Philips SAA4990H Datasheet

INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
DATA SH EET
SAA4990H
Progressive scan-Zoom and Noise
reduction IC (PROZONIC)
Preliminary specification
File under Integrated Circuits, IC02
1996 Oct 25
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Progressive scan-Zoom and Noise
SAA4990H
reduction IC (PROZONIC)
FEATURES
• Progressive scan conversion
(262.5 to 525 or 312.5 to 625 lines/field)
• Field rate up-conversion (50 to 100 Hz or 60 to 120 Hz)
• Line flicker reduction
• Noise and cross-colour reduction
• Variable vertical sample rate conversion
• Movie phase detection
• Synchronous No parity Eight bit Reception and
Transmission (SNERT) interface.
QUICK REFERENCE DATA
SYMBOL PARAMETER MIN. MAX. UNIT
V
T
DDD
amb
digital supply voltage 4.5 5.5 V
operating ambient temperature 0 70 °C
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The Progressive scan-Zoom and Noise reduction IC,
abbreviated as PROZONIC, is designed for applications
together with:
SAA4951WP Economy Controller (ECO3)
SAA4952H (memory controller)
SAA7158WP Back END IC (BENDIC)
SAA4995WP PANorama IC (PANIC)
SAA4970T ECOnomical video processing Back END IC
(ECOBENDIC)
TMS4C2970/71 (serial field memories)
TDA8755/8753A (A/D converter 4 : 1 : 1 format)
83C652/54 type of microcontroller.
ORDERING INFORMATION
TYPE
NUMBER
SAA4990H QFP80 plastic quad flat package; 80 leads (lead length 1.95 mm); body 14 × 20 × 2.8 mm SOT318-2
NAME DESCRIPTION VERSION
PACKAGE
1996 Oct 25 2
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Progressive scan-Zoom and Noise
reduction IC (PROZONIC)
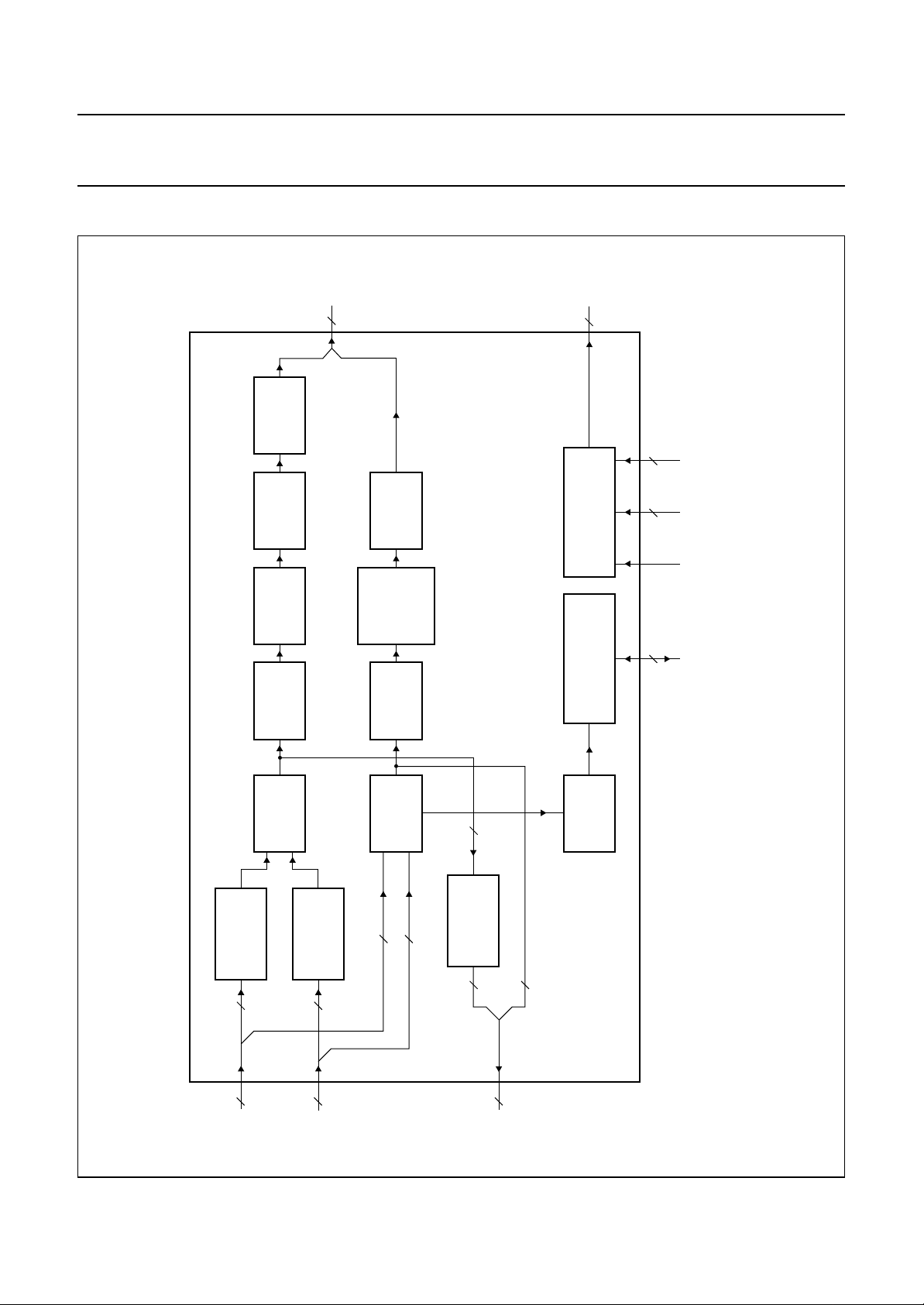
BLOCK DIAGRAM
D
YUV
12
FORMATTER
LINE
MIXER
MEMORY 3
LINE
MIXER
MEMORY 3
SAA4990H
RE1
RE2
WE2
3
CONTROL BLOCK
MGE024
SAA4990H
CK RE, WEVD, HD
book, full pagewidth
LINE
MIXER
MEMORY 2
LINE
MEMORY 1
NOISE
REDUCTION
REFORMATTER
4
UV1
REFORMATTER
4
UV2
LINE
MEDIAN
MEMORY 2
LINE
MEMORY 1
NOISE
REDUCTION
8
8
Y1
Y2
FILTER
84
FORMATTER
3 2 2
(SNERT)
INTERFACE
MICROPROCESSOR
SNRST
SNCL, SNDA,
Fig.1 Block diagram.
