Page 1

Internet Telephony PBX System
IPX-300 Series
User’s manual
Version 1.0.0
Page 2

Copyright
Copyright (C) 2007 PLANET Technology Corp. All rights reserved.
The products and programs described in this User’s Manual are licensed products of PLANET Technology, This
User’s Manual contains proprietary information protected by copyright, and this User’s Manual and all
accompanying hardware, software, and documentation are copyrighted.
No part of this User’s Manual may be copied, photocopied, reproduced, translated, or reduced to any electronic
medium or machine-readable form by any means by electronic or mechanical. Including photocopying, recording,
or information storage and retrieval systems, for any purpose other than the purchaser's personal use, and without
the prior express written permission of PLANET Technology.
Disclaimer
PLANET Technology does not warrant that the hardware will work properly in all environments and applications,
and makes no warranty and representation, either implied or expr essed, with respect to the quality, performance,
merchantability, or fitness for a particular purpose.
PLANET has made every effort to ensure that this User’s Manual is accurate; PLANET disclaims liability for any
inaccuracies or omissions that may have occurred.
Information in this User’s Manual is subject to change without notice and does not represent a commitment on the
part of PLANET. PLANET assumes no responsibility for any inaccuracies that may be contained in this User’s
Manual. PLANET makes no commitment to update or keep current the information in this User’s Manual, and
reserves the right to make improvements to this User’s Manual and/or to the products described in this User’s
Manual, at any time without notice.
If you find information in this manual that is incorrect, misleading, or incomplete, we would appreciate your
comments and suggestions.
CE mark Warning
The is a class B device, In a domestic environment, this product may cause radio interference, in which case the
user may be required to take adequate measures.
WEEE Warning
To avoid the potential effects on the environment and human health as a result of the presence of
hazardous substances in electrical and electronic equipment, end users of electrical and electronic
equipment should understand the meaning of the crossed-out wheeled bin symbol. Do not dispose of
WEEE as unsorted municipal waste and have to collect such WEEE separately.
Trademarks
The PLANET logo is a trademark of PLANET Technology. This documentation may refer to numerous hardware
and software products by their trade names. In most, if not all cases, their respective companies claim these
designations as trademarks or registered trademarks.
2
Page 3

Revision
User’s Manual for PLANET Internet Telephony PBX System:
Model: IPX-300/IPX-300W
Rev: 1.0 (December, 2007)
Part No. EM-IPX300 Series V1
3
Page 4

TABLE OF CONTENTS
Chapter 1................................................................................................ 3
Introduction............................................................................................ 3
Overview............................................................................................................................3
Package Content...............................................................................................................3
Physical Details.................................................................................................................3
Front Panel Indicators.................................................................................................3
Rear Panel Indicators..................................................................................................3
Chapter 2 Preparations & Installation.................................................. 3
Physical Installation Requirement..................................................................................3
Network Interface quick configurations.....................................................................3
Chapter 3 IP PBX Setup ........................................................................ 3
SIP Basic Setting........................................................................................................3
User Extensions Setup................................................................................................3
Attendant Extension ...................................................................................................3
Dialing Rules..............................................................................................................3
Time Rules..................................................................................................................3
Record Voice Menu....................................................................................................3
Call Parking................................................................................................................3
Gereral Setting............................................................................................................3
Chapter 4 Network Setup...................................................................... 3
WAN & LAN Setup....................................................................................................3
DHCP .........................................................................................................................3
WLAN Setting (For IPX-300W)................................................................................3
Access Policy (For AP and WISP&AP mode) ...........................................................3
Static Route.................................................................................................................3
NAT ............................................................................................................................3
Packet Filter................................................................................................................3
URL Filter...................................................................................................................3
Security.......................................................................................................................3
UPnP...........................................................................................................................3
Call Out Block List.....................................................................................................3
SNTP ..........................................................................................................................3
Chapter 5 Management......................................................................... 3
Admin Account...........................................................................................................3
Date & Time ...............................................................................................................3
Ping T est.....................................................................................................................3
Save & Restore...........................................................................................................3
4
Page 5

Factory Default...........................................................................................................3
Admin Account...........................................................................................................3
Appendix A............................................................................................. 3
How to use Call Parking function...................................................................................3
Appendix B............................................................................................. 3
How to use Call Pick-up function....................................................................................3
Appendix C............................................................................................. 3
Record Voice Guide Process............................................................................................3
Appendix D............................................................................................. 3
Voice Communication Samples.......................................................................................3
IP Phone and Wi-Fi Phone register to IPX-300W......................................................3
IP Phone and Wi-Fi Phone make off-Net calls via Gateway......................................3
Appendix E............................................................................................. 3
IPX-300 Series Specifications..........................................................................................3
5
Page 6

Chapter 1
1
Introduction
Overview
PLANET IPX-300/IPX-300W IP PBX telephony systems (“IP PBX” in the following term) are designed
and optimized for the small business in daily communications. It can support up to 100 user
registrations and easy to install and manage a fully working system with the convenience and cost
advantages. The future IP PBX telephony system offers all of the essential features of telephony which
is required by small business users for their telecommunication/data needs.
The IP PBX series are the feature-rich SIP based IP PBX telephony system that integrates NAT
functions to make it perfect for small business usage. The IP PBX integrates traditional PBX system
functions and provides many advanced functions including voice mail to email, web management etc.
Designed to run on a variety of VoIP applications, the IP PBX provide IP-based communications, voice
conferencing, call detailed record (CDR), centralized Auto-Attendant (AA), and Interactive Voice
Responses (IVR). The IP PBX utilizes standard PSTN / GSM lines via the interfaces of FXO / GSM
gateway to become a feature-rich IP PBX telephony system that supports seamless communications
among existing local calls, SIP-based endpoints including low cost of long distance service, telephone
number portability and one network for both voice and data.
With a built-in IEEE 802.11b/g wireless AP / CPE, the Wi-Fi IP PBX (IPX-300W) of fers wireless
connectivity via 54Mbps data transmissi ons. Users may integrate PLANET IP Phone VIP-154T series,
VIP-155PT/ 350PT/ 550PT, the VIP-156/ 157/ 158/ 161W of AT A (analog telephone adapter) series, the
VIP-191/ 192 of Wi-Fi Phone, and Gateway series VIP-281/ 281GS/ 480 to build up the VoIP network
deployment in minutes.
IP PBX Features
• PBX Features
- Automated Attendant (AA)
- Interactive Voice Responses (IVR)
- Voicemail support (VM)
- Voicemail to E-Mail
- Call Detailed Record (CDR)
- User Management via Web Browser
- Call/Pickup Group
Page 7

- Display 100 Registered User’s Status: Unregistered / Registered / On-Call
• Call Features
- Call Forward Immediate
- Call Forward on Busy
- Call Forward on No Answer
- Call Pickup / Call Park
- Caller ID
- Musi c on Hold / Music on Transfer
- Call Transfer / Call Hold / Call Waiting
- Three-way conference with feature phones (VIP-154T series, VIP-155PT/ 350PT/ 550PT and
VIP-156/ 157/ 158/ 161W series)
• Router/Firewall Features
- DHCP Server for LAN Users
- Access Control / URL Filter
- Virtual Server / DMZ / Port Mapping
- Static Route
- Pass-through
- UPnP
• Wireless Features (IPX-300W)
- IEEE 802.11b/ 802.11g
- AP / AP-Client / WISP & AP Mode
- 64/128 bits WEP Date Encryption
- WPA/ WPA-PSK/ WPA2/ WPA2-PSK/ Mix Mode
- WPAPSK/ WPS2PSK Mix Mode
7
Page 8

