Planet Technology IPX-1900 User Manual

Internet Telephony PBX System
IPX-1900
User’s manual
Version 1.0.

Copyright
Copyright (C) 2008 PLANET Technology Corp. All rights reserved.
The products and programs described in this User’s Manual are licensed products of PLANET Technology, This
User’s Manual contains proprietary information protected by copyright, and this User’s Manual and all
accompanying hardware, software, and documentation are copyrighted.
No part of this User’s Manual may be copied, photocopied, reproduced, translated, or reduced to any electronic
medium or machine-readable form by any means by electronic or mechanical. Including photocopying, recording,
or information storage and retrieval systems, for any purpose other than the purchaser's personal use, and without
the prior express written permission of PLANET Technology.
Disclaimer
PLANET Technology does not warrant that the hardware will work properly in all environments and applications,
and makes no warranty and representation, either implied or expressed, with respect to the quality, performance,
merchantability, or fitness for a particular purpose.
PLANET has made every effort to ensure that this User’s Manual is accurate; PLANET disclaims liability for any
inaccuracies or omissions that may have occurred.
Information in this User’s Manual is subject to change without notice and does not represent a commitment on the
part of PLANET. PLANET assumes no responsibility for any inaccuracies that may be contained in this User’s
Manual. PLANET makes no commitment to update or keep current the information in this User’s Manual, and
reserves the right to make improvements to this User’s Manual and/or to the products described in this User’s
Manual, at any time without notice.
If you find information in this manual that is incorrect, misleading, or incomplete, we would appreciate your
comments and suggestions.
CE mark Warning
The is a class B device, In a domestic environment, this product may cause radio interference, in which case the
user may be required to take adequate measures.
WEEE Warning
To avoid the potential effects on the environment and human health as a result of the presence of
hazardous substances in electrical and electronic equipment, end users of electrical and electronic
equipment should understand the meaning of the crossed-out wheeled bin symbol. Do not dispose of
WEEE as unsorted municipal waste and have to collect such WEEE separately.
Trademarks
The PLANET logo is a trademark of PLANET Technology. This documentation may refer to numerous hardware
and software products by their trade names. In most, if not all cases, their respective companies claim these
designations as trademarks or registered trademarks.
2

Revision
User’s Manual for PLANET Internet Telephony PBX System:
Model: IPX-1900
Rev: 1.0 (June, 2008)
Part No. EM-IPX1900 Series V1.0
3

Table of Contents
Chapter 1................................................................................................ 6
Introduction............................................................................................ 6
Overview............................................................................................................................6
Package Content...............................................................................................................7
Physical Details.................................................................................................................7
Front Panel Indicators.................................................................................................8
Rear Panel Indicators..................................................................................................8
Chapter 2 Preparations & Installation................................................ 10
Physical Installation Requirement................................................................................10
Network Interface quick configurations...................................................................11
RS-232 Console Port Configuration.........................................................................14
Chapter 3 IP PBX Setup ...................................................................... 16
SIP Basic Setting.............................................................................................................16
User Extensions Setup..............................................................................................19
Trunk Management – SIP Trunk ..............................................................................20
Trunk Management – FXO Trunk............................................................................22
Trunk Management – Gateway Trunk......................................................................24
Trunk Management – Trunk Group..........................................................................24
Trunk Management – Dialing Rules.........................................................................26
Attendant Management.............................................................................................30
Attendant Message ...................................................................................................31
Attendant Time.........................................................................................................32
Record Auto Attendant.............................................................................................33
Upload Voice File.....................................................................................................34
Call Parking..............................................................................................................34
Gereral Setting..........................................................................................................35
Hunt Group Setting...................................................................................................37
Chapter 4 Network Setup.................................................................... 40
WAN & LAN Setup........................................................................................................40
DHCP .......................................................................................................................45
Static Route...............................................................................................................47
NAT ..........................................................................................................................47
Packet Filter..............................................................................................................51
URL Filter.................................................................................................................52
Security.....................................................................................................................53
UPnP.........................................................................................................................54
DDNS .......................................................................................................................54
SNMP .......................................................................................................................55
4

Chapter 5 Management....................................................................... 57
Admin Account ...............................................................................................................57
Date & Time .............................................................................................................58
Ping T est...................................................................................................................59
Save & Restore.........................................................................................................59
Factory Default.........................................................................................................60
Firmware Update......................................................................................................60
Chapter 6 Information ......................................................................... 61
System Information........................................................................................................61
PBX Extension Status...............................................................................................62
PBX Trunk Status.....................................................................................................62
Call Detail Record....................................................................................................63
Appendix A........................................................................................... 64
How to use Call Parking function.................................................................................64
Appendix B........................................................................................... 65
How to use Call Pick-up function..................................................................................65
Appendix C........................................................................................... 66
Record Sound Sample....................................................................................................66
Appendix D........................................................................................... 68
Record Voice Guide Process..........................................................................................68
Appendix E........................................................................................... 69
Voice Communication Samples.....................................................................................69
IP Phone register to IPX-1900..................................................................................69
IP Phone make off-Net calls via Gateway................................................................71
IP Phone make external SIP Proxy calls via SIP Trunk............................................76
Appendix F........................................................................................... 78
IPX-1900 Series Specifications......................................................................................78
Appendix G........................................................................................... 80
IPX-1900 Module Card Specifications .........................................................................80
FXO Port Pin Assignments............................................................................................81
FXS Port Pin Assignments.............................................................................................81
5

Chapter 1
1
Introduction
Overview
PLANET IPX-1900 IP PBX telephony systems are designed and optimized for the small business in
daily communications. The IPX-1900 are able to accept 300 user registrations, and easy to install and
manage a fully working system with the convenience and cost advantages. The PLANET IPX-1900 is
also designed to operate on a variety of VoIP applications; it provides centralized call control,
auto-attendant, voice conferencing, and PSTN access, digital and IP-based communications.
Based on state-of-the-art embedded technology, the IPX-1900 provides a solid, uniform platform for
voice communications as well as data network communications. The IPX-1900 offers a seamlessly
integrated solution for the up-to-date telecommunication needs. The future IP PBX telephony system
offers all of the essential features of telephony which is required by small business/enterprise users for
their telecommunication/data needs.
Being more flexible, the IPX-1900 integrates up to 4 calls via the IPX-19FO (2*FXO) / IPX-19FS (2*FXS)
/ IPX-19SL (1FXO+1FXS) module to become a feature-rich PBX system that supports seamless
communications between existing PSTN calls, analog, IP phones and SIP-based endpoints.
The IP PBX is the feature-rich SIP based IP PBX telephony system that integrates NAT functions to
make it perfect for small business usage. The IP PBX integrates traditional PBX system functions and
provides many advanced functions including voice mail to email, web management etc.
Designed to run on a variety of VoIP applications, the IP PBX provide IP-based communications, voice
conferencing, and call detailed record (CDR), centralized Auto-Attendant (AA), and Interactive Voice
Responses (IVR). The IP PBX utilizes standard PSTN/GSM lines via the interfaces of FXO/GSM
gateway to become a feature-rich IP PBX telephony system that supports seamless communications
among existing local calls, SIP-based endpoints including low cost of long distance service, telephone
number portability and one network for both voice and data.
