查询PCF2113A供应商查询PCF2113A供应商
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
DATA SH EET
PCF2113x
LCD controllers/drivers
Product specification
Supersedes data of 1997 Apr 04
File under Integrated Circuits, IC12
2001 Dec 19

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
LCD controllers/drivers PCF2113x
CONTENTS
1 FEATURES
1.1 Note
2 APPLICATIONS
3 GENERAL DESCRIPTION
4 ORDERING INFORMATION
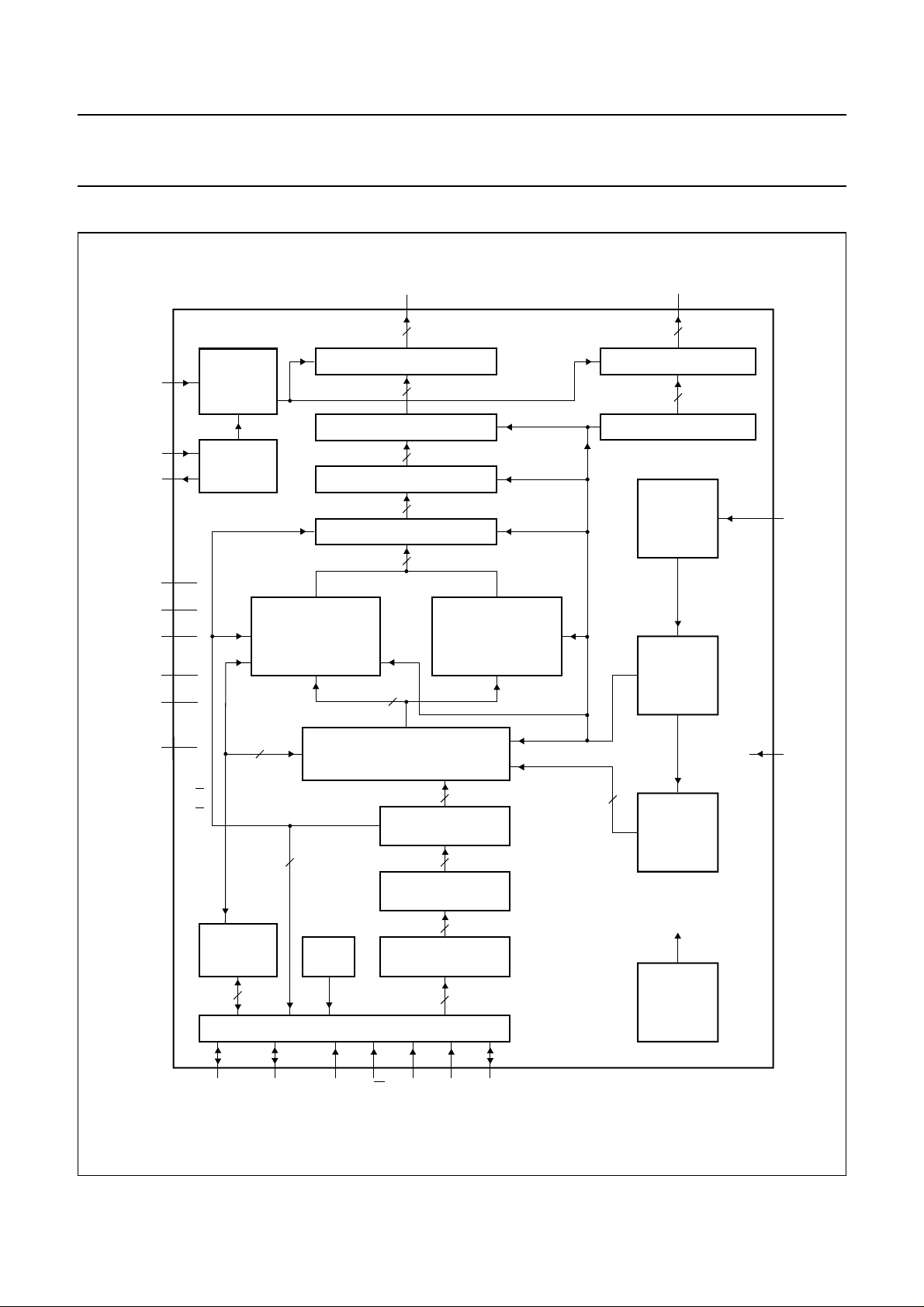
5 BLOCK DIAGRAM
6 PINNING
7 FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
7.1 LCD supply voltage generator
7.2 LCD bias voltage generator
7.3 Oscillator
7.4 External clock
7.5 Power-on reset
7.6 Power-down mode
7.7 Registers
7.8 Busy flag
7.9 Address Counter (AC)
7.10 Display Data RAM (DDRAM)
7.11 Character Generator ROM (CGROM)
7.12 Character Generator RAM (CGRAM)
7.13 Cursor control circuit
7.14 Timing generator
7.15 LCD row and column drivers
7.16 Reset function
8 INSTRUCTIONS
8.1 Clear display
8.2 Return home
8.3 Entry mode set
8.4 Display control (andpartial Power-down mode)
8.5 Cursor or display shift
8.6 Function set
8.7 Set CGRAM address
8.8 Set DDRAM address
8.9 Read busy flag and read address
8.10 Write data to CGRAM or DDRAM
8.11 Read data from CGRAM or DDRAM
9 EXTENDED FUNCTION SET
INSTRUCTIONS AND FEATURES
9.1 New instructions
9.2 Icon control
9.3 Bit IM
9.4 Bit IB
9.5 Direct mode
9.6 Voltage multiplier control
9.7 Screen configuration
9.8 Display configuration
9.9 Temperature control
9.10 Set V
9.11 Reducing current consumption
10 INTERFACES TO MICROCONTROLLER
10.1 Parallel interface
10.2 I2C-bus interface
11 LIMITING VALUES
12 HANDLING INSTRUCTIONS
13 DC CHARACTERISTICS
14 AC CHARACTERISTICS
15 DEVICE PROTECTION CIRCUITS
16 APPLICATION INFORMATION
16.1 General application information
16.2 4-bit operation, 1-line display using internal
16.3 8-bit operation, 1-line display using internal
16.4 8-bit operation, 2-line display
16.5 I2C-bus operation, 1-line display
17 BONDING PAD INFORMATION
18 TRAY INFORMATION
19 PACKAGE OUTLINE
20 SOLDERING
20.1 Introduction to soldering surface mount
20.2 Reflow soldering
20.3 Wave soldering
20.4 Manual soldering
20.5 Suitability of surface mount IC packages for
21 DATA SHEET STATUS
22 DEFINITIONS
23 DISCLAIMERS
24 BARE DIE DISCLAIMER
25 PURCHASE OF PHILIPS I2C COMPONENTS
LCD
reset
reset
packages
wave and reflow soldering methods
2001 Dec 19 2

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
LCD controllers/drivers PCF2113x
1 FEATURES
• Single-chip LCD controller/driver
• 2-line display of up to 12 characters + 120 icons, or
1-line display of up to 24 characters + 120 icons
• 5 × 7 character format plus cursor; 5 × 8 for kana
(Japanese) and user defined symbols
• Icon mode: reduced current consumption while
displaying
• Icon blink function
• On-chip:
– Configurable 4, 3 or 2 voltage multiplier generating
LCD supply voltage, independent of VDD,
programmable by instruction (external supply also
possible)
– Temperature compensation of on-chip generated
V
: −0.16 to −0.24 %/K (programmable by
LCD
instruction)
– Generation of intermediate LCD bias voltages
– Oscillator requires no external components
(external clock also possible).
• Display data RAM: 80 characters
• Character generator ROM: 240, 5 × 8 characters
• Character generator RAM: 16, 5 × 8 characters;
3 characters used to drive 120 icons, 6 characters used
if icon blink feature is used in application
• 4 or 8-bit parallel bus and 2-wire I2C-bus interface
• CMOS compatible
• 18 row and 60 column outputs
• Multiplex rates 1 : 18 (for normal operation), 1 : 9 (for
single line operation) and 1 : 2 (for icon only mode)
• Uses common 11 code instruction set (extended)
• Logic supply voltage range V
DD1
− V
= 1.8 to 5.5 V
SS1
(chip may be driven with two battery cells)
• V
• Display supply voltage range V
generator supply voltage range
LCD
V
DD2
− V
= 2.2 to 4.0 V
SS2
LCD
− V
= 2.2 to 6.5 V
SS2
• Direct mode to save current consumption for icon mode
and Mux 1 : 9 (depending on V
value and LCD liquid
DD2
properties)
• Very low current consumption (20 to 200 µA):
– Icon mode: <25 µA
– Power-down mode: <2 µA.
1.1 Note
Icon mode is used to save current. When only icons are
displayed, a much lower operating voltage V
LCD
can be
used and the switching frequency of the LCD outputs is
reduced. In most applications it is possible to use VDD as
V
.
LCD
2 APPLICATIONS
• Telecom equipment
• Portable instruments
• Point-of-sale terminals.
3 GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The PCF2113x is a low power CMOS LCD controller and
driver, designed to drive a dot matrix LCD display of 2-line
by 12 or 1-line by 24 characters with 5 × 8 dot format.
All necessary functions for the display are provided in a
single chip, including on-chip generation of LCD bias
voltages, resulting in a minimum of external components
and lower system current consumption. The PCF2113x
interfaces to most microcontrollers via a 4 or 8-bit bus or
via the 2-wire I2C-bus. The chip contains a character
generator and displays alphanumeric and kana
(Japanese) characters. The letter ‘x’ in PCF2113x
characterizes the built-in character set. Various character
sets can be manufactured on request.
2001 Dec 19 3
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
LCD controllers/drivers PCF2113x
4 ORDERING INFORMATION
TYPE NUMBER
NAME DESCRIPTION VERSION
PCF2113AU/10/F4 − chip on flexible film carrier −
PCF2113DU/10/F4 − chip on flexible film carrier −
PCF2113DU/F4 − chip in tray −
PCF2113DH/F4 LQFP100 plastic low profile quad flat package; 100 leads;
body 14 × 14 × 1.4 mm
PCF2113DU/2/F4 − chip with bumps in tray −
PCF2113EU/2/F4 − chip with bumps in tray −
PCF2113WU/2/F4 − chip with bumps in tray −
PACKAGE
SOT407-1
2001 Dec 19 4
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
LCD controllers/drivers PCF2113x
5 BLOCK DIAGRAM
handbook, full pagewidth
V
LCD1
V
LCDSENSE
V
LCD2
V
DD1
V
DD2
V
DD3
V
SS1
V
SS2
BIAS
VOLT AGE
GENERATOR
V
LCD
GENERATOR
SHIFT REGISTER 5 × 12 BIT
CURSOR AND DATA CONTROL
CHARACTER
GENERATOR
RAM (128 × 5)
(CGRAM)
16 CHARACTERS
C1 to C60 R1 to R18
60
COLUMN DRIVERS
60
DATA LATCHES
60
5
5
CHARACTER
GENERATOR
ROM
(CGROM)
240 CHARACTERS
8
SHIFT REGISTER 18-BIT
18
ROW DRIVERS
18
OSCILLATOR
TIMING
GENERATOR
OSC
T1
T2
T3
DB0 to DB3/SA0
7
DATA
REGISTER
(DR)
8
DB4 to DB7
DISPLAY DATA RAM
(DDRAM)
80 CHARACTERS/BYTES
ADDRESS COUNTER
BUSY
FLAG
I/O BUFFER
E
R/W
RS
Fig.1 Block diagram.
7
(AC)
77
INSTRUCTION
DECODER
8
INSTRUCTION
REGISTER(IR)
8
SCL
SDA
PD
7
DISPLAY
ADDRESS
COUNTER
PCF2113x
POWER-ON
RESET
MGE990
2001 Dec 19 5
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
LCD controllers/drivers PCF2113x
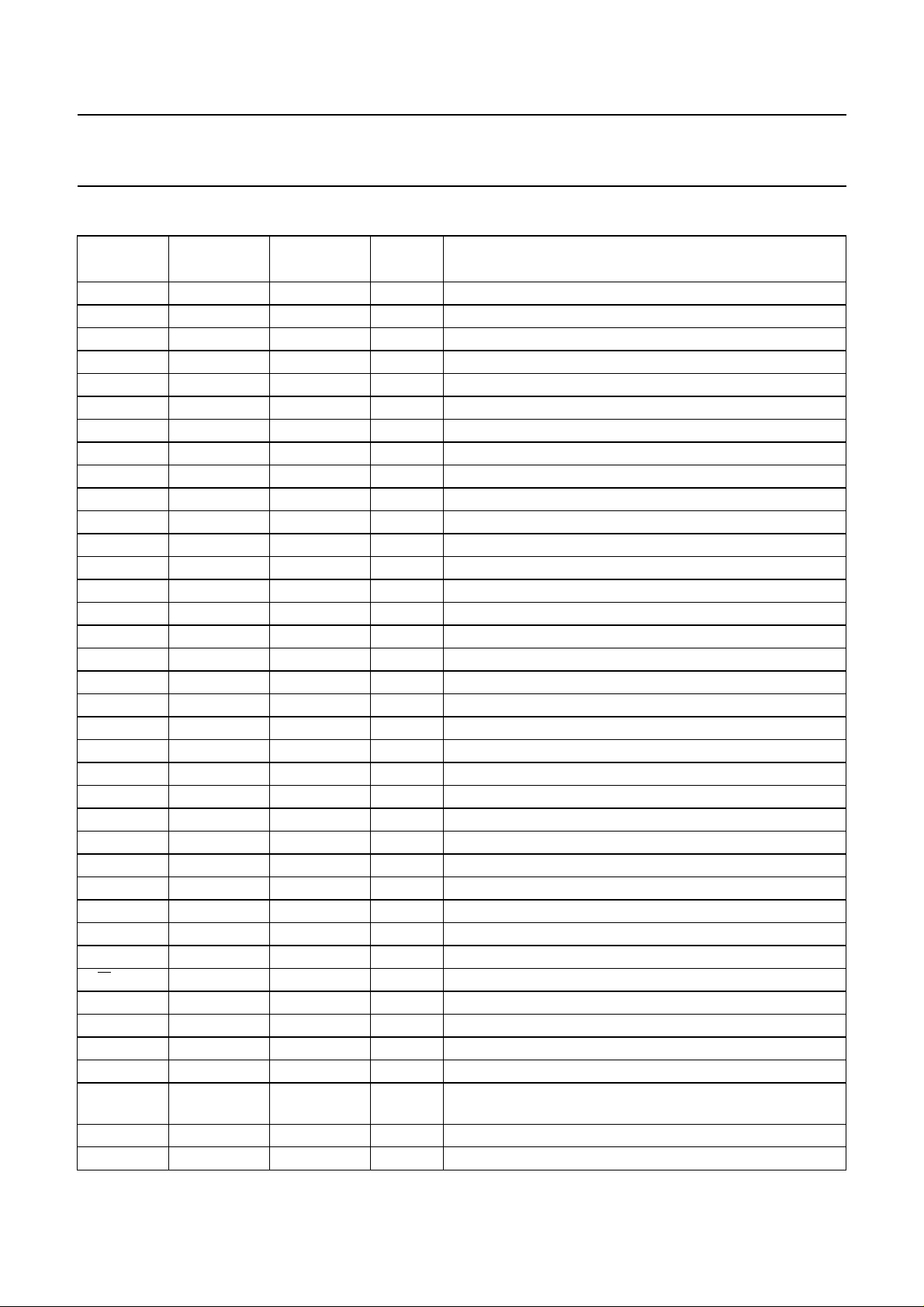
6 PINNING
SYMBOL
V
DD1
PIN
PCF2113DH
PCF2113XU
1 1 P supply voltage 1 for all except V
PAD
(1)
TYPE DESCRIPTION
generator
LCD
OSC 2 2 I oscillator/external clock input; note 2
PD 3 3 I power-down select input; for normal operation PD is LOW
T3 − 4 I test pad; open circuit and not user accessible
T1 4 5 I test pin; must be connected to V
T2 − 6 I test pad; must be connected to V
V
SS1
V
SS2
V
LCD2
V
LCDSENSE
V
LCD1
5 7 P ground 1 for all except V
6 8 P ground 2 for V
79OV
output if V
LCD
− 10 I input (V
LCD
LCD
) for voltage multiplier regulation; notes 3 and 7
LCD
LCD
generator
is generated internally; note 7
8 11 I input for generation of LCD bias levels; note 7
SS1
SS1
generator
R9 to R16 9 to 16 12 to 19 O LCD row driver outputs 9 to 16
R18 17 20 O LCD row driver output 18
C60 to C53 18 to 25 21 to 28 O LCD column driver outputs 60 to 53
dummy pad − 29 −
dummy pad − 30 −
C52 to C28 26 to 50 31 to 55 O LCD column driver outputs 52 to 28
dummy pad − 56 −
dummy pad − 57 −
C27 to C3 51 to 75 58 to 82 O LCD column driver outputs 27 to 3
dummy pad − 83 −
dummy pad − 84 −
C2 76 85 O LCD column driver output 2
C1 77 86 O LCD column driver output 1
R8 to R1 78 to 85 87 to 94 O LCD row driver outputs 8 to 1
R17 86 95 O LCD row driver output 17
SCL 87 96 I I
SDA 88 97 I/O I
2
C-bus serial clock input; note 4
2
C-bus serial data input/output; note 4
E 89 98 I data bus clock input; note 4
RS 90 99 I register select input
R/
W 91 100 I read/write input
DB7 92 101 I/O 8-bit bidirectional data bus bit 7; note 5
DB6 93 102 I/O 8-bit bidirectional data bus bit 6
DB5 94 103 I/O 8-bit bidirectional data bus bit 5
DB4 95 104 I/O 8-bit bidirectional data bus bit 4
DB3/SA0 96 105 I/O 8-bit bidirectional data bus bit 3 or I
2
C-bus address pin;
notes 4 and 5
DB2 97 106 I/O 8-bit bidirectional data bus bit 2
DB1 98 107 I/O 8-bit bidirectional data bus bit 1
2001 Dec 19 6
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
LCD controllers/drivers PCF2113x
SYMBOL
PIN
PCF2113DH
PCF2113XU
PAD
(1)
TYPE DESCRIPTION
DB0 99 108 I/O 8-bit bidirectional data bus bit 0
V
V
DD2
DD3
100 109 P supply voltage 2 for V
− 110 P supply voltage 3 for V
generator; note 6
LCD
generator; notes 3 and 6
LCD
Notes
1. Bonding pad location information is given in Chapter 17.
2. When the on-chip oscillator is used this pad must be connected to V
DD1
.
3. In the LQFP100 version this signal is connected internally and can not be accessed at any pin.
4. When the I2C-bus is used, the parallel interface pin E must be LOW. In the I2C-bus read mode DB7 to DB0 should
be connected to V
When the parallel bus is used, the pins SCL and SDA must be connected to V
or left open-circuit.
DD1
SS1
or V
; they must not be left
DD1
open-circuit.
When the 4-bit interface is used without reading out from the PCF2113x (R/W is set permanently to logic 0), the
unused ports DB0 to DB4 can either be set to V
SS1
or V
instead of leaving them open-circuit.
DD1
5. DB7 may be used as the busy flag, signalling that internal operations are not yet completed. In 4-bit operations the
four higher order lines DB7 to DB4 are used; DB3 to DB0 must be left open-circuit except for I2C-bus operations
(see note 4).
6. V
7. When V
and V
DD2
LCD
V
is supplied, pin V
LCD
should always be equal.
DD3
is generated internally, pins V
should be left open-circuit to avoid any stray current, pins V
LCD2
LCD1
, V
LCD2
and V
LCDSENSE
must be connected together. When external
LCD1
and V
LCDSENSE
must be
connected together.
2001 Dec 19 7
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
LCD controllers/drivers PCF2113x
handbook, full pagewidth
DD2
V
DB0
DB1
DB2
DB3/SA0
DB4
DB5
DB6
DB7
V
V
V
V
LCD2
V
LCD1
DD1
OSC
PD
T1
SS1
SS2
R9
R10
R11
R12
R13
R14
R15
R16
R18
C60
C59
C58
C57
C56
C55
C54
C53
R/WRSE
99989796959493929190898887868584838281
100
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
SDA
PCF2113x
SCL
R17R1R2R3R4
R5
R6R7R8C1C2
8079787776
75
C3
C4
74
C5
73
C6
72
71
C7
C8
70
C9
69
C10
68
67
C11
C12
66
C13
65
C14
64
63
C15
C16
62
C17
61
C18
60
59
C19
C20
58
C21
57
C22
56
55
C23
C24
54
C25
53
C26
52
C27
51
26
C52
C51
C50
31323334353637383940414243444546474849
C49
C47
C46
C45
C44
C43
C42
C48
C41
30
29
28
27
Fig.2 Pin configuration (LQFP100).
2001 Dec 19 8
C40
C39
C38
C37
C36
C35
C34
C33
C32
C31
C30
C29
50
C28
MGE989

