Philips SCN2652AC2A44, SCN2652AC2F40, SCN2652AC2N40, SCN6852AC2A44, SCN6852AC2F40 Datasheet
...
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
SCN2652/SCN68652Multi-protocol communications controller (MPCC)
1
1995 May 1 853-1068 15179
DESCRIPTION
The SCN2652/68652 Multi-Protocol Communications Controller
(MPCC) is a monolithic n-channel MOS LSI circuit that formats,
transmits and receives synchronous serial data while supporting
bit-oriented or byte control protocols. The chip is TTL compatible,
operates from a single +5V supply, and can interface to a processor
with an 8 or 16-bit bidirectional data bus.
APPLICATIONS
•Intelligent terminals
•Line controllers
•Network processors
•Front end communications
•Remote data concentrators
•Communication test equipment
•Computer to computer links
FEATURES
•DC to 2Mbps data rate
•Bit-oriented protocols (BOP): SDLC, ADCCP, HDLC
•Byte-control protocols (BCP): DDCMP, BISYNC (external CRC)
•Programmable operation
– 8 or 16-bit tri-state data bus
– Error control – CRC or VRC or none
– Character length – 1 to 8 bits for BOP or 5 to 8 bits for BCP
– SYNC or secondary station address comparison for BCP-BOP
– Idle transmission of SYNC/FLAG or MARK for BCP-BOP
•Automatic detection and generation of special BOP control
sequences, i.e., FLAG, ABORT, GA
•Zero insertion and deletion for BOP
•Short character detection for last BOP data character
•SYNC generation, detection, and stripping for BCP
•Maintenance mode for self-testing
•TTL compatible
•Single +5V supply
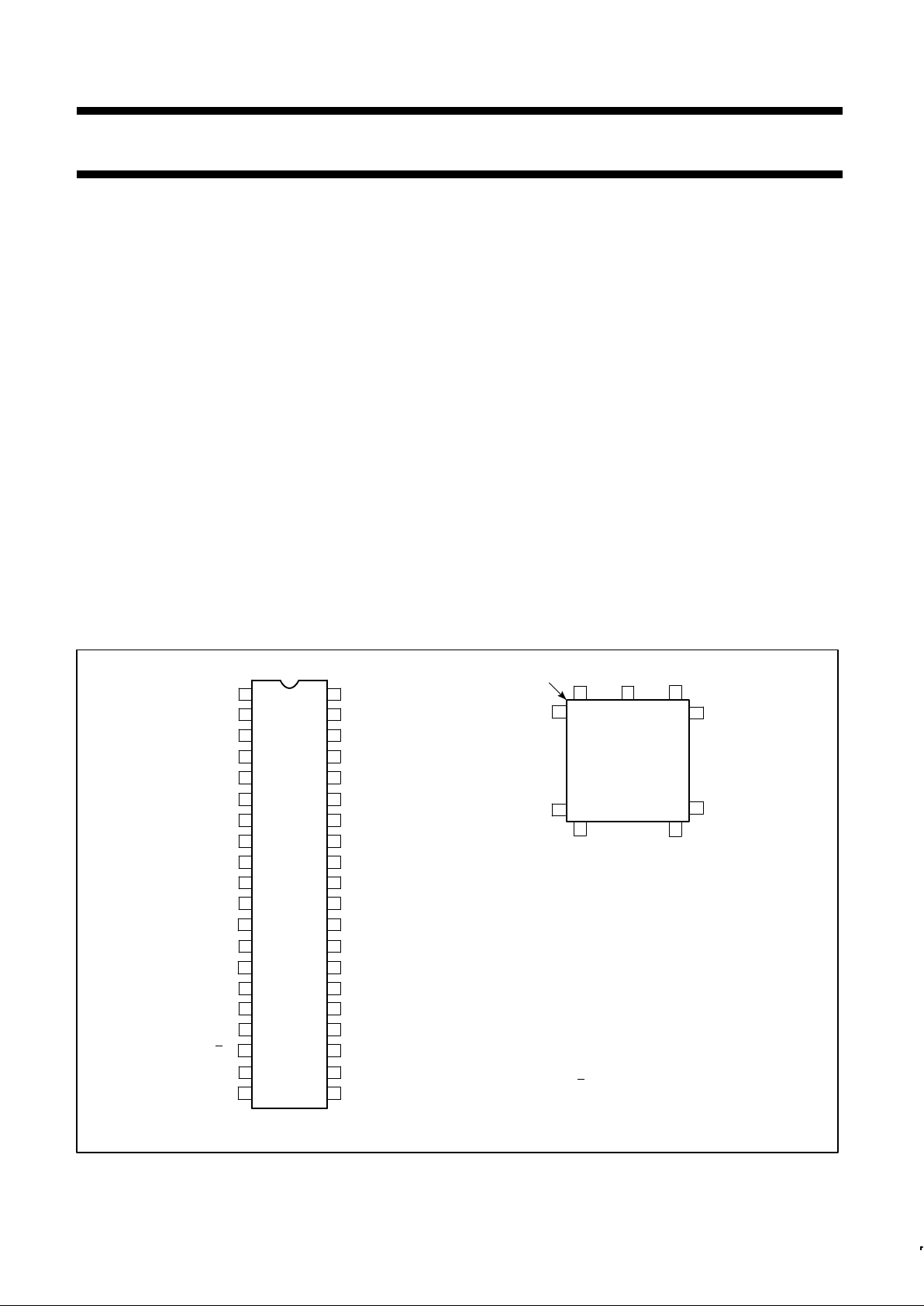
PIN CONFIGURA TION
Pin Function Pin Function
1 NC 23 NC
2 CE 24 A0
3 RxC 25 BYTE
4 RxSI 26 DBEN
5 S/F 27 DB07
6 RxA 28 DB06
7 RxDA 29 DB05
8 RxSA 30 DB04
9 RxE 31 DB03
10 GND 32 DB02
11 DB08 33 DB01
12 NC 34 NC
13 DB09 35 DB00
14 DB10 36 V
CC
15 DB11 37 RESET
16 DB12 38 TxA
17 DB13 39 TxBE
18 DB14 40 TxU
19 DB15 41 TxE
20 R
/W 42 TxSQ
21 A2 43 TxC
22 A1 44 MM
1
39
17
28
40
29
18
7
PLCC
6
TOP VIEW
INDEX
CORNER
NOTE: DB00 is least significant bit, highest number
(that is, DB15, A2) is most significant bit.
