Page 1

802.11n Wireless PCI Express Adapter
Page 2

802.11nWirelessPCIExpressAdapter
WNL‐9501
Copyright
Copyright 2014 by PLANET Technology Corp. All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be
reproduced, transmitted, transcribed, stored in a retrieval system, or translated into any language or
computer language, in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, magnetic, optical, chemical,
manual or otherwise, without the prior written permission of PLANET.
PLANET makes no representations or warranties, either expressed or implied, with respect to the
contents hereof and specifically disclaims any warranties, merchantability or fitness for any particular
purpose. Any software described in this manual is sold or licensed "as is". Should the programs prove
defective following their purchase, the buyer (and not PLANET, its distributor, or its dealer) assumes
the entire cost of all necessary servicing, repair, and any incidental or consequential damages
resulting from any defect in the software. Further, PLANET reserves the right to revise this publication
and to make changes from time to time in the contents hereof without obligation to notify any person of
such revision or changes.
All brand and product names mentioned in this manual are trademarks and/or registered trademarks
of their respective holders.
Federal Communication Commission Interference Statement
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device,
pursuant to Part 15 of FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against
harmful interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio
frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful
interference to radio communications. However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occur
in a particular installation. If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or television
reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try
to correct the interference by one or more of the following measures:
1. Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
2. Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
3. Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver is
connected.
4. Consult the dealer or an experienced radio technician for help.
FCC Caution
To assure continued compliance, use only shielded interface cables when connecting to computer or
peripheral devices. Any changes or modifications not expressly approved by the party responsible for
compliance could void the user’s authority to operate the equipment.
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following two
conditions: (1) This device may not cause harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept any
interference received, including interference that may cause undesired operation.
Federal Communication Commission (FCC) Radiation Exposure
Statement
This equipment complies with FCC radiation exposure set forth for an uncontrolled environment. In
order to avoid the possibility of exceeding the FCC radio frequency exposure limits, human proximity
to the antenna shall not be less than 20cm (8 inches) during normal operation.
2
Page 3

802.11nWirelessPCIExpressAdapter
WNL‐9501
CE Mark Warning
This is a class B device in a domestic environment; this product may cause radio interference, in which
case the user may be required to take adequate measures.
R&TTE Compliance Statement
This equipment complies with all the requirements of DIRECTIVE 1999/5/CE of THE EUROPEAN
PARLIAMENT AND THE COUNCIL of 9 March 1999 on radio equipment and telecommunication
terminal equipment and the mutual recognition of their conformity (R&TTE). The R&TTE Directive
repeals and replaces in the directive 98/13/EEC (Telecommunications Terminal Equipment and
Satellite Earth Station Equipment) as of April 8, 2000.
Safety
This equipment is designed with the utmost care for the safety of those who install and use it. However,
special attention must be paid to the dangers of electric shock and static electricity when working with
electrical equipment. All guidelines of this and of the computer manufacture must therefore be allowed
at all times to ensure the safe use of the equipment.
EU Countries Intended for Use
The ETSI version of this device is intended for home and office use in Austria Belgium, Denmark,
Finland, and France (with Frequency channel restrictions). Germany, Greece, Ireland, Italy,
Luxembourg .The Netherlands, Portugal, Spain, Sweden and United Kingdom.
The ETSI version of this device is also authorized for use in EFTA member states Iceland,
Liechtenstein, Norway and Switzerland.
WEEE regulation
To avoid the potential effects on the environment and human health as a result of the
presence of hazardous substances in electrical and electronic equipment, end users of
electrical and electronic equipment should understand the meaning of the crossed-out
wheeled bin symbol. Do not dispose of WEEE as unsorted municipal waste and have to
collect such WEEE separately.
Revision
User
’s Manual for PLANET 802.11n Wireless PCI Express Adapter
Model: WNL-9501
Rev: EM-WNL-9501_v2.0 (December, 2013)
Part No. 2081-E22140-002
3
Page 4

802.11nWirelessPCIExpressAdapter
WNL‐9501
CONTENTS
Chapter 1. PRODUCT INTRODUCTION ...............................................................................................5
1.1 Package Contents .................................................................................................................5
1.2 Product Description ...............................................................................................................5
1.3 Product Features...................................................................................................................6
1.4 Hardware Description............................................................................................................7
Chapter 2. INSTALLATION ..................................................................................................................8
2.1 Hardware Installation.............................................................................................................8
2.2 Utility Installation....................................................................................................................9
Chapter 3. CONNECTING TO WIRELESS NETWORK ................................................................... 13
3.1 Connecting with PLANET 11n PCI-E Wireless LAN Utility................................................. 13
3.2 Connecting with WPS......................................................................................................... 17
3.2.1 PBC (Push Button Configuration) method ............................................................. 17
3.2.2 PIN method ............................................................................................................ 18
3.3 Connecting with Windows built-in wireless utility ............................................................... 22
3.3.1 Windows XP - Use Windows Zero Configuration................................................... 22
3.3.2 Windows 7 - Use Windows 7 WLAN AutoConfig ................................................... 26
Chapter 4. MANAGEMENT............................................................................................................... 29
4.1 Profile.................................................................................................................................. 29
4.1.1 Add a profile ........................................................................................................... 29
4.1.2 Modify a profile....................................................................................................... 31
4.1.3 Delete a profile ....................................................................................................... 31
4.2 Advanced............................................................................................................................ 32
Chapter 5. SoftAP MODE (For Windows 7 only)............................................................................... 33
Appendix: Specifications................................................................................................................... 36
Appendix: Troubleshooting............................................................................................................... 37
Appendix: Glossary............................................................................................................................ 38
Appendix: FAQ.................................................................................................................................... 43
4
Page 5