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
LCD controllers/drivers PCF2113x
7 FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
7.1 LCD supply voltage generator
The LCD supply voltage may be generated on-chip. The
V
generator is controlled by two internal 6-bit registers:
LCD
VAand VB. The nominal LCD operating voltage at room
temperature is given by the relationship:
V
OP(nom)
= (integer value of register × 0.08) + 1.82
7.1.1 PROGRAMMING RANGES
Programmed value: 1 to 63. Voltage: 1.90 to 6.86 V.
T
=27°C.
ref
Values producing more than 6.5 V at operating
temperature are not allowed. Operation above this
voltage may damage the device. When programming the
operating voltage the V
tolerance and temperature
LCD
coefficient must be taken into account.
Values below 2.2 V are below the specified operating
range of the chip and are therefore not allowed.
Value 0 for VAand VB switches the generator off
(i.e. VA= 0 in character mode, VB= 0 in icon mode).
Usually register VA is programmed with the voltage for
character mode and register VB with the voltage for icon
mode.
When V
is generated on-chip the V
LCD
pins should be
LCD
decoupled to VSS with a suitable capacitor.
The generated V
temperature compensated. When the V
is independent of VDD and is
LCD
LCD
generator and
the direct mode are switched off, an external voltage may
besupplied at connected pinsV
V
may be higher or lower than V
LCD2
LCD1
andV
DD2
LCD2.VLCD1
.
and
During direct mode (program DM register bit) the internal
V
generator is turned off and the V
LCD
is directly connected to V
DD2
. This reduces the current
output voltage
LCD2
consumption during icon mode and Mux 1 : 9 (depending
on V
The V
value and LCD liquid properties).
DD2
generator ensures that, as long as VDDis in the
LCD
valid range (2.2 to 4 V), the required peak voltage
VOP= 6.5 V can be generated at any time.
7.2 LCD bias voltage generator
The intermediate bias voltages for the LCD display are
also generated on-chip. This removes the need for an
external resistive bias chain and significantly reduces the
system current consumption. The optimum value of V
LCD
depends on the multiplex rate, the LCD threshold voltage
(Vth) and the number of bias levels. Using a 5-level bias
scheme for 1 : 18 maximum rate allows V
LCD
< 5 V for
most LCD liquids. The intermediate bias levels for the
different multiplex rates are shown in Table 1. These bias
levels are automatically set to the given values when
switching to the corresponding multiplex rate.
Table 1 Bias levels as a function of multiplex rate; note 1
MULTIPLEX
RATE
1:18 5 V
1:9 5 V
1:2 4 V
NUMBER
OF LEVELS
V
LCD
LCD
LCD
1
V
2
3
/
4
3
/
4
2
/
3
Note
1. The values in the table are given relative to V
− VSS, e.g.3/4means3/4× (V
LCD
2001 Dec 19 9
V
3
1
/
2
1
/
2
2
/
3
V
4
1
/
2
1
/
2
1
/
3
− VSS).
LCD
V
5
1
/
4
1
/
4
1
/
3
V
6
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
LCD controllers/drivers PCF2113x
7.3 Oscillator
The on-chip oscillator provides the clock signal for the
display system. No external components are required and
the OSC pin must be connected to V
DD1
.
7.4 External clock
If an external clock is to be used this input is at the OSC
pin. The resulting display frame frequency is given by:
f
=
OSC
------------3072
f
frame
Only in the Power-down mode is the clock allowed to be
stopped (OSC connected to V
), otherwise the LCD is
SS
frozen in a DC state.
7.5 Power-on reset
The on-chip Power-on reset block initializes the chip after
power-onor power failure. This isasynchronous reset and
requires 3 oscillator cycles to be executed.
7.6 Power-down mode
Thechip can be putinto Power-down mode byapplying an
external active HIGH level to the PD pin. In Power-down
mode all static currents are switched off (no internal
oscillator, no bias level generation and all LCD outputs are
internally connected to VSS).
During power-down, information in the RAMs and the chip
state are preserved. Instruction execution during
power-down is possible when pin OSC is externally
clocked.
7.7 Registers
The PCF2113x has two 8-bit registers, an Instruction
Register (IR) and a Data Register (DR). The Register
Select (RS) signal determines which register will be
accessed.The instruction register storesinstruction codes
such as ‘display clear’, ‘cursor shift’, and address
information for the Display Data RAM (DDRAM) and
Character Generator RAM (CGRAM).The instruction
register can be written to but not read from by the system
controller.
The data register temporarily stores data to be read from
the DDRAM and CGRAM. When reading, data from the
DDRAM or CGRAM corresponding to the address in the
instruction register is written to the data register prior to
being read by the ‘read data’ instruction.
7.8 Busy flag
The busy flag indicates the internal status of the
PCF2113x. A logic 1 indicates that the chip is busy and
further instructions will not be accepted. The busy flag is
output to pin DB7 when bit RS = 0 and bit R/
W=1.
Instructions should only be written after checking that the
busy flag is at logic 0 or waiting for the required number of
cycles.
7.9 Address Counter (AC)
The address counter assigns addresses to the DDRAM
and CGRAM for reading and writing and is set by the
commands ‘set CGRAM address’ and ‘set DDRAM
address’. After a read/write operation the address counter
is automatically incremented or decremented by 1.
The address counter contents are output to the bus
(DB6 to DB0) when bit RS = 0 and bit R/W=1.
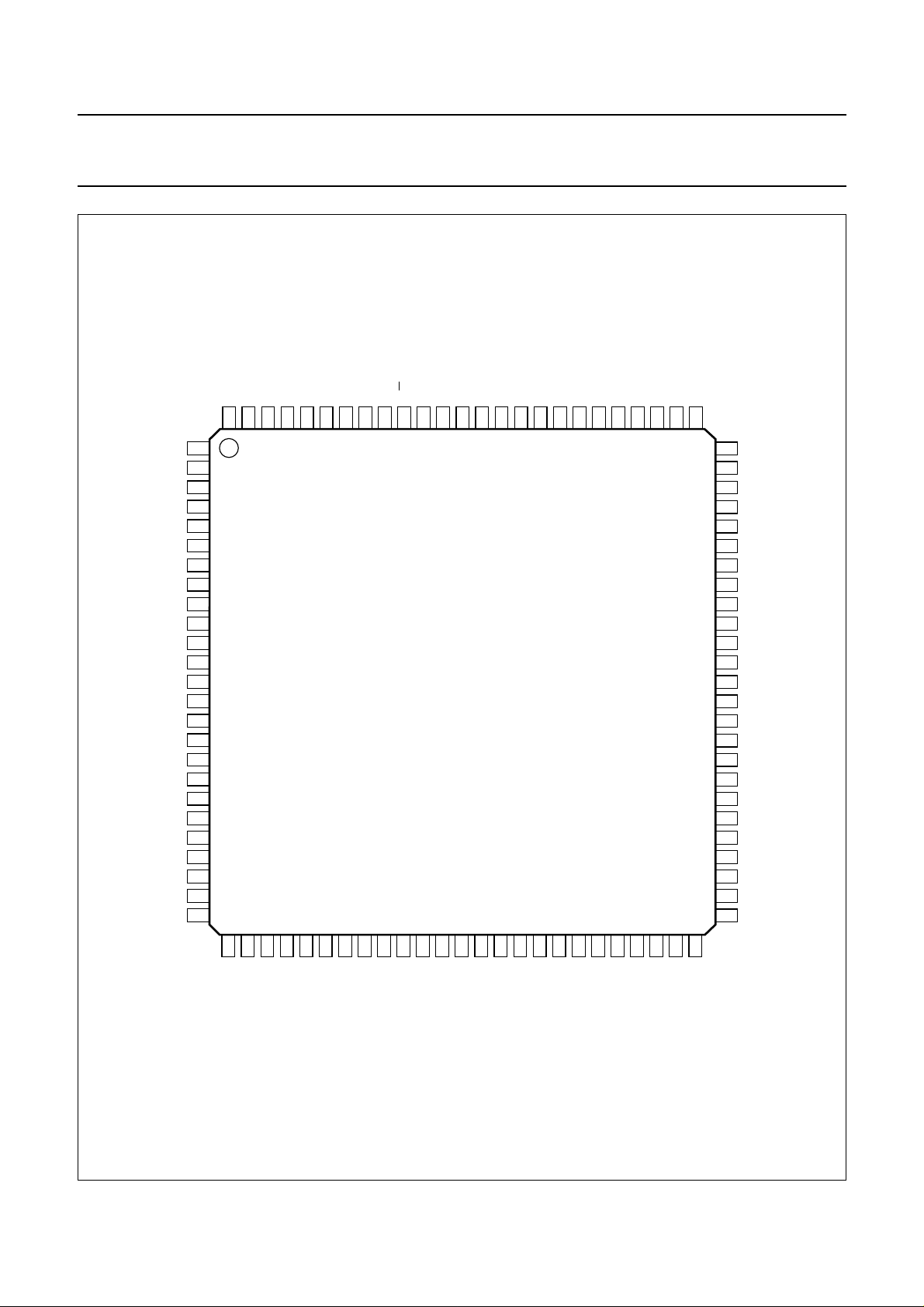
7.10 Display Data RAM (DDRAM)
The DDRAM stores up to 80 characters of display data
represented by 8-bit character codes. RAM locations
which are not used for storing display data can be used as
general purpose RAM. The basic RAM to display
addressing scheme is shown in Fig.3. With no display shift
the characters represented by the codes in the first
24 RAM locations starting at address 00H in line 1 are
displayed. Figures 4 and 5 show the display mapping for
right and left shift respectively.
When data is written to or read from the DDRAM,
wrap-around occurs from the end of one line to the start of
the next line. When the display is shifted each line wraps
around within itself, independently of the others. Thus all
lines are shifted and wrapped around together.
The address ranges and wrap-around operations for the
various modes are shown in Table 2.
Table 2 Address space and wrap-around operation
MODE 1 × 24 2 × 12 1 × 12
Address space 00 to 4F 00 to 27; 40 to 67 00 to 27
Read/write wrap-around (moves to next line) 4F to 00 27 to 40; 67 to 00 27 to 00
Display shift wrap-around (stays within line) 4F to 00 27 to 00; 67 to 40 27 to 00
2001 Dec 19 10
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
LCD controllers/drivers PCF2113x
handbook, full pagewidth
display
position
DDRAM
address
1-line display
DDRAM
address
2-line display
handbook, halfpage
12345 222324
non-displayed DDRAM addresses
00 01 02 03 04 15 16 17 18 19 4C 4D 4E 4F
non-displayed DDRAM address
12345 101112
00 01 02 03 04 09 0A 0B 0C 0D 24 25 26 27
line 1
12345 101112
64 65 66 6740 41 42 43 44 49 4A 4B 4C 4D
MGE991
line 2
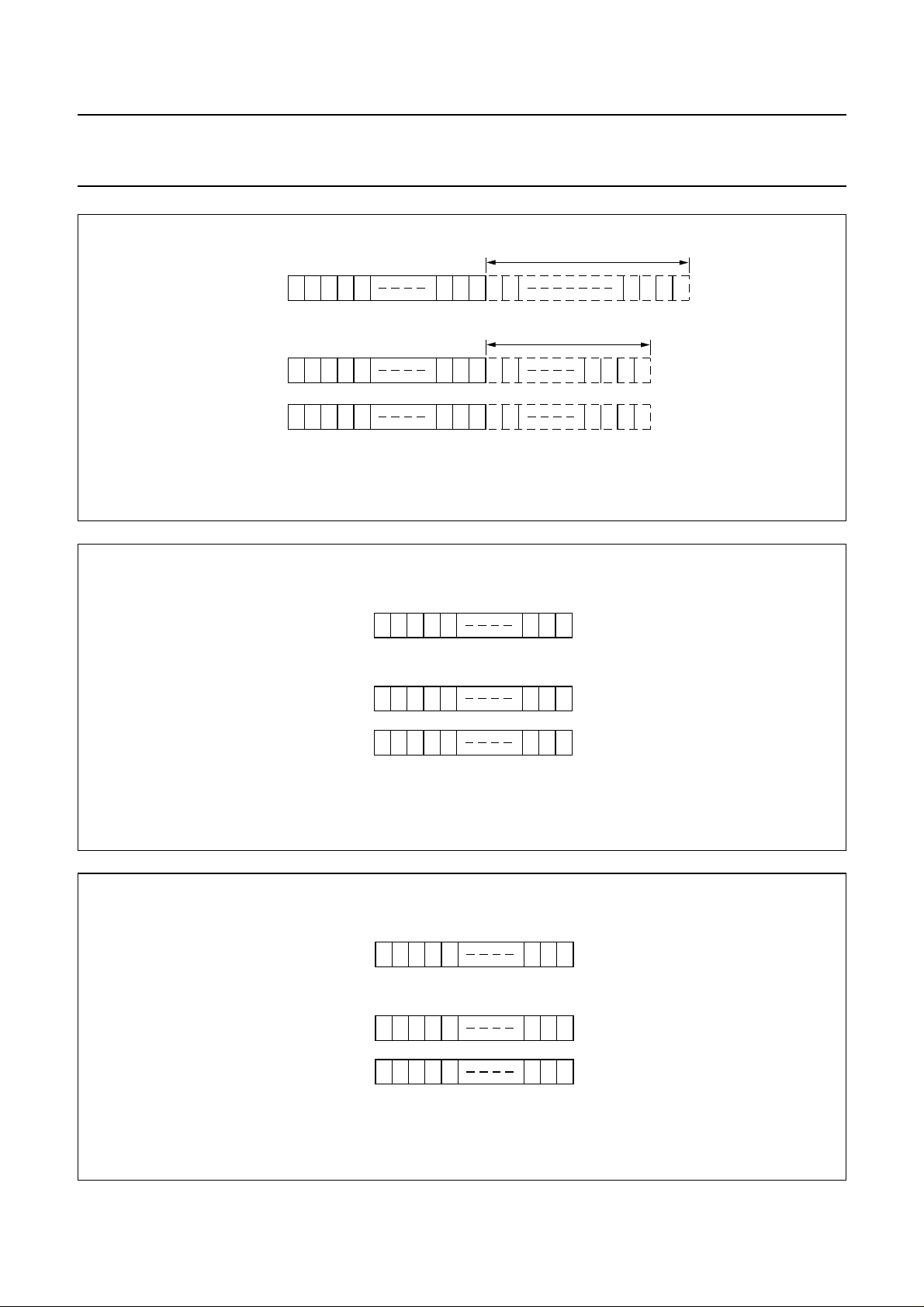
Fig.3 DDRAM to display mapping; no shift.
display
position
DDRAM
address
1-line display
DDRAM
address
2-line display
1 2 3 4 5 22 23 24
4F 00 01 02 03 14 15 16
1 2 3 4 5 10 11 12
27 00 01 02 03
08 09 0A
1 2 3 4 5 10 11 12
67 40 41 42 43
48 49 4A
MGE992
line 1
line 2
Fig.4 DDRAM to display mapping; right shift.
display
handbook, halfpage
position
DDRAM
address
1 2 3 4 5 22 23 24
01 04 05
02 03 16 17 18
1-line display
1 2 3 4 5 10 11 12
02 03
DDRAM
address
01 04 05
1 2 3 4 5 10 11 12
41 42 43 44 45
2-line display
Fig.5 DDRAM to display mapping; left shift.
2001 Dec 19 11
0A 0B 0C
4A 4B 4C
MGE993
line 1
line 2
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
LCD controllers/drivers PCF2113x
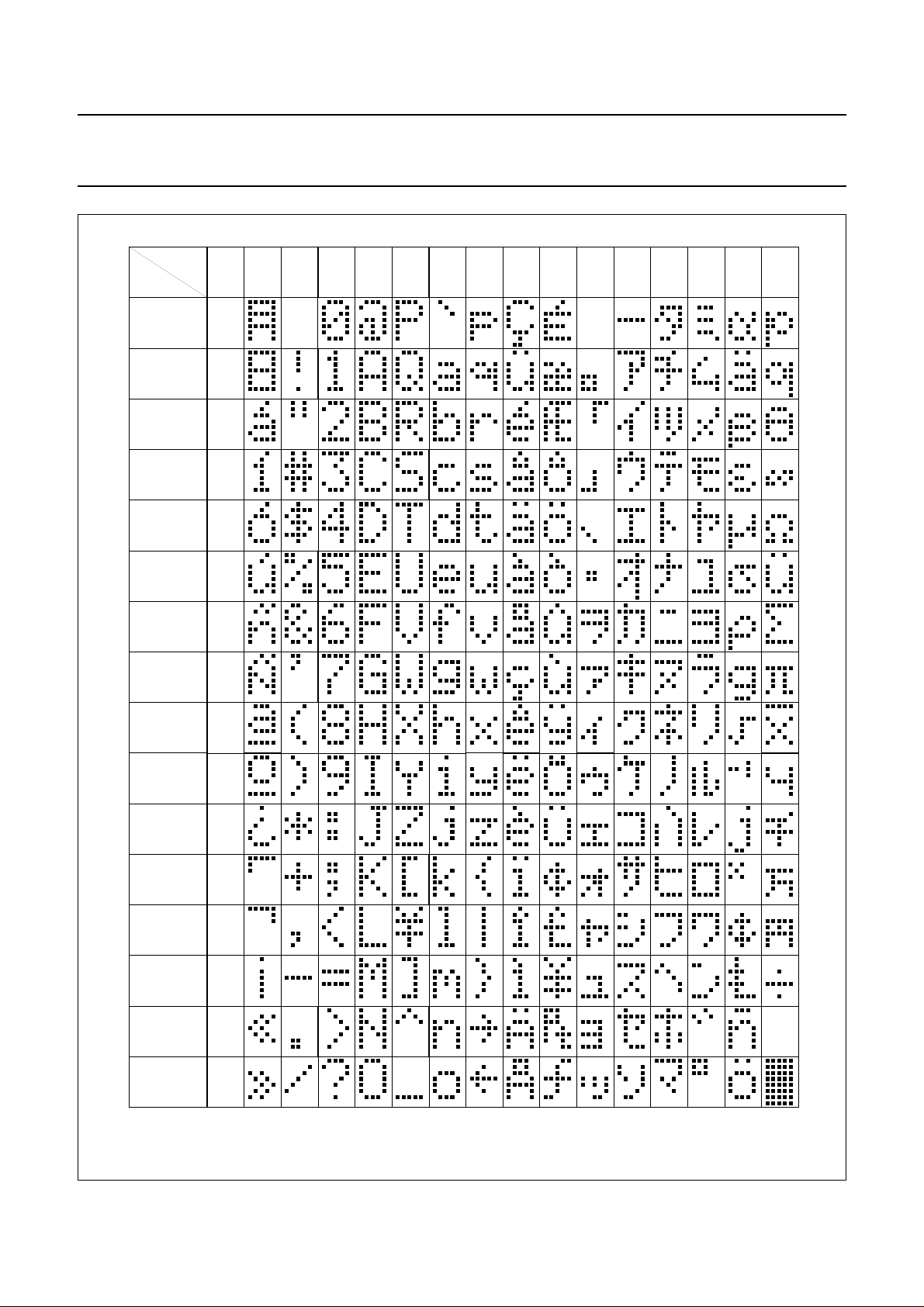
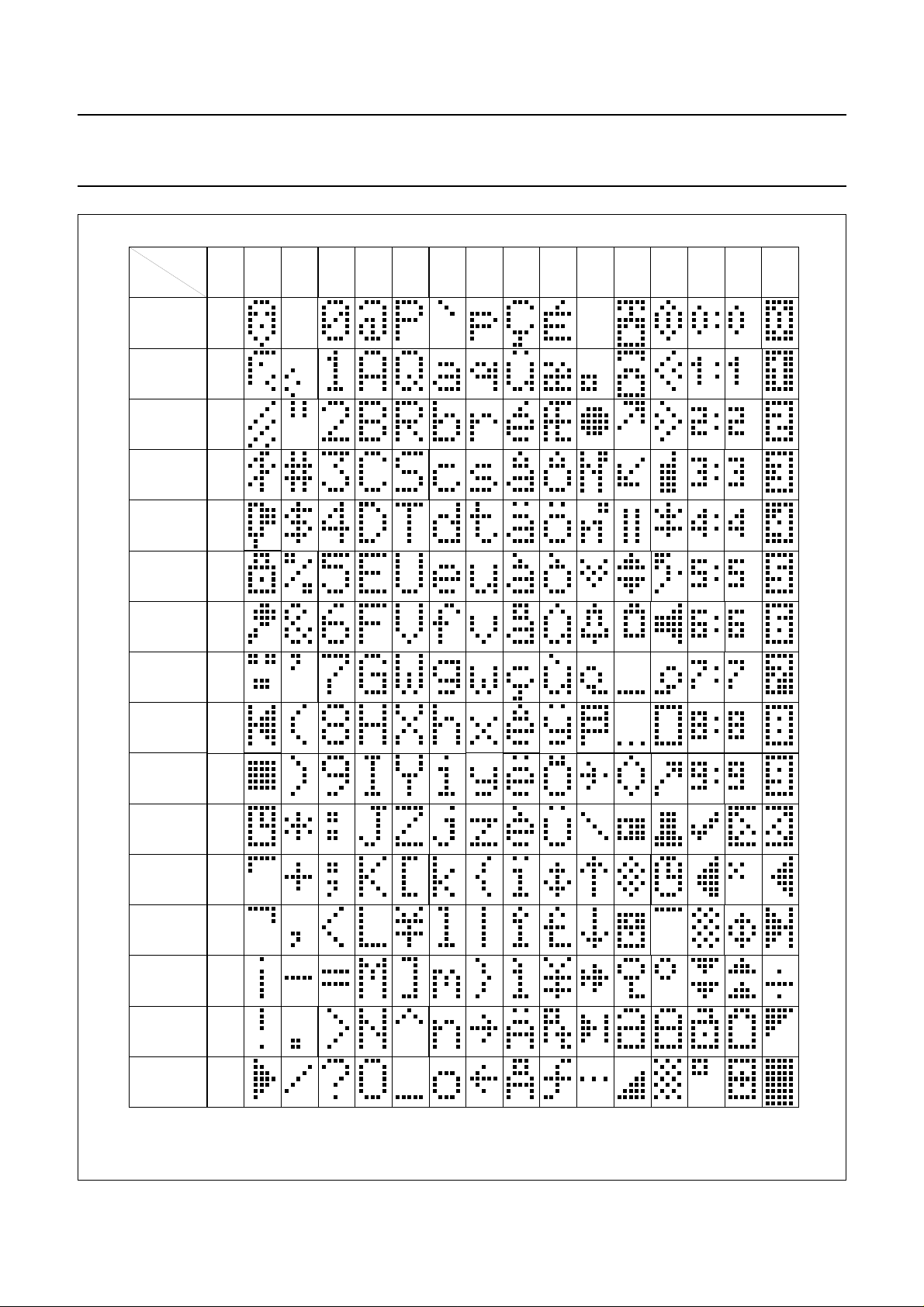
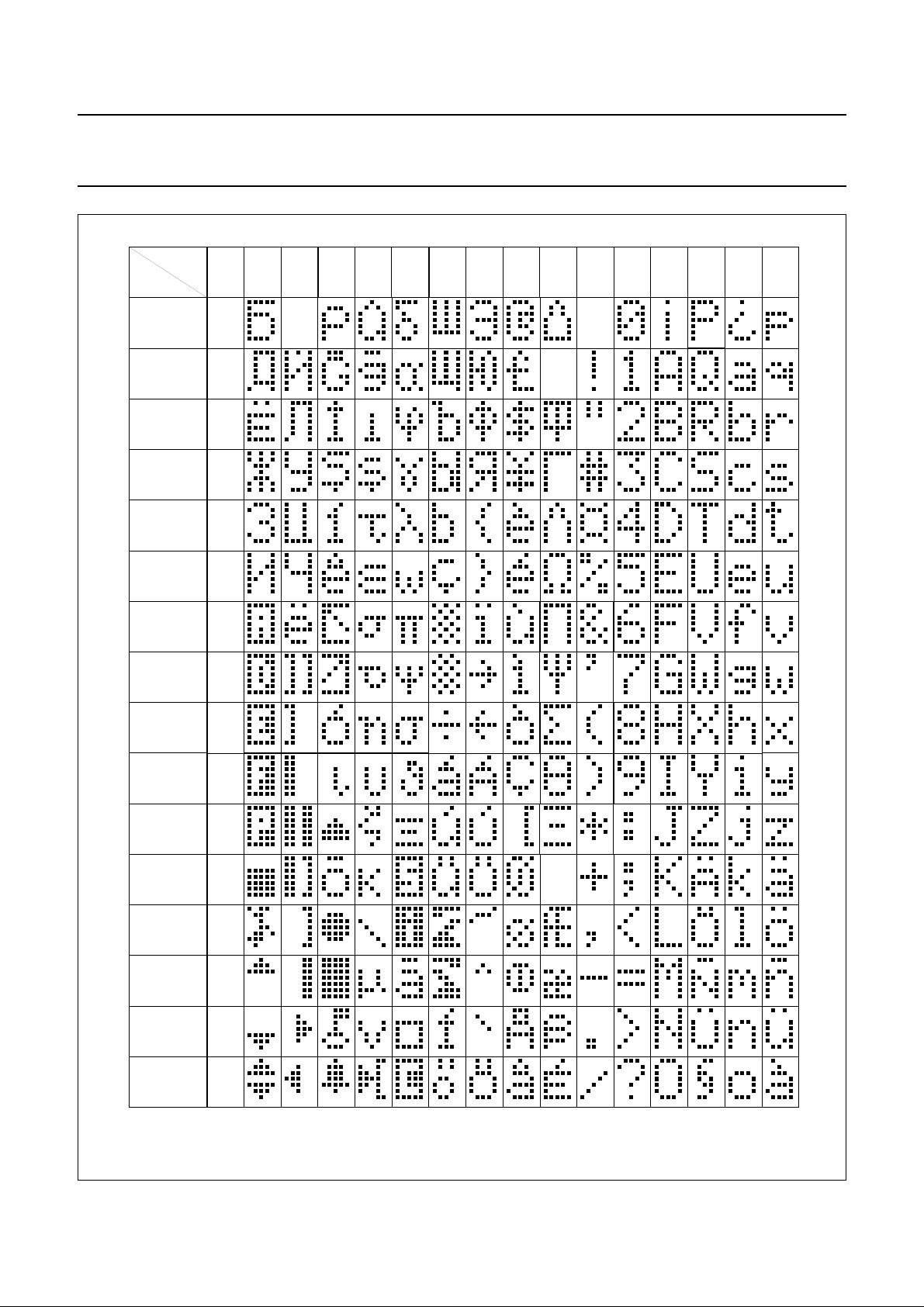
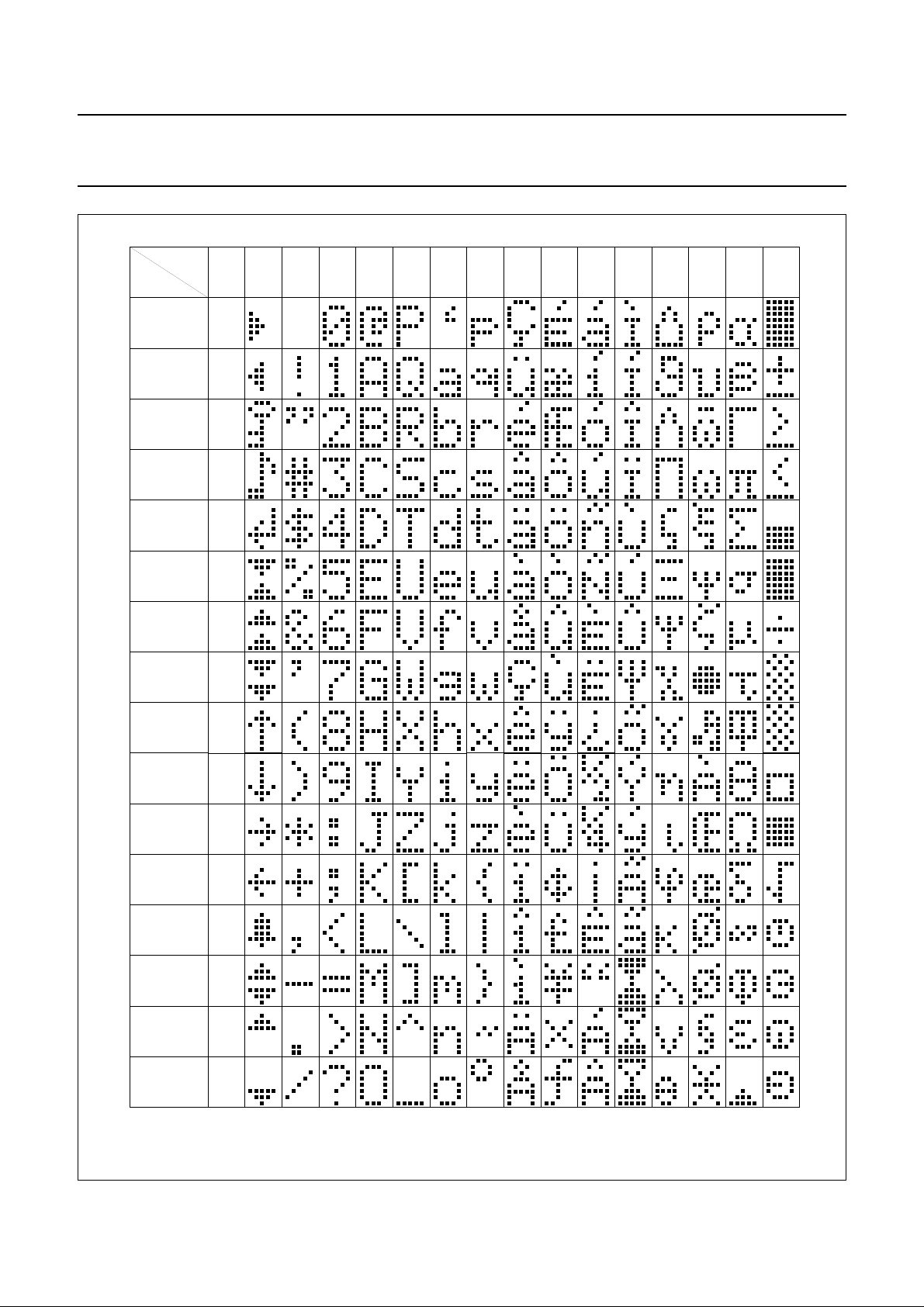
7.11 Character Generator ROM (CGROM)
The CGROM generates 240 character patterns in a
5 × 8 dot format from 8-bit character codes.
Figures 7, 8, 9 and 10 show the character sets that are
currently implemented.
7.12 Character Generator RAM (CGRAM)
Up to 16 user defined characters may be stored in the
CGRAM. Some CGRAM characters (see Fig.16) are also
used to drive icons (6 if icons blink and both icon rows are
used in the application; 3 if no blink but both icon rows are
used in the application; 0 if no icons are driven by the icon
rows). The CGROM and CGRAM use a common address
space, of which the first column is reserved for the
CGRAM (see Fig.7). Figure 11 shows the addressing
principle for the CGRAM.
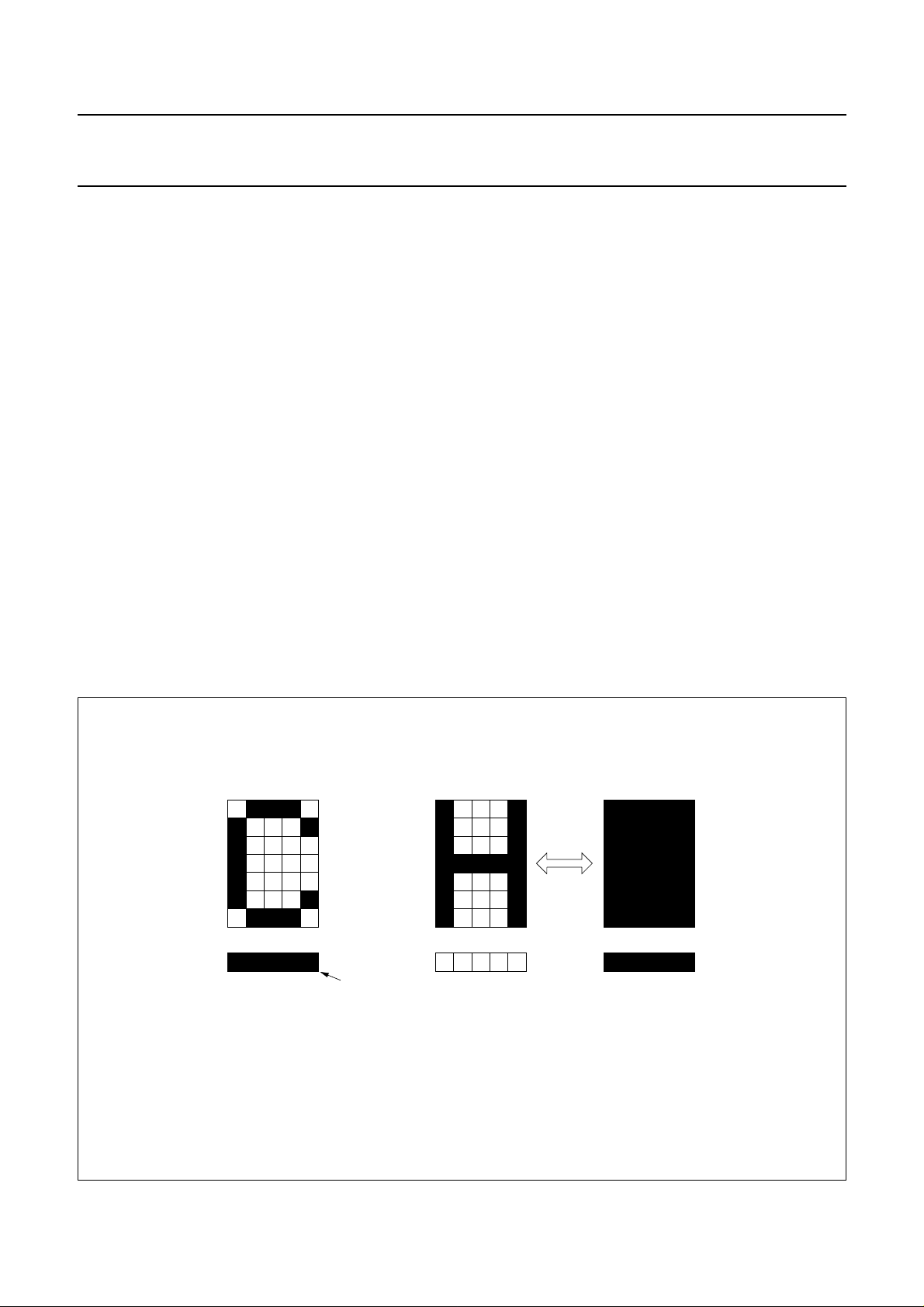
7.13 Cursor control circuit
The cursor control circuit generates the cursor underline
and/or cursor blink as shown in Fig.6 at the DDRAM
address contained in the address counter.
When the address counter contains the CGRAM address
the cursor will be inhibited.
7.14 Timing generator
The timing generator produces the various signals
required to drive the internal circuitry. Internal chip
operation is notdisturbed by operations on thedata buses.
7.15 LCD row and column drivers
The PCF2113x contains 18 row and 60 column drivers,
which connect the appropriate LCD bias voltages in
sequence to the display in accordance with the data to be
displayed. R17 and R18 drive the icon rows.
The bias voltages and the timing are selected
automatically when the number of lines in the display is
selected. Figures 12, 13, 14 and 15 show typical
waveforms. Unused outputs should be left unconnected.
cursor
5 x 7 dot character font alternating display
cursor display example blink display example
Fig.6 Cursor and blink display examples.
2001 Dec 19 12
MGA801
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
LCD controllers/drivers PCF2113x
handbook, full pagewidth
lower
4 bits
xxxx 0000
xxxx 0001
xxxx 0010
xxxx 0011
xxxx 0100
xxxx 0101
xxxx 0110
xxxx 0111
upper
4 bits
0000 0001 0010 0011 0100 0101 0110 0111 1000 1001 1010 1011 1100 1101 1110 1111
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
xxxx 1000
xxxx 1001
xxxx 1010
xxxx 1011
xxxx 1100
xxxx 1101
xxxx 1110
xxxx 1111 16
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
MGE994
Fig.7 Character set ‘A’ in CGROM.
2001 Dec 19 13
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
LCD controllers/drivers PCF2113x
handbook, full pagewidth
lower
4 bits
xxxx 0000
xxxx 0001
xxxx 0010
xxxx 0011
xxxx 0100
xxxx 0101
xxxx 0110
xxxx 0111
upper
4 bits
0000 0001 0010 0011 0100 0101 0110 0111 1000 1001 1010 1011 1100 1101 1110 1111
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
xxxx 1000
xxxx 1001
xxxx 1010
xxxx 1011
xxxx 1100
xxxx 1101
xxxx 1110
xxxx 1111 16
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
MGD688
Fig.8 Character set ‘D’ in CGROM.
2001 Dec 19 14
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
LCD controllers/drivers PCF2113x
handbook, full pagewidth
lower
4 bits
xxxx 0000
xxxx 0001
xxxx 0010
xxxx 0011
xxxx 0100
xxxx 0101
xxxx 0110
xxxx 0111
upper
4 bits
0000 0001 0010 0011 0100 0101 0110 0111 1000 1001 1010 1011 1100 1101 1110 1111
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
xxxx 1000
xxxx 1001
xxxx 1010
xxxx 1011
xxxx 1100
xxxx 1101
xxxx 1110
xxxx 1111 16
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
MGD689
Fig.9 Character set ‘E’ in CGROM.
2001 Dec 19 15
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
LCD controllers/drivers PCF2113x
handbook, full pagewidth
lower
4 bits
xxxx 0000
xxxx 0001
xxxx 0010
xxxx 0011
xxxx 0100
xxxx 0101
xxxx 0110
xxxx 0111
upper
4 bits
0000 0001 0010 0011 0100 0101 0110 0111 1000 1001 1010 1011 1100 1101 1110 1111
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
xxxx 1000
xxxx 1001
xxxx 1010
xxxx 1011
xxxx 1100
xxxx 1101
xxxx 1110
xxxx 1111 16
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
MGU204
Fig.10 Character set ‘W’ in CGROM.
2001 Dec 19 16
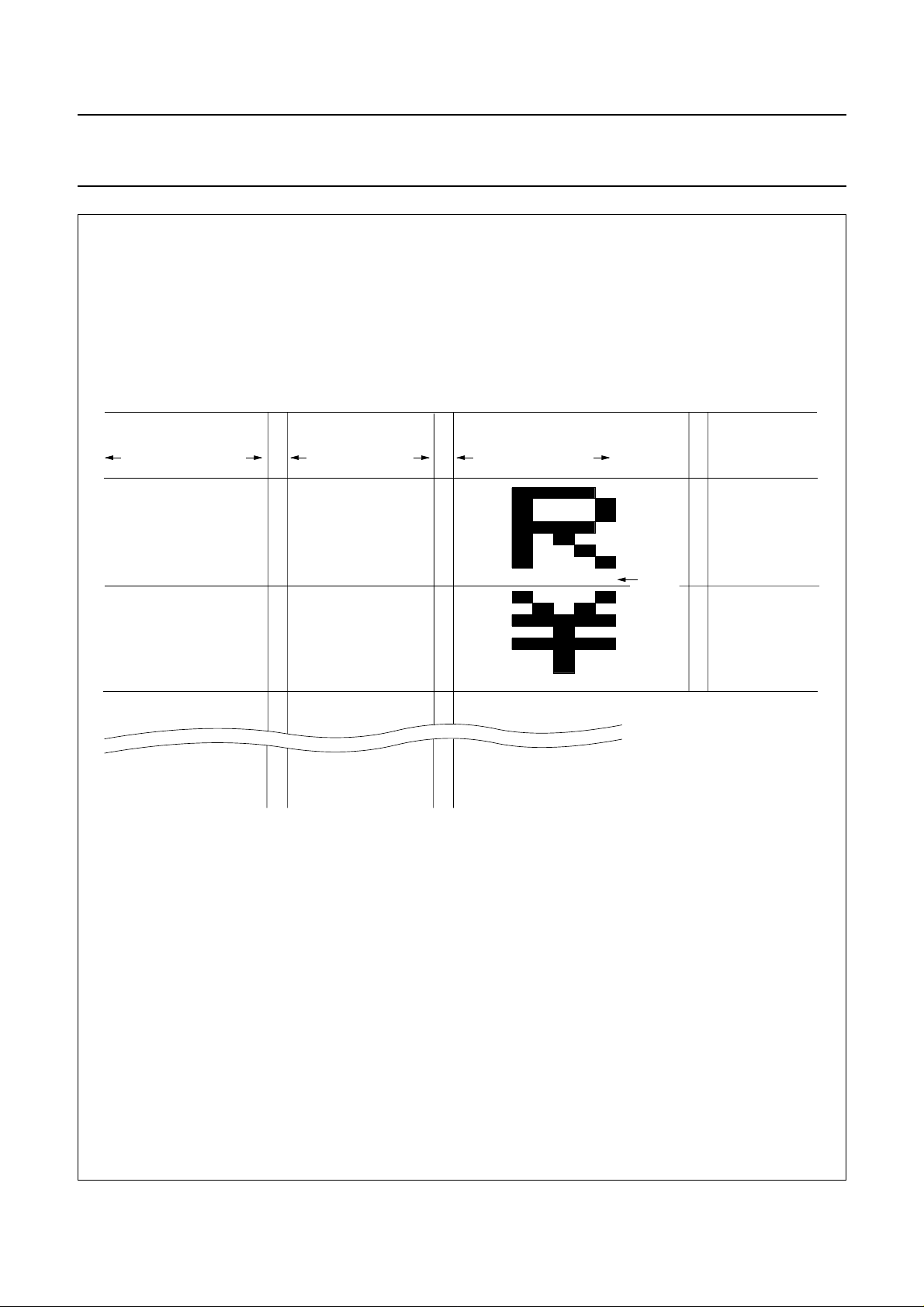
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
LCD controllers/drivers PCF2113x
handbook, full pagewidth
character codes
(DDRAM data)
76543210 6543210 43210
higher
order
bits
00000000 0000000 0
00000001 0001
00000010
00001111
00001111
00001111
00001111
lower
order
bits
CGRAM
address
higher
order
bits
010 0000
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
111
1
1
lower
order
bits
001 000
010 000
011 0
100 0 00
101 00 0
110 000
111 00000
000 000
001 0 0 0
010
100
101 00 00
110 00 00
111 00000
001
1
100
1
101
1
110
1
1
higher
order
bits
character patterns
(CGRAM data)
00 00011
lower
order
bits
character
pattern
example 1
cursor
position
character
pattern
example 2
character code
(CGRAM data)
43210
1
111
1
000
1
000
1111
0010
1
00 01
1
000
1
00
1
000
0
101
1
111
0100
1111
1
01 00
0
010
0
00
0
1
1
0
1
000
1
0
1
0
0
000
MGE995
Character code bits 0 to 3 correspond to CGRAM address bits 3 to 6.
CGRAM address bits 0 to 2 designate the character pattern line position. The 8th line is the cursor position and display is performed by logical ORwith
the cursor. Data in the 8th position will appear in the cursor position.
Character pattern column positions correspond to CGRAM data bits 0 to 4, as shown in this figure.
As shown in Figs 7 and 8, CGRAM character patterns are selected when character code bits 4 to 7 are all logic 0. CGRAM data = logic 1 corresponds
to selection for display.
Only bits 0 to 5 of the CGRAM address are set by the ‘set CGRAM address’ command. Bit 6 can be set using the ‘set DDRAM address’ command in
the valid address range or by using the auto-increment feature during CGRAM write. All bits 0 to 6 can be read using the ‘read busy flag’ and ‘address
counter’ command.
Fig.11 Relationship between CGRAM addresses, data and display patterns.
2001 Dec 19 17
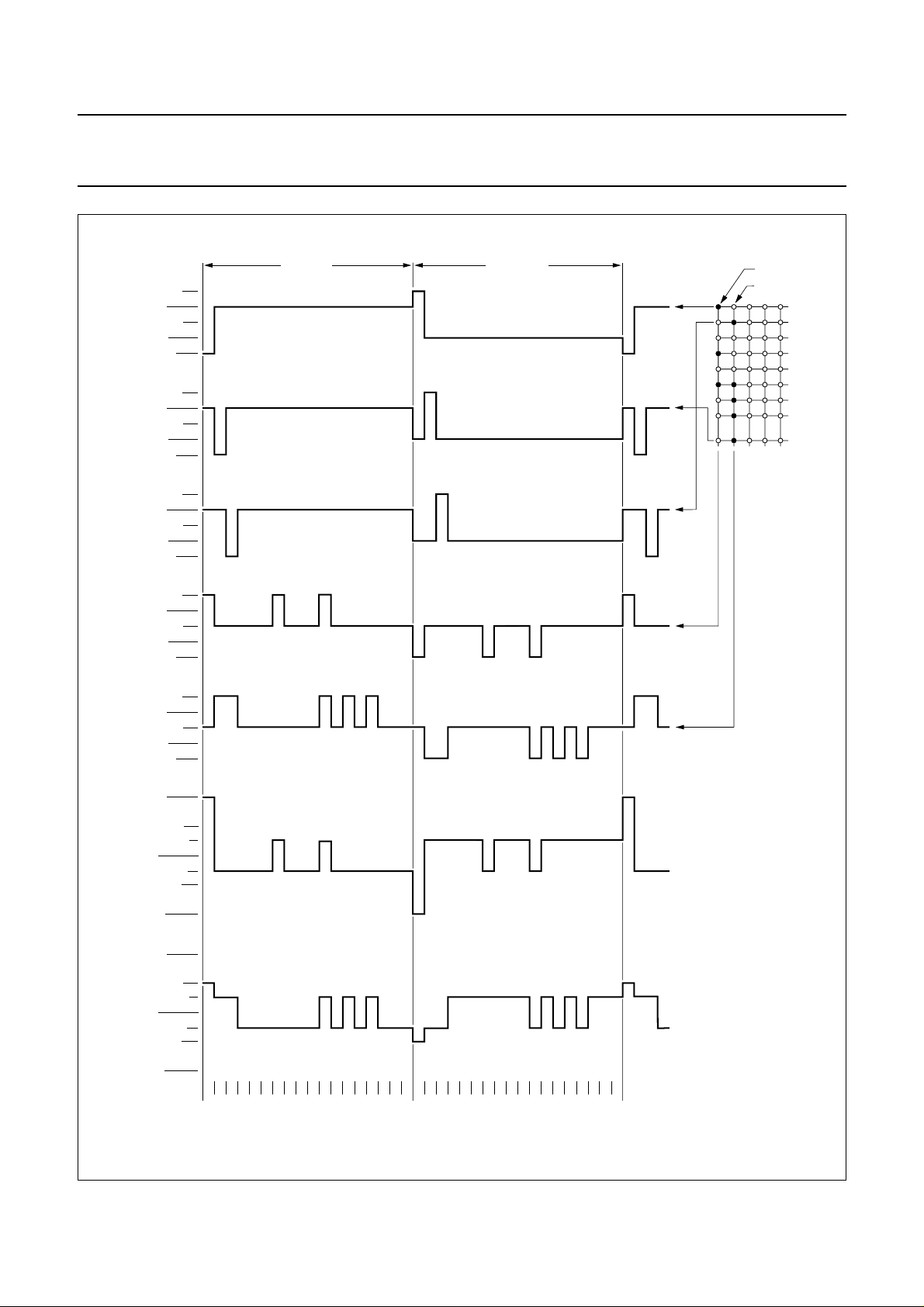
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
LCD controllers/drivers PCF2113x
handbook, full pagewidth
V
LCD
V
2
ROW 1
ROW 9
ROW 2
COL1
COL2
V3/V
V
5
V
SS
V
LCD
V
2
V3/V
V
5
V
SS
V
LCD
V
2
V3/V
V
5
V
SS
V
LCD
V
2
V3/V
V
5
V
SS
V
LCD
V
2
V3/V
V
5
V
SS
frame n + 1 frame n
state 1 (ON)
state 2 (OFF)
R1
4
R2
R3
R4
R5
R6
R7
R8
4
R9
4
4
4
V
OP
0.5V
OP
0.25V
OP
0 V
state 1
−0.25V
OP
−0.5V
OP
−V
OP
V
OP
0.5V
OP
0.25V
OP
0 V
state 2
−0.25V
OP
−0.5V
OP
−V
OP
123 18123 18
Fig.12 MUX 1 : 18 LCD waveforms; character mode.
2001 Dec 19 18
MGE996
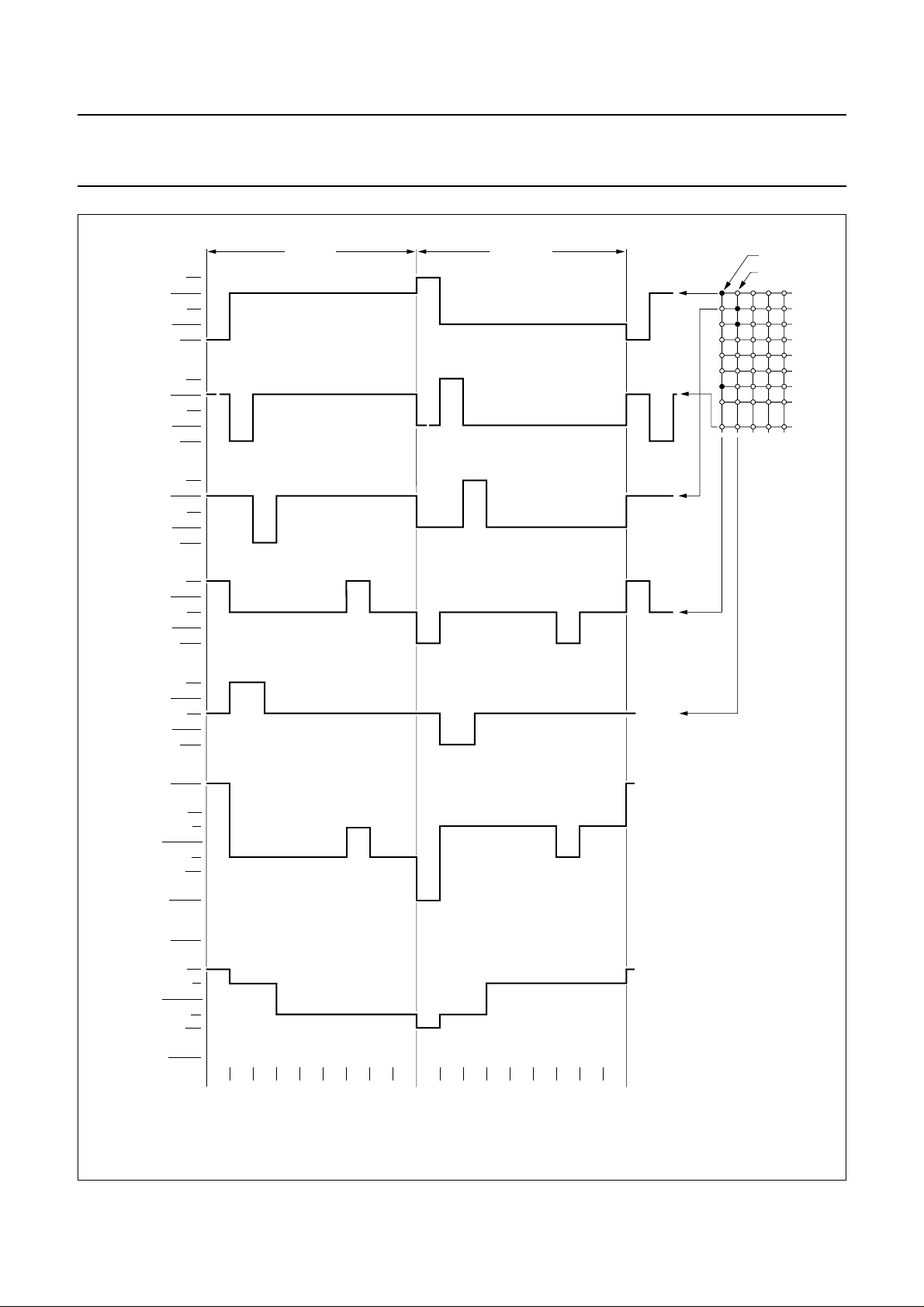
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
LCD controllers/drivers PCF2113x
handbook, full pagewidth
V
LCD
V
2
ROW 1
ROW 2
ROW 3
COL1
COL2
V3/V
V
5
V
SS
V
LCD
V
2
V3/V
V
5
V
SS
V
LCD
V
2
V3/V
V
5
V
SS
V
LCD
V
2
V3/V
V
5
V
SS
V
LCD
V
2
V3/V
V
5
V
SS
frame n + 1 frame n
state 1 (ON)
state 2 (OFF)
R1
4
R2
R3
R4
R5
R6
R7
R8
4
R9
4
4
4
V
OP
0.5V
OP
0.25V
OP
0 V
state 1
−0.25V
OP
−0.5V
OP
−V
OP
V
OP
0.5V
OP
0.25V
OP
0 V
state 2
−0.25V
OP
−0.5V
OP
−V
OP
123 9123 9
R10 to R18 to be left open.
Fig.13 MUX1:9LCD waveforms; character mode.
2001 Dec 19 19
MGU217
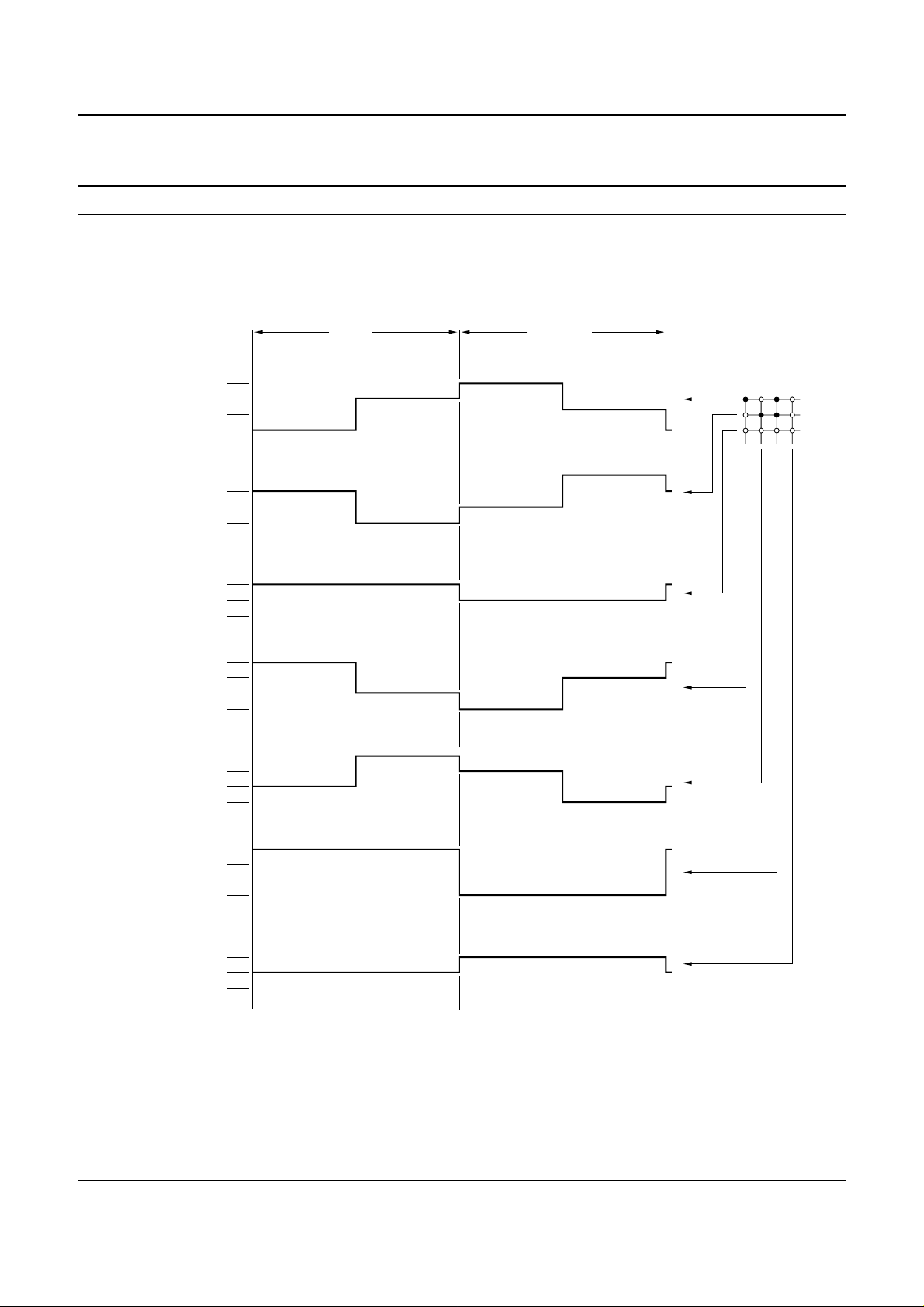
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
LCD controllers/drivers PCF2113x
handbook, full pagewidth
ROW 17
ROW 18
ROW 1 to 16
COL 1
ON/OFF
COL 2
OFF
/ON
V
V
V
V
V
LCD
2/3
1/3
V
SS
LCD
2/3
1/3
V
SS
LCD
2/3
1/3
V
SS
LCD
2/3
1/3
V
SS
LCD
2/3
1/3
V
SS
frame n + 1 frame n
only icons are
driven (MUX 1 : 2)
V
LCD
V
2/3
1/3
V
SS
LCD
2/3
1/3
V
SS
COL 3
COL 4
ON/ON
OFF/OFF
Fig.14 MUX 1 : 2 LCD waveforms; icon mode.
2001 Dec 19 20
MGE997
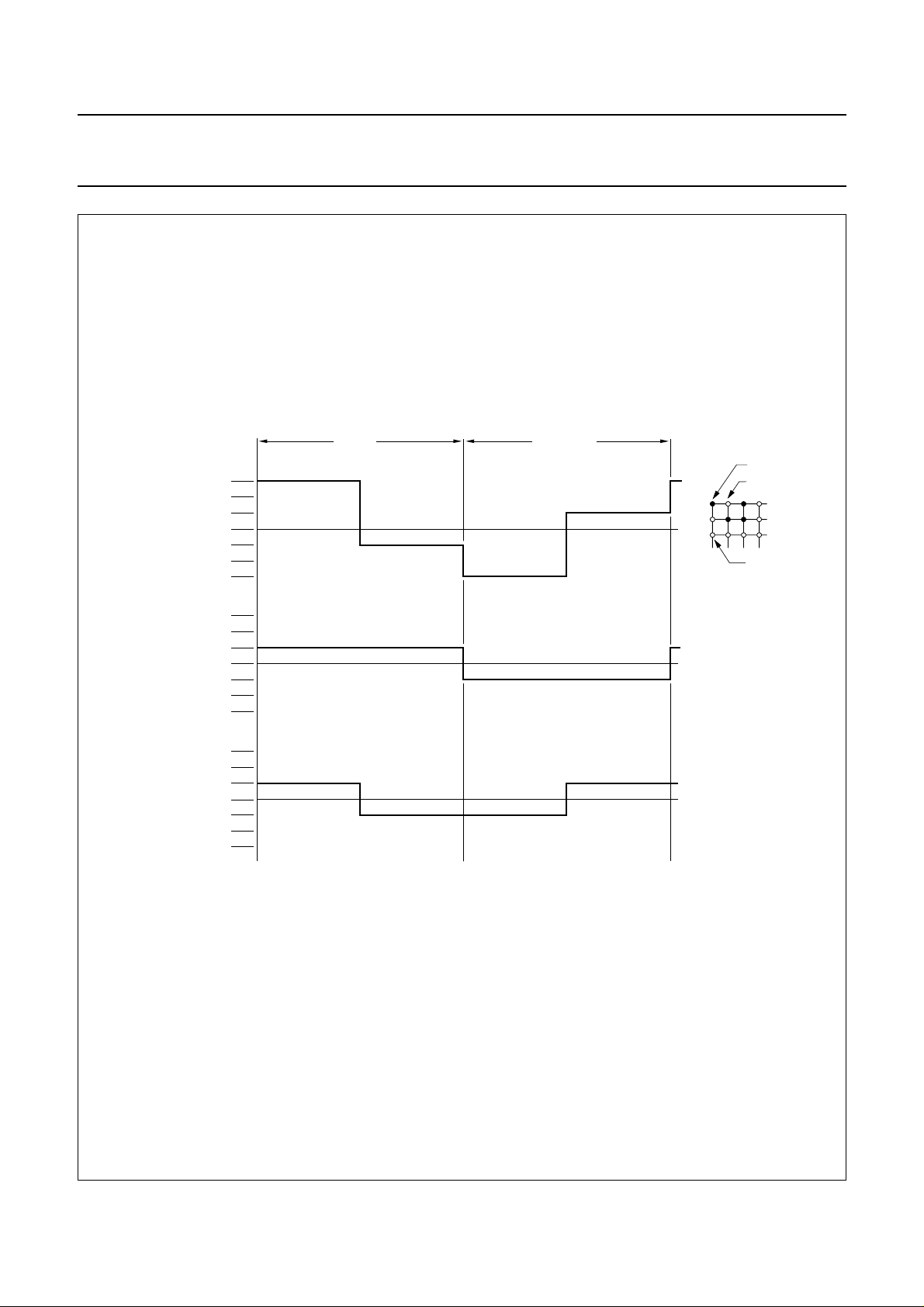
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
LCD controllers/drivers PCF2113x
handbook, full pagewidth
state 1
COL 1 -
ROW 17
state 2
COL 2 -
ROW 17
state 3
COL 1 -
ROW 1 to 16
V
PIXEL
2/3 V
1/3 V
−1/3 V
−2/3 V
−V
2/3 V
1/3 V
−1/3 V
−2/3 V
−V
2/3 V
1/3 V
−1/3 V
−2/3 V
−V
frame n + 1 frame n
state 1 (ON)
V
OP
OP
OP
0
state 2 (OFF)
R17
R18
R1-16
OP
OP
state 3 (OFF)
OP
V
OP
OP
OP
0
OP
OP
OP
V
OP
OP
OP
0
OP
OP
OP
MGE998
V
= 0.745V
ON(rms)
V
OFF(rms)
D
V
ON
------------V
OFF
= 0.333V
2.23==
OP
OP
Fig.15 MUX 1 : 2 LCD waveforms; icon mode.
2001 Dec 19 21
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
LCD controllers/drivers PCF2113x
7.16 Reset function
The PCF2113x automatically initializes (resets) when power is turned on. The chipexecutes a reset sequence, including
a ‘clear display’, requiring 165 oscillator cycles. After the reset the chip has the state shown in Table 3.
Table 3 State after reset
STEP FUNCTION CONTROL BIT STATE CONDITIONS
1 clear display
2 entry mode set I/D = 1 +1 (increment)
S = 0 no shift
3 display control D = 0 display off
C = 0 cursor off
B = 0 cursor character blink off
4 function set DL = 1 8-bit interface
M = 0 1-line display
H = 0 normal instruction set
SL = 0 MUX 1 : 18 mode
5 default address pointer to DDRAM; the Busy Flag (BF) indicates the busy state (BF = 1) until
initialization ends; the busy state lasts 2 ms; the chip may also be initialized by software;
see Tables 17 and 18
6 icon control IM = 0; IB = 0; DM = 0 icons, icon blink and direct
mode disabled
7 display/screen configuration L = 0; P = 0; Q = 0 default configurations
8V
9 set V
10 I
11 Set HVgen stages S1 = 1; S0 = 0 V
temperature coefficient TC1 = 0; TC2 = 0 default temperature coefficient
LCD
LCD
2
C-bus interface reset
VA= 0; VB=0 V
generator off
LCD
generator voltage
LCD
multiplier set at factor 4
2001 Dec 19 22

