Page 1

Color Television Chassis
LC9.2L
LA
18610_000_090602.eps
090604
Contents Page Contents Page
1. Revision List 2
2. Technical Specifications and Connections 2
3. Precautions, Notes, and Abbreviation List 5
4. Mechanical Instructions 9
5. Service Modes, Error Codes, and Fault Finding 21
6. Alignments 36
7. Circuit Descriptions 41
8. IC Data Sheets 43
9. Block Diagrams
Wiring Diagram 32" (P & S) 47
Wiring Diagram 42" (P & S) 48
Wiring Diagram 42"(Frame) 49
Wiring Diagram 47"(P & S) 50
Wiring Diagram 52"(Frame) 51
Block Diagram Video 52
Block Diagram Audio 53
Block Diagram Control & Clock Signals 54
Block Diagram I2C 55
Supply Lines Overview 56
10. Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts Drawing PWB
SSB: DC/DC
SSB: Tuner & Analog demodulator (B02A) 58 74
SSB: Class-D & Muting (B03) 59 74
SSB: MTK Power (B04A) 60 74
SSB: GDDR3 (B04B) 61 74
SSB: Flash & EJTAG (B04C) 62 74
SSB: Display interface - LVDS (B04D) 63 74
SSB: Ambilight (B04E) 64 74
SSB: HDMI & MUX (B05) 65 74
SSB: Digital I/O - Ethernet (provisional) (B06A) 66 74
SSB: Analog I/O - YPbPr (B06B) 67 74
SSB: Analog I/O - Cinch (B06C) 68 74
SSB: Side - A/V & USB (B06D) 69 74
SSB: VGA (B06E) 70 74
SSB: BDS iTV (B07) 71 74
SSB: SRP List Explanation 72
SSB: SRP List 73
(B01) 57 74
©
Copyright 2009 Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V.
All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a
retrieval system or transmitted, in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical,
photocopying, or otherwise without the prior permission of Philips.
Published by JA/WS 0968 BU TV Consumer Care Printed in the Netherlands Subject to modification EN 3122 785 18700
2010-Jul-01
Page 2
EN 2 LC9.2L LA1.
Revision List
1. Revision List
Manual xxxx xxx xxxx.0
• First release.
2. Technical Specifications and Connections
Index of this chapter:
2.1 Technical Specifications
2.2 Directions for Use
2.3 Connections
2.4 Chassis Overview
Notes:
• Figures can deviate due to the different set executions.
• Specifications are indicative (subject to change).
2.1 Technical Specifications
For on-line product support please use the links in Table 2-1.
Here is product information available, as well as getting started,
user manuals, frequently asked questions and software &
drivers.
Table 2-1 Described Model numbers
CTN Styling Published in:
32PFL5604D/78
42PFL5604D/78
42PFL7404D/78
47PFL5604D/78
52PFL7404D/78
P & S 3122 785 18700
P & S 3122 785 18700
Frame 3122 785 18700
P & S 3122 785 18700
Frame 3122 785 18700
2.2 Directions for Use
You can download this information from the following websites:
http://www.philips.com/support
http://www.p4c.philips.com
2010-Jul-01
Page 3

2.3 Connections
18700_001_090828.eps
090828
9
10
11
12
13
14
8
Rear connectors
Side connectors
1
2
6
3
4
5
7
1
2
6
3
4
5
7
1 2 3 4
10000_022_090121.eps
090121
Technical Specifications and Connections
EN 3LC9.2L LA 2.
2.3.1 Side Connectors
Figure 2-1 Connection overview
Note: The following connector color abbreviations are used
(according to DIN/IEC 757): Bk= Black, Bu= Blue, Gn= Green,
Gy= Grey, Rd= Red, Wh= White, Ye= Yellow.
1 - Cinch: Audio - In
Rd - Audio R 0.5 V
Wh - Audio L 0.5 V
2 - Cinch: Video CVBS - In
Ye - Video CVBS 1 V
3 - S-Video (Hosiden): Video Y/C - In
1 - Ground Y Gnd H
2 - Ground C Gnd H
3 - Video Y 1 V
4 - Video C 0.3 V
4 - Head phone (Output)
Bk - Head phone 32 - 600 Ω / 10 mW ot
/ 10 kΩ jq
RMS
/ 10 kΩ jq
RMS
/ 75 Ω jq
PP
/ 75 Ω j
PP
/ 75 Ω j
PP
5 - USB2.0
Figure 2-2 USB (type A)
1-+5V k
2 - Data (-) jk
3 - Data (+) jk
4 - Ground Gnd H
6 - HDMI: Digital Video, Digital Audio - In (see HDMI 1 & 2)
7 - Service Connector (UART)
1 - Ground Gnd H
2 - UART_TX Transmit k
3 - UART_RX Receive j
2010-Jul-01
Page 4

EN 4 LC9.2L LA2.
1
6
10
11
5
15
10000_002_090121.eps
090127
19
1
18 2
E_06532_017.eps
250505
Technical Specifications and Connections
2.3.2 Rear Connectors
8 - Aerial - In (Cable and Air)
- - F-type Coax, 75 Ω D
9 - Mini Jack: Audio - In
Wh - Audio L 0.5 V
Rd - Audio R 0.5 V
/ 10 kΩ jo
RMS
/ 10 kΩ jo
RMS
10 - VGA: Video RGB - In
Figure 2-3 VGA Connector
1 - Video Red 0.7 V
2 - Video Green 0.7 V
3 - Video Blue 0.7 V
4-n.c.
/ 75 Ω j
PP
/ 75 Ω j
PP
/ 75 Ω j
PP
5 - Ground Gnd H
6 - Ground Red Gnd H
7 - Ground Green Gnd H
8 - Ground Blue Gnd H
9-+5V
10 - Ground Sync Gnd H
+5 V j
DC
11 - n.c.
12 - DDC_SDA DDC data j
13 - H-sync 0 - 5 V j
14 - V-sync 0 - 5 V j
15 - DDC_SCL DDC clock j
11 - Cinch: S/PDIF - Out
Bk - Coaxial 0.4 - 0.6V
/ 75 ohm kq
PP
12 - Cinch: Video CVBS - In, Audio - In
Ye - Video CVBS 1 V
/ 75 ohm jq
PP
Wh - Audio L 0.5 V
Rd - Audio R 0.5 V
/ 10 kohm jq
RMS
/ 10 kohm jq
RMS
13 - CVI-1 & 2: Cinch: Video YPbPr - In, Audio - In
Gn - Video Y 1 V
Bu - Video Pb 0.7 V
Rd - Video Pr 0.7 V
Wh - Audio - L 0.5 V
Rd - Audio - R 0.5 V
/ 75 Ω jq
PP
/ 75 Ω jq
PP
/ 75 Ω jq
PP
/ 10 kΩ jq
RMS
/ 10 kΩ jq
RMS
14 - HDMI 1, 2, and 3: Digital Video, Digital Audio - In
Figure 2-4 HDMI (type A) connector
1 - D2+ Data channel j
2 - Shield Gnd H
3 - D2- Data channel j
4 - D1+ Data channel j
5 - Shield Gnd H
6 - D1- Data channel j
7 - D0+ Data channel j
8 - Shield Gnd H
9 - D0- Data channel j
10 - CLK+ Data channel j
11 - Shield Gnd H
12 - CLK- Data channel j
13 - Easylink/CEC Control channel jk
14 - n.c.
15 - DDC_SCL DDC clock j
16 - DDC_SDA DDC data jk
17 - Ground Gnd H
18 - +5V j
19 - HPD Hot Plug Detect j
20 - Ground Gnd H
2.4 Chassis Overview
Refer to chapter 9. Block Diagrams for PWB/CBA locations.
2010-Jul-01
Page 5

Precautions, Notes, and Abbreviation List
3. Precautions, Notes, and Abbreviation List
EN 5LC9.2L LA 3.
Index of this chapter:
3.1 Safety Instructions
3.2 Warnings
3.3 Notes
3.4 Abbreviation List
3.1 Safety Instructions
Safety regulations require the following during a repair:
• Connect the set to the Mains/AC Power via an isolation
transformer (> 800 VA).
• Replace safety components, indicated by the symbol h,
only by components identical to the original ones. Any
other component substitution (other than original type) may
increase risk of fire or electrical shock hazard.
Safety regulations require that after a repair, the set must be
returned in its original condition. Pay in particular attention to
the following points:
• Route the wire trees correctly and fix them with the
mounted cable clamps.
• Check the insulation of the Mains/AC Power lead for
external damage.
• Check the strain relief of the Mains/AC Power cord for
proper function.
• Check the electrical DC resistance between the Mains/AC
Power plug and the secondary side (only for sets that have
a Mains/AC Power isolated power supply):
1. Unplug the Mains/AC Power cord and connect a wire
between the two pins of the Mains/AC Power plug.
2. Set the Mains/AC Power switch to the “on” position
(keep the Mains/AC Power cord unplugged!).
3. Measure the resistance value between the pins of the
Mains/AC Power plug and the metal shielding of the
tuner or the aerial connection on the set. The reading
should be between 4.5 MΩ and 12 MΩ.
4. Switch “off” the set, and remove the wire between the
two pins of the Mains/AC Power plug.
• Check the cabinet for defects, to prevent touching of any
inner parts by the customer.
• Where necessary, measure the waveforms and voltages
with (D) and without (E) aerial signal. Measure the
voltages in the power supply section both in normal
operation (G) and in stand-by (F). These values are
indicated by means of the appropriate symbols.
3.3.2 Schematic Notes
• All resistor values are in ohms, and the value multiplier is
often used to indicate the decimal point location (e.g. 2K2
indicates 2.2 kΩ).
• Resistor values with no multiplier may be indicated with
either an “E” or an “R” (e.g. 220E or 220R indicates 220 Ω).
• All capacitor values are given in micro-farads (μ=× 10
nano-farads (n =× 10
• Capacitor values may also use the value multiplier as the
decimal point indication (e.g. 2p2 indicates 2.2 pF).
• An “asterisk” (*) indicates component usage varies. Refer
to the diversity tables for the correct values.
• The correct component values are listed on the Philips
Spare Parts Web Portal.
3.3.3 Spare Parts
For the latest spare part overview, consult your Philips Spare
Part web portal.
3.3.4 BGA (Ball Grid Array) ICs
Introduction
For more information on how to handle BGA devices, visit this
URL: http://www.atyourservice-magazine.com
“Magazine”, then go to “Repair downloads”. Here you will find
Information on how to deal with BGA-ICs.
BGA Temperature Profiles
For BGA-ICs, you must use the correct temperature-profile.
Where applicable and available, this profile is added to the IC
Data Sheet information section in this manual.
-9
), or pico-farads (p =× 10
. Select
-12
-6
),
).
3.2 Warnings
• All ICs and many other semiconductors are susceptible to
electrostatic discharges (ESD w). Careless handling
during repair can reduce life drastically. Make sure that,
during repair, you are connected with the same potential as
the mass of the set by a wristband with resistance. Keep
components and tools also at this same potential.
• Be careful during measurements in the high voltage
section.
• Never replace modules or other components while the unit
is switched “on”.
• When you align the set, use plastic rather than metal tools.
This will prevent any short circuits and the danger of a
circuit becoming unstable.
3.3 Notes
3.3.1 General
• Measure the voltages and waveforms with regard to the
chassis (= tuner) ground (H), or hot ground (I), depending
on the tested area of circuitry. The voltages and waveforms
shown in the diagrams are indicative. Measure them in the
Service Default Mode with a colour bar signal and stereo
sound (L: 3 kHz, R: 1 kHz unless stated otherwise) and
picture carrier at 475.25 MHz for PAL, or 61.25 MHz for
NTSC (channel 3).
3.3.5 Lead-free Soldering
Due to lead-free technology some rules have to be respected
by the workshop during a repair:
• Use only lead-free soldering tin. If lead-free solder paste is
required, please contact the manufacturer of your soldering
equipment. In general, use of solder paste within
workshops should be avoided because paste is not easy to
store and to handle.
• Use only adequate solder tools applicable for lead-free
soldering tin. The solder tool must be able:
– To reach a solder-tip temperature of at least 400°C.
– To stabilize the adjusted temperature at the solder-tip.
– To exchange solder-tips for different applications.
• Adjust your solder tool so that a temperature of around
360°C - 380°C is reached and stabilized at the solder joint.
Heating time of the solder-joint should not exceed ~ 4 sec.
Avoid temperatures above 400°C, otherwise wear-out of
tips will increase drastically and flux-fluid will be destroyed.
To avoid wear-out of tips, switch “off” unused equipment or
reduce heat.
• Mix of lead-free soldering tin/parts with leaded soldering
tin/parts is possible but PHILIPS recommends strongly to
avoid mixed regimes. If this cannot be avoided, carefully
clear the solder-joint from old tin and re-solder with new tin.
3.3.6 Alternative BOM identification
It should be noted that on the European Service website,
“Alternative BOM” is referred to as “Design variant”.
2010-Jul-01
Page 6

EN 6 LC9.2L LA3.
Precautions, Notes, and Abbreviation List
The third digit in the serial number (example:
AG2B0335000001) indicates the number of the alternative
B.O.M. (Bill Of Materials) that has been used for producing the
specific TV set. In general, it is possible that the same TV
model on the market is produced with e.g. two different types
of displays, coming from two different suppliers. This will then
result in sets which have the same CTN (Commercial Type
Number; e.g. 28PW9515/12) but which have a different B.O.M.
number.
By looking at the third digit of the serial number, one can
identify which B.O.M. is used for the TV set he is working with.
If the third digit of the serial number contains the number “1”
(example: AG1B033500001), then the TV set has been
manufactured according to B.O.M. number 1. If the third digit is
a “2” (example: AG2B0335000001), then the set has been
produced according to B.O.M. no. 2. This is important for
ordering the correct spare parts!
For the third digit, the numbers 1...9 and the characters A...Z
can be used, so in total: 9 plus 26= 35 different B.O.M.s can be
indicated by the third digit of the serial number.
Identification: The bottom line of a type plate gives a 14-digit
serial number. Digits 1 and 2 refer to the production centre (e.g.
AG is Bruges), digit 3 refers to the B.O.M. code, digit 4 refers
to the Service version change code, digits 5 and 6 refer to the
production year, and digits 7 and 8 refer to production week (in
example below it is 2006 week 17). The 6 last digits contain the
serial number.
MODEL :
PROD.NO:
32PF9968/10
AG 1A0617 000001
MADE IN BELGIUM
220-240V 50/60Hz
VHF+S+H+UHF
S
10000_024_090121.eps
~
BJ3.0E LA
Figure 3-1 Serial number (example)
3.3.7 Board Level Repair (BLR) or Component Level Repair (CLR)
If a board is defective, consult your repair procedure to decide
if the board has to be exchanged or if it should be repaired on
component level.
If your repair procedure says the board should be exchanged
completely, do not solder on the defective board. Otherwise, it
cannot be returned to the O.E.M. supplier for back charging!
3.3.8 Practical Service Precautions
• It makes sense to avoid exposure to electrical shock.
While some sources are expected to have a possible
dangerous impact, others of quite high potential are of
limited current and are sometimes held in less regard.
• Always respect voltages. While some may not be
dangerous in themselves, they can cause unexpected
reactions that are best avoided. Before reaching into a
powered TV set, it is best to test the high voltage insulation.
It is easy to do, and is a good service precaution.
128W
100105
3.4 Abbreviation List
0/6/12 SCART switch control signal on A/V
board. 0 = loop through (AUX to TV),
6 = play 16 : 9 format, 12 = play 4 : 3
format
AARA Automatic Aspect Ratio Adaptation:
algorithm that adapts aspect ratio to
remove horizontal black bars; keeps
the original aspect ratio
ACI Automatic Channel Installation:
algorithm that installs TV channels
directly from a cable network by
means of a predefined TXT page
ADC Analogue to Digital Converter
AFC Automatic Frequency Control: control
signal used to tune to the correct
frequency
AGC Automatic Gain Control: algorithm that
controls the video input of the feature
box
AM Amplitude Modulation
AP Asia Pacific
AR Aspect Ratio: 4 by 3 or 16 by 9
ASF Auto Screen Fit: algorithm that adapts
aspect ratio to remove horizontal black
bars without discarding video
information
ATSC Advanced Television Systems
Committee, the digital TV standard in
the USA
ATV See Auto TV
Auto TV A hardware and software control
system that measures picture content,
and adapts image parameters in a
dynamic way
AV External Audio Video
AVC Audio Video Controller
AVIP Audio Video Input Processor
B/G Monochrome TV system. Sound
carrier distance is 5.5 MHz
BDS Business Display Solutions (iTV)
BLR Board-Level Repair
BTSC Broadcast Television Standard
Committee. Multiplex FM stereo sound
system, originating from the USA and
used e.g. in LATAM and AP-NTSC
countries
B-TXT Blue TeleteXT
C Centre channel (audio)
CEC Consumer Electronics Control bus:
remote control bus on HDMI
connections
CL Constant Level: audio output to
connect with an external amplifier
CLR Component Level Repair
ComPair Computer aided rePair
CP Connected Planet / Copy Protection
CSM Customer Service Mode
CTI Color Transient Improvement:
manipulates steepness of chroma
transients
CVBS Composite Video Blanking and
Synchronization
DAC Digital to Analogue Converter
DBE Dynamic Bass Enhancement: extra
low frequency amplification
DCM Data Communication Module. Also
referred to as System Card or
Smartcard (for iTV).
DDC See “E-DDC”
D/K Monochrome TV system. Sound
carrier distance is 6.5 MHz
DFI Dynamic Frame Insertion
2010-Jul-01
Page 7

Precautions, Notes, and Abbreviation List
EN 7LC9.2L LA 3.
DFU Directions For Use: owner's manual
DMR Digital Media Reader: card reader
DMSD Digital Multi Standard Decoding
DNM Digital Natural Motion
DNR Digital Noise Reduction: noise
reduction feature of the set
DRAM Dynamic RAM
DRM Digital Rights Management
DSP Digital Signal Processing
DST Dealer Service Tool: special remote
control designed for service
technicians
DTCP Digital Transmission Content
Protection; A protocol for protecting
digital audio/video content that is
traversing a high speed serial bus,
such as IEEE-1394
DVB-C Digital Video Broadcast - Cable
DVB-T Digital Video Broadcast - Terrestrial
DVD Digital Versatile Disc
DVI(-d) Digital Visual Interface (d= digital only)
E-DDC Enhanced Display Data Channel
(VESA standard for communication
channel and display). Using E-DDC,
the video source can read the EDID
information form the display.
EDID Extended Display Identification Data
(VESA standard)
EEPROM Electrically Erasable and
Programmable Read Only Memory
EMI Electro Magnetic Interference
EPG Electronic Program Guide
EPLD Erasable Programmable Logic Device
EU Europe
EXT EXTernal (source), entering the set by
SCART or by cinches (jacks)
FDS Full Dual Screen (same as FDW)
FDW Full Dual Window (same as FDS)
FLASH FLASH memory
FM Field Memory or Frequency
Modulation
FPGA Field-Programmable Gate Array
FTV Flat TeleVision
Gb/s Giga bits per second
G-TXT Green TeleteXT
H H_sync to the module
HD High Definition
HDD Hard Disk Drive
HDCP High-bandwidth Digital Content
Protection: A “key” encoded into the
HDMI/DVI signal that prevents video
data piracy. If a source is HDCP coded
and connected via HDMI/DVI without
the proper HDCP decoding, the
picture is put into a “snow vision” mode
or changed to a low resolution. For
normal content distribution the source
and the display device must be
enabled for HDCP “software key”
decoding.
HDMI High Definition Multimedia Interface
HP HeadPhone
I Monochrome TV system. Sound
2
I
C Inter IC bus
2
I
D Inter IC Data bus
2
I
S Inter IC Sound bus
carrier distance is 6.0 MHz
IF Intermediate Frequency
IR Infra Red
IRQ Interrupt Request
ITU-656 The ITU Radio communication Sector
(ITU-R) is a standards body
subcommittee of the International
Telecommunication Union relating to
radio communication. ITU-656 (a.k.a.
SDI), is a digitized video format used
for broadcast grade video.
Uncompressed digital component or
digital composite signals can be used.
The SDI signal is self-synchronizing,
uses 8 bit or 10 bit data words, and has
a maximum data rate of 270 Mbit/s,
with a minimum bandwidth of 135
MHz.
ITV Institutional TeleVision; TV sets for
hotels, hospitals etc.
LS Last Status; The settings last chosen
by the customer and read and stored
in RAM or in the NVM. They are called
at start-up of the set to configure it
according to the customer's
preferences
LATAM Latin America
LCD Liquid Crystal Display
LED Light Emitting Diode
L/L' Monochrome TV system. Sound
carrier distance is 6.5 MHz. L' is Band
I, L is all bands except for Band I
LPL LG.Philips LCD (supplier)
LS Loudspeaker
LVDS Low Voltage Differential Signalling
Mbps Mega bits per second
M/N Monochrome TV system. Sound
carrier distance is 4.5 MHz
MHEG Part of a set of international standards
related to the presentation of
multimedia information, standardised
by the Multimedia and Hypermedia
Experts Group. It is commonly used as
a language to describe interactive
television services
MIPS Microprocessor without Interlocked
Pipeline-Stages; A RISC-based
microprocessor
MOP Matrix Output Processor
MOSFET Metal Oxide Silicon Field Effect
Transistor, switching device
MPEG Motion Pictures Experts Group
MPIF Multi Platform InterFace
MUTE MUTE Line
MTV Mainstream TV: TV-mode with
Consumer TV features enabled (iTV)
NC Not Connected
NICAM Near Instantaneous Compounded
Audio Multiplexing. This is a digital
sound system, mainly used in Europe.
NTC Negative Temperature Coefficient,
non-linear resistor
NTSC National Television Standard
Committee. Color system mainly used
in North America and Japan. Color
carrier NTSC M/N= 3.579545 MHz,
NTSC 4.43= 4.433619 MHz (this is a
VCR norm, it is not transmitted off-air)
NVM Non-Volatile Memory: IC containing
TV related data such as alignments
O/C Open Circuit
OSD On Screen Display
OAD Over the Air Download. Method of
software upgrade via RF transmission.
Upgrade software is broadcasted in
TS with TV channels.
OTC On screen display Teletext and
Control; also called Artistic (SAA5800)
P50 Project 50: communication protocol
between TV and peripherals
PAL Phase Alternating Line. Color system
mainly used in West Europe (color
carrier= 4.433619 MHz) and South
America (color carrier PAL M=
2010-Jul-01
Page 8

EN 8 LC9.2L LA3.
Precautions, Notes, and Abbreviation List
3.575612 MHz and PAL N= 3.582056
MHz)
PCB Printed Circuit Board (same as “PWB”)
PCM Pulse Code Modulation
PDP Plasma Display Panel
PFC Power Factor Corrector (or Pre-
conditioner)
PIP Picture In Picture
PLL Phase Locked Loop. Used for e.g.
FST tuning systems. The customer
can give directly the desired frequency
POD Point Of Deployment: a removable
CAM module, implementing the CA
system for a host (e.g. a TV-set)
POR Power On Reset, signal to reset the uP
PSDL Power Supply for Direct view LED
backlight with 2D-dimming
PSL Power Supply with integrated LED
drivers
PSLS Power Supply with integrated LED
drivers with added Scanning
functionality
PTC Positive Temperature Coefficient,
non-linear resistor
PWB Printed Wiring Board (same as “PCB”)
PWM Pulse Width Modulation
QRC Quasi Resonant Converter
QTNR Quality Temporal Noise Reduction
QVCP Quality Video Composition Processor
RAM Random Access Memory
RGB Red, Green, and Blue. The primary
color signals for TV. By mixing levels
of R, G, and B, all colors (Y/C) are
reproduced.
RC Remote Control
RC5 / RC6 Signal protocol from the remote
control receiver
RESET RESET signal
ROM Read Only Memory
RSDS Reduced Swing Differential Signalling
data interface
R-TXT Red TeleteXT
SAM Service Alignment Mode
S/C Short Circuit
SCART Syndicat des Constructeurs
d'Appareils Radiorécepteurs et
Téléviseurs
SCL Serial Clock I
SCL-F CLock Signal on Fast I
SD Standard Definition
SDA Serial Data I
SDA-F DAta Signal on Fast I
2
C
2
C bus
2
C
2
C bus
SDI Serial Digital Interface, see “ITU-656”
SDRAM Synchronous DRAM
SECAM SEequence Couleur Avec Mémoire.
Color system mainly used in France
and East Europe. Color carriers=
4.406250 MHz and 4.250000 MHz
SIF Sound Intermediate Frequency
SMPS Switched Mode Power Supply
SoC System on Chip
SOG Sync On Green
SOPS Self Oscillating Power Supply
SPI Serial Peripheral Interface bus; a 4-
wire synchronous serial data link
standard
S/PDIF Sony Philips Digital InterFace
SRAM Static RAM
SRP Service Reference Protocol
SSB Small Signal Board
SSC Spread Spectrum Clocking, used to
reduce the effects of EMI
STB Set Top Box
STBY STand-BY
SVGA 800 × 600 (4:3)
SVHS Super Video Home System
SW Software
SWAN Spatial temporal Weighted Averaging
Noise reduction
SXGA 1280 × 1024
TFT Thin Film Transistor
THD Total Harmonic Distortion
TMDS Transmission Minimized Differential
Signalling
TS Transport Stream
TXT TeleteXT
TXT-DW Dual Window with TeleteXT
UI User Interface
uP Microprocessor
UXGA 1 600 × 1 200 (4:3)
V V-sync to the module
VESA Video Electronics Standards
Association
VGA 640 × 480 (4:3)
VL Variable Level out: processed audio
output toward external amplifier
VSB Vestigial Side Band; modulation
method
WYSIWYR What You See Is What You Record:
record selection that follows main
picture and sound
WXGA 1280 × 768 (15:9)
XTAL Quartz crystal
XGA 1 024 × 768 (4:3)
Y Luminance signal
Y/C Luminance (Y) and Chrominance (C)
signal
YPbPr Component video. Luminance and
scaled color difference signals (B-Y
and R-Y)
YUV Component video
2010-Jul-01
Page 9

4. Mechanical Instructions
18700_101_090824.eps
090824
Mechanical Instructions
EN 9LC9.2L LA 4.
Index of this chapter:
4.1 Cable Dressing
4.1.1 32PFL5604D/78
4.1.2 42PFL5604D/78
4.1.3 42PFL7404D/78
4.1.4 47PFL5604D/78
4.1.5 52PFL7404D/78
4.2 Service Positions
4.3 Assy/Panel Removal
4.4 Set Re-assembly
4.1 Cable Dressing
4.1.1 32PFL5604D/78
Notes:
• Figures below can deviate slightly from the actual situation,
due to the different set executions.
Figure 4-1 General overview 32PFL5604D/78
2010-Jul-01
Page 10

EN 10 LC9.2L LA4.
1. Inverter cable route
at bottom with foam
2. Speaker cable reroute & taping
Ensure that wiretree does not
touch backcover – to avoid rattle.
18700_102_090824.eps
090824
Mechanical Instructions
2010-Jul-01
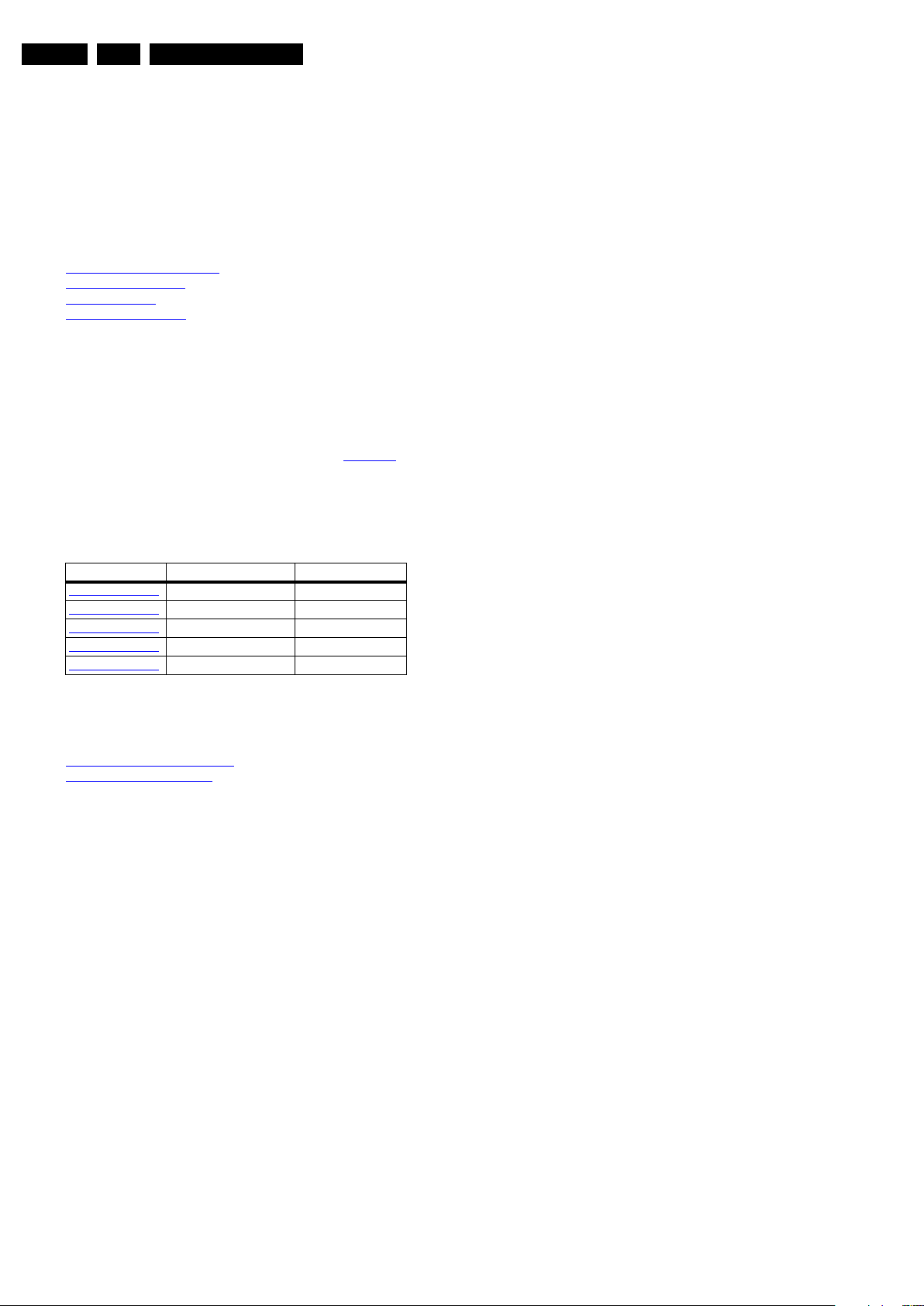
Figure 4-2 PSU section 32PFL5604D/78
Page 11

Mechanical Instructions
3. Speaker saddle
location shift downward
18700_103_090824.eps
090824
EN 11LC9.2L LA 4.
Figure 4-3 SSB section 32PFL5604D/78
2010-Jul-01
Page 12

EN 12 LC9.2L LA4.
18700_111_090824.eps
090824
18700_114_090824.eps
090824
4.1.2 42PFL5604D/78
Mechanical Instructions
Figure 4-4 General overview 42PFL5604D/78
2010-Jul-01
Figure 4-5 Light leakage taping 42PFL5604D/78
Page 13

Mechanical Instructions
Dress and
tape HV
cable &
Keyboard
cable at
least 2cm
apart.
Keyboard
Interference solution.
18700_112_090824.eps
090824
Dress and
tape HV
cable
starting
from this
end.
18700_113_090824.eps
090824
EN 13LC9.2L LA 4.
Figure 4-6 PSU section 42PFL5604D/78
Figure 4-7 SSB section 42PFL5604D/78
2010-Jul-01
Page 14

EN 14 LC9.2L LA4.
3
SYMBOL QTY
Tape 11
Saddle (S) 1
Saddle (M) 3
2X foam used for IR and side control cable
dressing. Insert the foam between panel slot.
- Cable hook
18700_121_090824.eps
090824
Reference photo (from LC09M Analog) for indication of tape location.
18700_124_090824.eps
090824
4.1.3 42PFL7404D/78
Mechanical Instructions
Figure 4-8 General overview 42PFL7404D/78
2010-Jul-01
Figure 4-9 Light leakage taping 42PFL7404D/78
Page 15

4.1.4 47PFL5604D/78
18700_131_090824.eps
090824
18700_134_090824.eps
090824
Mechanical Instructions
EN 15LC9.2L LA 4.
Figure 4-10 General overview 47PFL5604D/78
Figure 4-11 Light leakage taping 42PFL7404D/78
2010-Jul-01
Page 16
EN 16 LC9.2L LA4.
Dress and tape
HV cable &
Keyboard cable
at least 2cm
apart.
Keyboard
Interference solution.
18700_132_090824.eps
090824
Dress and
tape HV
cable
starting
from this
end.
18700_133_090824.eps
090824
Mechanical Instructions
Figure 4-12 PSU section 47PFL5604D/78
2010-Jul-01
Figure 4-13 SSB section 47PFL5604D/78
Page 17

4.1.5 52PFL7404D/78
Divison, MMMM dd, yyyy, Reference
4
SYMBOL QTY
Tape 18
Saddle (S) 2
Saddle (M) 3
2X saddle used for IR and side control cable
dres sin g. Dres s as s hown in photo.
18700_141_090824.eps
090824
Mechanical Instructions
EN 17LC9.2L LA 4.
Figure 4-14 General overview 52PFL7404D/78
2010-Jul-01
Page 18

EN 18 LC9.2L LA4.
18700_142_090824.eps
090824
LVDS short-end
at this location.
18700_143_090824.eps
090824
Mechanical Instructions
Figure 4-15 PSU section 52PFL7404D/78
2010-Jul-01
Figure 4-16 SSB section 52PFL7404D/78
Page 19

Mechanical Instructions
EN 19LC9.2L LA 4.
4.2 Service Positions
For easy servicing of this set, there are a few possibilities
created:
• The buffers from the packaging.
• Foam bars (created for Service).
4.2.1 Foam Bars
1
Required for sets
1
42"
4.3 Assy/Panel Removal
4.3.1 Rear Cover
Warning: Disconnect the mains power cord before you remove
the rear cover.
Note: it is not necessary to remove the stand while removing
the rear cover.
1. Remove all screws of the rear cover.
2. Lift the rear cover from the TV. Make sure that wires and
flat coils are not damaged while lifting the rear cover from
the set.
4.3.2 Speakers
Each speaker unit is mounted with two screws. If necessary, a
sticker on the unit indicates if it is the right (“R”) or left (“L”) box,
seen from the backside of the set, and sometimes an arrow
points to the bottom of the set.
When defective, replace the whole unit.
4.3.3 Subwoofer (if present)
Remove the screws and take out the unit. Be careful to use the
original screw and washer when re-assembling.
When defective, replace the whole unit.
4.3.4 IR & LED Board
E_06532_018.eps
171106
Figure 4-17 Foam bars
The foam bars (order code 3122 785 90580 for two pieces) can
be used for all types and sizes of Flat TVs. See Figure 4-17
for
details. Sets with a display of 42" and larger, require four foam
bars [1]. Ensure that the foam bars are always supporting the
cabinet and never only the display.
Caution: Failure to follow these guidelines can seriously
damage the display!
By laying the TV face down on the (ESD protective) foam bars,
a stable situation is created to perform measurements and
alignments. By placing a mirror under the TV, you can monitor
the screen.
1. Unplug all connectors.
2. Remove the fixation screws.
3. Take the board out.
When defective, replace the whole unit.
4.3.5 Key Board Control Panel
4. Remove the fixation screws.
5. Unplug the key board connector.
6. Take the unit out.
When defective, replace the whole unit.
4.3.6 Main Supply Panel
1. Unplug all connectors.
2. Remove the fixation screws.
3. Take the board out.
When defective, replace the whole unit.
4.3.7 Small Signal Board (SSB)
Caution: It is mandatory to remount screws at their original
position during re-assembly. Failure to do so may result in
damaging the SSB.
1. Unplug all connectors. Be careful with the fragile LVDS
connector(s)!
2. Remove all screws that secure the board.
3. Take the SSB out of the set, together with the side cover.
4. To remove the side cover, push the clamp with e.g. a
screwdriver in the middle of the cover and pull the cover
sidewards from the SSB.
2010-Jul-01
Page 20

EN 20 LC9.2L LA4.
18440_103_090223.eps
090709
1
2
3
3
3
3
2
Mechanical Instructions
4.3.8 LCD Panel
Refer to Figure 4-18
(slightly) different mechanical construction (some have the
boards directly mounted on the LCD display, others use
brackets), we only describe one model. Disassembly method of
other LCD panels is similar to the one described below (see
also cable dressing pictures for more details).
for details. As every screen size has a
1. Unplug all connectors.
2. Remove all boards as earlier described.
3. Remove the speakers as earlier described.
4. Remove the stand [1].
5. Remove all subframes from the LCD panel (e.g. [2]).
6. Remove the brackets [3] that secure the LCD Panel.
7. The LCD panel can now be lifted from the front cabinet.
Figure 4-18 LCD Panel removal (example model)
4.4 Set Re-assembly
To re-assemble the whole set, execute all processes in reverse
order.
Notes:
• While re-assembling, make sure that all cables are placed
and connected in their original position. See 4.1 Cable
Dressing.
• Pay special attention not to damage the EMC foams on the
SSB shields. Ensure that EMC foams are mounted
correctly.
2010-Jul-01
Page 21

