Page 1

Avid Unity™ LANshare
Workgroup Setup Guide
Page 2

Copyright and Disclaimer
Product specifications are subject to change without notice and do not represent a commitment on
the part of Avid Technology, Inc. The software described in this document is furnished under a
license agreement. You can obtain a copy of that license by visiting Avid’s Web site at
www.avid.com. The software may not be reverse assembled and may be used or copied only in
accordance with the terms of the license agreement. It is against the law to copy the software on any
medium except as specifically allowed in the license agreement. Avid products or portions thereof
are protected by one or more of the following United States patents: 4,746,994; 4,970,663;
5,045,940; 5,063,448; 5,077,604; 5,245,432; 5,267,351; 5,309,528; 5,325,200; 5,355,450;
5,396,594; 5,440,348; 5,452,378; 5,467,288; 5,513,375; 5,528,310; 5,557,423; 5,568,275;
5,577,190; 5,583,496; 5,584,006; 5,627,765; 5,634,020; 5,640,601; 5,644,364; 5,654,737;
5,701,404; 5,715,018; 5,719,570; 5,724,605; 5,726,717; 5,729,673; 5,731,819; 5,745,637;
5,752,029; 5,754,180; 5,754,851; 5,781,188; 5,799,150; 5,812,216; 5,828,678; 5,842,014;
5,852,435; 5,883,670; 5,889,532; 5,892,507; 5,905,841; 5,912,675; 5,929,836; 5,929,942;
5,930,445; 5,930,797; 5,946,445; 5,966,134; 5,977,982; 5,986,584; 5,987,501; 5,995,079;
5,995,115; 5,999,190; 5,999,406; 6,009,507; 6,011,562; 6,014,150; 6,016,152; 6,016,380;
6,018,337; 6,023,531; 6,023,703; 6,031,529; 6,035,367; 6,038,573; 6,052,508; 6,058,236;
6,061,758; 6,072,796; 6,084,569; 6,091,422; 6,091,778; 6,105,083; 6,118,444; 6,128,001;
6,128,681; 6,130,676; 6,134,379; 6,134,607; 6,137,919; 6,141,007; 6,141,691; 6,154,221;
6,157,929; 6,160,548; 6,161,115; 6,167,404; 6,174,206; 6,192,388; 6,198,477; 6,208,357;
6,211,869; 6,212,197; 6,215,485; 6,223,211; D352,278; D372,478; D373,778; D392,267; D392,268;
D392,269; D395,291; D396,853; D398,912. Additional U.S. and foreign patents pending. No part of
this document may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic or
mechanical, including photocopying and recording, for any purpose without the express written
permission of Avid Technology, Inc.
Copyright © 2001 Avid Technology, Inc. and its licensors. All rights reserved. Printed in
USA.
The following disclaimer is required by Apple Computer, Inc.
APPLE COMPUTER, INC. MAKES NO WARRANTIES WHATSOEVER, EITHER EXPRESS OR
IMPLIED, REGARDING THIS PRODUCT, INCLUDING WARRANTIES WITH RESPECT TO ITS
MERCHANTABILITY OR ITS FITNESS FOR ANY PARTICULAR PURPOSE. THE EXCLUSION OF
IMPLIED WARRANTIES IS NOT PERMITTED BY SOME STATES. THE ABOVE EXCLUSION MAY NOT
APPLY TO YOU. THIS WARRANTY PROVIDES YOU WITH SPECIFIC LEGAL RIGHTS. THERE MAY
BE OTHER RIGHTS THAT YOU MAY HAVE WHICH VARY FROM STATE TO STATE.
The following disclaimer is required by Sam Leffler and Silicon Graphics, Inc. for the
use of their TIFF library:
Copyright © 1988–1997 Sam Leffler
Copyright © 1991–1997 Silicon Graphics, Inc.
Permission to use, copy, modify, distribute, and sell this software [i.e., the TIFF library] and its
documentation for any purpose is hereby granted without fee, provided that (i) the above copyright
notices and this permission notice appear in all copies of the software and related documentation,
and (ii) the names of Sam Leffler and Silicon Graphics may not be used in any advertising or
publicity relating to the software without the specific, prior written permission of Sam Leffler and
Silicon Graphics.
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED “AS-IS” AND WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS,
IMPLIED OR OTHERWISE, INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION, ANY WARRANTY OF
MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
IN NO EVENT SHALL SAM LEFFLER OR SILICON GRAPHICS BE LIABLE FOR ANY SPECIAL,
INCIDENTAL, INDIRECT OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES OF ANY KIND, OR ANY DAMAGES
WHATSOEVER RESULTING FROM LOSS OF USE, DATA OR PROFITS, WHETHER OR NOT
ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF DAMAGE, AND ON ANY THEORY OF LIABILITY, ARISING OUT
OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE USE OR PERFORMANCE OF THIS SOFTWARE.
Page 3

The following disclaimer is required by the Independent JPEG Group:
Portions of this software are based on work of the Independent JPEG Group.
The following disclaimer is required by Paradigm Matrix:
Portions of this software licensed from Paradigm Matrix.
The following disclaimer is required by Ray Sauers Associates, Inc.:
“Install-It” is licensed from Ray Sauers Associates, Inc. End-User is prohibited from taking any
action to derive a source code equivalent of “Install-It,” including by reverse assembly or reverse
compilation, Ray Sauers Associates, Inc. shall in no event be liable for any damages resulting from
reseller’s failure to perform reseller’s obligation; or any damages arising from use or operation of
reseller’s products or the software; or any other damages, including but not limited to, incidental,
direct, indirect, special or consequential Damages including lost profits, or damages resulting from
loss of use or inability to use reseller’s products or the software for any reason including copyright or
patent infringement, or lost data, even if Ray Sauers Associates has been advised, knew or should
have known of the possibility of such damages.
The following disclaimer is required by Videomedia, Inc.:
“Videomedia, Inc. makes no warranties whatsoever, either express or implied, regarding this
product, including warranties with respect to its merchantability or its fitness for any particular
purpose.”
“This software contains V-LAN ver. 3.0 Command Protocols which communicate with V-LAN ver. 3.0
products developed by Videomedia, Inc. and V-LAN ver. 3.0 compatible products developed by
third parties under license from Videomedia, Inc. Use of this software will allow “frame accurate”
editing control of applicable videotape recorder decks, videodisc recorders/players and the like.”
The following notice is required by Altura Software, Inc. for the use of its Mac2Win software and Sample Source Code:
©1993–1998 Altura Software, Inc.
The following notice is required by Ultimatte Corporation:
Certain real-time compositing capabilities are provided under a license of such technology from
Ultimatte Corporation and are subject to copyright protection.
Attn. Government User(s). Restricted Rights Legend
U.S. GOVERNMENT RESTRICTED RIGHTS. This Software and its documentation are “commercial
computer software” or “commercial computer software documentation.” In the event that such
Software or documentation is acquired by or on behalf of a unit or agency of the U.S. Government,
all rights with respect to this Software and documentation are subject to the terms of the License
Agreement, pursuant to FAR §12.212(a) and/or DFARS §227.7202-1(a), as applicable.
Page 4

Trademarks
AirPlay, AudioVision, Avid, Avid Xpress, CamCutter, Digidesign, FieldPak, Film Composer, HIIP,
Image Independence, Marquee, Media Composer, Media Recorder, NewsCutter, OMF,
OMF Interchange, Open Media Framework, Pro Tools, and Softimage are registered trademarks and
888 I/O, AirSPACE, AirSPACE HD, AniMatte, AudioSuite, AutoSync, AVIDdrive, AVIDdrive Towers,
AvidNet, Avid Production Network, AvidProNet, AVIDstripe, Avid Unity, AVX, DAE, D-Fi, D-fx, D-Verb,
ExpertRender, FilmScribe, HyperSPACE, HyperSPACE HDCAM, Intraframe, iS9, iS18, iS23, iS36,
Lo-Fi, Magic Mask, make manage move | media, Matador, Maxim, MCXpress, MEDIArray,
MediaDock, MediaDock Shuttle, Media Fusion, Media Illusion, MediaLog, Media Reader,
MediaShare, Meridien, NaturalMatch, OMM, Open Media Management, ProEncode, QuietDrive,
Recti-Fi, rS9, rS18, Sci-Fi, Sound Designer II, SPACE, SPACEnet, SPACEShift, Symphony, Trilligent,
UnityRAID, Vari-Fi, Video Slave Driver, and VideoSPACE are trademarks of Avid Technology, Inc.
3ware is a trademark of 3ware, Inc. which may be registered in some jurisdictions. Acrobat and
Adobe are registered trademarks of Adobe Systems Incorporated in the United States and/or other
countries. Adaptec is a trademark of Adaptec, Inc., which may be registered in some jurisdictions.
Apple, AppleTalk, Mac, Macintosh, and Power Macintosh are registered trademarks of Apple
Computer, Inc., registered in the U.S. and other countries. DAVE is a trademark of Thursby Software
Systems, Inc. Ghost is a registered trademark of Symantec Corporation in the United States and
other countries. Intel is a registered trademark of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries in the United
States and other countries. Java is a trademark of Sun Microsystems, Inc. Windows is a registered
trademark of Microsoft Corporation in the United States and/or other countries. All other trademarks
contained herein are the property of their respective owners.
Avid Unity LANshare Workgroup Setup Guide • Part 0130-05099-01 Rev. A •
November 2001
Page 5

Contents
Using This Guide
Who Should Use This Guide . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .xi
About This Guide . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xii
Symbols and Conventions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xiii
If You Need Help . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .xiv
If You Have Documentation Comments . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xv
How to Order Documentation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xv
Related Information. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .xvi
Chapter 1 LANshare Workgroup Overview
Introduction to LANshare . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-2
The LANserver. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-3
Installation Prerequisites . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-4
Chapter 2 Installing the LANserver and Ethernet Switch
Before You Begin . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-2
Standard LANshare Components . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-2
Optional LANshare Components . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-2
Installing the LANserver Hardware. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-3
Installing on a Desktop . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-3
Installing the LANserver . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-3
Installing the Ethernet Switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-4
Installing the CD-ROM Drive . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-5
Connecting Power Cords . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-6
Page 6

vi
Installing in a Rack . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-7
Installing the LANserver Rack-Mount Rails . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-7
Mounting a LANserver . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-8
Installing the CD-ROM Drive. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-10
Installing the Ethernet Switch Rack-Mount Bracket . . . . . 2-10
Mounting the Ethernet Switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-11
Connecting Power Cords. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-12
Installing the Application Key . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-13
Connecting a LANshare Workgroup to an In-House Network. . . 2-13
Making the Connection to the In-House Network. . . . . . . . . . 2-14
Cascading Multiple Ethernet Switches. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-14
Turning On the LANserver Hardware . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-16
Configuring the LANserver Using Windows 2000 Setup. . . . . . . . 2-17
Chapter 3 Configuring a LANserver
Setting Up the LANserver . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-2
Setting the Date, Time, and Time Zone . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-2
Specifying a Unique Computer Name . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-3
IP Addressing Strategies When Connecting to a Network . . . . 3-4
Configuring the LANserver Network Properties. . . . . . . . . . . . 3-4
Installing the LANserver Software. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-6
Configuring the MediaNet Software . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-7
Creating a Drive Set. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-7
Creating an Allocation Group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-8
Creating Workspaces . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-9
Creating User Accounts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-10
Sharing MediaNet Workspaces . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-11
Configuring User Accounts and Permissions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-11
Allowing Network Installation of Ethernet Client Software . . . . . 3-18
Chapter 4 Setting Up Windows Ethernet Clients
Installation Prerequisites . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-2
Connecting a Windows Ethernet Client . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-2
Page 7

Setting the Date, Time, and Time Zone . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-4
Configuring Network Properties . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-5
Installing the Avid Composer Products Software . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-7
Installing the Windows Ethernet Client Software . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-7
Installing Ethernet Client Software from the CD-ROM . . . . . . . 4-7
Installing Ethernet Client Software over the Network . . . . . . . . 4-8
Mounting Workspaces on a Windows Client . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-9
Finishing Up. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-9
Reconfiguring the Client Connection to a LANserver. . . . . . . . . . . . 4-9
Chapter 5 Setting Up Macintosh Ethernet Clients
Installation Prerequisites . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-2
Connecting a Macintosh Ethernet Client . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-2
Setting the Date, Time, and Time Zone . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-4
Configuring Network Properties . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-5
Installing the Avid Composer Products Software . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-7
Installing the Macintosh Ethernet Client Software. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-7
Installing Ethernet Client Software from the CD-ROM . . . . . . . 5-8
Configuring DAVE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-9
Installing the Macintosh Runtime Java Library . . . . . . . . . 5-11
Mounting Workspaces on a Macintosh Client . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-12
Finishing Up. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-12
Reconfiguring the Client Connection to a LANserver. . . . . . . . . . . 5-13
vii
Chapter 6 Upgrading from MediaShare F/C
Connecting MediaShare F/C Clients to a LANshare Workgroup. . 6-2
Copying Data to MediaNet Workspaces . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-3
Disconnecting MediaShare F/C Cables . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-3
Chapter 7 Troubleshooting
Using ping and tracert . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-2
ping. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-2
tracert . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-4
Page 8

viii
Troubleshooting a LANshare Workgroup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-6
Avid Composer Products Software Has Performance Issues. . 7-6
Workspaces Are Not Available to an Ethernet Client . . . . . . . . 7-6
Macintosh Client Cannot Mount Shared Workspaces. . . . . . . . 7-7
SGI Client Cannot Mount Shared Workspaces. . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-7
LANserver Is Whistling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-8
Checking That the Operating System Is Properly Installed . . . 7-8
Setting Virtual Memory . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-9
Checking the Gigabit Ethernet Adapter Board Driver. . . . . . . 7-11
Checking the 3ware Adapter Board Driver. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-11
Checking the SCSI Adapter Board Driver . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-12
Removing and Replacing LANserver Drives. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-13
Removing a Drive . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-13
Replacing a Drive. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-14
Resetting the LANserver Power Supplies. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-15
Appendix A Avid Performance Meter
Starting the Avid Performance Meter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-2
User Interface Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-2
Setting Up Your Test . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-6
Setting Up a Standard Test. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-6
Setting Up a Custom Test. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-8
Starting and Stopping a Test. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-11
Interpreting the Test Results . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-11
Appendix B LANserver BIOS Settings
Using the BIOS Setup Utility. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . B-1
Setting the Peripheral Device Configuration. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . B-2
Setting the Floppy Drive. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . B-2
Setting the Boot Device Priority. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . B-3
Saving the Changes and Closing the BIOS Setup Utility. . . . . . B-3
Page 9

