Philips TEA0678 Technical data

查询TEA0678供应商
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
DATA SH EET
TEA0678
Dual Dolby* B-type noise reduction
circuit, automatic music search,
with differential outputs and mute
Preliminary specification
Supersedes data of August 1993
File under Integrated Circuits, IC01
1996 Jun 06
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Dual Dolby* B-type noise reduction circuit, automatic
music search, with differential outputs and mute
FEATURES
• Dual noise reduction (NR) channels
• Head pre-amplifiers
• Reverse head switching
• Automatic Music Search (AMS)
• Mute position
• Equalization with electronically switched time constants
• Dolby reference level = 387.5 mV
• 32 pins
• Switch inputs TTL compatible
• Differential output stage has:
– Capability to drive 1.2 nF capacitive load
– Capability to drive 1 kΩ load
– Short-circuit proof
– Short-circuit proof to 16 V via coupling capacitor.
• Improved EMC behaviour.
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The TEA0678 is a bipolar integrated circuit that provides
two channels of Dolby B noise reduction for playback
applications in car radios. It includes head and
equalization amplifiers with electronically switchable time
constants. Furthermore it includes electronically
switchable inputs for tape drivers with reverse heads.
This device also detects pauses of music in Automatic
Music Search (AMS) mode, with a delay time fixed
externally by a resistor. The short-circuit proof output
stage of the TEA0678 is differential and provides muting.
The device will operate with power supplies in the range of
7.6 to 12 V, output overload level increasing with increase
in supply voltage. Current drain varies with supply voltage,
noise reduction on/off and AMS on/off so it is advisable to
use a regulated power supply or a supply with a long time
constant.
.Current drain varies with these variables:
Supply voltage
Noise reduction on/off
AMS on/off.
TEA0678
Because of this current drain variation it is advisable to use
