Philips UMA1015M-C2 Datasheet

INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
DATA SH EET
UMA1015M
Low-power dual frequency
synthesizer for radio
communications
Product specification
Supersedes data of October 1994
File under Integrated Circuits, IC03
1995 Jun 22

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Low-power dual frequency synthesizer
for radio communications
FEATURES
• Two fully programmable RF dividers up to 1.1 GHz
• Fully programmable reference divider up to 35 MHz
• 2 : 1 or 1 : 1 ratio of selectable reference frequencies
• Fast three-line serial bus interface
• Adjustable phase comparator gain
• Programmable out-of-lock indication for both loops
• On-chip voltage doubler
• Low current consumption from 3 V supply
• Separate power-down mode for each synthesizer
• Up to 4 open-drain output ports.
APPLICATIONS
• Cordless telephone
• Hand-held mobile radio.
UMA1015M
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The UMA1015M is a low-power dual frequency
synthesizer for radio communications which operates in
the 50 to 1100 MHz frequency range. Each synthesizer
consists of a fully programmable main divider, a phase and
frequency detector and a charge pump. There is a fully
programmable reference divider common to both
synthesizers which operates up to 35 MHz. The device is
programmed via a 3-wire serial bus which operates up to
10 MHz. The charge pump currents (gains) are fixed by an
external resistance at pin 20 (I
designed to operate from 2.6 V (3 Ni-Cd cells) to 5.5 V at
low current. Digital supplies V
same potential. The charge pump supply (VCC) can be
provided by an external source or on-chip voltage doubler.
