Page 1

Avid® MediaCentral Platform Services
Security Architecture and Analysis
Purpose of This Document
This document provides the MediaCentral administrator with an overview of the security
architecture for the MediaCentral environment and recommended best practices for a secure
operation. The document also provides an analysis of the MediaCentral UX application against
the most common security flaws for Web-based applications.
Intended Audience
This document is intended for anyone responsible for system security, including MediaCentral
administrators, Chief Security Officers, and IT administrators.
Product Version
MediaCentral version 2.3 and version 2.4.
c
Beginning with version 2.0, the product name “MediaCentral” replaces “Interplay
Central.” Specific product names are Avid MediaCentral Platform (bus infrastructure) and
Avid MediaCentral | UX (Web and mobile applications).
Page 2
Revision History
Date Revised Changes Made
November 23, 2015 Added multiple-zone port information. See “MediaCentral Security
Architecture” on page 6
Updated version to MediaCentral version 2.4.
July 13, 2015 First publication of version 2.3.
• Added information about strong password validation. See
Authentication” on page 8
• Added information for Media Index. See
on page 16
June 27, 2014 Version 2.0 published.
.
“User
.
“Media Index Security”
Contents
Overview of MediaCentral . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Overview of MediaCentral Security . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
MediaCentral Security Architecture . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Strategies and Best Practices . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Media Index Security. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Security Risk Assessment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Where to Find More Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
2
Page 3

Overview of MediaCentral
MediaCentral Platform Services deliver workflow tools for media professionals through both
Web and mobile applications. The MediaCentral UX application allows individuals in different
media production roles to access the tools they need to complete tasks with greater access to
assets, team collaboration, and workflow agility. Through MediaCentral UX, users can access
existing Interplay Production assets and iNEWS story/rundown information.
Overview of MediaCentral Security
This section describes some common Web application concerns and how they are addressed by
the MediaCentral architecture.
Internet Security and Availability
The MediaCentral client accesses the MediaCentral server functionality through a Web-based
client. As with any Web-based application, information is passed over the Internet for the user to
log in and operate the application. MediaCentral utilizes standard HTTPS Internet transfer
protocols for secure information transfers, such as user login credentials. MediaCentral relies on
consistent Internet access for successful operation. If the application is disconnected due to
faulty Internet access, the user session closes and users are required to re-enter their credentials
when access is restored.
Overview of MediaCentral
MediaCentral version 2.0 and later uses Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) v6.5 as the server
operating system. For the latest information on approved security updates for RHEL 6.5 see the
Avid MediaCentral Platform Services ReadMe. You can download the ReadMe for version 2.3
from the following Knowledge Base page:
http://avid.force.com/pkb/articles/en_US/ReadMe/Avid-MediaCentral-Version-2-3-x-Document
ation
Data Privacy
MediaCentral provides the client with access to existing Interplay Production assets and iNEWS
story/rundown information. As part of the login to MediaCentral, the user is also logged into
associated Interplay Production and iNEWS sessions using their existing Interplay Production
and iNEWS credentials. Access to these assets is controlled by the underlying applications
themselves, based on the user’s existing account privileges. The MediaCentral client does not
provide users access to any assets for which they do not have existing privileges.
3
Page 4

Overview of MediaCentral Security
In order to provide for a single login experience, MediaCentral stores user login credentials
(MediaCentral, iNEWS, Interplay Production, and other customer user account information) in a
central user management database. All data is stored in this central database and all passwords
are maintained in an encrypted form. Note that MediaCentral leverages the existing iNEWS and
Interplay Production credentials (no modifications are made to existing accounts).
Control of Data
MediaCentral stores system configuration information, some of which includes login credentials
to other applications (such as iNEWS, Interplay Production). MediaCentral also stores user
configuration information (roles) and login credentials. A MediaCentral administrator does not
have access to any user private information. Access to user and system settings is limited as
described below.
There are three categories of settings:
• Home > User Settings (Basic, Video, Logging layouts), which are accessed only through a
user login. A MediaCentral administrator cannot access these settings.
• System Settings (System Settings layout), which are accessed only through an administrator
login. These settings define the overall MediaCentral environment.
• User Management settings (Users layout), which are accessed only through an administrator
login. These settings include settings for individual users, groups, and roles.
Specific information about the settings is available in the MediaCentral UX documentation. See
“Where to Find More Information” on page 22.
Security Incident Tracking
MediaCentral does not have the ability to track specific security incidents related to the
application.
Through the MediaCentral UI, the administrator has access to user session information (who is
logged in and at what time) and has the ability to manually terminate a specific user session if
required. The administrator also can review information contained in /var/log/audit/audit.log and
/var/log/secure, which contain a history of remote logins, authentication and authorization
privileges.
Example:
Jan 7 14:39:59 localhost sshd[3781]: Accepted password for root from
172.24.41.133 port 43239 ssh2
4
Page 5