a regulated power supply or a supply with a long time
constant.
QUICK REFERENCE DATA
SYMBOL PARAMETER MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
V
CC
I
CC
SN+
-------------N
ORDERING INFORMATION
TYPE
NUMBER
TEA0678 SDIP32
TEA0678T SO32 plastic small outline package; 32 leads; body width 7.5 mm SOT287-1
Remark Dolby*: Available only to licensees of Dolby Laboratories Licensing Corporation, San Francisco, CA94111,
USA, from whom licensing and application information must be obtained. Dolby is a registered trade-mark of Dolby
Laboratories Licensing Corporation.
supply voltage 7.6 10 12 V
supply current − 25 28 mA
signal plus noise-to-noise ratio 78 84 − dB
PACKAGE
NAME DESCRIPTION VERSION
plastic shrink dual in-line package; 32 leads (400 mil)
SOT232-1
1996 Jun 06 2
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Dual Dolby* B-type noise reduction circuit, automatic
music search, with differential outputs and mute
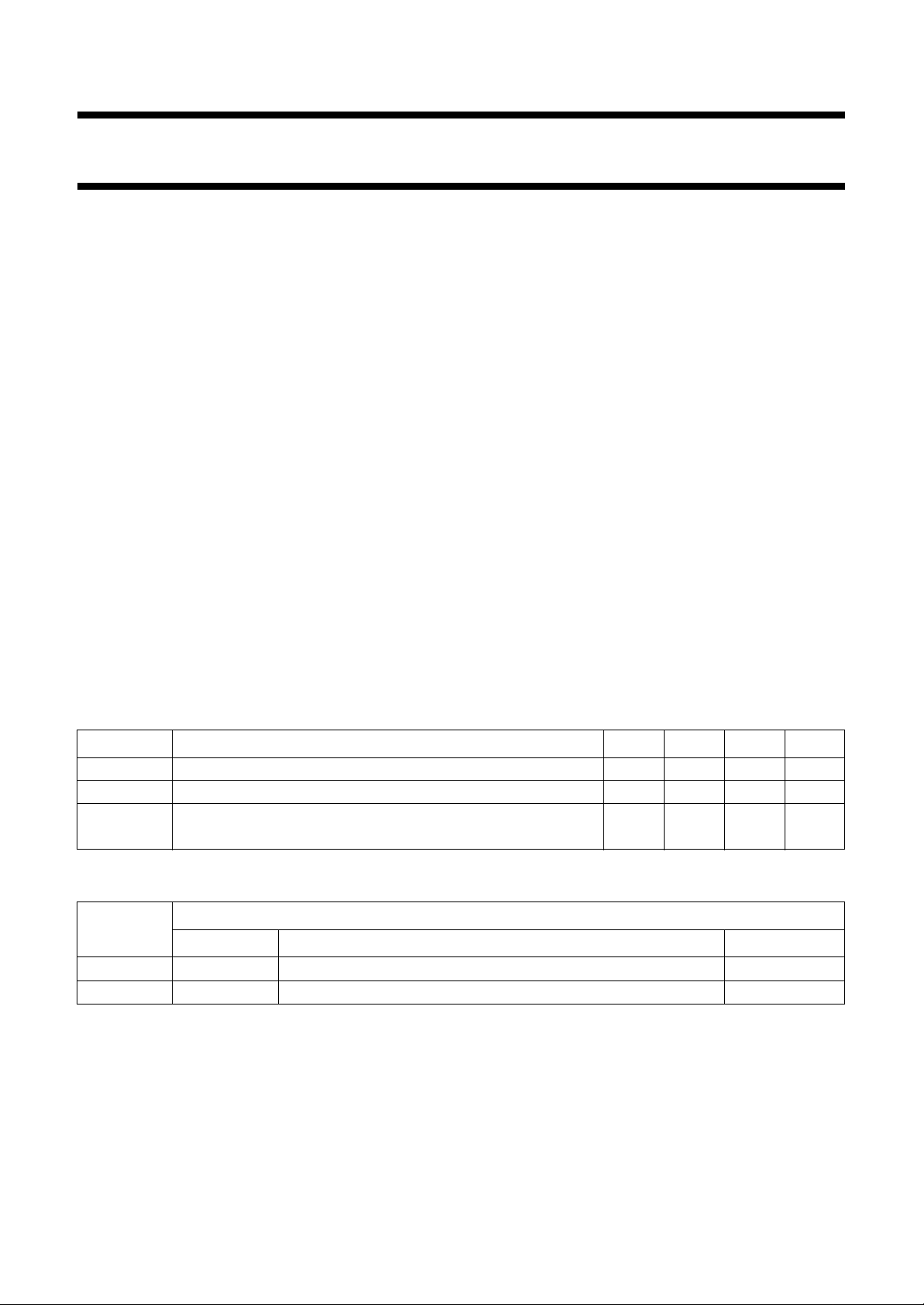
BLOCK DIAGRAM
pF
input
head switch
LOW: INPUT 1
10 µF
180 Ω
470
from
HIGH: INPUT 2
microprocessor
pF
470
1 kΩ
10
kΩ
330
nF
17
18
TEA0678
19
PRE
AMP.
20
21
kΩ
8.2
EQ
22
AMP.
GND
ref
V
POWER
SUPPLY
CC
V
PRE
TEA0678
MED769
pF
470
100
µF
15 16
14
pF
470
AMP.
10 µF
13
CC
V
12
10
kΩ
EQ
AMP.
8.2
11
180 Ω
1 kΩ
nF
kΩ
330
EQ switch from
microprocessor
handbook, full pagewidth
24
ref
V
from
microprocessor
LOW: MUTE ON
HIGH: MUTE OFF
18
kΩ
15 nF
23
24
AMS
25
LEVEL
PROCESSOR
DELAY
DETECTOR
TIME
910
15 nF
8
out
LOW: 120 µs
OPEN: 70 µs
AMS
kΩ
4.7 nF
AMS
t
R
4.7 nF
delay
time
24
kΩ
ref
V
Fig.1 Block and application diagram.
180 kΩ
26
nF
100
270 kΩ
27
nF
330
1 µF
10
µF
27
kΩ
output
B+
L
R
L
C
L
R
B−
output
28
29
30
4.7 µF
31
32
4.7 µF
DOLBY B NR CIRCUIT
AMS
15
LOGIC
kΩ
DOLBY B NR CIRCUIT
7
NR
EQ
MUTE
15
HEAD-
SWITCH
kΩ
6
5
4
23
1
180 kΩ
nF
100
270 kΩ
nF
330
1 µF
from
LOW: NR ON
OPEN: OFF
HIGH: AMS ON
microprocessor
4.7 µF
output
A+
L
R
L
C
L
R
A−
output
4.7 µF
1996 Jun 06 3
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Dual Dolby* B-type noise reduction circuit, automatic
