Philips tda8798 DATASHEETS
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
DATA SH EET
TDA8798
Dual 8-bit, 100 Msps A/D converter
with DPGA
Objective specification
Supersedes data of 1998 Apr 15
File under Integrated Circuits, IC02
1999 Sep 16
Philips Semiconductors Objective specification
Dual 8-bit, 100 Msps A/D converter with
TDA8798
DPGA
FEATURES
• Dual 8-bit Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC)
• Sampling rate up to 100 million samples per
second (Msps)
• Dual 34 dBV 6-bit Digitally Programmable Gain
Amplifier (DPGA) with optional power-off
• Optional external equalization filter with capacitive
coupling between DPGA and ADC
• Serial Interface (SI) for DPGA gain control using either
parallel load mode or count-up/count-down mode
• 3.3 V TTL/CMOS compatible I/O
• Differential or single-ended TTL/CMOS clock interface
• AC or DC coupling for DPGA inputs.
QUICK REFERENCE DATA
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
V
V
V
I
DDA
DDA
DDD
DDO
analog supply voltage 3.15 3.3 3.45 V
digital supply voltage 3.0 3.3 3.6 V
output stage supply voltage 2.7 3.3 3.6 V
analog supply current with DPGAEN LOW − 106 − mA
with DPGAEN HIGH − tbf − mA
I
DDD
I
DDO
digital supply current − 30 − mA
output stage supply current − 3 − mA
INL DC integral non-linearity from IC analog input to digital
output; ramp input;
f
CLK
DNL DC differential non-linearity from IC analog input to digital
output; ramp input;
f
CLK
V
n(o)(rms)
output referred noise (RMS value) DPGA at G
noise bandwidth = 15 MHz
B
(−3dB)(ADC)
B
(−3dB)(DPGA)
f
(sample)(max)
P
tot
ADC −3 dB analogue bandwidth at V
DPGA −3 dB bandwidth at V
maximum sampling rate 100 −−Msps
