Page 1

Page 2

Copyright
Copyright 2013 by PLANET Technology Corp. All rights reserved. No part of this publication may
be reproduced, transmitted, transcribed, stored in a retrieval system, or translated into any language
or computer language, in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, magnetic, optical,
chemical, manual or otherwise, without the prior written permission of PLANET.
PLANET makes no representations or warranties, either expressed or implied, with respect to the
contents hereof and specifically disclaims any warranties, merchantability or fitness for any particular
purpose. Any software described in this manual is sold or licensed "as is". Should the programs
prove defective following their purchase, the buyer (and not this company, its distributor, or its dealer)
assumes the entire cost of all necessary servicing, repair, and any incidental or consequential
damages resulting from any defect in the software. Further, this company reserves the right to revise
this publication and to make changes from time to time in the contents hereof without obligation to
notify any person of such revision or changes.
All brand and product names mentioned in this manual are trademarks and/or registered trademarks
of their respective holders.
Federal Communication Commission Interference Statement
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A digital device,
pursuant to part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable
protection against harmful interference when the equipment is operated in a commercial
environme
nt. This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not
installed and used in accordance with the instruction manual, may cause harmful interference to
radio communications. Operation of this equipment in a residential area is likely to cause harmful
interference in which case the user will be required to correct the interference at his/her own
expense. Any changes or modifications not expressly approved by PLANET could void the user’s
authority to operate this equipment under the rules and regulations of the FCC.
FCC Cau
tion:
To assure continued compliance, (example-use only shielded interface cables when connecting to
computer or peripheral devices) any changes or modifications not expressly approved by the party
responsible for compliance could void the user’s authority to operate the equipment.
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the Following two
conditions:
(1) This device may not cause harmful interference
(2) This Device must accept any interference received, including interference that may cause
undesired operation.
Federal Communication Commission (FCC) Radiation Exposure Statement
This equipment complies with FCC radiation exposure set forth for an uncontrolled environment. In
order to avoid the possibility of exceeding the FCC radio frequency exposure limits, human proximity
to the antenna shall not be less than 20 cm (8 inches) during normal operation.
I
Page 3

CE Mark Warning
This is a Class B product. In a domestic environment, this product may cause radio interference, in
which case the user may be required to take adequate measures.
Energy Saving Note of the Device
This power required device does not support Standby mode operation.
For energy saving, please remove the DC-plug to disconnect the device from the power circuit.
Without remove the DC-plug, the device still consuming power from the power circuit. In the view of
Saving the Energy and reduce the unnecessary power consuming, it is strongly suggested to
remove the DC-plug for the device if this device is not intended to be active.
R&TTE Compliance Statement
This equipment complies with all the requirements of DIRECTIVE 1999/5/CE OF THE EUROPEAN
PARLIAMENT AND THE COUNCIL OF 9 March 1999 on radio equipment and telecommunication
terminal Equipment and the mutual recognition of their conformity (R&TTE).
The R&TTE Directive repeals and replaces in the directive 98/13/EEC (Telecommunications
Terminal Equipment and Satellite Earth Station Equipment) As of April 8, 2000.
Safety
This equipment is designed with the utmost care for the safety of those who install and use it.
However, special attention must be paid to the dangers of electric shock and static electricity when
working with electrical equipment. All guidelines of this and of the computer manufacture must
therefore be allowed at all times to ensure the safe use of the equipment.
WEEE regulation
To avoid the potential effects on the environment and human health as a result of the
presence of hazardous substances in electrical and electronic equipment, end users of
electrical and electronic equipment should understand the meaning of the crossed-out
wheeled bin symbol. Do not dispose of WEEE as unsorted municipal waste and have to
collect such WEEE separately.
II
Page 4

Revision
User’s Manual for PLANET 802.11a/n Wireless Outdoor Access Point
Model: WNAP-7350
Rev: 2.0 (December, 2012)
Part No. EM-WNAP-7350_v2.0 (2081-E10510-002)
III
Page 5

CONTENTS
Chapter 1. Product Introduction...........................................................................................................1
1.1 Package Contents...............................................................................................................1
1.2 Product Description............................................................................................................ 2
1.3 Product Features................................................................................................................. 6
1.4 Product Specification ......................................................................................................... 7
Chapter 2. Hardware Installation ........................................................................................................10
2.1 Hardware Description.......................................................................................................10
2.1.1 The Bottom Panel ...................................................................................................10
Chapter 3. Connecting to the AP........................................................................................................12
3.1 Preparation before Installation ........................................................................................ 12
3.1.1 Professional Installation Required..........................................................................12
3.1.2 Safety Precautions.................................................................................................. 12
3.2 Installation Precautions....................................................................................................12
3.3 Installing the AP ................................................................................................................ 14
Chapter 4. Quick Installation Guide ................................................................................................... 17
4.1 Manual Network Setup - TCP/IP Configuration..............................................................17
4.1.1 Configure the IP Address Manually........................................................................17
4.2 Starting Setup in the Web UI ............................................................................................ 21
Chapter 5. Configuring the AP............................................................................................................ 23
5.1 Status.................................................................................................................................. 23
5.2 Easy Setup.........................................................................................................................26
5.3 Advanced ........................................................................................................................... 27
5.3.1 Advanced - Management........................................................................................27
5.3.1.1. Web Interface Settings (Password)................................................................................ 28
5.3.1.2. Firmware Upgrade .........................................................................................................28
5.3.1.3. Configuration.................................................................................................................. 29
5.3.1.4. Load Factory Defaults....................................................................................................30
5.3.1.5. Reboot System ..............................................................................................................30
5.3.1.6. Scheduling Reboot......................................................................................................... 31
5.3.2 Advanced – Advanced Settings.............................................................................. 31
5.3.2.1. Time Zone Settings........................................................................................................32
5.3.2.2. DDNS Settings...............................................................................................................32
5.3.2.3. UPNP Settings ...............................................................................................................34
5.3.2.4. SNMP Settings............................................................................................................... 35
5.3.3 Advanced – Operation Mode..................................................................................36
5.3.3.1. AP Router (AP+Router) .................................................................................................36
5.3.3.2. AP Bridge (AP+WDS) .................................................................................................... 37
5.3.3.3. Client Router (WISP) .....................................................................................................38
IV
Page 6

5.3.3.4. Client Bridge (Slave AP Bridge) ..................................................................................... 42
5.3.4 Advanced – System Log......................................................................................... 43
5.3.5 Advanced – Tools ...................................................................................................43
5.3.5.1. Ping................................................................................................................................44
5.3.5.2. Traceroute...................................................................................................................... 44
5.3.5.3. Throughput..................................................................................................................... 45
5.4 Firewall Settings................................................................................................................ 45
5.4.1 MAC/IP/Port Filtering ..............................................................................................45
5.4.2 Virtual Server ..........................................................................................................47
5.4.3 DMZ ........................................................................................................................ 48
5.4.4 Firewall....................................................................................................................48
5.4.5 QoS.........................................................................................................................49
5.4.6 Content Filtering .....................................................................................................51
5.4.6.1. Webs URL Filter Settings............................................................................................... 51
5.4.6.2. Web Host Filter Settings ................................................................................................52
5.5 Network Settings...............................................................................................................52
5.5.1 WAN........................................................................................................................52
5.5.1.1. Static (Fixed IP)..............................................................................................................53
5.5.1.2. Cable/Dynamic IP (DHCP).............................................................................................53
5.5.1.3. PPPoE (ADSL)............................................................................................................... 54
5.5.1.4. IPSEC ............................................................................................................................ 55
5.5.1.5. PPTP .............................................................................................................................59
5.5.1.6. L2TP ..............................................................................................................................60
5.5.2 LAN.........................................................................................................................61
5.5.2.1. DHCP Server ................................................................................................................. 62
5.5.2.2. DHCP Relay................................................................................................................... 62
5.5.3 VLAN.......................................................................................................................63
5.5.4 Advanced Routing ..................................................................................................64
5.5.5 IPv6.........................................................................................................................65
5.6 Wireless Settings ..............................................................................................................66
5.6.1 Basic ....................................................................................................................... 66
5.6.1.1. Wireless Mode – Access Point....................................................................................... 67
5.6.1.2. Wireless Mode – WDS Access Point .............................................................................69
5.6.1.3. Wireless Mode – WDS Repeater ...................................................................................71
5.6.1.4. Wireless Mode – WDS Client.........................................................................................73
5.6.2 Profile Settings........................................................................................................ 75
5.6.3 Advanced................................................................................................................77
5.6.4 Access Control........................................................................................................78
5.7 Logout ................................................................................................................................79
Appendix A: FAQ................................................................................................................................. 80
A.1 What and how to find my PC’s IP and MAC address? .....................................................80
V VI
Page 7

A.2 What is Wireless LAN?........................................................................................................ 80
A.3 What are ISM bands?...........................................................................................................80
A.4 How does wireless networking work?............................................................................... 80
A.5 What is BSSID?....................................................................................................................81
A.6 What is ESSID? .................................................................................................................... 81
A.7 What are potential factors that may causes interference?..............................................81
A.8 What are the Open System and Shared Key authentications?....................................... 82
A.9 What is WEP?.......................................................................................................................82
A.10 What is Fragment Threshold? ..........................................................................................82
A.11 What is RTS (Request to Send) Threshold? ................................................................... 83
A.12 What is Beacon Interval? ..................................................................................................83
A.13 What is Preamble Type?.................................................................................................... 83
A.14 What is SSID Broadcast?..................................................................................................83
A.15 What is Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA)? .........................................................................84
A.16 What is WPA2? ...................................................................................................................84
A.17 What is 802.1x Authentication?........................................................................................84
A.18 What is Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP)?...........................................................84
A.19 What is Advanced Encryption Standard (AES)?.............................................................84
A.20 What is Inter-Access Point Protocol (IAPP)?.................................................................. 85
A.21 What is Wireless Distribution System (WDS)?...............................................................85
A.22 What is Universal Plug and Play (UPnP)?.......................................................................85
A.23 What is Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) Size? ........................................................85
A.24 What is Clone MAC Address? .......................................................................................... 85
A.25 What is DDNS?................................................................................................................... 85
A.26 What is NTP Client?........................................................................................................... 85
A.27 What is VPN?...................................................................................................................... 86
A.28 What is IPSEC? .................................................................................................................. 86
A.29 What is WLAN Block Relay between Clients? ................................................................86
A.30 What is WMM?....................................................................................................................86
A.31 What is WLAN ACK TIMEOUT? ........................................................................................86
A.32 What is Modulation Coding Scheme (MCS)?..................................................................86
A.33 What is Frame Aggregation?............................................................................................ 86
A.34 What is Guard Intervals (GI)? ........................................................................................... 87
Appendix B: Configuring the PC in Windows 7...............................................................................88
Appendix C: Use Planet Smart Discovery to find AP......................................................................91
Appendix D: Specifications................................................................................................................92
Page 8

User Manual of WNAP-7350
Chapter 1. Product Introduction
1.1 Package Contents
Thank you for choosing PLANET WNAP-7350. Before installing the AP, please verify the contents inside the
package box.
WNAP-7350 Wireless AP Quick Installation Guide CD-ROM
(User Manual included)
PoE Injector & Power Cord Mounting Kit x 1 RJ-45 Waterproof Kit x 2
If there is any item missed or damaged, please contact the seller
immediately.
-1-
Page 9
User Manual of WNAP-7350
1.2 Product Description
High Power Outdoor Wireless Coverage
PLANET Technology introduces the latest high power outdoor wireless LAN solution - the 300Mbps outdoor
wireless AP, WNAP-7350. It provides higher transmit power, better performance, widely coverage and
stable connection than standard outdoor wireless AP. As an IEEE 802.11a/n compliant wireless device, the
WNAP-7350 is able to give stable and efficient wireless performance for long distance application; while
designed with IEEE 802.11n standard and 2T2R MIMO technology makes it possible to deliver six times faster
data rate up to 300Mbps than normal 802.11a wireless device. It also features adjustable output power up to
500mW to extend higher coverage in outdoor long range application.
-2-
Page 10
User Manual of WNAP-7350
Multiple Operating & Wireless Modes
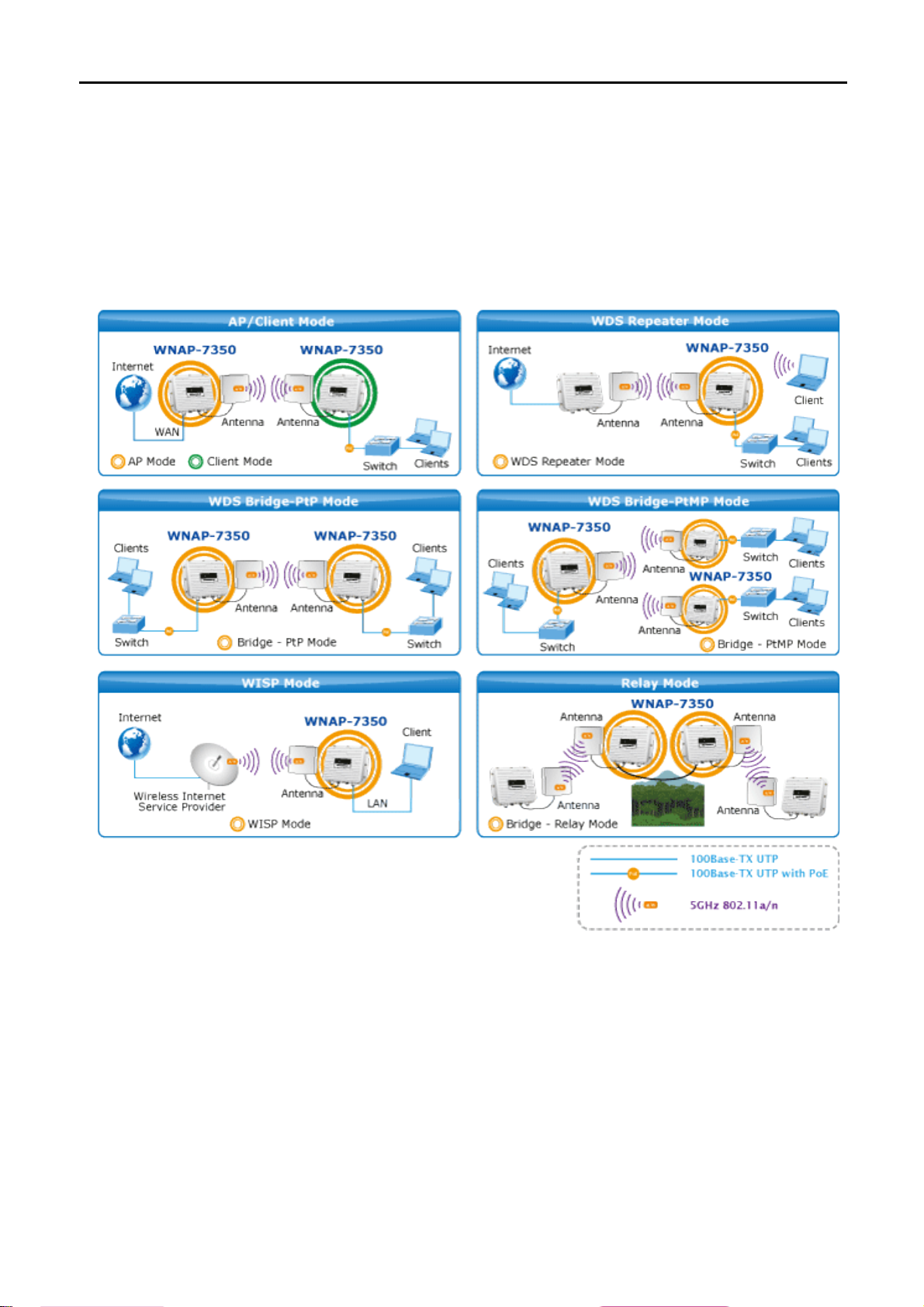
The WNAP-7350 supports multiple wireless communication connectivity (AP / Client CPE / WDS PtP / WDS
PtMP / Repeater) allowing for various application requirements and thus it gives users more comprehensive
experience when using the WNAP-7350. It helps users to easily build a wireless network and extend the
wireless range of existing wireless network.
The WNAP-7350 also supports WISP mode, so CPE users could easily connect to Internet via WISP provider
or connect to a wired network.
Advanced Security and Management
In aspect of security, besides 64/128- bit WEP encryption, the WNAP-7350 integrates WPA / WPA2,
WPA-PSK / WPA2-PSK and 802.1x authority to secure and protect your wireless LAN. The wireless MAC
filtering and SSID broadcast control consolidate t
wireless connection. To fulfill enterprise and various applications demand, the WNAP-7350 enhances security
and management features such as providing multiple SSID support.
he wireless network security and prevent unauthorized
-3-
Page 11

User Manual of WNAP-7350
Perfect Solution for Outdoor Environment
The WNAP-7350 is perfectly suitable in outdoor environments and exposed locations. By designing with IP67
and aluminum rugged strong housing, the WNAP-7350 can perform normally under rigorous weather
conditions including heavy rain, wind and snow. Moreover, the WNAP-7350 is rated to operate at the
temperature from -30 to 75 Degree C; thus it can operate more stably than general outdoor equipments. It is
the best way using the WNAP-7350 to build outdoor wireless access applications between buildings on
campuses, business, rural areas and etc.
Flexible Deployment with PoE Feature
Compliant with IEEE 802.3af/at Power over Ethernet standard, the WNAP-7350 can be powered by PSE
(Power Sourcing Equipment) via a single UTP cable. It thus reduces the needs of extra cables and dedicated
electrical outlets on the wall, ceiling or any other places where are difficult to reach. Furthermore, the
WNAP-7350 is also suitable to be integrated with PoE Solar Power System to offer farther Wireless service in
remote areas. It enables the wireless LAN deployment becomes more flexible and worries free from the power
outlet locations.
-4-
Page 12

User Manual of WNAP-7350
Easy Installation & Management
With user-friendly Web UI and step by step Setup Wizard, the WNAP-7350 is easier to install, even for users
who never experience setting up a wireless network. Furthermore, with SNMP-Based management interface,
the WNAP-7350 is convenient to be managed and configured remotely.
-5-
Page 13