music search, with differential outputs and mute
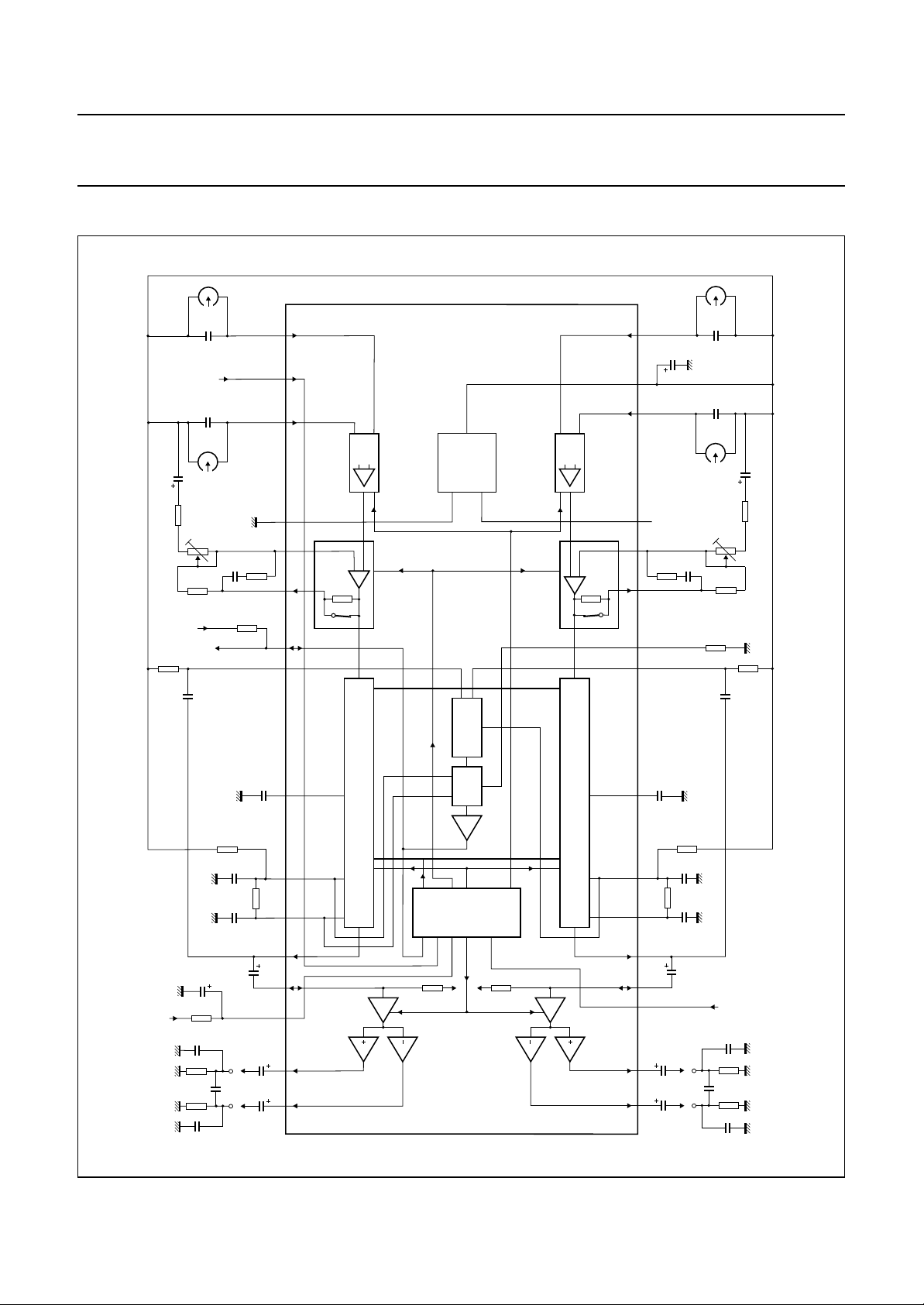
PINNING
SYMBOL PIN DESCRIPTION
OUTA− 1 negative output channel A
OUTA+ 2 positive output channel A
NR/AMS 3 noise reduction/music search switch
INCA 4 input mute/output stage channel A
OUTCA 5 output Dolby B processor channel A
INTA 6 integrating filter channel A
CONTRA 7 control voltage channel A
HPA 8 high-pass filter channel A
SCA 9 side chain channel A
TD 10 delay time constant
EQA 11 equalizing output channel A
EQFA 12 equalizing feedback channel A
V
CC
13 supply voltage
INA1 14 input channel A1 (forward or reverse)
V
ref
15 reference voltage
INA2 16 input channel A2 (reverse or forward)
INB2 17 input channel B2 (reverse or forward)
HS 18 head switch input
INB1 19 input channel B1 (forward or reverse)
GND 20 ground
EQFB 21 equalizing feedback channel B
EQB 22 equalizing output channel B
AMSEQ 23 AMS output and EQ switch input
SCB 24 side chain channel B
HPB 25 high-pass filter channel B
CONTRB 26 control voltage channel B
INTB 27 integrating filter channel B
OUTCB 28 output Dolby B processor channel B
INCB 29 input mute/output stage channel B
MUTE 30 mute switch
OUTB+ 31 positive output channel B
OUTB− 32 negative output channel B
handbook, halfpage
OUTA−
OUTA+
NR/AMS
OUTCA
CONTRA
1
2
3
INCA
4
5
INTA
6
7
HPA
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
TEA0678
MED770
SCA
TD
EQA
EQFA
V
CC
INA1
V
ref
INA2
Fig.2 Pin configuration.
TEA0678
OUTB−
32
OUTB+
31
MUTE
30
INCB
29
OUTCB
28
INTB
27
CONTRB
26
HPB
25
SCB
24
AMSEQ
23
EQB
22
EQFB
21
GND
20
INB1
19
HS
18
INB2
17
1996 Jun 06 4
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Dual Dolby* B-type noise reduction circuit, automatic
music search, with differential outputs and mute
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
Noise Reduction (NR) is enabled when pin NR/AMS is
connected to ground and disabled when open-circuit (left
floating from a 3-state output).
Dolby noise reduction only operates correctly if 0 dB Dolby
level is adjusted at 387.5 mV.
