Philips NUDOS, HQ 4885-B, HQ 4865-B, HQ 4845-B, HQ 3865-B Service Manual

NUDOS NiCd Shavers
HQ 3865/B
Service
HQ 4845/B
HQ 4865/B
Service
HQ 4885/B
Service
Domestic Appliances and Personal Care
Circuit Description
INTRODUCTION
The Nudos shavers with NiCd cells can be recharged
in 30 minutes by means of a Fly Back Self Oscillating
Power Supply (SOPS).
This electronic circuit enables cells to be recharged at
100-240 V .
It is possible to shave directly from the mains,
provided the voltage exceeds 100V .
The on/off slide has a locking device, which prevents
the shaver from being switched on accidentally.
Leaving it connected to the mains after it is fully
charged will not damage the shaver.
However, the life of the cells may be shortened if the
shaver is kept permanently connected.
If the shaver is kept in the case when charging, make
sure that the lid is open to prevent overheating.
HINTS FOR REPAIRS
a. Disassembly
- Remove the shaving unit, to prevent damages
during repairs.
- Remove screws A1 (4X, of which 2 are under
trimmer slide).
- Put the shaver on the table and remove the cover
(item 26) from the shaver.
- The trimmer can be removed by pushing the hinge
points (‘Y’ in exploded view, near item 11) slightly
inwards.
- Detach the motor clamping springs (item 18) on the
bearing block with a small screwdriver.
- The PC-boards with motor can now be removed
from the housing.
- Remove screws A2 (2X).
- Unlock the snap connection (3X) between frame
(item 14) and hair chamber (item 11).
- If the Power Module (item 23) and Time Control
Module (item 7) have to be separated, read the
instructions under IMPORTANT.
b. Assembly
- The assembly must be carried out in reverse order
of what is described under a. Disassembly.
- The trimmer slide can be snapped into the cover
last.
Published by Philips Domestic Appliances and Personal Care Printed in The Netherlands Copyright reserved Subject to modification
4822 729 22107
97/04 - 99/01
PCS 99 106
©
NUDOS NiCd shavers
2
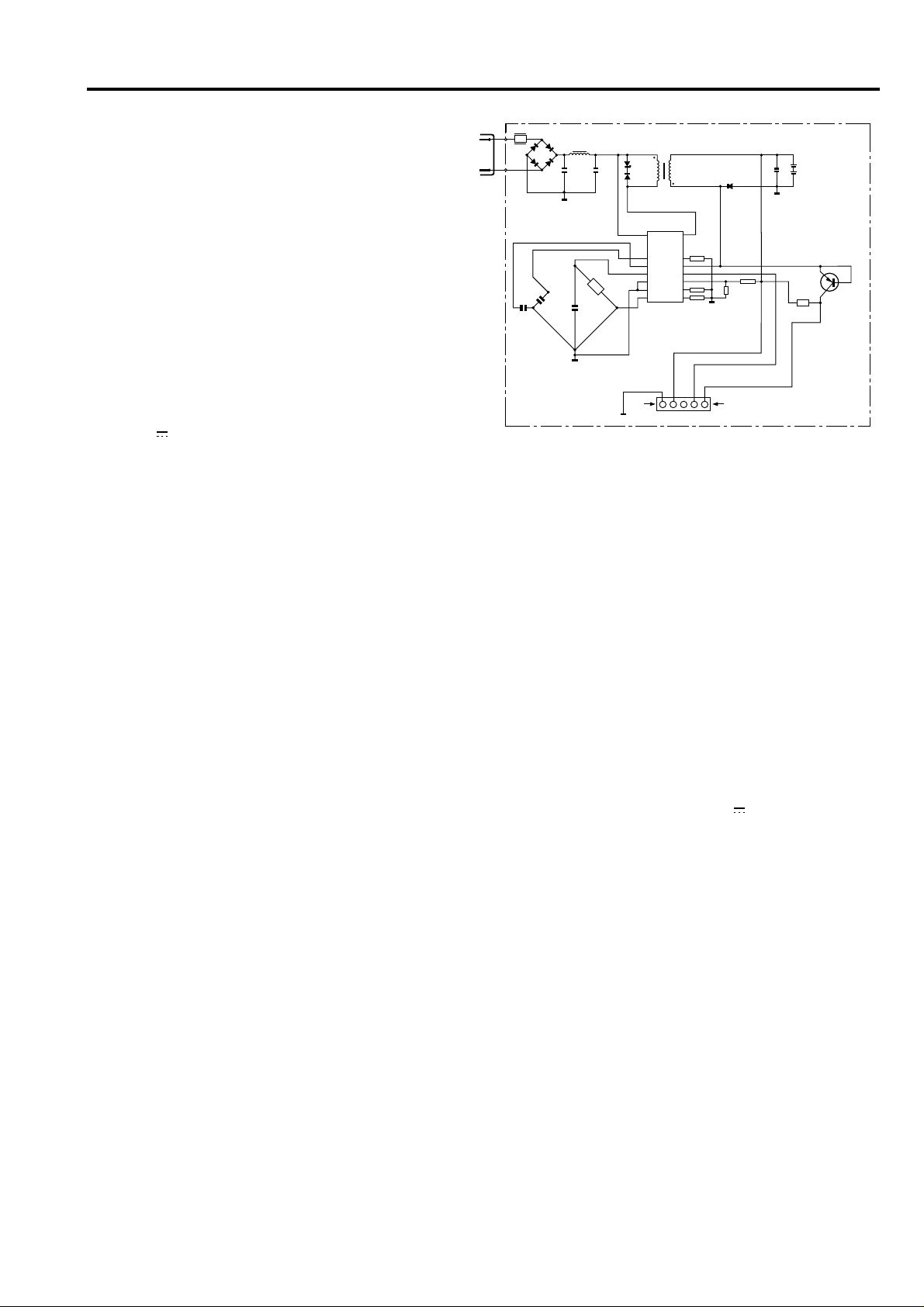
TECHNICAL DESCRIPTION
The electronics for the Nudos shavers with NiCd
cells consist of 2 modules:
a Power Module (PM) and a Time Control Module
(TCM), connected via a 5-pin connector.
POWER MODULE
The PM consists of a High Voltage Integrated Circuit
(HVIC) and some external components, regulating the
following functions:
a. a current controller to adjust the charge current at
1200 mA or at 100 mA.
b. a 2.5 V dynamic supply controller for shaving
from the mains.
c. a primary current limiter (max 400 mA) to protect
the transformer from saturation.
d. a frequency limiter (max 60 kHz).
e. an open cell protection (Vbat>5V).