1.3 Product Features
Industrial Compliant Wireless LAN & LAN
Compliant with IEEE 802.11n wireless technology capable of up to 300Mbps data rate
Backward compatible with 802.11a standard
Equipped with 10/100Mbps RJ-45 Ports for LAN & WAN, Auto MDI/ MDI-X supported
Fixed-network Broadband AP
Supported connection types: Dynamic IP / Static IP / PPPoE / PPTP / L2TP / IPSec
Supports Virtual Server, DMZ for various networking applications
Supports DHCP Server, UPnP, Dynamic DNS
RF Interface Characteristics
Built-in two N-Type Female Antenna connectors
High Output Power up to 500mW with multiple adjustable transmit power control
User Manual of WNAP-7350
Outdoor Environmental Characteristics
Aluminum Housing, IP67 Protection Grade
IEEE 802.3af/at Power over Ethernet design
Operating Temperature: -30~75 Degree C
Multiple Operation & Wireless Mode
Multiple Operation Modes: Bridge, Gateway, WISP
Multiple Wireless Modes: AP, Client CPE (WISP), WDS PtP, WDS PtMP, Repeater
Supports Dual-SSID allowing users to access different networks through one single AP
Supports WMM (Wi-Fi Multimedia)
Secure Network Connection
Supports Software Wi-Fi Protected Setup (WPS)
Advanced security: 64/128-bit WEP, WPA / WPA2, WPA-PSK / WPA2-PSK (TKIP/AES), and
802.1x Authentication
Supports NAT firewall features, with SPI function to protect against DoS attacks
Supports IP / Protocol-based access control and MAC Filtering
Easy Installation & Management
Web-Based UI and Quick Setup Wizard for easy configuration
Remote Management allows configuration from a remote site
SNMP-Based management interface
System status monitoring includes DHCP Client, System Log
-6-
Page 14
1.4 Product Specification
User Manual of WNAP-7350
Product
WNAP-7350
5GHz 300Mbps 802.11a/n Wireless Outdoor Access Point
Hardware Specifications
IEEE 802.11a/n Wireless LAN
IEEE 802.11i Wireless Security
Standard support
IEEE 802.3 10Base-T Ethernet
IEEE 802.3u 100Base-TX Ethernet
IEEE 802.3x Flow Control
IEEE 802.3af/at Power over Ethernet / PD
Memory
32 Mbytes DDR SDRAM
8 Mbytes Flash
Wireless IEEE 802.11a/n, 2T2R
Interface
LAN: 1 x 10/100Base-TX, Auto-MDI/MDIX, IEEE 802.3af/at PoE/PD port
WAN: 1 x 10/100Base-TX, Auto-MDI/MDIX
Antenna N-Type Female connectors x 2
Wireless RF Specifications
Wireless Technology
IEEE 802.11a
IEEE 802.11n
IEEE 802.11a: 54, 48, 36, 24, 18, 12, 9 and 6Mbps
Data Rate
IEEE 802.11n (20MHz): up to 150Mbps
IEEE 802.11n (40MHz): up to 300Mbp
Media Access Control CSMA / CA
Modulation
Transmission / Emission Type: OFDM
Data modulation type: OFDM with BPSK, QPSK, 16-QAM, 64-QAM
Frequency Band 5.180GHz ~ 5.825GHz
Operating Channel
RF Output Power
5.180GHz CH36 5.580GHz CH116
5.200GHz CH40 5.600GHz CH120
5.220GHz CH44 5.620GHz CH124
5.240GHz CH48 5.640GHz CH128
5.260GHz CH52 5.660GHz CH132
5.280GHz CH56 5.680GHz CH136
5.300GHz CH60 5.700GHz CH140
5.320GHz CH64 5.745GHz CH149
5.500GHz CH100 5.765GHz CH153
5.520GHz CH104 5.785GHz CH157
5.540GHz CH108 5.805GHz CH161
5.560GHz CH112 5.825GHz CH165
*The above 24 channels are defined in theory. The actual application will vary
depends on the regulation in different regions and countries.
IEEE 802.11a: 27 ± 1dBm
IEEE 802.11n: 24 ± 1dBm
-7-
Page 15
User Manual of WNAP-7350
Receiver Sensitivity
IEEE 802.11a: -91dBm
IEEE 802.11n: -92dBm
Output Power Control 3~27dBm
Software Features
LAN
Built-in DHCP server supporting static IP address distributing
Supports 802.1d STP (Spanning Tree)
Static IP
Dynamic IP
WAN
PPPoE
PPTP
L2TP
IPSec
Bridge
Operating Mode
Gateway
WISP
NAT firewall with SPI (Stateful Packet Inspection)
Firewall
Built-in NAT server supporting Virtual Server and DMZ
Built-in firewall with Port / IP address / MAC / URL filtering
AP
Client
Wireless Mode
WDS PTP
WDS PTMP
WDS Repeater (AP+WDS)
Channel Width 20MHz / 40MHz
Wireless Isolation
Enable it to isolate each connected wireless clients from communicating with
each other mutually.
Encryption Type 64/128-bits WEP, WPA, WPA-PSK, WPA2, WPA2-PSK, 802.1X
Provides wireless LAN ACL (Access Control List) filtering
Wireless Security
Wireless MAC address filtering
Supports WPS (WIFI Protected Setup )
Enable / Disable SSID Broadcast
Multiple SSID Up to 2
Max. Wireless Client 40
Max. WDS AP 8
Max. Wired Client 60
WMM Supports Wi-Fi Multimedia
QoS Supports Quality of Service for bandwidth control
NTP Network Time Management
Management Web UI, DHCP Client, Configuration Backup & Restore, Dynamic DNS, SNMP
Diagnostic tool System Log, Ping Watchdog
Mechanical & Power
IP Rate IP67
Material Aluminum
-8-
Page 16

Dimension (W x D x H) 239 x 269 x 80mm
Weight 2.4kg
Installation Pole mounting or Wall mounting
Power Requirements
AP: IEEE 802.3af/at PoE / 48VDC input (PoE Injector included)
PoE Injector: 100~240VAC
Power Consumption 7.68W
Environment & Certification
Operation Temperature -30~75 Degree C
Operating Humidity 10~95% non-condensing
Regulatory CE / RoHS
Accessory
48VDC 802.3af PoE injector & Power cord x 1
Mounting Kit x 1
Standard Accessories
Waterproof RJ-45 Connector Kit x 2
Quick Installation Guide x 1
CD (User’s Manual, Quick Installation Guide) x 1
User Manual of WNAP-7350
-9-
Page 17

User Manual of WNAP-7350
Chapter 2. Hardware Installation
Please follow the instructions below to connect WNAP-7350 to the existing network devices and your
computers.
2.1 Hardware Description
Dimension: 320 x 27.5 x 320 mm (W x D x H)
Figure 2-1 Three-way View
2.1.1 The Bottom Panel
The Bottom panel provides the physical connectors connected to the power adapter and any other network
devices. Figure 2-2 shows the Bottom panel of WNAP-7350.
-10-
Page 18
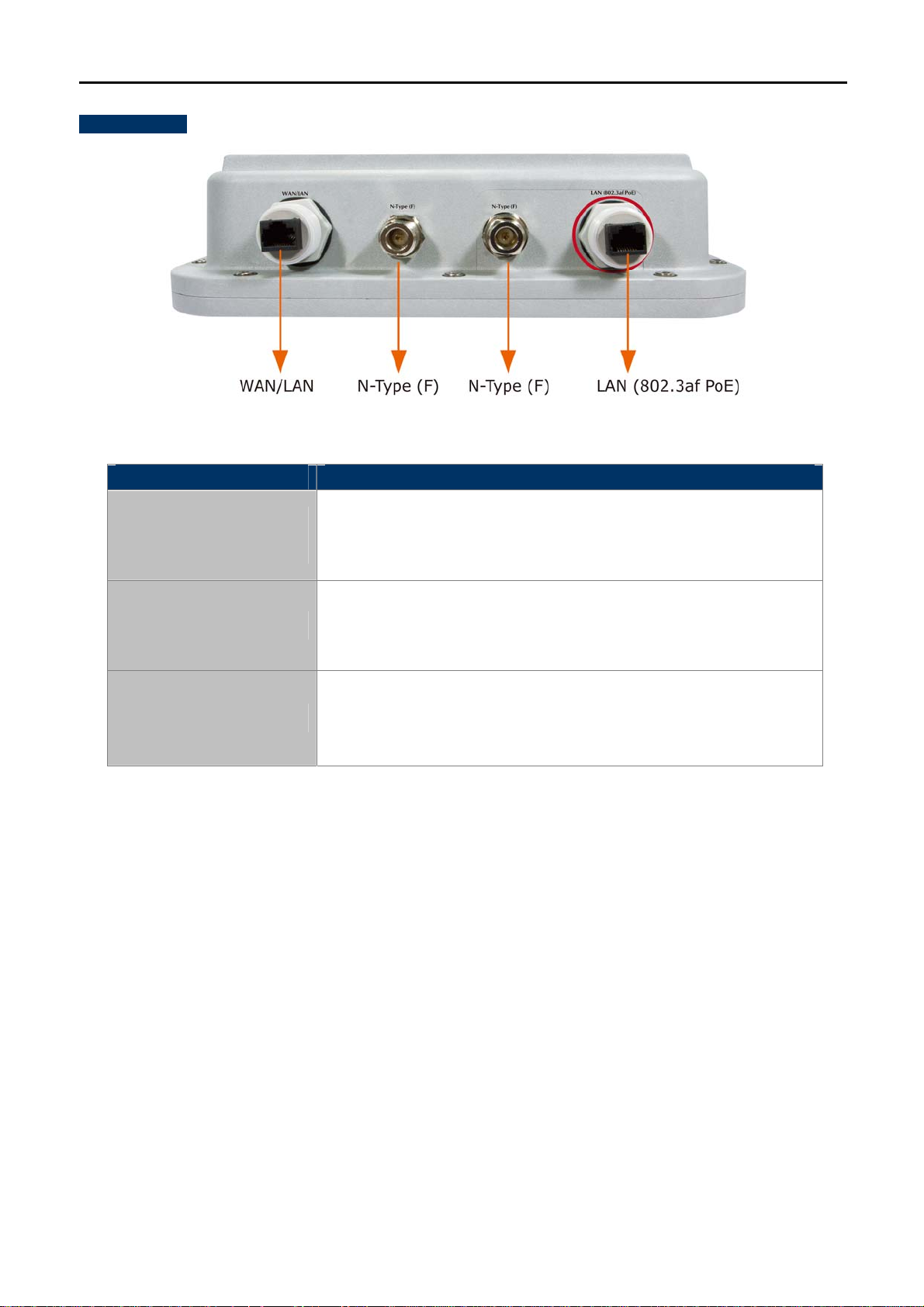
Bottom Panel
User Manual of WNAP-7350
Figure 2-2 Bottom Panel
Interface Description
LAN
(802.3af/at PoE/PD port)
N-Type (F)
WAN / LAN
10/100Mbps RJ-45 port , Auto MDI/ MDI-X & 802.3af/at PoE supported
Connect LAN port to the PoE injector or PoE switch to power on the
device.
N-Type Female Antenna Connectors.
Connect N-Type (F) Antenna Connectors with Outdoor Antenna through
the N-Type (Male) to N-Type (Male) RF cable.
10/100Mbps RJ-45 port , Auto MDI/ MDI-X
Connect this port to the xDSL modem in AP mode.
Connect this port to the network equipment in bridge mode.
Table 2-1 The Interface indication
-11-
Page 19

User Manual of WNAP-7350
Chapter 3. Connecting to the AP
3.1 Preparation before Installation
3.1.1 Professional Installation Required
Please seek assistance from a professional installer who is well trained in the RF installation and knowledgeable
in the local regulations.
3.1.2 Safety Precautions
1. To keep you safe and install the hardware properly, please read and follow these safety precautions.
2. If you are installing WNAP-7350 for the first time, for your safety as well as others’, please seek assistance
from a professional installer who has received safety training on the hazards involved.
3. Keep safety as well as performance in mind when selecting your installation site, especially where there
are electric power and phone lines.
4. When installing WNAP-7350, please note the following things:
Do not use a metal ladder;
Do not work on a wet or windy day;
Wear shoes with rubber soles and heels, rubber gloves, long sleeved shirt or jacket.
5. When the system is operational, avoid standing directly in front of it. Strong RF fields are present when the
transmitter is on.
3.2 Installation Precautions
Users MUST use a proper and well-installed surge arrestor and grounding kit with WNAP-7350;
otherwise, a random lightening could easily cause fatal damage to WNAP-7350. EMD (Lightning)
DAMAGE IS NOT COVERED UNDER WARRANTY.
Users MUST use the “Power cord & PoE Injector” shipped in the box with the WNAP-7350. Use of
other options will cause damage to the WNAP-7350.
Users MUST power off the WNAP-7350 first before connecting the external antennas to it; otherwise,
damage might be caused to the WNAP-7350 itself.
-12-
Page 20
User Manual of WNAP-7350
OUTDOOR INSTALLATION WARNING
!
IMPORTANT SAFETY PRECAUTIONS:
LIVES MAY BE AT RISK! Carefully observe these instructions and any special instructions that are included with the
equipment you are installing.
CONTACTING POWER LINES CAN BE LETHAL. Make sure no power
lines are anywhere where possible contact can be made. Antennas, masts,
towers, guy wires or cables may lean or fall and contact these limes.
People may be injured or killed if they are touching or holding any part of
equipment when it contacts electric lines. Make sure there is NO possibility
that equipment or personnel can come in contact directly or indirectly with
power lines.
Assume all overhead lines are power lines.
The horizontal distance from a tower, mast or antenna to the nearest power line should be at least twice the total length of
the mast/antenna combination. This will ensure that the mast will not contact power if it falls either during installation or later.
TO AVOID FALLING, USE SAFE PROCEDURES WHEN WORKING AT HEIGHTS ABOVE GROUND.
Select equipment locations that will allow safe, simple equipment installation.
Don’t work alone. A friend or co-worker can save your life if an accident happens.
Use approved non-conducting lasers and other safety equipment. Make sure all equipment is in good repair.
If a tower or mast begins falling, don’t attempt to catch it. Stand back and let it fall.
If anything such as a wire or mast does come in contact with a power line, DON’T TOUCH IT OR ATTEMPT TO
MOVE IT. Instead, save your life by calling the power company.
Don’t attempt to erect antennas or towers on windy days.
MAKE SURE ALL TOWERS AND MASTS ARE SECURELY GROUNDED, AND ELECTRICAL CABLES CONNECTED TO
ANTENNAS HAVE LIGHTNING ARRESTORS. This will help prevent fire damage or human injury in case of lightning, static
build-up, or short circuit within equipment connected to the antenna.
The base of the antenna mast or tower must be connected directly to the building protective ground or to one or more
approved grounding rods, using 1 OAWG ground wire and corrosion-resistant connectors.
Refer to the National Electrical Code for grounding details.
IF A PERSON COMES IN CONTACT WITH ELECTRICAL POWER, AND CANNOT MOVE:
DON’T TOUCH THAT PERSON, OR YOU MAY BE ELECTROCUTED.
Use a non-conductive dry board, stick or rope to push or drag them so they no longer are in contact with electrical
power.
Once they are no longer contacting electrical power, administer CPR if you are certified, and make sure that emergency
medical aid has been requested.
-13-
Page 21
User Manual of WNAP-7350
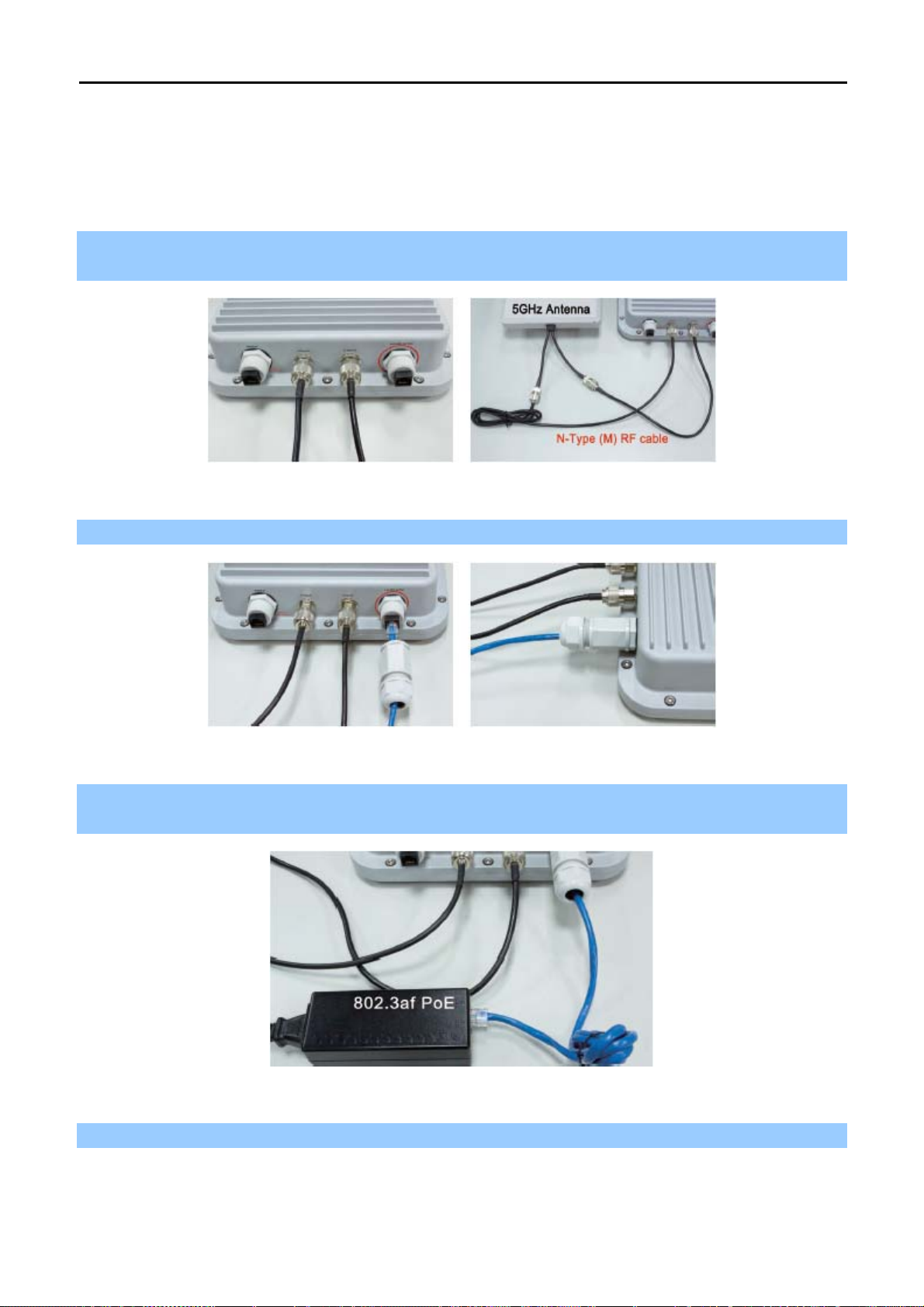
3.3 Installing the AP
Please install the AP according to the following steps. Don't forget to pull out the power plug and keep your
hands dry.
Step 1. Plug the N-Type (M) to N-Type (M) RF cables into the antenna connectors of the WNAP-7350, and
then connect the N-Type (F) antennas to the other side of the RF cables.
Figure 3-1
Step 2. Plug the RJ-45 Ethernet cable into the LAN Port of WNAP-7350 through the waterproof kit.
Figure 3-2
Step 3. Take out the power cord and PoE injector, plug the power cord into the DC port and plug the other side
of the RJ-45 cable into the POE port of the PoE injector.
Figure 3-3
Step 4. Plug the other waterproof kit to the WAN/LAN port to complete the installation.
-14-
Page 22

User Manual of WNAP-7350
Figure 3-4
Step 5a. Pole Mounting:
(a.1) Attach the mounting bracket to the back of the device by using four screws and flat washers.
(a.2) Assemble the M bracket to the outside of the mounting bracket by using four screws and flat washers.
(a.3)Install the antenna assembly to the pole by using the toothed bracket, and then tighten it by four long
screws.
Figure 3-5
Pole diameter less than 5cm may require the use ※ of hex nuts to lock the long screws to
the suitable location.
Step 5b. Wall Mounting:
(b.1) Attach the mounting bracket to the back of the device by using four screws and flat washers.
(b.2) Assemble the M bracket to the wall by using four screws and flat washers.
(b.3) Install the mounting bracket assembly inside the M bracket mounted in the wall by using four screws and
flat washers.
-15-
Page 23

User Manual of WNAP-7350
Figure 3-6
Step 5. Connect the power cord to the power socket on the PoE injector, and the other end into an electrical
outlet. Then power on the AP.
-16-
Page 24