Appendix C Mounting All Workspaces on a LANserver
Appendix D Using the Product Recovery CD-ROM
Reinstalling the Windows 2000 Operating System. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . D-2
Configuring the LANserver Using Windows 2000 Setup. . . . . . . . . D-3
Appendix E Reinstalling a LANshare Workgroup
Installing the LANshare Hardware . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . E-2
Configuring a LANserver. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . E-2
Setting Up Windows Ethernet Clients . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . E-4
Setting Up Macintosh Ethernet Clients . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . E-4
Appendix F Regulatory and Safety Notices
FCC Notice . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . F-1
Canadian ICES-003 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . F-2
European Union Notice . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . F-2
Australia and New Zealand EMC Regulations. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . F-4
ix
Page 10

x
Figures
Figure 1-1 LANshare Infrastructure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-2
Figure 2-1 Attaching Optical Cable to the Gigabit Ethernet
Adapter Board . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-5
Figure 2-2 Aligning the LANserver Rails to the Rack. . . . . . . . . . 2-7
Figure 2-3 Attaching Optical Cable to the Gigabit Ethernet
Adapter Board . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-11
Figure 2-4 Ethernet Switch Ports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-15
Figure 2-5 Cascading Ethernet Switches. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-15
Figure 3-1 Standalone User Accounts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-13
Figure 3-2 Standalone User Accounts and Groups . . . . . . . . . . . 3-14
Figure 3-3 Network User Accounts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-16
Figure 3-4 Network User Accounts and Groups . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-17
Figure 4-1 Connecting the Ethernet Cable to the Ethernet
Client . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-3
Figure 4-2 Connecting the Ethernet Cable to the Ethernet
Switch. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-3
Figure 5-1 Connecting the Ethernet Cable to the Ethernet
Client . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-3
Figure 5-2 Connecting the Ethernet Cable to the Ethernet
Switch. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-3
Figure 6-1 LANshare to MediaShare F/C Connection . . . . . . . . . 6-2
Figure A-1 Avid Performance Meter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-3
Page 11

Using This Guide
Congratulations on your purchase of an Avid Unity™ LANshare
workgroup. You can connect up to 10 offline or low-resolution Avid
workstations as Ethernet clients, allowing them to cost-effectively
share media files over an Ethernet network.
Who Should Use This Guide
This guide is intended for anyone who is installing, configuring, or
maintaining a LANshare workgroup. It provides installation and
configuration information specific to the standard LANserver
hardware and MediaNet software.
®
Page 12

xii
About This Guide
This guide provides task-oriented instructions for setting up and
configuring a LANshare workgroup.
The Contents provides a complete listing of all the topics in this book:
• Chapter 1, “LANshare Workgroup Overview,” provides an
overview of a LANshare workgroup and its components.
• Chapter 2, “Installing the LANserver and Ethernet Switch,”
provides step-by-step instructions for connecting the LANserver,
the external CD-ROM drive, and the Ethernet switch.
• Chapter 3, “Configuring a LANserver,” provides step-by-step
instructions for installing and configuring the MediaNet software
on the LANserver.
• Chapter 4, “Setting Up Windows Ethernet Clients,” provides
step-by-step instructions for connecting Windows-based Ethernet
clients, installing the client software, and configuring the clients.
Using This Guide
• Chapter 5, “Setting Up Macintosh Ethernet Clients,” provides
step-by-step instructions for connecting Macintosh-based Ethernet
clients, installing the client software, and configuring the clients.
• Chapter 6, “Upgrading from MediaShare F/C,” describes how to
upgrade a MediaShare F/C workgroup to a LANshare
workgroup.
• Chapter 7, “Troubleshooting,” provides information for fixing
some problems that might arise while using a LANshare
workgroup.
• Appendix A, “Avid Performance Meter,” describes the
Performance Meter, an Avid-supplied utility for checking the
network connection between the File Manager and the Ethernet
clients.
• Appendix B, “LANserver BIOS Settings,” describes the BIOS
settings for the LANserver and how to change them.
Page 13

• Appendix C, “Mounting All Workspaces on a LANserver,”
describes how to make the LANserver automatically mount up to
21 workspaces.
• Appendix D, “Using the Product Recovery CD-ROM,” describes
how to reinstall the operating system using the recovery
CD-ROM.
• Appendix E, “Reinstalling a LANshare Workgroup,” lists the
major steps to reinstall a LANshare workgroup if it is moved from
one location to another.
• Appendix F, “Regulatory and Safety Notices,” provides regulatory
compliance information.
Symbols and Conventions
xiii
The material in this document applies to the Windows®2000 and
Macintosh
operating system, it is marked as follows:
• (Windows 2000) means the information applies to the
• (Macintosh) means the information applies to the Macintosh
This guide uses the following special symbols and conventions:
1. Numbered lists, when the order of the items is important.
• Bulleted lists, when the order of the items is unimportant.
t One arrow indicates a single-step procedure. Multiple arrows in a
®
operating systems. When the text applies to a specific
Windows 2000 operating system.
operating system.
a. Alphabetical lists, when the order of secondary items is
important.
- Indented dashed lists, when the order of secondary items is
unimportant.
list indicate that you perform one of the actions listed.
Symbols and Conventions
Page 14

xiv
The k symbol refers to the Apple or Command key. Press and hold
the Command key and another key to perform a keyboard shortcut.
Courier Bold font identifies text that you type.
Look here in the margin
for tips.
n
c
w
In the margin, you will find tips that help you perform tasks more
easily and efficiently.
A note provides important related information, reminders, recommendations,
and strong suggestions.
A caution means that a specific action you take could cause harm to
your computer or cause you to lose data.
A warning describes an action that could cause you physical harm.
Follow the guidelines in this guide or on the unit itself when
handling electrical equipment.
If You Need Help
If you are having trouble setting up your LANshare workgroup, you
should:
1. Retry the action, carefully following the instructions given for that
task in this guide.
2. Check the documentation that came with your hardware for
maintenance or hardware-related issues.
Using This Guide
3. Check the release notes supplied with your Avid application for
information on accessing the Avid Web site and the Avid
Knowledge Center.
4. For support services, call Avid Customer Support:
- Broadcast products — call 800-NEWS-DNG (639-7364).
- Post production products — call 800-800-AVID (2843).
Page 15

If You Have Documentation Comments
Avid Technology continuously seeks to improve its documentation.
We value your comments about this manual or other Avid-supplied
documentation.
Simply e-mail your documentation comments to Avid Technology at
TechPubs@avid.com
Please include the title of the document, its part number, revision, and
the specific section you’re commenting on in all correspondence.
How to Order Documentation
To order additional copies of this documentation from within the
United States, call Avid Telesales at 800-949-AVID (2843). If you are
placing an order from outside the United States, contact your local
Avid representative.
xv
n
Adobe® Acrobat® (PDF format) versions of this documentation are included
on the MediaNet Release 2.2 CD-ROM. You can read these online or print
them, as required.
If You Have Documentation Comments
Page 16

xvi
Related Information
The following documents provide more information about the
LANshare workgroup and MediaNet environment:
• Avid Unity LANshare Site Preparation Guide
• Avid Unity Macintosh Ethernet Client Quick Start Card
• Avid Unity Windows Ethernet Client Quick Start Card
• Avid Unity LANshare Release Notes
• Avid Unity MediaNet Management Guide
• Avid Products Collaboration Guide
The Avid Products Collaboration Guide provides step-by-step
instructions for transferring project files, audio files, and graphics
and effects files between various Avid products.
The most recent update of the Avid Products Collaboration Guide is
provided online. Check the release notes supplied with your Avid
application for information on accessing online documentation.
Using This Guide
Page 17

CHAPTER 1
LANshare Workgroup Overview
This chapter introduces the Avid Unity LANshare workgroup.
LANshare is a low-cost alternative to Avid Unity MediaNet that
allows you to connect up to 10 Ethernet clients to a LANserver and its
storage. It is designed to provide real-time media editing over an
Ethernet network using the MediaNet software.
Topics in this chapter include:
• Introduction to LANshare
• The LANserver
• Installation Prerequisites
Page 18
1-2
Introduction to LANshare
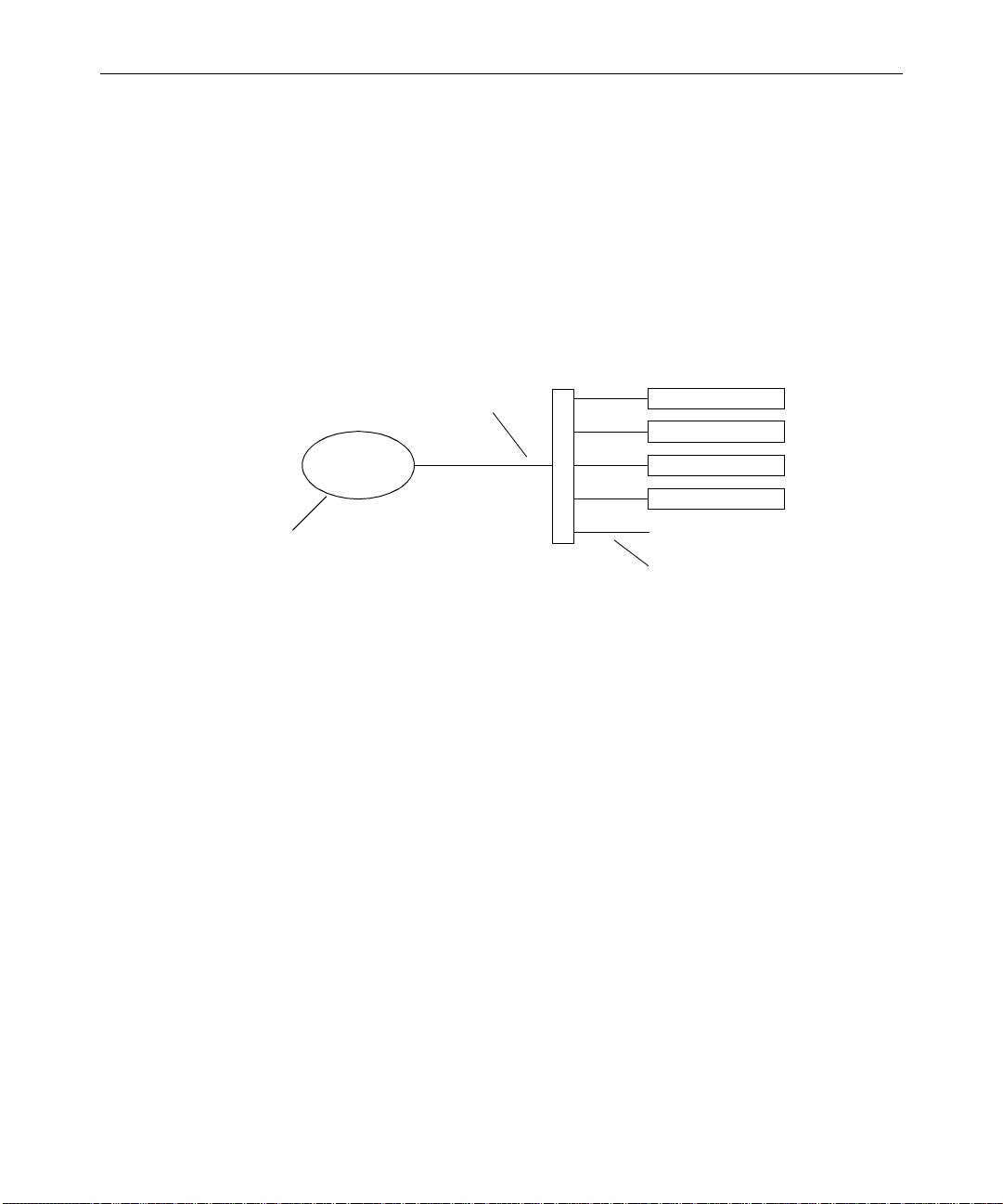
The LANshare workgroup provides clients access to MediaNet
workspaces (shared folders) over a fast Ethernet network (see
Figure 1-1). The LANserver allows Ethernet clients to mount up to 21
MediaNet workspaces. You can have several LANshare workgroups
at your site, each accommodating multiple Ethernet clients.
Storage and
MediaNet file system
Gigabit Ethernet
LANserver
Ethernet switch
Ethernet client
Ethernet client
Ethernet client
Ethernet client
…
100BASE-T Ethernet
Figure 1-1 LANshare Infrastructure
MediaNet workspaces, exported by the LANserver, can be mounted
on Ethernet clients and then accessed in the same manner as local
drives. Ethernet clients can then play, record, and edit media on the
MediaNet workspaces using a high-performance networking protocol
optimized by Avid for real-time media transfer. Real-time media reads
and writes are not possible unless the connected clients are running a
qualified Avid editing application and have the MediaNet Ethernet
client software installed.
Ethernet clients can edit media in one or more of the following video
resolutions:
• 4:1s or lower – dual-stream, up to six clients
• 10:1 or lower – dual-stream, up to six clients
LANshare Workgroup Overview
Page 19

• 14:1 or lower – single-stream, up to ten clients
• 10:1m or lower – four streams, up to six clients; nine streams, up to
The LANserver requires an application key (commonly called a
dongle). Ethernet clients do not require LANshare application keys –
their licenses are handled separately by the LANserver. However, the
clients do require application keys to run the Avid Composer Products
software.
The LANserver
The LANserver is a standalone system that runs the MediaNet
software. It is a dual-processor, rack-mount PC system that contains
nine hard drives; one for the operating system and eight for storing
data.
1-3
five clients
On the front of the LANserver are two doors that cover the hard
drives. The doors contain fans to provide air circulation for the drives
and can be locked to prevent the accidental removal of a drive while
the LANserver is running.
The front of the LANserver has a block of 12 LEDs. Each hard drive
has a green LED to show that the drive is operating. The drives are
numbered from left to right and top to bottom. Drive 1 to drive 8 are
the data drives. Drive 9 is the operating system drive.
Three other LEDs on the front of the LANserver indicate power
(PWR), network connection (LAN), and hard drive use (HDD, the
operating system drive). The PWR LED is green when the power is on.
The LAN LED is orange when the LANserver is attached to a network.
The HDD LED flashes red when data is read from or written to
drive 9.
The LANserver
Page 20

1-4
Each of the hard drives has a lock and two green LEDs on the left side
of the drive carrier. The lock can be used to secure the drive carrier,
preventing its removal from the LANserver. The right LED is on when
a drive is receiving power from the LANserver. The left LED flashes
when a drive is in use.
Installation Prerequisites
To set up a LANshare workgroup, you need:
• A LANserver.
• An external CD-ROM drive.
• The MediaNet Release 2.2 (or later) CD-ROM.
• A fast Ethernet switch (a nonblocking gigabit Ethernet-to10/100BASE-T Ethernet switch) that connects the LANshare to the
Ethernet clients.
• Up to 10 Ethernet clients (Avid workstations running a qualified
LANshare Workgroup Overview
Avid Composer Product) with 100BASE-T capable Ethernet
connectivity. See the Avid Unity MediaNet Release Notes for
information on qualified Avid Composer Products.
Page 21

CHAPTER 2
Installing the LANserver and Ethernet Switch
This chapter describes how to install a LANserver, external CD-ROM
drive, and Ethernet switch to create a LANshare workgroup. The
workgroup can be standalone or connected to an in-house network.
Topics in this chapter include:
• Before You Begin
• Installing the LANserver Hardware
• Connecting a LANshare Workgroup to an In-House Network
• Turning On the LANserver Hardware
• Configuring the LANserver Using Windows 2000 Setup
Page 22

