Page 1

Internet Telephony PBX System
IPX-2000
User’s Manual
Page 2

Copyright
Copyright (C) 2008 PLANET Technology Corp. All rights reserved.
The products and programs described in this User’s Manual are licensed products of PLANET
Technology, This User’s Manual contains proprietary information protected by copyright, and this
User’s Manual and all accompanying hardware, software, and documentation are copyrighted.
No part of this User’s Manual may be copied, photocopied, reproduced, translated, or reduced to any
electronic medium or machine-readable form by any means by electronic or mech anical. Including
photocopying, recording, or information storage and retrieval systems, for any purpose other than the
purchaser's personal use, and without the prior express written permission of PLANET Technology.
Disclaimer
PLANET Technology does not warrant that the hardware will work properly in all environments and
applications, and makes no warranty and representation, either implied or expressed, with respect to
the quality, performance, merchantability, or fitness for a particular purpose.
PLANET has made every effort to ensure that this User’s Manual is accurate; PLANET disclaims
liability for any inaccuracies or omissions that may have occurred.
Information in this User’s Manual is subject to change without notice and does not represent a
commitment on the part of PLANET. PLANET assumes no responsibility for any inaccuracies that may
be contained in this User’s Manual. PLANET makes no commitmen t to update or keep current the
information in this User’s Manual, and reserves the right to make improvements to this User’s Manual
and/or to the products described in this User’s Manual, at any time without notice.
If you find information in this manual that is incorrect, misleading, or incomplete, we would appreciate
your comments and suggestions.
CE Declaration of conformity
This equipment complies with the requirements relating to electromagnetic compatibility, EN 55022
class A for ITE and EN 50082-1. This meets the essential protection requirements of the European
Council Directive 89/336/EEC on the approximation of the laws of the Member States relating to
electromagnetic compatibility.
The is a class B device, In a domestic environment, this product may cause radi o interference, in which
case the user may be required to take adequate measures.
ii
Page 3

FCC Notice
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A digital device,
pursuant to Part 15 of FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against
harmful interference when the equipment is operated in a commercial environment. This equipment
generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed in accordance with the
instruction manual, may cause harmful interference to radio communication. Operation of this
equipment in a residential area is likely to cause harmful interference in which case the user will be
required to correct the interference at the user’s own expense.
WEEE Warning
To avoid the potential effects on the environment and human health as a result of the
presence of hazardous substances in electri cal and el ectronic equipment, end users of
electrical and electronic equipment should understand the meaning of the cro s sed-out
wheeled bin symbol. Do not dispose of WEEE as unsorted municipal waste and have to
collect such WEEE separately .
Trademarks
The PLANET logo is a trademark of PLANET Technology. This documentation may refer to numerous
hardware and software products by their trade names. In most, if not all cases, their respective
companies claim these designations as trademarks or registered trademarks.
Revision
PLAENT IP PBX User’s Manual
Revision: 1.0 (June. 2008)
iii
Page 4

TABLE OF CONTENTS
Introduction.......................................................................................................................................1
1
1.1 Overview.......................................................................................................................1
1.2 Physical Interfaces........................................................................................................1
2 Managing with Web Interface...........................................................................................................3
3 Wizard Configuration........................................................................................................................4
3.1 Add Account Wizard......................................................................................................4
Step 1: Add User Group............................................................................................................4
Setp 2: Add User.......................................................................................................................6
Step 3: Choose Device.............................................................................................................6
Step 4: Add Device ...................................................................................................................7
Setp 5: Add Extension..............................................................................................................7
3.1.5.1 Add Extension of IP Phone..........................................................................7
3.1.5.2 Add Analog Phone.....................................................................................10
3.2 Add Route & Trunk......................................................................................................11
Step 1: Add Route...................................................................................................................11
Setp 2: Add Route Group.......................................................................................................12
Setp 3: Choose Trun k.............................................................................................................13
Setp 4: Add Trunk...................................................................................................................13
3.2.4.1 Add SIP Trunks..........................................................................................13
3.2.4.2 Add Analog PSTN Trunks..........................................................................16
3.2.4.3 Add ISDN PSTN Trunks............................................................................18
Setp 5: Assign Trunk...............................................................................................................20
3.3 Mass Extension Adding...............................................................................................21
Step 1: Add User & Extension ................................................................................................21
4 System Configuration.....................................................................................................................22
4.1 PBX System................................................................................................................22
4.2 Time Setup..................................................................................................................22
4.2.1 System Time Zone .............................................................................................22
4.2.2 Real Time Clock (RTC) Setup............................................................................22
4.3 On-board WAN Setup.................................................................................................22
4.3.1 Static IP..............................................................................................................23
4.3.2 DHCP .................................................................................................................23
iv
Page 5

4.3.3 PPPoE................................................................................................................23
4.3.4 Allow WAN to Respond PING............................................................................23
4.3.5 LAN Only............................................................................................................23
4.3.6 MAC Clone.........................................................................................................24
4.4 On-board LAN Setup...................................................................................................24
4.5 LAN Routing................................................................................................................24
4.5.1 Add a Route .......................................................................................................24
4.5.2 Edit a Route........................................................................................................25
4.5.3 Delete a Route ...................................................................................................25
4.6 Dynamic DNS Setup...................................................................................................25
4.6.1 Enable Dynamic DNS.........................................................................................25
4.6.2 Disable Dynamic DNS........................................................................................25
4.7 QoS Setup...................................................................................................................26
4.7.1 Enable QoS........................................................................................................26
4.7.2 Disable QoS.......................................................................................................26
4.8 Virtual Server ..............................................................................................................26
4.8.1 Add a Service.....................................................................................................27
4.8.2 Edit a Service .....................................................................................................27
4.8.3 Delete a Service.................................................................................................27
4.9 Maintenance................................................................................................................27
4.9.1 Storage Backup..................................................................................................27
4.9.1.1 Back up to USB Mass Storage..................................................................28
4.9.1.2 Back up to NFS Server..............................................................................28
4.9.2 SIP UA................................................................................................................28
4.9.3 CDR Log.............................................................................................................29
4.9.4 System Events....................................................................................................29
4.9.5 Active Calls.........................................................................................................29
4.10 Firmware Upgrade ......................................................................................................30
4.11 Stackable Management...............................................................................................30
4.11.1 Operation Modes................................................................................................30
4.11.2 Consolidated Manageme nt................................................................................30
4.11.3 Configuration Procedure ....................................................................................31
4.11.3.1 Case I: Stack multiple IP PBX boxes from scratch....................................31
v
Page 6

4.11.3.2 Case II: Stack a new IP PBX box with an existing running box.................32
4.11.3.3 Case III: Add new slave boxes to an existing stack...................................32
4.11.3.4 Remove slave boxes from stack................................................................32
4.12 Shutdown....................................................................................................................33
4.13 Logout.........................................................................................................................33
5 Service Configuration.....................................................................................................................34
5.1 NTP Service................................................................................................................34
5.1.1 Enable NTP Service...........................................................................................34
5.1.2 Disable NTP Service..........................................................................................34
5.2 SNMP Service.............................................................................................................34
5.2.1 Enable SNMP Service........................................................................................34
5.2.2 Disable SNMP Service.......................................................................................34
5.3 STUN Service .............................................................................................................35
5.3.1 Enable STUN Service ........................................................................................35
5.3.2 Disable STUN Service........................................................................................35
5.4 TFTP Service..............................................................................................................35
5.4.1 Enable TFTP Service .........................................................................................35
5.4.1.1 Change Directory.......................................................................................35
5.4.1.2 Add a Folder..............................................................................................36
5.4.1.3 Delete a Folder..........................................................................................36
5.4.1.4 Download a File.........................................................................................36
5.4.1.5 Delete a File...............................................................................................36
5.4.1.6 Upload a File..............................................................................................36
5.4.2 Disable TFTP Service.........................................................................................36
5.5 DHCP Service.............................................................................................................37
5.5.1 DHCP Service....................................................................................................37
5.5.1.1 Enable DHCP Service ...............................................................................37
5.5.1.2 Disable DHCP Service...............................................................................37
5.5.2 Add New.............................................................................................................37
5.5.2.1 Add DHCP Range......................................................................................37
5.5.2.2 Edit DHCP Range......................................................................................37
5.5.2.3 Delete DHCP Range..................................................................................38
5.5.3 Show Leased Clients..........................................................................................38
vi
Page 7

5.6 IP PBX Service............................................................................................................38
5.6.1 Operations..........................................................................................................38
5.6.1.1 Reload IP PBX Configuration....................................................................38
5.6.1.2 Backup IP PBX Configuration....................................................................38
5.6.1.3 Restore IP PBX Configuration...................................................................38
5.6.1.4 Restart IP PBX Configuration....................................................................39
5.6.1.5 Revert IP PBX Configuration.....................................................................39
5.6.2 Settings...............................................................................................................39
6 IP PBX Configuration......................................................................................................................41
6.1 User Group Configuration...........................................................................................41
6.1.1 Add a User Group ..............................................................................................41
6.1.2 Edit a User Group...............................................................................................41
6.1.3 Delete a User Group ..........................................................................................41
6.1.4 Search a User Group .........................................................................................42
6.2 User Configuration......................................................................................................43
6.2.1 Add a User..........................................................................................................43
6.2.2 Edit a User..........................................................................................................44
6.2.3 Clone a User ......................................................................................................44
6.2.4 Delete a User .....................................................................................................44
6.2.5 Search a User ....................................................................................................44
6.3 Device Configuration...................................................................................................45
6.3.1 IP Phone.............................................................................................................45
6.3.1.1 Add a Device .............................................................................................45
6.3.1.2 Edit a Device..............................................................................................45
6.3.1.3 Delete a Device .........................................................................................46
6.3.1.4 Search a Device ........................................................................................46
6.3.2 Extension of IP Phone........................................................................................47
6.3.2.1 Add an Extension.......................................................................................47
6.3.2.2 Edit an Extension.......................................................................................48
6.3.2.3 Clone an Extension....................................................................................48
6.3.2.4 Delete an Extension...................................................................................48
6.3.2.5 Search an Extension..................................................................................48
6.3.3 Analog Phone.....................................................................................................51
vii
Page 8

6.3.3.1 Add an Analog Phone................................................................................52
6.3.3.2 Edit an Analog Phone................................................................................52
6.3.3.3 Delete an Analog Phon e............................................................................52
6.3.4 IP Phone Firmware.............................................................................................54
6.3.4.1 Add IP Phone Firmware.............................................................................54
6.3.4.2 Delete IP Phone Firmware.........................................................................55
6.4 Route Configuration....................................................................................................55
6.4.1 Add a Route .......................................................................................................56
6.4.2 Edit a Route........................................................................................................56
6.4.3 Delete a Route ...................................................................................................56
6.4.4 Search a Route ..................................................................................................56
6.5 Route Group Configuration.........................................................................................57
6.5.1 Add a Route Group ............................................................................................57
6.5.2 Edit a Route Group.............................................................................................57
6.5.3 Delete a Route Group ........................................................................................58
6.5.4 Search a Route Group .......................................................................................58
6.6 SIP Trunk Configuration..............................................................................................58
6.6.1 Add a SIP Trunk .................................................................................................59
6.6.2 Edit a SIP Trunk..................................................................................................59
6.6.3 Clone a SIP Trunk..............................................................................................59
6.6.4 Delete a SIP Trunk .............................................................................................59
6.6.5 Search a SIP Trunk............................................................................................59
6.7 Analog PSTN Trunk configuration...............................................................................63
6.7.1 Add an Analog PSTN Trunk...............................................................................63
6.7.2 Edit an Analog PSTN Trunk................................................................................64
6.7.3 Delete an Analog PSTN Trunk...........................................................................64
6.8 ISDN PSTN Trunk Configuration ................................................................................66
6.8.1 Add an ISDN PSTN Trunk..................................................................................66
6.8.2 Edit an ISDN PSTN Trunk..................................................................................67
6.8.3 Delete an ISDN PSTN Tru nk..............................................................................68
6.9 POTS Setting..............................................................................................................70
6.9.1 FXO Port Configuration Settings........................................................................71
6.9.2 FXS Port Configuration Settings........................................................................72
viii
Page 9

6.9.3 ISDN Port Configuration Settings.......................................................................73
6.10 Digitmap Configuration ...............................................................................................73
6.10.1 Add a Digitmap...................................................................................................73
6.10.2 Edit a Digitmap...................................................................................................74
6.10.3 Delete a Digitmap...............................................................................................74
7 Feature Configuration.....................................................................................................................75
7.1 Call Park......................................................................................................................75
7.2 Life Line.......................................................................................................................75
7.2.1 Add a Life Line Pattern.......................................................................................76
7.2.2 Edit a Life Line Pattern.......................................................................................76
7.2.3 Delete a Life Line Pattern...................................................................................76
7.3 Meet-me Conference..................................................................................................76
7.3.1 Add a Meet-me Conference...............................................................................77
7.3.2 Edit a Meet-me Conference ...............................................................................77
7.3.3 Delete a Meet-me Conference...........................................................................77
7.4 Music On Hold.............................................................................................................78
7.4.1 Music on Hold Management...............................................................................78
7.4.1.1 Add a MOH File.........................................................................................78
7.4.2 Media File Management.....................................................................................78
7.4.2.1 Edit a MOH File .........................................................................................78
7.4.3 MOH ID List........................................................................................................78
7.4.3.1 Edit a MOH ID............................................................................................78
7.4.3.2 Delete a MOH File.....................................................................................78
7.5 Voicemail.....................................................................................................................79
7.6 Meet-me Prompts........................................................................................................80
7.7 Voicemail Prompts ......................................................................................................81
7.8 Broadcast....................................................................................................................82
7.8.1 Add a Broadcast.................................................................................................82
7.8.2 Edit a Broadcast.................................................................................................82
7.8.3 Delete a Broadcast.............................................................................................82
7.9 Worktime.....................................................................................................................83
7.9.1 Add a Worktime..................................................................................................83
7.9.2 Edit a Worktime..................................................................................................84
ix
Page 10

7.9.3 Delete a Worktime..............................................................................................84
7.10 Memo Call...................................................................................................................84
7.10.1 Add a Memo Call................................................................................................85
7.10.2 Edit a Memo Call................................................................................................85
7.10.3 Delete Memo Call...............................................................................................85
7.11 Automatic Call Distribution..........................................................................................86
7.11.1 Set Agent Login and Logout...............................................................................86
7.11.2 Add an Agent......................................................................................................86
7.11.3 Edit an Agent......................................................................................................86
7.11.4 Delete an Agent..................................................................................................87
7.11.5 Add a Queue......................................................................................................87
7.11.6 Edit a Queue ......................................................................................................87
7.11.7 Delete a Queue..................................................................................................87
7.12 Interactive Voice Response (IVR)...............................................................................88
7.12.1 Add a new IVR Menu .........................................................................................89
7.12.2 Edit an IVR Menu...............................................................................................89
7.12.3 Clone an IVR Menu............................................................................................89
7.12.4 Delete an IVR Menu...........................................................................................90
7.12.5 IVR Prompts Management.................................................................................92
7.12.5.1 Add an IVR Prompt...........................................................................92
7.12.5.2 Delete an IVR Prompt.......................................................................92
7.12.6 IVR Parameters..................................................................................................93
7.12.7 Auto Attendant Prompts .....................................................................................93
8 Example Provisioning.....................................................................................................................94
8.1 Internal Extension Configuration.................................................................................94
8.2 Case I: Singe-site Configuration.................................................................................94
8.3 Case II: Two-site configuration....................................................................................96
9 Appendix.........................................................................................................................................99
9.1 Keypad Default Settings for IP PBX............................................................................99
9.2 Managing with CLI Commands...................................................................................99
9.2.1 Introduction.........................................................................................................99
9.2.2 Console Interface...............................................................................................99
9.2.2.1 Connection...............................................................................................100
x
Page 11