Automatic Music Search (AMS) is enabled when pin
NR/AMS is connected to HIGH (5 V) and disabled when
open-circuit (left floating from a 3-state output). In AMS
mode the signal of both channels are rectified and then
added. This means, even if one channel signal appears
inverted to the other channel, with the TEA0678 the normal
AMS function is ensured (see Figs 4, 5 and 6).
Equalization time constant switching (70 µs or 120 µs)
is achieved when pin AMSEQ is connected to GND via an
18 kΩ resistor (120 µs), or left open-circuit (70 µs).
This does not affect the AMS output signal during AMS
mode (see Fig.1).
Head switching is achieved when pin HS is connected to
GND (input IN1 active) or connected to HIGH (5 V) level
(input IN2 active). If left open-circuit IN1 is active.
Mute is enabled when pin MUTE is connected to ground
and off when connected to HIGH (5 V) level. For smooth
switching a time constant is recommended. If left
open-circuit MUTE is active.
The differential output stage of each channel is
connected via a provision to the Dolby and pre-amplifier
part. This provision may be used for any processing of the
tape signal or to add another signal. Each output drives a
resistive load of nominal 10 kΩ and is capable of driving
1kΩ, also a capacitive load of 1.2 nF to ground and
between differential outputs. Each output can be
short-circuited to a battery (16 V) via a coupling capacitor
(4.7 µF).
TEA0678
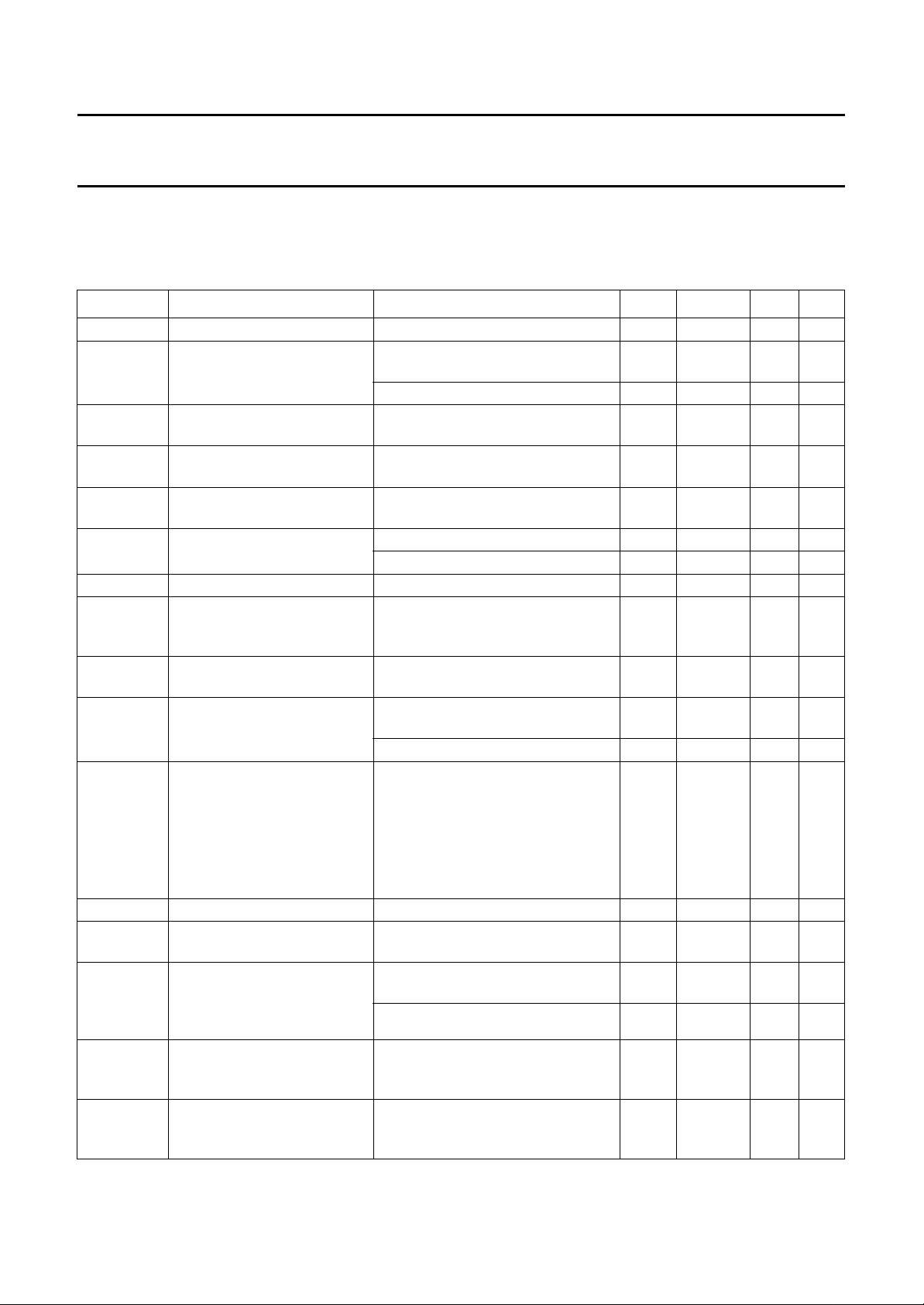
LIMITING VALUES
In accordance with the Absolute Maximum Rating System (IEC 134); note1.