2-2
Before You Begin
Keep the shipping
boxes that come with
your LANserver kit.
You mig ht need to
repackage and ship the
components in the
future.
Before you begin to install the LANserver hardware, do the following:
• Unpack the LANshare kit (the LANserver, CD-ROM drive, and
Ethernet switch).
• Check the contents of the kit against the packing sticker on the
outside of each shipping box to confirm you have received all the
components.
Standard LANshare Components
The standard LANshare components include:
• A LANserver with nine drives
• A gigabit Ethernet switch and two 25-foot (7.5 meter) optical
cables
• An external SCSI CD-ROM drive, SCSI cable, and 68-pin to 50-pin
SCSI adapter
Optional LANshare Components
The optional LANshare components include:
• A monitor, keyboard, and mouse
• A keyboard, monitor, and mouse assembly (KMM)
• A keyboard, video, and mouse switch (KVM)
All of these components are available from Avid. You can contact Avid
Telesales at 800-949-AVID (2843), your Avid sales representative, or
your Avid Reseller to purchase these components.
Installing the LANserver and Ethernet Switch
Page 23

Installing the LANserver Hardware
Each LANserver ships with a gigabit Ethernet adapter board and a
SCSI adapter installed. For fault-tolerence, the LANserver has two
autosensing power supplies that set the voltage automatically for
either 120 volts or 220 volts at 50 to 60 Hz.
The LANserver hardware can be set on a desktop or mounted in a
rack. Select one of the following:
t If you are installing the LANserver on a desktop, continue
with“Installing on a Desktop” on page 2-3.
t If you are installing the LANserver in a rack, continue with
“Installing in a Rack” on page 2-7.
Installing on a Desktop
The following sections describe how to install the LANserver, Ethernet
switch, and CD-ROM drive on a desktop.
2-3
Installing the LANserver
To install the LANserver on a desktop:
1. Locate the rubber feet in the LANshare kit.
2. Attach one rubber foot to the bottom of the LANserver at each
3. Place the LANserver on the desktop. Leave adequate room at the
4. Place the monitor, keyboard, and mouse on the desktop next to the
5. Attach the 15-pin connector on the monitor cable to the video port
corner.
front for air circulation and access to the drives, and at the back for
cables.
LANserver.
on the back of the LANserver. Secure the connector with the
thumbscrews on the connector.
Installing the LANserver Hardware
Page 24

2-4
6. Attach the connector on the keyboard cable to the keyboard
connector on the back of the LANserver. The keyboard connector
is at the bottom left of the connectors on the LANserver.
7. Attach the connector on the mouse cable to the mouse connector
on the back of the LANserver. The mouse connector is directly
above the keyboard connector.
Installing the Ethernet Switch
To install the Ethernet switch on a desktop:
1. Locate the rubber feet in the Ethernet switch kit.
2. Cut the feet apart.
3. Attach one rubber foot to the bottom of the switch at each corner.
4. Place the switch on top of the LANserver. Leave adequate room at
the front for cables and at the back for air circulation.
5. Locate a 25-foot (7.5-meter) optical gigabit Ethernet cable in the
Ethernet switch kit. Look for an orange cable with a dual plug on
each end (see Figure 2-1).
c
Installing the LANserver and Ethernet Switch
Handle the optical cable carefully. It can be easily damaged if it is
pinched or crimped.
6. Remove the protective covers from the connectors on one end of
the optical cable.
7. Remove the protective cover from the Ethernet adapter board in
the LANserver. The board is located in the top slot.
8. Firmly push the cable connector into the gigabit Ethernet adapter
board connector on the LANserver (see Figure 2-1). Make sure the
alignment tabs on the cable connector face down.
9. Route the cable to the front of the switch.
Page 25
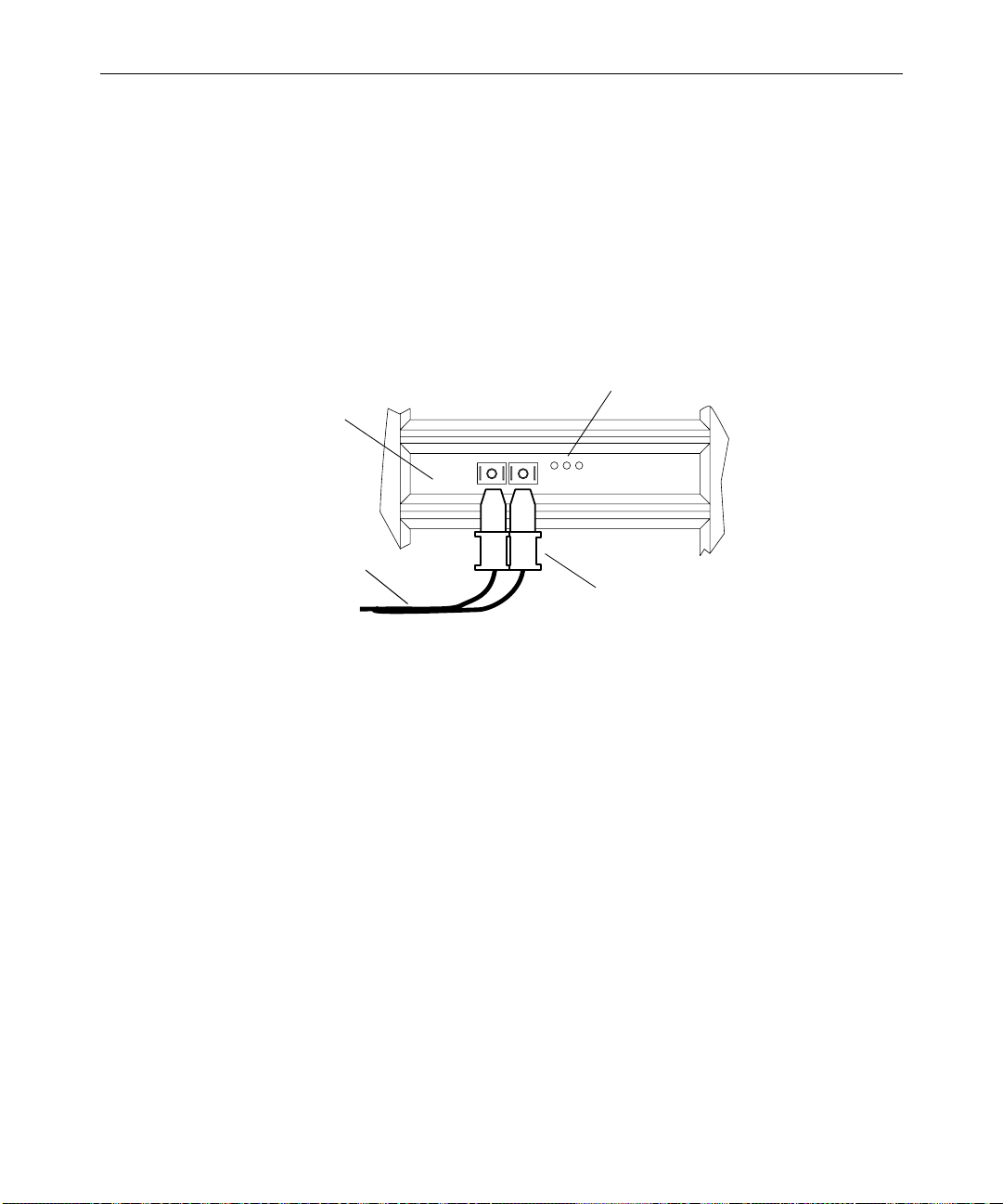
Gigabit Ethernet
adapter board
Optical cable
2-5
10. Remove the protective covers from the connectors on the other
end of the optical cable.
11. Remove the protective cover from switch port 17 (the top
connector).
12. Firmly push the cable connector into the top gigabit Ethernet port
on the switch. Make sure the alignment tabs on the cable
connector face up.
LEDs
Optical connector
Figure 2-1 Attaching Optical Cable to the Gigabit Ethernet
Installing the CD-ROM Drive
To install the CD-ROM drive:
1. Position the CD-ROM drive on top of the LANserver, near the
back of the case. Leave adequate room at the front of the CD-ROM
drive for the tray to open and at the back for cables.
2. Locate the Avid-supplied SCSI cable and the 68-pin to 50-pin SCSI
adapter.
3. Attach the 68-pin connector on one end of the SCSI cable to the
68-pin connector on the SCSI adapter. Secure the connector with
the thumbscrews on the cable connector.
Adapter Board
Installing the LANserver Hardware
Page 26

2-6
4. Attach the 68-pin connector on the other end of the SCSI cable to
the 68-pin connector on the SCSI adapter board in the LANserver.
The board is in the bottom slot.
5. Attach the 50-pin connector on the SCSI adapter to the bottom
50-pin connector on the back of the CD-ROM drive. You should
hear a click when the connector is secure.
Connecting Power Cords
Before you attach the power cords to the LANshare components, make
sure the Power switches on the LANserver and the CD-ROM drive are
in the off (O) position.
n
The Ethernet switch has no Power switch and will turn on when you plug the
power cords into a power outlet.
To connect the power cords to the LANserver and other components:
1. Plug one power cord into the right power connector on the back of
the LANserver.
2. Plug one power cord into the left power connector on the back of
the LANserver.
3. Plug the power cords into power outlets.
4. Plug a power cord into the back of the Ethernet switch.
5. Plug the power cord into a power outlet. You should see some of
the LEDs on the front of the switch light and hear the fan when the
switch is plugged in.
6. Plug a power cord into the back of the CD-ROM drive.
7. Plug the power cord into a power outlet.
8. Plug the monitor power cord into a power outlet.
You can continue with “Installing the Application Key” on page 2-13.
Installing the LANserver and Ethernet Switch
Page 27
Installing in a Rack
The following sections describe how to install the LANserver,
CD-ROM drive, and Ethernet switch in a rack.
Installing the LANserver Rack-Mount Rails
If you are installing the LANserver in a rack, follow the instructions
supplied in the LANserver rail kit to install the rack-mount rails while
ensuring that:
• The rails do not interfere with the power strips, power cords, or
other cables at the back of the rack.
• The bottom of the LANserver is at the bottom of a U-alignment
space.
• The rails span two U-alignment spaces and use the middle two
slots for screws (see Figure 2-2).
• The rails allow the LANserver to slide completely into the rack.
2-7
Rack channel hole spacing
EIA rack unit
Baseline of LANserver
is at U-alignment
position between two
1/2-inch spaced holes.
• The front edge of the slides are set back approximately 1/2 inch
from the rack front channels.
• The rails attach as far forward on the LANserver as possible.
1/2 in
5/8 in
1 3/4 in
1 3/4 in
2 U
5/8 in
1/2 in
5/8 in
1 U
5/8 in
1/2 in
Rack front channel
Support rail
Figure 2-2 Aligning the LANserver Rails to the Rack
Installing the LANserver Hardware
Page 28

2-8
Mounting a LANserver
w
Mounting the LANserver on the rack-mount rails is a two-person
task. It is heavy, fits tightly into the rack rails, and the rails might
need to be spread slightly to fit the LANserver. If you try to mount
the LANserver alone, you might damage the LANserver or injure
yourself.
To mount a LANserver on the rack-mount rails:
1. Slide the rack-mount rails out of the rack.
2. Lift the LANserver into position with one person on each side of
the rack.
3. Place the rail slides on the LANserver onto the extended rails.
4. Slide the LANserver into the rack. You should hear the slides click
onto the rails as you push the LANserver into the rack.
5. Attach the monitor, keyboard, and mouse to the LANserver by
selecting one of the following:
t If you are using a standard monitor, keyboard, and mouse,
connect them as described in “Connecting a Standard
Keyboard, Monitor, and Mouse” on page 2-8.
t If you are using a KVM switch with the monitor, keyboard,
and mouse, connect them as described in “Connecting to an
Optional KVM Switch” on page 2-9.
Connecting a Standard Keyboard, Monitor, and Mouse
To connect the LANserver to a standard keyboard, monitor, and
mouse:
1. Place the monitor, keyboard, and mouse on a suitable desktop or
table next to the LANserver rack.
You can also place the monitor on a shelf, and the keyboard and
mouse on a sliding tray in the rack. These items are optional. You
can supply them yourself or you can purchase them from Avid.
Installing the LANserver and Ethernet Switch
Page 29

2. Attach the 15-pin connector on the monitor cable to the video port
on the back of the LANserver. Secure the connector with the
thumbscrews on the connector.
3. Attach the connector on the keyboard cable to the keyboard
connector on the back of the LANserver. The keyboard connector
is at the bottom left of the connectors on the LANserver.
4. Attach the connector on the mouse cable to the mouse connector
on the back of the LANserver. The mouse connector is directly
above the keyboard connector.
Connecting to an Optional KVM Switch
This section assumes you already have your keyboard, monitor, and
mouse connected to the KVM switch. This switch might be on a
desktop or mounted in a rack.
To connect a LANserver to a KVM switch:
1. Locate a KVM cable (customer-supplied).
2-9
2. Attach the KVM cable connector to a free connector on the back of
the KVM switch. Secure the connector with the thumbscrews on
the connector.
3. Attach the 15-pin connector on the monitor cable to the video port
on the back of the LANserver. Secure the connector with the
thumbscrews on the connector.
4. Push the keyboard cable connector into the keyboard connector on
the back of the LANserver. The keyboard connector is at the
bottom left of the connectors on the LANserver.
5. Push the mouse cable connector into the mouse connector on the
back of the LANserver. The mouse connector is directly above the
keyboard connector.
Installing the LANserver Hardware
Page 30

2-10
Installing the CD-ROM Drive
To install the CD-ROM drive:
1. Position the CD-ROM drive on the top front of the LANserver,
centered between the rack rails.
2. Locate the Avid-supplied SCSI cable and the 68-pin to 50-pin SCSI
adapter.
3. Attach the 68-pin connector on one end of the SCSI cable to the
68-pin connector on the SCSI adapter. Secure the connector with
the thumbscrews on the cable connector.
4. Attach the 68-pin connector on the other end of the SCSI cable to
the 68-pin connector on the SCSI adapter board in the LANserver.
The board is in the bottom slot.
5. Attach the 50-pin connector on the SCSI adapter to the bottom
50-pin connector on the back of the CD-ROM drive. You should
hear a click when the connector is secure.
Installing the Ethernet Switch Rack-Mount Bracket
Follow the instructions supplied with the Ethernet switch to install the
rack-mount bracket and ensure that:
• The bottom of the switch is at the bottom of a U-alignment space.
• The switch is mounted directly above the CD-ROM drive or below
the LANserver.
• There is adequate space to run and connect Ethernet cables to the
front of the switch.
Installing the LANserver and Ethernet Switch
Page 31

