Philips TEA1112T-C1, TEA1112AT-C1, TEA1112A-C1, TEA1112-C1 Datasheet
DATA SH EET
Product specification
Supersedes data of 1996 Feb 16
File under Integrated Circuits, IC03
1997 Mar 26
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
TEA1112; TEA1112A
Low voltage versatile telephone
transmission circuits with dialler
interface
1997 Mar 26 2
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Low voltage versatile telephone
transmission circuits with dialler interface
TEA1112; TEA1112A
FEATURES
• Low DC line voltage; operates down to 1.6 V (excluding
polarity guard)
• Voltage regulator with adjustable DC voltage
• Provides a supply for external circuits
• Symmetrical high impedance inputs (64 kΩ) for
dynamic, magnetic or piezo-electric microphones
• Asymmetrical high impedance input (32 kΩ) for electret
microphones
• DTMF input with confidence tone
• Mute input for pulse or DTMF dialling (MUTE for
TEA1112 and MUTE for TEA1112A)
• Receiving amplifier for dynamic, magnetic or
piezo-electric earpieces
• AGC line loss compensation for microphone and
earpiece amplifiers
• LED on-hook/off-hook status indication
• Microphone mute function (MMUTE for TEA1112 and
MMUTE for TEA1112A).
APPLICATION
• Line powered telephone sets, cordless telephones, fax
machines and answering machines.
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The TEA1112; TEA1112A are bipolar integrated circuits
that perform all speech and line interface functions
required in fully electronic telephone sets. They perform
electronic switching between speech and dialling. The ICs
operate at a line voltage down to 1.6 V DC (with reduced
performance) to facilitate the use of telephone sets
connected in parallel.
A current (proportional to the line current and internally
