Philips TEA1098UH, TEA1098TV Datasheet
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
DATA SH EET
TEA1098
Speech and handsfree IC
Product specification
Supersedes data of 2000 Sep 26
File under Integrated Circuits, IC03
2001 Aug 24

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Speech and handsfree IC TEA1098
FEATURES
Line interface
• Low DC line voltage
• Voltage regulator with adjustable DC voltage
• Symmetrical high impedance inputs (70 kΩ) for
dynamic, magnetic40 or electret microphones
• DTMF input with confidence tone on earphone and/or
loudspeaker
• Receive amplifier for dynamic, magnetic or
piezo-electric earpieces(with externally adjustable gain)
• Automatic Gain Control (AGC) for true line loss
compensation.
Supplies
• Provides a strong 3.35 V regulated supply for
microcontrollers or diallers
• Provides filtered power supply, optimized according to
line current
• Filtered 2.0 V power supply output for electret
microphone
• PD logic input for power-down.
Handsfree
• Asymmetrical high input impedance for electret
microphone
• Loudspeaker amplifier with single-ended rail-to-rail
output and externally adjustable gain
• Dynamic limiter on loudspeaker amplifier to prevent
distortion
• Logarithmic volume controlon loudspeakeramplifier via
linear potentiometer
• Duplex controller consisting of:
– Signal and noise envelope monitors for both
channels (with adjustable sensitivities and timing)
– Decision logic (with adjustable switch-over and Idle
mode timing)
– Voice switch control (with adjustable switching range
and constant sum of gain during switching).
APPLICATIONS
• Line powered telephone sets.
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The TEA1098 is an analog bipolar circuit dedicated to
telephonyapplications. It includesa line interface,handset
(HS) microphone and earpiece amplifiers, handsfree (HF)
microphone and loudspeaker amplifiers and a duplex
controller with signal and noise monitors on both channels.
This IC provides a 3.35 V supply for a microcontroller or
dialler and a 2.0 V filtered voltage supply for an electret
microphone.
ORDERING INFORMATION
TYPE
NUMBER
TEA1098TV VSO40 plastic very small outline package; 40 leads SOT158-1
TEA1098UH − bare die; on foil −
2001 Aug 24 2
NAME DESCRIPTION VERSION
PACKAGE

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Speech and handsfree IC TEA1098
QUICK REFERENCE DATA
I
= 15 mA; R
line
connected to pin LN;