Mounting the Ethernet Switch
To mount the Ethernet switch on the rack-mount bracket:
1. Position the switch above the CD-ROM drive or below the
LANserver.
2. Attach the switch to the rack with the large mounting screws and
washers supplied in the Ethernet switch kit.
3. Locate a 25-foot (7.5-meter) optical gigabit Ethernet cable in the
Ethernet switch kit. Look for an orange cable with a dual plug on
each end (see Figure 2-3).
2-11
c
Gigabit Ethernet
adapter board
Handle the optical cable carefully. It can be easily damaged if it is
pinched or crimped.
Optical cable
4. Remove the protective covers from the connectors on one end of
the optical cable.
5. Remove the protective cover from the Ethernet adapter board in
the LANserver. The board is located in the top slot.
6. Firmly push the cable connector into the gigabit Ethernet adapter
board connector on the LANserver (see Figure 2-3). Make sure the
alignment tabs on the cable connector face down.
LEDs
Optical connector
Figure 2-3 Attaching Optical Cable to the Gigabit Ethernet
Adapter Board
Installing the LANserver Hardware
Page 32

2-12
7. Route the cable to the front of the switch.
8. Remove the protective covers from the connectors on the other
end of the optical cable.
9. Remove the protective cover from switch port 17 (the top
connector).
10. Firmly push the cable connector into the top gigabit Ethernet port
on the switch. Make sure the alignment tabs on the cable
connector face up.
Connecting Power Cords
Before you attach the power cords to the LANshare components, make
sure the Power switches on the LANserver and the CD-ROM drive are
in the off (O) position.
n
The Ethernet switch has no Power switch and will turn on when you plug the
power cords into a power outlet.
To connect the power cords to the LANserver and other components:
1. Plug one power cord into the right power connector on the back of
the LANserver.
2. Plug one power cord into the left power connector on the back of
the LANserver.
3. Plug the power cords into power outlets.
4. Plug the power cord into the back of the Ethernet switch.
5. Plug the power cord into a power outlet. You should see some of
the LEDs on the front of the switch light and hear the fan when the
switch is plugged in.
6. Plug the power cord into the back of the CD-ROM drive.
7. Plug the power cord into a power outlet.
8. Plug the monitor power cord into a power outlet.
Installing the LANserver and Ethernet Switch
Page 33

2-13
Installing the Application Key
To install the application key (dongle):
1. Locate the application key in the LANshare kit.
2. Attach the application key to the parallel port on the back of the
LANserver. Secure the application key with the thumbscrews on
the key.
Connecting a LANshare Workgroup to an In-House Network
To allow the clients in your LANshare workgroup to easily share
project information with other Ethernet clients or to use other network
services, you can connect the LANshare workgroup to your 10BASE-T
or 100BASE-T in-house Ethernet local area network (LAN).
n
c
c
If you have multiple LANshare workgroups, you can connect each
Ethernet switch directly to the LAN, or cascade the Ethernet switches
and connect only one of them to the LAN.
A connection to a LAN is not a requirement to allow access by Ethernet
clients to MediaNet workspaces shared by the LANserver. Avid does not
install, configure, or troubleshoot LANs. If you are having trouble with your
LAN, consult your Information Services department or your network vendor.
When you are connecting the LANserver to an in-house network,
make sure you use only Category 5 or Category 5e Ethernet cables.
Using other cable types can cause LANserver performance
problems.
Avid recommends you connect the LANserver to an in-house
network using only port 16 on the Ethernet switch. Using either of
the built-in 10/100BASE-T Ethernet connections can cause an
increase in login time.
Connecting a LANshare Workgroup to an In-House Network
Page 34

2-14
Making the Connection to the In-House Network
You connect your Ethernet switch to your LAN through port 16, which
can be configured to have uplink (MDI) wiring.
n
If you have multiple LANshare workgroups and would like to cascade the
switches to have a single Ethernet connection, skip this section and continue
with “Cascading Multiple Ethernet Switches” on page 2-14.
To connect a single Ethernet switch to the site network:
1. Attach an RJ-45 cable to port 16 on the Ethernet switch.
2. Attach the other end of the RJ-45 cable to a suitable LAN jack.
3. Press the Normal/Uplink button so it is pushed in, thus
configuring port 16 for uplink wiring. Confirm that the switch is in
the appropriate position by checking that the port’s connection
LED lights up (see Figure 2-4).
Cascading Multiple Ethernet Switches
If you have multiple LANshare workgroups (and, therefore, multiple
Ethernet switches), you can attach them all to your LAN using a single
network port by cascading the Ethernet switches.
To cascade Ethernet switches:
1. Attach an RJ-45 cable to port 16 on the first Ethernet switch.
2. Press the Normal/Uplink button so it is pushed in, thus
configuring port 16 for uplink wiring. Confirm that the switch is in
the appropriate position by checking that the port’s connection
LED lights up (see Figure 2-4).
Installing the LANserver and Ethernet Switch
Page 35

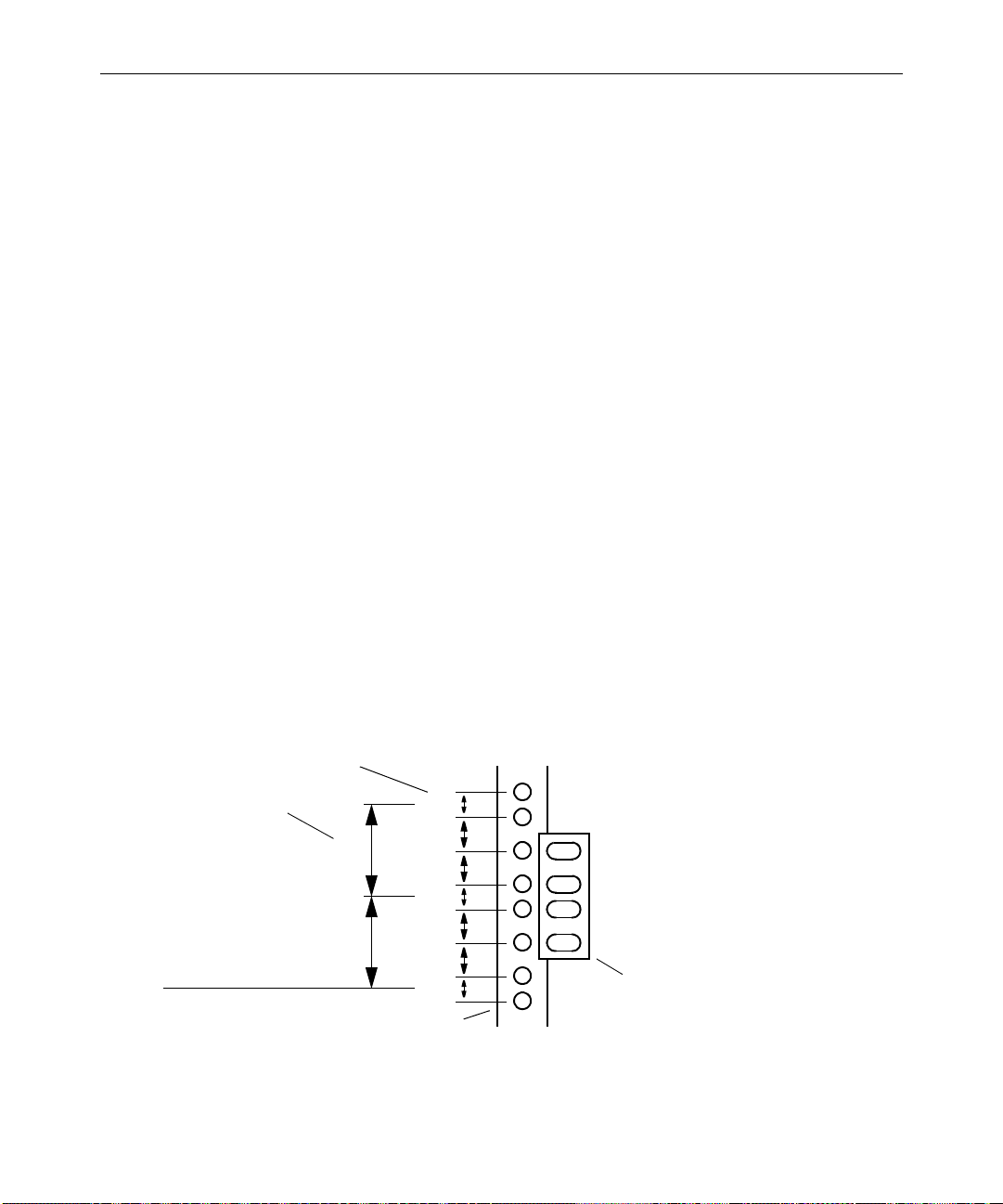
2-15
Ports 1 to 8
Ports 9 to 15
Normal/Uplink button
Port 16
Figure 2-4 Ethernet Switch Ports
3. Attach the other end of the RJ-45 cable to a free port (port 1 to
port 15) on the next uncascaded Ethernet switch (see Figure 2-5).
4. Attach an RJ-45 cable to port 16 on the Ethernet switch you just
cascaded, and then determine whether there are more Ethernet
switches to cascade:
t If there is another Ethernet switch to cascade, repeat steps 2
to 4.
t If there are no more Ethernet switches to cascade, proceed to
step 5.
5. Locate the other end of the RJ-45 cable you connected to port 16 on
the last Ethernet switch, and attach it to a suitable LAN jack (see
Figure 2-5).
Ethernet switch 1
Figure 2-5 Cascading Ethernet Switches
Ethernet switch 2 Ethernet switch
Connection from port 16
on Ethernet switch 1 to a
free port on Ethernet
switch 2 (ports 1 to 15)
Connecting a LANshare Workgroup to an In-House Network
Connection from port 16
on Ethernet switch 2 to a
free port on Ethernet
N
switch
(ports 1 to 15)
N
(up to 10)
Connection
to in-house
network
Page 36

2-16
6. Press the Normal/Uplink button so it is pushed in, thus
configuring port 16 for uplink wiring. Confirm that the switch is in
the appropriate position by checking that the port’s connection
LED lights up.
Turning On the LANser ver Hardware
You can now turn on power to your LANserver hardware. When you
turn on the power, it is order-dependent so the LANserver will see all
of its connected components.
To turn on the power for each component:
1. The Ethernet switch has no Power switch. It turns on when you
plug the power cord into a power outlet.
2. Turn on the Power switch for the monitor.
3. Turn on the Power switch for the external CD-ROM drive.
n
n
Installing the LANserver and Ethernet Switch
If the doors on the LANserver are locked, locate one of the keys (supplied in
the LANserver) to unlock the front doors.
4. Open the front doors on the LANserver and push the Power
switch to |. It is a rocker switch and returns to the O position after
you push it.
Watch the monitor. You should see the LANserver boot sequence
begin. Wait for the Windows operating system to load before you
attempt to use the LANserver.
It takes approximately 3 minutes for the boot sequence to complete and
another minute for the Windows operating system to load.
Page 37

Configuring the LANserver Using Windows 2000 Setup
The first time you boot your LANserver, it runs the Windows 2000
Setup utility to set several Windows operating system parameters.
You’ll need to have the Windows software kit available when you run
the utility. It contains the Windows license number that you need to
type as part of the configuration.
To set up the Windows operating system:
1. The Windows 2000 Setup utility starts and the Windows 2000
Server Setup dialog box appears showing the License Agreement
screen.
2. Click the Agree radio button to accept the license.
3. Click Next. The Regional Settings screen appears.
t If you are outside the United States, customize the system and
locale settings, and the keyboard for your location.
2-17
t If you are in the United States, continue.
4. Click Next. The Personalize Your Software screen appears.
5. Type the system administrator’s name in the Name text box.
6. Type the company name in the Organization text box.
7. Click Next. The Your Product Key screen appears.
8. Type the Product Key from the Certificate of Authenticity in the
Product key text box. The certificate might be on the back of the
Windows 2000 Server Getting Started Guide in the Windows software
kit, or it might be affixed to the LANserver.
If the certificate is not already affixed to the LANserver, remove it
from the Windows 2000 Server Getting Started Guide and affix it
now.
9. Click Next. The License Modes screen appears.
Configuring the LANserver Using Windows 2000 Setup
Page 38

2-18
10. Click the Per Server radio button and set the number of concurrent
connections to 10.
11. Click Next. The Computer Name and Administrator Password
screen appears.
12. Type the name you want to use for the LANserver in the
Computer name text box.
n
Avid recommends you use an administrator password to prevent
unauthorized use of the Administrator account.
13. Type the password you want to use for the administrator account
in the Administrator Password text box.
14. Confirm the password by retyping the password in the Confirm
password text box.
15. Click Next. The Date and Time Settings screen appears. Set the
correct date, time, and time zone for the LANserver.
16. Click the “Automatically adjust clock for daylight saving changes”
check box if your location observes daylight saving time.
17. Click Next. The Network Settings screen appears.
18. Click the Typical radio button. The network settings are site
dependent and will be set later during the LANserver
configuration in Chapter 3.
19. Click Next. The Workgroup and Computer Domain screen
appears.
20. Click No. The workgroup and domain settings are site dependent
and will be set later during the LANserver configuration in
Chapter 3. The Performing Final Tasks screen appears, followed
by the Complete the Windows 2000 Setup Wizard screen.
21. Click Finish. The Windows 2000 operating system is loaded.
Your LANshare workgroup hardware installation is complete.
Continue with Chapter 3 to configure the LANserver and to install the
LANshare software.
Installing the LANserver and Ethernet Switch
Page 39

CHAPTER 3
Configuring a LANserver
This chapter describes how to configure some of the LANserver
operating system parameters and install the LANshare software on
the LANserver.
Topics in this chapter include:
• Setting Up the LANserver
• Installing the LANserver Software
• Configuring the MediaNet Software
• Sharing MediaNet Workspaces
• Configuring Windows Network Permissions for Workspace
Sharing
• Allowing Network Installation of Ethernet Client Software
Page 40

3-2
Setting Up the LANserver
Your LANserver ships with the Windows 2000 Server operating
system, Service Pack 2, and all the necessary drivers preinstalled. You
do not need to perform any configuration operations on these items.
You do need to configure the LANserver for the correct date and time,
computer name, and network properties so that it will function
properly at your site. To set up the LANserver, you should perform all
the operations in the following sections.
Quick Summary
• Accurately set the date, time, and time zone.
• Specify a unique Computer Name by which all Ethernet clients
will identify the LANserver.
• Configure a static IP address and, if necessary, a gateway IP
address for the gigabit Ethernet network adapter.
Setting the Date, Time, and Time Zone
You need to correctly set the date, time, time zone, and daylight saving
time option on each LANserver.
To set the date, time, time zone, and daylight saving time option on a
LANserver:
1. Double-click the time in the taskbar. The Date/Time Properties
dialog box appears.
2. Set the date and time by using the Date & Time tab.
3. Click the Time Zone tab.
Configuring a LANserver
Page 41