Chapter 1. PRODUCT INTRODUCTION
1.1 Package Contents
The following items should be contained in the package:
802.11nWirelessPCIExpressAdapter
WNL‐9501
WNL-9501 (802.11n
Wireless PCI Express
Adapter)
If there is any item missing or damaged, please contact the seller immediately.
Quick Installation Guide CD (including
driver/utility/user’s manual)
1.2 Product Description
Stable PCI Express Adapter with 11n Performance
For higher wireless transfer performance, we are glad to introduce PLANET 802.11n wireless PCI
Express adapter ─ WNL-9501. It is a PCI Express wireless adapter that can operate in either Ad-Hoc
mode (Point to Point/Point to Multipoint without an Access Point) or Infrastructure mode (Point to
Point/Point to Multipoint with an Access Point) 2.4GHz frequency band; it’s backward compatible with
802.11b and 802.11g for users to create a new wireless environment based on the existing wireless
network. With the integration of the latest innovative 802.11n technology, the maximum data rate of the
WNL-9501 is up to 150Mbps which is almost three times of standard G.
High Speed 802.11n Wireless Experience
Featuring smart antenna technology, the 802.11n design helps combat distortion and interference, so
this Network Card can send its data streams with greater distances and be more reliable. The
WNL-9501 supports the most convenient security, ” Wi-Fi Protected Setup (WPS)“, which is the way to
build connection between wireless network clients and this wireless router. This WNL-9501 supports
two types of WPS, Push-Button Configuration (PBC) and PIN code (key wireless adapter card pin
number).
5
Page 6
802.11nWirelessPCIExpressAdapter
WNL‐9501
Advanced Wireless Security
For WLAN security issues, the WNL-9501 supports 64/128-bit WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) and
WPA/WPA2 (Wi-Fi Protected Access) for securing wireless network connections. The driver and utility
support the most popular operating systems, such as Windows XP, Vista and Windows 7. With
advanced features and high performance capability, the WNL-9501 is an excellent choice for
constructing a wide range of wireless solutions.
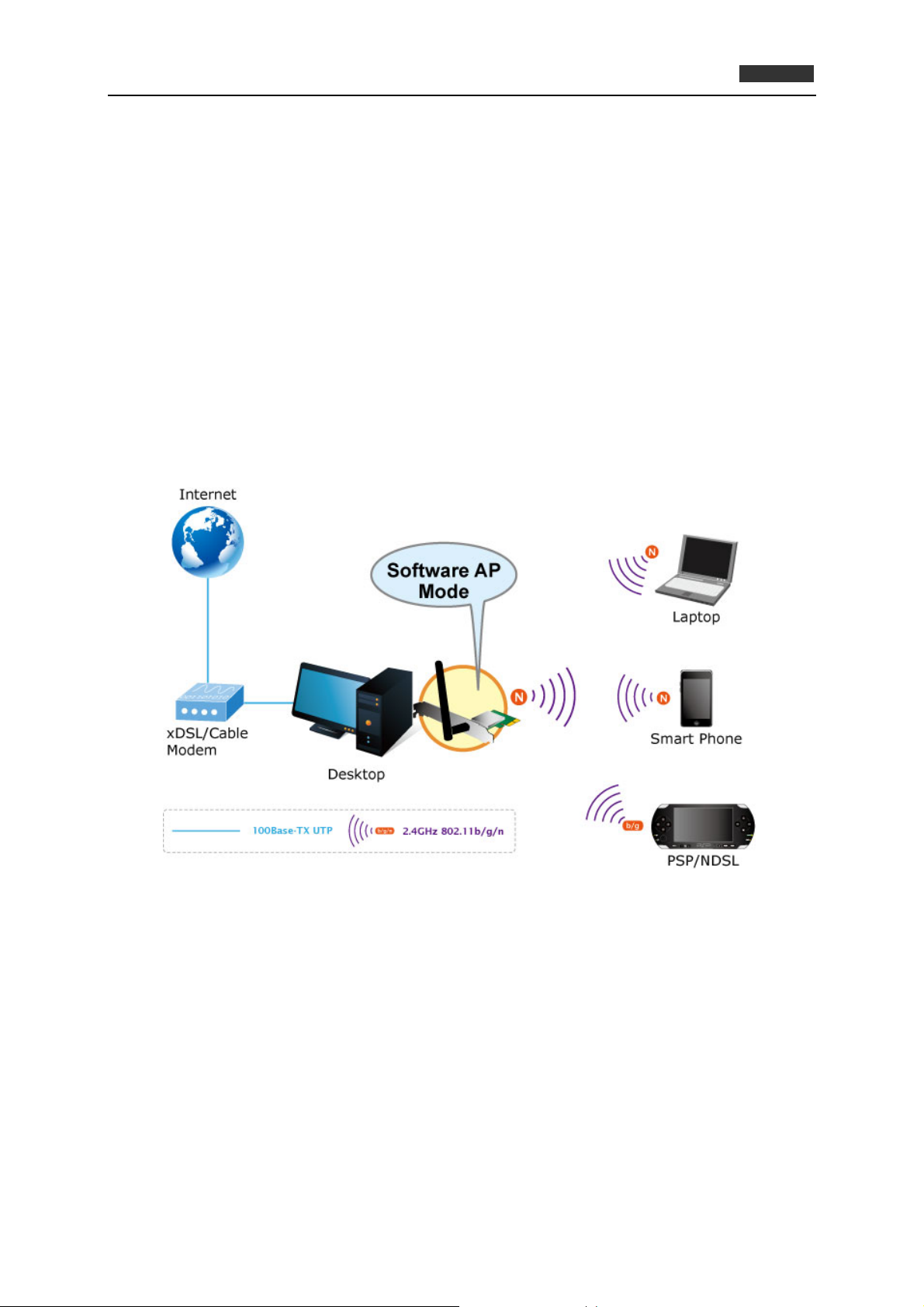
Software Access Point Function for Wireless Connection Sharing (For Windows 7 only)
More than just being an adapter for PC and laptop connecting to high speed wireless network, the
WNL-9501 can also become a wireless access point. By applying the PCI Express Wireless LAN
Utility included in the package, users can switch the WNL-9501 operation mode between Station mode
and Access Point mode. When the WNL-9501 is in the Access Point mode, it turns to a Wi-Fi Hotspot.
The Wi-Fi supported devices such as iPhone / Android / Windows Phone / iPad / PSP can connect to it
and share the wireless access easily.
1.3 Product Features
Compliant with PCI Express 1.0a - x1 PCI Express standard
2.4GHz ISM band, unlicensed operation
Supports Wi-Fi Protected Setup (WPS) utility and hardware button
Compliant with IEEE 802.11b, IEEE 802.11g, IEEE 802.11n
802.11n provides up to 150Mbps data rate
Supports 64/128-bit WEP , WAP/WAP2 , and WPA/WPA2-PSK high-level security mechanisms
Supports Ad-Hoc (supports 802.11b and 802.11b/g mode) / Infrastructure mode (supports
802.11b , 802.11b/g and 802.11b/g/n mix mode)
Supports WMM (WiFi Multi-Media) function to meet the multi-media data bandwidth requirement.
(the connected AP and the application must support WMM as well)
Support of Power Save mode
Support of the most popular operating systems including Windows XP, Vista and Windows 7.
6
Page 7