specified.
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
I
line
V
SLPE
V
BB
V
DD
I
BB
I
BB(pd)
G
v(MIC-LN)
G
v(IR-RECO)
∆G
v(QR)
G
v(TXIN-TXOUT)
G
v(HFTX-LN)
G
v(HFRX-LSAO
SWRA switching range − 40 − dB
∆SWRA switching range adjustment R
∆G
v(trx)
SLPE
=20Ω;Z
= 600 Ω; f = 1 kHz;T
line
=25°C forTEA1098TV;Tj=25°C forTEA1098UH; pin AGC
amb
PD = HIGH; HFC = LOW; MUTE = HIGH; measured according to test circuit; unless otherwise
line current operating range normal operation 11 − 130 mA
with reduced performance 1 − 11 mA
stabilized voltage between
pins SLPE and GND
regulated supply voltage for
internal circuitry
regulated supply voltage on
pin V
DD
current available on pin V
BB
I
= 15 mA 3.4 3.7 4.0 V
line
I
= 70 mA 5.7 6.1 6.5 V
line
I
= 15 mA 2.75 3.0 3.25 V
line
I
= 70 mA 4.9 5.3 5.7 V
line
VBB> 3.35 V + 0.25 V (typ.) 3.1 3.35 3.6 V
otherwise − V
− 0.25 − V
BB
in speech mode − 11 − mA
in handsfree mode − 9 − mA
current consumption on V
BB
PD = LOW − 460 −µA
during power-down phase
voltagegain from pins MIC+/MIC−
V
= 5 mV (RMS) 43.3 44.3 45.3 dB
MIC
to LN
voltage gain from pin IR
VIR= 8 mV (RMS) 28.7 29.7 30.7 dB
(referenced to LN) to RECO
gain voltage range between
−3 − +15 dB
pins RECO and QR
voltage gain from pin TXIN to
TXOUT
voltage gain from pin HFTX to LN V
) voltage gain from pinHFRX
to LSAO
gain control range for transmitand
V
= 3 mV (RMS);
TXIN
R
= 30.1 kΩ
GATX
= 15 mV (RMS) 33.5 34.7 35.9 dB
HFTX
V
= 30 mV (RMS);
HFRX
R
= 255 kΩ; I
GALS
= 365 kΩ−40 − +12 dB
SWR
I
= 70 mA 5.45 6.45 7.45 dB
line
=70mA
line
12.7 15.2 17.7 dB
25.5 28 30.5 dB
receive amplifiers affected by the
AGC; with respect to I
=15mA
line
2001 Aug 24 3
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Speech and handsfree IC TEA1098
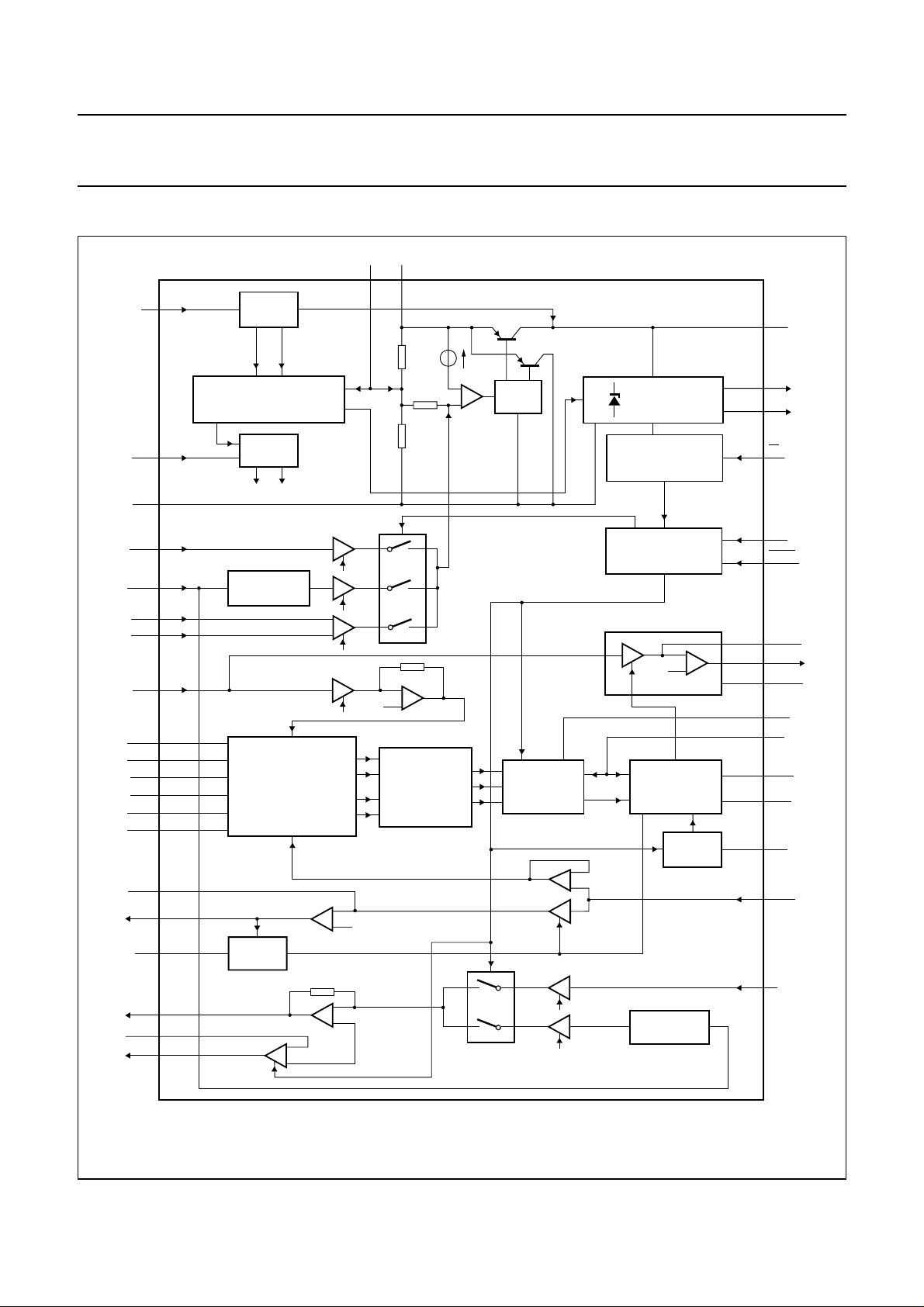
BLOCK DIAGRAM
REG
handbook, full pagewidth
LN 18
STARTER
LINE CURRENT DETECTION
LOW VOLTAGE BEHAVIOUR
19 17
SLPE
R1
SWITCH
SUPPLY
MANAGEMENT
13
V
BB
V
22
DD
MICS
23
AGC
GND
HFTX
DTMF
MIC+
MIC−
TXIN
TSEN
TENV
TNOI
RNOI
RENV
RSEN
GALS
LSAO
30
24
25
40
29
32
27
28
26
1
2
5
PD
HFC
MUTE
GATX
TXOUT
GNDTX
SWT
IDT
STAB
SWR
VOL
HFRX
21
16
39
35
34
33
31
8
7
6
9
11
10
14
15
AGC
Tail currents for preamps
ATTENUATOR
TX AND RX
ENVELOPE AND NOISE
DETECTORS
BUFFERS
AND
COMPARATORS
TEA1098TV
DUCO LOGIC
SWT STATUS
POWER-DOWN
CURRENT SOURCES
LOGIC
INPUTS
DECODING
VOICE
SWITCH
VOLUME
CONTROL
12
DLC
RECO
GARX
QR
38
37
36
DYNAMIC
LIMITER
Fig.1 Block diagram.
