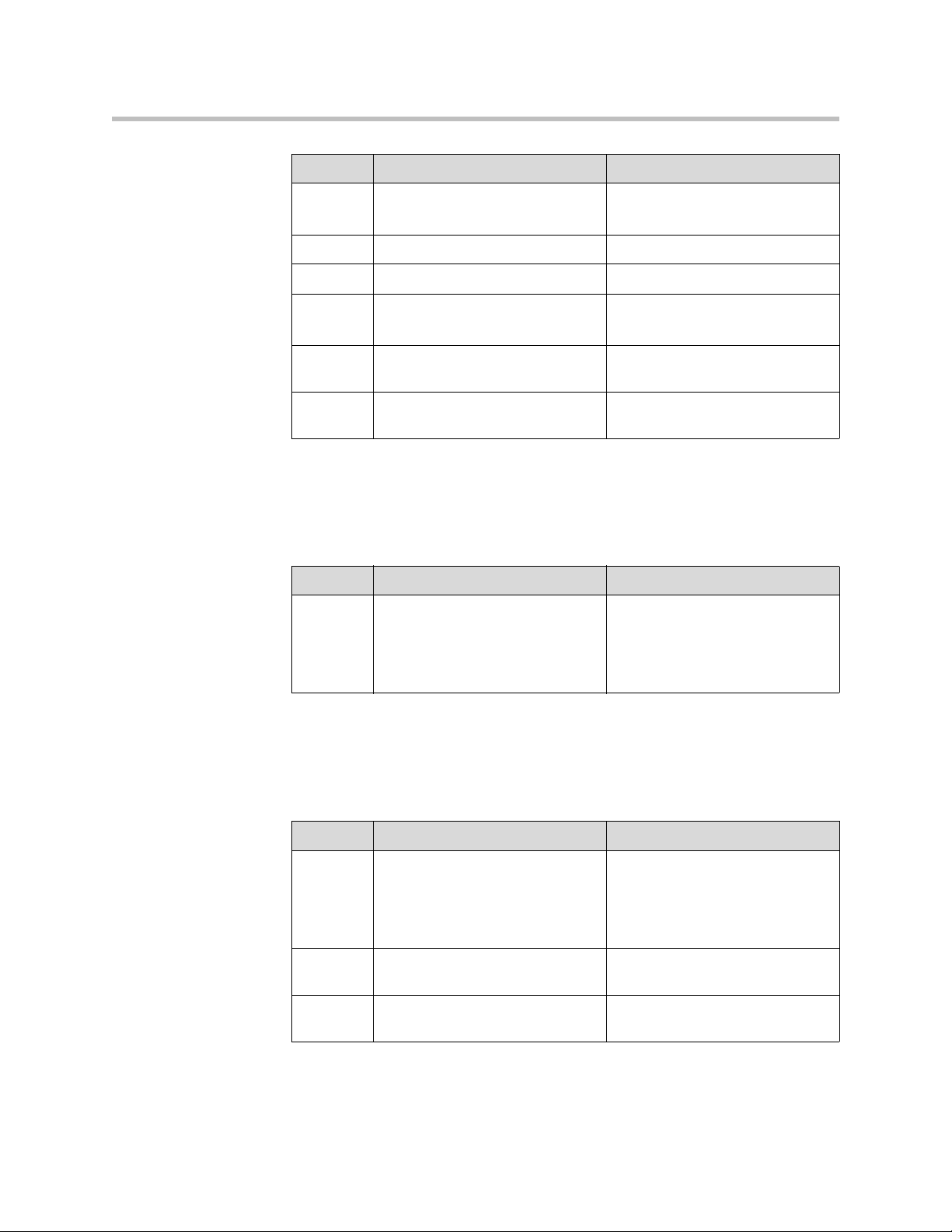
Developer’s Guide SoundPoint IP / SoundStation IP
Attribute Value/s Description
class class_rule
style_rule
title tooltip_text A text to display in a tool tip
style style_definition An inline style definition
dir ltr (left to right)
rtl (left to right)
lang language_code (Ex: EN, deu/ger,
hin)
xml:lang language_code (Ex: EN, deu/ger,
hin)
The class of the element
Sets the text direction
Sets the language code
Sets the language code
<tr>
This tag defines a row in a table.
The following attributes are supported:
Attribute Value/s Description
align right
left
center
justify
char
Defines the text alignment in cells.
2 - 10
<td>
This tag defines a cell in a table.
The following attributes are supported:
Attribute Value/s Description
align left
right
center
justify
char
colspan number Indicates the number of columns
rowspan number Indicates the number of rows this
Specifies the horizontal alignment
of cell content
this cell should span.
cell should span.
Page 23

Application Development
<thead>
This tag defines a table header. The thead, tfoot and tbody elements enable you
to group rows in a table. When you create a table, you might want to have a
header row, some rows with data, and a row with totals at bottom. This
division enables browsers to support scrolling of table bodies independently
of the table header and footer. When long tables are printed, the table header
and footer information may be repeated on each page that contains table data.
Note
The <thead> must have a <tr> tag inside. If you use the thead, tfoot and tbody
elements, you must use every element. They should appear in this order: <thead>,
<tfoot> and <tbody>, so that browsers can render the foot before receiving all the
data. You must use these tags within the table element.
The following attributes are supported:
Attribute Value/s Description
align right
left
center
justify
char
char. character Specifies which character to align
charoff Pixels (number, EX: “30” )
%
valign top
middle
bottom
baseline
Defines the text alignment in cells.
text on
Note: Only used if align="char"!
Specifies the alignment offset to
the first character to align on.
Note: Only used if align="char"!
Specifies the vertical text
alignment in cells
id unique_name Defines a unique name for the
map tag.
class class_rule
style_rule
title tooltip_text A text to display in a tool tip
style style_definition An inline style definition
The class of the element
2 - 11
Page 24

Developer’s Guide SoundPoint IP / SoundStation IP
Attribute Value/s Description
dir ltr (left to right)
rtl (left to right)
lang language_code (Ex: EN, deu/ger,
hin)
xml:lang language_code (Ex: EN, deu/ger,
hin)
Sets the text direction
Sets the language code
Sets the language code
<tbody>
This tag defines a table body. The thead, tfoot and tbody elements enable you
to group rows in a table.
The following attributes are supported:
Attribute Value/s Description
align right
left
center
Defines the text alignment in cells.
<tfoot>
This tag defines a table footer. The thead, tfoot and tbody elements enable you
to group rows in a table.
2 - 12
The following attributes are supported:
Attribute Value/s Description
align right
left
center
justify
char
char. character Specifies which character to align
charoff Pixels (number, EX: “30” )
%
valign top
middle
bottom
baseline
Defines the text alignment in cells.
text on
Note: Only used if align="char"!
Specifies the alignment offset to
the first character to align on.
Note: Only used if align="char"!
Specifies the vertical text
alignment in cells
Page 25

Application Development
Attribute Value/s Description
id unique_name Defines a unique name for the
map tag.
class class_rule
title tooltip_text A text to display in a tool tip
style style_definition An inline style definition
dir ltr (left to right)
lang language_code (Ex: EN, deu/ger,
xml:lang language_code (Ex: EN, deu/ger,
Meta Information Tags
The following meta information tags are supported:
• <head>—Defines information about the document
Note
The class of the element
style_rule
Sets the text direction
rtl (left to right)
Sets the language code
hin)
Sets the language code
hin)
Due to space constraints, there isn’t a static title bar at the top of the Microbrowser
window, as there is in most other browsers. The title is displayed in large bold text in
the first line of the page, and is scrolled off the screen as the focus is moved down
the page.
<head>
The head element can contain information about the document. The browser
does not display the “head information” to the user. The following tag can be
in the head section: <title>.
No attributes are supported.
SoundPoint IP/SoundStation IP XML API Application Interface
In SIP 3.1, there is expanded support in the Microbrowser for applications on
the SoundPoint IP 320/330, 430, 501, 550, 560, 650, and 670 desktop phones,
and SoundStation IP 4000, 6000, and 7000 conference phones.
2 - 13
Page 26

Developer’s Guide SoundPoint IP / SoundStation IP
The SoundPoint IP/SoundStation IP XML API is intended to provide
developers with flexibility in developing applications on SoundPoint IP and
SoundStation IP phones, while tightly integrating into the phone’s telephony
capabilities and functions.
This expanded support includes:
• Programmable Soft Keys
• Telephone Integration URIs
• Push Requests
• Telephony Notification Events
• Phone State Polling
For a discussion of the security aspects of this API, refer to API Security on
page 2-32.
Programmable Soft Keys
The following programmable soft key tag is supported:
• <softkey>—Defines a soft key
<softkey>
The softkey element creates a soft key with a customizable label, position, and
action. Users execute actions by pressing the soft key on their phone.
The soft keys are modified within the interactive Microbrowser only.
The following format is supported:
<softkey index="X" label="Y" action="Z" />
The following attributes are supported:
Attribute Value/s Description
index numeric, 1 to 8 Position of the soft key.
label string Text displayed on soft key. The
maximum length is 9 characters.
Note: If empty or absent, default
action name is displayed.
action URI Supported actions (must be one of
those listed in the next table).
2 - 14
Page 27