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
LCD controllers/drivers PCF2113x
8 INSTRUCTIONS
OnlytwoPCF2113x registers, the Instruction Register (IR)
and the Data Register (DR) can be directly controlled by
the microcontroller. Before internal operation, control
information is stored temporarily in these registers, to
allow interfacing to various types of microcontrollers which
operate at different speeds or to allow interface to
peripheral control ICs.
The instruction set for I2C-bus commands is given in
Table 4.
The PCF2113x operation is controlled by the instructions
shown in Table 5 together with their execution time.
Details are explained in subsequent sections.
Instructions are of 4 types, those that:
1. Designate PCF2113x functions such as display
format, data length, etcetera.
2. Set internal RAM addresses
3. Perform data transfer with internal RAM
4. Others.
2
Table 4 Instruction set for I
CONTROL BYTE COMMAND BYTE I
CoRS000000DB7DB6DB5DB4DB3DB2DB1DB0note 1
C-bus commands
In normal use, category 3 instructions are used most
frequently. However, automatic incrementing by 1
(or decrementing by 1) of internal RAM addresses after
each data write lessens the microcontroller program load.
The display shift in particular can be performed
concurrently with display data write, enabling the designer
to develop systems in minimum time with maximum
programming efficiency.
During internal operation, no instructions other than the
‘read busy flag’ and ‘read address’ instructions will be
executed.Because the busy flagisset to a logic 1whilean
instructionis being executed, checkto ensure it isa logic 0
before sending the next instruction or wait for the
maximum instruction execution time, as given in Table 5.
An instruction sent while the busy flag is logic 1 will not be
executed.
2
C-BUS COMMANDS
Note
1. R/
W is set together with the slave address.
2001 Dec 19 23