2001 Aug 24 4
ATTENUATOR
20
MGL317
IR
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Speech and handsfree IC TEA1098
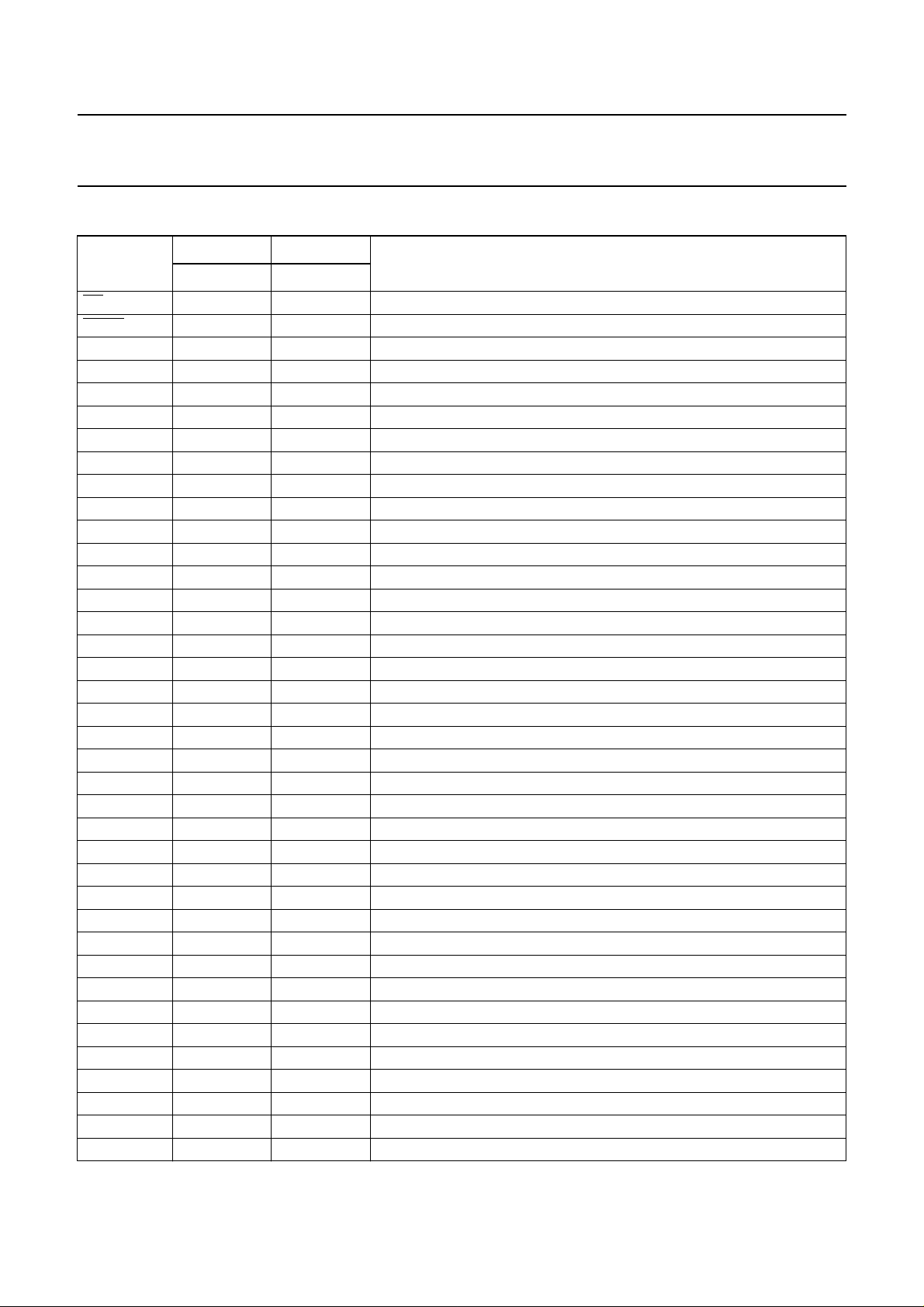
PINNING
SYMBOL
PD 1 40 power-down input (active LOW)
MUTE 2 41 logic input (active LOW)
n.c. 3 42 not connected
n.c. 4 43 not connected
n.c. − 44 not connected
HFRX 5 1 receive input for loudspeaker amplifier
TNOI 6 2 transmit noise envelope timing adjustment
TENV 7 3 transmit signal envelope timing adjustment
TSEN 8 4 transmit signal envelope sensitivity adjustment
RNOI 9 5 receive noise envelope timing adjustment
RSEN 10 6 receive signal envelope sensitivity adjustment
RENV 11 7 receive signal envelope timing adjustment
DLC 12 8 dynamic limiter capacitor for the loudspeaker amplifier
V
BB
GALS 14 10 loudspeaker amplifier gain adjustment
LSAO 15 11 loudspeaker amplifier output
n.c. − 12 not connected
GND 16 13 ground reference
SLPE 17 14 and 15 line current sense
LN 18 16 positive line terminal input
REG 19 17 line voltage regulator decoupling
IR 20 18 receive amplifier input
AGC 21 19 automatic gain control or line loss compensation input
V
DD