4. Set the time zone for the location of the LANserver. By default,
Windows 2000 sets the time zone to “(GMT - 8:00) Pacific Time (US
& Canada), Tijuana.”
5. Make sure the “Automatically adjust clock for daylight saving
changes” option is selected if your location observes daylight
saving time.
6. Click OK to close the Date/Time Properties dialog box and save
the settings.
Specifying a Unique Computer Name
To specify a unique computer name by which clients identify your
LANserver:
1. Right-click the My Computer icon on the desktop, and choose
Properties from the pop-up menu that appears. The System
Properties dialog box appears.
3-3
2. Click the Network Identification tab.
3. Click the Properties button. The Identification Changes dialog box
appears.
4. Specify the LANserver name by typing it in the Computer name
text box.
5. Determine if you need to select the Domain or Workgroup in the
“Member of” section at the bottom of the dialog box. Contact your
network administrator for assistance.
6. Click OK.
7. Close all open windows and dialog boxes.
Setting Up the LANserver
Page 42

3-4
IP Addressing Strategies When Connecting to a Network
If your LANserver and Ethernet clients are connected to your in-house
network, the LANserver and each client must be properly configured
with a unique, valid IP address and subnet mask.
Your site network administrator should determine how best to allocate
IP addresses for systems on your in-house network, bearing in mind
the following:
• You must assign a static IP address to the gigabit Ethernet adapter
on the LANserver — the Ethernet clients are configured to locate
the LANserver using this address.
• You can assign static IP addresses to the Ethernet clients or use
DHCP to obtain them dynamically if you have a DHCP server on
the network.
• However you assign the Ethernet client IP addresses, the
LANserver and all clients must have addresses in the same
subnet.
Configuring the LANserver Network Properties
You need to configure each LANserver’s network properties so that it
can communicate with the network. Each LANserver has three
possible network connections: a gigabit Ethernet adapter and two
built-in 10/100BASE-T adapters. You need to provide a static IP
address and subnet mask for the gigabit Ethernet adapter.
To configure Network Properties for the gigabit Ethernet adapter:
1. Right-click the My Network Places icon on the desktop and choose
Properties from the pop-up menu that appears. The Network and
Dial-up Connections dialog box appears.
2. Click the View menu and choose Details. The window changes to
show details about its contents.
Configuring a LANserver
Page 43

3-5
3. Locate the Local Area Connection that is identified as Intel(R)
Pro/1000 F Server Adapter.
4. Double-click this Local Area Connection’s icon. The Local Area
Connection Status dialog box appears.
5. Click Properties. The Local Area Connection’s Properties dialog
box appears.
6. Select the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) option.
7. Click Properties. The Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties dialog
box appears.
8. Select the “Use the following IP address” option.
9. Type a unique IP address in the IP address text box (see “IP
Addressing Strategies When Connecting to a Network” on
page 3-4), and press Enter. The LANserver should fill in the subnet
mask appropriately. If not, type the appropriate subnet mask in
the Subnet mask text box.
10. If necessary, type a gateway IP address in the Default gateway text
box.
11. If necessary, type a Preferred and Alternate DNS server IP address
in the Preferred DNS server and Alternate DNS server text boxes.
12. Click Advanced. The Advanced TCP/IP Settings dialog box
appears.
13. Click the DNS tab.
14. If necessary, type a DNS name in the “DNS suffix for the
connection” text box.
15. Click OK to close each of the open dialog boxes and save the
changes.
16. Close all the remaining open windows and dialog boxes.
17. Click the Start button and then select Shut Down. The Shut Down
Windows dialog box appears.
18. Choose Restart from the menu and then click OK. The LANserver
reboots.
Setting Up the LANserver
Page 44

3-6
Installing the LANserver Software
The MediaNet software allows the LANserver to share MediaNet
workspaces. This software is supplied on the MediaNet Release
CD-ROM in the LANshare installation kit.
To install the MediaNet software on the LANserver:
1. Locate the MediaNet Release 2.2 (or later) CD-ROM.
2. Insert the CD-ROM into the LANserver external CD-ROM drive.
The CD-ROM is set to auto-start and opens the Avid Unity
Installation window. This takes approximately 30 seconds.
If the CD-ROM does not auto-start, you can start the installation
manually as follows:
a. Double-click the My Computer icon on the desktop. The My
Computer window opens.
b. Right-click the CD-ROM icon and choose AutoPlay from the
pop-up menu that appears. The Avid Unity Installation
window opens.
Configuring a LANserver
3. Click LANshare. The screen changes to the LANshare options.
4. Click LANserver. The Question dialog box appears noting the
prerequisite software that needs to be installed.
t If all the prerequisite software is installed, click Yes and
continue with step 5. The InstallShield Wizard dialog box
appears.
t If some of the software is not installed, click No to quit the
installer and install the prerequisite software. Then, begin the
LANshare installation again.
5. Accept the default values presented by the InstallShield Wizard.
6. Click Finish to install the LANshare and MediaNet software, and
reboot the LANserver.
7. Log in to the LANserver as Administrator.
Page 45

8. To verify that the MediaNet software is correctly installed:
a. Right-click the My Computer icon on the desktop, and choose
Manage from the pop-up menu that appears. The Computer
Management window opens.
b. Expand Services and Applications.
c. Click Services. A list of services appears in the right portion of
the window.
d. Locate the Avid Unity PortServer service. It should have a
Status of Started and a Startup Type of Automatic.
Configuring the MediaNet Software
You need to configure the MediaNet software to establish a
functioning LANshare workgroup. This configuration requires that
you:
3-7
• Create a drive set
• Create an allocation group
• Create several workspaces
• Create user accounts
While you are performing the configuration, you will need to refer to
the Avid Unity MediaNet Management Guide for information about the
MediaNet configuration tools. You should also read the first two
chapters of the guide. They describe the MediaNet software and the
tools.
Creating a Drive Set
The drive set defines the drives that the MediaNet software can use to
store data. Each MediaNet workgroup can have only one drive set.
Configuring the MediaNet Software
Page 46

3-8
To create a drive set for your LANshare workgroup:
1. Start the Setup Manager. See the Avid Unity MediaNet Management
Guide for additional information about using the Setup Manager.
2. Click Raw Drives in the left portion of the window.
3. Select all eight drives that appear in the right portion of the
window.
4. Click the Drive Set menu and choose Create Data Drive Set.
5. Click OK. The drive set is created.
6. Click Data Drive Set in the left portion of the window. All of the
drives should move from Raw Drives to Data Drive Set.
7. Quit the Setup Manager.
Creating an Allocation Group
An allocation group defines how the drives in a drive set are
partitioned to store data.
n
Configuring a LANserver
To create an allocation group:
1. Open the Administration Tool. See the Avid Unity MediaNet
Management Guide for additional information about using the
Administration Tool.
2. Click the Allocation Groups tab.
3. Click the Partition Disk Set icon in the left portion of the window.
All of the drives should appear in the right portion of the window.
4. Select each of the drives by clicking the check box before the drive
number.
For best performance, Avid recommends you create a single allocation group
using all eight drives. You can then create multiple workspaces within the
allocation group.
Page 47

5. Click the New Group button. A dialog box appears asking if you
are sure you want to create the allocation group.
6. Click Yes. The allocation group is created.
7. Leave the Administration Tool running.
Creating Workspaces
Workspaces are locations to store and segregate data. You can allow
users to access some or all of the workspaces, and assign permissions
for how each user can access the data in a workspace.
3-9
n
All new workspaces are created with protection enabled. Avid recommends
you leave your workspaces protected. Protection creates a copy of the files you
store in a workspace. The file copy resides on different drives from the original
file. When several clients want to play the same file, MediaNet steers clients
to either the original or the copy of the file to provide maximum playback
performance. Protection also allows you to rebuild the data on a drive, if one
of your drives should fail.
To create a workspace:
1. Click the Workspace tab in the Administration Tool. See the Avid
Unity MediaNet Management Guide for additional information
about using the Administration Tool.
2. Click the turn-down arrow before Partition Disk Set. The
allocation group appears.
3. Click the Allocation Group icon and then click the New
Workspace button. A 1-GB workspace is created.
4. Click the turn-down arrow before the allocation group. The
workspace appears.
5. Click the workspace name, type the name you want for the
workspace, and press Enter. The workspace name changes.
6. Resize the workspace, to make it larger, by clicking the resize
handle and dragging it to the right.
Configuring the MediaNet Software
Page 48

3-10
7. Repeat steps 3 to 6 to create as many workspaces as you might
need.
8. Leave the Administration Tool running.
n
You can create as many workspaces as you need to support different projects.
Due to the physical restrictions of drive letters, the LANserver can only
mount a maximum of 21 workspaces at a time.
Creating User Accounts
User accounts allow individual users, or groups of users, access to the
LANshare workgroup. These accounts allow users to mount or map
MediaNet workspaces on their Avid workstations.
To create a user account:
1. Click the User tab in the Administration Tool. See the Avid Unity
MediaNet Management Guide for additional information about
using the Administration Tool.
2. Click the turn-down arrow before Partition Disk Set. The
allocation group appears.
3. Click the turn-down arrow before the allocation group. The
workspaces appear.
4. Click the New User button in the right portion of the window. A
new user is created and appears in the column head area.
Configuring a LANserver
5. Double-click the user name. The Change User Name dialog box
appears.
6. Type the desired user name in the text box and click OK. The user
name changes.
7. Click the user name and then click the Set Password button. The
Set Password dialog box appears.
8. Type the desired password in the text box and click OK. The user’s
password is saved.
Page 49

9. Click the permissions below the user name for each workspace,
and set them accordingly to No Access (N), Read (R), or
Read/Write (R/W).
10. Repeat steps 4 to 9 for each user.
11. Close the Administration Tool.
Sharing MediaNet Workspaces
The LANserver software includes the Avid Unity PortServer service
that automatically mounts and shares MediaNet workspaces. The
workspaces are mounted in response to mount requests received from
the Connection Manager application on Ethernet clients. The service
can mount up to 21 workspaces.
The Avid Unity PortServer service starts automatically when you boot
the LANserver. On startup (and every 60 seconds thereafter), the
service reads MediaNet configuration information to obtain
workspace, user, and access privilege information. It then uses this
information to remount and reshare MediaNet workspaces to
LANshare clients with the correct access privileges.
3-11
Configuring User Accounts and Permissions
This section assumes you are a Windows network administrator with
a working knowledge of managing Windows users, groups, and
permissions. Windows user accounts and permissions can be local to
the LANserver or supplied by a Windows domain (if the LANserver is
part of a network). For more information about Windows users,
groups, and permissions, contact your network administrator or
consult the Windows 2000 Help system
Sharing MediaNet Workspaces
Page 50

3-12
On the LANserver, the Connection Manager matches MediaNet users,
and Windows users or groups to validate access to MediaNet
workspaces. When the Connection Manager finds a match between a
MediaNet user account and a Windows user account or group, it
applies the appropriate permissions to each MediaNet workspace to
which the user has access. The requested workspaces can then be
mounted on the MediaNet client.
When the Connection Manager cannot find a match between a
MediaNet user account and a Windows user account or group, it
displays a Login dialog box requesting the user to type a valid
Windows/MediaNet user account and password. If these are not
supplied, the user login request is denied.
The following examples provide information about how and where to
create the necessary user accounts for MediaNet and Windows.
Example 1 – Standalone LANshare Workgroup Using Local User
Accounts
n
Configuring a LANserver
You are creating a standalone LANshare workgroup and want to
allow individual users access to MediaNet workspaces. In this
workgroup you need to create three user accounts:
• A MediaNet user account for each Windows and Macintosh user
on the LANserver
• A Windows user account for each Windows and Macintosh user
on the LANserver
• A Windows user account for each user on the Windows client
No user account is required on a Macintosh client.
The MediaNet user account and the Windows user account (on the
LANserver and the Windows client) must have the same user name
and password to allow user login and permission setting. Users
should log in to the client using their client user account and
password. Figure 3-1 shows where the Windows and MediaNet user
accounts are created.
Page 51

3-13
Windows User
LANserver
MediaNet User
Windows User
Windows
Client
Macintosh
Client
Figure 3-1 Standalone User Accounts
For this example, you have several people working on different
projects that need access to different workspaces. You could create all
the user accounts in the following manner:
• On the LANserver, create a MediaNet user account “Fred” with a
password of “seven.” Assign this account read/write permission
to the necessary MediaNet workspaces, and read or no access
permission to other workspaces on the LANserver.
• On the LANserver, create a Windows user account “Fred” with a
password of “seven.”
• On the client, create a Windows user account “Fred” with a
password of “seven.”
Example 2 – Standalone LANshare Workgroup Using Local
Groups
You are creating a standalone LANshare workgroup and want to
allow a group of users access to MediaNet workspaces. In this
workgroup you need to create three user accounts and one Windows
group:
Configuring User Accounts and Permissions
Page 52

3-14
• A MediaNet user account for the group on the LANserver
• A Windows group on the LANserver
• A Windows user account for each Windows and Macintosh user
on the LANserver
• A Windows user account for each user on the Windows client
n
No user account is required on a Macintosh client.
The MediaNet user account and the Windows group (on the
LANserver and the Windows client) must have the same name to
allow user login and permission setting. Users should log in to the
client using their client user account and password. Figure 3-2 shows
where the Windows and MediaNet user accounts and the Windows
group are created.
Windows Group
Windows User
LANserver
MediaNet User
Windows User
Windows
Client
Macintosh
Client
Configuring a LANserver
Figure 3-2 Standalone User Accounts and Groups
For this example, you want to give several people working on a project
access to the same workspaces with the same permissions. You could
create all the user accounts in the following manner:
Page 53

3-15
• On the LANserver, create a MediaNet user account “ProjectA”
with a password of” six.” Assign this account read/write
permission to the necessary MediaNet workspaces, and read or no
access permission to other workspaces on the LANserver.
• On the LANserver, create a Windows user account “Fred” with a
password of “seven” and a Windows user account “Jill” with the
password “twelve.”
• On the LANserver, create a Windows group “ProjectA.” Add
“Fred” and “Jill” to the “ProjectA” group.
• On the client, create a Windows user account “Fred” with a
password of “seven” and a Windows user account “Jill” with the
password “twelve.”
Example 3 – Network LANshare Workgroup Using Domain User
Accounts
You are creating a network LANshare workgroup (the LANserver is
part of a Windows domain) and want to allow individual users access
to MediaNet workspaces. In this workgroup you need to create two
user accounts:
n
n
• A MediaNet user account for each Windows and Macintosh user
on the LANserver
• A Windows user account for each Windows and Macintosh user
on the domain server
No user account is required on a Macintosh client.
The LANserver and all of its clients must be a part of the same Windows
domain.
The MediaNet user account and the Windows user account must have
the same user name and password to allow user login and permission
setting. Users should log in to the client using their Windows domain
user account and password. Figure 3-3 shows where the Windows and
MediaNet user accounts are created.
Configuring User Accounts and Permissions
Page 54

3-16
Windows User
Windows
Client
Domain
Server
LANserver
Macintosh
Client
MediaNet User
Figure 3-3 Network User Accounts
For this example, you have several people working on different
projects that need access to different workspaces. You could create all
the user accounts in the following manner:
• On the LANserver, create a MediaNet user account “Fred” with a
password of “seven.” Assign this account read/write permission
to the necessary MediaNet workspaces, and read or no access
permission to other workspaces on the LANserver.
• On the Windows domain server, create a Windows user account
“Fred” with a password of “seven.”
Example 4 – Network LANshare Workgroup Using Domain
Groups
Configuring a LANserver
You are creating a network LANshare workgroup (the LANserver is
part of a Windows domain) and want to allow a group of users access
to MediaNet workspaces. In this workgroup you need to create two
user accounts and one Windows group:
• A MediaNet user account for the group on the LANserver
• A Windows group on the domain server
Page 55