MOVIE
PHASE
DETECTOR
8
12
A
YUV
12
B
YUV
1996 Oct 25 3
12
C
YUV
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Progressive scan-Zoom and Noise
reduction IC (PROZONIC)
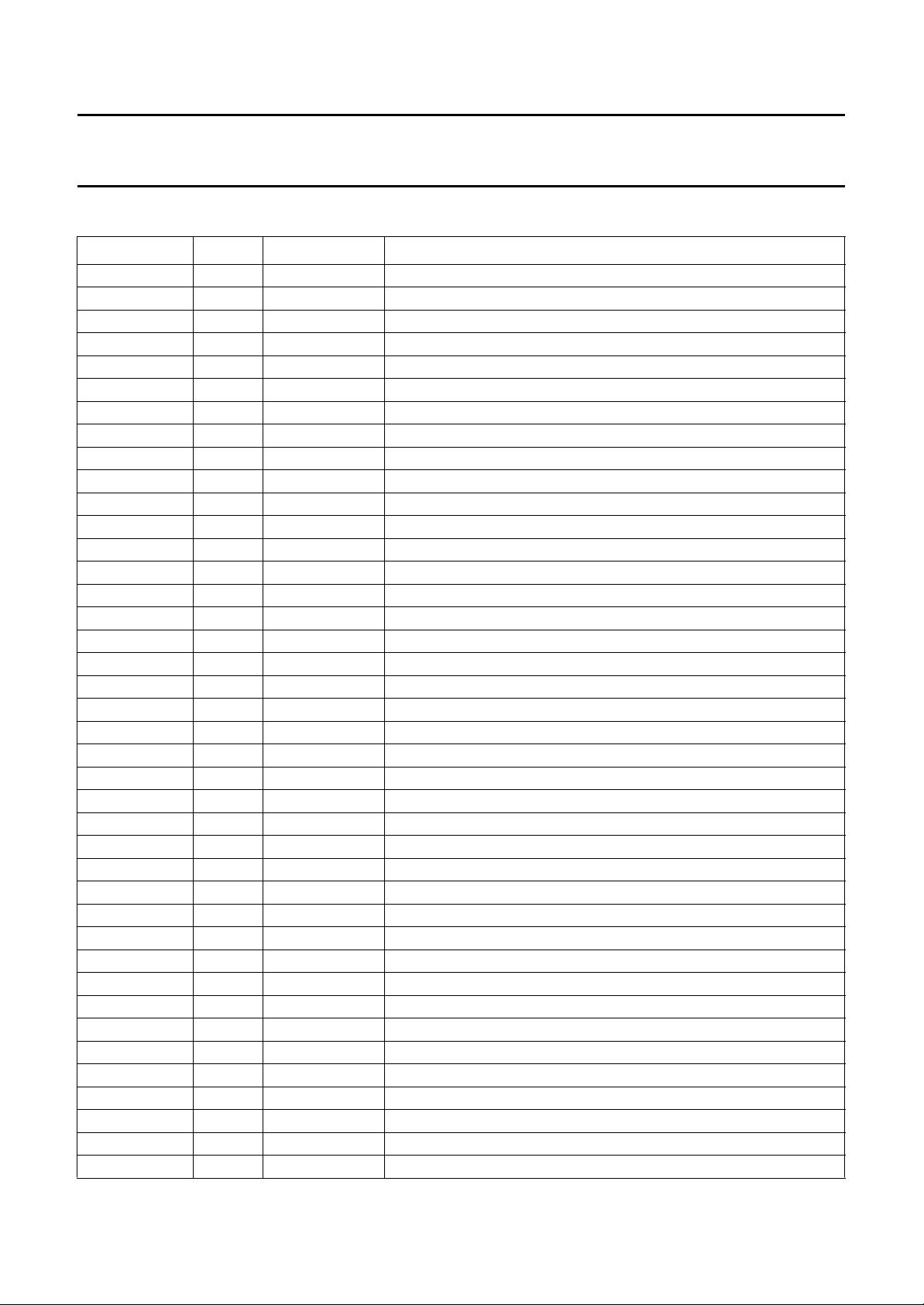
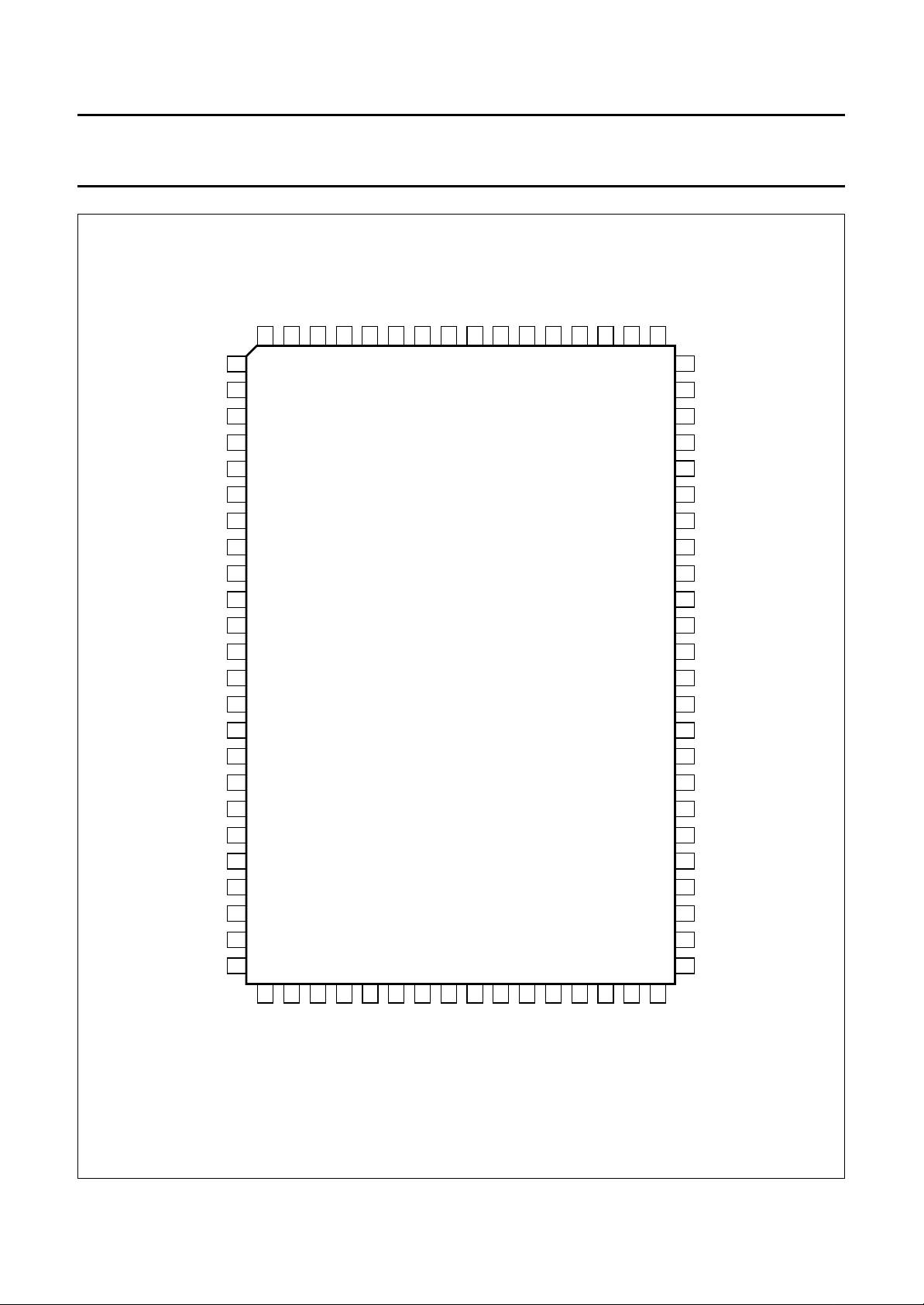
PINNING
SYMBOL PIN TYPE DESCRIPTION
TEST1/AP 1 input action pin for testing, to be connected to V
TEST2/SP 2 input shift pin for testing, to be connected to V
RE1 3 output read enable to FM1
V
SS1
V
DD1
YUV
C7
YUV
C6
YUV
C5
YUV
C4
YUV
C3
V
SS2
V
DD2
YUV
C2
YUV
C1
YUV
C0
YUV
C11
YUV
C10
YUV
C9
YUV
C8
CK 20 input master clock, nominal 27 or 32 MHz
V
SS3
V
DD3
WE2 23 output write enable to FM2
RE2 24 output read enable to FM2
YUV
B8
YUV
B9
YUV
B10
YUV
B11
YUV
B0
YUV
B1
YUV
B2
YUV
B3
V
DD4
V
SS4
YUV
B4
YUV
B5
YUV
B6
YUV
B7
RE 39 input master read enable
VD 40 input field frequent reset, vertical display
4 ground ground 1
5 supply supply voltage 1
6 output Y bit 7 to FM2
7 output Y bit 6 to FM2
8 output Y bit 5 to FM2
9 output Y bit 4 to FM2