MICS 23 21 microphone supply
STAB 24 22 reference current adjustment
SWR 25 23 switching range adjustment
VOL 26 24 loudspeaker volume adjustment
SWT 27 25 switch-over timing adjustment
IDT 28 26 Idle mode timing adjustment
TXOUT 29 27 HF microphone amplifier output
GATX 30 28 HF microphone amplifier gain adjustment
TXIN 31 29 HF microphone amplifier input
GNDTX 32 30 and 31 ground reference for microphone amplifiers
MIC− 33 32 negative handset microphone amplifier input
MIC+ 34 33 positive handset microphone amplifier input
DTMF 35 34 dual tone multi-frequency input
QR 36 35 earpiece amplifier output
PIN PAD
DESCRIPTION
TEA1098TV TEA1098UH
13 9 stabilized supply for internal circuitry
22 20 3.35 V regulated voltage supply for microcontrollers
2001 Aug 24 5
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Speech and handsfree IC TEA1098
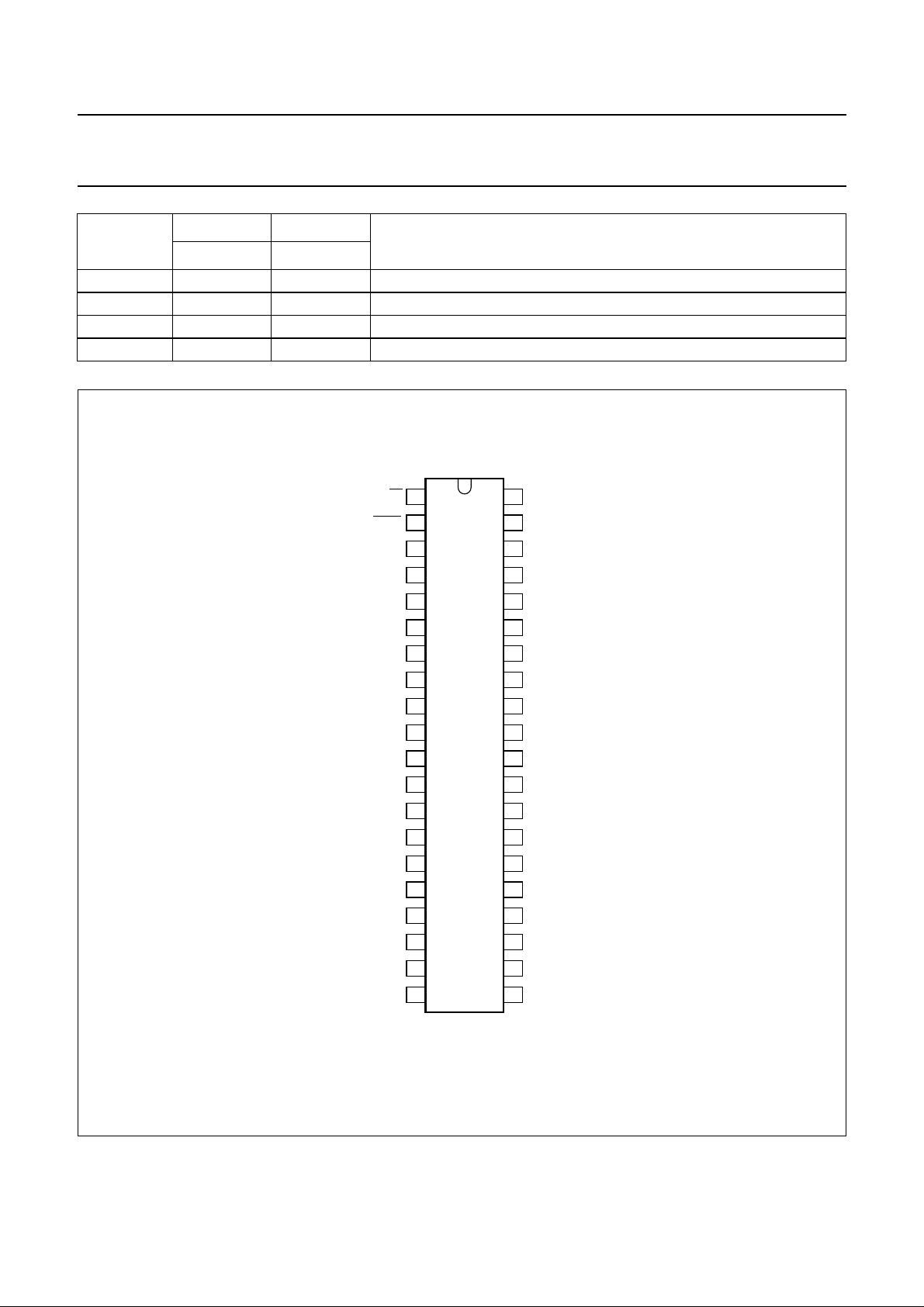
SYMBOL
DESCRIPTION
TEA1098TV TEA1098UH
GARX 37 36 earpiece amplifier gain adjustment
RECO 38 37 receive amplifier output
HFTX 39 38 transmit input for line amplifier
HFC 40 39 logic input
PIN PAD
handbook, halfpage
PD
MUTE
n.c.
n.c.