9.2.2.2 Login........................................................................................................100
9.2.2.3 Basic Commands.....................................................................................100
CLI Command:....................................................................................................................................100
CLI Command:....................................................................................................................................100
CLI Command:....................................................................................................................................101
CLI Command:....................................................................................................................................101
9.2.2.4 Admin Commands...................................................................................101
CLI Command:....................................................................................................................................101
CLI Command:....................................................................................................................................101
9.2.2.5 PBX Commands......................................................................................102
Import CLI Command:.........................................................................................................................103
Export CLI Command:.........................................................................................................................103
9.3 IP PBX Voicemail System Menu Tree.......................................................................106
xi
Page 12
1 Introduction
1.1 Overview
PLANET IPX-2000 series IP PBX system are designed and optimized for the enterprise, and SMB
daily communications. The IPX-2000 is the next generation voice communication plat form for the small
to medium enterprise. Designed as an open, scalable, and highly reliable telephony solution, the
IPX-2000 series are able to accept 200 extension registrations, and effectively meeting scales from
various enterprises. Designed to run on a variety of VoIP applications, the IPX-1800 and IPX-2000
provides centralized call control, auto-attendant, voice conferencing, PSTN, and IP-based
communications.
The IPX-2000 integrates up to 8 FXO to become a feature-ric h PBX system that supports seamless
communications between existing PSTN call s, analog, IP phones and SIP-based endpoints
The IPX-2000 system integrates telephony call processing , call control, voice mail, and a widel y PBX
application programming interface into a hig hly scalable architecture designed to s upport both
traditional circuit-based and the Internet telephon y service within a distributed enterprise
communications network.
With IPX-2000 system, s tandard SIP phones can be easily integrated i n your office; plus the
auto-config feature, you may integrate our IP Phone series - VIP-254T/VIP-254T, and the ATA (analog
telephone adapter) series - VIP-156/VIP-157 to build up th
Allowing distributed IP technology to meet traditional voice services, with proactive management
interface, the IPX-2000 system in the daily business processes, enterprises can make people more
productive, more intelligent tasks, and more customer satisfaction.
e VoIP network deployment in minutes.
1.2 Physical Interfaces
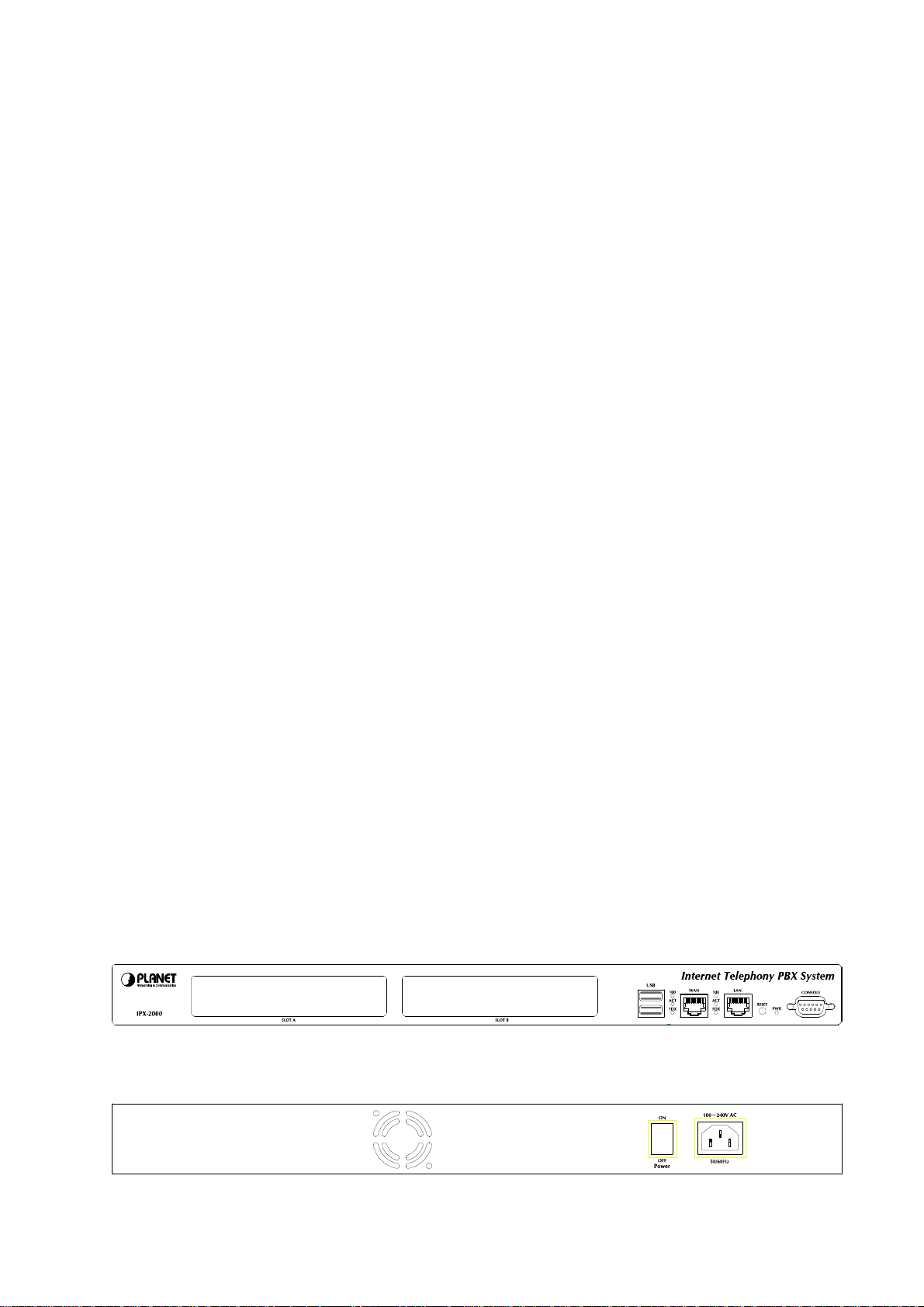
Figure 7. Front Panel of IPX-2000
Figure 8. Rear Panel of IPX-2000
Page 13

Power cord
Telephony interface ports
USB ports
WAN
LAN
Table 1. Physical interfaces description of IP PBX
100-240 Volt, 50-60 Hz
IPX-2000 2 x slots integrates up 8 FXO
4 ports per daughter card, numbered from right to
the left. The rightmost port at slot 0 is port 1 and
FXO module
the leftmost port at slot 1 (if installed) is port 8. FXO
ports are to be connected to FXS jacks on wall or
analog PBX using RJ-11 cables.
1 external port with compliance to USB 1.1/2.0. Plug in a USB
hard drive for voicemail backup from the internal one
Connect to a broadband modem or a WAN router
Connect to a LAN switch
2
Page 14

2 Managing with Web Interface
The factory default of LAN IP address is 192.168.1.1. Connect to LAN port and the configuration We b
interface is at https://192.168.1.1/
Click Yes to see the home page. Ty pe in the default administ rator I D and p assword (both are admin) to
log in for administration. The administrator password can be changed in the User Management ->
User.
1. Click admin in the Login ID.
2. Change the password in Password.
3. Click Apply to change the password.
Note: For the system security, please change the password after the first log-in.
After login, you will see four icons, Add Account Wizard, Add Route & Trunk, Mass Extensions
Adding and Customize Setup. The first three icons can lead you step by step to configure some ba sic
settings of IP PBX. Click the Customize Setup icon to see all the PBX configurations into detail.
Administrator can click
Web Interface.
. Once connected, the browser will ask for accepting a certificate.
on the top-left side of the webpage to go back to the home page of IP PBX
3
Page 15
3 Wizard Configuration
With IP PBX Wizard configuration, the administrator can set basic configurations for IP PBX easily.
With basic setup, IP PBX can function, and connect to the relevant devices and trunks. The Wizard
Configuration including Add Account Wizard, Add Route & T runk and Mass Extension Adding.
When entering Wizard configuration, you will see
you to configure with Wizard. Any configuration change in Wizard requires clicking
bottom of the homepage.
at the bottom of each page that helps
at the
3.1 Add Account Wizard
In Add User & Device page, the administrator can setup usergro ups, users and devices. You can
follow the following steps to finish configuration. After finishing configuration, click
bottom of the homepage to take the configuration effect.
Step 1: Add User Group
1. Enter a group ID and then click ADD.
2. The name will show in the table of the webpage.
3. Click the name to view the edit page.
at the
4. Enter settings shown in Table 3-1.
5. Click Back to return to the ADD USER GROUP page.
For deleting a usergroup, select a group ID and click DEL.
Note: Make sure there is no user associate with the usergroup, or it cannot be deleted.
Click Next to add a user .
Table 3-1Add Usergroup Settings
Field Description
Description
Arbitrary description information. Click SET to add/update
4
Page 16
Associated Trunk s
the information.
1
Select routegroups and outbound trunks accessible by this
usergroup. Note the order matters the hunting sequence in
run-time.
Routegroup: display available routegroups.
Trunk: Display available trunks.
Group ID: The default number is “0”. A trunk with Group ID
“0” does not form a balance group with any other trunks in
Group 0. If Group ID is 1~9, trunks with the same Group ID
form a usage balance group.
Weight: the weight of a trunk to be selected in a trunk
balance group for an outgoing call.
Reachable User Groups
Associated PBX Features
Click
or to add or delete the associate trunks.
After add all trunks, click APPLY.
) If there is not any appropriate SIP trunk and PSTN
trunks to select, you may assign trunks at Setp 5:
Assign Trunk in Add Route & Trunk wizard
configuration after trunks are created in the previous
step.
Select a usergroup and click ADD that is reachable from this
usergroup. By default, only users in the same usergroup can
reach one another .
) If there is not any appropriate usergroup to select,
come back later to revise this selection, once more
usergroups have been created.
2
Select PBX features enabled to this usergroup.
Member List Show the users associated with this usergroup.
Auth. Dial Passcode Select and enter a password in number for caller to have the
same privilege as this usergroup to dial out.
1
Please refer to 6.6, 6.7, and 6.8 for detail s.
2
Please refer to 7 for details.
5
Page 17
Setp 2: Add User
1. Enter settings shown in Table 3-2.
2. Click ADD to see the user information in the table of the webpage.
For deleting a user, select a Login ID and click DEL.
Click Next to choose a device.
Table 3-2 Add User Settings
Field Description
Login ID A unique ID containing alphabets, numbers, and underscore
only without spaces; 20 characters maximum. This is the ID
for personal configuration through IP PBX Web
management.
Name Name of the user , either a real or a virtu al one, e.g. Alice Lee
or Conference Room.
Password Password for the user to access IP PBX Web management.
Description Arbitrary description information.
E-mail Address E-mail address of the user for voicemail notification.
Attach Voicemail in E-mail Notification Select to enclose the message received in the notification
e-mail as an attachment.
Usergroup Select the usergroup this user belongs to.
) If there is not any appropriate usergroup to select,
come back later to revise this selection if no
appropriate usergroup could be chosen for now.
Step 3: Choose Device
Based on the devices you have, click ADD IP PHONE or A DD ANALOG PHONE, and Next to add/set
the device.
Note: If selecting ADD ANALOG PHONE, the wizard will skip to Step 5.
6
Page 18
Step 4: Add Device
1. Enter a device name in the Device ID box.
2. Select Auto Provision if you want to enable Automatic Client Configuration.
3. Click ADD to see the newly added device in the table of the webpage, or to see the Enable
Automatic Client Configuration (ACC) page if Auto Provision is selected.
Enter settings shown in Table 3-3 ACC (Automatic Client Configuration) Settings and click ENABLE.
Note: Consult with your vendor to make sure your SIP phone support Auto Provision function.
For deleting a device, select a device ID and click DEL.
Note: Make sure there is no extension associate with the device, or it cannot be deleted.
Click Next to set a device.
Table 3-3 ACC (Automatic Client Configuration) Settings
Field Description
Vendor Prefix Ask your IP Phone vendor for the Prefix. e.g. eip7012.
MAC Address MAC address of the device.
Supplementary Configuration
Codec Preference
Enable Voice Activity Detection
(VAD)
Supplementary configuration files for IP Phone. The file name
must start with “psc-“.
Preference order of supported codec and packet times of the
phone.
VAD is a technique that detects absence of audio and con se rves
bandwidth by preventing the transmission of "silent packets" over
the network.
) Select if your IP Phone supports VAD.
DTMF mode Choose a DTMF mode used by the phone.
Setp 5: Add Extension
3.1.5.1 Add Extension of IP Phone
1. Enter settings shown in Table 3-4.
2. Click ADD to see the newly added extension in the table of the webpage.
7
Page 19
For deleting an extension, select an extension number and click DEL.
Click Finish to finalize all the settings, and go back to the homepage.
Table 3-4 Add Extension of IP Phone Settings
Field Description
Extension Number A unique line number composed of digits only, e.g. 101; 20
digits maximum. This is the login ID on the device
configuration side.
Associated Device Select the Device this extension asso ciates with.
3
User
Select the user this extension associates with.
) If there is not any appropriate users to select, one can
come back later once the expected user has been
added.
Password Password of this extension. Same password must be
configured on the device side as well.
Pickup Group The usergroup that the extension can pick up. The
extension can set a usergroup that when any extension in
the usergroup rings, the extension can press *8 to pick up
the call in ringing state.
Select Include Reachables check box to be able to pickup
calls that belong to other usergroups which is configured in
Reachable User Groups of the selected usergroup.
Language Preferred language for system instructions heard from the
extension.
Voicemail Select enable to allocate voicemail account for the
extension.
Voicemail PIN PIN to access voicemails. This is mandatory if above
voicemail option is enabled.
Max Voicema il Space Enter maximum space in KBytes for voicemail. Enter 0 or
leave it as blank for not limiting the voicemail space. The
3
Please refer to 6.1 for details.
8
Page 20
voicemail will be recorded until the storage is full.
Disable Fast Bridging Select to disable express media forwarding.
) With Fast Bridging feature enabled, if the two parties
involved in a call (for example, one IP extension and
one SIP trunk) use different DTMF modes
(RFC2833/SIP INFO/Inband), inline transfer (*#) or
2nd-dialing might fail. To avoid such problem, it is
recommended to set the same DTMF mode for all IP
extensions and SIP trunks in the IPBX, as well as for
all IP phones registered to the IPBX. If it is not
feasible to set the same DTMF mode for some IP
extensions or SIP trunks, and inline transfer or
2nd-dialing is necessary for those IP extensions or
SIP trunks, the Fast Bridging feature can be disabled
on a per IP extension and per SIP trunk basis. Note
that Fast Bridging is enabled by default.
Try Peer-to-peer RTP
DTMF Mode Choose preferre d DTMF mode for this extension. Currently
If click YES, IP PBX will attempt to notify the two peers in a
conversation to try peer-to-peer RTP tra nsmission. This is
suggested as long as phones support INVITE or UPDATE
method during a connected call to save the resource of IP
PBX. However, only SIP INFO DTMF mode phones should
enable this since other DTMF modes require IP PBX being
RTP relay server to support in-line transfer.
supported types include RFC2833, SIP INFO, and in-band
tone. It must match configuration on the device side.
) In-band DTMF mode consumes the limited DSP
resource when using a highly compressed codec,
such as G.729 or G.723.1. Therefore, calls will not
connect with such setting if DSP is not installed.
Although using a low-complexity codec such as G.711
does not require DSP, DTMF detection still takes
considerable CPU resource and impacts several
system specs. Be cautious when configuring an
extension with in-band DTMF mode.
9
Page 21