Package Content
The contents of your product should contain the following items:
Internet Telephony PBX system unit
Power Adapter
Quick Installation Guide
User’s Manual CD
Physical Details
The following figure illustrates the front/rear panel of IP PBX.
Front Panel Indicators
Figure 1-1. Front Panel of IPX-300
Figure 1-2. Front Panel of IPX-300W
Front Panel LED State Descriptions
PWR
WAN Port
LAN Port
WLAN Port
(IPX-300W only)
On
Off
On
Flashing
Off
On
Flashing
Off
On
Flashing
Off
PBX Power ON
PBX Power OFF
PBX network connection established
Data traffic on cable network
Waiting for network connection
LAN is connected successfully
Data is transmitting
Ethernet not connected to PC
WLAN is connected successfully
Data is transmitting
Ethernet not connected to PC
Table1-1. Front Panel description of IP PBX
8
Page 9
Rear Panel Indicators
Figure 1-3. Rear Panel of IPX-300
Figure 1-4. Rear Panel of IPX-300W
1 12V DC
2 Reset
3 WAN
4 LAN
External
5
Antenna 2db
(IPX-300W only)
12V DC Power input outlet
The reset button, when pressed, resets the IP PBX without the
need to unplug the power cord.
The WAN port supports auto negotiating Fast Ethernet
10/100Base-T networks. This port allows your IP PBX to be
connected to an Internet Access device, e.g. router, cable modem,
ADSL modem, through a CAT.5 twisted pair Ethernet cable.
The LAN port allows your PC or Switch/Hub to be connected to the
IP PBX through a CAT.5 twisted pair Ethernet cable.
Used to Wirelessly Connect to 802.11b/g networks
802.11b: 11/5.5/2 Mbps
802.11g: 54/48/36/24/19/12/6Mbps
Table 1-2. Rear Panel description of IP PBX
9
Page 10
Chapter 2
2
Preparations & Installation
Physical Installation Requirement
This chapter illustrates basic installation of IP PBX
• Network cables. Use standard 10/100BaseT network (UTP) cables with RJ45 connectors.
• TCP/IP protocol must be installed on all PCs.
For Internet Access, an Internet Access account with an ISP, and either of a DSL or Cable modem (for
WAN port usage)
Administration Interface
PLANET IP PBX provides GUI (Web ba sed, G raphi cal User Interface) for machine management and
administration.
Web configuration access:
To start IP PBX web configuration, you must have the web browsers installed on computer for
management
• Microsoft Internet Explorer 6.0.0 or higher with Java support
Default LAN interface IP address of IP PBX is 192.168.0.1. You may now open your web browser, and
insert 192.168.0.1 in the address bar of your web browser to logon IP PBX web configuratio n page.
IP PBX will prompt for logon username/password, please enter: admin / 123 to continue machine
administration.
Figure 2-1. Input prompt
Page 11
ÍNote
In order to connect machine for administration, please
locate your PC in the same network segment (192.168.0.x)
of IP PBX. If you’re not familiar with TCP/IP, please refer
to related chapter on user’s manual CD or consult your
network administrator for proper network configurations.
Network Interface quick configurations
Wizard for Quick Setup of the IP PBX, after finishing the authentication, please click “Wizard” to enter
quick start:
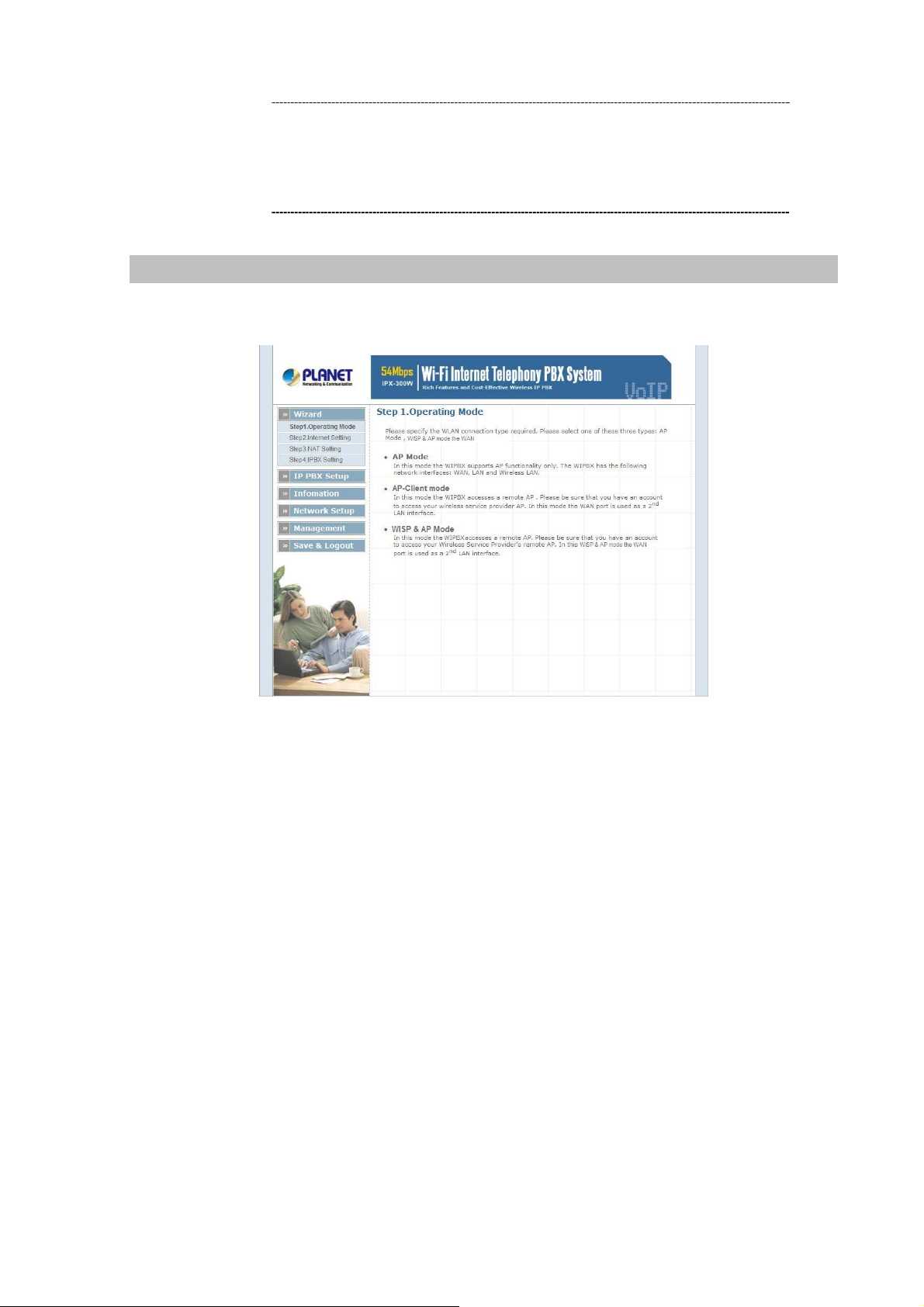
Figure 2-2. Wizard-Operating Mode settings
¾ Step1. Operation Mode (For IPX-300W)
For most users, Internet access is the primary application. The IP PBX supports the WAN, LAN and
WLAN interface for Internet access and remote access. When you click “Operation Mode” from within
the Wizard Setup, the following setup page will be show.
Three WLAN modes of operation are available for Internet Access:
AP Mode:
In this mode the IP PBX supports AP functionality only. The IP PBX has the following
network interfaces: WA N, LAN and Wireless LAN.
AP-Client Mode:
In this mode the IP PBX accesses a remote AP. Please be sure that you have an account to
access your wireless service provider AP. In this mode the WAN interface is used a 2nd
LAN interface.
WISP & AP Mode:
11
Page 12
The IP PBX must access remote AP .Please be sure that have account to access from
remote AP. In this WISP & AP mode the network interface will change from WAN port to
LAN port and all of network access will through by remote AP.
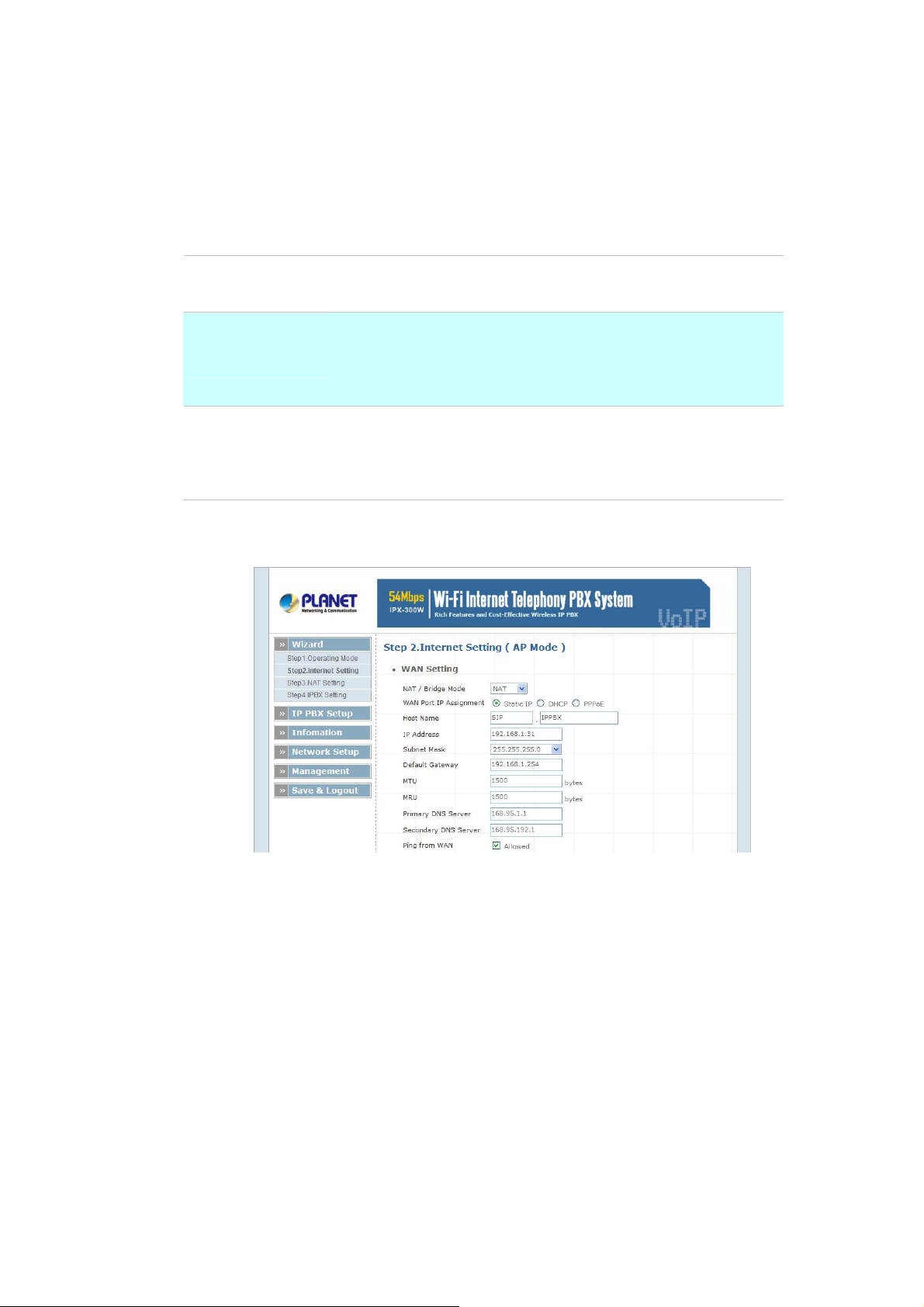
¾ Step2. Internet Setting (AP Mode)
WAN Setting
NAT Mode
Bridge Mode
WAN Port IP
Assignment
Network Address Translation (NAT) serves co nnect ing multiple
computers to the Internet using one IP address.
Bridge mode serves to connect a local area network (LAN /
Wireless) to another local area network that uses the same
protocol.
Three methods are available for Internet Access. Static IP /
DHCP / PPPoE type for your select .you should refer to “Network
Setting” in user menu.
Table 2-1. WAN description of IP PBX
Figure 2-3. Wizard-Internet settings
AP Setting (For IPX-300W)
For configuring correctly the WLAN port in client mode. the below instructions will provide a quick
start. It is advised if possible to use the simplest network settings for first try.
For making sure the IP PBX is connecting to your wireless router (AP). You need to set up the
following: SSID, Frequency Channel, Authentication method and Encryption parameters
(Type/Encryption length/Keys.)
12
Page 13
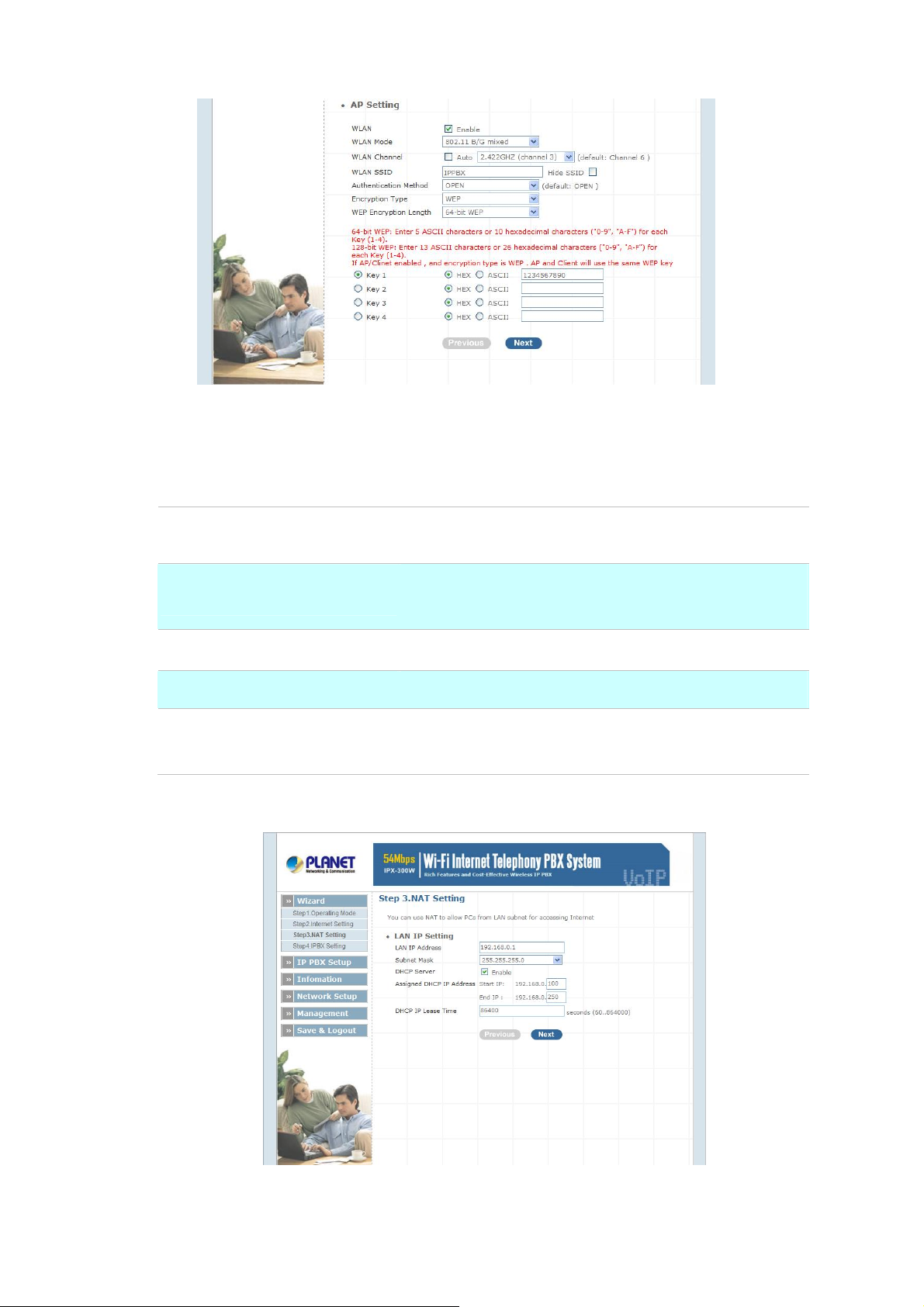
¾ Step3. NAT Setting
LAN IP Setting
Figure 2-4. Wizard-AP settings
LAN IP Address
Subnet Mask
DHCP Server
Assigned DHCP IP Address
DHCP IP Lease Time
Table 2-2. LAN IP description of IP PBX
Private IP address for connecting to a local private network.
(Default: 192.168.0.1)
Subnet mask for the local private network (Default:
255.255.255.0)
Enable to open LAN port DHCP server
DHCP server range from start IP to end IP
Client to ask DHCP server refresh time, range from 60 to
86400 seconds
Figure 2-5. Wizard-NA T settings
13
Page 14
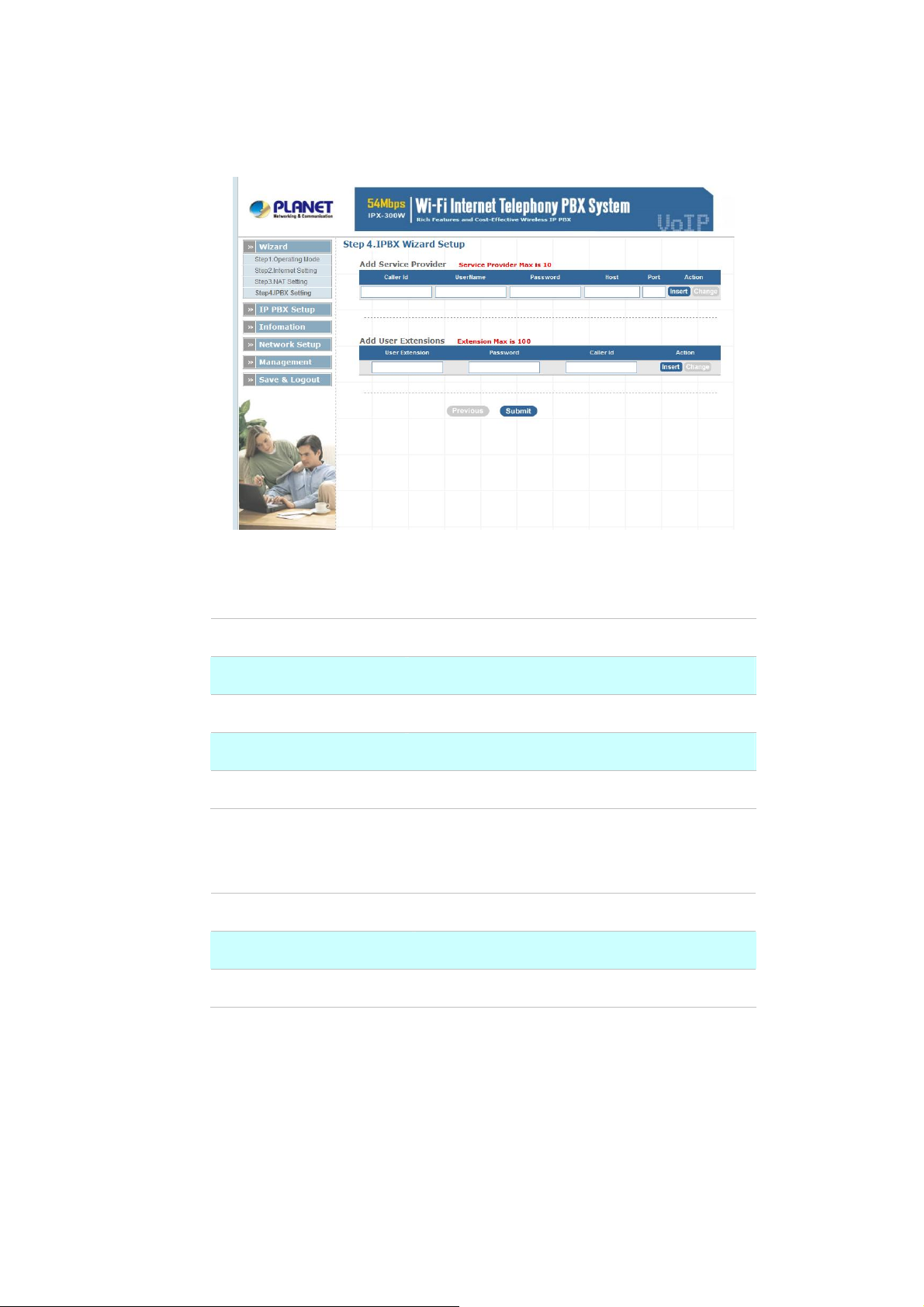
¾ Step4. IPPBX Setup
The IP PBX allows multiple ITSP providers / User Extensions registration by simply fill-in the required
information in the provided table.
Figure 2-6. Wizard-IP PBX settings
Service Provider:
User Extensions:
Caller ID
Username
Password
Host
Port
Table 2-3. Service provider description
User Extension
Password
Caller Id
Table 2-4. User extension description
Service provider name
Input Provider name
Input Provider password
Input Providers server address
Providers server port
Input Extension number
Input Extension password
Input Extension caller id
After completing the wizard setup, cli ck “ Submit” button, The IP PBX will save configuration and reboot
IP PBX automatically, after 50 seconds, you can re-load setting page again.
14
Page 15