HFRX
TNOI
TENV
TSEN
RNOI
RSEN
RENV
DLC
V
BB
GALS
LSAO
GND
SLPE
LN
REG
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
IR
TEA1098TV
MGL341
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
HFC
HFTX
RECO
GARX
QR
DTMF
MIC+
MIC−
GNDTX
TXIN
GATX
TXOUT
IDT
SWT
VOL
SWR
STAB
MICS
V
DD
AGC
Fig.2 Pin configuration.
2001 Aug 24 6

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Speech and handsfree IC TEA1098
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
All data values given in this chapter are typical, except
when otherwise specified.
Supplies
LINE INTERFACE AND INTERNAL SUPPLY (PINS LN, SLPE,
REG AND VBB)
Thesupply for theTEA1098 and itsperipheralsis obtained
from the line. The IC generates a stabilized reference
voltage (V
) between pins SLPE and GND. This
ref
reference voltage is equal to 3.7 V for line currents below
18 mA. When the line current rises above 45 mA, the
reference voltage rises linearly to 6.1 V. For line currents
below9 mA,V
isautomaticallyadjusted to alowervalue.
ref
The performance of the TEA1098 in this so-called low
voltage area is limited (see Section “Low voltage
behaviour”). The reference voltage is temperature
compensated.
The voltage between pins SLPE and REG is used by the
internal regulator to generate the stabilized reference
voltage and is decoupled by a capacitor connected
between pins LN and REG. This capacitor, converted into
an equivalent inductance realizes the set impedance
conversionfrom its DC value(R
)to its AC value(done
SLPE
by an external impedance).
The IC regulates the line voltage at pin LN which can be
calculated as follows:
V
V
LN
I
SLPEIlineILN
refRSLPEISLPE
×+=
–=
where:
I
= line current
line
ILN= current consumed on pin LN (approximately a
few µA)
I
= current flowing through the R
SLPE
The preferred value for R
is 20 Ω. Changing this value
SLPE
SLPE
resistor.
not only affects the DC characteristics, it also influences
the transmit gains to the line, the gain control
characteristic,the sidetonelevel, and themaximum output
swing on the line.
Figure 3 shows that the internal circuit is supplied by
pin V
, whichcombined with the line interface is a strong
BB
supply point.
The line current through resistor R
is sunk by the
SLPE
VBBvoltage stabilizer, and is suitable for supplying a
loudspeaker amplifieror any peripheral IC. VBBis 3.0 Vat
line currents below 18 mA and rises linearly to 5.3 V when
the line current rises above 45 mA. It is temperature
compensated.
The current switch (TR1 and TR2) is intended to reduce
distortionof large AC linesignals. Current I
SLPE
issupplied
to VBB via TR1 when the voltage on pin SLPE is above
VBB+ 0.25 V. Whenthe voltage on pin SLPE is below this
value, I
Voltage V
is shunted to GND via TR2.
SLPE
can be increased by connecting an external
ref
resistor between pins REG and SLPE. For large line
currents, this increase can slightly affect some dynamic
performances such as maximumsignal level on the line at
THD = 2%. The external resistor does not affect the
voltage on pin VBB; see Fig.4 for the main DC voltages.
V
SUPPLY FOR MICROCONTROLLERS (PIN V
DD
The voltage on the V
supply point follows the voltage on
DD
DD
)
VBBwith a difference typically of 250 mV, internallylimited
to 3.35 V. This voltage is temperature compensated. This
supply point can provide a current of up to typically 3 mA.
Itsinternal consumption stayslow (a few 10 nA)as long as
VDD does not exceed 1.5 V (see Fig.5).
An external voltage can be connected to VDD with limited
extra consumptionon VDD(typically 100 µA).This voltage
source should not be below 3.5 V or above 6 V.
VBBand VDDcan supply current to external circuits within
the line limits, taking into account the internal current
consumption.
2001 Aug 24 7

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Speech and handsfree IC TEA1098
handbook, full pagewidth
LN
REG
GND
C
REG
4.7 µF
SLPE
TP1
R3
R2
TN1
R1
from
preamp
R
SLPE
20 Ω
J1
Fig.3 Line interface principle.
SUPPLY FOR MICROPHONE (PINS MICS AND GNDTX)
The MICS output can be used as a supply for an electret
microphone. Its voltage is equal to 2.0 V; it can source a
current of up to 1 mA and has an output impedance equal
to 200 Ω.
LOW VOLTAGE BEHAVIOUR
For line currents below 9 mA, the reference voltage is
automatically adjusted to a lower value; the VBB voltage
follows the SLPE voltagewith adifference of250 mV. Any
excess current available, other than for the purposes of
DC biasing the IC, will be small. At low reference voltage,
the IC has limited performance.
When voltage VBB falls below 2.7 V, it is detected by the
receive dynamic limiter circuit connected to pin LSAOand
is continuously activated, discharging the capacitor
connected to pin DLC. In the DC condition, the
loudspeaker is then automatically disabled below this
voltage.