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. MAX. UNIT
V
CC
V
i
supply voltage 0 16 V
input voltage (pins 1 to 32) except pin 15 (V
(NR/AMS), pin 18 (HS) and pin 30 (MUTE) to V
input voltage at pin 3 (NR/AMS), pin 18 (HS) and
); pin 3
ref
−0.3 +V
CC
note 2 −0.3 +6.5 V
CC
V
pin 30 (MUTE)
t
short
T
stg
T
amb
V
es
pin 15 (V
storage temperature −55 +150 °C
operating ambient temperature −40 +85 °C
electrostatic handling voltage for all pins note 3 −2+2kV
) to VCC short-circuiting duration − 5s
ref
note 4 −500 +500 V
Notes
1. The device may not operate correctly when subjected to these ratings when the ratings exceed the electrical
characteristics of the device as specified in Chapter “Characteristics”. The device will recover automatically when the
environment is reduced to the requirements of the characteristics.
2. The TEA0678 allows a HIGH-level at switching pins without supply voltage (V
= 0; stand-by mode). This means a
CC
maximum input voltage of 6.5 V for the switching input pins.
3. Human body model (1.5 kΩ, 100 pF).
4. Machine model (0 Ω, 200 pF).
1996 Jun 06 5
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Dual Dolby* B-type noise reduction circuit, automatic
TEA0678
music search, with differential outputs and mute
CHARACTERISTICS
VCC= 10 V; f = 20 Hz to 20 kHz; T
differential outputs (Vo=Vo+− Vo−), this corresponds to Dolby level 387.5 mV (RMS) (0 dB) at test point (OUTC);
see Fig.1; NR on/AMS off; EQ switch in the 70 µs position; unless otherwise specified.
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
V
CC
I
CC
α
m
G
v
G
mm
supply voltage 7.6 10 12 V
supply current pins 14, 16, 17 and 19 connected to
channel matching f = 1 kHz; Vo= 0 dB; NR off;
voltage gain (output stage) between OUT and OUTC; f = 1 kHz;
voltage gain mismatch
(output stage)
THD total harmonic distortion (2nd
and 3rd harmonic)
H
R
SN+
-------------N
V
no(rms)
headroom at output VCC= 9 V; THD = 1%; f = 1 kHz 13 −−dB
signal plus noise-to-noise
ratio
equivalent input noise voltage
in decode mode (RMS value)
PSRR power supply ripple rejection V
f
o
frequency response
measured in encode mode;
referenced to TP
α
cs
α
cc
channel separation Vo= +10 dB; f = 1 kHz; see Fig.8 61 67 − dB
crosstalk between active and
inactive input
R
L
load resistance at each output
OUTA+, OUTA−, OUTB+ and
OUTB− (corresponds to 2 kΩ
at differential output)
C
L
capacitive load at each output