Overview of MediaCentral Security
Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity
• The MediaCentral application can operate within a clustered server configuration, providing
Active/Passive failover for continuity of services.
• The MediaCentral Playback Services (MCPS), which supports the player functionality in the
MediaCentral UI, is also load balanced, providing performance and failover support for
video streaming.
• The underlying MediaCentral database, which stores the user settings and system
configuration data, can be configured for data replication and failover. Continuous database
®
replication is performed by LINBIT
DRBD® (www.drbd.org).
Additional details are provided in the Avid MediaCentral Platform Services Installation and
Configuration Guide.
• The MediaCentral Messaging Broker can operate in an active/active configuration with load
balancing. Other MediaCentral services (such as Attributes) are highly available using
Active/Passive failover and are not load balanced. All services are managed as a single
combined resource and will fail over as a group.
Regulatory Compliance
Due to the nature of the application and the information that is accessed and stored, the
MediaCentral application is not currently validated against any existing security compliance
standards (such as HIPAA, DSS, ISO 19779/27001).
5
Page 6
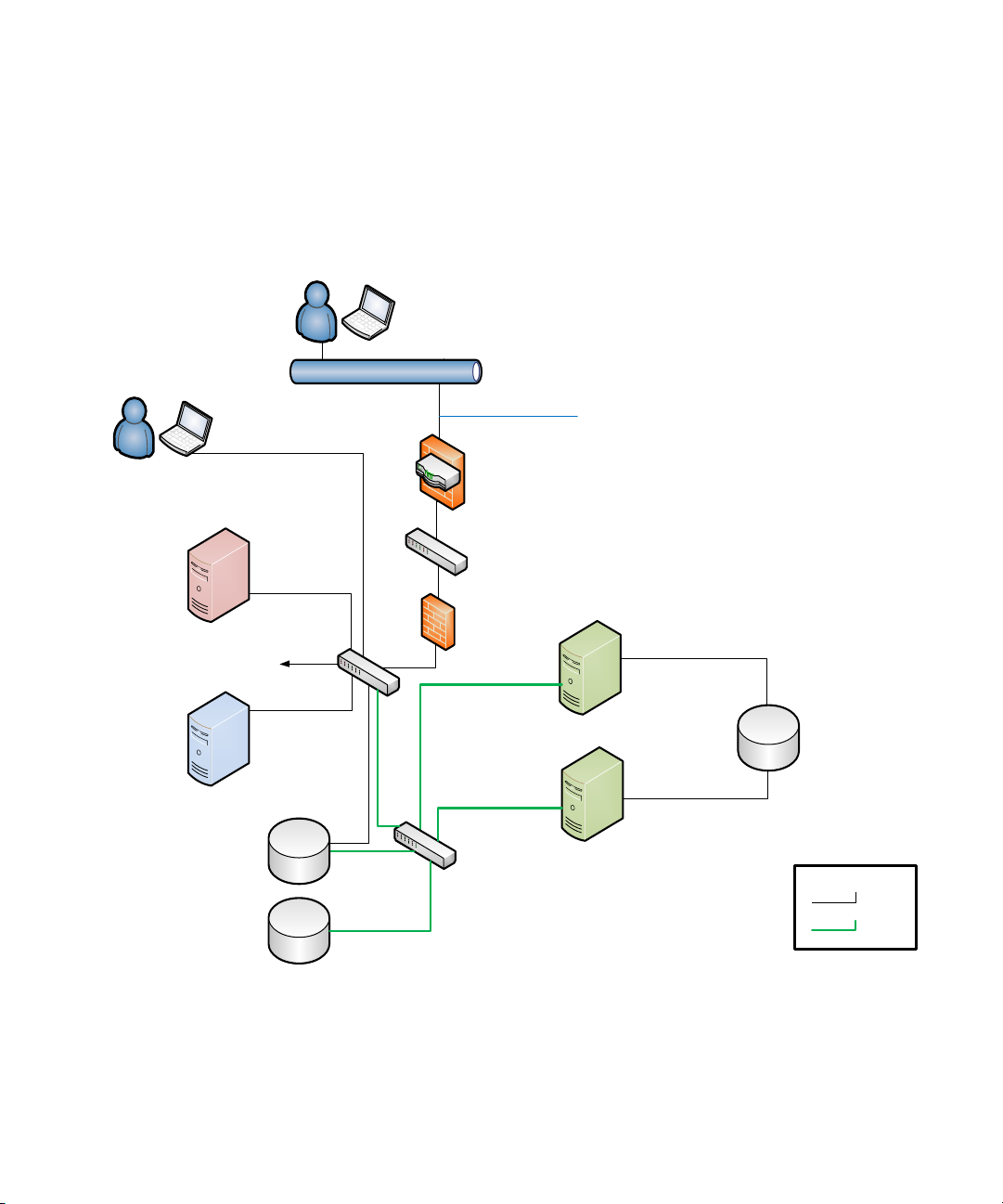
MediaCentral Security Architecture
MediaCentral Security Architecture
MediaCentral Server
(Node 2)
MediaCentral Server
(Node 1)
Interplay
Production
Workgroup
ISIS 7000
MediaCentral Client
(External)
1Gb
10 GigE
10 Gb
Network
VPN Router /
Firewall
Internet
To House
Network
Data In Transit:
x User Credentials
x JPEG Images
x Machine
Instructions
x User
Credentials
x User Settings
x System
Attributes
Edge Switch
HTTPS
Session Creation
and Termination
Logs
1 Gb
Netwok
MediaCentral Client
(WAN/LAN)
ISIS 5000
ISIS 2000
10Gb
port
The diagram below provides an overview of the MediaCentral architecture with specific
references to application and data security. This diagram shows a clustered MediaCentral server
configuration.
MediaCentral Security Architecture
6
Page 7

