Philips pcf2116 DATASHEETS

INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
DATA SH EET
PCF2116 family
(PCF2114X; PCF2116X)
LCD controller/drivers
Product specification
Supersedes data of October 1994
File under Integrated Circuits, IC12
1996 Oct 25

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
LCD controller/drivers
FEATURES
• Single chip LCD controller/driver
• 1 or 2-line display of up to 24 characters per line, or
2 or 4 lines of up to 12 characters per line
• 5 × 7 character format plus cursor; 5 × 8 for kana
(Japanese syllabary) and user defined symbols
• On-chip:
– generation of LCD supply voltage (external supply
also possible)
– generation of intermediate LCD bias voltages
– oscillator requires no external components (external
clock also possible)
• Display data RAM: 80 characters
• Character generator ROM: 240 characters
• Character generator RAM: 16 characters
2
• 4 or 8-bit parallel bus or 2-wire I
• CMOS/TTL compatible
• 32 row, 60 column outputs
• MUX rates 1 : 32 and 1 : 16
• Uses common 11 code instruction set
• Logic supply voltage range, VDD− VSS: 2.5 to 6 V
• Display supply voltage range, VDD− V
• Low power consumption.
C-bus interface
: 3.5 to 9 V
LCD
PCF2116 family
(PCF2114X; PCF2116X)
The letter X in PCF2116X or PCF2114X specifies the
character set in the character generator ROM (CGROM).
The different character sets currently available are
specified by the letters A, C, G and J (see Figs 8 to 11).
Set ‘A’ in PCF2116A characterises the built-in standard
character set. Other character sets are available on
request.
The PCF2116 is a low-power CMOS LCD controller and
driver, designed to drive a split screen dot matrix LCD
display of 1 or 2 lines by 24 characters or 2 or 4 lines by
12 characters with 5 × 8 dot format. All necessary
functions for the display are provided in a single chip,
including on-chip generation of LCD bias voltages,
resulting in a minimum of external components and lower
system power consumption. The chip contains a character
generator and displays alphanumeric and kana
characters. The PCF2116 interfaces to most
microcontrollers via a 4 or 8-bit bus or via the 2-wire
2
C-bus.
I
The PCF2116K differs from the existing PCF2116 family
only in the V
LCD/VOP
generation section.
APPLICATIONS
• Telecom equipment
• Portable instruments
• Point of sale terminals.
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The PCF2116 family of LCD controller/drivers consists of
2 similar members: PCF2116X and PCF2114X, later
referred to as PCF2116. The specific differences are
expressed in separate paragraphs for PCF2116X and
PCF2114X respectively.
ORDERING INFORMATION
TYPE NUMBER
NAME DESCRIPTION VERSION
PCF2114XU/2116XU 116 FFC116 −
PCF2116KH/KHZ LQFP128 plastic low profile quad flat package; 128 leads;
body 14 × 20 × 1.4 mm
1996 Oct 25 2
Packages
• PCF2116XU/10; chip on FFC
• PCF2114XU/10; chip on FFC
• PCF2116XU/12; chip with bumps on FFC
• PCF2114XU/12; chip with bumps on FFC
• PCF2116K; LQFP128 (14 × 20 mm)
• Pin grid array PGA144 (samples only).
For further details see Chapters “Bonding pad locations”
and “Package outline”.
PACKAGE
SOT425-1
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
LCD controller/drivers
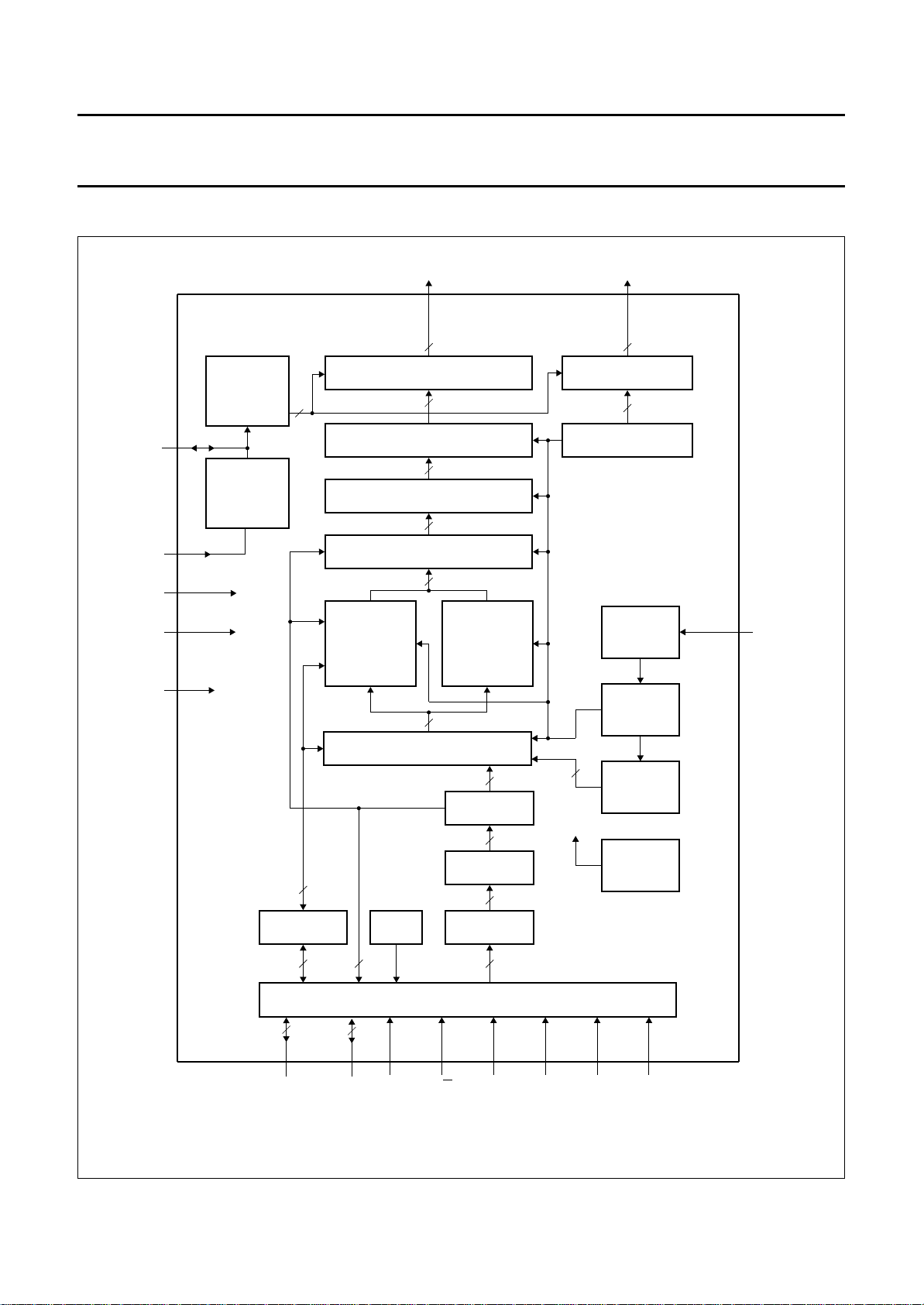
BLOCK DIAGRAM
handbook, full pagewidth
BIAS
VOLTAGE
GENERATOR
LCD
V
DD
V
V
SS
T1
0
93, 95, 97
GENERATOR
92
104, 106
109, 112
111
V
LCD
V
6
8
DATA
REGISTER (DR)
C1 to C60
68, 65 to 38
35 to 5
60
COLUMN DRIVERS
60
DATA LATCHES
60
SHIFT REGISTER
5 x 12-bit
5
CURSOR + DATA CONTROL
5
CHARACTER
GENERATOR
RAM
(CGRAM)
16
CHARACTERS
8
DISPLAY DATA RAM
(DDRAM) 80 CHARACTERS
BUSY
FLAG
CHARACTER
GENERATOR
ROM
(CGROM)
240
CHARACTERS
7
ADDRESS
COUNTER (AC)
7
INSTRUCTION
DECODER
8
INSTRUCTION
REGISTER (IR)
PCF2116 family
(PCF2114X; PCF2116X)
R1 to R32
84 to 77, 115 to 122
76 to 69, 123 to 128,
1 and 4
32
ROW DRIVERS
32
SHIFT REGISTER
32-BIT
PCF2116
OSCILLATOR
GENERATOR
7
DISPLAY
ADDRESS
COUNTER
POWER - ON
TIMING
RESET
102
OSC
1996 Oct 25 3
105, 103,
4
98, 96
DB0 to DB3 DB4 to DB7 E
94, 91,
89, 87
78 8
I/O BUFFER
4
108 110 113
R/W
Fig.1 Block diagram.