(between OUT+ and OUT−)
and ground
G
v
voltage gain of pre-amplifier from pin INA1 or INA2 to pin EQFA
=25°C; nominal load 10 kΩ; all levels are referenced to 775 mV (RMS) (0 dB) at
amb
− 25 28 mA
V
ref
f = 1 kHz; V
= 0 dB at each output − 26 37 mA
o
−0.5 − +0.5 dB
OUTA/OUTB
5.5 6 6.5 dB
NR off
mismatch between OUT+ and
−0.5 − +0.5 dB
OUT−; f = 1 kHz; NR off
f = 1 kHz; V
f = 10 kHz; V
internal gain 40 dB; linear;
=0dB − 0.08 0.15 %
o
=6dB − 0.15 0.3 %
o
78 84 − dB
CCIR/ARM weighted; decode mode;
see Fig.10
NR off; unweighted;
f = 20 Hz to 20 kHz; R
= 0.25 V; f = 1 kHz; see Fig.7
i(rms)
source
=0Ω
−− 1.4 µV
52 57 − dB
for unsymmetrical signal at OUTC
at differential OUT; note 1 49 52 − dB
see Fig.10
= −25 dB; f = 0.2 kHz −22.9 −24.4 −25.9 dB
V
o
= 0 dB; f=1kHz −1.5 0 +1.5 dB
V
o
V
= −25 dB; f=1kHz −17.8 −19.3 −20.8 dB
o
= −25 dB; f=5kHz −18.1 −19.6 −21.1 dB
V
o
= −35 dB; f = 10 kHz −24.4 −25.9 −27.4 dB
V
o
NR off; f = 1 kHz; Vo= +10 dB;
70 77 − dB
see Fig.8
AC-coupled f = 1 kHz; Vo= 12 dB;
10 −−kΩ
THD=1%
THD = 1%; note 2 1 −−kΩ
C
at each output to ground
Lmin
0.3 − 1.3 nF
(pins 1, 2, 31 and 32)
29 30 31 dB
and from pin INB1 or INB2 to
pin EQFB; f = 1 kHz
1996 Jun 06 6
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Dual Dolby* B-type noise reduction circuit, automatic
TEA0678
music search, with differential outputs and mute
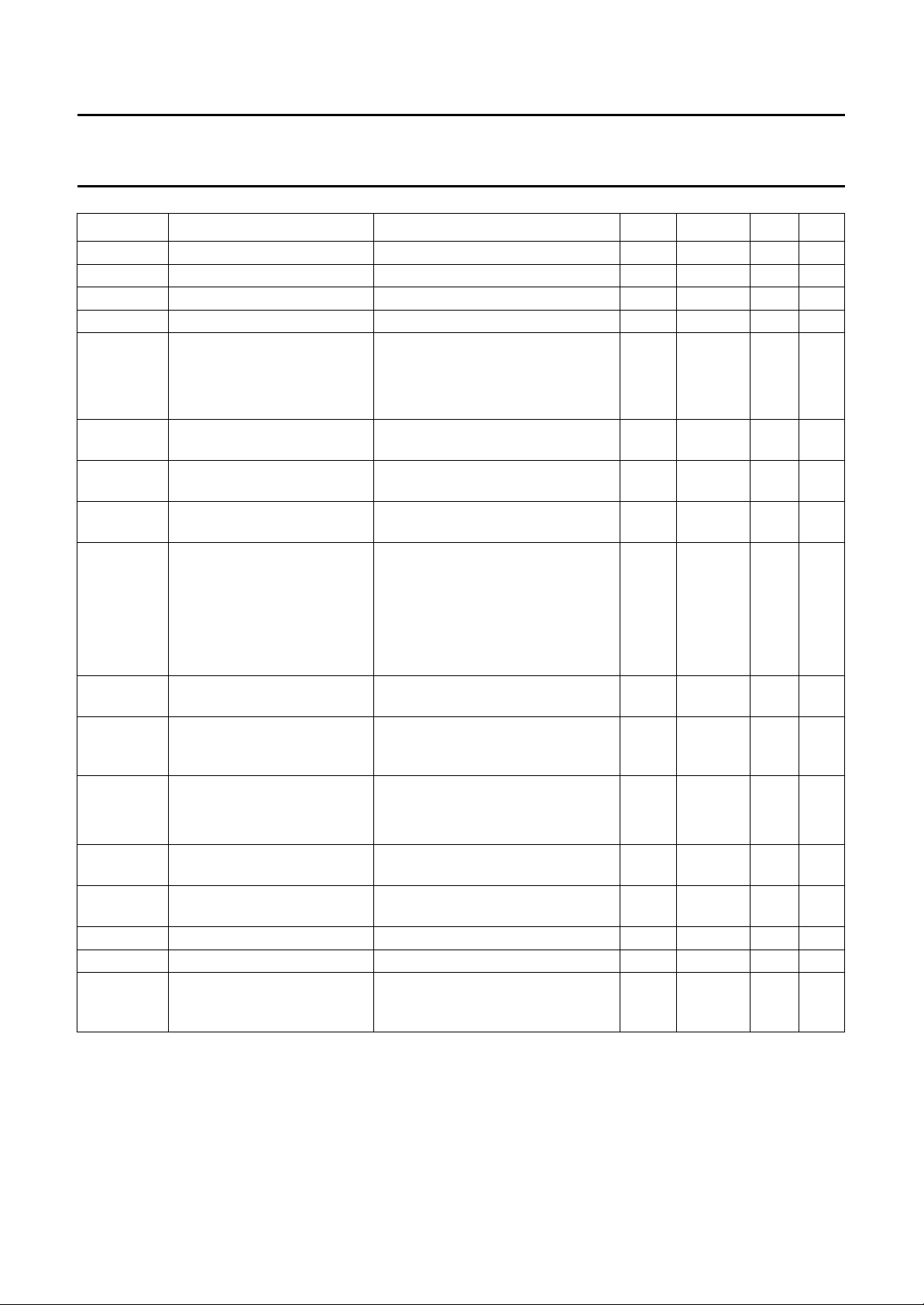
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
V
I(offset)(DC)
I
i(bias)
R
EQ
R
I
A
v
V
O(offset)(DC)
V
mute(offset)
V
− V
ref
I
O
R
i
Z
o
d
mute
AMSL AMS threshold level at
AMSH AMS threshold level at
t
d
t
r
EMC DC offset voltage at
DC input offset voltage − 2 − mV
input bias current −− 0.4 µA
equalization resistor 4.7 5.8 6.9 kΩ
input resistance head inputs 60 100 − kΩ
open-loop amplification pin INA1 or INA2 to pin EQA and
pin INB1 or INB2 to pin EQB
f = 10 kHz 80 86 − dB
f = 400 Hz 104 110 − dB
DC offset voltage at pins
OUT+ to OUT−
MUTE offset voltage at pins
OUT+ to OUT−
DC output offset voltage at
OUTC
pins OUTCA and OUTCB
pins INA1, INA2, INB1 and INB2
connected to V
ref
pins INA1, INA2, INB1 and INB2
connected to V
ref
NR off; pins INA1, INA2, INB1 and
INB2 connected to V
ref
−10 − +10 mV
−10 − +10 mV
−0.15 − +0.15 V
DC output current pins INA1, INA2, INB1 and INB2
connected to V
ref
pin OUTC to ground −2 −−mA
pin OUTC to V
CC
0.3 −−mA
pin OUT± to ground −2.5 −−mA