1.4 Hardware Description
Product Outlook
802.11nWirelessPCIExpressAdapter
WNL‐9501
LED Definition
There is an LED equipped on the wireless adapter. When the data is transmitting, the LED
will be flashing.
LED Description
ON System is working
OFF System is not working / No Power
7
Page 8
802.11nWirelessPCIExpressAdapter
WNL‐9501
Chapter 2. INSTALLATION
2.1 Hardware Installation
Please follow the instructions below to install the PCI Express Wireless Adapter:
1. If you have ever installed other wireless adapters before, please uninstall the
existing drivers and utilities first.
2. The following installation is performed in Windows 7. The procedures in other
operating systems are similar.
3. It’s recommended to touch some metal material before installing the network
card, or the static on your body may damage the components on network card
and computer.
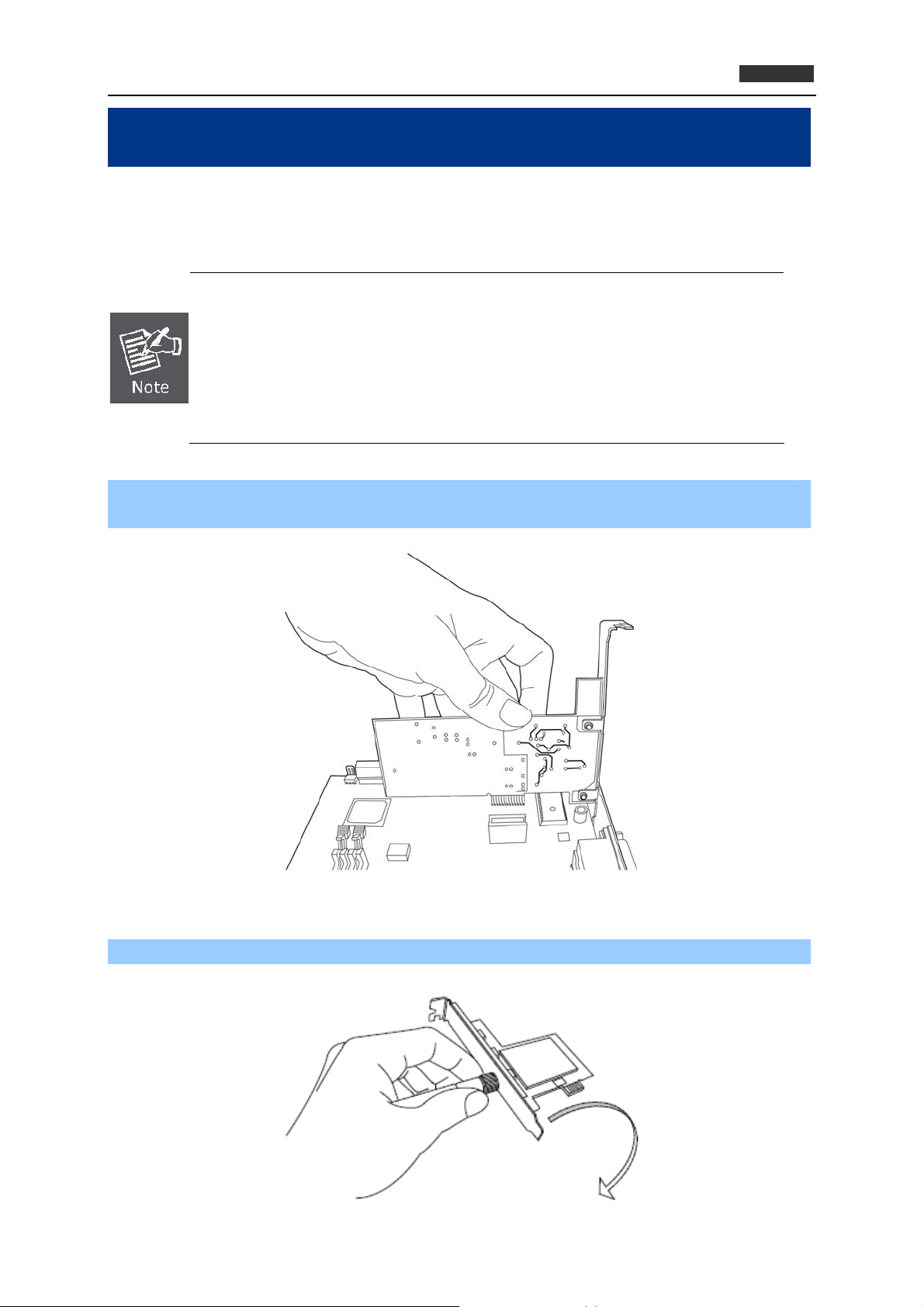
Step 1. Switch the computer off, remove the cover and insert the wireless network card into an
empty PCIe slot of your computer.
Figure 2-1-1
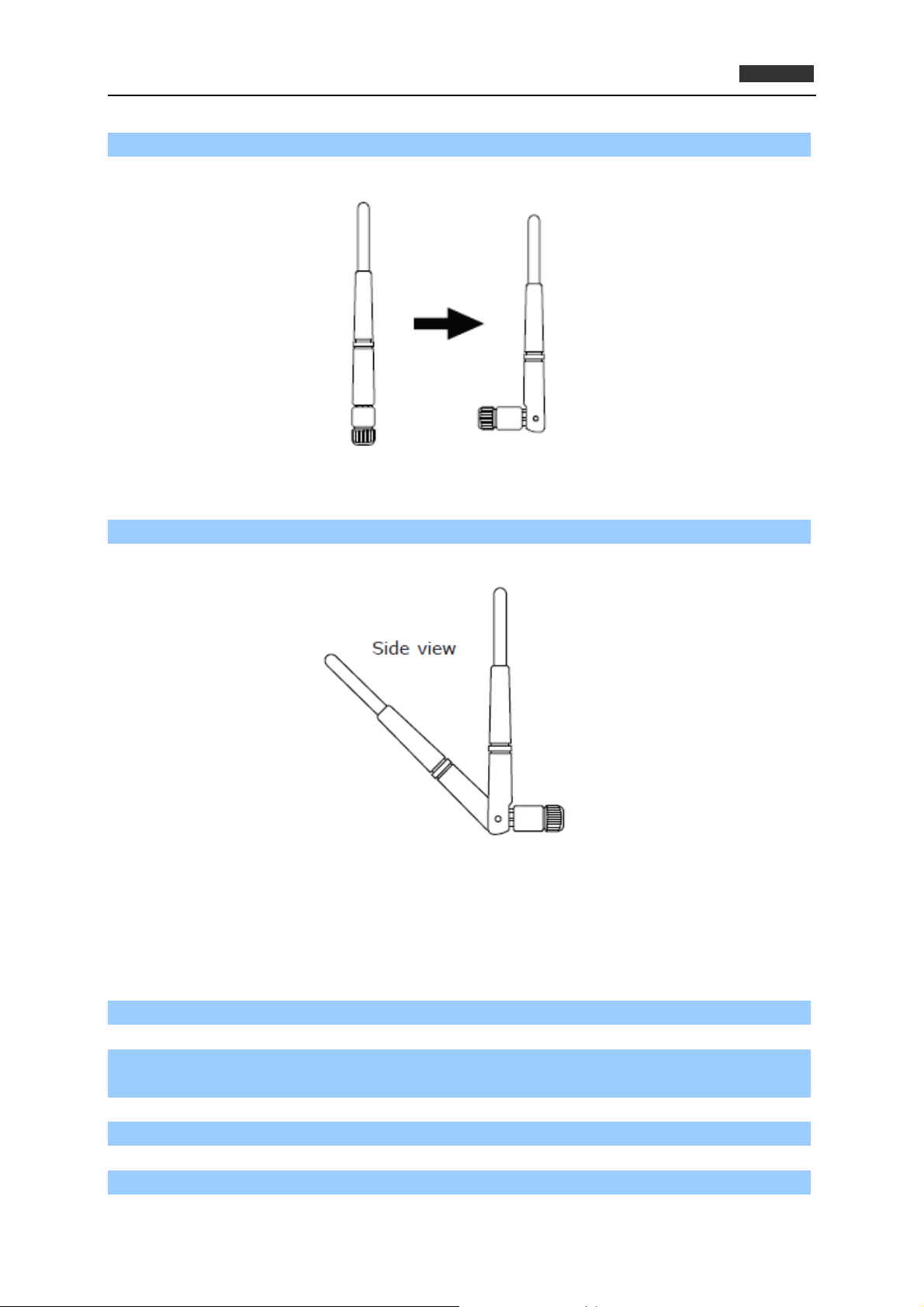
Step 2. Fasten the antennas to the antenna connectors on the network card by clockwise direction.
Figure 2-1-2
8
Page 9
802.11nWirelessPCIExpressAdapter
WNL‐9501
Step 3. You can bend the antenna to best suit your actual needs.
Figure 2-1-3
Step 4. To improve radio reception, please adjust antenna to the position shown in the picture.
Figure 2-1-4
2.2 Utility Installation
Step 1. Power on the computer. The system will find the new hardware.
Step 2. Insert the bundled CD into the CD-ROM drive to launch the auto run program. Once
completed, a menu screen will appear.
Step 3. Click the “setup.exe Utility” hyperlink to initiate the install wizard.
Step 4. Read the License Agreement carefully. Click “Yes” to accept it and continue.
9
Page 10
802.11nWirelessPCIExpressAdapter
WNL‐9501
Figure 2-2-1
Step 5. It is suggested to install PLANET Utility and Driver, which provide full access to all functions
to manage the WNL-9501. Click “Next” to continue.
Figure 2-2-2
10
Page 11
802.11nWirelessPCIExpressAdapter
WNL‐9501
Step 6. Click “Install” to continue.
Figure 2-2-3
Figure 2-2-4
11
Page 12
802.11nWirelessPCIExpressAdapter
WNL‐9501
Step 7. When “Windows Security” pops up, click “Install this driver software anyway” to accept it and
continue.
Figure 2-2-5
Figure 2-2-6
Step 8. After the driver of wireless adapter has been installed successfully, you’ll see an icon on the
