Philips tda8425 DATASHEETS
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
DATA SH EET
TDA8425
Hi-fi stereo audio processor;
2
I
C-bus
Product specification
File under Integrated Circuits, IC02
October 1988
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Hi-fi stereo audio processor; I2C-bus
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The TDA8425 is a monolithic bipolar integrated stereo sound circuit with a loudspeaker channel facility, digitally
controlled via the I2C-bus for application in hi-fi audio and television sound.
Feature:
• Source and mode selector for two stereo channels
• Pseudo stereo, spatial stereo, linear stereo and forced mono switch
• Volume and balance control
• Bass, treble and mute control
• Power supply with power-on reset
TDA8425
QUICK REFERENCE DATA
PARAMETER SYMBOL MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
Supply voltage (pin 4) V
Input signal handling V
Input sensitivity
full power at the output stage V
Signal plus noise-to-noise ratio (S+N)/N − 86 − dB
Total harmonic distortion THD − 0.05 − %
Channel separation α−80 − dB
Volume control range G −64 − 6dB
Treble control range G −12 − 12 dB
Bass control range G −12 − 15 dB
PACKAGE OUTLINE
20-lead dual in-line; plastic (SOT146); SOT146-1; 1996 November 26.
CC
l
i
10.8 12.0 13.2 V
2 −− V
− 300 − mV
October 1988 2
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Hi-fi stereo audio processor; I2C-bus
TDA8425
October 1988 3
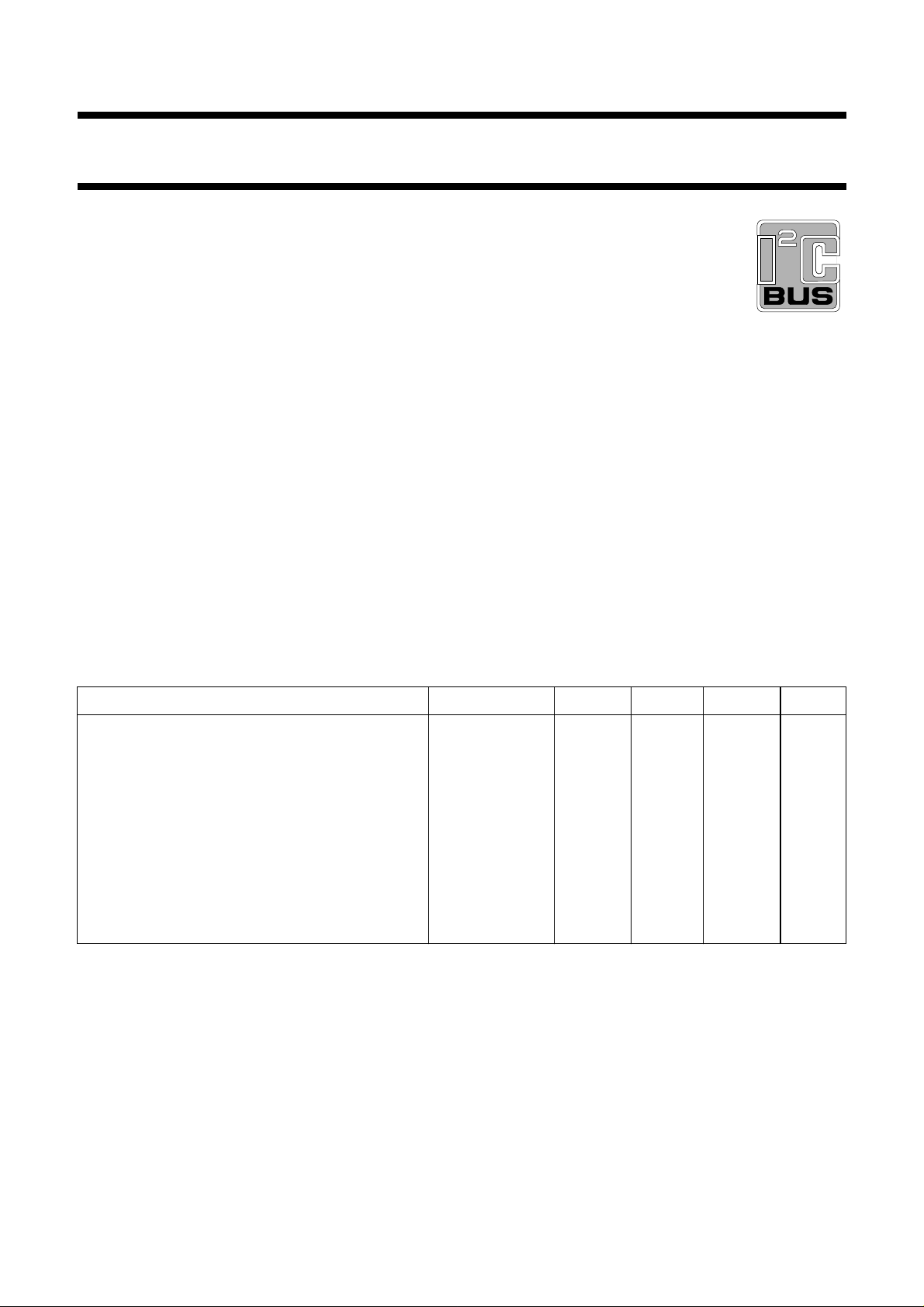
Fig.1 Block diagram.
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Hi-fi stereo audio processor; I2C-bus
PINNING
TDA8425
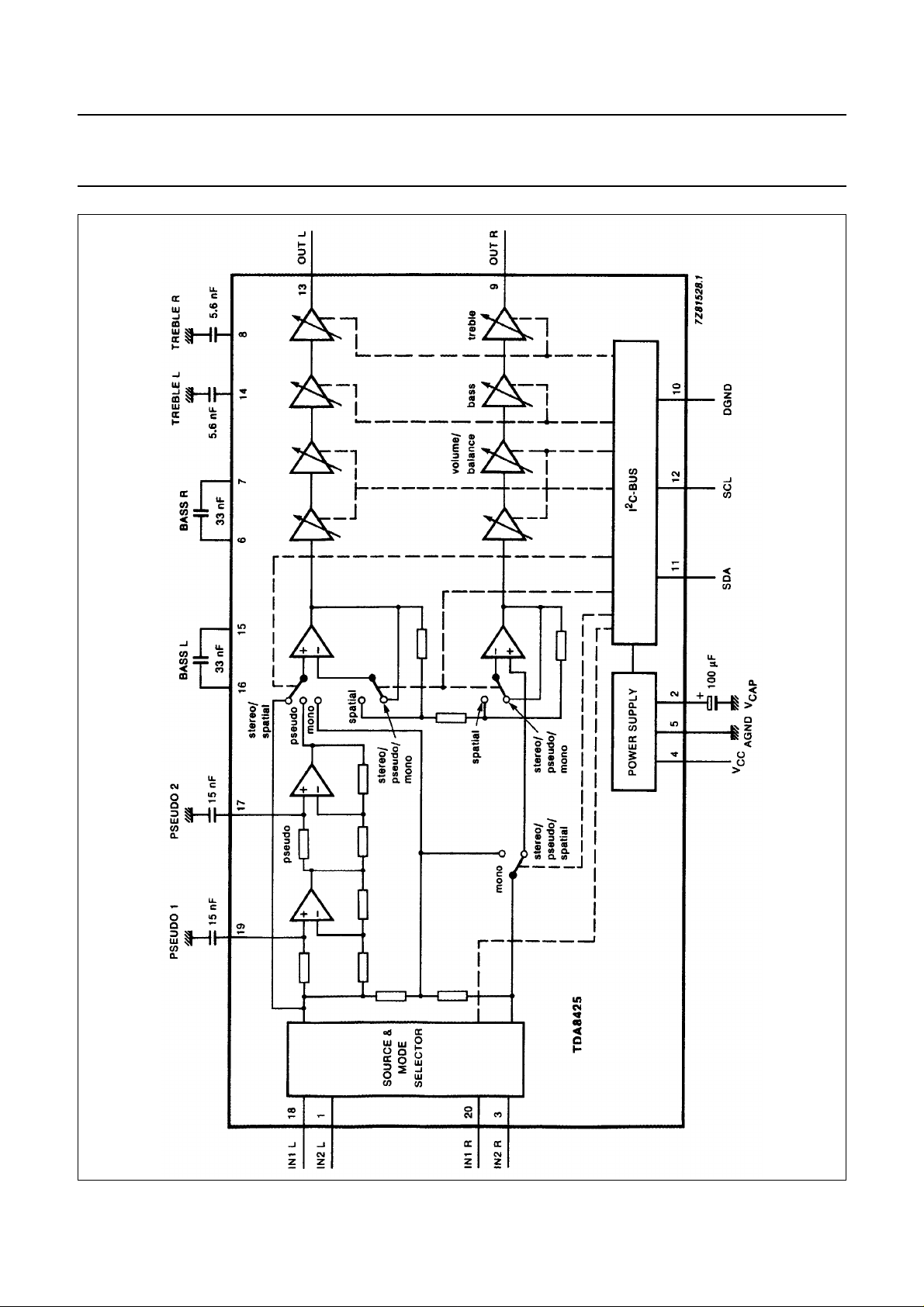
Fig.2 Pinning diagram.