10 output Y bit 3 to FM2
11 ground ground 2
12 supply supply voltage 2
13 output Y bit 2 to FM2
14 output Y bit 1 to FM2
15 output Y bit 0 to FM2
16 output UV bit 3 to FM2
17 output UV bit 2 to FM2
18 output UV bit 1 to FM2
19 output UV bit 0 to FM2
21 ground ground 3
22 supply supply voltage 3
25 input UV bit 0 from FM2
26 input UV bit 1 from FM2
27 input UV bit 2 from FM2
28 input UV bit 3 from FM2
29 input Y bit 0 from FM2
30 input Y bit 1 from FM2
31 input Y bit 2 from FM2
32 input Y bit 3 from FM2
33 supply supply voltage 4
34 ground ground 4
35 input Y bit 4 from FM2
36 input Y bit 5 from FM2
37 input Y bit 6 from FM2
38 input Y bit 7 from FM2
SAA4990H
SS
SS
1996 Oct 25 4
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Progressive scan-Zoom and Noise
SAA4990H
reduction IC (PROZONIC)
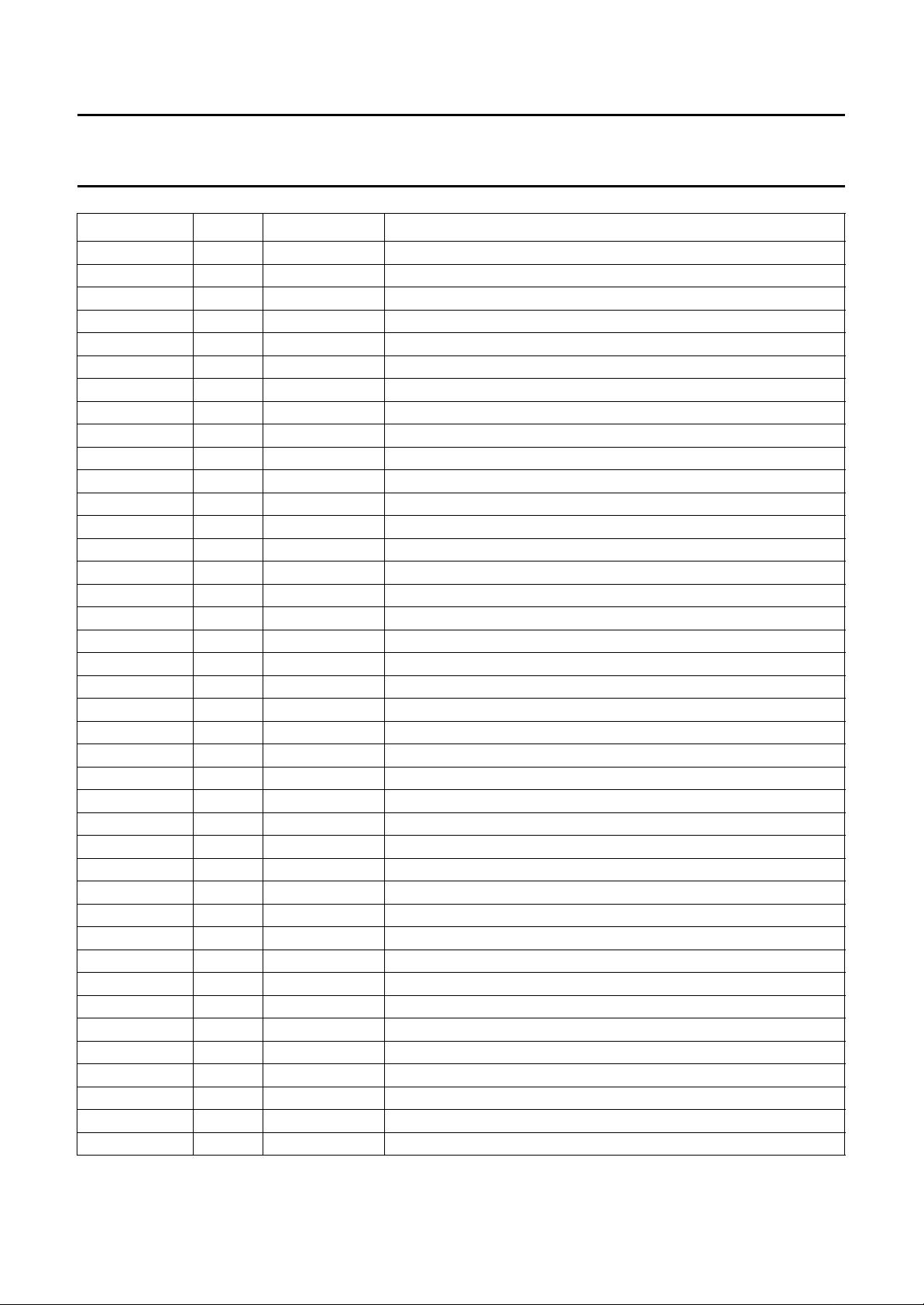
SYMBOL PIN TYPE DESCRIPTION
HD 41 input horizontal reference signal
YUV
D8
YUV
D9
YUV
D10
V
DD5
V
SS5
YUV
D11
YUV
D0
YUV
D1
YUV
D2
V
DD6
V
SS6
YUV
D3
YUV
D4