Application Development
The supported actions are described in the following table:
Action Default Action Name Description
SoftKey:Home Home Moves to configured home page
Softkey:Back Back Move to previous page
Softkey:Exit Exit Exits Microbrowser
SoftKey:Refresh Refresh Refreshes current page
SoftKey:Fetch;
<URI>
Fetch Fetches the page from the given
URI
SoftKey:Reset Reset Clears all input fields in the form
SoftKey:Submit Submit Submits the form
Key:VolDown VolDown Decreases volume by 1 unit
Key:VolUp VolUp Increases volume by 1 unit
Key:DoNotDisturb Do not disturb Enables Do Not Disturb feature
Key:Headset Headset Enables use of microphone
Key:Handsfree Hands-fre e Enables use of speaker
Key:Messages Messages Open the Messages menu
Key:Applications Applications Open the Applications menu
Key:Mute Mute Mutes the phone when the call
state
Key:Directories Dire ctories Open the Directories menu
Depending on the browser state, a number of predefined soft keys exist:
Action Predefined Soft Key
Browser Active—fetching pages or rendering
Home, Refresh, Back, Stop
data
Browser Stop—no longer active Home, Refresh, Back, Exit or
programmable soft key
Edit Active—when entering text Home, A->a1, Back, Exit
2 - 15
Page 28

Developer’s Guide SoundPoint IP / SoundStation IP
Note
The soft keys from the “Browser Active” and “Edit Active” soft key groups override
any custom soft keys defined in the current XHTML.
The soft keys from the “Browser Stop” soft key group appear if no custom soft keys
are defined.
The exact soft keys that appear vary between the SoundPoint IP and SoundStation
IP phones.
The following should be noted with respect to softkey tags:
• All actions are case insensitive.
• If the soft key action name is empty, the soft key tag is ignored.
• The Reset and Submit softkey tags must exist inside the
<form>
tag that
they are to act upon.
• Indexes need not be sequential. A missing index will result in an empty
space, no soft key displayed.
• An index greater than eight is ignored.
• By default, a Back soft key is placed on the graphic display (even if one is
not defined).
For example, to create a simple page:
<html>
<p> Hello World! </p><br/>
<softkey index="1" label="Home" action="SoftKey:Home" />
<softkey index="2" label="Refresh" action="SoftKey:Refresh" />
<softkey index="4" label="Exit" action="SoftKey:Exit" />
<softkey index="3" label="Back" action="SoftKey:Back" />
</html>
Telephone Integration URIs
Internal URIs provide the interface to execute predefined actions on the phone.
These actions are similar to the manual execution of key presses by the user.
There are three ways to execute an internal URI action:
• If the file sent to the phone contains only internal URI actions, the file
content type must be “
internal URIs are executed in ascending order.
• If an XHTML file will include internal URI, they must be defined in (and
executed from) anchor tags, in the
hef=”Key:Setup”>Menu</a>
action is processed and executed.
• Refer to Programmable Soft Keys on page 2-14.
application/x-com-polycom-spipx
href
attribute (for example,
). When the user selects the anchor, the
”. The
<a
2 - 16
Page 29

Application Development
Note
Internal URI actions contained in a file with content type
application/x-com-polycom-spipx
“
” can be executed only through a URL push.
The following format is supported:
ActionType:Action
where:
• ActionType is a type of key or action to execute (Key, Softkey, Tel, or Play)
• Action is the name of the action to be executed.
The supported internal URIs are described in the following table:
Action Type Action Description
Key Line1 to Line36 T he Key URIs send the key press
DialPad0 to DialPad9
SoftKey1 to SoftKey4
DialPadStar
DialPadPound
VolDown
event to the phone. The phone
processes this event as if the
button had been physically
pressed.
VolUp
Headset
Handsfree
Mute
Messages
Applications
Directories
Setup
ArrowUp
ArrowDwn
ArrowLeft
ArrowRight
Backspace
DoNotDisturb
Select
2 - 17
Page 30

Developer’s Guide SoundPoint IP / SoundStation IP
Action Type Action Description
SoftKey Back The SoftKey URIs send the soft
Tel Number;LineIndex The Tel URI initiates a new call to
Cancel
Exit
Submit
Reset
Refresh
key press event to the phone. The
phone processes this event as if
the associated soft key had been
physically pressed. These URIs
function when the interactive
Microbrowser is on the screen.
the specified number on the
specified line. The line number is
optional (the first available line is
used).
Note: The LineIndex value is case
sensitive. The range of LineIndex
is “Line1” to “Line36”.
Note: If the line corresponding to
the LineIndex in the Tel action is
busy, the request is ignored.
Play Play:<audiofile_path> Download and play the audio file.
The supported audio formats are
G.711 uLaw and Liner16.
The <audiofile_path> is the
relative path on the application
server, relative to
apps.push.serverRootURL
The supported maximum file size
is determined by
res.finder.sizeLimit.
.
The following should be noted with respect to internal URIs:
• The action name and key type are case insensitive.
• For non-XHTML content containing only internal URIs, the internal URIs
are executed in ascending order without any delay.
• If any URI is invalid and it is in a file of only internal URIs, the entire file
is rejected.
• If any invalid URI is present in a XHTML file, the execution of that URI is
ignored.
2 - 18
Page 31

Push Requests
Application Development
For example, to create a link that behaves as if you pressed the Do Not Disturb
key:
<html>
<body> <br/>
Click on the link to engage the DND feature
<a href="Key:DoNotDisturb">DNDSettings</a>
</body>
<softkey index="1" label="Back" action="SoftKey:Back" />
<softkey index="2" label="Exit" action="SoftKey:Exit" />
</html>
A push request is defined as a request that you send to a remote site asking for
data to be sent to you.
HTTP URL Push
The HTTP URL push allows you to send asynchronous relative ULIs to a
specific phone.
Note
The following format is supported:
<URL priority=”X” >URI data</URL>
The following attributes are supported:
Attribute Value/s Description
priority 0 = Disable push functionality
1 = Accept critical priority push
requests only
2 = accept normal priority push
requests only,
3 = accept all push requests
URI data string Any relative URI on the configured
This tag must be defined under a
<PolycomIPPhone>
Priority
Note: If set to a value other than 0
to 3 or if absent, “normal”is used.
application server.
Note: Currently multiple URIs in a
single push request are not
supported.
root tag.
2 - 19
Page 32

Developer’s Guide SoundPoint IP / SoundStation IP
The following table describes when to use a specific priority:
Phone State Priority Description
Idle State Critical The phone will display push
Non-Idle State Critical The phone will display push
The following should be noted with respect to HTTP URI push:
• By default, a Back soft key is placed on the graphic display.
• The phone can hold a maximum of 10 push requests at any time.
request immediately.
Normal The phone will display push
request immediately.
request immediately.
Normal The phone will keep push request
in push queue. Once the phone is
idle, the push request will be
displayed.
• Push requests are displayed as “first-in-first-out”.
• Changes must be made in the sip.cfg configuration file to enable this
feature. Refer to Push Request Configuration Parameters on page 2-21.
• All HTTP requests are challenged through HTTP Digest Authentication.
• If the phone cannot fetch the content from the pushed URI, the request is
ignored.
For example, to push the display of soft keys that fetch pages:
<PolycomIPPhone>
<URL priority=”normal”>/examples/media.xhtml</URL>
</PolycomIPPhone>
where
<html>
<!--Data for displaying on the screen-->
action="SoftKey:Fetch;http://www.cbc.ca/news/world/top/>
"action="SoftKey:Fetch;http://www.theweathernetwork.com/canada/bc/burn
aby/current/"/>
action="SoftKey:Fetch;http://www.tsn.ca/topstory/"/>
</html>
media.xhtml
Press any soft key to fetch the corresponding page
<softkey index="1" label="Top News"
<softkey index="2" label="Weather
<softkey index="4" label="Sports"
<softkey index="3" label="Back" action="SoftKey:Back"/>
is defined as follows:
2 - 20
Page 33

Application Development
Data Push
The data push allows you to send messages in XHTML format to a specific
phone.
The following format is supported:
<Data priority=”X” >Y</Data>
The following attributes are supported:
Attribute Value/s Description
Note
priority 0 = Disable push functionality
1 = Accept critical priority push
requests only
2 = accept normal priority push
requests only,
3 = accept all push requests
text text in HTML format Text
This tag must be defined under a
<PolycomIPPhone>
Priority
Note: If set to a value other than 0
to 3 or if absent, “normal”is used.
Note: The maximum file size is
1KB.
root tag.
For example, to push the display of an important message:
<PolycomIPPhone>
<Data priority=”critical”> <h1> Fire Drill at 2pm </h1> Please exit
and congregate at your appropriate location outside </Data>
</PolycomIPPhone>
Push Request Configuration Parameters
The push request configuration parameters in sip.cfg must be set as followed:
• Set
• Set
apps.push.messageType
For example,
apps.push.messageType
apps.push.serverRootURL
to the appropriate display priority.
=2
to the application server root relative
URL.
For example,
• Set
apps.push.username
For example,
apps.push.serverRootURL
to the appropriate username.
apps.push.username
=bob
=/sampleapps
The username and password are required to authenticate incoming push
requests to the phone.
2 - 21
Page 34