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
Source selector
The input to channel 1 (CH1) and channel 2 (CH2) is determined by the source selector. The selection is made from the
following AF input signals:
• IN 1 L (pin 18); IN1 R (pin 20)
or
• IN2 L (pin 1); IN2 R (pin 3)
Mode selector
The mode selector selects between stereo, sound A and sound B (in the event of bilingual transmission) for OUT R and
OUT L.
Volume control and balance
The volume control consists of two stages (left and right). In each part the gain can be adjusted between +6 dB and
−64 dB in steps of 2 dB. An additional step allows an attenuation of ≥ 80 dB. Both parts can be controlled independently
over the whole range, which allows the balance to be varied by controlling the volume of left and right output channels.
Linear stereo, pseudo stereo, spatial stereo and forced mono mode
(1)
It is possible to select four modes: linear stereo, pseudo stereo, spatial stereo or forced mono. The pseudo stereo mode
handles mono transmissions, the spatial stereo mode handles stereo transmissions and the forced mono can be used
in the event of stereo signals.
(1) During forced mono mode the pseudo stereo mode cannot be used.
October 1988 4
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Hi-fi stereo audio processor; I2C-bus
Bass control
The bass control stage can be switched from an emphasis of 15 dB to an attenuation of 12 dB for low frequencies in
steps of 3 dB.
Treble control
The treble control stage can be switched from +12 dB to −12 dB in steps of 3 dB.
Bias and power supply
The TDA8425 includes a bias and power supply stage, which generates a voltage of 0.5 × V
impedance and injector currents for the logic part.
Power-on reset
The on-chip power-on reset circuit sets the mute bit to active, which mutes both parts of the treble amplifier. The muting
can be switched by transmission of the mute bit.
2
I
C-bus receiver and data handling
Bus specification
The TDA8425 is controlled via the 2-wire I2C-bus by a microcomputer.
The two wires (SDA − serial data, SCL− serial clock) carry information between the devices connected to the bus. Both
SDA and SCL are bidirectional lines, connected to a positive supply voltage via a pull up resistor.
When the bus is free both lines are HIGH.
The data on the SDA line must be stable during the HIGH period of the clock. The HIGH or LOW state of the data line
can only change when the clock signal on the SCL line is LOW. The set up and hold times are specified in AC
CHARACTERISTICS.
with a low output
CC
TDA8425
A HIGH-to-LOW transition of the SDA line while SCL is HIGH is defined as a start condition.
A LOW-to-HIGH transition of the SDA line while SCL is HIGH is defined as a stop condition.
The bus receiver will be reset by the reception of a start condition. The bus is considered to be busy after the start
condition.
The bus is considered to be free again after a stop condition.