Figure 2-7. Wizard-Rebooting
ÍNote
Please consult your ISP personnel to obtain proper PPPoE/IP
address related information, and input carefully.
If Internet connection cannot be established, please check
the physical connection or contact the ISP service staff
for support information.
15
Page 16
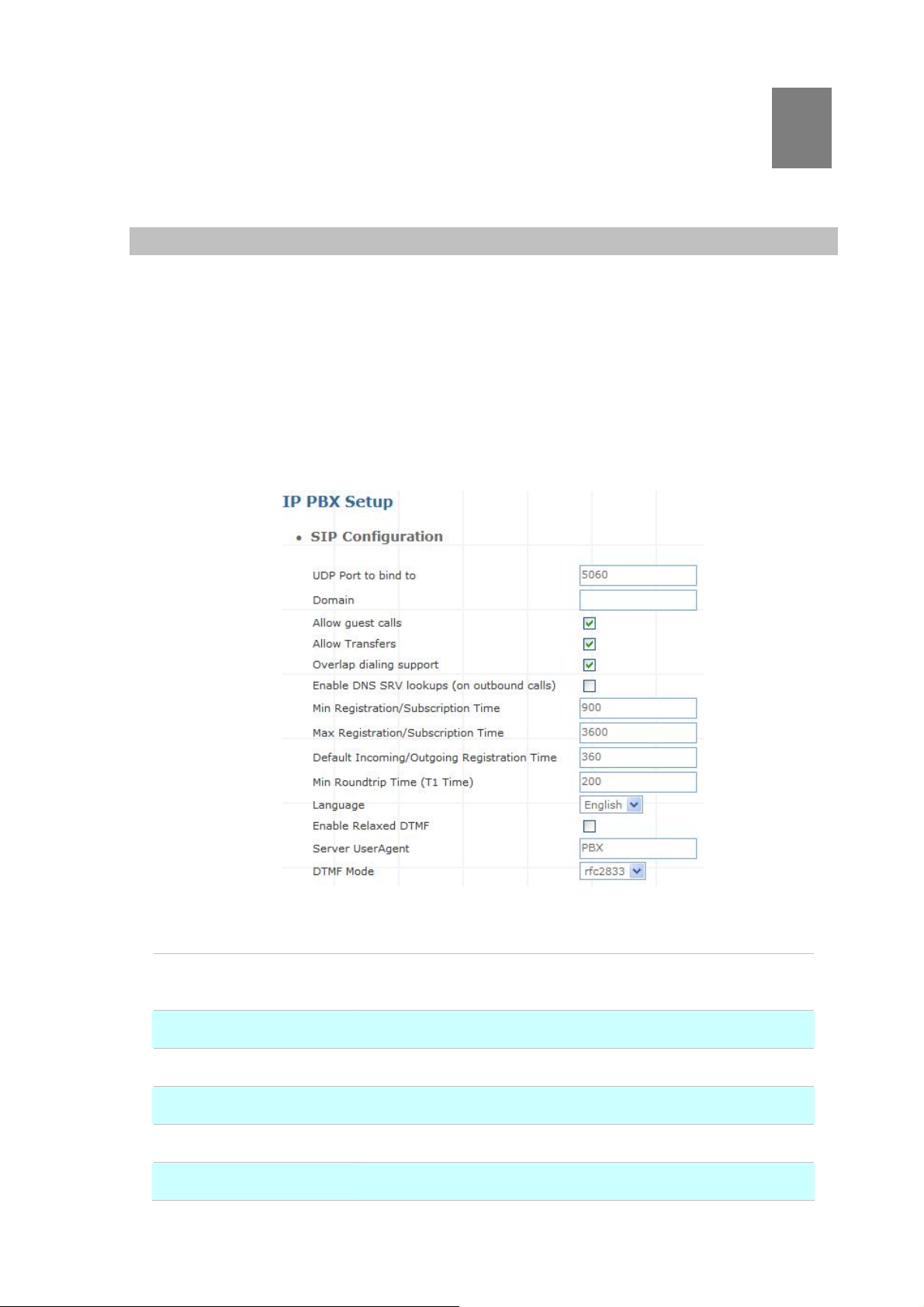
Chapter 3
3
IP PBX Setup
SIP Basic Setting
SIP (Session Initiation Protocol) is a request-response protocol, dealing with requests from clients and
responses from servers. Participants are identified by SIP URLs. Requests can be sent throu gh any
transport protocol. SIP determines the end system to be used for the session, the communication
media and media parameters, and the called party's desire to engage in the communication. Once
these are assured, SIP establishes call parameters at either end of the communication, and handles
call transfer and termination.
¾ SIP Configuration
UDP Port to bind to
Domain
Allow guest calls
Overlap dialing support
Allow Transfers
Enable DNS SRV lookups
Figure 3-1. SIP configuration settings
This is SIP Local Port 5060, if you have any specific reason for
change this port.
IP PBX Server’s IP address.
Enable/Disable guest calls. Default is Enable. Default is all IP.
Enable/Disable overlaps dialing support. Default is Enable.
Enable Call Transfers.
Enable DNS SRV lookups on calls
Page 17