3.1.5.2 Add Analog Phone
1. Enter settings shown in Table 3-5.
2. Click ADD to see the newly added analog phone in the table of the webpage.
For deleting an analog phone, select a POTS port and click DEL.
Click Finish to finalize all the settings, and go back to the homepage.
Table 3-5 Add Analog Phone Settings
Field Description
POTS Port FXS port index.
Pickup Group The pickup group that the extension belongs to. Select
Include Reachables check box to be able to pickup calls
that belong to other usergroups which is configured in
Reachable User Groups of the selected usergroup.
Extension Number A unique line number composed of digits only, e.g. 101; 20
digits maximum.
Unavailable T imeout Timeout for ringing before a call is a nswered.
4
User
Select a user that this extension associates with.
) If there is not any appropriate users to select, one can
come back later once the expected user has been
added.
Language Preferred language for system instructions heard from the
extension.
Voicemail
Voicemail PIN PIN to access voicemails. This is mandatory if above
Select Enable to allocate voicemail account for the
extension.
voicemail option is enabled.
Max Voicema il Space Enter maximum space in KBytes for voicemail. Enter 0 or
leave it as blank for not limiting the voicemail space. The
4
Please refer to 6.1 for details.
10
Page 22
voicemail will be recorded until the storage is full.
3.2 Add Route & Trunk
In Add Route & T r unk page, the administrator can setup routes, routgroups and trunks. Moreover,
worktime and IVR are included in this part for assigning to trunks. You can follow the following steps to
finish configuration. After finishing configuration, click
take the configuration effect.
at the bottom of the homepage to
Step 1: Add Route
1. Enter settings shown in Table 3-6.
2. Click ADD to see the newly added route in the table in the webpage.
For deleting a route, select a route ID and click DEL.
Click Next to set a routegroup.
Table 3-6 Add Route Settings
Field Description
Route ID A unique ID containing alphabets, numbers, and underscore
only without spaces; 16 characters maximum.
Description Arbitrary description information.
Destination Number Pattern
Prefix A sequen ce of digit s to be prefixed to the final dialed number
5
For more information about the available digit set and wildcard characters, please refer to Table 6-7.
5
A destination number pattern consisting of digits, digit set,
and wildcard characters, e.g. 9NXXXXXX matches any
7-digit called number starting from a digit larger or equal to 2
and with an extra prefix digit 9.
after stripping. Using 9NXXXXXX as an example route
pattern with number of stripped digits equal to 1 and prefix
1408, dialing 95270001 will be 14085270001 when it
actually got dialed out.
A special pref ix character “w” could be used for PSTN trunks
to pause 0.5 second during dialing. Say, 4 leading
11
Page 23
consecutive “w” result in 2 seconds delay before dialing.
Number of Stripped Digits Select number of leading digits to be stripped from the
original dialed number when matches this route. Using
9NXXXXXX as an example route pattern with number of
stripped digits equal to 1, dialing 95270001 will be stripped
to be 5270001 when it actually got dialed out.
Setp 2: Add Route Group
1. Enter a group ID and then click ADD.
2. The name will show in the table of the webpage.
3. Click the name to view the edit page.
4. Enter settings shown in Table 3-7.
5. Click Back to return to the ADD ROUTE GROUP page.
For deleting a routegroup, select a group ID and click DEL.
Click Next to choose a trunk.
Note: Make sure there is no route associate with the routegroup, or it cannot be deleted.
Table 3-7 Add Routegroup Settings
Field Description
Description
Arbitrary description information. Click SET to add/update
the information.
Associated Routes
6
Select routes belonged to this routegroup. Click or
button to add or remove a route to or from the
routegroup. The right box lists current selected routes. Click
SET to update the information. Note the order of the
selected routes is important since it decides which route
would be matched first for an outgoing call.
) If there is no appropriate routes to select initially, one
6
Please refer to 6.4 for details.
can come back later to revise it, once the expected
routes are added.
12
Page 24
Setp 3: Choose Trunk
In the Choose T runk page, click SIP TRUNK, ANALOG PSTN TRUNK or ISDN PSTN TRUNK to see
one of the following pages to add various types of trunks.
Setp 4: Add Trunk
3.2.4.1 Add SIP Trunks
1. Enter settings shown in Table 3-8.
2. Click ADD to see the newly added SIP trunk in the table in the webp age.
For deleting a SIP trunk, select a trunk identifier and click DEL.
Click Next to assign trunks to usergroups.
Table 3-8 Add SIP Trunk Settings
Field Description
Trunk Identifier A unique num ber consisting of digits only. Usually give the
phone number issued by the ITSP for consistency.
Description Arbitrary description information.
Auth. Name
Auth. Password Give the password used for authentication on the remote
Dynamic Peer Select if the trunk is a passive trunk which means the
Specify the name for authentication if different to the Trunk
Identifier.
SIP proxy or registrar. Usually this is given by the ITSP.
registration will be from a dynamic remote peer. T y pical
application is to accept registration from an IP PBX at a
remote site with dynamic IP address. Once the remote IP
PBX registers, calls from local to remote can be made
reversely over the trunk.
SIP Proxy IP
SIP Proxy Port
Registration Required Select if registration to a registrar is required to activate the
Specify IP address (or fully qualified d omain name) a nd UDP
port of the remote SIP proxy, which usually refer to the SIP
server on the ITSP side.
trunk. This is true for a remote IP PBX or an ITSP account,
13
Page 25
however, may be not required in case of a SIP gateway.
SIP Registrar IP
SIP Registrar Port
Language Preferred language for system instructions heard from the
DID T ype DID means direct inward dialing (also called DDI in Europe).
None DID
Extension DID
Specify IP address (or fully qualified d omain name) a nd UDP
port of the remote SIP registrar, which usually refer to the
SIP server on the ITSP side (same as proxy).
trunk.
Select a preferred type, None DID, Extension DID, DID by
Number DID by Privilege or Centrex DID from the list and
then enter configuration in DID Prefix and DID Stripping to
have the incoming calls directed to the corresponding trunk.
When selected None DID, all incoming calls will enter IVR
system instead of directly dial to a specified extension.
Select a preferred IVR from IVR list for this trunk.
When selected Extension DID, select an extension in the
list to be an unconditional destination for incoming calls to
this trunk. If prefix or stripping has been given, the result of
DID By Number
DID By Privilege
digit manipulation is dialed in a DTMF string after the call
has been answered by the DID extension as an automatic
nd
2
dialing.
) If you set a DID extension in a trunk, then only that
extension can use this trunk to call out, and all incoming
calls to this trunk will connect to that extension directly.
When selected DID By number, enter configurations in DID
Prefix and DID Stripping to have the incoming calls
directed to the corresponding extension derived by number
manipulation. The SIP trunk numbers is therefore regarded
as the direct line of the extension.
When selected DID By Privilege, select a usergroup i n the
list as the privilege of inbound calls from this trunk. Enter
configuration in DID Prefix and DID Stripping to have the
incoming calls redirected to dial out.
DID Prefix A digit string to be prefixed to the incoming called number
after stripping.
DID Stripping A number of leadin g digits to be stripped from the original
14
Page 26
called number. Click All to strip all digits of the original called
number.
Centrex DID
IVR List
7
Select this function to make the numbers of
incoming/outgoing calls more flexible by prefixing/stripping
digits.
All-number
Digitmap
Default Number
Inbound
Manipulation
Digitmap
Outbound
Manipulation
Digitmap
Associate an IVR menu with incoming calls to this trunk.
This is mandatory unless the trunk is configured for DID.
Leave it blank and the system will automatically create an
Select a digitmap ID for calls via the
trunk changing numbers.
Enter digits for calls from this trunk
displaying this caller ID.
Select a digitmap ID to have the
incoming calls direct to the
corresponding extensions.
Select a digitmap ID to have the
outgoing calls display the
corresponding numbers.
IVR for the trunk.
Usergroup8 of Privilege When disabled DID, click a usergroup in the list whose
reachability to other usergroups and trunks will be used as
the privilege of inbound calls from this trunk.
) There may not be appropriate usergroups to select
initially. One can come back later once the expected
usergroup has been added.
Disable Fast Bridging Select to disable express media forwarding.
) With Fast Bridging feature enabled, if the two parties
involved in a call (for example, one IP extension and
one SIP trunk) use different DTMF modes
(RFC2833/SIP INFO/Inband), inline transfer (*#) or
7
Please refer to 7.12 for details.
8
Please refer to 6.1 for details.
15
Page 27
2nd-dialing might fail. To avoid such problem, it is
recommended to set the same DTMF mode for all IP
extensions and SIP trunks in the IPBX, as well as for
all IP phones registered to the IPBX. If it is not
feasible to set the same DTMF mode for some IP
extensions or SIP trunks, and inline transfer or
2nd-dialing is necessary for those IP extensions or
SIP trunks, the Fast Bridging feature can be disabled
on a per IP extension and per SIP trunk basis. Note
that Fast Bridging is enabled by default.
3.2.4.2 Add Analog PSTN Tr unk s
1. Enter settings shown in Table 3-9.
2. Click ADD to see the newly added analog PSTN trunk in the table in the webpage.
For deleting an analog PSTN trunk, select a trunk identifier and click DEL.
Click Next to assign trunks to usergroups.
Table 3-9 Add Analog PSTN Trunk Settings
Field Description
Trunk Group ID number of this PSTN trunk group. A valid number ranges
from 1 to 31. It should not overlap with existing ISDN PSTN
trunk groups.
Trunk Type Select the port type, FXO or FXS. If selecting FXS, users
can see By Number and By Privilege in the DID of
Extension list, and be able to configure DID Prefix and DID
Stripping.
Trunk Ports Select one or more FXO or FXS ports for this Analog PSTN
trunk.
Description Arbitrary description information.
Port Selection
Click to search for an available port in the group. Rotating
means to force ports being selected in turns to even cost.
DID T ype DID means direct inward dialing (also called DDI in Europe).
Select a preferred type, None DID, Extension DID, and DID
by Privilege from the list and then enter configuration in DID
Prefix and DID Stripping to have the incoming calls
16
Page 28
directed to the corresponding trunk.
None DID
When selected None DID, all incoming calls will enter IVR
system instead of directly dial to a specified extension.
Select a preferred IVR from IVR list for this trunk.
Extension DID
When selected Extension DID, select an extension in the
list to be an unconditional destination for incoming calls to
this trunk. If prefix or stripping has been given, the result of
digit manipulation is dialed in a DTMF string after the call
has been answered by the DID extension as an automatic
nd
2
dialing.
) If you set a DID extension in a trunk, then only that
extension can use this trunk to call out, and all incoming
calls to this trunk will connect to that extension directly.
DID By Privilege When selected DID By Privilege, select a usergroup in the
list as the privilege of inbound calls from this trunk. Enter
configuration in DID Prefix and DID S t ripping to have the
incoming calls redirected to dial out.
DID Prefix A digit string to be prefixed to the incoming called number
after stripping.
DID Stripping A number of leadin g digits to be stripped from the original
called number. Click All to strip all digits of the original called
number.
Language Preferred language for system instructions heard from the
trunk.
IVR List
9
Associate an IVR menu with incoming calls to this trunk.
This is mandatory unless the trunk is configured for DID.
Leave it blank and the system will automatically create an
IVR for the trunk.
Usergroup10 of Privilege When disabled DID, click a usergroup in the list whose
reachability to other usergroups and trunks will be used as
9
Please refer to 7.12 for details.
10
Please refer to 6.1 for details.
17
Page 29
the privilege of inbound calls from this trunk.
) There may not be any appropriate usergroups to select
initially. One can come back later to revise it, once the
expected usergroups are added.
Caller ID Detection Select to detect the Caller ID calling from PSTN lines.
Answering by Battery Reversal
Detection
If selected, billable time will count from the call is answered.
) Please enable this function when Central Office (CO)
site provides battery reversal.
3.2.4.3 Add ISDN PSTN Trunks
1. Enter settings shown in Table 3-10.
2. Click ADD to see the newly added ISDN PSTN trunk in the table in the webpage.
For deleting an ISDN PSTN trunk, select a trunk identifier and click DEL.
Click Next to assign trunks to usergroups.
Table 3-10 Add ISDN PSTN Trunk Settings
Field Description
Trunk Group ID number of this ISDN trunk group. A valid number ranges
Trunk Channels
from 1 to 31. It should not overlap with existing Analog
PSTN trunk groups.
The Trunk Channels is the logical ran ge of the sum of B
and D channels. Each physical ISDN port occupies three
Trunk Ports, two B and on e D channels. User only needs to
specify the B channel number here, since D channel is
reserved in the 3
E.g. Assume there are four ISDN ports in the PBX and no
other FXO/FXS modules installed, then one can set each
pair of numbers here, like 1,2 but excluding 3,6,9,12.
rd
trunk port for each physical ISDN port.
) If a four-port FXO/FXS module is also installed, then
the Trunk Ports here shoul d be numbered from 5 to 16
instead of 1 to 12. Make sure to specify the indices of
ports correctly, or PBX will not start. One can refer to
18
Page 30
the POTS Setting page before configuration.
Description Arbitrary description information.
Port Selection
DID T ype DID means direct inward dialing (also called DDI in Europe).
None DID
Extension DID
Select to search for an available port in the group. Rotating
means to force ports being selected in turns to even cost.
Select a preferred type, None DID, Extension DID, DID by
Number DID by Privilege or Centrex DID from the list and
then enter configuration in DID Prefix and DID Stripping to
have the incoming calls directed to the corresponding trunk.
When selected None DID, all incoming calls will enter IVR
system instead of directly dial to a specified extension.
Select a preferred IVR from IVR list for this trunk.
When selected Extension DID, select an extension in the
list to be an unconditional destination for incoming calls to
this trunk. If prefix or stripping has been given, the result of
digit manipulation is dialed in a DTMF string after the call
has been answered by the DID extension as an automatic
nd
2
dialing.
) If you set a DID extension in a trunk, then only that
extension can use this trunk to call out, and all incoming
calls to this trunk will connect to that extension directly.
DID By Number
DID By Privilege
DID Prefix A digit string to be prefixed to the incoming called number
DID Stripping A number of leadin g digits to be stripped from the original
When selected DID By number, enter configurations in DID
Prefix and DID Stripping to have the incoming calls
directed to the corresponding extension derived by number
manipulation. The SIP trunk numbers is therefore regarded
as the direct line of the extension.
When selected DID By Privilege, select a usergroup i n the
list as the privilege of inbound calls from this trunk. Enter
configuration in DID Prefix and DID Stripping to have the
incoming calls redirected to dial out.
after stripping.
called number. Click All to strip all digits of the original called
number.
19
Page 31

Language Preferred language for system instructions heard from the
trunk.
IVR List
11
Associate an IVR menu with incoming calls to this trunk.
This is mandatory unless the trunk is configured for DID.
Leave it blank and the system will automatically create an
IVR for the trunk.
Usergroup12 of Privilege When disabled DID, clicks a usergroup in the list whose
reachability to other usergroups and trunks will use as the
privilege of inbound calls from this trunk.
) There may not be any appropriate usergroups to select
initially. One can come back later to revise it, once the
expected usergroups are added.
Setp 5: Assign Trunk
In Assign Trunk page, all usergroups display here. T he administrator can assign trunks to any
usergroup at this stage.
1. Click a group ID to see the Assign Trunk Management.
2. Enter settings shown in Table 3-11.
3. Click
or to add or delete the associate trunks. After adding all trunks, click APPLY.
Note: The order of the assigning trunks matters the hunting sequence in run-time.
Table 3-11 Assign Trunk Settings
Field Description
Routegroup Click to select available routegroups.
Trunk Click to select available trunks.
Group ID The default number is “0”. A trunk with Group ID “0” does not
form a balance group with any other trunks in Group 0. If
Group ID is 1~9, trunks with the same Group ID form a
usage balance group.
11
Please refer to 7.12 for details.
12
Please refer to 6.1 for details.
20
Page 32

Weight The weight of a trunk to be selected in a trunk balance group
for an outgoing call.
3.3 Mass Extension Adding
The Mass Extension Adding Manag ement p ag e help s the administrator to ad d many extensi ons and
assign users for these extensions under a usergroup and a device. After finishing configuration, click
at the bottom of the homepage to take the configuration effect.
Note: Make sure the range of extension numbers does not exist in Extension of IP Phone or user Login
ID, or the configuration will fail to continue.
Step 1: Add User & Extension
1. Enter the digits for the starting extension.
2. Click a number in the Number of EXT list for the mass extension adding.
3. Click a usergroup in the USERGROUP list.
4. Select enable to allocate voicemail account for the extension.
5. Click an IP phone device in the DEVICE list.
6. Select to enable Try-Peer-to-peer RTP. If click INVITE or UPDATE, IP PBX will attempt to notify
the two peers in a conversation to try peer-to-peer RTP transmissio n.
7. Click a usergroup in the Pickup Group list.
8. Select Include Reachables check box to enable pickup calls that belong to other usergroup
which is configured in Reachable User Groups of the selected usergroup.
9. Choose preferred DTMF mode for extensions. Currently supported types include RFC2833, SIP
INFO and Inband.
10. Click ADD, and IP PBX will start to add these extensions automatically.
11. Click Back to the homepage.
21
Page 33

4 System Configuration
This section describes how to configure system parameters used by IP PBX. Click Customize Setup
after login the web interface to configure the following system parameters.
4.1 PBX System
The PBX System page briefs IP PBX status to the administrator. Firmware versions, IP addresses of
WAN and LAN interfaces, and default gateway router are sh own in this page. Click PBX System to
see the basic information of IP PBX.
4.2 Time Setup
The Time Setup page allows administrator to configure time zone and date for IP PBX. With correct
time setup, functions such as IVR, worktime, and voicemail can present the actions at the right time.
Select System -> Time Setup to see the current setting of time zone and date.
4.2.1 System Time Zone
1. Click a region/country in the Time Zone list.
2. Click Apply in System Timezone Setup.
3. Go to System -> Shutdown, select Rebooting Af ter Shutdown and Click Yes to activate
changes.
4.2.2 Real Time Clock (RTC) Setup
1. Click year, month, day, hour, minute, and second in the correspondent list.
2. Click Apply in Real Time Clock Setup.
Note: When reset the time 15 minutes later than the time showed in RTC Setup, the system will ask for
re-login.
4.3 On-board WAN Setup
The On-board WAN Setup page allows administrator to configure WAN network interface for IP PBX.
Select System -> On-board WAN Setup, and the current setting of WAN network interface is
displayed, e.g. type, IP address etc.
22
Page 34

Unless the LAN Only is selected, you can choose one of the three options, Static IP, DHCP, and
PPPoE from the Type list for your configuration. Select LAN Only check box to disable WA N, and only
default router and DNS settings are applicable. Select MAC Clone to change the WAN MAC address.
Select Yes to allow WAN to respond PING request.
4.3.1 Static IP
You can click Static IP in the Type list, and manually configure the following information:
• IP Address
• Netmask
• Default gateway IP address
• Primary, secondary or third DNS servers
Click Apply to submit.
4.3.2 DHCP
Simply click DHCP in the Type list, and click Apply. The acquired IP address, netmask, default
gateway and DNS server information will show when revisit this page later.
4.3.3 PPPoE
1. Click PPPoE in the Type list.
2. Enter a user name and its password in User Name and Password boxes.
3. Click Apply.
The PPPoE dialing will start right away. When there is an active connection, the page will show the
acquired IP address, network mask, default gateway and DNS server information.
4.3.4 Allow WAN to Respond PING
Select this option if appropriate and click Set. If enabled, the WAN port of IP PBX will respond PING to
the originator.
4.3.5 LAN Only
Select LAN Only to disable WAN IP settings but allow the configu ration of default gateway and
primary/secondary/third DNS servers.
23
Page 35

4.3.6 MAC Clone
Select MAC Clone and enter a MAC/physical address to change the WAN MAC address.
4.4 On-board LAN Setup
The On-board LAN Setup page allows administrator to configure LAN network interface for IP PBX.
1. Select System -> On-board LAN Setup to see the current settings of LAN network interface.
2. Enter a new IP address and network mask.
3. Click Apply to change the settings.
Note: By default IP PBX grants IP addresses to LAN devices via DHCP, and translates those
addresses into its WAN IP address for access beyond the LAN subnet. Make sure to change
DHCP pool and LAN routing (if any) accordingly after changing the system LAN IP subnet. After
configuration, go to Service -> IP PBX Service, and click Restart to activate the changes.
4.5 LAN Routing
To enable static routing among LAN subnets, enter network information and the IP address of the
corresponding gateway in the IP PBX’s LAN. It is important to assure that the given gateway IP
address sits in the IP PBX’s LAN. Each subnet requires an entry even multiple subnet s share the same
gateway, unless masking does the same.
Examples are adding IP Route IDs net1 and net2 with parameters 192.168.128.0/255.255.255.0,
192.168.129.0/255.255.255.0, shared gateway 192.168.1.254 respectively. Or, IP Route ID net1n2
with 192.168.128.0/255.255.254.0 and gateway 192.168.1.254 would do the same. Added routes
enable routing immediately after clicking Add. However, the IP PBX Service needs to be restarted to
regard calls from designated LAN subnets as LA N traffic. Go to Service -> IP PBX Service, and click
Restart to regard calls as LAN traffic.
4.5.1 Add a Route
1. Enter the IP Route ID, Network, Netmask, and Gateway.
2. Click Add to have the newly added route in IP Route ID.
24
Page 36

4.5.2 Edit a Route
1. Edit the information in a row.
2. Click Apply in the row to update the information.
4.5.3 Delete a Route
1. Select a route ID.
2. Click Delete to remove the route ID from the IP Route ID column.
4.6 Dynamic DNS Setup
Dynamic WAN IP address causes difficulty for inbound connections from remote clients or IP PBX
systems. A popular work-around is to adopt domain names provided by Dynamic DNS service
providers and run a client on or behind the gateway router (or IP PBX). It is required to apply an
account and create a hostname in the account before configuration.
Click Enable, give account information and refresh interval to activate a Dynamic DNS client. The
client then uses Username and Password to access its account and update periodically the
Hostname with the latest WAN IP address at DynDNS or 3322.net Service.
4.6.1 Enable Dynamic DNS
Typical hostn ame has a form of <hostname>.dyndns.org or <hostname>.3322.net. The refresh interval
is usually between 60 – 600 seconds depending on the volatility of WAN IP assignment.
1. Click Enable.
2. Click DynDNS or 3322.net in the Service list.
3. Enter the Username, Password, and Hostname.
4. Click Apply.
4.6.2 Disable Dynamic DNS
Click Disable, and then click Apply.
25
Page 37