User Manual of WNAP-7350
Chapter 4. Quick Installation Guide
This chapter will show you how to configure the basic functions of your Wireless AP using Easy Setup within
minutes.
A computer with wired Ethernet connection to the Wireless AP is required for the first-time
configuration.
4.1 Manual Network Setup - TCP/IP Configuration
The default IP address of the WNAP-7350 is 192.168.1.1. And the default Subnet Mask is 255.255.255.0. These
values can be changed as you desire. In this guide, we use all the default values for description.
Connect the WNAP-7350 with your PC by an Ethernet cable plugging in LAN port of PoE injector in one side and
in LAN port of PC in the other side. Please power on the WNAP-7350 by PoE from PoE injector or PoE switch.
In the following sections, we’ll introduce how to install and configure the TCP/IP correctly in Windows XP. And
the procedures in other operating systems are similar. First, make sure your Ethernet Adapter is working, and
refer to the Ethernet adapter’s manual if needed.
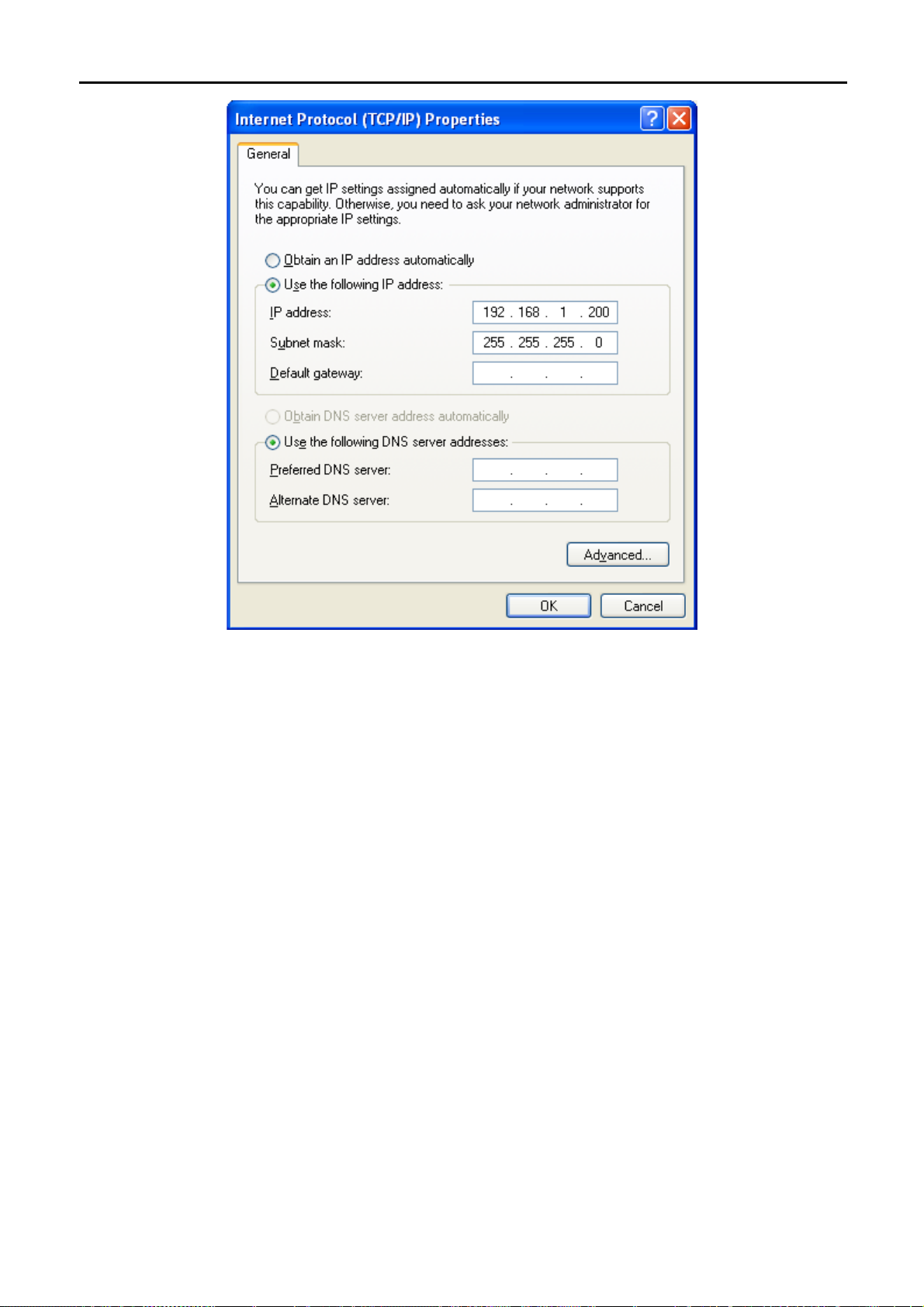
4.1.1 Configure the IP Address Manually
Summary:
Set up the TCP/IP Protocol for your PC.
Configure the network parameters. The IP address is 192.168.1.xxx ("xxx" is any number from 2 to
254), Subnet Mask is 255.255.255.0, and Gateway is 192.168.1.1 (The AP's default IP address)
1 Select Use the following IP address radio button.
2 If the AP's LAN IP address is 192.168.1.1, enter IP address 192.168.1.x (x is from 2 to 254), and Subnet
mask 255.255.255.0.
3 Select Use the following DNS server addresses radio button. In the Preferred DNS Server field, you can
enter the DNS server IP address which has been provided by your ISP
-17-
Page 25
User Manual of WNAP-7350
Figure 4-1
Now click OK to save your settings.
Now, you can run the Ping command in the command prompt to verify the network connection between your
PC and the AP. The following example is in Windows XP OS. Please follow the steps below:
1. Click on Start > Run.
-18-
Page 26
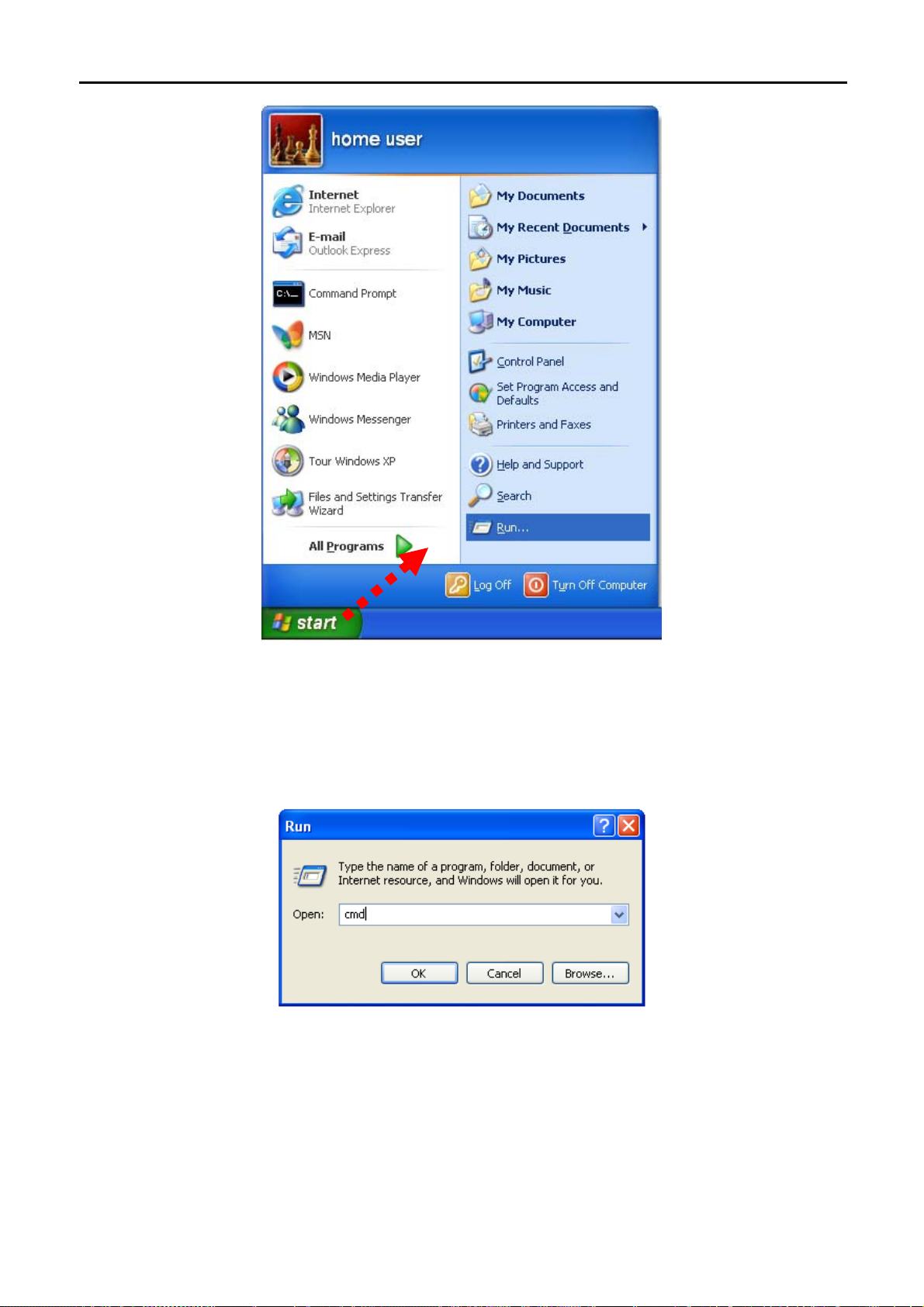
User Manual of WNAP-7350
2. In the run b
prompt.
Figure 4-2
ox type “cmd” and click OK. (Windows Vista users type “cmd” in the Start .Search box.)At the
Figure 4-3
Open a command prompt, and type ping 192.168.1.1, and then press Enter.
If the result displayed is similar to Figure 4-4, it means the connection between your PC and the AP
has been established well.
-19-
Page 27
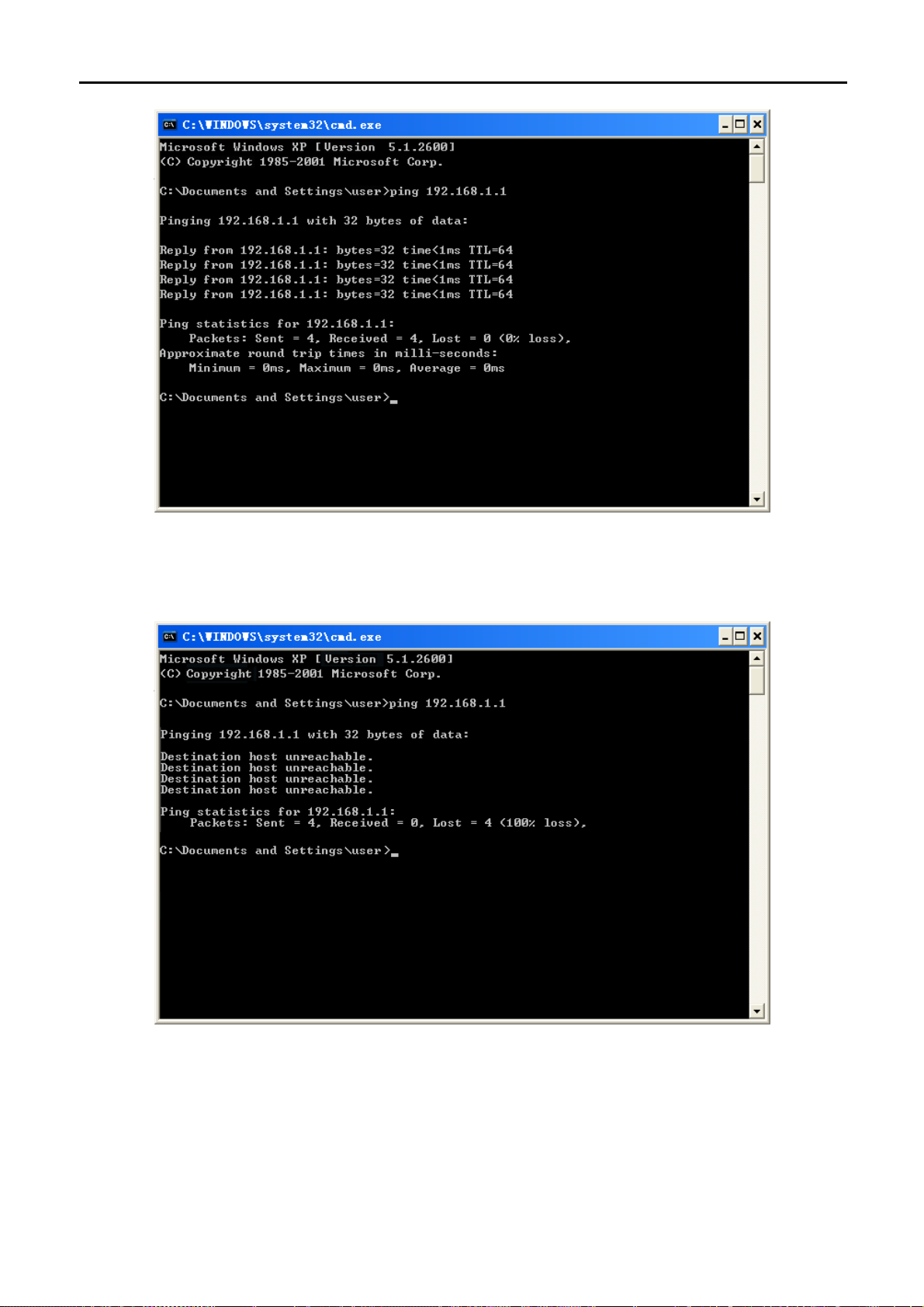
User Manual of WNAP-7350
Figure 4-4 Success result of Ping command
If the result displayed is similar to Figure 4-5, it means the connection between your PC and the AP
has failed.
Figure 4-5 Failure result of Ping command
If the address is 0.0.0.0, check your adapter installation, security settings, and the settings on your AP. Some
firewall software programs may block a DHCP request on newly installed adapters.
-20-
Page 28

User Manual of WNAP-7350
4.2 Starting Setup in the Web UI
It is easy to configure and manage the WNAP-7350 with the web browser.
Step 1. To access the configuration page, open a web-browser and enter the default IP address
http://192.168.1.1 in the web address field of the browser.
Figure 4-6 Login the AP
After a moment, a login window will appear. Enter admin for the User Name and Password, both in lower case
letters. Then click the OK button or press the Enter key.
Default IP Address: 192.168.1.1
Default User name: admin
Default Password: admin
If the above screen does not pop up, it may mean that your web-browser has been set to a
proxy. Go to Tools menu>Internet Options>Connections>LAN Settings, in the screen
that appears, cancel the Using Proxy checkbox, and click OK to finish it.
Figure 4-7 Login Window
-21-
Page 29
User Manual of WNAP-7350
After entering the username and password, the Status page screen appears as Figure 4-8
Figure 4-8 WNAP-7350 Web UI Screenshot
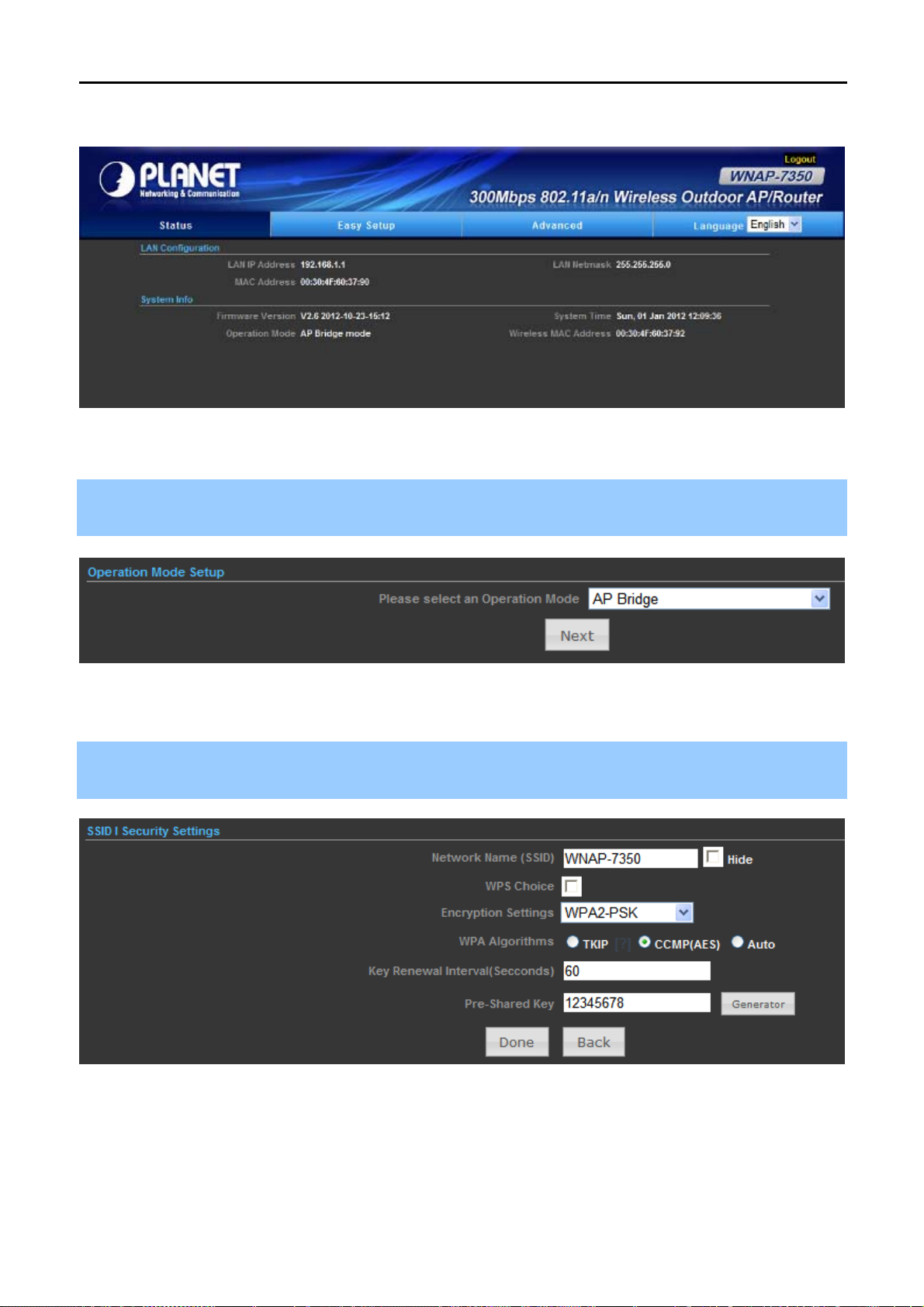
Step 2. Go to “Easy Setup” to choose an Operation Mode. Please refer to the instructions in the next chapter
for configuring the other Operation Modes.
Figure 4-9 Choose Operation Mode
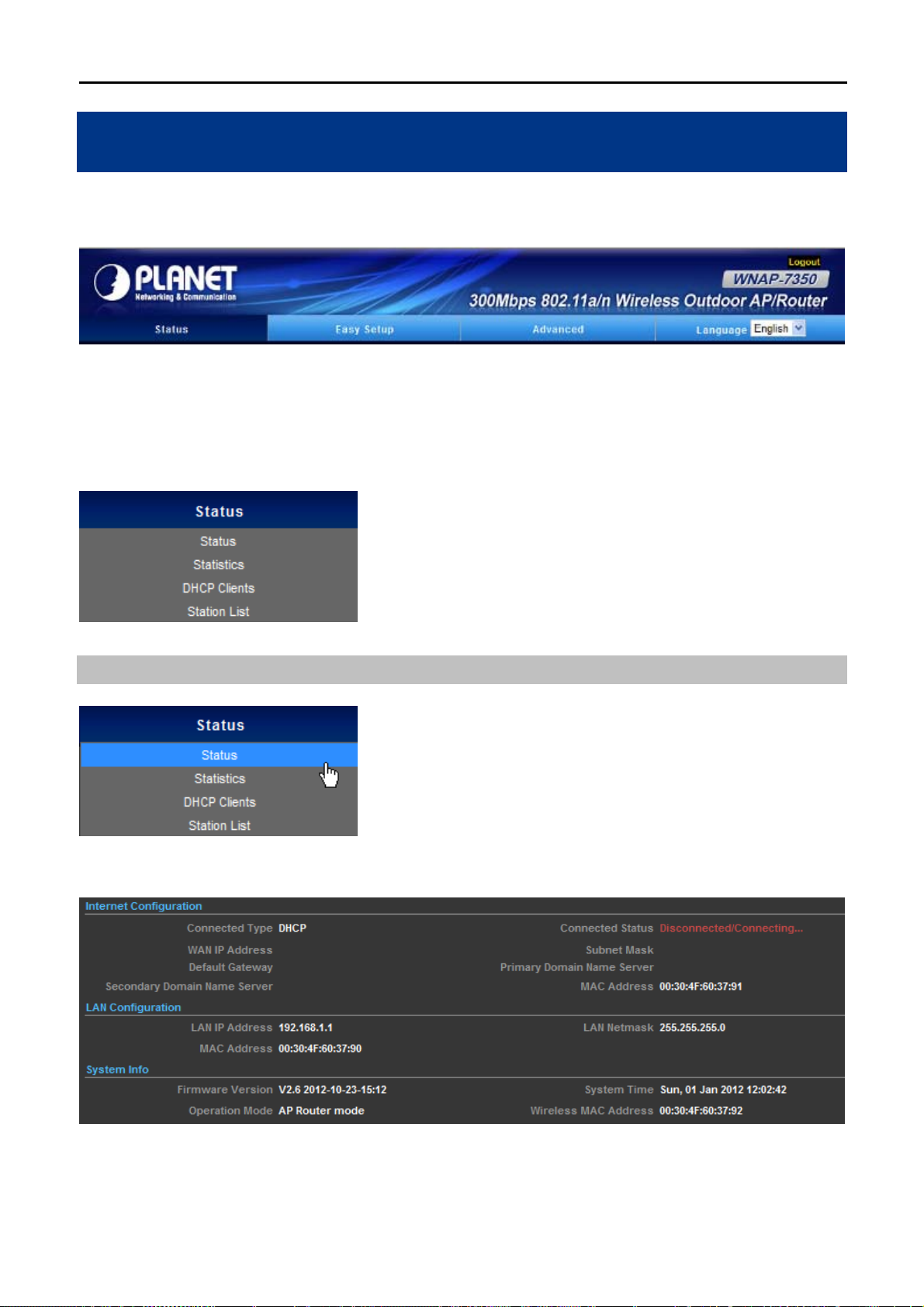
Step 3. Please enter the SSID, configure your Encryption Settings, Pre-Shared Key and etc. Then click Done
button to make the configuration take effect immediately.
Figure 4-10 Configure Wireless Settings
-22-
Page 30
User Manual of WNAP-7350
Chapter 5. Configuring the AP
This chapter delivers a detailed presentation of AP’s functionalities and features under 3 main menus (Status,
Easy Setup, and Advanced) below, allowing you to manage the AP with ease.
Figure 5-1
5.1 Status
In this page, you can view information about the current running status of WNAP-7350, including WAN interface,
LAN interface, Wireless interface, and firmware version information.
Status
This section allows you to view the AP’s System info listed below:
Figure 5-1-1
-23-
Page 31