Developer’s Guide SoundPoint IP / SoundStation IP
• Set
apps.push.password
For example,
Telephony Notification Events
The phone can be configured to send information to a specific URI if one of the
following telephony notification events occurs:
• Incoming Call Event
• Outgoing Call Event
• Offhook Event
• Onhook Event
These events are XML data posted to web server by the phone’s Microbrowser.
Changes must be made in the sip.cfg configuration file to enable this feature.
Refer to Telephony Event Notification Configuration Parameters on page 2-26.
Incoming Call Event
The following format is supported:
to the appropriate password.
apps.push.password
=1234
<IncomingCallEvent>
<PhoneIP> </PhoneIP>
<MACAddress> </MACAddress>
<CallingPartyName> </CallingPartyName>
<CallingPartyNumber> </CallingPartyNumber>
<CalledPartyName> </CalledPartyName>
<CalledPartyNumber> </CalledPartyNumber>
<TimeStamp> </TimeStamp>
</IncomingCallEvent>
The following attributes are supported:
Attribute Value/s Description
Phone IP IP address IP address of the phone.
For example, “172.24.128.160”
MACAddress MAC address MAC address of the phone.
For example, “0004f214b8e7”
2 - 22
Page 35

Application Development
Attribute Value/s Description
CallingPartyName name The name displayed in phone's
"From" label in screen.
• If the line is registered and the
call is initiated from that line,
then the registered line display
name of the calling party is
shown. For example,
“SoundPoint IP”
• If the line is not registered and
the call is initiated from that
line, then IP address of the
calling party is shown. For
example,
“sip:172.24.128.160”
CallingPartyNumber number The number displayed on the
phone.
• If the line is registered and the
call is initiated from that line,
the registered line number of
the calling party is shown.
• If the line is not registered and
the call is initiated using IP
address from that line, the IP
address of the calling party is
shown.
CalledPartyName name • If the call is received by
registered line, the registered
line display name of the called
party is shown.
• If the call is received on a nonregistered line, the IP address
of the called party is shown.
CalledPartyNumber number • If the call is received by
registered line, the registered
line number of the called party
is shown.
• If the call is received on a nonregistered line, the IP address
of the called party is shown.
TimeStamp time The date and time that the event
occurred on the phone.
For example,
“2008-07-11T13:19:53-08:00”
2 - 23
Page 36

Developer’s Guide SoundPoint IP / SoundStation IP
When the telephone notification URI is set and the incoming call event is
enabled to gather information, the following example shows the transmitted
data for a call between two registered lines:
<PolycomIPPhone>
<IncomingCallEvent>
<PhoneIP>172.24.132.135</PhoneIP>
<MACAddress>0004f214b89e</MACAddress>
<CallingPartyName>20701</CallingPartyName>
<CallingPartyNumber>20701@172.18.186.94</CallingPartyNumber>
<CalledPartyName>20300</CalledPartyName>
<CalledPartyNumber>20300</CalledPartyNumber>
<TimeStamp>2008-07-11T13:19:53-08:00</TimeStamp>
</IncomingCallEvent>
</PolycomIPPhone>
Outgoing Call Event
The following format is supported:
<OutgoingCallEvent>
<PhoneIP> </PhoneIP>
<MACAddress> </MACAddress>
<CallingPartyName> </CallingPartyName>
<CallingPartyNumber> </CallingPartyNumber>
<CalledPartyName> </CalledPartyName>
<CalledPartyNumber> </CalledPartyNumber>
<TimeStamp> </TimeStamp>
</OutgoingCallEvent>
2 - 24
The following attributes are supported:
Attribute Value/s Description
Phone IP IP address IP address of the phone.
For example, “172.24.128.160”
MACAddress MAC address MAC address of the phone.
For example, “0004f214b8e7”
CallingPartyName name • If the line is registered and the
call is initiated from that line,
then the registered line display
name of the calling party is
shown.
• If the line is not registered and
the call is initiated from that
line, then IP address of the
calling party is shown.
Page 37

Application Development
Attribute Value/s Description
CallingPartyNumber number • If the line is registered and the
call is initiated from that line,
the registered line number of
the calling party is shown.
• If the line is not registered and
the call is initiated using IP
address from that line, the IP
address of the calling party is
shown.
CalledPartyName name The name displayed at phone’s
"To" name.
• If the call is received by
registered line, the registered
line display name of the called
party is shown.
• If the call is received on a nonregistered line, the IP address
of the called party is shown.
CalledPartyNumber number The number displayed on the
phone.
• If the call is received by
registered line, the registered
line number of the called party
is shown.
• If the call is received on a nonregistered line, the IP address
of the called party is shown.
TimeStamp time The date and time that the event
occurred on the phone.
For example,
“2008-07-11T13:19:53-08:00”
Offhook Event
The following format is supported:
<OffHookEvent>
<PhoneIP> </PhoneIP>
<MACAddress> </MACAddress>
<TimeStamp> </TimeStamp>
</OffHookEvent>
2 - 25
Page 38

Developer’s Guide SoundPoint IP / SoundStation IP
The following attributes are supported:
Attribute Value/s Description
Phone IP IP address IP address of the phone.
MACAddress MAC address MAC address of the phone.
TimeStamp time The date and time that the event
Onhook Event
The following format is supported:
<OnHookEvent>
<PhoneIP> </PhoneIP>
<MACAddress> </MACAddress>
<TimeStamp> </TimeStamp>
</OnHookEvent>
For example, “172.24.128.160”
For example, “0004f214b8e7”
occurred on the phone.
For example,
“2008-07-11T13:19:53-08:00”
The following attributes are supported:
Attribute Value/s Description
Phone IP IP address IP address of the phone.
For example, “172.24.128.160”
MACAddress MAC address MAC address of the phone.
For example, “0004f214b8e7”
TimeStamp time The date and time that the event
occurred on the phone.
For example,
“2008-07-11T13:19:53-08:00”
Telephony Event Notification Configuration Parameters
The telephone event notification configuration parameters in sip.cfg must be
set as followed:
• Set
apps.telNotification.URL
to the location where notifications
should be sent.
For example,
apps.telNotification.URL
=http://172.24.128.85:8080
If this URL is set to Null, the notifications events will not be sent.
2 - 26
Page 39

Application Development
Phone State Polling
• Set
• Set
• Set
• Set
The phone can be configured to send the current state of the phone to a specific
URI:
• Call Line Information—The line registration and call state are requested
apps.telNotification.incomingEvent
Disable respectively).
For example,
apps.telNotification.outgoingEvent
Disable respectively).
For example,
apps.telNotification.offhookEvent
Disable respectively).
For example,
apps.telNotification.onhookEvent
respectively).
For example,
by the call state handler (http://<Phone_IP>/callstateHandler).
apps.telNotification.incomingEvent
apps.telNotification.outgoingEvent
apps.telNotification.offhookEvent
apps.telNotification.onhookEvent
to 1 or 0 (for Enable or
=1
to 1 or 0 (for Enable or
=1
to 1 or 0 (for Enable or
=1
to 1 or 0 (for Enable or Disable
=1
• Device Information—Device- specific information is requested by the
device handler (http://<Phone_IP>/deviceHandler).
• Network Configuration—Network-specific information is requested by
the network handler (http://<Phone_IP>/networkHandler).
Two HTTP transactions occur here:
• The application sends an HTTP request to a particular handler
• The Microbrowser posts the state, in XML format, to a preconfigured web
server.
Changes must be made in the sip.cfg configuration file to enable this feature.
Refer to Phone State Polling Configuration Parameters on page 2-32.
2 - 27
Page 40

Developer’s Guide SoundPoint IP / SoundStation IP
Call Line Information
The following format is supported:
<CallLineInfo>
<LineKeyNum> </LineKeyNum>
<LineDirNum> </LineDirNum>
<LineState>Active</LineState>
<CallInfo>
<CallState> </CallState>
<CallType> </CallType>
<CalledPartyName> </CalledPartyName>
<CalledPartyDirNum> </CalledPartyDirNum>
<CallingPartyName> </CallingPartyName>
<CallingPartyDirNum> </CallingPartyDirNum>
<CallReference> </CallReference>
<CallDuration> </CallDuration>
</CallInfo>
</CallLineInfo>
The
Note
<CallInfo>
is not included.
block is included if and only if <LineState> is “Active”. Otherwise it
The following attributes are supported:
Attribute Value/s Description
LineKeyNum number Registered phone line key
number.
LineDirNum number Registered line directory number.
LineState Active,
Inactive
CallState Outgoing call states:
Dialtone, Setup,
RingBack
Incoming call states:
Offering
Outgoing/Incoming call
states: Connected,
CallConference,
CallHold, CallHeld,
CallConfHold,
CallConfHeld
Shared line states:
CallRemoteActive
CallType Incoming, Outgoing Call type.
Line state.
Call state.
2 - 28
Page 41