TR2
GND
D1
TR1
E1
TN2
J2
GND
E2
MGM298
D1
V
BB
When VBBfalls below 2.5 V, the TEA1098 is forced into a
lowvoltage mode irrespectiveof the logicinput levels. This
is a speech mode with reduced performance which only
enables the microphone channel (between the MICinputs
and pin LN) and the earpiece amplifier. These two
channels are able to deliver signals for line currents as
small as 3 mA. The HFC input is tied to GND sinking a
current of typically 300 µA.
POWER-DOWN MODE (PIN PD)
To reduce consumption during dialling or register recall
(flash), the TEA1098 is provided with a power-down input
(pin PD). Whenthe voltage on pin PD is LOW, the current
consumption from VBB and VDD is reduced to typically
460 µA. Therefore a capacitor of 470 µF on VBB is
sufficient to power the TEA1098 during pulse dialling or
flash. The PD input has a pull-up structure. In this mode,
the capacitor C
is internally disconnected.
REG
2001 Aug 24 8
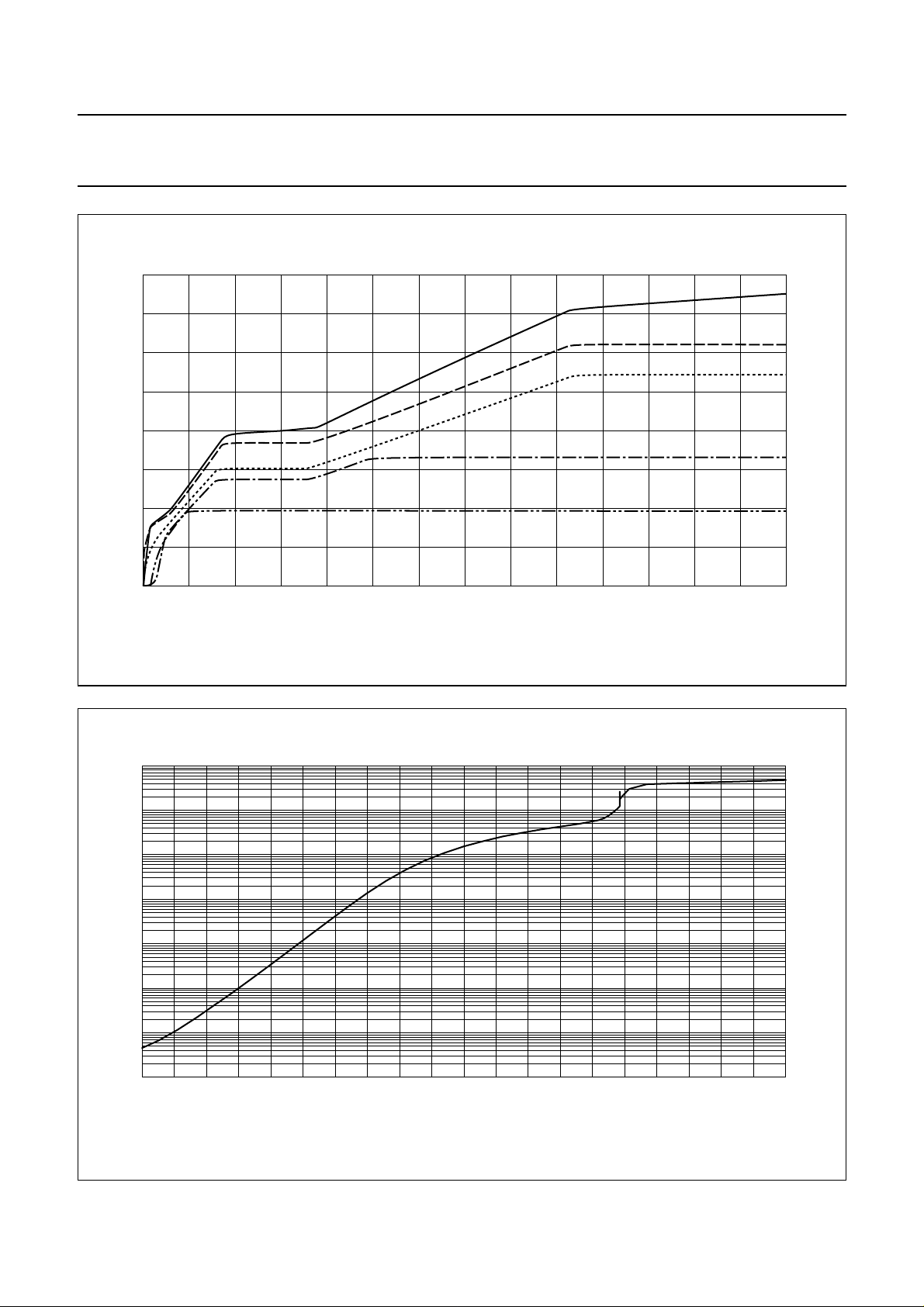
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Speech and handsfree IC TEA1098
handbook, full pagewidth
8
voltages
(V)
6
4
2
0
0 0.01
0.02 0.05
0.040.03
Fig.4 Main DC voltages.