With the IP PBX, standard SIP phones can be easily integrated in your office. Users may integrate
PLANET IP Phone VIP-254T series, VIP-255PT/ 350PT/ 550PT, the VIP-156/ 157/ 158/ 161W of ATA
(analog telephone adapter) series, the VIP-191/ 192 of Wi-Fi Phone, and Gateway series VIP-281/
281GS/ 480 to build up the VoIP network deployment in minutes. Allowing distributed IP technology to
meet traditional voice services with proactive managed interface, the IP PBX for enterprises in the daily
business processes can make people more productive, more intelligent tasks and more customer
satisfaction.
6

IP PBX Features
• PBX Features
Automated Attendant (AA)
Interactive Voice Responses (IVR)
Voicemail support (VM)
Call Detailed Record (CDR)
User Management via Web Browsers
Display 300 Registered User’s Status: Unregistered / Registered / On-Call
Multiple Service Providers Lines / SIP Accounts (30)
Simultaneous Trunk Links: 30 concurrent trunk calls
SIP Trunk / Gateway Trunk / FXO Trunk Management
Two-stage / One-stage call to Trunk by Trunk Group Configuration
Build in 2 / 4 FXO PSTN trunk (Modular)
By adding external FXO analog gateway to use Terminal trunk Line
By adding external GSM VoIP gateway to use GSM trunk line
Built-in SIP Proxy Server Following RFC-3261
Support password authentication using MD5 digest and RFC2833 for DTMF Relay
• Call Features
Call Forward Immediate
Call Forward on Busy
Call Forward on No Answer
Call Pickup / Call Park
Call / Pickup Group
Caller ID / T.38 FoIP
Music on Hold / Music on Transfer
Call Transfer / Call Hold / Call Waiting
Three-way conference with feature phones
• Router Features
DHCP Server for LAN Users
Packet / URL Filter Virtual Server / DMZ/ Port Trigger
Static Route
NAT/Bridge mode
UPnP
Package Content
The contents of your product should contain the following items:
Internet Telephony PBX system unit
Power Adapter
Quick Installation Guide
User’s Manual CD
RJ-45 Cable
RS-232 Cable
Rack mount brackets
Physical Details
The following figure illustrates the front/rear panel of IP PBX.
7
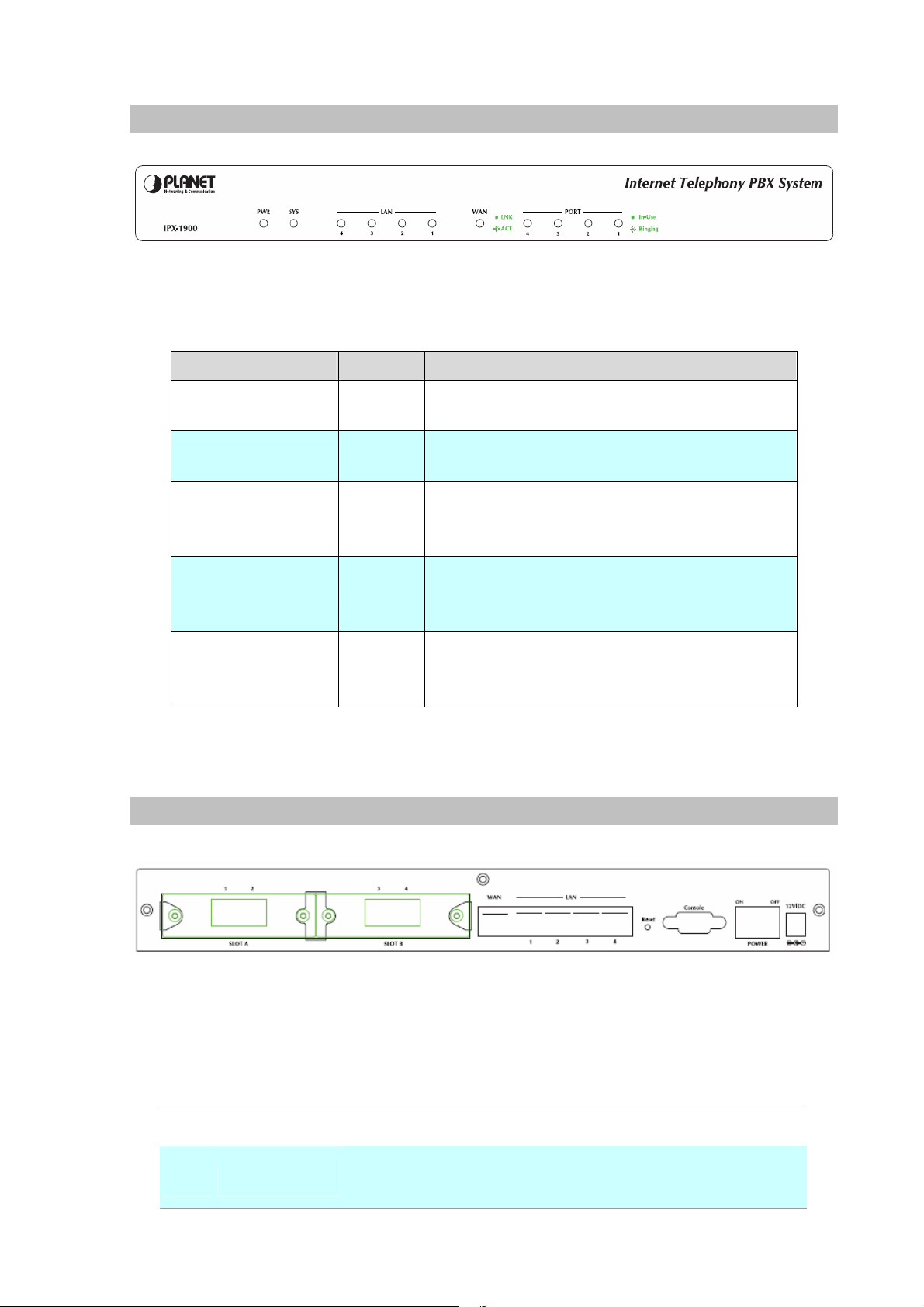
Front Panel Indicators
Front Panel LED State Descriptions
Figure 1-1. Front Panel of IPX-1900
PWR
SYS
LAN
WAN
FXO/FXS Port
Rear Panel Indicators
On
Off
On
Flashing
On
Flashing
Off
On
Flashing
Off
On
Flashing
Off
Table1-1. Front Panel description of IP PBX
PBX Power ON
PBX Power OFF
System is booting
System is ready
LAN is connected successfully
Data is transmitting
Ethernet not connected to PC
PBX network connection established
Data traffic on cable network
Waiting for network connection
Port is busy
Ring indication. (FXS only)
Port is not enabled.