Service Modes, Error Codes, and Fault Finding
5. Service Modes, Error Codes, and Fault Finding
EN 21LC9.2L LA 5.
Index of this chapter:
5.1 Test Points
5.2 Service Modes
5.3 Service Tools
5.4 Error Codes
5.5 The Blinking LED Procedure
5.6 Fault Finding and Repair Tips
5.7 Software Upgrading
5.1 Test Points
In the chassis schematics and layout overviews, the test points
are mentioned. In the schematics, test points are indicated with
“Fxxx” or “Ixxx”, in the layout overviews with a “half-moon” sign.
As most signals are digital, it will be difficult to measure
waveforms with a standard oscilloscope. Several key ICs are
capable of generating test patterns, which can be controlled via
ComPair. In this way it is possible to determine which part is
defective.
Perform measurements under the following conditions:
• Service Default Mode.
• Video: Color bar signal.
• Audio: 3 kHz left, 1 kHz right.
5.2 Service Modes
The Service Mode feature is split into four parts:
• Service Default Mode (SDM).
• Service Alignment Mode (SAM).
• Customer Service Mode (CSM).
• Computer Aided Repair Mode (ComPair).
SDM and SAM offer features, which can be used by the Service
engineer to repair/align a TV set. Some features are:
• A pre-defined situation to ensure measurements can be
made under uniform conditions (SDM).
• Activates the blinking LED procedure for error identification
when no picture is available (SDM).
• The possibility to overrule software protections when SDM
is entered via the Service pins.
• Make alignments (e.g. White Tone), (de)select options,
enter options codes, reset the error buffer (SAM).
• Display information (“SDM” or “SAM” indication in upper
right corner of screen, error buffer, software version,
operating hours, options and option codes, sub menus).
The CSM is a Service Mode that can be enabled by the
consumer. The CSM displays diagnosis information, which the
customer can forward to the dealer or call centre. In CSM
mode, “CSM”, is displayed in the top right corner of the screen.
The information provided in CSM and the purpose of CSM is to:
• Increase the home repair hit rate.
• Decrease the number of nuisance calls.
• Solved customers' problem without home visit.
ComPair Mode is used for communication between a computer
and a TV on I2C /UART level and can be used by a Service
engineer to quickly diagnose the TV set by reading out error
codes, read and write in NVMs, communicate with ICs and the
uP (PWM, registers, etc.), and by making use of a fault finding
database. It will also be possible to up and download the
software of the TV set via I2C with help of ComPair. To do this,
ComPair has to be connected to the TV set via the ComPair
connector, which will be accessible through the rear of the set
(without removing the rear cover).
5.2.1 Service Default Mode (SDM)
Purpose
Set the TV in SDM mode in order to be able to:
• Create a pre-defined setting for measurements to be
made.
• Override software protections.
• Start the blinking LED procedure.
• Read the error buffer.
• Check the life timer.
Specifications
Table 5-1 SDM default settings
Region Freq. (MHz) Default syst.
Europe (except France),
AP-PAL/-Multi
France SECAM L
NAFTA, AP-NTSC 61.25 (channel 3) NTSC M
LATAM PAL M
• Set linear video and audio settings to 50%, but volume to
25%. Stored user settings are not affected.
• All service-unfriendly modes (if present) are disabled, since
they interfere with diagnosing/repairing a set. These
service unfriendly modes are:
– (Sleep) timer.
– Blue mute/Wall paper.
– Auto switch “off” (when there is no “ident” signal).
– Hotel or hospital mode.
– Child lock or parental lock (manual or via V-chip).
– Skipping, blanking of “Not favorite”, “Skipped” or
“Locked” presets/channels.
– Automatic storing of Personal Preset or Last Status
settings.
– Automatic user menu time-out (menu switches back/
OFF automatically.
– Auto Volume levelling (AVL).
How to Activate SDM
For this chassis there are two kinds of SDM: an analog SDM
and a digital SDM. Tuning will happen according Table 5-1
• Analog SDM: use the standard RC-transmitter and key in
the code “062596”, directly followed by the “MENU” (or
HOME) button.
Note: It is possible that, together with the SDM, the main
menu will appear. To switch it “off”, push the “MENU” (or
HOME) button again.
• Digital SDM: use the standard RC-transmitter and key in
the code “062593”, directly followed by the “MENU” (or
HOME) button.
Note: It is possible that, together with the SDM, the main
menu will appear. To switch it “off”, push the “MENU” (or
HOME) button again.
• Analog SDM can also be activated by grounding for a
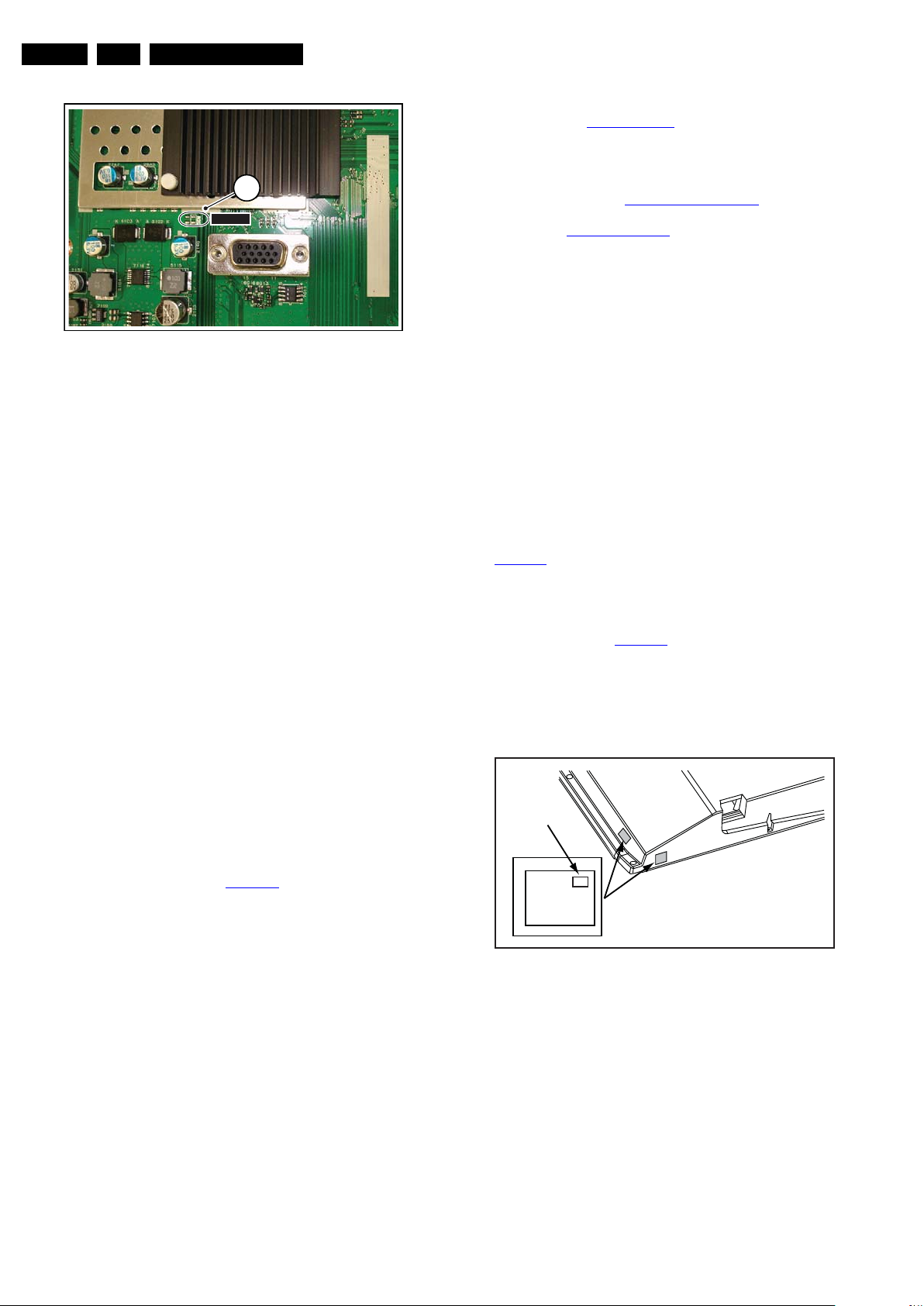
moment the solder pad on the SSB, with the indication
“SDM” (see figure Service mode pad
475.25 PAL B/G
).
.
2010-Jul-01
Page 22
EN 22 LC9.2L LA5.
18490_201_090409.eps
090409
1
SDM1SDM
10000_038_090121.eps
090819
PHILIPS
MODEL:
32PF9968/10
PROD.SERIAL NO:
AG 1A0620 000001
040
39mm
27mm
(CTN Sticker)
Display Option
Code
Service Modes, Error Codes, and Fault Finding
Figure 5-1 Service mode pad
After activating this mode, “SDM” will appear in the upper right
corner of the screen (when a picture is available).
• Errors (followed by maximum 10 errors). The most recent
error is displayed at the upper left (for an error explanation
see section “5.4 Error Codes
”).
• Reset Error Buffer. When “cursor right” (or the “OK
button) is pressed and then the “OK” button is pressed, the
error buffer is reset.
• Alignments. This will activate the “ALIGNMENTS” submenu. See chapter 6.3 Software Alignments
.
• Dealer Options. Extra features for the dealers.
• Options.6.4 Option Settings
Extra features for Service. For
more info regarding option codes, see chapter .
Note that if the option code numbers are changed, these
have to be confirmed with pressing the “OK” button before
the options are stored. Otherwise changes will be lost.
• Initialize NVM. The moment the processor recognizes a
corrupted NVM, the “initialize NVM” line will be highlighted.
Now, two things can be done (dependent of the service
instructions at that moment):
– Save the content of the NVM via ComPair for
development analysis, before initializing. This will give
the Service department an extra possibility for
diagnosis (e.g. when Development asks for this).
– Initialize the NVM.
How to Navigate
When the “MENU” (or HOME) button is pressed on the RC
transmitter, the TV set will toggle between the SDM and the
normal user menu.
How to Exit SDM
Use one of the following methods:
• Switch the set to STAND-BY via the RC-transmitter.
• Via a standard customer RC-transmitter: key in “00”sequence.
5.2.2 Service Alignment Mode (SAM)
Purpose
• To perform (software) alignments.
• To change option settings.
• To easily identify the used software version.
• To view operation hours.
• To display (or clear) the error code buffer.
How to Activate SAM
Via a standard RC transmitter: Key in the code “062596”
directly followed by the “INFO” button. After activating SAM
with this method a service warning will appear on the screen,
continue by pressing the “OK” button on the RC.
Contents of SAM (see also Table 6-4
• Hardware Info.
– A. SW Version. Displays the software version of the
main software (example: LC92L-1.2.3.4=
AAAAB_X.Y.W.Z).
• AAAA= the chassis name.
• B= the region (A= Asian Pacific, E= Europe, L=
Latam, U= United States).
• X.Y.W.Z= the software version, where X is the
main version number (different numbers are not
compatible with one another) and Y.W.Z is the sub
version number (a higher number is always
compatible with a lower number).
– B. Standby Processor Version. Displays the
software version of the Stand-by processor.
– C. Production Code. Displays the production code of
2010-Jul-01
the TV, this is the serial number as printed on the back
of the TV set. Note that if an NVM is replaced or is
initialized after corruption, this production code has to
be re-written to NVM. ComPair will foresee in a
possibility to do this.
• Operation Hours. Displays the accumulated total of
operation hours (not the stand-by hours). Every time the
TV is switched “on/off”, 0.5 hours is added to this number.
)
Note: When the NVM is corrupted, or replaced, there is a high
possibility that no picture appears because the display code is
not correct. So, before initializing the NVM via the SAM, a
picture is necessary and therefore the correct display option
has to be entered. To adapt this option bit, it is advised to use
ComPair (the correct values for the options can be found in
Table 6-3
) or a method via a standard RC (described below).
Changing the display option via a standard RC: Key in the
code “062598” directly followed by the “MENU” (or HOME)
button and “XXX” (where XXX is the 3 digit decimal display
code as mentioned in Table 6-3
). Make sure to key in all three
digits, also the leading zero’s. If the above action is successful,
the front LED will go out as an indication that the RC sequence
was correct. After the display option is changed in the NVM, the
TV will go to the Stand-by mode. If the NVM was corrupted or
empty before this action, it will be initialized first (loaded with
default values). This initializing can take up to 20 seconds.
Figure 5-2 Location of Display Option Code sticker
• Store - go right. All options and alignments are stored
when pressing “cursor right” (or the “OK” button) and then
the “OK”-button.
• SW Maintenance.
– SW Events. Not useful for Service purposes. In case
of specific software problems, the development
department can ask for this info.
– HW Events. Not useful for Service purposes. In case
of specific software problems, the development
department can ask for this info.
• Operation hours display. Displays the accumulated total
of display operation hours. So, this one keeps up the
lifetime of the display itself, mainly to compensate the
degeneration behavior.
Page 23

Service Modes, Error Codes, and Fault Finding
EN 23LC9.2L LA 5.
• Test settings. For development purposes only.
• Development file versions. Not useful for Service
purposes, this information is only used by the development
department.
• Upload to USB. To upload several settings from the TV to
an USB stick, which is connected to the SSB. The items are
“Channel list”, “Personal settings”, “Option codes”,
“Display-related alignments” and “History list”. First a
directory “repair\” has to be created in the root of the
USB stick. To upload the settings select each item
separately, press “cursor right” (or the “OK” button),
confirm with “OK” and wait until “Done” appears. In case
the download to the USB stick was not successful “Failure”
will appear. In this case, check if the USB stick is
connected properly and if the directory “repair” is present in
the root of the USB stick. Now the settings are stored onto
the USB stick and can be used to download onto another
TV or other SSB. Uploading is of course only possible if the
software is running and if a picture is available. This
method is created to be able to save the customer’s TV
settings and to store them into another SSB.
• Download to USB. To download several settings from the
USB stick to the TV, same way of working needs to be
followed as with uploading. To make sure that the
download of the channel list from USB to the TV is
executed properly, it is necessary to restart the TV and
tune to a valid preset if necessary.
Note: The “History list item” can not be downloaded from
USB to the TV. This is a “read-only” item. In case of
specific problems, the development department can ask
for this info.
How to Navigate
• In SAM, the menu items can be selected with the
“CURSOR UP/DOWN” key on the RC-transmitter. The
selected item will be highlighted. When not all menu items
fit on the screen, move the “CURSOR UP/DOWN” key to
display the next/previous menu items.
• With the “CURSOR LEFT/RIGHT” keys, it is possible to:
– (De) activate the selected menu item.
– (De) activate the selected sub menu.
• With the “OK” key, it is possible to activate the selected
action.
How to Exit SAM
Use one of the following methods:
• Switch the TV set to STAND-BY via the RC-transmitter.
• Via a standard RC-transmitter, key in “00” sequence, or
select the “BACK” key.
5.2.3 Customer Service Mode (CSM)
Purpose
The Customer Service Mode shows error codes and
information on the TV’s operation settings. A call centre can
instruct the customer (by telephone) to enter CSM in order to
identify the status of the set. This helps them to diagnose
problems and failures in the TV before making a service call.
The CSM is a read-only mode; therefore, modifications are not
possible in this mode.
How to Activate
To activate CSM, press the following key sequence on a
standard remote control transmitter: “123654” (do not allow the
display to time out between entries while keying the sequence).
Contents of CSM
The contents are reduced to 3 pages: General, Software
versions and Quality items. The group names itself are not
shown anywhere in the CSM menu.
General
• Set Type. This information is very helpful for a helpdesk/
workshop as reference for further diagnosis. In this way, it
is not necessary for the customer to look at the rear of the
TV-set. Note that if an NVM is replaced or is initialized after
corruption, this set type has to be re-written to NVM.
ComPair will foresee in a possibility to do this.
• Production Code. Displays the production code (the serial
number) of the TV. Note that if an NVM is replaced or is
initialized after corruption, this production code has to be
re-written to NVM. ComPair will foresee a in possibility to
do this.
• Installed date. Indicates the date of the first installation of
the TV. This date is acquired via time extraction.
• Options 1. Gives the option codes of option group 1 as set
in SAM (Service Alignment Mode).
• Options 2. Gives the option codes of option group 2 as set
in SAM (Service Alignment Mode).
• 12NC SSB. Gives an identification of the SSB as stored in
NVM. Note that if an NVM is replaced or is initialized after
corruption, this identification number has to be re-written to
NVM. ComPair will foresee in a possibility to do this. This
identification number is the 12nc number of the SSB.
• 12NC display. Shows the 12NC of the display.
• 12NC supply. Shows the 12NC of the supply.
Software versions
• Current main SW. Displays the built-in main software
version. In case of field problems related to software,
software can be upgraded. As this software is consumer
upgradable, it will also be published on the Internet.
Example: LC92L_1.2.3.4
• Ambilight SW. Displays the Ambilight SW-version.
Quality items
• Signal quality. Poor / average /good
• Child lock. Not active / active. This is a combined item for
locks. If any lock (Preset lock, child lock, lock after or
parental lock) is active, the item shall show “active”.
• HDMI HDCP key. Indicates if the HDMI keys (or HDCP
keys) are valid or not. In case these keys are not valid and
the customer wants to make use of the HDMI functionality,
the SSB has to be replaced.
• Ethernet MAC address. Displays the MAC address
present in the SSB.
• BDS key. Indicates if the “BDS level” key is valid or not.
How to Exit CSM
Press “MENU” (or HOME) / “Back” key on the RC-transmitter.
Specifications
• Ignore “Service unfriendly modes”.
• Line number for every line (to make CSM language
independent).
• Set the screen mode to full screen (all contents on screen
is visible).
• After leaving the Customer Service Mode, the original
settings are restored.
• Possibility to use “CH+” or “CH-” for channel surfing, or
enter the specific channel number on the RC.
2010-Jul-01
Page 24

EN 24 LC9.2L LA5.
Service Modes, Error Codes, and Fault Finding
5.3 Service Tools
5.3.1 ComPair
Introduction
ComPair (Computer Aided Repair) is a Service tool for Philips
Consumer Lifestyle products. and offers the following:
1. ComPair helps you to quickly get an understanding on how
to repair the chassis in a short and effective way.
2. ComPair allows very detailed diagnostics and is therefore
capable of accurately indicating problem areas. You do not
have to know anything about I2C or UART commands
yourself, because ComPair takes care of this.
3. ComPair speeds up the repair time since it can
automatically communicate with the chassis (when the uP
is working) and all repair information is directly available.
4. ComPair features TV software up possibilities.
Specifications
ComPair consists of a Windows based fault finding program
and an interface box between PC and the (defective) product.
The (new) ComPair II interface box is connected to the PC via
an USB cable. For the TV chassis, the ComPair interface box
and the TV communicate via a bi-directional cable via the
service connector(s).
How to Connect
This is described in the ComPair chassis fault finding database.
TO TV
TO
TO
UART SERVICE
CONNECTOR
2
C
I
RS232 /UART
ComPair II
RC in
Optional
Switch
Power ModeLink/
Activity
UART SERVICE
CONNECTOR
RC out
TO
I2C SERVICE
CONNECTOR
Multi
function
5.4 Error Codes
5.4.1 Introduction
The error code buffer contains all detected errors since the last
time the buffer was erased. The buffer is written from left to
right, new errors are logged at the left side, and all other errors
shift one position to the right.
When an error occurs, it is added to the list of errors, provided
the list is not full. When an error occurs and the error buffer is
full, then the new error is not added, and the error buffer stays
intact (history is maintained).
To prevent that an occasional error stays in the list forever, the
error is removed from the list after more than 50 hrs. of
operation.
When multiple errors occur (errors occurred within a short time
span), there is a high probability that there is some relation
between them.
New in this chassis is the way errors are displayed:
• There is a simple blinking LED procedure for board level
repair (home repair) so called LAYER 1 errors, next to the
existing errors which are LAYER 2 errors (see Table 5-3
– LAYER 1 errors are one digit errors (via CSM).
– LAYER 2 errors are 2 digit errors (via SAM/SDM).
• In protection mode:
– From consumer mode: LAYER 1.
– From SDM mode: LAYER 2.
• In CSM mode: When entering CSM: error LAYER 1 will be
displayed by blinking LED. Only the latest error is shown.
• In SDM mode: When SDM is entered via Remote Control
code or the hardware pins, LAYER 2 is displayed via
blinking LED.
• In the “ON” state: with the RC commands “mute_06250X
_OK”, LAYER 2 errors are displayed via blinking LED.
• Error display on screen:
– In CSM no error codes are displayed on screen.
– In SAM the complete error list is shown.
).
PC
ComPair II Developed by Philips Brugge
Optional power
HDMI
2
I
C only
5V DC
10000_036_090121.eps
091118
Figure 5-3 ComPair II interface connection
Caution: It is compulsory to connect the TV to the PC as
shown in the picture above (with the ComPair interface in
between), as the ComPair interface acts as a level shifter. If
one connects the TV directly to the PC (via UART), ICs will be
blown!
How to Order
ComPair II order codes:
• ComPair II interface: 3122 785 91020.
• ComPair UART interface cable: 3138 188 75051.
• Program software can be downloaded from the Philips
Service portal.
Note: If you encounter any problems, contact your local
support desk.
5.4.2 How to Read the Error Buffer
Use one of the following methods:
• On screen via the SAM (only when a picture is visible).
E.g.:
– 00 00 00 00 00: No errors detected
– 23 00 00 00 00: Error code 23 is the last and only
detected error.
– 37 23 00 00 00: Error code 23 was first detected and
error code 37 is the last detected error.
– Note that no protection errors can be logged in the
error buffer.
• Via the blinking LED procedure. See section 5.4.3 How to
Clear the Error Buffer.
•Via ComPair.
5.4.3 How to Clear the Error Buffer
Use one of the following methods:
• By activation of the “Reset error buffer” command in the
SAM menu.
• With a normal RC, key in sequence “MUTE” followed by
“062599” and “OK”.
• If the content of the error buffer has not changed for 50+
hours, it resets automatically.
2010-Jul-01
Page 25

5.4.4 Error Buffer
Service Modes, Error Codes, and Fault Finding
EN 25LC9.2L LA 5.
In case of non-intermittent faults, clear the error buffer before
Table 5-2 Layer 1 error codes
starting to repair (before clearing the buffer, write down the
content, as this history can give significant information). This to
ensure that old error codes are no longer present.
If possible, check the entire contents of the error buffer. In
some situations, an error code is only the result of another error
code and not the actual cause (e.g. a fault in the protection
Description Layer 1 code Remarks
SSB 2
Display supply 3 If only one supply is used
Platform supply 4 No separate supply
Ambilight 8
detection circuitry can also lead to a protection).
Take notice that some errors need several minutes before they
start blinking or before they will be logged. So in case of
problems wait 2 minutes from start-up onwards, and then
check if the front LED is blinking or if an error is logged.
Table 5-3 Error code overview
Description Layer 1 Layer 2 Monitored
by
I2C Bus related:
I2C 2 14 ARM E BL / EB SSB SSB
uP does not boot 2 15 ARM P BL MT5392 SSB
Supply related:
DC on speaker 2 11 Stby µP P BL / SSB
12V (*) 3 16 Stby µP P BL / Supply
Inverter or display supply 3 17 ADC E EB / Supply
IC related:
HDMI MUX 2 23 ARM E EB ADV3002 SSB
HDMI EDID 2 24 ARM E EB M24C02-WMN6 SSB
ARM (Ambilight) 8 28 ARM E EB NXP LPC2103 AL-module or DC/DC
Tuner (Frontend) 2 34 ARM E EB VA1G5BF8010 SSB
Main NVM 2 35 ARM E / M24C64 SSB
Error/
Prot
Error Buffer/
Blinking LED
Device Defective Board
Extra Info
• (*) 12V is necessary to start up the ARM, the ARM boots
the Stand-by processor.
– If 12V fails during normal operation or in stand-by, the
protection can be displayed via the “blinking LED”.
5.5 The Blinking LED Procedure
5.5.1 Introduction
The software is capable of identifying different kinds of errors.
Because it is possible that more than one error can occur over
time, an error buffer is available, which is capable of storing the
last five errors that occurred. This is useful if the OSD is not
working properly.
Errors can also be displayed by the blinking LED procedure.
The method is to repeatedly let the front LED pulse with as
many pulses as the error code number, followed by a period of
1.5 seconds in which the LED is “off”. Then this sequence is
repeated.
Example (1): error code 4 will result in four times the sequence
LED “on” for 0.25 seconds / LED “off” for 0.25 seconds. After
this sequence, the LED will be “off” for 1.5 seconds. Any RC5
command terminates the sequence. Error code LED blinking is
in red color.
Example (2): the content of the error buffer is “129600”
After entering SDM, the following occurs:
• 1 long blink of 5 seconds to start the sequence,
• 12 short blinks followed by a pause of 1.5 seconds,
• 9 short blinks followed by a pause of 1.5 seconds,
• 6 short blinks followed by a pause of 1.5 seconds,
• 1 long blink of 1.5 seconds to finish the sequence,
• The sequence starts again with 12 short blinks.
– If the mains cord is disconnected and reconnected
again, the ARM and Stand-by processor are not
booted, 12V can not be detected, and no indication is
possible.
5.5.2 Displaying the Entire Error Buffer
Additionally, the entire error buffer is displayed when Service
Mode “SDM” is entered. In case the TV set is in protection or
Stand-by: The blinking LED procedure sequence (as in SDMmode in normal operation) must be triggered by the following
RC sequence: “MUTE” “062500” “OK”.
In order to avoid confusion with RC5 signal reception blinking,
this blinking procedure is terminated when a RC5 command is
received.
2010-Jul-01
Page 26

EN 26 LC9.2L LA5.
Service Modes, Error Codes, and Fault Finding
5.6 Fault Finding and Repair Tips
Notes:
• It is assumed that the components are mounted correctly
with correct values and no bad solder joints.
• Before any fault finding actions, check if the correct
options are set.
5.6.1 Software Protections
Most of the protections and errors use either the stand-by or the
micro processor as detection device. Since in these cases,
checking of observers, polling of ADCs, and filtering of input
values are all heavily software based, these protections are
referred to as software protections.
There are several types of software related protections, solving
a variety of fault conditions:
• Protections related to supplies: check of the 12V.
• Protections related to breakdown of the safety check
mechanism. E.g. since the protection detections are done
by means of software, failing of the software will have to
initiate a protection mode since safety cannot be
guaranteed any more.
Remark on the Supply Errors
The detection of a supply dip or supply loss during the normal
playing of the set does not lead to a protection, but to a cold
reboot of the set. If the supply is still missing after the reboot,
the TV will go to protection.
Protections during Start-up
During TV start-up, some voltages and IC observers are
actively monitored to be able to optimise the start-up speed,
and to assure good operation of all components. If these
monitors do not respond in a defined way, this indicates a
malfunction of the system and leads to a protection.
5. Stop bits = 1
6. Flow control = none
During the start-up of the TV set, the logging will be displayed.
This is also the case during rebooting of the TV set (the same
logging appears time after time). Also available in the logging
is the “Display Option Code” (useful when there is no picture),
look for item “DisplayRawNumber” in the beginning of the
logging. Tip: when there is no picture available during
rebooting you are able to check for “error devices” in the
logging (LAYER 2 error) which can be very helpful to determine
the failure cause of the reboot. For protection state, there is no
logging.
5.6.4 Display option code
Caution: In case you have replaced the SSB, always check the
display option code in SAM, even if you have picture. With a
wrong display option code it is possible that you have picture,
but that in certain conditions you have unwanted side-effects.
5.6.5 Trouble Shooting Tuner section
When there is no picture in analog RF mode:
1. Check whether picture is present in AV mode. If not, tuner
section is okay. Check video processing section.
2. Check if option settings are correct.
3. Check if 5 V supply is available at test points F256, F228,
F229 and F219, and if 33 V is available at test point F257.
4. Check if the I
5. Manually store a known channel and check if there is IF
output at tuner pin 11. If not, tuner is faulty.
6. Feed in 105 dBuV at tuner pin 11 and check whether there
is CVBS output from IF demodulator IC. If not, IF
demodulator might be faulty. Check components in this
area.
2
C lines are working correctly (3.3 V).
5.6.2 Hardware Protections
The only real hardware protection in this chassis is (in case of
an audio problem) the audio protection circuit that will trigger
the uP to switch “off” the TV.
Repair Tip
• It is also possible that you have an audio DC protection
because of an interruption in one or both speakers (the DC
voltage that is still on the circuit cannot disappear through
the speakers).
Caution: (dis)connecting the speaker wires during the ON
state of the TV at high volume can damage the audio
amplifier.
5.6.3 Logging
When something is wrong with the TV set (f.i.the set is
rebooting) you can check for more information via the logging
in Hyperterminal. The Hyperterminal is available in every
Windows application via Programs, Accessories,
Communications, Hyperterminal. Connect a “ComPair UART”cable (3138 188 75051) from the service connector in the TV to
the “multi function” jack at the front of ComPair II box.
Required settings in ComPair before starting to log:
- Start up the ComPair application.
- Select the correct database (open file “Q549.3E LA”, this will
set the ComPair interface in the appropriate mode).
- Close ComPair
After start-up of the Hyperterminal, fill in a name (f.i. “logging”)
in the “Connection Description” box, then apply the following
settings:
1. COMx
2. Bits per second = 115200
3. Data bits = 8
4. Parity = none
2010-Jul-01
Page 27

Service Modes, Error Codes, and Fault Finding
18490_209_090409.eps
090409
5.6.6 Trouble Shooting Sound section
EN 27LC9.2L LA 5.
Figure 5-4 Fault finding tree sound section
2010-Jul-01
Page 28

EN 28 LC9.2L LA5.
No Video and Audio
for any HDMI input
(permanently)
Check TMDS signal at pin 1,
3, 4, 6, 7, 9, 10, 12 of
connector 1 (if HDMI 1)
Yes
No
Check TMDS signal at pin
37,38,41,42,44,45,47,48 of
ADV3002 (if HDMI 1)
Malfuntion of HDMI
connector, ensure
solderbility of Connector
Check TMDS signal at pin
25,26,28,29,31,32,34,35 of
ADV3002
Yes
No
Malfuntion of PCB trace,
ensure no broken trace of
these signals between
connector and ADV3002
Yes
No
The video and audio path is
intact, no video & audio is
cause by MTK 5392
malfunction
Malfuntion of ADV3002
No Video and Audio for any
HDMI input
(Intermittent and differ
within various DVD player)
Go to CSM mode using RC
key "123654",
check item 11: Key(HDCP)
Valid
Invalid
check item 19:
EDID Version / Check sum
As per latest?
Reload HDCP key
Check the following possible hardware failure:
1) Supply of EEPROM IC (pin 8 of 7B02). Should be +5V.
2) Connectivity of I2C between EEPROM (7B02) and ADV3002
(7B05). Between pin 5, 6 of 7B02 and pin 61 , 62 of 7B05.
Should be +3.8V.
3) Connectivity of DDC line between HDMI connector and
ADV3002. (ex: pin 15, 16 of connector HDMI 1 to pin 69 , 70 of
ADV3002.)
4) Connectivity of DDC line between ADV3002 and MTK5392.
(pin 67, 68 of ADV3002 to test point F836 & F837)
No
Update EDID
Yes
18490_211_090409.eps
090409
5.6.7 Trouble Shooting HDMI section
Service Modes, Error Codes, and Fault Finding
2010-Jul-01
Figure 5-5 Fault finding tree HDMI section
Page 29

Service Modes, Error Codes, and Fault Finding
18490_204_090409.eps
090409
EN 29LC9.2L LA 5.
5.6.8 Start-up/Shut-down Flowcharts
On the next pages you will find start-up and shut-down
flowcharts, which might be helpful during fault finding.
POWER STATES
In this chassis, there are six possible power states as follows:
• Power OFF
• Power ON
• STANDBY
• SEMI-STANDBY
• Special Panel Mode
• PROTECTION
Figure 5-6 Power States
POWER OFF
In “Power OFF” mode, the system is completely switched “off”
from AC mains. When AC power is applied, the system checks
for last status. Depending on the last standby status stored in
the system EEPROM, this mode can then transit to “ON” or
“STANDBY” mode.
ON
This is the normal operating mode, indicated by the “on” LED.
All the power supply lines are available and depending on the
sub-mode, all the circuits in the system may be active. From
this mode it shall be possible to transit to “STANDBY” and
“PROTECTION” mode, or to “Power OFF” mode if AC mains
are switched “off”. The sub-modes are:
• Active Mode (Normal Consumer Mode)
• Service Modes
• Panel Modes
• Factory Modes
SPECIAL PANEL MODE
The Special Panel Mode is only used during manufacturing
process to program the system EEPROM. In this mode, the
SDA0 and SCL0 ports of MT5392 are set to high impedance
after SDM and PANEL pins are both detected as “low” during
start-up. This mode can be exited using a power recycle.
PROTECTION
This state is entered when an error has been detected at startup or in the “ACTIVE” mode. All switched power supply lines
are turned “off” with only +3V3stby remaining “on”; similar to
“STANDBY” mode. This state is indicated by the blinking red
front LED with the blinking sequence denoting the type of error
detected.
When the system enters the protection mode due to a critical
error, it should be turned “off” and the failure cause needs to be
resolved. The system will function normally again after
performing a power recycling once all protection causing
failures have been resolved.
START-UP SEQUENCE
There are two cases of start-up sequences, namely:
• AC On and
• Standby Wake-up.
See also Figure 5-7
.
AC ON
In the case of start-up from AC mains, all PSU voltages start to
turn “on” as the hardware default of the active “low” STANDBY
(controlled by Standby Controller STANDBY signal) signal to
the PSU is pulled “low” with respect to ground.
The MT5392 starts running boot loader once the hardware
reset circuit is released. The system will then check the last
standby status from the system EEPROM to determine
whether to complete the system start-up (load image, turn on
the audio, display etc) or proceed to standby and wait for wakeup command from user. The Standby Controller then proceeds
to verify the power status of the +12V and sends the system to
protection in case of any failures. Special Panel, SDM, and
PANEL modes are detected as well.
STANDBY WAKEUP
When the system receives a command to wake-up from
standby, the Standby Controller sets the STANDBY signal
“low” to turn “on” the switched power, and similarly detects for
the presence of +12V. The MT5392 waits for +3V3_SW to be
available before loading its image. The significance of this
voltage detection is due to the flash is also being powered by
the same mentioned voltage.
The following figure shows the start-up flowchart for both “AC
On” and “Standby Wake-up”:
STANDBY
The total power consumption of the system in this mode shall
be equal or less than 150 mW. This state is indicated by white
LED when AC mains is switched “on”. Only the standby
controller is operational in this state, where only +3V3stby
power supply is available. From this mode it shall be possible
to transit to the “ACTIVE” or “Power OFF” mode if AC mains are
switched “off”.
SEMI-STANDBY
The semi-standby state is required to perform the following
tasks:
• AmbiLight wakeup control
• PBS SemiStandby.
2010-Jul-01
Page 30

EN 30 LC9.2L LA5.
START
HW Default PSU is ON, and
MT5392 POR
MT5392 POR and config
DRAM decompress
bootloader into DRAM
(preLoader)
MT5392 Bootloader
decompressed and running
from DRAM
Special Panel mode
Detection
SDM
& PANEL =
LOW?
All IIC Port set to High
Impedance
Yes
END
Check T8032 Status
T8032 in reset State?
(Cold Boot?)
Yes
Download T8032 Code
And kick uP to start to run.
Check T8032/ARM
communication ready?
1. Version cmd ok.
2. Setup CEC parameters.
T8032/ARM
Communicate ok?
Communicate
Failed Count <= 3
Communicate
Failed Count > 3
Error #, failed into Protection
mode, Record error in NVM.
Yes
Cold Start?
No
Yes
Check Last Status and Boot
Ctrl Bits from NVM
Enter Standby?
Yes
Setup Wakeup Scenarios on
PDWNC module of 5392
Standby
(HW)
NVM Error
[ Protection ]
Enable T8032 receive IR key
No
5392 checks
POWER_DOWN =
HIGH ?
Wakeup
Events
(RC/LKB/CEC/Ambilight)
No
No
No
Wait 100ms
No
12V Error
[ Protection ]
No
To Reboot
SDM and PANEL Mode Detection
1. Check SDM Port and Set SDM Mode Flag
If SDM Pin = LOW and System EEPROM Firs t 20
bytes = 0xFF or CH+ on LKB pressed, Load
Software Default System EEPRO M Data (only
when cold start)
2. Check Panel Port
If Panel Pin = LoW, Set Panel Mode Flag
Enable POWER_DOWN INT
Enable DC_PROT INT
MT5392 begins initializing the
System
Initialize Tuner
Initialize HDMI Switch
Initialize Middleware Layer
Initialize Philips
drivers/Application
Initialize Application Layer
Switch RC/OPCTRL control
from T8032 to MT5392 and
Enable RC Key
Switch to Video Path
Blank Picture and Switch to Last
Source
Picture Mode Setup & Detecti on
UnBlank Picture and UnMute
Audio MUTEn = HIGH
SW_MUTE = HIGH
Set Last Status = ON
Start PWM_DIMMING and
BACKLIGHT_BOOST
Note: Startup time from image
decompression long enough to
satisfy 1sec high time after
LAMP ON for proper panel
startup
Initialize CEC driver
Check T8032 CEC buffer
T8032 with
CEC data
Copy CEC data from T8032 to
MT5392 CEC driver buffer
Switch CEC h/w control from
T8032 to MT5392
Initialize NVM
Yes
No
NVM Error
[ Protection ]
Tuner
HDMI Switch
Watchdog timeout
Reboot
Panel turn on Sequence
Turn on LED1
Retrieve/Display Startup
Logo
PWM_DIMMING keep at 100%
BACKLIGHT_BOOST at
nominal
Turn on LVDS Power
LCD_PWR_ON = LOW
Retrieve Panel ID from NVM
Retrieve Panel Info from Flash
data
Wait for Panel_On_Time_1
based on Panel ID in ms (from
Panel Info on Flash)
Switch on LVDS Signal
Wait for Panel_On_Time_2
based on Panel ID in ms (from
Panel Info on Flash)
BACKLIGHT_ON_OFF = HIGH
MT5392 Decompress Image
from Flash into DRAM
Successful?
Set Program Counter to
DRAM Image to boot into
TV Image
Yes
Notify T8032 that
MT5392 start up is OK
T8032 reset state
T8032
T8032 booting
T8032 main loop
T8032 main loop in standby
mode
Control PDWNC
module to
wakeup ARM11
Send error code info to
T8032 & CEC on/off status
Receive ARM info
(Error code etc)
Wakeup event
If not watchdog reboot,
Enable 20 seconds watchdog
Check Wakeup Reason from
PDWNC module (IR/Keypad
HW and CEC) and confirm
from T8032
Any of Upgrade
bits at NVM is on?
USB Upgrade
Upgrade
Failed
Upgrade success
AP: TV Navigator
Is it Ambilight wakeup?
No
Yes
1. If Boot Ctrl Bits to set always enter
standby, then go to standby directly.
2. If Boot Ctrl Bits to set always boot
directly, then continue booting.
3. If Boot Ctrl Bits to follow Last Status,
then check the Last status go decide to
enter standby or continue booting.
Drop All RC key received before
this block
NVM
Error
[ Protecti
on ]
AP: Reload UI param eter into
program
Timeout
= 6 Sec ?
yes
No
2.568 second
3.774 second
Turn off Philips
logo
Video Ready
Initialize OSD
3.776 second
Enable 5392 Self-Watchdog thread
Thread action:
1. If watchdog reboot, delay 500
seconds to work.
2. Enable Self-watc hdog and initial 15
seconds counter
3. Refresh watchdog counter / 0.5 sec
4. Alive check T8032 / 15 seconds
Check Boot Bank Flag in
EEPROM
Calculate Boot Bank addr ess
Is it Ambilight wakeup?
Panel Initialization
Yes
Semi-Standby
Received wakeup event
Power on
Is it Ambilight
wakeup ?
Audio MUTEn = LOW
SW_MUTE = LOW
AP: Background Manager
Yes
No
DTV_IRQ = Low
Yes
DTV_IRQ = High
Wait 100ms
No
Standby
(HW)
Ambilight off
Check
PowerDown
Start up OK
Yes
Yes
Blinking LED No
NVM status to
check Upgrade bit
Yes
Yes
Standby
(HW)
BACKLIGHT_ON_OFF = HIGH
Panel Initialization
No
ON Mode
18490_205_090409.eps
090409
Service Modes, Error Codes, and Fault Finding
Figure 5-7 Start-up flowchart
2010-Jul-01
Page 31

Service Modes, Error Codes, and Fault Finding
Active
Disable AP RC/LKB key
Disable DC_PROT &
POWER_DOWN INT
Pass Error Buffer and CEC Info
to T8032
Switch IR/GPIO control from
RISC to T8032
Notify T8032 to go to Standby
STANDBY
Wait 3000 ms to block next
startup to ensure PSU properly
discha rged
T8032 bli nks LED2 a ccording t o
Error Buffer
STANDBY due
to Pr otection?
No
Yes
Receive Standby Command
Turn off LED1
Set Last Status = STANDBY
Semi Standby
W ait x m s ( disp lay file )
Mute all sound outputs via softmute
See FMS audio for all details
Mute all video outputs
switch o ff LC D b acklight
Force ext audio outputs to ground
(I/O: audio reset) and wait 5ms
sw itch off Am bilig ht (if present)
Se t ma in am plifie r mu te ( I/O: a udio -mu te)
Wait 100ms
Delay state transition until Ambilight has faded
out: Output power Observer of MTK5392 AL
should be zero.
Switch off the display power by
switching LCD-PWR-ON high
Wait x ms
Sw itch off LV DS outp ut
Switch off POK line detection algorithm
Delay transition until ramping down of ambient light is
finished. *)
If ambientlight functionality was used in semi-standby
(lounge mode), switch off ambient light
*) If this is not performed and
the set is switched to standby
when the switch off of the
am biligh ts is st ill ong oing , th e
ligh ts will s witch off a bru ptly
when the supply is cut.
18700_202_090828.eps
090828
EN 31LC9.2L LA 5.
STANDBY SEQUENCE
The following flowchart depicts the Standby (plus SemiStandby condition) sequence:
Figure 5-8 Standby flowchart
2010-Jul-01
Page 32

EN 32 LC9.2L LA5.
START
Note: To
Avoid False
Triggering
Log Error Code
Mute Audio Output
Go to STANDBY
Check
DC_PROT = LOW
for 3 sec?
Ye s
No
END
DC Protection
[Protection]
H_17740_037.eps
240108
MTK 5392 detects
POWER_D OWN int err upt
POWER_DOWN
interrupt ba sedon
falling edge triggering
St art
Reconfirm
POWE R_DOWN=LOW
Trigger Standby µP to handle
PowerDown
System Idle Mode
yes
Resume
No
Wait for TBD ms
Mute Audio Output
Set Write Protect for Flash and
System EEPROM
Receive command to handle
PowerDown
Switch Off Power
Wait for 5 sec onds
Reboot System
End
18700_201_090828.eps
090828
Service Modes, Error Codes, and Fault Finding
DC PROTECTION
The following figure shows the DC_PROT interrupt flowchart:
Figure 5-9 DC Protection flowchart
POWERDOWN SEQUENCE
The following figure shows the power-down sequence
flowchart:
• Upon detection, the power detection circuitry should switch
the low power DC/DC converters “off” and/or switch the
MT5392 in reset.
• The SW detection is done on the T8032 (built-in stand-by
microprocessor). The T8032 is fed by the stand-by voltage
and is less critical to power drops than the +12V and
derivatives.
• If T8032 detects a power drop, it shuts down the supplies
immediately (enter HW stand-by mode), waits for 5
seconds and restarts the system.
• If the power drop is caused by a mains voltage drop, the
system performs a cold boot which prevents a HW hangup
due to the power drop. At the restart, if power is readily
available again, the set will resume its function.
• If the power drop is caused by a failing supply, the failure
will be detected during the restart and the appropriate error
logging will be given.
• If the power drop is caused by mains voltage removal by
the customer, the set will restart but will ‘die’ during the 5s
wait time (specification of the power supplies).
Figure 5-10 Power-down flowchart
• Power detection circuitry should be quick enough to rapidly
detect any powerdip which is large enough to jeopardize
2010-Jul-01
the functionality of the set.
Page 33