Application Development
Attribute Value/s Description
CallingPartyName number If the line is registered, the value is
the registered line display name.
If the line is not registered, the
value is the IP address of the
calling party.
CallingPartyDirNum number If the line is registered, the value is
the registered line number.
If the line is not registered, the
value is the IP address of the
calling party.
CalledPartyName name If the line is registered, the value is
the registered line display name.
If the line is not registered, the
value is the IP address of the
called party.
CalledPartyDirNum number If the line is registered, the value is
the registered line number.
If the line is not registered, the
value is the IP address of the
called party.
CallReference number An internal identifier for the call.
CallDuration number in seconds Duration of the call in seconds.
When the phone state polling URL is set and the phone receives a Call
Processing Request, the following example shows the transmitted data:
<PolycomIPPhone>
<CallLineInfo>
<LineKeyNum>1</LineKeyNum>
<LineDirNum>10</LineDirNum>
<LineState>Connected</LineState>
<CallInfo>
<CallState>Offering</CallState>
<CallType>Incoming</CallType>
<CalledPartyName>10</CalledPartyName>
<CalledPartyNumber>10</CalledPartyNumber>
<CallingPartyName>21</CallingPartyName>
<CallingPartyNumber>21@172.24.128.61</CallingPartyNumber>
<CallReference>0</CallReference>
<CallDuration>0</CallDuration>
</CallInfo>
</CallLineInfo>
<CallLineInfo>
<LineKeyNum>2</LineKeyNum>
<LineDirNum>35</LineDirNum>
2 - 29
Page 42

Developer’s Guide SoundPoint IP / SoundStation IP
<LineState>NotConnected</LineState>
</CallLineInfo>
<CallLineInfo>
<LineKeyNum>3</LineKeyNum>
<LineDirNum>36</LineDirNum>
<LineState>NotConnected</LineState>
</CallLineInfo>
</PolycomIPPhone>
Device Information
The following format is supported:
<DeviceInformation>
<MACAddress> </MACAddress>
<PhoneDN> </PhoneDN>
<AppLoadID> </AppLoadID>
<BootROMID> </BootROMID>
<ModelNumber> </ModelNumber>
<TimeStamp> </TimeStamp>
</DeviceInformation>
The following attributes are supported:
Attribute Value/s Description
MACAddress MAC address MAC address of the phone.
PhoneDN string List of all registsred lines, including
expansion modules, and their
directory numbers delimited by
commas.
For example,
“Line1:1,Line2:2,Line3:3”
AppLoadID string Application load ID on the phone.
For example, “Tip 27-Feb-08
20:07”
BootROMID string BootROM on the phone.
For example, “4.1.0.0213”
ModelNumber string Phone’s model number.
For example, “SoundPoint IP 650”
TimeStamp time The date and time that the event
occurred on the phone.
2 - 30
Page 43

Application Development
Network Configuration
The following format is supported:
<NetworkConfiguration>
<DHCPServer></DHCPServer>
<MACAddress>0004f214b8e7</MACAddress>
<DNSSuffix></DNSSuffix>
<IPAddress>172.24.128.160</IPAddress>
<SubnetMask>255.255.255.0</SubnetMask>
<ProvServer></ProvServer>
<DefaultRouter>172.24.128.1</DefaultRouter>
<DNSServer1>172.21.6.218</DNSServer1>
<DNSServer2>0.0.0.0</DNSServer2>
<VLANID></VLANID>
<DHCPEnabled>0</DHCPEnabled>
</Networkconfiguration>
The following attributes are supported:
Attribute Value/s Description
DHCPServer IP address DHCP server IP address.
MACAddress MAC address MAC address of the phone.
DNSSuffix host name DNS domain suffix.
IPAddress IP address IP address of the phone.
SubnetMask IP address IP address of the subnet.
ProvServer IP address Provisioning server.
DefaultRouter IP address IP address of default router (or IP
gateway).
DNSServer1 IP address Configured IP address of DNS
Server 1.
DNSServer2 IP address Configured IP address of DNS
Server 2.
VLANID Null, 0 through 4094 Phone’s 802.1Q VLAN identifier.
DHCPEnabled Yes, No If DHCP is enabled, set to “Yes”.
2 - 31
Page 44

Developer’s Guide SoundPoint IP / SoundStation IP
Phone State Polling Configuration Parameters
The phone state polling configuration parameters in sip.cfg must be set as
followed:
API Security
• Set
apps.statePolling.URL
to the location where requested information
should be sent.
For example,
apps.statePolling.URL
=http://172.24.128.85:8080
If this URL is set to Null, the requested information will not be sent.
• Set
apps.statePolling.username
For example,
apps.statePolling.username
to the appropriate username.
=bob
The username and password are required to authenticate incoming
polling requests to the phone.
• Set
apps.statePolling.password
For example,
apps.statePolling.password
to the appropriate password.
=1234
With respect to the security of the SoundPoint IP/SoundStation IP XML API,
the following should be noted:
• Authenticating remote control and monitoring— There is no support of
TLS on the phone’s web server. The execution of each of each HTTP
GET/POST request requires an MD5 digest authentication. All pushed
URLs are relative URLs with the root specified in the sip.cfg configuration
file.
2 - 32
Note
• Achieving confidentiality of executed content—The phone’s HTTP client
supports TLS, so any data retrieved from the URL can be protected. Make
sure of the confidentiality of all traffic past the initial push request by
specifying a root URL that uses https.
• Unsolicted event reporting—The confidentiality of all events reported by
the phone can be also be protected by TLS in the same way that push
content is.
• Direct data push—When direct data push is enabled—disabled by
default— small amounts of executable content (1KB) can be sent directly
to the phone by the application server. The request will still be
authenticated through HTTP digest, but all content will be in clear text on
the network. Polycom recommends that you only use data push for
broadcast type alerts that do not pose any confidentiality risks.
Both
apps.push.username
push to be enabled.
and
apps.push.password
must be set for data
Page 45

HTTP Support
Application Development
The Microbrowser is a fully compliant HTTP/1.1 user agent:
• It supports:
— Cookies
Note
Cookies are stored in RAM, therefore they are not are not preserved when the
phone reboots or is reconfigured. Cookies are not shared between the idle display
Microbrowser and the main Microbrowser.
— Refresh headers
— HTTP proxies
— HTTP over SSL/TLS
— Self-signed or custom CA certificates
• There are the following exceptions:
— There is no sophisticated caching. The HTML cache refresh META tag
is not supported.
— Any images in the body of a document with the same URL are
assumed to be the same image. The image is loaded from the
Microbrowser’s memory instead of making another request to the
server.
— When a new page is requested, the Microbrowser’s internal memory
is cleared and all components of the new page are downloaded from
the server.
Microbrowser User Interface
Two instances of the Microbrowser may run concurrently:
• An instance with standard interactive user interface
2 - 33
Page 46

Developer’s Guide SoundPoint IP / SoundStation IP
SoundPoint IP 430
SoundPoint IP 501SoundPoint IP 650
SoundStation IP 4000
SoundPoint IP 430
SoundPoint IP 501SoundPoint IP 650
SoundStation IP 4000
• An instance that does not support user input, but appears in a window on
the idle display
Launching the Microbrowser
2 - 34
The first time the Applications key is pressed, the main Microbrowser loads
the home page specified in the
mb.main.home
configuration parameter.
Subsequent presses of the Applications key simply toggle between the
Microbrowser and SIP telephony applications. The active page remains loaded
in memory when you toggle.
Page 47

Whenever there is an event in the telephony application that requires the
user's attention, the telephony application is brought to the foreground
automatically.
The Microbrowser can be displayed again by simply pushing the Applications
key. While the Microbrowser application is not displayed, it is still active and
pending transactions will complete in the background and be immediately
visible when the browser is brought to the foreground.
Navigation and Form Editing
The user navigates through pages by moving the focus among the focusable
items with the up and down arrow keys. Focusable items include links, form
elements, and buttons. The focus moves between all focusable items on a page
in the order that they appear in the XHTML source, including tables. For
newly displayed pages, the focus will automatically move to the first focusable
item visible on the current page.
When the user has focused on a link that they would like to follow, or a form
element they would like to toggle, they press the Select key. This will either
generate a request for the linked page or toggle the selection of an element in
the form. When the focus moves to fields which are editable, the user may
simply enter text at will, then move the focus to the next selectable item when
complete using the up and down arrow keys. If there is a large area of the page
without a focusable element, the page is only scrolled by one screen for each
push of the arrow key.
Application Development
To submit form data, navigate to and select a submit button on the page or
press the Submit soft key when available.
The Back soft key takes the user to the previous page viewed. The left arrow
key performs a similar function unless the user is editing a text field. The
Refresh and Home soft keys behave in the expected manner, reloading the
current page and returning to the user's home page respectively.
Text is entered into text boxes using the dial pad through the same entry
method used elsewhere on the phone. When editing text, a soft key allows the
user to cycle through uppercase letter, lowercase letter or numeric entry
modes. A Cancel soft key is available to undo the current edits.
Idle Display Microbrowser
The idle display Microbrowser is independent of the main Microbrowser, but
is capable of rendering the same content. Its home page is configured via the
mb.idleDisplay.home
Microbrowser does not accept any user input and will only appear when the
user has no phone calls in progress and the phone is in the idle user interface
state. The idle display Microbrowser can update its content based on a
configurable refresh timer or by honoring the value of the Refresh header.
configuration parameter. The idle display
2 - 35
Page 48