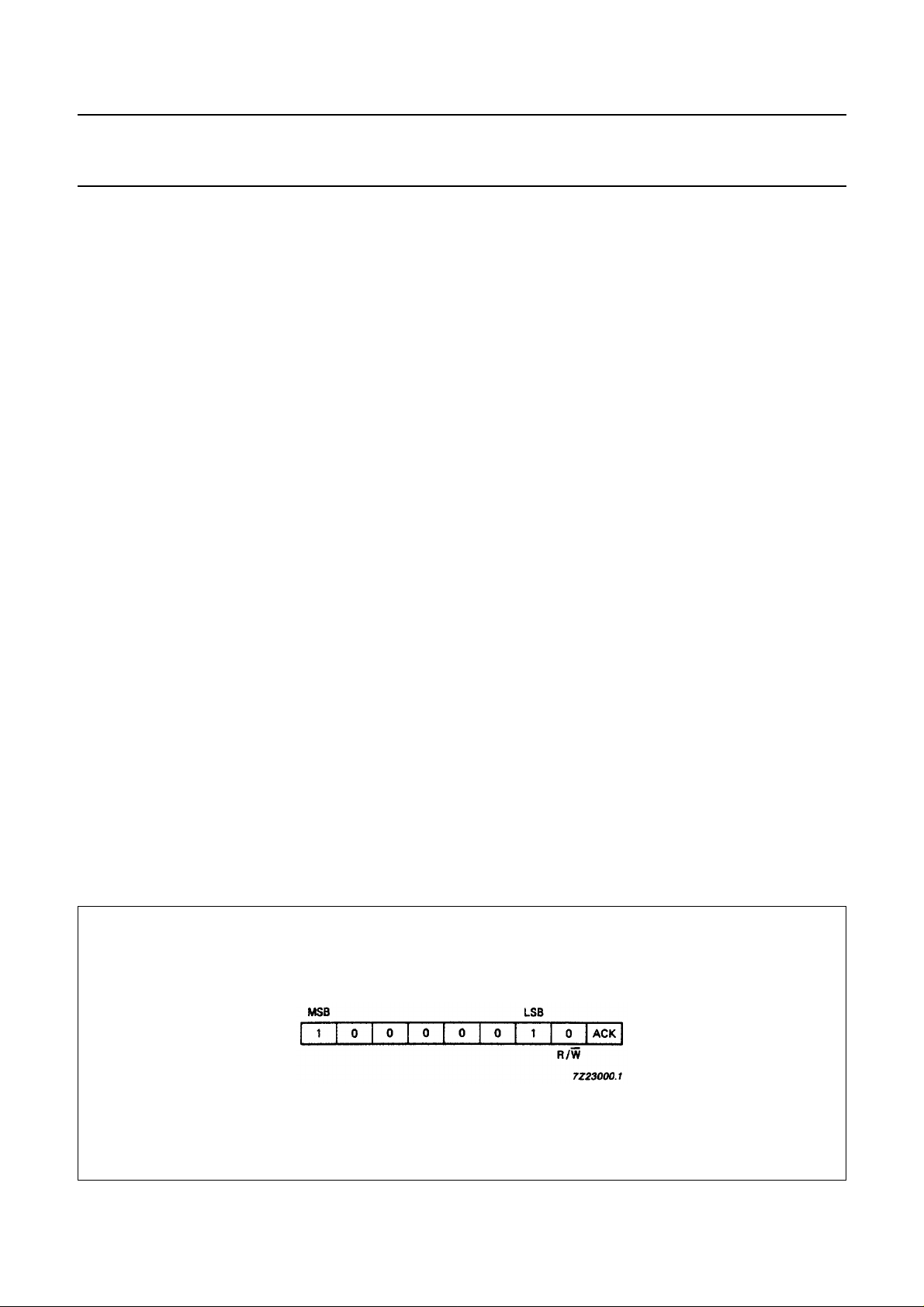
Module address
Data transmission to the TDA8425 starts with the module address MAD.
Fig.3 TDA8425 module address.