f. a temperature protection (Tchip>140˚C).
R1
100-240 V
50/60Hz
L1
D4
C1
C2
C4
C6
R7
C5
D1
D2
T1
18
1
17
2
16
3
15
4
14
5
6
13
12
7
11
8
IC1
10
9
TEA 1402
12345
C3
D3
R5
R8
R9
R10
R12
MPMP
The TCM has 3 variants:
HQ3865 with 4 green LEDs and 1 red/green duoLED.
HQ4845 with 1 red LED and 1 green LED.
HQ4865 with 4 green LEDs and 1 red/green duoLED.
HQ4885 with LCD, 1 red LED and 1 green LED.
2 x AA
NiCd
A
TS1
R14
The mains voltage is full-wave rectified by D4 and
smoothed by π-filter C1-L1-C2.
This filter also serves as a radio interference filter
(RIF) for the SOPS and motor and as a suppressor of
voltage transients from the mains.
Resistor R1, which functions as a fuse, limits the
switch-on (inrush) current and the transient (surge)
current.
The resistor interrupts in case of a too large mains
current due to improper use or internal short circuit.
The primary-current circuit consists of the primary
winding of T1 and the high-voltage switch inside the
HVIC (IC1).
Snubber circuit D1-D2 limits the voltage across the
primary winding during commutation.
During the flyback of the converter (when the switch
is open) the secondary winding of T1 will deliver the
primary energy across D3 and R2 to the cells or to
the R26 sensed motor.
TIME CONTROL MODULE
The primary function of the TCM is:
Monitoring the capacity of the cells during charging
and discharging.
- controlling the 3 charging modes:
1. 1200 mA during max. 30 minutes.
2. 100 mA if the voltage across the 2 cells
exceeds 2.5.V and charging exceeds 30 minutes.
3. 200-1800 mA at 2.5 V when the motor is
switched on at the same time.
When the PM is connected to the mains, a signal will
be generated by the SOPS, which is recognised by
the TCM as ‘mains on’.
Depending on the frequency of this signal, the TCM
forces the PM into the quick charge mode as long as
the capacity counter has not reached the ‘full’ state.
After max. 30 minutes the PM is set to the slow
charge mode.
If during charging the shaver is switched on, the PM
is set to the dynamic 2.5 V mode, in which the control
switches from TCM to PM.
With empty cells this means that no charging takes
place till the cells reach the 2.5 V level,
consequently the capacity counter is not activated.
If the cell voltage is higher than 2.5 V, the motor
current will come from the cells.
The capacity counter will now count down, as
signalled via R26.
If the voltage drops below 2.5 V again, the PM takes
over the supply of the motor current.
During charging and discharging the IC calculates the
capacity available in the cells and subsequently
generates signals to activate the LEDs and/or LCD,
the sequence being:
 Loading...
Loading...