VCC must be equal to or higher than V
synthesizer can be powered-down independently via the
serial bus to save current. It is also possible to power-down
the device via the HPD input (pin 5).
). The BiCMOS device is
SET
DD1
and V
must be at the
DD2
. Each
DD1
QUICK REFERENCE DATA
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
V
V
V
DD1
CC
CCvd
, V
DD2
digital supply voltage V
charge pump supply
voltage
charge pump supply from
DD1=VDD2
external supply; doubler
disabled; VCC≥ V
DD
2.6 − 5.5 V
2.6 − 6.0 V
doubler enabled − 2V
− 0.6 6.0 V
DD1
voltage doubler
I
DDO1
I
CCO
I
DD1pd
+ I
CCpd
I
DD1pd
f
RFA
+I
, f
+ I
RFB
DDO2
DD2pd
+
operating supply current both synthesizers ON; doubler
current in power-down
mode per supply
current in power-down
mode from supply V
DD
disabled; V
doubler disabled;
V
DD1=VDD2
doubler enabled;
V
DD1=VDD2
DD1=VDD2
= 5.5 V
=3V
RF input frequency for
− 9.6 − mA
= 5.5 V
− 0.01 − mA
− 0.15 − mA
50 − 1100 MHz
each synthesizer
f
XTALIN
f
pc(min)
f
pc(max)
T
amb
crystal input frequency 3 − 35 MHz
minimum phase
comparator frequency
maximum phase
comparator frequency
operating ambient
temperature
fRF= 50 to 1100 MHz;
f
=3to35MHz
XTALIN
fRF= 50 to 1100 MHz;
f
=3to35MHz
XTALIN
synthesizer A
2.6 V ≤ VDD≤ 5.5 V
synthesizer B
2.6 V ≤ V
DD
≤ 4.5 V
synthesizer B
2.6 V ≤ V
DD
≤ 5.0 V
− 10 − kHz
− 750 − kHz
−30 − +85 °C
−30 − +85 °C
0 − +85 °C
1995 Jun 22 2

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
B
B
B
B
Low-power dual frequency synthesizer
UMA1015M
for radio communications
ORDERING INFORMATION
TYPE NUMBER
PINS PIN POSITION MATERIAL CODE
UMA1015M/C2 20 SSOP20 plastic SOT266-1
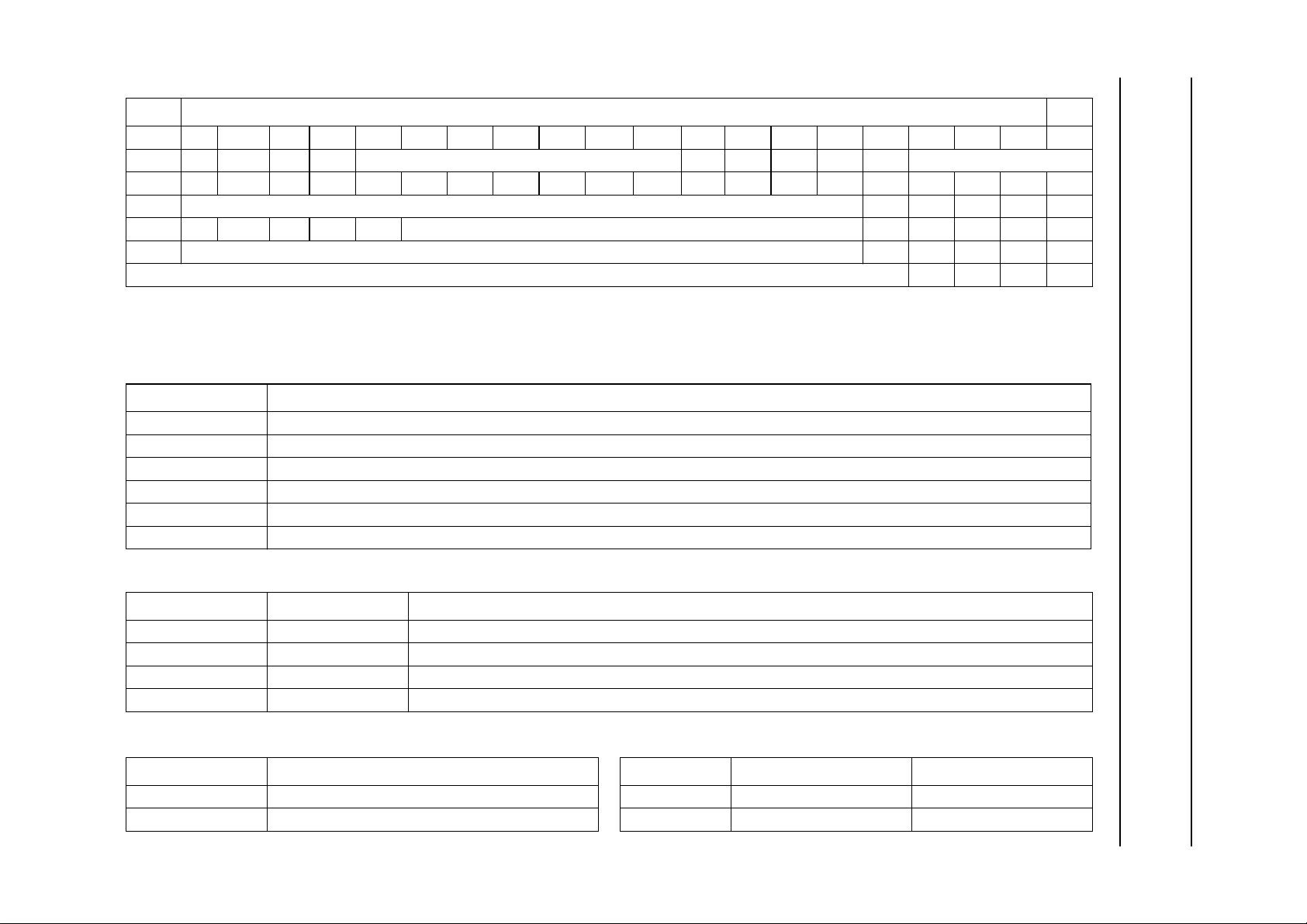
BLOCK DIAGRAM
PACKAGE
Fig.1 Block diagram.