(on outbound calls)
Max Registration Time
Min Registration Time
Default
Incoming/Outgoing
Registration Time
Min RoundtripTime
(T1 Time)
Language
Enable Relaxed DTMF
Server UserAgent
DTMF Mode
Maximum duration of incoming registration/subscriptions we allow.
Default 3600 seconds.
Minimum duration of registrations/subscriptions. Default 60
seconds
Default duration (in seconds) of incoming / outgoing registration.
Minimum roundtrip time for messages to monitored hosts, Defaults
to 200 ms
Set default language for all users.
Use relaxed DTMF detection. Default is Disable.
Enable you to change the trunk User agent string, Default is PBX.
Set default DTMF mode for sending DTMF. Default: rfc2833.
Table 3-1. SIP configuration description
¾ SIP Codecs
The Codec is used to compress the voice signal into data packets. Each Codec has different bandwidth
requirement. There are 7 kinds of codec. To determine the priority, selects one codec algorithm from
the pull-down menus individually.
Figure 3-2. SIP codecs settings
¾ Outbound SIP Registrations
Figure 3-3. Outbound SIP Registrations settings
17
Page 18

Register TimeOut
Register Attempts
Table 3-2. Outbound DIP registration description
Retry registration calls at every 'x' seconds (default 20).
Number of registration attempts before we give up; 0 =
continue forever.
¾ NAT Support
The externip, externhost and localnet settings are used if you use IP PBX behind a NAT device to
communicate with services on the outside.
Figure 3-4. NAT support settings
Extern IP
Extern Host
Extern Refresh
Local Network
Address
Address that we're going to put in outbound SIP messages if we're
behind a NAT.
Alternatively you can specify an external host, and IP PBX will perform
DNS queries periodically. Not recommended for production
environments! Use externip instead.
How often to refresh externhost if used. You may specify a local network
in the field below.
localnet=192.168.0.0/255.255.0.0; All RFC 1918 addresses are local
networks
localnet=11.0.0.0/255.0.0.0 ; Also RFC1918
localnet=171.16.0.0/12 ; Another RFC1918 with CIDR notation
localnet=168.254.0.0/255.255.0.0; Zero conf local network
Table 3-3. NAT support description
User Extensions Setup
¾ Extension List
18
Page 19
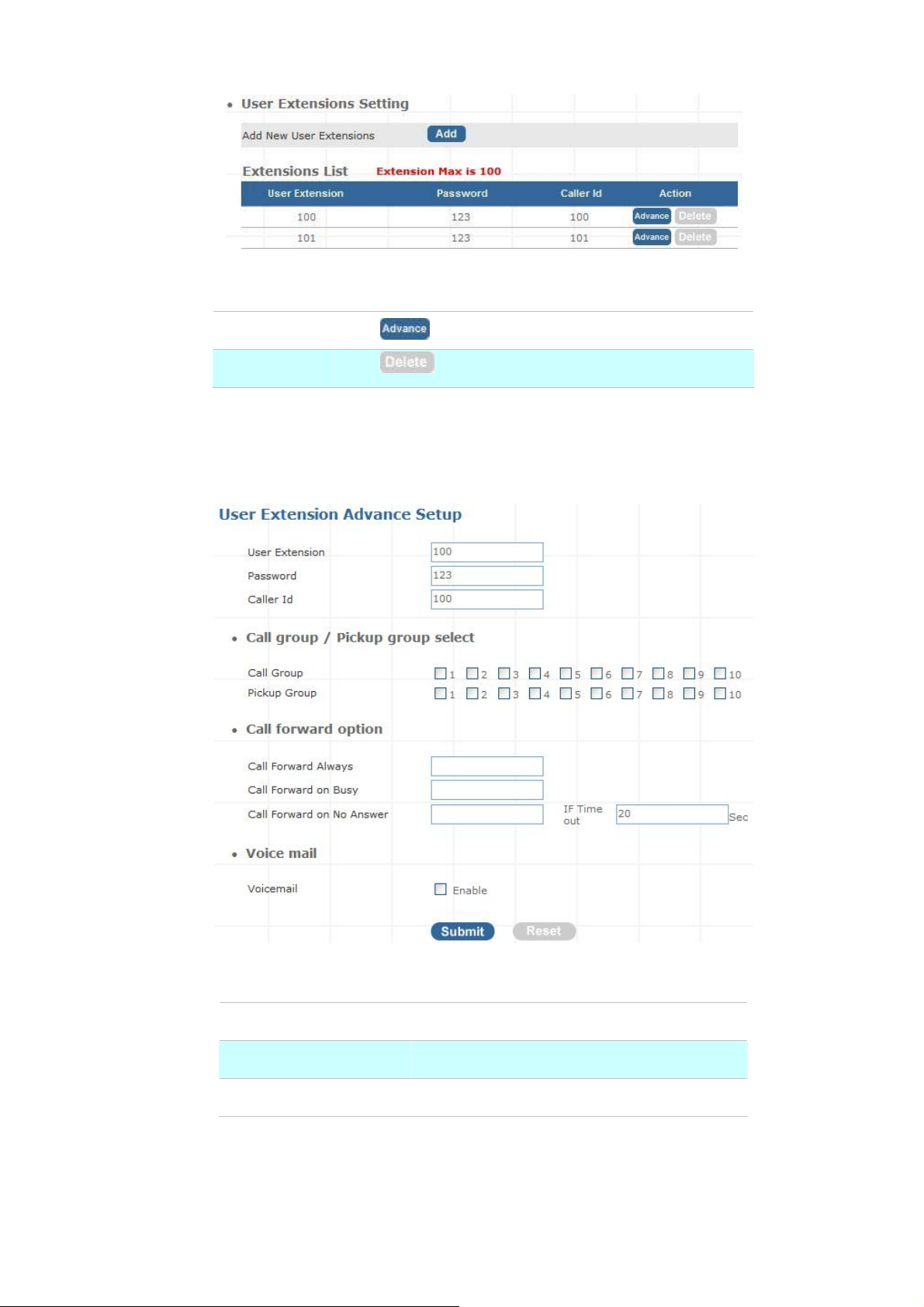
Figure 3-5. User extension settings
Advance
Delete
¾ Advance Setup
Click
Click to delete an extension.
Table 3-4. User extension description
to edit an extension other setting.
Figure 3-6. Extension advance settings
User Extension
Password
Caller Id
Table 3-5. Extension advance description
Input Extension number
Input Extension password
Input Extension caller id
19
Page 20

- Call group / Pickup group select :
Call Group
Pickup Group
- Call forward option :
Call forward always
Call forward on busy
Call forward no answer
If time out “XXX” sec
- Voice mail :
Voice mail select
Voice mail name
An Extension can set single/multiple call group(s) 1-10 id
An Extension can set single/multiple Pickup group(s) 1-10 id
Table 3-6. Call / Pickup group description
Input forward always number
Input forward on busy number
Input forward no answer number
This is the maximum number allowed no answer time out used
Table 3-7. Call forward description
Enable / Disable voice mail function
Input voice mail name
E-Mail address
Send voice to mail
Delete voice mail after send
Input E-mail address
Enable / Disable send voice to mail
Save / Delete voice mail after send
Table 3-8. Voice mail de scription
Attendant Extension
Attendant Extension in IP PBX system helps you to configure internal dial plan for extension setup. It
can allow more calls to be handled by IVR from Gateway's FXO, and FXS port. Attendant Extension
Provide 10 sets of IVR.
Figure 3-7. Attendant exten sion settings
20
Page 21
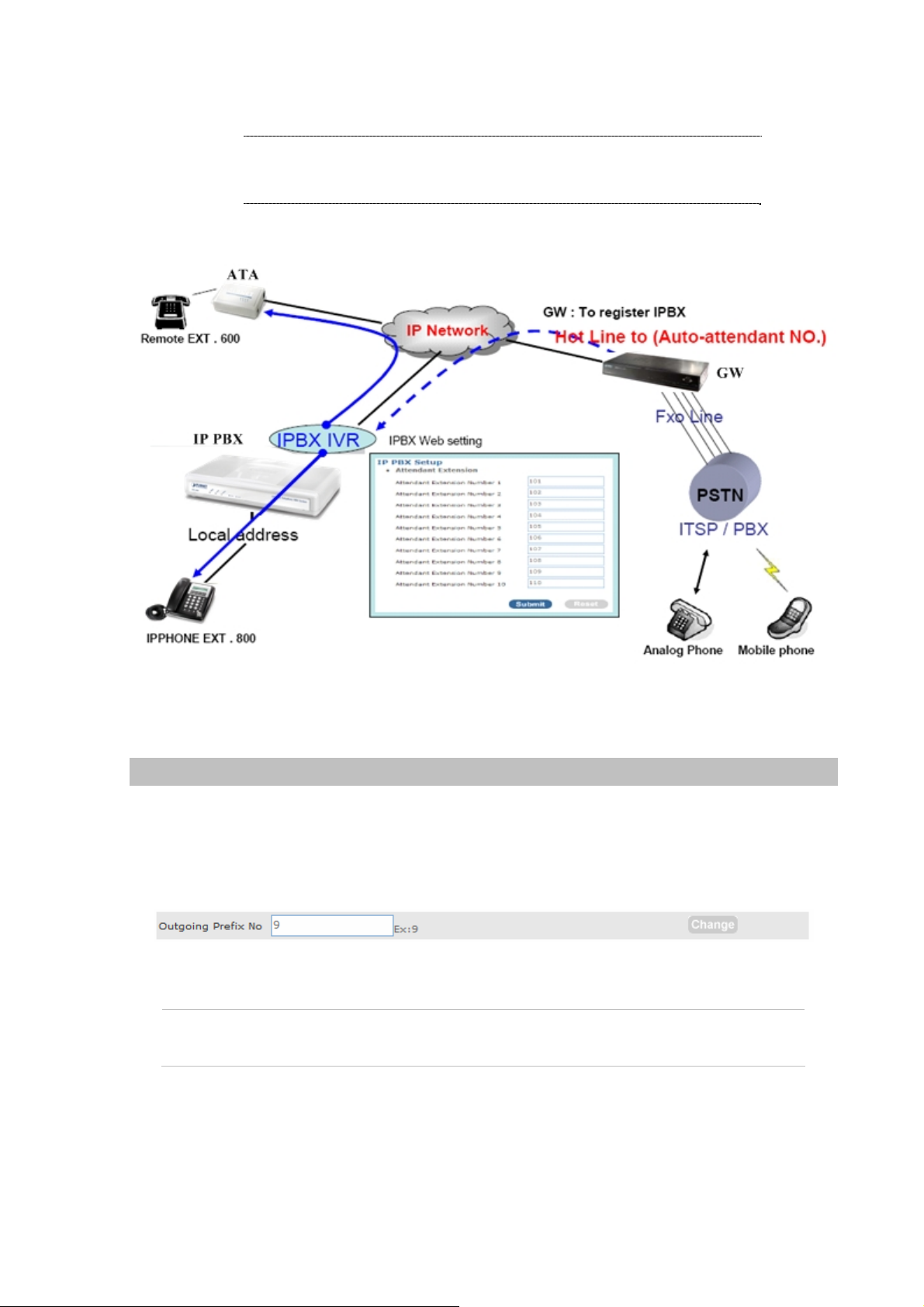
The IP PBX will handle incoming Caller ID and show to remote / local registered IP-Phone.
ÍNote
If your Gateway can bypass Mobile/Analog Phone number, The
IP PBX will handle incoming caller ID and show to remote
/ local registered IP-Phone.
¾ Sample:
Figure 3-8. Auto-attendant sample
Dialing Rules
The “Dialing Rules” need to be setup when the user uses the method of Peer-to-Peer SIP VoIP call or
SIP Proxy Server Mode.
¾ Outgoing Prefix
Figure 3-9. Outgoing prefix settings
Outgoing Prefix No
Set a prefix number for when making outgoing call via server. This
number is used set to initiate the call with the server provider.
Table 3-9. Outgoing prefix description
¾ Dialing Rules
In the “Dialing Rules” settings: Maximum Entries: 100 records
21
Page 22