total power dissipation with DPGAEN LOW − 460 500 mW
with DPGAEN HIGH − tbf tbf mW
APPLICATIONS
• High-dynamic range acquisition front-ends
• Digital data storage read channels.
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The TDA8798 is a dual 8-bit ADC with DPGA.
The 100 Mspsmaximumsamplingrateand34 dBVDPGA
gain range optimizes the ADC for high dynamic range
applications.
= 100 MHz
with DPGA at G
(min)
−±3.0 tbf LSB
without DPGA −±1.0 tbf LSB
= 100 MHz
with DPGA at G
(min)
−±0.5 tbf LSB
without DPGA −±0.5 tbf LSB
i(dif)(FS)
i(dif)(max)
; Zi =50Ω;
(max)
− tbf 2 mV
− 120 − MHz
30 tbf − MHz
rms
1999 Sep 16 2
Philips Semiconductors Objective specification
Dual 8-bit, 100 Msps A/D converter with
DPGA
ORDERING INFORMATION
to BUF2
to BUF2N
V
oref2
64
BUFFER
TDA8798
BUFFER
1718161514
V
oref1
PACKAGE
TE
TEST
54
62
REGULATOR
REGULATOR
DDA3
V
SSA3
V
V
SR
52
ADC2
ADC1
DDO1
V
V
SSA4
A
A
DDO2
TYPE
NUMBER
NAME DESCRIPTION VERSION
TDA8798HL LQFP64 plastic low profile quad flat package; 64 leads;
body 10 × 10 × 1.4 mm
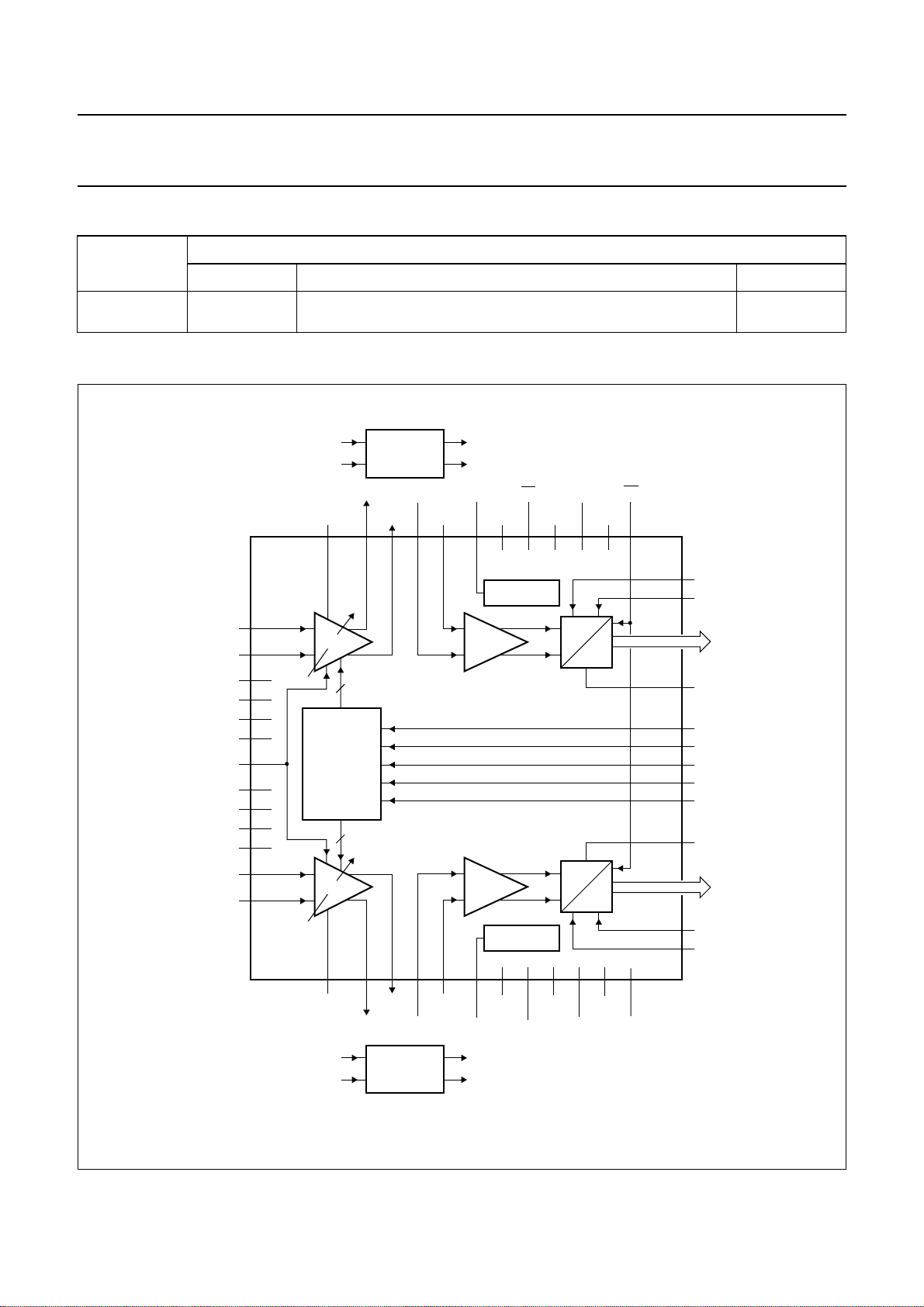
BLOCK DIAGRAM
handbook, full pagewidth
analog
input 2
analog
input 1
VIN2N
VIN2
V
DDA2
V
SSA2
V
SSD1
V
DDD1
DPGAEN
V
DDD2
V
SSD2
V
SSA1
V
DDA1
VIN1
VIN1N
6
7
5
8
24
25
53
56
57
9
12
10
11
to DPGA2
to DPGA2N
DPGAC2
DPGA2
SERIAL
INTERFACE
DPGA1
3
DPGA2
DPGA2N
2
6
6
OPTIONAL
EXTERNAL
FILTER 2
BUF2N
1
BUF1NDPGA1
BUF2
63
BUF1DPGA1NDPGAC1
V
6055
D
D
V
SSO1
DDA4
61 51
325031212019
OE
V
SSO2
41 to 48
40 to 33
49
MGM863
TDA8798
SOT314-2
58
CLK2
59
CLK2N
digital
output 2
B0 to B7
4
V
ref2
27
SEN2
29
SCLK
26
SMODE
28
SDATA
30
SEN1
13
V
ref1
digital
output 1
A0 to A7
23
CLK1
22
CLK1N
to DPGA1N
to DPGA1
OPTIONAL
EXTERNAL
FILTER 1
Fig.1 Block diagram.