October 1988 5
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Hi-fi stereo audio processor; I2C-bus
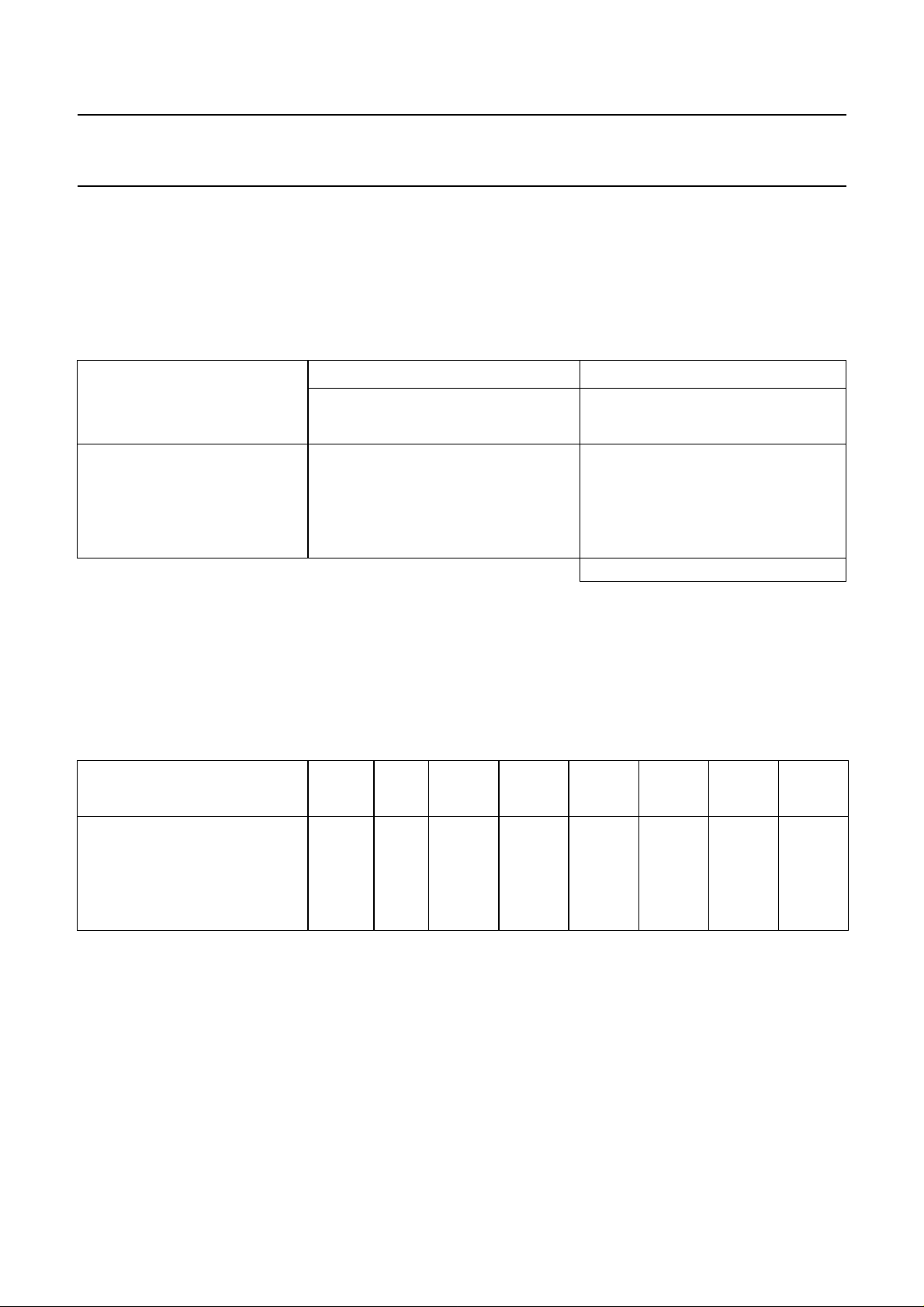
Subaddress
After the module address byte a second byte is used to select the following functions:
• Volume left, volume right, bass, treble and switch functions
The subaddress SAD is stored within the TDA8425. Table 1 defines the coding of the second byte after the module
address MAD.