Object Description
Internet Configuration
User Manual of WNAP-7350
Connected Type
Connected Status
WAN IP
Subnet Mask
Default Gateway
Primary Domain Name
Server
Secondary Domain
Name Server
MAC Address
Displays current Internet connection type.
Disconnected: Indicates that the Ethernet cable from your
ISP side is / is not correctly connected to the WAN port on
the AP or the AP is not logically connected to your ISP.
Connecting: Indicates that the WAN port is correctly
connected and is requesting an IP address from your ISP.
Connected: Indicates that the AP has been connected to
your ISP.
Displays WAN IP address.
Displays WAN subnet mask.
Displays WAN gateway address.
Displays WAN DNS address.
Displays WAN DNS address.
Displays AP’s WAN MAC address.
LAN Configuration
LAN IP Address
LAN Netmask
MAC Address
System Info
Firmware Version
System Time
Operation Mode
Wireless MAC Address
Statistics
Displays LAN IP address.
Displays LAN subnet mask.
Displays AP’s LAN MAC address.
Displays current F/W version.
Displays the System Time.
Displays current Operation Mode.
Displays AP’s Wireless MAC address.
This section allows you to view the AP’s Statistics listed below:
-24-
Page 32

Object Description
Memory
User Manual of WNAP-7350
Figure 5-1-2
Memory Left/
Memory Total
WAN/LAN
WAN Rx packets
WAN Rx bytes
WAN Tx packets
WAN Tx bytes
LAN Rx packets
LAN Rx bytes
LAN Tx packets
LAN Tx bytes
DHCP Clients
Displays the retain memory and total memory.
Displays the real-time packets received from WAN port.
Displays the real-time bytes received from WAN port.
Displays the real-time packets transmitted from WAN port.
Displays the real-time bytes transmitted from WAN port.
Displays the real-time packets received from LAN port.
Displays the real-time bytes received from LAN port.
Displays the real-time packets transmitted from LAN port.
Displays the real-time bytes transmitted from LAN port.
This section displays a DHCP dynamic client list, which includes MAC address, IP address, and lease time info.
-25-
Page 33

Object Description
User Manual of WNAP-7350
Figure 5-1-3
MAC address
Displays MAC address of a given host.
Displays IP address(es) that client(s) obtained from the DHCP
IP Address
server.
Expires in
Remaining time for a corresponding IP address lease.
Station List
This section allows you to view the Station List. The Station List submenu is only available in AP mode.
Figure 5-1-4
Object Description
MAC address
Rate
Expires in
Displays MAC address of a connected client.
Displays connection speed of a connected client.
Displays the signal strength of a connected client.
5.2 Easy Setup
The Easy Setup helps you configure the basic functions of your Wireless AP within minutes.
Please refer to the Step 2 in the section “4.2 Starting Setup in the Web UI” for the detail procedure.
Figure 5-2-1
-26-
Page 34

User Manual of WNAP-7350
5.3 Advanced
“Advanced” includes the following four submenus (Advanced, Firewall Settings, Network Settings, and Wireless
Settings). Clicking any of them enters corresponding interface for configuration. Below explains, in details, each
such feature.
Figure 5-3-1
5.3.1 Advanced - Management
This section allows you to manage the Wireless AP.
-27-
Page 35

5.3.1.1. Web Interface Settings (Password)
User Manual of WNAP-7350
Figure 5-3-2
Object Description
User Name
Password
Re-enter to confirm
Display the User Name info.
Enter the new password that you prefer for login.
Re-enter the new password to confirm.
If you changed the login password, you must enter the new one in the next login.
5.3.1.2. Firmware Upgrade
Figure 5-3-3
-28-
Page 36

Click the “Browse…” button to select the new firmware for upgrading.
Object Description
User Manual of WNAP-7350
Software Version
Location
Upload
!
IMPORTANT SAFETY PRECAUTIONS:
Do Not Turn off the power or close the browser during upgrade process!
5.3.1.3. Configuration
Display the current Software Version info.
Click the “Browse…” button to select the new firmware in this field.
Click the “Upload” button to upgrade the new firmware.
Figure 5-3-4
Click the “Export” button to backup the configuration of the Wireless AP, and click “Import” to restore the
configuration.
Object Description
Export
Browse…
Import
Click the “Export” button to backup the configuration.
Click the “Browse…” button to select the configuration file in this
field for restoring settings.
Click the “Import” button to restore the configuration.
-29-
Page 37

5.3.1.4. Load Factory Defaults
Figure 5-3-5
Click the “Load Default” button to reset it to factory default settings.
5.3.1.5. Reboot System
User Manual of WNAP-7350
Figure 5-3-6
Click the “Reboot Now!” button to restart the Wireless AP.
-30-
Page 38
User Manual of WNAP-7350
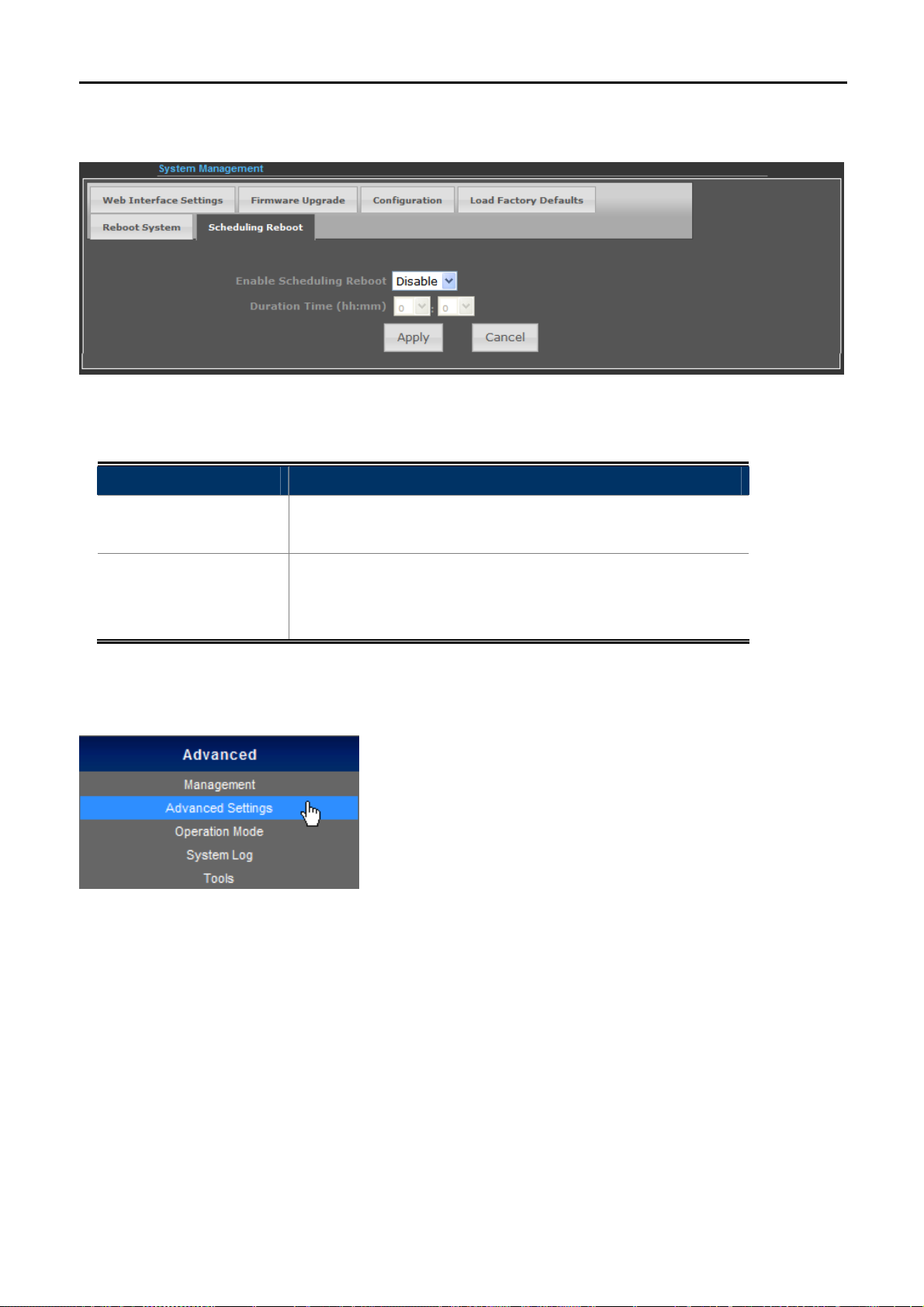
5.3.1.6. Scheduling Reboot
Figure 5-3-7
Select “Enable” to configure the system auto reboot according to the Duration Time (Time interval).
Object Description
Enable Scheduling
Reboot
Enable: select it to enable the Scheduling Reboot.
Disable: select it to disable the Scheduling Reboot.
Configure the particular time interval for the system auto reboot.
Duration Time
hh: means hours
(hh:mm)
mm: means minutes
5.3.2 Advanced – Advanced Settings
This section allows you to configure advanced settings of the Wireless AP.
-31-
Page 39

5.3.2.1. Time Zone Settings
The page includes the following fields:
User Manual of WNAP-7350
Figure 5-3-8
Object Description
Current Time
Sync with host
Time Zone
SNTP Server
SNTP Synchronization
(minutes)
Display the current Time.
Click it to sync your PC’s time to the device.
Select your current time zone.
Configure your SNTP Server.
Determines a time length when device periodically updates its
time and date info from Internet.
5.3.2.2. DDNS Settings
The page includes the following fields:
Object Description
Figure 5-3-9
-32-
Page 40

User Manual of WNAP-7350
Dynamic DNS Provider
Select your Dynamic DNS Provider.
Enter the host name or domain name provided by your DDNS
Host Name
service provider.
User Name
Password
Enter the name of your DDNS account.
Password: Enter the password of the DDNS account.
Example of Planet DDNS Settings:
Please go to http://www.planetddns.com/
Please refer to the FAQ (http://www.planetddns.com/index.php/faq
to register a Planet DDNS account.
) for how to register a free account.
Please refer to the procedure listed as following to configure using Planet DDNS service.
Step 1. Select “planetddns.com” to choose Planet DDNS service.
Step 2. Configure the DDNS account that has been registered in Planet DDNS website.
Host Name: Enter your DDNS host (format: xxx.planetddns.com, xxx is the registered domain name)
User Name: Enter your DDNS account
Password: Enter your DDNS account’s password
Figure 5-3-10
Step 3. Go to “Advanced-> Firewall Settings-> Firewall” to allow remote access from WAN port.
Figure 5-3-11
Step 4. Go to “Advanced-> Network Settings-> WAN” to configure WAN Connection using Static (Fixed IP).
-33-
Page 41

User Manual of WNAP-7350
Figure 5-3-12
Step 5. Apply the settings, and connect your WAN port of the Wireless AP to the internet by Ethernet cable.
Step 6. In a remote computer, enter the DDNS host name as the figure shown as below. Then, you should
beable to login the WNAP-7350 remotely.
Please remember to enter the remote management port number that you have configured in Step 3.
Figure 5-3-13
You can go to My Devices page of Planet DDNS website to check if the “Last Connection IP” is displayed.
This indicates your DDNS service is work properly.
5.3.2.3. UPNP Settings
Select “Enable” to enable the UPNP function.
Figure 5-3-14
-34-
Page 42

User Manual of WNAP-7350
Figure 5-3-15
In the computer connected with WNAP-7350, go to “Network” to check the WNAP-7350 is displayed in the list.
Double-click it to logon the Web UI of WNAP-7350.
Figure 5-3-16
5.3.2.4. SNMP Settings
Enable SNMP function will allow the network management station to retrieve statistics and status from the
SNMP Agent in the device.
-35-
Page 43

The page includes the following fields:
Object Description
Choose Enable to open this function if you want to have
User Manual of WNAP-7350
Figure 5-3-17
SNMP Settings
remote control through SNMPv1/v2 agent.
Choose Disable to close this function.
Enter the community name that allows Read-Only access to
Get Community
the Device's SNMP information. The community name can be
considered a group password. The default setting is public.
Enter the community name that allows Read/Write access to
Set Community
the Device's SNMP information. The community name can be
considered a group password. The default setting is private.
5.3.3 Advanced – Operation Mode
There are 4 operation modes (AP Router, AP Bridge, Client Router, Client Bridge) can be configured to meet
various applications.
5.3.3.1. AP Router (AP+Router)
In the Access Point Mode with Router Function, WNAP-7350 acts as central connection point, which wireless
clients can connect to. The DHCP & NAT is enabled, so the clients wirelessly connected to WNAP-7350 can
share the internet connection by connecting WNAP-7350 to a DSL/Cable modem.
-36-
Page 44

User Manual of WNAP-7350
1. Connect the LAN port of WNAP-7350 to the POE port of the PoE Injector with an Ethernet cable.
2. Connect the DSL/Cable Modem to the WAN port of the WNAP-7350.
3. Plug one end of the power cord into the PoE Injector, and the other end in electrical socket.
4. Go to “Advanced-> Operation Mode” to configure it to AP Router Mode.
Figure 5-3-18
In this mode, the LAN2 of the WNAP-7350 works as the WAN port.
To configure the Wireless Settings of AP Router Mode, please refer to the section 5.6 Wireless Settings
.
5.3.3.2. AP Bridge (AP+WDS)
In the Access Point Mode with WDS Function, WNAP-7350 function likes a central connection for any stations or
clients. Stations and Client must configure the same SSID and Security Password to associate within the range.
WNAP-7350 supports 2 different SSIDs to separate different clients at the same time.
-37-
Page 45

User Manual of WNAP-7350
1. Connect the LAN port of WNAP-7350 to the POE port of the PoE Injector with an Ethernet cable.
2. Connect the PC to the LAN port of the PoE Injector with an Ethernet cable.
3. Plug one end of the power cord into the PoE Injector, and the other end in electrical socket.
4. Go to “Advanced-> Operation Mode” to configure it to AP Bridge Mode.
Figure 5-3-19
In this mode, the Wireless interface of the WNAP-7350 works as the WAN port.
To configure the Wireless Settings of AP Bridge Mode, please refer to the section 5.6 Wireless Settings
.
5.3.3.3. Client Router (WISP)
In the Client Router Mode, the WNAP-7350 has DHCP Server build inside that allows many LANs automatically
generate an IP address to share the same Internet. Connect an AP/WISP Wirelessly and connect to LANs via
wired. Client Router Mode is act completely opposite to the AP Router Mode.
-38-
Page 46

User Manual of WNAP-7350
1. Connect the LAN port of WNAP-7350 to the POE port of the PoE Injector with an Ethernet cable.
2. Connect the PC to the LAN port of the PoE Injector with an Ethernet cable.
3. Plug one end of the power cord into the PoE Injector, and the other end in electrical socket.
4. Go to “Advanced-> Operation Mode” to configure it to Client Router Mode.
Figure 5-3-20
WISP Setup Procedure:
Step 1. Go to Advanced-> Wireless Settings-> Profile Settings.
Figure 5-3-21
Step 2. Click “Site Survey” to discover the Wireless Internet Service Provider.
Step 3. Select the WISP’s AP, and the click “Select”.
-39-
Page 47

User Manual of WNAP-7350
Figure 5-3-22
Step 4. Enter the Passphrase, and then click “Add” to add this setting to the profile.
Figure 5-3-23
Step 5. The profile should be listed in the Profile List as the figure shown as below.
-40-
Page 48

User Manual of WNAP-7350
Figure 5-3-24
Step 6. Go to “Advanced-> Network Settings-> LAN” to enable DHCP Server.
Figure 5-3-25
Step 7. Go to “Advanced-> Network Settings-> WAN” to configure the WAN Connection.
Figure 5-3-26
-41-
Page 49

