Page 1

16-Channel VoIP Gateway Card
Programming Guide
Model No. KX-TDA0490
Thank you for purchasing a Panasonic 16-Channel VoIP Gateway Card.
Please read this manual carefully before using this product and save this manual for future use.
Page 2

Table of Contents
1 IP-GW16 Maintenance Utility .................................................................3
1.1 Starting the IP-GW16 Maintenance Utility.......................................................................4
2 Administrator Functions........................................................................ 7
2.1 Main Menu for the Administrator.....................................................................................8
2.2 Programming................................................................................................................... 10
2.2.1 Network Parameters .........................................................................................................10
2.2.2 H.323 Parameters .............................................................................................................14
2.2.3 Voice Communication Parameters.................................................................................... 18
2.2.4 VoIP Gateway/IP-PBX Interface Parameters....................................................................26
2.2.5 Hunt Pattern Parameters .................................................................................................. 28
2.2.6 Address Translation Table—GW Entry ............................................................................. 34
2.2.7 Address Translation Table—DN2IP Entry ......................................................................... 37
2.2.8 Initialization .......................................................................................................................41
2.3 Maintenance ....................................................................................................................42
2.3.1 Status Control.................................................................................................................... 42
2.3.2 Maintenance Settings .......................................................................................................43
2.3.3 Diagnosis ..........................................................................................................................46
2.3.4 Log Information .................................................................................................................47
2.4 Data Management ........................................................................................................... 48
2.4.1 Upload of Configuration Data............................................................................................48
2.4.2 Download of Configuration Data ....................................................................................... 50
2.4.3 Upload of Address Translation Table ................................................................................ 51
2.4.4 Download of Address Translation Table............................................................................ 53
2.5 Others ..............................................................................................................................54
2.5.1 Reboot ..............................................................................................................................54