YUV
D5
YUV
D6
YUV
D7
V
DD7
V
SS7
SNRST 60 input field frequent reset from microcontroller; reset for SNERT interface
SNDA 61 I/O data for SNERT interface
SNCL 62 input clock for SNERT interface
AUX 63 output spare output from line-sequencer
H
O
n.c. 65 − not connected
n.c. 66 − not connected
YUV
A7
YUV
A6
YUV
A5
YUV
A4
YUV
A3
YUV
A2
V
SS8
V
DD8
YUV
A1
YUV
A0
YUV
A11
YUV
A10
YUV
A9
YUV
A8
42 output UV bit 0
43 output UV bit 1
44 output UV bit 2
45 supply supply voltage 5
46 ground ground 5
47 output UV bit 3
48 output Y bit 0
49 output Y bit 1
50 output Y bit 2
51 supply supply voltage 6
52 ground ground 6
53 output Y bit 3
54 output Y bit 4
55 output Y bit 5
56 output Y bit 6
57 output Y bit 7
58 supply supply voltage 7
59 ground ground 7
64 output output hold to e.g. LC display
67 input Y bit 7 from FM1
68 input Y bit 6 from FM1
69 input Y bit 5 from FM1
70 input Y bit 4 from FM1
71 input Y bit 3 from FM1
72 input Y bit 2 from FM1
73 ground ground 8
74 supply supply voltage 8