Developer’s Guide SoundPoint IP / SoundStation IP
Developing an XHTML Application
Changing Configuration Parameters
Create a new configuration file in the style of sip.cfg so that users will connect
to your application when they press the Application key (or select the
Application feature item).
Note
For more information on why to create another configuration file, refer to the
“Configuration File Management on SoundPoint IP Phones” whitepaper at
www.polycom.com/support/voice/ .
Setting
sec.tagSerialNo
address to the user agent header field in all HTTP messages sent by the phone.
To allow an application to be run from the Microbrowser:
1. Open a new configuration file in an XML editor.
2. Add the Microbrowser <mb> parameter.
3. Set
4. Set
5. Set
mb.proxy
Microbrowser.
For example,
where 10.11.32.103 is proxy server IP address and 8080 is the port number.
mb.idleDisplay.home
display home page.
For example,
mb.idleDisplay.home=http://10.11.32.128:8080/sampleapps/idle
mb.idleDisplay.refresh
of the idle display Microbrowser's content.
to the address of the desired HTTP proxy to be used by the
mb.proxy=10.11.32.103:8080
in sip.cfg will cause the phone to append its MAC
to the URL used for Microbrowser idle
to the period in seconds between refreshes
2 - 36
For example,
6. Set
7. Set
8. Set
9. (Optional.) If you are including HTTP URL push messages in your
mb.main.home
For example,
mb.main.home=http://10.11.32.128:8080/sampleapps/login
mb.limits.nodes
parser will handle.
For example,
mb.limits.cache
for each page (both XHTML and images).
For example,
application, do the following:
mb.idleDisplay.refresh=10
to the URL used for Microbrowser home page.
to the maximum number of tags that the XML
mb.limits.nodes= 256
to the maximum total size of objects downloaded
mb.limits.cache= 200
Page 49

Application Development
a Set
b Set
apps.push.messageType
For example,
apps.push.messageType
apps.push.serverRootURL
to the appropriate display priority.
=3
to the application server root URL.
For example,
apps.push.serverRootURL
c Set
apps.push.username
For example,
apps.push.username
=http://172.24.128.85:8080/sampleapps
to the appropriate username.
=bob
The username and password are required to authenticate incoming
push requests to the phone.
d Set
apps.push.password
For example,
apps.push.password
to the appropriate password.
=1234
10. (Optional.) If you are including telephone event notifications in your
application, do the following:
a Set
apps.telNotification.URL
to the location where notifications
should be sent.
For example,
apps.telNotification.URL
=http://172.24.128.85:8080
If this URL is set to Null, the notifications events will not be sent.
b Set
apps.telNotification.incomingEvent
to 1 or 0 (for Enable or
Disable respectively).
For example,
c Set
apps.telNotification.outgoingEvent
apps.telNotification.incomingEvent
to 1 or 0 (for Enable or
=1
Disable respectively).
For example,
d Set
apps.telNotification.offhookEvent
apps.telNotification.outgoingEvent
to 1 or 0 (for Enable or
=1
Disable respectively).
For example,
e Set
apps.telNotification.onhookEvent
apps.telNotification.offhookEvent
to 1 or 0 (for Enable or
=1
Disable respectively).
For example,
apps.telNotification.onhookEvent
=1
11. (Optional.) If you are including phone state polling requests in your
application, do the following:
a Set
apps.statePolling.URL
to the location where requested
information should be sent.
For example,
apps.statePolling.URL
=http://172.24.128.85:8080
If this URL is set to Null, the requested information will not be sent.
2 - 37
Page 50

Developer’s Guide SoundPoint IP / SoundStation IP
Sample Applications
b Set
apps.statePolling.username
For example,
apps.statePolling.username
to the appropriate username.
=bob
The username and password are required to authenticate incoming
polling requests to the phone.
c Set
apps.statePolling.password
For example,
apps.statePolling.password
to the appropriate password.
=****
12. Save your changes and close the XML editor.
13. Add the new file to the master configuration file’s CONFIG_FILES list in
the appropriate order.
Since the files are processed left to right, any parameter which appears in
first file will override the same parameter in later files.
For more information on configuration parameters, refer to the latest
Administrator’s Guide for the SoundPoint IP / SoundStation IP Family at
http://www.polycom.com/support/voicedocumentation/.
This section presents three sample applications that you can use as a starting
point for writing your own application.
• Static XHTML Application
• Dynamic XHTML Application
• SoundPoint IP/SoundStation IP XML API Application
Static XHTML Application
To develop a static XHTML application:
1. Create a
Sample.xhtml
page with static information to be displayed.
In this case, the static information will be "Hello World!".
<html>
<head>
<title>Sample Application</title>
</head>
<body>
<p>HelloWorld!</p>
</body>
</html>
2 - 38
Page 51

Application Development
2. Configure the Web server to serve the above XHTML file.
For example, if you are using Apache Tomcat to try this example, then put
this file into the
webapps\PLCM
folder of Tomcat.
3. Configure SoundPoint IP and SoundStation IP phones to point to the
XHTML file in the sip.cfg configuration file.
Note
For this example, change
http://<WEBSERVER_ADDRESS:PORT>/PLCM/Sample.xhtml
mb.main.home
to
.
4. Reboot the phones.
5. On a SoundPoint IP phone, press the Applications (or Services) key.
The text “Hello World!” appears on the graphic display.
Static XHTML applications can be developed using any Web server. Even though
Tomcat is used in the example, the developer is free to use any Web server.
Dynamic XHTML Application
To develop a dynamic XHTML application:
1. Create a
AddStock.xhtml
page.
This XHTML page is designed for getting a stock symbol as input from the
SoundPoint IP or SoundStation IP phone, then retrieve the information for
this stock symbol.
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<!- - HEADER START - ->
<head>
<title>Stocks</title>
</head>
<!- - HEADER END - ->
<!- - BODY START - ->
<body>
<!- - ADD STOCK FORM START - ->
<form method="POST" action="GetQuote.jsp">
<p>Symbol<input type="text" name="stockname"/>
<input type="submit" value="Get Quote"/></p>
</form>
<!- - ADD STOCK FORM END - ->
</body>
<!- - BODY END - ->
</html>
2. Configure the Web server to serve the above XHTML file.
For example, if you are using Apache Tomcat to try this example, put this
file into the
webapps\PLCM
folder of Tomcat.
2 - 39
Page 52

Developer’s Guide SoundPoint IP / SoundStation IP
3. Write an application that is going to retrieve the stock information from a
data service provider.
For this example, this application will be retrieving stock information from
Yahoo and will send it to the Microbrowser. This application is written
using a Java Server Page (JSP).
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="iso-8859-1"?>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Strict//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-strict.dtd">
<%@page
import="java.io.File,java.io.IOException,java.net.URL,java.awt.image.B
ufferedImage,javax.imageio.ImageIO"%>
<html>
<head>
<title>Stock Quote</title>
</head>
<body>
<%
// GETTING THE PATH WHERE BMP FILE HAS TO BE SAVED
String bmpFilePath = application.getRealPath(File.separator) +
"quote.bmp";
// DEFINE URL FROM WHERE CONTENT TO BE RETRIEVED
String stockUrl = "http://ichart.yahoo.com/t?s=";
// RETRIEVE THE STOCK SYMBOL FROM REQUEST
String stockSymbol = "PLCM"; // DEFAULT TO PLCM
if ( request.getParameter("stockname") != null ) {
stockSymbol = request.getParameter("stockname");
}
readAndConvertContentToBmp(stockUrl + stockSymbol, bmpFilePath,
stockSymbol);
%>
<%!
// READ THE CONTENT FROM GIVEN URL AND THEN CONVERT THE CONTENT TO A
BMP FILE
private void readAndConvertContentToBmp(String a_stockUrl, String
a_filePath, String a_name) throws IOException {
try {
BufferedImage stockImage = ImageIO.read(new URL(a_stockUrl));
ImageIO.write(stockImage, "bmp", new File(a_filePath));
}
catch (IOException ex) { throw ex;}
}
%>
<!-- START DISPLAY BMP FILE -->
<img src="quote.bmp"/>
<!-- END DISPLAY BMP FILE -->
</body>
</html>
2 - 40
Page 53