Table 1 Second byte after module address MAD
128 64 32 16 8 4 2 1
MSB LSB
function
volume left 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
volume right 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1
bass 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0
treble 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1
switch functions 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0
76543210
subaddress SAD
TDA8425
The automatic increment feature of the slave address enables a quick slave receiver initialization, within one
transmission, by the I
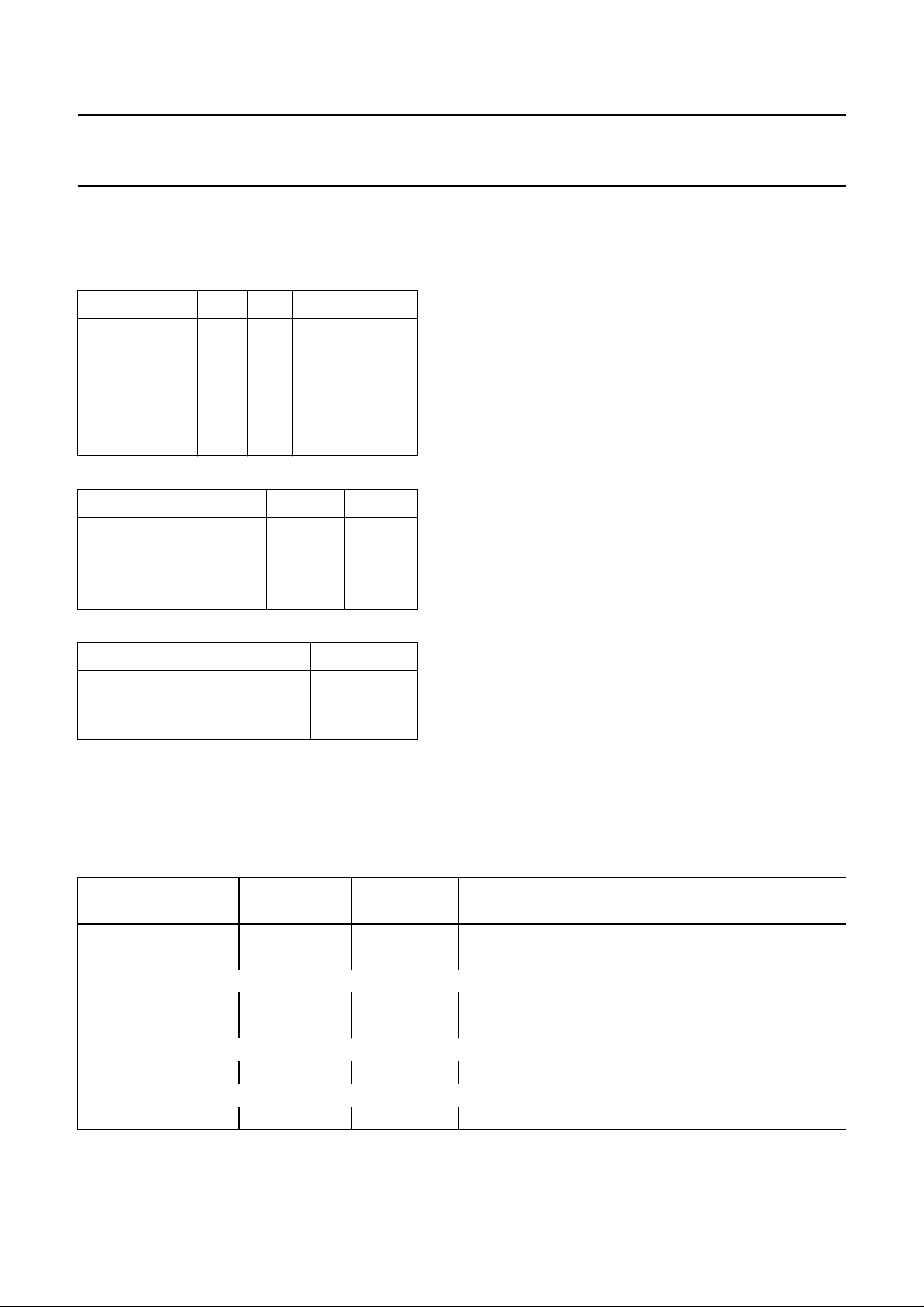
Definition of 3rd byte
A third byte is used to transmit data to the TDA8425. Table 2 defines the coding of the third byte after module address
MAD and subaddress SAD.