75 input Y bit 1 from FM1
76 input Y bit 0 from FM1
77 input UV bit 3 from FM1
78 input UV bit 2 from FM1
79 input UV bit 1 from FM1
80 input UV bit 0 from FM1
1996 Oct 25 5
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Progressive scan-Zoom and Noise
reduction IC (PROZONIC)
handbook, full pagewidth
TEST1/AP
TEST2/SP
YUV
YUV
YUV
YUV
YUV
YUV
YUV
YUV
YUV
YUV
YUV
YUV
V
V
V
V
V
V
WE2
RE1
SS1
DD1
C7
C6
C5
C4
C3
SS2
DD2
C2
C1
C0
C11
C10
C9
C8
CK
SS3
DD3
RE2
YUVA8YUVA9YUV
80
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
A10
A11
YUV
YUVA0YUVA1V
79
78
77
76
75
DD8VSS8
74
73
SAA4990H
YUVA2YUVA3YUVA4YUVA5YUVA6YUVA7n.c.
71
72
70
69
68
67
66
n.c.
65
SAA4990H
H
64
O
63
AUX
62
SNCL
61
SNDA
60
SNRST
V
59
SS7
V
58
DD7
YUV
57
D7
YUV
56
D6
YUV
55
D5
YUV
54
D4
YUV
53
D3
V
52
SS6
V
51
DD6
YUV
50
D2
YUV
49
D1
YUV
48
D0
YUV
47
D11
V
46
SS5
V
45
DD5
YUV
44
D10
YUV
43
D9
YUV
42
D8
HD
41
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
B9
B10
B11
YUVB8YUV
YUV
YUVB0YUVB1YUVB2YUV
YUV
Fig.2 Pin configuration.