Application Development
4. Configure the Web server to deploy the above JSP file.
For example, if you are using Apache Tomcat to try this example, put this
file into the
webapps\PLCM
folder of Tomcat.
5. Configure SoundPoint IP and SoundStation IP phones to point to the
XHTML file in the sip.cfg configuration file.
Note
For this example, change
http://<WEBSERVER_ADDRESS:PORT>/PLCM/AddStock.xhtml
mb.main.home
to
.
6. Reboot the phones.
7. On a SoundPoint IP phone, press the Applications (or Services) key.
The
AddStock.xhtml
appears on the graphic display.
8. Enter a stock symbol, then select the Get Quote soft key.
The stock quote for the entered stock symbol appears on the graphic
display.
Dynamic XHTML applications can be developed using any Web server. Even
though Tomcat is used in the example, the developer is free to use any Web server.
Dynamic XHTML applications can be developed using any Web technologies—for
example, ASP.net, Java Servlets, Java Server Pages, CGI-PERL, and PHP.
SoundPoint IP/SoundStation IP XML API Application
This example uses a Telephone Integration URI:
• This is an ASP.NET sample for an IIS Server.
• A customer is browsing a company’s web site on the internet. They come
upon this web page (http://A_Web_Site/WebCallback.aspx), and enter
their name and phone number as shown below.
2 - 41
Page 54

Developer’s Guide SoundPoint IP / SoundStation IP
• After the customer clicks Send Request, the page shown below is pushed
to the customer support agent’s phone.
The customer support agent can call the customer by just pressing the
Select key, because the highlighted link contains a Tel URI with the
customer’s phone number.
To develop an XML API application:
1. Using Microsoft Visual Studio, create a file called
<%@ Page Language="C#" AutoEventWireup="true"
CodeFile="WebCallback.aspx.cs" Inherits="WebCallback" %>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd">
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" >
<head runat="server">
<title>Web Call Back Request</title>
</head>
<body>
<form id="form1" runat="server">
<div>
Please Enter Your Name and Phone # to Ask an Agent to Call
Back Immediately:<br />
<br />
Name:<br />
<asp:TextBox ID="BoxName" runat="server" Height="23px"
Width="192px"></asp:TextBox><br />
<br />
Phone #<br />
<asp:TextBox ID="BoxNumber" runat="server" Height="22px"
Width="192px"></asp:TextBox><br />
<br />
<asp:Button ID="Button1" runat="server" Height="30px"
OnClick="Button1_Click" Text="Send Request"
Width="162px" /></div>
</form>
webcallback.aspx
.
2 - 42
Page 55

</body>
</html>
Application Development
2. Using Microsoft Visual Studio, create a file called
using System;
using System.IO;
using System.Text;
using System.Data;
using System.Configuration;
using System.Net;
using System.Web;
using System.Web.Security;
using System.Web.UI;
using System.Web.UI.WebControls;
using System.Web.UI.WebControls.WebParts;
using System.Web.UI.HtmlControls;
using System.Threading;
public partial class WebCallback : System.Web.UI.Page
{
public static ManualResetEvent allDone = new
ManualResetEvent(false);
protected void Page_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
}
protected void Button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
String phoneNum = BoxNumber.Text ;
String name = BoxName.Text;
webcallback.aspx.cs
.
//send a push request to the phone with the IP address
callbackReq("172.18.103.32", phoneNum, name);
}
private void callbackReq(String phoneIP, String phoneNum, String
name)
{
String strLoc = "http://" + phoneIP + "/push";
String[] cred = { "Polycom", "456" };
NetworkCredential myCred = new NetworkCredential(cred[0],
cred[1]);
CredentialCache myCache = new CredentialCache();
myCache.Add(new Uri(strLoc), "Digest", myCred);
2 - 43
Page 56

Developer’s Guide SoundPoint IP / SoundStation IP
string result = "";
// Create the web request
HttpWebRequest request =
(HttpWebRequest)WebRequest.Create(strLoc);
WebRequestState myRequestState = new WebRequestState();
myRequestState.request = request;
request.Method = "POST";
request.Credentials = myCache;
myRequestState.createPostData(phoneNum, name);
IAsyncResult r = (IAsyncResult)request.BeginGetRequestStream(
new AsyncCallback(ReadCallback), myRequestState);
allDone.WaitOne();
// Get response
HttpWebResponse response =
(HttpWebResponse)request.GetResponse();
// Get the response stream
StreamReader reader = new
StreamReader(response.GetResponseStream());
// Read the whole contents and return as a string
result = reader.ReadToEnd();
reader.Close();
response.Close();
}
private static void ReadCallback(IAsyncResult asynchronousResult)
{
WebRequestState myRequestState =
(WebRequestState)asynchronousResult.AsyncState;
WebRequest myWebRequest = myRequestState.request;
// End the Asynchronus request.
Stream streamResponse =
myWebRequest.EndGetRequestStream(asynchronousResult);
byte[] byteArray =
Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(myRequestState.getPostData());
2 - 44
Page 57

Application Development
// Write the data to the stream.
streamResponse.Write(byteArray, 0, byteArray.Length);
streamResponse.Close();
allDone.Set();
}
}
public class WebRequestState
{
public String postData = null;
public WebRequest request;
public WebRequestState()
{
request = null;
}
public String getPostData()
{
return postData;
}
public void createPostData(String phoneNum, String name)
{
postData =
"<PolycomIPPhone><Data Priority=\"critical\">" +
"<title>Customer Web Call Back Request</title>" +
" <h1>Customer Name : " + name + " </h1> <br></br>" +
"<a href=\"tel://" + phoneNum + ";Line1\">Callback to
Customer</a>" +
"</Data></PolycomIPPhone>";
}
}
3. Configure the IIS Web server to deploy the above files.
4. Change the sip.cfg configuration file as follows:
a Set
b Set
The phone’s IP address is hardcoded in
apps.push.username
apps.push.password
to Polycom.
to 456.
webcallback.aspx.cs
to
172.18.103.32 for this example. You must change this to another value.
5. Reboot the phone.
After a customer enters their name and phone number on the web page,
the Customer Web Call Back Request page appears on the phone with IP
address 172.18.103.32 .
2 - 45
Page 58

Developer’s Guide SoundPoint IP / SoundStation IP
2 - 46
Page 59

Troubleshooting
This chapter presents problems, likely causes, and corrective actions.
Problems are grouped as follows:
• XML Errors
If you still need assistance, contact your system administrator.
XML Errors
3
Symptom Problem Corrective Action
Improperly formatted tables
could cause the phone to stop
and restart or display the error
“XML Error (17,75) mismatched
tag”.
A table tag was improperly
formatted.
Correct the improperly formatted table.
3 - 1
Page 60

Developer’s Guide SoundPoint IP / SoundStation IP
3 - 2
Page 61

Appendix
This appendix provides information on unsupported XHTML elements.
Unsupported XHTML Elements
The unsupported elements and attributes are:
Tag Type Tag Description
Basic Tags <html>—Defines HTML document.
A
<body>—Defines documents’ body.
<h1> to <h6>—Defines header 1 to header 6.
<p>—Defines a paragraph.
<br>—Inserts a single line break.
<hr>—Defines a horizontal rule.
Character Format Tags <b>—Defines bold text.
<font>—Deprecated. Defines text font, size, and color.
<i>—Defines italic text.
<em>—Defines emphasized text.
<big>—Defines big text.
<strong>—Defines strong text.
<small>—Defines small text.
<sup>—Defines superscripted text.
<sub>—Defines subscripted text.
<bdo>—Defines the direction of text display.
<u>—Deprecated. Defines underlined text.
A - 1
Page 62

Developer’s Guide SoundPoint IP / SoundStation IP
Tag Type Tag Description
Output Tags <pre>—Defines preformatted text.
Block Tags <acronym>—Defines an acronym.
<code>—Defines computer code text.
<tt>—Defines teletype text.
<kbd>—Defines keyboard text.
<var>—Defines a variable.
<dfn>—Defines a definition term.
<samp>—Defines sample computer code.
<xmp>—Deprecated. Defines preformatted text.
<abbr>—Defines an abbreviation.
<address>—Defines an address element.
<blockquote>—Defines a long quotation.
<center>—Deprecated. Defines centered text.
<q>—Defines a short quotation.
<cite>—Defines a citation.
<ins>—Defines inserted text.
<del>—Defines deleted text.
<s>—Deprecated. Defines strikethrough text.
<strike>—Deprecated. Defines strikethrough text.
Link Tags <a>—Defines an anchor.
The following attributes are not supported: charset,
coords, hreflang, rel, rev, shape, target, type, id, class,
title, style, dir, lang, xml:lang, tabindex, and accesskey.
<link>—Defines a resource reference.
Frame Tags <frame>—Defines a sub window (frame).
<frameset>—Defines a set of frames.
<noframes>—Defines a noframe section.
<iframe>—Defines an inline sub window (frame).
A - 2
Page 63