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
LCD controllers/drivers PCF2113x
CLOCK
REQUIRE
CYCLES
3
lines (M), single line/MUX 1 : 9 (SL) and extended
instruction set control (H)
0
) contents
C
reads the Busy Flag (BF) indicating internal
operating is being performed and reads Address
counter (A
3
165
returns shifted display to original position; DDRAM
address counter
3
contents remain unchanged
3
of display (S); these operations are performed
during data write and read
blink of cursor position character (B); D = 0 (display
off) puts chip into the Power-down mode
3
(R/L) without changing DDRAM contents
3
sets CGRAM address; bit DB6 is to be set by the
command ‘set DDRAM address’; look at the
description of the commands
sets DDRAM address 3
This text is here in white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here in
_white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here inThis text is here in
white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader. white to force landscape pages to be ...
Table 5 Instruction set with parallel bus commands
2001 Dec 19 24
INSTRUCTION RS R/W DB7 DB6 DB5 DB4 DB3 DB2 DB1 DB0 DESCRIPTION
H=0or1
NOP 0000000000no operation 3
CG
C
000001S/CR/L00moves cursor or shifts display (S/C) to right or left
Cursor/display
shift
0001 A
Set CGRAM
0 1 BF A
Read data 1 1 read data reads data from CGRAM or DDRAM 3
Write data 1 0 write data writes data from CGRAM or DDRAM 3
Function set 00001DL0MSLHsets interface Data Length (DL), number of display
Read busy flag
and address
counter
H=0
Return home 0000000010sets DDRAM address 0 in address counter; also
Clear display 0000000001clears entire display and sets DDRAM address 0 in
Entry mode set 00000001I/DSsets cursor move direction (I/D) and specifies shift
Display control 0000001DCBsets entire display on/off (D), cursor on/off (C) and
address
DD
001 A
Set DDRAM
address