3-17
• A Windows user account for each Windows and Macintosh user
on the domain server
n
n
No user account is required on a Macintosh client.
The LANserver and all of its clients must be a part of the same Windows
domain.
The MediaNet user account and the Windows group must have the
same name to allow user login and permission setting. Users should
log in to the client using their Windows domain user account and
password. Figure 3-4 shows where the Windows and MediaNet user
accounts and the Windows group are created.
Windows Group
Windows User
Windows
Client
Domain
Server
LANserver
Macintosh
Client
MediaNet User
Figure 3-4 Network User Accounts and Groups
For this example, you want to give several people working on a project
access to the same workspaces with the same permissions. You could
create all the user accounts in the following manner:
• On the LANserver, create a MediaNet user account “ProjectA”
with a password of “six.” Assign this account read/write
Configuring User Accounts and Permissions
Page 56

3-18
permission to the necessary MediaNet workspaces, and read or no
access permission to other workspaces on the LANserver.
• On the Windows domain server, create a Windows user account
“Fred” with a password of “seven” and a Windows user account
“Jill” with the password “twelve.”
• On the Windows domain server, create a Windows group
“ProjectA.” Add “Fred” and “Jill” to the “ProjectA” group.
Allowing Network Installation of Ethernet Client Software
The Windows Ethernet client software installer is included as part of
the LANserver installation (in D:\Program Files\Avid
Technology\AvidUnity\Ethernet Client Setup), if you accepted the
defaults during the installation. If you share the Ethernet Client Setup
folder you (or other users with the appropriate access permissions)
can install the Windows Ethernet client software on any connected
Windows Ethernet client over the network without using the
MediaNet Release CD-ROM.
Configuring a LANserver
To share the Ethernet Client Setup folder to allow network
installation of the Windows 2000 Ethernet client software:
1. Open Windows Explorer.
2. Navigate to D:\Program Files\Avid Technology\AvidUnity.
3. Right-click the Ethernet Client Setup folder and choose Sharing
from the pop-up menu that appears. The Ethernet Client Setup
Properties dialog box appears.
4. Select the “Share this folder” option.
5. Type the name you want to use for the folder in the Share name
text box.
6. Click OK. The dialog box closes and the sharing hand appears
under the folder.
Page 57

CHAPTER 4
Setting Up Windows Ethernet Clients
Each Windows Ethernet client needs to be properly configured and
have the correct software installed to function properly in the
LANshare workgroup.
Topics in this chapter include:
• Installation Prerequisites
• Connecting a Windows Ethernet Client
• Setting the Date, Time, and Time Zone
• Installing the Avid Composer Products Software
• Installing the Windows Ethernet Client Software
•Finishing Up
• Reconfiguring the IP Address of the LANserver
Page 58

4-2
Installation Prerequisites
The MediaNet software requires that several software packages be
installed before you attempt to perform an installation. Attempting to
perform an Ethernet client installation without these prerequisite
software packages will cause the Ethernet client installer to quit.
Windows 2000 Ethernet Client Prerequisites
The Ethernet client requires the following software:
• Windows 2000 Service Pack 2
• Windows 2000 hotfixes, if necessary
• Internet Explorer Version 5.5 or later
You should take the time to install Internet Explorer on the Windows
Ethernet client now, if you are not running Version 5.5 or later. A copy
of Internet Explorer Version 5.5 is provided on the MediaNet Release
CD-ROM in the directory \Extras\IE55\.
If necessary, you should take the time to install the Windows 2000
hotfixes on the Windows Ethernet client now. These hotfixes are
required. See the Avid Unity MediaNet Release Notes for more
information on the hotfixes and how to install them.
c
Failing to install the hotfixes can cause unpredictable results or
performance problems when you attempt to use the client.
Connecting a Windows Ethernet Client
You connect a Windows Ethernet client to the LANshare workgroup
by connecting its Ethernet 10BASE-T/100BASE-T (RJ-45) port to a
10/100BASE-T port on the Ethernet switch.
Setting Up Windows Ethernet Clients
Page 59

4-3
c
c
RJ-45 port
The Ethernet path between the LANserver and Ethernet clients must
be a direct, full-duplex connection using the Avid-supplied Ethernet
switch. Adding other half-duplex devices between the LANserver
and its clients, or attempting to connect clients using other switches
or hubs, is not supported.
When you are connecting the Ethernet client to the Ethernet switch,
make sure you use only Category 5 or Category 5e Ethernet cables.
Using other cable types can cause client performance problems.
To connect a Windows Ethernet client’s RJ-45 port to the Ethernet
switch:
1. Connect the RJ-45 cable to the RJ-45 port on the rear of the client
(see Figure 4-1).
RJ-45 connector
To Ethernet switch
Figure 4-1 Connecting the Ethernet Cable to the Ethernet Client
2. Connect the other end of the RJ-45 cable to an empty
10/100BASE-T port, between port 1 and port 15, on the Ethernet
switch (see Figure 4-2).
Ports 1 to 8
Ports 9 to 15
Figure 4-2 Connecting the Ethernet Cable to the Ethernet
Switch
Connecting a Windows Ethernet Client
Page 60

4-4
Setting the Date, Time, and Time Zone
You need to correctly set the date, time, time zone, and daylight saving
time option on the Ethernet client. This allows the “Synchronize the
system clock with the PortServer or LANserver” function on the
clients to work correctly.
To set the date, time, time zone, and daylight saving time option on
the Ethernet client:
1. Double-click the time in the taskbar. The Date/Time Properties
dialog box appears.
2. Set the date and time using the Date & Time tab.
3. Click the Time Zone tab.
4. Set the time zone for the location of the Windows Ethernet client.
By default, Windows 2000 sets the time zone to “(GMT - 8:00)
Pacific Time (US & Canada), Tijuana.”
5. Make sure the “Automatically adjust clock for daylight saving
changes” option is selected if your location observes daylight
saving time.
6. Click OK to close the Date/Time Properties dialog box and save
the settings.
After you correctly reset the date, time, and time zone, and activate the
daylight saving time option on the Ethernet client, reboot the client.
This ensures the Ethernet client software is using the correct time.
Setting Up Windows Ethernet Clients
Page 61

Configuring Network Properties
You need to configure each Ethernet client’s network properties so it
can communicate with the LANserver network.
Before you start to configure your client’s network properties:
• Determine whether you should use static or dynamic
(DHCP/DNS-based) IP addressing.
• If you are using static addressing, obtain an IP address and subnet
mask.
• If you are using dynamic IP addressing, find out whether you
should obtain DNS server addresses automatically or specify them
manually.
• If you are specifying DNS server addresses manually, obtain the
addresses of the site preferred and alternate DNS servers.
To configure the network properties:
4-5
1. Consult your site network administrator to determine whether
you should use static or dynamic (DNS-based) IP addressing.
2. Right-click the My Network Places icon on the desktop and choose
Properties from the pop-up menu that appears. The Network and
Dial-up Connections dialog box appears.
3. Double-click the Local Area Connection icon. The Local Area
Connection Status dialog box appears.
4. Click Properties. The Local Area Connections Properties dialog
box appears.
5. Select the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) option.
6. Click Properties. The Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties dialog
box appears.
Configuring Network Properties
Page 62

4-6
t If you are using static addressing, specify the IP address
assigned by your network administrator:
a. Select the “Use the following IP address” option.
b. Type a unique IP address in the IP address text box, and press
Enter. The subnet mask should fill in appropriately. If not,
type the appropriate subnet mask in the Subnet mask text box.
c. If necessary, type a gateway IP address in the Default gateway
text box.
d. Continue with step 7.
t If you are using dynamic (DHCP/DNS-based) IP addressing and
obtaining the DHCP/DNS server addresses automatically:
a. Select the “Obtain an IP address automatically” option.
b. Select the “Obtain DNS server address automatically” option.
c. Continue with step 7.
t If you are using dynamic address allocation and must manually
specify the addresses of preferred and alternate DNS servers
obtained from the network administrator:
a. Select the “Obtain an IP address automatically” option.
b. Select the “Use the following DNS server addresses” option.
c. Specify the Preferred and Alternate DNS server IP addresses
7. Click OK to set the changes.
8. Close all open windows and dialog boxes.
9. Click the Start button and select Shut Down. The Shut Down
Windows dialog box appears.
10. Choose Restart from the menu and click OK to reboot the Ethernet
client. The Ethernet client restarts with its new IP address.
Setting Up Windows Ethernet Clients
in the appropriate text boxes.
Page 63

Installing the Avid Composer Products Software
Your Windows Ethernet clients require a qualified release of the Avid
Composer Products software to allow them to use the LANserver
storage when connected to a LANshare workgroup. Install the
qualified release of the Avid Composer Products software before you
install the Ethernet client software. Check the Avid Unity MediaNet
Release Notes to determine a qualified release of Avid Composer
Products software.
Installing the Windows Ethernet Client Software
Each Ethernet client requires software to allow it to log in to the
LANserver, mount accessible workspaces, and to read and write data
to those workspaces in real time. The Windows Ethernet client
software is supplied on the MediaNet Release CD-ROM and is also
available for network installation from the LANserver.
4-7
Installing Ethernet Client Software from the CD-ROM
To install the Windows Ethernet client software from the MediaNet
Release CD-ROM:
1. Locate the MediaNet Release 2.2 (or later) CD-ROM.
2. Insert the CD-ROM into the Ethernet client CD-ROM drive. The
CD-ROM is set to auto-start and opens the Avid Unity Installation
window. This takes approximately 1 minute.
If the CD-ROM does not auto-start, you can start the installation
manually as follows:
a. Double-click the My Computer icon on the desktop. The My
Computer window opens.
Installing the Avid Composer Products Software
Page 64

4-8
b. Right-click the CD-ROM icon and choose AutoPlay from the
pop-up menu that appears. The Avid Unity Installation
window opens.
3. Click LANshare. The screen changes to the LANshare options.
4. Click Ethernet Attached Client. The InstallShield Wizard dialog
box appears showing the Welcome screen.
5. Accept the default values presented by the InstallShield Wizard.
6. When prompted, type the IP address of the LANserver to which
the client is connected in the IP address text box.
7. Continue by accepting the default values presented by the
InstallShield Wizard. The Ethernet client software is installed.
8. Reboot the client.
Installing Ethernet Client Software over the Network
The Windows Ethernet client software installer is available on the
LANserver as part of the MediaNet installation.
n
Setting Up Windows Ethernet Clients
For security reasons, the LANserver’s internal drive is not shared by default.
If you want to allow network installation of client software from the
LANserver, you must configure sharing of the Ethernet client installer
directory. For more information, see “Allowing Network Installation of
Ethernet Client Software” on page 3-18.
To install the Windows Ethernet client software from the LANserver
over the network:
1. Using My Network Places, navigate to the LANserver D:\Avid
Technology\AvidUnity and open the Ethernet Client Setup folder
containing the Ethernet client software installer.
2. Double-click Setup. The Ethernet Client Installer window opens
showing the Welcome screen.
3. Accept the default values presented by the InstallShield Wizard.
Page 65

4. When prompted, type the IP address of the LANserver to which
the client is connected in the IP address text box.
5. Continue by accepting the default values presented by the
InstallShield Wizard. The Ethernet client software is installed.
6. Reboot the client.
Mounting Workspaces on a Windows Client
The LANshare kit contains several Avid Unity Windows Ethernet Client
Quick Start Cards. These cards describe how to mount and use
workspaces on the client.
Finishing Up
4-9
You have completed the installation of the Ethernet clients.
Avid recommends you mount a workspace on the client (see the Avid
Unity Windows Ethernet Client Quick Start Card) and perform a
throughput test on it using the Avid Performance Meter utility. This
checks that the client connection is properly established and the
workgroup is functioning correctly. For more information about using
the Avid Performance Meter utility, see Appendix A.
Reconfiguring the Client Connection to a LANserver
You configure the IP address for the LANserver to which a client is
connected when you install the Ethernet client software. Normally,
you should not need to change this address. (The LANshare software
does not currently support connecting a client to any LANserver other
Mounting Workspaces on a Windows Client
Page 66

4-10
than the one to which it is directly connected via the Ethernet switch.)
However, it is possible the client could be moved and connected
directly to another LANserver.
To reconfigure the IP address of the LANserver to which a client is
connected:
1. Click the Connection Manager icon in the Windows taskbar and
choose Configure from the pop-up menu that appears. The
Configure Connection Manager dialog box appears.
2. Type the new IP address of the LANserver to which the client is
connected in the PortServer or LANserver text box.
3. Click OK to close the dialog box and save the change.
4. Quit the Connection Manager by clicking the Connection Manager
icon and choosing Exit from the pop-up menu that appears.
5. Restart the Connection Manager by clicking the Start button,
pointing to Programs, pointing to Startup, and then choosing
Connection Manager from the pop-up menu that appears. The
Connection Manager starts and its icon reappears in the Windows
taskbar.
Setting Up Windows Ethernet Clients
Page 67

CHAPTER 5
Setting Up Macintosh Ethernet Clients
Each Macintosh Ethernet client needs to be properly configured and
have the correct software installed to function properly in the
LANshare workgroup.
Topics in this chapter include:
• Installation Prerequisites
• Connecting a Macintosh Ethernet Client
• Setting the Date, Time, and Time Zone
• Installing the Avid Composer Products Software
• Installing the Macintosh Ethernet Client Software
•Finishing Up
• Reconfiguring the IP Address of the LANserver
Page 68

5-2
Installation Prerequisites
The MediaNet software requires that several software packages be
installed before you attempt to perform an installation. Attempting to
perform an Ethernet client installation without these prerequisite
software packages will cause the Ethernet client installer to quit.
Macintosh Ethernet Client Prerequisites
The Ethernet client requires the following software:
®
•Mac
• Internet Explorer Version 5.0 or later
You should take the time to install Internet Explorer on the Macintosh
Ethernet client now, if you are not running Version 5.0 or later. A copy
of Internet Explorer Version 5.0 is provided on the MediaNet Release
CD-ROM in the directory Extras:IE50:Mac.
OS 9.0.4, 9.1, or 9.2.1
Connecting a Macintosh Ethernet Client
You connect a Macintosh Ethernet client to the LANshare workgroup
by connecting its Ethernet 10BASE-T/100BASE-T (RJ-45) port to a
10/100BASE-T port on the Ethernet switch.
c
Setting Up Macintosh Ethernet Clients
The Ethernet path between the LANserver and Ethernet clients must
be a direct, full-duplex connection using the Avid-supplied Ethernet
switch. Adding other half-duplex devices between the LANserver
and its clients, or attempting to connect clients using other switches
or hubs, is not supported.
Page 69

