Philips SA9025BE Datasheet

SA9025
900 MHz transmit modulator and
2.2 GHz fractional–N synthesizer
Objective specification 1997 Aug 01
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
Philips Semiconductors Objective specification
SA9025
900 MHz transmit modulator and 2.2 GHz
fractional–N synthesizer
2
1997 Aug 01
DESCRIPTION
This specification defines the requirements for a transmitter
modulator and fractional–N synthesizer IC to be used in cellular
telephones which employ the North American Dual Mode Cellular
System (IS–136).
FEA TURES
•Low current from 3.75V supply
•Low phase noise
•Main loop with internal charge pump and fractional compensation
•3–line serial interface bus
•Power down for the synthesizers
•Speedup mode for faster switching
APPLICATIONS
•Cellular phones
•Portable battery–powered radio equipment.
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The SA9025 BICMOS device integrates:
•Main channel synthesizer
•Auxiliary synthesizer
•Transmit offset synthesizer and oscillator
•I/Q modulator
•Power control
•Reference and clock buffers
•Control logic for programming and power down modes
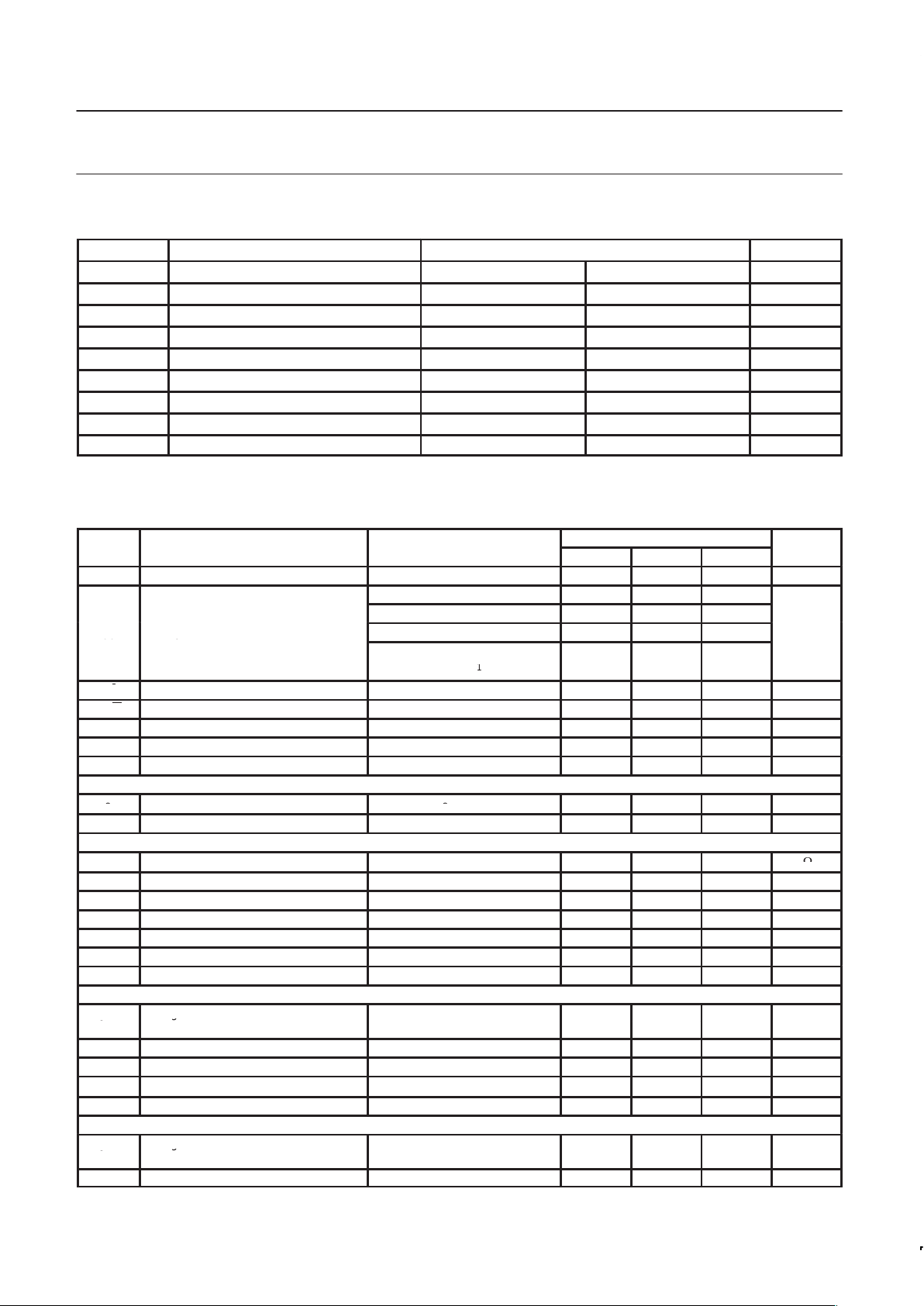
PIN CONFIGURATION
SR01446
45464748
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
13 14 15 16 17 18 19
25
26
27
28
29
30
424344
31
32
33