24
23
22
2120
19
18
17
16
15
28
27
12
10
11
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
14
13
26
25
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40CE
RxC
RxSI
S/F
RxA
RxDA
RxSA
RxE
GND
DB08
DB09
DB10
DB11
DB12
DB13
DB14
DB15
R
/W
A2
A1 A0
BYTE
DBEN
DB07
DB06
DB05
DB04
DB03
DB02
DB01
DB00
V
CC
RESET
TxA
TxBE
TxU
TxE
TxSQ
TxC
MM
DIP
TOP VIEW
SD00057
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
SCN2652/SCN68652Multi-protocol communications controller (MPCC)
1995 May 1
2
ORDERING CODE
VCC = 5V +5%
PACKAGES
Commercial
0°C to +70°C
Industrial
-40°C to +85°C
DWG #
40-Pin Ceramic Dual In-Line Package (DIP) SCN2652AC2F40 / SCN68652AC2F40 0590B
40-Pin Plastic Dual In-Line Package (DIP) SCN2652AC2N40 / SCN68652AC2N40 Contact Factory SOT129-1
44-Pin Square Plastic Lead Chip Carrier (PLCC) SCN2652AC2A44 / SCN68652AC2A44 Contact Factory SOT187-2
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
1
SYMBOL
PARAMETER RATING UNIT
T
A
Operating ambient temperature
2
Note 4 °C
T
STG
Storage temperature –65 to +150 °C
V
CC
All inputs with respect to GND
3
–0.3 to +7 V
NOTES:
1. Stresses above those listed under “Absolute Maximum Ratings” may cause permanent damage to the device. This is a stress rating only
and functional operation of the device at these or at any other condition above those indicated in the operation sections of this specification
is not implied.
2. For operating at elevated temperatures the device must be derated based on +150
°
C maximum junction temperature.
3. This product includes circuitry specifically designed for the protection of its internal devices from the damaging effects of excessive static
charge. Nonetheless, it is suggested that conventional precautions be taken to avoid applying any voltages larger than the rated maxima.
4. Parameters are valid over operating temperature range unless otherwise specified. See ordering code table for applicable temperature
range and operating supply range.
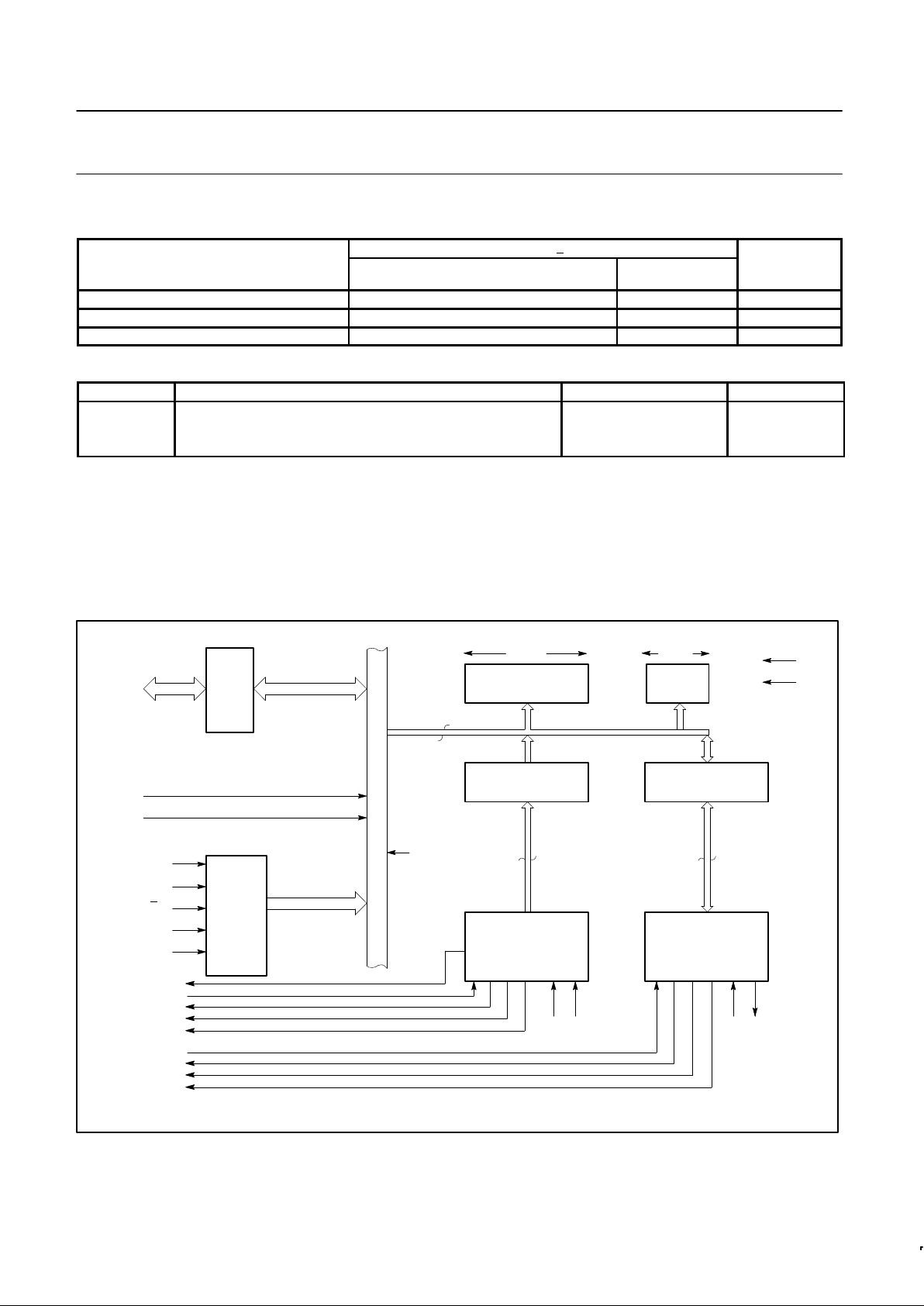
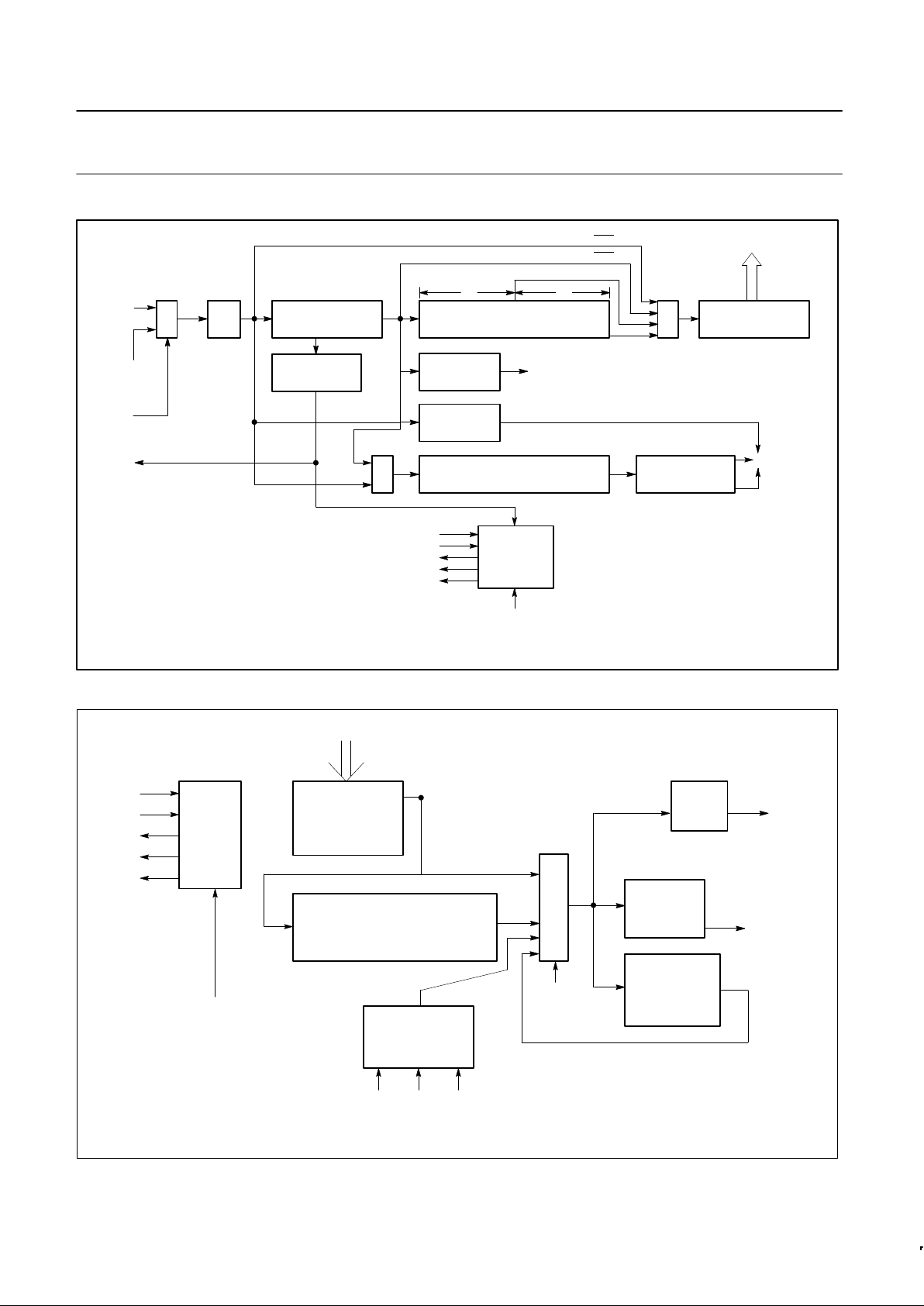
BLOCK DIAGRAM
DATA
BUS
BUFFER
DB15–
DB00
RESET
MM
READ/
WRITE
LOGIC
AND
CONTROL
A2–A0
BYTE
R
/W
CE
DBEN
PARAMETER CONTROL