limited to a typical value of 19.5 mA) is available to drive
an LED which indicates the on-hook/off-hook status.
The microphone amplifier can be disabled during speech
condition by means of a microphone mute function.
All statements and values refer to all versions unless
otherwise specified.
QUICK REFERENCE DATA
I
line
= 15 mA; VEE=0V; R
SLPE
=20Ω; AGC pin connected to VEE; Z
line
= 600 Ω; f = 1 kHz; T
amb
=25°C;
unless otherwise specified.
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
I
line
line current operating range normal operation 11 − 140 mA
with reduced performance 1 − 11 mA
I
LED(max)
maximum supply current available I
line
=18mA − 0.5 − mA
I
line
>76mA − 19.5 − mA
V
LN
DC line voltage 3.35 3.65 3.95 V
I
CC
internal current consumption VCC= 2.9 V − 1.15 1.4 mA
V
CC
supply voltage for peripherals Ip=0mA − 2.9 − V
G
vtrx
typical voltage gain range
microphone amplifier V
MIC
= 2 mV (RMS) 38.8 − 51.8 dB
receiving amplifier V
IR
= 6 mV (RMS) 19.2 − 31.2 dB
∆G
vtrx
gain control range for microphone and
receiving amplifiers with respect to
I
line
=15mA
I
line
=85mA − 5.8 − dB
∆G
vtxm
microphone amplifier gain reduction − 80 − dB
1997 Mar 26 3
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Low voltage versatile telephone
transmission circuits with dialler interface
TEA1112; TEA1112A
ORDERING INFORMATION
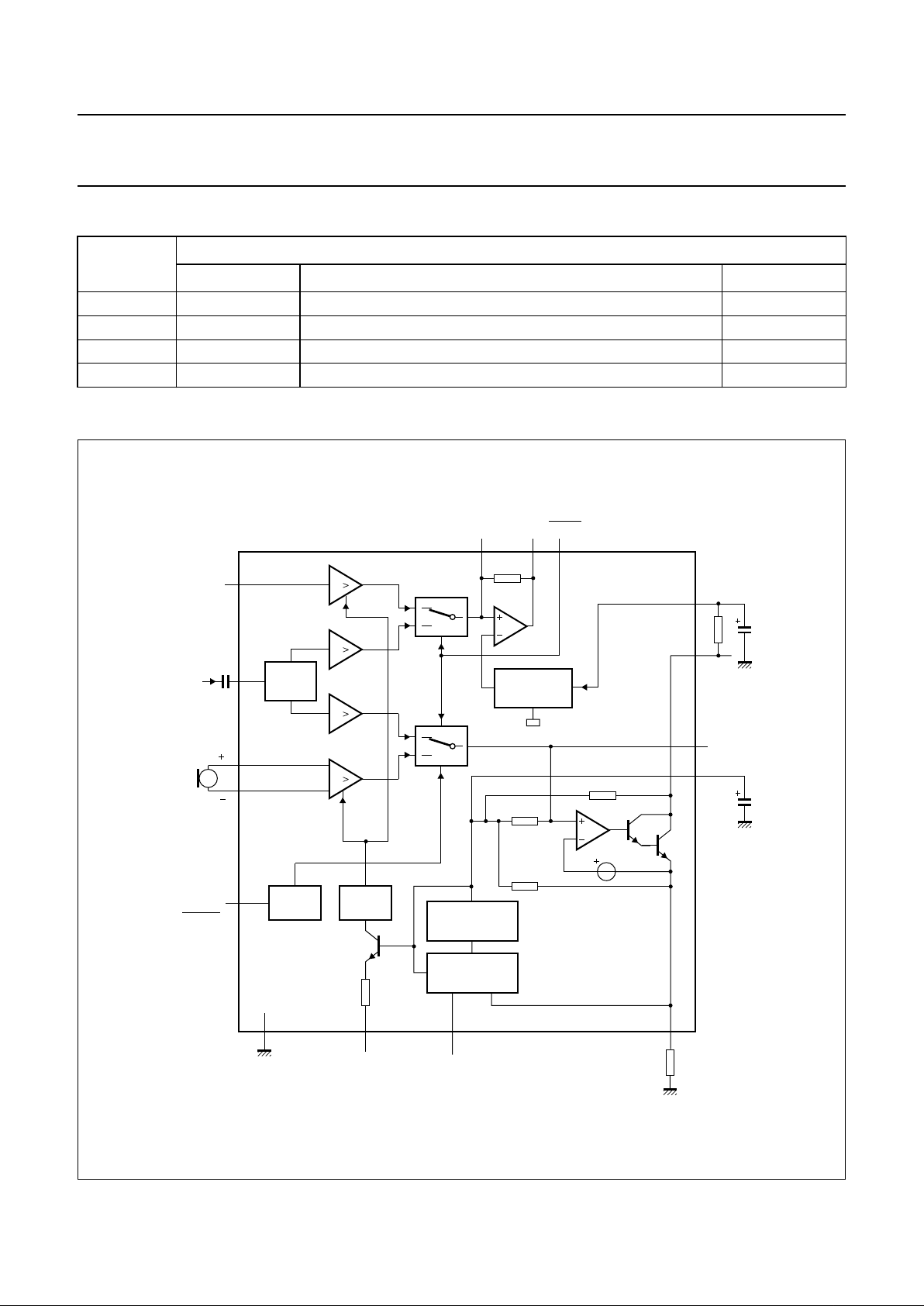
BLOCK DIAGRAM
TYPE
NUMBER
PACKAGE
NAME DESCRIPTION VERSION
TEA1112 DIP16
plastic dual in-line package; 16 leads (300 mil)
SOT38-4
TEA1112A DIP16
plastic dual in-line package; 16 leads (300 mil)
SOT38-4
TEA1112T SO16
plastic small outline package; 16 leads; body width 3.9 mm
SOT109-1
TEA1112AT SO16
plastic small outline package; 16 leads; body width 3.9 mm
SOT109-1
Fig.1 Block diagram.
handbook, full pagewidth
ATT.