34
35
36
20 21 22 23 24
8
9
10
11
12
394041 3738
PHP
V
RX
GND
GND
Ipeak
TANK1
XTAL
TX
DATA
CLOCK
LOCK
STROBE
GND
I
Q
PHI
GNDRNGND
INA
GND
PHA
RCLK
MCLK
TANK2
Vcc
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
DUAL
GND
GND
CC
V
CC
Vcc
V
CC
V
CC
V
CC
SA9025
LO1
RX
LO2
TX
LO1
TX
LO2
PHS out
TX1
DUAL
TX2
EN
2
XTAL
1
Q
I
Figure 1. Pin Configuration
QUICK REFERENCE DA TA
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
V
CC
Supply voltage V
CC
3.6 3.75 3.9 V
I
CC
Supply current – TBD – mA
I
CC_save
Total supply current in power–down
mode
– TBD – mA
f
VCO
Input frequency 800 – 2200 MHz
f
AUX
Input frequency 10 – 500 MHz
f
XTAL
Crystal reference input frequency 10 – 40 MHz
f
PC
Maximum phase comparator frequency Main and Aux loops – – 5 MHz
T
amb
Operating ambient temperature –40 – +85 °C
ORDERING INFORMATION
TYPE NUMBER
PACKAGE
NAME DESCRIPTION VERSION
SA9025 LQFP48 Plastic low profile quad flat package; 48 leads; body 7x7x1.4 mm SOT313-2
Philips Semiconductors Objective specification
SA9025
900 MHz transmit modulator and 2.2 GHz
fractional–N synthesizer
1997 Aug 01
3
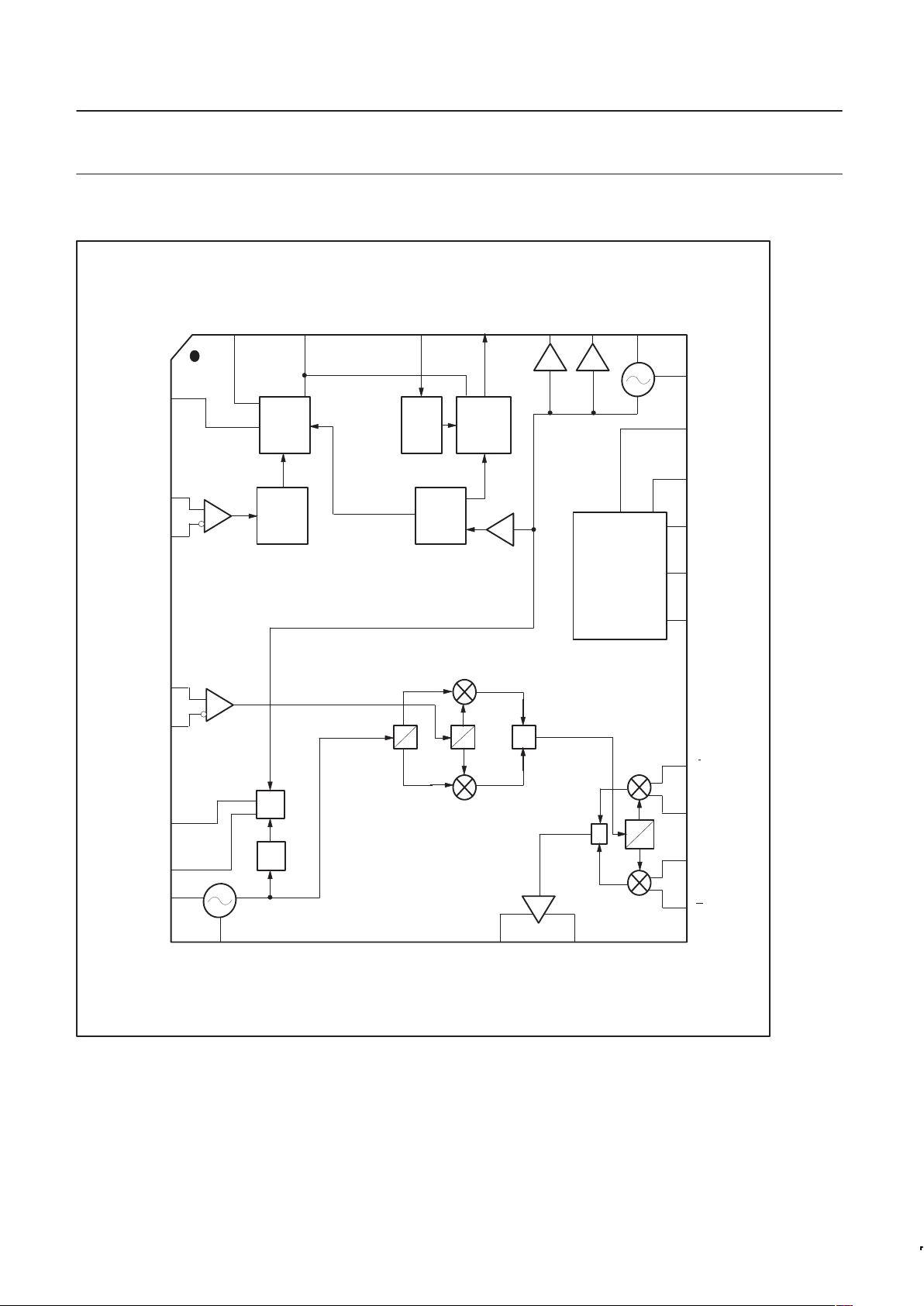
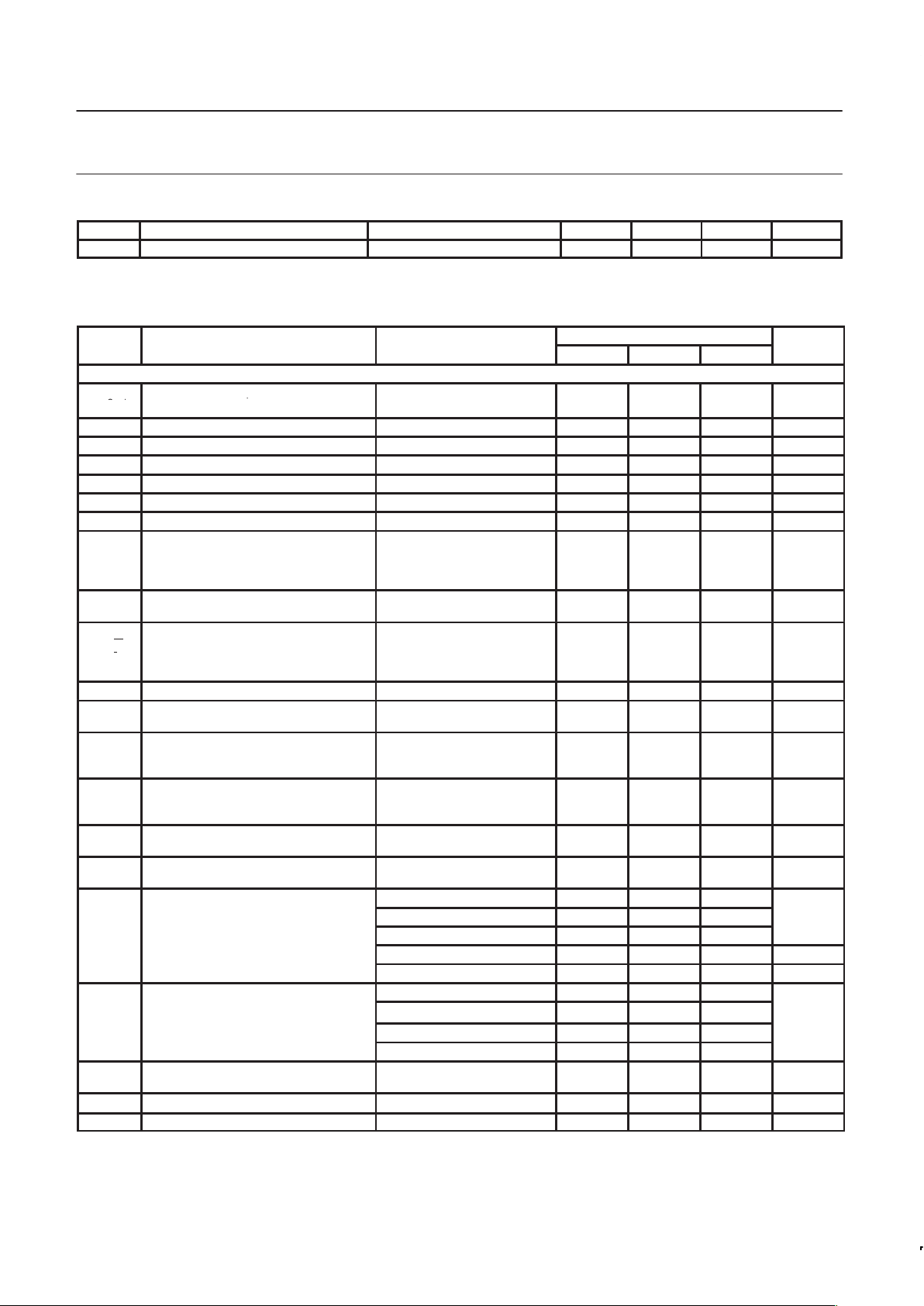
CONNECTIONS
SR01455
PHP
V
RX
GND
GND
Ipeak
TANK1
XTAL
TX
DATA
CLOCK
LOCK
STROBE
GND
I
Q
PHI
GND
RN
GND
INA
GND
PHA
RCLK
MCLK
TANK2