Phone NO
Figure 3-10. Dialing rules settings
Phone Number. Is the leading digit of the call out diali ng number.
Phone NO Pattern: “N” single digit from 2 to 9.
“z” single digit from 1 to 9.
“X” single digit from 0 to 9.
“.” unlimited length of digit.
Delete Length
Prefix NO
Dest. IP/DNS
Port
Delete Length is the number of digits that will be stripped from
beginning of the dialed number.
Prefix NO is the digits that will be added to the beginning of the
dialed number.
Destination IP Address / Domain Name is the IP address / Domain
Name of the destination ATA (Gateway) that owns this phone
number.
Port is port of the destination Gateway / ATA use. (Default is 5060)
Table 3-10. Dialing rules description
Time Rules
Defined Service providers based on date and time voice rule.
Figure 3-11. Attendant time settings
22
Page 23

Day setting
Defined Start day / end time
Time setting
Month setting
Date setting
Defined Start time / End time
Defined Start Month / End Month
Defined Start Date / End Date
Table 3-11. Attendant time description
Record Voice Menu
Allow you to record On / Off duty voice menu over a register ip-phone.
Figure 3-12. Record voice menu settings
Pick up your register IP-Phone handset and press “function key + password “ to enter into voice menu
guide.
Record voice
Play voice
Default voice
Password
Answer Extension enable you to record the customized voice menu remotely from a registered
IP-Phone.
Answer extension
Record your voice menu , Default is *9
Play your record voice menu ,Default is *10
To set default voice menu, Default is *11
This is record / default voice password , Default is 1234
Table 3-12. Record voice menu description
Call from registered IP-Phone to record the voice menu.
Table 3-13. Answer extensi on description
23
Page 24

Call Parking
Build a calling rule for IP Phone to park the calls during the phone conversation.
Figure 3-13. Call parking settings
Extension to Dial for Parking Calls
What extension to park calls on
Number of seconds a call can be
parked for
Pickup Extension
Timeout for answer on attended
transfer
Table 3-14. Call parking description
Set an extension number to dial when need to park the
call. Default number is 700.
Set the Extension range for call parking retrieving.
(Example: '701-720').
Set allowed parking time for the parking call. Default is
30/sec.
Set up a number for IP Phone to retrieve back the call.
Default is *8.
Set a timeout value for answer the transferred call.
Default is 30 Sec.
Gereral Setting
IP Phone or sip device extension connected IP PBX, extension have call forward / transfer and pickup /
voice key …
¾ Call Forward Key
Figure 3-14. Call forward key settings
24
Page 25

Call forward always
Enable: Dial the “ *1 + number ” enable call forward always function
Disable: Dial the “ * 2” disable call forward always function
Call forward Busy
Call forward no answer
¾ Transfer Feature
Attendant Transfer
Blind Transfer
Enable: Dial the “ *3 + number ” enable call forward busy function
Disable: Dial the “ * 4 ” disable call forward busy function
Enable: Dial the “ *5 + number ” enable call forward no answer function
Disable: Dial the “ * 6 ” disable call forward no answer function
Table 3-15. Call forward description
Figure 3-15. Transfer feature settings
When you attendant transfer fail, you can definition other transfer number
Blind Transfer , When Ex: Ext 100 call Ext 200, Ext 200 blind transfer to
Ext 300 , Ignore the Ext.300 status, the Ext.200 will immediately on-hook
Transfer Digit time out
¾ Pickup Key
Pickup Extension
¾ Voice Mail
Set (Attendant/blind) transfer digit time out sec
Table 3-16. Transfe r feature description
Figure 3-16. Pickup key settings
Set call pickup (Default is *8 )
Table 3-17. Pickip description
25
Page 26

Figure 3-17. Voice mail settings
Max time of a voice mail
Max number of messages per folder
Dial voice mail number
Dial my voice mail number
Table 3-18. Voice mail description
Set a voice mail max time
Max number of voice mail per folder
Dial “ *12 “ into voice mail guide
Dial “ *13 + Ext number “ into voice mail guide
¾ SMTP Setting
SMTP is a relatively simple, text-based protocol, where one or more recipients of a message are
specified. Input the valid account number , the extension setting voice mail will be been in use d.
SMTP server IP / Address
SMTP Authentication user name
SMTP Authentication password
Figure 3-18. SMTP settings
Input server IP / Address
Input SMTP Authentication user name
Input SMTP Authentication password
Table 3-19. SMTP description
26
Page 27

Chapter 4
4
Network Setup
WAN & LAN Setup
WAN (Wide Area Network) is a network connection connecting one or more LANs together ov er some
distance. For example, the means of connecting two office buildings separated by several kilometers
would be referred to as a WAN connection. The size of a WAN and the number of distinct LANs
connected to a WAN is not limited by any definition. Therefore, the Internet may be called a WAN.
WAN Settings are settings that are used to connect to your ISP (Internet Service Provider). The WAN
settings are provided to you by your ISP and often times referred to as "public settings". Please select
the appropriate option for your specific ISP.
For most users, Internet access is the primary application. IP PBX supports the WAN interface for
internet access and remote access. The following sections will explain more details of WAN Port
Internet access and broadband access setup. When you click “WAN & LAN Setup”, the follo wing setup
page will be shown. Three methods are available for Internet Access.
Figure 4-1. Network settings
Page 28

¾ Static IP
If you are a leased line user with a fixed IP address, enter in the IP address, subnet mask, gateway
address, and DNS (domain name server) address(es) provided to you by your ISP. Each IP address
entered in the fields must be in the appropriate IP form, which are four IP octets separated by a dot
(x.x.x.x). The Router will not accept the IP address if it is not in this format. Example: 168.95.1.2
Figure 4-2. WAN-Static IP settings
IP Address
Subnet Mask
Default Gateway
Check with your ISP provider.
Check with your ISP provider.
Check with your ISP provider.
Table 4-1. WAN-Static IP description
¾ DHCP
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP), Dynamic IP (Get WAN IP Address automatically). If you
are connected to the Internet through a Cable modem line, then a dynamic IP will be assigned.
Note: WAN port gets the IP Address, Subnet Mask and default gateway IP address automatically, if
DHCP client is successful.
28
Page 29

Figure 4-3. WAN-DHCP settings
¾ PPPoE
Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet (PPPoE). Some ISPs provide DSL-based services and use
PPPoE to establish communication link with end-users. If you are connected to the Internet through a
DSL line, check with your ISP to see if they use PPPoE. If they do, you need to make sure the following
items, PPPoE User name: Enter username provided by your ISP. PPPoE Password: Enter password
provided by your ISP.
Figure 4-4. WAN-PPPoE settings
¾ Host Name
The Host Name field is optional but may be required by some Internet Service Providers. The default
host name is the model number of the device. It is a computer that is connected to a TCP/IP network,
including the Internet. Each host has a unique IP address. Assign the domain name or IP address of
your host computer. When the host operating system is set up it is given a name. This name may
reflect the prime use of the computer. For example, a host computer that converts host names to IP
addresses using DNS may be called cvs.IP-PBX.com
and a host computer that is a web server may be
29
Page 30

called www.IP-PBX.com
to the host using its IP address. The host will respond with its host name.
. When we need to find the host name from an IP address we send a request
¾ WAN Port MAC
The MAC (Media Access Control) Address field is required by some Internet Service Providers (ISP).
The default MAC address is set to the MAC address of the WAN interface in the device. It is only
necessary to fill the field if required by your ISP.
The WAN port allows your voice gateway to be connected to an Internet Access Device, e.g. router,
cable modem, ADSL modem, through a CAT.5 twisted pair Ethernet Cable. MAC addresses are
uniquely set by the network adapter manufacturer and are sometimes called "physical addresses" for
this reason. MAC assigns a unique number to each IP network adapter called the MAC address. The
MAC address is commonly written as a sequence of 12 hexadecimal digits as follows:
00:3f:4f:88:81:18. The first six hexadecimal digits of the address correspond to a manufacturer's
unique identifier, while the last six digits correspond to the device's serial number.
Some Internet service providers track the MAC address of a home router for security purposes. Many
routers support a process called cloning that allows the MAC address to be simulated so that it
matches one the service provider is expecting. This allows end-user to change their router (and their
real MAC address) without having to notify the provider. For example, you could allow packets which
have your name server's IP on them, but come from another MAC address (one way of spoofing
packets).
Figure 4-5. WAN port MAC settings
¾ MTU and MRU
MTU stands for Maximum Transmission Unit, the largest physical packet size, m easured in bytes that a
network can transmit. Any messages larger than the MTU are divided into smaller packets b efore bei ng
sent.
MRU stands for Maximum Receiving Unit. The largest physical packet size, measured in byte s that a
network can receive. Any messages larger than the MRU are divided into smaller packets before being
received.
The key is to be deciding how big your bandwidth pipe is and sele ct the best MTU for your configuration.
For example, you have a 33.6 modem, you use a MTU and MRU of 576, and if you have a larger pipe
you may want to try 1500.
30
Page 31

Figure 4-6. MTU and MRU settings
ÍNote
For Static IP, both MTU and MRU are set to 1500 bytes as default value.
For DHCP, both MTU and MRU are set to 1500 bytes as default value.
For PPPoE, both MTU and MRU are set to 1492 bytes as default value.
¾ DNS Server
DNS stands for Domain Name System. Every Internet host must have a unique IP address; also they
may have a user-friendly, easy to remember name such as www.ippbx.com
the user-friendly name into its equivalent IP address. The original DNS specifications require that each
domain name is served by at least 2 DNS servers for redundancy. When you run your DNS, web, and
mail servers all on the same MAChine - if this MAChine goes down, it doesn't really matter that the
backup DNS server still works.
The recommended practice is to configure the primary and secondary DNS servers on separate
MAChines, on separate Internet connections, and in separate geographic locations.
. The DNS server converts
Figure 4-7. DNS server settings
Primary DNS Server
Secondary DNS Server
Sets the IP address of the primary DNS server.
Sets the IP address of the secondary DNS server.
Table 4-2. DNS server description
¾ Ping From WAN
Ping is a basic Internet program that lets you verify that a particular IP address exists and can accept
requests. Ping is used diagnostically to ensure that a host computer you are trying to reach is actually
operating.
The default setting is allowed user can ping the host computer from remote site. If you disallow, the
host computer doesn’t response any user who issues Ping IP addre ss command from any remote sites.
Figure 4-8. Ping from wan settings
31
Page 32

¾ LAN Setting
A
These are the IP settings of the LAN (Local Area Network) interface for the device. These settings may
be referred to as "private settings". You may change the LAN IP address if needed. The LAN IP
address is private to your internal network and cannot be seen on the Internet. The default IP address
is 192.168.0.1 with a subnet mask of 255.255.255.0.
LAN is a network of computers or other devices that are in relatively close range of each other. For
example, devices in a home or office building would be considered part of a local area network.
Figure 4-9. LAN settings
LAN IP Address
Subnet Mask
ssign the IP address of LAN server, default is
222.222.222.1
Select a subnet mask from the pull-down menu, default is
255.255.255.0
Table 4-3. LAN description
¾ DNS Proxy
A proxy server is a computer network service that allows clients to make indirect network connections
to other network services. The default setting is Enable the DNS proxy server.
Figure 4-10. DNS proxy settings
DHCP
DHCP stands for Dynamic Host Control Protocol. The DHCP server gives out IP addresses when a
device is starting up and request an IP address to be logged on to the network. The device must be set
as a DHCP client to "Obtain the IP address automatically". By default, the DHCP Server is enabled in
the unit. The DHCP address pool contains the range of the IP address that will automatically be
assigned to the clients on the network.
DHCP client computers connected to the unit will have their information displayed in the DHCP Client
List table. The table will show the Type, Host Name, IP Address, MAC Address, Description, and
32
Page 33