User Manual of WNAP-7350
Step 8. Configure the wired client’s TCP/IP setting to “Obtain an IP address automatically”.
Figure 5-3-27
After got the IP assigned by the WNAP-7350, ping the DNS server to check whether internet connection is
reachable.
5.3.3.4. Client Bridge (Slave AP Bridge)
In the Client Bridge Mode, the WNAP-7350 function likes a wireless adapter. Connected to an Access Point
wirelessly and surf internet whenever you want. Using Site Survey to scan all the Access Point within the range
and configure its SSID and Security Password to associate with it.
1. Connect the LAN port of WNAP-7350 to the POE port of the PoE Injector with an Ethernet cable.
2. Connect the PC to the LAN port of the PoE Injector with an Ethernet cable.
3. Plug one end of the power cord into the PoE Injector, and the other end in electrical socket.
4. Go to “Advanced-> Operation Mode” to configure it to Client Bridge Mode.
-42-
Page 50

User Manual of WNAP-7350
Figure 5-3-28
To configure the Wireless Settings of Client Bridge Mode, please refer to the section 5.6 Wireless Settings
5.3.4 Advanced – System Log
Choose menu “Advanced-> System Log” to view the logs of the Wireless AP.
Click “Refresh” to update the system log.
Click “Clear” to erase the current system log.
.
Figure 5-3-29
5.3.5 Advanced – Tools
The Tools included Ping, Traceroute, and Throughput can help user diagnostic the network connection.
-43-
Page 51
User Manual of WNAP-7350
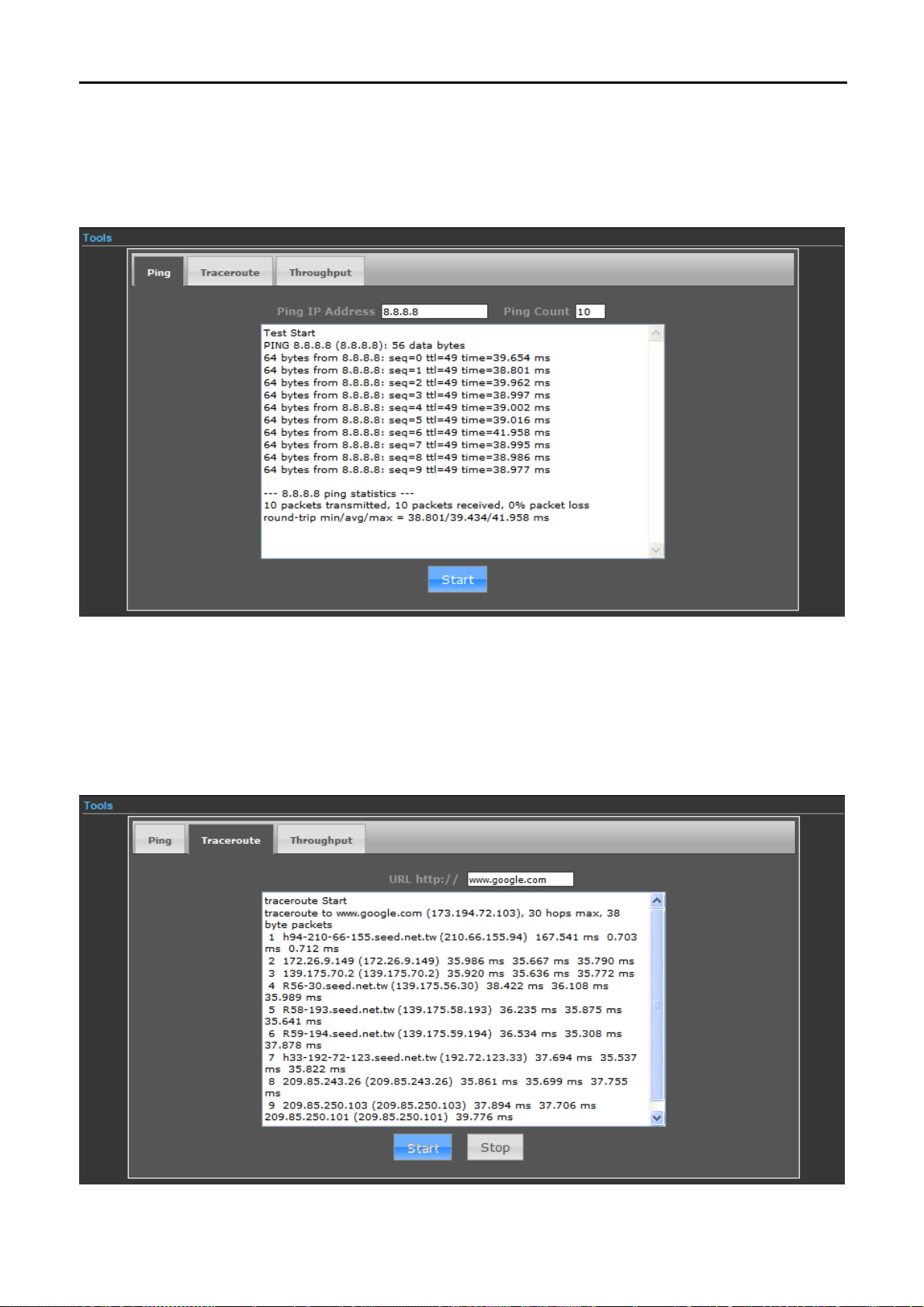
5.3.5.1. Ping
Ping is a network tool used to test whether a particular host is reachable across an IP network.
Enter the IP, Ping Count, and click “Start” to diagnostic your internet connection.
Figure 5-3-30
5.3.5.2. Traceroute
Traceroute is a computer network diagnostic tool for displaying the route (path) and measuring transit delays of
packets across an Internet Protocol (IP) network. It can help identify connection problems.
Enter the IP
stname, and click “Start” to diagnostic your internet connection.
or Ho
Figure 5-3-31
-44-
Page 52

5.3.5.3. Throughput
User Manual of WNAP-7350
Click “VISIT THE SITE TO TEST SPEED” button to go http://www.speedtest.net/
speed.
Figure 5-3-32
5.4 Firewall Settings
to test the internet connection
5.4.1 MAC/IP/Port Filtering
-45-
Page 53
User Manual of WNAP-7350
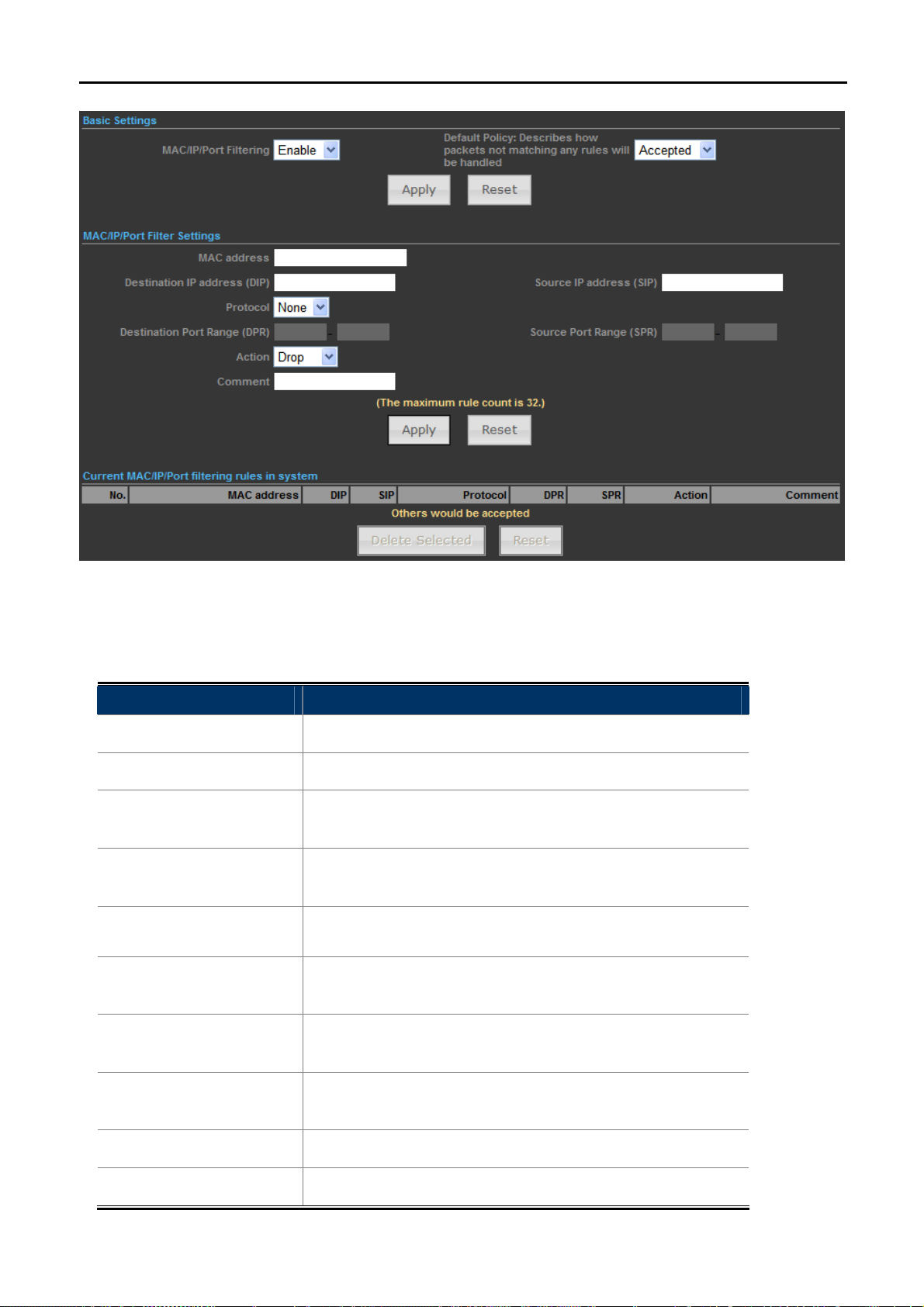
The page includes the following fields:
Object Description
MAC/IP/Port Filtering
Default Policy
Select Enable to enable the MAC/IP/Port Filtering function.
Select a policy for filtering rule.
Fill in the MAC address of source NIC, to restrict data
MAC Address
transmission.
Destination IP address
(DIP)
Source IP address
Fill in the IP address of destination, to restrict data
transmission.
Fill in the IP address of source, to restrict data transmission.
(SIP)
Select the protocol that you want to restrict. There are four
Protocol
options: None, TCP, UDP and ICMP.
Figure 5-4-1
Destination Port Range
Source Port Range
Action
Comment
Fill in the start-port and end-port number of destination, to
restrict data transmission.
Fill in the start-port and end-port number of source, to restrict
data transmission.
Select Accept or Drop to specify the action of filtering policies.
Make a comment for the filtering policy.
-46-
Page 54
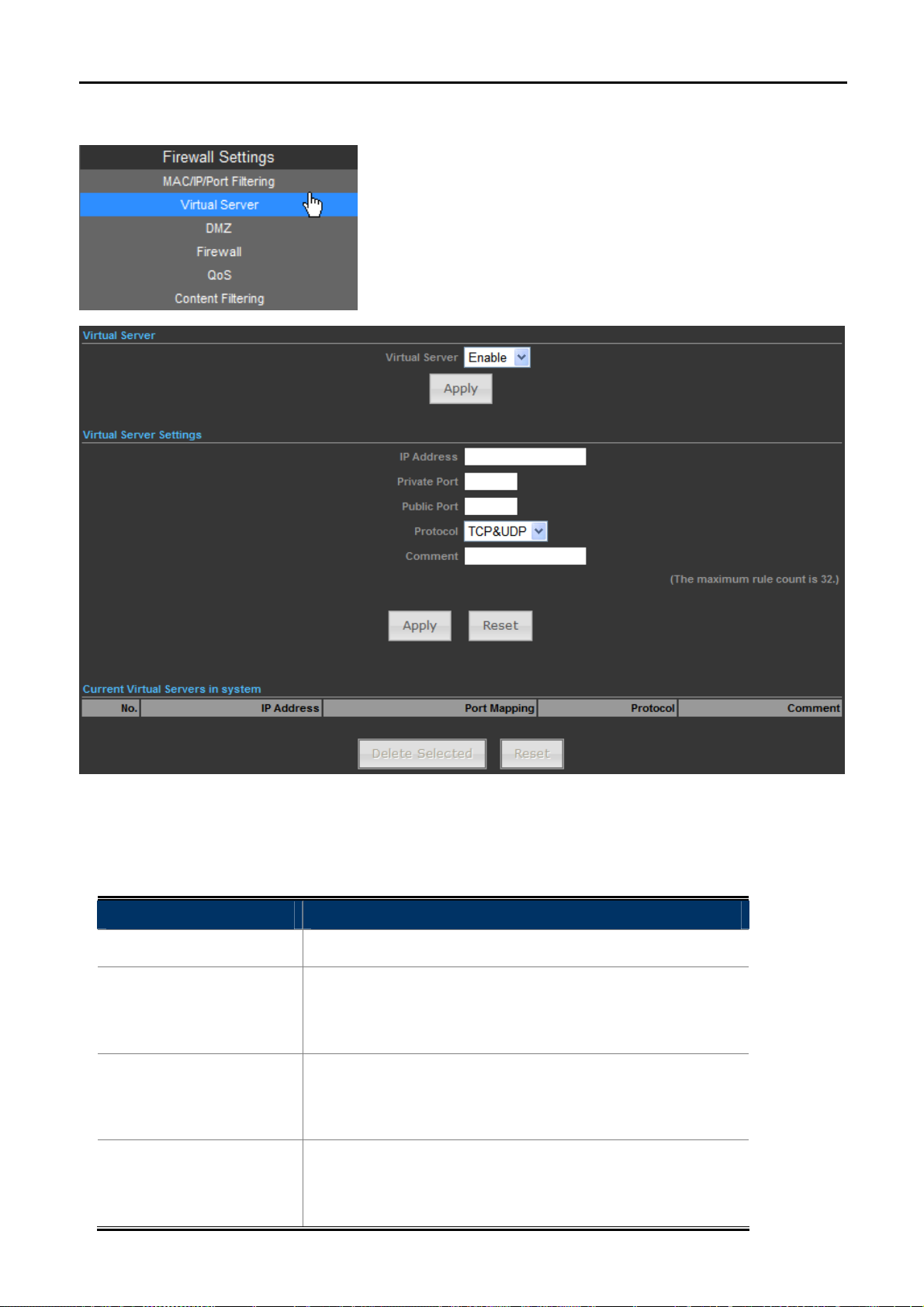
5.4.2 Virtual Server
User Manual of WNAP-7350
The page includes the following fields:
Object Description
Virtual Server
Select Enable to enable the Virtual Server function.
To forward data packets coming from WAN to a specific IP
IP address
address that hosted in local network behind the NAT firewall, fill
in the IP address.
To forward data packets coming from WAN to a specific IP
Private Port
address that hosted in local network behind the NAT firewall, fill
in the private port.
To forward data packets coming from WAN to a specific IP
Public Port
address that hosted in local network behind the NAT firewall, fill
in the public port.
Figure 5-4-2
-47-
Page 55

User Manual of WNAP-7350
Protocol
Comment
5.4.3 DMZ
The protocol used for this application, either of TCP, UDP, or
TCP&UDP (all protocols are supported by the Device.).
Make a comment to help identify the setting.
The page includes the following fields:
Object Description
DMZ Settings
Select Enable to enable the DMZ function.
To support DMZ in your firewall design, fill in the IP address of
DMZ IP Address
DMZ host that can be access from the WAN interface.
5.4.4 Firewall
Figure 5-4-3
-48-
Page 56

Figure 5-4-4
User Manual of WNAP-7350
The page includes the following fields:
Object Description
Remote Management
Select Deny or Allow for remote management function.
(via WAN)
Remote Management
Configure the port for remote management.
Port
Ping from WAN Filter
SPI Firewall
Select Deny or Allow for Ping permit from WAN.
Select Disable or Enable for SPI firewall function.
Enable it to let the LAN devices connect to the internet.
All computers must be assigned with a public IP address to get
connected to the Internet without NAT. However, Internet Service
Network Address
Providers only provide very few IP addresses to every user.
Translation
Therefore it is necessary to use NAT to share a single public IP
address to multiple computers on local network, so everyone can get
connected to the Internet.
PPPoE Passthrough
Enable it to allow Multiple PPP connections on remote hosts.
5.4.5 QoS
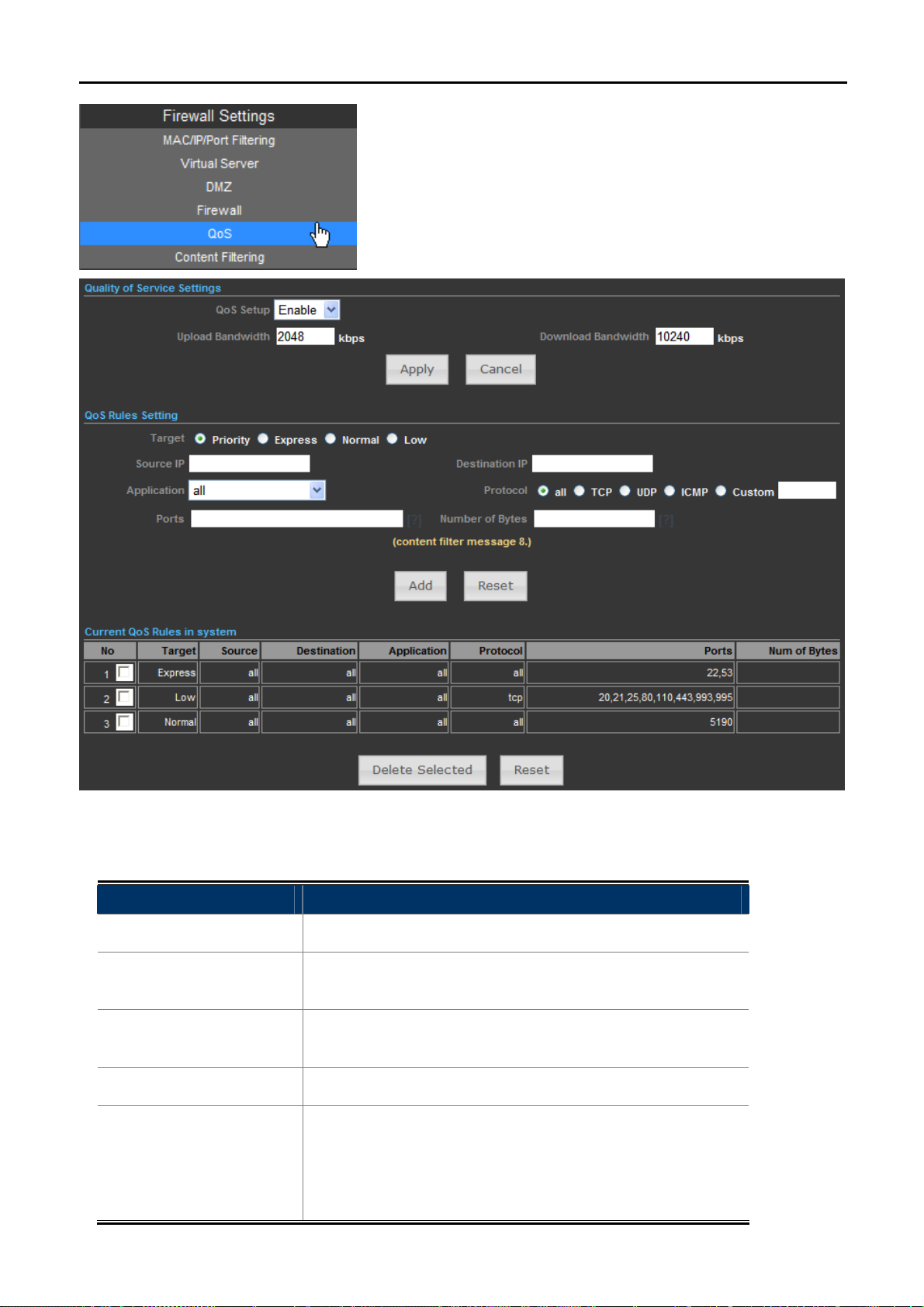
Quality of Service provides an efficient way for clients on the network to share the bandwidth with a promised
quality of Internet service. Without QoS, all computers and devices on the network will compete with each other
to get the bandwidth, and some applications which require guaranteed bandwidth (like video streaming and
network telephone) will be affected. With this function, you can limit the maximum bandwidth or give a
guaranteed bandwidth for a specific computer, to avoid such unpleasing result from happening.
-49-
Page 57
User Manual of WNAP-7350
The page includes the following fields:
Object Description
QoS Setup
Select Enable to enable the QoS function.
Set the limit of total upload bandwidth in kbits. To disable
Upload Bandwidth
upload bandwidth limitation, input ‘0’ here.
Set the limit of total download bandwidth in kbits. To disable
Download Bandwidth
download bandwidth limitation, input ‘0’ here.
Ta rget
Set the target of QoS rule.
Specify the local (source) IP address that will be affected by
this rule. Please input the starting IP address in the left field,
Source IP
and input the end IP address in the right field to define a range
of IP addresses, or just input the IP address in the left field to
Figure 5-4-5
-50-
Page 58