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
DUAL
GND
GND
CC
V
CC
V
CC
V
CC
V
CC
LO1
RX
LO2
TX
LO1
TX
LO2
PHS out
TX1
DUAL
TX2
EN
XTAL
V
CC
V
CC
2
MAIN
DIV.
MAIN PD
and CP
AUX.
DIV.
AUX PD
and CP
REF.
DIV.
CONTROL
LOGIC
0
90
0
90
∑
∑
0
90
∅
1
Q
I
÷M
÷N
÷A
Figure 2. SA9025 Block Diagram
Philips Semiconductors Objective specification
SA9025
900 MHz transmit modulator and 2.2 GHz
fractional–N synthesizer
1997 Aug 01
4
PIN DESCRIPTIONS
PIN
NO.
PIN DESCRIPTION
1 PHP Proportional charge pump output
2 V
CC
Digital supply voltage
3 RX
LO1
Differential LO input
4 RX
LO2
Differential LO input
5 GND Digital Ground
6 V
CC
Tank supply voltage
7 TX
LO1
Differential Transmit LO Input
8 TX
LO2
Differential Transmit LO Input
9 GND Tank Ground
10 PHS OUT Charge pump output (transmit offset)
11 I
PEAK
PHS out current set resistor
12 TANK1 VCO differential tank
13 TANK2 VCO differential tank
14 V
CC
Tx supply voltage
15 GND Tx Ground
16 GND Tx Ground
17 GND Tx Ground
18 GND Tx Ground
19 GND Tx Ground
20 DUALTX1 Dual mode RF output
21 GND Tx Ground
22 DUALTX2 Dual mode RF output
23 GND Tx Ground
24 V
CC
Tx supply voltage
25 Q Inverting quadrature input
26 Q Non–Inverting quadrature input
27 I Non–inverting in phase modulation input
28 I Inverting in phase modulation input
29 V
CC
Tx supply voltage
30 GND Tx Ground
