Philips N74F193N, N74F193D Datasheet
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
74F193Up/down binary counter with separate up/down clocks
1
1995 Jul 17
853-0353 15459
FEATURES
•Synchronous reversible 4-bit counting
•Asynchronous parallel load capability
•Asynchronous reset (clear)
•Cascadable without external logic
DESCRIPTION
The 74F193 is a 4-bit synchronous up/down counter in the binary
mode. Separate up/down clocks, CP
U
and CPD respectively,
simplify operation. The outputs change state synchronously with the
Low-to-High transition of either clock input. If the CP
U
clock is
pulsed while CP
D
is held High, the device will count up. If CPD clock
is pulsed while CP
U
is held High, the device will count down. The
device can be cleared at any time by the asynchronous reset pin. It
may also be loaded in parallel by activating the asynchronous
parallel load pin.
Inside the device are four master-slave JK flip-flops with the
necessary steering logic to provide the asynchronous reset,
asynchronous preset, load, and synchronous count up and count
down functions.
Each flip-flop contains JK feedback from slave to master, such that a
Low-to-High transition on the CP
D
input will decrease the count by
one, while a similar transition on the CP
U
input will advance the
count by one.
One clock should be held High while counting with the other,
because the circuit will either count by twos or not at all, depending
on the state of the first JK flip-flop, which cannot toggle as long as
either clock input is Low. Applications requiring reversible operation
must make the reversing decision while the activating clock is High
to avoid erroneous counts.
The Terminal Count Up (TC
U
) and Terminal Count Down (TCD)
outputs are normally High. When the circuit has reached the
maximum count state of 15, the next High-to-Low transition of CP
U
will cause TCU to go Low. TCU will stay Low until CPU goes High
again, duplicating the count up clock, although delayed by two gate
delays. Likewise, the TC
D
output will go Low when the circuit is in
