Philips MIIC-201D-U User Manual

User’s Guide
DLL/USB
2
C Host Adapter
I
with iPort Utility Pack Software
www.mcc-us.com

Introduction
The MCC iPort™ DLL/USB to I2C Host Adapter (#MIIC-201D/U) allows any
Windows 98se, 2000, XP, or higher PC, with a free USB port or self-powered USB
2
hub, to become an I
messages between the PC and one or more I
This user’s guide describes the installation and operation of the iPort DLL/USB I
Bus host adapter and the iPort Utility Pack Software for Windows.
Are you new to I
www.mcc-us.com/I2CBusTechnicalOverview.pdf.
C Master or Slave device, transmitting or receiving I2C
2
C devices across an I2C Bus.
2
2
C? Want to know more? We suggest you review “What is I2C?” at
C
MCC products use Philips components and are licensed to use the I²C Bus.
“Purchase of Philips I²C components conveys a license under the Philips’ I²C patent
to use the components of the I²C system, provided the system conforms to the I²C
specifications defined by Philips.”
I²C is a trademark of Philips Corporation.
09-JAN-07

Copyright© 2006 by Micro Computer Control Corporation. All rights are reserved.
No part of this publication may be reproduced by any means without the prior
written permission of Micro Computer Control Corporation, PO Box 275,
Hopewell, New Jersey 08525 USA.
DISCLAIMER: Micro Computer Control Corporation makes no representations or
warranties with respect to the contents hereof and specifically disclaims any implied
warranties of merchantability or fitness for any particular purpose. Further, Micro
Computer Control Corporation reserves the right to revise the product described in
this publication and to make changes from time to time in the content hereof
without the obligation to notify any person of such revisions or changes.
WARNING - Life Support Applications: MCC products are not designed for use
in life support appliances, devices, or systems where the malfunction of the product
can reasonably be expected to result in a personal injury.
WARNING - Radio Frequency Emissions: This equipment can radiate levels of
radio frequency energy that may cause interference to communications equipment.
Operation of this equipment may cause interference with radio, television, or other
communications equipment. The user is responsible for correcting such interference
at the expense of the user.
WARNING - Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) Precautions: Any damage caused by
Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) through inadequate earth grounding is NOT covered
under the warranty of this product. See the “Electrostatic (ESD) Precautions”
section of this guide for more information.
Printed in the United States of America

Table of Contents
Part 1 - iPort DLL/USB I2C Bus Host Adapter ..........................1
1 Overview .......................................................2
2
iPort DLL/USB I
iPort DLL/USB Virtual Communications Port (VCP) ....................2
iPort Utility Pack Software .........................................3
iPort Software Development Kit for Windows ..........................3
Packing Slip.....................................................3
System Requirements .............................................3
2 Interconnects ....................................................3
USB Connector ..................................................4
Virtual Communications Port (VCP) ...............................4
C Bus Host Adapter ................................2
+5VDC Power Jack ...............................................4
2
C Interface Connector ............................................4
I
3 Hardware Configuration ...........................................6
Pull-up Resistors .................................................6
Connecting to a 3.3 Volt Target System ...............................6
Connecting to an SMBus Target System...............................6
4 ESD (Electrostatic Discharge) Precautions .............................7
Host Computer Grounding .........................................7
Grounding Solutions ..............................................8
5 Hardware Set-Up.................................................8
Part 2 - iPort Utility Pack for Windows ...............................11
1 iPort Utility Pack for Windows .....................................13
iPort Message Center.............................................13
iPort Message Manager ...........................................14
2 System Requirements ............................................15
3 iPort Utility Pack Installation ......................................15
Installing from CD...............................................15
Installing from the Web...........................................15