31 STROBE Data input latch enable
32 LOCK Lock detect
33 CLOCK Serial clock input
34 DAT A Serial data input
35 TX
EN
Transmit enable
36 XTAL
2
Crystal Oscillator emitter input
37 XTAL
1
Crystal Oscillator base Input
38 MCLK Buffered oscillator output
39 RCLK Buffered oscillator output
40 V
CC
REF supply voltage
41 PHA Auxiliary charge pump output
42 GND REF Ground
43 INA RX
IF
input
44 V
CC
CP supply voltage
45 GND CP Ground
46 RN CP current set resistor
47 GND CP Ground
48 PHI Integral charge pump output
Philips Semiconductors Objective specification
SA9025
900 MHz transmit modulator and 2.2 GHz
fractional–N synthesizer
1997 Aug 01
5
OPERATING MODES & POWER DOWN CONTROL
There are two power saving modes of operation which the SA9025
can be put into, dependent on the status of the system. The
intention of these different modes is to disable circuity that is not in
use at the time in order to reduce power consumption. During sleep
mode, only circuitry which is required to provide a master clock to
the digital portion of the system is enabled. During receive mode,
circuitry which is used to perform the receive function and provide a
master clock is enabled. In transmit mode all the functions of the
chip are enabled which are required to perform transmit, receive and
provide master clock.