5-3
c
RJ-45 port
When you are connecting the Ethernet client to the Ethernet switch,
make sure you use only Category 5 or Category 5e Ethernet cables.
Using other cable types can cause client performance problems.
To connect a Macintosh Ethernet client’s RJ-45 port to the Ethernet
switch:
1. Connect the RJ-45 cable to the RJ-45 port on the rear of the client
(see Figure 5-1).
RJ-45 connector
To Ethernet switch
Figure 5-1 Connecting the Ethernet Cable to the Ethernet Client
2. Connect the other end of the RJ-45 cable to an empty
10/100BASE-T port, between port 1 and port 15, on the Ethernet
switch (see Figure 5-2).
Ports 1 to 8
Ports 9 to 15
Figure 5-2 Connecting the Ethernet Cable to the Ethernet
Switch
Connecting a Macintosh Ethernet Client
Page 70

5-4
Setting the Date, Time, and Time Zone
You need to correctly set the date, time, time zone, and daylight saving
time option on the Ethernet client. This allows the “Synchronize the
system clock with the server clock” function on the clients to work
correctly.
n
The following procedure is based on Mac OS 9.1. If you are running a
different version of Mac OS, the process might vary.
To set the date, time, time zone, and daylight saving time option on
the Ethernet client:
1. Choose Date & Time from Control Panels in the Apple menu. The
Date & Time Control Panel opens.
2. Set Current Date and Current Time correctly for the Ethernet client
location.
3. Make sure the “Set Daylight-Saving Time Automatically” option is
selected if your location observes daylight saving time.
4. Click Set Time Zone. A dialog box with a list of cities and countries
appears.
5. Select the name of a city and country closest to the Ethernet client
location from the list box.
6. Click OK to set the time zone.
7. Click the close box on the Date & Time Control Panel to close it
and save the settings.
After you correctly reset the date, time, and time zone, and activate the
daylight saving time option on the Ethernet client, reboot the client.
This ensures the Ethernet client software is using the correct time.
Setting Up Macintosh Ethernet Clients
Page 71

Configuring Network Properties
You need to configure each Ethernet client’s network properties so it
can communicate with the LANserver network.
Before you start to configure your client’s network properties:
• Determine whether you should use static or dynamic
(DHCP/DNS-based) IP addressing.
• If you are using static addressing, obtain an IP address and subnet
mask.
• If you are using dynamic IP addressing, find out whether you
should obtain DNS server addresses automatically or specify them
manually.
• If you are specifying DNS server addresses manually, obtain the
addresses of the site preferred and alternate DNS servers.
To configure the network properties:
5-5
1. Consult your site network administrator to determine whether
you should use static or dynamic (DNS-based) IP addressing.
2. Click the Apple menu, point to Control Panels, and then choose
TCP/IP from the menu that appears. The TCP/IP dialog box
appears.
3. Choose Ethernet from the “Connect via” menu.
t If you are using static addressing, specify the IP addresses
assigned by your network administrator:
a. Choose Manually from the Configure menu.
b. Type the workstation IP address in the IP Address text box.
c. Type the network subnet mask in the Subnet mask text box.
d. If needed, type the gateway IP address in the Router text box.
Configuring Network Properties
Page 72

5-6
e. If needed, type the DNS name server IP address in the “Name
server addr” text box. If you have more than one DNS name
server, type all the name server IP addresses in the text box in
the order you want the servers to be searched.
f. If needed, type the domain name in the Search domains text
box.
g. Continue with step 4.
t If you are using dynamic (DHCP/DNS-based) IP addressing and
obtaining DHCP/DNS server addresses automatically:
a. Choose Using DHCP Server from the Configure menu.
b. If needed, type the system name to associate with the IP
address in the DHCP Client IP text box.
c. If needed, type the domain name in the Search domains text
box.
d. Continue with step 4.
t If you are using dynamic address allocation and must manually
specify the addresses of preferred and alternate DNS servers
obtained from the network administrator:
a. Choose Using DHCP Server from the Configure menu.
b. Choose User Mode from the Edit menu. The User Mode
c. Click Advanced and click OK to save the change.
d. Type the DNS name server IP address in the “Name server
e. If needed, type the domain name in the Search domains text
Setting Up Macintosh Ethernet Clients
dialog box appears.
addr” text box. If you have more than one DNS name server,
type all the name server IP addresses in the text box in the
order you want the servers to be searched.
box.
Page 73

4. Close the dialog box. A message appears asking if you want to
save the changes.
5. Click Save. The dialog box closes and saves the changes.
6. Click the Apple menu, point to Control Panels, and then choose
AppleTalk from the menu that appears. The AppleTalk dialog box
appears.
7. Choose Ethernet from the “Connect via” menu.
8. Close the dialog box. A message appears asking if you want to
save the changes.
9. Click Save. The dialog box closes and saves the changes.
Installing the Avid Composer Products Software
Your Macintosh Ethernet clients require a qualified release of the Avid
Composer Products software to allow them to use the LANserver
storage when connected to a LANshare workgroup. Install the
qualified release of the Avid Composer Products software before you
install the Ethernet client software. Check the Avid Unity MediaNet
Release Notes to determine a qualified release of Avid Composer
Products software.
5-7
Installing the Macintosh Ethernet Client Software
Each Ethernet client requires software to allow it to log in to the
LANserver, mount accessible workspaces, and to read and write data
to those workspaces in real time. The Macintosh Ethernet client
software is supplied on the MediaNet Release CD-ROM.
Installing the Avid Composer Products Software
Page 74

5-8
Installing Ethernet Client Software from the CD-ROM
To install the Macintosh Ethernet client software from the MediaNet
Release CD-ROM:
1. Locate the MediaNet Release 2.2 (or later) CD-ROM.
2. Insert the CD-ROM into the Ethernet client CD-ROM drive. The
MN 2.2 CD-ROM icon appears on the desktop.
3. Double-click the MN 2.2 CD-ROM icon. The MN 2.2 window
opens.
4. Double-click the Avid Unity 2.2 Install icon. The Avid splash
screen appears.
5. Click Continue.
6. Read the license agreement and click Accept. The Avid Unity 2.2
Install window opens. If you click Decline, you will end the
installation.
7. Select the Easy Install option to install all of the necessary software
on the Avid drive.
8. Click Install. A dialog box appears asking which client software do
you want to install.
9. Click LANshare and then click Continue. The LANshare software
is installed in the Avid Unity folder on the Avid drive. After the
LANshare software is installed, a dialog box appears stating that
DAVE
now.
10. Click Yes. The DAVE splash screen appears.
11. Click Continue. The License screen appears.
12. Click Accept to acknowledge the license. The Read Me screen
appears.
13. Click Continue. The DAVE software is installed.
Setting Up Macintosh Ethernet Clients
™
is required and asking if you want to install the software
Page 75

Configuring DAVE
5-9
14. After the DAVE software is installed, a dialog box might appear
informing you that you need to install the Macintosh Runtime
™
library. You must complete the steps in the section
Java
“Installing the Macintosh Runtime Java Library” after you
complete the client software and DAVE configuration.
15. Click OK. A dialog box appears asking if you would like to
Continue, Quit, or Restart the Macintosh client. Click Restart.
After rebooting your Macintosh Ethernet client, you need to configure
DAVE to function in a LANshare workgroup. The DAVE Setup dialog
box appears immediately after you reboot the client.
To configure the DAVE software:
1. Click the right arrow at the bottom of the DAVE Setup
Introduction screen. The Entering Your License Code screen
appears.
2. Type your name in the Name text box.
3. Type your company name in the Organization text box.
4. Type your license code in the License Code text box. The license
code is supplied on a card in the Macintosh Ethernet client kit.
5. Click the right arrow at the bottom of the screen. The Choosing
Your Network Type screen appears.
6. Click Yes and click the right arrow at the bottom of the screen. The
Configuring WINS screen appears.
Installing the Macintosh Ethernet Client Software
Page 76

5-10
7. Do one of the following:
t If your LANshare workgroup is not connected to an in-house
network, click the right arrow at the bottom of the screen. The
Choosing a NetBIOS Name screen appears.
t If your LANshare workgroup is connected to an in-house
network, click the “My Network Uses WINS” check box and
type the IP address for the primary and secondary WINS
servers on your network in the appropriate text boxes. Click
the right arrow at the bottom of the screen. The Choosing a
NetBIOS Name screen appears.
8. Type the computer name you want DAVE to use to identify your
Macintosh Ethernet client on the network in the Name text box.
9. Click the right arrow at the bottom of the screen. The Setting Your
Workgroup screen appears.
10. Do one of the following:
t If your LANshare workgroup is not connected to an in-house
network, click the right arrow at the bottom of the screen. The
Choosing a Description For Your Computer screen appears.
t If your LANshare workgroup is connected to an in-house
11. Type the name you want to appear in the Windows Network
Neighborhood in the Description text box. Make sure there are no
spaces in the name.
12. Click the right arrow at the bottom of the screen. The Configuring
Network Logon screen appears.
13. Click the “I don’t want to log on to the network at startup” check
box.
Setting Up Macintosh Ethernet Clients
network, type the Windows domain name for your network in
the Workgroup text box. Click the right arrow at the bottom of
the screen. The Choosing a Description For Your Computer
screen appears.
Page 77

14. Click the right arrow at the bottom of the screen. The Review
Setting screen appears.
15. Make sure all of the settings are OK before you continue.
t If you need to make changes to the entries, click the left arrow
at the bottom of the screen to back up through the screens and
repeat any of steps 5 to 13.
t If the entries are OK, click the right arrow at the bottom of the
screen. The Share Your Local Files screen appears.
16. Do one of the following:
t If you don’t want to share your files with other systems, click
the right arrow at the bottom of the screen. The Setup
Complete screen appears.
t If you want to share your files with other systems, click the “I
want to set up DAVE to share my local files” option and then
click the right arrow at the bottom of the screen. The DAVE
Sharing Setup screen appears. See the DAVE user guide for
information on setting up DAVE to share your local files.
5-11
17. The DAVE configuration is complete. Reboot the Macintosh
Ethernet client. After the client reboots, both DAVE and the
Connection Manager are running.
Installing the Macintosh Runtime Java Library
To install the Macintosh Runtime Java library:
1. Double-click the Extras folder in the MN 2.2 window. The Extras
window opens.
2. Double-click the MRJ 2.2.4 Installer folder. The MRJ 2.2.4 Installer
window opens.
3. Double-click the MRJ 2.2.4 Install icon. The license agreement
appears.
Installing the Macintosh Ethernet Client Software
Page 78

5-12
4. Read the license agreement and click Agree. The MRJ 2.2.4 Install
window opens. If you click Decline, you will end the installation.
5. Click Install. The library is installed in the Extensions folder. A
message box appears indicating the installation was successful.
6. Click OK. The installation is complete.
Mounting Workspaces on a Macintosh Client
The LANshare kit contains several Avid Unity Macintosh Ethernet Client
Quick Start Cards. These cards describe how to mount and use
workspaces on the client.
Finishing Up
You have completed the installation of the Ethernet clients.
Avid recommends you mount a workspace on the client (see the Avid
Unity Macintosh Ethernet Client Quick Start Card) and perform a
throughput test on it using the Avid Performance Meter utility. This
checks that the client connection is properly established and the
workgroup is functioning correctly. For more information about using
the Avid Performance Meter utility, see Appendix A.
Setting Up Macintosh Ethernet Clients
Page 79

Reconfiguring the Client Connection to a LANserver
You configure the IP address of the LANserver to which a client is
connected when you install the Ethernet client software. Normally,
you should not need to change this address. (The LANshare software
does not currently support connecting a client to any LANserver other
than the one to which it is directly connected via the Ethernet switch.)
However, it is possible the client could be moved and connected
directly to another LANserver.
To reconfigure the IP address of the LANserver to which a client is
connected:
1. Switch to the Connection Manager using the Application menu in
the upper right of the monitor screen. If the Connection Manager
is not running, open the Avid Unity folder on the Avid drive and
double-click the Connection Manager icon.
5-13
2. Click the LANshare menu and choose Configure. The Configure
Connection dialog box appears.
3. Type the new IP address of the LANserver to which the client is
connected in the LANshare Server text box.
4. Click OK to close the dialog box and save the change.
Reconfiguring the Client Connection to a LANserver
Page 80

5-14
Setting Up Macintosh Ethernet Clients
Page 81

CHAPTER 6
Upgrading from
MediaShare F/C
If you are currently using MediaShare™ F/C as your shared storage
solution, you can connect these clients to a LANshare workgroup and
copy your existing project and data files to the LANserver storage.
When your data is copied, you can disconnect the MediaShare F/C
cables and work exclusively from the LANserver storage.
n
MediaShare F/C supports connecting only Macintosh clients to the
MediaShare F/C hub. The following sections apply only to Macintosh clients.
Topics in this chapter include:
• Connecting MediaShare F/C Clients to a LANshare Workgroup
• Copying Data to MediaNet Workspaces
• Disconnecting MediaShare F/C Cables
Page 82

6-2
Connecting MediaShare F/C Clients to a LANshare Workgroup
When you are copying data from a MediaShare F/C workgroup to a
LANshare workgroup, you need to have one or more clients
connected directly to both workgroups. This requires an Ethernet
connection to LANshare and a Fibre Channel connection to the
MediaShare F/C hub (see Figure 6-1).
LANserver
Gigabit Ethernet
100BASE-T Ethernet
Figure 6-1 LANshare to MediaShare F/C Connection
To connect a MediaShare F/C client to a LANshare workgroup:
MediaShare
storage
Ethernet switch
Macintosh client
Macintosh client
Ethernet client
Ethernet client
…
Fibre Channel
MediaShare hub
1. Leave the MediaShare F/C cable connected to the
MediaShare F/C hub (see Figure 6-1).
2. Connect the client to a LANshare workgroup, and install and
configure the Macintosh Ethernet client software as described in
Chapter 5.
Upgrading from MediaShare F/C
Page 83

Copying Data to MediaNet Workspaces
To copy data from MediaShare F/C workspaces to MediaNet
workspaces:
1. Mount the MediaShare F/C workspace from which you want to
copy data on the client desktop.
2. Mount the MediaNet workspace to which you want to copy data
on the client desktop.
3. Open both workspace windows.
4. Click the files you need in the MediaShare F/C workspace
window, and drag them to the MediaNet workspace window.
5. Repeat steps 1 to 4 until all the data you want is copied to the
MediaNet workspace.
Disconnecting MediaShare F/C Cables
6-3
To disconnect the MediaShare F/C client:
1. Loosen the thumbscrews holding the MediaShare F/C cable to the
adapter board in the client.
2. Remove the cable from the adapter board.
Copying Data to MediaNet Workspaces
Page 84

6-4
Upgrading from MediaShare F/C
Page 85

CHAPTER 7
Troubleshooting
This chapter provides information on troubleshooting your LANshare
workgroups.
Topics in this chapter include:
• Using ping and tracert
• Troubleshooting a LANshare Workgroup
• Removing and Replacing LANserver Drives
• Resetting the LANserver Power Supplies
Page 86