MediaCentral Security Architecture
A MediaCentral client requires user login credentials in order to gain access to the underlying
functionality. All data transfer to and from the MediaCentral client (user credentials, session
information, user configuration settings, media images and files, text, and machine instructions)
are transported in a secure manner to the MediaCentral server using HTTPS protocol.
MediaCentral clients that connect through the public Internet require VPN access into the server
network. All connections pass through the VPN router/firewall through identified ports. Once the
data has passed into the “house network” it is secured using the customer’s existing network
security infrastructure.
Users connected within the corporate LAN/WAN would not typically use VPN access but would
likely need to pass through firewalls and other network security devices with ACLs before
accessing the Avid Interplay network.
The following table lists the ports used by MediaCentral server that should be allowed through
the VPN firewall.
Table 1: VPN Firewall Port Settings
Protocol and
Component Port
Direction Usage
MediaCentral Web application 80 TCP Inbound MediaCentral Playback
Services (MCPS) HTTP calls
File streaming from MCPS
443 Secure TCP Inbound MediaCentral HTTPS calls
Communication with
MediaCentral server
843 TCP Inbound Serving Flash Player socket
policy files
5000 TCP Inbound Playback service (loading
assets, serving JPEG images
and audio, etc.). Outbound
flow to client serving inbound
request.
MediaCentral mobile
applications
80 TCP Inbound MediaCentral Playback
Services (MCPS) HTTP calls
File streaming from MCPS
443 Secure TCP Inbound MediaCentral HTTPS calls
Communication with
MediaCentral server
7
Page 8