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
LCD controllers/drivers PCF2113x
CLOCK
REQUIRE
CYCLES
3
Direct Mode (DM)
3
generator voltage multiplier stages
LCD
(S1 = 1 and S0 = 1 not allowed)
(V) 3
B
or V
A
in register V
LCD
W DB7 DB6 DB5 DB4 DB3 DB2 DB1 DB0 DESCRIPTION
INSTRUCTION RS R/
This text is here in white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here in
_white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here inThis text is here in
white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader. white to force landscape pages to be ...
2001 Dec 19 25
H=1
Reserved 0000000001do not use −
000000001Lset screen configuration (L) 3
Screen
configuration
00000001PQset display configuration, columns (P) and rows (Q) 3
Display
configuration
Icon control 0000001IMIBDMset Icon Mode (IM), Icon Blink (IB),
00000100TC1TC2set Temperature Coefficient (TCx) 3
Temperature
control
0 0 1 V voltage store V
LCD
Set V
Set HVgen stages 00010000S1S0setinternal V

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
LCD controllers/drivers PCF2113x
Table 6 Explanations of symbols used in Tables 4 and 5.
BIT LOGIC STATE 0 LOGIC STATE 1
Co last control byte; see Table 4 another control byte follows after data/command
DL 4 bits 8 bits
M (noimpact,
if SL = 1)
SL MUX 1 : 18 (1 × 24 or 2 × 12 character display) MUX1:9 (1×12 character display)
H use basic instruction set use extended instruction set
I/D decrement increment
S display freeze display shift
D display off display on
C cursor off cursor on
B cursor character blink off; character at cursor
S/C cursor move display shift
R/L left shift right shift
L (no impact,
if M = 1 or
SL = 1)
P column data: left to right; column data is displayed
Q row data; top to bottom; rowdata is displayedfrom
IM character mode; full display icon mode; only icons displayed
IB icon blink disabled icon blink enabled
DM direct mode disabled direct mode enabled
V set V
1-line by 24 display 2-line by 12 display
cursor character blink on; character at cursor
position does not blink
position blinks
left/right screen: standard connection left/right screen; mirrored connection
1st 12 characters of 24; columns are from 1 to 60 1st 12 characters of 24; columns are from 1 to 60
2nd 12 characters of 24; columns are from 1 to 60 2nd 12 characters of 24; columns are from 60 to 1
column data; right to left; column data is displayed
from 1 to 60
from 60 to 1
row data; bottom to top; row data is displayed
1 to 16 and icon row data is in 17 and 18
A
from 16 to 1 and icon row data is in 18 and 17
set V
B
8.1 Clear display
‘Clear display’ writes character code 20H into all DDRAM
addresses (the character pattern for character code 20H
must be a blank pattern), sets the DDRAM address
counter to logic 0 and returns the display to its original
position, if itwas shifted. Thus, the displaydisappears and
the cursor or blink position goes to the left edge of the
display. Sets entry mode I/D = 1 (increment mode). S of
entry mode does not change.
The instruction ‘clear display’ requires extra execution
time. This may be allowed by checkingthe Busy Flag (BF)
or by waiting until the 165 clock cycles have elapsed.
The lattermust be applied wherenoread-back options are
foreseen, as in some Chip-On-Glass (COG) applications.
2001 Dec 19 26
8.2 Return home
‘Return home’ sets the DDRAM address counterto logic 0
and returns the display to its original position if it was
shifted. DDRAM contents do not change. The cursor or
blink position goes to the left of the first display line.
I/D and S of entry mode do not change.

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
LCD controllers/drivers PCF2113x
8.3 Entry mode set
8.3.1 BIT I/D
When I/D = 1 (0) the DDRAM or CGRAM address
increments (decrements) by 1 when data is written into or
read from the DDRAM or CGRAM. The cursor or blink
position moves to the right when incremented and to the
left when decremented. The cursor underline and cursor
character blink are inhibited when the CGRAM is
accessed.
8.3.2 BIT S
When S = 1, the entire display shifts either to the right
(I/D = 0)orto the left (I/D = 1) duringaDDRAMwrite. Thus
it appears as if the cursor stands still and the display
moves. The display does not shift when reading from the
DDRAM, or when writing to or reading from the CGRAM.
When S = 0, the display does not shift.
8.4 Display control (and partial Power-down mode)
8.4.1 BIT D
The display is on when D = 1 and off when D = 0. Display
data in the DDRAM is not affected and can be displayed
immediately by setting D = 1.
8.4.3 BIT B
The character indicated by the cursor blinks when B = 1.
The cursor character blink is displayed by switching
between display characters andall dots onwith a period of
f
approximately 1 second, with
f
blink
=
OSC
---------------- 52224
Thecursor underline andthe cursor character blinkcan be
set to display simultaneously.
8.5 Cursor or display shift
‘Cursor/display shift’ moves the cursor position or the
display to the right or left without writing or reading display
data. This function is used to correct a character or move
the cursor through the display. In 2-line displays, the
cursor moves to the next line when it passes the last
position (40)of the line.When the displayed datais shifted
repeatedly all lines shift at the same time; displayed
characters do not shift into the next line.
The Address Counter (AC) content does not change if the
only action performed is shift display, but increments or
decrements with the ‘cursor display shift’.
8.6 Function set
When the display is off (D = 0) the chip is in partial
Power-down mode:
• The LCD outputs are connected to V
SS
• The LCD generator and bias generator are turned off.
Three oscillator cycles are required after sending the
‘display off’ instruction to ensure all outputs are at VSS,
afterwards the oscillator can be stopped. If the oscillator is
running during partial Power-down mode (‘display off’) the
chip can still execute instructions. Even lower current
consumption is obtained by inhibiting the oscillator
(OSC = VSS).
To ensure IDD<1µA, the parallel bus pins DB7 to DB0
should be connected to VDD; pins RS and R/W to VDD or
left open-circuit and pin PD to VDD. Recovery from
Power-down mode: PD back to VSS, if necessary pin OSC
back to VDD and send a ‘display control’ instruction with
D=1.
8.4.2 BIT C
The cursor is displayed when C = 1 and inhibited when
C = 0. Even if the cursor disappears, the display functions
I/D,etcetera, remain in operationduringdisplay data write.
The cursor is displayed using 5 dots in the 8th line (see
Fig.6).
8.6.1 B
IT DL (PARALLEL MODE ONLY)
Sets interface data width. Data is sent or received in bytes
(DB7 to DB0) when DL = 1 or in two nibbles (DB7 to DB4)
when DL = 0. When 4-bit width is selected, data is
transmitted in two cycles using the parallel bus. In a 4-bit
applicationDB3 to DB0shouldbeleftopen-circuit(internal
pull-ups). Hence in the first ‘function set’ instruction after
power-on M, SL and H are set to logic 1. A second
‘function set’ must then be sent (2 nibbles) to set M,
SL and H to their required values.
‘Function set’ from the I2C-bus interface sets the DL bit to
logic 1.
8.6.2 BIT M
Selects either 1-line by 24 display (M = 0) or 2-line by
12 display (M = 1).
8.6.3 BIT SL
Selects MUX 1 : 9, 1-line by 12 display (independent of
M and L). Only rows 1 to 8and 17 are tobe used. All other
rows must be left open-circuit. The DDRAM map is the
same as in the 2-line by 12 display mode, however, the
second line cannot be displayed.
2001 Dec 19 27

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
LCD controllers/drivers PCF2113x
8.6.4 BIT H
When H = 0 the chip can be programmed via the standard
11 instruction codes used in the PCF2116 and other LCD
controllers.
When H = 1 the extended range of instructions will be
used. These are mainly for controlling the display
configuration and the icons.
8.7 Set CGRAM address
‘Set CGRAM address’ sets bits DB5 to 0 of the CGRAM
address ACG into the address counter (binary A5 to A0).
Data can then be written to or read from the CGRAM.
Attention: the CGRAM address uses the same address
register as the DDRAM address and consists of 7 bits
(binary A6 to A0). With the ‘set CGRAM address’
command, only bits DB5 to DB0 are set. Bit DB6 can be
set using the ‘set DDRAM address’ command first, or by
using the auto-increment feature during CGRAM write. All
bits DB6 to DB0can be read usingthe ‘read busy flag’and
‘read address’ command.
When writing to the lower part of the CGRAM, ensure that
bit DB6of the address is notset(e.g.by an earlier DDRAM
write or read action).
8.8 Set DDRAM address
‘Set DDRAM address’ sets the DDRAM address ADD into
the address counter (binary A6 to A0). Data can then be
written to or read from the DDRAM.
8.9 Read busy flag and read address
8.10 Write data to CGRAM or DDRAM
‘Write data’ writes binary 8-bit data DB7 to DB0 to the
CGRAM or the DDRAM.
Whether the CGRAM or DDRAM is to be written into is
determined by the previous ‘set CGRAM address’ or ‘set
DDRAM address’ command. After writing, the address
automatically increments or decrements by 1, in
accordance with the entry mode. Only bits DB4 to DB0 of
CGRAM data are valid, bits DB7 to DB5 are ‘don’t care’.
8.11 Read data from CGRAM or DDRAM
‘Read data’ reads binary 8-bit data DB7 to DB0 from the
CGRAM or DDRAM.
The most recent ‘set address’ command determines
whether the CGRAM or DDRAM is to be read.
The ‘read data’ instruction gates the content of the Data
Register (DR) to the bus while pin E is HIGH. After pin E
goes LOW again, internal operation increments (or
decrements) the AC and stores RAM data corresponding
to the new AC into the DR.
There are only three instructions that update the data
register:
• ‘Set CGRAM address’
• ‘Set DDRAM address’
• ‘Read data’ from CGRAM or DDRAM.
Other instructions (e.g. ‘write data’, ‘cursor/display shift’,
‘clear display’ and ‘return home’) do not modify the data
register content.
‘Read busy flag and address counter’ read the Busy Flag
(BF) and Address Counter (AC). BF = 1 indicates that an
internal operation is in progress. The next instruction will
not be executed until BF = 0. It is recommended that the
BF status is checked before the next write operation is
executed.
At the same time, the value of the address counter
expressed in binary A6 to A0 is read out. The address
counter is used by both CGRAM and DDRAM, and its
value is determined by the previous instruction.
2001 Dec 19 28
9 EXTENDED FUNCTION SET INSTRUCTIONS AND
FEATURES
9.1 New instructions
H = 1 sets the chip into alternate instruction set mode.
9.2 Icon control
The PCF2113x can drive up to 120 icons. See Fig.16 for
CGRAM to icon mapping.