Service Modes, Error Codes, and Fault Finding
H_16771_007a.eps
100402
START
C onn ect the U SB sti ck to the set,
go to SAM and save the current TV settings via “Upload to USB”
Set is sti ll opera ting?
Yes
1.
Discon nect the WiF i module f rom the PC I conn ector (only for Q549.x SSB)
2. Replace the SSB by a Service SSB.
3. Place the WiFi module in the PCI connector.
4. Mount the Service SSB in the set.
Set behaviour?
Yes
No
No
Ins truction note SSB replacem ent Q543.x, Q548.x, Q549.x, and Q55x.x
Before starting:
- prepare a USB memory stick with the latest software
- download the latest Main Software (Fus) from www.p4c.philips.com
- unzip this file
- create a folder ”upgrades” in the root of a USB stick (size > 50 MB) and
save the autorun.upg file in this "upgrades" folder.
Note: it is possible to rename this file, e.g."Q54x_SW_version.upg"; this in
case there are more than one "autorun.upg" files on the USB stick.
No pic ture displayed
Pic ture displayed
Set is starting up without software
upgrade menu appearing on screen
Pic ture displayed
Set is starting up with software
upgrade menu appearing on screen
Due to a possible wrong display option code in the received Service
SSB (NVM), it’s possible that no picture is displayed. Due to this
the download application will not be shown either. This tree enables you
to load the main software step-by-step via the UART logging on the PC
(this for visual feedback).
Start-up the set
1) Start up the TV set, equiped with the Service
SSB,
and enable the UART logging on the PC.
2) The TV set will start-up automatically in the
download application if main TV software is not loaded.
3) Plug the prepared USB stick into the TV set. Follow the
instructions in the UART log file, press “Right” cursor key to enter
the list. Navigate to the “autorun.upg” file in the UART logging
printout via the cursor keys on the remote control. When the
correct file is selected, press
“Ok”.
4) Press "Down" cursor and “Ok” to start flashing the main
TV software. Printouts like: “L: 1-100%, V: 1-100% and
P: 1-100%” should be visible now in the UART logging.
5) Wait until the message “Operation successful !” is logged in
the UART log and remove all inserted media. Restart the TV set.
1) Plug the USB stick into the TV set a
nd select
the “autorun .upg” file in the displayed browser.
2) Now the main software will be loaded automatically,
supported by a progress bar.
3) Wait until the message “Operation successful !” is displayed
and remove all inserted media. Restar t the TV set.
Set the correct “Display code” via “06259
8 -HOME- xxx” where
“xxx” is the 3 digit display panel code (see sticker on the side
or bottom of the cabinet)
After entering the “Display Option” code, the set is going to
Standby
(= validation of code)
Restart the set
Connect PC via the ComPair interface to Service connector.
Start TV in Jett mode (DVD I + (OSD))
Open ComPair browser Q54x
Program set type number, serial number, and di
splay 12 NC
Program E - DFU if needed.
Go to SAM and reload settings
via “Download from USB” function.
In case of settings reloaded from USB, the set type,
serial number, display 12 NC, are automatically stored
when entering display options.
- Check if correct “display option” code is programmed.
- Verify “option codes” according to sticker inside the set.
- Default
settings for “white drive” > see Service Manual.
Q54x.E SSB Board swap – VDS
Updated 22-03-2010
If not already done:
Check latest software on Service website.
Update main and Stand-by software via USB.
Check and perform alignments in SAM according to the
Service Manual. Option codes, colour temperature, etc.
Final check of a
ll menus in CSM.
Special attention for HDMI Keys and Mac address.
Check if E - D F U is present.
End
Attention point for Net TV: If the set type and serial number are not
filled in, the Net TV functionality will not work. It will not be possible
to connect to the internet.
Saved settings
on USB stick?
5.6.9 SSB replacement
Follow the instructions in the flowchart in case a SSB has to be
swapped.
Note: flowchart below has originally been created for the Q5xx
chassis, but can also be used for this LC9.2L chassis.
EN 33LC9.2L LA 5.
2010-Jul-01
Page 34

EN 34 LC9.2L LA5.
H_16771_007b.eps
100322
Resta rt the set
Set is starting up in Factory mode
Set is starting u p in Factory mode?
Noisy picture with bands/lines is visible and the
RED LED is continuous on.
An “F” is displayed (and the HDMI 1
input is displayed).
- Press the “volume minus” button on the TVs local keyboard for 5 ~10
seconds
- Press the “SOURCE” button for 10 seconds until the “F” disappears
from the screen or the noise on the screen is replaced by “blue mute”
The noise on the screen is replaced
with the
blue mute or the “F” is disappeared!
Unplug the mains cord to verify the correct
disabling of the Factory mode.
Program display option code
via “062598 MENU”, followed by
the 3 digits code of the display
(this code can be found
on a sticker on - or inside - the set).
After entering “display option” code, the set is
going in stand-by mode (= validation of code)
Service Modes, Error Codes, and Fault Finding
Figure 5-11 SSB replacement flowchart [1/2]
2010-Jul-01
Figure 5-12 SSB replacement flowchart [2/2]
Page 35

Service Modes, Error Codes, and Fault Finding
5.7 Software Upgrading
5.7.1 Introduction
It is possible for the user to upgrade the main software via the
USB port. This allows replacement of a software image in a
stand alone set, without the need of an E-JTAG debugger. A
description on how to upgrade the main software can be found
in the DFU.
Important: When the NAND-Flash must be replaced, a new
SSB must be ordered, due to the presence of the security keys!
(copy protection keys, MAC address, ...).
Perform the following actions after SSB replacement:
1. Set the correct option codes (see sticker inside the TV).
2. Update the TV software => see the DFU for instructions.
3. Perform the alignments as described in chapter 6.
4. Check in CSM if the HDMI key, MAC address.. are valid.
For the correct order number of a new SSB, always refer to the
Spare Parts list on the Philips Service web portal!
5.7.2 Software Upgrade
SW versions can be divided in three types:
• SW that can not crash the working of the set.
– EDID NVM. If the download fails, the set is still running
and the download can start again.
– Main NVM: If the download fails the default NVM value
can be loaded. NVM can be loaded via USB, be aware
PCBA alignments stored in NVM will not be overridden.
• SW that is “fool proof”: There is a backup version, a main
interruption during upgrade shall not crash the normal
working, a new upgrade can be started.
– Main SW image: Upgradable via USB.
– Standby SW.
– ARM Ambilight (if applicable): Upgradable via USB.
• SW that is not “fool proof”.
– Bootloader: Upgradable via USB in SAM (Note: must
be done by service personnel).
EN 35LC9.2L LA 5.
SW for all model numbers is loaded to the Philips Service portal
(P4S) and contains the following software:
• Process_NVM_LC09Mxxx.bin: mainly for factory use to
load main NVM. Can be used by service if applicable.
• LC09M_VGAxxxx.bin: for loading VGA NVM using
ComPair tool.
• LC09M_HDMIxxxx.bin: for loading HDMI NVM via
ComPair (HDMI MUX EDID) tool.
• The Autorun.upg file, which is available on P4C (the
consumer web site), contains:
– Main SW.
– Standby SW.
– Bootloader SW (via SAM upgradable).
– Ambilight SW (if applicable).
2010-Jul-01
Page 36

EN 36 LC9.2L LA6.
6. Alignments
Alignments
Index of this chapter:
6.1 General Alignment Conditions
6.2 Hardware Alignments
6.3 Software Alignments
6.4 Option Settings
Note: Figures below can deviate slightly from the actual
situation, due to the different set executions.
General: The Service Default Mode (SDM) and Service
Alignment Mode (SAM) are described in chapter 5. Menu
navigation is done with the CURSOR UP, DOWN, LEFT or
RIGHT keys of the remote control transmitter.
6.1 General Alignment Conditions
Perform all electrical adjustments under the following
conditions:
• Power supply voltage: 120 - 230 V
• Connect the set to the mains via an isolation transformer
with low internal resistance.
• Allow the set to warm up for approximately 15 minutes.
• Measure voltages and waveforms in relation to correct
ground (e.g. measure audio signals in relation to
AUDIO_GND).
Caution: It is not allowed to use heatsinks as ground.
• Test probe: Ri > 10 Mohm, Ci < 20 pF.
• Use an isolated trimmer/screwdriver to perform
alignments.
/ 50 Hz (± 10%).
AC
Picture Setting
Brightness 50
Colour 0
Contrast 100
• Go to the SAM and select “Alignments”-> “White point”.
White point alignment LCD screens:
• Use a 100% white screen as input signal and set the
following values (in SAM mode):
– “Color temperature” to “Cool”.
– “Whitepoint red”, “Whitepoint green”, and “Whitepoint
blue” values to “127”.
– “Red BL offset” and “Green BL offset” values to “8”.
With a color analyzer:
• Measure with a calibrated, contactless (max. 25 mm
distance) color analyzer in the centre of the screen.
Consequently, the measurement needs to be done in a
dark environment.
• Adjust one or two registers (so holding one of the White
point registers R, G or B on 127) to obtain the “Cool” x,y
values (see Table 6-1
). Tolerance: dx: ± 0.004, dy: ± 0.004.
• Repeat this step for the “Normal” and “Warm” color
temperatures.
• When finished press “OK” on the RC and then press
“Store” (in the SAM root menu) to store the aligned values
into the NVM.
• Restore the initial picture settings after the alignments.
Table 6-1 White D alignment values
6.2 Hardware Alignments
Not applicable.
6.3 Software Alignments
Put the set in SAM mode (see chapter 5. Service Modes, Error
Codes, and Fault Finding). The SAM menu will now appear on
the screen. Select ALIGNMENTS and go to one of the sub
menus. The alignments are explained below.
The following item can be aligned:
• Whitepoint.
To store the data:
• Press OK on the RC before the cursor is moved to the left.
• In main menu select “Store” and press OK on the RC.
• Press MENU on the RC to switch back to the main menu.
• Switch the set to stand-by mode.
For the next alignments, supply the following test signals via a
video generator to the RF input:
• LATAM models: an NTSC M TV-signal with a signal
strength of at least 1 mV and a frequency of 61.25 MHz
(channel 3).
6.3.1 White Point
• Set “Active control” to “Off”.
• Choose “TV menu”, “TV Settings” and then “Picture” and
set picture settings as follows:
Picture Setting
Dynamic backlight Off
Dynamic Contrast Off
Colour Enhancement Off
Picture Format Unscaled
Light Sensor Off
Value Cool (11000 K) Normal (9000 K) Warm (6500 K)
x 0.278 0.289 0.314
y 0.278 0.291 0.319
Without a color analyzer, you can use below default values.
This is the next best solution. The default values are average
values coming from production (statistics).
• Select a “Color Temperature” (e.g. “Cool”, “Normal”, or
“Warm”).
• Set the “Whitepoint Red”, “- Green” and “- Blue” default
values according to the values in the “Tint settings” table.
• When finished press “OK” on the RC, then press “Store” (in
the SAM root menu) to store the aligned values into the
NVM.
• Restore the initial picture settings after the alignments.
Table 6-2 Tint settings (default values)
Colour Temp. R G B
32-inch
Cool 121 127 119
Normal 125 127 106
Warm 127 121 74
42-inch
Cool 127 122 112
Normal 122 122 127
Warm 127 111 70
47-inch
Cool 127 121 118
Normal 127 116 100
Warm 127 107 62
52-inch
Cool 127 121 118
Normal 127 116 100
Warm 127 107 62
2010-Jul-01
Page 37

Alignments
EN 37LC9.2L LA 6.
6.4 Option Settings
6.4.1 Introduction
The microprocessor communicates with a large number of I
ICs in the set. To ensure good communication and to make
digital diagnosis possible, the microprocessor has to know
which ICs to address. The presence/absence of these specific
ICs (or functions) is made known by the option codes.
Notes:
• After changing the option(s), save them with the STORE
command.
• The new option setting becomes active after the TV is
switched “off” and “on” again with the mains switch (the
EAROM is then read again).
6.4.2 Dealer Options
For dealer options, in SAM select “Dealer options”.
See Table 6-4
6.4.3 (Service) Options
Select the sub menu's to set the initialisation codes (options) of
the model number via text menus.
See Table 6-4
.
.
option numbers on a sticker inside the TV set and in Table
“Option code overview”.
Example: The options sticker gives the following option
2
C
numbers:
• 25604 00386 00235 56068
• 08395 05120 00000 00000
The first line (group 1) indicates hardware options 1 to 4.
Example: option no. “2” contains the “cabinet type”.
The second line (group 2) indicates software options 5 to 8.
Example: option no. “5” contains the “display code”.
Every 5-digit number represents 16 bits (so the maximum value
will be 65536 if all options are set).
When all the correct options are set, the sum of the decimal
values of each Option Byte (OB) will give the option number.
See Table 6-3
for the options. Always refer to the sticker in the
TV-set as leading.
Diversity
Not all sets with the same Commercial Type Number (CTN)
necessarily have the same option code!
Use of Alternative BOM
An alternative BOM number usually indicates the use of an
alternative display. This results in another Display Code thus in
another Option code. Refer to chapter 3. Precautions, Notes,
and Abbreviation List.
6.4.4 Opt. No. (Option numbers)
Select this sub menu to set all options at once (expressed in
two long strings of numbers).
An option number (or “option byte”) represents a number of
different options. When you change these numbers directly,
you can set all options very quickly. All options are controlled
via eight option numbers.
When the NVM is replaced, all options will require resetting. To
be certain that the factory settings are reproduced exactly, you
must set both option number lines. You can find the correct
6.5 Total Overview SAM modes
Table 6-4 SAM mode overview (usage is model dependent)
Main Menu Sub-menu 1 Sub-menu 2 Sub-menu 3 Description
Hardware Info A. SW VERSION e.g. “QL92L_1.33.0.0” Displays TV & Standby SW version and CTN serial
B. Standby processor version e.g. “STDBY_88.68.0.0”
C. Production code e.g. “VN010935123456”
Operation hours Displays the accumulated total o f operation hours.TV
Errors Displayed the most recent errors.
Reset error buffer Clears all content in the error buffer.
Alignment Tuner AGC RF-AGC Take over point adjustment (AGC default
White point Colour temperature Normal 3 different modes of colour temperature can be se-
White point red
White point green
White point blue
Red black level offset
Green black level offset
6.4.5 Option code overview
Table 6-3 Option code overview (subject to change)
Model Number Option Codes Displ.
32PFL5604D/78 2560 4 00385 00235 56068 08396 05120 00000 00000 204
42PFL5604D/78 2560 4 00386 00235 56068 08397 05120 00000 00000 205
42PFL7404D/78 0922 0 00899 00239 56068 08375 05120 00000 00000 183
47PFL5604D/78 2560 4 00386 00235 56068 08395 05120 00000 00000 203
52PFL7404D/78 0922 0 00899 00239 56068 08400 05120 00000 00000 208
number.
switched “on/off” & every 0.5 hours is increase one
value is 80)
Warn
Cool
lected
LCD White Point Alignment. For values,
see Table 6-2
.
Code
2010-Jul-01
Page 38

EN 38 LC9.2L LA6.
Main Menu Sub-menu 1 Sub-menu 2 Sub-menu 3 Description
Dealer options Personal options Picture mute Off/On Select Picture mute On/Off. Picture is muted / not
Options Digital broadcast DVB Off/On Select DVB On/Off
Digital features USB Off/On Select USB On/Off
Data EPG Off/On Select EPG On/Off
Display Screen e.g. “130 - LGD WUE SAA1 42"“ Displayed the panel code & type model.
Video reproduction Picture processing None/PNX5100 Select Picture processing None/PNX5100 (Q549.xE
Alignments
muted in case no input signal is detected at input
connectors.
Virgin mode Off/On
E-sticker Off/On Select E-sticker On/Off (USPs on-screen)
Auto store mode None
PDC/VPS
TXT page
PDC/VPS/TXT
DVB - T installation Off/On or Country dependent Select DVB T installation On/Off or by country
DVB - T light Off/On Select DVB T light On/Off
DVB - C Off/On Select DVB C On/Off
DVB - C installation Off/On or Country dependent Select DVB C installation On/Off or by country
Over the air download Off/On or Country dependent Select Over the air download On/Off or by country
8 days EPG Off/On Select 8 day EPG On/Off
Ethernet Off/On Select Ethernet On/Off
Wi-Fi Off/On Select Wi-Fi On/Off
DLNA Off/On Select DLNA On/Off
On-line service Off On-line service is Off
PTP (Picture Transfer Protocol) Off/On Select PTP On/Off
Update assistant Off/On Select Update assistant On/Off
Internet software update Off Internet software update is Off
TvTv EPG Off/On Select TvTv EPG On/Off
Dimming backlight Off/On Select Dimming Backlight On/Off
LightGuide Off/On Select LightGuide On/Off
Display fans Not present/Present Select Display fans Present/Not present.
Temperature sensor Sensor present in display (only for
Temperature LUT 0 N.A
E-box & monitor Off/On Select E-box & monitor On/Off
MOP local contrast Off/On Select MOP local contrast On/Off
Light sensor Off/On Select Light sensor On/Off
Light sensor type 0/1/2/3 Select Light sensor type form 0 to 3 (for difference
Pixel Plus type Pixel Plus HD Select type of picture improvement.
Pixel Plus Off/On Select Pixel Plus On/Off
Ambilight Off/Mono/Stereo/Triple/Quad/Pixe-
Ambilight technology CCFL/LED Select Ambilight technology.
Ambilight driver Pacific 3/MOP/DFI Select Ambilight driver.
Pacific 3 Not present/Present Select Pacific 3 presence.
MOP Not present/Present Select MOP presence.
MOP ambilight Off/On Select MOP ambilight On/Off
21:9)
Perfect Pixel HD
Pixel Precise HD
lated quad
Select Virgin mode On/Off. TV starts up / does not
start up (once) with a language selection menu after
the mains switch is turned “on” for the first time (virgin
mode)
N.A.
chassis).
styling).
Select type of Ambilight modules use.
2010-Jul-01
Page 39

Alignments
Main Menu Sub-menu 1 Sub-menu 2 Sub-menu 3 Description
Audio reproduction Acoustic system Cabinet design used for setting dynamic audio pa-
Source selection EXT1/AV1 type SCART CVBS RGB LR Select input source when connected with external
CVBS Y/C YPbPr LR
CVBS Y/C YPbPr HV LR
(CVBS) YPbPr LR
EXT2/AV2 type SCART CVBS RGB LR Select input source when connected with external
CVBS Y/C LR
(CVBS) YPbPr LR
CVBS Y/C LR
EXT3/AV3 type None Select input source when connected with external
CVBS
CVBS LR
YPbPr
YPbPr LR
YPbPr HV LR
VGA Off/On Select VGA On/Off
SIDE I/O Off/On Select SIDE I/O On/Off
HDMI 1 Off/On Select HDMI 1 On/Off
HDMI 2 Off/On Select HDMI 2 On/Off
HDMI 3 Off/On Select HDMI 3 On/Off
HDMI 4 Off/On Select HDMI 4 On/Off
HDMI side Off/On Select HDMI side On/Off
HDMI CEC Off/On Select HDMI CEC On/Off
HDMI CEC RC pass through Off/On Select HDMI CEC RC pass through On/Off
HDMI CEC Pixel Plus link Off/On Select Pixel Plus link On/Off
USB version USB 1.0/USB 2.0 Select USB version
S/PDIF inputs None/1 connector Select no. of inputs
Miscellaneous Region Europe/AP-PAL-MULTI/Australia Select Region/country
ATSC/DVB-T Off/On Select feature On/Off
Over the air download (AOD) Off/On Select feature On/Off
DVB-T installation Off/Country dependent/On Select feature On/Off
DVB-C Off/On Select feature On/Off
DVB-C installation Off/Country dependent/On Select feature On/Off
MPEG4 Off/On Select feature On/Off
Tuner type HD1816-MK1/TD1716-MK4/etc. Select type of Tuner used
Nyquist SAW filter Off/On Select feature On/Off
I2C configuration With PCA9540/9515/channel dec. Select configuration
Channel decoder TDA10048/etc. Select channel decoder
Remote control assistant Off/On Select feature On/Off
System RC support Off/On Select System RC support On/Off
Embedded user manual Off/On Select Embedded user manual On/Off
Start-up screen Off/On Select Start-up screen On/Off
Wallpaper Off/On Select Wallpaper On/Off
Hotel mode Off Hotel mode is Off
Video playback Off/On Select feature On/Off
Update assistant Off/On Select feature On/Off
Board identifier TV520/82 / TV520/82M Select chassis
Light guide Off/On Select feature On/Off
Option number Group 1 e.g. “08192.02181.01387.45160” The first line (group 1) indicates HW options 1 - 4
Group 2 e.g. “10185.12448.00164.00000” The second line (group 2) indicates SW options 5 - 8
Store Store after changing
Initialise NVM N.A.
Store
SW maintenance Software events Display Displayed information is for development purposes
Clear
Test reboot
Hardware events Display Displayed information is for development purposes
Clear
Operation hours display 0003 In case the display must be swapped for repair, you
Test settings Digital info Displayed information is for development purposes.
Install start frequency 000 Install start frequency from “0” MHz
Install end frequency 999 Install end frequency as 999 MHz
Default install frequency
Installation Digital only Select Digital only or Digital + Analogue b efore instal-
Digital + Analogue
rameters
equipment
equipment
equipment
Select Store in the SAM root menu after making any
changes
can reset the “”Display operation hours” to “0”. So,
this one does keeps up the lifetime of the display itself (mainly to compensate the degeneration behaviour)
lation.
EN 39LC9.2L LA 6.
2010-Jul-01
Page 40

EN 40 LC9.2L LA6.
Main Menu Sub-menu 1 Sub-menu 2 Sub-menu 3 Description
Development file versions
Upload to USB Channel list To upload several settings from the TV to an USB
Download from USB Channel list To download several settings from the USB stick to
Development 1 file version Display parameters DISPT 3.26.8.7 Displayed information is for development purposes.
Development 2 file version 12NC one zip software Displayed information is for development purposes.
Personal settings
Option codes
Display-related alignment
History list
Personal settings
Option codes
Display-related alignments
Alignments
Acoustics parameters ACSTS 3.6.6.5
PQ - PRFPP 1.26.10.4
Ambilight parameters PRFAM 2.6.1.3
Initial main software
NVM version Q5492_0.4.0.0
Flash units SW Q5492_0.26.15.0
stick
the TV.
2010-Jul-01
Page 41

7. Circuit Descriptions
18700_203_090828.eps
090828
Index of this chapter:
7.1 Introduction
7.2 PSU
Notes:
•Only new circuits (circuits that are not published recently)
are described.
• Figures can deviate slightly from the actual situation, due
to different set executions.
• For a good understanding of the following circuit
descriptions, please use chapter 9. Block Diagrams
10. Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
you will find a separate drawing for clarification.
7.1 Introduction
. Where necessary,
Circuit Descriptions
and
EN 41LC9.2L LA 7.
The LC9.2L LA chassis is a digital derivative from the LC9.1A
LA chassis. Only the DTM part (digital Brazil) is different, but is
all incorporated in the MT5392 (+ other tuner). For all other
circuitry, refer to the LC9.1A LA Service Manual.
7.1.1 Architecture Overview
For details about the chassis block diagrams refer to chapter
Block Diagrams
in figure 7-1 Architecture
. An overview of the architecture can be found
.
Figure 7-1 Architecture
2010-Jul-01
Page 42

EN 42 LC9.2L LA7.
CVI 1 CVI 2
UART
18700_204_090828.eps
090828
7.1.2 SSB Cell Layout
Circuit Descriptions
7.2 PSU
All PSUs are so-called IPBs (Integrated Power Boards). That
are PSUs with integrated LCD inverters.
The power supplies are a black box for Service. When
defective, a new board must be ordered and the defective one
must be returned, unless the main fuse of the board is broken.
Always replace a defective fuse with one with the correct
specifications! This part is available in the regular market.
For an overview of the output voltages of the Power Supplies,
refer to the wiring diagrams in chapter Block Diagrams
The following PSUs are used:
• 32-inch/50Hz: LGIT PLHL-T810B (155 W).
• 42-inch/50Hz: LGIT PLHL-T814B (205 W).
• 47-inch/50Hz: LGIT PLHL-T819B (270 W).
• 42-inch/100Hz: LGIT PLHL-T814A (220 W).
• 52-inch/100Hz: Delta DPS-411AP-3A (280 W).
2010-Jul-01
Figure 7-2 SSB cell layout
.
Page 43

IC Data Sheets
G_16860_045.eps
100326
Block diagram
Pinning information
TDA8932T
V
SSD(HW)
V
SSD(HW)
OICSOP1NI
1PVHN1NI
VGAID
DDP1
1TOOBEGAGNE
1TUOPUREWOP
VDNGC
SSP1
V
DDA
STAB1
V
SSA
STAB2
OSCREF
V
SSP2
2TUOFERPVH
2TOOBFERNI
VTSET
DDP2
2PVHN2NI
FERDP2NI
V
SSD(HW)
V
SSD(HW)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
18
17
20
19
22
21
24
23
26
25
32
31
30
29
28
27
2
81301
28
29
27
3
12
TDA8932
OSCILLATOR
26
BOOT1
V
DDP1
OUT1
V
SSP1
PWM
MODULATOR
DRIVER
HIGH
DRIVER
LOW
CTRL
MANAGER
CTRL
PWM
MODULATOR
PROTECTIONS:
OVP, OCP, OTP,
UVP, TF, WP
STABILIZER 11 V
STABILIZER 11 V
REGULATOR 5 V
MODE
V
DDA
15
14
IN1P
VOICSOFERCSO
DDA
V
SSD
IN1N
INREF
IN2P
IN2N
6
POWERUP
4
DIAG
7
CGND
21
20
22
23
BOOT2
V
DDP2
OUT2
25
STAB1
24
STAB2
18
11
DREF
HVPREF
30
HVP1
19
HVP2
V
SSP2
DRIVER
HIGH
DRIVER
LOW
V
DDA
V
SSP1
V
SSP2
V
SSD
V
DDA
V
SSA
HALF SUPPLY VOLTAGE
5
ENGAGE
13
9
TEST
V
SSA
1, 16, 17, 32
V
SSD(HW)
8. IC Data Sheets
This section shows the internal block diagrams and pin layouts
of ICs that are drawn as "black boxes" in the electrical diagrams
(with the exception of "memory" and "logic" ICs).
8.1 Diagram B03, Type TDA8932BT (IC7510), Audio Amplifier
EN 43LC9.2L LA 8.
Figure 8-1 Internal block diagram and pin configuration
2010-Jul-01
Page 44

EN 44 LC9.2L LA8.
18700_302_090828.eps
100326
Block diagram
DRAM Bus
IO Bus
UART
PWMPVR
Audio DSP
Watchdog
Audio I/F
SPDIF, I
2
S
RTC
2-D Graphic
Vplane
scaler
OSD
scaler
VADCx4
TS
Demux
TV
Decoder
HDMI In
I/F
LVDS
Audio
Input
MJC and Post
Processing
DDR
DRAM
Controller
BIM
ARM11
HDMI
Rx
Panel
VDO-In
NAND Flash
Audio DAC
CKGEN
Audio
Demod
De-interlace
Audio In
DTD
Audio
A
DC
Serial Flash
Servo ADC
BScan
JTAG
USB2.0
I2CIrDA
CVBS/
YC Input
Video Decoder
SDIO
Ethernet MAC
T8032
Tuner
In
Component
Analog
Input
Tuner
In
DDR2
GDDR3
CEC
IC Data Sheets
8.2 Diagram B04x, Type MT5392 (IC7701), CPU / Demodulator / Decoder
Figure 8-2 Internal block diagram
2010-Jul-01
Page 45

8.3 Diagram B05, Type ADV3002 (IC7B05), HDMI MUX
18700_301_090828.eps
100326
Block diagram
Pinning information
2
IN_B_CLK+
3
HPD_B
4
IN_B_DATA0–
7
IN_B_DATA1–
6
HPD_A
5
IN_B_DATA0+
1
IN_B_CLK–
8
IN_B_DATA1+
9
AVCC
10
IN_B_DATA2–
12
SEL0
13
IN_A_CLK–
14
IN_A_CLK+
15
SEL1
16
IN_A_DATA0–
17
IN_A_DATA0+
18
AVCC
19
IN_A_DATA1–
20
IN_A_DATA1+
11
IN_B_DATA2+
59
58
57
54
55
56
60
53
52
IN_C_DATA2–
HPD_C
IN_C_DATA1+
IN_C_DATA0+
HPD_D
IN_C_DATA1–
IN_C_DATA2+
IN_C_DATA0–
AVCC
51
IN_C_CLK+
49
I2C_ADDR0
48
IN_D_DATA2+
47
IN_D_DATA2–
46
AVE E
45
IN_D_DATA1+
44
IN_D_DATA1–
43
AVCC
42
IN_D_DATA0+
41
IN_D_DATA0–
50
IN_C_CLK–
21
AVEE
22
IN_A_DATA2–
23
IN_A_DAT
A2+
24
TX_EN
25
OUT_D
AT
A2+
26
OUT_DATA2–
27
I2C_SCL
28
OUT_D
ATA1+
29
OUT_DATA1–
30
AVEE
31
OUT_D
AT
A0+
32
OUT_DATA0–
33
AVCC
34
OUT_CLK+
35
OUT_CLK–
36
RESETB
37
IN_D_CLK–
38
IN_D_CLK+
39
I2C_ADDR1
40
I2C_SDA
80
P5V_A
79
P5V_B78P5V_C77P5V_D
76
DDC_SDA_A75DDC_SCL_A
74
DDC_SDA_B73DDC_SCL_B72DDC_SDA_C71DDC_SCL_C70DDC_SDA_D
69
DDC_SCL_D
68
DDC_SDA_COM67DDC_SCL_COM66CEC_IN
65
CEC_OUT
64
AMUXVCC
63
EDID_ENABLE
62
EDID_SDA
61
EDID_SCL
PIN 1
ADV3002
TOP VIEW
(Not to Scale)
SERIAL
I2C_SDA
I2C_SCL
I2C_ADDR[1:0]
AVCC
AVCC
CEC_IN
IN_x_CLK+
IN_x_CLK–
IN_x_DATA2+
IN_x_DATA2–
IN_x_DATA1+
IN_x_DATA1–
IN_x_DATA0+
IN_x_DATA0–
DDC_xxx_ A
DDC_xxx_B
DDC_xxx_C
DDC_xxx_D
P5V_A
P5V_B
P5V_C
P5V_D
HPD_A
HPD_B
HPD_C
HPD_D
HOT PLUG DETECT
EDID
DDC/CEC
TMDS
EDID EEPROM I NTERFACE
ADV3002
4
4
2
4
4
4
2
2
2
2
2
2
4
4
+
–
+
–
+
–
+
–
+
–
+
–
+
–
+
–
AVCC
AVCC
AVCC
AVEE
OUT_CLK+
OUT_CLK–
OUT_DATA2+
OUT_DATA2–
OUT_DATA1+
OUT_DATA1–
OUT_DATA0+
OUT_DATA0–
DDC_SCL_COM ,
DDC_SDA_COM
CEC_OUT
EDID_ENABLE
EDID_SCL,
EDID_SDA
AMUXVCC
BIDIRECTI ONAL
SEL[1:0] TX_EN
RESETB
CONFIG
INTERFACE
CONTRO L
LOGIC
LOS
EQ
SWITCH
CORE
SWITCH
CORE
3.3V 3.3V
REPLICATOR
CONTRO L
5V
COMBI NER
HPD
CONTROL
PARALLEL
IC Data Sheets
EN 45LC9.2L LA 8.
Figure 8-3 Internal block diagram and pin configuration
2010-Jul-01
Page 46

EN 46 LC9.2L LA8.
Personal Notes:
10000_012_090121.eps
IC Data Sheets
2010-Jul-01
Page 47

9. Block Diagrams
1M99
(B01)
12. GND
11. N.C
10. N.C
9. POWER-OK
8. GND
7. BACKLIGHT_BOOST
6. PWM_DIMMING
5. BL_ON_OFF
4. GND
3. GND
2. +12VDISP
1. +12VDISP
1M95
(B01)
11. N.C
10. GNDSND
9. +24VAUDIO
8. +12VS
7. +12VS
6. +12VS
5. GND
4. GND
3. GND
2. STANDBY
1. +3V3STBY
CN4
11. FAN_PWM
10. GND_SND
9. +VSND
8. +12V
7. +12V
6. +12V
5. GND1
4. GND1
3. GND1
2. STANDBY
1. 3V3_ST
CN5
12. GND1
11. I2C_DATA
10. I2C_SCL
9. INV_OK
8. A/P_DIM
7. BOOST
6. DIM
5. BL_ON_OFF
4. GND1
3. GND1
2. +12V
1. +12V
CN1
1. N
2. L
1M20
(B04c)
8. +5V_SW
7. KEYBOARD
6. LED1
5. +3V3STBY
4. LED2
3. IR
2. GND
1. LIGHT-SENSOR
1736
(B03)
3. SPEAKER_RIGHT-
2. N.C.
1. SPEAKER_LEFT+
1735
(B03)
4. SPEAKER_RIGHT-
3. SPEAKER_RIGHT+
2. SPEAKER_LEFT-
1. SPEAKER_LEFT+
WIRING DIAGRAM 32"
(P&S)
SSB
(1150)
B
INLET
MAIN POWER SUPPLY
IPB 32 PLHL-T810B
(1005)
TO
BACKLIGHT
CN2
1. HV1
2. N.C.
3. HV1
CN3
1. HV2
2. N.C.
3. HV2
IR LED PANEL
LCD DISPLAY
(1004)
P2
3P
KEYBOARD CONTROL
P1
8P
8M95
8M99
TO
BACKLIGHT
1G51
(B04D)
51. GND
...
...
...
4. +VDISP
3. +VDISP
2. +VDISP
1. +VDISP
1G50
(B04D)
1. GND
2. GND
...
...
38. +VDISP
39. +VDISP
40. +VDISP
41. +VDISP
18700_400_090818.eps
090824
Board Level Repair
Component Level Repair
Only For Authorized Workshop
8319
8316
LEFT SPEAKERRIGHT SPEAKER
8G51
Wiring Diagram 32" (P & S)
Block Diagrams
EN 47LC9.2L LA 9.
2010-Jul-01
Page 48

Wiring Diagram 42" (P & S)
WIRING DIAGRAM 42"
Board Level Repair
(P&S)
Block Diagrams
EN 48LC9.2L LA 9.
KEYBOARD CONTROL
BACKLIGHT
Component Level Repair
Only For Authorized Workshop
8316
CN2
1. HV1
2. N.C.
3. HV1
TO
CN3
1. HV2
2. N.C.
3. HV2
MAIN POWER SUPPLY
IPB 42 PLHL-T814B
(1005)
8319
CN4
11. FAN_PWM
10. GND_SND
9. +VSND
8. +12V
7. +12V
6. +12V
5. GND1
4. GND1
3. GND1
2. STANDBY
1. 3V3_ST
CN5
12. GND1
11. I2C_DATA
10. I2C_SCL
9. INV_OK
8. A/P_DIM
7. BOOST
6. DIM
5. BL_ON_OFF
4. GND1
3. GND1
2. +12V
1. +12V
CN1
1. N
2. L
8308
FUSE
LCD DISPLAY
51P
8M95
SUB WOOFER
8M99
(1004)
8G51
1G50
(B04D)
1. GND
2. GND
...
...
38. +VDISP
39. +VDISP
40. +VDISP
41. +VDISP
1M20
(B04c)
8. +5V_SW
7. KEYBOARD
6. LED1
5. +3V3STBY
4. LED2
3. IR
2. GND
1. LIGHT-SENSOR
1M95
(B01)
11. N.C
10. GNDSND
9. +24VAUDIO
8. +12VS
7. +12VS
6. +12VS
5. GND
4. GND
3. GND
2. STANDBY
1. +3V3STBY
1M99
(B01)
12. GND
11. N.C
10. N.C
9. POWER-OK
8. GND
7. BACKLIGHT_BOOST
6. PWM_DIMMING
5. BL_ON_OFF
4. GND
3. GND
2. +12VDISP
1. +12VDISP
1735
(B03)
4. SPEAKER_RIGHT-
3. SPEAKER_RIGHT+
2. SPEAKER_LEFT-
1. SPEAKER_LEFT+
1736
(B03)
3. SPEAKER_RIGHT-
2. N.C.
1. SPEAKER_LEFT+
(B04D)
51. GND
1G51
B
...
...
...
SSB
(1150)
1. +VDISP
3. +VDISP
2. +VDISP
4. +VDISP
TO
BACKLIGHT
IR LED PANEL
INLET
+ -
P2
3P
P1
8P
RIGHT SPEAKER
LEFT SPEAKER
+ -
18700_401_090818.eps
090821
2010-Jul-01
Page 49

Wiring Diagram 42"(Frame)
1M99
(B01)
12. GND
11. N.C
10. N.C
9. POWER-OK
8. GND
7. BACKLIGHT_BOOST
6. PWM_DIMMING
5. BL_ON_OFF
4. GND
3. GND
2. +12VDISP
1. +12VDISP
1M95
(B01)
11. N.C
10. GNDSND
9. +24VAUDIO
8. +12VS
7. +12VS
6. +12VS
5. GND
4. GND
3. GND
2. STANDBY
1. +3V3STBY
CN4
11. FAN_PWM
10. GND_SND
9. +VSND
8. +12 V
7. +12V
6. +12V
5. GND1
4. GND1
3. GND1
2. STANDBY
1. 3V3_ST
CN5
12. GND1
11. I2C_DATA
10. I2C_SCL
9. INV_OK
8. A/P_DIM
7. BOOST
6. DIM
5. BL_ON_OFF
4. GND1
3. GND1
2. +12V
1. +12V
CN1
1. N
2. L
1M20
(B04c)
8. +5V_SW
7. KEYBOARD
6. LED1
5. +3V3STBY
4. LED2
3. IR
2. GND
1. LIGHT-SENSOR
1736
(B03)
3. SPEAKER_RIGHT-
2. N.C.
1. SPEAKER_LEFT+
1735
(B03)
4. SPEAKER_RIGHT-
3. SPEAKER_RIGHT+
2. SPEAKER_LEFT-
1. SPEAKER_LEFT+
WIRING DIAGRAM 42"
(FRAME)
SSB
(1150)
B
INLET
MAIN POWER SUPPLY
IPB 42 PLHL-T814A
(1005)
TO
BACKLIGHT
CN2
1. HV1
2. N.C.
3. HV1
CN3
1. HV2
2. N.C.
3. HV2
IR LED PANEL
(1112)
P2
3P
KEYBOARD CONTROL
(1114)
P1
8P
FUSE
8M20
8M95
8M99
TO
BACKLIGHT
1G51
(B04D)
51. GND
...
...
...
4. +VDISP
3. +VDISP
2. +VDISP
1. +VDISP
1G50
(B04D)
1. GND
2. GND
...
...
38. +VDISP
39. +VDISP
40. +VDISP
41. +VDISP
18700_402_090818.eps
090821
Board Level Repair
Component Level Repair
Only For Authorized Workshop
8319
8316
SPEAKER RIGHT (5212) SPEAKER LEFT (5211)
+ -
+ -
8308
8735
8G50
8G51
LCD DISPLAY
(1004)
51P 41P
Block Diagrams
EN 49LC9.2L LA 9.
2010-Jul-01
Page 50

Wiring Diagram 47"(P & S)
1M99
(B01)
12. GND
11. N.C
10. N.C
9. POWER-OK
8. GND
7. BACKLIGHT_BOOST
6. PWM_DIMMING
5. BL_ON_OFF
4. GND
3. GND
2. +12VDISP
1. +12VDISP
1M95
(B01)
11. N.C
10. GNDSND
9. +24VAUDIO
8. +12VS
7. +12VS
6. +12VS
5. GND
4. GND
3. GND
2. STANDBY
1. +3V3STBY
CN4
11. FAN_PWM
10. GND_SND
9. +VSND
8. +12V
7. +12V
6. +12V
5. GND1
4. GND1
3. GND1
2. STANDBY
1. 3V3_ST
CN5
12. GND1
11. I2C_DATA
10. I2C_SCL
9. INV_OK
8. A/P_DIM
7. BOOST
6. DIM
5. BL_ON_OFF
4. GND1
3. GND1
2. +12V
1. +12V
CN1
1. N
2. L
1M20
(B04c)
8. +5V_SW
7. KEYBOARD
6. LED1
5. +3V3STBY
4. LED2
3. IR
2. GND
1. LIGHT-SENSOR
1736
(B03)
3. SPEAKER_RIGHT-
2. N.C.
1. SPEAKER_LEFT+
1735
(B03)
4. SPEAKER_RIGHT-
3. SPEAKER_RIGHT+
2. SPEAKER_LEFT-
1. SPEAKER_LEFT+
WIRING DIAGRAM 47" (P&S)
SSB
(1150)
B
INLET
MAIN POWER SUPPLY
IPB 47 PLHC-T819A
(1005)
TO
BACKLIGHT
CN2
1. HV1
2. N.C.
3. HV1
CN3
1. HV2
2. N.C.
3. HV2
KEYBOARD CONTROL
IR LED PANEL
P2
3P
P1
8P
FUSE
8M95
8M99
TO
BACKLIGHT
1G51
(B04D)
51. GND
...
...
...
4. +VDISP
3. +VDISP
2. +VDISP
1. +VDISP
1G50
(B04D)
1. GND
2. GND
...
...
38. +VDISP
39. +VDISP
40. +VDISP
41. +VDISP
18700_403_090818.eps
090821
Board Level Repair
Component Level Repair
Only For Authorized Workshop
8319
8316
8308
8G51
LCD DISPLAY
(1004)
51P
RIGHT SPEAKER
SUB WOOFER
LEFT SPEAKER
+ -
+ -
Block Diagrams
EN 50LC9.2L LA 9.
2010-Jul-01
Page 51