DTMF
V− I
MICRO
MUTE
AGC
CIRCUIT
CURRENT
REFERENCE
LOW VOLTAGE
CIRCUIT
LED
DRIVER
IR
MIC
MIC
MMUTE
or
MMUTE
V
EE
I
LED
AGC
SLPE
TEA1112
TEA1112A
5
4
231013
11
6
12
15 14 8
16
1
7
9
GAS
GAR
QR
LN
V
CC
REG
MUTE
or
MUTE
V− I
V− I
V− I
MBE793
1997 Mar 26 4
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Low voltage versatile telephone
transmission circuits with dialler interface
TEA1112; TEA1112A
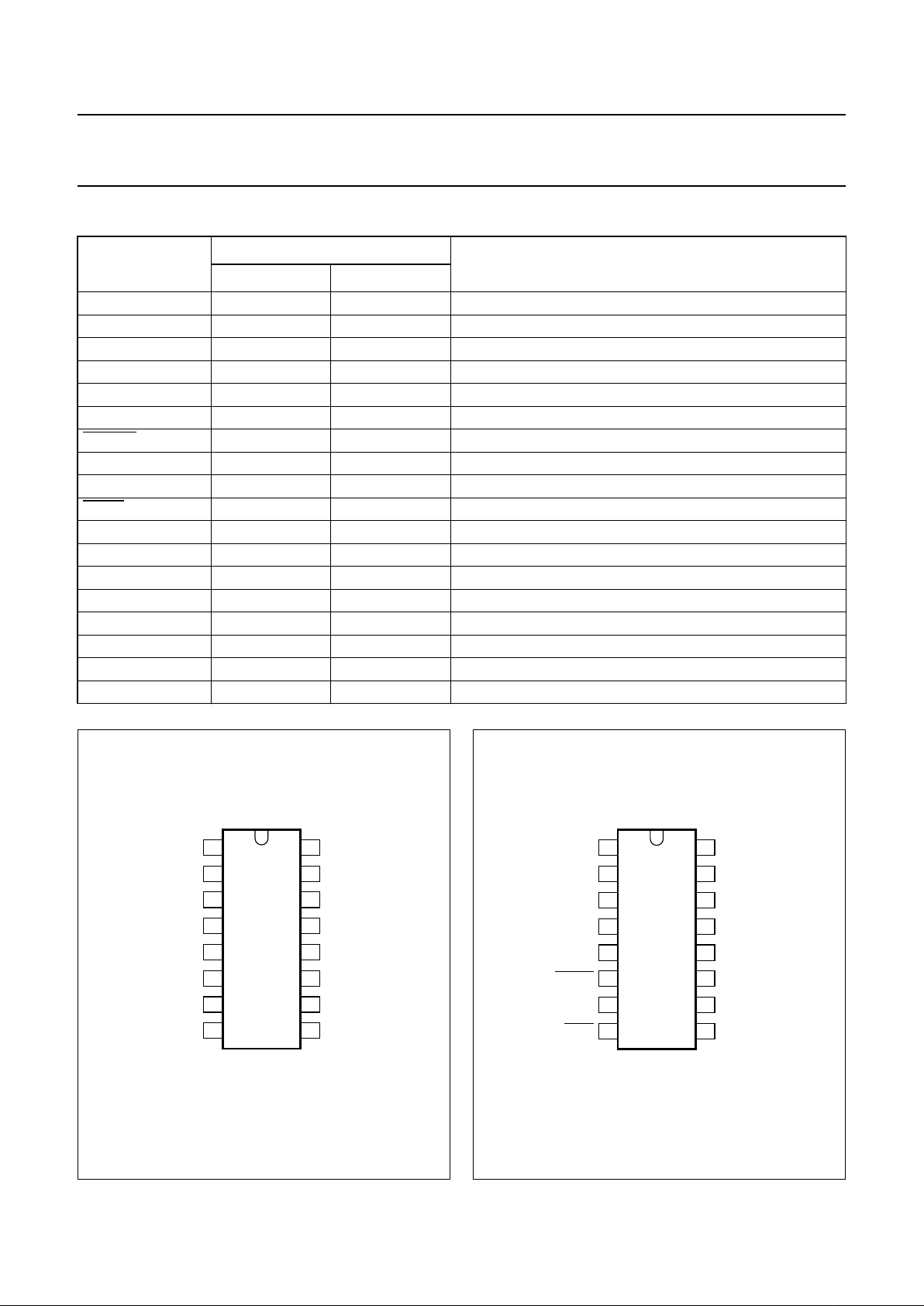
PINNING
SYMBOL
PIN
DESCRIPTION
TEA1112 TEA1112A
LN 1 1 positive line terminal
SLPE 2 2 slope (DC resistance) adjustment
I
LED
3 3 available output current to drive a LED
REG 4 4 line voltage regulator decoupling
GAS 5 5 sending gain adjustment
MMUTE 6 − microphone mute input
MMUTE − 6 microphone mute input (active LOW)
DTMF 7 7 dual-tone multi-frequency input
MUTE 8 − mute input to select speech or dialling mode
MUTE − 8 mute input to select speech or dialling mode (active LOW)
IR 9 9 receiving amplifier input
AGC 10 10 automatic gain control/line loss compensation
MIC− 11 11 inverting microphone amplifier input
MIC+ 12 12 non-inverting microphone amplifier input
V
EE
13 13 negative line terminal
QR 14 14 receiving amplifier output
GAR 15 15 receive gain adjustment
V
CC
16 16 supply voltage for speech circuit and peripherals
Fig.2 Pin configuration (TEA1112).