MediaCentral Security Architecture
Outbound ACLs should be used to allow packets from the MediaCentral server to the
n
MediaCentral client over “established” TCP sessions only. The “established” keyword indicates
that packets belong to an existing connection if the TCP datagram has the Acknowledgment
(ACK) or Reset (RST) bit set.
In addition to the ports listed above, Multi-Zone and Media Index configurations require
additional ports to enable communication between the zones. While the ports in the table below
are considered “external,” they are similar to internal ports in that they should be open only
between controlled data centers.
Table 2: Multi-Zone Ports
Protocol and
Component Port
Direction Purpose
Multi-Zone
configurations
Media Index Custom ports configured in /etc/elasticsearch-tribe/elasticsearch.yml must be allowed
Avid does not test or support firewalled connections between zones in a Multi-Zone
n
configuration. If required, zone communication can be limited by source IP ranges.
Note that the MediaCentral Web service and MediaCentral application services operate on the
same server so there are no proxies or firewalls between these components. Access to the
MediaCentral database is also direct, with no database firewall protection required.
All system data stored within the user management database (user credentials, user settings,
system attributes) can only be accessed and modified by a MediaCentral administrator.
The following items describe the MediaCentral security architecture in more detail.
User Authentication
Access to the MediaCentral client application requires the use of user or administrator identity
credentials. All user credentials are passed from the web browser to the MediaCentral server
using SSL / HTTPS protocol. User authentication is through single factor authentication
(username/password) and is provided by the MediaCentral User Management Service, which
resides on the MediaCentral server. MediaCentral can authorize users through Active Directory
as well as through local MediaCentral user management.
5672 AMQP Multi-Zone configurations require that AMQP
protocol and port 5672 be accessible between
zones/machines.
5432 UMS/Postgres Replication.
to cross the firewall. See
“Media Index Server Ports” on page 18 for details.
8
Page 9

MediaCentral Security Architecture
User passwords created in MediaCentral UX v2.1 and later require strong password validation:
• Minimum length of user names: 1 character
• Minimum length of passwords: 6 characters
• Maximum length of user names and passwords: 255 characters
• Passwords are case-sensitive.
• Passwords cannot contain all or part of the user’s account name.
• Passwords cannot consist of spaces only.
• Passwords must contain characters from three of the following four categories:
- English uppercase characters (A through Z)
- English lowercase characters (a through z)
- Base 10 digits (0 through 9)
- Nonalphanumeric characters (for example !, $, #, %)
These requirements do not affect passwords for MediaCentral users whose accounts were
n
created in MediaCentral UX v2.0.x or earlier. The new requirements are enforced when user
passwords are changed or created in MediaCentral UX v2.1 or later.
These requirements do not apply to passwords for users imported from Active Directory. These
users use their Active Directory credentials.
User sessions are managed with an Avid Session ID, which is stored within a client cookie.
These client-side cookies are used to identify a specific user session within the MediaCentral
Middleware Service, which stores necessary user connection information. The client cookie
carries an identifier of the server-side session and does not contain any user credentials. All
session communication is encrypted over HTTPS, and HTTPOnly is configured so as to expose
the cookie only to the server, thus protecting the cookie from client-side scripts (where supported
by the browser).
MediaCentral also uses a form of federated identity management in order to log the user into the
underlying Interplay Production and iNEWS applications. User authentication is managed by
each of these applications locally. At initial login, user login credentials are passed over the
house network from the MediaCentral server to the Interplay Production and iNEWS server.
User Access
User rights and privileges are managed through role-based access lists stored within the
MediaCentral User Management Service. Roles can be assigned to users directly, or a user can
inherit a role from a user group assignment. Roles control user access to features and specific
MediaCentral UI layouts. (Additional information can be found in the Avid MediaCentral | UX
Administration Guide.)
9
Page 10

MediaCentral Security Architecture
MediaCentral queries the User Management Service to determine which MediaCentral layouts
are to be made available to the user upon login. Access to all assets (media, metadata, rundowns,
stories) is managed by the backend systems themselves (Interplay Production, iNEWS). The
MediaCentral User Management Service authorizes all client requests against the privileges for
the current session.
All requests to a MediaCentral service require a session ID that is authenticated by the
MediaCentral User Management Service.
User Accountability (Non-Repudiation)
MediaCentral logs both user session creation and termination. MediaCentral user activity is not
logged as part of the MediaCentral session management function. Session logs are stored locally
on the MediaCentral server and are not replicated. Log access is file-system based; any
individual who has access to the MediaCentral server can access the User Management logs.
Securing Data at Rest
The MediaCentral database stores user credentials, user settings, and system attributes
information.
• User credentials are stored in a protected manner. The user name is stored as created, but the
user password is stored only as the hash digest of the password. This hash is calculated using
a SHA512 secure hash algorithm.
• User settings and system attributes are not encrypted. System attributes only contain server
path information.
If e-mail forwarding is turned on for the “Messages & Sharing” feature, then the SMTP
credentials are stored in the system attributes. Account information is also stored if SSL is used
for mail forwarding.
When using Active Directory (AD) synchronization, the MediaCentral User Management
Service does not store the main passwords of the users (nor can the AD password be
overwritten).
Interplay Production and iNEWS passwords are also stored in the MediaCentral user
management database using the following encryption techniques:
• iNEWS – AES encrypted with a fixed 32-character password
• Interplay Production – NXNCrypt encrypted
10
Page 11