Figure 1-2. Rear Panel of IPX-1900
1 12V DC
2 Reset
12V DC Power input outlet
The reset button, when pressed, resets the IP PBX without the
need to unplug the power cord.
8
The WAN port supports auto negotiating Fast Ethernet
3 WAN
4 LAN
Slost A/B
5
FXS Port
(Modular
IPX-19FS)
10/100Base-TX networks. This port allows your IP PBX to be
connected to an Internet Access device, e.g. router, cable modem,
ADSL modem, through a CAT.5 twisted pair Ethernet cable.
The LAN port allows your PC or Switch/Hub to be connected to the
IP PBX through a CAT.5 twisted pair Ethernet cable.
2 external slosts with compliance FXO/FXS module.
FXO module is connects to PBX or CO line with RJ-11(Write)
analog line. FXO port was connected to the extension port of a PBX
or directly connected to a PSTN line of carrier
FXS module is connects to Phone with RJ-11 (Black) analog line.
FXS port was connected to your telephone sets, FAX, or Trunk Line
of PBX.
Connect to Phone with RJ-11 (Black) analog line. FXS port was
connected to your telephone sets, FAX, or Trunk Line of PBX.
FXO Port
(Modular
IPX-19FO)
Connect to PBX or CO line with RJ-11(Write) analog line. FXO port
was connected to the extension port of a PBX or directly connected
to a PSTN line of carrier
Note : IPX-19SL 2-Port PBX Life Line Module IPX-1900 (1FXO, 1FXS)
Table 1-2. Rear Panel description of IP PBX
9
Chapter 2
Preparations & Installation
2
Physical Installation Requirement
This chapter illustrates basic installation of IP PBX
• Network cables. Use standard 10/100Base-TX network (UTP) cables with RJ45 connectors.
• TCP/IP protocol must be installed on all PCs.
For Internet Access, an Internet Access account with an ISP, and either of a DSL or Cable modem (for
WAN port usage)
Administration Interface
PLANET IP PBX provides GUI (Web based, Graphical User Interface) for machine management and
administration.
Web configuration access:
To start IP PBX web configuration, you must have the web browsers installed on computer for
management
• Microsoft Internet Explorer 6.0.0 or higher with Java support
Default LAN interface IP address of IP PBX is 192.168.0.1. You may now open your web browser, and
insert 192.168.0.1 in the address bar of your web browser to logon IP PBX web configuration page.
IP PBX will prompt for logon username/password, please enter: admin / 123 to continue machine
administration.
Figure 2-1. Input prompt
In order to connect machine for administration, please
ÍNote
locate your PC in the same network segment (192.168.0.x)
of IP PBX. If you’re not familiar with TCP/IP, please refer
to related chapter on user’s manual CD or consult your
network administrator for proper network configurations.
Network Interface quick configurations
Wizard is a tool to quickly setup IP PBX.
After pass the authentication, please click for quick IPX PBX setup.
For most users, Internet access is the primary application. The IP PBX supports the WAN interface for
Internet access and remote access. The following sections will explain more details of WAN Port
Internet access and broadband access setup. When you click “Wizard Setup “the following setup page
will be show.
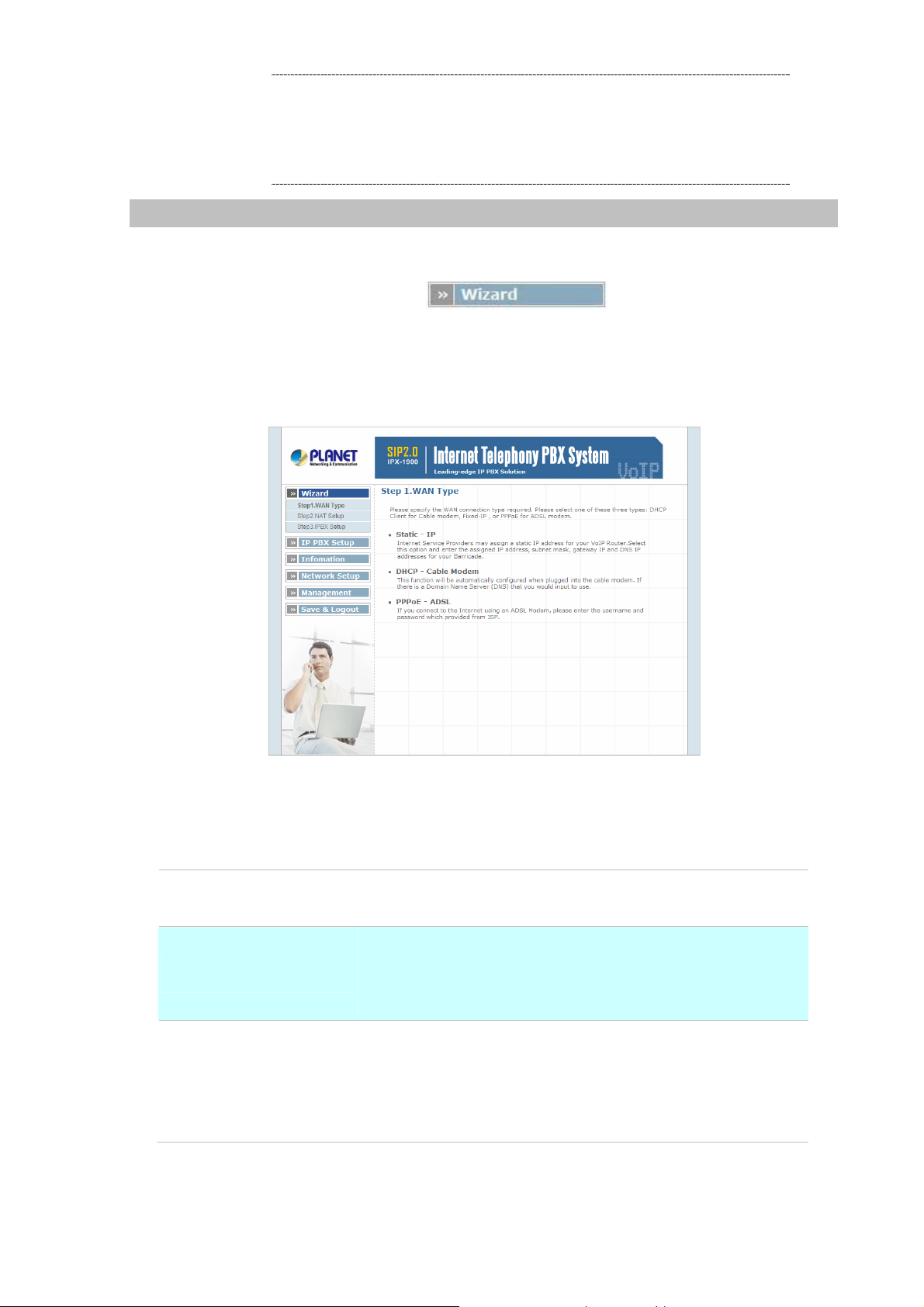
¾ Step1. Wan Type
WAN Setting
Static - IP
DHCP – Cable Modem
PPPoE - ADSL
Figure 2-2. Wizard-Operating Mode settings
If you are a leased line user with a fixed IP address, fill out the
following items with the information provided by your ISP.