1995 Jun 22 3

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Low-power dual frequency synthesizer
for radio communications
PINNING
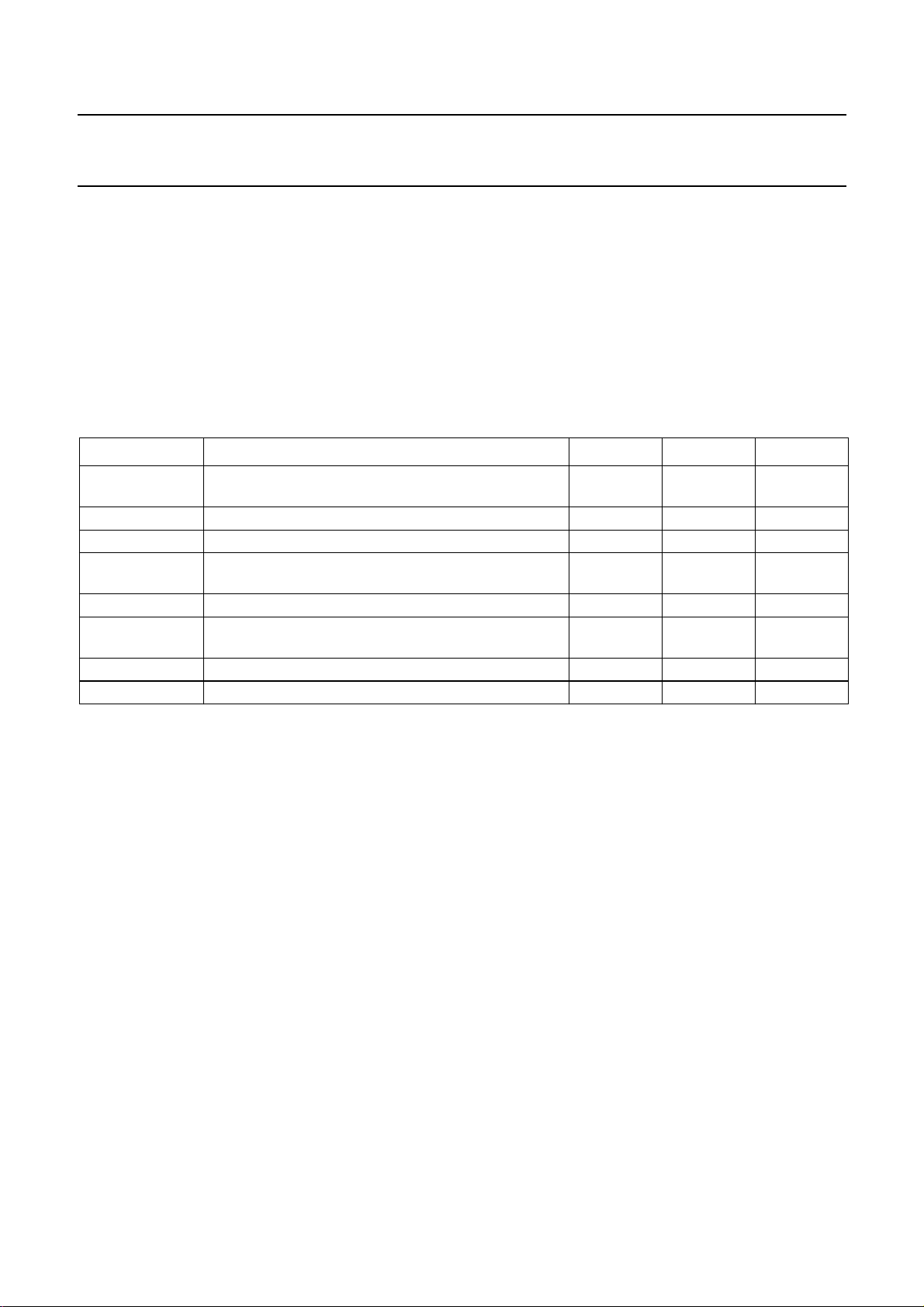
SYMBOL PIN DESCRIPTION
P1 1 output Port 1
P2 2 output Port 2
CPA 3 charge-pump output synthesizer A
V
DD1
HPD 5 hardware power-down
RFA 6 RF input synthesizer A
DGND 7 digital ground
f
XTALIN
P3 9 output Port 3
f
XTALO
CLK 11 programming bus clock input
DATA 12 programming bus data input
E 13 programming bus enable input
V
DD2
RFB 15 RF input synthesizer B
AGND 16 analog ground to charge pumps
CPB 17 charge pump output synthesizer B
V
CC
P0/OOL 19 Port output 0/out-of-lock output
I
SET
4 digital supply voltage 1
(input LOW = power-down)
8 common crystal frequency input from
TCXO
10 open-drain output of f
XTAL
signal
(active LOW)
14 digital supply voltage 2
18 analog supply to charge pump;
external or voltage doubler output
20 regulator pin to set charge-pump
currents
UMA1015M
Fig.2 Pin configuration.