the zero state and the CP
D
goes Low. The TC outputs can be used
as the clock input signals to the next higher order circuit in a
multistage counter, since they duplicate the clock waveforms.
Multistage counters will not be fully synchronous since there is a
two-gate delay time difference added for each stage that is added.
The counter may be preset by the asynchronous parallel load
capability of the circuit. Information present on the parallel Data
inputs (D0 - D3) is loaded into the counter and appears on the
outputs regardless of the conditions of the clock inputs when the
Parallel Load (PL
) input is Low. A High level on the Master Reset
(MR) input will disable the parallel load gates, override both clock
inputs, and set all Q outputs Low. If one of the clock inputs is Low
during and after a reset or load operation, the next Low-to-High
transition of the clock will be interpreted as a legitimate signal and
will be counted.
TYPE
TYPICAL f
MAX
TYPICAL
SUPPLY CURRENT
(TOTAL)
74F193 125MHz 32mA
ORDERING INFORMATION
DESCRIPTION
COMMERCIAL RANGE
V
CC
= 5V ±10%, T
amb
= 0°C to +70°C
16-pin plastic DIP N74F193N
16-pin plastic SO N74F193D
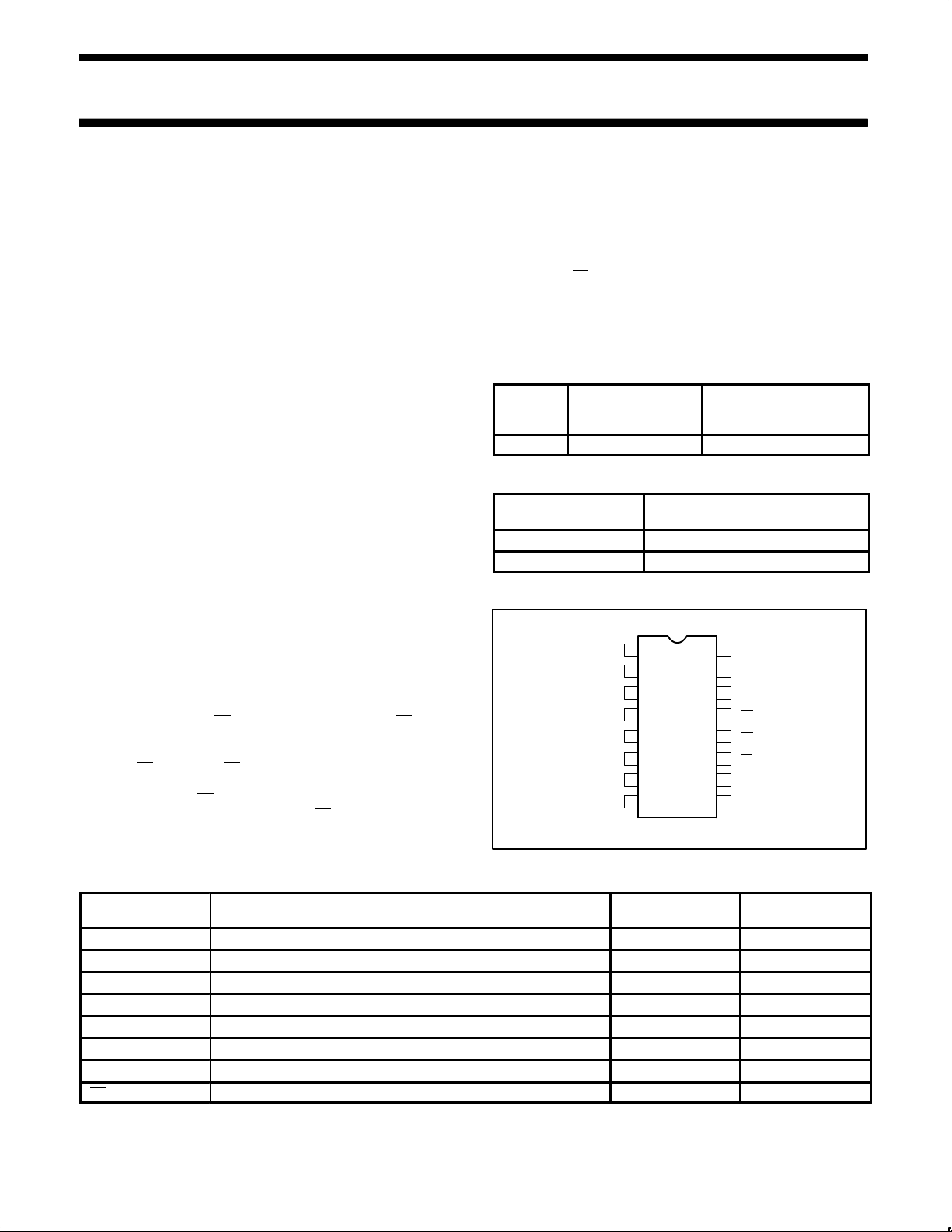
PIN CONFIGURATION
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
98
7
6
5
4
3
2
1D1
Q1
Q0
CP
D
CP
U
Q2
Q3
D0
TC
D
TC
U
D2
D3
PL
GND
MR
V
CC
SF00745
INPUT AND OUTPUT LOADING AND FAN-OUT TABLE
PINS DESCRIPTION
74F(U.L.)
HIGH/LOW
LOAD VALUE
HIGH/LOW
D0 - D3 Data inputs 1.0/1.0 20µA/0.6mA
CP
U
Count up clock input (active rising edge) 1.0/3.0 20µA/1.8mA
CP
D
Count down clock input (active rising edge) 1.0/3.0 20µA/1.8mA
PL Asynchronous parallel load control input (active Low) 1.0/1.0 20µA/0.6mA
MR Asynchronous master reset input 1.0/1.0 20µA/0.6mA
Q0 - Q3 Flip-flop outputs 50/33 1.0mA/20mA
TC
U
Terminal count up (carry) output (active Low) 50/33 1.0mA/20mA
TC
D
Terminal count down (borrow) output (active Low) 50/33 1.0mA/20mA
NOTE: One (1.0) FAST Unit Load (U.L.) is defined as: 20µA in the High state and 0.6mA in the Low state.