RS
88
SCL90SDA
107
MGA797 - 1
SA0
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
LCD controller/drivers
(PCF2114X; PCF2116X)
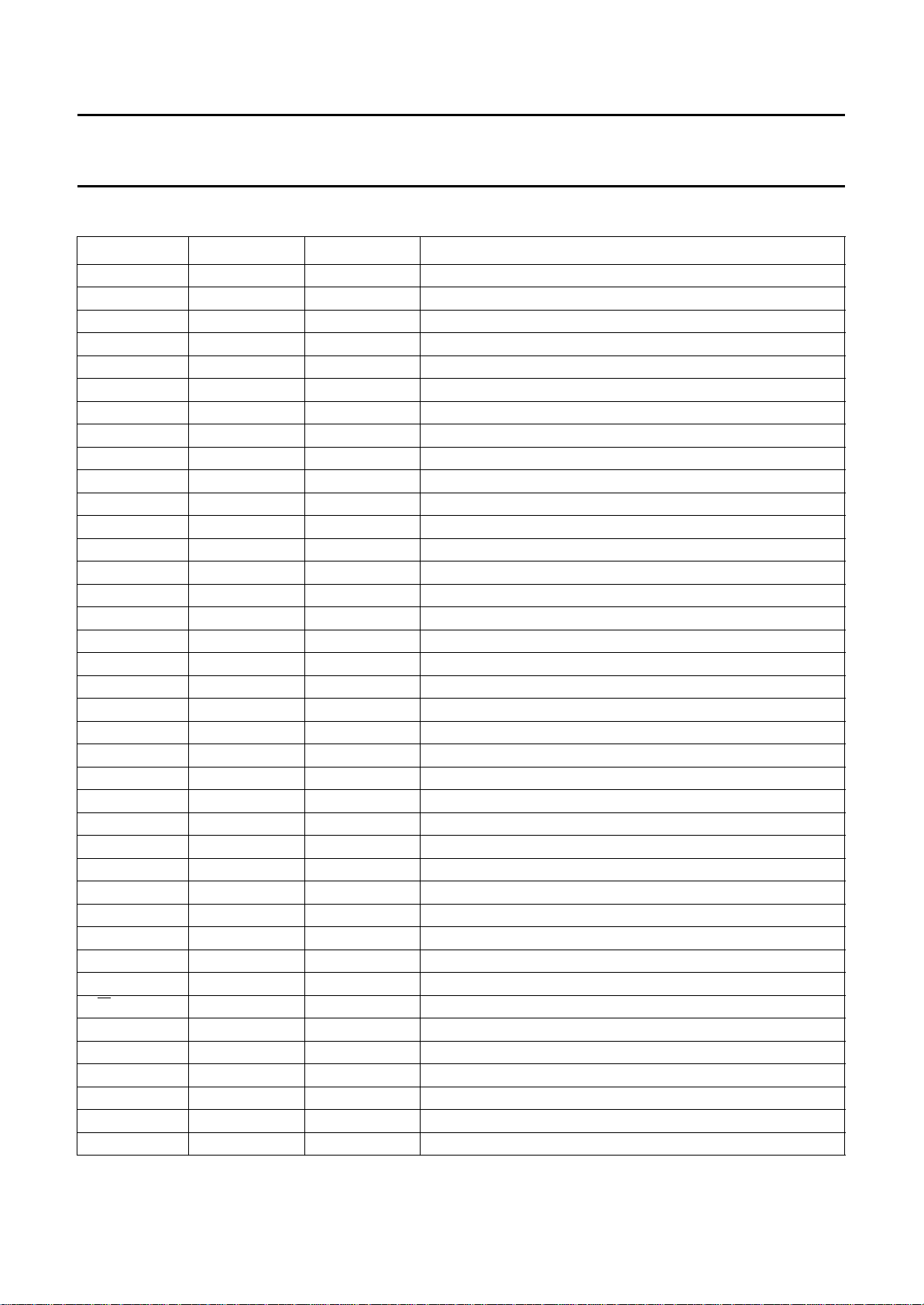
PINNING
SYMBOL LQFP128 PIN FFC PAD DESCRIPTION
R31 1 27 LCD row driver output
n.c. 2 and 3 − not connected
R32 4 28 LCD row driver output
C60 to C30 5 to 35 29 to 59 LCD column driver outputs 60 to 30
n.c. 36 and 37 − not connected
C29 to C2 38 to 65 60 to 87 LCD column driver outputs 29 to 2
n.c. 66 and 67 − not connected
C1 68 88 LCD column driver output 1
R24 to R17 69 to 76 89 to 96 LCD row driver outputs
R8 to R1 77 to 84 97 to 104 LCD row driver outputs
n.c. 85 and 86 − not connected
DB7 87 105 bidirectional data bus
2
SCL 88 106 I
DB6 89 107 bidirectional data bus
SDA 90 108 I
DB5 91 109 bidirectional data bus
V
V
0
LCD1
92 110 control input for V
93 111 LCD supply voltage
DB4 94 112 bidirectional data bus
V
LCD2
95 113 LCD supply voltage
DB3 96 114 bidirectional data bus
V
LCD3
97 115 LCD supply voltage
DB2 98 116 bidirectional data bus
n.c. 99 to 101 − not connected
OSC 102 1 oscillator/external clock input
DB1 103 2 bidirectional data bus
V
DD2
104 3 supply voltage
DB0 105 4 bidirectional data bus
V
DD1
106 5 supply voltage
SA0 107 6 I
E 108 7 data bus clock
V
SS1
W 110 9 read/write
R/
109 8 ground (logic)
T1 111 10 test pad (connect to V
V
SS2
112 11 ground (logic)
RS 113 12 register select
n.c. 114 − not connected
R9 to R16 115 to 122 13 to 20 LCD row driver outputs
R25 to R30 123 to 128 21 to 26 LCD row driver outputs
C-bus serial clock input
2
C-bus serial data input/output
LCD
2
C-bus address pin
)
SS
PCF2116 family
1996 Oct 25 4
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
LCD controller/drivers
handbook, full pagewidth
R30
R29
R28
128
127
126
1
R31
2
n.c.
3
n.c.
4
R32
5
C60
6
C59
7
C58
8
C57
9
C56
10
C55
11
C54
12
C53
13
C52
C51
14
15
C50
16
C49
17
C48
18
C47
19
C46
20
C45
21
C44
22
C43
23
C42
24
C41
25
C40
26
C39
27
C38
28
C37
29
C36
30
C35
31
C34
32
C33
33
C32
34
C31
35
C30
36
n.c.
n.c.
37
38
C29
R27
125
R26
124
R25
123
R16
122
R15
121
R14
120
R13
119
R12
R11
118
117
PCF2116
R10
116
R9
115
n.c.
114
RS
113
V
112
SS2
PCF2116 family
(PCF2114X; PCF2116X)
DD2
T1
111
R/W
110
V
109
SS1
E
108
SA0
107
DD1
V
DB0VDB1
106
105
104
103
102
101
100
99
98
97
96
95
94
93
92
91
90
89
88
87
86
85
84
83
82
81
80
79
78
77
76
75
74
73
72
71
70
69
68
67
66
65
OSC
n.c.
n.c.
n.c.
DB2
V
LCD3
DB3
V
LCD2
DB4
V
LCD1
V
0
DB5
SDA
DB6
SCL
DB7
n.c.
n.c.
R1
R2
R3
R4
R5
R6
R7
R8
R17
R18
R19
R20
R21
R22
R23
R24
C1
n.c.
n.c.