Tag Type Tag Description
Input Tags <form>—Defines a form.
The following attributes are not supported: accept,
accept charset, enctype, target, class, id, style, title, dir,
lang, and accesskey.
<input>—Defines an input field.
The following attributes are not supported: accept, align,
alt, disabled, maxlength, readonly, size, arc,
type:button, type:file, type:image, class, is, style, title,
dir, lang, accesskey.
<textarea>—Defines a text area.
<button>—Defines a push button.
<select>—Defines a selectable list.
<optgroup>—Defines an option group.
<option>—Defines an item in a list box.
<label>—Defines a label for a form control.
Appendix
<fieldset>—Defines a fieldset.
<legend>—Defines a title in a fieldset.
<isindex>—Deprecated. Defines a single-line input
field.
List Tags <ul>—Defines an unordered list.
<ol>—Defines an ordered list.
<li>—Defines a list item.
<dir>—Deprecated. Defines a directory list.
<dl>—Defines a definition list.
<dt>—Defines a definition term.
<dd>—Defines a definition description.
<menu>—Deprecated. Defines a menu list.
Image Tags <img>-Defines an image.
The following attributes are not supported: alt, align,
border, hspace, ismap, longdesc, usemap, vspace, id,
class, title, style, xml:lang, and lang
<map>—Defines an image map.
<area>—Defines an area inside an image map.
A - 3
Page 64

Developer’s Guide SoundPoint IP / SoundStation IP
Tag Type Tag Description
Tab le Tags <table>—Defines a table.
The following atrributes are not supported: bgcolor,
frame, rules, summary, id, class, title, style, dir, lang,
and xml:lang.
<col>—Defines attributes for table columns.
<tr>—Defines a table row.
The following attributes are not supported: bgcolor,
cahr, charoff, valign, id, class, title, style, dir, lang, and
xml:lang.
<td>—Defines a table cell.
The following attributes are not supported: abbr, axis,
bgcolor, char, charoff, headers, height, nowrap, scope,
valign, width, id, class, title, style, dir, lang, and
xml:lang.
<tbody>—Defines a table body.
The following attributes are not supported: align:justify,
align:char, char, charoff, valign, id, class, title, style, dir,
lang, and xml:lang.
<colgroup>—Defines groups of table columns.
Style Tags <style>—Defines a style definition.
<div>—Defines a section in a document.
<span>—Defines a section in a document.
Meta Information Tags <head>—Defines information about the document.
No attributes are supported.
<title>—Defines the document title.
<meta>—Defines meta information
<base>—Defines a base URL for all the links in a page
<basefont>—Deprecated. Defines a base font
Programming Tags <script>—Defines a script
<noscript>—Defines a noscript section
<applet>—Deprecated. Defines an applet
<object>—Defines an embedded object
<param>—Defines a parameter for an object
A - 4
Page 65

Index
A
application development process 2–36
B
basic tags
supported 2–2
unsupported A–1
block tags
unsupported A–2
C
character format tags
unsupported A–1
configuration parameters, changes to 2–36
F
frame tags
unsupported A–2
H
HTTP support 2–33
I
image tags
supported 2–6
unsupported A–3
input tags
supported 2–3
unsupported A–3
L
launching Microbrowser 2–34
link tags
supported 2–3
unsupported A–2
list tags
unsupported A–3
M
meta information tags
supported 2–13
unsupported A–4
Microbrowser
definition 1–1
idle display 2–35
launching 2–34
overview 1–1
Microbrowser <mb> 2–36
N
navigation and form editing 2–35
O
output tags
unsupported A–2
P
programmable soft key tags
supported 2–14
programming tags
unsupported A–4
S
sample application
dynamic 2–39
static 2–38
XML API 2–41
style tags
unsupported A–4
supported XHTML elements 2–1, A–1
T
table tags
supported 2–7
unsupported A–4
troubleshooting 3–1
XML errors 3–1
Index – 1
Page 66

Developer’s Guide SoundPoint IP / SoundStation IP
U
unsupported attributes A–1
unsupported elements A–1
X
XHTML, definition 1–2
Index – 2
Page 67

1. Agreement
Terms included with the Product(s) and this document (together, the “Agreement”). In the event of any conflicts between the End User
License and Warranty Terms and this document, this document shall govern with respect to the API.
2. Parties.
API. The relationship between you and Polycom is that of licensee/licensor. No legal partnership or agency relationship is created
between you and Polycom. Neither you nor Polycom is a partner, an agent or has any authority to bind the other. You agree not to
represent otherwise.
3. License/Ownership
solely for the purposes of developing and testing your own proprietary software to be used in conjunction with the Product(s). The
foregoing license does not grant you any distribution rights or other rights to use the API for any other purpose and you agree that you
shall not rent, lease, loan, sell, sublicense, assign or otherwise transfer any rights in the API. Polycom retains ownership of the API, and
except as expressly set forth herein, no other rights or licenses are granted. Pol ycom may change, s uspend or discontinue providing th e
API at any time.
4. Term/Survival
terms and conditions of this Agreement. In such an event, you must destroy all copies of the API. You may terminate this Agreement at
any time by destroying the API. In the event of any termination of this Agreement, Sections 1, 2, 5, and 7-11 shall survive termination.
5. Development
products, software or technologies that perform the same or similar functions as, or otherwise compete with any other products, software
or technologies that you may develop, produce, market, or distribute. In the absence of a separate written agreement to the contrary,
Polycom shall be free to use any information, suggestions or recommendations you provide to Polycom for any purpose, subject to any
applicable patents or copyrights.
6. Harmful Code
to any code that: (i) contains hidden files, “time bombs” or viruses; or (ii) can alter, damage, disclose or erase any data or other computer
programs without control of a person operating the computing equipment on which it resides, or (iii) retrieves or collects information
without the consent of the user or for any illegal or unauthorized purpose; or (iv) contains a key, node lock, time-out or other function
whether implemented by electronic, mechanical or other means which restricts or may restrict use or access to programs or data on the
Products, frequency or duration of use, or other limiting criteria; or (v) any code which may restrict, inhibit, disrupt or interfere with the
functionality of the Products as provided by Polycom. You agree not to use the API for any illegal or unauthorized purpose.
7. Marketing/Trademarks
logo, the marks "Polycom," "SoundPoint," "SoundStation," any other marks belonging or licensed to Polycom, or any marks that are
confusingly similar to marks belonging or licensed to Polycom in any way except as otherwise expressly authorized by Polycom in each
instance. In no event shall you (i) expressly state or imply that any products developed by you were created by or on behalf of Polycom
or are being marketed by or on behalf of Polycom; or (ii) expressly state or imply that Polycom has reviewed, sanctioned, or endorsed
your product in any way.
8. No Warranty
WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, WHETHER EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES
OF MERCHANTIBILITY, NON-INFRINGEMENT, ACCURACY, COMPLETENESS, PERFORMANCE, AND FITNESS FOR A
PARTICULAR PURPOSE, AND POLYCOM PROVIDES NO SUPPORT FOR THIS API. You understand that Polycom is under no
obligation to provide updates, enhancements, or corrections, or to notify you of any API changes that Polycom may make. In the event
you market a product you develop using the API, any obligations, representations or warranties provided by you to an end user shall be
solely your obligations, and in no event shall Polycom be responsible to fulfill any such obligations.
9. Indemnity
expenses (including reasonable attorneys’ fees) arising from your use of the API (including without limitation any actions arising from acts
or omissions of your employees or agents) or any failure by you to comply with the terms of this Agreement.
10. Disclaimer of Liability
OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES, INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION, DAMAGES RESULTING FROM DE LAY OF DELIVERY OR
FROM LOSS OF PROFITS, DATA, BUSINESS OR GOODWILL, ON ANY THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER ARISING UNDER
TORT (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE), CONTRACT OR OTHERW ISE, WHETHER OR NOT POLYCOM HAS BEEN ADVISED OR IS
AWARE OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES. POLYCOM’S ENTIRE LIABILITY FOR DIRECT DAMAGES UNDER THIS
AGREEMENT IS LIMITED TO FIVE DOLLARS ($5.00).
11. Miscellaneous
extent necessary so that this Agreement shall otherwise remain in full force and effect and enforceable. This Agreement constitutes the
entire agreement between the parties with respect to its subject matter and supersedes all prior or contemporaneous understandings
regarding such subject matter. No addition to or removal or modification of any of the provisions of this Agreement will be binding upon
Polycom unless made in writing and signed by an authorized representative of Polycom.
YOUR USE OF THIS API ACKNOWLEDGES THAT YOU HAVE READ, UNDERSTAND AND AGREE TO BE BOUND BY THE
TERMS AND CONDITIONS INDICATED ABOVE.
For purposes of this Agreement “you” or “your” shall mean the individual or entity accepting this Agreement or using the
FOR SOUNDPOINT IP AND SOUNDSTATION IP PRODUCTS (“Product” or “Products”).
. You understand and agree that by using the API you will be bound by the terms of the End User License and Warranty
. Subject to your compliance with this Agreement, Polycom hereby grants you a limited license to use the API
. Without prejudice to any other rights, Polycom may terminate this Agreement if you fail to comply with any of the
. Nothing in this Agreement shall impair Polycom’s right to develop, acquire, license, market, promote or distribute
. You agree not to include any “Harmful Code” in any products you develop by use of the API, including but not limited
. You understand the API provided to you is supplied "AS IS" AND “WITH ALL FAULTS” WITHOUT ANY
. You shall indemnify and hold Polycom harmless from and against any and all costs, damages, losses, liability or
. UNDER NO CIRCUMSTANCES SHALL POLYCOM BE LIABLE FOR SPECIAL, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL,
. If any provision is found to be unenforceable or invalid, that provision shall be limited or eliminated to the minimum
APPLICATION PROGRAMMING INTERFACE LICENSE (“API”)
. You are free to market any products you develop using the API, provided you agree not use the Polycom
POLYCOM, INC.
Polycom, Inc. © 2008. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. www.polycom.com
Corporate Headquarters: Phone 408-526-9000
4750 Willow Road Fax: 408-526-9100
Pleasanton, CA 94588
U.S.A.
Page 68

