Philips TSA5055T-C2, TSA5055T-C3 Datasheet

DATA SH EET
Product specification
Supersedes data of November 1991
File under Integrated Circuits, IC02
1999 Aug 11
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
TSA5055T
2.65 GHz bidirectional I
2
C-bus
controlled synthesizer

1999 Aug 11 2
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
2.65 GHz bidirectional I2C-bus controlled
synthesizer
TSA5055T
FEATURES
• Complete 2.65 GHz single-chip system
• Low power 5 V, 60 mA
• I2C-bus programming
• In-lock flag
• Varicap drive disable
• Low radiation
• 5-level Analog to Digital Converter (ADC)
• Address selection for Picture-In-Picture (PIP),
DBS tuner, etc.
• 6 controllable outputs, 4 bidirectional
• Power-down flag
• Available in SOT109-1 (SO16) package
• Symmetrical or asymmetrical drive.
APPLICATIONS
• Satellite TV
• High IF cable tuning systems.
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
TheTSA5055Tisasingle-chipPLL frequencysynthesizer
designed for satellite TV tuning systems. It may be used
with a symmetrical input (pins 13 and 14) or with an
asymmetrical input (pin 13).
ControldataisenteredviatheI2C-bus;fiveserialbytesare
required to address the device, select the oscillator
frequency, program the six output ports and set the
charge-pumpcurrent.Fouroftheseportscanalsobe used
as input ports (three general purpose I/O ports, one ADC).
Digital information concerning these ports can be read out
of the TSA5055T on the SDA line (one status byte) during
a READ operation. A flag is set when the loop is ‘in-lock’
and is read during a READ operation. The device has one
fixed I2C-bus address and three programmable
addresses, programmed by applying a specific voltage to
port 3. The phase comparator operates at 7.8125 kHz
when a 4 MHz crystal is used.
QUICK REFERENCE DATA
ORDERING INFORMATION
SYMBOL PARAMETER MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
V
CC
supply voltage 4.5 5 5.5 V
I
CC
supply current − 60 80 mA
f
RF
RF input frequency range 1 − 2.65 GHz
V
I (rms)
input voltage level (RMS value)
1 to 1.8 GHz 50 − 300 mV
1.8 to 2.65 GHz 70 − 300 mV
f
XTAL
crystal oscillator frequency 3.2 4 4.48 MHz
z
XTAL
crystal oscillator impedance (absolute value) 600 1000 −Ω
I
O
open-collector output current P7, P6, P5 and P4 −−10 mA
output current P3 and P0 − 1 − mA
T
amb
ambient temperature −20 − +85 °C
T
stg
storage temperature −40 − +150 °C
TYPE NUMBER
PACKAGE
NAME DESCRIPTION CODE
TSA5055T SO16 plastic small outline package; 16 leads; body width 3.9 mm SOT109-1

1999 Aug 11 3
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
2.65 GHz bidirectional I
2
C-bus controlled
synthesizer
TSA5055T
This text is here in white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here in
_white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here inThis text is here in
white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader. white to force landscape pages to be ...
BLOCK DIAGRAM
handbook, full pagewidth
15-BIT
PROGRAMMABLE
DIVIDER
DIGITAL
PHASE
COMPARATOR
CHARGE-
PUMP
LOGIC
LATCH 3
CONTROL DATA
GATE
3
TTL LEVEL
COMPARATORS
3-BIT
ADC
ADDRESS
SELECTION
I
2
C-BUS
TRANSCEIVER
POWER DOWN
DETECTOR
15-BIT LATCH
DIVIDER RATIO
DIVIDER
N = 512
OSCILLATOR
4 MHz
TO CP
T1
SDA
SCL
Q1
Q2
RF
IN1
RF
IN2
7.8125 kHz
7-BIT LATCH
PORT INFORMATION
IN-LOCK
DETECTOR
P0 P3 P4 P5 P6 P7
f
REF
f
DIV
PRESCALER
16
PD
UD
TSA5055T
MBC307
OS
13
14
2
3
5
4
12
15
1
16
10
11 9
8
7
6
GND
V
CC
Fig.1 Block diagram.