This function will be automatically configured when plugged into
the cable modem. If there is a Domain Name Server (DNS) that
you would input to use.
Some ISP's provide DSL-based service and use PPPoE to
establish communication link with end-users. If you are connected
to the Internet through a DSL line, check with your ISP to see if
they use PPPoE. If they do, you need to select this item.
Table 2-1. WAN description of IP PBX
11
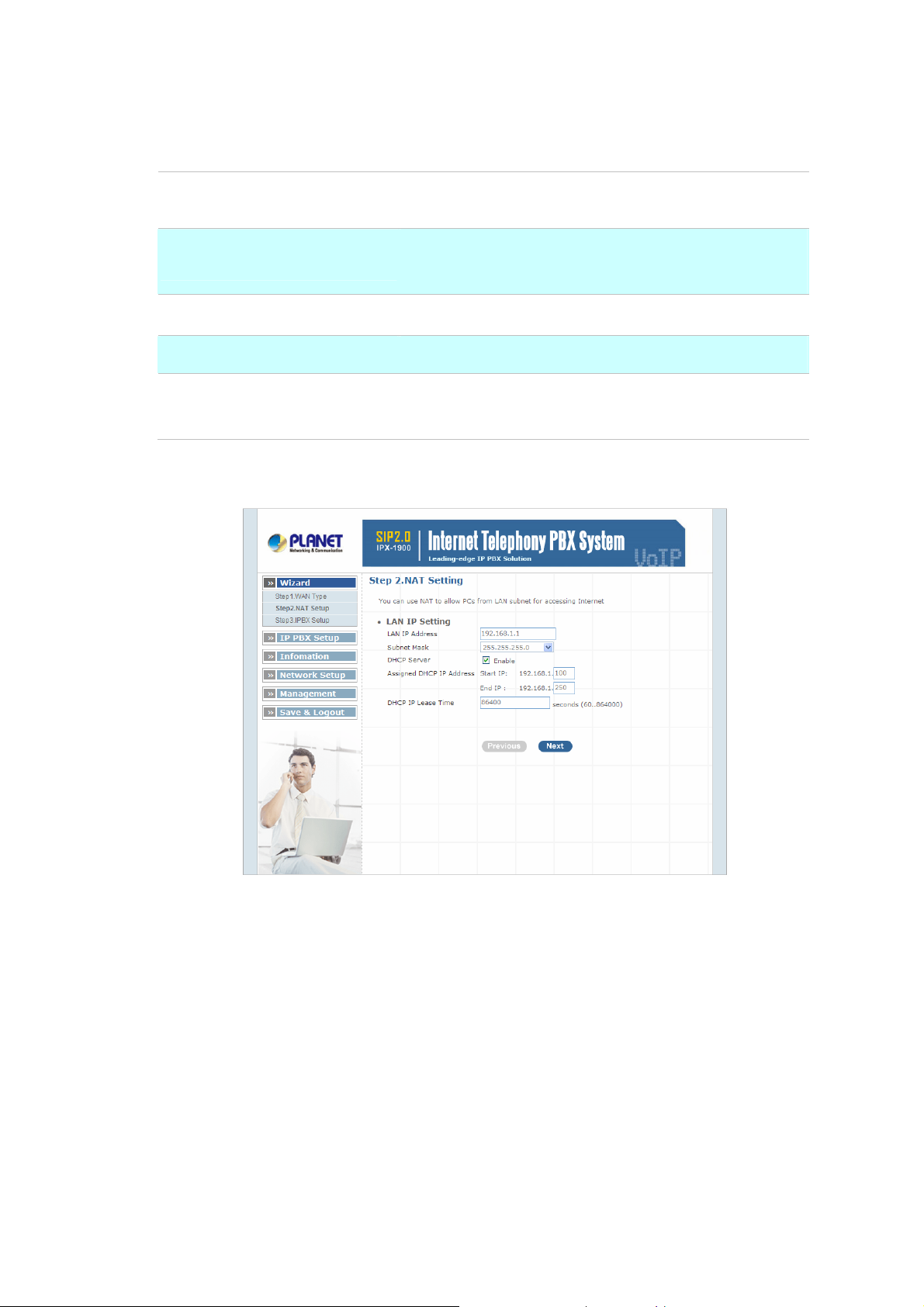
¾ Step2. NAT Setting
LAN IP Setting
LAN IP Address
Subnet Mask
DHCP Server
Assigned DHCP IP Address
DHCP IP Lease Time
Table 2-2. LAN IP description of IP PBX
Private IP address for connecting to a local private network.
(Default: 192.168.0.1)
Subnet mask for the local private network (Default:
255.255.255.0)
Enable to open LAN port DHCP server
DHCP server range from start IP to end IP
Client to ask DHCP server refresh time, range from 60 to
86400 seconds
Figure 2-3. Wizard-NAT settings
¾ Step4. IPPBX Setup
The IP PBX allows multiple ITSP providers / User Extensions registration by simply fill-in the required
information in the provided table.