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
Main dividers
Each synthesizer has a fully programmable 17-bit main
divider. The RF input drives a pre-amplifier to provide the
clock to the first divider bit. The pre-amplifier has a high
input impedance, dominated by pin and pad capacitance.
The circuit operates with signal levels from below
50 mV (RMS) up to 250 mV (RMS), and at frequencies up
to 1.1 GHz. The high frequency sections of the divider are
implemented using bipolar transistors, while the slower
section uses CMOS technology. The range of division
ratios is 512 to 131071.
Reference divider
There is a common fully programmable 12-bit reference
divider for the two synthesizers. The input f
XTALIN
drives a
1995 Jun 22 4
pre-amplifier to provide the clock input for the reference
divider. This clock signal is also buffered and output on pin
(open drain). An extra divide-by-2 block allows a
f
XTALO
reference comparison frequency for synthesizer B to be
half that of synthesizer A. This feature is selectable using
the program bit SR. If the programmed reference divider
ratio is R then the ratio for each synthesizer is as given in
Table 1.
The range for the division ratio R is 8 to 4095. Opposite
edges of the divider output are used to drive the phase
detectors to ensure that active edges arrive at the phase
detectors of each synthesizer at different times. This
minimizes the potential for interference between the
charge pumps of each loop. The reference divider consists
of CMOS devices operating beyond 35 MHz.

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Low-power dual frequency synthesizer
for radio communications
Table 1 Synthesizer ratio of reference divider
SR SYNTHESIZER A SYNTHESIZER B
0R R
1R 2R
Phase comparators
For each synthesizer, the outputs of the main and
reference dividers drive a phase comparator where a
charge pump produces phase error current pulses for
integration in an external loop filter. The charge pump
current is set by an external resistance R
where a temperature-independent voltage of 1.2 V is
generated. R
give an I
SET
should be between 12 kΩ and 60 kΩ (to
SET
of 100 µA and 20 µA respectively).
The charge-pump current, ICP, can be programmed to be
either (12 × I
) or (24 × I
SET
) with the maximum being
SET
2.4 mA. The dead zone, caused by finite switching of
current pulses, is cancelled by an internal delay in the
phase detector thus giving improved linearity. The charge
pump has a separate supply, VCC, which helps to reduce
the interference on the charge pump output from other
parts of the circuit. Also, VCC can be higher than V
wider range on the VCO input is required. VCC must not be
less than V
DD1
.
Voltage doubler
If required, there is a voltage doubler on-chip to supply the
charge pumps at a higher level than the nominal available
supply. The doubler operates from the digital supply V
and is internally limited to a maximum output of 6 V.
An external capacitor is required on pin VCC for smoothing,
the capacitor required to develop the extra voltage is
integrated on-chip. To minimize the noise being introduced
to the charge pump output from the voltage doubler, the
doubler clock is suppressed (provided both loops are
in-lock) for the short time that the charge pumps are active.
The doubler clock (RF/64) is derived from whichever main
divider is operating (synthesizer A has priority). While both
synthesizers are powered down (and the doubler is
enabled), the doubler clock is supplied by a low-current
internal oscillator. The doubler can be disabled by
programming the bit VDON to logic 0, in order to allow an
external charge pump supply to be used.
SET
at pin I
DD1
SET
,
if a
DD1
UMA1015M
output is forced LOW). The lock condition output is
software selectable (see Table 4). An out-of-lock condition
is flagged when the phase error is greater than T
value of which is approximately equal to 80 cycles of the
relevant RF input. The out-of-lock flag is only released
after 8 consecutive reference cycles where the phase error
is less than T
via the serial bus, and the pin P0/OOL can be used as an
output port. Three other port outputs P1, P2 and P3
(open-drain transistors) are also available.