1996 Oct 25 6
B3
33
DD4
V
34
35
36
SS4
V
YUVB4YUVB5YUVB6YUV
37
38
39
40
B7
RE
MGE023
VD
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Progressive scan-Zoom and Noise
reduction IC (PROZONIC)
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
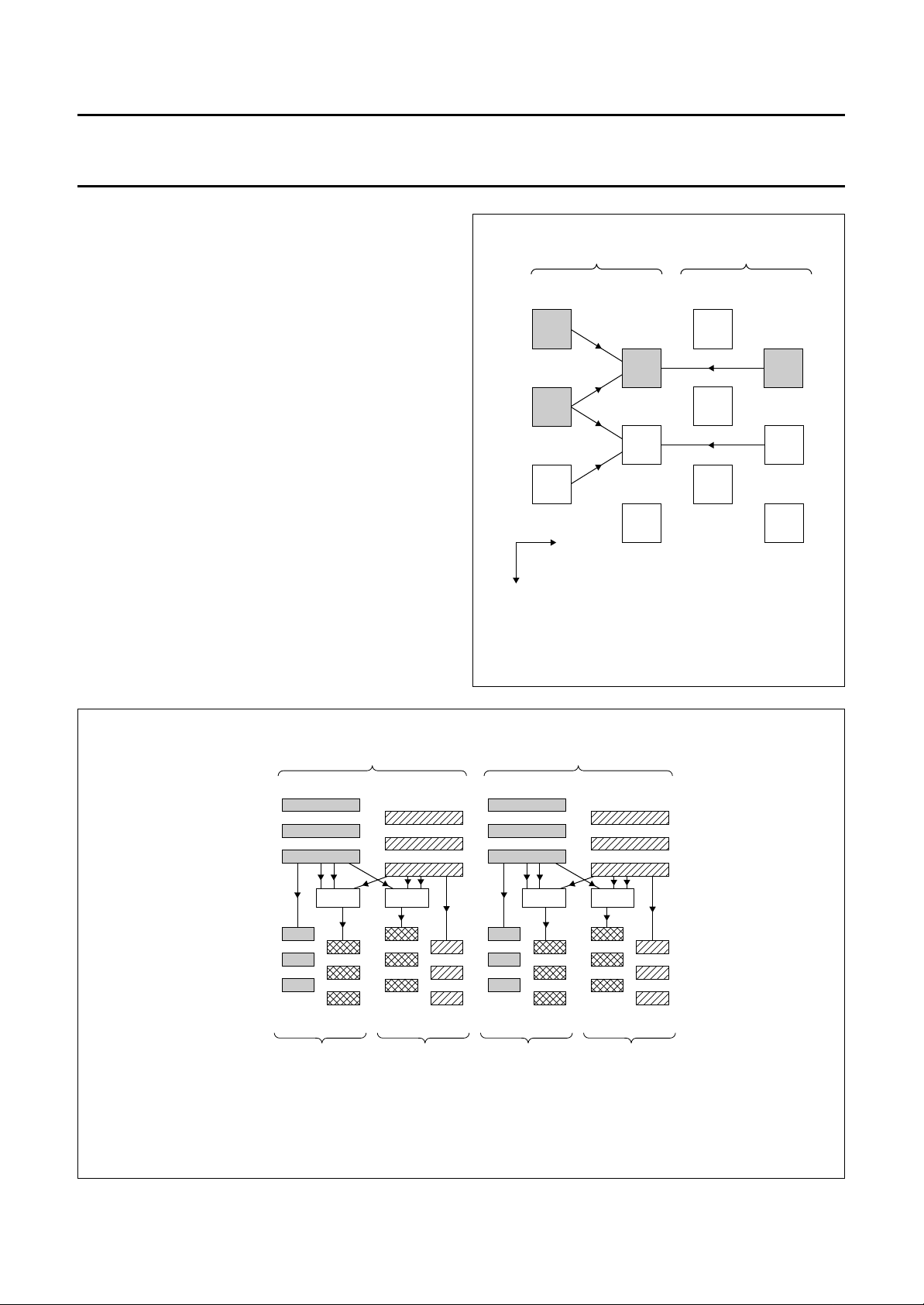
Field rate up-conversion with line flicker reduction
The line flicker reduction in conjunction with field rate
up-conversion is performed by generating a 50 Hz
interlace on the 100 Hz field rate display. Median filtering
supplies the data for the interlaced output fields.
D
EFINITIONS
Framel: l is the number of an input/output frame
temporarily combinating an A and B field.
x
: x is the field raster where A means an odd field and
Field
n
B means an even field.
Frame
combinating an origin/interpolated A and B field;
k indicates the origin input field with
k = 1: odd input field and raster A
k = 2: even input field and raster B within framel.
Field
2 lines of field
(see Fig.3); x is the field raster where A means an odd field
and B means an even field.
: l is the number of an output frame temporarily
l, k
x
: n, m = lines of field
n, m
and 1 line of fieldm using the median filter
n
are interpolated by
n, m
field
n
frame
A
t
handbook, halfpage
y
Fig.3 Generation of (median filter).field
l, k = 1
field
n,m
SAA4990H
frame
l, k = 2
B
B
n, m
A
field
m,n
B
field
m
MGE026
handbook, full pagewidth
input
1fH, 1f
output
2fH, 2f
v
v
field
1
A
frame
field
1
median
field
1, 2
frame
1
A
1, 1
B
field
2, 1
field
2
median
A
frame
B
field
2
1, 2
B
field
3
Fig.4 Scan rate up-conversion.