4 iPort Message Center ............................................16
Message Center Operations........................................17
Starting the Message Center .....................................17
Selecting the Adapter ..........................................17
Select the Communications Port ..................................18
Options Menu ................................................18
Establish Adapter Communications Link ...........................18
2
Entering or Editing I
2
Set I
C Address ...............................................19
C Messages .................................18
Set Message Read/Write Direction ................................19
Specify Repeated Start Messages .................................19
Set Time Delay ...............................................20
Specify Write Data or Read Byte Count ............................20
Inserting and Deleting Messages..................................21
Saving or Loading Message Lists .................................21
Send the Message List..........................................21
Special Event Handling.........................................21
Slave Not Acknowledging ......................................22
Command Line Arguments ........................................23
Set Adapter Type..............................................24
Set RS-232 Communication Port .................................24
Set RS-232 Baud Rate ..........................................24
2
Set I
C Bus Clock Rate .........................................24
Enable /INT Signal Monitor .....................................25
Stop On Busy ................................................25
Stop On Arbitration Loss .......................................25
Stop On Slave Negative Acknowledgment ..........................25
Beep On Busy ................................................25
Beep On Arbitration Loss .......................................26
Beep On Slave Negative Acknowledgment .........................26
Beep On /INT Assert...........................................26
2
Load I
Saved I
C Message List File......................................26
2
C Message List File .....................................27
Auto Open...................................................27
Auto Send ...................................................27
Auto Exit....................................................27
5 iPort Message Manager ..........................................28
Message Manager Operations ......................................29
Starting the Message Manager ...................................29

Select the Adapter .............................................29
Establish Adapter Communications Link ...........................30
Basic Setup ..................................................30
Advanced Setup ..............................................31
2
Adapter’s Own I
C Slave Address ..............................31
General Call Enable .........................................31
2
C Bus Master Bit Rate ......................................31
I
2
C Bus Time-Out...........................................31
I
Enable INT Signal Monitor ...................................31
Diagnostic Setup ..............................................32
Log File Level .............................................32
Log File Name .............................................32
Log File Size...............................................32
2
Sending I
C Messages..........................................33
Master Operations.............................................33
Specifying the Destination Address ...............................33
Repeated Start Messages........................................33
Auto Repeat..................................................34
Master Transmitting Data .......................................34
Specifying Master Tx Message Bytes ...........................34
Sending Master Transmit Messages .............................35
Master Receive Data ...........................................35
Specifying Data to Read ......................................35
Negative Acknowledge Last Byte ..............................36
Master Transmit and Receive ....................................36
Slave Operations ..............................................36
Slave Transmit Data ...........................................36
Slave Receive Data ............................................36
6 Uninstalling Software Components ..................................37
Uninstalling iPort Utility Pack for Windows ...........................37
Uninstalling iPort DLL/USB VCP Device Driver.......................37
iPort DLL/USB Revision Report ....................................39
Additional Information ............................................39
2
Appendix A - I
C Connector Information .............................40

Part 1 - iPort DLL/USB I2C Bus Host Adapter
Part 1
DLL/USB
2
I
C Bus Host Adapter
User’s Guide
Model: MIIC-201D/U
1

1 Overview
2
The MCC iPort DLL/USB I
C Bus Host Adapter (#MIIC-201D/U) allows any
Windows 98se, 2000, XP, or higher PC with a free USB port or self-powered USB
2
hub, to become an I
messages between the PC and one or more I
C Master or Slave device, transmitting or receiving I2C
2
C devices across an I2C Bus.
iPort DLL/USB Product Features:
• Compatible with existing iPort (#MIIC-201) applications.Upgrade existing iPort
applications from RS-232 to USB. No software changes required.
• Windows DLL Application Program Interface (API).
• Compatible with Windows 98se, 2000, XP, or higher based PC.
• Compatible with USB 2.0 Specifications.
2
• Supports I
• User Selectable Master I
• Compatible with 3.3V to 5V I
• Includes switch-enabled internal I
• Includes our free I
Applications. Get on the I
C Bus Master and Slave, Transmit and Receive operations.
2
C bit rates of 12.5 KHz and 100 KHz.
2
C Bus voltages.
2
C Pull-Up resistors.
2
C Message Center and Message Manager Windows
2
C Bus in Seconds.
• Includes our easy to use Virtual Communications Port (VCP) driver.
2
The I
1.1 iPort DLL/USB I
C adapter system consists of the following components:
2
C Bus Host Adapter
The iPort DLL/USB adapter is a bus-powered USB device that plugs into a host
2
computer’s USB port or self-powered USB hub and generates I
C Bus signals.
1.2 iPort DLL/USB Virtual Communications Port (VCP)
The iPort DLL/USB Virtual Communications Port (VCP) driver creates a virtual
serial port within the iPort DLL/USB device. To a Windows software application,
the VCP looks just like a legacy serial communications port, allowing standard
iPort DLL programming methods to work unchanged. No special USB
programming is required. The iPort DLL/USB VCP is available to the host
computer whenever the iPort DLL/USB is attached to the host computer.
2