Serial programming bus
A simple 3-line unidirectional serial bus is used to program
the circuit. The 3 lines are DATA, CLK and
data sent to the device is loaded in bursts framed by E.
Programming clock edges are ignored until E goes active
LOW. The programmed information is loaded into the
addressed latch when E returns inactive HIGH. This is
allowed when CLK is in either state without causing any
consequences to the register data. Only the last 21 bits
serially clocked into the device are retained within the
programming register. Additional leading bits are ignored,
and no check is made on the number of clock pulses. The
fully static CMOS design uses virtually no current when the
bus is inactive. It can always capture new programming
data even during power-down of both synthesizers.
However when either synthesizer A or synthesizer B or
both are powered-on, the presence of a TCXO signal is
required at pin 8 (f
,
Data format
Data is entered with the most significant bit first. The
leading bits make up the data field, while the trailing four
bits are an address field. The address bits are decoded on
the rising edge of
to store the data in the addressed latch. To ensure that
data is correctly loaded on first power-up,E should be held
LOW and only taken HIGH after having programmed an
appropriate register. To avoid erroneous divider ratios, the
pulse is inhibited during the period when data is read by
the frequency dividers. This condition is guaranteed by
respecting a minimum E pulse width after data transfer.
The data format and register bit allocations are shown in
Table 2.
. The out-of-lock function can be disabled,
00L
E (enable). The
) for correct programming.
XTALIN
E. This produces an internal load pulse
00L
, the
Out-of-lock indication/output ports
There is a lock detector on-chip for each synthesizer. The
lock condition of each, or both loops, is output via an
open-drain transistor which drives the pin P0/OOL (when
out-of-lock, the transistor is turned on and therefore the
1995 Jun 22 5
1995 Jun 22 6
Table 2 Bit allocation
FIRST REGISTER BIT ALLOCATION LAST
p1 p2 p3 p4 p5 p6 p7 p8 p9 p10 p11 p12 p13 p14 p15 p16 p17 p18 p19 p20 p21
dt16 dt15 dt14 dt13 dt12 DATA FIELD dt4 dt3 dt2 dt1 dt0 ADDRESS
X X VDON PO OLA OLB CRA CRB X X sPDA sPDB P3 P2 P1 X X 0 0 0 1
MA16 SYNTHESIZER A MAIN DIVIDER COEFFICIENT MA0 0 1 0 0
0 0 0 0 SR R11 REFERENCE DIVIDER COEFFICIENT R0 0 1 0 1
MB16 SYNTHESIZER B MAIN DIVIDER COEFFICIENT MB0 0 1 1 0
RESERVED FOR TEST
Note
1. The test register should not be programmed with any other values except all zeros for normal operation.
Table 3 Bit allocation description
SYMBOL DESCRIPTION
sPDA, sPDB software power-down for synthesizers A and B (0 = power-down)
P3, P2, P1 and P0 bits output to pins 1, 2, 9 and 19 (1 = high impedance)
VDON voltage doubler enable (1 = doubler enabled)
OLA, OLB out-of-lock select; selects signal output to pin 19 (see Table4)
CRA, CRB charge pump A/B current to I
SR reference frequency ratio select (see Table 6)
ratio select (see Table 5)
SET
(1)
0000
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Low-power dual frequency synthesizer
for radio communications
Table 4 Out-of-lock select
OLA OLB OUTPUT AT PIN 19
00P0
0 1 lock status of loop B; OOLB
1 0 lock status of loop A; OOLA
1 1 logic OR function of loops A and B
Table 5 Charge pump current ratio
CRA/CRB CURRENT AT PUMP
0I
1I
=12×I
CP
=24×I
CP
SET
SET
UMA1015M
Table 6 Reference division ratio
SR SYNTHESIZER A SYNTHESIZER B
0R R
1R 2R
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Low-power dual frequency synthesizer
UMA1015M
for radio communications
Power-down modes
The device can be powered down either via pin HPD
(active LOW = power-down) or via the serial bus (bits
SPDA and SPDB, logic 0 = power-down). The
synthesizers are powered up when both hardware and
software Power-down signals are at logic 1. When only
one synthesizer is powered down, the functions common
to both will be maintained. When both synthesizers are
LIMITING VALUES
In accordance with the Absolute Maximum Rating System (IEC 134).