SA9025 POWER MODE TRUTH TABLE
Sleep Mode Receive Mode Transmit Mode
Enabled yes no yes no yes no
Crystal Oscillator
✓ ✓ ✓
Phase detector and charge pump (transmit offset)
✓ ✓ ✓
VCO
✓ ✓ ✓
SSB Up-converter
✓ ✓ ✓
MCLK Buffer
✓ ✓ ✓
RCLK Buffer
✓ ✓ ✓
÷M offset loop divider
✓ ✓ ✓
TXLO Buffer
✓ ✓ ✓
RXLO Buffer
✓ ✓ ✓
I/Q Modulator
✓ ✓ ✓
Variable Gain Amp.
✓ ✓ ✓
Control Logic
✓ ✓ ✓
Main Divider
✓ ✓ ✓
Reference Divider
✓ ✓ ✓
Auxiliary Divider
✓ ✓ ✓
Main Phase Detector and charge pump
✓ ✓ ✓
Auxiliary Phase Detector and charge pump
✓ ✓ ✓
Lock Detect
✓ ✓ ✓
Philips Semiconductors Objective specification
SA9025
900 MHz transmit modulator and 2.2 GHz
fractional–N synthesizer
1997 Aug 01
6
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
SYMBOL PARAMETER VALUE UNIT
MIN. MAX.
V
CC
Supply voltage -0.3 +4.5 V
V
IN
Voltage applied to any other pin -0.3 VCC+0.3 V
P
N
Power dissipation, TA = 25°C (still air) 980 mW
T
JMAX
Operation junction temperature TBD °C
P
MAX
Power input/output +10/+14 dBm
I
MAX
DC current into any I/O pin -10 +10 mA
T
STG
Storage temperature –65 +150 °C
T
o
Operating temperature -40 +85 °C
DC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
V
CC
= +3.75 V; TA = 25°C; unless otherwise stated.
SYMBO
LIMITS
L
PARAMETER
TEST CONDITIONS
MIN TYP MAX
UNITS
V
CC
Power supply range 3.6 3.75 3.9 V
Sleep mode 2
Standby mode 17
I
CC
Supply current
Operating: full power analog 95
mA
CC
y
Operating: full power digital
DUAL
1
52
I / I In-phase dif ferential input quiescent VCC /2 V
Q / Q Quadrature phase differential input quiescent VCC /2 V
V
IL
Clock, Data, Strobe, TX
EN
Input logic low –0.3 0.3 × V
CC
V
V
IH
Clock, data, strobe, TX
EN
Input logic high 0.7 × V
CC
VCC+0.3 V
T
A
Ambient temperature range -40 +25 +85 °C
Digital Outputs Lock
p
VOLOutput voltage LOW
I
O
=
2mA
0.4
V
V
OH
Output voltage HIGH IO = -2mA V
CC
– 0.4 V
Charge Pump Current Setting Resistor Input; RN, R
Ipeak
RN
External resistor to ground
6
7.5
24
k
R
Ipeak
External resistor to ground 4.7
k
V
RN
Regulated voltage
RN = 7.5 k
1.23 V
V
Ipeak
Regulated voltage
R
ipeak
= 4.7 k
1.3 V
I
peak
PHSOUT programming
R
ipeak
= 4.7 k
0.26 mA
PHS
gain
PHSOUT gain
R
ipeak
= 4.7 k
24xI
peak
mA
K
PD phase gain Transmit offset PLL in phase lock 4.33 mA/rad
Charge Pump Outputs (including fractional compensation pump, not PHS) RN = 7.5 k
Charge pump output current error
I
OPH
g
versus expected current.