1.3 iPort Utility Pack Software
This free software package includes the iPort Message Center and Message
2
Manager applications to help you easily send and receive I
C Bus messages.
1.4 iPort Software Development Kit for Windows
This optional software package includes:
• iPort DLL (Dynamic Linked Library) for Windows
• Programmer’s Guide
• Sample Application Programs
This iPort Software Development Kit for Windows is only needed if you are
developing a custom Windows software application for the iPort DLL/USB. Find
additional sample programs and complete projects on our web site’s Sample
Program page.
1.5 Packing Slip
This package includes the following items:
2
• iPort DLL/USB I
C Bus Host Adapter (#MIIC-201D/U).
• USB Interface Cable.
2
C Clip-Lead Cable.
•I
2
C Interface Cable.
•I
• iPort DLL/USB User’s Guide (this document).
• iPort Utility Pack for Windows CD.
• Global Power Supply (Optional supplement power for target system).
1.6 System Requirements
a. A host computer with one free USB port or self-powered USB hub.
b. Windows 98se, 2000, XP or higher.
2 Interconnects
The iPort DLL/USB includes three interconnections:
3
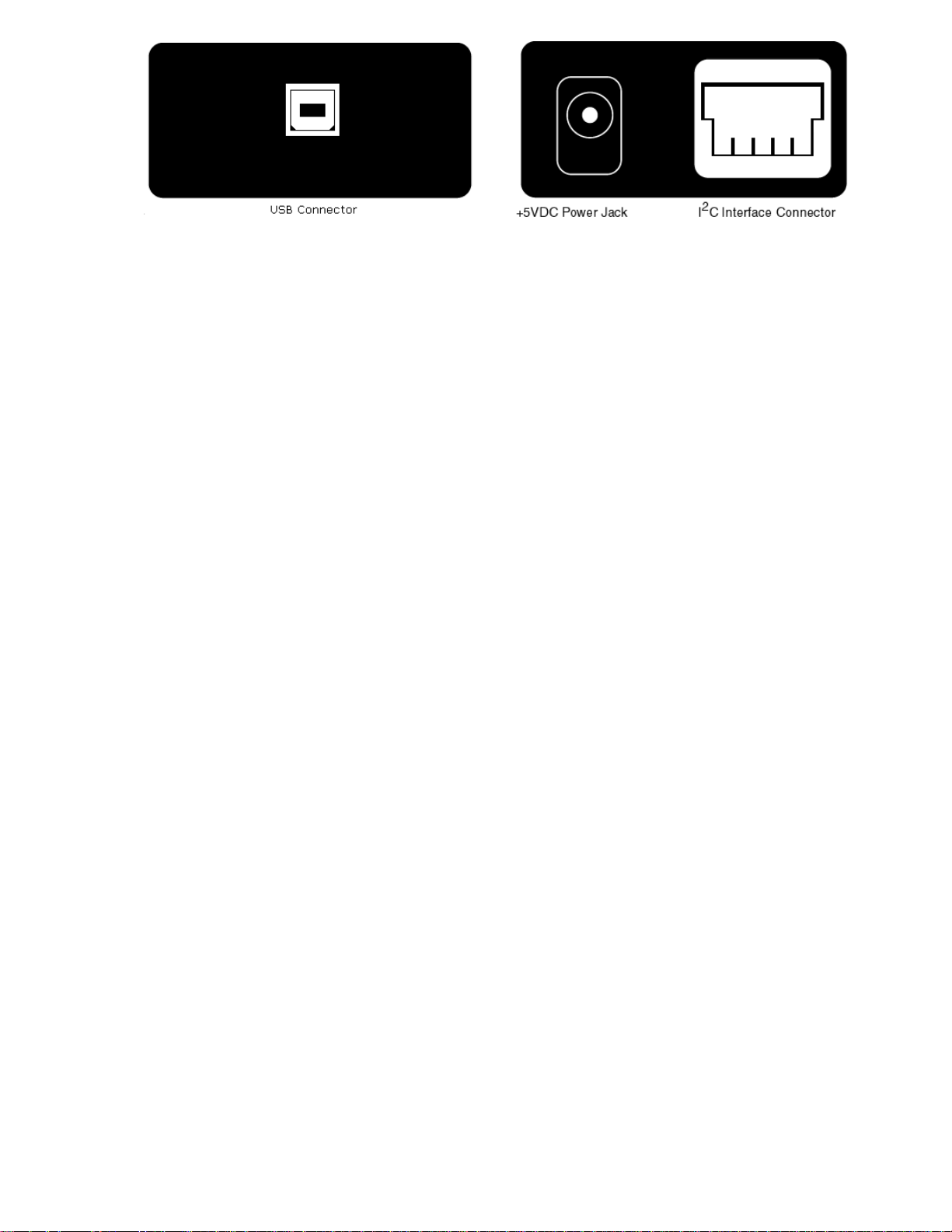
2.1 USB Connector
2
The USB connector provides connection from the I
C adapter to a USB port on the
host computer or self-powered USB hub. The iPort DLL/USB operates as a
bus-powered USB device, with limited target system power. Additional target
system power can be provided via an included external power supply.
2.1.1 Virtual Communications Port (VCP)
The iPort DLL/USB provides a Virtual Communications Port (VCP) interface via a
host computer driver. Application programs running on the host computer
communicate with the iPort DLL/USB via the standard iPort DLL.
2.2 +5VDC Power Jack
The iPort DLL/USB is a bus-powered USB device. When deriving power from the
Universal Serial Bus only, a limited amount of power is available to a target system
2
via +5V wire in the I
C Interface Connector. Additional power for a target system
can be provided via the +5VDC Power Jack. When connected to the +5VDC Power
Jack, an external power supply will remove all target system power load from the
USB and replace it with power from the external power supply. See the “Hardware
Setup” section for additional details.
2
2.3 I
The I
(see Appendix A) for interfacing to an external I
Clock (SCL), I
Minimum wiring for I
C Interface Connector
2
C adapter includes a four wire, positive locking, modular receptacle connector
2
C Bus. Lines provided include I2C
2
C Data (SDA), Ground, and +5V.
2
C communications include I2C Clock, Data, and Ground.
4
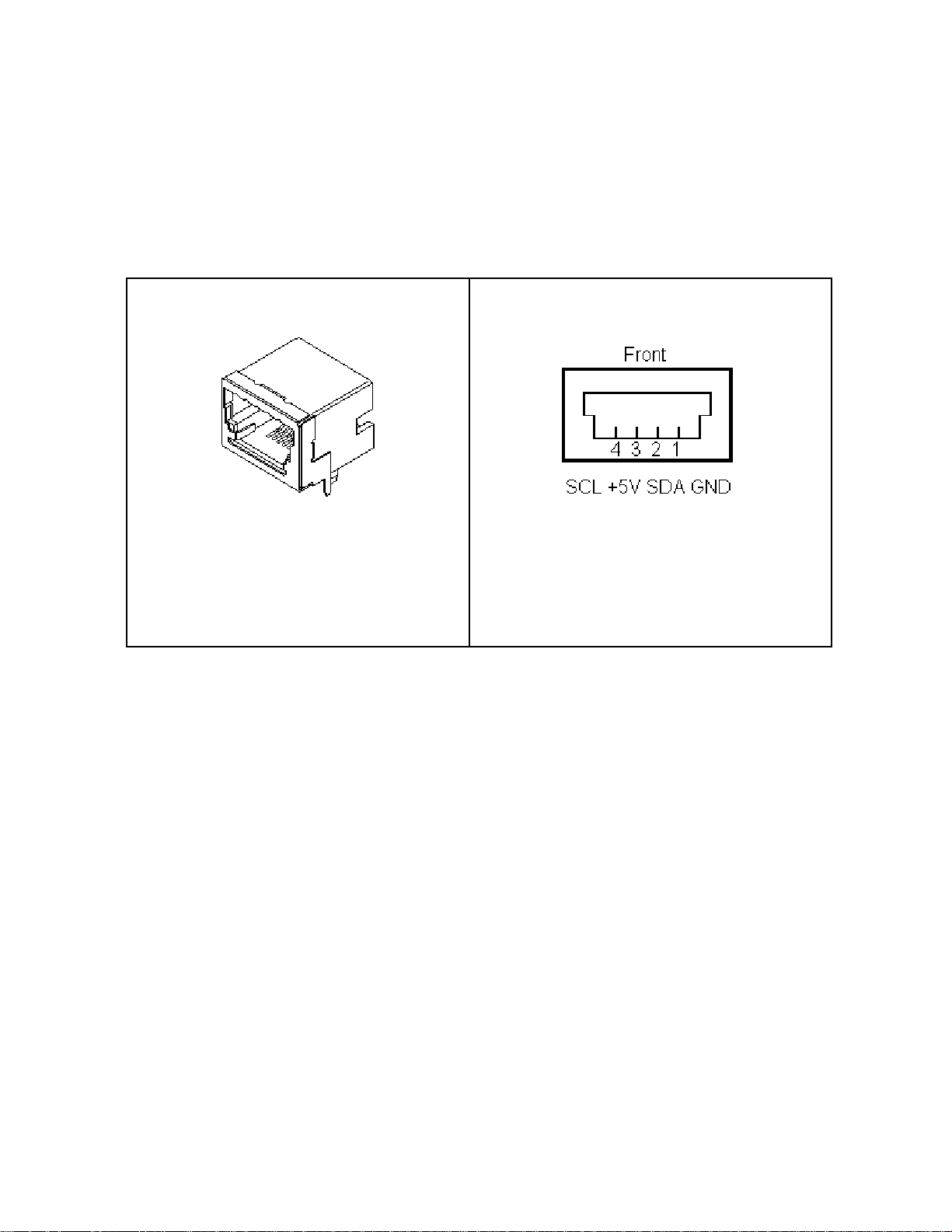
Use of the +5V wire in the I2C Interface connector is optional. Connect this wire to
the target system to power the target system from either:
1 USB derived power. Maximum available target system power is 100 ma at
+5V.
2 A +5VDC Power Jack connected external +5V regulated power supply.
Maximum available target system power is 250 ma at +5V.
Receptacle Connector
An I2C Clip-Lead cable is provided to connect the I2C adapter to a target system.
Each clip-lead is clearly marked (C=SCL, V=+5VDC, D=SDA, G=Ground).
2
An I
also provided to connect the I
standard I
connector compatible with your target system. Additional I
C Interface Cable (White=SCL, Red=+5VDC, Green=SDA, Black=Ground) is
2
C adapter to an external I2C Bus. Since there is no
2
C Bus connector, you may want to cut off one end of the cable and add a
2
C Interface Cables (4
ft., 8 ft., or 16 ft.), and modular connectors are available from MCC. Additional
Clip-Lead cables are also available. (see Appendix A)
5