1999 Sep 16 3
to BUF1N
to BUF1
Philips Semiconductors Objective specification
Dual 8-bit, 100 Msps A/D converter with
DPGA
handbook, full pagewidth
I
OUT
−
I
OUT
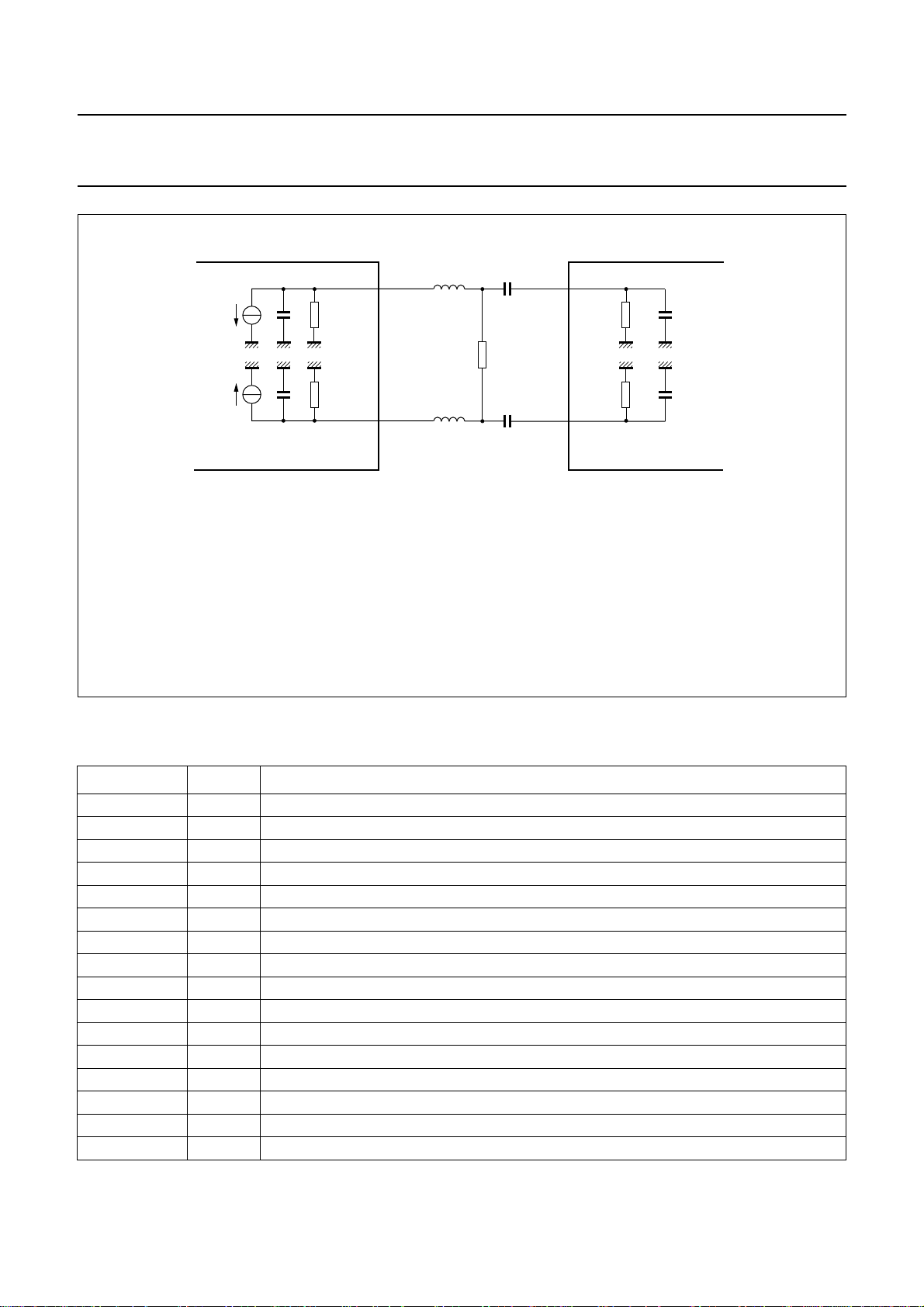
External filtering may be used between DPGA and ADC to limit the noise bandwidth.
The external filterhasalow-passcut-offfrequency of .
and a high-pass cut-off frequency of
Other types of filter may be used if DC biasing is correct.
C
o(DPGA)
C
o(DPGA)
f
10 µH
(1)
DPGA
L
R
o(DPGA)
R
o(DPGA)
DPGAN
(3)
L
10 µH
TDA8798 TDA8798
R2⁄ R
+
l 3dB–()
1
C×
1
×≈
------ -
------------------------------------------
2π
.
L
h 3dB–()
1
×≈
------ -
----------------------------- -
2π
R
f
iADC()
100 nF
C
R
1 kΩ
C
100 nF
oDPGA()
(2)
BUF
R
i(ADC)
R
i(ADC)
(4)
BUFN
(1) DPGA1/DPGA2
(2) BUF1/BUF2
(3) DPGA1N/DPGA2N
(4) BUF1N/BUF2N
C
i(ADC)
C
i(ADC)
TDA8798
FCE267
Fig.2 External filter.
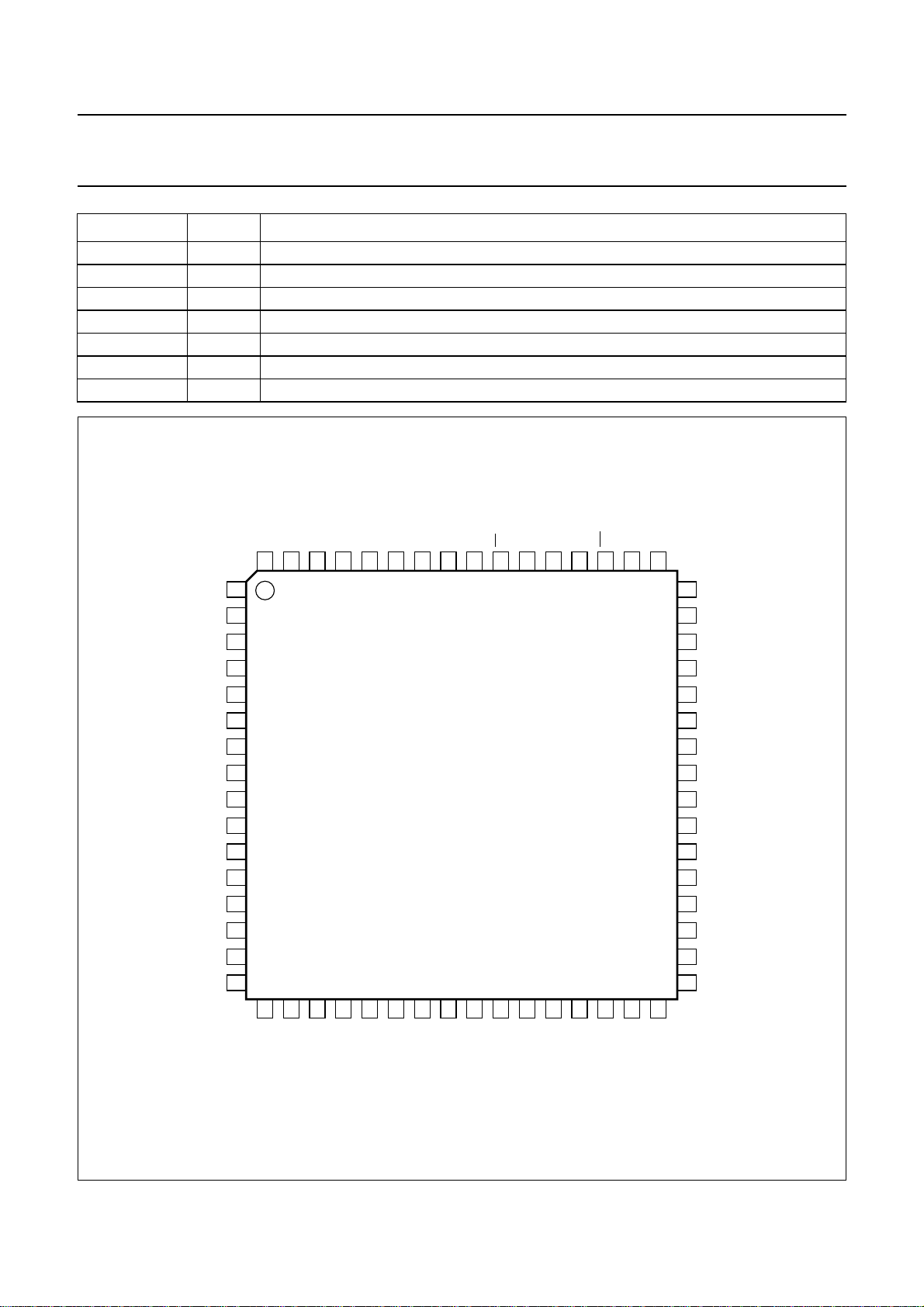
PINNING
SYMBOL PIN DESCRIPTION
DPGA2N 1 DPGA2 inverting output
DPGA2 2 DPGA2 non-inverting output
DPGAC2 3 DPGA2 bandwidth limitation control
V
V
ref2
DDA2
4 ADC2 reference output
5 DPGA2 analog supply voltage
VIN2N 6 DPGA2 inverting input voltage
VIN2 7 DPGA2 non-inverting input voltage
V
V
SSA2
SSA1