4.7 QoS Setup
To assure the bandwidth reserved for the outgoing VoIP traffic over regular data traffic from LAN, the
QoS Setup page offers three parameters to characterize the WAN link. The default QoS setting is
disabled because these parameters must be correctly given according to the actual WAN speed.
4.7.1 Enable QoS
1. Click Enable.
2. Enter the WAN Uplink Speed, WAN Downlink Speed, and Uplink VoIP Reserved (bandwidth).
3. Click Apply.
For a popular 2M/256K ADSL program, the WAN uplink speed would be 256 and the WAN downlink
speed would be 2048. The Uplink VoIP reserved could be, say, 192 out of the total 256 kbps to allow 2
concurrent G.711 calls. Following is the t able of WAN speed related to various codecs.
Codec Information Bandwidth Calculations
Codec & Bit Rate
(Kbps)
G.711 (64 Kbps) 80 10 4.1 160 20 50 87.2
G.729 (8 Kbps) 10 10 3.92 20 20 50 31.2
G.723.1 (6.3 Kbps) 24 30 3.9 24 30 34 21.9
G.723.1 (5.3 Kbps) 20 30 3.8 20 30 34 20.8
G.726 (32 Kbps) 20 5 3.85 80 20 50 55.2
G.726 (24 Kbps) 15 5 60 20 50 47.2
Codec
Sample
Size
(Bytes)
Codec
Sample
Interval
(ms)
Mean
Opinion
Score
(MOS)
Voice
Payload
Size
(Bytes)
Voice
Payload
Size (ms)
Packets
Per
Second
(PPS)
Bandwidth
Required
(Kbps)
4.7.2 Disable QoS
Click Disable, and then click Apply.
4.8 Virtual Server
You can configure IP PBX as a virtual server for remote users to access services such as the Web or
FTP at your local site via Public IP Addresses. With proper settings, IP PBX can automatically redirect
inbound traffic from W A N to local servers configured with private IP addre s ses. In other words,
26
Page 38

depending on the requested service (TCP/UDP) port number, the IP PBX redirects the external service
request to the appropriate internal server (located at one of your LAN's Private IP Address).
To enable access servers in LAN from a machine beyond WAN, select System -> Virtual Server to
configure port mappings. Service ID names the service. Protocol and Port specify the TCP/UDP port
number on WAN IP to be forwarded to the Forward to Port of Forward to IP in LAN. Say 192.168.1.5
is a Mail Server to be seen from outside, one should configure TCP port 25 to be forwarded to
192.168.1.5 port 25.
Note: Following ports are default server ports in use: TCP port 9, 7788, 80, 53, 23, 443 and 13422;
UDP port 1024, 9, 53, 67, 5060 and 69.
4.8.1 Add a Service
1. Enter the Service ID, Protocol, Port, Forward to IP, and Forward to Port.
2. Click Add to add the newly service in the Service ID.
Note: the usage of port range: using the syntax from-port : to-port. For example, enter the following
for the TCP ports 6881 to 6999. It should be 6881:6999.
4.8.2 Edit a Service
1. Change any information in a row.
2. Click Apply in the row to update the information.
4.8.3 Delete a Service
1. Select a service ID.
2. Click Delete to remove the service from the Service ID.
4.9 Maintenance
This page includes maintenance functions of IP PBX, including Storage Backup, SIP UA, CDR Log,
System Events, and Active Calls.
4.9.1 Storage Backup
To back up internal main storage, the administrator can back up the internal main storage to USB Mass
storage or NFS server. You can select to keep or remove CDR and/or voicemails after backup.
27
Page 39

4.9.1.1 Back up to USB Mass Storage
Click USB Mass Storage, and then BACKUP to follow the instructions to insert the USB connector of
an external USB drive. After a confirmation of the insertion, backup starts a few seconds later if the
external USB drive is accessible and has enough free spa ce. If the backu p is successful, a new folder
(yyyy-mm-dd-hhmmss, eg. 2007-06-26-151100) will be created in ippbx-backup folder on the external
drive. Af ter the backup, remove the USB connector of the external drive.
4.9.1.2 Back up to NFS Server
1. Click NFS Server.
2. Enter a URL path in NFS Directory Path.
3. Click Backup to have the internal main storage stored in the NFS server.
4.9.2 SIP UA
SIP UA lists the registration statu s of ea ch client/remote IP PBX, and the IP Address/Port from where
they register. SIP trunk registrations, if any, also show at the end of the list. The Dynamic column
shows the listed IP address is dynamic or static. Reg. Progress is the response code and message if
registration has been attempted but not successful so far. Slave Registrar column is used only under
the stackable mode. It indicates with which slave box a SIP client is registe red. Blank means a client is
registered to the master box locally. IP PBX supports share-line function and all information of
share-line extension/trunk is recorded on SIP UA page, To remove the specific registered
extension/trunk ID, please click Delete button in that row.
Table 4-1 The Registration Status of SIP UA
IP PBX The Description of Reg. Progress
UAS
Empty If there is no registration activities existing.
401 Unauthorized Authentication failed.
407 Authentication
Required
Empty If there is no registration activities existing. UAC
Status code and
message from UAS
Authentication required.
The response information is depended on UAS.
28
Page 40

4.9.3 CDR Log
The CDR(Call Detail Record) Log shows each call record including Calling and Dialed Numbers,
Caller ID, Destination Interface(trunk if outbound) in use, epochs when the call was made,
answered and ended, and which yield the Call Duration and Billable Time. The Result denotes the
disposition of a call like answered or not. The administrator can also click Get File to export the record
as a *.csv file, click Delete CDR to remove all records and click Show CDR to display all records on
the screen.
4.9.4 System Events
The log records an audit entry in the audit trail whenever certain events o ccur, such as service reload,
firmware upgrade, administrator logging on, logging off, and accessing resources from NTP, DNS,
DHCP, and PPPoE service.
4.9.5 Active Calls
The Active Calls page shows current active calls. Columns Client and Party indicate the involved
extensions or trunks of a call. State shows the state of a call, while Service gives the current action of
the listed Client.
Table 4-2 The State of Active Call
Field Description
Caller Show the caller’s extension number, port number, or SIP trunk ID.
Caller state
Dial The client is caller.
IVR Calls from FXO are picked up by Auto-Attendant.
Pause The client is being paused for some time.
Prompt The client is being prompted for a pre-recorded audio.
Voicemail The client enters voicemail service.
Meet-me The client enters meet-me service.
Busy Call-back The client enters b u sy call-back service.
ACD The client enters ACD service.
Trunk Shows trunk ID that is using in this call.
Callee state Answer The client is callee.
Callee Show the callee’s extension number, port number, or SIP trunk ID.
Answer Time Show the answer time of active calls.
29
Page 41

4.10 Firmware Upgrade
The version of the running PBX firmware could be found in System -> Firmware Upgrade. To upgrade
current firmware, click Browse to locate a relea se file obtained from the vendor, and click Upgrade to
have the latest version of PBX firmware.
Note: Consult with your IP PBX service provider for upgrade procedure.
Note: Do not change the firmware file name, otherwise the system will reject it.
4.11 Stackable Management
IP PBX is scalable and allows you to enlarge capacity by stacking up to four IP PBX boxes to form a
cluster.
4.11.1 Operation Modes
IP PBX provides three modes, standalone mode, master mode and slave mod e. The default mode is
standalone mode while there is no cluster and IP PBX box works independently. Once a cluster is
formed, only one IP PBX box runs in master mode, and rest of boxes run in slave mode in the cluster.
For instance, with full-capacity case, there would be one maste r bo x and 3 slave boxes in a cluster.
Select System -> Stackable to see the current operation mode of each IP PBX box.
4.11.2 Consolidated Management
Stackable Management page of the master box not only indicates IP addresses of current slave boxes
in a cluster but also allows you to add new slave boxes to the cluster or remove slave boxes from the
cluster. You can simply manage a cluster in Stackable Management page of the master box.
Within a cluster, any extension/user update of configuration information to the master box would affect
all slave boxes automatically. As a result, you shall only configure the master box to take control over
the whole cluster in most cases. Meanwhile, all boxes within the same cluster share the same
registration information and work as one single box.
Note: For SIP and PSTN trunks, and Meet-me conferences, you need to configure them respectively
on each box in stack. It is similar to how you configure them in standalone mode.
Note: For Meet-me conferences in stack, do not enter the same room number in slave and master
boxes, though the function need to be configured respectively.
30
Page 42

4.11.3 Configuration Procedure
The following examples illustrate how to configure a stack.
4.11.3.1 Case I: Stack multiple IP PBX boxes from scratch
1. Ensure all boxes have factory default settings before being stacked.
2. Ensure all boxes have TCP routing to e ach other via LAN interfaces if they are in different local
networks.
3. Select one of the boxes to be the master box. Others are slave boxes consequently.
4. For each slave box, go to System -> Stackable page to specify the master’s IP address and cli ck
Apply. Make sure to configure slave boxes before assigning to master box.
5. For the master box, go to System -> Stackable page. Select Enable Master Mode check box.
6. Enter IP address and port of a slave box, and then click Add. If clients support SIP 305 or SIP
302 response, select the By 305 Use Proxy or By 302 Moved Temporarily check box in
Registration Load Balance.
Do this step again if more than one slave box is stacked.
7. After adding all slave boxes, click Apply.
8. Go to Service -> IP PBX Service and click Restart to reflect the changes.
All boxes are stacked and a cluster is formed. You can start to configure extensions etc. on master box
to make internal calls possible. You can also configure SIP and PSTN trunks on each box to enable
inbound and outbound calls. Any configuration change in stack requires Reload in Service -> IP PBX
Service of master box.
In order to share SIP and FXO PSTN trunks with other boxes, you need to do the following settings.
For instance, a FXO PSTN trunk (with a route pattern) is configured on box A and assigned to some
usergroups. You would like to share this FXO PSTN trunk with box B.
1. On box B, configure a route with the pattern equals to the one associated with this FXO PSTN
trunk, and then assign this route to the routegroup associated with the intra trunk from box B
toward box A.
2. Click Reload in Service -> IP PBX Service of master box.
To explain step one more clearly, for example, box A is 192.168.1.100 and box B is 192.168.1.101.
There is a FXO PSTN trunk “pstn1” with a route pattern “9./1”
13
configured on box A. In order to share
this FXO PSTN trunk among box A and B, on box B we can configure a route “BoxA-pstn1” with pattern
13
9./1 means pattern is 9. and number of stripped digits is 1.
31
Page 43

14
“9./0”
intra trunk “_192168001101_192168001100”
and assign it to the routegroup “_192168001101_192168001100” which associates with the
15
.
4.11.3.2 Case II: Stack a new IP PBX box with an existing running box
This case means that there is a standalone box up run ning for a while. Now you would like to add a
new box to form a cluster. Therefore, the standalone box will become a master box later.
1. Ensure the new box has factory default settings before being stacked.
2. Ensure the new box has TCP routing to the existing box via LAN interface if they are in different
local networks.
3. Now, backup the IP PBX configuration on the existing box. Then restore this configuration to the
new one.
4. On new box, remove all trunk configurations including routes and routegroup s, an d all Meet-me
conference configurations first.
5. Go to System -> Stackable of the new box, specify master’s IP address and click Apply.
6. Go to System -> Stackable of the existing box, select Enable Master Mode check box, enter IP
address and SIP port of the new box, and then click Add.
7. Click Apply.
8. Go to Service -> IP PBX Service of the existing box, and click Restart to reflect the changes.
The existing box turns to be a master box and the new box is a slave box in the cluster.
4.11.3.3 Case III: Add new slave boxes to an existing stack
Similar to Case II, you can also add more slave boxes to an existing cluster.
4.11.3.4 Remove slave boxes from stack
1. Go to System -> Stackable of the master box.
2. Select IP address of a slave box you would like to remove in Slave Peers, and then click Delete.
3. Click Apply.
4. Go to Service -> IP PBX Service of the master box, and click Restart to reflect the changes.
The cluster no longer owns the removed box. The removed box get s off the cluster and would turn
back to be standalone. Moreover, the master box would also turn back to be standalone if all slave
boxes are removed and the cluster does not exist any more.
14
Here, please note that we always use 0 for number of stri pped digits.
15
You probably notice IP addresses of two boxes meshed by an intra trunk determine name of the intra trunk.
In this case, the name of intra trunk from box B (192.168.1.101) toward box A (192.168.1.100) is
_192168001101_192168001100. Meanwhile, the routegroup associated with this intra trunk has the same name.
32
Page 44

4.12 Shutdown
In System -> Shutdo wn, you can shutdown the machine by clicking YES, or reboot the machine by
selecting the Rebooting After Shutdown check box and clicking YES. In case the software reboot
fails, you can also press the hardware Reset button. It is advised to shut down IP PBX system before a
power-off.
Note: If the hardware RESET button is hold for 5 seconds, the system will revert to factory default.
4.13 Logout
Logout button, , locates at the top-right of the webpage. Administrator can logout, and go
back to the login page by clicking it.
Note: The GUI will automatically log out after 15 minutes, if you do not do any action.
33
Page 45

5 Service Configuration
This section describes details to configure various services built in the IP PBX.
5.1 NTP Service
Select Service -> NTP Service to specify a NTP server for network time synchronization. You can
enable or disable NTP service at any time.
5.1.1 Enable NTP Service
1. Click Enable.
2. Select the Automatic check box to use server pool at pool.ntp.org; or, enter a fully qualified
domain name or the IP address of a NTP server.
3. Click Apply.
5.1.2 Disable NTP Service
Click Disable, and click Apply.
5.2 SNMP Service
Select Service -> SNMP Service to specify Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)
parameters for network status retrieval. You can enable or disable SNMP service at any time.
5.2.1 Enable SNMP Service
1. Click Enable.
2. Enter System Location, System Administrator Contact, SNMPv2 Read-only Community
with allowed network specifications, and also those of the SNMPv2 Read-write Community.
3. Click Apply.
5.2.2 Disable SNMP Service
Click Disable, and click Apply.
34
Page 46

5.3 STUN Service
IP PBX has a built-in STUN client to solve NAT problems. Select Service -> STUN Service to specify a
Simple Traversal of UDP through NATs (STUN) server for NAT traversal. You can enable or disable
STUN Service at any time.
5.3.1 Enable STUN Service
1. Click Enable.
2. Enter a fully qualified domain name or the IP address of a STUN server.
3. Click Apply.
4. Go to Service -> IP PBX Service, and click Restart to reflect the changes.
5.3.2 Disable STUN Ser vice
1. Click Disable.
2. Enter the fully qualified domain name or the static IP address of the external WAN interface.
Usually this address refers to the static WAN IP add ress if there is a NAT device between the IP
PBX and the Internet. If the WAN port of IP PBX directly connect s to Internet or it is unused, leave
the address blank.
3. Click Apply.
4. Go to Service -> IP PBX Service, and click Restart to reflect the changes.
5.4 TFTP Service
Select Service -> TFTP Service to view the current status of TFTP Service. You can enable or disable
TFTP Service at any time.
5.4.1 Enable TFTP Servi ce
Click Enable, and then click Apply to manage files, e.g. upload and download files to and from the IP
PBX. Uploaded files can then be retrieved through TFTP Service.
5.4.1.1 Change Directory
Current directory is shown in the field on the right side of Directory, for instance, it is /.at the beginning.
Click a directory in the Directory list to change to a different folder.
35
Page 47

Note: The default directory is /. Initially, you may not be able to change the directory, since no folder is
created under /. yet.
5.4.1.2 Add a Folder
1. Click a directory under which you want to add a new folder in the Directory list.
2. Click Add Folder.
3. Enter a folder name in the pop-up dialog box, e.g. myfolder .
4. Click OK to see the newly added folder in the Directory list, e.g. /myfolder/.
5.4.1.3 Delete a Folder
1. Click a directory of a folder in the Directory list.
2. Click Delete Folder to remove the folder from the Directory list.
Note: A folder cannot be deleted if there is still file inside.
5.4.1.4 Download a File
1. Click a directory in the Directory list.
2. Click a file in the Download / Delete File From The Above Folder list.
3. Click Get File to download the file.
5.4.1.5 Delete a File
1. Click a directory in the Directory list.
2. Select a file in the Download / Delete File From The Above Folder list.
3. Click Delete File to remove the file.
5.4.1.6 Upload a File
1. Click a directory in the Directory list.
2. Click Browse.
3. Select a directory in the Look in list, and then a file.
4. Click Open.
5. Click Put File to upload the file.
Now, the uploaded file should appear in current directory and is displayed in the Download / Delete
File From The Above Folder list.
Note: The maximum file size for uploading a file to PC#1 is 12M, and to PC#2 is 6M.
5.4.2 Disable TFTP Service
Click Disable, and then Apply.
36
Page 48

5.5 DHCP Service
Select Service -> DHCP Service to view the current status of the DHCP Service. You can enable or
disable the DHCP Service at any time.
Note: If the IP PBX was shut down abnormally, Select Service -> DHCP Service and click Apply, or
Go to Service -> IP PBX Service, and click Restart to activate the DHCP service.
5.5.1 DHCP Service
5.5.1.1 Enable DHCP Service
Click Enable, choose the main interface offering addresses, and then Apply to configure DHCP
settings.
5.5.1.2 Disable DHCP Service
Click Disable and click Apply.
5.5.2 Add New
5.5.2.1 Add DHCP Range
1. Click Add New tab.
2. Enter a pool name (must have an alphabet initial) in Pool Name.
3. Select Range or Single-host to enter an IP address of the host with MAC, if the binding is
intended for a specific host only.
4. Enter a DHCP range of addresses available for lease in IP. The right addres s box will not show if
Single-host is selected.
5. Optionally, DHCP options
Code,Value and click
option, choose it from the Options list and click
6. Click Add at the bottom of the page to commit changes.
You can see the newly added DHCP POOL displayed in the DHCP POOL list.
5.5.2.2 Edit DHCP Range
16
could be configured by entering an option code and value in
. The new DHCP option will show in the Options list. To delete an
after the box.
1. Click any pool name in the DHCP POOL list to see the settings on the right.
16
Refer to RFC 2132 for the details of available DHCP options.
37
Page 49

2. Edit the settings.
3. Click Update to change the settings.
5.5.2.3 Delete DHCP Range
1. Click any pool name in the DHCP POOL list.
2. Click Delete to remove the pool name from the DHCP POOL list.
5.5.3 Show Leased Clients
Click the Show Leased Clients tab to see all leased LAN IP addresses and client details.
5.6 IP PBX Service
In Service -> IP PBX Service, you can click the Operations tab to reload, backup, restore, restart or
revert the IP PBX configuration, or click the Settings tab for the IP PBX parameters settings.
5.6.1 Operations
Select Service -> IP PBX Service, and then click the Operations tab.
5.6.1.1 Reload IP PBX Configuration
Click Reload, and IP PBX will reload the configuration once there is no active call. If there is any active
call, it will retain up to 3 minutes, and then IP PBX will reload. This is the most frequently used function
in this page since any IP PBX configuration change has to be reloaded to take effect.
5.6.1.2 Backup IP PBX C onfiguration
Click Backup, and IP PBX archives and encrypt s current configurat ion into a tim e-st amped backup file
under tftpboot root directory. To secure configuration files, download them to a local host through the
Get File function in Service -> TFTP Service once a while. Select the PBX Settings Only check box
for only back up Configurations in PBX, which are parts mainly from User Management to Feature in
the tree view; clear the check box to back up both PBX and system (interfaces and services) settings.
Note: Do not change the configuration file name, or the Restore function will reject the configuration
file.
5.6.1.3 Restore IP PBX Co nfiguration
Click a configuration backup file in the list, click Restore, and IP PBX will restore the configuration as
current setup. After restoring, the system will ask for reboot the PBX service, click Yes to reboot IP
PBX.
38
Page 50