SYNC/ADDRESS
REGISTER
16 BITS
16
PCSAR
INTERNAL
BUS
RECEIVER
DATA/STATUS
REGISTER
RDSR
RECEIVER
LOGIC AND
CONTROL
16
PARAMETER
CONTROL
REGISTER
8 BITS
PCR
V
CC
GND
TRANSMITTER
DATA/STATUS
REGISTER
TDSR
TRANSMITTER
LOGIC AND
CONTROL
16
RxC RxSI TxC TxSO
S/F
RxE
RxA
RxDA
RxSA
TxE
TxA
TxBE
TxU
SD00058
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
SCN2652/SCN68652Multi-protocol communications controller (MPCC)
1995 May 1
3
PIN DESCRIPTION
MNEMONIC PIN NO. TYPE NAME AND FUNCTION
DB15–DB00
17–10
24–31
I/O
Data Bus: DB07–DB00 contain bidirectional data while DB15–DB08 contain control and status
information to or from the processor. Corresponding bits of the high and low order bytes can be wire
OR’ed onto an 8-bit bus. The data bus is floating if either CE or DBEN are low.
A2–A0 19–21 I
Address Bus: A2–A0 select internal registers. The four 16-bit registers can be addressed on a word or
byte basis. See Register Address section.
BYTE 22 I
Byte: Single byte (8-bit) data bus transfers are specified when this input is high. A low level specifies
16-bit data bus transfers.
CE 1 I Chip Enable: A high input permits a data bus operation when DBEN is activated.
R/W 18 I
Read/Write: R/W controls the direction of data bus transfer . When high, the data is to be loaded into the
addressed register. A low input causes the contents of the addressed register to be presented on the
data bus.
DBEN 23 I
Data Bus Enable: After A2–A0, CE, BYTE and R/W are set up, DBEN may be strobed. During a read,
the 3-state data bus (DB) is enabled with information for the processor. During a write, the stable data is
loaded into the addressed register and TxBE will be reset if TDSR was addressed.
RESET 33 I Reset: A high level initializes all internal registers (to zero) and timing.
MM 40 I
Maintenance Mode: MM internally gates TxSO back to RxSI and TxC to RxC for off line diagnostic
purposes. The RxC and RxSI inputs are disabled and TxSO is high when MM is asserted.
RxE 8 I
Receiver Enable: A high level input permits the processing of RxSI data. A low level disables the
receiver logic and initializes all receiver registers and timing.
RxA 5 O