12
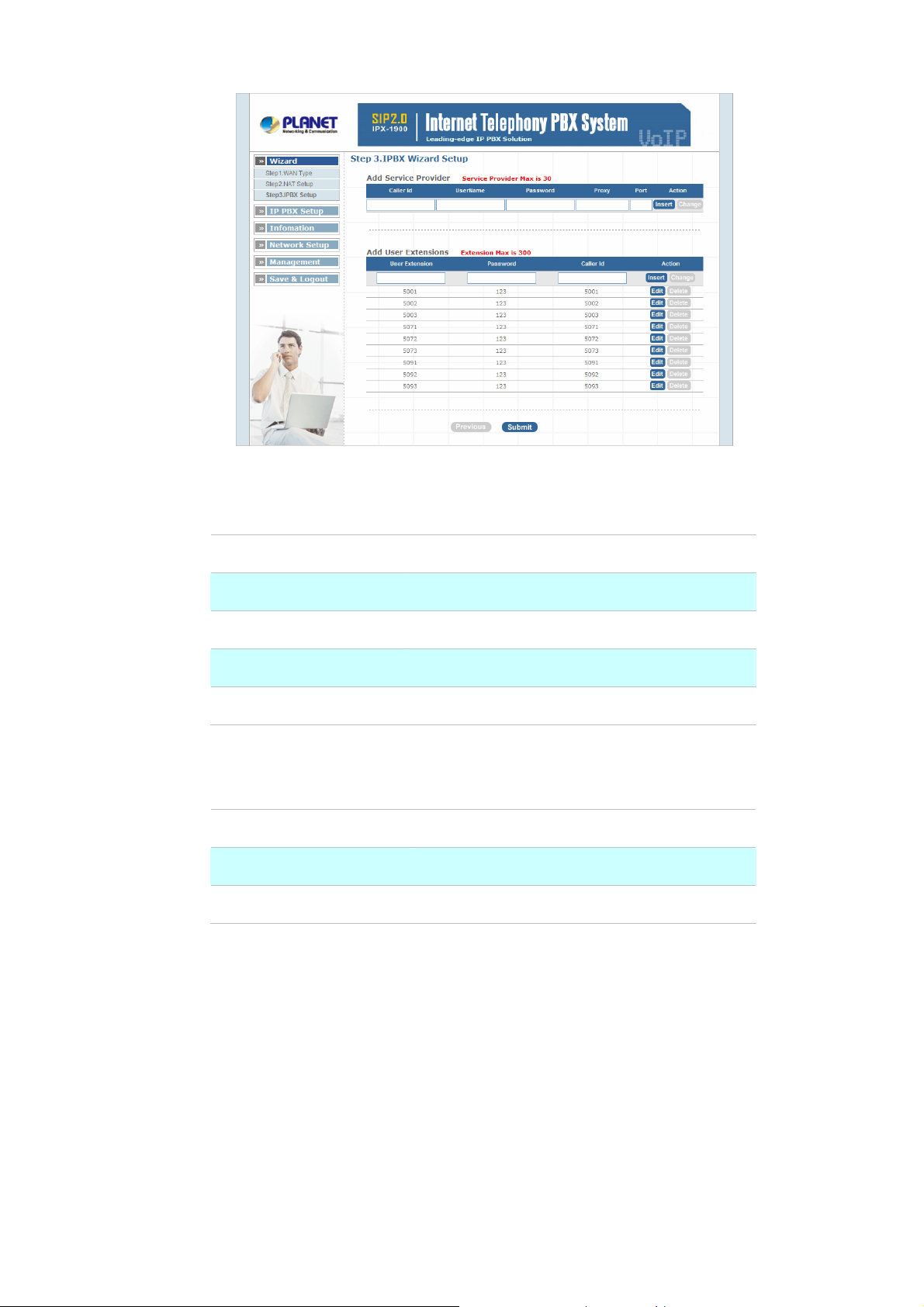
Service Provider:
Figure 2-4. Wizard-IP PBX settings
Caller ID
Username
Password
Host
User Extensions:
User Extension
Password
Caller Id
Port
Service provider name
Input Provider name
Input Provider password
Input Providers server address
Providers server port
Table 2-3. Service provider description
Input Extension number
Input Extension password
Input Extension caller id
Table 2-4. User extension description
After completing the wizard setup, click “Submit” button, The IP PBX will save configuration and reboot
IP PBX automatically, after 50 seconds, you can re-load setting page again.
13

Figure 2-5. Wizard-Rebooting
ÍNote
Please consult your ISP personnel to obtain proper PPPoE/IP
address related information, and input carefully.
If Internet connection cannot be established, please check
the physical connection or contact the ISP service staff
for support information.
RS-232 Console Port Configuration
RS-232 port (DB-9pin Female connector), Configure the COM Port Properties as following:
Bits per second: 57600, Flow control: None
1. Connect Gateway RS-232 port to PC COM Port.
2. Power on gateway.
3. Open Terminal Program (ie. Windows XP Hyper Terminal)
[Start] → [Program file] → [Accessories] → [communications] → [Hyper Terminal]
Figure 2-6. Windows Hyper Terminal Path
14
4. Create new connection. Select “COM” port that connect PC to gateway
Figure 2-7. Hyper Terminal Screen
5. Make connection(Bits Pre second:57600 Flow contact: None)
6. Input “Enter” and Show Welcome display.
7. Login, input the Password to login.(Password as the same as Access, default is admin)
8. Setting Gateway Configure like telnet mode
(Setting Table following as Telnet Setting table)
15

Chapter 3
IP PBX Setup
3
SIP Basic Setting
SIP (Session Initiation Protocol) is a request-response protocol, dealing with requests from clients and
responses from servers. Participants are identified by SIP URLs. Requests can be sent through any
transport protocol. SIP determines the end system to be used for the session, the communication
media and media parameters, and the called party's desire to engage in the communication. Once
these are assured, SIP establishes call parameters at either end of the communication, and handles
call transfer and termination.
¾ SIP Configuration
UDP Port to bind to
Domain
Allow guest calls
Overlap dialing support
Allow Transfers
Enable DNS SRV lookups
(on outbound calls)
Figure 3-1. SIP configuration settings
This is SIP Local Port 5060, if you have any specific reason for
change this port.
IP PBX Server’s IP address.
Enable/Disable guest calls. Default is Enable. Default is all IP.
Enable/Disable overlaps dialing support. Default is Enable.
Enable Call Transfers.
Enable DNS SRV lookups on calls

Max Registration Time
Maximum duration of incoming registration/subscriptions we allow.
Default 3600 seconds.
Min Registration Time
Default
Incoming/Outgoing
Registration Time
Min RoundtripTime
(T1 Time)
Language
Enable Relaxed DTMF
Server UserAgent
DTMF Mode
¾ SIP Codecs
Minimum duration of registrations/subscriptions. Default 60
seconds
Default duration (in seconds) of incoming / outgoing registration.
Minimum roundtrip time for messages to monitored hosts, Defaults
to 200 ms
Set default language for all users.
Use relaxed DTMF detection. Default is Disable.
Enable you to change the trunk User agent string, Default is PBX.
Set default DTMF mode for sending DTMF. Default: rfc2833.
Table 3-1. SIP configuration description
The Codec is used to compress the voice signal into data packets. Each Codec has different bandwidth
requirement. There are 7 kinds of codec. To determine the priority, selects one codec algorithm from
the pull-down menus individually.
Figure 3-2. SIP codecs settings
¾ Outbound SIP Registrations
Figure 3-3. Outbound SIP Registrations settings
17
Register TimeOut
Retry registration calls at every 'x' seconds (default 20).
Register Attempts
Table 3-2. Outbound DIP registration description
Number of registration attempts before we give up; 0 =
continue forever.