Expired Time of the DHCP lease for each client computer. DHCP Server is a useful tool that automates
A
the assignment of IP addresses to numbers of computers in your network. The server maintains a pool
of IP addresses that you use to create scopes. (A DHCP scope is a collection of IP addresses and
TCP/IP configuration parameters that are available for DHCP clients to lease.) Then, the server
automatically allocates these IP addresses and related TCP/IP configuration settings to DHCP-enabled
clients in the network. The DHCP Server leases the IP addresses to clients for a period that you specify
when you create a scope. A lease becomes inactive when it expires. Through the DHCP Server, you
can reserve specific IP addresses permanently for hardware devi ces that must have a static IP addre ss
(e.g., a DNS Server).
An advantage of using DHCP is that the service assigns addresses dynamically. The DHCP Server
returns addresses that are no longer in use to the IP addresses pool so that the server can reallocate
them to other machines in the network. If you disable this DHCP, you would have to manually configure
IP for new computers, keep track of IP addresses so that you could reassign addresses that clients
aren't using, and reconfigure computers that you move from one subnet to another. The DHCP Static
MAP table lists all MAC and IP address which are active now.
Figure 4-11. DHCP server settings
When you enable the DHCP server, you are able to enter:
Assigned DHCP IP
Address
Enter the starting IP address for the DHCP server’s IP
assignment and the ending IP address for the DHCP
server’s IP assignment.
DHCP IP Lease
Time
ssign the length of time for the IP lease, default setting is
86400 seconds.
Table 4-4. DHCP server description
33
Page 34

WLAN Setting (For IPX-300W)
A WLAN is a data communication system that reduces the need for a wired connection, thereby adding
new flexibility and convenience to your network. Using electromagnetic waves, WLAN's transmits and
receives data over the air, minimizing the need for wired connections and combines data connectivity
with user mobility.
¾ AP Mode
Access Point only Mode, The AP functions as a wireless hub to which wireless clients can co nnect. The
clients must make sure that they are configured to match the AP’s wireless settings. The AP must be
connected to switch or other LAN segment patch cable.
Figure 4-12. AP mode settings
WLAN
WLAN Mode
WLAN SSID
Hide SSID
WLAN Frequency
WLAN Frequency
Auto
Enable / Disable WLAN Function
For wireless connected type 802.11 B/G mixed / 802.11b only /
802.11G only
Wireless stations associating to the access point must have the
same SSID. Enter a descriptive name for the wireless
LAN.(support 20 ACSII characters)
Hide SSID prevents outside users from joining the network without
knowing the wireless Network's ID, default is check SSID.
The range of radio frequencies used by IEEE 802.11b/g wireless
devices is called a Selection channel. Select a channel ID that is
not already in use by a neighboring device.
When the users select this option, the IP PBX automatically finds
the channel with the least interference and uses that channel for
wireless IP PBX transmission.
34
Page 35

Example:
Authentication
Select OPEN, WPA, WPA-PSK, WPA2, WPA2-PSK, WPA/WPA2
mix mode, WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK mix mode .Default is OPEN
Method
mode.
Table 4-5. AP mode description
Figure 4-13. AP mode application
¾ AP-Client Mode
In this mode the IP PBX is used to access the Wireless Service Provider network by connecting
wirelessly to the remote (Outdoor AP).
When the IPBX operate in AP-Client Mode, the WAN and LAN RJ-45 interface will be configured as a 2
port switch for connecting with 2 PCs for access wireless network
Figure 4-14. AP-client mode setting s
35
Page 36

ÍNote
When IP PBX operate in AP-Client Mode, the WAN and LAN RJ-45
interface will be configured as a 2 port switch for connecting
with 2 PCs for access wireless network
WLAN Mode
Remote AP SSID
Remote AP KEY
W-LAN Channel
W-LAN IP Assignment
Static IP
DHCP Client
For wireless connected type 802.11 B/G mixed/ 802.11b only /
802.11G only
Define the same as your Wireless Router uses.
Enter the remote AP Authorization Key (WPA-PSK / WPA2-PSK /
WPAPSK ,WPA2PSK Mix Mode to Show)
Define the same as your Wireless Router uses.
1. DHCP client
2. Static IP Address
Key in the W-LAN IP address, W-LAN Subnet mask and W-LAN
Gateway from AP of WISP
When the DHCP Client is enabled, the IP PBX will get the IP Address
from Outdoor AP of WISP.
PPPoE Client
Remote AP SSID
Authentication Method
Encryption Type
Scan usable network
Enter User Name / Password provided by your ISP, the IP PBX will
get the IP Address from Outdoor AP of WISP
Define the same as your Wireless Router uses
Define the same as your Wireless Router uses.(OPEN / SHARED
Mode)
Define the same as your Wireless Router uses. (OPEN / SHARED
Mode)
Select list to remote AP SSID (magnifying glass)
Table 4-6. AP-Clie nt mode description
36
Page 37

Figure 4-15. AP-Client mode setting s
Figure 4-16. Search remote AP list page
ÍNote
Example:
After scan and select the Outdoor AP, the channel and
encryption method should be set the identical with the remote
AP.
37
Page 38

Figure 4-17. Ap-Client mode application
¾ WISP & AP Mode
The IP PBX can operate in AP-Client and access to another (Outdoor) AP. The wireless client needs to
have the same SSID, Channel, Encryption settings as the main AP. The user may need to change the
default IP to avoid IP conflicts.
Figure 4-18. WISP & AP mode settings
38
Page 39

ÍNote
When IP PBX operates in AP-Client (or WISP & AP) Mode, the
WAN and LAN RJ-45 interface will be configured as a 2 port
switch for connecting with 2 PCs for access wireless network.
WLAN Mode
Remote AP SSID
Remote AP MAC
Remote AP Key
W-LAN Channel
W-LAN IP Assignment
Static IP
For wireless connected type 802.11 B/G mixed/ 802.11b only /
802.11G only
Define the same as your Wireless Router uses
Define the same as your Wireless Router uses
Enter the remote AP Authorization Key (WPA-PSK / WPA2-PSK /
WPAPSK ,WPA2PSK Mix Mode to Show)
Define the same as your Wireless Router uses
1.DHCP client
2.Static IP Address
Key in the W-LAN IP address, W-LAN Subnet mask and W-LAN
Gateway from WISP
DHCP Client
WLAN SSID
Hide SSID
Authentication Method
Encryption Type
When the DHCP Client is enabled, the IP PBX will get the IP Address
from Outdoor AP of WISP
The service set identifier assigned to the wireless network (WLAN).
Default SSID is IPPBX
Hide SSID prevents outside users from joining the network without
knowing the wireless Network's ID, default is check SSID
Define the same as your Wireless Router uses. (OPEN / SHARED
Mode)
Define the same as your Wireless Router uses. (OPEN / SHARED
Mode
Table 4-7. WISP & AP mode description
39
Page 40

Figure 4-19. WISP & AP mode settings
Scan usable network:Select list to remote AP SSID (magnifying glass)
Figure 4-20. Search remote AP list page
ÍNote
Example:
After scan and select the Outdoor AP, the channel and
encryption method should be identical with the remote AP
40
Page 41

Figure 4-21. WISP & AP mode application
Access Policy (For AP and WISP&AP mode)
Access Policy
Access Control List
In IP PBX security, an access control list is a list of “allow
all / Reject all" to an MAC.
MAX MAC List:64
Table 4-8. Access p olicy description
Figure 4-22. Access policy settings
41
Page 42

Figure 4-23. Access policy settings
Static Route
Static routes are special routes that the network administrator manually enters into the router
configuration for local network management. You could build an entire network based on static routes.
The problem with doing this is that when a network failure occurs, the static route will not change
without you performing the change. This could be IP-PBX if the failure occurs when the administrator is
not available.
The route table allows the user to configure and define all the static routes supported by the router.
Figure 4-24. St atic route settings
Enable
Type
Target
NetMask
Gateway
Enable/Disable the static route.
Indicates the type of route as follows, Host for local connection and
Net for network connection.
Defines the base IP address (Network Number) that will be
compared with the destination IP address (after an AND with
NetMask) to see if this is the target route.
The subnet mask that will be AND'd with the destination IP address
and then compared with the Target to see if this is the target route.
The IP address of the next hop router that will be used to route
traffic for this route. If this route is local (defines the locally
connected hosts and Type = Host) then this IP address MUST be
the IP address of the router.
Action
Insert a new Static Router entry or update a specified entry.
Table 4-9. Static route description
42
Page 43

NAT
NAT (Network Address Translation) serves three purposes:
1. Provides security by hiding internal IP addresses. Acts like firewall.
2. Enables a company to access internal IP addresses. Internal IP addresses that are only available
within the company will not conflict with public IP.
3. Allows a company to combine multiple ISDN connections into a single internet connection.
¾ NAT Setting
Figure 4-25. NAT settings
Figure 4-26. NAT settings
43
Page 44

Network Address
Translation
IPSec Pass Through
PPTP Pass Through
Enable/Disable NAT.
IPsec (Internet Protocol Security) is a framework for a set of protocols for
security at the network or packet processing layer of network
communication. Enable/Disable this framework verification.
PPTP (Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol) is a protocol that allows
corporations to extend their own corporate network through private
"tunnels" over the public Internet. Enable/Disable this protocol verification.
L2TP (The Layer 2 Tunnel Protocol) is an emerging Internet Engineering
Task Force (IETF) standard that combines the best features of two
existing tunneling protocols: Cisco's Layer 2 Forwarding (L2F) and
L2TP Pass Through
SIP ALG
DMZ
Microsoft's Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP). L2TP is an
extension to the Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP), which is an important
component for VPNs. VPNs allow users and telecommuters to connect to
their corporate intranets or extranets. Enable/Disable this function.
SIP, the Session Initiation Protocol, is a signaling protocol for Internet
conferencing, telephony, presence, events notification and instant
messaging. Enable/Disable this protocol verification.
In computer networks, a DMZ (Demilitarized Zone) is a computer host or
small network inserted as a "neutral zone" between a company's private
network and the outside public network. It prevents outside users from
getting direct access to a server that has company dIP-PBX. Think of DMZ
as the front yard of your house. It belongs to you and you may put some
things there, but you would put anything valuable inside the house where
it can be properly secured. Setting up a DMZ is very easy. If you have
multiple computer s, you can choose to simply place one of the computers
between the Internet connection and the firewall.
If you have a computer that cannot run Internet applications properly from
behind the device, then you can allow the computer to have unrestricted
DMZ IP LAN
Internet access. Enter the IP address of that computer as a DMZ host with
unrestricted Internet access. Adding a client to the DMZ may expose that
computer to a variety of security risks; so only use this option as a last
resort.
Table 4-10. NAT description
¾ Virtual Server Mapping
The device can be configured as a virtual server so that remote users accessing services such as Web
or FTP services via the public (WAN) IP address can be automatically redirected to local servers in the
44
Page 45