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
LCD controllers/drivers PCF2113x
handbook, full pagewidth
handbook, full pagewidth
icon no. phase ROW/COL character codes CGRAM address CGRAM data
1-5 even 17/1-5 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 1
6-10 even 17/6-10 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 0
11-15 even 17/11-15 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 1 1 0
56-60 even 17/56-60 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
display:
ROW 17 –
ROW 18 –
COL 1 to 5
12345
61 62 63 64 65
block of 5 columns
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
MSB LSB LSB
COL 6 to 10
678910
66 67 68 69 70
6 5 4 3 2 1 0 4 3 2 1 0
MSB MSBLSB
COL 56 to 60
56 57 58 59 60
116 117 118 119 120
MGE999
icon view
61-65 even 18/1-5 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 0
116-120 even 18/56-60 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1
1-5 odd (blink) 17/1-5 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
116-120 odd (blink) 18/56-60 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0
CGRAM data bit = logic 1 turns the icon on, data bit = logic 0 turns the icon off.
Data in character codes 0 to 3 define the icon state when icon blink is disabled or during the even phase when icon blink is enabled.
Data in character codes 4 to 7 define the icon state during the odd phase when icon blink is enabled (not used for icons when icon blink is disabled).
0 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 0
MGG001
Fig.16 CGRAM to icon mapping.
2001 Dec 19 29

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
LCD controllers/drivers PCF2113x
9.3 Bit IM
When IM = 0, the chip is in character mode. In the
character mode characters and icons are driven
(MUX 1 : 18). The V
V
voltage programmed in register VA.
LCD
generator, if used, produces the
LCD
When IM = 1, the chip is in icon mode. In the icon mode
only the icons are driven (MUX 1 : 2) and the V
generator, if used, produces the V
voltage as
LCD
LCD
programmed in register VB.
Table 7 Normal/icon mode operation
IM MODE V
0 character mode generates V
1 icon mode generates V
LCD
A
B
9.4 Bit IB
Icon blink control is independent of the cursor/character
blink function.
When IB = 0, the icon blink is disabled. Icon data is stored
in CGRAM character 0 to 2 (3 × 8 × 5 = 120 bits for
120 icons).
When IB = 1, the icon blink is enabled. In this case each
icon is controlled by two bits. Blink consists of two half
phases (corresponding to the cursor on and off phases
called even and odd phases hereafter).
Icon states for the even phase are stored in CGRAM
characters 0 to 2 (3 × 8 × 5 = 120 bits for 120 icons).
These bits also define icon state when icon blink is not
used (see Table 9).
Icon states for the odd phase are stored in CGRAM
character4 to 6(another 120 bits for the 120 icons). When
icon blink is disabled CGRAM characters 4 to 6 may be
used as normal CGRAM characters.
WhenDM = 1, the chipis in direct mode.The internal V
generator is turned off and the V
connected to the V
generator supply voltage V
LCD
output is directly
LCD2
DD2
LCD
.
The direct mode can be used to reduce the current
consumption when the required V
close to the V
supply voltage. This can be the case in
DD2
output voltage is
LCD2
icon mode or in Mux 1:9 (depending on LCD liquid
properties).
9.6 Voltage multiplier control
Bits S1 and S0
A software configurable voltage multiplier is incorporated
in the V
generator and can be set via the ‘Set HVgen
LCD
stages’ command.
The voltage multiplier control can be used to reduce
current consumption by disconnecting internal voltage
multiplier stages, depending on the required V
LCD
output
voltage (see Table 8).
Table 8 S1 and S0 control of voltage multiplier
S1 S0 DESCRIPTION
0 0 set V
generator stages to 1
LCD
(2 x voltage multiplier)
0 1 set V
generator stages to 2
LCD
(3 x voltage multiplier)
1 0 set V
generator stages to 3
LCD
(4 x voltage multiplier)
1 1 do not use
9.7 Screen configuration
Bit L
L = 0: the two halves of a split screen are connected in a
standard way i.e. column 1/61, 2/62 to 60/120; default.
9.5 Direct mode
When DM = 0, thechip is notin the direct mode. Eitherthe
internal V
used to achieve V
generator or an external voltage may be
LCD
.
LCD
L = 1: the two halves of a split screen are connected in a
mirrored way i.e. column 1/120, 2/119 to 60/61. This
allows single layer PCB or glass layout.
Table 9 Blink effect for icons and cursor character blink
PARAMETER EVEN PHASE ODD PHASE
Cursor character blink block (all on) normal (display character)
Icons state 1; CGRAM character 0 to 2 state 2; CGRAM character 4 to 6
2001 Dec 19 30

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
LCD controllers/drivers PCF2113x
9.8 Display configuration
Bit P
P = 0: default.
P = 1: mirrors the column data.
Bit Q
Q = 0: default.
Q = 1: mirrors the row data.
9.9 Temperature control
Default is TC1 = 0 and TC2 = 0. Selects the default
temperature coefficient for the internally generated V
(see Table 10).
The ranges for TC are given in Chapter 13.
Table 10 TC1 and TC2 selection of V
temperature
LCD
coefficient
TC1 TC2 DESCRIPTION
00V
10V
01V
11V
9.10 Set V
TheV
LCD
valueisprogrammed by instruction. Two on-chip
LCD
registers, VAand VBhold V
temperature coefficient 0
LCD
temperature coefficient 1
LCD
temperature coefficient 2
LCD
temperature coefficient 3
LCD
values for the character
LCD
mode and the icon mode respectively. The generated
V
value is independent of VDD, allowing battery
LCD
operation of the chip.
LCD
V
programming:
LCD
1. Send ‘function set’ instruction with H = 1
2. Send ‘set V
a) DB7, DB6 = 10: DB5 to DB0 are V
’ instruction to write to voltage register:
LCD
of character
LCD
mode (VA)
b) DB7, DB6 = 11: DB5 to DB0 are V
LCD
of icon
mode (VB)
c) DB5 to DB0 = 000000 switches V
generator off
LCD
(when selected)
d) During ‘display off’ and power-down the V
LCD
generator is also disabled.
3. Send ‘function set’ instruction with H = 0 to resume
normal programming.
9.11 Reducing current consumption
Reducing current consumption can be achieved by one of
the options given in Table 11.
When V
lies outside the VDD range and must be
LCD
generated, it is usually more efficient to use the on-chip
generator than an external regulator.
Table 11 Reducing current consumption
ORIGINAL MODE ALTERNATIVE MODE
Character mode Icon mode (control bit IM)
Display on Display off (control bit D)
V
generator operating Direct mode
LCD
Any mode power-down (PD pin)
2001 Dec 19 31

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
LCD controllers/drivers PCF2113x
10 INTERFACES TO MICROCONTROLLER
10.1 Parallel interface
ThePCF2113xcansenddataineithertwo 4-bit operations
or one 8-bit operation and can thus interface to 4-bit or
8-bit microcontrollers.
In 8-bit mode data is transferred as 8-bit bytes using the
8 data lines DB7 to DB0. Three further control lines E,
RS and R/W are required (see Chapter 6).
In 4-bit mode data is transferred in two cycles of 4 bits
each using pins DB7 to DB4 for the transaction.
The higher order bits (corresponding to DB7 to DB4 in
8-bit mode) are sent in the first cycle and the lower order
bits (DB3 to DB0 in 8-bit mode) in the second cycle. Data
transfer is completeafter two 4-bit data transfers.It should
be noted thattwo cycles are also requiredfor the busy flag
check. 4-bit operation is selected by instruction, see
Figs 17 to 19 for examples of bus protocol.
In 4-bit mode, pins DB3 to DB0 must be left open-circuit.
They are pulled up to VDD internally.
2
10.2 I
C-bus interface
The I2C-bus is for bidirectional, two-line communication
between different ICs or modules. The two lines are the
Serial Data line (SDA) and the Serial Clock Line (SCL).
Both lines must be connected to a positive supply via
pull-up resistors. Data transfer may be initiated only when
the bus is not busy.
Each byte of eight bits is followed by an acknowledge bit.
The acknowledge bit is a HIGH level signal put on the bus
by the transmitter during which time the master generates
anextraacknowledge related clock pulse. Aslavereceiver
which is addressed must generate an acknowledge after
the reception of each byte.
Also a master receiver must generate an acknowledge
after the reception of each byte that has been clocked out
of the slave transmitter.
The device that acknowledges must pull-down the SDA
line during the acknowledge clock pulse, so that the SDA
line is stable LOW during the HIGH period of the
acknowledge related clock pulse (set-up and hold times
must be taken into consideration).
RS
R/W
E
DB7
DB6
DB5
DB4
IR7 IR3 BF AC3 DR7 DR3
IR6 IR2 AC6 AC2 DR6 DR2
IR5 IR1 AC5 AC1 DR5 DR1
IR4 IR0 AC4 AC0 DR4 DR0
instruction
write
busy flag and
address counter read
data register
read
Fig.17 4-bit transfer example.
MGA804
2001 Dec 19 32

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
LCD controllers/drivers PCF2113x
RS
R/W
E
internal
DB7
IR7, IR3: instruction 7th, 3rd bit.
AC3: address counter 3rd bit.
D7, D3: data 7th, 3rd bit.
RS
R/W
internal operation
IR7 IR3 AC3 D7 D3
instruction
write
busy
busy flag
AC3
check
not
busy
busy flag
check
instruction
Fig.18 An example of 4-bit data transfer timing sequence.
write
MGA805
E
internal
DB7
data busy busy
instruction
write
internal operation
busy flag
check
Fig.19 Example of busy flag checking timing sequence.
2001 Dec 19 33
busy flag
check
not
busy
busy flag
check
data
instruction
write
MGA806

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
LCD controllers/drivers PCF2113x
A master receiver must signal an end of data to the
transmitter by not generating an acknowledge bit on the
last byte that has been clocked out of the slave. In this
event the transmitter must leave the data line HIGH to
enable the master to generate a STOP condition.
2
10.2.1 I
C-BUS PROTOCOL
Before any data is transmitted on the I2C-bus, the device
whichshouldrespond is addressed first. Theaddressingis
always carried out with the first byte transmitted after the
START procedure. The I2C-bus configuration for the
different PCF2113x read and write cycles is shown in
Figs 24 to 26. The slow down feature of the I2C-bus
protocol (receiver holds SCL LOW during internal
operations) is not used in the PCF2113x.
SDA
SCL
MASTER
TRANSMITTER/
RECEIVER
SLAVE
RECEIVER
TRANSMITTER/
10.2.2 D
EFINITIONS
• Transmitter: the device which sends the data to the bus
• Receiver: the device which receives the data from the
bus
• Master: the device which initiates a transfer generates
clock signals and terminates a transfer
• Slave: the device addressed by a master
• Multi-master: more than one master can attempt to
control the bus at the same time without corrupting the
message
• Arbitration: procedure to ensure that if more than one
master simultaneously tries to control the bus, only one
is allowed to do so and the message is not corrupted
• Synchronization: procedure to synchronize the clock
signals of two or more devices.
SLAVE
RECEIVER
MASTER
TRANSMITTER
MASTER
TRANSMITTER/
RECEIVER
MGA807
Fig.20 System configuration.
handbook, full pagewidth
SDA
SCL
data line
stable;
data valid
Fig.21 Bit transfer.
2001 Dec 19 34
change
of data
allowed
MBC621

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
LCD controllers/drivers PCF2113x
handbook, full pagewidth
SDA
SDA
handbook, full pagewidth
SCL
START condition
DATA OUTPUT
BY TRANSMITTER
DATA OUTPUT
BY RECEIVER
SCL FROM
MASTER
S
STOP condition
Fig.22 Definition of START and STOP conditions.
not acknowledge
S
START
condition
P
acknowledge
acknowledgement
SCL
MBC622
9821
clock pulse for
MBC602
Fig.23 Acknowledgement on the I2C-bus.
2001 Dec 19 35

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
LCD controllers/drivers PCF2113x
MGG002
A
DATA BYTE
A
update
data pointer
handbook, full pagewidth
from PCF2113x
acknowledgement
S
1 byte n ≥ 0 bytes2n ≥ 0 bytes
CONTROL BYTE
0
A
DATA BYTE
A
CONTROL BYTE
RS RS
1
0A
0
A
Co
Co
R/W
Fig.24 Master transmits to slave receiver; write mode.
0
0
S
A
R/W
This text is here in white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here in
_white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here inThis text is here in
white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader. white to force landscape pages to be ...
2001 Dec 19 36
011101
slave address
S P
PCF2113x
011101
slave address

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
LCD controllers/drivers PCF2113x
A
handbook, full pagewidth
(1)
DATA BYTE
A
1 byte n ≥ 0 bytes
CONTROL BYTE
0
A
DATA BYTE
A
Co
2n 0 bytes
P
DATA BYTE
1A DATA BYTE A 1
0
S
acknowledgement acknowledgement no acknowledgement
A
MGG003
update
data pointer
data pointer
n bytes last byte
Co update
R/W
This text is here in white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here in
_white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here inThis text is here in
white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader. white to force landscape pages to be ...
2001 Dec 19 37
CONTROL BYTE
RS RS
1
A
0
S
acknowledgement
A
011101
S
0
Co
R/W
slave address
SLAVE
ADDRESS
S
Fig.25 Master reads after setting word address; writes word address, set RS; ‘read data’.
Last data byte is a dummy byte (may be omitted).

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
LCD controllers/drivers PCF2113x
handbook, full pagewidth
S
SLAVE
ADDRESS
acknowledgement
from PCF2113x
S
A
1A DATA BYTE A 1
0
R/W
Co update
acknowledgement
from master
DATA BYTE
n bytes last byte
data pointer
no acknowledgement
from master
P
update
data pointer
MGG004
Fig.26 Master reads slave immediately after first byte; read mode (RS previously defined).
11 LIMITING VALUES
In accordance with the Absolute Maximum Rating System (IEC 60134).
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. MAX. UNIT
V
DD1
V
, V
DD2
V
LCD
V
i/o(n)
I
I
I
O
I
, ISSand I
DD
P
tot
P
O
V
es
DD3
logic supply voltage −0.5 +5.5 V
V
generator supply voltages −0.5 +4 V
LCD
LCD supply voltage −0.5 +6.5 V
voltage on
any V
any V
related input or output −0.5 VDD+ 0.5 V
DD
related input or output −0.5 V
LCD
LCD
DC input current −10 +10 mA
DC output current −10 +10 mA
LCDVDD
, VSS or V
supply current −50 +50 mA
LCD
total power dissipation − 400 mW
power dissipation per output − 100 mW
electrostatic handling voltage human body model;
− 2000 V
+ 0.5 V
C = 100 pF; R = 1.5 kΩ
electrostatic handling voltage machine model;
− 150 V
C = 200 pF; L = 0.75 µH
T
stg
storage temperature −65 +150 °C
12 HANDLING INSTRUCTIONS
Inputs and outputs are protected against electrostatic discharge in normal handling. However, to be totally safe, it is
desirable to take normal precautions appropriate to handling MOS devices (see
“Handling MOS Devices”
).
2001 Dec 19 38

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
LCD controllers/drivers PCF2113x
13 DC CHARACTERISTICS
V
= 1.8 to 5.5 V; V
DD1
DD2=VDD3
specified.
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
Supplies
V
DD1
V
DD2,VDD3VLCD
logic supply voltage note 1 1.8 − 5.5 V
generator supply
voltages
V
V
LCD
POR
LCD supply voltage 2.2 − 6.5 V
Power-on reset voltage note 1 and 2 0.9 − 1.6 V
GROUND SUPPLY CURRENT; EXTERNAL V
I
SS1
I
SS3
I
SS4
I
SS5
ground supply current 1 − 70 120 µA
ground supply current 3 VDD=3V; V
ground supply current 4 icon mode; VDD=3V;
ground supply current 5 Power-down mode;
GROUND SUPPLY CURRENT; INTERNAL V
I
SS6
I
SS8
I
SS9
ground supply current 6 − 190 400 µA
ground supply current 8 VDD=3V; V
ground supply current 9 icon mode; VDD= 2.5 V;
Logic
V
IL
V
IH
V
IL(OSC)
LOW-level input voltage V
HIGH-level input voltage 0.7V
LOW-level input voltage on
pin OSC
V
IH(OSC)
I
OL(DB)
HIGH-level voltage pin OSC V
LOW-level output current on
pins DB7 to DB0
I
OH(DB)
HIGH-level output current on
pins DB7 to DB0
I
pu
pull-up current at
pins DB7 to DB0
I
L
leakage current VI=V
= 2.2 to 4.0 V; VSS=0V;V
LCD
; note 3
internal V
(V
DD2
V
LCD
VDD=3V; V
LCD
and V
DD3<VLCD
LCD
= 2.5 V; note 4
LCD
DB7 to DB0,RS and R/W=1;
OSC = 0; PD = 1
; notes 3 and 5
LCD
LCD
V
= 2.5 V; note 4
LCD
VOL= 0.4 V; V
VOH=4V; V
VI=V
SS1
DD1
DD1
or V
= 2.2 to 6.5 V; T
LCD
generation
= −40 to +85 °C; unless otherwise
amb
2.2 − 4.0 V
)
= 5 V; note 4 − 45 80 µA
− 25 45 µA
− 25 µA
= 2.5 V;
= 5 V; note 4 − 160 400 µA
− 120 −µA
SS1
DD1
V
SS1
− 0.1 − V
DD1
= 5 V 1.6 4 − mA
DD1
− 0.3V
− V
− V
DD1
DD1
DD1
DD1
− 1.2 V
=5V −1 −8 − mA
0.04 0.15 1 µA
SS1
−1 − +1 µA
V
V
V
2001 Dec 19 39

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
LCD controllers/drivers PCF2113x
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
I2C-bus; pins SDA and SCL
V
IL
V
IH
I
LI
C
i
I
OL (SDA)
LOW-level input voltage 0 − 0.3V
HIGH-level input voltage 0.7V
input leakage current VI=V
DD1
or V
SS1
−1 − +1 µA
DD1
− 5.5 V
DD1
input capacitance note 6 − 5 − pF
LOW-level output current on
pin SDA
VOL= 0.4 V; V
V
= 0.2 V
OL
DD1
>2V 3 −− mA
DD1
; V
<2V 2 −− mA
DD1
LCD outputs
R
O(ROW)
row output resistance of
note 7 − 10 30 kΩ
pins R1 to R18
R
O(COL)
column output resistance of
note 7 − 15 40 kΩ
pins C1 to C60
V
bias(tol)
bias voltage tolerance on
note 8 − 20 130 mV
pins R1 to R18 and C1 to C60
V
LCD2(tol)
TC0 V
TC1 V
TC2 V
TC3 V
voltage tolerance T
LCD
temperature coefficient 0 −−0.16 − %/K
LCD
temperature coefficient 1 −−0.18 − %/K
LCD
temperature coefficient 2 −−0.21 − %/K
LCD
temperature coefficient 3 −−0.24 − %/K
LCD
=25°C; note 5
amb
V
<3V −−160 mV
LCD
V
<4V −−200 mV
LCD
V
<5V −−260 mV
LCD
V
<6V −−340 mV
LCD
V
Notes
1. Spikes on V
2. Resets all logic when V
3. LCD outputs are open-circuit; inputs at V
4. T
amb
=25°C; f
5. LCD outputs are open-circuit; V
DD1
or V
= 200 kHz.
OSC
which cause V
SS1
DD1<VPOR
DD1
− V
≤ 1.6 V can cause a Power-on reset.
SS1
; 3 OSC cycles required.
or V
DD1
generator is on; load current I
LCD
; bus inactive.
SS1
VLCD
=5µA (at V
LCD
).
6. Tested on sample basis.
7. Resistance of output pins (R1 to R18 and C1 to C60) with a load current of 10 µA; outputs measured one at a time;
external V
8. LCD outputs open-circuit; external V
LCD
= 3 V, V
DD1, 2, 3
=3V.
LCD
.
V
2001 Dec 19 40

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
LCD controllers/drivers PCF2113x
14 AC CHARACTERISTICS
V
= 1.8 to 5.5 V; V
DD1
DD2=VDD3
specified.
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
f
FR
f
osc
f
OSC(ext)
t
osc(st)
t
W(PD)
t
SW(PD)
LCD frame frequency (internal clock) VDD= 5.0 V 45 95 147 Hz
oscillator frequency (not available at any pin) 140 250 450 kHz
external clock frequency 140 − 450 kHz
oscillator start-up time after power-down note 1 − 200 300 µs
power-down HIGH-level pulse width 1 −−µs
tolerable spike width on PD pin note 1 −−90 ns
Timing characteristics of parallel interface; note 2
WRITE OPERATION (WRITING DATA FROM MICROCONTROLLER TO PCF2113X); see Fig.27
T
cy(en)
t
W(en)
t
su(A)
t
h(A)
t
su(D)
t
h(D)
enable cycle time 500 −−ns
enable pulse width 220 −−ns
address set-up time 50 −−ns
address hold time 25 −−ns
data set-up time 60 −−ns
data hold time 25 −−ns
READ OPERATION (READING DATA FROM PCF2113X TO MICROCONTROLLER); see Fig.28
T
cy(en)
t
W(en)
t
su(A)
t
h(A)
t
d(D)
t
h(D)
enable cycle time 500 −−ns
enable pulse width 220 −−ns
address set-up time 50 −−ns
address hold time 25 −−ns
data delay time V
data hold time 5 − 100 ns
Timing characteristics of I
f
SCL
t
LOW
t
HIGH
t
SU;DAT
t
HD;DAT
t
r
t
f
C
b
t
SU;STA
t
HD;STA
SCL clock frequency −−400 kHz
SCL clock LOW period 1.3 −−µs
SCL clock HIGH period 0.6 −−µs
data set-up time 100 −−ns
data hold time 0 −−ns
SCL and SDA rise time note 1 and 3 15 + 0.1 Cb− 300 ns
SCL and SDA fall time note 1 and 3 15 + 0.1 Cb− 300 ns
capacitive bus line load −−400 pF
set-up time for a repeated START condition 0.6 −−µs
START condition hold time 0.6 −−µs
= 2.2 to 4.0 V; VSS=0V;V
2
C-bus interface; see Fig.29; note 2
V
LCD
DD1
DD1
= 2.2 to 6.5 V; T
= −40 to +85 °C; unless otherwise
amb
> 2.2 V −−150 ns
> 1.5 V −−250 ns
2001 Dec 19 41