desktop.
Figure 2-2-7
12
Page 13
802.11nWirelessPCIExpressAdapter
WNL‐9501
Chapter 3. CONNECTING TO WIRELESS NETWORK
With both the hardware and software successfully installed into your computer, you can quickly connect
to a wireless network using one of the following methods.
Method One: Connecting with PLANET 11n PCI-E Wireless LAN Utility
The WNL-9501 uses the Planet 11n Wireless PCI-E Utility as the management software. The utility
provides you with an easy interface to connect to a network and to change any settings related to
the wireless adapter.
Method Two: Connecting with WPS
By this method, you can connect to your network quickly on the condition that your router or
access point supports WPS as it is called by some other products.
Method Three: Connecting with Windows built-in wireless utility
Windows users may use the built-in wireless utility to connect to a wireless network. For specific
operations, please go to Section 3.3 Connecting with Windows built-in wireless utility.
3.1 Connecting with PLANET 11n PCI-E Wireless LAN Utility
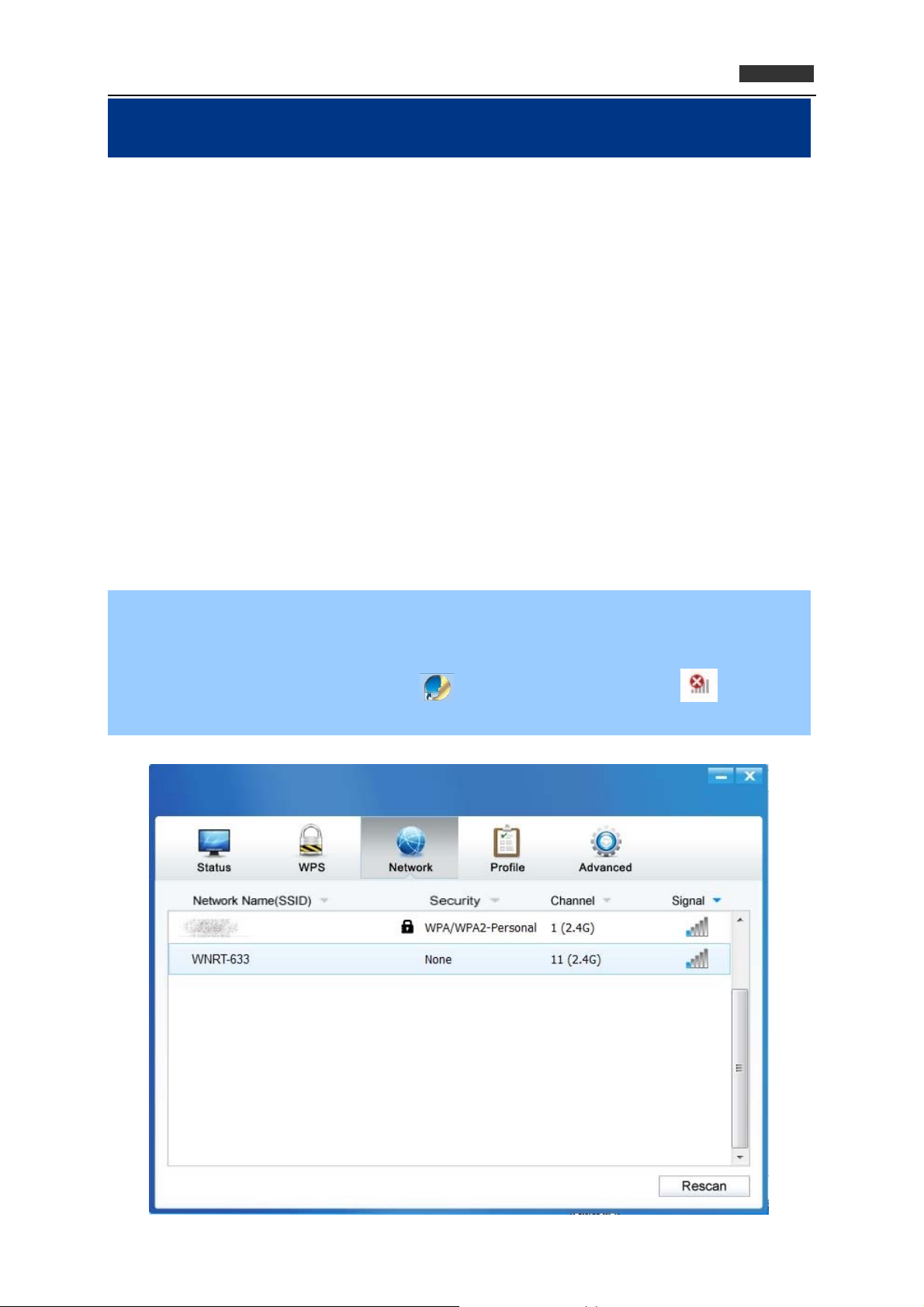
Step 1. Left-click the PLANET Wireless Utility icon located at the lower-right corner of the screen,
and configuration menu will appear: After installation, the utility configuration page will
automatically pop up on the screen. If the utility page does not pop up, you can also launch
the utility by double-clicking on the icon on your desktop or the icon in your
system tray.
Figure 3-1-1
13
Page 14
802.11nWirelessPCIExpressAdapter
WNL‐9501
Step 2. The Network page will display all wireless networks that are available in your area. To
connect to a network, simply highlight the wireless network name (SSID) and click Connect.
If you tick Connect automatically, the adapter will automatically connect to your target
network next time.
Figure 3-1-2
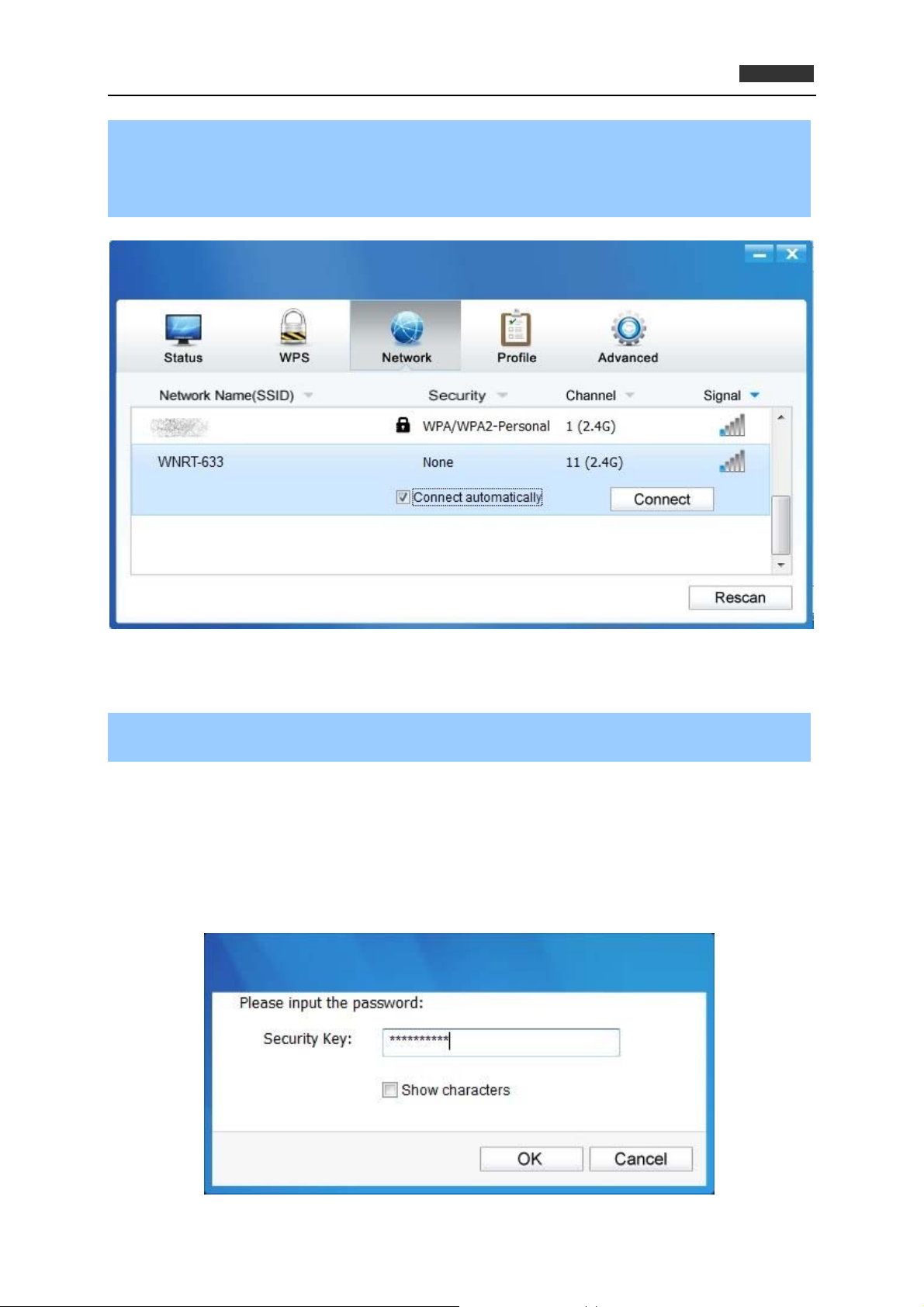
Step 3. You will be prompted different windows when you choose wireless network of different
security types.
Wireless network of WPA/WPA2-Personal
If you select a wireless network of the security type WPA/WPA2-Personal, you will be prompted to
enter the password in the security key field, as shown in Figure 3-1-3. Or you can push the WPS
button on your router (if it features the WPS function) to quickly build a connection without entering
the security key (password).
Figure 3-1-3
14
Page 15