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
74F193Up/down binary counter with separate up/down clocks
1995 Jul 17
2
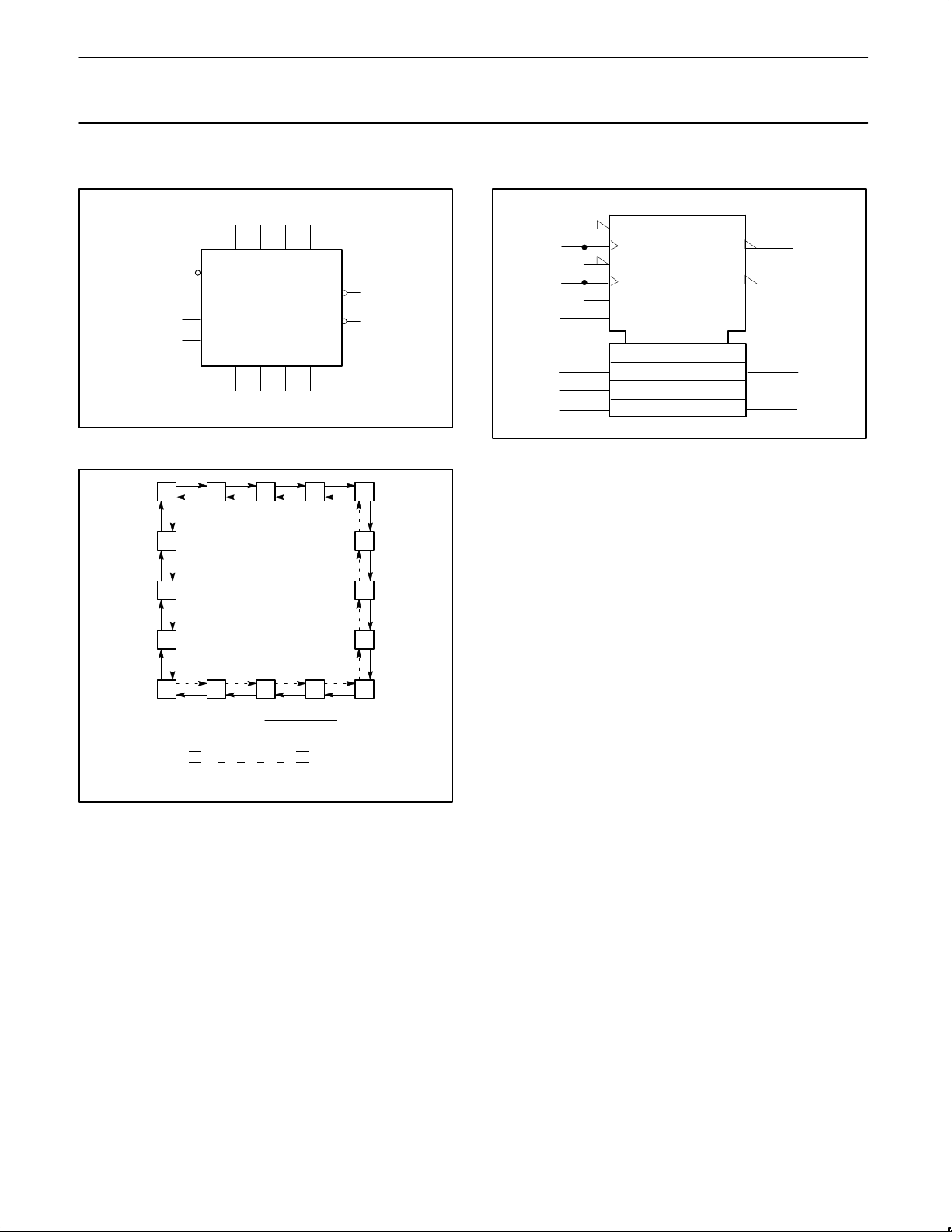
LOGIC SYMBOL
VCC = Pin 16
GND = Pin 8
11
15 1 10 9
7623
14
4
5
CP
U
CP
D
Q0
D0 D1Q1D2
Q2 Q3
D3
PL
12
13
MR
TC
U
TC
D
SF00746
STATE DIAGRAM
TCU = Q0 . Q1 . Q2 . Q3 . CP
U
TCD = Q0 . Q1 . Q2 . Q3 . CP
D
Logic Equations for Terminal Count
COUNT UP
COUNT DOWN
0 1 2 3 4
5
6
7
89101112
13
14
15
SF00748
LOGIC SYMBOL (IEEE/IEC)
11
5
4
14
[1]
R
15
1
10
9
3D
3
2
6
7
1–
G2
C3
SF00747
2+
G1
CTR DIV 16
[2]
[4]
[8]
12
13
1CT=15
2CT=0
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
74F193Up/down binary counter with separate up/down clocks
1995 Jul 17
3
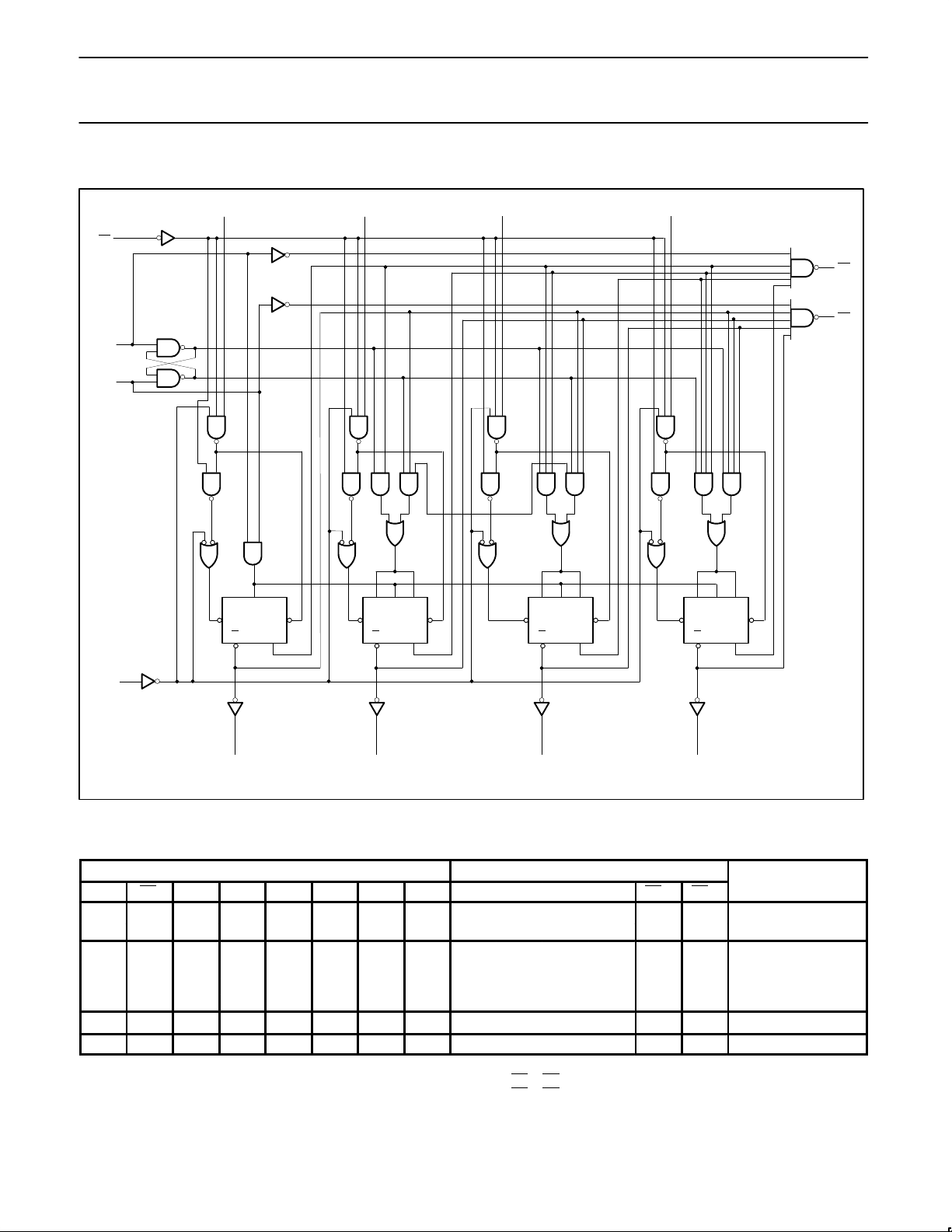
LOGIC DIAGRAM