input resistance output stage
pin OUT± to V
CC
2.5 −−mA
10 16 − kΩ
at pins INCA and INCB
output impedance at each
− 90 110 Ω
output OUTA+, OUTA−,
OUTB+ and OUTB−
mute depth at differential
output
NR off
f = 1 kHz −80 −−dB
f = 10 kHz −80 −−dB
NR off;f=10kHz; see Fig.9 −25 −22 −19 dB
music to pause
note 3 −24 −21 −18 dB
pause to music
AMS delay time range f = 10 kHz; 0 dB burst; see Table 1 − 23 to 160 − ms
AMS rise/delay time f = 10 kHz; 0 dB burst 2 − 10 ms
pins OUTA−, OUTA+,
f = 900 MHz; V
=3V
i
see Figs 11, 12 and13
(RMS)
;
− 100 − mV
OUTB+ and OUTB−
1996 Jun 06 7
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Dual Dolby* B-type noise reduction circuit, automatic
TEA0678
music search, with differential outputs and mute
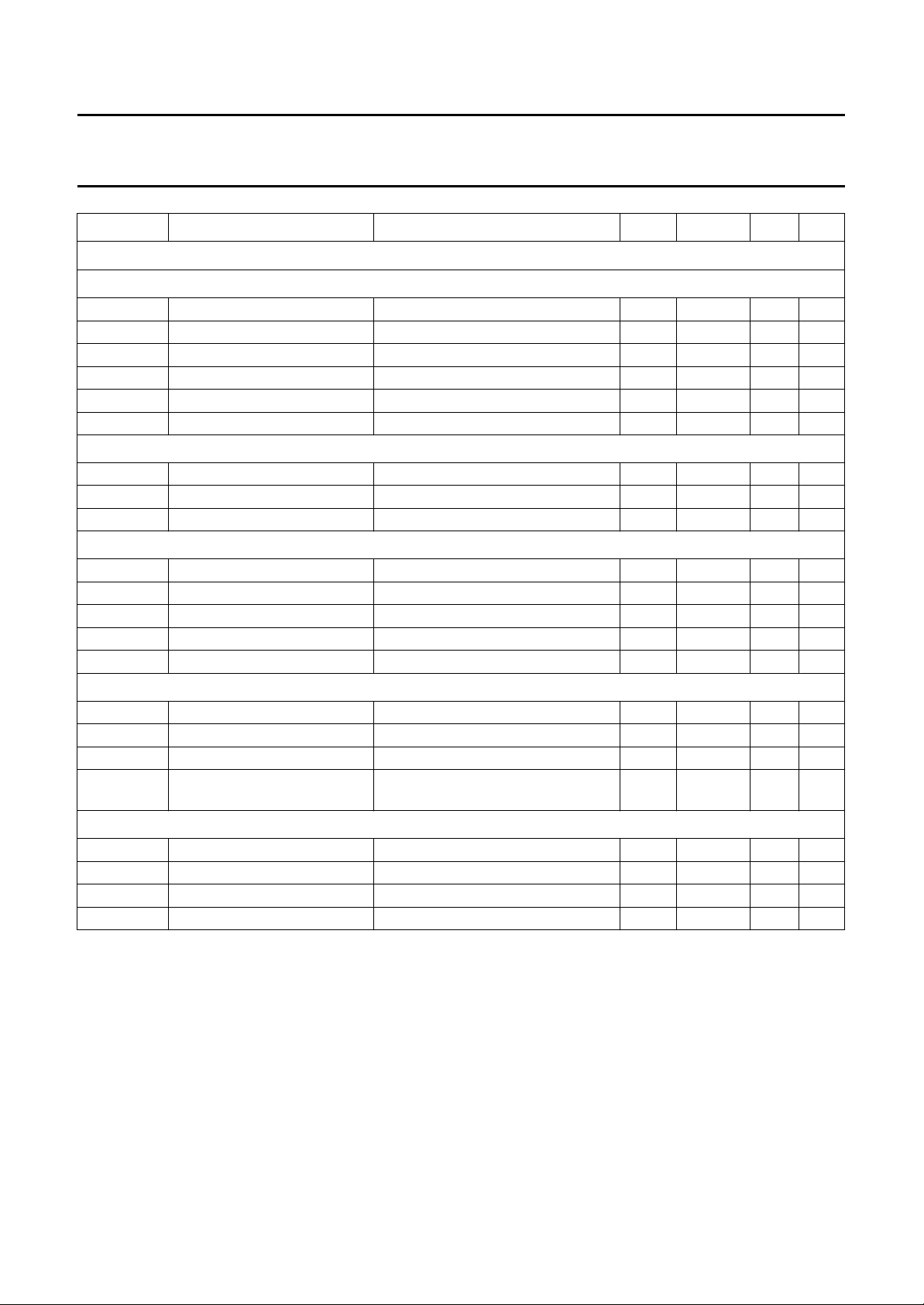
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
Switching thresholds
NR/AMS SWITCH (PIN 3)
V
IL
I
IL
I
i(float)
V
float
V
IH
I
IH
EQUALIZATION (PIN 23)
I
EQ70
V
EQ70
I
EQ120
AMS OUTPUT (PIN 23)
V
OH
I
OH
I
OH
V
OL
I
OL
MUTE SWITCH (PIN 30)
V
IL
I
IL
V
IH
I
IH
HEAD SWITCH (PIN 18)
V
IL
I
IL
V
IH
I
IH
LOW level input voltage NR on −0.3 − +0.8 V
LOW level input current NR on −10 −20 −40 µA
allowed floating input current pin left open-circuit; NR/AMS off −10 0 +10 µA
floating voltage pin left open-circuit; NR/AMS off − 2.4 5 V
HIGH level input voltage AMS on 4 − 5.5 V
HIGH level input current AMS on 10 20 40 µA
floating leakage current time constant 70 µs active +0.002 −−0.15 mA
floating voltage time constant 70 µs active − 4.6 5 V
input current time constant 120 µs active −0.25 −−1mA
HIGH level output voltage music present 4 4.6 5 V
HIGH level output current current capability +0.01 −−1mA
HIGH level output current current capability; note 4 +0.01 −−0.15 mA
LOW level output voltage music not present −− 0.8 V
LOW level output current current capability −0.01 − +1 mA
LOW level input voltage MUTE on −0.3 − +0.8 V
LOW level input current MUTE on −−4 −100 µA
HIGH level input voltage MUTE off 4 − 5.5 V
HIGH level input current MUTE off; smooth switching with a
− 10 100 µA
time constant is recommended
LOW level input voltage INPUT 1 on −0.3 − +0.8 V
LOW level input current INPUT 1 on −− −100 µA
HIGH level input voltage INPUT 2 on 4 − 5.5 V
HIGH level input current INPUT 2 on − 30 100 µA
1996 Jun 06 8

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Dual Dolby* B-type noise reduction circuit, automatic