8 DPGA2 analog ground
9 DPGA1 analog ground
VIN1 10 DPGA1 non-inverting input voltage
VIN1N 11 DPGA1 inverting input voltage
V
V
DDA1
ref1
12 DPGA1 analog supply voltage
13 ADC1 reference output
DPGAC1 14 DPGA1 bandwidth limitation control
DPGA1 15 DPGA1 non-inverting output
DPGA1N 16 DPGA1 inverting output
1999 Sep 16 4
Philips Semiconductors Objective specification
Dual 8-bit, 100 Msps A/D converter with
DPGA
SYMBOL PIN DESCRIPTION
BUF1 17 buffer1 non-inverting input
BUF1N 18 buffer1 inverting input
V
oref1
V
DDA3
V
SSA3
CLK1N 22 ADC1 inverting clock input
CLK1 23 ADC1 non-inverting clock input
V
SSD1
V
DDD1
SMODE 26 serial interface mode input
SEN2 27 serial interface enable 2 (active low)
SDATA 28 serial interface data input
SCLK 29 serial interface clock input
SEN1 30 serial interface enable 1 (active low)
V
DDO1
V
SSO1
A7 33 channel 1 output bit 7 (MSB)
A6 34 channel 1 output bit 6
A5 35 channel 1 output bit 5
A4 36 channel 1 output bit 4
A3 37 channel 1 output bit 3
A2 38 channel 1 output bit 2
A1 39 channel 1 output bit 1
A0 40 channel 1 output bit 0 (LSB)
B0 41 channel 2 output bit 0 (LSB)
B1 42 channel 2 output bit 1
B2 43 channel 2 output bit 2
B3 44 channel 2 output bit 3
B4 45 channel 2 output bit 4