Receiver Active: RxA is asserted when the first data character of a message is ready for the processor.
In the BOP mode this character is the address. The received address must match the secondary station
address if the MPCC is a secondary station. In BCP mode, if strip-SYNC (PCSAR
13
) is set, the first
non-SYNC character is the first data character; if strip-SYNC is zero, the character following the second
SYNC is the first data character. In the BOP mode, the closing FLAG resets RxA. In the BCP mode, RxA
is reset by a low level at RxE.
RxDA* 6 O
Receiver Data Available: RxDA is asserted when an assembled character is in RDSRL and is ready to
be presented to the processor. This output is reset when RDSRL is read.
RxC 2 I
Receiver Clock: RxC (1X) provides timing for the receiver logic. The positive going edge shifts serial
data into the RxSR from RxSI.
S/F 4 O SYNC/FLAG: S/F is asserted for one RxC clock time when a SYNC or FLAG character is detected.
RxSA* 7 O
Receiver Status Available: RxSA is asserted when there is a zero to one transition of any bit in RDSR
H
except for RSOM. It is cleared when RDSRH is read.
RxSI 3 I Receiver Serial Input: RxSI is the received serial data. Mark = ‘1’, space = ‘0’.
TxE 37 I
Transmitter Enable: A high level input enables the transmitter data path between TDSRL and TxSO. At
the end of a message, a low level input causes TxSO = 1(mark) and TxA = 0 after the closing FLAG
(BOP) or last character (BCP) is output on TxSO.
TxA 34 O
Transmitter Active: TxA is asserted after TSOM (TDSR8) is set and TxE is raised. This output will reset
when TxE is low and the closing FLAG (BOP) or last character (BCP) has been output on TxSO.
TxBE* 35 O
Transmitter Buffer Empty: TxBE is asserted when theTDSR is ready to be loaded with new control
information or data. The processor should respond by loading theTDSR which resets TxBE.
TxU* 36 O
Transmitter Underrun: TxU is asserted during a transmit sequence when the service of TxBE has been
delayed for one character time. This indicates the processor is not keeping up with the transmitter. Line
fill depends on PCSAR
11
. TxU is reset by RESET or setting of TSOM (TDSR8), synchronized by the
falling edge of TxC.