A
frame
field
3
median
A
B
field
3, 4
2, 1
frame
2
median
A
field
4, 3
frame
field
4
B
field
4
2, 2
MGE027
B
1996 Oct 25 7
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Progressive scan-Zoom and Noise
reduction IC (PROZONIC)
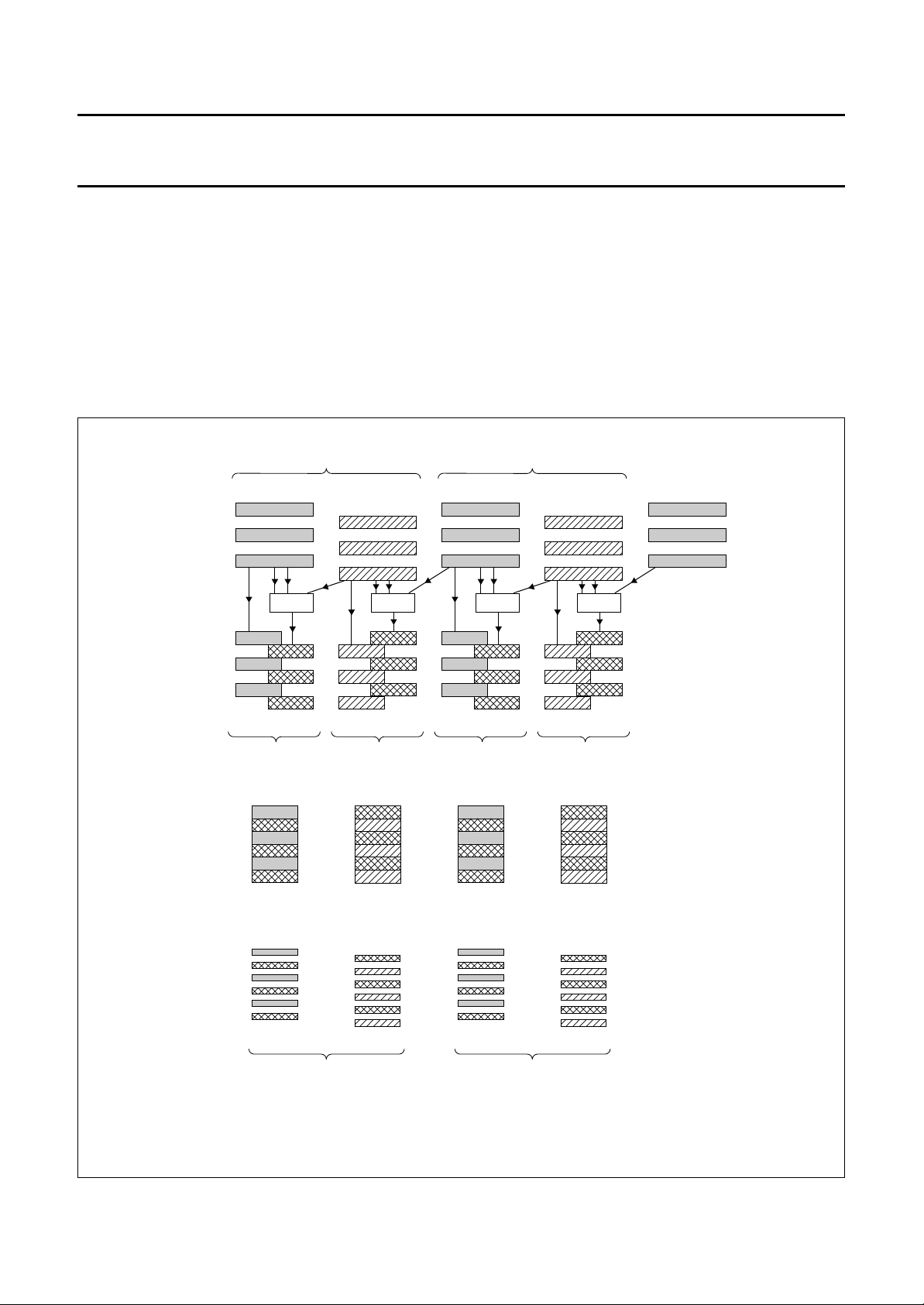
Progressive scan
Progressive scan conversion produces a double number
of lines per field on the output. The field frequency is not
changed, while the line frequency is doubled.
Processing for progressive scan is different for two
successive output fields, e.g. the first output field has a
median operation on the odd lines, while the second has
the median operation on the even lines.
ROGRESSIVE SCAN CONVERSION
P
handbook, full pagewidth
output
1fH, 1f
field
1
v
frame
1
A
field
2
B
SAA4990H
NON-INTERLACE MODE
With non-interlaced progressive scan output, line flicker is
removed because interlace is removed.
I
NTERLACE MODE
With interlaced progressive scan the output line structure
and line flicker is less visible (projection TV).
frame
2
field
3
A
field
4
B
field
5
A
output
2fH, 1f
v
field
1
A
median
frame
B
field
1, 2
1, 1
field
2
B
median
frame
A
field
2,3
1, 2
field
3
A
frame
a. Non-interlaced output; (625/50/1:1) or (525/60/1:1):
frame
1, 1
frame
1, 2
frame
b. Interlaced output; (1250/50/2:1) or (1050/60/2:1):
1
B
field
1,2
field
2,1
A
field
1,1
frame
median
field
3, 4
2, 1
2, 1
A
B
frame
field
4
2
B
frame
frame
field
2,2
median
field
4,5
2, 2
2, 2
B
A
MGE028
Fig.5 Progressive scan conversion.