handbook, halfpage
TEA1112
MBE791
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
V
CC
GAR
QR
V
EE
MIC+
MIC−
AGC
IR
LN
SLPE
I
LED
REG
GAS
MMUTE
DTMF
MUTE
Fig.3 Pin configuration (TEA1112A).
handbook, halfpage
TEA1112A
MBE790
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
V
CC
GAR
QR
V
EE
MIC+
MIC−
AGC
IR
LN
SLPE
I
LED
REG
GAS
MMUTE
DTMF
MUTE

1997 Mar 26 5
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Low voltage versatile telephone
transmission circuits with dialler interface
TEA1112; TEA1112A
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
All data given in this chapter are typical values, except
when otherwise specified.
Supply (pins LN, SLPE, V
CC
and REG)
The supply for the TEA1112; TEA1112A and their
peripherals is obtained from the telephone line.
The ICs generate a stabilized reference voltage (V
ref
)
between pins LN and SLPE. This reference voltage is
equal to 3.35 V, is temperature compensated and can be
adjusted by means of an external resistor (RVA). It can be
increased by connecting the RVA resistor between
pins REG and SLPE (see Fig.5), or decreased by
connecting the RVA resistor between pins REG and LN.
The voltage at pin REG is used by the internal regulator to
generate the stabilized reference voltage and is decoupled
by a capacitor (C
REG
) which is connected to VEE. This
capacitor, converted into an equivalent inductance (see
Section “Set impedance”), realizes the set impedance
conversion from its DC value (R
SLPE
) to its AC value (R
CC
in the audio-frequency range). The voltage at pin SLPE is
proportional to the line current. Figure 4 illustrates the
supply configuration.
The ICs regulate the line voltage at pin LN, and can be
calculated as follows:
V
LN
V
refRSLPEISLPE
×+=
I
SLPEIlineICC
– Ip– I∗– I
LED
I+
sh
==
Where:
I
line
= line current
ICC= current consumption of the IC
Ip= supply current for peripheral circuits
I* = current consumed between LN and V
EE
I
LED
= supply current for the LED component
Ish= the excess line current shunted to SLPE (and VEE)
via LN.
The preferred value for R
SLPE
is 20 Ω. Changing R
SLPE
will
affect more than the DC characteristics; it also influences
the microphone and DTMF gains, the LED supply current
characteristic, the gain control characteristics, the
sidetone level and the maximum output swing on the line.
The internal circuitry of the TEA1112; TEA1112A is
supplied from pin VCC. This voltage supply is derived from
the line voltage by means of a resistor (RCC) and must be
decoupled by a capacitor C
VCC
. It may also be used to
supply peripheral circuits such as dialling or control
circuits. The VCC voltage depends on the current
consumed by the IC and the peripheral circuits as shown
by the formula (see also Figs.6 and 7). R
CCint
is the
internal impedance of the voltage supply point, and I
rec
is
the current consumed by the output stage of the earpiece
amplifier.