5.6.1.4 Restart IP PBX Configuration
Click Restart, and the IP PBX Service will restart completely. Currently active calls will be
disconnected immediately. This function is rarely required unless the network setting has been
changed, or the service operates abnormally without problematic configuration could be identified.
5.6.1.5 Revert IP PBX Configurati on
Click Revert, and IP PBX will erase current IP PBX settings, DDNS, QoS, STUN service and revert
configuration back to the factory default. Note the reversion affects IP PBX service only, but not other
system services such as DHCP, TFTP, and NTP. The backup IP PBX configuration files under TFTP
remain intact after reversion, so that one can restore to a specific time if a backup file had been
generated then.
To revert the whole system back to the factory default, hold the hardware RESET button more than 5
seconds. All of the configuration settings will be re-set exactly the way they are when users receive the
IP PBX from providers. Users have to re-configure the IP PBX from scratch again. If one needs to
restore the backup configuration after factory default, he/she must download the backup configuration
file to the local computer in Service -> TFTP Service page.
5.6.2 Settings
Select Service -> IP PBX Service, and then click the Settings tab to configure IP PBX parameters.
After the configuration, go to Service -> IP PBX Service, and click Restart to activate changes.
Table 5-1 IP PBX Configuration Settings
Field Description
PBX SIP Port Specify the UDP port where the SIP service listens on.
RTP Port Range Limit the UDP ports used by the IP PBX for media
transport.
) The port range needs to have at least equals to the
(number of extensions (also count shared-lines) +
number of SIP trunks) * 2. If selecting Enable Video
Codec, the total amount needs to multiply by 2 to
have the least requirements for RTP port range.
Insufficient range of ports may cause call blocking
due to port depletion.
Max/Default Expiration Time Guard and advertise SIP registration respectively.
PBX Caller ID The default Caller ID for an unknown incoming call.
39
Page 51

Enable Video Codec Select if there will be video clients registering to the
system
Support Devices Multiplex Call-ID Select to force discrimination of SIP tags. Do this only
when there is such a client device in the system and other
devices supporting the same. Otherwise, one may find the
special device only got registered with this option but other
clients or even SIP trunks fail due to such change. Clear
the box if you are not sure.
Max Active Users Enter a number for registration admission control to limit
the maximum number of active registered clients.
Max Active Calls Enter a number for call admission control to limit the
maximum number of concurrent calls.
Max Wireless Calls Enter a number to limit the calls made by explicitly
specified wireless extensions.
MAX CDR Size Enter maximum space in KBytes available for CDR.
IP TOS Value Set the TOS value in the IP header of RTP packets
originated from IP PBX.
Call Keep Alive Enter a time in second to periodically confirm the call is still
connected. The time is between 10 and 180 seconds.
Registered Keep Alive Enter a time in second to confirm the registration status
periodically. The time is between 10 and 180 seconds.
NAT Traversal Keep Alive Enter a time in se conds to retain NAT hole punched
periodically. The time is between 10 and 180 seconds.
Disable WAN Bandwidth Saver Select to disable attempts to use low-bit-rate codec
(G.729A or G.723.1) for remote parties.
Disable DSP saver for LAN calls Select to honor the preferred codec of caller’s phone
instead of overriding by DSP utilization concerns.
Enable DNS SRV Resolution Select to enable looking up IP of dynamic clients or trunks
by DNS Service records before their successful
registrations.
Disable Line-in-use Call Back PBX supports call back function when an extension
without multi-line function is in use. Select to disable
Line-in-use Call Back function.
Disable Exponential Backoff in SIP
Select to disable exponential SIP retransmission.
Retransmission
40
Page 52

6 IP PBX Configuration
This section introduces steps to provision the IP telephony part of the IP PBX. Note that reloading
configuration is required in order to make new configuration effective
6.1 User Group Configuration
A userg roup is a logically groupi ng of users and th eir privileges. For inst an ce, one could have couple of
usergroups in an IP telephony network, e.g. Sales, Marketing, Administration, Accounting, and
Engineering, etc. Each usergroup associates with a set of PBX features and call routing scopes. In
other words, all users in the same usergroup share the same reachability of PBX features and final
destinations.
Select User Management -> User Group, and one can add, edit, delete or search usergroups. Go to
Service -> IP PBX Service, and click Reload to activate changes.
Note: The maximum usergroup is 64 for PC#1 and 32 is for PC#2.
6.1.1 Add a User Group
17
.
1. Enter a usergroup name beside the Add button, and then click Add.
2. The name will show in Group ID.
3. Click the name in Group ID to view the edit page.
4. Enter settings shown in Table 6-1.
5. Click Back to return to the Usergroup Management page.
Now, you can see the newly added usergroup displayed in the Group ID.
6.1.2 Edit a User Group
1. Click a usergroup name in the Group ID.
2. Edit settings shown in Table 6-1.
3. Click Back to see the updated information.
6.1.3 Delete a User Group
1. Select a Group ID.
2. Click Delete to remove the usergroup from the Group ID.
17
Please refer to 5.6.1.1 for details.
41
Page 53

6.1.4 Search a User Group
1. Type a group ID in the Search box, or cli ck a group ID in Group ID list.
2. Click Go to see the Update page.
Table 6-1 Usergroup Configuration Settings
Field Description
Group ID A unique group name containing alphabets, numbers, and
underscore only without spaces; 20 characters maximum.
Description
Associated Trunk s
Arbitrary description information. Click Set to add/update the
information.
18
Select routegroups and outbound trunks accessible by this
usergroup. Note the order matters the hunting sequence in
run-time. Click Routegroup: display available routegroups.
Trunk: Display available trunks. Select blocking to block
calls that meet the route patterns in selected routegroup.
Loop back is especially for hop on and off function. Select
loopback to have the number after performing the route
pattern in selected routegroup to go through the rules in
Associate Trunks again. Once find the matched rule, the
number will go to the relevant trunk. Normally, block is at the
very first in the list, while loopback is at the last in the list.
Group ID: The default number is “0”. A trunk with Group ID
“0” does not form a balance group with any other trunks in
Group 0. If Group ID is 1~9, trunks with the same Group ID
18
Please refer to 6.6, 6.7, and 6.8 for detail s.
form a usage balance group.
Weight: the weight of a trunk to be selected in a trunk
balance group for an outgoing call.
Click
After add all trunks, click Apply.
or to add or delete the associate trunks.
) If there is not any appropriate SIP trunk and PSTN
trunks to select, come back later to revise selection
once trunks have been created.
42
Page 54

Reachable User Groups
Select a usergroup and click
that is reachable from
this usergroup. By default, only users in the same usergroup
can reach one another .
) If there is not any appropriate usergroup to select,
come back later to revise this selection, once more
usergroups have been created.
Associated PBX Features
Member List Show the users associated with this usergroup.
Auth. Dial Passcode Select and enter a password in number for caller to have the
Group Call A gourp call number is a virtual number that presents all
19
Select PBX features enabled to this usergroup.
same privilege as this usergroup to dial out.
extensions belong to this group. Enter a group call number
(not an existed extension/service number). Select
extensions and click
to add into the group call. After
adding all extensions, click Apply.
6.2 User Configuration
A user is a logical entity in IP telephony which associates extensions with a usergroup. It also
propagates its attributes such as e-mail and voicemail PIN to extensions. Usually a user refers to a real
person who has a name and e-mail; however, one can always create virtual users to associate with
public extensions. For example, extensions in reception, break room, and lab areas.
Select User Management -> User, and one can add, edit, delete or search users. Go to Service -> IP
PBX Service, and click Reload to activate changes.
6.2.1 Add a User
1. Click the Add New tab.
2. Enter settings shown in Table 6-2.
3. Click Add.
19
Please refer to 7 for details.
43
Page 55

4. Click Back to see the newly added user in the Login ID.
6.2.2 Edit a User
1. Click a user in the Login ID.
2. Edit settings shown in Table 6-2.
3. Click Apply.
6.2.3 Clone a User
1. Click a user in the Login ID.
2. Click Clone.
3. Edit settings shown in Table 6-2.
4. Click Add.
5. Click Back to see the newly added user in the Login ID.
6.2.4 Delete a User
1. Select a Login ID.
2. Click Delete to remove the user from the Login ID.
6.2.5 Search a User
1. Type a login ID in the Search box, or click a login ID in User list.
2. Click Go to see the Update page.
Table 6-2 User Configuration Settings
Field Description
Login ID A unique ID containing alphabets, numbers, and underscore
only without spaces; 20 characters maximum. This is the ID
for personal configuration through IP PBX Web
management.
Name Name of the user , either a real or a virtu al one, e.g. Alice Lee
or Conference Room.
Password Password for the user to access IP PBX Web management.
Description Arbitrary description information.
E-mail Address E-mail address of the user for voicemail notification.
Attach Voicemail in E-mail Notification Select to enclose the message received in the notification
44
Page 56

e-mail as an attachment.
Usergroup Select the usergroup this user belongs to.
) If there is not any appropriate usergroup to select,
come back later to revise this selection if no
appropriate usergroup could be chosen for now.
Extensions Show the extensions associated with this user.
6.3 Device Configuration
A device coul d be an IP phone, gateway, analog telephone adapter, or even another IP PBX, etc. It has
one or more extensions to be registered to the IP PBX.
6.3.1 IP Phone
The DEVICE PHONE MANAGEMENT page lets the administrator to create IP Phone devices. Before
connecting a device to the IP PBX, you need to configure the same account information into the device
through the configuration interface enabled by the device. Select Device -> IP Phone to add, edit,
delete and search devices. Go to Service -> IP PBX Service, and click Reload to activate changes.
6.3.1.1 Add a Device
1. Enter a device name in the Device ID box, and a URL for fast connection to device configuration
page or description for the device in the Device Administration URL box.
2. Click Add to see the newly added device in the Device ID.
6.3.1.2 Edit a Device
Once create the device, you can modify its information through the following steps.
1. Modify the Device Administration URL and click Link as a shortcut to the device administration
URL.
2. Click Edit to see the Enable Automatic Client Config uration (ACC) p age. Table 6-3 is a reference
for detailed A CC settings whi ch is use d for auto- configurin g IP phones. One can specify the MAC
address and audio preferences of the phone. Note that for phones using HTTP for
auto-configuring, DHCP setting needs a new option 151 with a value of http://<IP PBX LAN
IP>/tftpboot/ in the Code,Value box in Service -> DHCP Service. If the phone uses TFTP for
auto-configuration, the option is 150 by default.
3. Click Enable to see Enable shows in the Auto Client Conf column. Click Edit and then Disable
to disable the function.
45
Page 57

6.3.1.3 Delete a Device
1. Select a Device ID.
2. Click Delete to remove the device from the Device ID.
6.3.1.4 Search a Device
1. Type a group ID in the Search box, or cli ck a device ID in Device ID list.
2. Click Go to see the data.
Table 6-3 ACC (Automatic Client Configuration) Settings
Field Description
Device
Vendor Prefix Ask your IP Phone vendor for the Prefix. e.g. eip7012.
MAC Address MAC address of the device.
Supplementary Configuration
Codec Preference
Redundant Servers
A unique ID containing alphabets, numbers, and underscore only
without spaces; 20 characters maximum.
Supplementary configuration files for IP Phone. The file name
must start with “psc-“.
Preference order of supported codec and packet times of the
phone.
Enter the information as follows.
Proxy IP/FQDN
Proxy Port
Registrar IP/FQDN
Registrar Port
SIP Domain Specify the SIP domain used by the proxy
Specify IP address (or fully qualified domain
name) and UDP port of the remote IP PBX.
Specify IP address (or fully qualified domain
name) and UDP port of the remote IP PBX
and registrar. If not specified, IP address will
be used as the domain by default.
VAD is a technique that detects absence of audio and con se rves
bandwidth by preventing the transmission of "silent packets" over
Enable Voice Activity Detection
(VAD)
the network.
) Select if your IP Phone supports VAD.
DTMF mode Choose a DTMF mode used by the phone.
IP PBX supports auto adjustment for daylight saving time. To
Daylight Saving
enable this function, the administrator must configure the Daylight
Format, Start Time and End Time. The following example
46
Page 58

configures daylight saving time for the U,S, adding one hour
starting at midnight on the first Sunday in April and ending at
midnight on the last Sunday of October. Select By weekday of a
specific month on the Daylight Format, set First Sunday of April
at 00 O’clock on the St art Time, and set Last Sunday of October
at 00 O’clock on the End Time.
6.3.2 Extension of IP Phone
The Extension of IP Phone Management page lets the administrator to create extensions. Select
Device -> Extension of IP Phone, and one can add, edit, delete and search extensions. Go to
Service -> IP PBX Service, and click Reload to activate changes.
IP PBX also offers its own extensions Line-in-use Call Back and Transfer Call Back function. For
example, extension A and B are within one IP PBX or a stacked cluster. When extension A calls
extension B, and extension B is in use. Extension A can press 1 to be in the waiting list. Once
extension B finishes the call, IP PBX will ring extension B within a minute. When extension B is picked
up, IP PBX will ring extension A to connect the call. Extension A call also press * to cancel, and will
connect to voice mail.
Note: The IP Phone should disable call waiting (multi-line) function in order to activate the line-in-use
call back function. If the extension B does not disable the call waiting function on IP Phone, wh en
extension A calls to extension, and extension B is in use, the second line of extension B’s IP
Phone will ring.
For transfer-call-back function, extension A calls to extension B, extension B (transferer) tries to
transfer the call to extension C (transferee). After the transferee’s unavailable timeout reached,
extension B gets re-ringback tone from IP PBX.
Note: To trigger the transfer-call-back-to function, all of the following conditions must be true:
1. It is phone-based ring-transfer.
2. The transferee is a local extension.
3. The transferee does not answer until the unavailable timeout is reached.
4. No forwarding settings to voicemail/extension for the transferee.
6.3.2.1 Add an Extension
1. Click the Add New tab to set an extension.
47
Page 59

2. Enter settings shown in Table 6-4.
3. Click Add to see the newly added extension.
6.3.2.2 Edit an Extension
1. Click an extension in the Extension Number.
2. Edit settings shown in Table 6-4.
3. Click Apply to see the updated information.
6.3.2.3 Clone an Extension
1. Click an extension in the Extension Number.
2. Click Clone.
3. Edit settings shown in Table 6-4.
4. Click Add to see the updated information.
6.3.2.4 Delete an Extension
1. Select an extension numbers.
2. Click Delete to remove the extension from the Extension Number.
6.3.2.5 Search an Extension
1. Type an extensio n number in the Search box, or click an extension number in Device ID list.
2. Click Go to see the data.
Table 6-4 Device Extension Configuration Settings
Field Description
Extension Number A unique line number composed of digits only, e.g. 101; 20
digits maximum. This is the login ID for device registra tion.
Associated Device Select the Device this extension asso ciates with.
Password Password of this extension. Same password must be
configured on the device side as well.
20
User
Select the user this extension asso ciates with.
) If there is not any appropriate users to select, one can
come back later once the expected user has been
added.
Pickup Group The usergroup that the extension can pick up. The
20
Please refer to 6.1 for details.
48
Page 60

extension can set a usergroup that when any extension in
the usergroup rings, the extension can press *8 to pick up
the call in ringing state.
Select Include Reachables check box to be able to pickup
calls that belong to other usergroups which is configured in
Reachable User Groups of the selected usergroup.
Line Type Specify the type of connection, wired or wireless, of the
client with the extension.
Language Preferred language for system instructions heard from the
extension.
Voicemail Select enable to allocate voicemail account for the
extension.
Voicemail PIN PIN to access voicemails. This is mandatory if above
voicemail option is enabled.
Max Voicema il Space Enter maximum space in KBytes for voicemail. Enter 0 or
leave it as blank for not limiting the voicemail space. The
voicemail will be recorded until the storage is full.
Unavailable T imeout Timeout for ringing before a call is a nswered.
Allow LAN Use Only Check to reject registration and calls from WAN in a SIP ID
same as the extension number. I.e., this extension must be
on LAN.
Disable NAT Traversal IP PBX uses NAT traversal for outgoing traffics by default.
Select to disable NAT traversal if there is a machine that
could handle NAT issues.
Call Keep Alive Select to check if the call is still active. Frequency check is
specified in 5.6.2.
Registered Keep Alive Select to check if the register still exists in a certain time.
Disable Fast Bridging Select to disable express media forwarding.
) With Fast Bridging feature enabled, if the two parties
involved in a call (for example, one IP extension and
one SIP trunk) use different DTMF modes
(RFC2833/SIP INFO/Inband), inline transfer (*#) or
2nd-dialing might fail. To avoid such problem, it is
recommended to set the same DTMF mode for all IP
49
Page 61

extensions and SIP trunks in the IPBX, as well as for
all IP phones registered to the IPBX. If it is not
feasible to set the same DTMF mode for some IP
extensions or SIP trunks, and inline transfer or
2nd-dialing is necessary for those IP extensions or
SIP trunks, the Fast Bridging feature can be disabled
on a per IP extension and per SIP trunk basis. Note
that Fast Bridging is enabled by default.
Try Peer-to-peer RTP
DTMF Mode Choose preferred DTMF mode for this extension. Currently
If click YES, IP PBX will attempt to notify the two peers in a
conversation to try peer-to-peer RTP tra nsmission. This is
suggested as long as phones support INVITE or UPDATE
method during a connected call to save the resource of IP
PBX. However, only SIP INFO DTMF mode phones should
enable this since other DTMF modes require IP PBX being
RTP relay server to support in-line transfer.
supported types include RFC2833, SIP INFO, and in-band
tone. It must match configuration on the device side.
) In-band DTMF mode consumes the limited DSP
resource when using a highly compressed codec,
such as G.729 or G.723.1. Therefore, calls will not
connect with such setting if DSP is not installed.
Although using a low-complexity codec such as G.711
does not require DSP, DTMF detection still takes
considerable CPU resource and impacts several
system specs. Be cautious when configuring an
extension with in-band DTMF mode.
Advanced Settings Select to see more optional settings shown below.
Selective Call Blocking
Block SIP redirection from the
extension
Select Block Anonymous Calls to block all calls without a
Caller ID.
Block one or more calling numbers by entering the calling
numbers and clicking
numbers by clicking the number from the list, and then click
.
Select to ignore the forward settings of IP phone and honor
the forward settings of IP PBX.
50
. Removing the blocked
Page 62