8G50
8G51
WIRING DIAGRAM 52" (FRAME)
KEYBOARD CONTROL
(1114)
18700_404_090818.eps
090821
1M99 (B01)
12. GND
11. N.C
10. N.C
9. POWER-OK
8. GND
7. BACKLIGHT_BOOST
6. PWM_DIMMING
5. BL_ON_OFF
4. GND
3. GND
2. +12VDISP
1. +12VDISP
1M95 (B01)
11. N.C
10. GNDSND
9. +24VAUDIO
8. +12VS
7. +12VS
6. +12VS
5. GND
4. GND
3. GND
2. STANDBY
1. +3V3STBY
CN4
11. FAN_PWM
10. GND_SND
9. +VSND
8. +12V
7. +12V
6. +12V
5. GND1
4. GND1
3. GND1
2. STANDBY
1. 3V3_ST
CN5
12. GND1
11. I2C_DATA
10. I2C_SCL
9. INV_OK
8. A/P_DIM
7. BOOST
6. DIM
5. BL_ON_OFF
4. GND1
3. GND1
2. +12V
1. +12V
CN1
1. N
2. L
1M20 (B04c)
8. +5V_SW
7. KEYBOARD
6. LED1
5. +3V3STBY
4. LED2
3. IR
2. GND
1. LIGHT-SENSOR
1736 (B03)
3. SPEAKER_RIGHT-
2. N.C.
1. SPEAKER_LEFT+
1735 (B03)
4. SPEAKER_RIGHT-
3. SPEAKER_RIGHT+
2. SPEAKER_LEFT-
1. SPEAKER_LEFT+
SSB
(1150)
B
INLET
MAIN POWER SUPPLY
PSU DPS-411AP4A B
(1005)
IR LED PANEL
(1112)
LCD DISPLAY (1004)
P2
3P
P1
8P
FUSE
1G51 (B04D)
51. GND
...
...
...
4. +VDISP
3. +VDISP
2. +VDISP
1. +VDISP
1M59 (B04E)
1. AMBI_SCL_OUT
2. GND
3. AMBI_SDA_OUT
4. I2S_SEL1
5. I2S_SEL2
6. +3V3_SW
7. GND
1G50 (B04D)
1. GND
2. GND
...
...
38. +VDISP
39. +VDISP
40. +VDISP
41. +VDISP
Board Level Repair
Component Level Repair
Only For Authorized Workshop
SPEAKER RIGHT (5212) SPEAKER LEFT (5211)
+ -
+ -
8308
8M95
8M99
8M20
8735
CN3/1316
12. N.C.
11. N.C.
10. GND3
9. GND3
8. GND3
7. GND3
6. GND3
5. 24Vinv
4. 24Vinv
3. 24Vinv
2. 24Vinv
1. 24Vinv
CN2/1319
14. PDIM_Select
13. PWM
12. On/Off
11. Vbri
10. GND3
9. GND3
8. GND3
7. GND3
6. GND3
5. 24Vinv
4. 24Vinv
3. 24Vinv
2. 24Vinv
1. 24Vinv
INVERTER
CONNECTOR
INVERTER
CONNECTOR
8319 8316
INVERTER
CN7
6. GND
5. +24V
4. GND
3. +24V
2. GND
1. +24V
41P 51P
Wiring Diagram 52"(Frame)
Block Diagrams
EN 51LC9.2L LA 9.
2010-Jul-01
Page 52

B02A
TUNER & ANALOG DEMOD
B04D
DISPLAY INTERFACE - LVDS
B04
MT5392:
B05
HDMI & MUX
B06B
ANALOG I/O - YPBPR
B06C
ANALOG I/O - CINCH
B06D
SIDE-AV & USB
B06E
VGA
B04B
GDDR3
B04C
FLASH & EJTAG
B06D
SIDE-AV & USB
7701
MT5392RHMJ
LVD S
B04D
AVI
B06B
CVBS_SPDIF_USB
B06D
PM_DEMOD
B04A
GPIO
B04C
HDMI_XTAL_LDO
B05
DREAM_IF
B04B
CVBS-SPDIF_USB
B06D
FLASH_IF
B04C
PB
PR
Y
35
RXC-
RX0+
RX0-
RX1+
RX1-
RX2+
RX2-
34
32
31
29
28
26
25
RXC+
AJ8
AK9
AJ9
AK8
AJ7
AJ6
AK6
AK7
HDMI_RX1_B_P
HDMI_RX2_B_N
HDMI_RX2_B_P
XTAL1
XTALO
HDMI_RX1_B_N
HDMI_RX0_B_P
HDMI_RXC_B_P
HDMI_RXC_B_N
HDMI_RX0_B_N
7B05
ADV3002BSTZ01
HDMI
SWITCH
OUT_CLK_-
OUT_CLK_+
IN_DIN_C
IN_B
IN_A
OUT_DATAD0_-
OUT_DATAD0_+
OUT_DATAD1_-
OUT_DATAD1_+
OUT_DATAD2_-
OUT_DATAD2_+
CRX2+
CRX2-
CRX1+
CRX1-
CRX0+
CRX0-
CRXC+
CRXC-
BRX2+
BRX2-
BRX1+
BRX1-
BRX0+
BRX0-
BRXC+
BRXC-
ARX2+
ARX2-
ARX1+
ARX1-
ARX0+
ARX0-
ARXC+
ARXC-
60
59
57
56
54
53
51
50
11
10
8
7
5
4
2
1
23
22
20
19
17
16
14
13
DRX2+
DRX2-
DRX1+
DRX1-
DRX0+
DRX0-
DRXC+
DRXC-
48
47
45
44
42
41
38
37
19
1
18 2
1
1B02
3
4
7
9
10
12
6
DRX2+
DRX2-
DRX1+
DRX1-
DRX0+
DRX0-
DRXC+
DRXC-
HDMI 1
CONNECTOR
19
1
18 2
1
1B07
3
4
7
9
10
12
6
CRX2+
CRX2-
CRX1+
CRX1-
CRX0+
CRX0-
CRXC+
CRXC-
HDMI 2
CONNECTOR
1
1B04
3
4
7
9
10
12
6
BRX2+
BRX2-
BRX1+
BRX1-
BRX0+
BRX0-
BRXC+
BRXC-
1
1B05
3
4
7
9
10
12
6
ARX2+
ARX2-
ARX1+
ARX1-
ARX0+
ARX0-
ARXC+
ARXC-
19
1
18 2
HDMI 3
CONNECTOR
(OPTIONAL)
19
1
18 2
HDMI SIDE
CONNECTOR
MT5392
7810
NAND01GW3B2BN6F
FLASH
1G
18700_405_090818.eps
090818
NAND_PDD(0-7)
4321
USB_DM0
TO
7F01-6
USB_DP0
USB 2.0
CONNECTOR SIDE
SW UPLOAD
JPEG
MP3
AAJ5
AK5
VIDEO
MPX0_P
1
5
SVHS IN
2
4
3
1F12
1F18
CVBS
CVBS2
SY0
AE29
AF30
2
CVBS_2
1D14
CVBS
PR
AE230
2
CVBS_3
SY_0
SC0
AF29
SC_0
1E17
SC1_B
SC1_G Y0P
PB0P
PR0P
Y0N
PBR0N
AJ19
AJ21
7
12
9
SC1_CVBS_OUT PR0P-SC1
PB0P-SC1
PBR0N-SC1
Y0P-SC1
Y0P-SC1
AH22
PR0P
Y0P
PB0P
AH21
AK22
PBR0N
Y0N
1
1G16
2
3
14
13
VGA_R
VGA_G
VGA_R p
VGA_R n
VGA_G n
VGA_B n
RN
GN
BN
VGA_G p
VGA_B
H-SYNC
V-S YNC
VGA_B p
HSYNC
VSYNC
RP
GP
BP
1
6
10
11
5
15
VGA
CONNECTOR
AJ14
AK14
AH15
AJ15
AJ16
AJ17
AK16
AK17
RP
VSYNC
GP
BP
HSYNC
BN
RN
GN
USB_DP0
USB_DM0
RDQ
RA
PDD
1G50
LVDS_A_TXe
LVDS_A_TXo
LVDS_B_TXo
LVDS_B_TXe
QUAD LVDS
1920x1080
100/120Hz
1G51
+VDISP
+VDISP
TO DISPLAY
TO DISPLAY
I2C
1
2
3
32
38
40
39
41
50
51
49
40
11
3
4
2
1
1B10
27M
W30
W29
1F21
1
2
4
3
SIF_OUT_1 SIF_OUT
1205
VA1G5BF8010
TUNER
6
SIF_OUT
AB26
RF-SW
3246
CVBS_0
CVBS0T CVBS_RF
7
VIDEO_OUT
AD29
EF
7213
GPIO_11
RF_SW
1
D29
GAIN-SW
GPIO_12
GAIN_SW
2
E27
AFT
ADIN_6
AFT
5
AK28
SYRSTN
GPIO_4
DEMOD_RESET
11
G29
SBYTE
TSO_SYNC
TSO_SYNC
15
C30
SPBVAL
TSO_VALID
TSO_VALID
16
A30
SRCK
TSO_CLK
TSO_CLK
18
B30
SRDT
TSO_DATA
TSO_DATA0
17
C29
PB
PR
Y
1E19
PB1P_SC2
SY1P_SC2 SY1P
SPB1P
SPR1P
SY1N
SPBR1N
AJ19
AJ18
7
12
9
PR1P_SC2
AH19
PR1P
Y1P
PB1P
AJ19
AH19
PR1P
PB1P
SOY0
CVBS3
AH20
SOY0
(0-12)
DDR3
SDRAM
7702
H5RS1H23MFR
DDR3
SDRAM
7703
H5RS1H23MFR
DQ(0-31)
(0-31)
RA(0-12)
Block Diagram Video
Block Diagrams
EN 52LC9.2L LA 9.
2010-Jul-01
Page 53

B02A
TUNER & ANALOG DEMOD
B03
CLASS-D & MUTING
B04
MT5392:
B05
HDMI & MUX
B06B
ANALOG I/O - YPBPR
B06C
ANALOG I/O - CINCH
B06D
SIDE-AV & USB
B04B
GDDR3
B04C
FLASH & EJTAG
B06D
SIDE-AV & USB
1D14
5
3
1D01
2
7701
MT5392RHMJ
ALI_ADAC
B06B
ALI_DAC
B06B
HDMI_XTAL_LDO
B05
DREAM_IF
B04B
CVBS-SPDIF_USB
B06D
FLASH_IF
B04C
35
RXC-
RX0+
RX0-
RX1+
RX1-
RX2+
RX2-
34
32
31
29
28
26
25
RXC+
AJ8
AK9
AJ9
AK8
AJ7
AJ6
AK6
AK7
HDMI_RX1_B_P
HDMI_RX2_B_N
HDMI_RX2_B_P
XTAL1
XTALO
HDMI_RX1_B_N
HDMI_RX0_B_P
HDMI_RXC_B_P
HDMI_RXC_B_N
HDMI_RX0_B_N
7B05
ADV3002BSTZ01
HDMI
SWITCH
OUT_CLK_-
OUT_CLK_+
IN_DIN_C
IN_B
IN_A
OUT_DATAD0_-
OUT_DATAD0_+
OUT_DATAD1_-
OUT_DATAD1_+
OUT_DATAD2_-
OUT_DATAD2_+
CRX2+
CRX2-
CRX1+
CRX1-
CRX0+
CRX0-
CRXC+
CRXC-
BRX2+
BRX2-
BRX1+
BRX1-
BRX0+
BRX0-
BRXC+
BRXC-
ARX2+
ARX2-
ARX1+
ARX1-
ARX0+
ARX0-
ARXC+
ARXC-
60
59
57
56
54
53
51
50
11
10
8
7
5
4
2
1
23
22
20
19
17
16
14
13
DRX2+
DRX2-
DRX1+
DRX1-
DRX0+
DRX0-
DRXC+
DRXC-
48
47
45
44
42
41
38
37
19
1
18 2
1
1B02
3
4
7
9
10
12
6
DRX2+
DRX2-
DRX1+
DRX1-
DRX0+
DRX0-
DRXC+
DRXC-
HDMI 1
CONNECTOR
19
1
18 2
1
1B07
3
4
7
9
10
12
6
CRX2+
CRX2-
CRX1+
CRX1-
CRX0+
CRX0-
CRXC+
CRXC-
HDMI 2
CONNECTOR
1
1B04
3
4
7
9
10
12
6
BRX2+
BRX2-
BRX1+
BRX1-
BRX0+
BRX0-
BRXC+
BRXC-
1
1B05
3
4
7
9
10
12
6
ARX2+
ARX2-
ARX1+
ARX1-
ARX0+
ARX0-
ARXC+
ARXC-
19
1
18 2
HDMI 3
CONNECTOR
(OPTIONAL)
19
1
18 2
HDMI SIDE
CONNECTOR
MT5392
18700_406_090818.eps
090819
4321
USB_DM0
USB_DP0
USB 2.0
CONNECTOR SIDE
SW UPLOAD
JPEG
MP3
AJ5
AK5
AUDIO
USB_DP0
USB_DM0
RDQ
RA
PDD
1B10
27M
W30
W29
1F21
1
2
4
3
1D11
2
3
1
1F22
2
3
4
1
U29
U28
AIN_2_L
AIN_2_R
AV2_L_IN
AV2_R_IN
J28
ASPDIF_OUT
ASPDID_OUT
DVI_AUL_IN
DVI_AUR_IN
AUDIO
L/R IN
1E17
52
U27
U26
53
SC2-IN-L
SC2-IN-R
V30
AIN1_L
V29
AIN1_R
AV OUT
AUDIO
L/R
AV IN
AUDI O
L/R
AIN0_L
AIN0_L
R28
T28
AIN_6_L
AIN_6_R
SAV_L_IN
SAV_R_IN
1F18
SIDE AV
AUDIO
L/R
5
8
5
3
1E19
5
3
M30
M29
PGA_2OUTL
PGA_2OUTR
AOUTL
AOUTR
AUDIO_LS_L
AUDIO_LS_R
SPEAKER_LEFT+
SPEAKER_LEFT-
SPEAKER_RIGHT+
SPEAKER_RIGHT-
7510
TDA8932BTW/N2
CLASS D
POWER
AMPLIFIER
2
14
27
22
MUTE
5
1
2
1735
3
4
DC-DETECTION
HP_LOUT
HP_ROUT
SW_MUTE
MUTE_C
MUTE_M
M28
M27
HPOUTL
HPOUTR
HEADPHONE
STANDBYn
6
MUTEn
POWER_DOWN
B04A
B06C
B06B
B04A
B04A
B04A
DC_PROT
B04C
7511÷7513
HP_DET
B04C
(CONTROL)
(CONTROL)
(CONTROL)
(CONTROL)
ANTI_PLOP
MUTE
7507
AVI
B06B
PM_DEMOD
B04A
GPIO
B04C
MPX0_P
SIF_OUT_1 SIF_OUT
1205
VA1G5BF8010
TUNER
6
SIF_OUT
AB26
RF-SW
3246
CVBS_0
CVBS0T CVBS_RF
7
VIDEO_OUT
AD29
EF
7213
GPIO_11
RF_SW
1
D29
GAIN-SW
GPIO_12
GAIN_SW
2
E27
AIN3_L
AIN3_R
CVBS_SPDIF_USB
B06D
AFT
ADIN_6
AFT
5
AK28
SYRSTN
GPIO_4
DEMOD_RESET
11
G29
SBYTE
TSO_SYNC
TSO_SYNC
15
C30
SPBVAL
TSO_VALID
TSO_VALID
16
A30
SRCK
TSO_CLK
TSO_CLK
18
B30
SRDT
TSO_DATA
TSO_DATA0
17
C29
7810
NAND01GW3B2BN6F
FLASH
1G
NAND_PDD(0-7)
(0-12)
DDR3
SDRAM
7702
H5RS1H23MFR
DDR3
SDRAM
7703
H5RS1H23MFR
DQ(0-31)
(0-31)
RA(0-12)
AIN1_R
AIN1_L
Block Diagram Audio
Block Diagrams
EN 53LC9.2L LA 9.
2010-Jul-01
Page 54

Block Diagram Control & Clock Signals
CONTROL + CLOCK SIGNALS
B04B
GDDR3
B04C
FLASH & EJTAG
B06D
SIDE-AV & USB
B04C
FLASH & EJTAG
1812
3
2
FOR
DEBUGGING
ONLY
TO IR/LED PANEL
AND
KEYBOARD CONTROL
+5V_SW
+3V3STBY
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
1M20
MT5392
7701
MT5392RHMJ
FLASH_IF
B04C
PM_DEMOD
B04A
M2 J11
OPWRSB
SPIO_UART_IIC
B04C
AJ13
AK13
UART
SERVICE
CONNECTOR
UART_RX
UART_TX
UART_RX
UART_TX
UART_RX
UART_TX
1813
3
2
1
RES
AH14
STANDBYn
B03
B01
STANDBY
OPWM_2
U0RX
U0TX
C5
PWM_DIMMMING
B01
AH5
GPIO_0
GPIO_16
GPIO_15
GPIO
B04C
GPIO_14
AK2
EDID_WC
B05 B06E
GPIO_20
B28
LCD_PWR_ON
B04D
GPIO_24
D28
BL_ON_OFF
B01
DC_PROT
B03
AG6
AJ2
AJ1
GPIO_1
USB_PWE
B06D
AF7
GPIO_2
USB_OC
B06D
G30
GPIO_17
G30
GPIO_17
AK11
OIRI
HP_DET
B06D
AJ29
ADIN_3
CVBS_SPDIF_USB
B06D
LIGHT_SENSOR
AK29
ADIN_4
POWER-OK
B01
AJ28
ADIN_5
KEYBOARD
AK28
ADIN_6
RF_AGC_MON
B02A
IR
OPCTRL_0
AJ12
HDMI_CEC
B05
OPCTRL_2
AG12
LED1
OPCTRL_3
AG11
MUTEn
B03
OPCTRL_4
AF13
SW_MUTE
B03
B03
B03
OPCTRL_5
AF12
POWER_DOWN
B03
OPCTRL_8
AH13
LED2
DDR3
7702
HYB18H1G321AF
DREAM_IF
B04B
DQ(0-31)
RA(0-12)
RDQ
RA
RCLK0
7810
NAND01GW3B2CN6F
FLASH
1G
NAND_PDDD(0-7)
PDD
OPWM_1
D_1
K27
BACKLIGHT_BOOST
B01
E9
LVD S_SELECT
B01
2843
SDM
2833
PAN EL
RCLK0p
M3 J10
RCLK0
RCLK0n
4 3 21
USB20-DM0
OPCTRL_8
AH13
USB_DM0
AJ5
USB_DP0
AK5
USB20-DP0
USB 2.0
CONNECTOR
SIDE
1F21
3
4
2
1
USB_PWE
7F01
TPS2041BD
USB_OC
EN
OUT
OC
18700_407_090818.eps
090819
7602
7816
Personal Notes:
E_06532_012.e
1310
Block Diagrams
EN 54LC9.2L LA 9.
2010-Jul-01
Page 55

Block Diagram I2C
I²C
HDMI & MUX
B05
VGA
B06E
TUNER & ANALOG DEMOD
B02A
MTK POWER
B04A
FLASH & EJTAG
B04C
CONTROLLER
B04
DISPLAY INTERFACE - LVDS
B04D
AMBILIGHT
B04E
GDDR3
B04B
7701
MT5392RHMJ
OSDA0
OSCL0
GPIO-18
PM_DEMOD
SPIO_UART
IIC
L28
L28 7
68
67
J29
J30
L29
TUNER_SDA
TUNER_SCL
SYS_EEPROM_WE
SDA
SCL
3606
3607
+3V3_SW
3831
3830
+3V3_SW
389D
389F
+3V3_SW
UA0RX
UA0TX
CLK
DATA
18700_408_090819.eps
090819
12 13
1205
VA1G5BF8010
MAIN
TUNER
56
7812
M24C64
EEPROM
(NVM)
3839
3838
AJ10
AK10
DDC-SDA
DDC-SCL
OSCL2
OSDA2
K30
K29
AMBI-SDA
AMBI-SCL
AJ13
AK13
UART_RX
UART_TX
OSCL1
OSDA1
38A9
3823
38A8
3864
3865
+3V3STBY
UART
SERVICE
CONNECTOR
TO AMBILIGHT
DRIVERS
TO DISPLAY
3869
3868
1813
3
2
1
1818
3
1
4
6
2
38A3
38A4
FOR DEBUGGING ONLY
1G51
49
50
3916
3917
3888
3889
+3V3STBY
3A11
3A10
3A13
+3V3_SW
+3V3_SW
1812
3
1
4
66
7
2
1M59
1
5
6
2
3
3890
3891
FOR DEBUGGING ONLY
RES
LVD S3_SDA_DISP
LVD S3_SCL_DISP
ERR
16
B04A
B04C
ERR
15
7815
5A16
5A14
5A10
40 27
7B05
ADV3002BSTZ
HDMI
MUX
3B38
3B39
VDDO_3V3
RES
L28
L29
EDID_SDA
EDID_SCL
3B35
3B34
+5V_COMBINED
56
7B02
M24C02
EEPROM
(EDID)
7
EDID_WC
7B07
HDMI
CONNECTOR 1
1B05
16
15
3B47
3B46
ARX-5V
3B19
3B20
+5V_COMBINED
76
75
HDMI
CONNECTOR 3
(OPTIONAL)
1B04
16
15
3B51
3B50
BRX-5V
74
73
HDMI
CONNECTOR 2
1B07
16
15
3B53
3B52
CRX-5V
72
71
HDMI
CONNECTOR
SIDE
1B02
16
15
3B55
3B54
DRX-5V
70
69
ARX-DDC-DAT
ARX-DDC-CLK
BRX-DDC-DAT
BRX-DDC-CLK
CRX-DDC-DAT
CRX-DDC-CLK
DRX-DDC-DAT
DRX-DDC-CLK
1
6
10
11
5
15
VGA
CONNECTOR
SDA_VGA
SCL_VGA
1G16
12
15
3G15
3G16
DC_5V
56
7G11
M24C02
EEPROM
ERR
17
4G12
4G11
4G14
4G13
RES
7
EDID_WC
7G12
B04C
B04C
MT5392
B04B
DREAM_IF
3270
3271
RES
ERR
14
7810
NAND01GW3B2BN6F
FLASH
512Mx8
NAND_PDD
DQ(0-31)
RA(0-12)
7702
H5RS1H23MFR
DDR3
7703
H5RS1H23MFR
Block Diagrams
EN 55LC9.2L LA 9.
2010-Jul-01
Page 56

Supply Lines Overview
SUPPLY LINES OVERVIEW
CN5
+12V
+12V
GND1
GND1
BL-ON_OFF
DIM
BOOST
A/P_DIM
INV_OK
MAIN
POWER SUPPLY
I2C
I2C
GND1
CN4
3V3_ST
STANDBY
GND1
GND1
GND1
+12V
+12V
+12V
+VSND
GND_SND
CN7
+24V
GND
+24V
GND
+24V
GND
Block Diagrams
DC / DC
B01
11
22
33
44
55
66
77
88
99
10 10
11 11
12 12
11
22
33
44
55
66
77
88
99
10 10
11 11
1
2
3
TO AMBILIGHT
4
MODULE
5
(OPTIONAL)
6
1M99
BL_ON_OFF
PWM_DIMMING
BACKLIGHT_BOOST
POWER-OK
N.C.
N.C.
1M95
STANDBY
5100
7103
ST1S10PH
5108 5101
7117
TPS54386PWP
Synchronous
5103
GNDSND
N.C.N.C.
IN OUT
7100
COM
DCDC
Converter
Non
Converter
7116
TPS54386PWP
7201
IN OUT
COM
7
3
5117
31,14
5116
12
Non
Synchronous
Converter
+12VDISP
B04C
CONTROL
B04C
CONTROL
B04C
CONTROL
B06D
CONTROL
+3V3STBY
+1V2-STANDBY
B04A
CONTROL
+12VS
+8V_SW
+1V0_SW
SENSE+1V0_MT5392
+5V5_TUN
+5V_SW
+3V3_SW
+12V_1
5104
5115
+1V8_SW
+1V2_SW
+24VAUDIO
31,14
12
B04d
B03,B04a,c,
B05,B07
B03,B04a
B04a
B04a
B04a
B02a
B02a,B03,B04c,
B05,B06d,e,B07
B02a,B03,
B04a,c,e,
B05,B06a,b,d
B04a,b
B02a,B04a,B05
B03
EN 56LC9.2L LA 9.
B01
B01
B01
B01
B01
B01
B01
B01
B01
B01
B01
B01
B01
B01
B01
B01
B01
B01
B01
B01
B02A
B03
+24VAUDIO
B04A
+1V0_SW
B04B
B04C
TUNER & ANALOG DEMOD
7216
COM
5223
5217
5225
7217
IN OUT
COM
5224
IN OUT
CLASS-D & MUTING
3530
5502
MTK POWER
GDDR3
FLASH & EJTAG
5810
5814
5815
+5V5_TUN+1V2_SW
+5V5_TUN+3V3_SW
+5V5_TUN+5V5_TUN
+5VTUN_DIGITAL
+5V_SW+5V_SW
+2V5_SW
+5VS
+24VAUDIO
VDDA
VDD
+3V3_SW+3V3_SW
+3V3STBY+3V3STBY
+5V_SW+5V_SW
+12VS+12VS
+1V0_SW
SENCE+1V0_MT5
+1V2_SW+1V2_SW
+3V3_SW+3V3_SW
+3V3STBY+3V3STBY
+1V8_SW+1V8_SW
+8V_SW+8V_SW
+12VS+12VS
+1V8_SW+1V8_SW
+3V3_SW+3V3_SW
+3V3_FLASH
+3V3STBY+3V3STBY
+5V_SW+5V_SW
392
1M20
5
8
TO
IR/LED
PA NE L
B01
B01
B01
B01
B01
B01
B01
B01
B01
B01
B01
B01
B01
B01
DISPLAY INTERFACE - LVDS
B04D
+12VDISP
7910
7911
LCD_PWR_ON
AMBILIGHT
B04E
+3V3_SW
HDMI & MUX
B05
+3V3_SW
+5V_SW
+1V2_SW
HDMI SIDE
CONNECTOR
HDMI 3
CONNECTOR
BOLT-ON
MOD. DTV
HDMI 1
CONNECTOR
HDMI 2
CONNECTOR
+3V3STBY
B06A
+3V3_SW
B06B
+3V3_SW
B06D
+3V3_SW
+5V_SW
B06E
+5V_SW
B07
+3V3STBY
+5V_SW
1B05
18
1B04
18
1B01
1B02
18
1B07
18
DIGITAL IO - ETHERNET (PROVISIONAL)
ANALOG I/O - YPbPr
SIDE-AV & USB
VGA
BDS iTV
5910
5911
5912
5B01
6B07
3
5NA1
5NA2
6G13
+12VDISP
+VDISP
+3V3_SW
1M59
5A10
+3V3_SW
VDDO_3V3
+5V_SW
+5V_COMBINED
+1V2_SW
ARX-5V
BRX-5V
DRX-5V
CRX-5V
+3V3STBY
+3V3_SW
+3V3AN
+3V3DN
+3V3_SW
+3V3_SW
+5V_SW
+5V_SW
DC_5V
+3V3STBY
+5V_SW
TO
6
AMBI
LIGHT
18700_409_090818.eps
090819
2010-Jul-01
Page 57

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
10. Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
SSB: DC/DC
EN 57LC9.2L LA 10.
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
J
K
All rights reserved. Reproduction in whole or in parts
is prohibited without the written consent of the copyright
owner.
L
M
N
1
2
3
12
DC-DC
A
7100
5107
10u
6102
BAV99
6125
SS36
10p
10p
I111
3 1
1u0
2125
10p
RES
2154
10p
RES
2163
6.3V100u
2136
L78L08ACU
2158
2137
OUTIN
COM
2
I100
I103
2N7002
2128
100p
6.3V
2162
100u
5104
10u
10u
+12VS
B
5100
30R
C
ONLY FOR ANALOG TUNER
+12VS
+VTUN
34V
D
F123
6101
2129
22u35V
PDZ33-B
E
+5V5_TUN
F132
+5V_SW
I
F
1%
3140
2170
100K
100u 16V
I131
1%
1%
3138
RES
3107
1K0
18K
G
+12VS
H
+1V8_SW
I
F125
1%
RES
3105
2134
1K5
I104
1%
RES
2135
3106
1K2
123 4567
5102
7101
GNDTUN
5117
10u
5103
4
5
3 45
F122
2127
220u
I102
3103
3
220R
1
2
1K0
3104
6100
BZX384-C6V2
3135
1R0
I124
10u
6123
SS34
10u
2131
2132
100u
16V
I106
3108
I105
1R0
2138
470p
I136
10R
3109
6103
SS34
+8V_SW
10u
2171
100n
+12VS_1
RES
2150
100u
16V
7117
114
TPS54386PWP
2152
33n
I107
I122
2141
I132
F124
10
11
I126
2160
2133
10u
PVDD1 PVDD2
2
BOOT1
SW1
EN1
FB1
9
ILIM2
SEQ
BP
4u7
PVDD1 PVDD2
BOOT1
SW1
EN1
FB1
9
ILIM2
10
SEQ
11
BP
GND GND_HS
415
4u7
+12VS_1
1
14
Φ
BOOT2
GND GND_HS
15
4
Φ
BOOT2
SW2
VIA1
VIA2
7116
TPS54386PWP
SW2
EN2
FB2
VIA1
VIA2
I127
312
213
65
EN2
87
FB2
16
17
I117
13
2165
213
65
87
16
17
2139
3129
I125
2156
470p
I134
10R
3130
10u
33n2167
76
678
2123
2168
10u
10u
2153
3136
I129
33n
I128
470p
2157
I135
10R
3131
6124
5116
1R0
10u
I130
2159
100u
6.3V
SS34
2164
F133
1%
3122
4K7
1K5
3125
10u
+3V3_SW
10p
RES
2155
10p
RES
2161
+12VS
5108
33R
REF EMC HOLE
2106
91011
1M99
1-1735446-2
1M95
0V
1-1735446-1
7103-1
16
ST1S10PH
INH
SYNCSWVFB
GND
4
7103-2
ST1S10PH
10 11
VIA
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
A
SW
VIN
HSPA
928
1X12
REF EMC HOLE
1M99
PIN ON STBY
112V0V
5
3V0V
>1.5V 0V
6
7
1.5V 0V
3V0V
9
1M95
PIN ON STBY
1 3V33V3
20V 3V
612V 0V
712V 0V
8 12V 0V
925V
I108
10u
10u
10u
2108
2107
1X05
1X06
REF EMC HOLE
Round screw hole of 4.02mm
I119
I118
3134
33n
470p
I123
10R
6122
SS34
5115
1R0
10u
I120
2140
100u
6.3V
F131
3139
220R
3119
390R
10u
2144
+1V2_SW
1%
10p
RES
2166
1%
10p
RES
2142
1X01
REF EMC HOLE
Round screw hole of 4.5mm
8 9
10 11 12
F126
F111
F112
F113
F114
F115
F116
F117
F118
F119
F120
F100
F101
F102
F103
F104
F105
F106
F107
F108
F109
F110
RES
2112
7
35
100p
100p2116
2124
GNDSND
1n0
RES
I109
REF EMC HOLE
14131211109
3101
68R
68R
3102
RES
4100
4101
100p2118
2119 100p
RES
RES
1n0
RES
2109
RES
2110
2169
2113
100n
100n
2114
RES
GNDSND
F134
5101
2u0
2100
2K2
3172
Oval screw hole of
5mm x 4.02mm
1X02
REF EMC HOLE
100p2121
2120 100p
3100
68R
1n0
RES
1n0
RES
2115
3199
4n7
RES
I110
3173
1X03
REF EMC HOLE
1X07
15
168
1817
12 13
+12VDISP
BL_ON_OFF
PWM_DIMMING
BACKLIGHT_BOOST
POWER-OK
2122 10n
+3V3STBY
STANDBY
1n0
2111
+12VS
+24VAUDIO
1n0
A
B
C
D
E
+1V0_SW
1%
10K
1%
1K0
22u
22u
2102
2101
1X08
REF EMC HOLE
2103
3171
1%220R
22u
22u
2104
2105
220u 25V
SENSE+1V0_MT5392
F
G
H
19
1M95 C10
1M99 A10
1X01 I10
1X02 I10
1X03 G11
1X05 G9
1X06 G9
1X07 I11
1X08 G12
1X12 G10
2100 F11
2101 F12
2102 F12
2103 F12
2104 F12
2105 F13
2106 F8
2107 F9
2108 F9
2109 B11
2110 C11
2111 C11
2112 D10
2113 D10
2114 D11
2115 D11
2116 B10
2118 B10
2119 B11
2120 B11
2121 B11
2122 B11
2123 E5
2124 B10
2125 B1
2127 B3
2128 D2
2129 D1
2131 H3
2132 H3
2133 H3
2134 H1
2135 I1
2136 I1
2137 I2
2138 I3
2139 I4
2140 I6
2141 I3
2142 I6
2144 I6
2150 E4
2152 E3
2153 E5
2154 F1
2155 F7
2156 F3
2157 F5
2158 F2
2159 F6
2160 F3
2161 F7
2162 F2
2163 F1
2164 F6
2165 H4
2166 H6
2167 H3
2168 E5
2169 D11
2170 F1
2171 B3
3100 C11
3101 A11
3102 A11
3103 D3
3104 E2
3105 H1
3106 I1
3107 F1
3108 H2
3109 I3
3119 I6
3122 F6
3125 F6
3129 I4
3130 F3
3131 F5
3134 H5
3135 E3
3136 E5
3138 F1
3139 H6
3140 F1
3171 F12
3172 F11
3173 F11
3199 F11
4100 A11
4101 A11
5100 B1
5101 F10
5102 D2
5103 G2
I
5104 H2
5107 D1
5108 F8
5115 H5
5116 F6
5117 F2
6100 E3
13
6101 D1
6102 D1
6103 I2
6122 I5
6123 F2
6124 F5
6125 F1
7100 B2
7101 D2
7103-1 E10
7103-2 F10
7116 H4
7117 E4
F100 C10
F101 C10
F102 C10
F103 C10
F104 C10
F105 C10
F106 C10
F107 C10
F108 C10
F109 C10
F110 C10
F111 A10
F112 A10
F113 A10
F114 A10
F115 A10
F116 A10
F117 A10
F118 A10
F119 A10
F120 A10
F122 B3
F123 D1
F124 G3
F125 H1
F126 A10
F131 H6
F132 F1
F133 F7
F134 F11
I100 D2
I102 D3
I103 D2
I104 I1
I105 H2
I106 H3
I107 H3
I108 F9
I109 F10
I110 F11
I111 B1
I117 H4
I118 H5
I119 H5
I120 H5
I122 I3
I123 I5
I124 F2
I125 E3
I126 E3
I127 E4
I128 F5
I129 F5
I130 F5
I131 F1
I132 F3
I134 F3
I135 F5
I136 I3
20
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
M
N
O
P
MULTI 12NC : 3139_123_64641
BD 12NC : 3139_123_64651
1
2 13121110
3 45678 9
2010-Jul-01
CLASS_NO
2009-02-23
2009-06-0423
NAME
SV
DC391162
3PC332
-- -- --
Tee Chor Kimp
EMANTESNHC
1
CHECK DATE
LC09M
PCB SB SSB DIGITAL
SUPERS.
2009-02-23
3139 123 6465
15 1
C
ROYAL PHILIPS ELECTRONICS N.V. 2009
13010
O
2009-06-04
1
1 2009-02-23
P
A2
20191817161514
18700_500_090825.eps
090825
Page 58

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
SSB: Tuner & Analog demodulator
EN 58LC9.2L LA 10.
876
5225 E12
5226 C3
5227 D3
6201 E3
7201 D3
7213 C6
7216 D11
7217 D11
A210 D14
A211 D14
A212 D14
A213 D14
A214 D14
A225 D14
A258 D14
A259 D14
F201 C2
F202 C2
F203 C2
F204 C2
74
F205 D2
F206 D2
F207 D2
F208 D2
F209 D2
F210 D2
F211 D2
F213 C2
F214 C14
F215 C6
8
F216 C14
F217 C14
F218 C14
F219 D14
F227 D8
3236 D6
3246 E6
3247 E6
3254 D7
3255 D7
54
3256 D7
3257 C10
3258 C10
3263 B4
3264 C4
3271 E4 F251 C14
3278 B2
3265 D4
3266 D4
3267 D4
3268 C3
3270 D4
3273 C6
3274 C6
3276 B4
3277 B4
3279 B2
3280 D7
3281 E4
3282 D2
5217 E10
5221 C3
5222 C3
5223 D10
5224 D12
56 9101112
321
2252 E7
2264 E10
2265 E11
2266 D10
2267 D11
2268 D10
2270 D4
2271 E4
2272 E11
2273 E10
1205 C1
2235 C7
2240 D7
A
2241 F11
2242 F11
2274 D11
2275 D12
2276 E12
2277 E11
2278 B3
2279 B3
2280 B3
2282 C3
2284 C3
2285 D3
2286 C3
2287 D3
2288 B3
3234 B7
3235 C6
123
B
1211109 151413
F228 E11
F236 C14
F229 D14
F237 C14
F230 C14
F240 D2
F234 C14
F241 D2
F235 C14
F242 D2
F243 D2
F244 D2
F245 D2
F250 C14
F252 C14
F255 C14
F256 C14
F257 D14
F260 D8
I210 C13
I212 C13
I213 C13
I214 C13
I215 C13
I216 D13
I218 D13
I226 D13
16
I234 C14
I228 D13
I230 C14
I235 C14
I231 C14
I237 C6
I232 C14
I233 D13
I239 D6
I241 E9
31D 222I2D 642F
I242 D14
I244 D14
I247 E7
I248 D14
I250 D14
I252 E6
I253 E6
I261 D10
20191817
A
13 14
B
TUNER & ANALOG DEMOD
A
C
+5V_SW
+3V3_SW
10K
10K
RES
3279
3278
F201
F202
F203
F204
F205
F206
F207
F208
F209
F210
F211
F240
F241
F242
F243
F244
F245
F246
2279
100n
2288RES
3268330R
32821K0
D
B
E
C
VA1G5BF8010
F
G
H
D
F240 same location as I227
F241 same location as I249
F242 same location as I251
F243 same location as I240
F244 same location as I238
F245 same location as I243
F246 same location as I245
F213
1205
23
22
MT
1
RF-SW
2
GAIN-SW
3
BB
4
B1
5
AFT
6
SIF_OUT
7
VIDEO_OUT
8
B2
9
B3
10
B4
11
SYRSTN
TUNER
12
SDA
13
SCL
14
RSEORF
15
SBYTE
16
SPBVAL
17
SRDT
18
SRCK
MT
19
20 21
E
47u
100n2280
2278
100n
+5VTUN_DIGITAL
5221 1K0
100n2282
5226
33R
228622u
2284100n
5227
33R
22u2287
100n2285
7201
BC847B
SML-310
6201
3277
10K
RES
3276
100K
1K05222
+2V5_SW
+3V3_SW
+1V2_SW
+3V3_SW
3281
1K0
FOR DEV. ONLY
+3V3_SW
3263
3264
200K
100K
3265
10K
1R0
3266
RES
3267
1K0
3270
100R
2270
15p
3271
100R
2271
15p
I
+3V3_SW
GAIN_SW
RF_SW
SIF_OUT_1
CVBS0T
DEMOD_RESET
TUNER_SDA
TUNER_SCL
TSO_SYNC
TSO_VALID
TSO_DATA0
TSO_CLK
AFT
CVBS0T
SIF_OUT_1
SIF_OUT
SIF_OUT_GND
3234
+5VS
15R
3274
F215
3273
RES
10n
7213
BC847B
1V5
I237
10K
1R0
3235
3280
1R0
RES
3254
I239
75R
3236
I252
I253
RES
3255
220R
3246
1R0
3247
1R0
I247
15p
RES
2252
F227
CVBS_RF
47p
75R
2240
F260
3256
GND_CVBS_RF
1R0
2235
1R0
RES
+5V_SW
+5V5_TUN
+5V_SW
FRONTEND_SCL
FRONTEND_SDA
I241
5223
33R
2273
5217
10u
I261
2266
22u
2264
3257
1R0
3258
1R0
LD1117DT25
3
2268
100n
100u 16V
7216
LD29150DT50R
1 3
OUTIN
COM
1u0
2
2242
TUNER_SCL
TUNER_SDA
7217
2
OUTIN
COM
2267
1
22u
2265
2272
F228
22u
5224
33R
2274
100n
47u 16V
5225
33R
22u
10n
2277
2241
10n
+2V5_SW
2275
100n
+5VTUN_DIGITAL
2276
100n
+5VS
Common Testpoint With
LC09M Analog
I235
F250
I210
I231
F251
I212
F252
I230
I213
F255
I232
I214
I234
F256
I215
F257
I216
I244
I242
A258
I218
I248
A259
I222
A225
I226
I250
I228
I233
F214
F234
F216
F235
F217
F236
F237
F218
F230
A210
A211
A212
A213
A214
F219
F229
A
C
B
D
E
C
F
D
G
H
E
I
F
J
K
All rights reserved. Reproduction in whole or in parts
owner.
is prohibited without the written consent of the copyright
L
M
N
O
P
MULTI 12NC : 3139_123_64501
BD 12NC : 3139_123_64511
123 45 11 12
1 1312
2 3 456
678 910
7 8 91011
DC391162
CLASS_NO
3PC332
-- -- --
1
PCB SB SSB DIGITAL
CHECK DATE
"200" ~ "299"
2009-02-23
2009-06-0423
Evelyn/Lee Boon Hiong
NAME
SV
13 14 15 16
EMANTESNHC
LC09M
SUPERS.
2009-02-23
17
14
3139 123 6465
10
15
C
ROYAL PHILIPS ELECTRONICS N.V. 2009
18 19 20
F
2009-06-04
1
1 2009-02-23
2
130
A2
18700_501_090825.eps
090825
J
K
L
M
N
O
P
2010-Jul-01
Page 59