LAN network. Depending on the requested service (TCP/UDP port number), the device redirects the
external service request to the appropriate server within the LAN network. You will only need to input
the LAN IP address of the computer running the service and enable it.
A Virtual Server is defined as a service port, and all requests to this port will be redirected to the
computer specified by the server IP.
Figure 4-27. Virtual server mapping settings
Enable
WAN Port
Protocol
LAN IP
LAN Port
Action
¾ Port Trigger
Enable/Disable the virtual server mapping, default setting is Disable.
The port number on the WAN side that will be used to access the
virtual service. Enter the WAN Port number, e.g. enter 80 to
represent the Web (http server), or enter 25 to represent SMTP
(email server). Note: You can specify maximum 32 WAN Ports.
The protocol used for the virtual service. Select a protocol type is
TCP or UDP.
The server computer in the LAN network that will be providing the
virtual services. Enter the IP address of LAN.
The port number of the service used by the Private IP computer.
Enter the LAN port number.
Insert a new WAN port or update a specified WAN port.
Table 4-11. Virtual server mapping description
Some applications require multiple connections, such as Internet gaming, video conferencing, Internet
telephony and others. These applications have difficulties working through NAT (Network Address
Translation). If you need to run applications that require multiple connections, specify the port normally
associated with an application in the "Trigger Port" field, select the protocol type as TCP (Transmission
Control Protocol) or UDP (User DIP-PBXgram Protocol), then enter the public ports associated with the
trigger port to open them for inbound traffic.
45
Page 46

Figure 4-28. Port trigger settings
Enable
Trigger Port
Trigger Type
Public Port
Public Type
Action
Enable/Disable the port trigger, default setting is Disable.
This is the port used to trigger the application. It can be either a single
port or a range of ports.
This is the protocol used to trigger the special application.
This is the port number on the WAN side that will be used to access
the application. You may define a single port or a range of ports. You
can use a comma to add multiple ports or port ranges.
This is the protocol used for the special application.
Insert a new Port Trigger or update a specified Port Trigger.
Table 4-12. Port trigger description
Packet Filter
Controlling access to a network by analyzing the incoming packets and letting they p ass or halting them
based on the IP addresses of the source. (This function can be useful for re sidential screening as well –
for parental screening or other)
Figure 4-29. Packet filter settings
46
Page 47

¾ WAN
A
WAN
Enable/Disable
Enable
Source IP
Dest. Port
Protocol
Block
Day
Time
The WAN IP port packet filter function, control a network IP port,
default setting is Enable.
Enable/Disable the Internet to WAN IP source port rules, default
setting is Disable.
This is the filter WAN IP address. Example: 209.131.36.158
This is the port used for source IP service.
This Protocol Used for the source IP service. Select either TCP or
UDP.
Wan IP Port Block time setting. Select Always or By Schedule.
Block Day setting, select a All / Mon-Sat./ Mon-Fri./Mon./ Tues./
Wed./Thu./Fri./Sat./Sun.
Block Time setting, select time range is 00:00 to 23:59.
Table 4-13. Packet filter-WAN description
¾ LAN
LAN
Enable/Disable
Enable
Source IP
Dest. Port
Protocol
Day
Time
Internet to LAN filter function, default setting is Enable.
prohibitive rule set should only allow the necessary
Internet/DMZ services to LAN (Local Area Network) clients.
Enable/Disable the WAN IP source port rules, default setting
is Disable.
This is the filter source IP address to LAN.
This is the port used for source IP.
This Protocol Used for the WAN Filter service. Select either
TCP or UDP.
Block Day setting, select All / Mon-Sat./ Mon-Fri./Mon./
Tues./ Wed./Thu./Fri./Sat./Sun.
Block Time setting, select time range is 00:00 to 23:59
Table 4-14. Packet filter-LAN description
¾ MAC
MAC
Enable/Disable
Block
Form internet MAC filter function, default setting is Enable.
Wan IP Port Block time Setting. Select Always or By
Schedule.
47
Page 48

Day
Block Day setting, select a All / Mon-Sat./ Mon-Fri./Mon./
Tues./ Wed./Thu./Fri./Sat./Sun.
Time
Block Time setting, select time range is 00:00 to 23:59
Table 4-15. Packet filter-MAC description
URL Filter
URL filter allows you to block sites based on a black li st and white list. Sites matching the black list but
not matching the white list will be automatically blocked and closed.
Figure 4-30. URL filter settings
Enable
Enable/Disable the URL filter function, default setting is
Disable.
Enable
Client IP
URL Filter String
Enable/Disable Block URL to the Clinet IP, default setting is
Disable
This is the Clinet IP is LAN address. Example:
192.168.0.100
This is the filter URL. Example: “http://www.yahoo.com/”
Table 4-16. URL filter description
Security
Intrusion Detection has powerful management and analysis tools that let your IT administrator see
what's going on in your network. Such as whose surfing the Web, and gives you the tools to block
access to inappropriate Web sites.
Malicious code (also called vandals) is a new breed of Internet threat that cannot be efficiently
controlled by conventional antivirus software alone. In contrast to viruses th at require a user to execute
a program in order to cause damage, vandals are auto-executable applications
48
Page 49

Figure 4-31. Security settings
Intrusion Detection
Drop Malicious
Packet
Enable / Disable , network / internet security protection.
Enable / Disable , Detect and drop malicious application
layer traffic.
Table 4-17. Security description
UPnP
UPnP provides support for communication between control point s and devi ces. The network media, the
TCP/IP protocol suite and HTTP provide basic network connectivity and addressing needed. On top of
these open, standard, Internet based protocols, UPnP defines a set of HTTP servers to handle
discovery, description, control, events, and presentation.
Figure 4-32. UPnP settings
UPNP Internet Gate
Device
Enable/Disable UPNP Service to working, default
setting is Disable.
Table 4-18. UPnP description
Call Out Block List
The DDNS (Dynamic DNS) service allows you to alias a dynamic IP address to a static hostname,
allowing your computer to be more easily accessed from various locations on the Internet. Without
49
Page 50

DDNS, the users should use the WAN IP to reach internal server. It is inconvenient for the users if this
IP is dynamic. With DDNS supported, you apply a DNS name (e.g., www.IPPBX.com
) for your server
(e.g., Web server) from a DDNS server. The outside users can always acce ss the web server using the
www.IP-PBX.com regardless of the WAN IP.
When you want your internal server to be accessed by using DNS name rather than using the dynamic
IP address, you can use the DDNS service. The DDNS server allows to alias a dynamic IP address to a
static hostname.
Unlike DNS that only works with static IP addresses, DDNS works with dynamic IP addresses, such as
those assigned by an ISP or other DHCP server. DDNS is popular with home networkers, who typically
receive dynamic, frequently-changing IP addresses from their service provider.
DDNS is a method of keeping a domain name linked to a changing (dynamic) IP address. With most
Cable and DSL connections, you are assigned a dynamic IP address and that address is used only for
the duration of that specific connection. With the IP-PBX, you can setup your DDNS service and the
IP-PBX will automatically update your DDNS server every time it receives a different IP address.
Figure 4-33. DDNS settings
Enable
DDNS Server Type
Enable/Disable the DDNS service, default setting is Disable.
The IP-PBX support two types of DDNS, DynDns.org or
No-IP.com
DDNS Username
The username which you register in DynDns.org or No-IP.com
website.
The password which you register in DynDns.org or No-IP.com
DDNS Password
website.
Confirmed Password
Hostname to register
Confirm the password which you typing.
The hostname which you register in DynDns.org or No-IP.com
50
Page 51

website
Table 4-19. DDNS description
SNTP
The simple network management protocol (SNMP) forms part of the internet protocol suite as defined
by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF). SNMP is used by network management systems to
monitor network-attached devices for conditions that warrant administrative attention. It consists of a
set of standards for network management, including an Application Layer protocol, a dIP-PBXbase
schema, and a set of dIP-PBX objects.
Enable
SNMP Read Community
SNMP Write Community
SNMP Trap Host
SNMP Trap Community
.
Figure 4-34. SNMP settings
Enable/Disable the SNMP service, default setting is Disable.
(Support SNMP version 1 or SNMP version 2c).
SNMP Read Community string so that EPICenter can
retrieve information.(default :public)
Specifies the name of the SNMP write community to which
the printer device that this actual destination represents
belongs.(Default:private)
Defines an SNMP trap host to which AppCelera will send
trap messages. (Default address is empty)
The SNMP trap community name. The community name
functions as a password for sending trap notifications to the
target SNMP manager. (Default: public).
Table 4-20. SNMP description
51
Page 52

Chapter 5
A
Management
Admin Account
The administrator account can access the management interface through the web bro wser.
Figure 5-1. Management settings
5
Administrator Name
Administrator
Password
Confirm Password
Remote Administration
Http port for remote
ssign a name to represent the administrator account. Maximum 16
characters. Legal characters can be the upper letter “A” to “Z”, lower
letter “a” to “z”, digit number “0” to “9” and an underscore sign¡ ”_”.
Assign an administrator password. Maximum 16 characters and
minimum 6 characters with mix of digits and letters characters. Legal
characters can be the upper letter “A” to “Z”, lower letter “a” to “z”,
digit number “0” to “9” and an underscore sign”_”.
Enter the administrator password again. Remote Administrator
allows the device to be configured through the WAN port from the
Internet using a web browser. A username and password is still
required to access the browser-based management interface.
Enable/Disable to access from remote site. Default setting is
“Disable”.
If you allowed the access from the remote site, assign the http port
used to access the IP-PBX. Default port number is “8080”.
Internet IP address of the computer that has access to the IP-PBX.
Remote administration
only from IP
Assign the legal IP address.
Example: http://x.x.x.x:8080 where as x.x.x.x is the WAN IP
address and 8080 is the port used for the Web-Management
interface.
Table 5-1. Management description
Page 53

z The administrator name and password are case-sensitive
ÍNote
and the “blank” character is an illegal character
z Only the administrator account has the ability to
change account password.
Date & Time
¾ Manual Time Setting
Manual Time Setting
¾ NTP Time Server
Figure 5-2. Date/Time-Manual time settings
Set up the time manually.
Table 5-2. Date/Time-Manual time description
Figure 5-3. Date/Time-NTP time settings
53
Page 54

NTP Time Server
Protocol used to help match your system clock with an accurate
time source. For example atomic clock or a server.
Time Zone
Daylight Saving
NTP Update Interval
NTP Server 1
NTP Server 2
Choose your time zone, Default is (GMT+8:00) Beijing,
Singapore, Taipei.
Enable / Disable. Default is Disabling, time during which clocks
are set one hour ahead of local standard time; widely adopted
during summer to provide extra daylight in the evenings.
Default is 24 hours; This is used to select the frequency of. NTP
updates.
Default is “pool.ntp.org”, NTP Server address.
Default is empty.
Table 5-3. Date/Time-NTP time descri ption
Ping Test
This useful diagnostic utility can be used to check if a computer is on the Internet. It send s ping packet s
and listens for replies from the specific host. Enter in a host name or the IP address that you want to
ping (Packet Internet Groper) and click Ping. Example: www.yahoo.com or 209.131.36.158
Figure 5-4. Ping test settings
Ping Destination
Assign a legal IP address.
Table 5-4. Ping test description
Save & Restore
All settings can be saving to a local file. Pervious device configuration can also be restored by upload a
local file back to the device.
Figure 5-5. Save/Restore settings
54
Page 55