V
CC
V
CC0RCCintIpIrec
–()×–=
V
CC0
VLNR
CCICC
×–=
Fig.4 Supply configuration.
handbook, full pagewidth
LED
DRIVER
I
sh
R
p
R
d
I
SLPE
REG
LN
R
GASint
from pre amp
SLPE
45.5 kΩ
15.5 kΩ
V
EE
V
d
V
CC
R
CC
C
VCC
I
CC
C
REG
R
SLPE
V
exch
R
exch
I
LED
I
LED
I
line
R
line
TEA1112
TEA1112A
I*
I
P
peripheral
circuits
100 µF
4.7 µF
20 Ω
69 kΩ
619 Ω
MBE789
1997 Mar 26 6
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Low voltage versatile telephone
transmission circuits with dialler interface
TEA1112; TEA1112A
The DC line current flowing into the set is determined by
the exchange supply voltage (V
exch
), the feeding bridge
resistance (R
exch
), the DC resistance of the telephone line
(R
line
) and the reference voltage (V
ref
). With line currents
below 7.5 mA, the internal reference voltage (generating
V
ref
) is automatically adjusted to a lower value. This means
that more sets can operate in parallel with DC line voltages
(excluding the polarity guard) down to an absolute
minimum voltage of 1.6 V. At currents below 7.5 mA, the
circuit has limited sending and receiving levels. This is
called the low voltage area.
Set impedance
In the audio frequency range, the dynamic impedance is
mainly determined by the R
CC
resistor. The equivalent
impedance of the circuits is illustrated in Fig.8.
LED supply (pin I
LED
)
The TEA1112; TEA1112A give an on-hook/off-hook status
indication. This is achieved by a current made available to
drive an LED connected between pins I
LED
and LN. In the
low voltage area, which corresponds to low line current
conditions, no current is available for this LED.
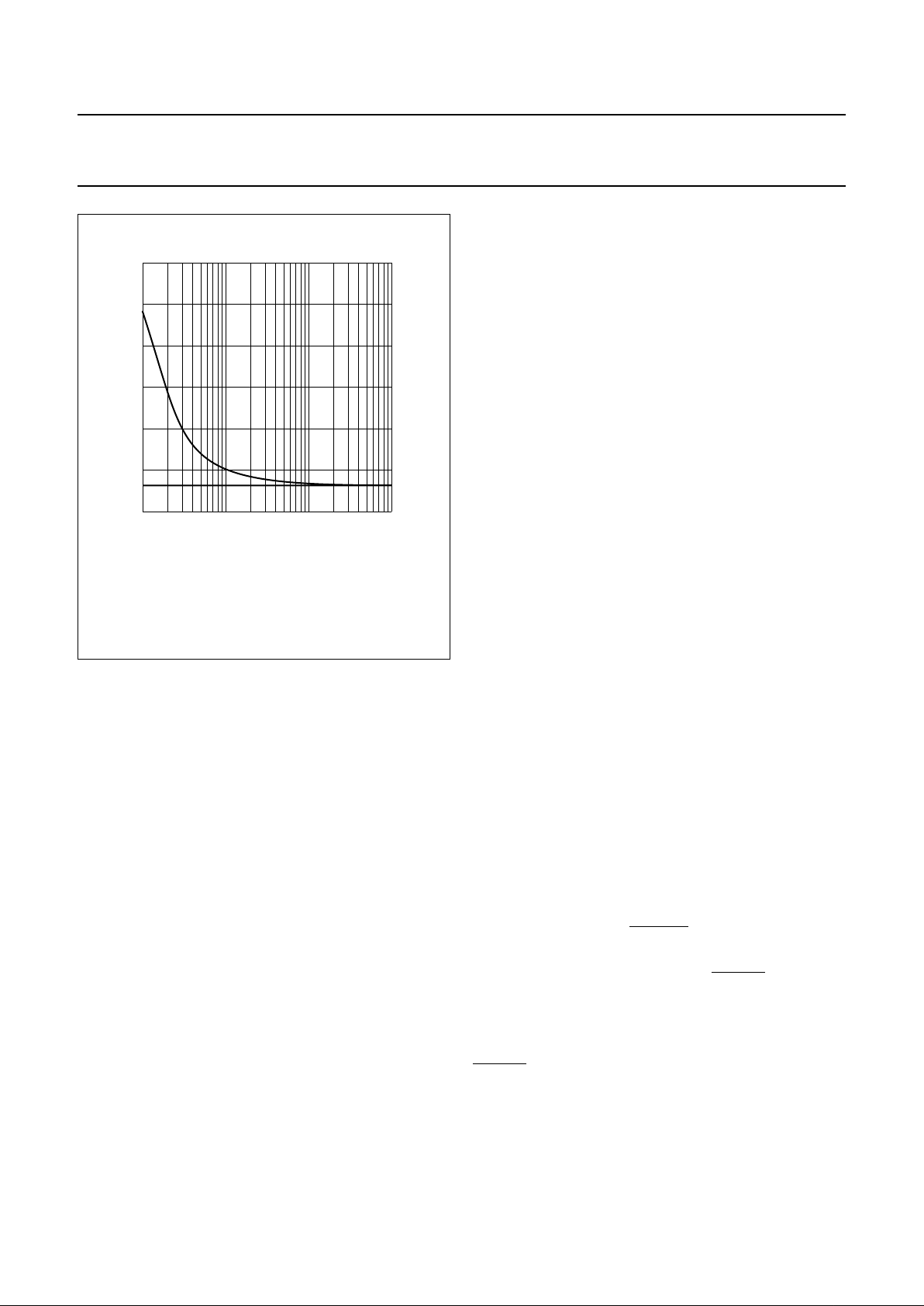
Fig.5 Reference voltage adjustment by RVA.
(1) Influence of RVA on V
ref
.
(2) V
ref
without influence of RVA.
handbook, halfpage
6.0
V
ref
(V)
3.0
4.0
(1)
(2)
5.0
RVA (Ω)
MGD176
10
5
10
4
10
6
10
7
For line currents higher than a threshold, I
LEDstart
, the I
LED
current increases proportionally to the line current (with a
ratio of one third). The I
LED