TxC 39 I
Transmitter Clock: TxC (1X) provides timing for the transmitter logic. The positive going edge shifts
data out of the TxSR to TxSO.
TxSO 38 O Transmitter Serial Output: TxSO is the transmitted serial data. Mark = ‘1’, space = ‘0’.
V
CC
32 I +5V: Power supply.
GND 9 I Ground: 0V reference ground.
*Indicates possible interrupt signal
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
SCN2652/SCN68652Multi-protocol communications controller (MPCC)
1995 May 1
4
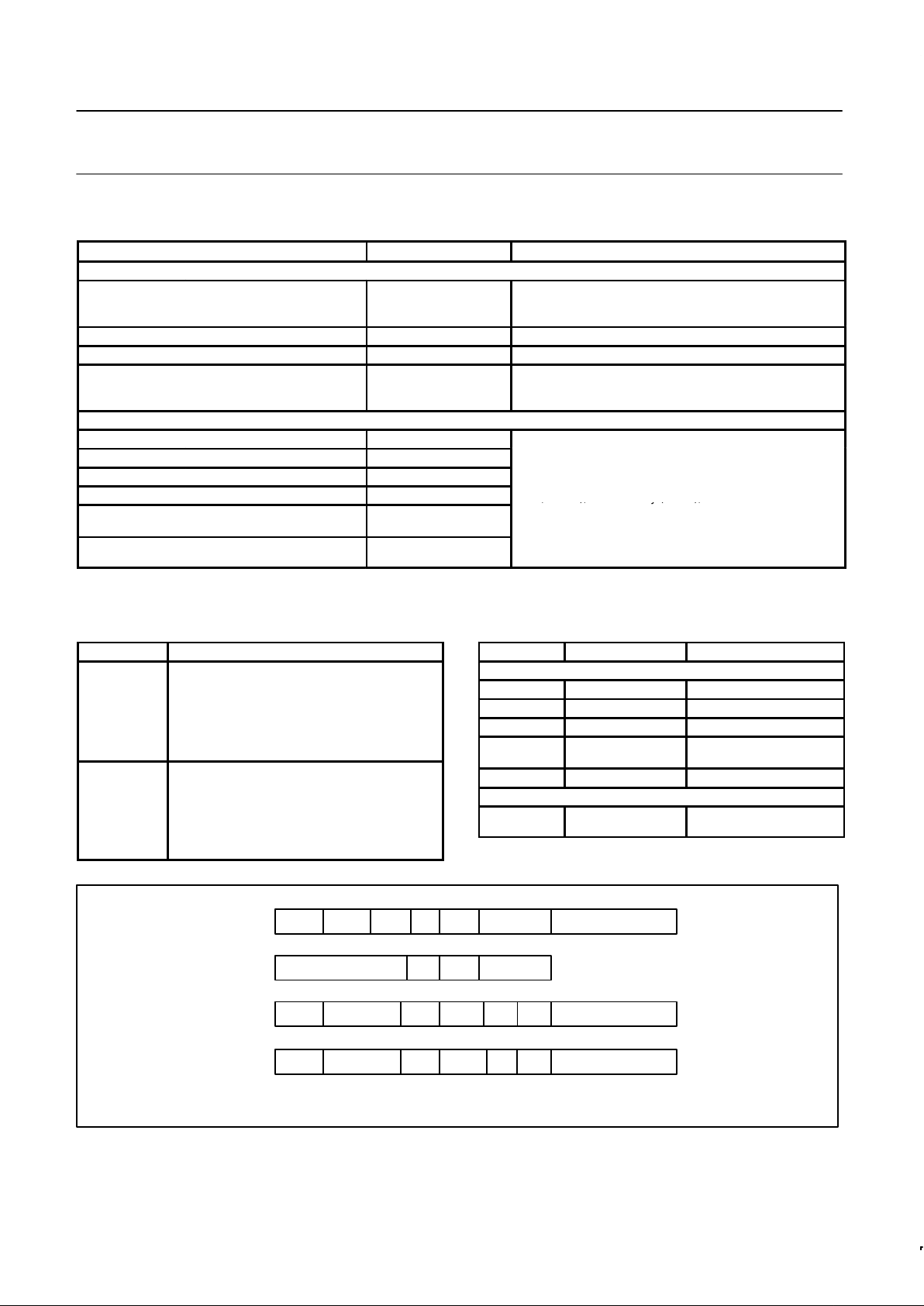
Table 1. Register Access
REGISTERS NO. OF BITS DESCRIPTION*
Addressable
PCSAR
Parameter control sync/
address register
16
PCSARH and PCR contain parameters common to the
receiver and transmitter. PCSAR
L
contains a programmable
SYNC character (BCP) or secondary station address (BOP).
PCR Parameter control register 8 RDSRH contains receiver status information.
RDSR Receive data/status register 16 RDSRL = RxDB contains the received assembled character.
TDSR Transmit data/status register 16
TDSRH contains transmitter command and status
information. TDSRL = TxDB contains the character to be
transmitted
Non-Addressable
CCSR Control character shift register 8
HSR Holding shift register 16
RxSR Receiver shift register 8
TxSR Transmitter shift register 8
These registers are used for character assembly (CSSR,
HSR, RxSR), disassembly (TxSR), and CRC
RxCRC
Receiver CRC accumulation
register
16
HSR, RxSR), disassembly (TxSR), and CRC
accumulation/generation (RxCRC, TxCRC).