802.11nWirelessPCIExpressAdapter
Wireless network of WPA/WPA2-Enterprise
If you select a wireless network of the security type WPA/WPA2-Enterprise, you will be prompted
to choose a type of authentication, either certificate or password. With Certificate as your
authentication, you need to select one specific certificate from the drop-down list, as shown in
Figure 3-1-4. With Password as your authentication, you should
enter the right user name and
password in the corresponding field, as shown in Figure 3-1-5
WNL‐9501
Figure 3-1-4
Figure 3-1-5
Wireless network of None
If you select a wireless network of None (that is, no security is set.), you can get directly connected
to this network without any further configuration.
15
Page 16

802.11nWirelessPCIExpressAdapter
WNL‐9501
Step 4. Please wait a few minutes for the connection process.
Figure 3-1-6
Step 5. You have now successfully connected to your network. Click Close to enjoy the Internet.
Figure 3-1-7
Step 6. To view more information about the network currently connected, click Status in the tools
section and the page will display information such as the network type, channel, rate, etc.
Figure 3-1-8
16
Page 17

802.11nWirelessPCIExpressAdapter
WNL‐9501
3.2 Connecting with WPS
WPS (Wi-Fi Protected Setup) function allows you to add a new wireless device to an existing network
quickly.
If your wireless router supports WPS, you can establish a wireless connection between wireless card
and router using either Push Button Configuration (PBC) method or PIN method. Three WPS
connection methods are listed in the following parts, while the third method is only supported in
Windows XP and Windows Vista.
3.2.1 PBC (Push Button Configuration) method
Step 1. Press the WPS button on the router.
Step 2. Open PLANET Wireless Utility and click WPS tab. Select Push the button on my access
point or wireless router and then click Connect.
Figure 3-2-1
Step 3. The adapter will be connecting to the target network.
17
Page 18

802.11nWirelessPCIExpressAdapter
WNL‐9501
Figure 3-2-2
Step 4. When the following window appears, you have successfully connected to the network.
Figure 3-2-3
3.2.2 PIN Method
There are two ways to configure the WPS by PIN method:
Enter the PIN from your router or AP device.
Step 1. Open Planet Wireless Utility and click WPS tab. Select Enter the PIN of my access
point or wireless router. In the empty field beside PIN, enter the PIN labeled on the
bottom of the router (Takes 46728470 for example). If you have generated a new PIN
code for your router, please enter the new one instead. Click Connect to continue.
18
Page 19

802.11nWirelessPCIExpressAdapter
WNL‐9501
Figure 3-2-4
Step 2. The adapter will be connecting to the target network.
Figure 3-2-5
Step 3. When Figure 3-2-3 appears, you have successfully connected to the network.
Enter a PIN into your router or AP device.
This method is only available in Windows XP and Windows Vista.
19
Page 20

802.11nWirelessPCIExpressAdapter
WNL‐9501
Step 1. Open Planet Wireless Utility and click WPS tab. Select Enter the PIN of this device into
my access point or wireless router. In the field beside PIN, you will see the PIN value
of the adapter which is randomly generated. Click Connect to continue.
Figure 3-2-6
Step 2. Open your router’s Web-based Utility and click WPS link on the left of the main menu.
Then click Add device and the following figure will appear. Enter the PIN value of the
adapter in the empty field beside PIN and then click Connect.
Figure 3-2-7
Step 3. When Connect successfully appears on the screen (as shown in Figure 3-2-8), the
WPS configuration is complete. Or you can view the adapter’s utility page to see whether
the connection has been successful (as shown in Figure 3-2-9).
20
Page 21

802.11nWirelessPCIExpressAdapter
WNL‐9501
Figure 3-2-8
Figure 3-2-9
21
Page 22

802.11nWirelessPCIExpressAdapter
WNL‐9501
3.3 Connecting with Windows Built-in Wireless Utility
Windows XP / Vista / 7 has a built-in wireless network configuration utility, called as “Windows Zero
Configuration” (WZC). You can also use WZC to configure your wireless network parameter:
3.3.1 Windows XP - Use Windows Zero Configuration
Step 1. Click “Start” button (should be located at the bottom-left corner of Windows desktop), click
“Control Panel”, and then click “Network and Internet Connections” in Control Panel.
Figure 3-3-1
Step 2. Double-click “Network Connections”.
22
Page 23

802.11nWirelessPCIExpressAdapter
WNL‐9501
Figure 3-3-2
Step 3. Right-click “Wireless Network Connection” (It may have a number as suffix if you have
more than one wireless network adapter. Please make sure you right-click PLANET
Wireless LAN 802.11n PCI-E Network Adapter), and then select “View Available
Wireless Networks”.
Figure 3-3-3
Step 4. All wireless access points in proximity will be displayed here. If the access point you want to
use is not displayed here, please try to move your computer closer to the access point, or
you can click “Refresh network list” to rescan access points. Click the access point you
want to use if it’s shown, and then click “Connect”.
23
Page 24

802.11nWirelessPCIExpressAdapter
WNL‐9501
Figure 3-3-4
Step 5. If the access point is protected by encryption, you have to input its network key or
passphrase here. It must match the encryption setting on the access point. If the access
point you selected does not use encryption, you’ll not be prompted for network key or
passphrase.
Figure 3-3-5
Step 6. If you see “Connected” message, the connection between your computer and wireless
access point you selected is successfully established.
24
Page 25

802.11nWirelessPCIExpressAdapter
WNL‐9501
Figure 3-3-6
25
Page 26

802.11nWirelessPCIExpressAdapter
WNL‐9501
3.3.2 Windows 7 - Use Windows 7 WLAN AutoConfig
WLAN AutoConfig service is built-in in Windows 7 that can be used to detect and connect to wireless
network. This built-in wireless network connection tool is similar to wireless zero configuration tool in
Windows XP.
Step 1: Right-click on the network icon displayed in the system tray
Figure 3-3-7
Step 2: Highlight and select the wireless network (SSID) to connect.
(1) All wireless access points in proximity will be displayed here. If the access point you want
to use is not displayed here, please try to move your computer closer to the access point,
or you can click “Refresh network list” to rescan access points.
(2) Click the access point you want to use if it’s shown, and then click “Connect”.
Figure 3-3-8
If you will be connecting to this Wireless Router in the future, check [Connect
automatically].
26
Page 27

802.11nWirelessPCIExpressAdapter
Step 4: Enter the network security key of the wireless access point.
(1) The Connect to a Network box will appear
(2) Enter the security key
If the access point is protected by encryption, you have to input its network key or
passphrase here. It must match the encryption setting on the access point.
(3) Click the [OK] button
WNL‐9501
Figure 3-3-9
Figure 3-3-10
27
Page 28

Step 5: Check if “Connected” is displayed
802.11n Wireless PCI Express Adapter
WNL‐9501
Figure 3-3-11
Page 29

802.11nWirelessPCIExpressAdapter
WNL‐9501
Chapter 4. MANAGEMENT
This section will show you how to configure your WNL-9501adapter using the Planet Wireless Utility.
The WNL-9501adapter uses the Planet Wireless Utility as the management software. The utility
provides users with an easy interface to change any settings related to the adapter.
the icon on your desktop will start the utility.
4.1 Profile
Your wireless networks may vary in different places like home, office or coffee shop. With Profile
management, you can easily save and manage various networks to be connected, saving you the
trouble of having to repeat the same configurations. Click Profile in the tools section, and the following
page will appear.
Double-clicking on
Figure 4-1-1
4.1.1 Add a profile
To add a profile, click the Add button on the bottom of the screen. Then the configuration window will
appear.
If you are connecting to a wireless router or access point, select Infrastructure as the Network Type,
and if you are connecting to another wireless client such as an adapter, select ad hoc as the Network
Type. Then, the screen below will appear. Follow the instructions below to finish the setting.
29
Page 30

Figure 4-1-2
The following items can be found on the screen.
802.11nWirelessPCIExpressAdapter
WNL‐9501
Object Description
Enter a name for your profile (e.g. Coffee Shop, Home, and
Profile Name:
Office). The same name is not allowed. Please also note that
no space is allowed between words.
SSID:
Select the target network from the drop-down list.
Select the network type. If you are connecting to a wireless
router or access point, select Infrastructure. If you are
Network Type:
connecting to another wireless client such as an adapter,
select ad hoc.
Select the security type from the list. In Infrastructure mode,
four options are available: WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK,
WPA/WPA2, WEP and None. In ad hoc mode, two options
Security Type:
are available: WEP and None. The security type should be
the same as on your router or access point; otherwise, you
will not be able to build a successful connection.
From the drop-down menu, select the encryption type that is
Encryption Type:
the same as on your router or access point.
You can select ASCII or Hexadecimal format on the right.
ASCII format stands for any combination of keyboard
Key Index:
characters in the specified length. Hexadecimal format stands
for any combination of hexadecimal digits (0-9, a-f, A-F) in the
specified length.
Enter the passphrase exactly as it is on your wireless router or
Security Key:
access point. Click the Show characters box to see the
passphrase. Unchecking it will hide it.
Select a type of authentication, either certificate or
Authentication:
password.
30
Page 31