B5 46 channel 2 output bit 5
B6 47 channel 2 output bit 6
B7 48 channel 2 output bit 7 (MSB)
V
SSO2
V
DDO2
OE 51 digital output enable (active LOW)
SR 52 digital output bit slew-rate control
DPGAEN 53 DPGA enable (active LOW)
TEST 54 test input (to be grounded)
TE 55 track-and-hold enable (active LOW)
V
DDD2
V
SSD2
19 buffer1 common mode reference output
20 ADC1 analog supply voltage 3
21 ADC1 analog ground 3
24 digital ground 1
25 digital supply voltage 1
31 output stage supply voltage 1
32 output stage ground 1
49 output stage ground 2
50 output stage supply voltage 2
56 digital supply voltage 2
57 digital ground 2
TDA8798
1999 Sep 16 5
Philips Semiconductors Objective specification
Dual 8-bit, 100 Msps A/D converter with
DPGA
SYMBOL PIN DESCRIPTION
CLK2 58 ADC2 non-inverting clock input
CLK2N 59 ADC2 inverting clock input
V
SSA4
V
DDA4
V
oref2
BUF2N 63 buffer2 inverting input
BUF2 64 buffer2 non-inverting input
handbook, full pagewidth
60 ADC2 analog ground 4
61 ADC2 analog supply voltage 4
62 buffer2 common mode reference output
oref2
DDA4
SSA4
V
V
61
60
CLK2N
59
CLK2
58
TDA8798HL
DPGA2N
DPGA2
DPGAC2
V
ref2
V
DDA2
VIN2N
VIN2
V
SSA2
V
SSA1
VIN1
VIN1N
V
DDA1
V
ref1
DPGAC1
DPGA1
DPGA1N
BUF2N
BUF2