2.5.2 Log Out .............................................................................................................................55
3 Installer Functions................................................................................ 57
3.1 Main Menu for the Installer.............................................................................................58
3.2 Maintenance ....................................................................................................................59
3.2.1 Status Control.................................................................................................................... 59
3.2.2 Maintenance Settings .......................................................................................................60
3.3 Data Management ........................................................................................................... 62
3.3.1 Upload of Firmware Data .................................................................................................. 62
3.3.2 Handling of Firmware Page...............................................................................................65
3.4 Others ..............................................................................................................................67
3.4.1 Reboot ..............................................................................................................................67
3.4.2 Log Out .............................................................................................................................68
Index ............................................................................................................ 69
2 Programming Guide
Page 3

Section 1
IP-GW16 Maintenance Utility
Programming of the VoIP Gateway Card is carried out through
a web programming utility called the IP-GW16 Maintenance
Utility. This section provides the start-up procedure for the IPGW16 Maintenance Utility.
Programming Guide 3
Page 4
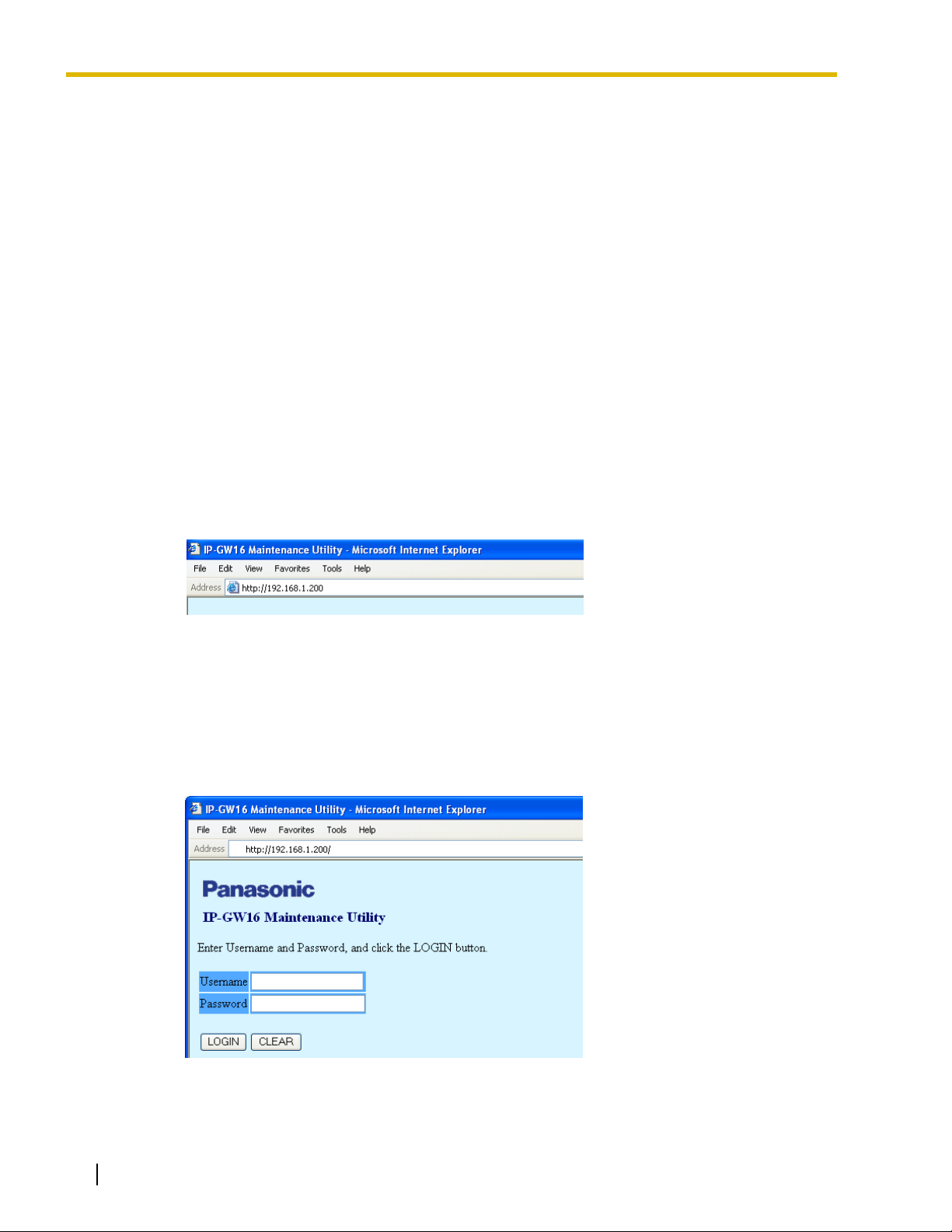
1.1 Starting the IP-GW16 Maintenance Utility
1.1 Starting the IP-GW16 Maintenance Utility
There are 2 different log-in levels to the IP-GW16 Maintenance Utility, a web programming utility for
the VoIP Gateway Card: Administrator level and Installer level. These levels provide different
programming options.
For full discussions of Administrator-level programming and Installer-level programming, refer to "2
Administrator Functions" and "3 Installer Functions", respectively.
System Requirements
• The IP-GW16 Maintenance Utility requires Microsoft® Internet Explorer 5.0 or above.
Trademarks
• Microsoft is either a registered trademark or trademark of Microsoft Corporation in the
United States and/or other countries.
• All other trademarks identified herein are the property of their respective owners.
• Screen shots reprinted with permission from Microsoft Corporation.
1. Run Internet Explorer from the Start menu.
2. In the Address box of Internet Explorer, type http://192.168.1.200.
192.168.1.200 is the default IP address of the VoIP Gateway Card.
3. Press the ENTER key on the keyboard.
4. In the Username box, type the user name.
• Default Administrator-level user name: Administrator
• Default Installer-level user name: Installer
5. In the Password box, type the password.
• Default Administrator-level password: Administrator
• Default Installer-level password: Installer
6. Click LOGIN.
To clear your entry, click CLEAR.