User Manual of WNAP-7350
define a single IP address.
Specify the remote (destination) IP address that will be affected
by this rule. Please input the starting IP address in the left field,
Destination IP
Application
Protocol
Ports
Number of Bytes
5.4.6 Content Filtering
and input the end IP address in the right field to define a range
of IP addresses, or just input the IP address in the left field to
define a single IP address.
Select the pre-defined application for this rule.
Please select the protocol type of this rule. If you don’t know
what protocol your application uses, please try ‘TCP’ first, and
switch to ‘UDP’ if this rule doesn’t seems to work.
Fill out the ports for this rule.
Fill out the max. Number of bytes for this rule.
There are two types (Webs URL Filter Settings and Web Host Filter Settings) of content filtering.
5.4.6.1. Webs URL Filter Settings
The Webs URL Filter option allows you to set up a list of Web sites you would like to deny through your network.
Please enter a URL for filtering.
-51-
Page 59

User Manual of WNAP-7350
Figure 5-4-6
5.4.6.2. Web Host Filter Settings
The Webs Host Filter option allows you to set up a list of keyword you would like to deny through your network.
Please enter a Host (keyword) for filtering.
Figure 5-4-7
5.5 Network Settings
5.5.1 WAN
There are 5 submenus under the Network menu: WAN, LAN, VLAN, Advanced Routing and IPv6. Click any of
them, and you will be able to configure the corresponding function.
WAN Connection Types:
-52-
Page 60

User Manual of WNAP-7350
5.5.1.1. Static (Fixed IP)
If your ISP provides a static or fixed IP Address, Subnet Mask, Gateway and DNS setting, select Static
(Fixed IP). The Static IP settings page will appear as the figure shown as below.
Figure 5-5-1
The page includes the following fields:
Object Description
WAN Connections
Select Static (Fixed IP) from the list.
IP Address
Enter the IP address in dotted-decimal notation provided by
your ISP.
Enter the subnet Mask in dotted-decimal notation provided by
Subnet Mask
your ISP, usually is 255.255.255.0
(Optional) Enter the gateway IP address in dotted-decimal
Default Gateway
notation provided by your ISP.
(Optional) Enter the DNS IP address in dotted-decimal notation
Primary DNS Server
provided by your ISP.
(Optional) Enter another DNS IP address in dotted-decimal
Secondary DNS Server
notation provided by your ISP.
5.5.1.2. Cable/Dynamic IP (DHCP)
If your ISP provides the DHCP service, please choose Cable/Dynamic IP (DHCP) type, and the AP Router will
automatically obtain IP parameters from your ISP. You can see the page shown as the below.
-53-
Page 61

User Manual of WNAP-7350
Figure 5-5-2
The page includes the following fields:
Object Description
WAN Connections
Host Name
Select Cable/Dynamic IP (DHCP) from the list.
This option specifies the Host Name of the AP Router.
(Optional) Enter the DNS IP address in dotted-decimal notation
Primary DNS Server
provided by your ISP.
(Optional) Enter another DNS IP address in dotted-decimal
Secondary DNS Server
notation provided by your ISP.
5.5.1.3. PPPoE (ADSL)
If local ISP provides a PPPoE connection, choose PPPoE (ADSL) and fill the necessary parameters below.
-54-
Page 62

The page includes the following fields:
Object Description
User Manual of WNAP-7350
Figure 5-5-3
WAN Connections
Host Name
User Name / Password
Verify Password
Operation Mode
Keep Alive Mode
MTU
Primary DNS Server
Secondary DNS Server
Select PPPoE (ADSL) from the list.
This option specifies the Host Name of the AP Router.
Enter the User Name and Password provided by your ISP.
These fields are case-sensitive.
Enter the same password entered above for the confirmation.
Keep Alive: Being constantly connected.
Set up the redial period after the disconnection.
The default setting is "60 seconds".
Please input the MTU value of your network connection here. If
you don’t know, please keep the default value.
(Optional) Enter the DNS IP address in dotted-decimal notation
provided by your ISP.
(Optional) Enter another DNS IP address in dotted-decimal
notation provided by your ISP.
5.5.1.4. IPSEC
If your ISP provides IPSEC connection, please select IPSEC. And enter the following parameters.
-55-
Page 63

User Manual of WNAP-7350
The page includes the following fields:
Figure 5-5-4
Figure 5-5-5
Object Description
WAN Connections
Select IPSEC from the list.
(Optional) Enter the DNS IP address in dotted-decimal notation provided
Primary DNS Server
by your ISP.
(Optional) Enter another DNS IP address in dotted-decimal notation
Secondary DNS Server
provided by your ISP.
-56-
Page 64

User Manual of WNAP-7350
Connection address
family
IPSec Operation Mode
IPSec Connection Type
For an IPSec connection, all host addresses must be of the same
Address Family (IPv4 and IPv6 use different Address Families).
Select the IPSec Operation Mode from the drop-down list.
This field allows you to set the connection type to any of the following:
Select Tunn el to specify a Host to Host, Host to Subnet (Road
Warrior), or Subnet to Subnet Tunnel. This is by far the most common
connection type.
Select Transport to specify a Host to Host Transport mode tunnel. This
connection type is much less common, and would generally only be used
if you are attempting to establish and IPSec connection to another host
which specifically requires this mode.
Select Passthrough to disable IPSec processing on packets associated
with the tunnel. We can't imagine a scenario where you would use this
connection type. I mean seriously, if you don't allow IPSec to process the
PFS|DH Group
packets then you don't really have a tunnel, right? Still, the underlying
protocol supports this mode, and so here we are.
Select Drop to cause the kernel to drop IPSec packets associated with
the tunnel.
Select Reject to cause the kernel to reject IPSec packets associated with
the tunnel.
Perfect Forward Secrecy (PFS)—PFS ensures that a given IPSec SA
key was not derived from any other secret, like some other keys. In other
words, if someone breaks a key, PFS ensures that the attacker is not
able to derive any other key. If PFS is not enabled, someone can
potentially break the IKE SA secret key, copy all the IPSec protected
data, and then use knowledge of the IKE SA secret in order to
compromise the IPSec SAs setup by this IKE SA. With PFS, breaking
IKE does not give an attacker immediate access to IPSec. The attacker
needs to break each IPSec SA individually.
Diffie-Hellman (DH) key exchange protocol allows two parties without any
initial shared secret to create one securely. The following Modular
Exponential (MODP) and Elliptic Curve (EC2N) Diffie-Hellman (also
known as "Oakley") Groups are supported:
Diffie-Hellman Group Name Reference
Group 1 768 bit MODP group RFC 2409
-57-
Page 65
IPSec Authentication
User Manual of WNAP-7350
Group 2 1024 bits MODP group RFC 2409
Group 3 EC2N group on GP(2^155) RFC 2409
Group 4 EC2N group on GP(2^185) RFC 2409
Group 5 1536 bits MODP group RFC 3526
The AP supports SHA1 & MD5 authentication algorithms.
The AP supports DES, 3DES, AES, Blowfish, Tw of is h, Camellia
Encryption methods.
DES - 56-bit DES-CBC encryption algorithm
3DES - 168-bit DES encryption algorithm
IPSec Encryption
SA connection Life
Time
IKE Key Tries
Local IP Address
Peer IP Address
Local Subnet
AES - 128, 192 and 256-bit key AES-CBC encryption algorithm
Blowfish - a symmetric block cipher that can be used as a drop-in
replacement for DES or IDEA. It takes a variable-length key, from 32 bits
to 448 bits.
Twofi sh - Twofish has a 128-bit block size, a key size ranging from 128 to
256 bits, and is optimized for 32-bit CPUs.
Camellia - 128, 192 and 256-bit key Camellia encryption algorithm
This value describes the timeframe in hours for which the IKE SA is valid
and when the next rekeying should take place.
The field is used to specify the retry times of IKE Key.
This field is used to configure the IP address of the Untangle server on
the network configured in the Local Network field.
This field should contain the public IP address of the host to which the
IPSec VPN will be connected.
This field is used to configure the local network that will be reachable
from hosts on the other side of the IPSec VPN.
Peer Subnet
Local Gateway
Peer Gateway
IPSec Tunnel Name
IPSec Secret Key
This field is used to configure the remote network that will be reachable
from hosts on the local side of the IPSec VPN.
This field is used to configure the Gateway of the Untangle server on the
network configured in the Local Network field.
This field should contain the public Gateway of the host to which the
IPSec VPN will be connected.
This field should contain a short name or description.
This field should contain the shared secret or PSK (pre-shared key) that
is used to authenticate the connection, and must be the same on both
sides of the tunnel for the connection to be successful. Because the PSK
is actually used as the encryption key for the session, using long strings
of a random nature will provide the highest level of security.
-58-
Page 66

User Manual of WNAP-7350
Lifetime settings determine when a new key is generated. Any time a key
lifetime is reached, the associated SA is also renegotiated. The process
of generating new keys at intervals is called dynamic rekeying or key
IPSec Key Life time
NAT Traversal
Perfect Forward
Secrets
IPSec Compression
IPSec Conn. Keep
Alive
IPSec Tunnel UP
regeneration. Lifetimes allow you to force the generation of a new key
after a specific interval. For example, if the communication takes 12
hours and you specify the key lifetime as 1 hour, 12 keys will be
generated (one every 1 hour) during the exchange.
NAT Traversal also known as UDP encapsulation allows traffic to get to
the specified destination when a device does not have a public address.
This is usually the case if your ISP is doing NAT, or the external interface
of your firewall is connected to a device that has NAT enabled.
Select the checkbox to enable PFS (Perfect Forward Secrets).
Select the checkbox to enable compression of content on the connection.
When the firewall is located behind a NAT device, it sends keep alive
packets to maintain the connection. You can also force it to send keep
alive packets for all NAT-T connections.
This field indicates the IPSec Tunnel is UP and running.
5.5.1.5. PPTP
If your ISP provides PPTP connection, please select PPTP. And enter the following parameters.
Figure 5-5-6
The page includes the following fields:
Object Description
WAN Connections
Select PPTP from the list.
-59-
Page 67

User Manual of WNAP-7350
Server IP
User Name / Password
Address Mode
IP Address
Subnet Mask
Operation Mode
Keep Alive Mode
Primary DNS Server
Enter the IP address of the PPTP server.
Enter the User Name and Password provided by your ISP.
These fields are case-sensitive.
Static IP/ Dynamic IP: Choose either as you are given by your
ISP and If you choose static IP and enter the domain name,
you should also enter the DNS assigned by your ISP. And click
the Save button.
Enter the User Name and Password provided by your ISP.
These fields are case-sensitive.
Enter the subnet Mask in dotted-decimal notation provided by
your ISP, usually is 255.255.255.0
Keep Alive: Being constantly connected.
Set up the redial period after the disconnection.
The default setting is "60 seconds".
(Optional) Enter the DNS IP address in dotted-decimal notation
provided by your ISP.
Secondary DNS Server
(Optional) Enter another DNS IP address in dotted-decimal
notation provided by your ISP.
5.5.1.6. L2TP
If your ISP provides L2TP connection, please select L2TP. And enter the following parameters.
The page includes the following fields:
Object Description
WAN Connections
Select L2TP from the list.
Figure 5-5-7
-60-
Page 68

User Manual of WNAP-7350
Server IP
User Name / Password
Address Mode
IP Address
Subnet Mask
Operation Mode
Keep Alive Mode
Primary DNS Server
Enter the IP address of the L2TP server.
Enter the User Name and Password provided by your ISP.
These fields are case-sensitive.
Static IP/ Dynamic IP: Choose either as you are given by your
ISP and If you choose static IP and enter the domain name,
you should also enter the DNS assigned by your ISP. And click
the Save button.
Enter the User Name and Password provided by your ISP.
These fields are case-sensitive.
Enter the subnet Mask in dotted-decimal notation provided by
your ISP, usually is 255.255.255.0
Keep Alive: Being constantly connected.
Set up the redial period after the disconnection.
The default setting is "60 seconds".
(Optional) Enter the DNS IP address in dotted-decimal notation
provided by your ISP.
Secondary DNS Server
5.5.2 LAN
(Optional) Enter another DNS IP address in dotted-decimal
notation provided by your ISP.
Figure 5-5-8
The page includes the following fields:
Object Description
MAC Address
Display the LAN port MAC address of the Wireless AP.
The Wireless AP’s LAN IP.
IP Address
The default is 192.168.1.1. You can change it according to your need.
-61-
Page 69

User Manual of WNAP-7350
Subnet Mask
Enter the subnet mask of the LAN IP.
5.5.2.1. DHCP Server
The page includes the following fields:
Object Description
DHCP Server
Local Domain Name
(Optional)
Select DHCP Server to enable DHCP server feature.
(Optional) Input the domain name of your network.
Figure 5-5-9
Start IP Address
End IP Address
Enter the starting IP address for the DHCP server’s IP assignment.
Enter the ending IP address for the DHCP server’s IP assignment.
The length of time for the IP address lease. Configuring a proper
Lease Time
lease time improves the efficiency for the DHCP server to reclaim
disused IP addresses.
To benefit from the DHCP server feature, you must set all LAN PCs to DHCP clients by selecting the “Obtain an
IP Address Automatically” radio buttons thereon.
5.5.2.2. DHCP Relay
Figure 5-5-10
The page includes the following fields:
Object Description
DHCP Server
DHCP Relay
Select DHCP Relay to enable DHCP relay feature.
A DHCP relay agent is any host that forwards DHCP packets
-62-
Page 70

5.5.3 VLAN
User Manual of WNAP-7350
between clients and servers.
Configure the IP address of DHCP Relay host.
The page includes the following fields:
Object Description
VLAN Setup
Management VLAN ID
Enable Management
Check this box to enable the VLAN function.
Configure a specified VLAN to be the management VLAN.
Check this box to enable the Management VLAN function.
VLAN ID
The ID of a VLAN. Only in the same VLAN can a wireless PC and a
wired PC communicate with each other. The value can be between 1
VLAN ID
and 4095. If the VLAN function is enabled, when AP forwards
packets, the packets out from the LAN port will be added with an
Figure 5-5-11
-63-
Page 71

5.5.4 Advanced Routing
User Manual of WNAP-7350
IEEE 802.1Q VLAN Tag, whose VLAN ID is just the ID of the VLAN
where the sender belongs.
The page includes the following fields:
Object Description
Destination
The IP address of packets that can be routed.
Defines the type of destination. ( Host: Signal IP address / Net: Portion
Type
of Network )
Gateway
Interface
Defines the packets destination next hop
Select interface to which a static routing subnet is to be applied
Figure 5-5-12
-64-
Page 72

User Manual of WNAP-7350
Comment
Help identify the routing
Enable or disable the RIP (Routing Information Protocol) for the
Dynamic Routing
WAN or LAN interface.
Protocol
It supports RIP v1 and v2.
5.5.5 IPv6
Use this section to configure your IPv6 Connection type. If you are unsure of your connection method, please
contact your Internet Service Provider.
The page includes the following fields:
Object Description
Choose the mode to be used by the AP/Router to the IPv6 Internet.
There are 7 connection modes available:
IPv6 Connection Mode
Static, SLAAC, DHCPv6, 6to4 Tunnel, 6in4 Tunnel, PPPoE, and
Pass Through.
DNS Address Server
Enter the IPv6 Primary DNS & IPv6 Secondary DNS to this section.
Setting
Prefix Delegation
Enter the IPv6 Prefix Delegation information provided by your
Figure 5-5-13
-65-
Page 73

User Manual of WNAP-7350
Setting
LAN IPv6 Address
Setting
LAN Address Auto
configuration
Internet Service Provider (ISP).
Use this section to configure the internal network settings of your
AP/Router. If you change the LAN IPv6 Address here, you may need
to adjust your PC network settings to access the network again.
IPv6 offers two types of autoconfiguration: Stateful (DHCPv6) &
Stateless (RADVD).
Stateful (DHCPv6):
This type of configuration is suitable for small organizations and
individuals. It allows each host to determine its address from the
contents of received user advertisements. It makes use of the IEEE
EUI-64 standard to define the network ID portion of the address.
Stateless(RADVD):
With Stateless Autoconfiguration, a host gains an address via an
interface automatically "leasing" an address and does not require the
establishment of an server to delve out address space.
5.6 Wireless Settings
You could configure the minimum number of Wireless settings for communication, such as Network Name (SSID)
and Channel. The Access Point can be set simply with only the minimum setting items.
5.6.1 Basic
-66-
Page 74

5.6.1.1. Wireless Mode – Access Point
User Manual of WNAP-7350
The page includes the following fields:
Object Description
Click to select Wireless Mode from pull down menu.
There are 4 options available:
Access Point:
This mode allows wireless clients or Stations(STA) to access
WDS Access Point:
This mode enables the wireless interconnection of Access Point in an
Wireless Mode
IEEE802.11 network .and accept wireless clients at the same time.
WDS Repeater:
Set to this mode to enable the wireless access point repeat the signal
of root access point using WDS.
WDS Client:
Figure 5-6-1
Multiple SSID
Country Code
Frequency (Channel)
Set to this mode to enable wireless client using WDS to connect to
the WDS Access Point.
There is one more SSID available. Select the checkbox to enable it,
enter the descriptive names that you want to use.
Set your country code by clicking the “Set Country Code”.
Set the channel you would like to use. The channel range will be
changed by selecting different domain.
-67-
Page 75