–
1515%
I
MATCH
Sink to source current matching V
PHX =
VCC/2 –5 5 %
Current output variation versus V
PHX
V
PHX
in compliance range –10 10 %
Charge pump off, leakage current V
PHX
= VCC/2 –10
1
10 nA
V
PH
Charge pump voltage compliance
3
0.7 VCC – 0.8 V
Charge Pump Outputs (only PHS) R
ipeak
= 4.7 k
Charge pump output current error
I
OPH
g
versus expected current.
–
1515%
I
MATCH
Sink to source current matching V
PHS
= VCC/2 –10 10 %
Philips Semiconductors Objective specification
SA9025
900 MHz transmit modulator and 2.2 GHz
fractional–N synthesizer
1997 Aug 01
7
Current output variation versus V
PH
V
PHS
in compliance range –25 25 %
V
PH
Charge pump voltage compliance 0.5 VCC–0.5 V
AC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
VCC = +3.75 V; TA = 25°C; unless otherwise stated.
LIMITS
SYMBOL
PARAMETER
TEST CONDITIONS
MIN TYP MAX
UNITS
Modulator
Transmit LO input (AC-coupled; 50Ω Input power -13 -10 dBm
TX
LO 1/2
(
single-ended, 100Ω differential) Frequency range 900 1100 MHz
VSWR 2:1
TANK1/2 VCO tank differential inputs Frequency range 90 180 MHz
÷M PLL offset divider Maximum input frequency 180 MHz
XTAL1Osc. transistor base Osc. frequency 10 40 MHz
XTAL2Osc. transistor emitter Osc. frequency 10 40 MHz
XO Negative resistance –100
RCLK,
MCLK
Reference buffer output
Frequency range
Output levels
Harmonic content
Z
LOAD
= 5kΩ| | 7 pF
10
0.7
1.0
40
1.4
–10
MHz
V
P–P
dBc
TX
EN
Transmit enable
Transmit enable
Transmit disable
TX
EN
= 1
TX
EN
= 0
Logic
Q / Q
I / I
Baseband in-phase differential inputs
Maximum frequency
Diff. mod. level
Diff. input impedance
DC bias point
1.8
0.8
10.0
1.8
0.9
VCC/2
1.0
2.55
MHz
V
P-P
kΩ
V
TX
RF
TX
RF
operating range 820 920 MHz
DUAL
TX
DUAL output SE=1, TXEN=1 (with
external matching) (50Ω)
AMPS/DAMPS 820 853 MHz
DUAL
TX
Differential output, (DUALTX)
open-collector, matched to 200Ω
differential impedance
Output level (avg. min., I and Q
quad., 0dB VGA)
Gain flatness
+9.0 +11.0
1
+13.0 dBm
dB
DUAL
TX
Linearity worst case intermod. products
(0dB VGA OR +9 dBm, whichever is
less, I & Q in-phase)
3rd-order
5th-order
7th-order
-42
-55
-65
-34
-45
-53
dBc
DUAL
TX
Carrier suppression
(I & Q in quadrature)
VGA = 0dB
VGA = -38dB
-45
-33
-35
dBc
DUAL
TX
Sideband suppression
(I & Q in quadrature)
-45 -35 dBc
2 to 284 MHz -45
824 to 849 MHz -47 dBc
DUALTXSpurious output 849 to 869 MHz -45
869 to 894 MHz -104 dBm
894 to 8490 MHz -45 dBc
TX
LO
-21
p
p
Upper Side Band –21
DUAL
TX
TX
LO
u-
conversion roducts
TXLO ±3 × TX
OFFSET
-36
dBc
Harmonics ≤ 10th -21
DUAL
TX
Broad-band noise (0dB VGA or +9 dBm,
whichever is less)
869 to 894 MHz -123 dBm/Hz
p
DUAL
TX
Adjacent channel noise power
@ 30 kH
z -
95
dBc/H
z
DUALTXAlternate channel noise power @ 60 kHz –101 dBc/Hz
 Loading...
Loading...