802.11nWirelessPCIExpressAdapter
WNL‐9501
4.1.2 Modify a profile
You may edit an existing profile by clicking the Modify button from the Profile page. For instance, you
may like to change the profile name from Home to Home1 or you may want to specify another SSID for
profile Home. After all the changes, click Save to make the changes take effect.
4.1.3 Delete a profile
To delete an existing profile, highlight the profile name and click Remove on the bottom of the screen
or press the Delete button on your keyboard. When the following figure appears, click OK to continue.
31
Page 32

4.2 Advanced
802.11nWirelessPCIExpressAdapter
WNL‐9501
Figure 4-2-1
The following configurations can be made on the Advanced page:
Select wireless configuration tool
Here you can decide which tool to use, either the Planet Wireless Utility or the Windows wireless
configuration tool. (This option is available only in Windows XP.)
Wireless network adapter switch
Here you can switch to another adapter installed in your computer. The adapters successfully installed
in your computer will be listed in the drop-down list if the adapters are supported by this utility.
SoftAP mode (This option is only available in Windows 7.)
Once enabled, the adapter will be able to work as an AP.
Power Save mode
32
Page 33

802.11nWirelessPCIExpressAdapter
WNL‐9501
Chapter 5. SoftAP MODE (For Windows 7 only)
In Soft AP mode, the adapter will work as an AP.
This function is available only in Windows7.
Suppose that only one computer in your house can access the Internet for various reasons like only
one WLAN port is available on your wired broadband router; however, other wireless-capable devices
also want to share the Internet. Then the adapter can be configured as an AP under the Soft AP mode,
saving you the trouble of having to get a separate access point or a router.
With this feature, a computer can use a single physical wireless adapter to connect as a client to a
hardware access point while at the same time acting as a software AP allowing other wireless-capable
devices to connect to it. To switch to this mode, right-click on the utility icon in your system tray and
select Switch toSoftAP mode.
33
Page 34

802.11nWirelessPCIExpressAdapter
WNL‐9501
Figure 5-1-1
The Soft AP icon then will appear beside Advanced icon in the utility.
.
Figure 5-1-2
34
Page 35

The following items can be found on the screen.
Object Description
802.11nWirelessPCIExpressAdapter
WNL‐9501
SoftAP mode:
Internet Connecting
Share (ICS):
SSID:
Security Type:
Encryption Type:
Security Key:
Select to enable or disable the function.
Specify a connection through which devices connected to
your AP can access the Internet.
Enter the name for your soft AP (for example, Jones) so that
others can know which AP is yours when trying to connect to
it. The default name (SSID) is “SoftAP”.
The security type here is set to be WPA2-PSK which is based
on 802.11i and uses Advanced Encryption Standard instead
of TKIP. It was designed to improve the security features of
WEP. WPA2-PSK uses a passphrase or key to authenticate
your wireless connection. You needn’t make any configuration
here.
The encryption type here is set to be AES.
Enter the Key in the field to make your AP security enabled. It
is recommended that you specify another key instead of the
default key 12345678. Only by entering the corresponding key
can other computers establish a successful connection with
your AP.
IP Address:
Here displays the IP address of the SoftAP.
35
Page 36

Appendix: Specifications
Normal
Interface PCI-E Interface
Standards IEEE 802.11n; IEEE 802.11g; IEEE 802.11b;
Throughput 150Mbps (maximum)
Operating System Windows XP, Vista and Windows 7
11b: 1/2/5.5/11Mbps
802.11nWirelessPCIExpressAdapter
WNL‐9501
Radio Data Rate
Modulation
Media Access Protocol CSMA/CA with ACK
Data Security 64/128 bit WEP; WPA/WPA2, WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK
Frequency 2.4 ~ 2.4835GHz
Spread Spectrum Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum (DSSS)
Safety & Emissions FCC, CE
Environmental and Physical
Operating Temp. 0 degrees C ~ 40 degrees C
Storage Temp. -40 degrees C ~ 70 degrees C
11g: 6/9/12/18/24/36/48/54Mbps
11n: Up to 150Mbps
11b: CCK, QPSK, BPSK;
11g: OFDM;
11n: QPSK, BPSK, 16-QAM, 64-QAM;
Working Humidity 10% ~ 90% RH, non-condensing
Storage Humidity 5% ~ 90% RH, non-condensing
36
Page 37

802.11nWirelessPCIExpressAdapter
WNL‐9501
Appendix: Troubleshooting
Symptom :
Remedy :
Symptom :
Remedy :
Symptom :
Remedy :
Symptom :
Remedy :
The LED is off.
Make sure the PC Card is inserted properly. Otherwise contact your
vendor.
The LED is always on, but not blinking.
Make sure that you have installed the driver from the attached CD.
Otherwise contact your vendor.
The LED is blinking but the PC Card icon does not appear in your icon
tray.
Make sure that you have installed the Utility from the attached CD.
The PC Card is linking, but can’t share files with others.
Make sure the file and printer sharing function is enabled.
You can enable the function by checking the icon of My Computer ->
Control Panel -> Network -> file and printer sharing -> I want to be
able to give others to access to my files.
Symptom :
Remedy :
Slow or poor performance under AP mode
Try to select another channel for the communicating group or move your
device closer to the Access Point.
37
Page 38

802.11nWirelessPCIExpressAdapter
WNL‐9501
Appendix: Glossary
1. IEEE 802.11 Standard
The IEEE 802.11 Wireless LAN standards subcommittee formulates a standard for the industry.
2. Access Point
An internetworking device that seamlessly connects wired and wireless networks together.
3. Ad Hoc
An Ad Hoc wireless LAN is a group of computers, each with a WLAN adapter, connected as an
independent wireless LAN
Ad Hoc wireless LAN is applicable on a departmental scale for a branch or SOHO operation.
4. BSSID
A specific Ad Hoc LAN is called a Basic Service Set (BSS). Computers in a BSS must be configured
with the same BSSID.
5. DHCP
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol -- a method in which IP addresses are assigned by server
dynamically to clients on the network. DHCP is used for Dynamic IP Addressing and requires a
dedicated DHCP server on the network.
6. Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum
This is the method the wireless cards use to transmit data over the frequency spectrum. The other
method is frequency hopping. Direct sequence spreads the data over one frequency range (channel)
while frequency hopping jumps from one narrow frequency band to another many times per second.
7. ESSID
An Infrastructure configuration could also support roaming capability for mobile workers. More than
one BSS can be configured as an Extended Service Set (ESS). Users within an ESS could roam
freely between BSSs while served as a continuous connection to the network wireless stations and
Access Points within an ESS must be configured with the same ESSID and the same radio channel.
8. Ethernet
Ethernet is a 10/100Mbps network that runs over dedicated home/office wiring. Users must be wired
to the network at all times to gain access.
9. Gateway
A gateway is a hardware and software device that connects two dissimilar systems, such as a LAN
and a mainframe. In Internet terminology, a gateway is another name for a router. Generally a
gateway is used as a funnel for all traffic to the Internet.
38
Page 39