4 Programming Guide
Page 5

1.1 Starting the IP-GW16 Maintenance Utility
Notes
• If another user is already logged in, you will be rejected.
• For readability of the text on the screen, it is recommended that you adjust the text size
of Internet Explorer to below medium.
• If you finish a programming session without logging out from the card (e.g., quitting
Internet Explorer, or returning to the log-in screen with the "Back" button of Internet
Explorer), you cannot log in again for the period of time specified by the parameter
Programming Auto Disconnect Time (default: 10 min).
For the log-out procedure and Programming Auto Disconnect Time setting, refer to
"2.5.2 Log Out"/"3.4.2 Log Out" and "2.3.2 Maintenance Settings", respectively.
Programming Guide 5
Page 6

1.1 Starting the IP-GW16 Maintenance Utility
6 Programming Guide
Page 7

Section 2
Administrator Functions
This section provides operating instructions for the IP-GW16
Maintenance Utility when logged in as the Administrator.
Programming Guide 7
Page 8
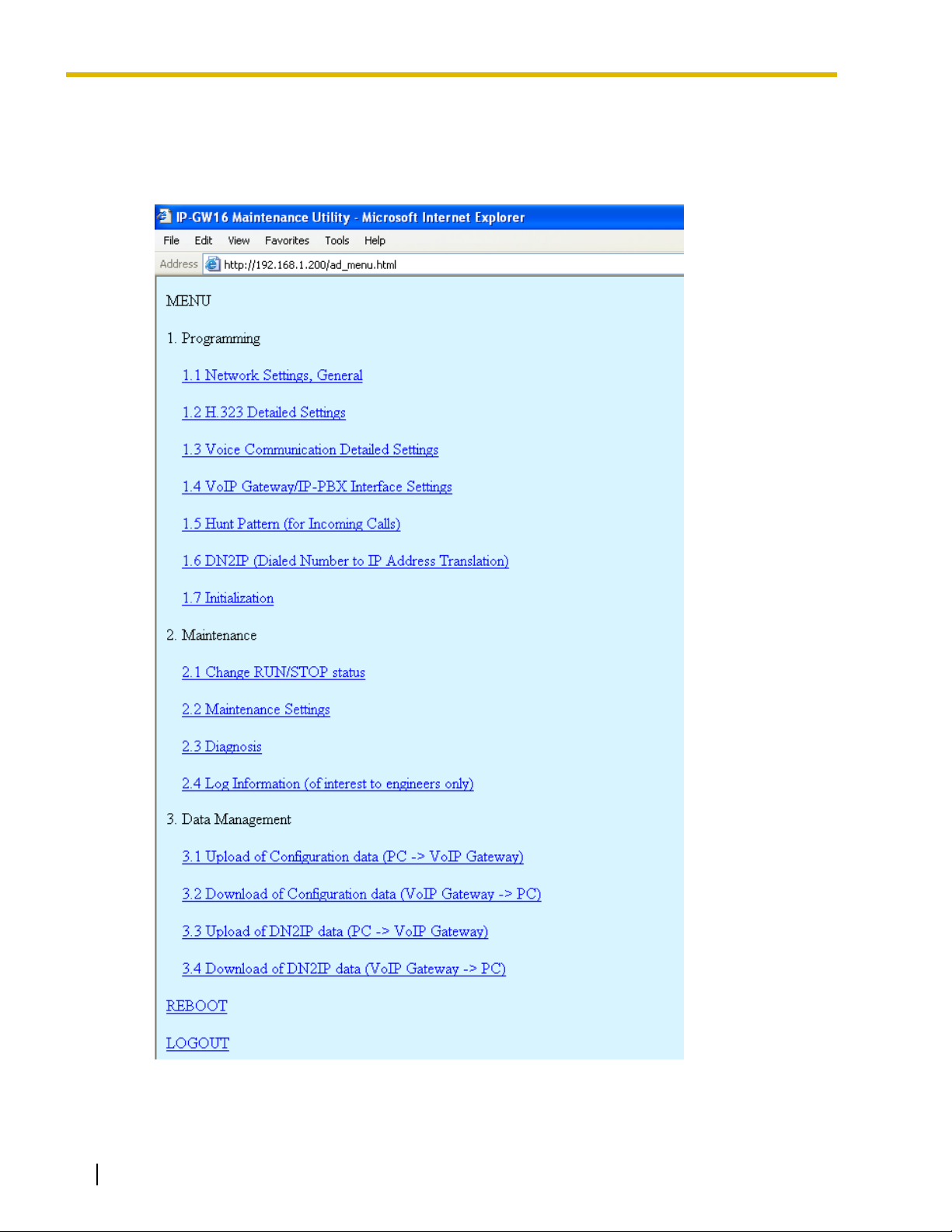
2.1 Main Menu for the Administrator
2.1 Main Menu for the Administrator
The IP-GW16 Maintenance Utility provides the following menu to a user logged in as the
Administrator.