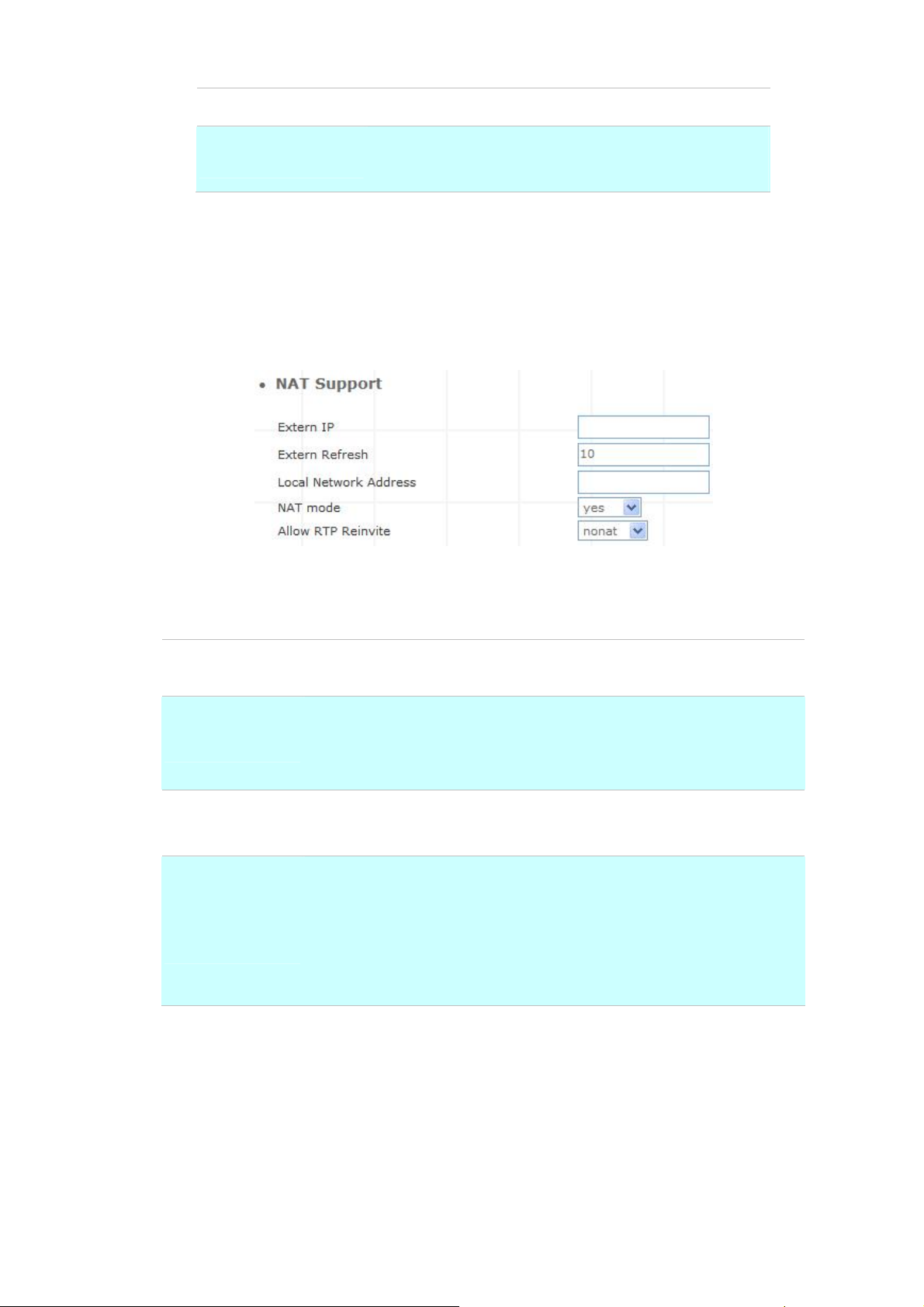
¾ NAT Support
The externip, externhost and localnet settings are used if you use IP PBX behind a NAT device to
communicate with services on the outside.
Figure 3-4. NAT support settings
Extern IP
Extern Host
Extern Refresh
Local Network
Address
Address that we're going to put in outbound SIP messages if we're
behind a NAT.
Alternatively you can specify an external host, and IP PBX will perform
DNS queries periodically. Not recommended for production
environments! Use externip instead.
How often to refresh externhost if used. You may specify a local network
in the field below.
localnet=192.168.0.0/255.255.0.0; All RFC 1918 addresses are local
networks
localnet=11.0.0.0/255.0.0.0 ; Also RFC1918
localnet=171.16.0.0/12 ; Another RFC1918 with CIDR notation
localnet=168.254.0.0/255.255.0.0; Zero conf local network
Table 3-3. NAT support description
18
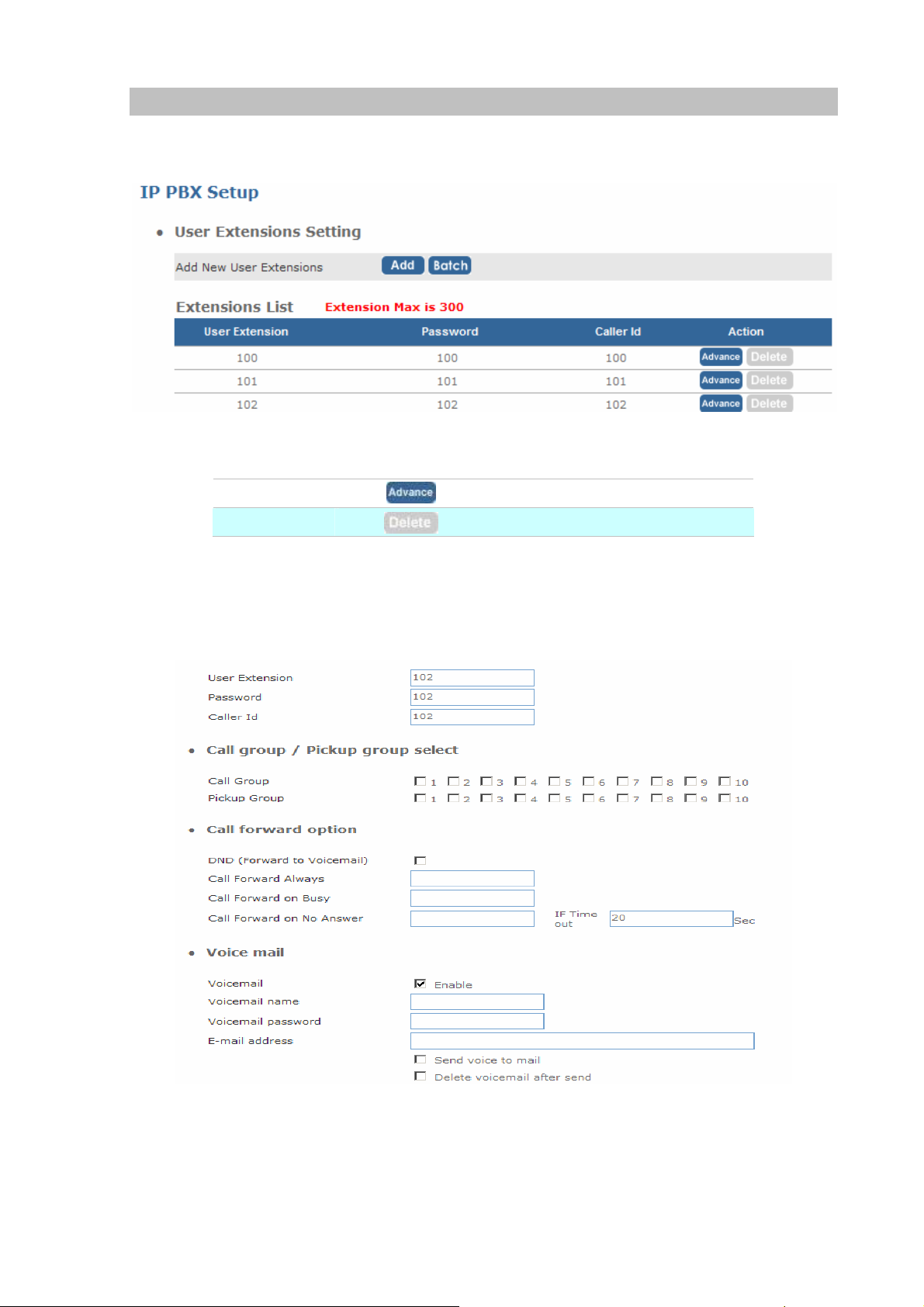
User Extensions Setup
¾ Extension List
Figure 3-5. User extension settings
Advance
Delete
¾ Advance Setup
Click to edit an extension other setting.