Factory Default
This function is used to restore all the parameters back to factory default setting. You can use the
Save/Restore Setting to check the factory default configuration, after you click on the Set button.
Figure 5-6. Factory default settings
Admin Account
Y ou can upgrade the firmware of the device usin g this tool. Make sure that the firmware you want to use
is saved on the local hard drive of your computer. Click o n Bro wse to search the local ha rd driv e for the
firmware to be used for the update. Upgrading the firmware will not change any of your system settings
but it is recommended that you save your system settings before doing a firmware upgra de.
Figure 5-7. Firmware update settings
Firmware Name
Select that you want to upgrade Firmware version.
Table 5-5. Firmware update description
55
Page 56

Appendix A
How to use Call Parking function
The followings are the Call Park function settings, and all of VoIP devices (ATA, GW and IP Phone)
were registered with Wi-Fi IP PBX.
¾ Extension to Dial for Parking Calls: 700
¾ Extensions to park calls on :701-720
Figure A-1. Call Parking sample scenario
1. Ext.100 and Ext.300 are talking.
2. Ext.300 press Transfer button and dial “700#” to carry out the Call Parking function, and the voice
guide will tell Ext.300 a retrieve number (ex:701) to set parking call (At this moment, the remote
extension will hear the holding music.)
3. Ext.200 dial retrieve number (ex:701) to pick up call.
4. Ext.100 are talking with Ext.200
56
Page 57

Appendix B
How to use Call Pick-up function
The followings are the Call Pickup function settings, and all of VoIP devices (ATA, GW and IP Phone)
were registered with IP PBX.
¾ Pickup Extension: *8
Figure B-1. Call Pickup sample scenario
1. Ext.300 call to Ext.100, and Ext.100 is ringing.
2. Ext.200 dial “*8#” to pickup the call for Ext.100, and Ext.200 is talking with Ext.300.
Page 58

Appendix C
Record Voice Guide Process
IPX-300W provides Record Voice Menu by Phone function. Please register your VoIP devices to
Wi-Fi IP PBX at first, and then check the Record voice code from “IP PBX Setup -> record Voice
Menu” page.
Figure C-1. Record voice menu settings
VoIP devices dial
record the Voice Menu.
*9 to entry the Record Voice Menu, then refer to the following record processes to
Figure C-2. Voice record processe s
Page 59

Appendix D
Voice Communication Samples
The chapter shows you the concept and command to help you configure your IP PBX System through
sample configuration. And provide several ways to make calls to desired destination in IP PBX. In this
section, we’ll lead you step by step to establish your first voice communication via web browsers
operations.
IP Phone and Wi-Fi Phone register to IPX-300W
In the following samples, we’ll introduce IP Phone and Wi-Fi Phone register to IP PBX applications.
Figure D-1. Topology of instruction example
¾ Machine Configuration:
STEP 1:
Please log in IP PBX via web browser and browse to “Network Setup -> WLAN Setting”
configuration menu. Enable the WLAN and setup the related configuration. The sample configuration
screen is shown below:
Page 60

Figure D-2. WLAN Setting of IPX-300W
STEP 2:
Browse to “IP PBX Setup Æ User Extensions Setup” configuration menu.
Figure D-3. User extension setting of IP PBX
STEP 3:
Click the “Add” button to create extension account ext.100 and ext.101.
60
Page 61

Figure D-4. Add extension setting of IP PBX
STEP 4:
Please log in VIP-154T and browser to “SIP setting Æ Domain Service” configuration menu.
Insert the account/password information then save and reboot machine. The sample co nfiguration
screen is shown below:
Data match with Figure D-3.
IP PBX’s extension settings
The IP address
of IP PBX
Figure D-5. Web page of VIP-154T
STEP 5:
Please take VIP-192 and setup the wireless network to connect with IP PBX (IPX-300W) by
keypad menu method. Then log in VIP-192 via web browser and b rowser to “SIP Settings”
configuration menu. Insert the Register and Outbound Proxy IP Address information.
61
Page 62

The IP address
of IP PBX
Figure D-6. SIP settings of VIP-192
Then browse to “SIP Account Settings” configuration menu and fill in the account/password
information. The sample configuration screen is shown below:
Data match with Figure D-3. IP
PBX’s extension settings
Figure D-7. SIP account settings of VIP-192
STEP 6:
After both of devices have registered to IP PBX successfully, it could browse to “Information ->
PBX Extension Status” page to show the registration status:
Figure D-8. Extension status
¾ Test the Scenario:
1. VIP-154T pick up the telephone
2. Dial the number: 100 (VIP-192) shall be able to connect to the VIP-192
3. Then the VIP-192 should ring. Please repeat the same dialing steps on VIP-192 to
establish the first voice communication from VIP-154T
62
Page 63

IP Phone and Wi-Fi Phone make off-Net calls via Gateway
In the following samples, we’ll introduce VIP-154T and VIP-192 makes off-Net Calls (PSTN calls) via
VIP-480FO applications.
Figure D-9. Installation example with VIP-480FO
¾ Machine Configuration:
STEP 1:
Please refer to the first sample and let VIP-154T and VIP-192 register to IP PBX.
STEP 2:
Please log in IP PBX via web browser and browse to “IP PBX Setup Æ User Extensions Setup”
configuration menu to add four accounts for VIP-480FO using.
Figure D-10. Add accounts for VIP-480FO
63
Page 64

STEP 3:
Browse to “IP PBX Setup Æ Attendant Extension” configuration menu. Assign an attendant
number which inexistence extension in Extension List and the sample configuration screen is shown
below:
Figure D-11. Assign an attendant number
Pressing the “Submit” button for activate the configuration.
STEP 4:
Browse to “IP PBX Setup Æ Dialing Rules” configuration menu. Add a dialing rule for
off-Net calls via VIP-480FO, and press the “Insert” button for activate the configuration.
Figure D-12. Add dialing rule for grab the FXO ports of VIP-480FO
making
STEP 5:
Please log in VIP-480FO via web browser and browse to “Advance Setup Æ VoIP Setup Æ VoIP
Basic” configuration menu. Insert the account/password information and set up the hunting function.
The sample configuration screen is shown below:
64
Page 65

Figure D-13. Set up the number of FXO ports of VIP-480FO
Figure D-14. Set up the Hunting Member of FXO ports
Figure D-15. Set up the Proxy Server IP address for register to IPX-300W
STEP 6:
Browse to “Dialing Plan” configuration menu. Add an Incoming Dial Plan (no.0) for redirect the
PSTN outgoing calls to FXO ports.
Figure D-16. Add an incoming dial plan
65
Page 66

STEP 7:
Browse to “Port Status” configuration menu. Fill in the auto attendant number 555 to all of ports.
( Where 555 is the auto-attendant number of IP PBX )
Figure D-17. Hot Line to auto-attendant of IPX-300W
STEP 8:
After all of devices have registered to IP PBX successfully, the Extension Status page will show
the registration status:
Figure D-18. Extension status page with Phone and Gateway registered
¾ Test the Scenario:
1. VIP-154T pick up the telephone
2. Dial the number: 0 shall be able to connect to the port 1 of VIP-480FO
3. Then the telephone will hear the dial tone from PSTN lines, and dial the number: 12345678
shall be able connect to the User A.
4. Then the telephone of User A will ringing, User A can pick up the handset and talk with
VIP-154T.
5. Both VIP-154T and User A hang up the calls.
6. User A pick up the telephone and dial the number: 23456789 should be able to connect to the
Auto Attendant System of IP PBX.
7. The User A will hear the prompts, and dial the extension number: 100 shall be able connect to
the VIP-192.
8. Then the VIP-192 should will ringing, and it to pick up the call then talk with User A.
66
Page 67

IPX-300 Series Specifications
Appendix E
Product
Model
Hardware
WLAN Standards
Wireless Frequency
Range
Security
Operating Frequencies
/ Channel
Data Rate
Internet Telephony PBX System Wi-Fi Internet Telephony PBX System
IPX-300 IPX-300W
- IEEE 802.11 b/g
- 2.4GHz ~ 2.4835 GHz
64/128 bit WEP data encryption, WPA,
-
-
-
WPA-PSK, WPA2, WPA2-PSK, WPA /
WPA2 mix mode, WPAPSK / WPA2PSK
mix mode
USA / Canada: 2.412 GHz - 2.426 GHz
(11 channels)
Europe: 2.412 GHz - 2.472 GHz (13
channels)
Japan: 2.412 GHz - 2.477 GHz (14
channels)
802.11b: CCK (11Mbps,5.5Mbps),
DQPSK (2Mbps), DBPSK (1Mbps)
802.11g: OFDM (54Mbps, 48Mbps,
36Mbps, 24Mbps, 18Mbps, 12Mbps,
9Mbps, 6Mbps)
Wireless Signal Range*
LAN 1 RJ-45 (10/100Base-TX, Auto-Sensing/Switching)
WAN 1 RJ-45 (10/100Base-TX, Auto-Sensing/Switching)
Standards and Protocol
Call control
Registration
Calls
Voice CODEC Support
Voice Processing
PBX features
SIP 2.0 (RFC3261) , SDP (RFC 2327), Symmetric RTP
Max. 100 nodes / SIP IP phones/ ATA / FXO gateways
Max. 30 concurrent calls
G.723, G.726, G.729, G.711, GSM, iLBC
DTMF detection and generation
In-Band and Out-of-Band (RFC 2833), (SIP INFO)
Supports password authentication using MD5 digest
Auto Attendant (AA)
Interactive Voice Respon se (IVR)
Records IVR via IP Phone
Voicemail Su pport (VM)
Voicemail Send to E-mail
Call Detailed Record (CDR)
-
Indoors: Up to 230 ft (70 meters)
Outdoors: Up to 1050 ft (320 meters)
User Management via Web Browsers
Web Firmware Upgrade
67
Page 68

Backup and Restore Configuration file
Call/Pickup Group
Displays 100 Registered User’s Status: Unregistered / Regi stered / On-Call
Displays 20 Registered Trunk’s Status: Unregistered / Registered
Fax Support using G.711 Pass-Through or T.38**
Caller ID
Call Group
Call Hold
Call Waiting
Call Transfer
Call features
Call Forward (Always, Busy, No Answer)
Call Pickup
Call Park
Call Resume
Music on Hold
Three-way conference with feature phones (VIP-154T series, VIP-155PT/
350PT/ 550PT and ATA se ries: VIP-156/ 157/ 158 / 161W)
Internet Sharing
Protocol TCP/IP, UDP/RTP/RTCP, HTTP, ICMP, ARP, NAT, DHCP, PPPoE, DNS
Advanced Function
NAT/Bridge mode, DHCP server, Static Route, DMZ, Virtual Server, Port
Trigger, Packet / URL Filter, UPnP, DDNS, SNMP, Ping test
Network and Configuration
Connection Type
Management
Static IP, PPPoE, DHCP
HTTP Web Browser
System: 1, PWR
System: 1, PWR
WAN: 1, LNK/ACT
LED Indications
WAN: 1, LNK/ACT
LAN: 1, LNK/ACT
LAN: 1, LNK/ACT
WLAN: 1, LNK/ACT
Environment
Dimension (W x D x H)
180 x 110 x 25 mm
Operating Temperature
Power Requirement
EMC/EMI
Remark
0~40 degree C, 0~90% humidity
12V DC
CE, FCC Class B
* Signal Range depends on the used antenna
**T.38 support is dependent on fax machine, SIP provider and network /
transport resilience
68
 Loading...
Loading...