3 Hardware Configuration
3.1 Pull-up Resistors
2
C Bus systems are based on open-collector technology requiring pull-up devices
I
on each signal wire. These pull-up devices usually take the form of pull-up resistors
connected to bus power.
2
The I
2
I
Every I
C adapter includes a slide switch used to enable or disable internal +5VDC
C Bus 1.8K ohm pull-up resistors attached to the SCL, SDA, and /INT lines.
2
C Bus system must have at least one pull-up on the signal lines. Use this
switch to configure the pull-up resistors for your system.
3.2 Connecting to a 3.3 Volt Target System
2
If you are connecting the I
C adapter to a 3.3 volt target system, you should follow
these steps BEFORE applying power:
2
• Shut off the I
C adapter’s internal pull-ups (See Pull-up Resistor section). Use
external pull-ups to the target system’s 3.3V power. These pull-ups may already
be present in the target system.
2
• Disconnect the I
C connector +5V wire from the target system. The I2C adapter
will be powered from its own +5V power supply, and the target system will be
powered by its own 3.3V power supply.
2
The I
C adapter is a 5-volt device. Any signal above 3.3V on the SCL, SDA, and
/INT lines is high enough for the adapter to see a Logical 1.
3.3 Connecting to an SMBus Target System
2
If you are connecting the I
C adapter to a SMBus target system, you should follow
these steps BEFORE applying power:
2
• Shut off the I
C adapter’s internal pull-ups (See Pull-up Resistor section).
• Use external SMBus rated (appoximately15k ohms) pull-up resistors. These
pull-ups may already be present in the target system.
2
• Visit our I
C versus SMBus FAQ page (www.mcc-us.com/I2CSMBusFAQ.htm).
• See the SMBus Specification for additional details.
2
Special Note for SMBus Users: MCC’s I
C adapters are designed to be I2C Bus
6