TxCRC
Transmitter CRC generation
register
16
NOTES:
*H = High byte – bits 15–8
L = Low byte – bits 7–0
Table 2. Error Control
CHARACTER DESCRIPTION
FCS Frame check sequence is transmitted/received
as 16 bits following the last data character of a
BOP message. The divisor is usually
CRC–CCITT (X
16
+ X12 + X5 + 1) with dividend
preset to 1’s but can be other wise determined
by ECM. The inverted remainder is transmitter as
the FCS.
BCC Block check character is transmitted/received as
two successive characters following the last data
character of a BCP message. The polynomial is
CRC–16 (X
16
+ X15 + X2 + 1) or CRC–CCITT
with dividend preset to 0’s (as specified by
ECM). The true remainder is transmitted as the
BCC.
Table 3. Special Characters
OPERATION BIT PATTERN FUNCTION
BOP
FLAG 01111110 Frame message
ABORT 11111111 generation Terminate communication
01111111 detection
GA 01111111
Terminate loop mode
repeater function
Address (PCSARL)
1
Secondary station address
BCP
SYNC
(PCSARL) or
(TxDB)
2
generation
Character synchronization
NOTES:
1. ( ) = contents of.
2. For IDLE = 0 or 1 respectively.
APAPCSAR
PCR
RDSR
TDSR
15
PROTO14SS/GA13SAM12IDLE
11
E C M
10
9 8
S/AR
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
TxCL
15 14 13 12 11
RxCL
10 9 8
T
x
C
L
E
R
x
C
L
E
RERR
15
A B C
14 13
ROR
12
RAB/
GA
11
REOM
10 9 8
RxDBRSOM
TERR15NOT DEFINED
14 13
TGA12TABORT11TEOM
10 9 8
TxDBTSOM
NOTE:
Refer to Register Formats for mnemonics and description.
SD00059
Figure 1. Short Form Register Bit Formats
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
SCN2652/SCN68652Multi-protocol communications controller (MPCC)
1995 May 1
5
M
U
X
RxSI
FROM
XMITTER
MM
SEL
SYNC
FF
CCSR (8)
SYNC/FLAG
1
COMPARATOR
HSR (16)
8 8
M
U
X
RxSR (8)
TO
RDSR
L
BCP . CRC
BOP . CRC
BCP . CRC
BOP
.
CRC
ZERO (BOP)
DELETION
LOGIC
ZERO
DELETION
CONTROL
PARITY (BCP)
LOGIC
M
U
X
BCP
BOP
RxCRC ACC
CRC–16 (BCP) OR
CCRC–CCITT
(BOP)
CRC–16 = 0
COMPARATOR
CRC–CCIT = F0B8
RERR
RECEIVER
CONTROL
LOGIC
RxC
NOTES:
1. Detected in SYNC FF and 7 MS bits of CCSR.
2. In BOP mode, a minimum of two data characters must be received to turn the receiver active.
RESET
RxE
RxA
RxDA
RxSA
S/F
1-BIT
DELAY
SD00060
Figure 2. MPCC Receiver Data Path
TXSR (8)
M
U
X
BOP
ZERO
INSERTION
LOGIC
ZERO
INSERTION
CONTROL
TRANSMITTER
CONTROL
LOGIC
TxC
NOTES:
1. TxCRC selected if TEOM = 1 and the last data character has been shifted out of TxSR.
2. In BCP parity selected will be generated after each character is shifted out of TxSR.
RESET
TxE
TxA
TxBE
TxU
SD00088
TXCRC ACC (16)
CRC–16 OR CRC–CCITT
CONTROL
CHARACTER
GENERATOR
BCP
PARITY
GENERATION
FLAG ABORT GA
SEL
1, 2
SYNC
FF
1 BIT
DELAY
FROM
TDSAR
L
OR PCSAR
L
(SYNC)
TxSO
Figure 3. MPCC Transmitter Data Path

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
SCN2652/SCN68652Multi-protocol communications controller (MPCC)
1995 May 1
6
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
The MPCC can be functionally partitioned into receiver logic,
transmitter logic, registers that can be read or loaded by the
processor, and data bus control circuitry. The register bit formats are
shown in Figure 1 while the receiver and transmitter data paths are
depicted in Figures 2 and 3.
RECEIVER OPERATION
General
After initializing the parameter control registers (PCSAR and PCR),
the RxE input must be set high to enable the receiver data path. The
serial data on the RxSI is synchronized and shifted into an 8-bit
Control Character Shift Register (CCSR) on the rising edge of RxC.
A comparison between CCSR contents and the FLAG (BOP) or
SYNC (BCP) character is made until a match is found. At that time,
the S/F output is asserted for one RxC time and the 16-bit Holding
Shift Register (HSR) is enabled. The receiver then operates as
described below.
BOP Operation
A flowchart of receiver operation in BOP mode appears in Figure 4.
Zero deletion (after five ones are received) is implemented on the
received serial data so that a data character will not be interpreted
as a FLAG, ABORT, or GA. Bits following the FLAG are shifted
through the CCSR, HSR, and into the Receiver Shift Register
(RxSR). A character will be assembled in the RxSR and transferred
to the RDSR
L
for presentation to the processor. At that time the
RxDA output will be asserted and the processor must take the
character no later than one RxC time after the next character is
assembled in the RxSR. If not, an overrun (RDSR
11
= 1) will occur
and succeeding characters will be lost.