SSB: Class-D & Muting
C
DIGITAL
DE-EMPHASIS
INTERPOLATION
DAC
NOISE SHAPER
FILTER
INTERFACE
DAC
IN1P
VSSD|HW
IN1N
IN2P
IN2N
INREF
OSCREF
OSCIO
HVPREF
DREF
ENGAGE
POWERUP
VIA
TEST
GND_HS
VDDP
VSSP
VDDA
STAB2
STAB1
BOOT2
BOOT1
HVP2
HVP1
DIAG
OUT2
OUT1
CGND VSSA
G
3521 F2
3523 G4
3524 I6
3525 J5
3526 J3
3527 J3
15 16
123 4
3534 E8
3535 E8
3536 E8
6
J
K
L
45678 9
-2V8
-2V8
3555 D5
3556 D6
3557 E6
3558 C3
3559 C5
3560 F5
2567 F7
2568 F5
2569 G5
3500 A6
3565 G5
3566 D5
4502 E4
3501 B6
3502 C5
3507 C2
3508 C2
3509 D5
3510 E3
3511 H6
I
J
K
L
1502 C16
1735 E16
A
H
3528 K5
3
7511 F15
7513 G16
3530 C12
3531 D14
3532 E12
3533 E8
3537 E8
3538 F8
3540 F8
3541 F14
7 8 9101112
10
3529 K5
12 13 14
5
10 11 12 13 14 15
F579 E9
F580 D6
3561 F5
3562 F6
3563 F5
3564 G6
5502 D12
5503 D12
5505 F12
5507 E15
3512 E2
3513 E3
3514 E1
3515 E1
3516 I5
3517 F1
1736 D16
B
C
D
E
F
F544 E16
N
O
P
201918171611109
I523 I5
I524 E1
I525 F4
I526 F5
I527 G5
I530 G3
13
11
3V9
15 16
A
D
C
18 19 20
432
I572 E8
I573 E9
I575 E9
I576 E12
I577 E8
I578 E8
F539 H13
2500 A5
TO INDIA SUBWOOFER OUT
RES
12
2518 D13
2519 D14
2544 F11
2545 F9
2546 F11
2547 F12
G
H
15141312
2556 G15
2559 C15
2566 E7
8765
I535 J5
14
F
G
F
E
2520 D15
2521 D15
2522 E10
B
C
D
E
F
2
RIGHT -
4V7
2V6
1
1
I582 F11
I583 F13
I584 F12
I585 F14
I586 F11
I587 F11
I580 F9
F540 D12
-8V2
F541 E7
F542 E16
F543 E16
2516 D13
7505 J6
7506 J4
7507 K5
7508 G16
7510 E10
I546 J4
2549 G9
2550 G8
2552 G12
2553 G15
2554 E13
2555 E14
7519 G6
F512 B3
F515 B3
2532 E11
2534 E12
2530 E8
2531 E8
I
J
K
L
M
I543 J3
0V
NC
MUTING CIRCUIT
24V
H
2565 G4
2503 B5
2508 C4
2509 C4
2510 H5
2511 E3
2523 E10
2524 E13
2527 E8
2528 E12
2529 E9
RIGHT+
BD 12NC : 3139_123_64651
-2V8
I
3 4
P
O
N
I581 F9
7504 F4
TO SUBWOOFER OUT
-2V6
2502 B5
2501 A5
7500 A4
7501-1 E2
I552 J5
7515-1 H5
7515-2 D5
7516 D6
7517 E4
7518 F6
-7V6
I544 J3
16
F516 B3
F518 B3
F522 E2
3542 F12
3544 G15
3548 G16
3549 G15
56
A
B
C
D
E
EMC
I519 D3
I521 E2
I522 E2
5508 E15
6500 E4
6501 E1
2537 F13
2539 F8
2540 F8
2541 F11
2542 F13
2543 F14
owner.
is prohibited without the written consent of the copyright
All rights reserved. Reproduction in whole or in parts
-2V8
G
H
2536 F8
3V3
2564 F16
2560 C16
2561 F15
2562 F16
2563 F16
3519 F2
M
L
2512 I5
2513 J3
2515 C13
F536 F9
F538 K3
7501-2 E2
7503 I6
LEFT +
LEFT-
3V2
TO SPEAKERS
7102 F5
DC-DETECTION
F545 E7
F546 E16
F547 E11
F548 F7
F550 G16
F569 E9
17
I554 K5
I559 F4
I560 E3
I562 F2
I563 C13
I564 D13
I565 D13
I566 D14
I568 E8
I570 E12
7 8 9
J
I
F524 H6
F525 I6
F535 J6
CLASS-D & MUTING
I597 D5
I598 D6
I599 H4
"500 - 599"
I510 A5
24V
2533 E9
B
A
K
3553 H4
3554 D5
I588 F9
I589 F9
I590 F12
I595 G12
I596 G15
3520 F3
3552 H4
8V9
MULTI 12NC : 3139_123_64641
3550 G15
F593 G9
I511 B5
I512 B2
I513 C2
I515 C3
I516 C5
I518 D2
6502 F2
6503 K4
I571 E11
F523 E4
I564
GNDSND
470R
3502
3513
1K8
2500
47u 16V
220n
2518
F515
I596
F516
5
3
4
BC857BS
7501-2
10R
F523
+3V3STBY
3532
3510
1K0
30R
GNDSND
5502
RES
2559
1n0
F512
1n0
2560
2
6
1
RES
BC857BS
7501-1
4K7
3514
GNDSND
I598
F538
I516
1n0
2532
3526
4K7
F535
F548
RES
220p
2533
F580
2542
220n
F518
3508
1R0
GNDSND
3507
1R0
F545
GNDSND
2523 100n
2545
100n
+12VS
GNDSND
100n
2501
10K
I522
2531
3535
1u0
25361u0
3558
470R
I586
RES
6501
BAS316
4u72553
RES
5503
22u
F569
10K
3555
I566
2552
1n0
BC857BW
7506
3527
4K7
56K
3515
I570
RES
47K
3556
2519
220n
6500
BAT54C
25V
RES
2520
1n0
GNDSND
470u2554
I560
GNDSND
22u
5505
I515
RES
10n
2567
2503
100n
VDDA
I577
I578
I562
GNDSND
F543
F542
7508
BC847BW
F547
+3V3_SW
I589
4u7
2556
3533
10K
7513
BC857BW
F525
3553
10K
2562 1n0
7503
RES
2540 100n
2SD2653K
3538
RES
VDDA
10K
3509 470R
I587
3563
1K0
I595
4
I590
BC857BS
7515-2
5
3
1n0
2521
GNDSND
RES
F593
I588
2516
220u
GNDSND
35V
I544
BC847BW
7507
I543
I580
I535
4n7
2510
I554
RES
I518
2SD2653K
I510
7505
3525
1K0
I573
F579
10K
3536
I599
F544
RES
47K
3517
RES
100K
3521
3542
10R
I523
I521
F524
2555
470u
1
2
3
4
25V
1735
1735446-4
I546
3530
I552
10R
1K0
3565
2SD2653K
7518
3552
47K
1K0
3566
I571
GNDSND
4n7
3562
47K
RES
2568
I525
47K
3564
47K
3511
RES
2512
4n7
47K
3524
22R
3519
1R0
3531
F536
RES
2537
470n
I575
WS2
I519
SYSCLK6
VDDA
13
VDDD
4
VOL14 VOR 16
VREF-DAC
12
VSSA15VSSD
5
BCK1
DATAI3
DEEM9
MUTE8
PCS10
SFOR0 11
SFOR1 7
GNDSND
UDA1334BTS
7500
GNDSND
F546
470n
2549
GNDSND
7511
BC857BW
1n0
2547
1u02530
1u0
2527
100n
2515
F540
F522
I583
I511
100K
3544
I563
ROYAL PHILIPS ELECTRONICS N.V. 2009
SV
2009-06-04
DC391162
Roger Poon & Jason Ong
2009-06-0423
VDD
I585
2009-02-23
-- -- --
2009-02-23
A2
LC09M
PCB SB SSB DIGITAL
3139 123 6465
CHECK DATE
NAME
1
SUPERS.
1
CLASS_NO
EMANTESNHC
15
3PC332
3
2009-02-23
13010
1
6
1
BC857BS
7515-1
2
BC857BW
1
3
2
47K
3560
7102
10K
3561
I527
I526
RES
4n7
2569
7519
2SD2653K
I524
I512
1R0
3501
2534
1n0
47K
3554
1n0
GNDSND
RES2561
I513
GNDSND
100K
3549
100K
3548
+3V3STBY
+5V_SW
RES2564 1n0
39
40
41
9
1
161732
26
23
24
13
8
29
20
34
35
36
37
38
3
2
14
15
12
31
10
27
22
6
25
28
21
7
4
18
5
33
30
19
11
CLASS D
POWER
AMPLIFIER
TDA8932BTW
7510
Φ
2
3
I582
1735446-3
1736
1
2509
100n
I572
47u
2508
16V
3534
12K
3537
100n2546
12K
2544
GNDSND
15n
1502
MTJ-032-21B-43 NI FE LF
1
2
3500
1R0
GNDSND
GNDSND
16V47u
2502
I597
I576
+3V3_SW
1n0
2528
I565
VDD
I568
100K
3550
2522 100n
15n2541
1
3
2
4502
F550
7517
BC847BW
470R
GNDSND
RES
3559
2524
470n
GNDSND
2565
100n
220n
2543
22K
3529
22R
3541
1u0
GNDSND
+24VAUDIO
2513
GNDSND
F539
100n2539
I584
1K0
3516
39K3540
10n
I559
RES
2566
3557
10K
+12VS
I530
220p
2529
GNDSND
RES
3
2
RES2563 1n0
BC857BW
7516
1
10K
3528
6503
BAT54C
220R
5508
5507
220R
2550
47u 25V
3512
4K7
7504
SI2301BDS
312
I581
RES
100K
3520
10K
3523
BAS316
6502
F541
470u
2511
GNDSND
AOUTR
16V
MUTE
HP_LOUT
HP_ROUT
POWER_DOWN
MUTEn
AOUTL
AOUTL
AOUTR
SW_MUTE
AUDIO_LS_L
AUDIO_LS_R
AOUTR
MUTE_M
MUTE_C
SPEAKER_RIGHT-
SPEAKER_RIGHT+
SPEAKER_LEFT-
SPEAKER_LEFT+
DC_PROT
AOUTL
STANDBYn
MUTE
AOSDATA0
AOBCK
AOLRCK
AOMCLK
OFF_MUTE
18700_502_090825.eps
090825
Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
EN 59LC9.2L LA 10.
2010-Jul-01
Page 60

SSB: MTK Power
AVDD12
AVSS12
AVDD33
AVSS33
AVDD80
AVSS80
CVBS1
CVBS2
CVBS3
DEMOD1
DIG
HDMI
LVDS_1
LVDS_2
LVDS_3
LVDS_4
LVDS_5
REF_AADC
REG
SRV
STB
SYSPLL1
SYSPLL2
USB_1
USB_2
VDAC
VDAC_BG
XTAL
ADAC1
ADAC2
DVSS12_VGA
DLL1
DLL2
HDMI
LVDSA
LVDSB
MEMPLL
PLLG
RGBADC_1
RGBADC_2
RGBFE
SYSPLL
USB
VGAPLL
VOPLL
XTAL
VDAC_BG
VDAC
USB_2
USB_1
SYSPLL2
SY
SPLL1
STB
SRV
REG
REF_AADC
ADAC1
ADAC2
DVDD12_VGA
LVDSD
LVDSC
LVDSB
LVDSA
HDMI
DIG
DEMOD1
CVBS3
CVBS2
CVBS1
APLL
ADAC2
ADAC1
AADC
DLL1
DLL2
LVDSA
LVDSB
MEMPLL
PLLG
RGBADC_1
RGBADC_2
RGBFE
SYSPLL
USB
VGAPLL
VOPLL
AADC
ADAC1
ADAC2
APLL
C
OPCTRL
OPWR_5V
TS0
TUNER
CLK
DATA
IF_AGC
CLK
VALID
SYNC
DATA
OPWRSB
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
0
1
2
DVSSDVSS
VCC3IO
VCC2IO
VCCK
3629-4 F9
5603 D2
5604 D2
5605 E2
5606 E2
5607 E2
5608 F2
5609 F2
5610 G2
6600 H4
6601 H7
F614 D9
F615 H6
F616 G5
I614 F7
I616 F7
I617 F7
I618 E2
I623 F2
F
G
H
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
I629 H5
I630 H6
I631 D2
I632 D2
I633 E2
I636 F2
I637 F3
3627 E9
3628 E9
3629-3 F9
"600 - 699"
1
3629-1 F9
3629-2 F9
45
4601 G7
4602 G7
4603 G7
5600 B5
5601 B1
5602 D9
12
123 45678 9
7602 E5
7605-1 H5
7605-2 H6
7701-12 B6
7701-13 B11
7701-14 C4
7701-4 E8
F611 A3
F612 B4
F613 C2
8 91213
A
B
C
D
E
98
2609 A3
2610 A3
2611 A3
2612 A3
2613 A3
2614 A4
2615 A4
2616 A4
H
2600 B8
2601 B8
2602 B8
2603 B8
2604 B8
2605 B8
2606 B9
2607 B9
2608 A3
C
D
2 3
G
H
678 91011
2620 A4
2621 A4
2622 A4
2623 A4
2624 A5
2625 A5
2626 A5
2627 A5
2628 A5
2629 A5
10 11 12
H
I
All rights reserved. Reproduction in whole or in parts
J
7
2633 A5
2634 A5
10 11
2637 C8
2638 C8
6543
1110
2645 B3
2646 B3
2647 B3
2648 B4
2649 B4
2650 B4
2651 B4
2652 B4
2653 B4
2654 C1
2617 A4
2618 A4
2619 A4
I
J
A
B
E
F
is prohibited without the written consent of the copyright
1
RES FOR ITV
RES FOR ITV
21
2678 D2
2679 D2
2680 D2
2681 D1
2682 D1
2683 D2
2684 D2
2685 D2
2686 E2
2687 E2
2630 A5
2631 A5
2632 A5
452 13123 6
2694 F2
2695 F2
owner.
2698 H6
2699 C8
2639 B2
2640 B2
2641 B2
2642 B3
2643 B3
2644 B3
26A6 F9
3600 D5
3601 E6
3602 E6
3603 E6
3604 E6
3605 E6
3606 E9
3607 E9
3608 F7
3621 G5
3622 H5
2668 D9
2669 D2
3623 H6
3624 H6
2672 B1
2673 B2
2674 B2
2675 B2
2676 B2
2677 B2
BD 12NC : 3139_123_64651
MULTI 12NC : 3139_123_64641
2671 B1
2666 D8
2667 D9
2635 C8
2636 C8
2688 E2
2689 E2
2690 E2
2691 F2
2692 F2
2693 F1
2696 G2
2697 G2
26A0 C8
26A1 A3
26A2 D2
26A3 D2
26A4 E2
26A5 A3
MTK POWER
7
2655 C2
2656 C2
2657 C2
2658 C2
3609 F7
3610 F7
3611 F7
3612 F7
3613 F7
3614 F7
3615 F7
3617 G6
3618 G6
3619 G6
2659 C2
2660 D8
2661 D8
2662 D8
2663 D8
2664 D8
2665 D8
2670 D2
3625 E6
3626 E6
G
F
E
D
C
B
A
I633
I630
I629
30R
5602
F615
2610 100n
2613 100n
10K3618
1u02689
5605
30R
3615 100R
2601 100n
+3V3STBY
26A2 100n
2648 100n
100n
2647
100n2609
+3V3STBY
100n2678
100n2670
+3V3STBY
2682 100n
100R3613
100R3611
2697
2622 100n
I618
1u0
10K
3601
3602
10K
F612
2675 100n
1u02674
+3V3STBY
1K0
15K
3622
3621
100n2683
100n
2605
2604 100n
100n2619
2620 100n
100n
2642
6.3V100u
26A5
+3V3_SW
100n2657
SENSE+1V0_MT5392
+1V2_SW
100n
2611
100n
2612
3625 4K7
4601
2644 100n
100R3614
100R3608
4K7
3626
2635100n
30R
5609
4u72685
I632
+1V0_SW
30R
5604
2615
100n
47R3629-2 2
7
BZX384-C8V2
6601
3
6
1
8
47R3629-3
47R3629-1
7602
+3V3STBY
BC847BW
2696
100n
5610
30R
F614
+5V_SW
F613
100n
2677
RES
+5V_SW
1K0
3627
2691 1u0
100n2692
100n
2633
2632100n
100n2649
2607
+1V8_SW
4u7
100n2606
100n2629
2653
4u7
2680100n
100n2679
4u7
2654
4u7
5601
30R
2668
I614
3617
4K7
2651
2650
100n
100n
5607
30R
100n2623
2624 100n
100R3609
4602
I623
BZX384-C3V3
6600
100n2618
4
5
100n2621
47R3629-4
100n2660
100n
2637100n
2638
100n2636
+12VS
F616
100n
2645
2634100n
26A4 100n
100n2676
100n2603
100n2602
100n26A3
100n26A1
100n2681
100n2631
2630100n
RES3619 10K
26861u0
100n2625
100n2627
2626 100n
2628 100n
100n2643
2617 100n
3623
1K0
100n2640
2639100n
5603
30R
I636
2656 100n
+3V3_SW
K25
AG20 AF20
100n
2616
AF16
AG26
AH26
Y29
Y28
AG8
AG7
AF23
AG22
Y30
L25
AC26
AB28
V26
AH8
K14
K15
K16
K17
K18
T26
AF19
AG24
AB11
AH25
E20
R25
N25
P25
Y27
AD26
AC27
W28
L26
K26
N10
V11
E16
E23
U11
AB18
AF17
AG17
R26
AG16
AG27
AJ27
AA28
AA27
AH6
AH7
AG23
AG21
Y26
AD27
AC28
AC29
AC30
U25
AH9
E18
E15
E24
E21
AB20
AF18
AG18
AG19
AH24
AB10
AJ25
E19
T25
N26
P26
MT5391
7701-14
N11
W10
AB12
E17
E22
T10
Φ
POWER & GROUND
4K7
3607
100n2664
2663 100n
2693
4u7
3624
1K0
2667 100n
100n2699
26A0 100n
10K
3603
RES
3612 100R
F611
+3V3STBY
+3V3STBY
2671 100n
2641 100n
2690 100n
26871u0
2600 100n
4u7
2608
2673 1u0
100n2672
+3V3_SW
100n2655
I616
2646 100n
3606
4K7
26844u7
I631
3628
1K0
RES
100n2666
2665 100n
2669 100n
100n2659
3610 100R
10K
3605
3604
10K
220n
+3V3STBY
2698
100n2688
B1
AA10
AA14
AB13
B2
C2
C3
D3
D4
D5
A2
P19
P10
R11
M11
R18
V18
Y11
K13
AA12
AB15
E4
E5
E6
F5
F6
G6
L11
L12
L15
M19
E8
F26
G8
G25
H25
F9
AJ3
AH4
AG5
AF6
A1
AE6
AF5
AG4
AB3
E3
V4
F4
G5
H6
L2
L3
T2
U4
U3
U5
AB6
D2
AB5
AC4
AD2
AD3
7701-12
MT5391
DIGITAL POWER
Φ
C1
M4
N6
P6
W16
W17
Y10
Y12
Y13
Y14
Y15
Y16
V12
V13
V14
V15
V16
V17
W12
W13
K5
W14
W15
T17
U10
U12
U13
U14
U15
U16
U17
J6
U18
V10
L17
N19
R19
T19
T12
T13
T14
J4
T15
T16
P18
R10
R12
R13
R14
R15
R16
H3
R17
T11
L19
N15
N16
N17
P11
P12
P13
P14
H2
P15
P16
P17
M13
M14
M15
M16
M17
M18
G3
N12
N13
N14
AB17
AD6
AE5
AF4
AG2
AG3
F11
L13
L14
L16
M12
N18
D27
E26
W11
AA15
AB14
T18
K12
L18
AA3
AA5
Y20
Y21
Y22
Y23
Y24
T21
W18
T23
T24
M10
V21
V22
V23
V24
W20
W21
R6
W22
W23
W24
Y6
AA13
AA16
AA17
AA18
AB16
U21
R5
U22
U23
U24
V20
7701-13
Φ
DIGITAL GROUND
E1
R4
Y17
Y18
AA4
AA11
MT5391
2695
1u0
100n
2694
7605-2
BC847BS
5
3
4
7605-1
BC847BS
2
6
1
I617
4603
RES
100n
2614
L28
100n
26A6
AH13
AH11
AG10
AH10
AH14
B30
C29
C30
A30
L29
K28
AJ12
AF11
AG12
AG11
AF13
AF12
AG13
AH12
7701-4
MT5391
PM_DEMOD
Φ
I637
2661 100n
100n
2662
3600
4K7
30R
5608
NAME
1
SUPERS.
1
CLASS_NO
EMANTESNHC
15
3PC332
4
2009-02-23
ROYAL PHILIPS ELECTRONICS N.V. 2009
SV
2009-06-04
DC391162
Hwang Zhen
2009-06-0423
13010
1 2009-02-23
-- -- --
2009-02-23
A3
LC09M
PCB SB SSB DIGITAL
3139 123 6465
CHECK DATE
30R
5606
2652 100n
30R
5600
2658 100n
LCD_CLK_SCL
FRONTEND_SDA
LCD_CLK_SDA
STANDBY
FRONTEND_SCL
TSO_CLK
TSO_VALID
TSO_SYNC
TSO_DATA0
LED2
STANDBYn
POWER_DOWN
POWER_DOWN
DTV_IRQ
ARX-5V
BRX-5V
CRX-5V
+3V3_SW
+8V_SW
HDMI_CEC
LED1
MUTEn
SW_MUTE
18700_503_090825.eps
090825
Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
EN 60LC9.2L LA 10.
2010-Jul-01
Page 61

SSB: GDDR3
Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
EN 61LC9.2L LA 10.
1098762
171615141312115431
A
2710 C12
2711 C13
2712 C10
2713 C10
2714 C10
2716 C11
2717 C11
2720 C12
2722 C12
2724 C12
2725 C13
2726 C13 I714 C6
2727 C13
2728 C14
2729 C14
2731 C12
2732 C12
2734 C12
2735 C13
2736 C13
2738 C13
2739 C13
2740 C13
2741 E9
2742 E10
2745 E10
2746 C5
6C 347231C 7372
2747 C10
2749 C142719 C11
2750 E10
2751 B11
2752 B11
2753 B11
2755 B12
2756 B12
2757 B12
2758 B12
2759 B12
2760 B13
2761 B13
2762 B13
2763 B13
2764 B14
2765 B14 2768 B14
2766 B14
2767 B14
3710 E10
3711 E2
3712 E10
3713 C6
3714 E102715 C11
3715 E10
3716 C5
3717 D4
3718 H8
3720 C5
3722 D5
3724 E2
3725 H42754 B11
3730 E7
3731 E6
5712 E9
5713 C6
5714 E9
7702-1 E7
7702-2 E12
7703-1 E37701-5 A3
7703-2 E14
F710 B10
B
12
GDDR3
C
A
D
B
E
F
C
G
D
RA(0)
RA(1)
RA(2)
RA(3)
RA(4)
RA(5)
RA(6)
RA(7)
RA(8)
RA(9)
RA(10)
RA(11)
RA(12)
DQ0
DQ1
DQ2
DQ3
DQ4
DQ5
DQ6
DQ7
DQ8
DQ9
DQ10
DQ11
DQ12
DQ13
DQ14
DQ15
DQ16
DQ17
DQ18
DQ19
DQ20
DQ21
DQ22
DQ23
DQ24
DQ25
DQ26
DQ27
DQ28
DQ29
DQ30
DQ31
3 4567
7701-5
MT5391
Φ
P2
P5
P1
T4
V3
V1
U2
T3
V2
T1
N3
R2
R3
K1
L1
K2
K3
M6
M5
L4
L5
AA1
Y2
AA2
Y3
W4
W5
Y4
Y5
AD5
AA6
AE4
AD4
AD1
AE2
AE1
AE3
H5
J5
G4
H4
F2
E2
F3
D1
DRAM_IF
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
RA
7
8
9
10
11
12
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
RDQ
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
RCLK0
RCLK1
RDQM
RBA
RDQS
WDQS
RRESET
REXTDN
RCKE
RCS1
RRAS
RCAS
RCAS1
RWE
RVREF
M2
RCLK0p
M3
RCLK0n
AF2
RCLK1p
AF3
RCLK1n
N1
RCKE
W2
RCS
0
AB4
1
AC5
2
3
0
W1
1
W3
2
0
AB1
1
AC3
2
G1
3
0
AB2
1
AC2
2
G2
3
V5
AG1
RCS
T5
RCS1
RRAS
N2
P4
RCAS
N5
CAS1
RWE
U1
K4
RDQM0
RDQM1
RDQM2
RDQM3
H1
P3
RBA0
RBA1
RBA2
RDQS0
J3
RDQS1
RDQS2
RDQS3
J2
WDQS0
WDQS1
WDQS2
WDQS3
D_RVREF0
N4
RRESET
1%150R
3717
1%
47K
3720
2746
100n
RES
3716
2k4
2K2
3722
5713
3713
I714
1K0
1%
2743
+1V8_SW
30R
100n
8
910
+1V8_SW
F710
6.3V
100n
2712
100n
2713
2747
100u
131211
2756
100n
2758
2751
2753
2752
100n
100n
100n
2716
100n
100n
2714
2715
2717
100n
2755
100n
100n
2754
2720
2719
100n
100n
100n
100n
2760
100n
100n
2759
100n
2757
100n
100n
2722
2710
100n
2732
100n
2731
100n
2740
2724
100n
2735
2734
100n
100n
2763
2762
100n
100n
2761
2726
2725
2711
100n
100n
100n
2737
2736
100n
2738
14
100n
2766
100n
2765
2764
100n
100n
100n
100n
2729
100n
2728
100n
2727
2739
100n
100n
100n
2768
2767
100n
2749
100n
201918
A
B
C
A
D
B
E
C
F
G
D
H
K
All rights reserved. Reproduction in whole or in parts
owner.
is prohibited without the written consent of the copyright
L
M
N
H
5712
+1V8_SW
3711
3724
62R
E
I
J
F
G
H
RCLK0p
RCLK0n
RWE
CAS1
RBA2
RCS1
RCKE
RDQM1
RDQM0
RDQM3
RDQM2
WDQS1
WDQS0
WDQS3
WDQS2
RBA1
RBA0
RRAS
RA(4)
RA(5)
RA(6)
RA(9)
RA(0)
RA(1)
RA(2)
RA(11)
RA(10)
RA(3)
RA(8)
RA(7)
RRESET
RA(12)
62R
+1V8_SW
1
J11
J10
H4
F9
H3
F4
H9
E3
E10
N10
N3
D2
D11
P11
P2
G4
G9
H10
K4
H2
K3
M4
K9
H11
K10
L9
K11
M9
K2
L4
V9
A9
V4
J2
J3
32
7703-1
HYB18H512321BF-14
Φ
MAIN
CK
CKE
CS
RAS
CAS
WE
0
1
DM
2
3
0
1
WDQS
2
3
0
BA
1
2
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
AP
RESET
MF
SEN
RFU
RCLK1p
RCLK1n
RCKE
RCS
RRAS
RCAS
RWE
RDQM0
RDQM1
RDQM2
RDQM3
WDQS0
WDQS1
WDQS2
WDQS3
RBA0
RBA1
RBA2
RA(0)
RA(1)
RA(2)
RA(3)
RA(4)
RA(5)
RA(6)
RA(7)
RA(8)
RA(9)
RA(10)
RA(11)
RRESET
RA(12)
RDQS
B2
0
B3
1
C2
2
C3
3
E2
4
F3
5
F2
6
G3
7
B11
8
B10
9
C11
10
C10
11
E11
12
F10
13
F11
14
G10
15
DQ
M11
16
L10
17
N11
18
M10
19
R11
20
R10
21
T11
22
T10
23
M2
24
L3
25
N2
26
M3
27
R2
28
R3
29
T2
30
T3
31
D3
0
D10
1
P10
2
P3
3
A4
ZQ
3725
280R 1%
DQ10
DQ11
DQ12
DQ13
DQ14
DQ15
DQ24
DQ25
DQ26
DQ27
DQ28
DQ29
DQ30
DQ31
DQ16
DQ17
DQ18
DQ19
DQ20
DQ21
DQ22
DQ23
RDQS1
RDQS0
RDQS3
RDQS2
DQ8
DQ9
DQ0
DQ1
DQ2
DQ3
DQ4
DQ5
DQ6
DQ7
456
+1V8_SW
3730
3731
62R
62R
J11
J10
H4
F9
H3
F4
H9
E3
E10
N10
N3
D2
D11
P11
P2
G4
G9
H10
K4
H2
K3
M4
K9
H11
K10
L9
K11
M9
K2
L4
V9
A9
V4
J2
J3
7702-1
HYB18H512321BF-14
Φ
MAIN
CK
CKE
CS
RAS
CAS
WE
0
1
DM
2
3
0
1
WDQS
2
3
0
BA
1
2
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
AP
RESET
MF
SEN
RFU
RDQS
B2
0
B3
1
C2
2
C3
3
E2
4
F3
5
F2
6
G3
7
B11
8
B10
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
DQ
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
0
1
2
3
ZQ
DQ10
C11
DQ11
C10
DQ12
E11
DQ13
F10
DQ14
F11
DQ15
G10
DQ16
M11
DQ17
L10
DQ18
N11
DQ19
M10
DQ20
R11
DQ21
R10
DQ22
T11
DQ23
T10
DQ24
M2
DQ25
L3
DQ26
N2
DQ27
M3
DQ28
R2
DQ29
R3
DQ30
T2
DQ31
T3
D3
RDQS0
D10
RDQS1
P10
RDQS2
P3
RDQS3
A4
280R 1%
7 8
+1V8_SW
DQ0
DQ1
DQ2
DQ3
DQ4
DQ5
DQ6
DQ7
DQ8
DQ9
3718
+1V8_SW
9
3710
30R
1K0 1%
100n
2741
5714
3714
30R
1%1K0
2750
100n
10 11
D_RVREF1
3712
2742
100n
2k4 1%
D_RVREF2
1%
2745
3715
100n
2k4
+1V8_SW
H1
H12
A2
A11
F1
F12
K1
K12
M1
M12
V2
V11
A1
A12
C1
C4
C9
C12
E1
E4
E9
E12
J4
J9
N1
N4
N9
N12
R1
R4
R9
R12
V1
V12
7702-2
HYB18H512321BF-14
Φ
POWER
VREF
VDD
VDDQ
A3
A10
G1
G12
+1V8_SW
J1
VSS
J12
L1
L12
V3
V10
B1
B4
B9
B12
D1
D4
D9
D12
G2
G11
L2
VSSQ
L11
P1
P4
P9
P12
T1
T4
T9
T12
12 13
H1
H12
A2
A11
F1
F12
K1
K12
M1
M12
V2
V11
A1
A12
C1
C4
C9
C12
E1
E4
E9
E12
J4
J9
N1
N4
N9
N12
R1
R4
R9
R12
V1
V12
7703-2
HYB18H512321BF-14
Φ
POWER
VREF
VDD
VDDQ
14
VSSQ
A3
A10
G1
G12
J1
VSS
J12
L1
L12
V3
V10
B1
B4
B9
B12
D1
D4
D9
D12
G2
G11
L2
L11
P1
P4
P9
P12
T1
T4
T9
T12
E
I
J
F
K
G
L
H
M
N
O
P
MULTI 12NC : 3139_123_64641
BD 12NC : 3139_123_64651
1
2 3 456
DC391162
CLASS_NO
3PC332
1
-- -- --
2009-02-23
2
3
2009-06-04
NAME
"700 - 799"
7 16 17 18 19 20
8 910111213 14 15
SV
Hwang Zhen
SETNAMECHN
LC09M
PCB SB SSB DIGITAL
SUPERS.
DATECHECK
2009-02-23
1
3139 123 6465
15
C
ROYAL PHILIPS ELECTRONICS N.V. 2009
03101
5
18700_504_090825.eps
2010-Jul-01
2009-06-04
2009-02-231
O
P
A2
090825
Page 62

SSB: Flash & EJTAG
EVSS
JTMS
JTDI
JTDO
JTCK
JTRST
ORESET
TN_0
TP_0
TN_1
TP_1
TN_2
TP_2
TN_HDMI
TP_HDMI
TN_VGA
TP_VGA
TN_PLLG
TP_PLLG
B
R
WP
VCC
VSS
IO
NC
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
CLE
ALE
CE
RE
WE
POCE
PDD
PDD
ONDA
ONDD
ONDCE
10
11
12
13
14
15
ONDOE
0
1
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
8
9
3
4
5
6
7
0
1
POOE
0
1
POWE
PALE
PCLE
PARB
2
1
2
CLK
CMD
0
1
2
3
U0RX
U0TX
U2RX
U2TX
U2CTS
U2RTS
D
SDIO
OPWM
OIRI
OSDA0
OSCL0
O
SDA1
OSCL1
OSDA2
OSCL2
0
GPIO
GPIO
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
13
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
SCL
ADR
0
1
2SDA
WC
D
C
S
W
HOLD
VSS
Q
VCC
SUBERGND
VOUT
VDD
C
3892 B3
3893 G2
TRAP2
3897 C13
3898 E14
3899 F14
FOR DEBUGGING
ONLY
I819 D15
I835 F7
I829 E6
I832 F14
I833 F8
I834 F14
38A8 G2
38A9 F5
4102 F2
4800 C5
4802 E10
4803 E10
4804 E10
4805 E10
PALE(0)
1
0
0
0
F827 D2
F828 D2
ONLY
FOR DEBUGGING ONLY
12 13
0
3856 G10
3857 H14
3858 H6
BD 12NC : 3139_123_64511
4806 E10
1
I812 B3
F813 B13
F814 C13
F819 D2
F820 D2
F821 D2
F822 D2
F823 D2
F824 D2
ONDA[ 2 ]
1
7822 C12
F810 A12
F811 C11
F812 B12
3882 G11
3883 G11
3884 G2
3885 G2
3888 J8
3889 J8
3890 K7
3891 K7
3852-4 G9
3859 H4
3861 H15
4807 E10
4808 E10
I838 G7
I839 G7
I840 G6
I841 G6
I842 H5
I8
43 H15
OLT Mode
CPU model mode
1
1
3878 F6
3879 F6
3880 D10
3881 G11
45678 91011
ONDA[ 1 ]
PANEL
PWM DIMMING
389C G6
389D I9
I813 B3
I814 B7
I816 B11
RES FOR SERIAL FLASH
RES FOR
ETHERNET
1
0
F825 D7
F826 D6
TRAP1
3839 E5
3840 F8
3841 F8
87543
1
OLT TEST MODE
4809 E10
4810 F10
4811 F10
7701-8 B4
7810 D15
7812 D7
7814 E6
7815 F8
7816 G6
7820 H15
16
123
17 18 19 20
A
B
D
E
F
0
0
389F I10
389G B13
389H A7
389I A7
389J D7
389K E2
389L F2
38A1 G4
38A2 G4
38A3 I9
161514131211109
MULTI 12NC : 3139_123_64641
0
6
Serial Boot
0
OneNAND Boot
21
0
1812 K8
1813 H5
3869 I3
3871 I8
3872 I8
3873 I8
3874 C5
3876 H14
3877 H14
13 14 15 16
D
C
B
A
K
owner.
is prohibited without the written consent of the copyright
All rights reserved. Reproduction in whole or in parts
2826 G6
2827 H14
C
1
0
1
G
H
TN0
XTAL 54MHZ
NAND Boot
0
TRAP3
TRAP0
0
Normal mode
0
ICE mode
20191817
5811 D14
5812 D7
5813 D3
5814 D3
5815 D3
6810 H14
6811 H6
6812 I3
Large NAND Boot (1G bit)
0
I
12
9 10111213 14 15
H
G
F
E
2817 E2
2818 E2
2819 E2
2820 E2
2821 E2
2822 E6
2823 E6
2824 F8
F867 B5
F868 B3
2833 B7
I811 A11
FT MODE
TRAP4
0
1
F829 E5
F831 E5
4819 F10
4820 H11
4822 F4
5810 B11
C
D
F
G
H
1
FOR DEBUGGING
1
3833 D5
3 45678 9 101112
2812 D15
2813 D7
2815 E2
2816 E2
F855 K8
F856 K8
F859 I9
F860 E6
F861 G2
F862 G2
F864 J10
F865 B5
3813 B7
3814 B3
I810 B11
3818 B7
3820 B12
3821 C11
UART (SERVICE)
0ZHM72 LATX
0
F832 E5
F835 F4
F836 F4
J
K
L
M
N
O
P
1
1
3
PDWNC Normal
0
XTAL 60MHZ
0
0
XTAL 48MHZ
SDM
E
D
E
F
I
J
K
L
3834 E14
3835 D3
3837 E14
P
O
N
M
L
J
I
F847 H4
F848 I4
F849 I4
F853 K8
RES
NORMAL
PDWNC SCAN
1
2837 G5
3810 B2
3811 B2
3812 B3
3831 D5
0
3816 A12
PCLE(0)
TP0
2834 B7
3822 C13
3823 F2
3824 D3
3825 D3
456
4812 F10
4813 F10
4814 F10
4815 F10
4816 F10
4817 F10
4818 F10
TEST MODE
1
OPCTRL8(0)
OPWM2 (0)
RES FOR
ETHERNET
16
A
B
C
B
1
21
"800 - 899"
3863 H10
3864 H2
3865 H2
G
H
I
J
1811 I4
0
I849 K2
3838 E5
1814 I4
1817 H7
1818 I10
1M20 D1
2810 B11
2811 D15
3866 C5
3868 H3
3832 D5
2835 H15
2836 H16
OPWM1 (0)
SCAN mode
ONDA[ 0 ]
14 15
3829 D6
3830 D5
7701-3 F3
I820 D4
I821 D4
I822 D4
I823 D4
I824 D4
I825 E11
I827 E11
38A4 J9
38A5 E4
3826 D6
3827 D3
3828 D3
7 8
38A6 E4
38A7 E4
3842 F7
3845 G7
3846 G4
3847 G4
3848 G5
3850 G7
3851 G9
3852-1 G10
3852-2 G9
RES
K
L
A
I850 K2
I852 I13
I853 J10
I855 F14
F837 F4
F841 H4
F843 H14
FLASH & EJTAG
3894 G2
FRONT CONTROL
3852-3 G9
1
389A G13
389B G13
6813 I3
6814 H16
7701-1 H12
7701-2 D12
3814
100R
100n2813
2822
10p
RES38814K7
F868
BAS316
6814
2811
3883 4K7
100n
I811
F841
4K7
3850
4814
4K7
3864
+3V3_SW
+3V3_SW
4K7
3888
10K3852-2
3828 100R
F856
3856 10K
I852
F837
38A4 100R
F861
F826
I850
1n02819
100R
3823
+3V3_SW
100R38A8
6811
BAS316
F812
100R3835
1R0
3845
BC847BW
7814
3859
100R
+3V3_SW
38A1 1R0
3892
10K
F855
10K3852-4
4K7
3889
I814
389A 4K7
+3V3_SW
F864
I843
3885
100R
4806
10K3833
100n2833
1
2
3
4
56
B4B-PH-SM4-TBT(LF)
1818
1K0
3851
F820
4800
+3V3_SW
3897
4K7
F819
I829
RES
680R
1%
3824
RES
30R5815
AC6
AG9
AK26
AG14
1814
C27
D26
AK27
AF27
K6
AB7
AF9
AJ26
AF14
AE27
L6
Φ
AF8
B27
C26
A27
4817
7701-1
MT5391
MISC_JTAG
+3V3_SW
7816
BC847BW
F847
+3V3_SW
6813
BZX384-C6V8
30R5813
4816
38A3 100R
4K7
3882
7
12
37
13
36
18
19
47
48
3
4
5
6
10
11
14
8
27
28
2
33
34
35
38
39
40
45
46
44
1
15
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
17
9
16
29
30
31
32
41
42
43
7810
NAND01GW3B2BN6F
Φ
[FLASH]
1G
I812
1R0
389C
4820
RES
3825 100R
389K
4K7
+3V3_SW
RES
100n
2827
+3V3_SW
RES
4805
4802
F853
4K7
389G
389F
7
8
9
12
13
4K7
502382-1170
1817
1
10
11
2
3
4
5
6
F862
+3V3_SW
33R
3829
33R
3863
4818
10K
3871
4822
4
56
1812
B4B-PH-SM4-TBT(LF)
1
2
3
1811
1n02821
3852-3 10K
2823
E10
B10
B9
E14
10p
C12
A3
B13
B11
A13
C10
A11
C13
A10
C11
B12
B3
D11
E11
F12
E12
E13
D10
D13
F13
C4
A4
B4
B7
D8
B5
B6
A8
B8
C9
C8
C6
7701-2
MT5391
FLASH_IF
A5
C7
A7
F10
Φ
I823
I841
100R3812
2812
100n
4803
3826
10K
RES
4K7
3899
389J
4K7
BC847BW
7815
1
3
2
BAS316
6810
RES
F831
4K7
3866
4K7
3878
4813
1K0
3857
F843
4808
+3V3_FLASH
4807
3842
10K
30R
5810
RES
F810
3879
4K7
38A7
1R0
I816
4804
4K7389B
F867
3874
4815
+3V3_SW
100R
F828
F827
3872
10K
10K
3841
3852-1
1K0
1R0
3821
1R0
3820
3816
1R0
H26
G26
I810
F814
F8
D7
F7
E9
D6
E7
AJ13
AK13
H27
G27
AK11
AJ11
K27
C5
J29
K29
AK10
J30
K30
AJ10
Φ
SPIO_UART_IIC
MT5391
7701-3
3893
4K7
3877 4K7
1n02815
2816 1n0
+3V3_SW
1R0
38A6
4u7
2835
383010K
3873
10K
680R
3848
4810
4812
47p
2837
22R38A9
F865
3838 22R
4K73876
220R
5811
3818
+3V3_SW
10K
2820 1n0
F836
F835
AH2
G29
AH1
E29
F29
F30
F28
G30
H28
A28
AF7
B28
A29
B29
D30
D28
E28
H29
AH5
AG6
G28
D29
E27
AH3
AK2
AJ1
AJ2
7701-8
MT5391
GPIO
Φ
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
1M20
1735446-8
4K7
3846
RES
100R3827
I813
2
1
8
4
3
+3V3_SW
Φ
16M
FLASH
M25P16
7822
6
5
7
383110K
+3V3_SW
8
4
7
2836
4u7
M24C64-RDW
1
2
3
6
5
7812
EEPROM
Φ
(8Kx8)
3869 33R
3847
I821
RES 4K7
+3V3_FLASH
F848
4K7
389H
I820
+3V3STBY
1
2
3
4
5
7
8
MSJ-035-10A B AG PPO
1813
5814 30R
+3V3STBY
I839
F824
+3V3_SW
389D
4K7
I838
+3V3_SW
4819
+5V_SW
I834
38A5
3822
10K
RES
1R0
2817
F813
2818 1n0
1n0
+3V3_SW
BZX384-C6V8
6812
F821
F822
3858
1K0
+3V3_SW
RES
I824
3891
1R0
4K7
3880
4K7
3894
I853
22R3839
I855
I819
I833
3898 10K
5812
30R
+3V3_SW
2u2
2826
F849
+3V3_SW
F860
I825
I827
4809
4K7
389I
F829
33R3868
I832
I822
+3V3_FLASH
4K7
+3V3STBY
3865
1R0
3890
4102
1
3
2
5
4
Φ
7820
BD45292G
100K
3861
4811
100R
+3V3STBY
3884
2824
1u0
1K0
F811
RES
3840
F823
10K
3811
1R0
+3V3_SW
38A2
3139 123 6465
PCB SB SSB DIGITAL
LC09M
A2
2009-02-23
-- -- --
2009-02-231
03101
3
2
2009-06-04
Hwang Zhen
DC391162
2009-06-04
SV
ROYAL PHILIPS ELECTRONICS N.V. 2009
2009-02-23
6
3PC332
15
SETNAMECHN
CLASS_NO
1
SUPERS.
1
NAME
DATECHECK
+3V3STBY
4K7
3834
I835
10K3813
10K
F825
3832
I849
389L
4K7
RES
I842
2810
100n
100n
F859
+3V3_SW
2834
3837 330R
I840
3810
10K
F832
HDMI_RESET
DDC-SCL
JTRST
UART_TX
UART_RX
LVDS_SELECT
SCL
JTDO
GAIN_SW
USB_OC
USB_PWE
JTCK
JTMS
JTDI
RF_SW
BL_ON_OFF
UART_TX
PBS_SPI_CLK
PBS_SPI_DI
PBS_SPI_DO
BOLT_ON_UART_RXD
DRX-5V
LAN-RST
MII-MDINT
MII-TXD(0)
MII-TXD(1)
MII-TXD(2)
MII-TXD(3)
MII-RXD(2)
MII-RXD(3)
MII-RXCLK
MII-RX-ER
BOLT_ON_UART_TXD
RC2
MII-MDC
MII-MDIO
MII-CRS
MII-RX-DV
MII-RXD(0)
MII-RXD(1)
MII-TXEN
MII-COL
MII-TXCLK
SDA
RC1
UART_TX
UART_RX
DC_PROT
ORESET
UART_RX
DEMOD_RESET
DDC-SDA
HP_DET
LIGHT_SENSOR
LED1
KEYBOARD
LED2
SPDIF_IN
PBS_I2C_SCL
BOOST_CONTROL
BACKLIGHT_CONTROL
PWM_DIMMING
BACKLIGHT_BOOST
AOSDATA0
HP_DETECTDDC_RESET
AOMCLK
AOLRCK
AOBCK
AMBI_SDA
AMBI_SCL
SYS_EEPROM_WE
EDID_WC
IR
LCD_PWR_ON
SERIAL_POOE
SERIAL_PDD1
SDA
SCL
NAND_PDD(1)
NAND_PDD(0)
JTMS
JTCK
JTRST
JTDO
JTDI
NAND_PDD(4)
NAND_PDD(5)
NAND_PDD(6)
NAND_PDD(7)
SERIAL_POCE
SERIAL_POCE
NAND_POOE
NAND_POOE
NAND_PDD(0)
NAND_PDD(1)
NAND_POWE
NAND_PALE
NAND_PCLE
NAND_PARB
NAND_PDD(2)
NAND_PDD(3)
NAND_PCLE
NAND_PALE
NAND_POWE
NAND_POCE
NAND_PARB
NAND_PDD(0)
NAND_PDD(1)
NAND_PDD(2)
NAND_PDD(3)
NAND_PDD(4)
NAND_PDD(5)
NAND_PDD(6)
NAND_PDD(7)
NAND_POOE
NAND_POCE
18700_505_090825.eps
090825
Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
EN 62LC9.2L LA 10.
2010-Jul-01
Page 63