1996 Oct 25 8
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Progressive scan-Zoom and Noise
reduction IC (PROZONIC)
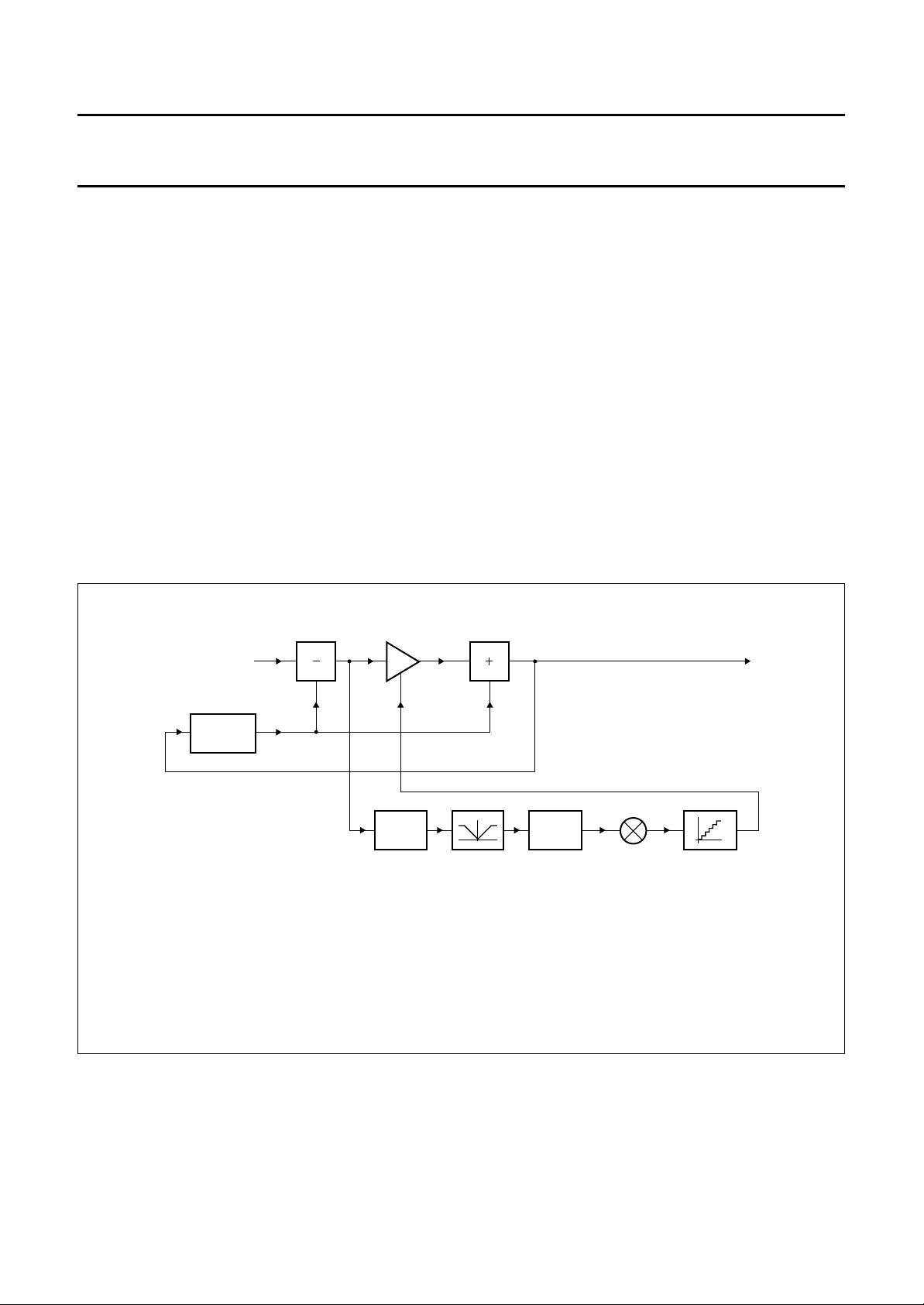
Noise and cross-colour reduction
The noise reduction is field recursive with an average ratio
between fresh and over previous fields averaged
luminance and chrominance.
Two operating modes can be used in principal: the fixed
and the adaptive mode (see Table 6).
In the fixed mode, the averaging produces a constant
linear combination of the inputs. Except for k = 1, the fixed
mode should not be used for normal operation, because of
its smearing effects.
In the adaptive mode, the averaging ratio switches softly
on the basis of absolute differences in luminance among
the inputs. When the absolute difference is low, only a
small part of the fresh data will be added. When the
difference is high, much of the fresh data will be taken.
This occurs in either the situation of movement or where a
significant vertical contrast is seen.
SAA4990H
To latter remark, note that recursion is done over a field,
and the pixel positions one field apart always have a
vertical offset of one frame line. So averaging is not only
done in the dimension of time but also in the vertical
direction. Therefore averaging vertically on e.g. a vertical
black to white edge would provide a grey result if this was
not adapted for.
The averaging in chrominance is slaved to the luminance
averaging. This implies that differences in the
chrominance are not taken into account for the k-factor
setting.
The noise reduction scheme effectively decreases both
noise and cross-colour patterns.
The cross-colour pattern does not produce an increase of
the measured luminance difference, therefore this pattern
will be averaged over many fields.
handbook, full pagewidth
(1) Y
(2) see Table 9.
(3) see Fig.11.
out=YA
×k+YB×(1 −k).
FIELD
MEMORY
Y
A
Y
B
k
TF2TF1
FILTER LIMITER FILTER MULTIPLIER
(2)
Y
k-CURVE
(3)
out
(1)
MGE029
Fig.6 Noise reduction scheme.
1996 Oct 25 9
 Loading...
Loading...