MediaCentral Security Architecture
Security Data in Transit
MediaCentral uses default HTTPS transfer from the Web client to the MediaCentral server and
all underlying MediaCentral services (for example, User Management). HTTPS calls are sent
over port 443; see Table 1 on
page 7 on for a complete list of ports. Note that a network firewall
is recommended for all configurations.
Communication between MediaCentral and Interplay Production and iNEWS is sent over the
house network in an unsecured fashion. Any user password information that is transported for
login to Interplay Production and iNEWS is sent in an encrypted state.
All communication across MediaCentral services (bus-based messaging) occurs within the
MediaCentral server and does not traverse the house network. This information is not encrypted
and can only be accessed by logging into the MediaCentral server. Applications and services do
not need a service authorization token to register on the bus, but since all services are contained
on the MediaCentral server it is difficult for external services to obtain access to the
MediaCentral Platform bus.
For video playback with the MCPS client, the client will forward video MOBID and associated
relink policy to the MCPS server, which responds with the timeline object, JPEG image, and
audio to the MCPS player within the web client. The MCPS request data is not encrypted and the
response data (JPEG images and PCM audio) is also not encrypted. However, MCPS media
services transport over port 5000 can be secured with a signed certificate. See Table 4 on
page 13.
If the Flash player Transfer Layer Security setting is enabled, the MCPS request data is
encrypted and the response data (JPEG images and PCM audio) is also encrypted.
The following table summarizes the types of data transfer security.
Table 3: Data Transfer Security
Communication Data Transfer Security
MediaCentral Client <-> MediaCentral Server HTTPS transfer
MediaCentral Client <-> MediaCentral Playback
Services (MCPS)
Interplay Central Server <-> Interplay Production HTTP transfer
No data encryption.
Data encryption if the Flash player Transfer
Layer Security setting is enabled.
Secured with a signed certificate.
Only Interplay Production password is encrypted
(TEA 128 bit)
11
Page 12

MediaCentral Security Architecture
MediaCentral v2.0 and later allows search and delivery of assets through a multi-zone
configuration. By default, a MediaCentral system is configured as a single zone. Large
organizations can combine two or more single-zone systems into a multi-zone environment.
Multi-zone functionality is designed for deployment across an internal secure network
(“corporate network”) with all traffic occurring behind the firewall.
Multi-zone functionality is not designed to be used over unsecured Internet connections.
Customers need to make sure the network used is secure, such as through dedicated lines or VPN
tunnels between the sites.
Data Integrity
Any MediaCentral user with iNEWS access has the ability to modify and delete stories in an
iNEWS rundown. They do not have the ability to delete an entire rundown.
Note that asset or story updates or deletions are not logged.
In order to prevent improper modification or destruction, all changes to video assets from the
MediaCentral client create new versions of the video (no master essence is changed). In addition,
there is no delete operation available in MediaCentral for Interplay Production media assets.
For user management, an MediaCentral administrator has the ability to delete users and groups,
but only for the MediaCentral user management. An MediaCentral administrator does not have
access to Interplay Production or iNEWS user management features.
Data Availability
All MediaCentral user management information, system settings, and user settings data is
contained within an SQLdatabase, which is replicated using continuous data mirroring. The
MediaCentral UX Messages & Sharing feature uses a separate noSQL database which is also
replicated using continuous data mirroring. Database backup and recovery procedures are
recommended and are documented in the Avid MediaCentral Platform Services Installation and
Configuration Guide. No other data or state information is required for long-term storage in
order to operate MediaCentral.
Network Security
MediaCentral relies on VPN and associated firewalls for access to the house network (see
diagram). The MediaCentral network configuration does not utilize proxy servers or server
firewalls. Additional network protection can be implemented within the house network.
MediaCentral can use either self-signed, no certificate, or commercially issued certificates for
HTTPS communication. Each certificate type provides a different user experience and has its
own set of security implications, as listed in the following table.
12
Page 13