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
AO BO
AE BE
3N
4P
4N
CKP
CKN
0P
0N
1P
1N
2P
2N
3P
3N
4P
4N
CKP
CKN
0P
0N
1P
1N
2P
2N
3P
4N
CKP
CKN
0P
0N
1P
1N
2P
2N
3P
3N
4P
4N
CKP
CKN
TP_VPLL
TN_VPLL
0P
0N
1P
1N
2P
2N
3P
3N
4P
C
123
P
12 13 14
L
J
6
LVDS#1
11
876543
4
H
G
K
F
P
DISPLAY INTERFACE - LVDS
2
LVDS#2
BD 12NC : 3139_123_64651
LVDS
7910 C14
5911 B14
5912 C14
6912 C15
6913 C13
H
F918 H10
17
F911 H10
D
18
B
MULTI 12NC : 3139_123_64641
13
1927 J8
4915 B12
4916 B13
4917 B13
LVDS_A_TXoCLKp_1
LVDS_A_TXoCLKn_1
LVDS_A_TXo3p_1
LVDS_A_TXo3n_1
LVDS_A_TXo2p_1
LVDS_A_TXo4p_1
LVDS_A_TXo4n_1
1906 D8
1907 D8
1908 D8
1909 E8
1910 E8
1911 E8
21
1923 H8
1924 I8
16
1926 I8
O
N
M
8
F912 H10
F913 H10
F914 H10
3917 G10
B
DISPLAY I2C CONTROL
# RESERVED FOR
A
15 16
F910 H10
M
1211109
H
I
J
K
L
A
4918 B13
5910 B14
D
6
F
8
1925 I8
6915 G10
I
J
15
LVDS_B_TXeCLKn_1
17
P
17
K
LVDS_A_TXo0n_1
LVDS_A_TXo0p_1
LVDS_A_TXo1n_1
LVDS_A_TXo1p_1
LVDS_A_TXo2n_1
7911 C15
7
1903 C8
1904 C8
1905 C8
E
F
G
L
N
12
1912 F8
1922 H8
15 16 17 18
A
C
D
2
10
4913 B12
4914 B12
C
F916 H10
4911 B13
10 11
K
NC
E
6
5
E
F
G
K
M
O
B
C
FOR DEV. USE ONLY
L
J
I
LVDS_B_TXo4p_1
19
18
LVDS_B_TXe0p_1
201918171615148
A
B
C
D
7
P
9
F976 C9
11
F978 C9
13 14
F980 C9
F981 C9
F982 C9
F983 C9
19 20
H
14 15
10
NC
O
20
1413
109
E
H
I
J
F969 B9
F971 B9
F973 B9
H
G
F
E
LVDS_B_TXe0n_1
LVDS_B_TXo1p_1
LVDS_B_TXo2n_1
N
LVDS_B_TXo2p_1
LVDS_B_TXo4n_1
1928 J8
All rights reserved. Reproduction in whole or in parts
456
I
F915 H10
F975 B9
F917 H10
F977 C9
F919 H10
F979 C9
LVDS_B_TXo1n_1
O
8
F
I
F984 C9
F985 C9
F986 C9
F987 D9
9
3
12
B
A
19
D
I915 C15
F968 B9
6914 F10
F970 B9
7701-6 A3
F972 B9
1929 J8
F974 B9
6131
L
1
D
C
B
A
K
owner.
is prohibited without the written consent of the copyright
3916 G10
E
4910 B13
G
4912 B13
1901 B8
F920 I10
N
4
20
12
1
M
G
C
7
F988 D9
F989 D9
F990 D9
F991 D9
I914 C13
F932 J10
F933 J10
F934 J11
F966 C16
5
LVDS_B_TXe4p_1
7
LVDS_B_TXe4n_1
9
LVDS_B_TXe3p_1
1930 K8
5
LVDS_A_TXe2p_1
LVDS_A_TXe2n_1
LVDS_A_TXe1p_1
LVDS_A_TXe1n_1
3
J
1931 K8
1932 K8
3912 C15
3913 C13
3914 C14
3915 C13
LVDS_B_TXe1n_1
LVDS_B_TXe1p_1
LVDS_B_TXe2n_1
LVDS_B_TXe2p_1
LVDS_B_TXeCLKp_1
L
1902 B8
11
8 910112 3 45
1
F921 I10
F922 I10
F923 I10
F992 E12
F993 F10
F994 G10
I910 B14
I911 B13
I912 C14
I913 C13
F931 J10
123 4
16
LVDS_B_TXe3n_1
LVDS_A_TXe4p_1
LVDS_A_TXe4n_1
LVDS_A_TXe3p_1
LVDS_A_TXe3n_1
LVDS_A_TXeCLKp_1
LVDS_A_TXeCLKn_1
1G51 F12
2901 G10
2902 G10
2903 K11
2904 K11
2916 C13
2917 E11
2919 E11
2920 C10
LVDS_B_TXo0p_1
50HZ 100HZ
2921 I10
LVDS_A_TXoCLKn_1
LVDS_B_TXoCLKp_1
LVDS_B_TXo3n_1
LVDS_B_TXo3p_1
1G50
1G51
YES
YESNOYES
67
F924 I10
F925 I10
F926 I10
F927 I10
F928 I10
F929 I10
F930 J10
1712 13 14 15
LVDS_A_TXe0p_1
LVDS_A_TXe0n_1
LVDS_B_TXo0n_1
ITEM #
1933 L8
1G50 B12
6913
BZX384-C6V8
I910
1927
DLW21S
2902
10p RES
F991
F928
F919
DLW21S
1925
RES
RES
2919
100n
C23
B20
A20
4912
D20
C20
D21
C21
D22
C22
D24
C24
D25
C25
D23
B22
A22
B23
A23
B25
A25
B26
A26
B24
A24
C15
D16
C16
D18
C18
D19
C19
D17
C17
B21
A21
B16
A16
B18
A18
B19
A19
B17
A17
D14
C14
D15
Φ
LVDS
MT5391
7701-6
B14
A14
B15
A15
47
48
49
50
5
6
7
8
9
42
51
43
44
45
46
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
4
40
41
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
3
30
31
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
2
20
21
22
FX15SC-41S-0.5SH
1
10
11
12
1G50
1901
DLW21S
DLW21S
1902
BZX384-C6V8
6914
F911
4
1
2
3
F972
SI4835BDY
7910
5
6
7
8
F925
SML-310
6912
130
F934
15
SETNAMECHN
CLASS_NO
1
SUPERS.
1
NAME
DATECHECK
3139 123 6465
PCB SB SSB DIGITAL
LC09M
A2
2009-02-23
-- -- --
2009-02-231
10
3
2
2009-06-04
Kyaw Aung Aung
DC391162
2009-06-04
SV
ROYAL PHILIPS ELECTRONICS N.V. 2009
2009-02-23
7
3PC332
F982
1909
DLW21S
F914
DLW21S
1910
1932
DLW21S
I915
F989
F990
5911
30R
F924
F920
4916
1904
DLW21S
F988
F986
1912
DLW21S
I912
2901
RES
F923
10p
F971
F976
F970
F968
F979
30R
5910
F978
F993
6915
BZX384-C6V8
4913
RES
4918
RES
F983
4911
I911
RES
2921 10n
DLW21S
1907
F917
F927
2903
16V
+VDISP
100u
F987
DLW21S
1929
RES
I913
2917
1n0
4917
F977
+VDISP
F915
3913
47K
F992
F932
F930
4910 RES
1u0
2916
F973
1908
DLW21S
F912
+5V_SW
1923
DLW21S
3914
47K
1905
DLW21SDLW21S
1906
DLW21S
1911
F981
F966
30R
5912
3916 22R
DLW21S
1926
F985
F984
1924
DLW21S
22R3917
1K0
3912
DLW21S
1922
PDTC114ET
7911
F913
F916
4915
RES
4914RES
F994
RES
F980
2920 10n
55
56 57
58 59
60
6
7
8
9
526153
54
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
5
50
51
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
4
40
41
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
3
30
31
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
2
20
21
1G51
FI-RE51S-HF
1
10
11
12
F975
F929
+VDISP
F922
F969
47R
F921
3915
F931
+12VDISP
F974
DLW21S
1903
I914
F918
DLW21S
1933
DLW21S
1930
1931
DLW21S
1928
DLW21S
F910
2904
100n
F926
LVDS_A_TXe2n
LVDS_A_TXe2p
LVDS_A_TXe1n
LVDS_A_TXe1p
LVDS_A_TXe0n
F933
LVDS_A_TXeCLKn
LVDS_A_TXeCLKp
LVDS_A_TXe4n
LVDS_A_TXe4p
LVDS_A_TXe3n
LVDS_A_TXe3p
LVDS_A_TXo3p
LVDS_A_TXo2p
LVDS_A_TXo1n
LVDS_A_TXo1p
LVDS_A_TXo0n
LVDS_A_TXo0p
LVDS_A_TXo2n
LVDS_A_TXe0p
LVDS_A_TXoCLKn
LVDS_A_TXoCLKp
LVDS_A_TXo4n
LVDS_A_TXo4p
LVDS_A_TXo3n
LVDS_B_TXe3n
LVDS_B_TXe3p
LVDS_B_TXe2n
LVDS_B_TXe2p
LVDS
_B_TXe1n
LVDS_B_TXe1p
LVDS_B_TXe0n
LVDS_B_TXo1n
LVDS_B_TXo1p
LVDS_B_TXo0n
LVDS_B_TXo0p
LVDS_B_TXeCLKn
LVDS_B_TXeCLKp
LVDS_B_TXe4n
LVDS_B_TXe4p
LVDS_B_TXe0p
LVDS_B_TXoCLKn
LVDS_B_TXoCLKp
LVDS_B_TXo4n
LVDS_B_TXo4p
LVDS_B_TXo3n
LVDS_B_TXo3p
LVDS_B_TXo2p
LVDS_B_TXo2n
LVSD3_SDA_DISP
LVDS3_SCL_DISP
LVDS_SELECT
LVDS_B_TXo4p
LVDS_B_TXo0n
LVDS_B_TXo1p
LVDS_SELECT
LVDS_B_TXo0p
LVDS_B_TXo1n
LVDS_B_TXo2n
LVDS_B_TXo2p
LVDS_B_TXoCLKn
LVDS_B_TXoCLKp
LVDS_B_TXo3n
LVDS_B_TXo3p
LVDS_B_TXo4n
LVDS_A_TXe0p
LVDS_A_TXe0n
LVDS_A_TXe1p
LVDS_A_TXe1n
LVDS_A_TXe2p
LVDS_A_TXe2n
LVDS_A_TXeCLKp
LVDS_A_TXeCLKn
LVDS_A_TXo3p
LVDS_A_TXo3n
LVDS_A_TXo4n
LVDS_A_TXo1n
LVDS_A_TXo2p
LVDS_A_TXoCLKn
LVDS_A_TXo2n
LVDS_A_TXoCLKp
LVDS_A_TXo0p
LVD
S_A_TXo0n
LVDS_A_TXe4n
LVDS_A_TXe3n
LVDS_A_TXe3p
LVDS_A_TXe4p
LVDS_A_TXo1p
LVDS_A_TXo4p
LVDS_B_TXe0n
LVDS_B_TXe0p
LVDS_B_TXe1n
LVDS_B_TXe1p
LVDS_B_TXe2n
LVDS_B_TXe2p
SCL
SDA
LVDS_B_TXeCLKn
LVDS_B_TXeCLKp
LVDS_B_TXe3n
LVDS_B_TXe3p
LVDS_B_TXe4n
LVDS_B_TXe4p
LCD_PWR_ON
18700_506_090825.eps
090825
SSB: Display interface - LVDS
EN 63LC9.2L LA 10.
2010-Jul-01
Page 64

SSB: Ambilight
Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
EN 64LC9.2L LA 10.
A
B
C
D
All rights reserved. Reproduction in whole or in parts
is prohibited without the written consent of the copyright
owner.
E
123
123 45
AMBILIGHT
A
AMBI_SCL
B
AMBI_SDA
FA20
4
5
6
TO DRIVE AMBILIGHT DRIVERS
+3V3_SW
5A14
120R
RES
3A14
100R
RES
3A16
100R
5A16
120R
3A10
2A10
4K7
4K7
1R01R0
3A12
3A11
RES
33p
33p
3A18
2A11
2A12
3A13
33p
3A19
RES
7
1312111098
A
67
A
0R10R1
1M59
AMBI_SCL_OUT
AMBI_SDA_OUT
I2S_SEL1
I2S_SEL2
+3V3_SW
33p
2A13
5A10
3A15
3A17
1R0
1R0
30R
2A14
1
FA17
2
FA18
3
FA19
4
FA13
5
FA14
6
FA16
7
FA15
1735446-7
1n0
B
1M59 B7
2A10 C3
2A11 C3
2A12 C4
2A13 C4
2A14 C6
3A10 B3
3A11 B3
3A12 B4
3A13 B4
3A14 B2
3A15 B6
3A16 B2
3A17 B6
3A18 C4
3A19 C4
5A10 B6
5A14 B2
5A16 B2
FA13 B7
FA14 B7
FA15 B7
FA16 B7
FA17 B7
FA18 B7
FA19 B7
FA20 B1
B
C
D
E
C
F
G
H
I
J
MULTI 12NC : 3139_123_64641
BD 12NC : 3139_123_64651
1
C
123 4567
DC391162
CLASS_NO
3PC332
-- -- --
1
2009-02-23
2009-06-04
"A00 - A99"
32 13
54
6
7
NAME
SV
2
3
SETNAMECHN
LC09M
PCB SB SSB DIGITAL
SUPERS.
2009-02-23
DATECHECK
98
15
3139 123 6465
C
ROYAL PHILIPS ELECTRONICS N.V. 2009
F
G
H
I
2009-06-04
1
2009-02-231
J
8
03101Fong King Hou
A3
121110
2010-Jul-01
18700_507_090825.eps
090825
Page 65

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
RX0
LDO
XTALI
XTALO
VCXO
STB_SCAN
VOUT12_STB
ACT_SCAN
VOUT12_ACT
SCAN_MAIN
VOUT10
C
CB
0
0B
1
1B
2
2B
-
+
OUT_DATA0
-
+
OUT_CLK
DDC_SCL
DDC_SDA
D
DDC_SCL
DDC_SDA
COM
OUT_DATA1
-
+
OUT_DATA2
HPD
A
B
C
D
PSV
AVEE
AVCC
DATA1
ENABLE
AMUXVCC
TX_EN
D
-
+
A
B
C
SCL
SDA
DDC_SCL
DDC_SDA
-
IN
OUT
RESETB
0
1
SCL
SDA
0
1
IN_C
+
+
CLK
DATA0
+
DATA2
+
-
DATA1
IN_D
+
+
CLK
DATA0
+
DATA2
+
EDID
A
DDC_SCL
DDC_SDA
B
DDC_SCL
DDC_SDA
C
CEC
SEL
I2C
I2C_ADDR
IN_A
+
+
CLK
DATA0
+
DATA2
+
-
DATA1
IN_B
+
+
CLK
DATA0
+
DATA2
+
-
DATA1
C
SCL
ADR
0
1
2SDA
WC
C
HDMI 2
D
1H02
D
Y
HDMI 2
17
IB11 G8
IB12 G8
IB14 I12
4B34 E5
4B35 E5
Y
N
3B73 F10
IB16 I12
19
1H04
11
HDMI CONNECTOR 2
F
H
FB08 E11
FB09 F11
FB10 G15
FB54 J7
FB55 J7
Y
FB33 C12
FB37 I4
FB38 I4
FB40 I4
VERTICAL
I
5131
O
11
P
1H01
10
F
I
532
D
Y
K
9
HDMI CONNECTOR 1
E
FB56 K7
FB57 D11
IB01 G15
IB02 H12
IB03 H12
IB04 H15
IB09 G8
FB53 J7
7B09 F14
FB05 K7
FB06 K7
FB07 D11
4B04-4 E5
4B11-1 B3
4B11-2 B3
4B11-3 B3
15
15
HORIZONTAL N
K
4B30 K7
2
B
4 14
N
3B75 E12
3B76 F9
"B00 - B99"
FB51 H15
FB52 I15
Y
Y
N
6
6
FB30 C12
FB31 C12
All rights reserved. Reproduction in whole or in parts
4B16-3 C3
4B16-4 B3
4B17-1 D3
4B17-2 D3
3B68 F8
3B69 F8
3B70 F6
3B71 F7
7
is prohibited without the written consent of the copyright
8
18
NC
P
Y
7
HDMI 1
F
Y
16
1H00
FB11 B15
FB16 C2
FB17 C9
6B07 J10
7701-7 H14
7B02 E12
7B03 E14
7B04 F14
7B05 F9
7B06 G14
FB32 C11
4B03-4 D5
4B04-1 E5
4B04-2 E5
4B04-3 E5
3B46 G10
3B47 G10
3B48 G14
3B49 G15
4B11-4 B3
C
E
17
1
N
19
2 13
A
191
18
5B01 B15
5B07 I15
6B06 F7
7
5
M
B
16
HDMI PNS 1+1
4B16-1 C3
FB25 C9
3B64 G8
3B65 I10
3B66 G8
3B67 G8
2B51 J10
3B10 F10
3B11 F7
3B19 F13
3B72 F10
B
8
M
G
VERTICAL
E
HDMI-DTV
Y
8
N
N
1
4B01-1 H2
4B01-2 H2
4B01-3 H2
4B01-4 H2
4B02-1 I2
4B02-2 I2
4B02-3 I2
4B02-4 H2
4B03-1 E5
4B03-2 E5
7B07 D11
3B41 F7
3B43 F14
3B44 F15
3B45 F8
B
C
D
E
3B50 G10
1914
M
3
HDMI 1
N
CONNECTOR
J
K
10
HORIZONTAL
3B53 G11
3B54 G11
3B55 G11
3B33 E15
3B34 E10
3B35 E10
3B36 F14
3B37 F15
3B38 F7
3B39 F7
4B03-3 E5
B
C
D
E
7 8 910
3B20 F13
10
H
6 13
HDMI FRAME 3+1
I
C
G
O
3B22 H16
3B24 I15
3B32 E14
1B12 C5
1B13 C5
1B14 D5
2B11 B15
2B16 B14
2B17 B14
2B24 E9
3B63 G8
5678
1B05 B11
1B06 H2
1B07 H3
1B08 J6
J
9
6
F
N
L
1B01 B6
N
1H05
A
E
16 17
L
14 15 16
2B25 E9
3 456
8
Y
Y
P
11
VERTICAL
L
14
N
1
3 4
J
N
13
13 14 15 16
123
12
1B10 H16
14
O
D
E
F
12
N
For DTV only
2010
O
5
owner.
5
1
A
2
J
732
L
J
I
56
G
H
I
4
18 19 2012
RES FOR FLECS
N
M
1615
I
J
K
G
H
1B02 B9
1B03 D6
1B04 B1
2
98
F
E
B
A
K
owner.
17
654
4B38 I2
4B39 I2
4B40 D12
20
HDMI FLECS 2+0 22"
H
G
10 11 12 13 14 15 16
BD 12NC : 3139_123_64651
HDMI SIDE
H
20
FB42 I4
FB44 I3
RES FOR FLECS
C
P
B
C
1817
M
12
J
13
RES
L
M
20191413121110
K
L
A
9101112
L
is prohibited without the written consent of the copyright
All rights reserved. Reproduction in whole or in parts
G
16
4B36 E5
4B37 I2
4
N
4
3B51 G11
3B52 G11
9
MULTI 12NC : 3139_123_64641
7 8 9
FB45 I3
FB47 J9
FB48 K7
FB49 K7
O
11
1
12
N
FB18 C2
FB19 C9
FB20 C2
FB21 C9
FB22 C9
FB23 D2
FB24 D2
D
A
N
3 9
L
2B50 J10
F
G
H
IB10 G8
7
J
N
O
P
4B17-4 C3
4B18 B3
4B28 K7
4B29 K7
A
K
12
A
11
N
B
C
Y
HDMI 3
3B40 F7
G
3
HDMI CONNECTOR 3
P
Y
H
17
F
I
N
HDMI FLECS 2+0 32"_42"
HDMI CONNECTOR SIDE
K
Y
I
20
N
4
N
HDMI PNS 2+1ITEM NO
18D18
1H03HORIZONTAL
15
1B11 B5
3B56 I10
3B57 I10
3B58 I10
3B59 I11
3B60 D12
3B61 E12
3B62 D10
4B16-2 C3
2B26 E10
2B29 G16
2B48 H16
FB26 C9
FB27 D2
FB28 C12
FB29 C12
4B17-3 C3
HDMI & MUX
FB57
IB04
AK6
AJ6
AE26
J27
AF15
W27
AF26
W29
W30
Φ
MT5391
7701-7
W26
AG15
AK7
AJ7
AK8
AJ8
AK9
AJ9
HDMI_XTAL_LDO
+5V_COMBINED
4B18
FB48
FB05
FB25
IB03
IB02
DLW21S
1
2
4
3
1B13
3 6
27
4B02-3
45
4B02-2
4B04-336
4B01-4
4B04-1 18
47K 3B50
3B49
2K2
FB49
4B34
1n0
2B26
10n
2B25
36
10K3B66
4B03-3
2K0
3B19
IB10
4B01-33 6
IB09
FB16
+3V3STBY
23
2425
26
FB19
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
2021
22
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
1B02
DC1R019WBER220
1
4B04-4 45
18
+5V_COMBINED
4B03-1
4B39
IB12
IB11
7B06
1K03B57
BC847BW
1
2
4
3
FB33
1B11
DLW21S
+5V_COMBINED
3B44
2K2
4
5
6
7
8
9
20 21
22 23
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
2
3
1B03
DC1R019JBAR190
1
10
11
6B06
BAT54
27K
3B71
30R
5B07
3K3
3B34
VDDO_3V3
1
2
4
3
4B11-4
DLW21S
1B12
2B11
1u0
45
3B56 1K0
4B03-4
4B16-1
4B17-3
3B5147K
4B04-2 27
4B17-2
23
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
2021
22
1
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
DC1R019JBAR190
1B06
100n
4B38
2B24
4B37
+3V3_SW
4B11-2
FB37
4B02-11 8
4B17-4
+5V_COMBINED
1K03B59
FB27
54B02-44
10K
3B11
FB26
4B16-4
VDDO_3V3
RES
3B38
2K0
3K3
3B35
25
26
80
79
78
77
36
12
15
24
45
44
48
47
34
35
31
32
28
29
54
53
57
56
60
59
38
37
42
41
22
2
1
5
4
8
7
11
10
51
50
39
27
40
14
13
17
16
20
19
23
68
70
63
61
62
6
3
58
55
49
46
66
65
75
73
71
67
69
76
74
72
64
9
183343
52
21
30
ADV3002BST
7B05
Φ
3B69
1R0
2K2
RES
820K
3B33
FB40
3B22
FB52
47K 3B47
10K3B65
10K3B64
470n
2B16
BC847BW
7B07
FB07
27 4B03-2
3B24
4K7
3B5247K
FB17
3B46 47K
2B51
10n
47K 3B53
2
4
3
DLW21S
1B141
2B48
27p
FB08
IB16
FB09
27p
2B29
2K2
3B37
FB30
3B73
10K
3B72
10K
3B60
10K
FB47
3B36
100R
7B09
BC847BW
6
7
8
9
15 16
1
10
11
12
13
14
2
3
4
5
1B08
501331-1409
VDDO_3V3
3B5547K
FB10
4B29
4B28
4B16-2
100R
3B43
25V
2B17
220u
RES
3B40
6K8
6K8
3B76
RES
3B67 10K
27M0
1B10
4B36
+5V_COMBINED
FB31
7B03
BC847BW
FB21
FB53
FB54
100R
3B32
24
25
26
27
28 29
30
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
22
31
23
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
2
20
21
1B01
FI-RE21S-HF-R1500
1
10
11
12
100R
FB22
3B45
+5V_COMBINED
1R0
3B70
RES
3B68
1R0
FB24
+1V2_SW
5B01
30R
RES
3B41
3K3
4B30
FB06
2B50
1u0
IB01
9
2009-02-23
ROYAL PHILIPS ELECTRONICS N.V. 2009
SV
2009-06-04
DC391162
Fong King Hou
2009-06-0423
13010
1 2009-02-23
-- -- --
2009-02-23
A2
LC09M
PCB SB SSB DIGITAL
3139 123 6465
CHECK DATE
NAME
1
SUPERS.
1
CLASS_NO
EMANTESNHC
15
3PC332
FB23
FB28
+5V_COMBINED
33R
3B61
FB45
FB56
FB55
3B75
FB51
4B40
RES
6K8
4
7
1
2
3
6
5
8
M24C02-WMN6
7B02
EEPROM
Φ
(256x8)
2425
26
+5V_COMBINED
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
2021
2223
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
1B04
DC1R019WBER220
1
10
4B17-1
+3V3_SW
FB38
3B39
2K0
RES
FB11
4B35
100R
3B48
1 84B01-1
FB42
10K
3B62
6B07
BAT54
7
8
9
2021
2223
14
15
16
17
18
19
2
3
4
5
6
1B05
DC1R019JBAR190
1
10
11
12
13
4B11-1
4B11-3
2425
26
4
5
6
7
8
9
2021
2223
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
2
3
1B07
DC1R019WBER220
1
10
BC847BW
7B04
47K 3B54
3B63 10K
4B01-227
FB18
FB20
FB44
3B10
1K0
3B20
2K0
IB14
FB32
FB29
4B16-3
+5V_SW
3B58 1K0
EDID_SDA
RXC+
RXCRX0+
RX0RX1+
RX1RX2+
RX2-
HDMI_RESET
EDID_SCL
CEC
CRX-DDC-DAT
CRX-DDC-CLK
CEC
HDMI_CEC
BRX-HPD
BRX-5V
BRXC+
BRX0-
BRX0+
BRX1-
BRX1+
BRXC-
BRX2-
BRX2+
CEC
BRX-DDC-CLK
BRX-DDC-DAT
DRX2+
BRX-DDC-CLK
BRX-DDC-DAT
BRX-5V
BRX-HPD
BRX2+
BRX2-
BRX1+
BRX1-
BRX0+
BRX0-
BRXC+
BRXC-
ARXC+
ARXC-
CEC
DRX-HPD
DRX-5V
DRX-DDC-DAT
DRX-DDC-CLK
DRX1+
DRX1-
DRX0+
DRX0-
DRXC+
DRXC-
DRX2-
DRX2+
DRX2-
DRXC+
DRXC-
ARX0+
ARX0-
ARX1+
ARX1-
ARX2+
ARX2-
EDID_WC
SCL
DRX0+
DRX0-
DRX1+
DRX1-
ARX-DDC-CLK
BRX-DDC-CLK
CRX-DDC-CLK
DRX-DDC-CLK
DDC_RESET
CRX-HPD
DRX-HPD
CRX-DDC-CLK
CRX-5V
CRX-DDC-DAT
DRX-DDC-CLK
DRX-5V
DRX-DDC-DAT
SDA
ARX-HPD
ARX-DDC-CLK
ARX-DDC-DAT
ARX-5V
BRX-HPD
BRX-DDC-CLK
BRX-DDC-DAT
BRX-5V
BOLT_ON_UART_TXD
DTV_L_IN
DTV_R_IN
SPDIF_IN
DDC-SDA
DDC-SCL
DTV_IRQ
CVBS_IN_DTV
BOLT_ON_UART_RXD
DDC-SCL
ARX2+
ARX2-
ARXC-
ARXC+
ARX0-
ARX0+
ARX1-
ARX1+
CEC
ARX-DDC-CLK
ARX-DDC-DAT
ARX-5V
ARX-HPD
CRX-5V
CRX-HPD
DDC-SDA
CRXC+
CRXC-
CRX2+
CRX2-
CRXC-
CRXC+
CRX0-
CRX0+
CRX1-
CRX1+
CEC
RXC-
RXC+
CRX0+
CRX0-
CRX1+
CRX1-
CRX2+
CRX2-
BRX2-
BRXC+
BRXC-
RX0-
RX0+
RX1-
RX1+
RX2-
RX2+
XTALI
XTALO
BRX0+
BRX0-
BRX1+
BRX1-
BRX2+
18700_508_090825.eps
090825
EN 65LC9.2L LA 10.
SSB: HDMI & MUX
2010-Jul-01
Page 66

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
C
0
RE_XRRE_XT
CFG
TXD
RX
MD
MF
LED
TX
RXD
VCCE VCCA
GNDA
0
GNDE
N
0
1
2
3
4
RX_CLK
RX_DV
COL
CRS
NC
IREF
TEST_SE
TEST
S
C
L
TR
R10
RIP
P
X1
PWRDWN
FDE
4
3
1
2
X2
RESET
1
0
1
2
3
4
TX_EN
TX_CLK
P
N
C
IO
INT
2NAF B6
3NA2 C4
RJ45
NC
123 456
9101112
A
B
C
D
A
B
C
D
E
F
1NA1 A10
1NA2 B6
2NA1 A3
2NA2 A3
2NA3 A3
2NA4 A4
2NA5 A4
2NA6 B3
14 15
2NA7 B3
2NA8 B3
2NA9 B4
2NAA B12
2NAB B11
2NAC B11
2NAD B11
2NAE A6
7 8 9101112
123 45678
1918
E
F
32
8 910111213
I
H
16 17 18 19 20
A
K
L
M
N
O
P
20
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
987654 11101
123 4567
P
O
N
M
L
J
FNA4 B11
FNA5 B10
FNA6 B11
FNA7 B10
G
F
E
D
C
B
INAP D2
INAQ D2
INAR D5
INAS C7
INAT D7
INAU D7
INAV E7
INAW E7
INAY D7
INAZ E5
NC
" XNA0 ~ XNBZ "
owner.
is prohibited without the written consent of the copyright
All rights reserved. Reproduction in whole or in parts
A
3NAU F2
3NAV F2
NC
J
K
171615141312
3NAW F2
3NAY F2
3NB1 F2
3NB2 F2
3NB3 B6
3NB4 F4
3NB5 F4
5NA1 A3
5NA2 A3
5NA3 B4
7NA1 C5
9NA2 A11
9NA3 E5
DIGITAL IO - ETHERNET (PROVISIONAL)
BD 12NC : 3139_123_64651
MULTI 12NC : 3139_123_64641
3NA3 D5
3NA4 D5
3NA5 C7
3NA6 D7
FNA8 B11
FNA9 B10
FNAA B10
FNAB B9
FNAC B9
FNAD A4
FNAE A4
FNAF C4
3NA7 D7
3NA8 D8
3NA9 E7
3NAA E8
3NAB E7
3NAC E7
3NAD A12
3NAE A11
3NAH D2
3NAJ D2
3NAK D2
3NAL D2
3NAM E2
3NAN E2
3NAP E2
3NAQ E2
3NAR E2
3NAT E2
RES
1K0
3NAJ3NAH
GNDLANGNDLAN
1K0
3NA3 1K0
30R
5NA1
+3V3DN
1u0
5NA3
+3V3AN
2NAE
27p
3NB3
820K
GNDLAN
INAW
2NAF
27p
10n
2NA7
+3V3AN
1K0
3NAV
1K0
3NAR
10n
2NA3
GNDLAN
RES
3NAY
1K0
3NA4 100R
10n
2NA9
10n
2NA8
FNAA
FNAC
3NAL
+3V3DN
RES
1K0
FNA7
FNA6
3NAB 1K5
1K0
100u 16V
2NA6
3NAW
10n
2NA4
3NB5
4K7
GNDLAN
RES
3NAQ
1K0
1K0
3NAT
RES
+3V3DN
10n
2NA2
2NAA
10p
GNDLAN
INAT
INAU
3NA6 1K5
DATE
NAME
1
SUPERS.
1
CLASS_NO
EMANTESNHC
15
3PC332
10
2009-02-23
ROYAL PHILIPS ELECTRONICS N.V. 2009
SV
2009-06-04
DC391162
Hwang Zhen
2009-06-0423
+3V3DN
13010
1 2009-02-23
-- -- --
2009-02-23
A2
LC09M
PCB SB SSB DIGITAL
3139 123 6465
CHECK
+3V3DN +3V3DN
GNDLAN
3NAE
49R9
GNDLAN
1K0
+3V3DN
GNDLAN
RES
3NAN
270R3NA9
+3V3DN
1K53NAA
+3V3_SW
+3V3DN
FNA9
FNAB
FNA8
FNA5
FNA4
4K7
3NB4
10n
2NA5
+3V3DN
1K0
3NAP
5NA2
3NB2
30R
RES
1K0
1K0
+3V3AN
RES
3NAU
3NAM
1K0
3NAD
+3V3_SW
49R9
INAQ
INAP
INAZ
3NA7 270R
+3V3DN
INAS
FNAE
4K99
3NA5
FNAF
1%
2NAB
10p
100u
2NA1
GNDLAN
16V
5
6
7
8
9
11
10
12
1314
1NA1
1840419-1
GREEN
1
2
3
4
YELLOW
25M
1NA2
9NA2
1K53NA8
3NAK
+3V3DN
1K0
INAR
INAY
100n
2NAD
100n
2NAC
FNAD
INAV
3NB1
+3V3DN
+3V3DN
1K0
3NAC 1K5
3NA2
10K
9NA3
131617
22
39
45
62
12
11
55
56
57
58
52
23
21
53
54
9
46
44
43
51
18
19
49
48
26
332
1
8
30
31
3227
28
29
47
36
38
34
37
42
61
41
5
4
3
6
7
101420
24
254050
15
35
Φ
ETHERNET
TRANSCEIVER
E-STE100P
7NA1
64
63
59
60
TPIM
TPIP
TPOM
TPOP
MII-MDIO
RJLED_Y
RJLED_G
MII-RX-ER
MII-RXCLK
MII-RX-DV
MII-TXD(0)
MII-TXD(1)
MII-TXD(2)
MII-TXD(3)
TPOP
TPOM
LAN-RST
MII-TXEN
MII-TXCLK
TPIP
TPIM
MII-MDC
MII-MDINT
MII-COL
MII-CRS
MII-RXD(0)
MII-RXD(1)
MII-RXD(2)
MII-RXD(3)
18700_509_090825.eps
090825
SSB: Digital I/O - Ethernet (provisional)
EN 66LC9.2L LA 10.
2010-Jul-01
Page 67