8 Programming Guide
Page 9

Programming
Menu Section Reference
1.1 Network Settings, General 2.2.1 Network Parameters
1.2 H.323 Detailed Settings 2.2.2 H.323 Parameters
1.3 Voice Communication Detailed Settings 2.2.3 Voice Communication Parameters
1.4 VoIP Gateway/IP-PBX Interface Settings 2.2.4 VoIP Gateway/IP-PBX Interface Parameters
1.5 Hunt Pattern (for Incoming Calls) 2.2.5 Hunt Pattern Parameters
2.1 Main Menu for the Administrator
1.6 DN2IP (Dialed Number to IP Address
Translation)
1.7 Initialization 2.2.8 Initialization
Maintenance
Menu Section Reference
2.1 Change RUN/STOP status 2.3.1 Status Control
2.2 Maintenance Settings 2.3.2 Maintenance Settings
2.3 Diagnosis 2.3.3 Diagnosis
2.4 Log Information 2.3.4 Log Information
Data Management
Menu Section Reference
3.1 Upload of Configuration data (PC → VoIP
Gateway)
3.2 Download of Configuration data (VoIP
Gateway → PC)
2.2.6 Address Translation Table—GW Entry
2.2.7 Address Translation Table—DN2IP Entry
2.4.1 Upload of Configuration Data
2.4.2 Download of Configuration Data
Others
3.3 Upload of DN2IP data (PC → VoIP
Gateway)
3.4 Download of DN2IP data (VoIP Gateway
→ PC)
Menu Section Reference
REBOOT 2.5.1 Reboot
LOGOUT 2.5.2 Log Out
2.4.3 Upload of Address Translation Table
2.4.4 Download of Address Translation Table
Programming Guide 9
Page 10
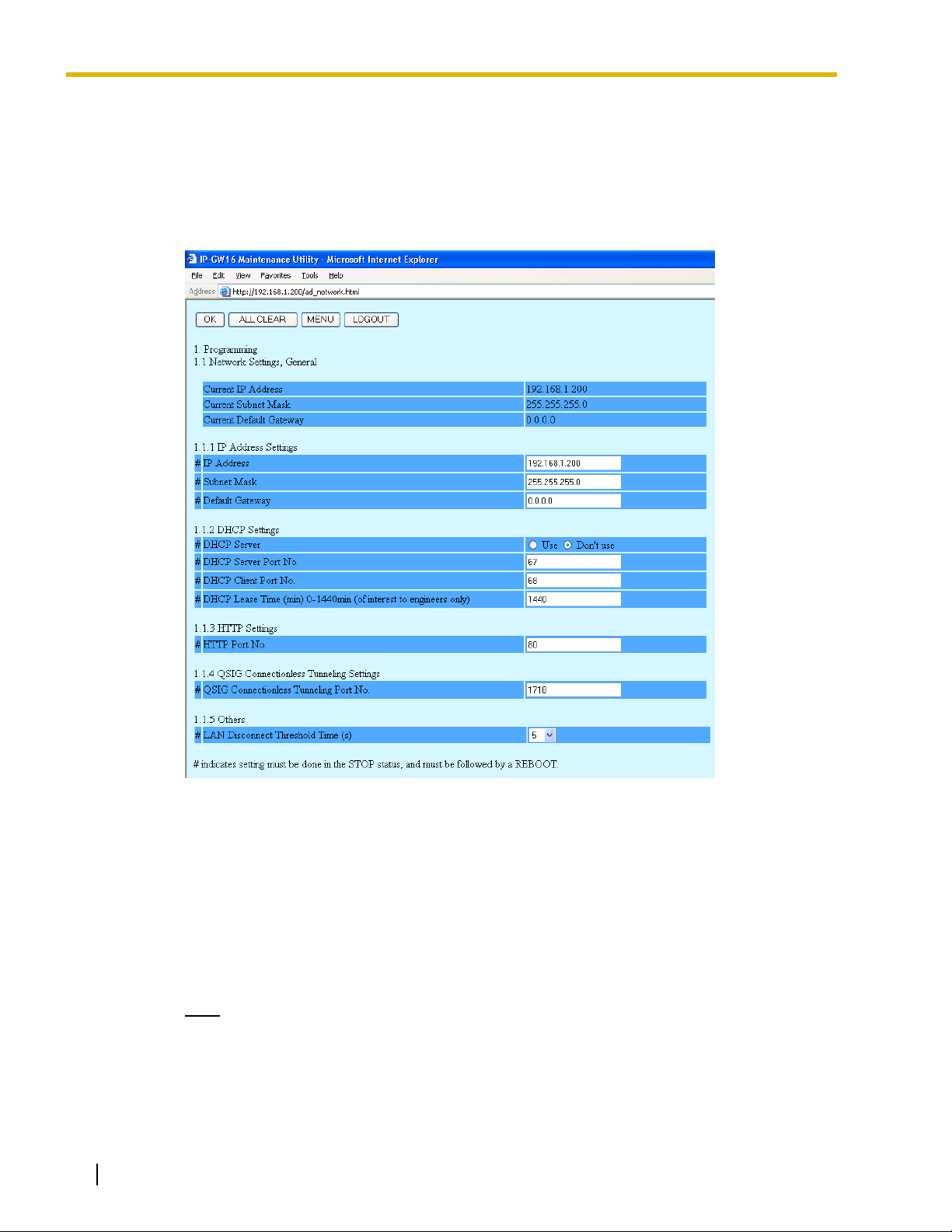
2.2 Programming
2.2 Programming
2.2.1 Network Parameters
1. Click 1.1 Network Settings, General in the main menu.
Current IP Address, Current Subnet Mask, and Current Default Gateway show the current