MediaCentral Security Architecture
Table 4: Security Implications for Certificate Types
No Certificate Self-Signed Commercially Issued
User experience User is prompted with
“This site is untrusted” with
options to back out or
“Proceed Anyway.”
Security Implications MediaCentral operates
behind the firewall and is a
“trusted application” so
security implications are
minimal. Even with no
certificate, HTTPS
connections are still
properly encrypted.
If the Flash player Transfer Layer Security is enabled, a commercially issued (CA-signed)
certificate is required or a self-signed certificate must be imported to the local certificate store
Service Security
All MediaCentral service calls are made using signed API calls which rely on an authenticated
session token.
Antivirus
User is prompted with
“This site is untrusted” with
options to back out or
“Proceed Anyway.” Login
is transparent.
Deployment involves both
server-side and client-side
certificate management by
a system administrator.
Login is transparent.
A system administrator
must ensure that the
certificate is installed on the
MediaCentral server.
Server side: Antivirus is not required due to the nature of the Linux operating system and the
data that is passed from the MediaCentral client to the MediaCentral server. Avid recommends
that no other application be loaded on the MediaCentral server to ensure optimal performance.
Data Separation/Isolation
Data access control is managed by the Interplay Production and iNEWS systems and does not
depend on any MediaCentral user controls.
OS Patching
Avid qualifies particular OS patches (see “Internet Security and Availability” on page 3). Other
patches are not supported. Any unqualified update or patch can break drivers and ISIS
connectivity.
13
Page 14

Strategies and Best Practices
Administrator Accounts
As part of the MediaCentral installation process, default administrator accounts are created.
After a successful installation, these account passwords must be updated.
• A default operating system account is created on the MediaCentral server using the
following credentials:
user: root
password: Avid123
Note that each cluster node will have a similar account. These are the credentials that the
administrator uses to log into the server itself.
• A default MediaCentral Administrator is created in the MediaCentral User Management
Service using the following credentials:
user: Administrator
password: Avid123
This account is created in the UMS as the first default Administrator user account.
Other credentials are also configured as part of the MediaCentral installation process. The
MediaCentral administrator should verify that all updated passwords align with corporate
security policy. Note that generic passwords might have been set by an Avid representative
during the installation process.
Strategies and Best Practices
c
The password information in this document is freely available through the Avid Knowledge
Base web site, so changing the default passwords is critical for the security of the overall
MediaCentral system. The system administrator must change these passwords
immediately after the installation. Passwords must meet corporate password complexity
standards.
Player Demo Page
Prior to Interplay Central v1.6, access to the player demo page was unrestricted by default. For
Interplay Central v1.6 and later, a server administrator must enable the page through the
MediaCentral server command line. For more information, see the Avid MediaCentral Platform
Services Installation and Configuration Guide.
14
Page 15

Strategies and Best Practices
Port Settings
The following table lists the ports that are required by the MediaCentral server. Check with your
Avid representative for the exact configuration. For ports used by Media Index, see
Server Ports” on page 18
.
“Media Index
Table 5: MediaCentral Server Ports
Service Name Port Notes
MediaCentral UX 80, 443 Externally exposed service
through ports 80 and 443
MediaCentral Playback
Services (MCPS)
MCPS Manager 80 Externally exposed service
MediaCentral Platform
Services
ISIS 5000 - 5399 (UPD and TCP)
RabbitMQ 5672 (AMQP), 15672 (Management UI/API)
MongoDB 27017
Postgresql 5432
System 22, ICMP, 111, 24007, 24008, 24009-(24009 + number of
For ports that require firewall configuration, see Table 1 on
843 (Flash), 80, 5000, 26000 Externally exposed service
through ports 843 and 5000
through port 80
8000 (optional Admin UI), 8183 (bus cluster info)
bricks across all volumes for gluster). If you will be using
NFS, open additional ports 38465-(38465 + number of
Gluster servers). Some MAM configuration might require
additional NFS ports (111, 2049 tcp&udp) or CIFS
(137,138 udp and 137,139 tcp). Other file systems will
have to be checked individually (Isilon, Harmonic
Omneon, etc.).
page 7.
15
Page 16