TEA0678
music search, with differential outputs and mute
Notes to the characteristics
1. For the signal to be doubled (+6 dB) at differential output as a function of OUTC, the signal-to-ripple ratio is improved
at differential output for approximately 3 dB.
2. By using the small load, the output voltage may be divided by −0.8 dB.
3. The high speed of the tape (FF, REW) at the tape head during AMS mode causes a transformation of level and
frequency of the originally recorded signal. It means a boost of signal level of approximately 10 dB and more for
recorded frequencies from 500 Hz up to 4 kHz. So the threshold level of −22 dB corresponds to signal levels in
PB mode of approximately −32 dB. The AMS inputs for each channel are pin SCA and pin SCB. As the frequency
spectrum is transformed by a factor of approximately 10 to 30 due to the higher tape speed in FF, REW, the
high-pass filter (4.7 nF/24 kΩ) removes the effect of offset voltages but does not affect the music search function.
In the application circuit (Fig.1) the frequency response of the system between tape heads input, e.g. pins INA2/INB2,
to the AMS input pins SCA and SCB is constant over the whole frequency range (see Fig.3). The frequency
dependence of threshold level is shown in Fig.3.
4. In AMS OFF mode, pin AMSEQ is HIGH level, the equalization time constant will be switched by pulling
approximately 200 µA out of pin AMSEQ. This means for the device connected to pin AMSEQ, a restriction of input
current at HIGH level less than 200 µA during AMS off; otherwise the switching of the time constants is disabled but
fixed at 120 µs. If the following devices, input consumes more than 200 µA, this input has to be disconnected in AMS
off mode. (To ensure switching the currents for the different switched modes are specified with a tolerance of±50 µA
in Chapter “Characteristics”.) For an application with a fixed EQ time constant of 120 µs the equalizing network may
be applied completely external. Change 8.2 kΩ resistor to 14 kΩ the internal resistor REQ= 5.8 kΩ is short-circuited
by fixing the EQ switch input at the 70 µs position (I
EQ70
).
Table 1 Blank delay time set by resistor R
RESISTOR VALUE R
(kΩ)
68 23 20
150 42 15
180 48 15
220 56 15
270 65 10
330 76 10
470 98 10
560 112 10
680 126 10
820 142 10
1000 160 10
t
at pin TD
t
DELAY TIME t
TYP. (ms)
d
TOLERANCE
(%)
1996 Jun 06 9
 Loading...
Loading...