The first character following the FLAG is the secondary station
address. If the MPCC is a secondary station (PCSAR
12
= 1), the
contents of RxSR are compared with the address stored in
PCSAR
L
. A match indicates the forthcoming message is intended
for the station; the RxA output is asserted, the character is loaded
into RDSR
L
, RxDA is asserted and the Receive Start of Message bit
(RSOM) is set. No match indicates that another station is being
addressed and the receiver searches for the next FLAG.
If the MPCC is a primary station, (PCSAR
12
= 0), no secondary
address check is made; RxA is asserted and RSOM is set once the
first non-FLAG character has been loaded into RDSR
L
and RxDA
has been asserted. Extended address field can be supported by
software if PCSAR
12
= 0.
When the 8 bits following the address character have been loaded
into RDSR
L
and RxDA has been asserted, RSOM will be cleared.
The processor should read this 8-bit character and interpret it as the
Control field.
Received serial data that follows is read and interpreted as the
information field by the processor. It will be assembled into character
lengths as specified by PCR
8–10
. As before, RxDA is asserted each
time a character has been transferred into RDSR
L
and is cleared
when RDSR
L
is read by the processor. RDSRH should only be read
when RxSA is asserted. This occurs on a zero to one transition of
any bit in RDSR
H
except for RSOM. RxSA and all bits in RDSR
H
except RSOM are cleared when RDSRH is read. The processor
should check RDSR
9–15
each time RxSA is asserted. If RDSR9 is
set, then RDSR
12–15
should be examined.
Receiver character length may be changed dynamically in response
to RxDA: read the character in RxDB and write the new character
length into RxCL. The character length will be changed on the next
receiver character boundary. A received residual (short) character
will be transferred into RxDB after the previous character in RxDB
has been read, i.e. there will not be an overrun. In general the last
two characters are protected from overrun.
The CRC–CCITT, if specified by PCSAR
8–10
, is accumulated in
RxCRC on each character following the FLAG. When the closing
FLAG is detected in the CCSR, the received CRC is in the 16-bit
HSR. At that time, the Receive End of Message bit (REOM) will be
set; RxSA and RxDA will be asserted. The processor should read
the last data character in RDSR
L
and the receiver status in
RDSR
9–15
. If RDSR15 = 1, there has been a transmission error; the
accumulated CRC–CCITT is incorrect. If RDSR
12–14
≠ 0, last data
character is not of prescribed length. Neither the received CRC nor
closing FLAG are presented to the processor. The processor may
drop RxE or leave it active at the end of the received message.
RxBCP Operation
The operation of the receiver in BCP mode is shown in Figure 5.
The receiver initially searches for two successive SYNC characters,
of length specified by PCR
8–10
, that match the contents of PCSARL.
The next non-SYNC character or next SYNC character, if stripping is
not specified (PCSAR
13
= 0), causes RxA to be asserted and
enables the receiver data path. Once enabled, all characters are
assembled in RxSR and loaded into RDSR
L
. RxDA is active when a
character is available in RDSR
L
. RxSA is active on a 0 to 1
transition of any bit in RDSR
H
. The signals are cleared when RDSRl
or RDSR
H
are read respectively.
If CRC–16 error control is specified by PCSAR
8–10
, the processor
must determine the last character received prior to the CRC field.
When that character is loaded into RDSR
L
and RxDA is asserted,
the received CRC will be in CCSR and HSR
L
. To check for a
transmission error, the processor must read the receiver status
(RDSR
H
) and examine RDSR15. This bit will be set for one
character time if an error free message has been received. If
RDSR
15
= 0, the CRC–16 is in error. The state of RDSR15 in BCP
CRC mode does not set RxSA. Note that this bit should be
examined only at the end of a message. The accumulated CRC will
include all characters starting with the first non-SYNC character if
PCSAR
13
= 1, or the character after the opening two SYNCs if
PCSAR
13
= 0. This necessitates external CRC generation/checking
when supporting IBM’s
BISYNC. This can be accomplished using the Philips
Semiconductors SCN2653 Polynomial Generator/Checker. See
Typical Applications.
If VRC has been selected for error control, parity (odd or even) is
regenerated on each character and checked when the parity bit is
received. A discrepancy causes RDSR
15
to be set and RxSA to be
asserted. This must be sensed by the processor. The received parity
bit is stripped before the character is presented to the processor.
When the processor has read the last character of the message, it
should drop RxE which disables the receiver logic and initializes all
receiver registers and timing.