SSB: Analog I/O - YPbPr
C
2
3
4
N
AF
P
N
D2S
DC_DEMOD
N_DEMOD
RP
RN
SOG
GP
GN
BP
BN
SOY0
Y0P
Y0N
PB0P
PBR0N
PR0P
SOY1
Y1P
Y1N
PB1P
PBR1N
PR1P
P_DEMOD
HSYNC
VSYNC
0
1
0
1
2
0
1
2
0
1
SY
SC
CVBS
MPX0
ADCIN
FB
SYNC
SCT0
SCT1
AIN
PGA
ALI_ADAC
ADAC_VCM
VCMCOUPLE
0OUTR
0OUTL
1OUTR
1OUTL
2OUTR
2OUTL
HPOUTR
HPOUTL
Φ
5_R
5_L
6_R
6_L
VMID_AADC
0_R
0_L
1_R
1_L
2_R
2_L
3_R
3_L
4_R
4_L
2019
6
I
H
is prohibited without the written consent of the copyright
3 4
1D23 D2
M
2D49 F10
20
D
E
D
17
L
M
N
ID38 F10
ID42 F4
ID43 G12
All rights reserved. Reproduction in whole or in parts
A
1
G
N
O
P
E
F
G
A
1D14 A1
1D15 B2
1D17 G1
1D18 B2
7 8 910
A
K
M
L
J
11 12 16 17 18 19
1D04 C14
16
L
J
19
1D08 C13
1D11 F1
1D13 F1
2D35 G10
2D37 G2
2D38 F2
2D39 G2
2D50 B4
2D51 B4
2D52 C4
2D53 D4
J
K
F
G
H
I
O
17161514
A
B
C
D
5432
1D19 G13
G
1D01 D14
1D03 E13
45
O
N
3D33 C4
3D34 D4
3D35 E5
3D36 E5
3D41 F82D41 D4
2D46 F7
2D47 F8
2D48 E10
RU / AP
3 4
B
C
All rights reserved. Reproduction in whole or in parts
A
B
C
2D40 D4
1D20 D2
1D21 D2
1D22 E13
K
owner.
is prohibited without the written consent of the copyright
E
7701-11 E7
FD14 A2
FD15 B2
FD17 B2
FD18 B4
owner.
9876
P
2019181
2D30 C6
2D31 B11
2D33 F2
2D34 E10
FD29 F14
ID12 C13
ID13 C13
ID29 D5
ID30 E10
ID31 E10
ID32 E12
2013 14 15
I
H
G
F
E
D
6D16 D2
6D17 D2
6D18 D2
6D22 E13
3D27 G12
3D28 C12
3D29 B12
3D30 F2
3D32 F2
7D10-1 E12
7D10-2 G12
7D11 D8
FD12 C10
FD13 A43D42 F8
3D43 E10
13121110
RESERVE FOR FLEX
2D55 F3
2D17 B6
2D18 B12
2D19 B12
2D20 B4
2D21 C6
2D22 C4
P
123
FD25 F1
FD26 F13
FD27 F1
FD28 E13
F
F
G
18
12
RES FOR MONITOR OUT
678 910
2D54 F3
15
J
5D05 D11
6D09 C13
6D10 F2
6D11 F13
D
C
B
A
3D23 D11
3D24 D11
3D25 E12
3D26 E10
3D46 F3
3D47 E11
3D48 F11
3D49 G10
3D50 D8
3D51 D9
3D52 B4
3D53 B12
3D54 A12
3D55 D12
MULTI 12NC : 3139_123_64641
65
10 11 12
3D17 B3
3D18 C4
2D25 D4
2D27 D13
2D28 C13
2D29 D4
B
C
D
E
678 9 10111213 14
123
ID37 F10ID28 D4
5D00 C13
5D01 A3
5D02 B3
5D03 C3
L
F
12
6D12 B2
6D13 G2
6D14 B2
6D15 G13
3D15 B4
9
6543 7 8
E
BD 12NC : 3139_123_64651
1D24 D12
1D25-1 E14
2D71 D11
21
1811
3D59 C5
4D00 C12
3D11 A4
3D12 A6
3D13 B3
3D14 B6
M
K
3D19 C6
3D20 C3
3D21 C4
3D22 C6
2
9
RES
5
2D13 C4
2D14 B4
2D15 B6
2D16 B12
SPDIF
45
1D25-2 E14
1D25-3 F14
2D10 A6
2D11 A6
2D12 B11
ID14 D12
ID22 C4
ID25 C4
ID26 C5
FD24 E13
N
13
2D56 E11
2D57 E11
2D58 G11
2D59 G11
2D60 C11
16
ID34 F3
ID35 F3
17
B
C
108
2D66 G5
2D67 A11
2D68 F7
11 12 13 14
7
O
P
14
Near IC
2D70 C12
3D56 E11
3D57 A5
3D58 B5
2D61 E7
2D62 E8
2D63 F8
2D64 F8
6B 61D34G 56D2
I
H
15
2D72 E11
2D73 E12
2D74 E12
3D10 A6
ANALOG I/O - YPbPr
3D44 F10
3D45 F3
13
2D69 F8
NC
ID36 F4
14
FD19 B2
FD20 B2
FD21 C4
FD22 C1
FD23 D12
ID34
3D43
470R
100n
2D63
PESD5V0S1BA
6D11
2D10
4n7
1R0
3D55
10K
3D51
3D15
1R0
1D24
1n0
2D57
RES
60R
5D02
1n0
2D39
RES
10u
2D49
3D53
100R
30R
5D00
3D52
1R0
2D15
10n
RES
PESD5V0S1BA
6D17
FD22
3D23 220R
3D42 33R
1D19
3D19
100R
3D17
75R
10n
2D21
2D51
15p
ID37
+3V3_SW
30K3D36
3D59
1R0
3D58
1R0
1R0
3D57
3D28
100R
2D70
100p
470R
3D44
3D54
100R
RES
6D16
PESD5V0S1BA
3D21
1R0
7D10-1
BC847BS
2
6
1
RES
1n0
2D41
FD29
2D40
1n0
6D09
PESD5V0S1BA
RES
1R0
3D18
30K
3D35
FD25
FD27
1D18
RES
2D56
1n0
ID32
RES
6D10
PESD5V0S1BA
2D3147n
10u
2D52
RES
1K0
3D27
PESD5V0S1BA
6D18
2D33
1n0
RES
RES
2D62 10u
FD15
FD14
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
1D14
MSP-636H2-01
1
10
11
12
2
30K
3D46
2D66
10u
100R
3D29RES
3D25
1K0
RES
6D14
PESD5V0S1BA
RES
2D34
4n7
60R
5D01
1R0
3D30
10n2D18
6D15
PESD5V0S1BA
1n0
2D58
RES
100R
3D24
2D48
10u
1D17
1D23
2D65
100n
3D34
1R0
3D33
1R0
1D15
ID12
68R
3D22
60R
5D03
FD17
RES
1n0
2D37
FD23
ID13
FD28
10u2D68
ID29
FD19
ID26
1R0
3D32
1R0
3D10
2
1
3
ID14
YKB21-5157V
1D11
3D47
1R0
2D19 10n
IN
VS
1734806-2
1D04
GND
5D05
1u8
4D00
33R3D41
FD24
3D49
47K
1D13
RES
1n0
2D25
3
4
ID22
1D25-2
WHITE
MSP-303H-BBB-432-03 NI
RES
15p
2D20
2D22
15p
180R
3D50
RES
RES
2D59
1n0
47n2D12
15p
2D50
6D22
PESD5V0S1BA
1D21
ID43
ID36
10u
2D64
ID25
100n
2D60
2D71
33p
1n0
10n
2D11
RES
2D38
FD26
PESD5V0S1BA
6D13
YELLOW
1D25-1
1
2
RES
MSP-303H-BBB-432-03 NI
ID38
FD12
3D20
75R
10u
2D54
15p
2D13
PESD5V0S1BA
6D12
RES
2D69 10u
47p
2D73
15p
2D74
FD18
2009-02-23
ROYAL PHILIPS ELECTRONICS N.V. 2009
SV
2009-06-04
DC391162
Kyam Aung Aung / Roger Poon
2009-06-0423
1R0
3D48
2009-02-23
-- -- --
2009-02-23
A2
LC09M
PCB SB SSB DIGITAL
3139 123 6465
CHECK DATE
NAME
1
SUPERS.
1
CLASS_NO
EMANTESNHC
15
3PC332
11
3D45
13010
1
30K
6.3V220u2D46
4
2D47 220u 6.3V
7D10-2
BC847BS
5
3
75R
3D56
47p
2D72
3D16
68R
BC847BW
7D11
FD13
1D03
10n
2D30
2D53
10u
3D12
68R
2D55
10u
1D25-3
RED
MSP-303H-BBB-432-03 NI
5
6
ID30
47K
3D26
2D61
100n
2D14
15p
10n
2D17
RES
2D29
1n0
RES
ID42
1u02D16
3D11
1R0
33p
2D27
1D08
T27
47n2D67
T28
M28
M27
N30
N29
N27
N28
M30
M29
P29
V30
V29
U29
U28
U27
U26
T30
T29
R30
R29
R28
MT5391
7701-11
P28
V28
V27
AH17
AF30
AG29
AH30
AJ14
AH21
AJ21
AH18
AJ18
AH22
AH19
AJ17
AK17
AF29
AG28
AH29
AH23
AJ20
AH16
AH20
AK20
AJ16
AK16
AK14
AB26
AB27
AJ22
AJ19
AK22
AK19
AA26
AJ15
AH15
AD29
AE28
AE29
AE30
AF28
AD28
AJ
30
AJ23
Φ
AVI
AB30
AB29
AA29
MT5391
ID35
100R
3D14
75R
3D13
1D20
FD21
2D28
100n
ID28
1
2
1D01
CON_JACK
MTJ-032-21B-43 NI FE LF
4n7
2D35
ID31
RES
FD20
1D22
DACOUT2
VSYNC
SY1P_1
SPB1P_1
SPR1P_1
ASPDIF_OUT
PR
PB
R_MON_OUT
L_MON_OUT
SC2_CVBS_OUT
CVBS_IN_DTV
DTV_R_IN
AUDIO_LS_R
AUDIO_LS_L
RN
GP
GN
BP
BN
DTV_L_IN
CVBS_RF
SY1P
SPB1P
SPR1P
SPBR1N
SY1N
SOY0
SOG
RP
OFF_MUTE
SIF_OUT_GND
HP_ROUT
HP_LOUT
AV3_R_IN
DVI_AUL_IN
DVI_AUR_IN
SAV_L_IN
SAV_R_IN
L_MON_OUT
R_MON_OUT
GND_CVBS_RF
SIF_OUT
SY0
Y0N
Y0P
AIN0_L
AIN0_R
AIN1_L
AIN1_R
AV3_L_IN
HSYNC
PB0P
PBR0N
PR0P
SC0
SCART_CVBS0
SCART_CVBS1
SPBR1N
PBR1N
S0Y1
SY1N
Y1N
CVBS2
CVBS3
CVBS4
SC1_FB
Y1P
PB1P
PR1P
MUTE_M
18700_510_090825.eps
090825
Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
EN 67LC9.2L LA 10.
2010-Jul-01
Page 68

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
C
2E49 J14
2E54 C8
2E55 D14
IE29 E8
IE34 H14
IE42 H13
IE56 G14
IE72 E14
IE78 F14
3E73 G14
3E75 E14
3E78 I14
3E79 H8
3E81 H14
A
B
C
D
E
F
3E94 D14
3E96 D12
2E28 H12
2E32 G12
2E33 F14
2E35 G12
2E39 E12
2E40 F14
IE17 H13
IE18 C8
IE20 H14
IE21 D14
IE24 H8
G
H
I
J
K
L
1E01 G9
1E02 F9
1E03 F9
2E43 F12
2E46 H6
2E47 H8
2E48 I12
2E53 C14
E
F
3E64 B14
3E66 C14
3E67 C8
3E68 D14
3E70 D14
3E71 E8
54321
IE89 I14
IE95 B12
IE96 C12
IE99 E6
"E00 - E99"
LOCATION NEAR 1D14
K
L
3E93 C6
B
A
FE51 D2
IE01 F6
IE11 B14
IE13 H14
IE14 G14
IE16 C14
2E50 I14
2E51 C14
K
L
M
N
1918
A
B
C
D
109
G
H
I
J
76
Near IC
CVI-2
7E02-2 B12
FE11 C6
FE14 E10
3E90 C14
3E92 C12
7 8 910 1415
F
E
D
C
K
owner.
is prohibited without the written consent of the copyright
All rights reserved. Reproduction in whole or in parts
4E06 D2
4E07 D2
IE25 E8
IE26 D14
19 20
O
P
20161514131211
6E14 F15
6E16 F15
6E26 D15
6E28 C15
6E30 C9
6E32 E9
7E02-1 D12
FE50 D2
G
H
I
J
LA
12
FE36 F15
FE38 F15
FE39 F15
FE47 F10
FE48 F10
11 12 13
15 16
A
B
C
D
E
F
1E10 C15
1E13 C9
1E14 D15
1E17 E16
1E18 E9
16 17 18
4E10 C2
4E11 E13
4E12 G13
4E13 H13
5E12 H14
17
5E17 E9
5E19 H13
6E02 G9
6E03 F9
6E04 F9
6E10 H15
910111213 14
2E57 E14
2E58 E8
Near IC
Near IC
2E88 H6
2E89 I12
3E01 G8
FE15 E10
FE18 F10
FE26 E16
FE32 B15
FE35 E16
LA
2E05 F8
2E06 F8
2E07 F8
2E10 C14
FE49 F10
8
LA
2E86 D13
AVout
14
3E43 F14
3E46 F13
3E47 F14
3E54 I13
3E55 H6
3E56 H14
3E57 H9
3E59 I13
16
123 4
MULTI 12NC : 3139_123_64641
AP
LA
2E26 H14
AP
2E02 G8
2E03 G8
2E04 F8
AP
15
5E13 G9
5E14 G9
5E15 G14
3 45678
10 11 12
3 456
P
O
N
M
L
J
2E71 H8
2E72 J14
2E80 B12
2E82 C13
2E83 C7
3E08 F8
3E10 B13
3E12 F9
3E17 D13
3E23 H13
2E87 E7
AVin
AP
3E26 H13
3E27 H14
3E35 G13
3E36 F14
3E38 G13
3E42 E13
ANALOG I/O - CINCH
2E14 C14
2E16 C9
2E18 D14
2E23 E14
2E24 E9
2E25 H12
3E97 E6
3E99 B12
3EA0 C12
3EA2 H6
3EA3 I13
3EA4 C2
1E19 E11
1E20 H15
1E24 F15
1E26 F15
1E35 B1
5678 9
BD 12NC : 3139_123_64651
12
3EA5 D2
3EA6 D2
3EA7 C4
3EA8 E4
3EA9 E4
2E59 H14
2E63 F14
2E65 F14
2E69 I13
2E70 I14
5E16 E14
4E08 B2
4E09 C2
2E84 D12
I
H
G
13
RES FOR FLECS
3E02 G8
3E03 G9
3E04 G8
3E06 F9
3E07 E8
3E60 J15
CVI-1
3E24 H14
IE01
RES
15p
2E65
1R0
3EA8
RES
FE38
75R
3E03
IE29
FE11
3E27
1R0
6E03
PESD5V0S1BA
RES
7E02-2
BC847BS
5
3
4
4E07
RES
3EA7
1R0
RES
1n0
2E16
4E06
1
03101
1E13
0001
ROYAL PHILIPS ELECTRONICS N.V. 2009
2009-02-23
12
3PC332
15
SETNAMECHN
CLASS_NO
1
SUPERS.
1
NAME
DATECHECK
3139 123 6465
PCB SB SSB DIGITAL
LC09M
A2
2009-02-23
-- -- --
2009-02-23
3
2
2009-06-04
Kyam Aung Aung / Roger Poon
DC391162
2009-06-04
SV
IE21
3E99
1K0
6E04
PESD5V0S1BA
3E60
RES
3E57
75R
75R
3EA2
100R
IE24
RES
1n0
2E53
RES
2E71
15p
4E13
4E12
4E11
1R0
3E08
+3V3_SW
10n
2E39
2E25
10n
RES
4n7
2E10
5E16
60R
IE78
1E01
FE15
10n
2E28
2E49
47p
3E35
68R
3E17
470R
RES
2E51
1n0
2E70
47p
3EA4 1R0
RES
2E03
15p
RES
2E14
1n0
1R0
3E67
3E70
1R0
60R
5E12
IE13
6E10
RES
PESD5V0S1BA
6E26
RES
PESD5V0S1BA
100R
3EA3
5E15
1E10
60R
6E28
RES
PESD5V0S1BA
3E59
1R0
1E18
PESD5V0S1BA
15p
RES
6E02
2E04
3E07
1R0
10u
2E82
2E55
1n0
1R0
3E47
RES
15p
2E33
2E80
10u
7
8
9
41
42
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
4
40
5
6
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
3
30
31
32
15
16
17
18
19
2
20
21
22
1
10
11
12
13
14
DF13-40DP-1.25V
1E35
FE48
2E83
10u
1E02
IE95
1E03
RES
2E72
15p
IE20
30K
3E93
RES
PESD5V0S1BA
6E32
IE72
47n
2E88
1R0
3E73
1u8
5E19
PESD5V0S1BA
RES
6E16
15p
2E50
2E26
15p
2E35
4n7
15p
2E06
1R0
3E38
1R0
3E66
FE32
FE47
15p
2E05
10n
2E32
RES
IE26
15p
2E02
1R0
3E71
FE39
IE56
10u
2E84
2E07
15p
3E24
75R
RES
470R
3E10
2E89
47n
60R
5E17
FE50
1E20
IE25
FE18
75R
3E12
12
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
1E17
MSP-636H1-01
1
10
11
15p
2E63
IE11
RES
3E79
100R
3E26
1R0
3E56
1R0
PESD5V0S1BA
RES
6E30
1n0
2E58
IE96
RES
3E43
75R
2E23
1n0
68R
RES
3E42
1R0
3E04
2
6
1
BC847BS
7E02-1
10u
2E87
6E14
PESD5V0S1BA
RES
30K
3E97
IE34
3E01
1R0
IE99
2E43
10n
1R0
IE42
3E81
IE89
FE35
RES
1n0
2E57
1R0
3E02
3E90
47K
47p
2E69
1E26
1E14
75R
3E54
60R
5E14
60R
5E13
2E40
15p
FE36
RES
1n0
2E24
FE51
1E24
30K
3E92
IE14
FE49
IE17
FE26
75R
3E36
100R
3E46
1R0
3E68
1R0
3E55
4E09
4E10
4E08
1K0
3EA0
RES
2E59
15p
IE16
3E96
30K
FE14
2E54
1n0
3E23
68R
RES
1R0
3E64
IE18
RES
3EA9
1R0
47K
3E94
4n7
2E46
2E48
4n7
3EA6 1R0
1R03EA5
3E75
1R0
2E86
10u
RES
4n7
2E18
47p
2E47
3E78
1R0
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
MSP-636H1-01
1E19
1
10
11
12
75R
HSYNC_B
HSYNC
PB0P-SC1
PR0P-SC1
Y0P-SC1
PBR0N-SC1
3E06
SC1_CVBS_OUT
SPB1P_1
SY1P_1
SPR1P_1
SPR1P_1
SPR1P
SPB1P_1
SPB1P
SY1P_1
SY1P
PR1P_SC2
PGA0OUTR-SC1
PGA0OUTL-SC1
PR
MUTE_C
MUTE_C
R_MON_OUT
L_MON_OUT
SC1_B
SC1_CVBS_OUT
YON-SC1
Y0P-SC1
Y0P
SC1_G
PR0P-SC1
PBR0N
PR0P
VSYNCVSYNC_B
CVBS4
CVBS_SC2
SCART_CVBS1
SOY0
Y0N
SPBR1N
PB1P_SC2
SY1P_SC2
DACOUT1
PB0P-SC1
SY1P
SY1N
SPB1P
SC1_CVBS_OUT
AIN1_R-
SC1
AIN1_L-SC1
ASPDIF_OUT
SC2_CVBS_OUT
AIN0_R-SC2
AIN0_L-SC2
CVBS_SC2
CVBS_SC1
PGA0OUTR-SC1
PGA0OUTL-SC1
SPR1P
AIN1_R-SC1
AIN1_L-SC1
AIN0_R-SC2
AIN0_L-SC2
CVBS3
CVBS_SC1
PB0P
AIN1_R
AIN1_L
SCART_CVBS0
AIN0_R
AIN0_L
18700_511_090825.eps
090825
EN 68LC9.2L LA 10.
SSB: Analog I/O - Cinch
2010-Jul-01
Page 69

SSB: Side - A/V & USB
1
2
IN
1
2
3
OUT
C
USB
ADIN
DAC
CVBS_SPDIF_USB
FS
VREF
OUT1
OUT2
VRT
DP0
DM0
DP1
DM1
Φ
ASPDIF_OUT
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
56
C
D
A
B
C
D
3 45678 91011
E
D
C
1F11 B3
1F12 B2
1F14 C3
1F16 D3
1F18-1 C2
1F18-2 C2
1F18-3 D2
1F19 D3
1F21 D6
G
E
F
G
H
1F01 D7
1F02 D7
1F03 D7
1F10 A3
1F22 F2
1F23 F4
1F24 F3
1M36 F11
2F10 A5
2F11 A4
(RED)
F
H
I
J
12
RES
12
A
B
3 478 9101112
12
2F33 C5
2F34 B11
2F35 F6
2F36 F9
2F37 F9
B
A
E
F
G
H
J
All rights reserved. Reproduction in whole or in parts
I
H
2F42 G9
2F43 B9
3F10 A5
RIGHT
RIGHT
10
3F11 A4
2F12 B5
2F13 B4
2F14 B5
3 4
12
2F19 D10
2F20 D8
2F21 A4
2F22 B4
2F23 C4
2F24 C4
2F25 D5
2F28 F6
2F29 F4
2F30 F4
2F31 F5
2F32 D5
E
F
G
"F00 - F99"
65
6F16 D8
6F17 D8
6F18 F5
6F19 F3
6F20 C3
MULTI 12NC : 3139_123_64641
LEFT
(WHITE)
2F38 F9
2F39 G9
2F40 G9
2F41 G9
1
7
65432 131211109
3F13 B5
3F14 B4
3F16 B5
3F19 C9
2F15 C4
2F16 C4
2F17 D10
2F18 D4
3F25 E9
3F26 F3
3F27 E9
3F28 E10
6F10 A4
6F11 B4
6F12 C4
6F13 D3
6F15 D7
B
C
D
FF32 F11
FF33 F11
FF34 F11
FF35 F11
FF36 F11
FF37 G11
FF38 F3
IF10 A5
IF12 B5
IF14 B11
IF16 B5
IF18 C4
7701-10 B10
7F01 C9
FF10 B3
FF11 B3
3F21 C4
3F22 C9
3F23 C9
3F24 E9
FF16 D7
FF17 D7
FF18 D4
FF19 D7
FF20 D2
FF21 D10
FF23 F2
FF24 F2
FF25 F2
A
owner.
is prohibited without the written consent of the copyright
5F15 G9
LEFT
9
0R
C
3F38 C5
3F39 B11
3F40 C11
3F41 F3
3F42 F8
3F43 F8
8
131211
3F47 G8
3F48 B8
3F49 C9
4F00 F9
FF27 B3
FF28 B11
FF29 D7
(YELLOW)
CVBS
FF26 F2
SVHS IN
Near IC
Y
0R
USB
HEADPHONE
FF30 F11
FF31 F11
SIDE-AV & USB
3F29 A4
3F30 B4
3F31 B4
3F32 C4
3F33 D4
3F35 F4
3F36 F5
3F37 D5
BD 12NC : 3139_123_64651
IF19 C5
IF20 D5
IF21 D5
IF22 E11
FF12 B11
FF13 B3
FF14 C4
FF15 C10
IF23 E11
IF24 B11
8
7
IF16
3F44 F8
3F45 F8
3F46 G8
4F01 F9
5F13 D9
5F14 G9
6F11
RES
6F10
PESD5V0S1BA
RES
PESD5V0S1BA
47p
3F43
2F11
47R
IF12
1F16
1R0
FF15
3F29
FF33
FF32
FF12
3F49 100R
560R
3F39
100n
2F43
RES
IF22
3F27
15K
FF21
1F01
1n0
2F29
RES
FF37
FF36
FF35
+5V_SW
FF34
5
1
3
4
2
MDC-013V1-B
1F12
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
1M36
1
10
11
1-1735446-1
FF28
75R
3F14
2F14
47n
1F10
1F03
3F41
1R0
RES
YELLOW
1F18-1
1
2
FF11
MTJ-032-37BAA-432 NI
3F37
RES
30K
1n0
2F16
FF31
FF30
1n0
2F35
RES
3F21
75R
3F48
10K
75R
3F11
IF18
2F37
FF18
100p
1F14
1F23
1F24
30R
5F14
2009-02-23
ROYAL PHILIPS ELECTRONICS N.V. 2009
SV
2009-06-04
DC391162
Kyam Aung Aung / Roger Poon
2009-06-0423
FF19
2009-02-23
-- -- --
2009-02-23
A3
LC09M
PCB SB SSB DIGITAL
3133 123 6465
CHECK DATE
NAME
1
SUPERS.
1
CLASS_NO
EMANTESNHC
15
3PC332
13
1F19
13010
1
2F33
10u
2
3
OC_
5
6
7
8
7F01
4
EN_
GND
1
TPS2041BD
15K
RES
3F46
100R
3F28
FF26
2F12
47n
FF17
3F23 1R0
3F32
1R0
4F00
1R0
3F30
15p
2F21
RES
100p
2F40
MTJ-032-37BAA-432 NI
WHITE
1F18-2
6
4
5
47p
2F13
1n0
2F24
RES
1F02
IF23
3F26 1R0
2F42
100p
5F15
30R
2F41 100p
AJ4
AK5
AK4
AK3AJ29
AK29
AJ28
AK28
J28 AF22
AJ24
AK24
AF21
AJ5
MT5391
7701-10
AH28
AH27
AK30
6F18
PESD5V0S1BA
8
1
2
3
4
5
7
BZX384-C6V8
1F22
MSJ-035-10A B AG PPO
6F15
1%
IF19
3F40
5K1
MTJ-032-37BAA-432 NI
RED
1F18-3
9
7
8
NUP1301ML3
6F16
3F47 47R
100p
2F39
100R
3F13
FF16
IF20
+3V3_SW
100R3F19
2F38
100p
2F10
47n
30R
5F13
100R
3F16
FF14
1R03F35
2F20
10u
3F44
100R
FF29
2F15
47p
PESD5V0S1BA
RES
3F38
30K
6F20
PESD5V0S1BA
6F19
FF13
1n0
RES
2F30
RES
PESD5V0S1BA
6F12
2F31
100R
3F10
RES
1n0
3F33
1R0
100R3F22
FF25
47R3F45
RES
PESD5V0S1BA
6F13
IF21
100n
2F19
1R0
1
2
3
4
56
3F31
292303-4
1F21
2F28
1n0
RES
2F36 100p
15p
2F23
RES
16V
IF14
RES
2F17
100u
2F22
15p
IF10
1F11
100R
3F42
4F01
FF38
3F36
1R0
FF23
IF24
6F17
NUP1301ML3
FF24
RES
2F18
1n0
2F34
100n
RES
3F25
2F25
1n0
RES
10u
2F32
FF27
FF20
FF10
3F24
RC2
HP_ROUT
HP_LOUT
R_MON_OUT
CVBS2
SC0
SC0
SAV_R_IN
POWER-OK
DP
SC2_CVBS_OUT
MUTE
L_MON_OUT
SAV_L_IN
CVBS2
HP_DET
RC1
DM
LIGHT_SENSOR
KEYBOARD
AFT
ASPDIF_OUT
DACOUT1
DACOUT2
5V
USB_DM0
USB_DP0
USB_PWE
USB_OC
HP_ROUT
SY0
SAV_L_IN
SAV_R_IN
HP_LOUT
18700_512_090825.eps
090825
Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
EN 69LC9.2L LA 10.
2010-Jul-01
Page 70

SSB: VGA
SCL
ADR
0
1
2SDA
WC
C
3G13 D4
3G14 D6
3G15 D9
3G16 D10
G
109
1
7
3G37 E9
3G38 E10
4G11 D9
4G12 E9
4G13 D9
4G14 D9
3G21 D5
3G22 E4
3G23 E6
3G24 E4
3G25 E5
3G26 E6
2G17 D3
2G18 E6
2G19 E3
2G21 E9
12111098
123 456
132 3
3G27 F4
3G28 F5
3G29 F6
3G30 G4
3G31 G5
3G32 A10
3G33 A8
3G34 D10
3G35 D11
3G11 C7
3G12 B7
1G12 B7
1G13 D7
654
13
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
3G18 D4
3G19 D5
3G20 D4
2G14 D11
2G16 D3
C
D
E
F
G
H
1G11 C7
MULTI 12NC : 3139_123_64641
8
7
11 12
2G22 E10
2G23 E3
2G24 F6
2G25 F6
2G26 F3
2G27 F6
2G29 G3
3G10 D5
owner.
is prohibited without the written consent of the copyright
FG15 E8
FG16 A8
FG17 D10
FG18 E10
FG19 E8
FG20 E8
IG01 D10
"G00" - "G99"BD 12NC : 3139_123_64651
12
123 45
F
E
H
I
All rights reserved. Reproduction in whole or in parts
J
1G14 E7
1G15 F7
1G16 D8
2G10 D6
2G11 C6
2G12 B6
2G13 D3
A
B
A
B
4G15 D11
5G11 C6
5G12 B6
5G13 E5
5G14 D6
5G15 D6
5G16 F6
6G11 C7
6G12 B7
6G13 A11
6G14 D7
6G15 E7
123 45678 91011
D
C
B
A
FG13 E8
FG14 E8
6G16 E5
6G17 F7
7G11 D11
7G12 A9
FG11 E8
FG12 D8
678 9101112
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
VGA
IG02 A9
3G32
10K
5p6
2G27
1R0
3G22
3G28
1R0
5G11
30R
3G11
2K2
2G11
15p
60R
5G15
60R
5G14
4G14
RES
4G13
RES
4G12
4G11
10K
3G16
1G13
0001
2G16
10n
2G17
10n
68R
3G13
3G24
100R
2G24
1n0
8
4
7
FG17
1
2
3
6
5
M24C02-WMN6
7G11
EEPROM
Φ
(256x8)
3G31
1R0
10K
3G33
3G12
2K2
1G15
FG12
1R0
3G25
FG20
3G23
75R
100n
2G25
6
7
8
9
16
17
FG11
11
12
13
14
15
2
3
4
5
1G16
1226-00B-15S-FAE-02
1
10
1R0
3G19
IG01
2G12
15p
1R0
3G21
2G18
5p6
3G10
1R0
DC_5V
330p
2G22
6G14
PESD5V0S1BA
RES
PESD5V0S1BA
RES
FG16
6G12
IG02
10n
2G13
6K2
3G35
RES
4G15
6K2
3G37RES
RES
6K2
3G38
100n
2G14
FG13
3G18
100R
DC_5V
60R
5G16
FG15
1G12
FG19
75R
3G14
BAS316
6G16
FG18
3G15
10K
FG14
RES
6G11
PESD5V0S1BA
DC_5V
5G13
60R
6G17
PESD5V0S1BA
RES
6G13
BAS316
4n7
2G19
68R
3G20
10n
2G23
3PC332
14
2009-02-23
ROYAL PHILIPS ELECTRONICS N.V. 2009
SV
2009-06-04
DC391162
Kyaw Aung Aung/ Roger Poon
2009-06-0423
BC847BW
7G12
10
1 2009-02-23
-- -- --
2009-02-23
A3
LC09M
PCB SB SSB DIGITAL
3139 123 6465
CHECK DATE
NAME
1
SUPERS.
1
CLASS_NO
EMANTESNHC
15
2G26
10n
130
68R
3G27
75R
3G29
2G29
5p6
2G10
10n
100R
3G30
30R
5G12
0001
1G11
RES
1G14
6G15
PESD5V0S1BA
330p
+5V_SW
2G21
150R
3G26
33R
3G34
EDID_SCL
EDID_SDA
SCL_VGA
SDA_VGA
H_SYNC
HSYNC
V_SYNC
VSYNC
VGA_G
VGA_B
EDID_WC
GN
VGA_Bp
VGA_Gp
VGA_Gn
VGA_Rn
VGA_R
BP
BN VGA_Bn
GP
VGA_Rp
SOG
RP
RN
18700_513_090825.eps
090825
Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
EN 70LC9.2L LA 10.
2010-Jul-01
Page 71

SSB: BDS iTV
C
1 98
13
6543
12111098
7
G
F
E
D
C
J
All rights reserved. Reproduction in whole or in parts
I
2
H
J
I
H
1H14 A6
1H16 A1
2H12 D4
2H24 D2
FH36 B1
B
A
G
F
E
D
C
B
A
owner.
is prohibited without the written consent of the copyright
7
2
C
FH21 C4
76
2 13121110
2H13 D5
A
6543
C
1
1H11 C1
1H12 C3
1H13 A3
FH33 A1
RES
RES
RES
2H14 D5
4H10 D6
4H11 D6
4H12 D6
4H13 D6
3H21 D5
2H25 D2
2H26 D2
2H27 D4
2H28 D4
2H29 D5
3H16 A4
3H17 A4
3H20 D5
45
3H22 D5
MULTI 12NC : 3139_123_64641
FH24 D4
FH22 D4
FH23 D4
FH25 D4
FH26 D4
FH27 B4
FH30 A7
FH31 A1
FH32 A1
RES
BD 12NC : 3139_123_64651
FH15 A4
FH16 A4
FH17 A4
FH18 C4
FH19 C4
FH20 C4
1
B
D
FH34 A1
FH35 B1
10
D
BDS iTV
5H10 A4
5H11 A4
5H12 C5
FH11 D1
FH14 A4
2H15 D5
2H19 B7
2H20 B7
2H21 D1
2H22 D2
2H23 D2
"H00" - "H99"
12
B
3H23 D5
3H24 D5
A
76543
3
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
BM08B-SRSS-TBT
1H16
2H13
100p
2H24
100p
2H27
15p
1
2
3
4
5
BM03B-SRSS-TBT
1H14
FH15
30R
5H10
1n0
2H21
100p
2H29
FH36
FH35
FH22
+3V3STBY
100p
2H25
3H22 100R
2H26
100p
5
6
7
8
9
11
12
1
10
2
3
4
1H12
BM10B-SRSS-TBT
3H17 100R
4H13
4H12
FH31
2H20
1n0
100p
2H23
FH20
FH21
CHECK
3139 123 6465
PCB SB SSB DIGITAL
LC09M
A3
2009-02-23
-- -- --
2009-02-231
03101
2H19
1n0
3
2
2009-06-04
Alexi Jebakumar
DC391162
2009-06-04
SV
ROYAL PHILIPS ELECTRONICS N.V. 2009
2009-02-23
15
3PC332
15
SETNAMECHN
CLASS_NO
1
SUPERS.
1
NAME
DATE
3H24 100R
2H14
100p
FH27
FH19
FH18
3H21 100R
FH11
2
3
4
5
67
1H13
BM05B-SRSS-TBT
1
2H22
1n0
FH16
8
9
10
100R3H16
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
BM08B-SRSS-TBT
1H11
4H10
100p
2H12
FH34
FH17
FH33
FH30
5H12
30R
100p
2H15
FH32
2H28
15p
FH23
FH26
3H23
4H11
100R
100R3H20
FH24
FH25
FH14
5H11
30R
RC2
PBS_SPI_DO
SCL
SDA
AMBI_SDA
AMBI_SCL
AOUTR
AOUTL
PBS_SPI_DI
PBS_SPI_CLK
PBS_I2C_SCL
RC1
SC1_FB
SC1_CVBS_OUT
SC1_G
SC1_B
SC1_AOUTL
SC1_AOUTR
SDA_CLOCK
SCL_CLOCK
LCD_CLK_SDA
LCD_CLK_SCL
+3V3STBY
+5V_SW
SC1_CVBS_OUT
RC1
DDC_RESET
STANDBY
18700_514_090825.eps
090825
Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
EN 71LC9.2L LA 10.
2010-Jul-01
Page 72

SSB: SRP List Explanation
1 . 1 . Introduction
Example
SRP (Service Re ference Protocol) is a softw are too l that creates a list w i th all refer e n c es to signal lines. The list contains
references to the signals w i thin all schemat ics of a PWB. It replaces the text refe r ences currentl y p r inted next t o the signal
names in the s
chematics. These printed refe rences are created man ually an d are t h e r efore n o t guar an teed to be 100 %
correct. In additio n , in the current crowded schema t ics there is often none or ver y little pl ace for these references.
Either there will be an SRP
reference list for a schematic, or there will be printed references in the schematic.
1.2. Non-SRP Schematics
There are several different signals available in a schematic:
1.2.1. Power Supply Lines
All power supply lines are available in the supply line overview (see chapter 9). In the schematics (see chapter 10) is not
indicated where supplies are coming from or going to.
It is however indicated if a supply is incoming (created elsewhere), or outgoing (created or adapted in the current schematic).
+5V +5V
Outgoing Incoming
1.2.2. Normal Signals
For normal signals, a schematic reference (e.g. B14b) is placed next to the signals.
signal_name
B14b
1.2.3. Grounds
For normal and special grounds (e.g. GNDHOT or GND3V3 etc.), nothing is indicated.
1.3. SRP Schematics
SRP is a tool, which automatically creates a list with signal references, indicating on which schematic the signals are used.
A reference is created for all signals indicated with an SRP symbol, these symbols are:
+5V +5V
Power supply line.
name name
Stand alone signal or switching line (used as less as possible).
name name
Signal line into a wire tree.
name name
Switching line into a wire tree.
name
Bi-directional line (e.g. SDA) into a wire tree.
name
Signal line into a wire tree, its direction depends on the circuit (e.g. ingoing for PDP, outgoing for LCD sets).
Remarks:
• When there is a black dot on the “signal direction arrow” it is an SRP symbol, so there will be a reference to the signal
name in the SRP list.
• All references to normal grounds (Ground symbols without additional text) are not listed in the reference list, this to keep
it concise.
•
Signals that are not used in multiple schematics, but only once or several times in the same schematic, are included
in the SRP reference list, but only with one reference.
Additional Tip:
When using the PDF service manual file, you can very easily search for signal names and follow the signal over all the
schematics. In Adobe PDF reader:
• Select the signal name you
want to search for, with the “Select text” tool.
• Copy and paste the signal name in the “Search PDF” tool.
• Search for all occurrences of the signal name.
• Now you can quickly jump between the different occurrences and follow the signal over all schematics. It is advised to
“zoom in” to e.g. 150% to see clearly, which text is selected. Then you can zoom out, to get a
n overview of the complete
schematic.
PS. It is recommended to use at least Adobe PDF (reader) version 6.x, due to better search possibilities in this version.
10000_031_090121.eps
100323
Net Name Diagram
+12-15V AP1 (4x)
+12-15V AP4 (4x)
+12-15V AP5 (12x)
+12-15V AP6 (4x)
+12-15V AP7 (8x)
+12V AP1 (4x)
+12V_NF AP1 (2x)
+12VAL AP1 (2x)
+25VLP AP1 (4x)
+25VLP AP2 (1x)
+3V3-STANDBY AP5 (3x)
+400V-F AP1 (2x)
+400V-F AP2 (2x)
+400V-F AP3 (2x)
+5V2 AP1 (6x)
+5V2 AP2 (1x)
+5V2-NF AP1 (1x)
+5V2-NF AP2 (1x)
+5V-SW AP1 (6x)
+5V-SW AP2 (1x)
+8V6 AP1 (3x)
+AUX AP1 (2x)
+AUX AP2 (1x)
+DC-F AP1 (2x)
+DC-F AP3 (2x)
+SUB-SPEAKER AP5 (1x)
+SUB-SPEAKER AP6 (2x)
-12-15V AP1 (4x)
-12-15V AP4 (6x)
-12-15V AP5 (14x)
-12-15V AP6 (6x)
-12-15V AP7 (8x)
AL-OFF AP1 (2x)
AUDIO-L AP4 (1x)
AUDIO-L AP5 (1x)
AUDIO-PROT AP5 (3x)
AUDIO-R AP4 (1x)
AUDIO-R AP5 (1x)
AUDIO-SW AP5 (1x)
AUDIO-SW AP7 (1x)
BOOST AP1 (2x)
CPROT AP4 (2x)
CPROT AP5 (1x)
CPROT-SW AP5 (1x)
CPROT-SW AP6 (2x)
-DC-F AP1 (2x)
-DC-F AP3 (2x)
DC-PROT AP1 (1x)
DC-PROT AP5 (2x)
DIM-CONTROL AP1 (2x)
FEEDBACK+SW AP6 (2x)
FEEDBACK-L AP4 (2x)
FEEDBACK-R AP4 (2x)
FEEDBACK-SW AP6 (2x)
GND-AL AP1 (2x)
GNDHA AP1 (40x)
GNDHA AP2 (20x)
GNDHA AP3 (2x)
GNDHOT AP3 (2x)
GND-L AP1 (2x)
GND-L AP4 (4x)
GND-L AP5 (34x)
GND-LL AP4 (7x)
GND-LL AP5 (1x)
GND-LR AP4 (7x)
GND-LR AP5 (1x)
GND-LSW AP5 (1x)
GND-LSW AP6 (15x)
GND-S AP1 (11x)
GND-SA AP4 (
8x)
GND-SA AP5 (2x)
GND-SA AP6 (8x)
GND-SA AP7 (6x)
GNDscrew AP3 (2x)
GNDscrew AP5 (2x)
GND-SSB AP5 (3x)
GND-SSP AP1 (51x)
GND-SSP AP2 (15x)
IN+SW AP6 (2x)
IN-L AP4 (2x)
IN-R AP4 (2x)
IN-SW AP6 (2x)
INV-MUTE AP4 (1x)
INV-MUTE AP5 (1x)
INV-MUTE AP6 (1x)
LEFT-SPEAKER AP4 (1x)
LEFT-SPEAKER AP5 (1x)
MUTE AP4 (2x)
MUTE AP5 (1x)
MUTE AP6 (2x)
ON-OFF AP1 (3x)
OUT AP6 (1x)
OUT AP7 (2x)
OUTN AP6 (1x)
OUTN AP7 (1x)
POWER-GOOD AP1 (2x)
POWER-OK-PLATFORM AP1 (2x)
RIGHT-SPEAKER AP4 (1x)
RIGHT-SPEAKER AP5 (1x)
SOUND-ENABLE AP5 (3x)
STANDBY AP1 (5x)
STANDBY AP2 (1x)
-SUB-SPEAKER AP5 (1x)
-SUB-SPEAKER AP6 (2x)
V-CLAMP AP1 (1x)
V-CLAMP AP3 (2x)
Personal Notes:
Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
EN 72LC9.2L LA 10.
2010-Jul-01
Page 73