By downloading the following Sample Applications, you agree to the below end user
license agreement.
LICENSE AGREEMENT FOR DEVELOPMENT PURPOSES
This License Agreement for Development Purposes (the "Agreement") is a legal
agreement between you and Polycom, Inc., a Delaware corporation ("Polycom").
The software you are about to download (the "Software") comprises sample code that
may be useful in the development of applications designed to operate on or in
conjunction with Polycom Products.
Polycom is willing to license the Software to you only upon the condition that you accept
all of the terms contained in this agreement. Select the "Accept" button at the bottom of
the page to confirm your acceptance. If you are not willing to be bound by these terms,
select the "Do Not Accept" button and the downloading process will not continue.
PLEASE NOTE:
* POLYCOM OFFERS NO SUPPORT FOR THIS SOFTWARE, AND THE
SOFTWARE IS BEING LICENSED WITHOUT DOCUMENTATION, WITHOUT
WARRANTY, "AS-IS," AND "WITH ALL FAULTS."
* THE SOFTWARE HAS NOT BEEN TESTED BY POLYCOM AND SHOULD NOT
BE LOADED ON PRODUCTION SYSTEMS.
1. GRANT OF LICENSE.
1.1. License. Subject to the terms of this Agreement, Polycom grants to you a
nonexclusive, nontransferable license to copy, install, use, and modify the Software,
including the Software in source code format, and to produce your own commercial or
other purposes derivative works thereof. Except as provided below, this License
Agreement does not grant you any rights to patents, copyrights, trade secrets, trademarks,
or any other rights related to the Software.
2. DESCRIPTION OF OTHER RIGHTS AND LIMITATIONS.
2.1. Copyright. All title and copyrights in and to the Software and any copies of the
Software are owned by Polycom or its suppliers. The Software is protected by copyright
laws and international treaty provisions. Title, ownership rights, and intellectual property
rights in the Software shall remain in Polycom or its suppliers.
2.2. Ownership of Derivative Works. As between you and Polycom, you will own
copyright and other intellectual property rights in derivative works of the Software that
you develop.
Page 69

2.3. Reservation. Polycom reserves all rights in the Software not expressly granted to you
in this Agreement.
3. SUPPORT SERVICES.
3.1. No Support Services. Polycom provides no support services for the Software.
4. TERMINATION.
4.1. Termination. Without prejudice to any other rights, Polycom may terminate this
Agreement if you fail to comply with any of the terms and conditions of this Agreement.
In such event, you must destroy all copies of the Software and all of its component parts.
You may terminate this Agreement at any time by destroying the Software and all of its
component parts.
5. NO WARRANTY.
THE SOFTWARE IS LICENSED WITHOUT WARRANTY, "AS IS," AND "WITH
ALL FAULTS." ALL WARRANTIES, TERMS OR CONDITIONS, EXPRESS OR
IMPLIED, EITHER IN FACT OR BY OPERATION OF LAW, STATUTORY OR
OTHERWISE, INCLUDING WARRANTIES, TERMS OR CONDITIONS OF
MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE,
SATISFACTORY QUALITY, CORRESPONDENCE WITH DESCRIPTION, AND
NON-INFRINGEMENT, ARE EXPRESSLY DISCLAIMED. POLYCOM NEITHER
ASSUMES NOR AUTHORIZES ANY OTHER PERSON TO ASSUME FOR IT ANY
OTHER LIABILITY IN CONNECTION WITH THE SALE, INSTALLATION,
MAINTENANCE, OR USE OF THIS SOFTWARE.
6. LIMITATION OF LIABILITY.
6.1. Limitations. TO THE MAXIMUM EXTENT PERMITTED BY APPLICABLE
LAW, IN NO EVENT SHALL POLYCOM OR ITS SUPPLIERS BE LIABLE FOR
ANY SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL, INDIRECT, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES
WHATSOEVER (INCLUDING. WITHOUT LIMITATION, DAMAGES FOR LOSS
OF BUSINESS PROFITS, BUSINESS INTERRUPTION, LOSS OF BUSINESS
INFORMATION, OR ANY OTHER PECUNIARY LOSS) ARISING OUT OF THE
USE OR INABILITY TO USE THE SOFTWARE, EVEN IF POLYCOM HAS BEEN
ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES. IN ANY CASE,
POLYCOM'S ENTIRE LIABILITY SHALL BE LIMITED TO THE GREATER OF
THE AMOUNT ACTUALLY PAID BY YOU FOR THE SOFTWARE OR U.S. $5.00.
7. DISCLAIMER.
7.1. Disclaimer. Some countries, states, or provinces do not allow the exclusion or
limitation of implied warranties or the limitation of incidental or consequential damages
Page 70

for certain products supplied to consumers or the limitation of liability for personal
injury, so the above limitations and exclusions may be limited in their application to you.
8. EXPORT CONTROLS.
8.1. Export Controls. The Software may not be downloaded or otherwise exported or reexported (i) into (or to a national or resident of) Cuba, Iraq, Libya, North Korea,
Yugoslavia, Iran, Syria, Republic of Serbia, or any other country to which the U.S. has
embargoed goods; or (ii) to anyone on the U.S Treasury Department's List of Specially
Designated Nationals or the U.S. Commerce Department's Table of Denial Orders. By
downloading or using this Software, you are agreeing to the foregoing and you are
representing and warranting that you are not located in, under the control of, or a national
or resident of any such country or on any such list. If you obtained this Software outside
of the United States, you are also agreeing that you will not export or re-export it in
violation of the laws of the country in which it was obtained.
9. MISCELLANEOUS.
9.1. Governing Law. This Agreement shall be governed by the laws of the State of
California as such laws are applied to agreements entered into and to be performed
entirely within California between California residents, and by the laws of the United
States. The United Nations Convention on Contracts for the International Sale of Goods
(1980) is hereby excluded in its entirety from application to this Agreement.
9.2. Venue for Resolving Disputes. Any disputes relating to this Agreement will be
resolved only in the state or federal courts located in Santa Clara County, California.
Each of the parties agrees to the exercise over them of the personal jurisdiction of such
courts for such purpose.
9.3. U.S. Government Restricted Rights. The Software and documentation are provided
with Restricted Rights. The Software programs and documentation are deemed to be
"commercial computer software" and "commercial computer software documentation,"
respectively, pursuant to DFAR Section 227.7202 and FAR 12.212(b), as applicable. Any
use, modification, reproduction, release, performance, display, or disclosure of the
Software programs and/or documentation by the U S. Government or any of its agencies
shall be governed solely by the terms of this Agreement and shall be prohibited except to
the extent expressly permitted by the terms of this Agreement. Any technical data
provided that is not covered by the above provisions is deemed to be "technical data
commercial items" pursuant to DFAR Section 227.7015(a). Any use, modification,
reproduction, release, performance, display, or disclosure of such technical data shall be
governed by the terms of DFAR Section 227.7015(b).
9.4. Relationship Between the Parties. The relationship between you and Polycom is that
of licensee/licensor. Neither party will represent that it has any authority to assume or
create any obligation, express or implied, on behalf of the other party, nor to represent the
other party as agent, employee, franchisee, or in any other capacity. Nothing in this
Page 71

agreement shall be construed to limit either party's right to independently develop or
distribute software that is functionally similar to the other party's products, so long as
proprietary information of the other party is not included in such software.
9.5. Entire Agreement. This Agreement represents the complete agreement concerning
this license and may be amended only by a writing executed by both parties. If any
provision of this Agreement is held to be unenforceable, such provision shall be reformed
only to the extent necessary to make it enforceable.
www.polycom.com
Corporate Headquarters: 4750 Willow Road, Pleasanton, CA 94588, USA Phone 408-
526.9000 Fax: 408-526-9100
 Loading...
Loading...