64
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
V
63
62
SSD2
V
57
DDD2
V
56
55
TE
TEST
54
SR
DPGAEN
53
52
OE
51
DDO2
V
50
SSO2
V
49
TDA8798
48
B7
47
B6
46
B5
45
B4
44
B3
43
B2
B1
42
B0
41
40
A0
39
A1
38
A2
37
A3
36
A4
35
A5
34
A6
33
A7
20
21
22
23
CLK1
24
V
17
BUF1
18
V
BUF1N
19
oref1
DDA3
V
SSA3
V
CLK1N
Fig.3 Pin configuration.
1999 Sep 16 6
SSD1
25
DDD1
V
26
27
SEN2
SMODE
28
SDATA
29
SCLK
30
SEN1
31
DDO1
V
32
SSO1
V
MGM864

Philips Semiconductors Objective specification
Dual 8-bit, 100 Msps A/D converter with
DPGA
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
The TDA8798 comprises two independent fully differential
signalchainseachhavingaDPGAandahigh-speed ADC.
A serial interface allows the gain of each DPGA to be
controlledindependently. To improve signal conditions, an
AC-coupled external filter can be connected between a
DPGAandADC.TheTDA8798canbeused as a dual 8-bit
ADC without DPGA functionality, using less power.
Digitally Programmable Gain Amplifier (DPGA)
The gain of the differential DPGA is programmable from
0 to 34 dBV in 63 equal steps by a 6-bit word output in
parallel from a gain control register in the SI. For all gain
settings, the DPGA signal bandwidth exceeds 30 MHz.