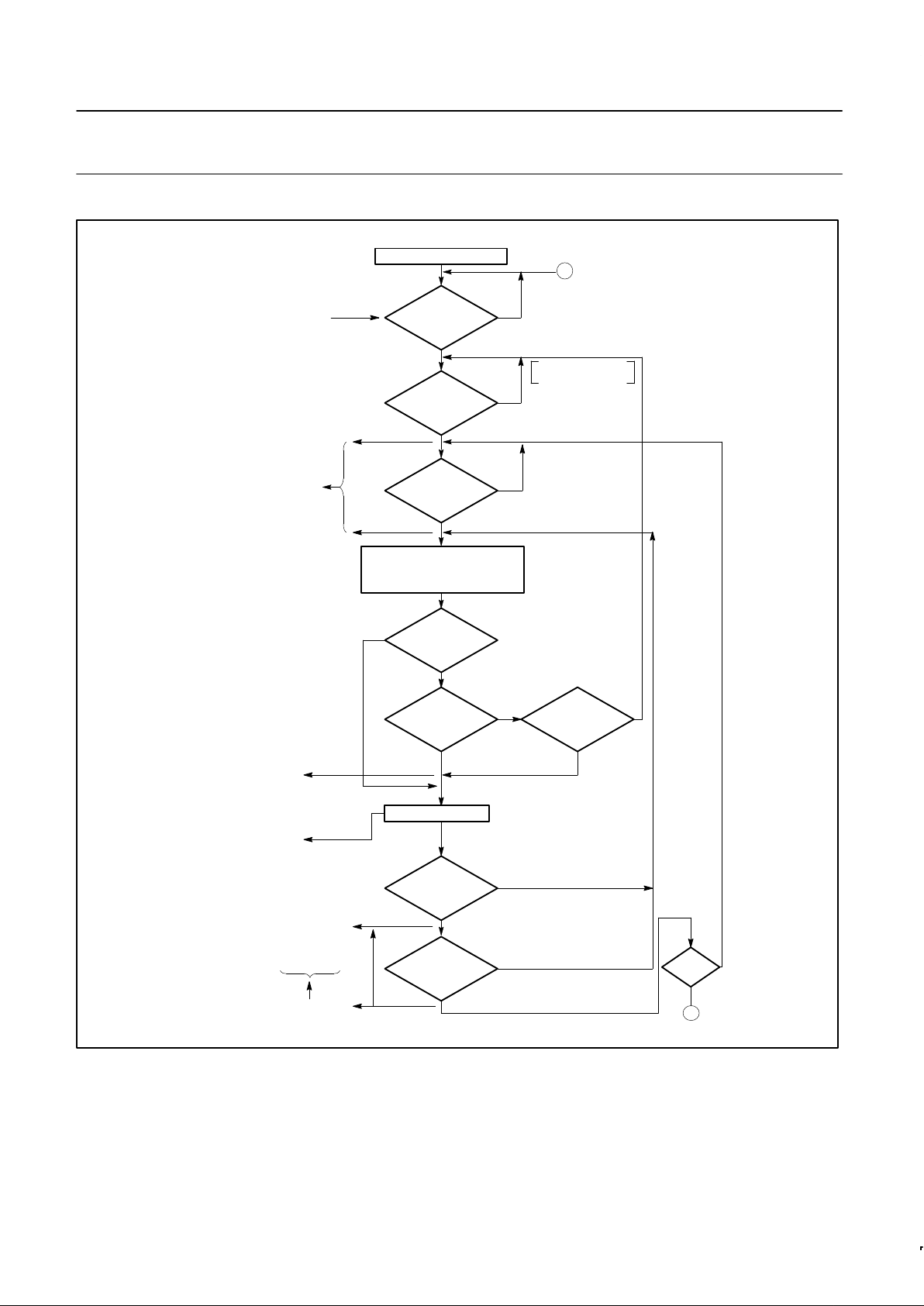
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
SCN2652/SCN68652Multi-protocol communications controller (MPCC)
1995 May 1
7
ASSEMBLE CHARACTER
IN RxSR. ZERO DELETION,
ACCUMULATE CRC IF
SPECIFIED
A
INITIALIZE PCSAR, PCR
RxE
= 1?
RECEIVER
STATUS BIT 0 → 1
EXCEPT RSOM
?
PROCESSOR
RxE = 1
NO
FLAG
IN CCSR*
?
YES
NO
* TEST MADE
EVERY RxC TIME
NO
S/F = 1
FOR ONE RxC
BIT TIME
(1) OVERRUN (ROVRN)
CAUSES LOSS OF
SUBSEQUENT
CHARACTERS
IS
IT 1st
CHARACTER
AFTER FLAG
?
NO
SEC.
STATION
MODE
?
YES
SECONDARY
STATION
ADDRESS
IS
CHARACTER
= PCSAR
L
?
NO
YES
YES
(PCSAR
12
= 1)
YES
NO
FLAG
IN CCSR*
?
YES – END OF MESSAGE
NO
RxSR → RxDB
NO
(PCSAR
12
= 0)
START OF
MESSAGE
RxA = 1
RSOM = 1
FOR ONE
CHARACTER
TIME
RxDA = 1
(PROCESSOR
SHOULD
READ RxDB)
FLAG
IN CCSR*
?
YES
YES
RxE → 0
?
NO
A
YES
RXSA = 1
(PROCESSOR SHOULD
READ AND EXAMINE
RDSR
H
– REOM, RAB/GA,
ROVRN, ABC, RERR)
S/F = 1 FOR ONE RxC
BIT TIME
REOM = 1, RxA = 0
SD00061
Figure 4. BOP Receive
TRANSMITTER OPERATION
General
After the parameter control registers (PCSAR and PCR) have been
initialized, TxSO is held at mark until TSOM (TDSR
8
) is set and TxE
is raised. Then, transmitter operation depends on protocol mode.
TxBOP Operation
Transmitter operation for BOP is shown in Figure 6. A FLAG is sent
after the processor sets the Transmit Start of Message bit (TSOM)
and raises TxE. The FLAG is used to synchronize the message that
follows. TxA will also be asserted. When TxBE is asserted by the
 Loading...
Loading...