7-2
Using ping and tracert
Ethernet networking is the backbone for the LANshare workgroup. If
your Ethernet network is not performing properly, it will affect your
workgroup. The following sections describe how to use two utilities,
ping and tracert, to troubleshoot your network.
ping
You can use the ping utility to confirm that the physical and logical
aspects of your network are correctly configured. Physical aspects
include network interface card, cables, and Ethernet switch. Logical
aspects include IP addresses, subnet masks, and routing.
ping works by sending a packet over the network from an originating
host to a destination host. The destination host receives the packet and
sends a response packet over the network back to the originating host.
If the originating host receives the response packet, it is a good
indication the network is correctly configured.
Troubleshooting
There are many options that can be used with ping. This section
discusses two types of ping syntax:
ping [System Name]
Where [System Name] is the network name of the remote system
to which you are testing connectivity.
or
ping [IP Address]
Where [IP Address] is the IP address of the remote system to
which you are testing connectivity.
Page 87

To run the ping command:
1. Open a Command Prompt window.
2. At the command line, type the ping command (for example,
ping 192.168.10.5).
The ping result should resemble the following:
Reply from 192.168.10.5: bytes=32 time<10ms
TTL=255
Reply from 192.168.10.5: bytes=32 time<10ms
TTL=255
Reply from 192.168.10.5: bytes=32 time<10ms
TTL=255
Reply from 192.168.10.5: bytes=32 time<10ms
TTL=255
Four responses of “Reply from…” indicate the network is
correctly configured and the originating and destination hosts can
see each other on the network.
7-3
If any of the responses in the ping result say:
Request timed out.
or
Destination host unreachable.
It is an indication the network is not correctly configured or there
are other network problems. Some items that can cause network
problems are:
- Bad, loose, or incorrectly connected cables
- Incorrectly configured IP address or subnet mask on local or
remote system
- Excessive network traffic
Using ping and tracert
Page 88

7-4
tracert
While ping can test for connectivity between two network hosts,
tracert (short for “trace route”) can verify the network path data uses
to travel between the two hosts.
Because Avid Composer Products applications are data intensive, it is
important that large amounts of data be transferred between the
LANserver and its clients in a timely fashion. An incorrectly
configured network might get the data to its destination, but be too
slow for your application to work effectively.
The tracert command can be used to confirm the data is traveling
along an optimal path. In a LANshare workgroup, the LANserver and
its clients should send traffic directly to each other. Routers should not
be used to direct traffic in between.
It is possible for network traffic to take two different paths going to
and coming back from one system to another. Because of this, it is
important to run this command on both the LANserver and its clients
to test the data path from both directions.
Troubleshooting
As with ping, there are many options that can be used with tracert.
This section discusses two types of tracert syntax:
tracert [System Name]
Where [System Name] is the network name of the remote system
to which you are testing connectivity.
or
tracert [IP Address]
Where [IP Address] is the IP address of the remote system to
which you are testing connectivity.
Page 89

To run the tracert command:
1. Open a Command Prompt window.
2. At the command line, type the tracert command (for example,
tracert 192.168.10.5).
The tracert result should resemble the following:
Tracing route to [remote system name or IP
address]
7-5
One entry indicates
an optimal route.
over a maximum of 30 hops:
1 10 ms <10 ms <10 ms [remote system name
or IP address]
Trace complete.
If your network is correctly configured, the tracert result will show
only one entry and then indicate the trace is complete. More than
one entry indicates the traffic is going through a router, which
significantly impacts performance.
If your tracert result shows more than one entry, most likely there
is an incorrect IP address or subnet mask configuration on the
local host.
Using ping and tracert
Page 90

7-6
Troubleshooting a LANshare Workgroup
The following sections describe how to troubleshoot some common
LANserver issues.
Avid Composer Products Software Has Performance Issues
Problem: The Avid Composer Products application you are running is
performing slowly or, potentially, not running.
Possible Cause: The LANserver and the client with the performance
problems are not on the same subnet mask, forcing the data to go
through additional routing while being transferred between the two
systems. If the data transfer is slow enough, it can cause the Avid
Composer Products application to perform poorly or to stop
functioning.
Data transfer between the LANserver and its clients must occur
directly. You can use the tracert utility to verify whether or not the data
transfer uses a direct, optimal path. See “tracert” on page 7-4 for more
information.
Workspaces Are Not Available to an Ethernet Client
Problem: No workspaces are available for mounting on an Ethernet
client.
Possible Cause: The user account the user has logged in to the
Ethernet client with, does not exist either in the MediaNet
Administration Tool or the LANserver’s Windows domain. See
“Configuring User Accounts and Permissions” on page 3-11 for more
information on properly setting up user accounts.
Possible Cause: The user account does not have permissions to mount
workspaces.
Troubleshooting
Page 91

Macintosh Client Cannot Mount Shared Workspaces
Problem: A Macintosh Ethernet client cannot mount workspaces
shared by the LANserver.
Possible Cause: Macintosh clients cannot connect to the LANserver
without installing additional software (DAVE) to allow them to see the
Windows network. DAVE is included with the MediaNet software and
must be correctly configured to function within a LANshare
workgroup. See “Configuring DAVE” on page 5-9 for information
about configuring the DAVE software.
7-7
n
Each Macintosh client needs to have a separate DAVE license to use the
DAVE software. If two clients use the same license, you will have conflicts
between these clients when they try to connect to the LANserver.
SGI Client Cannot Mount Shared Workspaces
Problem: An SGI Ethernet client cannot mount workspaces shared by
the LANserver.
Possible Cause: SGI clients cannot connect to the LANserver without
installing additional software (Samba) to allow them to see the
Windows network. Samba is not included with the MediaNet software.
It is freeware and is available from the Internet. See the Samba
application note on the Avid Customer Support Knowledge Center for
information about configuring the Samba software.
Troubleshooting a LANshare Workgroup
Page 92

7-8
LANserver Is Whistling
Problem: The LANserver is making a whistling sound.
Possible Cause: One of the power supplies might have failed. Press
the red button on the left of the power supplies on the back of the
LANserver. The whistling should stop. Contact Avid Customer
Support for further assistance and possible power supply
replacement.
Checking That the Operating System Is Properly Inst all ed
LANservers run the Windows 2000 Server operating system with
Service Pack 2. Avid ships each LANserver with the Windows 2000
Server, Service Pack 2, and any appropriate hotfixes preinstalled. If
you are concerned that the operating system might not be
appropriately installed, you can check it by following the procedure in
this section.
Troubleshooting
n
n
Windows 2000 Service Pack 2 and any hotfixes are provided in the
Extras\Win2k\ folder on the MediaNet Release 2.2 (or later) CD-ROM if
you need to reinstall them for any reason.
See the Avid Unity MediaNet Release Notes for a list of appropriate
hotfixes.
To determine that the appropriate Windows 2000 Server operating
system, service pack, and hotfix versions are correctly installed on
the LANserver:
1. Right-click the My Computer icon on the desktop, and choose
Properties from the pop-up menu that appears. The System
Properties dialog box appears.
2. Click the General tab. The System section lists the version of the
operating system and the service pack that are installed on the
LANserver.
Page 93

7-9
If your LANserver does not have the Windows 2000 Server operating
system, Service Pack 2, or the appropriate hotfixes installed, you
should install the Windows 2000 Server operating system, Service
Pack 2, the hotfixes, or all of them as required.
If you reinstall the Windows 2000 operating system for any reason,
make sure you perform a default installation (accept all the standard
installation recommendations) of the Windows 2000 Server operating
system. Follow the Windows 2000 installation instructions that came
with your LANserver.
You will also need to reinstall drivers for the gigabit Ethernet adapter
board, the 3ware
These drivers are provided on the MediaNet Release CD-ROM in the
Drivers_Firmware folder. Each driver is in its own folder, labeled by
its function.
Setting Virtual Memory
Virtual memory extends the physical memory (RAM) in your
LANserver using a portion of the hard drive as a location to move
unused data from physical memory. The Windows 2000 operating
system uses a swap file (pagefile.sys) to track the size and location of
the virtual memory, and to move data from the hard drive to RAM.
n
Avid ships each LANserver with virtual memory already configured. If you
are installing a new LANserver, continue with “Installing the LANserver
Software” on page 3-6. If you are rebuilding the LANserver, continue by
setting the virtual memory.
The LANserver requires you allocate 1536 MB of virtual memory on
the C: partition of each LANserver’s internal hard drive, and for the
LANserver file location table.
™
drive controller board, and the SCSI adapter board.
Troubleshooting a LANshare Workgroup
Page 94

7-10
To set virtual memory size:
1. Right-click the My Computer icon on the desktop, and choose
Properties from the pop-up menu that appears. The System
Properties dialog box appears.
2. Click the Advanced tab. The advanced settings appear.
3. Click the Performance Options button. The Performance Options
dialog box appears.
4. Click the Change button. The Virtual Memory dialog box appears.
5. Select C: in the Drive [Volume Label] list.
n
Make sure you select a drive or partition with sufficient free space for the
swap file.
6. Double-click the text box next to Initial Size (MB) and type 1536.
7. Double-click the text box next to Maximum Size (MB) and type
3072.
8. Click Set.
9. Click OK to close the Virtual Memory dialog box.
10. Click OK to close the Performance Options dialog box
11. Close the System Properties dialog box.
12. Click the Start button and select Shut Down. The Shut Down
Windows dialog box appears.
13. Choose Restart from the menu and click OK. The new virtual
memory size takes effect after the restart is complete.
Troubleshooting
Page 95

Checking the Gigabit Ethernet Adapter Board Driver
Avid ships each LANserver with the correct gigabit Ethernet adapter
board driver installed. If you are concerned that the gigabit Ethernet
adapter board driver might not be appropriately installed, you can
check it by following the procedure in this section.
To check the gigabit Ethernet adapter board driver version:
1. Right-click the My Computer icon on the desktop, and choose
Manage from the pop-up menu that appears. The Computer
Management window opens.
2. Select Device Manager in the left column.
3. Expand Network adapters in the right column.
4. Right-click the Intel(R) Pro/1000 F Server Adapter entry and
choose Properties from the pop-up menu that appears. The
Intel(R) Pro/1000 F Server Adapter Properties dialog box appears.
5. Select the Drivers tab and verify that the Driver Version listed is
2.84.284.0.
7-11
If the correct gigabit Ethernet adapter board driver is not present, you
should install the correct driver from the MediaNet Release CD-ROM.
Contact Avid Customer Support for assistance in installing the driver.
Checking the 3ware Adapter Board Driver
Avid ships each LANserver with the correct 3ware adapter board
driver installed. If you are concerned that the 3ware adapter board
driver might not be appropriately installed, you can check it by
following the procedure in this section.
Troubleshooting a LANshare Workgroup
Page 96

7-12
To check the 3ware adapter board driver version:
1. Right-click the My Computer icon on the desktop, and choose
Manage from the pop-up menu that appears. The Computer
Management window opens.
2. Select Device Manager in the left column.
3. Expand SCSI and RAID controllers in the right column.
4. Right-click the 3ware ATA-100 Storage Controller entry and
choose Properties from the pop-up menu that appears. The 3ware
ATA-100 Storage Controller Properties dialog box appears.
5. Select the Drivers tab and verify that the Driver Version listed is
1.10.1.42.
If the correct 3ware adapter board driver is not present, you should
install the correct driver from the MediaNet Release CD-ROM.
Contact Avid Customer Support for assistance in installing the driver.
Checking the SCSI Adapter Board Driver
Avid ships each LANserver with the correct SCSI adapter board driver
installed. If you are concerned that the SCSI adapter board driver
might not be appropriately installed, you can check it by following the
procedure in this section.
To check the SCSI adapter board driver version:
1. Right-click the My Computer icon on the desktop, and choose
Manage from the pop-up menu that appears. The Computer
Management window opens.
2. Select Device Manager in the left column.
3. Expand SCSI and RAID controllers in the right column.
Troubleshooting
Page 97

4. Right-click the Adaptec™ AIC-7892 Ultra160/m PCI SCSI Card
entry and choose Properties from the pop-up menu that appears.
The Adaptec AIC-7892 Ultra160/m PCI SCSI Card Properties
dialog box appears.
5. Select the Drivers tab and verify that the Driver Version listed is
5.0.2183.1.
If the correct SCSI adapter board driver is not present, you should
install the correct driver from the MediaNet Release CD-ROM.
Contact Avid Customer Support for assistance in installing the driver.
Removing and Replacing LANserver Drives
You might need to remove and replace a LANserver drive if you have
a bad drive in your Data Drive Set. You should only remove drives
from the LANserver when asked by Avid Customer Support.
7-13
c
Removing a drive from the LANserver while it is running might
cause a loss of data. Make sure you use the following procedure to
remove drives from the LANserver.
Removing a Drive
To remove a drive from the LANserver
1. Have all the Ethernet clients stop their work and unmount any
2. Start the Setup Manager and choose Stop File Manager from the
3. Click Yes. A dialog box appears while the File Manager is
LANserver workspaces.
File Manager menu. A message appears asking if you are sure you
want to stop the File Manager.
stopping.
Removing and Replacing LANserver Drives
Page 98

7-14
4. Click Data Drive Set in the left portion of the window and select
the drive you want to remove from the Data Drive Set by clicking
it.
5. Choose Identify from the Drives menu. On the front of the
LANserver, the LED for the drive flashes. Note the drive location
and number.
6. Click the Start button and select Shut Down. The Shut Down
Windows dialog box appears.
7. Choose Shutdown from the menu and click OK. The Windows
operating system shuts down and turns off the LANserver. This
takes approximately 1 minute.
8. Open the doors on the front of the LANserver. The doors are
unlocked when the key slot is in the 12-o’clock position. If the
doors are locked, locate the key to unlock the doors.
9. Check to make sure the drive you want to remove is unlocked.
The drive is locked when the key slot is in the 9-o’clock position.
10. Push down on the left side of the handle (you’ll hear a click when
it is free) and pull the handle forward. This unlatches the drive
and slides it approximately 1/2 inch out of the LANserver.
11. Grasp the drive carrier and slide it out of the LANserver.
Replacing a Drive
To replace a drive in the LANserver:
1. Locate the replacement drive. Make sure the handle on the drive
2. Slide the drive into the open drive location in the LANserver until
Troubleshooting
carrier is unlatched and pulled out as far as possible.
it stops moving. Approximately 1/2 inch of the drive carrier
should be outside the LANserver.
Page 99

3. Push the handle into the drive carrier. This seats the drive in the
LANserver. You’ll hear a click when the drive is fully seated and
the handle latches in place.
4. Start the LANserver by pushing the Power (PWR) switch on the
front of the LANserver.
Resetting the LANserver Power Supplies
If the LANserver does not start when you press the Power switch, the
power supplies might have tripped to prevent them from an
over-power condition.
To reset the power supplies:
1. Remove the power cord from both power supplies at the back of
the LANserver.
2. Wait 10 seconds.
7-15
3. Plug the power cords back into both power supplies.
4. Press the PWR switch on the front of the LANserver. If the
LANserver does not start, contact Avid Customer Support for
additional help.
Resetting the LANserver Power Supplies
Page 100

7-16
Troubleshooting
 Loading...
Loading...