SSB: SRP List
3139 123 6465.1
18700_545_090827.eps
090827
Netname Diagram
+12VDISP B01 (1 ×)
+12VDISP B04D (1 ×)
+12VS B01 (5 ×)
+12VS B03 (2 ×)
+12VS B04A (1 ×)
+12VS_1 B01 (2 ×)
+1V0_SW B01 (1 ×)
+1V0_SW B04A (1 ×)
+1V2_SW B01 (1 ×)
+1V2_SW B02A (1 ×)
+1V2_SW B04A (2 ×)
+1V2_SW B05 (1 ×)
+1V8_SW B01 (1 ×)
+1V8_SW B04A (1 ×)
+1V8_SW B04B (9 ×)
+24VAUDIO B01 (1 ×)
+24VAUDIO B03 (1 ×)
+2V5_SW B02A (2 ×)
+3V3_FLASH B04C (3 ×)
+3V3_SW B01 (1 ×)
+3V3_SW B02A (5 ×)
+3V3_SW B03 (2 ×)
+3V3_SW B04A (5 ×)
+3V
3_SW B04C (24 ×)
+3V3_SW B04E (2 ×)
+3V3_SW B05 (2 ×)
+3V3_SW B06A (2 ×)
+3V3_SW B06B (1 ×)
+3V3_SW B06C (1 ×)
+3V3_SW B06D (1 ×)
+3V3AN B06A (3 ×)
+3V3DN B06A (14 ×)
+3V3STBY B01 (1 ×)
+3V3STBY B03 (2 ×)
+3V3STBY B04A (9 ×)
+3V3STBY B04C (5 ×)
+3V3STBY B05 (1 ×)
+3V3STBY B07 (2 ×)
+5V_COMBINED B05 (8 ×)
+5V_SW B01 (1 ×)
+5V_SW B02A (3 ×)
+5V_SW B03 (1 ×)
+5V_SW B04A (4 ×)
+5V_SW B04C (1 ×)
+5V_SW B04D (1 ×)
+5V_SW B05 (1 ×)
+5V_SW B06D (1 ×)
+5V_SW B06E (1 ×)
+5V5_TUN B01 (1 ×)
+5V5_TUN B02A (1 ×)
+5VS B02A (2 ×)
+5VTUN_DIGITAL B02A (2 ×)
+8V_SW B01 (1 ×)
+VDISP B04D (3 ×)
+VTUN B01 (1 ×)
5V B06D (1 ×)
AFT B02A (1 ×)
AFT B06D (1 ×)
AIN0_L B06B (1 ×)
AIN0_L B06C (1 ×)
AIN0_L-SC2 B06C (1 ×)
AIN0_R B06B (1 ×)
AIN0_R B06C (1 ×)
AIN0_R-SC2 B06C (1 ×)
AIN1_L B06B (1 ×)
AIN1_L B06C (1 ×)
AIN1_L-SC1 B06C (1 ×)
AIN1_R B06B (1 ×)
AIN1_R B06C (1 ×)
AIN1_R-SC1 B06C (1 ×)
AMBI_SCL B04C (1 ×)
AMBI_SCL B04E (1 ×)
AMBI_SCL B07 (1 ×)
AMBI_SCL_OUT B04E (1 ×)
AMBI_SDA B04C (1 ×)
AMBI_SDA B04E (1 ×)
AMBI_SDA B07 (1 ×)
AMBI_SDA_OUT B04E (1 ×)
AOBCK B03 (1 ×)
AOBCK B04C (1 ×)
AOLRCK B03 (1 ×)
AOLRCK B04C (1 ×)
AOMCLK B03 (1 ×)
AOMCLK B04C (1 ×)
AOSDATA0 B03 (1 ×)
AOSDATA0 B04C (1 ×)
AOUTL B03 (3 ×)
AOUTL B07 (1 ×)
AOUTR B03 (
3 ×)
AOUTR B07 (1 ×)
ARX0- B05 (2 ×)
ARX0+ B05 (2 ×)
ARX1- B05 (2 ×)
ARX1+ B05 (2 ×)
ARX2- B05 (2 ×)
ARX2+ B05 (2 ×)
ARX-5V B04A (1 ×)
ARX-5V B05 (2 ×)
ARXC- B05 (2 ×)
ARXC+ B05 (2 ×)
ARX-DDC-CLK B05 (2 ×)
ARX-DDC-DAT B05 (2 ×)
ARX-HPD B05 (2 ×)
ASPDIF_OUT B06B (1 ×)
ASPDIF_OUT B06C (1 ×)
ASPDIF_OUT B06D (1 ×)
AUDIO_LS_L B03 (1 ×)
AUDIO_LS_L B06B (1 ×)
AUDIO_LS_R B03 (1 ×)
AUDIO_LS_R B06B (1 ×)
AV3_L_IN B06B (1 ×)
AV3_R_IN B06B (1 ×)
BACKLIGHT_BOOST B01 (1 ×)
BACKLIGHT_BOOST B04C (1 ×)
BL_ON_OFF B01 (1 ×)
BL_ON_OFF B04C (1 ×)
BN B06B (1 ×)
BN B06E (1 ×)
BOLT_ON_UART_RXD B04C (1 ×)
BOLT_ON_UART_RXD B05 (1 ×)
BOLT_ON_UART_TXD B04C (1 ×)
BOLT_ON_UART_TXD B05 (1 ×)
BP B06B (1 ×)
BP B06E (1 ×)
BRX0- B05 (2 ×)
BRX0+ B05 (2 ×)
BRX1- B05 (2 ×)
BRX1+ B05 (2 ×)
BRX2- B05 (2 ×)
BRX2+ B05 (2 ×)
BRX-5V B04A (1 ×)
BRX-5V B05 (2 ×)
BRXC- B05 (2 ×)
BRXC+ B05 (2 ×)
BRX-DDC-CLK B05 (2 ×)
BRX-DDC-DAT B05 (2 ×)
BRX-HPD B05 (2 ×)
CEC B05 (4 ×)
CRX0- B05 (2 ×)
CRX0+ B05 (2 ×)
CRX1- B05 (2 ×)
CRX1+ B05 (2 ×)
CRX2- B05 (2 ×)
CRX2+ B05 (2 ×)
CRX-5V B04A (1 ×)
CRX-5V B05 (2 ×)
CRXC- B05 (2 ×)
CRXC+ B05 (2 ×)
CRX-DDC-CLK B05 (2 ×)
CRX-DDC-DAT B05 (2 ×)
CRX-HPD B05 (2 ×)
CVBS_IN_DTV B05 (1 ×)
CVBS_IN_DTV B06B (1 ×)
CVBS_RF B02A (1 ×)
CVBS_RF B06B (1 ×)
CVBS_SC1 B06C (1 ×)
CVBS_SC2 B06C (1 ×)
CVBS0T B02A (2 ×)
CVBS2 B06B (1 ×)
CVBS2 B06D (2 ×)
DACOUT1 B06C (1 ×)
DACOUT1 B06D (1 ×)
DACOUT2 B06B (1 ×)
DACOUT2 B06D (1 ×)
DC_5V B06E (3 ×)
DC_PROT B03 (1 ×)
DC_PROT B04C (1 ×)
DDC_RESET B04C (1 ×)
DDC_RESET B05 (1 ×)
DDC_RESET B07 (1 ×)
DDC-SCL B04C (1 ×)
DDC-SCL B05 (2 ×)
DDC-SDA B04C (1 ×)
DDC-SDA B05 (2 ×)
DEMOD_RESET B02A (1 ×)
DEMOD_RESET B04C (1 ×)
DM B06D (1 ×)
DP B06D (1 ×)
DRX0- B05 (2 ×)
DRX0+ B05 (2 ×)
DRX1- B05 (2 ×)
DRX1+ B05 (2 ×)
DRX2- B05 (2 ×)
DRX2+ B05 (2 ×)
DRX-5V B04C (1 ×)
DRX-5V B05 (2 ×)
DRXC- B05 (2 ×)
DRXC+ B05 (2 ×)
DRX-DDC-CLK B05 (2 ×)
DRX-DDC-DAT B05 (1 ×)
DRX-HPD B05 (2 ×)
DTV_IRQ B04A (1 ×)
DTV_IRQ B05 (1 ×)
DTV_L_IN B05 (1 ×)
DTV_L_IN B06B (1 ×)
DTV_R_IN B05 (1 ×)
DTV_R_IN B06B (1 ×)
DVI_AUL_IN B06B (1 ×)
DVI_AUR_IN B06B (1 ×)
EDID_SCL B05 (1 ×)
EDID_SCL B06E (1 ×)
EDID_SDA B05 (1 ×)
EDID_SDA B06E (1 ×)
EDID_WC B04C (1 ×)
EDID_WC B05 (1 ×)
EDID_WC B06E (1 ×)
FRONTEND_SCL B02A (1 ×)
FRONTEND_SCL B04A (1 ×)
FRONTEND_SDA B02A (1 ×)
FRONTEND_SDA B04A (1 ×)
GAIN_SW B02A (1 ×)
GAIN_SW B04C (1 ×)
GN B06B (1 ×)
GN B06E (1 ×)
GND_CVBS_RF B02A (1 ×)
GND_CVBS_RF B06B (1 ×)
GNDLAN B06A (10 ×)
GNDSND B01 (2 ×)
GNDSND B03 (26 ×)
GNDTUN B01 (1 ×)
GP B06B (1 ×)
GP B06E (1 ×)
HDMI_CEC B04A (1 ×)
HDMI_CEC B05 (1 ×)
HDMI_RESET B04C (1 ×)
HDMI_RESET B05 (1 ×)
HP_DET B04C (1 ×)
HP_DET B06D (1 ×)
HP_DETECT B04C (1 ×)
HP_LOUT B03 (1 ×)
HP_LOUT B06B (1 ×)
HP_LOUT B06D (2 ×)
HP_ROUT B03 (1 ×)
HP_ROUT B06B (1 ×)
HP_ROUT B06D (2 ×)
HSYNC B06B (1 ×)
HSYNC B06C (1 ×)
HSYNC B06E (1 ×)
I2S_SEL1 B04E (1 ×)
I2S_SEL2 B04E (1 ×)
JTCK B04C (2 ×)
JTDI B04C (2 ×)
JTDO B04C (2 ×)
JTMS B04C (2 ×)
JTRST B04C (2 ×)
KEYBOARD B04C (1 ×)
KEYBOARD B06D (1 ×)
L_MON_OUT B06B (2 ×)
L_MON_OUT B06C (1 ×)
L_MON_OUT B06D (1 ×)
LAN-RST B04C (1 ×)
LAN-RST B06A (1 ×)
LCD_CLK_SCL B04A (1 ×)
LCD_CLK_SCL B07 (1 ×)
LCD_CLK_SDA B04A (1 ×)
LCD_CLK_SDA B07 (1 ×)
LCD_PWR_ON B04C (1 ×)
LCD_PWR_ON B04D (1 ×)
LED1 B04A (1 ×)
LED1 B04C (1 ×)
LED2 B04A (1 ×)
LED2 B04C (1 ×)
LIGHT_SENSOR B04C (1 ×)
LIGHT_SENSOR B06D (1 ×)
LV DS_A_TXe0n B04D (2 ×)
LV DS_A_TXe0p B04D (2 ×)
LV DS_A_TXe1n B04D (2 ×)
LV DS_A_TXe1p B04D (2 ×)
LV DS_A_TXe2n B04D (2 ×)
LV DS_A_TXe2p B04D (2 ×)
LV DS_A_TXe3n B04D (3 ×)
LV DS_A_TXe3p B04D (2 ×)
LV DS_A_TXe4n B04D (2 ×)
LV DS_A_TXe4p B04D (2 ×)
LV DS_A_TXeCLKn B04D (2 ×)
LV DS_A_TXeCLKp B04D (2 ×)
LV DS_A_TXo0n B04D (2 ×)
LV DS_A_TXo0p B04D (2 ×)
LV DS_A_TXo1n B04D (2 ×)
LV DS_A_TXo1p B04D (2 ×)
LV DS_A_TXo2n B04D (2 ×)
LV DS_A_TXo2p B04D (2 ×)
LV DS_A_TXo3n B04D (3 ×)
LV DS_A_TXo3p B04D (2 ×)
LV DS_A_TXo4n B04D (2 ×)
LV DS_A_TXo4p B04D (2 ×)
LV DS_A_TXoCLKn B04D (2 ×)
LV DS_A_TXoCLKp B04D (2 ×)
LV DS_B_TXe0n B04D (2 ×)
LV DS_B_TXe0p B04D (2 ×)
LV DS_B_TXe1n B04D (2 ×)
LV DS_B_TXe1p B04D (2 ×)
LV DS_B_TXe2n B04D (2 ×)
LV DS_B_TXe2p B04D (2 ×)
LV DS_B_TXe3n B04D (3 ×)
LV DS_B_TXe3p B04D (2 ×)
LV DS_B_TXe4n B04D (2 ×)
LV DS_B_TXe4p B04D (2 ×)
LV DS_B_TXeCLKn B04D (2 ×)
LV DS_B_TXeCLKp B04D (2 ×)
LV DS_B_TXo0n B04D (2 ×)
LV DS_B_TXo0p B04D (2 ×)
LV DS_B_TXo1n B04D (2 ×)
LV DS_B_TXo1p B04D (2 ×)
LV DS_B_TXo2n B04D (2 ×)
LV DS_B_TXo2p B04D (2 ×)
LV DS_B_TXo3n B04D (3 ×)
LV DS_B_TXo3p B04D (2 ×)
LV DS_B_TXo4n B04D (2 ×)
LV DS_B_TXo4p B04D (2 ×)
LV DS_B_TXoCLKn B04D (2 ×)
LV DS_B_TXoCLKp B04D (2 ×)
LV DS_SELECT B04C (1 ×)
LV DS_SELECT B04D (1 ×)
MII-COL B04C (1 ×)
MII-COL B06A (1 ×)
MII-CRS B04C (1 ×)
MII-CRS B06A (1 ×)
MII-MDC B04C (1 ×)
MII-MDC B06A (1 ×)
MII-MDINT B04C (1 ×)
MII-MDINT B06A (1 ×)
MII-MDIO B04C (1 ×)
MII-MDIO B06A (1 ×)
MII-RXCLK B04C (1 ×)
MII-RXCLK B06A (1 ×)
MII-RXD(0) B04C (1 ×)
MII-RXD(0) B06A (1 ×)
MII-RXD(1) B04C (1 ×)
MII-RXD(1) B06A (1 ×)
MII-RXD(2) B04C (1 ×)
MII-RXD(2) B06A (1 ×)
MII-RXD(3) B04C (1 ×)
MII-RXD(3) B06A (1 ×)
MII-RX-DV B04C (1 ×)
MII-RX-DV B06A (1 ×)
MII-RX-ER B04C (1 ×)
MII-RX-ER B06A (1 ×)
MII-TXCLK B04C (1 ×)
MII-TXCLK B06A (1 ×)
MII-TXD(0) B04C (1 ×)
MII-TXD(0) B06A (1 ×)
MII-TXD(1) B04C (1 ×)
MII-TXD(1) B06A (1 ×)
MII-TXD(2) B04C (1 ×)
MII-TXD(2) B06A (1 ×)
MII-TXD(3) B04C (1 ×)
MII-TXD(3) B06A (1 ×)
MII-TXEN B04C (1 ×)
MII-TXEN B06A (1 ×)
MUTE B03 (2 ×)
MUTE B06D (1 ×)
MUTE_C B03 (1 ×)
MUTE_C B06C (1 ×)
MUTE_M B03 (1 ×)
MUTE_M B06B (1 ×)
MUTEn B03 (1 ×)
MUTEn B04A (1 ×)
NAND_PALE B04C (2 ×)
NAND_PARB B04C (2 ×)
NAND_PCLE B04C (2 ×)
NAND_PDD(0) B04C (3 ×)
NAND_PDD(1) B04C (3 ×)
NAND_PDD(2) B04C (2 ×)
NAND_PDD(3) B04C (2 ×)
NAND_PDD(4) B04C (2 ×)
NAND_PDD(5) B04C (2 ×)
NAND_PDD(6) B04C (2 ×)
NAND_PDD(7) B04C (2 ×)
NAND_POCE B04C (2 ×)
NAND_POOE B04C (3 ×)
NAND_POWE B04C (2 ×)
OFF_MUTE B03 (1 ×)
OFF_MUTE B06B (1 ×)
PB0P B06B (1 ×)
PB0P B06C (1 ×)
PB0P-SC1 B06C (1 ×)
PB1P B06B (1 ×)
PBR0N B06B (1 ×)
PBR0N B06C (1 ×)
PBR1N B06B (1 ×)
PBS_I2C_SCL B04C (1 ×)
PBS_I2C_SCL B07 (1 ×)
PBS_SPI_CLK B04C (1 ×)
PBS_SPI_CLK B07 (1 ×)
PBS_SPI_DI B04C (1 ×)
PBS_SPI_DI B07 (1 ×)
PBS_SPI_DO B04C (1 ×)
PBS_SPI_DO B07 (1 ×)
PGA0OUTL-
SC1 B06C (1 ×)
PGA0OUTR-SC1 B06C (1 ×)
POWER_DOWN B03 (1 ×)
POWER_DOWN B04A (1 ×)
POWER-OK B01 (1 ×)
POWER-OK B06D (1 ×)
PR0P B06B (1 ×)
PR0P B06C (1 ×)
PR0P-SC1 B06C (1 ×)
PR1P B06B (1 ×)
PWM_DIMMING B01 (1 ×)
PWM_DIMMING B04C (1 ×)
R_MON_OUT B06B (2 ×)
R_MON_OUT B06C (1 ×)
R_MON_OUT B06D (1 ×)
RC1 B04C (1 ×)
RC1 B06D (1 ×)
RC1 B07 (2 ×)
RC2 B04C (1 ×)
RC2 B06D (1 ×)
RC2 B07 (1 ×)
RF_SW B02A (1 ×)
RF_SW B04C (1 ×)
RJLED_G B06A (1 ×)
RJLED_Y B06A (1 ×)
RN B06B (1 ×)
RN B06E (1 ×)
RP B06B (1 ×)
RP B06E (1 ×)
RX0- B05 (1 ×)
RX0+ B05 (1 ×)
RX1- B05 (1 ×)
RX1+ B05 (1 ×)
RX2- B05 (1 ×)
RX2+ B05 (1 ×)
RXC- B05 (1 ×)
RXC+ B05 (1 ×)
S0Y1 B06B (1 ×)
SAV_L_IN B06B (1 ×)
SAV_L_IN B06D (2 ×)
SAV_R_IN B06B (1 ×)
SAV_R_IN B06D (2 ×)
SC0 B06B (1 ×)
SC0 B06D (2 ×)
SC1_AOUTL B07 (1 ×)
SC1_AOUTR B07 (1 ×)
SC1_B B06C (1 ×)
SC1_B B07 (1 ×)
SC1_CVBS_OUT B06C (1 ×)
SC1_CVBS_OUT B07 (2 ×)
SC1_FB B06B (1 ×)
SC1_FB B07 (1 ×)
SC1_G B06C (1 ×)
SC1_G B07 (1 ×)
SC2_CVBS_OUT B06B (1 ×)
SC2_CVBS_OUT B06C (1 ×)
SC2_CVBS_OUT B06D (1 ×)
SCART_CVBS0 B06B (1 ×)
SCART_CVBS0 B06C (1 ×)
SCART_CVBS1 B06B (1 ×)
SCART_CVBS1 B06C (1 ×)
SCL B04C (3 ×)
SCL B04D (1 ×)
SCL B05 (1 ×)
SCL B07 (1 ×)
SDA B04C (3 ×)
SDA B04D (1 ×)
SDA B05 (1 ×)
SDA B07 (1 ×)
SENSE+1V0_MT5392 B01 (1 ×)
SENSE+1V0_MT5392 B04A (2 ×)
SERIAL_POCE B04C (2 ×)
SIF_OUT B02A (1 ×)
SIF_OUT B06B (1 ×)
SIF_OUT_1 B02A (2 ×)
SIF_OUT_GND B02A (1 ×)
SIF_OUT_GND B06B (1 ×)
SOG B06B (1 ×)
SOG B06E (1 ×)
SOY0 B06B (1 ×)
SOY0 B06C (1 ×)
SPB1P B06B (1 ×)
SPB1P B06C (1 ×)
SPB1P_1 B06B (1 ×)
SPB1P_1 B06C (2 ×)
SPDIF_IN B04C (1 ×)
SPDIF_IN B05 (1 ×)
SPR1P B06B (1 ×)
SPR1P B06C (1 ×)
SPR1P_1 B06B (1 ×)
SPR1P_1 B06C (2 ×)
STANDBY B01 (1 ×)
STANDBY B04A (1 ×)
STANDBY B07 (1 ×)
STANDBYn B03 (1 ×)
STANDBYn B04A (1 ×)
SW_MUTE B03 (1 ×)
SW_MUTE B04A (1 ×)
SY0 B06B (1 ×)
SY0 B06D (1 ×)
SY1P B06B (1 ×)
SY1P B06C (1 ×)
SY1P_1 B06B (1 ×)
SY1P_1 B06C (2 ×)
TPIM B06A (2 ×)
TPIP B06A (2 ×)
TPOM B06A (2 ×)
TPOP B06A (2 ×)
TSO_CLK B02A (1 ×)
TSO_CLK B04A (1 ×)
TSO_DATA0 B02A (1 ×)
TSO_DATA0 B04A (1 ×)
T
SO_SYNC B02A (1 ×)
TSO_SYNC B04A (1 ×)
TSO_VALID B02A (1 ×)
TSO_VALID B04A (1 ×)
TUNER_SCL B02A (2 ×)
TUNER_SDA B02A (2 ×)
UART_RX B04C (3 ×)
UART_TX B04C (3 ×)
USB_OC B04C (1 ×)
USB_OC B06D (1 ×)
USB_PWE B04C (1 ×)
USB_PWE B06D (1 ×)
VDD B03 (2 ×)
VDDA B03 (2 ×)
VDDO_3V3 B05 (3 ×)
VSYNC B06B (1 ×)
VSYNC B06C (1 ×)
VSYNC B06E (1 ×)
Y0N B06B (1 ×)
Y0N B06C (1 ×)
Y0P B06B (1 ×)
Y0P B06C (1 ×)
Y0P-SC1 B06C (1 ×)
Y1N B06B (1 ×)
Y1P B06B (1 ×)
Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
EN 73LC9.2L LA 10.
2010-Jul-01
Page 74

Layout Small Signal Board
1G51
29012902
1901
1902
1903
1904
1905
1906
1907
1908
1909
1910
1G50
1911
1912
2919
6912
1H16
1B08
1M20
2136
6915
3917
3916
3912
5911
2717
2719
2720
2722
2727
2728
2729
1922
1924
1925
1923
6914
5910
5912
7911
3914
3913
2916
3915
6913
7910
2713
2714
2716
3731
7702
3730
2731
2732
2747
6103 6122
1927
1926
1928
2749
2712
2735
26A5
1929
2904
1930
1931
1932
1933
2711
2710
2611
2618
2620
2621
2622
3718
3711
3724
2736
2737
2740
2738
2626
2833
2834
2140
5104
7116
7103
7117
3542
2544
2547
2552
2546
2534
2528
2541
3532
1502
5115
2103
5101
5116
21592170
2545
2509
2531
3537
2536
2533
7510
2529
2530
3534
2527
2500
2501
2508
2131
5103
1M951M99
5107
2555
1735
2554
1736
2107
7100
2106
2150
5100
5108
5117
2158
2129
6123 6124
2516
3513
2511
5505
5503
1D14
Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
1M59
7701
7602
38A638A7
3600
3601
38A5
5A10
2A12 2A13
2A14
3A183A19
5NA1
3A12 3A13
2903
2NA1
2NA6
2D10
2D15
2D21
2E25
2E32
2E39
2E46
38A8
3D10
3D19
3D14
3E23
3E42
3E55
3E35
2D11
2D17
2D30
2G26
2G23
2G13
2G19
2E28
2E35
2E43
3D16
3D22
3D12
3G13
3G27
3G223G23
3G24
3E26
3E46
3E38
2G16
2G17
2G29
3G28
3G25
3608
2G27
3G30
3G20
3G18
3G29
3G31
3G19
3G21
3602
3G10
2G18
2G10
3G14
5G15
5G16
5G14
1818
2268
5223
2266
7814
3826
3829
2822
3838
38303831
2D64
2D62
2E86
2E82
2267
7201
7D11
3D50 3D51
2E83
3E93
2E87
3E97
7217
2274
5224
2275
3281
3282
5NA2
5812
2813
389J
3832
7812
2823
3839
3629
26A6
38133818
3893
3894
3833
2F43
36063607
3627 3628
2D69
2D68
3E17
2E84
3E10
2E80
2D63
2D61
2B29 2B48
3B22
3E96
1B10
3E92
2D18
2D19
2D16
2D12
3D53
4F00
2F14
3F16
3EA3
2E89
2D31
3D29
2F10
3F10
4F01
2F12
3F13
3EA2
2E88
3D54
2D67
3F19
3F48
3F49
2E48
3E54
3F23
3E59
1G16
2G21
3G37
2G24
5G13
3G15
6G13
6G16
3G26
7G11
3G16
2G22
3G32
3G33
2G25
7G12
3G38
3G34
4G15
2G14
3G35
4H11
4H13
4H12
4H10
2H12
2H13
2H14
2H28
3H20
3H21
2H27
3536
3H22
2H15
3538
2H29
1H12
3H23
3H24
2550
3535
2567
3533
2566
3558
2H22
2H21
2H19
2H20
2502
1E17 1E19
1H11
1H14
1E35
1D04
2282
6201
2D55
3D46
1B06
3D44
2D59
3D49
2D58
2D35
3D48
2D39
3D32
2D37
6D13
1D01
1B02
1B07
1205
2D49
2D48
3D25
3D27
7D10
6D11
6D15
1D19
1D25
3D45
3D30
1D13
6D10
1D11
3D23
3D24
2D71
1D24
2D27
4B02
4B01
2D57
2D54
2D33
3D43
3D47
3D26
2D56
2D34
1D03
5NA3
2D38
9NA2
2NAC
2NAA
2NAB
3NAE
3NAD
1NA1
7B05
1B04
4B04
4B03
1B03
3D55
2D74
2D73
6D22
1D22
2NAD
2B17
3B19
3B20
3B54
3B68
3B71
3B70
3B69
4B114B164B17
5D05
3B55
3B59
2D72
3D56
2F19
3B52
3B53
6B06
3H16
3H17
3B46
3B47
3B50
3B51
3B57
3B56
2F36
2F37
2F38
3F45
3F44
2F39
3F47
2F40
2F41
2D47
5F14
5F15
2F42
3F21
2F23
6F12
2F15
3F31
2D46
3F11
6F10
1F10
2F11
3F29
2F21
1F11
6F11
3F14
2F13
3F30
2F22
1817
1H13
2F17
1B01
EN 74LC9.2L LA 10.
1M36
1F14
1F12
1F22
1812
1F21
1B05
1813
1F18
F924
F927
F926
F915
F921
F920
IF18
IF19
2F24
3F38
3F32
3F42
2F33
FF14
1F16
2F16
6F20
3F43
IF20
2F25
3F33
2F32
3F37
FF18
3F46
2F18
1F19
6F13
FF20
FF37
FF30
FF31
FF32
FF33
FF34
FF35
FF36
FF13
FF27
FF11
FF10
FF26
3856
3863
3872
3873
3888
3889
F856
FF19
FF17
FB32
FB28
FB29
3B48
FB30
FB31
3B49
FB33
F847
F848
F849
IF21
7216
F201
3276
3277
F202
3278
3279
2272
2264
2265
2273
I597
3555
I535
3554
F525
3D42
3525
3552
3553
7515
I599
7505
3524
2512
2510
3516
7503
I523
F524
3D41
3511
IF16
3236
3280
3235
3254
I239
2240
3255
F227
3256
F260
I248
IF10
I231
F228
IF12
2F35
3F26
I814
FF23
FF38
3F35
3F41
2F30
FF24
6F19
2F29
2F31
2F28
3F36
FF25
1F23 1F24
6F18
3852
3851
3871
F853
I850
3890
I849
3891
F855
5H10
FH14
FH15
FH16
FH17
5H11
FF15
FF21
FF29
6F15
5F13
6F17
3F27
IF23
3F25
3F24
IF22
3F28
1F02 1F03
6F16
3B65
2F20
FF16
1F01
2B24
IB10
IB09
3B663B67
2B26
IB16
IB14
7B06
FB10
3B44
7B09
3B43
18111814
6813
3868
3864
3865
FB18
FB16
3869
4B18
6812
4B34
3274
3273
7213
3234
2235
2241
2242
5217
7F01
2B16
3B39
FB24
FB20
I232
I233
I230
F215
I235
I234
I237
I228
I242
A213
I250
A212
I241
F229
F230
I218
I222
ID14
2B11
IB02
FH27
FD24
INAS
FNA7
FNA9
FNA5
FNA4
FNA6
FNA8
FNAA
FNAB
3810
3811
FB21
5B01
3B38
3B64
FB11
IB12
F868
3B45
3B11
2B25
IB11
FB47
3B63
3B33
3B40
3B58
3B41
6B07
2B51
2B50
FG16
IB03
3B62
3B76
FB07
3B60
3B10
3B73
3B72
7B07
3B34
3B61
3B35
FB08
FB57
FB09
4B40
3B75
7B02
FB23
3B37
FB27
1B13
1B11
1B12
1B14
4B35
4B36
F203
5225
2276
2277
I212
I215
2280
2288
I216
I210
F205
3263
F214
3264
3268
2252
5221
I247
3246
3247
2286
F241
F242
F243
F244
F246
A214
2285
5227
A210
A211
F216F217
ID30
ID43
ID31
ID35
ID34
FD12
FB22
FB19
FB17
3B32
7B03
FB42
FB38
3B36
4B39
FB37
4B38
7B04
FB45
F206
5222
I253
I252
F207
5226
F236
F240
2284
F208
I226
F209
F245
I244
F210
2287
ID37
ID32
ID38
FD26
FD29
FD25
FD27
1D17
FD23
FB25
FB26
FB40
4B37
IE29
6E32
2E54
FB44
I853
389D
F859
F864
389F
38A4
38A3
I261
A259
F250
F251
2278
F213
2279
F234
F204
F235
F255
F256
3265
3267
F257
3266
F252
3258
3270
A258
F211
2270
3257
3271
2271
F237
F832
ID42
ID36
FE51
4E07
FE50
4E06
2E58
3E71
2E24
FE18
IE18
3E67
2E16
6E30
F218
F219
I214
F829
F826
F860
I829
A225
C002
4820
F831
I562
F836
FF28
1E01
FE47
6E02
5E13
5E14
2E04
3E06
FE48
6E03
2E05
3E08
1E02
IE89
IE99
FE49
6E04
1E03
5E17
FF12
IE25
FD28
IE16
2E53
1E18
FE14
ID13
2D28
5D00
FE15
1E13
FNAD
I213
2NA4
3NA4
2NA3
9NA3
INAZ
FNAF
3NA2
4800
INAW
F825
INAV
3NAB
3NAC
FNAE
FNAC
5
F83
F862
3866
3874
2697
5610
I637
2693
FA20
38A1
3846
FE11
26A3
2D65
2685
2D66
IB04
2691
2692
IB01
5608
2671
2D60
2681
2672
3877
3876
2835
3F22
2689
2690
2836
5607
6814
6810
3857
2827
3861
7820
I843
4G12
4G14
FG18
FH18
2E02
3E01
3E03
2E03
4E13
3E02
4E09
3E04
FE26
4E08
4E12
4E10
4E11
3EA8
3D58
3EA4
3EA9
3D57
3EA5
3EA6
3D59
3EA7
IE01
3E07
2E07
2E71
2E06
3E12
3E79
IE24
3E57
2E47
2E23
FE35
IE26
3E70
2E57
3E66
2E14
4D00
3D28
2D70
ID12
6D09
1D08
3A17
1NA2
2NA2
3NA5
7NA1
INAY
INAU
INAT
2NA7
3NB5
3NAA
3NA6
3NA7
3NA9
3NA8
2664
2680
2662
F614
2696
2667
2695
I636
2694
5609
I631
26A2
I632
5603
5604
2676
2684
2670
2654
2683
I623
3B24
2682
2669
2674
5B07
IF14
5600
3F39
FB51
2F34
I618
2642
26A4
2652
2658
2659
F843
2686
I633
5605
6G17
1G15
1G14
3G11
5G11
2G11
FG17
4G11
IG01
4G13
FE36
1E20
FE38
1E24
FE39
1E26
1E14
FE32
1E10
3NB3
2647
2651
6G15
FG11 FG12
6E10
6E14
IE56
IE72 IE78
5E19
6E26
6E28
FA13FA14FA15 FA16
FA19
FA17FA18
2A10
3A10
3A14
5A14
3A15
2A11
3A11
5A16
3A16
3NB1
3NAM
3NAN
3NB2
3NAP
3NAR
2NA5
2NAE2NAF
3NAQ
3NAT
3NAV
3NAU
3NAW
3NAY
INAP
3NAJ
3NAH
3NAK
INAQ
3NAL
2NA9
3NB4
4806
4817
4815
4814
4813
4812
4816
4819
INAR
3NA3
4805
4818
4804
4807
4808
4809
2NA8
4811
4810
4803
4802
3883
I827
4102
3882
2628
2619
2663
2624
2660
2675
2646
2678
2679
2648
2609
2634
F134
2653
2673
2668
26A1
2617
2623
2601
2605
2630
2631
2602
2635
2639
26322633
2610
2644
2649
3603
3618
FG13FG14FG15
1G13
6G11
IG02
2603
2616
2725
2726
2640
2637
2743
5713
I714
3713
2612
2641
2746
2636
2629
3720
3716
2615
2608
2638
CXXX
2645
2613
2614
2643
2625
2627
2699
2604
2606
2677
F612
FB52
2687
2650
2688
I617
2655
2656
2661
2665
2666
2657
F613
4822
3610
3612
3613
5606
I614
3604
3609
3619
3625
3626
3F40
5601
5602
I813
I616
3617
I812
3611
3823
3892
3812
3814
4601
4603
3614
4602
3605
3615
F837
38A9
2837
6G14
FG19
1G11
1G12
FG20
3G12
5G12
2G12
6G12
F931
F930
F934
F933
F932
2811
I810
5810
2810
F813
389G
I841
F811
3821
389C
2826
3847
3850
I840
I842
38A2
I839
3858
3848
7816
3878
6811
3859
3880
3881
389L
389K
I825
2607
2754
2600
26A0
IF24
I852
2739
2751
F865
F867
389H
3717
3722
389I
I117
2165
I119
3134
I118
I123
3129
2139
2144
F131
2166
3139
F611
2104
2105
I128
3136
2157
I135
3131
F133
3122
2155
2164
F538
I544
F616
FH19
FH20
FH23
IE13
FH24
2E26
2H25
3E24
FH25
3E81
FH26
5E12
2E59
IE42
3E27
IE34
5E15
2H26
IE14
2E33
3E36
3E73
2E63
3E47
2E65
3E75
2E40
2H24
3E43
2H23
5E16
2E50
6E16
3E56
IE20
2E70
2E69
IE17
2E18
3E94
IE21
2E55
3E68
IE95
IE96
7E02
3EA0
3E99
IE11
2E51
3E64
5D01
FD14
3D52
2D14
2D50
3D11
3D13
2E10
3E90
FD13
3621
I543
3527
2513
I546
6600
7605
3622
FH22
2698
I629
3624
I630
3623
FH21
5H12
F615
I575
6601
I577
F579
I578
I563
2539
2515
F540
2540
3530
3540
F536
2549
2532
I572
I573
F569
3502
I568
F545
3509
F541
3562
I526
7518
FH11
2568
3565
I527
I525
3564
3500
7519
2569
F548
3559
F512
F515
3501
F516
I511
2503
7500
F518
3507 3508
I512
6D12
1D15
FD22
3526
3529
3528
I552
7506
F535
7507
I580
I581
I589
F547
F593
3563
7102
3560
3561
I516
I515
I510
I513
FH30
2D51
3D17
5D02
6D14
2D20
3D15
FD18
FD15
1D18 1D20
6503
I554
25222523
I587
F917
F928
F925
F916
F918
F922
F929
F923
F919
2921
7810
F812
F810
7822
F814
F841
2759
2760
2765
7703
3725
2755
2761
2757
21322133
I105
I122
2141
I120
I109
2108
2123
I127
I129
I132
2160
I130
3125
I584
3541
I586
I582
3531
3D18
FD17
2E49
3E60
I104
I108
I110
2168
I126
I134
I131
2542
I583
2543
I585
I590
I595
5502
I576
I570
I566
I565
2519
2518
I598
5D03
2D13
3D20
6D16
FD21
2D22
3D21
ID22
2142
3119
2153
2161
I588
I564
I571
2E72
3E78
F914
I816
3820
3816
I811
3897
3822
I913
2764
2766
2752
I107
3108
2138
2135
3106
F122
2102
3199
2101
2100
3171
3172
3173
I125
2152
2156
3130
2154
2559
F523
6500
4502
F522
3566
7516
35563557
3D36
ID25
2D25
F913
F912
F993 F994
F910
F911
3899
3898
I855
389B
389A
I819
I832
3834
3837
I834
F966
I912
I911
I914
2767
2742
3712
3710
2741
5712
5714
2750
3714
2745
3715
2762
2167
I106
I136
3109
2137
2134
3105
F125
6125
I124
3135
I102
6100
3103
3104
2163
3107
3138
6101
3140
2560
7501
I518
3510
I559
I519
3520
3519
6502
7504
3523
2565
I530
7517
F580
ID26
ID28
2D52
3D33
2D40
6D17
FD19
1D21
F970
F968
F971
F969
F974
5811
2812
I915
I910
4918
4910
4912
4911
4917
4916
2724
2756
2734
2768
2763
2715
2758
2753
F710
2127
2171
2125
I111
7101
I103
2128
F123
6102
F132
7508
3550
7513
I596
3512
I522
35143515
I524
3517
6501
3521
I521
I560
3D35
ID29
2D53
2D29
3D34
2D41
6D18
FD20
F972
F975
F973
F976
F977
F978
2920
F979
F980
F982
F981
F983
F984
F985
F987
F986
F990
F989
F991
2917
F988
F992
4913
4915
4914
FH36
FH35
FH34
FH33
FH32
FH31
F861
FB49
4B30
FB05
FB06
4B29
4B28
FB56
FB55
3885
3884
FB54
FB53
FB48
F828
5815
2815
I824
F827
3835
2816
3824
F824
I823
2817
3828
F823
5814
28182819
F822
I822
3827
F821
I821
5813
2820
F820
F819
I820
2821
3825
2113
F110
F124
2112
F109
F108
2169
2114
F107
2115
F106
F105
F104
F103
F102
2110
F101
F100
2109
3100
2111
2162
F120
4101
I100
F119
2119
4100
F118
2118
F117
5102
F116
2824
3841
I833
3840
F115
7815
F114
3845
3879
I838
I835
3842
F113
2124
3102
21202121
2116
F112
3101
2122
F111
F550
F126
3548
7511
2553
5508
F546
3544
2561
F544
2537
2562
C051
2563
F543
2556
2564
3549
2524
F542
5507
F539
2520
2521
1D23
3139 123 6465.1
2010-Jul-01
18700_550_090818.eps
090821
 Loading...
Loading...