Media Index Security
Media Index Overview
Media Index delivers an API for fast and efficient search across multiple data sources, including
Interplay Production, iNEWS, and Media Archive. It also provides an integration point for
third-party systems. Media Index, in conjunction with MediaCentral, allows users to search
metadata and access assets transparently, regardless of the data source and physical asset
location.
For more information about Media Index, see the Avid Media | Index Configuration Guide
n
(available internally).
Media Index Security Overview
A MediaCentral client accesses the Media Index through the web-based client application. User
authentication and authorization is provided by MediaCentral server functionality and uses
HTTPS for secure information transfer.
Data Privacy
MediaCentral provides the client unlimited access to the Media Index metadata. However, when
the client accesses the actual asset delivered as a part of the Media Index search results,
MediaCentral uses separate Interplay Production, iNEWS, and MAM sessions to authorize the
access for the user. Media Index provides a Content Based Access (CBA) authorization to
restrict the searches to a specific subset of the metadata according to the user’s permissions in the
respective system. CBA functionality in Media Index v.2.2 – v.2.3.x is only integrated with
Media Archive.
Media Index Security
®
All Media Index data is stored in Elasticsearch
search and analytics engine, designed for horizontal scalability, reliability, and easy
management.
Media Index stores its configuration in the com.avid.attributes service using ACS bus
technology. Configuration does not contains any login credentials. Media Index with CBA
enabled stores the user’s login names in Elasticsearch. Media Index configuration is accessible
through the ACS bus without authentication.
16
. Elasticsearch is a distributed, open source
Page 17

Media Index Security
Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity
Media Index can operate within a clustered environment, providing Active/Active failover.
High availability of the Media Index API is provided by Pacemaker. Elasticsearch as an
underlying data storage provides continuous data replication and high availability.
Media Index Architecture
Media Index is delivered with the MediaCentral installer and operates on the MediaCentral
servers. The following illustration shows how data is shared between two servers.
17
Page 18

Media Index Security
Media Index Server Ports
The Media Index API is exposed through ACS bus technology. A client accesses the Media
Index API through the MediaCentral middleware and ACS bus. The following table lists the
ports used
Table 6: Media Index Server Ports
Component Port Protocol Usage
Elasticsearch 9200 HTTP Elasticsearch HTTP calls
9300 TCP Internal Elasticsearch node to node
communication
Elasticsearch-tribe 9201 HTTP Elasticsearch-tribe HTTP calls. In a
multi-zone configuration, the set-up tribe
node federates the HTTP calls to other
connected Elasticsearch clusters
9305 TCP Internal Elasticsearch-tribe node to node
communication
9312 TCP Elasticsearch tribe local cluster binding port
931x TCP In a multi-zone configuration, each remote
zone will have its own Elasticsearch tribe
binding port. Port number is incremented by 1
from the local binding port number, for
example:
• local: 9312
• remote 1: 9313
• remote 2: 9314
• remote n: 931n
avid-acs-media-index-feed 3000 HTTP The Media Index feed API provides an HTTP
endpoint that exposes the RSS/ATOM feed
with the latest updates from the Media Index
database
18
Page 19

Security Risk Assessment
Security Risk Assessment
The following table describes how MediaCentral addresses security risks as described in the
Open Web Application Security Project (OWASP). Each threat is a link to the corresponding
section of the project Web site, available at
https://www.owasp.org/index.php/Top_10_2010-Main.
Table 7: Security Risk Assessment
Typical Security
Threat Risk
Measures MediaCentral Environment Impact
Injection Flaws Executing of
unintended
commands
Cross-Site
Scripting (XSS)
Broken
Authentication and
Session
Management
Hijacking of
browser sessions
Compromised
passwords and user
identities
Avoid use of
interpreters
Input validation
User input
validation
Input escaping
Input whitelisting
Protection of
session IDs
Encrypted user
credentials
Session ID security
Log out/timeouts
The only user input commands within
MediaCentral are within the search
function. MediaCentral utilizes an
abstracted search API that cannot
accept direct SQL requests. There is
no direct service access from UI
components and no strings are passed
directly into SQL queries.
MediaCentral looks for improper
redirect strings and applies necessary
escapes to prevent XSS.
HTTP Track and Trace commands are
disabled in MediaCentral.
MediaCentral user sessions do not
persist and are lost upon network
drops, causing the user to re-log on.
All user sessions close after five
minutes on exit, if not logged out. User
sessions close after 15 minutes of
browser inactivity, reducing the risk of
unattended browser hijacking.
Administrators have the ability to end
user sessions if required.
Low
Low
Medium
Insecure Direct
Object References
Unauthorized data
access
Access controls
Indirect object
references
19
MediaCentral leverages existing
access controls for Interplay
Production and iNEWS.
Low. MOB
IDs are not
considered
security
risks.
Page 20