current is internally limited to
19.5 mA (see Fig.9). If no LED device is used in the
application, the I
LED
pin should be shorted to pin SLPE.
For 17 mA < I
line
< 77 mA:
This LED driver is referenced to SLPE. Consequently, all
the I
LED
supply current will flow through the R
SLPE
resistor.
The AGC characteristics are not disturbed (see Fig.4).
Microphone amplifier (pins MIC+, MIC− and GAS)
The TEA1112; TEA1112A have symmetrical microphone
inputs. The input impedance between pins MIC+ and
MIC− is 64 kΩ (2 × 32 kΩ). The voltage gain from
pins MIC+/MIC− to pin LN is set at 51.8 dB (typ). The gain
can be decreased by connecting an external resistor R
GAS
between pins GAS and REG. The adjustment range is
13 dB. A capacitor C
GAS
connected between pins GAS
and REG can be used to provide a first-order low-pass
filter. The cut-off frequency corresponds to the time
constant C
GAS
× (R
GASint
// R
GAS
). R
GASint
is the internal
resistor which sets the gain with a typical value of 69 kΩ.
Automatic gain control is provided on this amplifier for line
loss compensation.
Microphone mute (pin MMUTE; TEA1112)
The microphone amplifier can be disabled by activating
the microphone mute function. When MMUTE is LOW, the
normal speech mode is entered, depending on the level on
MUTE (see Table 1). When MMUTE is HIGH, the
microphone amplifier inputs are disabled while the DTMF
input is enabled (no confidence tone is provided).
The voltage gain between LN and MIC+/MIC− is
attenuated; the gain reduction is 80 dB (typ).
Microphone mute (pin
MMUTE; TEA1112A)
The microphone amplifier can be disabled by activating
the microphone mute function. When MMUTE is LOW, the
microphone amplifier inputs are disabled while the DTMF
input is enabled (no confidence tone is provided).
The voltage gain between LN and MIC+/MIC− is
attenuated; the gain reduction is 80 dB (typ). When
MMUTE is HIGH, the normal speech mode is entered,
depending on the level on MUTE (see Table 1).
I
LED
I
line
17–
3
----------------------
=
 Loading...
Loading...