1999 Aug 11 4
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
2.65 GHz bidirectional I2C-bus controlled
synthesizer
TSA5055T
PINNING
SYMBOL PIN DESCRIPTION
PD 1 charge-pump output
Q1 2 crystal oscillator input 1
Q2 3 crystal oscillator input 2
SDA 4 serial data input/output
SCL 5 serial clock input
P7 6 port output/input (general
purpose)
P6 7 port output/input (ADC)
P5 8 port output/input (general
purpose)
P4 9 port output/input (general
purpose)
P3 10 port output (also used for address
selection)
P0 11 port output
V
CC
12 voltage supply
RF
IN1
13 RF signal input 1
RF
IN2
14 RF signal input 2 (decoupled)
GND 15 ground
UD 16 drive output
Fig.2 Pin configuration.
handbook, halfpage
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
TSA5055T
PD
Q1
Q2
SDA
SCL
P7
P6
P5
UD
GND
RF
IN2
RF
IN1
V
CC
P0
P3
P4
MBC304
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
General
The TSA5055T is controlled via the 2-wire I2C-bus. For
programming, there is one (7-bit) module address and the
R/W bit for selecting READ or WRITE mode.
WRITE mode: R/W=0; see Table 1
After the address transmission (first byte), data bytes can
be sent to the device. Four data bytes are needed to fully
program the TSA5055T. The bus transceiver has an
auto-incrementfacilitythatpermits the programming of the
TSA5055T within one single transmission (address + four
data bytes).
The TSA5055T can also be partly programmed on the
condition that the first data byte following the address is
byte 2 or byte 4.
The meaning of the bits in the data bytes is given in
Table 1. The first bit of the first data byte transmitted
indicates whether frequency data (first bit = 0) or
charge-pump and port information (first bit = 1) will follow.
Until an I2C-bus STOP condition is sent by the controller,
additional data bytes can be entered without the need to
re-address the device. This allows a smooth frequency
sweep for fine tuning. At power-on, the ports are set to the
high-impedance state.
The 7.8125 kHz reference frequency is obtained by
dividing the output of the 4 MHz crystal oscillator by 512.
Because the input of the RF signal is first divided by 16,
thestepsizeis125 kHz. A 3.2 MHz crystal can offer a step
size of 100 kHz.
1999 Aug 11 5
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
2.65 GHz bidirectional I2C-bus controlled
synthesizer
TSA5055T
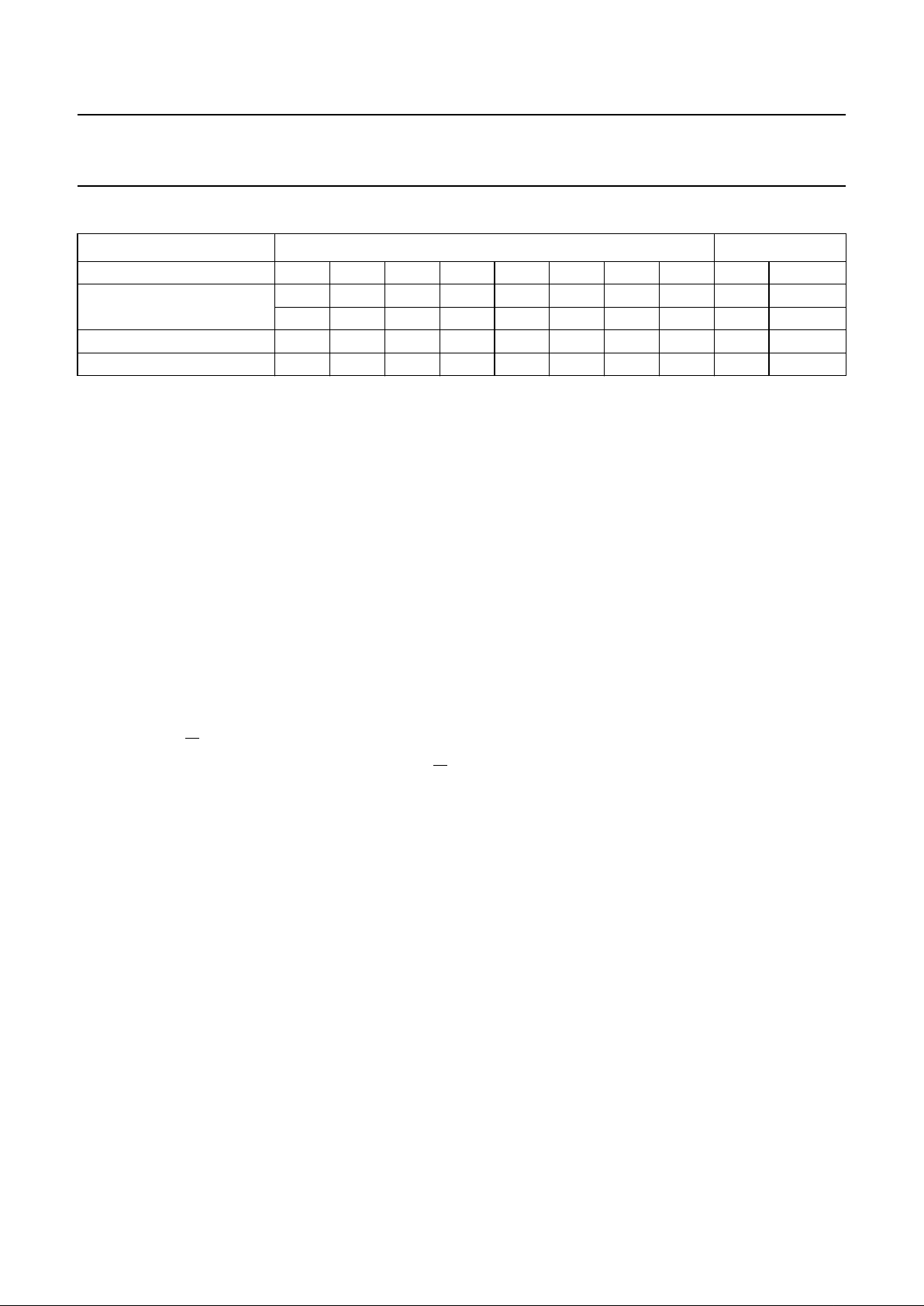
Table 1 Write data format; see notes 1 to 13
Notes
1. MA1 and MA0: programmable address bits (see Table 3).
2. A: Acknowledge bit.
3. N14 to N0: programmable divider bits.
4. N = N14 × 2
14
+ N13 × 213+ ... + N1 × 21+ N0.
5. CP: charge-pump current. CP = 0: 50 µA; CP = 1: 220 µA.
6. P7 to P4 = 1: open-collector outputs are active.
7. P7 to P3 and P0 = 0: outputs are in high-impedance state.
8. P3 and P0 = 1: current-limited outputs are active.
9. T1, T0 and OS = 0, 0 and 0: normal operation.
10. T1 = 1: P6 = f
REF
and P7 = f
DIV
.
11. T0 = 1: 3-state charge-pump.
12. OS = 1: Operational amplifier output is switched off (varicap drive disable).
13. X: don’t care.
BYTE MSB DATA BYTE LSB COMMAND
Address 11000MA1MA00Abyte1
Programmable divider 0 N14 N13 N12 N11 N10 N9 N8 A byte 2
N7 N6 N5 N4 N3 N2 N1 N0 A byte 3
Charge-pump and test bits 1 CP T1 T0 1 1 1 OS A byte 4
Output ports, control bits P7 P6 P5 P4 P3 X X P0 A byte 5
READ mode: R/W=1; see Table 2
Data can be read out of the TSA5055T by setting the R/W
bit to 1. After the slave address has been recognized, the
TSA5055T generates an Acknowledge signal (A) and the
first data byte (status byte) is transferred to the SDA line
(MSB first). Data is valid on the SDA line while the SCL
clock signal is HIGH.
A second data byte can be read out of the TSA5055T if the
processor generates an Acknowledge signal on the SDA
line. End of transmission will occur if the processor does
not send an Acknowledge signal.
The TSA5055T will then release the data line to allow the
processor to generate a STOP condition. When ports
P3 to P7 are used as inputs, they must be programmed to
their high-impedance state.
The POR flag (Power-On Reset) is set to 1 at power-on
and when VCC goes below 3 V. The flag is reset when an
end of data is detected by the TSA5055T (end of a READ
sequence). Control of the loop is made possible with the
in-lock flag FL, which indicates when the loop is
phase-locked (FL = 1).