C2
1996 Oct 25 5
394041424344454647
C28
C27
C26
C25
C24
C23
C22
C21
48
495051525354555657585960616263
C20
C19
C18
C17
C16
C15
C14
C13
C12
C9C8C7C6C5C4C3
C11
C10
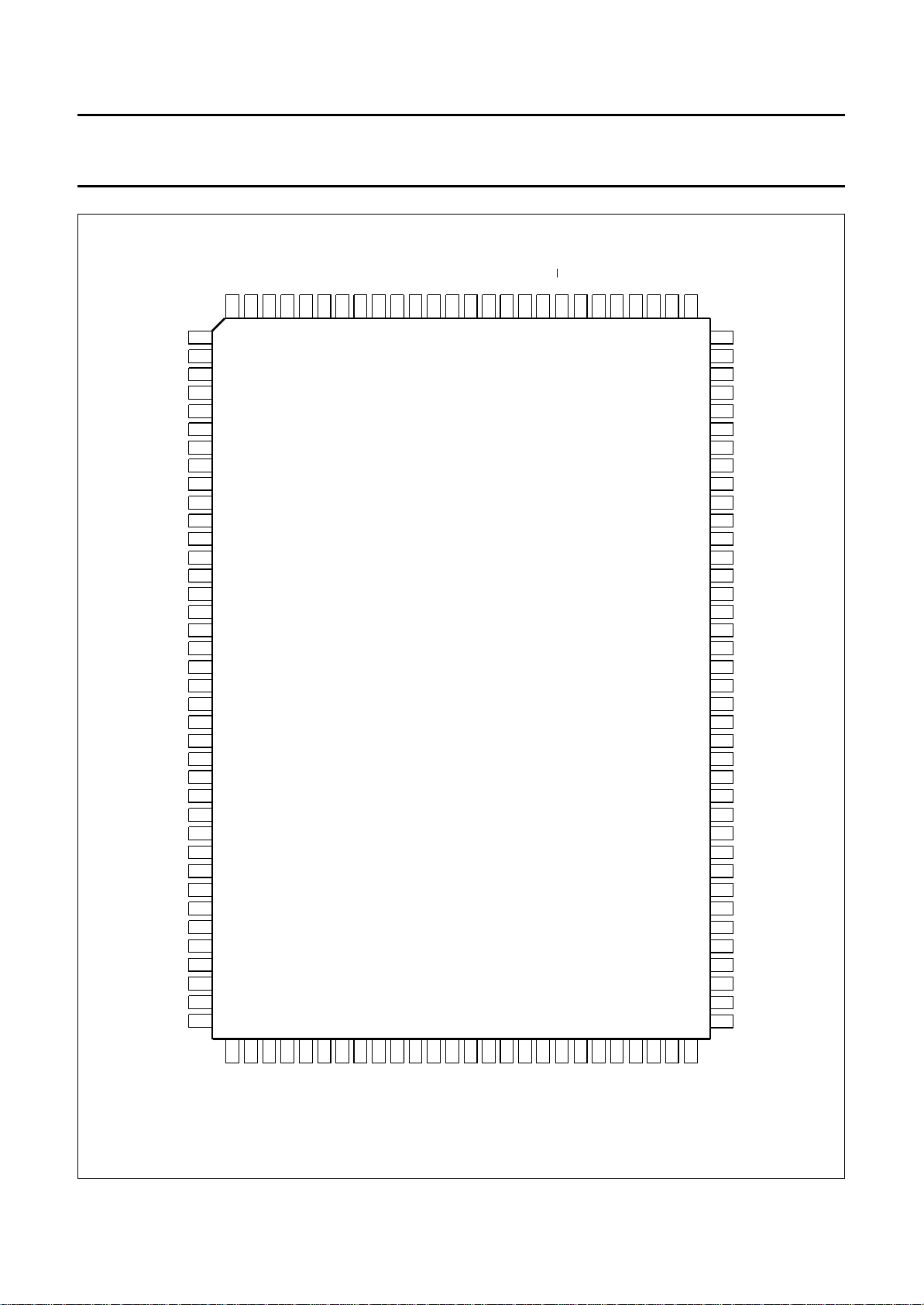
Fig.2 Pin configuration.
64
MBD451 - 1

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
LCD controller/drivers
PIN FUNCTIONS
RS: register select
RS selects the register to be accessed for read and write.
RS = logic 0 selects the instruction register for write and
the busy flag and address counter for read. RS = logic 1
selects the data register for both read and write. There is
an internal pull-up on pin RS.
W: read/write
R/
R/W selects either the read (R/W = logic 1) or write
(R/W = logic 0) operation. There is an internal pull-up on
this pin.
E: data bus clock
The E pin is set HIGH to signal the start of a read or write
operation. Data is clocked in or out of the chip on the
negative edge of the clock.
DB0 to DB7: data bus
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
PCF2116 family
(PCF2114X; PCF2116X)
OSC: oscillator
When the on-chip oscillator is used this pin must be
connected to VDD. An external clock signal, if used, is input
at this pin.
SCL: serial clock line
Input for the I
SDA: serial data line
Input/output for the I
SAO: address pin
The hardware sub-address line is used to program the
device sub-address for 2 different PCF2116s on the same
2
C-bus.
I
T1: test pad
Must be connected to V
2
C-bus clock signal.
2
C-bus data line.
. Not user accessible.
SS
The bidirectional, 3-state data bus transfers data between
the system controller and the PCF2116. DB7 may be used
as the busy flag, signalling that internal operations are not
yet completed. In 4-bit operations the 4 higher order lines
DB4 to DB7 are used; DB0 to DB3 must be left open
circuit. There is an internal pull-up on each of the data
lines.
C1 to C60: column driver outputs
These pins output the data for pairs of columns.
This arrangement permits optimized COG layout for 4-line
by 12 characters.
R1 to R32: row driver outputs
These pins output the row select waveforms to the left and
right halves of the display.
: LCD power supply
V
LCD
Negative power supply for the liquid crystal display.
This may be generated on-chip or supplied externally.
: V
V
0
The input level at this pin determines the generated V
control input
LCD
LCD
output voltage.
(1) When I2C-bus is used, the parallel interface pin E must be
defined: E = logic0; in I
be left open circuit.
2
C-bus read mode DB0 to DB7 must
BLOCK DIAGRAM FUNCTIONS
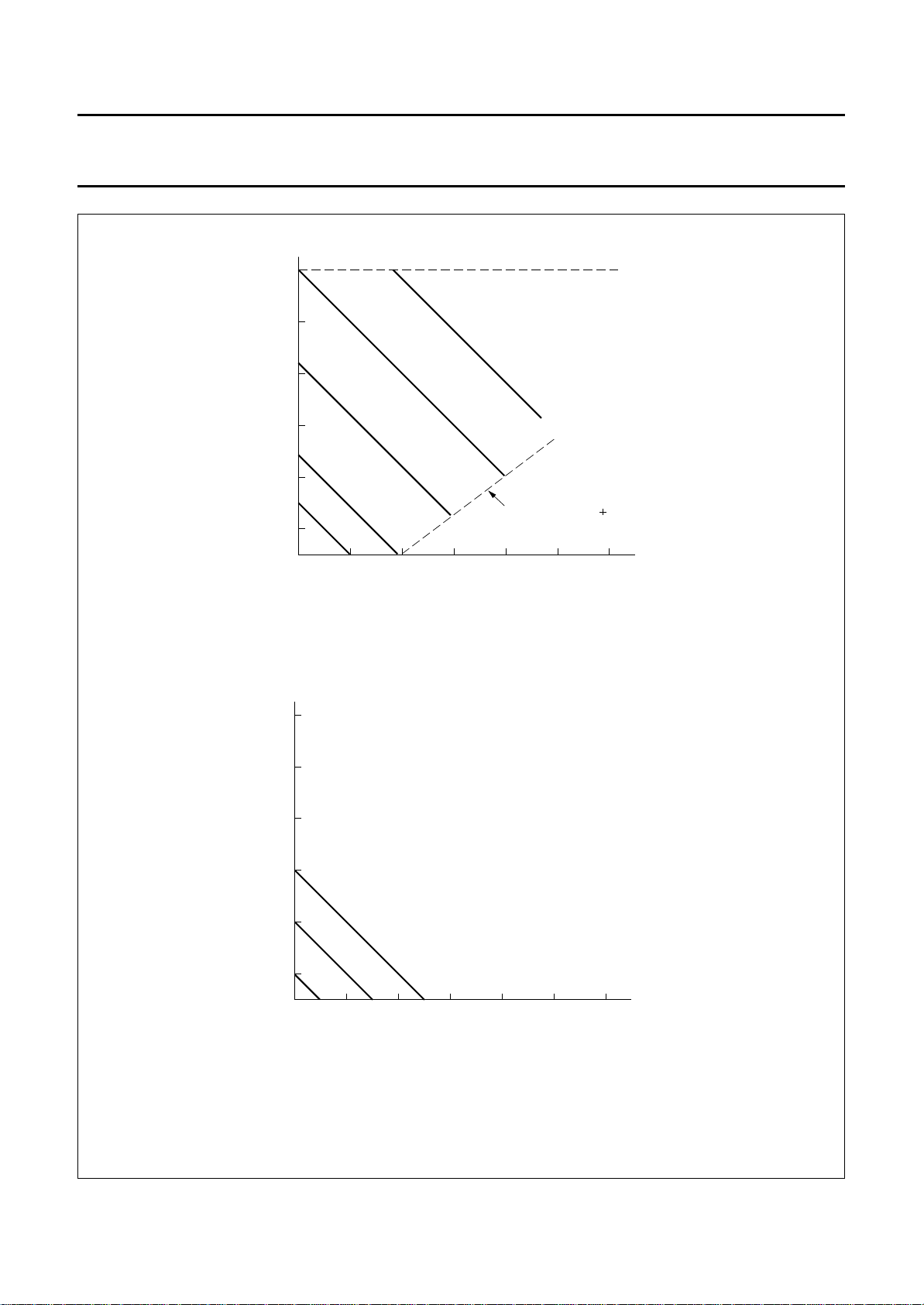
LCD supply voltage generator
The on-chip voltage generator is controlled by bit G of the
function set command and V
.