compatible, not SMBus compatible. Some features of the SMBus protocol not
supported include time-outs, device reset, and Packet Error Check byte processing.
2
The non-supported SMBus features may, or may not, permit the use of the I
C
adapter in your SMBus application. Consult the MCC FAQ web page and SMBus
Specification for details.
4 ESD (Electrostatic Discharge) Precautions
Electrostatic discharge is defined as the transfer of charge between bodies at
different electrical potentials. Electrostatic discharge can change the electrical
characteristics of a semiconductor device, degrading or destroying it. Electrostatic
discharge also may upset the normal operation of an electronic system, causing
equipment malfunction or failure.
2
When connecting the I
C adapter to a host computer and a target system, extreme
care must be taken to avoid electrostatic discharge. Failure to follow ESD protection
2
procedures when using the I
C adapter could damage the host computer, I2C
adapter, or the target system, and void product warranty coverage.
4.1 Host Computer Grounding
Case 1 - Desktop and Single-board Computers. The chassis on a desktop or
single-board host computer must be connected to earth ground to comply with
safety regulations. If the computer chassis is NOT connected to earth ground for
some reason (i.e., use of a two-prong power mains plug), the host computer power
supply ground will float to some unknown voltage potential.
Case 2 - Laptop Computers. Laptop computers present special ESD problems. Most
laptop computers use an external double-insulated mains power supply which is
NOT connected to the mains earth ground. This means that the laptop chassis is
floating at some unknown voltage potential.
2
In either case, upon connection to the I
computer will discharge energy through its serial port to the I
the target system. This discharge could damage the host computer, I
C adapter and the target system, the host
2
C adapter, and on to
2
C adapter, and
the target system.
7