I
line
FCA049
SLPE
V
V
MICS
(A)
LN
BB
DD
0.070.06
8
10
handbook, full pagewidth
I
DD
(pA)
7
10
6
10
5
10
4
10
3
10
2
10
10
1.0
FCA050
1.5 2.5 3.0
2.0
VDD (V)
Fig.5 Current consumption on VDD.
2001 Aug 24 9

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Speech and handsfree IC TEA1098
Transmit channels (pins MIC+, MIC−, DTMF, HFTX
and LN)
HANDSET MICROPHONE AMPLIFIER (PINS MIC+, MIC−
AND LN)
The TEA1098 has symmetrical microphone inputs. The
input impedance between pins MIC+ and MIC−is typically
70 kΩ. The voltage gainbetween pins MIC+/MIC−and LN
isset to44.3 dB. Without outputlimitation, themicrophone
input stage can accept signals of up to 18 mV (RMS) at
THD = 2% (room temperature). The microphone inputs
are biased at a voltage of one diode.
Automatic gain control is provided for line loss
compensation.
DTMF AMPLIFIER (PINS DTMF, LN AND RECO)
TheTEA1098 hasan asymmetrical DTMFinput. Theinput
impedance between DTMF and GND is typically 20 kΩ.
The voltage gain between pins DTMF and LN is set to
25.35 dB. Without output limitation, the input stage can
accept signals of up to180 mV (RMS) atTHD = 2% (room
temperature).
When the DTMF amplifier is enabled, dialling tones may
be sent on the line. These tones can be heard in the
earpiece or in the loudspeaker ata lowlevel. This is called
the confidence tone. The voltage attenuation between
pins DTMF and RECO is typically −16.5 dB. This input is
DC biased at 0 V.
The automatic gain control has no effect on these
channels.
HANDSFREE TRANSMIT AMPLIFIER (PINS HFTX AND LN)
The TEA1098 has an asymmetrical HFTX input, which is
mainly intended for use in combination with the TXOUT
output. The input impedance between HFTX and GND is
typically 20 kΩ. The voltage gain between pins HFTX
and LN is set to 34.7 dB. Without output limitation, the
input stage can accept signals of up to 95 mV (RMS) at
THD = 2% (room temperature).
Receive channels (pins IR, RECO, GARX and QR)
RX AMPLIFIER (PINS IR AND RECO)
The receive amplifier has one input (IR) which is
referenced to the line. The input impedance between pins
IR and LN is typically 20 kΩ and the DC bias between
these pins is equal to the voltage of one diode. The gain
between pins IR(referenced to LN) and RECO is typically
29.7 dB. Without output limitation, the input stage can
accept signals of up to 50 mV (RMS) at THD = 2% (room
temperature).
The receive amplifier has a rail-to-rail output (RECO),
which is designed for use with high ohmic (real) loads of
more than 5 kΩ. This output is biased at a voltage of two
diodes.
Automatic gain control is provided for line loss
compensation.
EARPIECE AMPLIFIER (PINS GARX AND QR)
The earpiece amplifier is an operational amplifier which
hasan output (QR)andaninverting input (GARX).Itsinput
signal is fed by a decoupling capacitor from the receive
amplifier output (RECO) to two resistors which set the
required gain or attenuation from −3 to +15 dB compared
to the receive gain.
Two external capacitors C
and QR) and C
ensure stability. The C
(connected between GAR and GND)
GARS
GAR
(connected between GAR
GAR
capacitor provides a first-order
low-pass filter. The cut-off frequency corresponds to the
time constant C
C
≥ 10 × C
GARS
× Re2. The relationship
GAR
must be satisfied.
GAR
The earpiece amplifierhas arail-to-rail output(QR) biased
at a voltage of two diodes. It is designed for use with low
ohmic (real) loads of 150 Ω, or capacitive loads of 100 nF
in series with 100 Ω.
The HFTX input is biased at a voltage of two diodes.
Automatic gain control is provided for line loss
compensation.
2001 Aug 24 10
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Speech and handsfree IC TEA1098
AGC (pin AGC)
The TEA1098 performsautomatic lineloss compensation,
which fits well with the true line attenuation. The automatic
gain control varies the gain of some transmit and receive
amplifiers in accordance with the DC line current. The
control range is6.45 dB forG
6.8 dB for G
v(HFTX-LN)
, which corresponds approximately
v(MIC-LN)
and G
v(IR-RECO)
, and
to a line length of 5.5 km for a 0.5 mm twisted-pair copper
cable.
To enable this gain control, pin AGC must be shorted to
pin LN. The start currentfor compensationcorresponds to
a line current of typically 23 mA and a stop current of
57 mA. The start current can be increased by connecting
an external resistor between pins AGC and LN. It can be
increased by up to 40 mA (using a resistor of typically
80 kΩ). The start and stop current will be maintained at a
ratio of 2.5. By leaving pin AGC open, the gain control is
disabled and no line loss compensation occurs.