0
V0 is a high-impedance input and draws no current from
the system power supply. Its range is between VSS and
VDD− 1 V. When V0 is connected to VDD the generator is
switched off and an external voltage must be supplied to
pin V
. This may be more negative than VSS.
LCD
When G = logic 1 the generator produces a negative
voltage at pin V
, controlled by the input voltage at
LCD
pin V0. The LCD operating voltage is given by the
relationship:
VOP= 1.8VDD− V
0
Where:
VOP=VDD− V
V
LCD=V0
When G = logic 0, the generated output voltage V
LCD
−(0.8VDD)
LCD
is
equal to V0 (between VSS and VDD). In this instance:
VOP=VDD− V
When V
LCD
decoupled to VDD with a suitable capacitor. VDD and V
0
is generated on-chip the V
pin should be
LCD
0
must be selected to limit the maximum value of VOPto 9 V.
Figure 3 shows the two control characteristics for
the generator.
1996 Oct 25 6

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
LCD controller/drivers
In the PCF2116K version, V0 is connected through an
on-chip resistor (R0) to V
value of 1 MΩ and draws a typical current of 4 µA from the
pin V0. A constant voltage (equal to 1.34VDD) is always
present across R0.
Its voltage range is between VSS and VDD− 0.5 V
(see Fig.4). When V0 is connected to VDD the generator is
switched off and an external voltage must be supplied to
pin V
. This may be more negative than VSS.
LCD
When G = logic 1 the generator produces a negative
voltage at pin V
, controlled by the input voltage at
LCD
pin V0. The LCD operating voltage is given by the
relationship:
VOP= 2.34VDD− V
Where:
VOP=VDD− V
V
LCD=V0
LCD
−(1.34VDD).
When G = logic 0, the generated output voltage V
equal to V0 (between VSS and VDD). In this instance:
VOP=VDD− V
0
Character generator ROM (CGROM)
The standard character set ‘C’ is available for the
PCF2116K.
. Resistor R0 has a nominal
LCD
0
LCD
is
PCF2116 family
(PCF2114X; PCF2116X)
Oscillator
The on-chip oscillator provides the clock signal for the
display system. No external components are required and
the OSC pin must be connected to V
External clock
If an external clock is to be used this is input at the OSC
pin. The resulting display frame frequency is given by
f
frame=fosc
/2304. A clock signal must always be present,
otherwise the LCD may be frozen in a DC state.
Power-on reset
The power-on reset block initializes the chip after
power-on or power failure.
Registers
The PCF2116 has two 8-bit registers, an Instruction
Register (IR) and a Data Register (DR). The Register
Select signal (RS) determines which register will be
accessed.
The instruction register stores instruction codes such as
display clear and cursor shift, and address information for
the Display Data RAM (DDRAM) and Character Generator
RAM (CGRAM). The instruction register can be written
from but not read by the system controller.
DD
.
LCD bias voltage generator
The intermediate bias voltages for the LCD display are
also generated on-chip. This removes the need for an
external resistive bias chain and significantly reduces the
system power consumption. The optimum levels depend
on the multiplex rate and are selected automatically when
the number of lines in the display is defined.
The optimum value of V
depends on the multiplex rate,
OP
the LCD threshold voltage (Vth) and the number of bias
levels and is given by the relationships in Table 1.
Using a 5-level bias scheme for 1 : 16 mux rate allows
VOP< 5 V for most LCD liquids. The effect on the display
contrast is negligible.
Table 1 Optimum values for V
MUX RATE
OP
NUMBER OF BIAS
LEVELS
1 : 16 5 3.67 1.277
1 : 32 6 5.19 1.196
The data register temporarily stores data to be read from
the DDRAM and CGRAM. When reading, data from the
DDRAM or CGRAM corresponding to the address in the
address counter is written to the data register prior to being
read by the read data instruction.
Busy flag
The busy flag indicates the internal status of the PCF2116,
a logic 1 indicating that the chip is busy and further
instructions will not be accepted. The busy flag is output to
pin DB7 when RS = logic 0 and R/
W = logic 1.
Instructions should only be written after checking that the
busy flag is logic 0 or waiting for the required number of
clock cycles.
VOP/V
th
DISCRIMINATION
Von/V
off
1996 Oct 25 7
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
LCD controller/drivers
9
V
OP
8
7
6
5
4
3.5
(PCF2114X; PCF2116X)
9 V
V = 1.8 x V
OP(max) DD
6 = V
DD
G = 1
5
4
3
2.5
0123456
V = 0.8 x V 1
OP(min) DD
V
0
MGA798
PCF2116 family
a. High-voltage mode VOP= 1.8VDD− V0.
9
V
OP
8
7
G = 0
6
5
4
4
3.5
0123456
6 = V
DD
5
V
0
b. Buffer mode VOP=VDD− V0.
MGA799
1996 Oct 25 8
Fig.3 VOP as a function of V0 control characteristics.
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
LCD controller/drivers
V
OP
3.5
(PCF2114X; PCF2116X)
9
8
5
7
4 = V
DD
6
5
4
0123456
2.5
3
V
OP(min)
= 1.34 × VDD + 0.5
6
V
9 V
G = 1
0
MBH667
PCF2116 family
a. High-voltage mode VOP= 2.34VDD− V0.
9
V
OP
8
7
G = 0
6
5
4
4
3.5
0123456
6 = V
DD
5
V
0
MGA799
1996 Oct 25 9
b. Buffer mode VOP=VDD− V0.
Fig.4 VOP as a function of V0 control characteristics (PCF2116K).

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
LCD controller/drivers
Address counter (AC)
The address counter assigns addresses to the DDRAM
and CGRAM for reading and writing and is set by the
commands ‘Set CGRAM Address’ and ‘Set DDRAM
Address’. After a read/write operation the address counter
is automatically incremented or decremented by 1.
The address counter contents are output to the bus
(DB0 to DB6) when RS = logic 0 and R/W = logic 1.