Forward Options
Select Unconditional Call Forward and clicks a default
destination in the list, e.g. Voicemail or Phone Number.
) If selecting Phone Number , enter a number to which
incoming calls are forwarded unconditionally. The
number could be an extension or a PSTN number with
appropriate outbound prefix.
Unavailable Call Forward Enter a number to which incoming calls are forwarded when
not answered. The number could be an extension or a
PSTN number with appropriate outbound prefix.
Timeout To Next Forward Enter a period of time in seconds for ringing the extension in
Unavailable Call Forward. Click
extension in Unavailable Call Forward and the time here
into the list. Remove the extension of Unavailable Call
Forward from the list by clicking
to add the
.
) The time must be shorter than Unavailable Timeout,
or the function will not work normally.
Play Unavailable/Line-in-use Forward
Prompt
Line-in-use Forward Enter a number to which incoming calls are forwarded when
Notify the caller that callee is not available and the call is
being forwarded to another extension.
the extension is busy. The number could be an extension or
a PSTN number with appropriate outbound prefix.
) If the function is enabled, the Line-in-use Call Back
function will be disabled.
Selective Call Forward Unconditional Call Forwarding according to the calling
number. Enters one or more calling numbers and a
forwarding number, and clicks
calls from 101 to a cellular number, while let the rest enter
the voice mail by default. Selects a forwarding and click
when the forwarding is no longer required.
. E.g., forward only
6.3.3 Analog Phone
The Analog Phone Management page lets the administrator to create analog p hones. Select Device
51
Page 63

-> Analog Phone, and one can add, edit, and delete analog phon es. Go to Service -> IP PBX Service,
and click Reload to activate changes. Connect an analog phone to a FXS port and configure the
properties of the port as detailed in Table 6-5.
6.3.3.1 Add an A nalog Phone
1. Click the Add New tab to see the detailed Analog Pho ne Management page.
2. Enter settings shown in Table 6-5.
3. Click Add to see the newly added analog phone in the Extension Number.
6.3.3.2 Edit an A nalog Phone
1. Click a port in POTS Port.
2. Edit settings shown in Table 6-5.
3. Click Apply to see the edited information.
6.3.3.3 Delete an Analog Phone
1. Select a POTS Port.
2. Click Delete to remove the extension from the POTS Port.
Table 6-5 FXS Extension Configuration Settings
Field Description
POTS Port FXS port index.
Extension Number A unique line number composed of digits only, e.g. 101; 20
digits maximum.
Pickup Group The pickup group that the extension belongs to. The
extension can set a usergroup that when any extension in
the usergroup rings, the extension can press *8 to pick up
the call in ringing state.
Select Include Reachables check box to be able to pickup
calls that belong to other usergroups which is configured in
Reachable User Groups of the selected usergroup.
Unavailable T imeout Timeout for ringing before a call is a nswered.
21
User
Select a user that this extension associates with.
21
Please refer to 6.1 for details.
) If there is not any appropriate users to select, one can
come back later once the expected user has been
52
Page 64

added.
Voicemail
Voicemail PIN PIN to access voicemails. This is mandatory if above
Max Voicema il Space Enter maximum space in KBytes for voicemail. Enter 0 or
Language Preferred language for system instructions heard from the
T.38 Enabled
UDPTL Redundancy Level Select number of the previous package(s) that will be sent
Input/Output Gain Voice amplification or attenuation in dB scale to adjust
Advanced Settings Select to see more optional settings shown below.
Select Enable to allocate voicemail account for the
extension.
voicemail option is enabled.
leave it as blank for not limiting the voicemail space. The
voicemail will be recorded until the storage is full.
extension.
Click Auto, Enable or Disable detecting fax tones in a call.
again. This function only takes effect when T.38 is enabled.
input/output volume.
Default Codec Select g711ulaw or g711alaw for connecting to other
devices.
Selective Call Blocking
Forward Options Select Unconditional Call Forward and click a default
Select Block Anonymous Calls to block all calls without a
Caller ID
Block one or more calling numbers by typing the calling
numbers and clicking
numbers by clicking the number from the list, and then click
.
destination in the list, e.g. Voicemail or Phone Number.
. Removing the blocked
) If selecting Phone Number, enter a number to which
incoming calls are forwarded unconditionally. The
number could be an extension or a PSTN number with
appropriate outbound prefix.
Unavailable Call Forward
Enter a number to which incoming calls are forwarded when
Timeout to Next Forward Enter a period of time in seconds for ringing the extension in
not answered. The number could be an extension or a
PSTN number with appropriate outbound prefix.
53
Page 65

Unavailable Call Forward. Click
extension in Unavailable Call Forward and the time here
into the list. Remove the extension of Unavailable Call
to add the
Forward from the list by clicking
.
) The time must be shorter than Unavailable Timeout,
or the function will not work normally.
Play Unavailable/Line-in-use Forward
Prompt
Line-in-use Forward Enter a number to which incoming calls are forwarded when
Selective Call Forward Unconditional call forwarding according to the calling
Hot/Warmline A hot line means that a specified numb er will be called
Notify the caller that callee is not available and the call is
being forwarded to another extension.
the extension is busy. The number could be an extension or
a PSTN number with appropriate outbound prefix.
number. Enters one or more calling numbers and a
forwarding number, and click
from 101 to a cellular number, while let the rest enter the
voice mail by default. Selects a forwarding and click
when the forwarding is no longer required.
. E.g., forward only calls
immediately when the phone goes off-hook. A warm line
functions similarly except it does so only after a specified
delay expired to allow dialing a different number with the
line.
Enter a number as the direct hot/warm line number, and
optionally, a timeout period in seconds if the warm line
behavior is expected.
6.3.4 IP Phone Firmware
The IP Phone Firmware Management page is for uploading firm ware of IP phone. When connecting
an IP phone to PBX, the IP phone can automatically upgrade to the latest firmware once there is a
version available for download on the IP PBX. Select Device -> IP Phone Firmware to add, edit, or
delete IP phone firmware configurations.
6.3.4.1 Add IP Phone Firmware
1. Enter settings shown in Table 6-6.
54
Page 66

2. Click Put File to see the newly added firmware in the table below.
Note: The uploaded file and auto generated file will be displayed at the TFTP Service page under root
directory.
6.3.4.2 Delete IP Phone Firmware
1. Select a vendor prefix of IP phone.
2. Click Delete at the top-left side of the table to remove the firmware.
Note: The deleted file and originally auto generated file will be also deleted from the TFTP Service
page under root directory.
Table 6-6 IP Phone Firmware Configuration Settings
Field Description
Vendor Prefix Ask your IP phone vendor for the prefix. e.g. eip7012.
Version Enter the firmware version that is going to be upgraded for
the IP phone, e.g. 1.0.0123
Firmware File to Upload
Click Browse to find a firmware file from the local host.
6.4 Route Configuration
A route is a destination number pattern for outbound call matching. A pattern consists of digits 0-9
(including “-”), “*”, “#”, digit set, and wildcard characters like “.”, “X”, “Z”, and “N”. Table 6-7 explains
digit set and wildcard characters.
Note: The “#” in route pattern is for some PSTN saver lines that may set “#” as their dial pattern. For
most of the IP Phones, press “#” will immediately send out the dialed number.
Table 6-7 Digit Set and Wildcard Characters for Route Patterns
Expression Description
[<digits>] Match any single digit listed explicitly. e.g., digit set [13579]
match odd digits. One may use ‘-‘ to indicate a range of
digits, e.g. [2-8].
. (dot) Match any digit in any length. Usually given in the end of a
pattern to include all numbers matched a specific prefix.
) . (dot) can not be used alone or at the beginning of the
route patterns.
X Match any single digit from 0 to 9.
55
Page 67

Z Match any single digit from 1 to 9.
N Match any single digit from 2 to 9.
By selecting Route Management -> Route, the administrator can add, edit, delete and search routes
in the Route Management page. Go to Service -> IP PBX Service, and click Reload to activate
changes.
6.4.1 Add a Route
1. Enter settings shown in Table 6-8.
2. Click Add to see the newly added route in the Route ID.
6.4.2 Edit a Route
1. Edit settings shown in Table 6-8 in a row.
2. Click Apply in the row to update the settings.
6.4.3 Delete a Route
1. Select a Route ID.
2. Click Delete to remove the route from the Route ID.
6.4.4 Search a Route
1. Type a route ID in the Search box, or select a route ID in Route ID list.
2. Click Go to see the data.
Table 6-8 Route Configuration Settings
Field Description
Route ID A unique ID containing alphabets, numbers, and underscore
only without spaces; 16 characters maximum.
Description Arbitrary description information.
Destination Number Pattern A destination number pattern consisting of digits, digit set,
and wildcard characters, 32 characters maximum, e.g.
9NXXXXXX matches any 7-digit called number starting from
a digit larger or equal to 2 and with an extra prefix digit 9.
Prefix A sequen ce of digit s to be prefixed to the final dialed number
56
Page 68

after stripping. Using 9NXXXXXX as an example route
pattern with number of stripped digits equal to 1 and prefix
1408, dialing 95270001 will be 14085270001 when it
actually got dialed out.
A special pref ix character “w” could be used for PSTN trunks
to pause 0.5 second during dialing. Say, 4 leading
consecutive “w” result in 2 seconds delay before dialing.
Number of Stripped Digits Number of leading digits to be stripped from the original
dialed number when matches this route. Using 9NXXXXXX
as an example route pattern with number of stripped digits
equal to 1, dialing 95270001 will be stripped to be 5270001
when it actually got dialed out.
6.5 Route Group Configuration
A routegrou p groups routes into a logical superset of route patterns. Such abbreviation simplifies the
association of multiple routes with a trunk, say, a PSTN line. A route must be included into at least one
routegroup in order to take the route pattern into effect. The administrator can click Group ID,
Description and Associated Routes arrows to sort the order of data.
Select Route Management-> Route Group, and the administrator can add, edit, delete and search
routegroups in the Route Group Management page. Go to Service -> IP PBX Service, and click
Reload to activate changes.
6.5.1 Add a Route Group
1. Type a route group name and click Add.
2. Click the route group in Group ID to see the settings.
3. Enter settings shown in Table 6-9, and click Back.
The newly added route group should be displayed in the Group ID.
6.5.2 Edit a Route Group
1. Click a route group name in Group ID.
2. Edit settings shown in Table 6-9.
3. Click Back to see the updated information.
57
Page 69

6.5.3 Delete a Route Group
1. Select a Group ID.
2. Click Delete to remove the route group from the Group ID.
6.5.4 Search a Route Group
1. Type a group ID in the Search box, or cli ck a group ID in Group ID list.
2. Click Go to see the Update page.
Table 6-9 Routegroup Configuration Settings
Field Description
Group ID A unique ID containing alphabets, numbers, and underscore
only without spaces; 32 characters maximum.
Description
Associated Routes
22
Arbitrary description information. Click Set to add/update the
information.
Select routes belonged to this routegroup. Click or
button to add or remove a route to or from the
routegroup. The right box lists current selected routes. Click
Set to update the information. Note the order of the selected
routes is important since it decides which route would be
matched first for an outgoing call.
) If there is no appropriate routes to select initially, one
can come back later to revise it, once the expected
routes are added.
6.6 SIP Trunk Configuration
A SIP trunk refers to a SIP account on a remote call routing or gateway device. A practical example is
an account at an Internet Telephony Service Provider (ITSP) where a call is routed to a SIP client or
off-ramped to an analog subscriber via PSTN. One could also build SIP trunk to a remote IP PBX to
reach its extensions and PSTN ports.
22
Please refer to 6.4 for details.
58
Page 70

The SIP Trunk Management page allows the administrator to configure SIP trunks used by IP PBX.
Select Trunk -> SIP Trunk, and one can add, edit, delete and search SIP trunks. Go to Service -> IP
PBX Service, and click Reload to activate changes.
6.6.1 Add a SIP Trunk
1. Click the Add New tab.
2. Enter settings shown in Table 6-10.
3. Click Add to see the newly added SIP trunk in the Trunk Identifier.
6.6.2 Edit a SIP Trunk
1. Click an identifier in T runk Identifier.
2. Edit settings shown in Table 6-10.
3. Click Apply to change the information.
6.6.3 Clone a SIP Trunk
1. Click an identifier in T runk Identifier.
2. Click Clone.
3. Edit settings shown in Table 6-10.
4. Click Add to see the updated information.
6.6.4 Delete a SIP Trunk
1. Click the Trunks tab, and select a trunk identifier.
2. Click Delete to remove the SIP trunk from the Trunk Identifier.
6.6.5 Search a SIP Trunk
1. Type a trunk identifier in the Search box, or click a trunk identifier in Group ID list.
2. Click Go to see the Update page.
Table 6-10 SIP Trunk Configuration Settings
Field Description
Trunk Identifier A unique number consisting of digits only. Usually give the phone
number issued by the ITSP for consistency.
Description Arbitrary description information.
59
Page 71

Auth. Name
Specify the name for authentication if different to the Trunk Identifier.
) IP PBX do not accept the following characters:
`;~!#$%^*()+|-=\{}[]" ',/<>.
Auth. Password Give the password used for authentication on the remote SIP proxy or
registrar. Usually this is given by the ITSP.
Dynamic Peer Select if the trunk i s a passive trunk which means the registration will
be from a dynamic remote peer . T y pical application is to accept
registration from an IP PBX at a remote site with dynamic IP address.
Once the remote IP PBX registers, calls from local to remote can be
made reversely over the trunk.
SIP Proxy IP
SIP Proxy Port
SIP Domain Specify the SIP domain used by the proxy and registrar. If not
Registration Required Select if registration to a registrar is required to activate the trunk. This
Specify IP address (or fully qualified domain name) and UDP port of
the remote SIP proxy, which usually refer to the SIP server on the ITSP
side.
specified, IP address will be used as the domain by default.
is true for a remote IP PBX or an ITSP account, however, may be not
required in case of a SIP gateway.
SIP Registrar IP
SIP Registrar Port
Language Preferred language for system instructions heard from the trunk.
DID Type DID means direct inward dialing (also called DDI in Europe). Select a
None DID
Extension DID
Specify IP address (or fully qualified domain name) and UDP port of
the remote SIP registrar, which usually refer to the SIP server on the
ITSP side (same as proxy).
preferred type, None DID, Extension DID, DID by Number DID by
Privilege or Centrex DID from the list and then enter configuration in
DID Prefix and DID Stripping to have the incoming calls directed to
the corresponding trunk.
When selected None DID, all incoming calls will enter IVR system
instead of directly dial to a specified extension. Select a preferred IVR
from IVR list for this trunk.
When selected Extension DID, select an extension in the list to be an
unconditional destination for incoming calls to this trunk. If prefix or
stripping has been given, the result of digit manipulation is dialed in a
DTMF string after the call has been answered by the DID extension as
an automatic 2
nd
dialing.
60
Page 72

) If you set a DID extension in a trunk, then only that extension can
use this trunk to call out, and all incoming calls to this trunk will
connect to that extension directly.
DID By Number
When selected DID By number, enter configurations in DID Prefix
and DID Stripping to have the incoming calls directed to the
corresponding extension derived by number manipulation. The SIP
trunk numbers is therefore regarded as the direct line of the extension.
DID By Privilege
When selected DID By Privilege, select a usergroup i n the list as the
privilege of inbound calls from this trunk. Enter configuration in DID
Prefix and DID Stripping to have the incoming calls redirected to dial
out.
DID Prefix A digit string to be prefixed to the incoming called number after
stripping.
DID Stripping A number of leadin g digits to be stripped from the original called
number. Click All to strip all digits of the original called number.
Centrex DID
Select this function to have more flexible calling numbers.
All-number Digitmap
Select a digitmap ID for calls via the trunk
changing numbers.
Default Number
Enter digits for calls from this trunk
displaying this caller ID.
Inbound Manipulation
Digitmap
Outbound
Manipulation
Select a digitmap ID to have the incoming
calls direct to the corresponding extensions.
Select a digitmap ID to have the outgoing
calls display the corresponding numbers.
Digitmap
IVR List
23
Associate an IVR menu with incoming calls to this trunk. This is
mandatory unless the trunk is configured for DID. Leave it blank and
the system will automatically create an IVR for the trunk.
Usergroup24 of Privilege When disabled DID, click a usergroup in the list whose reachability to
other usergroups and trunks will be used as the privilege of inbound
calls from this trunk.
23
Please refer to 7.12 for details.
24
Please refer to 6.1 for details.
61
Page 73

) There may not be appropriate usergroups to select initially. One
can come back later once the expected usergroup has bee n
added.
Disable Fast Bridging Select to disable express media forwarding.
) With Fast Bridging feature enabled, if the two part ies involved in a
call (for example, one IP extension and one SIP trunk) use
different DTMF modes (RFC2833/SIP INFO/Inband), inline
transfer (*#) or 2nd-dialing might fail. To avoid such problem, it
is recommended to set the same DTMF mode for all IP
extensions and SIP trunks in the IPBX, as well as for all IP
phones registered to the IPBX. If it is not feasible to set the
same DTMF mode for some IP extensions or SIP trunks, and
inline transfer or 2nd-dialing is necessary for those IP extensions
or SIP trunks, the Fast Bridging feature can be disabled on a per
IP extension and per SIP trunk basis. Note that Fast Bridging is
enabled by default.
Advanced Settings Select to see more settings shown below.
DTMF Mode
Try Peer-to-peer RTP
User Agent Override default User-Agent header content.
From Caller ID Send the entered number as Caller ID.
Select a preferred DTMF mode, Inband, RFC 2833 or SIP INFO, for
this trunk in the list. This must match configuration on the server side.
If the user does not know the DTMF mode on the server side, select
Auto from the list, and IP PBX will automatically detect the DTMF
mode on this SIP trunk is Inband or RFC2833.
Click NO to disable or IP PBX will attempt to notify the two peers in a
conversation to try peer-to-peer RTP transmission. This is suggested
as long as phone and ITSP side support re-INVITE or UPDATE
method during a connected call to save the resource of IP PBX.
However, only SIP INFO DTMF mode should enable this since other
DTMF modes require IP PBX being RTP relay server to support in-line
transfer.
Bandwidth Sensitive
Bandwidth Limitation (kbps)
Call Admissi on Control Select to enable the limitation of concurrent calls for a SIP trunk.
Click Bandwidth Sensitive and specify a limit of bandwi d th in kbp s for
call admission in Bandwidth Limitation.
62
Page 74