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
LCD controllers/drivers PCF2113x
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
t
SU;STO
t
SW
t
BUF
Notes
1. Tested on sample base.
2. All timing values are valid within the operating supply voltage and ambient temperature range and are referenced to
VILand VIH with an input voltage swing of VSSto VDD.
3. Cb= total capacitance of one bus line in pF.
set-up time for STOP condition 0.6 −−µs
tolerable spike width on bus −−50 ns
bus free time between STOP and START
1.3 −−µs
condition
handbook, full pagewidth
Fig.27 Parallel bus write operation sequence; writing data from microcontroller to PCF2113x.
RS
R/W
DB0 to DB7
V
IH1
V
IL1
t
su(A)
V
IL1
t
W(en)
V
E
IH1
V
IL1
V
V
V
V
t
su(D)
IH1
IL1
IH1
IL1
valid data
V
IH1
V
IL1
T
cy(en)
t
t
h(A)
t
h(A)
V
h(D)
IL1
V
IL1
V
IH1
V
IL1
MBK474
2001 Dec 19 42

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
LCD controllers/drivers PCF2113x
handbook, full pagewidth
Fig.28 Parallel bus read operation sequence; writing data from PCF2113x to microcontroller.
RS
R/W
DB0 to DB7
V
IH1
V
IL1
t
su(A)
V
IH1
t
W(en)
V
E
V
IL1
IH1
t
d(D)
V
V
V
IH1
OH1
OL1
V
IH1
V
IL1
T
cy(en)
t
h(A)
V
IH1
t
h(A)
V
IL1
t
h(D)
V
OH1
V
OL1
V
IL1
MBK475
handbook, full pagewidth
SDA
SCL
SDA
MGA728
t
BUF
t
HD;STA
t
LOW
t
r
Fig.29 I2C-bus timing diagram.
2001 Dec 19 43
t
SU;STA
t
HD;DAT
t
HIGH
t
f
t
SU;DAT
t
SU;STO

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
LCD controllers/drivers PCF2113x
15 DEVICE PROTECTION CIRCUITS
SYMBOL PAD INTERNAL CIRCUIT
V
DD1
1
V
DD1
V
SS1
MGU200
V
DD2
V
DD3
V
SS1
V
SS2
V
LCDSENSE
V
LCD1
V
LCD2
109
110
7
8
10
11
9
V
SS1
V
DD2
V
SS2
MGU201
V
DD3
V
SS1
MGU202
8
7
V
SS2
V
SS1
MGU203
V
SS1
MGU196
SCL 96
SDA 97
2001 Dec 19 44
V
DD1
V
SS1
MGU198

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
LCD controllers/drivers PCF2113x
SYMBOL PAD INTERNAL CIRCUIT
OSC 2
PD 3
T1 5
T2 6
T3 4
E98
RS 99
R/W 100
DB0 to DB7 108 to 101
R1 to R8 94 to 87
R9 to R16 12 to 19
R17 95
R18 20
C1 to C2 86 to 85
C3 to 27 82 to 58
C28 to C52 55 to 31
C53 to C60 28 to 21
V
DD1
V
SS1
MGU199
V
LCD2
V
SS1
MGU197
2001 Dec 19 45

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
LCD controllers/drivers PCF2113x
16 APPLICATION INFORMATION
handbook, full pagewidth
handbook, full pagewidth
2
2 × 12 CHARACTER
LCD DISPLAY
PLUS 120 ICONS
60
P80CL51
P11
RSP10
R17, R18
R/W
EP12
PCF2113x
DB7 to DB4P17 to P14
4
R1 to R16
16
C1 to C60
Fig.30 Direct connection to 8-bit microcontroller; 4-bit bus.
2
2 × 12 CHARACTER
LCD DISPLAY
PLUS 120 ICONS
60
P80CL51
P21
RSP20
R/W
EP22
PCF2113x
DB7 to DB0P17 to P10
8
R17, R18
R1 to R16
16
C1 to C60
MGG006
MGG005
Fig.31 Direct connection to 8-bit microcontroller; 8-bit bus.
handbook, full pagewidth
OSC
V
DD
100
nF
V
SS
100
nF
V
DD
PCF2113x
V
LCD
V
SS
8
RSDB7 to DB0 E
R17, R18
R1 to R16
C1 to C60
R/W
Fig.32 Typical application using parallel interface.
2001 Dec 19 46
2
2 × 12 CHARACTER
16
LCD DISPLAY
PLUS 120 ICONS
60
MGG007

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
LCD controllers/drivers PCF2113x
V
handbook, full pagewidth
V
DD
DD
V
DD
DB3/SAO
OSC
V
DD
100
nF
V
SS
V
DD
470
nF
V
SS
100
nF
100
nF
V
DD
V
LCD
V
SS
OSC
V
DD
V
LCD
V
SS
PCF2113x
SCL SDA
V
DB3/SAO
PCF2113x
SCL SDA
R17, R18
R1 to R16
16
C1 to C60
SS
R17, R18
R1 to R16
16
C1 to C60
2
2 × 12 CHARACTER
LCD DISPLAY
PLUS 120 ICONS
60
2
1 × 24 CHARACTER
LCD DISPLAY
PLUS 120 ICONS
60
SCL SDA
MASTER TRANSMITTER
PCF84C81A; P80CL410
Fig.33 Application using I2C-bus interface.
16.1 General application information
The required minimum value for the external capacitors in
an application with the PCF2113x are: C
V
LCD/VSS
= 100 nF min., for VDD/VSS= 470 nF. Higher
Ext
for
capacitor values are recommended for ripple reduction.
For COG applications the recommended ITO track
resistance is to be minimized for the I/O and supply
connections.
2001 Dec 19 47
MGG008
Optimized values for these tracks are below 50 Ω for the
supply and below 100 Ω for the I/O connections. Higher
track resistance reduceperformance and increase current
consumption.
To avoid accidental triggering of Power-on reset
(especially in COG applications), the supplies must be
adequately decoupled. Depending on power supply
quality, V
may have to be risen above the specified
DD1
minimum.

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
LCD controllers/drivers PCF2113x
16.2 4-bit operation, 1-line display using internal
reset
The program must set functions prior to a 4-bit operation
(see Table 12). When power is turned on, 8-bit operation
is automatically selected and the PCF2113x attempts to
perform the first write as an 8-bit operation. Since nothing
is connected to DB0 to DB3, a rewrite is then required.
However, since one operation is completed in two
accesses of 4-bit operation, a rewrite is required to set the
functions (see Table 12 step 3). Thus, DB4 to DB7 of the
‘function set’ are written twice.
16.3 8-bit operation, 1-line display using internal
reset
Tables 13 and 14 show an example of a 1-line display in
8-bit operation. The PCF2113x functions must be set by
the ‘function set’ instruction prior to display. Since the
DDRAM can storedata for 80 characters, the RAMcan be
used for advertising displays when combined with display
shift operation. Since the display shift operation changes
display position only and the DDRAM contents remain
unchanged, display data entered first can be displayed
when the ‘return home’ operation is performed.
16.4 8-bit operation, 2-line display
For a 2-line display the cursor automatically moves from
thefirst to thesecond line after the40th digit of the first line
hasbeen written. Thus, if thereareonly 8 characters in the
first line, the DDRAM address must be set after the 8th
character is completed (see Table 15). It should be noted
that both lines of the display are always shifted together;
data does not shift from one line to the other.
2
16.5 I
C-bus operation, 1-line display
A control byte is required with most commands
(see Table 16).
Table 12 4-bit operation, 1-line display example using internal reset
STEP INSTRUCTION DISPLAY OPERATION
1 power supply on (PCF2113x is initialized by
initialized; no display appears
the internal reset)
2 function set
RS R/
000010
W DB7 DB6 DB5 DB4 sets to 4-bit operation; in this instance operation
is handled as 8-bits by initialization and only this
instruction completes with one write
3 function set
000010 sets to 4-bit operation, selects 1-line display and
000000
V
LCD=V0
; 4-bit operation starts from this point
and resetting is needed
4 display control
000000_ turns on display and cursor; entire display is
001110
blank after initialization
5 entry mode set
000000_ sets mode to increment the address by 1 and to
000110
shift the cursor to the right at the time of write to
the DD/CGRAM; display is not shifted
6 ‘write data’ to CGRAM/DDRAM
100101P_ writes ‘P’; the DDRAM has already been selected
100000
by initialization at power-on; the cursor is
incremented by 1 and shifted to the right
2001 Dec 19 48

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
LCD controllers/drivers PCF2113x
0
=V
initialized; no display appears
LCD
V
initialization
cursor to the right at the time of the write to the
DD/CGRAM; display is not shifted
initialization at power-on; the cursor is incremented by 1
and shifted to the right
writes ‘ILIP’
writes ‘ICROK’
This text is here in white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here in
_white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here inThis text is here in
white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader. white to force landscape pages to be ...
STEP INSTRUCTION DISPLAY OPERATION
Table 13 8-bit operation, 1-line display example; using internal reset (character set ‘A’)
2001 Dec 19 49
reset)
1 power supply on (PCF2113x is initialized by the internal
W DB7 DB6 DB5 DB4 DB3 DB2 DB1 DB0 sets to 8-bit operation, selects 1-line display and
RS R/
0000110000
2 function set
0000001110_ turns on display and cursor; entire display is blank after
3 display control
0000000110_ sets mode to increment the address by 1 and to shift the
4 entry mode set
1001010000P_ writes ‘P’; the DDRAM has already been selected by
5 ‘write data’ to CGRAM/DDRAM
1001001000PH_ writes ‘H’
6 ‘write data’ to CGRAM/DDRAM
7to10 |
|
1001010011PHILIPS_ writes ‘S’
0000000111PHILIPS_ sets mode for display shift at the time of write
1000100000HILIPS _ writes space
11 ‘write data’ to CGRAM/DDRAM
12 entry mode set
13 ‘write data’ to CGRAM/DDRAM
|
1001001101ILIPS M_ writes ‘M’
14 ‘write data’ to CGRAM/DDRAM
15 to 19 |
1001001111MICROKO_ writes ‘O’
20 ‘write data’ to CGRAM/DDRAM

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
LCD controllers/drivers PCF2113x
O shifts only the cursor position to the left
KO shifts only the cursor position to the left
(address 0)
PHILIPS M returns both display and cursor to the original position
21 cursor/display shift
This text is here in white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here in
_white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here inThis text is here in
STEP INSTRUCTION DISPLAY OPERATION
white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader. white to force landscape pages to be ...
2001 Dec 19 50
0000010000MICROK
0000010000MICRO
22 cursor/display shift
23 ‘write data’ to CGRAM/DDRAM
0000011100MICROCO shifts the display and cursor to the right
1001000011ICROCO writes ‘C’ correction; the display moves to the left
24 cursor/display shift
0000010100MICROCO_ shifts only the cursor to the right
1001001101ICROCOM_ writes ‘M’
25 cursor/display shift
26 ‘write data’ to CGRAM/DDRAM
0000000010
27 return home

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
LCD controllers/drivers PCF2113x
0
=V
initialized; no display appears
LCD
V
initialization
cursor to the right at the time of the write to the
DD/CGRAM; display is not shifted
the CGRAM is selected
the CGRAM is selected
This text is here in white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here in
_white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here inThis text is here in
white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader. white to force landscape pages to be ...
STEP INSTRUCTION DISPLAY OPERATION
Table 14 8-bit operation, 1-line display and icon example; using internal reset (character set ‘A’)
2001 Dec 19 51
reset)
1 power supply on (PCF2113x is initialized by the internal
W DB7 DB6 DB5 DB4 DB3 DB2 DB1 DB0 sets to 8-bit operation, selects 1-line display and
RS R/
0000110000
2 function set
0000001110_ turns on display and cursor; entire display is blank after
3 display mode on/off control
0000000110_ sets mode to increment the address by 1 and to shift the
4 entry mode set
0001000000_ sets the CGRAM address to position of character 0;
5 set CGRAM address
1000001010_ writes data to CGRAM for icon even phase; icons appears
6 ‘write data’ to CGRAM/DDRAM
7|
|
0001110000_ sets the CGRAM address to position of character 4;
8 set CGRAM address
1000001010_ writes data to CGRAM for icon odd phase
9 ‘write data’ to CGRAM/DDRAM
|
0000110001 _ sets H = 1
10 |
11 function set
0000001010 _ icons blink
12 icon control
13 function set
0000110001 _ sets H = 0

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
LCD controllers/drivers PCF2113x
selected
the right
writes ‘ILIPS’
|
(address 0)
PHILIPS returns both display and cursor to the original position
14 set DDRAM address
This text is here in white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here in
_white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here inThis text is here in
STEP INSTRUCTION DISPLAY OPERATION
white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader. white to force landscape pages to be ...
2001 Dec 19 52
0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 sets the DDRAM address to the first position; DDRAM is
1001010000P_ writes ‘P’; the cursor is incremented by 1 and shifted to
15 ‘write data’ to CGRAM/DDRAM
1001001000PH_ writes ‘H’
16 ‘write data’ to CGRAM/DDRAM
17 to 21 |
22 return home
0000000010

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
LCD controllers/drivers PCF2113x
LCD
initialized; no display appears
generator off
initialization
cursor to the right at the time of write to the CG/DDRAM;
display is not shifted
initialization at power-on; the cursor is incremented by 1
and shifted to the right
writes ‘HILIP’
sets DDRAM address to position the cursor at the head of
the 2nd line
writes ‘M’
writes ‘ICROC’
_
|
M_
writes ‘O’
MICROCO_
|
This text is here in white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here in
_white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here inThis text is here in
white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader. white to force landscape pages to be ...
STEP INSTRUCTION DISPLAY OPERATION
Table 15 8-bit operation, 2-line display example; using internal reset
2001 Dec 19 53
reset)
1 power supply on (PCF2113x is initialized by the internal
W DB7 DB6 DB5 DB4 DB3 DB2 DB1 DB0 sets to 8-bit operation; selects 2-line display and V
RS R/
0000110100
2 function set
0000001110_ turns on display and cursor; entire display is blank after
3 display on/off control
0000000110_ sets mode to increment the address by 1 and to shift the
4 entry mode set
1001010000P_ writes ‘P’; the DDRAM has already been selected by
5 ‘write data’ to CGRAM/DDRAM
6 to 10 |
1001010011PHILIPS_ writes ‘S’
11 ‘write data’ to CGRAM/DDRAM
0011000000PHILIPS
12 set DDRAM address
1001001101PHILIPS
13 ‘write data’ to CGRAM/ DDRAM
1001001111PHILIPS
19 ‘write data’ to CGRAM/DDRAM
14 to 18 |

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
LCD controllers/drivers PCF2113x
sets mode for display shift at the time of write
MICROCO_
writes ‘M’; displayis shifted to the left; the first and second
lines shift together
returns both display and cursor to the original position
(address 0)
ICROCOM_
MICROCOM
20 ‘write data’ to CGRAM/DDRAM
This text is here in white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here in
_white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here inThis text is here in
STEP INSTRUCTION DISPLAY OPERATION
white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader. white to force landscape pages to be ...
2001 Dec 19 54
0000000111PHILIPS
1001001101HILIPS
21 ‘write data’ to CGRAM/DDRAM
0000000010PHILIPS
23 return home

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
LCD controllers/drivers PCF2113x
; SCL pulse during
0
=V
LCD
; note 1)
SS
C-BUS BYTE DISPLAY OPERATION
2
PCF2113x
acknowledge cycle starts execution of instruction
(blank in ASCII-like character sets)
to the right at the time of write to the DDRAM or CGRAM; display
is not shifted
control byte is needed
cursor is incremented by 1 and shifted to the right
C-bus operation; 1-line display (using internal reset, assuming SA0 = V
2
STEP I
This text is here in white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here in
_white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here inThis text is here in
white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader. white to force landscape pages to be ...
Table 16 Example of I
2001 Dec 19 55
C-bus start initialized; no display appears
2
SA6 SA5 SA4 SA3 SA2 SA1 SA0 R/W Ack during the acknowledge cycle SDA will be pulled-down by the
1I
2 slave address for write
C-bus start _ for writing data to DDRAM, RS must be set to 1; therefore a
2
011101001
Co RS 0 0 0 0 0 0 Ack control byte sets RS for following data bytes
000000001
DB7 DB6 DB5 DB4 DB3 DB2 DB1 DB0 Ack selects 1-line display and V
001X00001
3 send a control byte for ‘function set’
4 function set
000011101
DB7 DB6 DB5 DB4 DB3 DB2 DB1 DB0 Ack _ turns on display and cursor; entire display shows character 20H
5 display on/off control
000001101
DB7 DB6 DB5 DB4 DB3 DB2 DB1 DB0 Ack _ sets mode to increment the address by 1 and to shift the cursor
6 entry mode set
7I
SA6 SA5 SA4 SA3 SA2 SA1 SA0 R/WAck _
011101001
8 slave address for write
Co RS 0 0 0 0 0 0 Ack _
010000001
9 send a control byte for ‘write data’
010100001
DB7 DB6 DB5 DB4 DB3 DB2 DB1 DB0 Ack P_ writes ‘P’; the DDRAM has been selected at power-up; the
10 ‘write data’ to DDRAM
010010001
DB7 DB6 DB5 DB4 DB3 DB2 DB1 DB0 Ack PH_ writes ‘H’
11 ‘write data’ to DDRAM

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
LCD controllers/drivers PCF2113x
C-bus interface
C-write mode
2
C-bus interface to be shifted out; in the
2
2
C-BUS BYTE DISPLAY OPERATION
2
C-bus interface
2
display to original position; DDRAM contents unchanged); this
PHILIPS_
instruction does not update the Data Register (DR)
PHILIPS sets DDRAM address 0 in address counter (also returns shifted
previous instruction neither a ‘set address’ nor a ‘read data’ has
been performed; therefore the content of the DR was unknown;
into the internal I
the R/W has to be set to 1 while still in I
PHILIPS DDRAM content will be read from following instructions
acknowledge cycle is shifted out over SDA; MSB is DB7; during
ILIPS 8 × SCL; content loaded into interface during previous
master acknowledge content of DDRAM address 01 is loaded
into the I
LIPS 8 × SCL; code of letter ‘H’ is read first; during master
acknowledge code of ‘I’ is loaded into the I
|
C-bus start start + slave
2
STEP I
This text is here in white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here in
_white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here inThis text is here in
white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader. white to force landscape pages to be ...
12 to 15 |
2001 Dec 19 56
C-bus stop) I
2
C-bus start PHILIPS
010100111
DB7 DB6 DB5 DB4 DB3 DB2 DB1 DB0 Ack PHILIPS_ writes ‘S’
16 ‘write data’ to DDRAM
17 (optional I
address for write (as step 8)
Co RS 0 0 0 0 0 0 Ack PHILIPS_
100000001
DB7 DB6 DB5 DB4 DB3 DB2 DB1 DB0 Ack
18 control byte
19 return home
2
000000101
20 I
21 slave address for read
SA6 SA5 SA4 SA3 SA2 SA1 SA0 R/WAck PHILIPS during the acknowledge cycle the content of the DR is loaded
011101011
22 control byte for read
011000001
Co RS 0 0 0 0 0 0 Ack
XXXXXXXX0
DB7 DB6 DB5 DB4 DB3 DB2 DB1 DB0 Ack PH
23 ‘read data’: 8 × SCL + master acknowledge; note 2
010010000
DB7 DB6 DB5 DB4 DB3 DB2 DB1 DB0 Ack PHI
24 ‘read data’: 8 × SCL + master acknowledge; note 2

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
LCD controllers/drivers PCF2113x
C-bus
2
C-BUS BYTE DISPLAY OPERATION
2
interface register is shifted out no internal action is performed;
no new data is loaded to the interface register, data register is
not updated, address counter is not incremented and cursor is
not shifted
LIPS no master acknowledge; after the content of the I
25 ‘read data’: 8 × SCL + no master acknowledge; note 2
This text is here in white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here in
_white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here inThis text is here in
STEP I
white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader. white to force landscape pages to be ...
2001 Dec 19 57
C-bus stop PHILIPS
010010011
DB7 DB6 DB5 DB4 DB3 DB2 DB1 DB0 Ack PHI
2
26 I
Notes
1. X = don’t care.
2. SDA is left at high-impedance by the microcontroller during the read acknowledge.