1999 Aug 11 6
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
2.65 GHz bidirectional I2C-bus controlled
synthesizer
TSA5055T
Table 2 Read data format (see notes 1 to 5)
Notes
1. POR: Power-on reset flag (POR = 1 on power-on).
2. FL: in-lock flag (FL = 1 when the loop is phase-locked).
3. I2, I1 and I0: digital information for I/O ports P7, P5 and P4 respectively.
4. A2, A1 and A0: digital outputs of the 5-level ADC. Accuracy is1⁄2LSB (see Table 4).
5. MSB is transmitted first.
Bits I2, I1 and I0 represent the status of the I/O ports P7, P5 and P4, respectively. A logic ‘0’ indicates a LOW level and
a logic ‘1’ a HIGH level (TTL levels). A built-in 5-level ADC is available at I/O port P6. This ADC can be used to feed AFC
information to the controller from the IF section of the receiver, as shown in Fig.4. The relationship between bits A2, A1,
A0 and the input voltage at port P6 is given in Table 4.
Table 3 Address selection
Address selection; see Table 3
The module address contains programmable address bits (MA1 and MA0), which offer the possibility of having several
synthesizers (up to three) in one system. The relationship between MA1 and MA0 and the input voltage at port P3 is
given in Table 3.
Table 4 ADC levels
BYTE MSB DATA BYTE LSB COMMAND
Address 11000MA1MA01Abyte1
Status byte POR FL I2 I1 I0 A2 A1 A0 − byte 2
MA1 MA0 VOLTAGE APPLIED ON PORT P3
0 0 0 to 0.1V
CC
0 1 always valid
1 0 0.4V
CC
to 0.6V
CC
1 1 0.9VCCto 13.5 V
A2 A1 A0 VOLTAGE APPLIED ON PORT P6
1 0 0 0.6V
CC
to V
CC
0 1 1 0.45VCCto 0.6V
CC
0 1 0 0.3VCCto 0.45V
CC
0 0 1 0.15VCCto 0.3V
CC
0 0 0 0 to 0.15V
CC
 Loading...
Loading...