SYMBOL PARAMETER MIN. MAX. UNIT
V
DD1
, V
DD2
DC range of digital power supply voltage with respect
to DGND
V
∆V
V
CC
CC-DD
n
DC charge pump supply voltage with respect to AGND −0.3 +6.0 V
difference in voltage between VCC and V
DC voltage at pins 1, 2, 5, 6, 8 to 15, 19 and 20 with
respect to DGND
V
∆V
3, 17
GND
DC voltage at pins 3 and 17 with respect to AGND −0.3 VCC+ 0.3 V
difference in voltage between AGND and DGND
(these pins should be connected together)
T
T
stg
amb
storage temperature −55 +125 °C
operating ambient temperature −30 +85 °C
switched off, only the voltage doubler (if enabled) will
remain active drawing a reduced current. An internal
oscillator will drive the doubler in this situation. If both
synthesizers have been in a power-down condition, then
when one or both synthesizers are reactivated, the
reference and main dividers restart in such a way as to
avoid large random phase errors at the phase comparator.
−0.3 +6.0 V
DD1
, V
DD2
−0.3 +6.0 V
−0.3 V
+ 0.3 V
DD1
−0.3 +0.3 V
HANDLING
Inputs and outputs are protected against electrostatic discharge in normal handling. However, to be totally safe, it is
desirable to take normal precautions appropriate to handling MOS devices.
1995 Jun 22 7

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Low-power dual frequency synthesizer
UMA1015M
for radio communications
CHARACTERISTICS
V
DD1=VDD2
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
Supply; (V
V
, V
DD1
I
+ I
DD1
I
DDpda
I
DDpdb
I
DDpd
V
CC
I
CC
I
CCpd
= 2.6 to 5.5 V; VCC= 2.6 to 6.0 V; T
, V
DD1
digital supply voltage V
DD2
total digital supply current
DD2
from V
,
total digital supply current
from V
and VCC) voltage doubler disabled, external supply on V
DD2
and V
DD1
DD1
and V
DD2
DD2
one synthesizer in
power-down mode
digital supply current in
power-down mode
charge pump supply
voltage
charge pump supply
current
charge pump supply
current in power-down
mode
with
=25°C; unless otherwise specified.
amb
DD1=VDD2
f
= 12.8 MHz;
XTAL
both synthesizers on;
V
DD1=VDD2
= 12.8 MHz;
f
XTAL
=3V
both synthesizers on;
V
DD1=VDD2
f
= 12.8 MHz; one
XTAL
= 5.5 V
synthesizer powered down;
V
DD1=VDD2
f
= 12.8 MHz; one
XTAL
=3V
synthesizer powered down;
V
DD1=VDD2
= 5.5 V
both synthesizers powered
down; V
VCC≥ V
HPD
DD
=0V
both synthesizers on and in
lock; f
= 12.5 kHz
ref
both synthesizers powered
down
CC
2.6 − 5.5 V
− 8.5 − mA
−−12.5 mA
− 5.5 − mA
−−7.5 mA
−−60 µA
2.6 − 6.0 V
−−25 µA
−−25 µA
Voltage doubler enabled
I
DD
I
DDpd
V
CCvd
total digital supply current
from V
DD1
and V
DD2
total digital supply current
in power-down mode from
V
and V
DD1
DD2
charge pump supply
voltage
f
= 12.8 MHz; both
XTAL
synthesizers on and in lock;
V
=3V;
DD1
f
= 16 MHz
doubler
both synthesizers powered
down; V
V
HPD
DD1
=0V
=3V;
DC current drawn from
VCC=50µA
1995 Jun 22 8
− 8.5 12 mA
− 0.25 0.4 mA
2V
DD1
− 1.2 2V
− 0.6 6.0 V
DD1
 Loading...
Loading...