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
LCD controllers/drivers PCF2113x
STEP DESCRIPTION
|
W DB7 DB6 DB5 DB4 DB3 DB2 DB1 DB0 BF cannot be checked before this instruction
|
W DB7 DB6 DB5 DB4 DB3 DB2 DB1 DB0 BF cannot be checked before this instruction
|
W DB7 DB6 DB5 DB4 DB3 DB2 DB1 DB0 BF cannot be checked before this instruction
BF can be checked after the following instructions; when BF is not checked,
the waiting time between instructions is the specified instruction time
(see Table 3)
|
|
W DB7 DB6 DB5 DB4 DB3 DB2 DB1 DB0 function set (interface is 8 bits long); specify the number of display lines
This text is here in white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here in
_white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here inThis text is here in
white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader. white to force landscape pages to be ...
Table 17 Initialization by instruction, 8-bit interface (note 1)
2001 Dec 19 58
power-on or unknown state|wait 2 ms after internal reset has been applied
RS R/
0 0 0 0 1 1 X X X X function set (interface is 8 bits long)|wait 2 ms
RS R/
0 0 0 0 1 1 X X X X function set (interface is 8 bits long)|wait more than 40 µs
RS R/
0 0 0 0 1 1 X X X X function set (interface is 8 bits long)
RS R/
0000110M0H
0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 display off
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 clear display
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 I/D S entry mode set|Initialization ends
Note
1. X = don’t care.

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
LCD controllers/drivers PCF2113x
C-bus operation
2
STEP DESCRIPTION
|
W DB7 DB6 DB5 DB4 BF cannot be checked before this instruction
|
W DB7 DB6 DB5 DB4 BF cannot be checked before this instruction
|
W DB7 DB6 DB5 DB4 BF cannot be checked before this instruction
between instructions is the specified instruction time (see Table 3)
| BF can be checked after the following instructions; when BF is not checked, the waiting time
W DB7 DB6 DB5 DB4 function set (set interface to 4 bits long)
|
This text is here in white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here in
_white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here inThis text is here in
white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader. white to force landscape pages to be ...
Table 18 Initialization by instruction, 4-bit interface; not applicable for I
2001 Dec 19 59
power-on or unknown state|Wait 2 ms after internal reset has been applied
RS R/
000011function set (interface is 8 bits long)|Wait 2 ms
RS R/
000011function set (interface is 8 bits long)|Wait 40 µs
000011function set (interface is 8 bits long)
RS R/
RS R/
000010interface is 8 bits long
000010function set (interface is 4 bits long)
0 0 0 M 0 H specify number of display lines
000000
001000display off
000000clear display
000001
000000entry mode set
0 0 0 1 I/D S
Initialization ends

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
LCD controllers/drivers PCF2113x
17 BONDING PAD INFORMATION
COORDINATES
SYMBOL PAD
XY
V
DD1
1 −1345 −1550
OSC 2 −1155 −1550
PD 3 −1055 −1550
T3 4 −845 −1550
T1 5 −765 −1550
T2 6 −665 −1550
V
SS1
V
SS2
V
LCD2
V
LCDSENSE
V
LCD1
7 −525 −1550
8 −455 −1550
9 −295 −1550
10 −145 −1550
11 +15 −1550
R9 12 +175 −1550
R10 13 +245 −1550
R11 14 +315 −1550
R12 15 +385 −1550
R13 16 +455 −1550
R14 17 +525 −1550
R15 18 +595 −1550
R16 19 +665 −1550
R18 20 +735 −1550
C60 21 +805 −1550
C59 22 +875 −1550
C58 23 +995 −1550
C57 24 +1065 −1550
C56 25 +1135 −1550
C55 26 +1205 −1550
C54 27 +1275 −1550
C53 28 +1345 −1550
dummy pad 1 29 +1435 −1550
dummy pad 2 30 +1630 −1395
C52 31 +1630 −1255
C51 32 +1630 −1155
C50 33 +1630 −1055
C49 34 +1630 −955
C48 35 +1630 −735
C47 36 +1630 −635
C46 37 +1630 −535
C45 38 +1630 −435
C44 39 +1630 −335
C43 40 +1630 −235
C42 41 +1630 −135
C41 42 +1630 −35
(1)
COORDINATES
(1)
SYMBOL PAD
XY
C40 43 +1630 +65
C39 44 +1630 +165
C38 45 +1630 +265
C37 46 +1630 +365
C36 47 +1630 +465
C35 48 +1630 +565
C34 49 +1630 +665
C33 50 +1630 +765
C32 51 +1630 +865
C31 52 +1630 +965
C30 53 +1630 +1065
C29 54 +1630 +1165
C28 55 +1630 +1265
dummy pad 3 56 +1630 +1335
dummy pad 4 57 +1435 +1550
C27 58 +1335 +1550
C26 59 +1225 +1550
C25 60 +1115 +1550
C24 61 +1005 +1550
C23 62 +765 +1550
C22 63 +665 +1550
C21 64 +565 +1550
C20 65 +465 +1550
C19 66 +365 +1550
C18 67 +265 +1550
C17 68 +165 +1550
C16 69 +65 +1550
C15 70 −35 +1550
C14 71 −135 +1550
C13 72 −235 +1550
C12 73 −335 +1550
C11 74 −435 +1550
C10 75 −535 +1550
C9 76 −635 +1550
C8 77 −735 +1550
C7 78 −835 +1550
C6 79 −965 +1550
C5 80 −1065 +1550
C4 81 −1165 +1550
C3 82 −1265 +1550
dummy pad 5 83 −1465 +1550
dummy pad 6 84 −1630 +1355
C2 85 −1630 +1255
2001 Dec 19 60

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
LCD controllers/drivers PCF2113x
COORDINATES
(1)
SYMBOL PAD
XY
C1 86 −1630 +1185
R8 87 −1630 +1115
R7 88 −1630 +1045
R6 89 −1630 +975
R5 90 −1630 +905
R4 91 −1630 +835
R3 92 −1630 +765
R2 93 −1630 +695
R1 94 −1630 +625
R17 95 −1630 +555
SCL 96 −1630 +375
SDA 97 −1630 +305
E98−1630 +85
RS 99 −1630 −15
R/W 100 −1630 −115
COORDINATES
(1)
SYMBOL PAD
XY
DB7 101 −1630 −215
DB6 102 −1630 −315
DB5 103 −1630 −415
DB4 104 −1630 −515
DB3 105 −1630 −615
DB2 106 −1630 −715
DB1 107 −1630 −815
DB0 108 −1630 −915
V
DD2
V
DD3
109 −1630 −1015
110 −1630 −1235
dummy pad 7 111 −1630 −1395
dummy pad 8 112 −1465 −1550
Note
1. Allx and ycoordinates are referenced tocentre of chip
and dimensions are in µm (see Fig.34).
2001 Dec 19 61

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
LCD controllers/drivers PCF2113x
handbook, full pagewidth
dummy pad 4
C27
C26
C25
C24
C23
C22
C21
C20
C19
C18
C17
C16
C15
C14
C13
C12
C11
C10
C9
C8
C7
C6
C5
C4
C3
dummy pad 5
dummy pad 6
3.36
mm
dummy pad 7
V
V
R17
SCL
SDA
RS
RW
DB7
DB6
DB5
DB4
DB3
DB2
DB1
DB0
DD2
DD3
C2
C1
R8
R7
R6
R5
R4
R3
R2
R1
E
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
82
83
1
112
DD1
V
dummy pad 8
81
2
OSC
80
3
PD
77
78
79
PC2113x
45678
T3T1T2
76
75
SS1VSS2
V
74
71
70
72
73
y
0
0
9
V
11
10
LCD2VLCD1
LCDSENSE
V
3.52 mm
66
67
68
69
12131415161718
R9
R10
R11
R12
65
R13
R14
64
R15
63
19
R16
61
59
C59
C58
C57
60
C56
C55
C54
62
202122232425262728
R18
C60
57
58
56
55
54
53
52
51
50
49
48
47
46
45
44
43
x
42
41
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
C53
dummy pad 1
MGU205
dummy pad 3
C28
C29
C30
C31
C32
C33
C34
C35
C36
C37
C38
C39
C40
C41
C42
C43
C44
C45
C46
C47
C48
C49
C50
C51
C52
dummy pad 2
Fig.34 Bonding pad locations.
2001 Dec 19 62

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
LCD controllers/drivers PCF2113x
18 TRAY INFORMATION
handbook, full pagewidth
For dimensions see Table 19.
x
y
F
A
E
C
D
B
MGU206
Fig.35 Tray details.
Table 19 Tray dimensions
handbook, halfpage
PC2113x
MGU207
The orientation of the IC in a pocket is indicatedby the position of the
IC type name on the die surface with respect to the chamfer on the
upper left corner of the tray. Refer to the bonding pad location
diagram for the orientating and position of the type name on the die
surface.
Fig.36 Tray alignment.
DIMENSION DESCRIPTION VALUE
A pocket pitch x direction 6.35 mm
B pocket pitch y direction 5.59 mm
C pocket width x direction 3.82 mm
D pocket width y direction 3.66 mm
E tray width x direction 50.8 mm
F tray width y direction 50.8 mm
x pockets in x direction 7
y pockets in y direction 8
Table 20 Bump size
PARAMETER VALUE UNIT
Type galvanic pure Au −
Bump width 50 ±6 µm
Bump length 90 ±6 µm
Bump height 17.5 ±5 µm
Height difference in one die <2 µm
Convex deformation <5 µm
Pad size, aluminium 62 × 100 µm
Passivation opening CBB 36 × 76 µm
Wafer thickness 380 ±25 µm
2001 Dec 19 63

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
LCD controllers/drivers PCF2113x
19 PACKAGE OUTLINE
LQFP100: plastic low profile quad flat package; 100 leads; body 14 x 14 x 1.4 mm
c
y
X
A
SOT407-1
100
75
76
51
50
Z
E
e
H
E
E
A
2
A
A
1
(A )
3
w M
b
p
L
p
θ
L
pin 1 index
26
1
e
w M
b
p
D
H
D
25
Z
D
v M
A
B
v M
B
detail X
0 5 10 mm
scale
DIMENSIONS (mm are the original dimensions)
UNIT
mm
A
A1A2A3b
max.
0.15
1.6
0.05
1.45
1.35
0.25
cE
p
0.27
0.20
0.17
0.09
(1)
(1) (1)(1)
D
14.1
13.9
eH
H
14.1
13.9
0.5
16.25
15.75
Note
1. Plastic or metal protrusions of 0.25 mm maximum per side are not included.
OUTLINE
VERSION
IEC JEDEC EIAJ
REFERENCES
SOT407-1 136E20 MS-026
2001 Dec 19 64
D
E
16.25
15.75
LL
p
0.75
0.45
0.08 0.080.21.0
EUROPEAN
PROJECTION
Z
D
1.15
0.85
Zywv θ
E
1.15
0.85
o
7
o
0
ISSUE DATE
00-01-19
00-02-01

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
LCD controllers/drivers PCF2113x
20 SOLDERING
20.1 Introduction to soldering surface mount
packages
Thistextgives a very brief insighttoacomplex technology.
A more in-depth account of soldering ICs can be found in
our
“Data Handbook IC26; Integrated Circuit Packages”
(document order number 9398 652 90011).
There is no soldering method that is ideal for all surface
mount IC packages. Wave soldering can still be used for
certainsurfacemount ICs, but it is not suitableforfinepitch
SMDs. In these situations reflow soldering is
recommended.
20.2 Reflow soldering
Reflow soldering requires solder paste (a suspension of
fine solder particles, flux and binding agent) to be applied
tothe printed-circuit board byscreenprinting, stencilling or
pressure-syringe dispensing before package placement.
Several methods exist for reflowing; for example,
convection or convection/infrared heating in a conveyor
type oven. Throughput times (preheating, soldering and
cooling) vary between 100 and 200 seconds depending
on heating method.
Typical reflow peak temperatures range from
215 to 250 °C. The top-surface temperature of the
packages should preferable be kept below 220 °C for
thick/large packages, and below 235 °C for small/thin
packages.
20.3 Wave soldering
Conventional single wave soldering is not recommended
forsurfacemount devices (SMDs) or printed-circuit boards
with a high component density, as solder bridging and
non-wetting can present major problems.
To overcome these problems the double-wave soldering
method was specifically developed.
If wave soldering is used the following conditions must be
observed for optimal results:
• Use a double-wave soldering method comprising a
turbulent wave with high upward pressure followed by a
smooth laminar wave.
• For packages with leads on two sides and a pitch (e):
– larger than or equal to 1.27 mm, the footprint
longitudinal axis is preferred to be parallel to the
transport direction of the printed-circuit board;
– smaller than 1.27 mm, the footprint longitudinal axis
must be parallel to the transport direction of the
printed-circuit board.
The footprint must incorporate solder thieves at the
downstream end.
• Forpackageswith leads on four sides, the footprintmust
be placed at a 45° angle to the transport direction of the
printed-circuit board. The footprint must incorporate
solder thieves downstream and at the side corners.
During placement andbefore soldering, the package must
be fixed with a droplet of adhesive. The adhesive can be
applied by screen printing, pin transfer or syringe
dispensing. The package can be soldered after the
adhesive is cured.
Typical dwell time is 4 seconds at 250 °C.
A mildly-activated flux will eliminate the need for removal
of corrosive residues in most applications.
20.4 Manual soldering
Fix the component by first soldering two
diagonally-opposite end leads. Use a low voltage (24 V or
less) soldering iron applied to the flat part of the lead.
Contact time must be limited to 10 seconds at up to
300 °C.
When using a dedicated tool, all other leads can be
soldered in one operation within 2 to 5 seconds between
270 and 320 °C.
2001 Dec 19 65

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
LCD controllers/drivers PCF2113x
20.5 Suitability of surface mount IC packages for wave and reflow soldering methods
PACKAGE
WAVE REFLOW
(1)
BGA, LFBGA, SQFP, TFBGA not suitable suitable
SOLDERING METHOD
HBCC, HLQFP, HSQFP, HSOP, HTQFP, HTSSOP, SMS not suitable
(3)
PLCC
, SO, SOJ suitable suitable
LQFP, QFP, TQFP not recommended
SSOP, TSSOP, VSO not recommended
(2)
(3)(4)
(5)
suitable
suitable
suitable
Notes
1. All surface mount (SMD) packages are moisture sensitive. Depending upon the moisture content, the maximum
temperature (with respect to time) and body size of the package, there is a risk that internal or external package
cracks may occur due to vaporization of the moisture in them (the so called popcorn effect). For details, refer to the
Drypack information in the
“Data Handbook IC26; Integrated Circuit Packages; Section: Packing Methods”
.
2. These packages are not suitable for wave soldering as a solder joint between the printed-circuit board and heatsink
(at bottom version) can not be achieved, and as solder may stick to the heatsink (on top version).
3. If wave soldering is considered, then the package must be placed at a 45° angle to the solder wave direction.
The package footprint must incorporate solder thieves downstream and at the side corners.
4. Wave soldering is only suitable for LQFP, TQFP and QFP packages with a pitch (e) equal to or larger than 0.8 mm;
it is definitely not suitable for packages with a pitch (e) equal to or smaller than 0.65 mm.
5. Wave soldering is only suitable for SSOP and TSSOP packages with a pitch (e) equal to or larger than 0.65 mm; it is
definitely not suitable for packages with a pitch (e) equal to or smaller than 0.5 mm.
2001 Dec 19 66

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
LCD controllers/drivers PCF2113x
21 DATA SHEET STATUS
DATA SHEET STATUS
Objective specification Development This data sheet contains the design target or goal specifications for
Preliminary specification Qualification This data sheet contains preliminary data, and supplementary data will be
Product specification Production This data sheet contains final specifications. Philips Semiconductors
Note
1. Please consult the most recently issued data sheet before initiating or completing a design.
22 DEFINITIONS
Short-form specification The data in a short-form
specification is extracted from a full data sheet with the
same type number and title. For detailed information see
the relevant data sheet or data handbook.
Limiting values definition Limiting values given are in
accordance with the Absolute Maximum Rating System
(IEC 60134). Stress above one or more of the limiting
values may cause permanent damage to the device.
These are stress ratings only and operation of the device
attheseor at any otherconditionsabovethose given in the
Characteristics sections of the specification is not implied.
Exposure to limiting values for extended periods may
affect device reliability.
Application information Applications that are
described herein for any of these products are for
illustrative purposes only. Philips Semiconductors make
norepresentationorwarrantythat such applications will be
suitable for the specified use without further testing or
modification.
PRODUCT
STATUS
DEFINITIONS
product development. Specification may change in any manner without
notice.
published at a later date. Philips Semiconductors reserves the right to
make changes at any time without notice in order to improve design and
supply the best possible product.
reserves the right to make changes at any time without notice in order to
improve design and supply the best possible product.
23 DISCLAIMERS
Life support applications These products are not
designed for use in life support appliances, devices, or
systems where malfunction of these products can
reasonably be expected to result in personal injury. Philips
Semiconductorscustomersusingorselling these products
for use in such applications do so at their own risk and
agree to fully indemnify Philips Semiconductors for any
damages resulting from such application.
Right to make changes Philips Semiconductors
reserves the right to make changes, without notice, in the
products, including circuits, standard cells, and/or
software, described or contained herein in order to
improve design and/or performance. Philips
Semiconductors assumes no responsibility or liability for
theuseof any of these products, conveys nolicenceortitle
under any patent, copyright, or mask work right to these
products,and makes no representations orwarrantiesthat
these products are free from patent, copyright, or mask
work right infringement, unless otherwise specified.
(1)
24 BARE DIE DISCLAIMER
All die are tested and are guaranteed to comply with all data sheet limits up to the point of wafer sawing for a period of
ninety (90) days from the date of Philips' delivery. If there are data sheet limits not guaranteed, these will be separately
indicated in the data sheet. Thereare no post packing tests performed on individualdie or wafer.Philips Semiconductors
has no control of third party procedures in the sawing, handling, packing or assembly of the die. Accordingly, Philips
Semiconductorsassumes no liability fordevice functionality or performanceof the die orsystems after third partysawing,
handling, packing or assembly of the die. It is the responsibility of the customer to test and qualify their application in
which the die is used.
2001 Dec 19 67

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
LCD controllers/drivers PCF2113x
25 PURCHASE OF PHILIPS I2C COMPONENTS
Purchase of Philips I2C components conveys a license under the Philips’ I2C patent to use the
components in the I2C system provided the system conforms to the I2C specification defined by
Philips. This specification can be ordered using the code 9398 393 40011.
2001 Dec 19 68

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
LCD controllers/drivers PCF2113x
NOTES
2001 Dec 19 69

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
LCD controllers/drivers PCF2113x
NOTES
2001 Dec 19 70

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
LCD controllers/drivers PCF2113x
NOTES
2001 Dec 19 71

Philips Semiconductors – a w orldwide compan y
Contact information
For additional information please visit http://www.semiconductors.philips.com. Fax: +31 40 27 24825
For sales offices addresses send e-mail to: sales.addresses@www.semiconductors.philips.com.
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2001
All rights are reserved. Reproduction in whole or in part is prohibited without the prior written consent of the copyright owner.
The information presented in this document does not form part of any quotation or contract, is believed to be accurate and reliable and may be changed
without notice. No liability will be accepted by the publisher for any consequence of its use. Publication thereof does not convey nor imply any license
under patent- or other industrial or intellectual property rights.
Printed in The Netherlands 403502/03/pp72 Date of release: 2001 Dec 19 Document order number: 9397 750 06995
SCA73
 Loading...
Loading...