Handsfree application
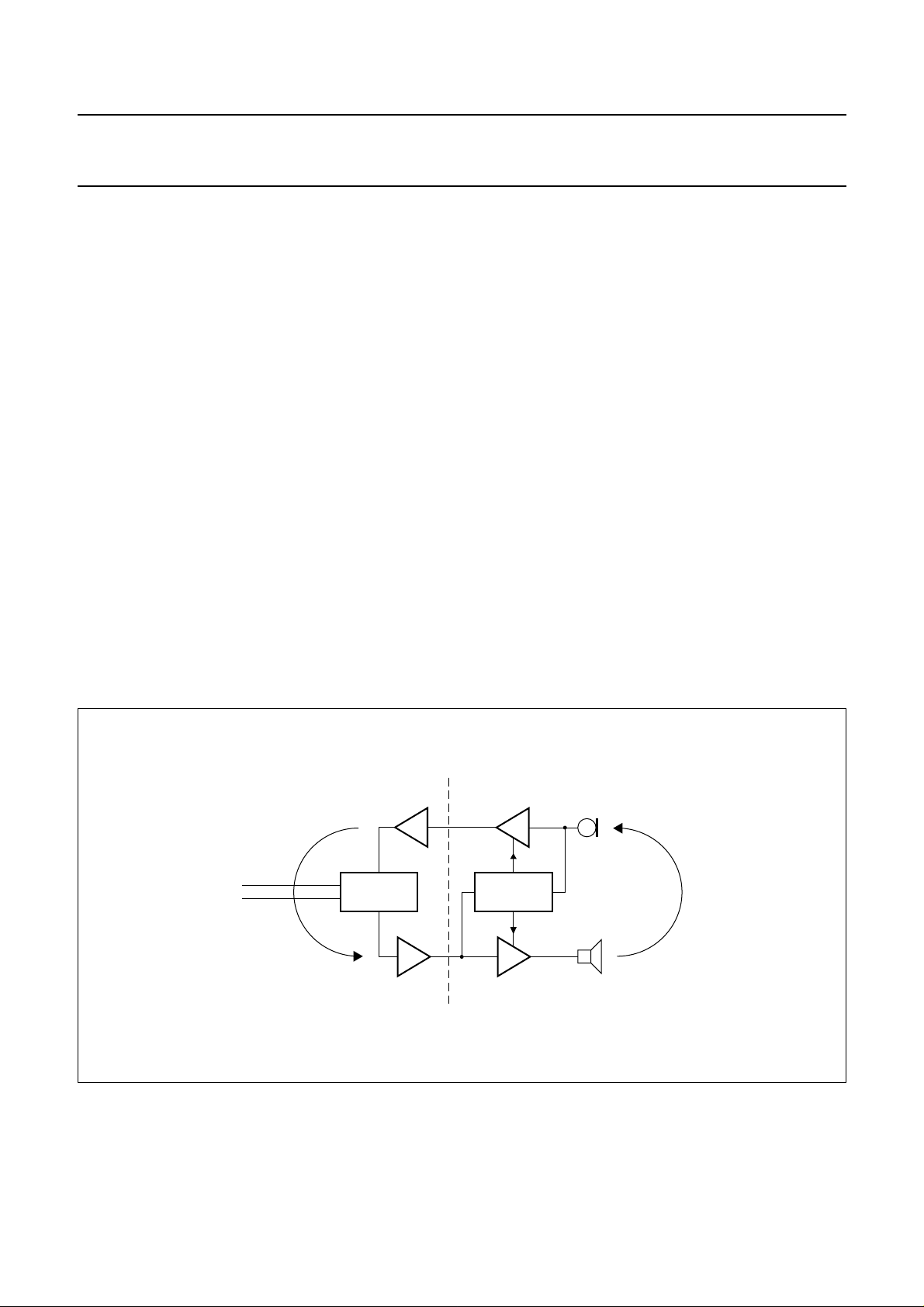
Figure 6 shows a loop is formed by the sidetone network
in the line interface section, and by the acoustic coupling
between loudspeaker and microphone in the handsfree
section. A loop-gain of greater than 1 causes howl.
To prevent howl in full duplex applications, the loop-gain
must be set much lower than 1. This is achieved by the
duplex controller which detects the channel with the
‘largest’ signal and controls the gains of the microphone
and the loudspeaker amplifiers so that the sum of their
gains remains constant.
Thereforein the handsfreeapplication,thecircuit can have
three stable modes:
1. Transmit mode (Tx mode):
The microphone amplifieris atmaximum gain, andthe
loudspeaker amplifier is at minimum gain.
2. Receive mode (Rx mode):
The microphoneamplifier is at minimum gain, and the
loudspeaker amplifier is at maximum gain.
3. Idle mode:
The microphone amplifier and the loudspeaker
amplifier are both midway between maximum and
minimum gain.
The difference between the maximum and minimum gain
is called the switching range.
handbook, full pagewidth
telephone
line
sidetone
HYBRID
Fig.6 Handsfree telephone set principles.
2001 Aug 24 11
acoustic
coupling
DUPLEX
CONTROL
MGM299
 Loading...
Loading...