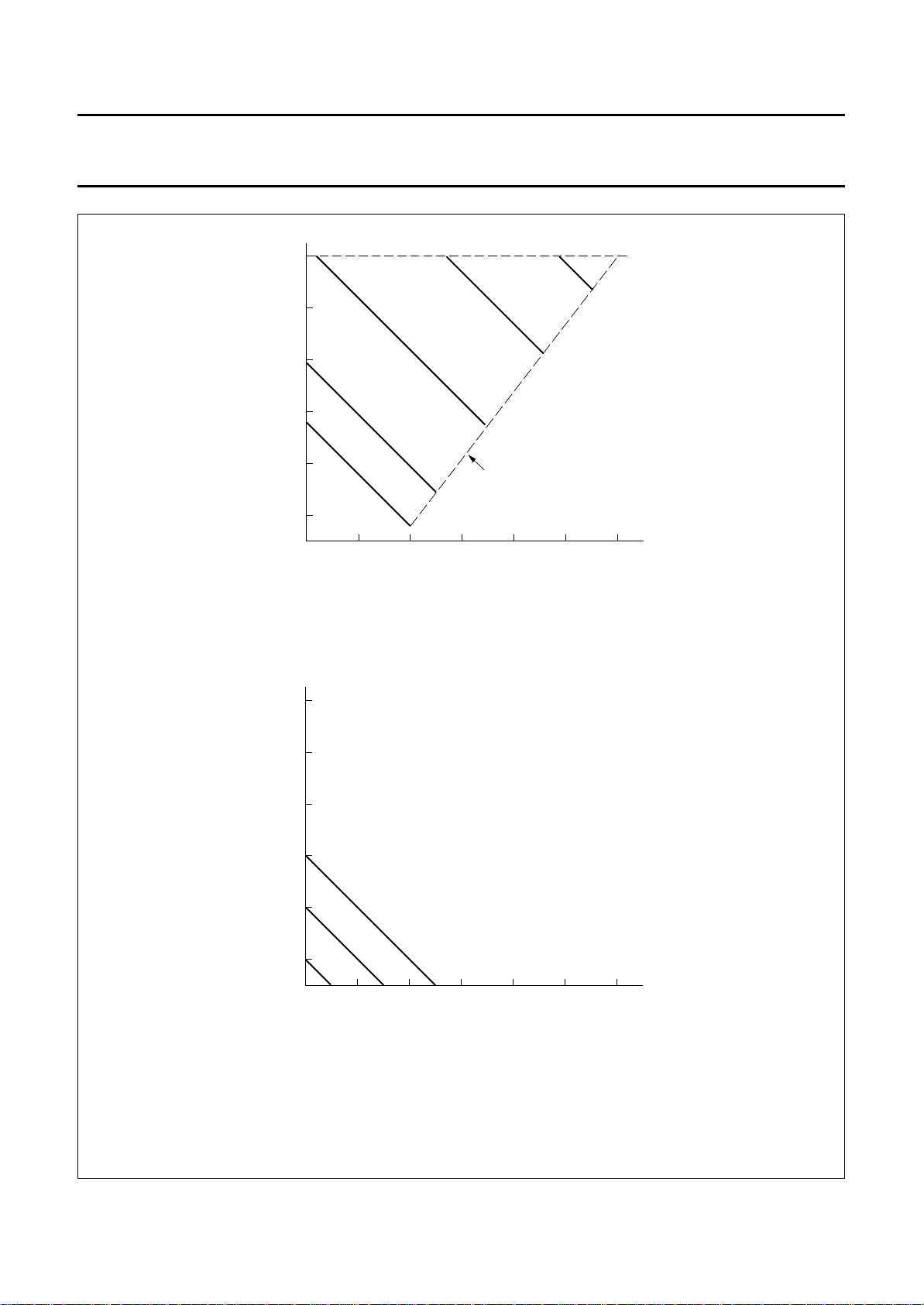
Display data RAM (DDRAM)
The display data RAM stores up to 80 characters of
display data represented by 8-bit character codes.
RAM locations not used for storing display data can be
used as general purpose RAM. The basic RAM to display
addressing scheme is shown in Fig.5. With no display shift
the characters represented by the codes in the first 12 or
24 RAM locations starting at address 00 in line 1 are
displayed. Subsequent lines display data starting at
addresses 20, 40, or 60H. Figs 6 and 7 show the DDRAM
to display mapping principle when the display is shifted.
The address range for a 1-line display is 00 to 4F; for a
2-line display from 00 to 27 (line 1) and 40 to 67 (line 2);
for a 4-line display from 00 to 13, 20 to 33, 40 to 53 and
60 to 73 for lines 1, 2, 3 and 4 respectively.
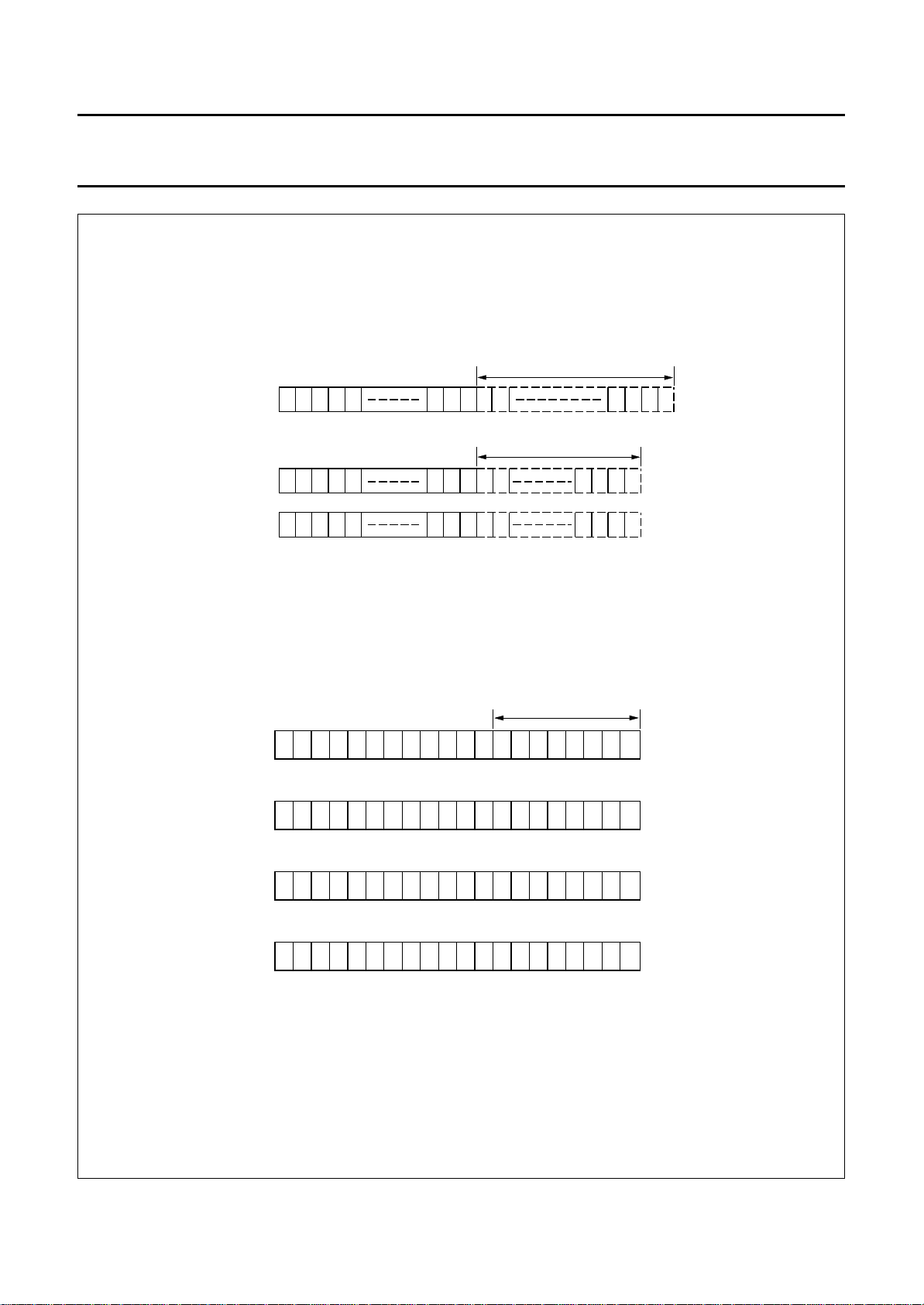
For 2 and 4-line displays the end address of one line and
the start address of the next line are not consecutive.
When the display is shifted each line wraps around
independently of the others (Figs 6 and 7).
When data is written into the DDRAM wrap-around occurs
from 4F to 00 in 1-line mode and from 27 to 40 and
67 to 00 in 2-line mode; from 13 to 20, 33 to 40, 53 to 60
and 73 to 00 in 4-line mode.