Table 2 Third byte after module address MAD and subaddress SAD
function
volume left VL 1 1 V05 V04 V03 V02 V01 V00
volume right VR 1 1 V15 V14 V13 V12 V11 V10
bass BA 1 1 1 1 BA3 BA2 BA1 BA0
treble TR 1 1 1 1 TR3 TR2 TR1 TR0
switch functions S1 1 1 MU EFL STL ML1 ML0 IS
2
C-bus controller (see Fig.5).
MSB LSB
76543210
October 1988 6
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Hi-fi stereo audio processor; I2C-bus
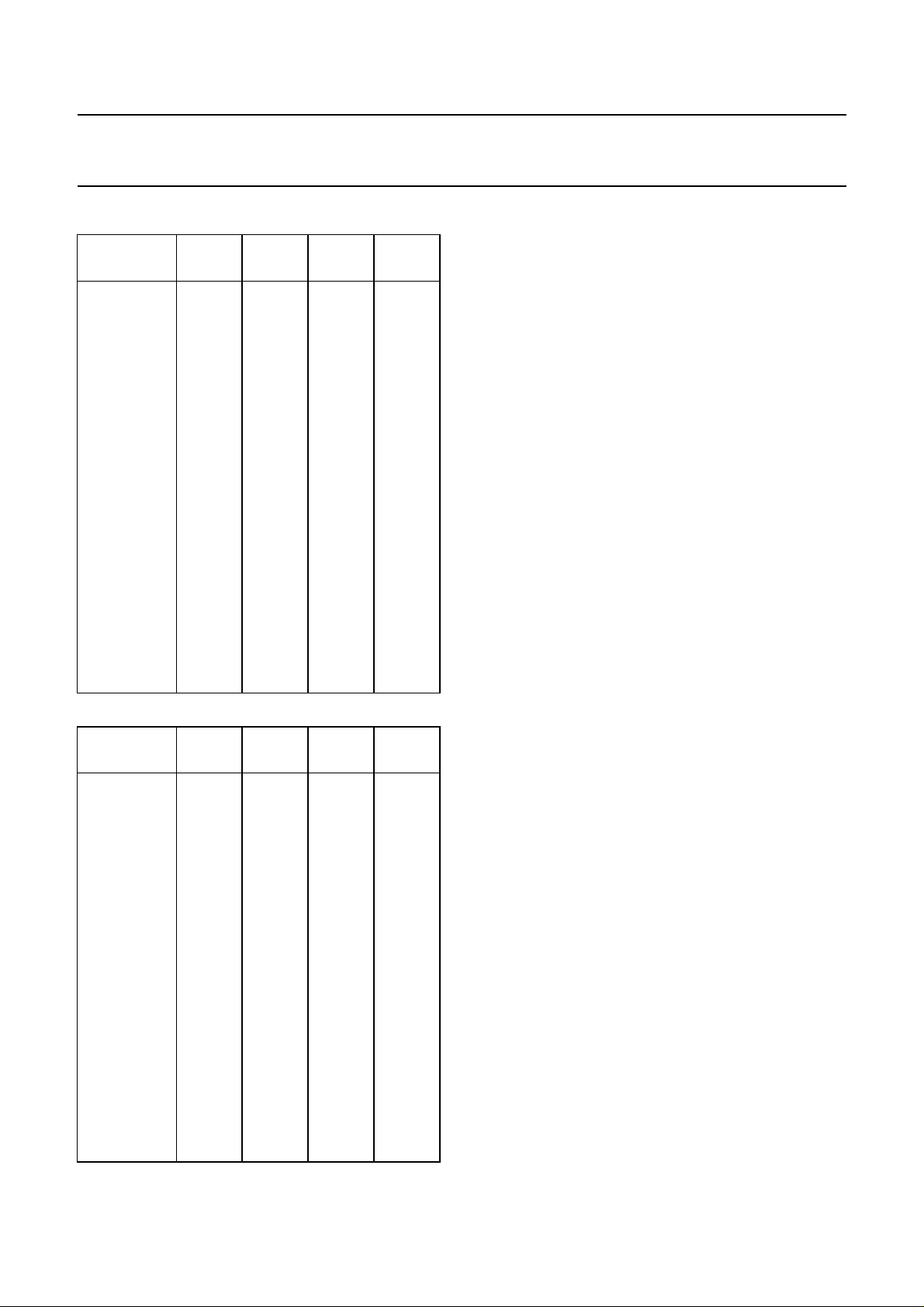
Truth tables
Truth tables for the switch functions
Table 3 Source selector
function ML1 ML0 IS channel
stereo 1 1 0 1
stereo 1 1 1 2
sound A 0 1 0 1
sound B 1 0 0 1
sound A 0 1 1 2
sound B 1 0 1 2
Table 4 Pseudo stereo/spatial stereo/linear stereo/forced mono
choice STL EFL
spatial stereo 1 1
linear stereo 1 0
pseudo stereo 0 1
forced mono
(1)