User Manual of WNAP-7350
Site Survey
Network Mode
Extension Channel
Distance
ACK/CTS Timeout
Click “Site Survey” button to observe the signal of remote sites.
Select the operating channel width to WiFi 11na (mixed), HT20 or
HT40MHz.
An extension channel is a secondary channel used to bond with the
primary channel to increase this range to 40MHz. Bonded channels
allow for greater bandwidth on the local network.
To decrease the chances of data retransmission at long distance, the
IEEE 802.11a/n Wireless Outdoor CPE can automatically adjust
proper ACK timeout value by specifying distance of the two nodes.
ACK/CTS Timeout settings are for long distance links. It is important
to tweak settings to achieve the optimal result based on requirement.
The device’s default settings should be sufficient for most
applications.
The value is auto determined by distance between the radios, data
rate of average environment.
It is the wireless network name. The SSID can be 32 bytes long.
Network Name (SSID)
WPS Choice
Encryption Settings
WPA Algorithms
Key Renewal Interval
(Seconds)
Pre-Shared Key
User can use the default SSID or change it.
The default SSID is WNAP-7350.
Enable it to use WPS associating with AP or Client device.
Select the encryption type that you would like to use.
Select the WPA Algorithms that you would like to use.
The key renewal time is the period of time that the AP uses the same
key before a new one is generated.
Data encryption and key are required for wireless authentication.
-68-
Page 76

5.6.1.2. Wireless Mode – WDS Access Point
User Manual of WNAP-7350
The page includes the following fields:
Object Description
Click to select Wireless Mode from pull down menu.
There are 4 options available:
Access Point:
This mode allows wireless clients or Stations(STA) to access
WDS Access Point:
This mode enables the wireless interconnection of Access Point in an
Wireless Mode
IEEE802.11 network .and accept wireless clients at the same time.
WDS Repeater:
Set to this mode to enable the wireless access point repeat the signal
of root access point using WDS.
Figure 5-6-2
Country Code
Frequency (Channel)
Site Survey
WDS Client:
Set to this mode to enable wireless client using WDS to connect to
the WDS Access Point.
Set your country code by clicking the “Set Country Code”.
Set the channel you would like to use. The channel range will be
changed by selecting different domain.
Click “Site Survey” button to observe the signal of remote sites.
-69-
Page 77

User Manual of WNAP-7350
Network Mode
Extension Channel
Distance
ACK/CTS Timeout
Network Name (SSID)
Select the operating channel width to WiFi 11na (mixed), HT20 or
HT40MHz.
An extension channel is a secondary channel used to bond with the
primary channel to increase this range to 40MHz. Bonded channels
allow for greater bandwidth on the local network.
To decrease the chances of data retransmission at long distance, the
IEEE 802.11a/n Wireless Outdoor CPE can automatically adjust
proper ACK timeout value by specifying distance of the two nodes.
ACK/CTS Timeout settings are for long distance links. It is important
to tweak settings to achieve the optimal result based on requirement.
The device’s default settings should be sufficient for most
applications.
The value is auto determined by distance between the radios, data
rate of average environment.
It is the wireless network name. The SSID can be 32 bytes long.
User can use the default SSID or change it.
Encryption Settings
WPA Algorithms
Key Renewal Interval
(Seconds)
Pre-Shared Key
The default SSID is WNAP-7350.
Select the encryption type that you would like to use.
Select the WPA Algorithms that you would like to use.
The key renewal time is the period of time that the AP uses the same
key before a new one is generated.
Data encryption and key are required for wireless authentication.
-70-
Page 78

5.6.1.3. Wireless Mode – WDS Repeater
User Manual of WNAP-7350
The page includes the following fields:
Object Description
Click to select Wireless Mode from pull down menu.
There are 4 options available:
Access Point:
This mode allows wireless clients or Stations(STA) to access
WDS Access Point:
This mode enables the wireless interconnection of Access Point in an
Wireless Mode
IEEE802.11 network .and accept wireless clients at the same time.
WDS Repeater:
Set to this mode to enable the wireless access point repeat the signal
of root access point using WDS.
Figure 5-6-3
Root AP MAC Address
(optional)
Country Code
WDS Client:
Set to this mode to enable wireless client using WDS to connect to
the WDS Access Point.
Fill out the Root AP’s MAC Address enable it to connect to the Root
AP using WDS.
Set your country code by clicking the “Set Country Code”.
-71-
Page 79

User Manual of WNAP-7350
Frequency (Channel)
Site Survey
Network Mode
Extension Channel
Distance
ACK/CTS Timeout
Set the channel you would like to use. The channel range will be
changed by selecting different domain.
Click “Site Survey” button to observe the signal of remote sites.
Select the operating channel width to WiFi 11na (mixed), HT20 or
HT40MHz.
An extension channel is a secondary channel used to bond with the
primary channel to increase this range to 40MHz. Bonded channels
allow for greater bandwidth on the local network.
To decrease the chances of data retransmission at long distance, the
IEEE 802.11a/n Wireless Outdoor CPE can automatically adjust
proper ACK timeout value by specifying distance of the two nodes.
ACK/CTS Timeout settings are for long distance links. It is important
to tweak settings to achieve the optimal result based on requirement.
The device’s default settings should be sufficient for most
applications.
The value is auto determined by distance between the radios, data
Network Name (SSID)
Root AP SSID
Encryption Settings
WPA Algorithms
Key Renewal Interval
(Seconds)
Pre-Shared Key
rate of average environment.
It is the wireless network name of itself. The SSID can be 32 bytes
long.
User can use the default SSID or change it.
The default SSID is WNAP-7350.
It is the wireless network name of Root AP.
The SSID must be the same with Root AP so that the connection can
be established successfully.
Select the encryption type that you would like to use.
Select the WPA Algorithms that you would like to use.
The key renewal time is the period of time that the AP uses the same
key before a new one is generated.
Data encryption and key are required for wireless authentication.
-72-
Page 80
5.6.1.4. Wireless Mode – WDS Client
User Manual of WNAP-7350
The page includes the following fields:
Object Description
Click to select Wireless Mode from pull down menu.
There are 4 options available:
Access Point:
This mode allows wireless clients or Stations(STA) to access
WDS Access Point:
This mode enables the wireless interconnection of Access Point in an
Wireless Mode
IEEE802.11 network .and accept wireless clients at the same time.
WDS Repeater:
Set to this mode to enable the wireless access point repeat the signal
of root access point using WDS.
Figure 5-6-4
Root AP MAC Address
(optional)
Country Code
Frequency (Channel)
WDS Client:
Set to this mode to enable wireless client using WDS to connect to
the WDS Access Point.
Fill out the Root AP’s MAC Address enable it to connect to the Root
AP using WDS.
Set your country code by clicking the “Set Country Code”.
Set the channel you would like to use. The channel range will be
changed by selecting different domain.
-73-
Page 81

User Manual of WNAP-7350
Network Mode
Extension Channel
Distance
ACK/CTS Timeout
Root AP SSID
Select the operating channel width to WiFi 11na (mixed), HT20 or
HT40MHz.
An extension channel is a secondary channel used to bond with the
primary channel to increase this range to 40MHz. Bonded channels
allow for greater bandwidth on the local network.
To decrease the chances of data retransmission at long distance, the
IEEE 802.11a/n Wireless Outdoor CPE can automatically adjust
proper ACK timeout value by specifying distance of the two nodes.
ACK/CTS Timeout settings are for long distance links. It is important
to tweak settings to achieve the optimal result based on requirement.
The device’s default settings should be sufficient for most
applications.
The value is auto determined by distance between the radios, data
rate of average environment.
It is the wireless network name of Root AP.
The SSID must be the same with Root AP so that the connection can
be established successfully.
Encryption Settings
WPA Algorithms
Key Renewal Interval
(Seconds)
Pre-Shared Key
Click “Scan” to site survey the Root AP.
Select the encryption type that you would like to use.
Select the WPA Algorithms that you would like to use.
The key renewal time is the period of time that the AP uses the same
key before a new one is generated.
Data encryption and key are required for wireless authentication.
-74-
Page 82

User Manual of WNAP-7350
5.6.2 Profile Settings
In Client Bridge and Client Router operation modes, please go to “Advanced-> Wireless Settings-> Profile
Settings” to configure the wireless client function to connect with the wireless AP.
The page includes the following fields:
Object Description
Fill out the Root AP’s MAC Address enable it to connect to the Root
Profile Name
AP using WDS.
Set the Network Type that you would like to use.
Infrastructure:
Infrastructure networks consist of the networked devices and the
wireless access point or wireless router. Each device must connect to
Network Type
the access point before having access to other computers on the
network.
Ad-hoc:
In an ad hoc network, each device's network adapter directly
communicates with other devices.
Figure 5-6-5
SSID
It is the wireless network name of Root AP.
-75-
Page 83

User Manual of WNAP-7350
BSSID (optional)
Encryption Settings
Distance
ACK/CTS Timeout
RTS/CTS
Indicate the Basic Service Set ID of the associated AP
Select the encryption type that you would like to use.
To decrease the chances of data retransmission at long distance, the
IEEE 802.11a/n Wireless Outdoor CPE can automatically adjust
proper ACK timeout value by specifying distance of the two nodes.
ACK/CTS Timeout settings are for long distance links. It is important
to tweak settings to achieve the optimal result based on requirement.
The device’s default settings should be sufficient for most
applications.
The value is auto determined by distance between the radios, data
rate of average environment.
RTS/CTS (Request to Send / Clear to Send) is the optional
mechanism used by the 802.11 wireless networking protocol to
reduce frame collisions introduced by the hidden node problem.
You can enter a setting ranging from 0 to 2347 bytes.
The fragmentation threshold determines the size at which packets
Fragmentation
Threshold
WDS Client
are fragmented (sent as several pieces instead of as one block). Use
a low setting in areas where communication is poor or where there is
a great deal of radio interference. This function will help you to
improve the network performance.
Check it to enable WDS Client function.
-76-
Page 84
5.6.3 Advanced
User Manual of WNAP-7350
The page includes the following fields:
Object Description
Wireless On/Off
AP MAC Address
Click this button to switch the Wireless Radio On or Off.
Display the AP MAC Address of wireless interface.
In a packet-based communications network, packet aggregation is
the process of joining multiple packets together into a single
Packet Aggregate
transmission unit, in order to reduce the overhead associated with
each transmission.
WMM function can guarantee the packets with high-priority
WMM
messages being transmitted preferentially. It is strongly
recommended enabled.
The beacons are the packets sent by the Device to synchronize a
Figure 5-6-6
Beacon Interval
wireless network. Beacon Interval value determines the time
interval of the beacons. You can specify a value between 20-1000
-77-
Page 85
User Manual of WNAP-7350
milliseconds. The default value is 100.
This value determines the interval of the Delivery Traffic Indication
DTIM
RTS/CTS
Fragmentation Threshold
Station Control (SSID I)
Station Control (SSID II)
Wireless Isolate
Message (DTIM). You can specify the value between 1-255
Beacon Intervals. The default value is 1, which indicates the DTIM
Interval is the same as Beacon Interval.
The RTS/CTS mechanism is widely used in wireless networks in
order to avoid packet collisions and, thus, achieve high
throughput.
This value is the maximum size determining whether packets will
be fragmented. Setting the Fragmentation Threshold too low may
result in poor network performance since excessive packets. 2346
is the default setting and is recommended.
Fill out the Station Control value of SSID I.
Fill out the Station Control value of SSID II.
Isolate all connected wireless stations so that wireless stations
cannot access each other through WLAN. This function will be
disabled if WDS/Bridge is enabled.
Set the AP to the external LED lights and wireless signal strength
Thresholds, dbm
received correspondence, when the AP receives the wireless
signal, according to the wireless signal strength, the
corresponding LED will be lit.
5.6.4 Access Control
Choose menu “Advanced-> Wireless Settings-> Access Control” to configure the filtering rules for the clients
would like to associate with Wireless AP.
-78-
Page 86

The page includes the following fields:
User Manual of WNAP-7350
Figure 5-6-7
Object Description
Select the SSID which you would like to configure access
SSID
control.
Allow Listed: allow the packets not specified by any access
control policy to pass through the AP Router.
Access Control Mode
Deny Listed: deny the packets not specified by any access
control policy to pass through the AP Router.
MAC Address
Current Access
Configure the MAC Address to apply the access control.
Display the current Access Control List.
Control List
5.7 Logout
Select “Logout”, and then click “Yes” to logout the system.
Figure 5-7-1
Figure 5-7-2
-79-
Page 87

User Manual of WNAP-7350
Appendix A: FAQ
A.1 What and how to find my PC’s IP and MAC address?
IP address is the identifier for a computer or device on a TCP/IP network. Networks using the TCP/IP protocol
route messages based on the IP address of the destination. The format of an IP address is a 32-bit numeric
address written as four numbers separated by periods. Each number can be zero to 255. For example,
191.168.1.254 could be an IP address
The MAC (Media Access Control) address is your computer's unique hardware number. (On an Ethernet LAN,
it's the same as your Ethernet address.) When you're connected to the Internet from your computer (or host as
the Internet protocol thinks of it), a correspondence table relates your IP address to your computer's physical
(MAC) address on the LAN.
To find your PC’s IP and MAC address,
(1) Open the Command program in the Microsoft Windows.
(2) Type in “ipconfig /all”, then press the Enter button.
(3) Your PC’s IP address is the one entitled IP Address and your PC’s MAC address is the one entitled
Physical Address.
A.2 What is Wireless LAN?
A wireless LAN (WLAN) is a network that allows access to Internet without the need for any wired connections to
the user’s machine.
A.3 What are ISM bands?
ISM stands for Industrial, Scientific and Medical; radio frequency bands that the Federal Communications
Commission (FCC) authorized for wireless LANs. The ISM bands are located at 915 +/-13 MHz, 2450 +/-50 MHz
and 5800 +/-75 MHz.
A.4 How does wireless networking work?
The 802.11 standard define two modes: infrastructure mode and ad hoc mode. In infrastructure mode, the
wireless network consists of at least one access point connected to the wired network infrastructure and a set of
wireless end stations. This configuration is called a Basic Service Set (BSS). An Extended Service Set (ESS) is
a set of two or more BSSs forming a single sub-network. Since most corporate WLANs require access to the
wired LAN for services (file servers, printers, Internet links) they will operate in infrastructure mode.
-80-
Page 88
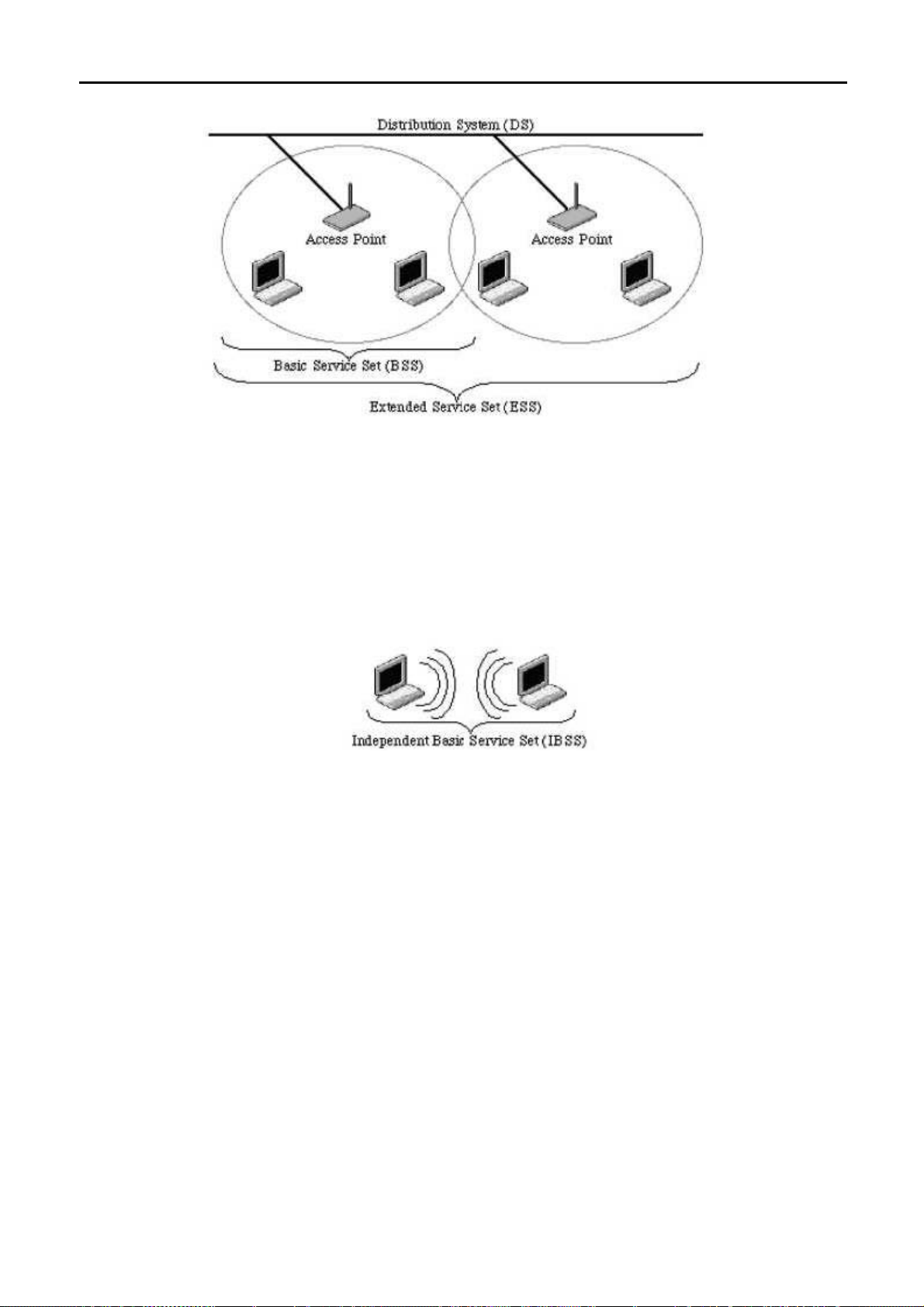
User Manual of WNAP-7350
Example 1: wireless Infrastructure Mode
Ad hoc mode (also called peer-to-peer mode or an Independent Basic Service Set, or IBSS) is simply a set of
802.11 wireless stations that communicate directly with one another without using an access point or any
connection to a wired network. This mode is useful for quickly and easily setting up a wireless network anywhere
that a wireless infrastructure does not exist or is not required for services, such as a hotel room, convention
center, or airport, or where access to the wired network is barred (such as for consultants at a client site).
Example 2: wireless Ad Hoc Mode
A.5 What is BSSID?
A six-byte address is that distinguish a particular a particular access point from others. Also know as just SSID.
Serve as a network ID or name.
A.6 What is ESSID?
The Extended Service Set ID (ESSID) is the name of the network you want to access. It is used to identify
different wireless networks.
A.7 What are potential factors that may causes interference?
Factors of interference:
Obstacles: walls, ceilings, furniture… etc.
Building Materials: metal door, aluminum studs.
Electrical devices: microwaves, monitors and electrical motors.
-81-
Page 89