PCF2116 family
(PCF2114X; PCF2116X)
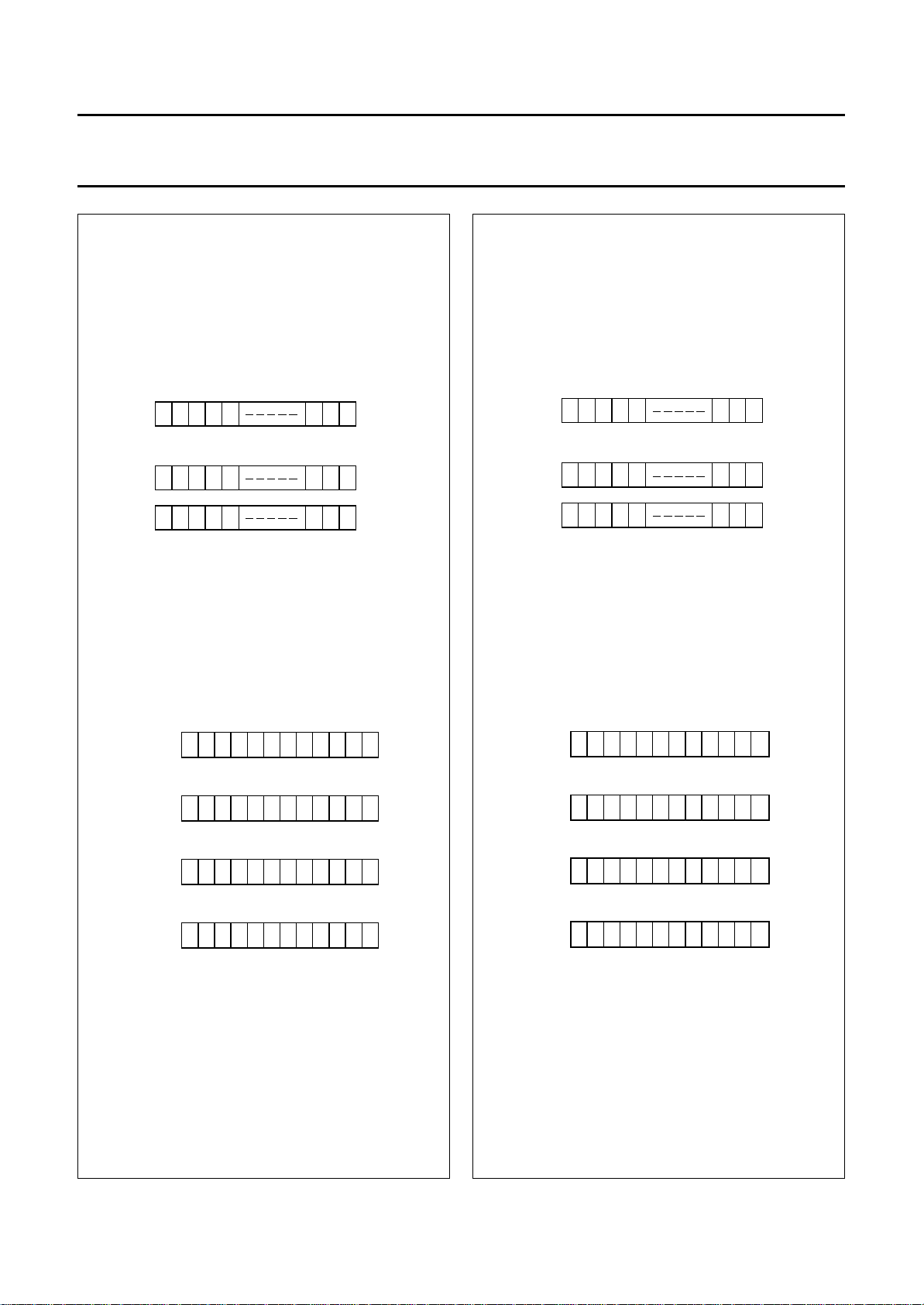
Character generator RAM (CGRAM)
Up to 16 user-defined characters may be stored in the
character generator RAM. The CGROM and CGRAM use
a common address space, of which the first column is
reserved for the CGRAM (see Fig.8). Figure 12 shows the
addressing principle for the CGRAM.
Cursor control circuit
The cursor control circuit generates the cursor (underline
and/or character blink as shown in Fig.13) at the DDRAM
address contained in the address counter. When the
address counter contains the CGRAM address the cursor
will be inhibited.
Timing generator
The timing generator produces the various signals
required to drive the internal circuitry. Internal chip
operation is not disturbed by operations on the data buses.
LCD row and column drivers
The PCF2116 contains 32 row and 60 column drivers,
which connect the appropriate LCD bias voltages in
sequence to the display, in accordance with the data to be
displayed. The bias voltages and the timing are selected
automatically when the number of lines in the display is
selected. Figures 14 and 15 show typical waveforms.
In 1-line mode (1 : 16) the row outputs are driven in pairs:
R1/R17, R2/R18 for example. This allows the output pairs
to be connected in parallel, providing greater drive
capability.
Unused outputs should be left unconnected.
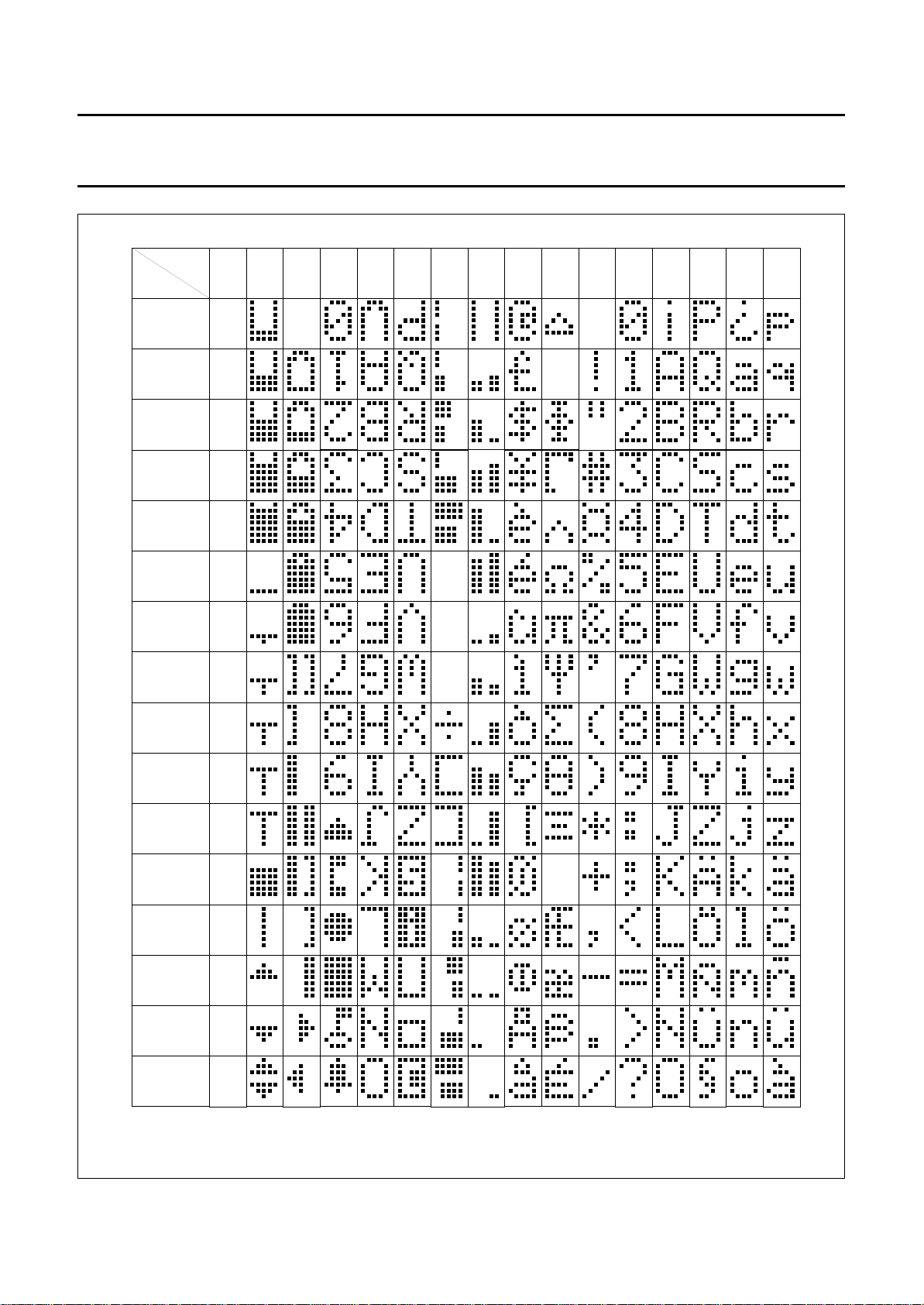
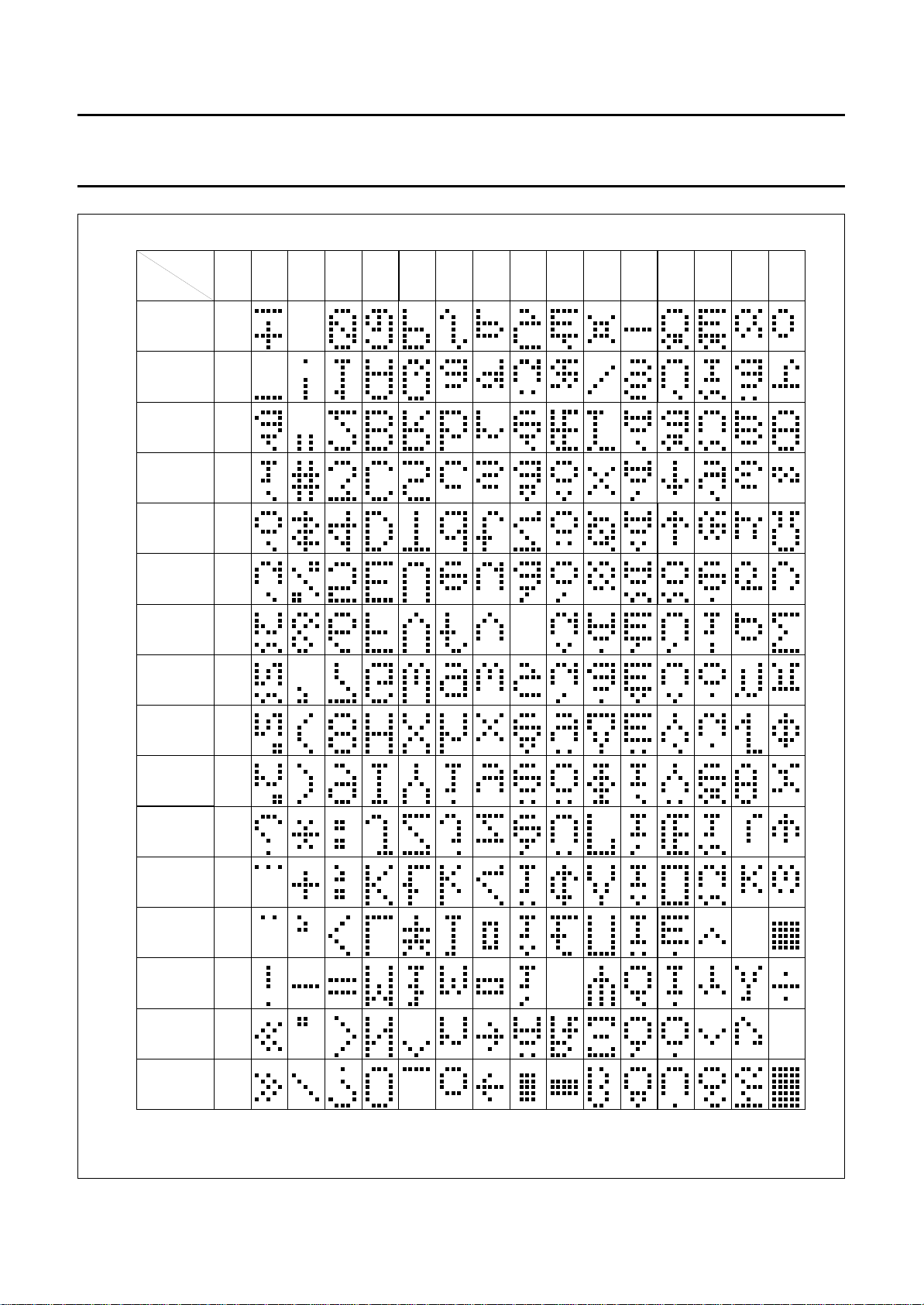
Character generator ROM (CGROM)
The character generator ROM generates 240 character
patterns in 5 × 8 dot format from 8-bit character codes.
Figures 8 to 11 show the character sets currently
available.
1996 Oct 25 10
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
LCD controller/drivers
Display
handbook, 4 columns
Position
(decimal)
DDRAM
Address
(hex)
DDRAM
Address
(hex)
12345 222324
00 01 02 03 04 15 16 17 18 19 4C 4D 4E 4F
00 01 02 03 04 15 16 17 18 19
1-line display
2-line display
(PCF2114X; PCF2116X)