802.11n Wireless PCI Express Adapter
WNL‐9501
10. IEEE
Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Infrastructure. An integrated wireless and wired LAN
is called an Infrastructure configuration. Infrastructure is applicable to enterprise scale for wireless
access to central database, or wireless.
11. ISM Band
The FCC and their counterparts outside of the U.S. have set aside bandwidth for unlicensed use in
the so-called ISM (Industrial, Scientific and Medical) band. Spectrum in the vicinity of 2.4 GHz, in
particular, is being made available (Industrial, Scientific and Medical) band. Spectrum in the vicinity of
2.4 GHz, in particular, is being made available of users around the globe.
12. Local Area Network (LAN)
A LAN is a group of computers, each equipped with the appropriate network adapter card connected
by cable/air, that share applications, data, and peripherals. All connections are made via cable or
wireless media, but a LAN does not use telephone services. It typically spans a single building or
campus.
13. Network
A network is a system of computers that is connected. Data, files, and messages can be transmitted
over this network. Networks may be local or wide area networks.
14. Protocol
A protocol is a standardized set of rules that specify how a conversation is to take place, including the
format, timing, sequencing and/ or error checking.
15. SSID
A Network ID unique to a network. Only clients and Access Points that share the same SSID are able
to communicate with each other. This string is case-sensitive.
16. Static IP Addressing
A method of assigning IP addresses to clients on the network. In networks with Static IP address, the
network administrator manually assigns an IP address to each computer. Once a Static IP address is
assigned, a computer uses the same IP address every time it reboots and logs on to the network,
unless it is manually changed.
17. Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP)
The Temporal Key Integrity Protocol, pronounced tee-kip, is part of the IEEE 802.11i encryption
standard for wireless LANs. TKIP is the next generation of WEP, the Wired Equivalency Protocol,
which is used to secure 802.11 wireless LANs. TKIP provides per-packet key mixing, a message
integrity check and a re-keying mechanism, thus fixing the flaws of WEP.
18. Transmission Control Protocol / Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)
TCP/IP is the protocol suite developed by the Advanced Research Projects Agency (ARPA). It is
widely used in corporate Internet works, because of its superior design for WANs. TCP governs how
packet is sequenced for transmission the network. The term “TCP/IP” is often used generically to
refer to the entire suite of related protocols.
Page 40

802.11n Wireless PCI Express Adapter
WNL‐9501
19. Transmit / Receive
The wireless throughput in Bytes per second averaged over two seconds.
20. Wi-Fi Alliance
The Wi-Fi Alliance is a nonprofit international association formed in 1999 to certify interoperability of
wireless Local Area Network products based on IEEE 802.11 specification. The goal of the Wi-Fi
Alliance’s members is to enhance the user experience through product interoperability. The
organization is formerly known as WECA.
21. Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA)
The Wi-Fi Alliance put together WPA as a data encryption method for 802.11 wireless LANs. WPA is
an industry-supported, pre-standard version of 802.11i utilizing the Temporal Key Integrity Protocol
(TKIP), which fixes the problems of WEP, including using dynamic keys.
22. Wide Area Network (WAN)
A WAN consists of multiple LANs that are tied together via telephone services and / or fiber optic
cabling. WANs may span a city, a state, a country, or even the world
23. Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP)
Now widely recognized as flawed, WEP was a data encryption method used to protect the
transmission between 802.11 wireless clients and APs. However, it used the same key among all
communicating devices. WEP’s problems are well-known, including an insufficient key length and no
automated method for distributing the keys. WEP can be easily cracked in a couple of hours with
off-the-shelf tools.
24. Wireless LAN (WLAN)
A wireless LAN does not use cable to transmit signals, but rather uses radio or infrared to transmit
packets through the air. Radio Frequency (RF) and infrared are the commonly used types of wireless
transmission. Most wireless LANs use spread spectrum technology. It offers limited bandwidth,
usually under 11Mbps, and users share the bandwidth with other devices in the spectrum; however,
users can operate a spread spectrum device without licensing from the Federal Communications
Commission (FCC).
25. Fragment Threshold
The proposed protocol uses the frame fragmentation mechanism defined in IEEE 802.11 to achieve
parallel transmissions. A large data frame is fragmented into several fragments each of size equal to
fragment threshold. By tuning the fragment threshold value, we can get varying fragment sizes. The
determination of an efficient fragment threshold is an important issue in this scheme. If the fragment
threshold is small, the overlap part of the master and parallel transmissions is large.
This means the spatial reuse ratio of parallel transmissions is high. In contrast, with a large fragment
threshold, the overlap is small and the spatial reuse ratio is low. However high fragment threshold
leads to low fragment overhead. Hence there is a trade-off between spatial re-use and fragment
overhead. Fragment threshold is the maximum packet size used for fragmentation. Packets larger
than the size programmed in this field will be fragmented If you find that your corrupted packets or
asymmetric packet reception (all send packets, for example). You may want to try lowering your
fragmentation threshold. This will cause packets to be broken into smaller fragments. These small
fragments, if corrupted, can be resent faster than a larger fragment. Fragmentation increases
Page 41

802.11nWirelessPCIExpressAdapter
WNL‐9501
overhead, so you'll want to keep this value as close to the maximum value as possible.
26. RTS(Request To Send) Threshold
The RTS threshold is the packet size at which packet transmission is governed by the RTS/CTS
transaction. The IEEE802.11-1997 standard allows for short packets to be transmitted without
RTS/CTS transactions. Each station can have a different RTS threshold. RTS/CTS is used when the
data packet size exceeds the defined RTS threshold. With the CSMA/CA transmission mechanism,
the transmitting station sends out an RTS packet to the receiving station, and waits for the receiving
station to send back a CTS (Clear to Send) packet before sending the actual packet data. This
setting is useful for networks with many clients. With many clients, and a high network load, there will
be many more collisions. By lowering the RTS threshold, there may be fewer collisions, and
performance should improve. Basically, with a faster RTS threshold, the system can recover from
problems faster. RTS packets consume valuable bandwidth, however, so setting this value too low
will limit performance.
27. Beacon Interval
In addition to data frames that carry information from higher layers, 802.11 includes management
and control frames that support data transfer. The beacon frame, which is a type of management
frame, provides the "heartbeat" of a wireless LAN, enabling stations to establish and maintain
communications in an orderly fashion. Beacon Interval represents the amount of time between
beacon transmissions. Before a station enters power save mode, the station needs the beacon
interval to know when to wake up to receive the beacon (and learn whether there are buffered frames
at the access point).
28. Preamble Type
There are two preamble types defined in IEEE 802.11 specification. A long preamble basically gives
the decoder more time to process the preamble. All 802.11 devices support a long preamble. The
short preamble is designed to improve efficiency (for example, for VoIP systems). The difference
between the two is in the Synchronization field. The long preamble is 128 bits, and the short is 56
bits.
29. WPA2
It is the second generation of WPA. WPA2 is based on the final IEEE 802.11i amendment to the
802.11 standard.
30. Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP)
The Temporal Key Integrity Protocol, pronounced tee-kip, is part of the IEEE 802.11i encryption
standard for wireless LANs. TKIP is the next generation of WEP, the Wired Equivalency Protocol,
which is used to secure 802.11 wireless LANs. TKIP provides per-packet key mixing, a message
integrity check and a re-keying mechanism, thus fixing the flaws of WEP.
31. 802.1x Authentication
802.1x is a framework for authenticated MAC-level access control, defines Extensible Authentication
Protocol (EAP) over LANs (WAPOL). The standard encapsulates and leverages much of EAP, which
was defined for dial-up authentication with Point-to-Point Protocol in RFC 2284. Beyond
encapsulating EAP packets, the 802.1x standard also defines EAPOL messages that convey the
shared key information critical for wireless security.
41
Page 42

802.11nWirelessPCIExpressAdapter
WNL‐9501
32. Advanced Encryption Standard (AES)
Security issues are a major concern for wireless LANs, AES is the U.S. government’s
next-generation cryptography algorithm, which will replace DES and 3DES.
42
Page 43

802.11nWirelessPCIExpressAdapter
WNL‐9501
Appendix: FAQ
1. What is WMM?
Wi-Fi Multimedia (WMM), a group of features for wireless networks that improve the user
experience for audio, video and voice applications. WMM is based on a subset of the IEEE
802.11e WLAN QoS draft standard. WMM adds prioritized capabilities to Wi-Fi networks and
optimizes their performance when multiple concurring applications, each with different latency and
throughput requirements, compete for network resources. By using WMM, end-user satisfaction is
maintained in a wider variety of environments and traffic conditions. WMM makes it possible for
home network users and enterprise network managers to decide which data streams are the most
important and assign them a higher traffic priority.
2. What is WMM Power Save?
WMM Power Save is a set of features for Wi-Fi networks that increase the efficiency and flexibility
of data transmission in order to conserve power. WMM Power Save has been optimized for
mobile devices running latency-sensitive applications such as voice, audio, or video, but can
benefit any Wi-Fi device. WMM Power Save uses mechanisms included in the IEEE 802.11e
standard and is an enhancement of IEEE 802.11 legacy power saves. With WMM Power Save,
the same amount of data can be transmitted in a shorter time while allowing the Wi-Fi device to
remain longer in a low-power “dozing” state.
3. What is GI?
GI stands for Guard Interval. It’s a measure to protect wireless devices from cross- interference. If
there are two wireless devices using the same or near channel, and they are close enough, radio
interference will occur and reduce the radio resource usability.
4. What is STBC?
STBC stands for Space-Time Block Coding, which is a technique used to transfer multiple copies
of data by multiple antennas, to improve data transfer performance. By using multiple antennas,
not only data transfer rate is improved, but also the wireless stability.
43
Page 44