The settling time between gain changes can be adjusted
by an external decoupling capacitor connected to
DPGAC1 (pin 14) and/or DPGAC2 (pin 3). The analog
input signals can be either AC or DC coupled. When used
only as a dual 8-bit ADC, both DPGAs can be disabled to
reduce power consumption.
Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC)
The 8-bit ADC converts the differential analog input signal
into a binary output format at a maximum conversion rate
of 100 Msps. All digital input and output signals are
TTL/CMOS compatible.
The ADC clock signal can be from either a differential or a
single-ended source; when single-ended, the unused
clockinputpinshouldbe decoupled externally. The analog
input to the ADC is AC coupled.
TDA8798
Serial Interface (SI)
The SI allows the gain of each DPGA to be controlled
independently using either a parallel load mode or a
count-up/count-down mode. The gain control mode is
selected by the state of SMODE. The operation of DPGA
gain control is shown in Timing diagram, (see Fig.4).
Parallel load mode
This mode loads gain control data serially into a decoder
in the SI. Each of the six bits are loaded on the rising edge
ofSCLK.After the load has completed, SEN goes inactive,
loading the data in parallel to a gain control register in the
SI, changing the gain of the DPGA.
Count-up/count-down mode
Count-up/count-down mode is selected when SMODE is
in the opposite state to parallel load mode. This mode
either increments or decrements the SI gain control
register in one-bit steps when SEN and SCLK are both
active; the state of SDATA determines the count direction
(up or down). This allows the gain of the DPGA to be
changed asynchronously and intermittently.
ADC digital outputs