User Manual of WNAP-7350
Solutions to overcome the interferences:
Minimizing the number of walls and ceilings.
Position the WLAN antenna for best reception.
Keep WLAN devices away from other electrical devices, eg: microwaves, monitors, electric
motors…etc.
Add additional WLAN Access Points if necessary.
A.8 What are the Open System and Shared Key authentications?
IEEE 802.11 supports two subtypes of network authentication services: open system and shared key. Under
open system authentication, any wireless station can request authentication. The station that needs to
authenticate with another wireless station sends an authentication management frame that contains the identity
of the sending station. The receiving station then returns a frame that indicates whether it recognizes the
sending station. Under shared key authentication, each wireless station is assumed to have received a secret
shared key over a secure channel that is independent from the 802.11 wireless network communications
channel.
A.9 What is WEP?
An option of IEEE 802.11 function is that offers frame transmission privacy similar to a wired network. The Wired
Equivalent Privacy generates secret shared encryption keys that both source and destination stations can use to
alert frame bits to avoid disclosure to eavesdroppers.
WEP relies on a secret key that is shared between a mobile station (e.g. a laptop with a wireless Ethernet card)
and an access point (i.e. a base station). The secret key is used to encrypt packets before they are transmitted,
and an integrity check is used to ensure that packets are not modified in transit.
A.10 What is Fragment Threshold?
The proposed protocol uses the frame fragmentation mechanism defined in IEEE 802.11 to achieve parallel
transmissions. A large data frame is fragmented into several fragments each of size equal to fragment threshold.
By tuning the fragment threshold value, we can get varying fragment sizes. The determination of an efficient
fragment threshold is an important issue in this scheme. If the fragment threshold is small, the overlap part of the
master and parallel transmissions is large. This means the spatial reuse ratio of parallel transmissions is high. In
contrast, with a large fragment threshold, the overlap is small and the spatial reuse ratio is low. However high
fragment threshold leads to low fragment overhead. Hence there is a trade-off between spatial re-use and
fragment overhead.
Fragment threshold is the maximum packet size used for fragmentation. Packets larger than the size
programmed in this field will be fragmented.
If you find that your corrupted packets or asymmetric packet reception (all send packets, for example). You may
-82-
Page 90

User Manual of WNAP-7350
want to try lowering your fragmentation threshold. This will cause packets to be broken into smaller fragments.
These small fragments, if corrupted, can be resent faster than a larger fragment. Fragmentation increases
overhead, so you'll want to keep this value as close to the maximum value as possible.
A.11 What is RTS (Request to Send) Threshold?
The RTS threshold is the packet size at which packet transmission is governed by the RTS/CTS transaction. The
IEEE 802.11-1997 standard allows for short packets to be transmitted without RTS/ CTS transactions. Each
station can have a different RTS threshold. RTS/CTS is used when the data packet size exceeds the defined
RTS threshold. With the CSMA/CA transmission mechanism, the transmitting station sends out an RTS packet
to the receiving station, and waits for the receiving station to send back a CTS (Clear to Send) packet before
sending the actual packet data.
This setting is useful for networks with many clients. With many clients, and a high network load, there will be
many more collisions. By lowering the RTS threshold, there may be fewer collisions, and performance should
improve. Basically, with a faster RTS threshold, the system can recover from problems faster. RTS packets
consume valuable bandwidth, however, so setting this value too low will limit performance.
A.12 What is Beacon Interval?
In addition to data frames that carry information from higher layers, 802.11 include management and control
frames that support data transfer. The beacon frame, which is a type of management frame, provides the
"heartbeat" of a wireless LAN, enabling stations to establish and maintain communications in an orderly fashion.
Beacon Interval represents the amount of time between beacon transmissions. Before a station enters power
save mode, the station needs the beacon interval to know when to wake up to receive the beacon (and learn
whether there are buffered frames at the access point).
A.13 What is Preamble Type?
There are two preamble types defined in IEEE 802.11 specification. A long preamble basically gives the decoder
more time to process the preamble. All 802.11 devices support a long preamble. The short preamble is designed
to improve efficiency (for example, for VoIP systems). The difference between the two is in the Synchronization
field. The long preamble is 128 bits, and the short is 56 bits.
A.14 What is SSID Broadcast?
Broadcast of SSID is done in access points by the beacon. This announces your access point (including various
bits of information about it) to the wireless world around it. By disabling that feature, the SSID configured in the
client must match the SSID of the access point.
Some wireless devices don't work properly if SSID isn't broadcast (for example the D-link DWL-120 USB
802.11b adapter). Generally if your client hardware supports operation with SSID disabled, it's not a bad idea to
-83-
Page 91

User Manual of WNAP-7350
run that way to enhance network security. However it's no replacement for WEP, MAC filtering or other
protections.
A.15 What is Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA)?
Wi-Fi’s original security mechanism, Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP), has been viewed as insufficient for
securing confidential business communications. A longer-term solution, the IEEE 802.11i standard, is under
development. However, since the IEEE 802.11i standard is not expected to be published until the end of 2003,
several members of the WI-Fi Alliance teamed up with members of the IEEE 802.11i task group to develop a
significant near-term enhancement to Wi-Fi security. Together, this team developed Wi-Fi Protected Access.
To upgrade a WLAN network to support WPA, Access Points will require a WPA software upgrade. Clients will
require a software upgrade for the network interface card, and possibly a software update for the operating
system. For enterprise networks, an authentication server, typically one that supports RADIUS and the selected
EAP authentication protocol, will be added to the network.
A.16 What is WPA2?
It is the second generation of WPA. WPA2 is based on the final IEEE 802.11i amendment to the 802.11
standard.
A.17 What is 802.1x Authentication?
802.1x is a framework for authenticated MAC-level access control, defines Extensible Authentication Protocol
(EAP) over LANs (WAPOL). The standard encapsulates and leverages much of EAP, which was defined for
dial-up authentication with Point-to-Point Protocol in RFC 2284.
Beyond encapsulating EAP packets, the 802.1x standard also defines EAPOL messages that convey the shared
key information critical for wireless security.
A.18 What is Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP)?
The Temporal Key Integrity Protocol, pronounced tee-kip, is part of the IEEE 802.11i encryption standard for
wireless LANs. TKIP is the next generation of WEP, the Wired Equivalency Protocol, which is used to secure
802.11 wireless LANs. TKIP provides per-packet key mixing, a message integrity check and a re-keying
mechanism, thus fixing the flaws of WEP.
A.19 What is Advanced Encryption Standard (AES)?
Security issues are a major concern for wireless LANs, AES is the U.S. government’s next-generation
cryptography algorithm, which will replace DES and 3DES.
-84-
Page 92

User Manual of WNAP-7350
A.20 What is Inter-Access Point Protocol (IAPP)?
The IEEE 802.11f Inter-Access Point Protocol (IAPP) supports Access Point Vendor interoperability, enabling
roaming of 802.11 Stations within IP subnet.
IAPP defines messages and data to be exchanged between Access Points and between the IAPP and high layer
management entities to support roaming. The IAPP protocol uses TCP for inter-Access Point communication
and UDP for RADIUS request/response exchanges. It also uses Layer 2 frames to update the forwarding tables
of Layer 2 devices.
A.21 What is Wireless Distribution System (WDS)?
The Wireless Distribution System feature allows WLAN AP to talk directly to other APs via wireless channel, like
the wireless WDS or repeater service.
A.22 What is Universal Plug and Play (UPnP)?
UPnP is an open networking architecture that consists of services, devices, and control points. The ultimate goal
is to allow data communication among all UPnP devices regardless of media, operating system, programming
language, and wired/wireless connection.
A.23 What is Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) Size?
Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) indicates the network stack of any packet is larger than this value will be
fragmented before the transmission. During the PPP negotiation, the peer of the PPP connection will indicate its
MRU and will be accepted. The actual MTU of the PPP connection will be set to the smaller one of MTU and the
peer’s MRU.
A.24 What is Clone MAC Address?
Clone MAC address is designed for your special application that request the clients to register to a server
machine with one identified MAC address. Since that all the clients will communicate outside world through the
WLAN Broadband Router, so have the cloned MAC address set on the WLAN Broadband Router will solve the
issue.
A.25 What is DDNS?
DDNS is the abbreviation of Dynamic Domain Name Server. It is designed for user owned the DNS server with
dynamic WAN IP address.
A.26 What is NTP Client?
NTP client is designed for fetching the current timestamp from internet via Network Time protocol. User can
specify time zone, NTP server IP address.
-85-
Page 93

User Manual of WNAP-7350
A.27 What is VPN?
VPN is the abbreviation of Virtual Private Network. It is designed for creating point-to point private link via shared
or public network.
A.28 What is IPSEC?
IPSEC is the abbreviation of IP Security. It is used to transferring data securely under VPN.
A.29 What is WLAN Block Relay between Clients?
An Infrastructure Basic Service Set is a BSS with a component called an Access Point (AP). The access point
provides a local relay function for the BSS. All stations in the BSS communicate with the access point and no
longer communicate directly. All frames are relayed between stations by the access point. This local relay
function effectively doubles the range of the IBSS.
A.30 What is WMM?
WMM is based on a subset of the IEEE 802.11e WLAN QoS draft standard. WMM adds prioritized capabilities to
Wi-Fi networks and optimizes their performance when multiple concurring applications, each with different
latency and throughput requirements, compete for network resources. By using WMM, end-user satisfaction is
maintained in a wider variety of environments and traffic conditions. WMM makes it possible for home network
users and enterprise network managers to decide which data streams are most important and assign them a
higher traffic priority.
A.31 What is WLAN ACK TIMEOUT?
ACK frame has to receive ACK timeout frame. If remote does not receive in specified period, it will be
retransmitted.
A.32 What is Modulation Coding Scheme (MCS)?
MCS is Wireless link data rate for 802.11n. The throughput/range performance of an AP will depend on its
implementation of coding schemes. MCS includes variables such as the number of spatial streams, modulation,
and the data rate on each stream. Radios establishing and maintaining a link must automatically negotiate the
optimum MCS based on channel conditions and then continuously adjust the selection of MCS as conditions
change due to interference, motion, fading, and other events.
A.33 What is Frame Aggregation?
Every 802.11 packet, no matter how small, has a fixed amount of overhead associated with it. Frame
Aggregation combines multiple smaller packets together to form one larger packet. The larger packet can be
sent without the overhead of the individual packets. This technique helps improve the efficiency of the 802.11n
radio allowing more end user data to be sent in a given time.
-86-
Page 94

User Manual of WNAP-7350
A.34 What is Guard Intervals (GI)?
A GI is a period of time between symbol transmission that allows reflections (from multipath) from the previous
data transmission to settle before transmitting a new symbol. The 802.11n specifies two guard intervals: 400ns
(short) and 800ns (long). Support of the 400ns GI is optional for transmit and receive. The purpose of a guard
interval is to introduce immunity to propagation delays, echoes, and reflections to which digital data is normally
very sensitive.
-87-
Page 95

User Manual of WNAP-7350
Appendix B: Configuring the PC in Windows 7
In this section, we’ll introduce how to configure the TCP/IP correctly in Windows 7. First make sure your Network
Adapter is working, refer to the adapter’s manual if needed.
1) On the Windows taskbar, click the Start button, and then click Control Panel.
2) Click the Network and Sharing Center icon, and then click the Change adapter settings on the left
side of the screen.
Figure B-1
3) Right click the icon of the network adapter shown in the figure below, and select Properties on the
prompt window.
-88-
Page 96

User Manual of WNAP-7350
Figure B-2
4) In the prompt page shown below, double click on the Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4).
Figure B-3
-89-
Page 97
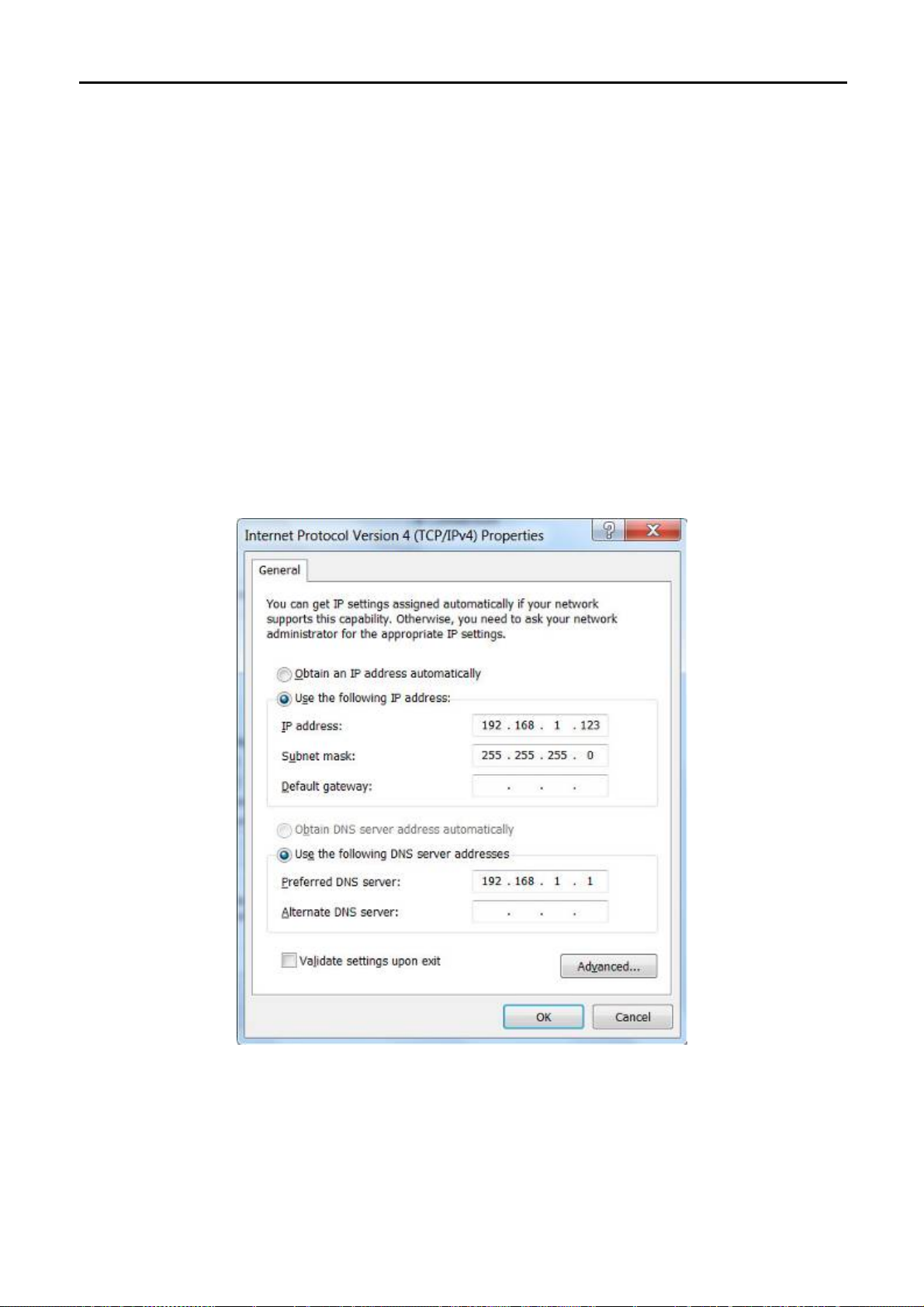
User Manual of WNAP-7350
5) The following TCP/IP Properties window will display and the IP Address tab is open on this window
by default.
Now you can configure the TCP/IP protocol below:
Setting IP address manually
1 Select Use the following IP address radio button.
2 If the AP's LAN IP address is 192.168.1.1, type in IP address 192.168.1.x (x is from 2 to 254), and Subnet
mask 255.255.255.0.
3 Select Use the following DNS server addresses radio button. In the Preferred DNS Server field you can
type the DNS server IP address which has been provided by your ISP
Now click OK to keep your settings.
Figure B-4
-90-
Page 98

User Manual of WNAP-7350
Appendix C: Use Planet Smart Discovery to find AP
For easily discover the WNAP-7350 in your Ethernet environment, the Planet Smart Discovery Utility from user’s
manual CD-ROM is an ideal solution.
The following install instructions guiding you to run the Planet Smart Discovery Utility.
Step 1: Deposit the Planet Smart Discovery Utility in administrator PC.
Step 2: Execute this utility.
Step 3: Click “Refresh” button to update the current connected devices list, the screen is shown as follow.
Figure C-1
Step 3: Select the WNAP-7350 from the list, and then click “Connect to Device” button to login the Web
Management Configuration Page.
The fields in white background can be modified directly, and then you can apply the new
setting by clicking the “Update Device” button.
-91-
Page 99
User Manual of WNAP-7350
Appendix D: Specifications
Product
Hardware Specifications
Standard support
Memory
Interface
Antenna N-Type Female connectors x 2
Wireless RF Specifications
Wireless Technology
Data Rate
Media Access Control CSMA / CA
Modulation
Frequency Band 5.180GHz ~ 5.825GHz
WNAP-7350
5GHz 300Mbps 802.11a/n Wireless Outdoor Access Point
IEEE 802.11a/n Wireless LAN
IEEE 802.11i Wireless Security
IEEE 802.3 10Base-T Ethernet
IEEE 802.3u 100Base-TX Ethernet
IEEE 802.3x Flow Control
IEEE 802.3af/at Power over Ethernet / PD
32 Mbytes DDR SDRAM
8 Mbytes Flash
Wireless IEEE 802.11a/n, 2T2R
LAN: 1 x 10/100Base-TX, Auto-MDI/MDIX, IEEE 802.3af/at PoE/PD port
WAN: 1 x 10/100Base-TX, Auto-MDI/MDIX
IEEE 802.11a
IEEE 802.11n
IEEE 802.11a: 54, 48, 36, 24, 18, 12, 9 and 6Mbps
IEEE 802.11n (20MHz): up to 150Mbps
IEEE 802.11n (40MHz): up to 300Mbp
Transmission / Emission Type: OFDM
Data modulation type: OFDM with BPSK, QPSK, 16-QAM, 64-QAM
5.180GHz CH36 5.580GHz CH116
5.200GHz CH40 5.600GHz CH120
5.220GHz CH44 5.620GHz CH124
5.240GHz CH48 5.640GHz CH128
5.260GHz CH52 5.660GHz CH132
5.280GHz CH56 5.680GHz CH136
Operating Channel
RF Output Power IEEE 802.11a: 27 ± 1dBm
5.300GHz CH60 5.700GHz CH140
5.320GHz CH64 5.745GHz CH149
5.500GHz CH100 5.765GHz CH153
5.520GHz CH104 5.785GHz CH157
5.540GHz CH108 5.805GHz CH161
5.560GHz CH112 5.825GHz CH165
*The above 24 channels are defined in theory. The actual application will vary
depends on the regulation in different regions and countries.
-92-
Page 100

IEEE 802.11n: 24 ± 1dBm
Receiver Sensitivity
IEEE 802.11a: -91dBm
IEEE 802.11n: -92dBm
Output Power Control 3~27dBm
Software Features
User Manual of WNAP-7350
LAN
Built-in DHCP server supporting static IP address distributing
Supports 802.1d STP (Spanning Tree)
Static IP
Dynamic IP
WAN
PPPoE
PPTP
L2TP
IPSec
Bridge
Operating Mode
Gateway
WISP
NAT firewall with SPI (Stateful Packet Inspection)
Firewall
Built-in NAT server supporting Virtual Server and DMZ
Built-in firewall with Port / IP address / MAC / URL filtering
AP
Client
Wireless Mode
WDS PTP
WDS PTMP
WDS Repeater (AP+WDS)
Channel Width 20MHz / 40MHz
Wireless Isolation
Enable it to isolate each connected wireless clients from communicating with
each other mutually.
Encryption Type 64/128-bits WEP, WPA, WPA-PSK, WPA2, WPA2-PSK, 802.1X
Provides wireless LAN ACL (Access Control List) filtering
Wireless Security
Wireless MAC address filtering
Supports WPS (WIFI Protected Setup )
Enable / Disable SSID Broadcast
Multiple SSID Up to 2
Max. Wireless Client 40
Max. WDS AP 8
Max. Wired Client 60
WMM Supports Wi-Fi Multimedia
QoS Supports Quality of Service for bandwidth control
NTP Network Time Management
Management Web UI, DHCP Client, Configuration Backup & Restore, Dynamic DNS, SNMP
Diagnostic tool System Log, Ping Watchdog
Mechanical & Power
IP Rate IP67
-93-
 Loading...
Loading...