4.2 Grounding Solutions
2
To avoid damage to the host computer, I
C adapter, or target system, follow these
instructions:
• Wear an earth grounded wrist strap, or discharge any static charge build-up,
2
when handling the I
C adapter or any target system devices.
• Ensure that both the host computer and target system are connected to a common
earth ground point.
• Make sure that all interconnections are made BEFORE applying power to the
2
host computer, I
C adapter, and target system.
• If you are using a laptop computer or host computer that is NOT connected to
mains earth ground, make a hard-wired connection from the host computer (i.e.,
port connector shell) and the target system ground connector to a common earth
ground point.
• Avoid plugging and unplugging system components while the host computer or
target system is powered.
• Ensure that any devices connected to the target system are properly grounded to
the common earth ground point.
• If unsure how to properly ground system components, seek electrical expert help.
WARNING: Any damage caused by Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) through
inadequate earth grounding is NOT covered under the warranty of this product.
5 Hardware Set-Up
2
This section provides information on connecting the I
2
computer and I
C Bus target system.
C adapter to your host
1. Attach the iPort DLL/USB adapter to a free USB port on your host computer
or self-powered USB hub. If this is the first time the iPort DLL/USB is
connected to the host computer, the Windows Hardware Wizard will appear.
Follow the on-screen directions. The required driver files can be found in the
root-directory of the iPort Utility Pack for Windows CD, and after iPort
Utility Pack software installation, in the installed iPortDLLUSB Driver folder.
NOTE: The Hardware Wizard may run multiple times to install the iPort
DLL/USB VCP driver, and the iPort DLL/USB device. If the Hardware
Wizard warns that the driver files is not certified, press continue.
8

The Windows Hardware Wizard will assign the iPort DLL/USB to a new
communications port number. You can find the ComPort number of the iPort
DLL/USB by running our Message Center or Message Manager software, and
selecting the iPort DLL/USB device. You can also find the ComPort number
by expanding the Ports Icon in the Windows Control Panel | System | Device
Manager application.
At this time you can install the iPort Utility Pack software. See the installation
instructions in “Part 2 - iPort Utility Pack for Windows” of this User’s Guide.
2
2. Connect the I
make this connection with the included I
C Bus cable to the I2C adapter and your I2C device. You can
2
C Clip-Lead cable or I2C Interface
Cable.
2
The I
C interconnect includes a +5V wire. You may not need to, or want to,
connect the +5V wire to your target system. Refer to the “+5VDC Power
Jack” and “Hardware Configuration” sections for details on pull-up resistors
and connecting the optional +5V wire.
3. Optionally connect the external power supply to the power jack. I
power is derived from the USB, with a limited amount of power available to
2
the target system via the I
provides additional power to the target system via the I
C connector. Use of the external power supply
2
C connector. See
“+5VDC Power Jack” section for additional details.
2
If you have any questions on I
C adapter setup and configuration, please contact our
technical support department via our web site.
2
C adapter
9
 Loading...
Loading...