Digital noise on the internal supply lines increases when
the V
between channels. This effect can be reduced by making
SR (pin 52) HIGH, changing the slew-rate of the ADC
digital outputs.
voltage increases, affecting the crosstalk
DDO
Whenused only as a dualADC, the ADC can beexternally
biased by regulator output V
V
(pin 62) using series resistors of, for example, 50 Ω,
oref2
(pin 19) and/or
oref1
connected to the ADCbuffer inputs providing a lower input
impedance. This requires V
oref1
and/or V
oref2
to be
decoupled to ground by a 10 nF capacitor.
V
(pin 13) and/or V
ref1
(pin 4) provide a voltage
ref2
corresponding to the bias of the ADC which can be used
as a reference output to an external control circuit.
Alternatively, an external control voltage can be applied to
these pins to adjust the full-scale range of the ADC.
1999 Sep 16 7
Philips Semiconductors Objective specification
Dual 8-bit, 100 Msps A/D converter with
DPGA
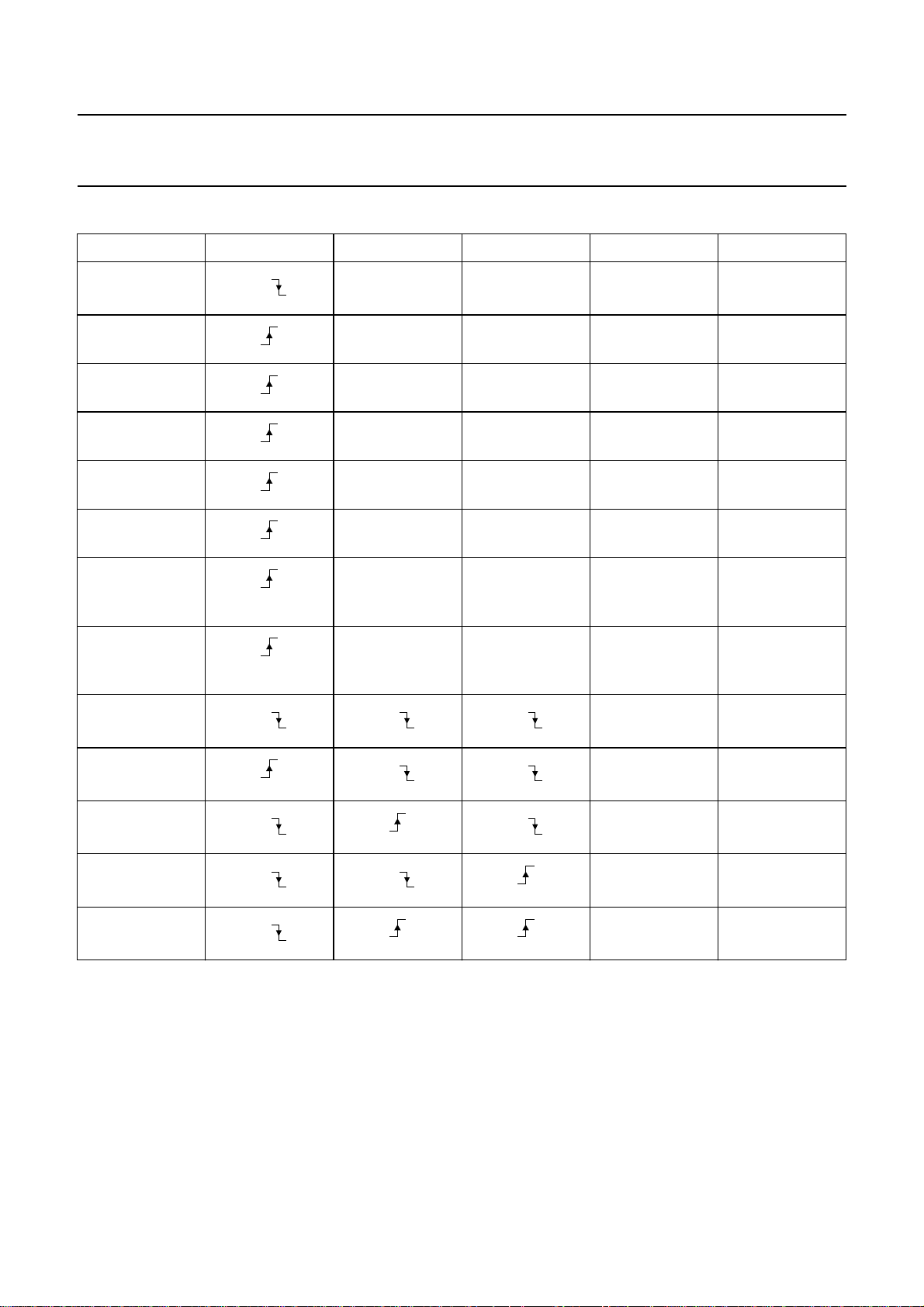
Table 1 Serial interface truth table; see notes 1 and 2
SMODE SCLK SEN1 SEN2 SDATA ACTION
0 1 1 U WAIT
X,
0 1 1 Di SISR: SISR ← Di
0 0 1 1 SISR: SISR ← 1
0 0 1 0 SISR: SISR ← 0
0 1 0 1 SISR: SISR ← 1
0 1 0 0 SISR: SISR ← 0
0 0 0 1 SISR: SISR ← 1
0 0 0 0 SISR: SISR ← 0
1 U WAIT
X, X, X,
TDA8798
GCR1: GCR1 + 1
GCR1: GCR1 − 1
GCR2: GCR2 + 1
GCR2: GCR2 − 1
GCR1: GCR1 + 1
GCR2: GCR2 + 1
GCR1: GCR1 − 1
GCR2: GCR2 − 1
1 Di SISR: SISR ← Di
X, X,
1 U GCR1: SISR
X, X,
1 U GCR2: SISR
X, X,
1 U GCR1: SISR
X,
Notes
1. ‘← Di’: shifting LSB and loading new LSB with value Di.
2. In count-up/count-down mode, thegain control register cannotbe incremented above themaximum gain value of 63,
or decremented below the minimum gain value of 0.
1999 Sep 16 8
GCR2: SISR
 Loading...
Loading...