non-displayed DDRAM addresses
non-displayed DDRAM address
24 25 26 27
64 65 66 6740 41 42 43 44 55 56 57 58 59
MLA792
PCF2116 family
line 1
line 2
handbook, 4 columns
DDRAM
Address
(hex)
123456789101112
00 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 0A 0B 0C 0D 0E 0F 10 11 12 13
20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 2A 2B 2C 2D 2E 2F 30 31 32 33
40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 4A 4B 4C 4D 4E 4F 50 51 52 53
60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 6A 6B 6C 6D 6E 6F 70 71 72 73
4 line display
non-displayed DDRAM addresses
line 1
line 2
line 3
line 4
MLA793
1996 Oct 25 11
Fig.5 DDRAM to display mapping; no shift (PCF2116X).
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
LCD controller/drivers
Display
Position
(decimal)
DDRAM
Address
(hex)
DDRAM
Address
(hex)
1 2 3 4 5 22 23 24
4F 00 01 02 03 14 15 16
1-line display
27 00 01 02 03
67 40 41 42 43
2-line display
14 15 16
54 55 56
MLA802
line 1
line 2
Display
Position
(decimal)
DDRAM
Address
(hex)
DDRAM
Address
(hex)
PCF2116 family
(PCF2114X; PCF2116X)
1 2 3 4 5 22 23 24
0501 02 03 04
1-line display
0501 02 03 04
41 42 43 44 45 56 57 58
2-line display
16 17 18
16 17 18
MLA815
line 1
line 2
123456789101112
13 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 0A
00
20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 2A33
DDRAM
Address
(hex)
40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 4A53
60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 6A73
4-line display
MLA803
Fig.6 DDRAM to display mapping; right shift
(PCF2116X).
line 1
line 2
line 3
line 4
123456789101112
01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 0A 0B 0C
21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 2A 2B 2C
DDRAM
Address
(hex)
41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 4A 4B 4C
61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 6A 6B 6C
4-line display
Fig.7 DDRAM to display mapping; left shift
(PCF2116X).