Allow <number> Concurrent
Select Call Admission Control and enter a number for allowed
Call(s)
Enable ENUM Resolution Select to use ENUM resolution, or leave it as blank.
Clear Bindings Prior
Registration
Disable NAT Traversal IP PBX uses NAT traversal for outgoing traffics by default. Select to
Anti-SIP Blocking Select to ignore illegitimately inserted CA NCEL messages from ISP.
Gateway Trunk Select to (1) trust the peer if IP matches and (2) retain caller ID.
Call Keep Alive Select to check if the call is still ongoing in a certain time.
Registered Keep Alive Select to check the registration status in a certain time.
Delay Before/After
Answering
RFC2833 Payload Type The default payload type is 101. Enter a value between 96 and 127 to
concurrent calls.
If failed to the registration and cannot identify any abnormal settings,
select to un-register before registering again.
disable NAT traversal if media ports in SDP are trusted.
Delay in seconds before and after answering a call from SIP trunk.
change the default payload type when selecting DTMF mode as RFC
2833 or Auto.
WAN LBR Preference Select a low bit rate codec to be used as the first pri ority for outbound
calls. e.g. select Auto to use caller’s low bit rate codec, if any, or G .729
as the first priority.
) To use WAN LBR Preference on a SIP trunk, the WAN Bandwidth
Saver function must be enabled.
6.7 Analog PSTN Trunk configuration
An Analog PSTN trunk group is a logical group of one or more FXO or FXS PSTN subscriber lines
connecting to FXO or FXS ports on IP PBX.
The Analog PSTN Trunk Management page allows the administrator to configure PSTN trunks.
Select Trunk -> Analog PSTN Trunk, and one can add, edit and delete PSTN trunks. Go to Service
-> IP PBX Service, and click Reload to activate changes.
6.7.1 Add an Analog PSTN Trunk
1. Click the Add New tab.
63
Page 75

2. Enter settings shown in Table 6-11.
3. Click Add to see the newly added Analog PSTN trunk in T runk Group.
6.7.2 Edit an Analog PSTN Trunk
1. Click a trunk group in Trunk Group.
2. Enter settings shown in Table 6-11.
3. Click Apply to change the information.
6.7.3 Delete an Analog PSTN Trunk
1. Click the Trunks tab, and select a trunk group.
2. Click Delete to remove the PSTN trunk from the Trunk Group.
Table 6-11 Analog PSTN Trunk Configuration Settings
Field Description
Trunk Group ID number of this PSTN trunk group. A valid number ranges
from 1 to 31. It should not overlap with existing ISDN PSTN
trunk groups.
Trunk Type
Trunk Ports Select one or more FXO or FXS ports for this Analog PSTN
Description Arbitrary description information.
Port Selection
DID Type
None DID
Select the port type, FXO or FXS.
trunk.
Click to search for an available port in the group. Rotating
means to force ports being selected by turns to even cost.
If selecting FXO, user can see None DID, Extension DID
and DID By Privilege in the DID Ty pe list. If selecting FXS,
users can see None DID, Extension DID and DID By
Privilege in the DID Type list.
When selected None DID, all incoming calls will enter IVR
system instead of directly dial to a specified extension.
Select a preferred IVR from IVR list for this trunk.
Extension DID
When selected Extension DID, select an extension in the
list to be an unconditional destination for incoming calls to
this trunk. If prefix or stripping has been given, the result of
digit manipulation is dialed in a DTMF string after the call
has been answered by the DID extension as an automatic
64
Page 76

nd
dialing.
2
) If you set a DID extension in a trunk, then only that
extension can use this trunk to call out, and all
incoming calls to this trunk will connect to that
extension directly.
DID By Number
When selected DID By number, enter configurations in DID
Prefix and DID Stripping to have the incoming calls
directed to the corresponding extension derived by number
manipulation. The trunk numbers is therefore regarde d as
the direct line of the extension.
DID By Privilege
When selected DID By Privilege, select a usergroup i n the
list as the privilege of inbound calls from this trunk. Enter
configuration in DID Prefix and DID Stripping to have the
incoming calls redirected to dial out.
DID Prefix A digit string to be prefixed to the incoming called number
after stripping.
DID Stripping A number of leadin g digits to be stripped from the original
called number. Click All to strip all digits of the original called
number.
Language Preferred language for system instructions heard from the
trunk.
IVR List
25
Associate an IVR menu with incoming calls to this trunk.
This is mandatory unless the trunk is configured for DID.
Leave it blank and the system will automatically create an
IVR for the trunk.
Usergroup26 of Privilege When disabled DID, click a usergroup in the list whose
reachability to other usergroups and trunks will be used as
the privilege of inbound calls from this trunk.
) There may not be any appropriate usergroups to select
initially. One can come back later to revise it, once the
25
Please refer to 7.12 for details.
26
Please refer to 6.1 for details.
65
Page 77

expected usergroups are added.
Delay Before/After Answering Delay in seconds before and after answering a call from
PSTN trunk.
Forced Disconnection of this Duration
(ms) of Silence Detected
Enter a time in ms for disconnecting the call when there is
no sound for the period of time.
6.8 ISDN PSTN Trunk Configuration
An ISDN PSTN trunk group is a logical group of one or more ISDN subscriber lines connecting to ISDN
ports (RJ45) on IP PBX. Currently only Basic Rate Interface (BRI) ISDN service is supported. BRI
consists of two 64 kb/s B channels and one 16 kb/s D cha nnel for a tot al of 144 kb/s. This basi c service
is intended to meet the needs of most individual users.
The ISDN PSTN Trunk Management page allows the administrator to configure ISDN trunks. Select
Trunk -> ISDN PSTN Trunk, and one can add, edit and delete ISDN trunks. Go to Service -> IP PBX
Service, and click Reload to activate changes.
6.8.1 Add an ISDN PSTN Trunk
1. Click the Add New tab.
2. Enter settings shown in
66
Page 78

Table 6-12.
3. Click Add to see the newly added ISDN PSTN trunk in the Trunk Group.
The newly added ISDN y in the Trunk Group.
6.8.2 Edit an ISDN PSTN T
1. Click a trunk
2. Enter settings shown in
Trunk shall displa
runk
group in Trunk Group.
67
Page 79

Table 6-12.
3. Click Apply to change the informatio
6.8.3 Delete an ISDN PS
1. Click the unk group.
2. Click Delete to remove the ISDN PSTN trunk from the Trunk Group.
Trunks tab, and select a tr
n.
TN Trunk
68
Page 80

Table 6-12 ISDN Trunk Configuration Settings
Field Description
Trunk Group ID number of this ISDN trunk group. A valid number ranges
t should not overlap with existing Analog from 1 to 31. I
PSTN trunk groups.
Trunk Channels s three channels, two B
Description Arbitrary description information.
Port Selection
Switch Type fault. Supports European switch type by de
DID T ype DID means direct inward dialing (also called DDI in Europe).
None DID
Each physical ISDN port occupie
and one D channels. The Trunk Channels displays B
channels only. User only needs to select one or more B
channels here. E.g. 1,2 is for the first physical port, 3,4 is for
the second physical port and so on.
Select to
means to force ports being selected by turns to even cost.
Select a preferred type, None DID, Extension DID, DID by
Number and DID by Privilege from the list and then ent
config
incomi
When selected None DID, all incoming calls will enter IVR
system instead of directly dial to a specified extension.
search for an available port in the group. Rotating
er
uration in DID Prefix and DID Stripping to have the
ng calls directed to the corresponding trunk.
Extension DID
DID By Number
Select a preferred IVR from IVR lis
When selected Extension DID, select an extension in the
list to be an u r incoming calls to
this trunk. If prefix or stripping has been given, the result of
digit manipulation is dialed in a DTMF string after the call
has been answered by the DID extension as an automatic
nd
2
dialing.
nconditional destination fo
t for this trunk.
) If you set a DID extension in a trunk, then only that
extension can use this trunk to call out, and all incoming
calls to this trunk will connect to that extension directly.
When selected DID By number, enter configurations in DID
Prefix and DID Stripping to have the incoming calls
directed to the corresponding extension derived by number
manipulation. The ISDN trunk numbers is theref ore
regarded as the
direct line of the extension.
69
Page 81

DID By Privilege
DID Prefix A digit string to be prefixed to the incoming called number
DID Stripping A number of leadin g digits to be stripped from the original
Language e for system instructions heard from the Preferred languag
IVR List
27
When selected DID By Privilege, select a usergroup i n th
list as the privilee ge of inbound calls from this trunk. Enter
configuration in DID Prefix and DID Stripping to have the
incoming calls redirected to dial out.
after stripping.
called number. Click All to strip all digits of the original called
r. numbe
trunk.
ming calls to this trunk. Associate an IVR menu with inco
This is mandatory unless the trunk is configured for DID.
Leave it blank and the system will automatically create an
IVR for the trunk.
Usergroup28 of Privilege sabled DID, clicks a usergrou p in the list whose
Caller ID Leaves it blank to have the default caller ID, or enters a
When di
reachability to other usergroups and trunks will use as
privilege o
) There may not be any appropriate use
calle ed by your ISDN service provider. r ID that is provid
f inbound calls from this trunk.
rgroups to select
initially. One can come back later to revise it, onc
expected usergroups are added.
the
e the
6.9 POTS Setting
The POTS Setting page allows users to s
requirement from the Central Office (CO) t impedance from drop-down list and
fine-tune the paramete ave modifications. Go to Service -> IP PBX Service, and
click Restart to activate new settings.
rs. Click Apply to s
et the parameters of FXO/FXS/ISDN ports based on t he
site. Users can selec
27
Please refer to 7.12 for details.
28
Please refer to 6.1 for details.
70
Page 82

6.9.1 FXO Port Configuration Settings
Table 6-13 FXO Port Configuration Settings
Field Description
Type The type of this port.
Port The ID number of physical port.
Impedance/CP Tone The Impedance/CP Tone setting determines the dial tone,
busy tone, and ringback tone to the originating party. Select
the appropriate impedance/call-progress tone for the local
region.
Default Codec Select g711ulaw or g711alaw for connecting to other
devices.
Input/Output Gain t Voice amplification or attenuation in dB scale to adjus
input/output volume of a PSTN line.
Caller ID Detection
Answering by Battery Reversal If selected, billable time will count from when the call is
Detection answered.
Select to detect the Caller ID calling from PSTN lines.
) Wh
en DID to an extension number, it is suggest to
enable this function, or the forwarding settings at
phone side may not work properly.
) Please enable this function when Central Office (CO)
site provides battery reversal.
Minimum Disconnection Tone Minimum volume level of the disconnection tone. If a PSTN
e , trunk is found to have disconnection problem and low-voic
choose a lower dB.
Call Time Restriction Enter a number (1-1440 ) in minute to limit the call peri od. If a
call lasts longer than the time, IP PBX will force to terminate
the call. Enter 0 or leave it blank to disable the function.
1st/ 2nd Frequency of On-cycle Tone Enter a number in Hz for call disconnection on-cycle tone.
1st/ 2nd Frequency of Off-cycle Tone Enter a number in Hz for call disconnection off-cycle tone.
Min/Max Duration of On-cycle Tone Enter a time in ms for minimum or maximum duration of
le tone. on-cyc
71
Page 83

Min/Max Duration of Off-cycle Tone Enter a time in ms for minimum or maximum duration of
off-cycle tone.
Forced Disconnection of this Duration Enter a time in ms for disconnecting the call when there is
no sound for the specific period of time. (ms) of Silence Detected
6.9.2 FXS Port Configuration Settings
Table 6-14 FXS Port Configuration Settings
Field Des
Type The type of this port.
Port The ID number of physical port.
Impedance/CP Tone The Impedance/CP Tone setting determines the dial tone,
Default Codec Select g711ulaw or g711alaw for connecting to other
Input/Output Gain Voice amplification or attenuation in dB scale to adjust
Caller ID Detection Select to detect the Caller ID calling from PSTN lines.
Answering by Battery Reversal when the call is
Detection
cription
busy tone, and ringback tone to the originating party. Select
appropriate impedance/call-progress tone for the local the
region.
devices.
input/output volume of a PSTN line.
If selected, billable time will count from
answered.
) Please enable this function when Central Office (CO)
site provides battery reversal.
Minimum Disconnection Tone TN
Call Time Restriction t the call period. If a
Minimum volume level of the disconnection tone. If a PS
trunk is found to have disconnection problem and low-voi
choose a lower dB.
Enter a number (1-1440) in minute to limi
call lasts longer than the time, IP PBX will force to terminate
the call. Enter 0 or leave it blank to disable the func
72
ce,
tion.
Page 84

6.9.3 ISDN Port Configuration Settings
Table 6-15 ISDN Port Configuration Settings
Field Description
Type The type of this port.
Port The ID number of physical port.
Impedance/CP Tone The Impedance/CP Tone setting determines the dial tone,
the appropriate impedance/call-progress tone for the local
region.
Default Codec Select g711ulaw or g711alaw for connecting to other
devices.
Compand Type Compand standards vary between countries. Select
MULAW or ALAW for the local region.
ct busy tone, and ringback tone to the originating party. Sele
Signaling
Caller ID Leave it blank to have the default caller ID, or enter a caller
6.10 Digitmap Configur
The digitmap is for Centrex DID in SIP trunks. A pattern consists of digits 0-9 (including “-”), “*”, “#”,
digit set, and wild Route Configuration explains digit set and
ildcard characters.
w
Note: The “#” in the patte
most of the IP Phones, p
card characters like “.”, “X”, “Z”, and “N”. in
rn is for some PSTN saver lines that may set “#” as their dial pattern. For
ress “#” will immediately send out the dialed number.
Select Point to point or Point to multipoint depends on
the link type between ISDN service provider and your
device.
ided by your ISDN service provider. ID that is prov
ation
6.10.1 Add a Digitmap
1. Click the Add New tab.
. Enter settings show in Table 6-16.
2
3. Click
4. Click Add to have newly added digitmap.
to see the pattern in the list.
73
Page 85

6.10.2 Edit a Digitmap
1. Select a digitmap ID.
2. Edit settings show in Table 6-16.
3. Click
4. Click
5. Click Apply.
6.10.3 te a Digitmap
Select a digitmap ID.
1.
2. Click Delete to remove
Table 6-16 Digitmap Configuration Setting
Field Description
Digitmap ID A unique ID cont aining alphabets, numbers, and underscore
Destination Number Pattern A des
or to add or delete the pattern.
or to adjust the order of sequence.
Dele
the ID.
s
only without spaces; 17 characters maximum.
and w
tination number pattern consisting of digits, digit set,
ildcard characters, e.g. 9NXXXXXX matches any
t number starting from a dig
7-digi it larger or equal to 2 and
with an extra prefix digit 9.
Number of Stripped Digits Number of leading digits to be stripped from the original
number when matches this digitmap. Using 9NXXXXXX as
xample pattern with number of stripped digits equ al to 1,
an e
dialing 95270001 will be stripped and change to 5270001
Prefix A sequence of digits to be prefixed to the number after
stripping. Using 9NXXXXXX as an example pattern with
number of stripped digits equal to 1 and prefix 1408, dialing
95270001 will change to 14085270001.
A special pref ix character “w” could be used
to pause 0.5 second during dialing. Say, 4 leading
consecutive “w” result in 2 seconds delay before diali
for PSTN trunks
ng.
.
74
Page 86

7 Feature Configuration
A feature is a logical entity pre sentin g a function module of
attendant, voice mail, music on hold, etc.
Reload in Service -> IP PBX Service to take ef
Any configuration change to a feature requires clicking
fect.
IP PBX, e.g. meet-me conference, auto
7.1 Call Park
During a call, the callee may want to continue the conversation using another p hone. The call park
feature enables so by letting the cal
IP PBX will respond an available park line from the pool of call par
the callee may hang up current phone, move to another phone, an
PBX to resume conversation with the caller. If the callee does no
retrieve his call before timeout, IP
call. To configure Call Park feature, select Feature -> Call Park.
1. s shown in Table 7-1.
Enter setting
2. Click Apply.
lee transfer the call to the call park pilot number (*# + Pilot Number).
k numbers to the callee. Af ter that
d dial the park line number told by IP
t call the given park line number to
PBX will ring the original extension where the callee answered the
Table 7-1
Field Description
Call Park Pilot Number arking, e.g. 700. A unique extension number for call p
Available Parking Lines 20 forms a An extension pool for call parking, e.g. 701-7
Parking Time out the parked call Timeout waiting for picking up
Call Park Configuration Settings
20-line pool available for system to park calls.
7.2 Life Line
Life line feature allows specification of emerg ute
priority . For e xample, someone dials an emerg s are in use. In such case, if
the called number matches any specified life line pattern, the PSTN line with longest t alk time so far will
be disconnected right away to allow th e
Select Feature -> Life Line to configure life-line featu
e mergency call.
ency number patterns to seize a PSTN line with absol
ency call while all PSTN line
re.
75
Page 87

7.2.1 Add a Life Line Pa
1. Enter settings shown in Table 7-2.
ttern
2. Click Add to see the newly added pa
7.2.2 Edit a Life Line P
1. Edit settings shown in a row.
2. Click Apply at the end of the row to update the information.
ttern in the Line Pattern.
attern
7.2.3 Delete a Life Line Pattern
1. Select a Line pattern.
2. Click Delete to remove the pattern from the Line Patte
Table 7-2 Life line Configuration Settings
Field Description
Line Pattern Pattern for e
Note: This i
rn.
mergency numbers.
s the pattern after digit stripping. For example,
configure 911 here even if users dial 9911 to reach the
911 service over PSTN when the PSTN trunk has an
outbound dialplan of “9.”.
Des ription Arbitrary description information. c
7.3 Meet-me Conference
Meet-me conference enables c
could reach this virtual conference room by dialing in a conferen
m
eet-me conference as administrator or normal user level. Administrator has more privilege during the
conference. Please refer to Table 7-3
IP PBX allows multiple conference room
entering a meeting room
N
ote: The administrator must drop all parties by pressing *5 when the meeting ends.
onferencing of multiple parties from various devices. A calling party
ce. Moreover , you can enter the
.
s going concurrently using different room numbers. Before
, the caller has to enter the correct PIN of the room number.
S
elect Feature -> Meet-me Conference to configure meet-me conference feature.
76
Page 88