Click to delete an extension.
Table 3-5. User extension description
Figure 3-6. Extension advance settings
19

User Extension
Input Extension number
Password
Caller Id
Table 3-5. Extension advance description
- Call group / Pickup group select :
Call Group
Pickup Group
An Extension can set single/multiple call group(s) 1-10 id
An Extension can set single/multiple Pickup group(s) 1-10 id
Table 3-6. Call / Pickup group description
- Call forward option :
DND(Forward to Voice mail)
Call forward always
Call forward on busy
Call forward no answer
Input Extension password
Input Extension caller id
Enable / Disable forward to voice mail.
Input forward always number
Input forward on busy number
Input forward no answer number
If time out “XXX” sec
This is the maximum number allowed no answer time out
used
Table 3-7. Call forward description
- Voice mail :
Voice mail select
Voice mail name
E-Mail address
Send voice to mail
Delete voice mail after send
Enable / Disable voice mail function
Input voice mail name
Input E-mail address
Enable / Disable send voice to mail
Save / Delete voice mail after send
Table 3-8. Voice mail description
Trunk Management – SIP Trunk
Services Providers Setting allows IP PBX register to different SIP systems and ITSP Services (SIP
Trunk).
On the “Providers List”, you can press “Add” to add a new service provider or press “Advance” to edit
the information of specific Service Provider or press “Delete” to delete the specified service provider
information. Maximum 10 registrations on Server Provider list
20

Figure 3-7. Server Providers Setting
¾ Add New Service Providers
Step 1. Press “Add” button to add an new service provider information.
Figure 3-8. Add new service providers
Step 2. Fill in the required information in Service Provider Advance Setup page.
Caller id
User name
Password
Registrar Server Address
Figure 3-9. Service provider advance setup
The caller ID will be sent between the callee and caller and will
be displayed on SIP device LCD panel for identification.
User name for authentication
User password for authentication
Assigns the SIP Register Server’s IP address / Domain name
21

Registrar Server Port
A
Port number of SIP Register Server. Assigns a value from 1024
to 65535, the common default SIP port is 5060.
Outbound Proxy server’s IP address / Domain name. Assign a
Outbound Proxy Address
Outbound Proxy Port
On duty / Off duty voice
select
Incoming call attendant
server’s IP / Domain name which is in charge of call-out
service.
Port number of Outbound Proxy Server.
1024 to 65535, the common default SIP port setting is 5060.
When the service provider registered to PBX, incoming calls
will hear On / Off duty voice, default settings are “Enable”.
(For how to record On/Off duty voice please refer “Record
Voice Menu”).
Choose a pre-set hunt groups, default is “blank”. There are 3
types of combination setup.
1. If On duty/ Off duty voice is “Enabled”, after caller hear
the voice menu one time, the call will be transferred to
the pre-defined group for call attendant.
2. If On duty/ Off duty voice is “Disabled”, caller will not
hear the voice menu, the call will be directly transferred
to the pre-defined group for call attendant.
ssign a number from
3. If On duty/Off duty voice is “Enabled” and no group is
pre-defined, voice menu will repeat itself until incoming
caller respond to it.
(For how to make hunt group please refer “Hunt Group
Setting”)
Table 3-9. Service provider advance setup description
Trunk Management – FXO Trunk
FXO (Foreign Exchange Office) Trunk Setting, can be Connected to PBX or CO line with RJ-11
analog line. FXO port can be connected to the extension port of a PBX or directly connected to a PSTN
line of carrier
Figure 3-10. FXO Trunk setting
22
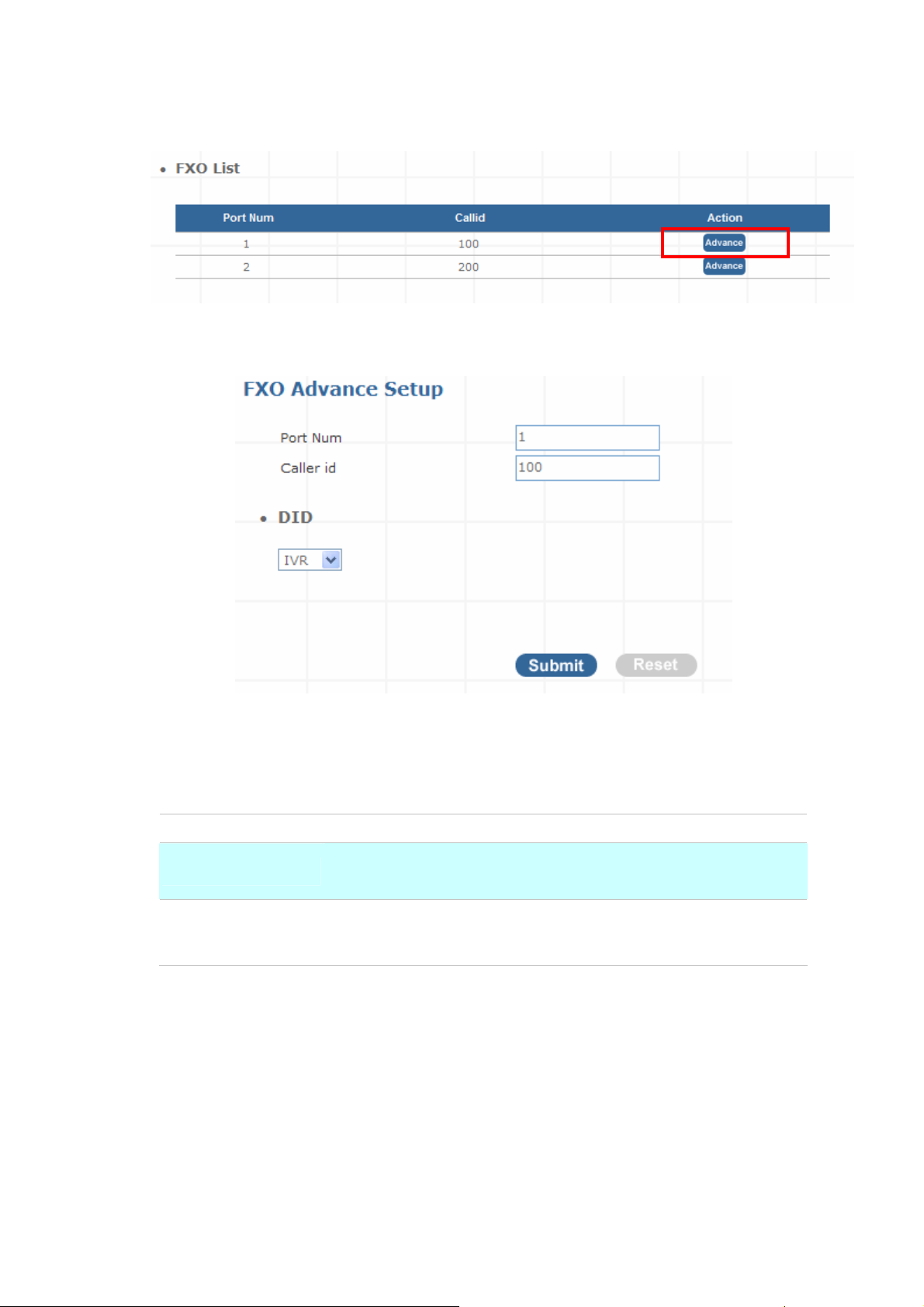
Press “Advance” to Edit an FXO Prot as below
Figure 3-11. FXO Trunk list
Port Num
Caller id
DID
Figure 3-12. FXO Advance setting
Analog Port Number (System Define)
The caller ID will be sent between the callee and caller and will be
displayed on SIP device LCD panel for identification.