12
13
J
Q
CP
Q
S
D
R
D
KJ
Q
CP
Q
S
D
R
D
D0 D1 D3
Q1Q0
CP
D
PL
15 1
23
14
4
11
V
CC
= Pin 16
GND = Pin 8
KJ
Q
CP
Q
S
D
R
D
Q1
10
6
K
JQCP
Q
S
D
R
D
Q1
9
7
MR
CP
U
5
TC
U
TC
D
D2
SF00749
FUNCTION TABLE
INPUTS OUTPUTS OPERATING
MR PL CPUCP
D
D0 D1 D2 D3 Q0 Q1 Q2 Q3 TCUTC
D
MODE
H X X L X X X X L L L L H L Reset (clear)
H X X H X X X X L L L L H H
L L X L L L L L L L L L H L
L L X H L L L L L L L L H H Parallel load
L L L X H H H H H H H H L H
L L H X H H H H H H H H H H
L H ↑ H X X X X Count up H
1
H Count up
L H H ↑ X X X X Count down H H2Count down
H = High voltage level
L = Low voltage level
X = Don’t care
↑ = Low-to-High clock transition
NOTES:
1. TC
U
=CPU at terminal count up (HHHH)
2. TC
D
=CPD at terminal count down (LLLL)
 Loading...
Loading...