7.3.1 Add a Meet-me Conf
1. Enter settings shown in Table 7-3.
2. Click Ad room.
The newly added room should display in t
d to add a new conference
7.3.2 Edit a Meet-me Co
1. Edit settings shown in a row.
2. Click Apply at the end of the row to te the information.
7.3.3 De Conference
1. Select a room number .
2. Click Delete to remo
Table 7-3 Meet-me Conference Configuration Settings
lete a Meet-me
ve the conference room from the Room Number.
erence
he Room Number.
nference
upda
Field Description
Room Number Meeting room number, e.g. 8000.
Description Arbitrary description information.
PIN to Join PIN for normal users to join the conference.
During a conference, a normal user has following options:
- # to quit conference
- *1 to mute/unmute
- *9 to log in as the administrator if there is no
administrator dialed in yet.
Administrator PIN PIN for the administrator of the conference.
ring a conference, the administrator has following
Du
options:
- # to quit conference
- *1 to mute/unmute
- *2 to lock/unlock the conference
- *3 to invite a us
- *4 to drop a party from the conference
-
*5 to drop all parties in the conference
77
er into the conference
Page 89

- *6 to drop the last invited party by *3
- ** to send DTMF string to the last invited party by
*3. This is useful when the invited party is behind
IVR system.
an
7.4 Music On Hold
Music-on-hold (MOH) is used in several occasions for a single purpose—to comfort the wait ing party
with music. One could upload some ca e music files and pick one as the default one.
Select Feature -> Music On Hold to manage MOH files.
7.4.1 Music on Hold Ma
ndidat
nagement
7.4.1.1 Add a MOH File
Enter settings shown in
1. Table 7-4.
2. Click Add to see the e in the MOH ID.
.4.2 Media File Management
7
newly added fil
7.4.2.1 Edit a MOH File
1. Upload Media File: Click Browse to select a file and Click Put File to upload.
2. Delete Media File: Select a file from the drop-down list an
3. Default MOH: Click a MOH ID from the drop-down list and click Set i
d Click Delete to remove it.
7.4.3 MOH ID List
7.4.
3.1 Edit a MOH ID
1. Click a file from the Media File and click Apply in the row .
7.4.3.2 Delete a MOH File
1. Select a MOH ID.
2. Click Delete to remove the MOH ID from the MOH ID List.
78
n the row.
Page 90

Table 7-4 MOH file Configuration Settings
Field Description
MOH ID A unique ID containing only alphabets, numbers, and
underscore without spaces; 32 characters maximum.
Media File Candidate music files in the repository. To upload a new
music file, click Browse to find a Windows PCM (8000 Hz,
16-bit) file from the local host and click Pu
successful uploading
File list. To delete a media file from the list, choose a file
from the Delete Media Fil
it.
Default MOH Select to use this music file for system default MOH globally.
, the filename will appear in the Media
e list, and click Delete to remove
t File. On
7.5 Voicemail
IP PBX has a built-in voice mail subsystem with a sophisticated IVR menu. A call to an extension in use
r no answer could be configured to enter voice mail recording procedure. After leaving a message, a
o
notification e-mail will be sent to the user owns the e
an attach
phones before the normal dial tone when picking up the analog
phone. The user could then dial the voicemail pilot number to enter voice mail system to manage
messages ve them from inbox to dif
ed WAV file. The Message Waiting Indicator (MWI) on IP phones (if any) will be lit. For a nalog
, the user will hear six short beeps
such as playback, delete, or mo ferent folders. In addition to
xtension with or without the message in the form of
indicating current v he management page, IP PBX can send an alarm e
the adminis mail space
feature, select Feature -> V
1. Enter settings shown in Table 7-5.
2. Click Ap
Table 7-5 V s
Field Description
Voicemail Pilot Numbe r voice mail system IVR, e.g. 6666. Number to access
Minimum Message Ti me is duration will not be saved as a
trator when the available voice reaches the threshold. To configure Voicemail
oice Mail Configuration Setting
oice mail capacity on t mail to
oicemail.
ply.
Messages less than th
message. e.g., 3 (sec)
79
.
Page 91

Maximum Message Time Maximum duration allowed for a single message. e.g., 60
(sec).
Maximum number of messages per Maximum number of messages allowed per extension.
account
SMTP Server Hostname or IP address of the SMTP server for voicemail
notification.
E-mail from Addre s s Most SMTP from address to accept a servers require a valid
mailing request.
Voicemail Available Space Check Select to enable the Alarm Email function described below.
Send Alarm Email whe n Space Below Set a threshold in minutes to send an alarm email to the
administrator when the space left is below it.
Voicemail Space L Show the available space in Kbytes and minutes.
SMTP Server Account Specify an account ID if the SMTP serv er requires
SMTP Server Password Specify the account password if the SMTP server requires
eft
) The storage inside IP PBX saves not only voice ma
but also some other stuff, such as CDR and logs. The
remained disk space is all for voice mails, and it is the
“maximum” available voice mail space.
authentication for outgoing mails.
authentication for outgoing mails.
ils
7.6 Meet-me Prompts
This page allows repl ng built-in meet-me conference prompts with user recordings.
1. Click a lan age and a prompt in the corresponding list
aci
gu s.
2. Click Browse to find a corresponding recording in the local storage .
3. Click Put File to complete the replacement.
4. T efault, click a l
o reset a prompt back to d anguage and a prompt in the corresponding lists, and
th
en click Use Default.
Note that the replacement is d Prompt only and the prompt is
marked st if it is not a default prompt. Currently only following prompts could be
replaced.
“*” in the dropdown li
done for the selected Language an
80
Page 92

Table 7-6 Replaceable Meet-
Prompt Des
Get PIN Number r. Please enter the conference pin numbe
Invalid PIN That pin is invalid for this conference.
Only Person You are currently the only person in this conference.
7.7 Voice mpts
This page allows r ilt-in voicemail system prompts with user recordin
1. Click a prompt in the corresponding lists.
2. Find a cording in the local storage.
3. Click Put File te the replacement.
4. To reset a pro to default, click a language and a prompt in the correspon d
then click Use Default.
mail Pro
eplacing bu gs.
language and a
corresponding re
to comple
mpt back ding lists, an
me Prompts
cription
ote that the replacement is done for the selected Language and Prompt only and the prompt is
N
marked “*” in the dropdown list if it is not a default prompt. Currently only following prompts could be
replaced.
Table 7-7 Replaceable Voicemail System Prompt s
Prompt
Login Welcome to voice mail system, please enter your mailbox.
Password Password.
Incorrect Mailbox Login incorrect, please enter your mailbox again.
Good-bye Good-bye.
Pre cording Introduction re Press star (*) to cancel recording and return to the main
Introduction Please leave your message after the tone. When done,
Extension Extension.
Description
enu. Or, press pound (#) to start recording right away. m
hang up or press the pound (#) key.
Unavailable It’s not available.
Busy It’s on the phone.
81
Page 93

Lin sdown ei Device Unreachable.
Isnotreg Device Unregistered.
7.8 Broadcast
A user can arrange an event at the exact time in IP PBX. IP PBX will inform all users that set in the
Callee Extensions
remind all attendants, he/she may enter settings. When the time set
to the extensions, and then executes the Action to each of the calls. Select Feature -> Broadcast to
onfigure Broadcast feature.
c
7.8.1
1. C
2. Enter settings shown in
3. Click Add at the bottom ast event in the Events.
Add a Broadcast
lick the Add New tab.
7.8.2 Edit a Broa
1. Click the Mana ab.
2. Click an Event.
3. Edit settings s able 7-8.
list by ringing their extensions. For example, one arranges a meeting and wants to
in Date/Time is up, IP PBX will call
Table 7-8.
of the page to see the newly added broadc
dcast
gement t
hown in T
4. Click Apply to change t
he information.
7.8.3 Delete a Broadcast
1. Click the Management tab.
2. Select an Event.
3. Click Delete to remove the broadcast event from the Events.
Table 7-8 Broadcast Configuration Settings
ield Description
F
Event A unique ID containing al phabets, numbers, and underscore only without
cters maximum. spaces; 32 chara
Action Select one of the three actions to execute when the Date/Time is up.
82
Page 94

Playback: Play the uploaded WAV file in the Customized Media File
box to the callee extensions.
Dial: IP PBX will ring the party set in the Callee Extensions box first,
Customized media File
and then cal
conversation.
It is sugge
the extension number in the Dial Extension field is multi-line.
Play defau
page to extensions
Upload a *.wav file, if Playback is selected in the Action list.
l back to the one in the Dial Extension field to establish a
sted to set one number only in the Callee Extensions unless
lt music: Play default music configured in the Music On Hold
in the Callee Extensions box.
) The recording format must be 8000 Hz, 16 bit, mono Wi ndows PCM
WAV file.
Dial Extension
Max Retry Times Maximum redial times if callees did not answer.
Retry Time A period of time in minutes between two retrying.
Wait Time in seconds when ringing a callee. Enter timeout
Date/Time Select a Date/Time to trigger this broadcast event.
Select an extension to call back if Dial is selected in the Action.
Callee Extensions
extensions to be called at the Date/Time. Click Intended to
select/remove the selected callee extension(s) from this list.
/
7.9 Worktime
Worktime page defines holid
date/time could be defined fo Feature -> Worktime to configure Worktime
features.
7.9.1 Add a Work e
1. Click the Add New tab.
2. Enter setting Table 7-9.
3. Click A of the page.
The newly ould display in the Group ID.
added worktime sh
s shown in
dd at the bottom
ays and business hours for generic IVR application. Several grou ps of
r different IVR menus. Select
tim
83
Page 95

7.9.2 Edit a Worktime
1. Click the Management tab.
2. Click a Group ID.
3. Edit settings shown in Table 7-9.
4. Click Apply to change the information.
7.9.3 Delete a Worktime
1. Click the Management tab.
2. Select a Group ID.
3. Click Delete.
The deleted worktime shall disappear from the Group ID.
Table 7-9 Worktime Configuration Settings
Field Description
Group ID A unique ID containing numbers only.
Mode Select one of the four modes:
1: No work on weekends.
2: Work off and on by turns on Saturd
3: Work half-day on Saturdays.
4: Work on all 7 days
General Worktime The work time from Monday to Friday.
Saturday Worktime The work time for Saturdays, this field only active when mode is set to 2
or 3.
Optional Worktime lidays or work day. User can set date and its work time, or set Special ho
item(s) from this list. selected
ays.
/ it to a whole-day holiday. Click to select/remove the
7.10 Memo Call
A user can set a memo at a specific time, e.g. a mornin
user set in the Extension list by call at the time. When the user picks up the phone, IP PBX plays
“voice file” or “music”. The user can also
user at the exact time every day. Select Feature -> Memo Call to configure memo calls.
set this memo as a daily routine so that IP PBX informs the
g call, in IP PBX to inform the user or another
84
Page 96

7.10.1 o Call
1. Click Add New tab.
2. Enter settings shown in Table 7-
3. Click Add at the bottom of the page t
7.10.2
. Click the Management tab.
1
2. Click a Memo.
3. Edit settings shown in Table 7-10.
4. Click Apply to update the informatio
7.10.3 Delete Mem
1. Click the Management tab.
. Select a Memo.
2
Add a Mem
the
10.
Edit a Memo Call
o Call
o see the newly added memo call in the Memo.
n.
3. Click Delete to remove the memo
Table 7-10 Memo Configuration Se
ld Description
Fie
Memo A unique ID containing alphabet s, num bers, a nd u ndersco re o nly wi thout
spaces.
Extension n to call. Click an extensio
Repeat Daily
Action mo.
Customized Media File
Select one out of the two available actions for the me
Playback: Play the uploaded WAV file in the Customized Media File
box to the extension(s).
Play default music: Play default music configured in the Music On Hold
page to the extension(s).
Upload a *.wav file, if Playback is selected in the Action list.
call from the Memo.
ttings
ery day at the exact time. Select Yes to enable looping playback ev
) The recording format must be 8000 Hz, 16 bit, mono Wi ndow
WAV file.
85
s PCM
Page 97

Max Retry Times Maximum redial times if callees did not answer.
Retry Time A period of time in minutes between two retries.
Wait Time Enter timeout in seconds when ringing a callee.
Date/Time Select a Date/T ime to trigger this memo call.
7.11 Automatic
IP PBX implements Automati es and agents. A pool of agents is
created first and then one or more queues could be added with distinct service numbers and a list of
agent extensi d be bound with an existed extension to take calls and each que
could have a specific distribu
random. With such settings one can enable agents located at any location to serve a unified queue of
calls. This comes with a benefit tha
changes immediately become effec tribution
centers to be ffectively, but also reduces the cost and complexity of implementing
home-based agents, who now ection to serve calls in queues. Refer to for
creating an agent p r setting queues. Select Feature -> ACD to configure agents and
queues.
Note that the agents are limit
7.11.1 Set Agent
Before ad es of the ACD, the administrator has to give universal Agent Logi
ons. Each agent shoul ue
operated cost-e
ool, and fo
ding agents or queu n and
Call Distribution
c Call Distribution (ACD) by queu
tion policy, such as round robin, ring all, least recent, fewest calls, and
t administrative changes can be made in a single place, and these
tive for all calls and all agents. This not only enables di s
only need an IP conn
ed to local extensions; login through trunk is not allowed.
Login and Logout
Logout num s.
1. Click the Agent Login /
2. Enter numbers in Agent L ut.
. Click Apply to apply login and logout numbers to all agents.
3
Note that the agent login and logout numbers can not be set the sam
bers for all agent
Logout tab.
ogin and Agent Logo
7.11.2 Add an Agent
1. Click the Agent Management tab.
2. Enter settings shown in Table 7-11.
3. Click Add to see the information in the table below.
7.11.3 Edit an Agent
1. Click the Agent Management tab.
86
e.
Page 98

2. Edit settings shown in Table 7-11 in a row oApf the table below.
3. Click ply in the row to update the information.
7.11.4
1.
2.
3. Click Delete to remove the agent from
Delete an Agent
Click the Agent Management tab.
Select an account in the table.
the table.
7.11.5 Add a Queue
1. Click the Add New Queue tab.
2.
Enter settings shown in Table 7-12.
3. lic
C k Add.
The new ueue ab.
7.1 .
1. Click the Manage tab and a queue.
ly added q displays in the Management t
1 6 Edit a Queue
2. Enter settings shown in Table 7-12.
3. Click Apply.
The updated queue displays in the Management tab.
7.11.7 Delete a Queue
1. Click the Management tab.
2. Select a queue.
3. Click Delete to remove the queue from the Management page.
Table 7-11 Agent Configuration Settings
Field Des
Account Enter an account number for the agent.
PIN password for the agent. Enter a login
Agent Name The name of agent. A unique ID containing alphabets, numbers, and
cription
underscore only without spaces; 20 characters maximum.
87
Page 99

Table 7-12 Queue Configuration Settings
Field Description
Qu e Name Name a queue. A uniqeu ue ID containing alphabet s, numbers, and
ly without spaces; 20 characters maximum. underscore on
Waiting Music The default media file in Music On Hold is the waiting music.
Distribution Policy Ways of distributing calls to the agents in a queue:
Round Robin:
Ring All: ring all available agents unt
Least Recent: ring the agent that was least recently called in this queue.
Fewest Calls:
Random: ring the agents randomly.
User Group ue. Only extensions that belong to the Select a usergroup for this que
usergroup can login the queue.
Timeout call.
Set a timeout period in seconds when no agent answers the
) The time must be shorter than Time
extension, or the call will forwarded to an extension that is s
Unavailable Call Forward in Extension of IP Phone.
Retry Time g time in seconds to ring agents in the queue again if the call
Service Extension S
Set a waitin
answ
is not ered.
et the representative number of this queue, e.g. a queue named
ort, and its service extension is 500. There are three agents with
Supp
take turns to ring each available agent.
il one answers (default).
ring the agent with fewest completed calls in this queue.
out To Nex t Forward of the
et in
extensions 7, and 166 in Support. The Distribution Pol
set to Ring a customer call s the service extension 500 for
Support, extensions 1
Max Len er of callsSelect numb for waiting when all agents are occupied.
Agent List
7.12 Interactive
Interactive Voice Response (
on a telephone keypad. With IVR, a caller can conn on or a service promptly.
IP PBX enables multiple conf menus in
hierarchy up to three layers. Select Feature -> IVR to add, edit and delete the IVR menus. You can
Click to s queue.
The left b vailable agents, and th
selected agents.
Voice Response (IVR)
IVR) helps a caller to select options from voice menus by pressing keys
igurable IVR a single system, and each of them could have a
of 155, 15 icy is
All. When
55, 157, and 166 will all ring simultaneously.
/
ox lists the a e right box shows the
select/remove the selected agent from thi
ect to an expected extensi
88
Page 100

also manage IVR prompts, used by IVR menus, in t
his page.
7.12 IVR Menu
1. Click Add New, enter a
2. Click
3. Enter se Table 7-13.
4. Click Save to add the n enu.
5. Click the IVR in the All IVR Menus list to see
6. For example, to create a basic Auto Attendant
.1 Add a new
name of an IVR menu in IVR Name, and click a file in the Prompt list.
next to the Info. System will prompt to
r confirmation whe
ask fo ther a Worktime setting is required or not. If W orktime setting is not
required, click Cancel in
ttings shown in
• Enter an IVR Name, say Basic_AA
• Choose Thank you from Prompt list in Act
• Click the
• Click Cancel in the pop-up window to confirm the Worktime setting is not required.
• Click Save.
IVR Name box to set the new IVR name in
the pop-up window.
ew IVR m
it as a tree view in Info.
IVR for a trunk with Usergroup of Privilege dial_in:
ion Data block.
next to the IVR Name box
.
• Now, Basic_AA should be available in the
IVR List of Trunk pages.
7.12.2 Edit an IVR Menu
1. Click an IVR name in the All IVR Menus list.
2. Click Modify if you want to change the promp orktime settings for the first level of IVR.
3. Select a prompt and modify the worktime setti
4. Click Update to change the prompt and workt
5. For other settings, edit settings shown in Tabl
6. Click Save to update th
e changes.
t and w
ngs.
ime settings.
e 7-13.
7.12.3 Clone an IVR Menu
1. Select an IV m the All IVR Menus list.
2. Cl
3. Enter a new IVR name.
ick Clone.
R name fro
4. Edit settings shown in Table 7-13.
5. Click Save to have the IVR in the All IVR Menus list.
89
 Loading...
Loading...