Security Risk Assessment
Table 7: Security Risk Assessment
Typical Security
Threat Risk
Measures MediaCentral Environment Impact
Cross Site Request
Forgery
Security
Misconfiguration
Legitimizes forged
browser requests
Inadequately
defined security
configurations
Insecure Storage Vulnerable
sensitive data
Unique session or
request tokens
Port management
Account
management
Auto Admin
settings deletion
OS patching
Error handling
Cookie
management
Strong standard
encryption
Encrypted backups
Password
hashing/salting
MediaCentral uses unique user session
tokens. All tokens are deleted upon
session exit.
Session IDs are mapped to specific
machines.
Port settings documented for
management
Application errors display limited
information regarding system
functions.
Session ID stored as a cookie. Cookies
are available only to the MediaCentral
server, using HTTPOnly.
Note: OS patching and code library
updates are not supported between
releases.
Uses encryption for stored data. Key
management is described in the Avid
MediaCentral Platform Services
Configuration and Installation Guide
Backups do not include encryption key
information.
Database master password is required
to restore backup.
Low
Medium.
Requires
Auto Admin
account
password
modification.
OS patching
limitations
may affect
security
status
Low
Non-Restricted
URL Access
Access to hidden
URLs
Page
Authentication /
Authorization
Default of no
access
20
MediaCentral UI components and
associated URL access are controlled
through user privileges.
MediaCentral bus monitoring URL is
available but requires administrator
credentials to launch (off by default).
Low. See
notes in
“Strategies
and Best
Practices” on
.
page 14
Page 21

Security Risk Assessment
Table 7: Security Risk Assessment
Typical Security
Threat Risk
Measures MediaCentral Environment Impact
Insufficient
Transport Layer
Protection
Unprotected
network traffic
SSL authentications
VPN
Backend SSL
transport
Secure database
connection
MediaCentral configuration utilizes
SSL transport protocol and VPN
network access.
All access requests to the
MediaCentral database requires a
suitable username and password.
Access from within the MediaCentral
server is considered trusted and does
not require a password.
Username/password for the
MediaCentral database is the same on
every installation and is automatically
sent to all MediaCentral bus connected
services for the cloud database. The
MediaCentral database contains bus
service registration data and system
attributes data. This
username/password does not have
privileges for other MediaCentral
databases containing user information
or MCPS information.
If the Flash player Transfer Layer
Security setting is enabled, the MCPS
request data is encrypted and the
response data (JPEG images and PCM
audio) is also encrypted.
Low.
Non-secure
transport of
MediaCentra
l to iNEWS
and Interplay
Production
across house
network.
Assumes
house
network is
secure.
Unvalidated
Redirects and
Forwards
Modified
forwarding data
Avoid
redirects/forwards
21
Redirects are difficult as MediaCentral
and all underlying services operate on
same physical machine.
Low
Page 22

Where to Find More Information
MediaCentral documentation can be found on the Avid Customer Support Knowledge Base.
Version 2.3 documentation is located here:
http://avid.force.com/pkb/articles/en_US/ReadMe/Avid-MediaCentral-Version-2-3-x-Document
ation
Legal Notices
Copyright © 2015 Avid Technology, Inc. and its licensors. All rights reserved.
Attn. Government User(s). Restricted Rights Legend
U.S. GOVERNMENT RESTRICTED RIGHTS. This Software and its documentation are “commercial computer software” or
“commercial computer software documentation.” In the event that such Software or documentation is acquired by or on behalf of a
unit or agency of the U.S. Government, all rights with respect to this Software and documentation are subject to the terms of the
License Agreement, pursuant to FAR §12.212(a) and/or DFARS §227.7202-1(a), as applicable.
All trademarks contained herein are the property of their respective owners.
Avid MediaCentral Security Architecture v2.4 • Created 11/23/15
Where to Find More Information
22
 Loading...
Loading...