line 1
line 2
line 3
line 4
MLA816
1996 Oct 25 12
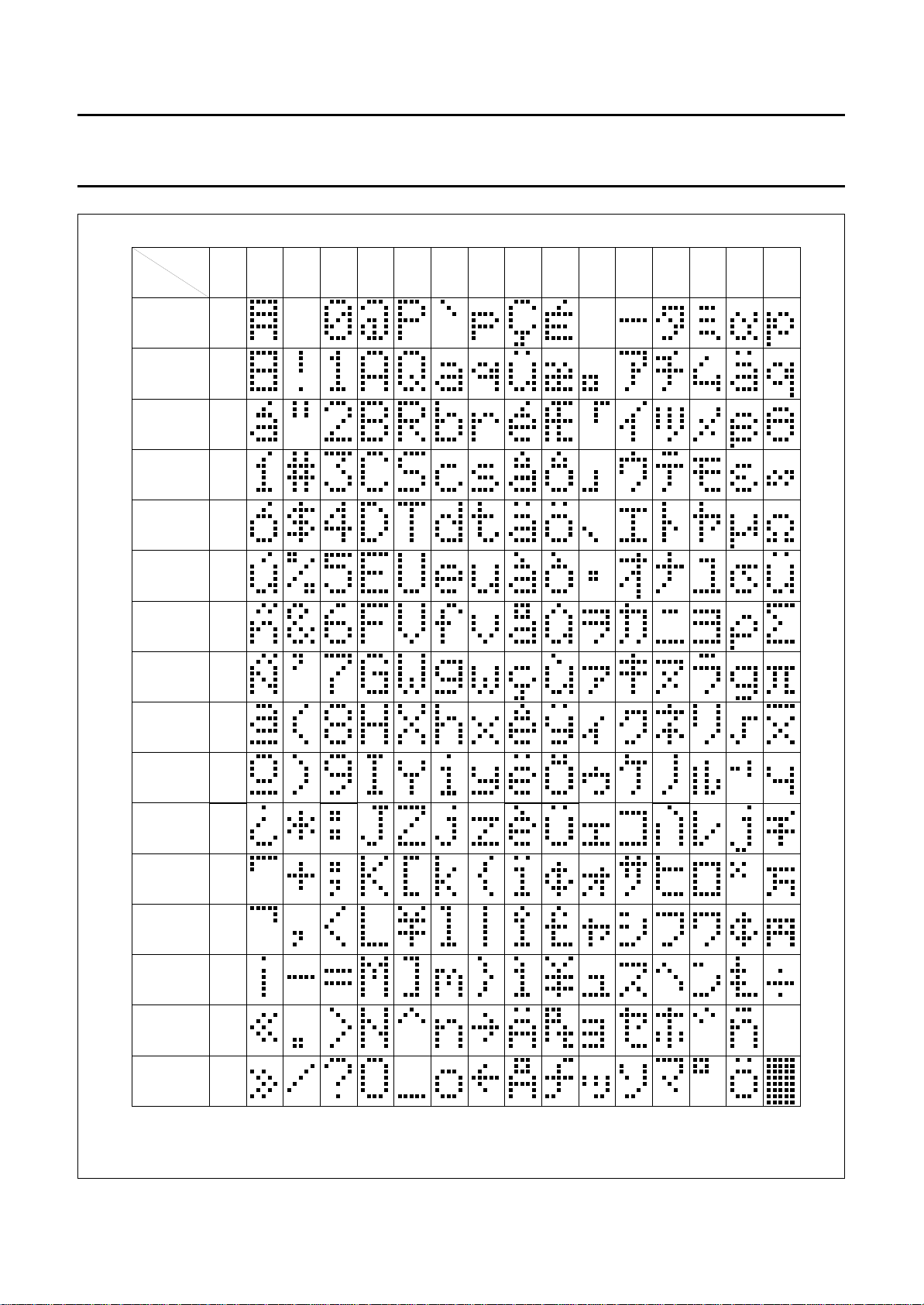
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
LCD controller/drivers
handbook, full pagewidth
upper
4 bits
lower
6 bits
xxxx 0000
xxxx 0001
xxxx 0010
xxxx 0011
xxxx 0100
xxxx 0101
0000 0001 0010 0011 0100 0101 0110 0111 1000 1001 1010 1011 1100 1101 1110 1111
1
2
3
4
5
6
PCF2116 family
(PCF2114X; PCF2116X)
xxxx 0110
xxxx 0111
xxxx 1000
xxxx 1001
xxxx 1010
xxxx 1011
xxxx 1100
xxxx 1101
xxxx 1110
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
xxxx 1111 16
1996 Oct 25 13
MLB245 - 1
Fig.8 Character set ‘A’ in CGROM; PCF2116A; PCF2114A.
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
LCD controller/drivers
handbook, full pagewidth
upper
4 bits
lower
4 bits
xxxx 0000
xxxx 0001
xxxx 0010
xxxx 0011
xxxx 0100
xxxx 0101
0000 0001 0010 0011 0100 0101 0110 0111 1000 1001 1010 1011 1100 1101 1110 1111
CG
RAM 1
2
3
4
5
6
PCF2116 family
(PCF2114X; PCF2116X)
xxxx 0110
xxxx 0111
xxxx 1000
xxxx 1001
xxxx 1010
xxxx 1011
xxxx 1100
xxxx 1101
xxxx 1110
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
xxxx 1111 16
1996 Oct 25 14
MLB895
Fig.9 Character set ‘C’ in CGROM; PCF2116C; PCF2114C.

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
LCD controller/drivers
handbook, full pagewidth
upper
4 bits
lower
6 bits
xxxx 0000
xxxx 0001
xxxx 0010
xxxx 0011
xxxx 0100
xxxx 0101
0000 0001 0010 0011 0100 0101 0110 0111 1000 1001 1010 1011 1100 1101 1110 1111
CG
RAM 1
2
3
4
5
6
PCF2116 family
(PCF2114X; PCF2116X)
xxxx 0110
xxxx 0111
xxxx 1000
xxxx 1001
xxxx 1010
xxxx 1011
xxxx 1100
xxxx 1101
xxxx 1110
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
xxxx 1111 16
1996 Oct 25 15
MLB896
Fig.10 Character set ‘G’ in CGROM; PCF2116G; PCF2114G.
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
LCD controller/drivers
handbook, full pagewidth
upper
4 bits
lower
4 bits
xxxx 0000
xxxx 0001
xxxx 0010
xxxx 0011
xxxx 0100
xxxx 0101
0000 0001 0010 0011 0100 0101 0110 0111 1000 1001 1010 1011 1100 1101 1110 1111
CG
RAM 1
2
3
4
5
6
PCF2116 family
(PCF2114X; PCF2116X)
xxxx 0110
xxxx 0111
xxxx 1000
xxxx 1001
xxxx 1010
xxxx 1011
xxxx 1100
xxxx 1101
xxxx 1110
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
xxxx 1111 16
1996 Oct 25 16
MLB968
Fig.11 Character set ‘J’ in CGROM; PCF2116J; PCF2114J.
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
LCD controller/drivers
handbook, full pagewidth
character codes
(DDRAM data)
76543210 6543210 43210
higher
order
bits
00000000 0000000 0
00000001 0001
00000010
lower
order
bits
CGRAM
address
higher
order
bits
010 0000
lower
order
bits
001 000
010 000
011 0
100 0 00
101 00 0
110 000
111 00000
000 000
001 0 0 0
010
100
101 00 00
110 00 00
111 00000
001
PCF2116 family
(PCF2114X; PCF2116X)
character patterns
(CGRAM data)
higher
order
bits
00 00011
lower
order
bits
character
pattern
example 1
cursor
position
character
pattern
example 2
1
1
1
00001111
00001111
00001111
00001111
Character code bits 0 to 3 correspond to CGRAM address bits 3 to 6.
CGRAM address bits 0 to 2 designate character pattern line position. The 8th line is the cursor position and display is performed by logical OR with
the cursor. Data in the 8th line will appear in the cursor position.
Character pattern column positions correspond to CGRAM data bits 0 to 4, as shown in Fig.12 (bit 4 being at the left end).
As shown in Figs 8 and 12, CGRAM character patterns are selected when character code bits 4 to 7 are all logic 0. CGRAM data = logic 1
corresponds to selection for display.
Only bits 0 to 5 of the CGRAM address are set by the ‘Set CGRAM Address’ command. Bit 6 can be set using the ‘Set DDRAM Address’ command
or by using the auto-increment feature during CGRAM write. All bits 0 to 6 can be read using the ‘Read BF and Address’ command.
1
1
111
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
100
1
101
1
110
1
1
MGA800 - 1
Fig.12 Relationship between CGRAM addresses and data and display patterns.
1996 Oct 25 17

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
LCD controller/drivers
5 x 7 dot character font alternating display
cursor display example blink display example
cursor
PCF2116 family
(PCF2114X; PCF2116X)
MGA801
Fig.13 Cursor and blink display examples.
1996 Oct 25 18

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
LCD controller/drivers
handbook, full pagewidth
V
DD
V
2
ROW 1
ROW 9
ROW 2
COL 1
V /V
34
V
5
V
LCD
V
DD
V
2
V /V
34
V
5
V
LCD
V
DD
V
2
V /V
34
V
5
V
LCD
V
DD
V
2
V /V
34
V
5
V
LCD
PCF2116 family
(PCF2114X; PCF2116X)
frame n 1frame n
state 1 (ON)
state 2 (ON)
1-line display
(1:16)
COL 2
state 1
state 2
V
V
V /V
V
V
V
op
0.25 V
0 V
0.25 V
V
op
V
op
0.25 V
0 V
0.25 V
V
op
DD
2
3
5
LCD
4
op
op
op
op
123 16123 16
MGA802 - 1
1996 Oct 25 19
Fig.14 Typical LCD waveforms; 1-line mode.
 Loading...
Loading...