Any calls originating from the registered ITSP to IP PBX will go into the
auto-attendant or direct to the selected user or hunting group.
Table 3-13. Trunk Management - FXO Trunk setup description
23

Trunk Management – Gateway Trunk
Gateway Trunk Setting allows IP PBX makes VoIP calls to external Gateway by peer-to-peer mode. If
the FXO ports of external Gateway have connected with PSTN lines, the user can make outgoing
PSTN calls via external Gateway by this function.
Figure 3-13. Gateway Trunk setting
IP
Port
Destination IP Address is the IP address of the destination
Gateway that owns this phone number.
Port is port of the destination Gateway use. (Default is 5060)
Table 3-11. Gateway Trunk setting description
Trunk Management – Trunk Group
Trunk Group is defines the leading digit of the call out dialing number through SIP / FXO / Gateway
Trunks of the same type between two given points. The IP PBX will in according to the leading digit to
determine to use which SIP or Gateway Trunks for outgoing route.
Figure 3-14. Trunk Group setting - 1
Press “more” to show the Service Provider Number under the group.
Figure 3-15. Trunk Group setting - 2
Figure 3-16. Trunk Group more information
24
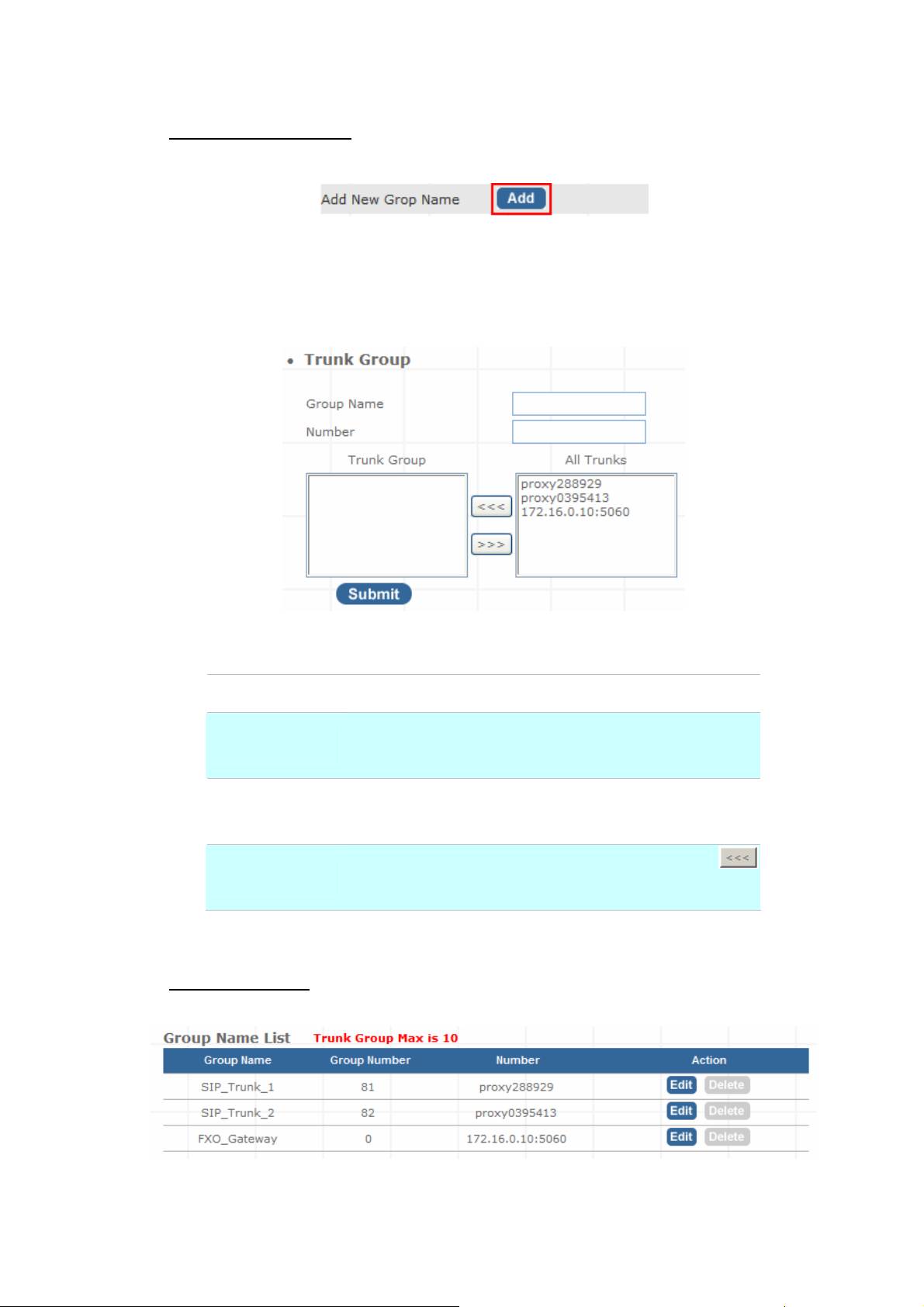
¾ Add New Trunk Group
Step 1. Press “Add” button to add an new Group Name information.
Figure 3-17. Add an new Group Name
Step 2. Fill in the required information in Trunk Group Setup page.
Figure 3-18. Trunk Group Setup
Group Name
Number
All Trunk
Trunk Group
The Trunk Group name
If the leading digits are match with this number, IP PBX will
delete this number and send out the following digits.
It will show all the available SIP Trunks and Gateway Trunks
for selection.
Choose the trunk at All Trunk box and press the
button to move the activated trunk to Trunk Group box.
Table 3-12. Trunk Group setting description
¾ Scenario Sample
IP PBX has created two different SIP trunks and one Gateway trunk for outgoing trunks.
Figure 3-19. Trunk Group sample setting
25
 Loading...
Loading...