EC Declaration of Conformity
For the following equipment:
*Type of Product : 802.11n Wireless PCI Express Adapter
*Model Number : WNL-9501
* Produced by:
Manufacturer‘s Name : Planet T
Manufacturer‘s Address: 10F., No.96, Minquan Rd., Xindian Dist.,
New Taipei City 231, Taiwan (R.O.C.).
is herewith confirmed to comply with the requirements set out in the Council Directive on the
Approximation of the Laws of the Member States relating to
For the evaluation regarding the R&TTE the following standards were applied:
EN 300 328 V1.7.1 (2006-10)
EN 62311 (2008)
EN 301 489-1 V1.9.2 (2011-09)
EN 301 489-17 V2.1.1 (2009-05)
EN 55022 (2010, Class B)
EN 61000-3-2 (2006 + A:2009 + A2:2009,Not applicable)
EN 61000-3-3 (2008,Not applicable)
EN 61000-4-2 (2009)
EN 61000-4-3 (2006 + A1:2008 + A2:2010)
EN 61000-4-4 (2004 + A1:2010,Not applicable )
EN 61000-4-5 (2006,Not applicable)
EN 61000-4-6 (2009)
EN 61000-4-11 (2004,Not applicable)
EN 60950-1 (2006 + A11: 2009 + A1:2010 + A12:2011)
Responsible for marking this declarati o n i f the:
echnology Corp.
1999/5/EC R&TTE.
Manufacturer Authorized representative established within the EU
Authorized representative established within the EU (if applicable):
Company Name: Planet Technology Corp.
Company Address: 10F., No.96, Minquan Rd., Xindian Dist., New Taipei City 231, Taiwan
Person responsible for making this declaration
Name, Surname Kent Kang
Position / Title : Product Manager
(R.O.C.)
Taiwan 6th Jan., 2014
Place Date Legal Signature
PLANET TECHNOLOGY CORPORATION
e-mail: sales@planet.com.tw http://www.planet.com.tw
10F., No.96, Minquan Rd., Xindian Dist., New Taipei City, Taiwan, R.O.C. Tel:886-2-2219-9518 Fax:886-2-2219-9528
Page 45

English
Česky
Dansk
Deutsch
Eesti keeles
Ελληνικά
Español
Français
Italiano
Latviski
EC Declaration of Conformity
Hereby, PLANET Technology Corporation,
declares that this 802.11n Wireless PCI Express
Adapter is in compliance with the essential
requirements and other relevant provisions of
Directive 1999/5/EC.
Společnost PLANET Technology Corporation,
tímto prohlašuje, že tato 802.11n Wireless PCI
Express Adapter splňuje základní požadavky a
další příslušná ustanovení směrnice 1999/5/EC.
PLANET Technology Corporation, erklærer
herved, at følgende udstyr 802.11n Wireless PCI
Express Adapter overholder de væsentlige krav
og øvrige relevante krav i direktiv 1999/5/EF
Hiermit erklärt PLANET Technology Corporation,
dass sich dieses Gerät 802.11n Wireless PCI
Express Adapter in Übereinstimmung mit den
grundlegenden Anforderungen und den anderen
relevanten
Vorschriften der Richtlinie 1999/5/EG befindet".
(BMWi)
Käesolevaga kinnitab PLANET Technology
Corporation, et see 802.11n Wireless PCI
Express Adapter vastab Euroopa Nõukogu
direktiivi 1999/5/EC põhinõuetele ja muudele
olulistele tingimustele.
ΜΕ ΤΗΝ ΠΑΡΟΥΣΑ , PLANET Technology
Corporation, ΔΗΛΩΝΕΙ ΟΤΙ ΑΥΤ Ο 802.11n
Wireless PCI Express
AdapterΣΥΜΜΟΡΦΩΝΕΤΑΙ ΠΡΟΣ ΤΙΣ
ΟΥΣ ΙΩ Δ ΕΙ Σ ΑΠΑΙΤΗΣΕΙΣ ΚΑΙ ΤΙΣ ΛΟΙΠ ΕΣ
ΣΧΕΤΙΚΕΣ ΔΙΑΤΑΞΕΙΣ ΤΗΣ ΟΔΗΓΙΑΣ 1999/5/ΕΚ
Por medio de la presente, PLANET Technology
Corporation, declara que 802.11n Wireless PCI
Express Adapter cumple con los requisitos
esenciales y cualesquiera otras disposiciones
aplicables o exigibles de
la Directiva 1999/5/CE
Par la présente, PLANET Technology
Corporation, déclare que les appareils du 802.11n
Wireless PCI Express Adapter sont conformes
aux exigences essentielles et aux autres
dispositions pertinentes de la directive 1999/5/CE
Con la presente , PLANET Technology
Corporation, dichiara che questo 802.11n
Wireless PCI Express Adapter è conforme ai
requisiti essenziali ed alle altre disposizioni
pertinenti stabilite dalla direttiva
1999/5/CE.
Ar šo PLANET Technology Corporation,
apliecina, ka šī 802.11n Wireless PCI Express
Adapter atbilst Direktīvas 1999/5/EK
pamatprasībām un citiem atbilstošiem
noteikumiem.
Lietuviškai
Magyar
Malti
Nederlands
Polski
Português
Slovensky
Slovensko
Suomi
Svenska
Šiuo PLANET Technology Corporation,,
skelbia, kad 802.11n Wireless PCI Express
Adapter tenkina visus svarbiausius 1999/5/EC
direktyvos reikalavimus ir kitas svarbias
nuostatas.
A gyártó PLANET Technology Corporation,
kijelenti, hogy ez a 802.11n Wireless PCI
Express Adapter megfelel az 1999/5/EK
irányelv alapkövetelményeinek és a kapcsolódó
rendelkezéseknek.
Hawnhekk, PLANET Technology
Corporation, jiddikjara li dan 802.11n Wireless
PCI Express Adapter jikkonforma mal-ħtiġijiet
essenzjali u ma provvedimenti oħrajn relevanti li
hemm fid-Dirrettiva 1999/5/EC
Hierbij verklaart , PLANET Technology
orporation, dat 802.11n Wireless PCI
Express Adapter in overeenstemming is met
de essentiële eisen en de andere relevante
bepalingen van richtlijn 1999/5/EG
Niniejszym firma PLANET Technology
Corporation, oświadcza, że 802.11n Wireless
High Power PCI Express Adapter spełnia
wszystkie istotne wymogi i klauzule zawarte w
dokumencie „Directive 1999/5/EC”.
PLANET Technology Corporation, declara
que este 802.11n Wireless PCI Express
Adapter está conforme com os requisitos
essenciais e outras disposições da Directiva
1999/5/CE.
Výrobca PLANET Technology Corporation,
týmto deklaruje, že táto 802.11n Wireless PCI
Express Adapter je v súlade so základnými
požiadavkami a ďalšími relevantnými predpismi
smernice 1999/5/EC.
PLANET Technology Corporation, s tem
potrjuje, da je ta 802.11n Wireless PCI
Express Adapter skladen/a z osnovnimi
zahtevami in ustreznimi določili Direktive
1999/5/EC.
PLANET Technology Corporation, vakuuttaa
täten että 802.11n Wireless PCI Express
Adapter tyyppinen laite on direktiivin 1999/5/EY
oleellisten vaatimusten ja sitä koskevien
direktiivin muiden ehtojen mukainen.
Härmed intygar, PLANET Technology
Corporation, att denna 802.11n Wireless PCI
Express Adapter står i överensstämmelse med
de väsentliga egenskapskrav och övriga
relevanta bestämmelser som framgår av
direktiv 1999/5/EG.
 Loading...
Loading...