00
TDA8425
Table 5 Mute
mute MU
active; automatic
after POR
not active 0
Notes
1. Pseudo stereo function is not possible in this mode.
2. Where: POR = Power-ON Reset.
Truth tables for the volume, bass and treble controls
Table 6 Volume control
6 1 1 1111
4 1 1 1110
−62 0 1 1101
−64 0 1 1100
≤−80 0 1 1011
(2)
2 dB/step
(dB)
1
V × 5V×4V×3V×2V×1V×0
≤−80 0 0 0000
October 1988 7
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Hi-fi stereo audio processor; I2C-bus
Table 7 Bass control
3 dB/step
(dB)
15 1111
⋅⋅ ⋅⋅ ⋅⋅ ⋅⋅ ⋅⋅
⋅⋅ ⋅⋅ ⋅⋅ ⋅⋅ ⋅⋅
⋅⋅ ⋅⋅ ⋅⋅ ⋅⋅ ⋅⋅
15 1011
12 1010
⋅⋅ ⋅⋅ ⋅⋅ ⋅⋅ ⋅⋅
⋅⋅ ⋅⋅ ⋅⋅ ⋅⋅ ⋅⋅
⋅⋅ ⋅⋅ ⋅⋅ ⋅⋅ ⋅⋅
0 0110
⋅⋅ ⋅⋅ ⋅⋅ ⋅⋅ ⋅⋅
⋅⋅ ⋅⋅ ⋅⋅ ⋅⋅ ⋅⋅
⋅⋅ ⋅⋅ ⋅⋅ ⋅⋅ ⋅⋅
−12 0010
⋅⋅ ⋅⋅ ⋅⋅ ⋅⋅ ⋅⋅
⋅⋅ ⋅⋅ ⋅⋅ ⋅⋅ ⋅⋅
⋅⋅ ⋅⋅ ⋅⋅ ⋅⋅ ⋅⋅
−12 0000
BA3 BA2 BA2 BA0
TDA8425
Table 8 Treble control
3 dB/step
(dB)
12 1111
⋅⋅ ⋅⋅ ⋅⋅ ⋅⋅ ⋅⋅
⋅⋅ ⋅⋅ ⋅⋅ ⋅⋅ ⋅⋅
⋅⋅ ⋅⋅ ⋅⋅ ⋅⋅ ⋅⋅
12 1010
⋅⋅ ⋅⋅ ⋅⋅ ⋅⋅ ⋅⋅
⋅⋅ ⋅⋅ ⋅⋅ ⋅⋅ ⋅⋅
⋅⋅ ⋅⋅ ⋅⋅ ⋅⋅ ⋅⋅
0 0110
⋅⋅ ⋅⋅ ⋅⋅ ⋅⋅ ⋅⋅
⋅⋅ ⋅⋅ ⋅⋅ ⋅⋅ ⋅⋅
⋅⋅ ⋅⋅ ⋅⋅ ⋅⋅ ⋅⋅
−12 0010
⋅⋅ ⋅⋅ ⋅⋅ ⋅⋅ ⋅⋅
⋅⋅ ⋅⋅ ⋅⋅ ⋅⋅ ⋅⋅
⋅⋅ ⋅⋅ ⋅⋅ ⋅⋅ ⋅⋅
−12 0000
TR3 TR2 TR2 TR0
October 1988 8
 Loading...
Loading...