IP address settings of the VoIP Gateway Card.
2. Assign each parameter referring to the descriptions below.
At any time during the session, you can:
• Click ALL CLEAR to return all parameters to their previous values.
• Click MENU to return to the main menu (see "2.1 Main Menu for the Administrator").
• Click LOGOUT to log out from the IP-GW16 Maintenance Utility (see "2.5.2 Log Out").
3. Click OK.
You will see a confirmation screen.
Note
4. Confirm your entry and click OK.
To return to the previous screen, click CANCEL.
10 Programming Guide
If your entry contains an invalid value, you will be prompted to correct your input. Enter
correct values for the parameters shown in red and try again.
Page 11

2.2 Programming
Parameter Descriptions
The parameters indicated with "#" must be changed while the card is in the "STOP" status (see "2.3.1 Status
Control"). The changes must be followed by a reboot to become effective (see "2.5.1 Reboot").
IP Address Settings
Parameter & Description Default Value Range
#
IP Address
Specifies the IP address of the card.
For more information, consult your network administrator.
#
Subnet Mask
Specifies the subnet mask address of the card.
For more information, consult your network administrator.
#
Default Gateway
Specifies the default gateway IP address of the card.
For more information, consult your network administrator.
192.168.1.200 The following addresses
are invalid:
• Class D addresses
• Class E addresses
• Loopback
addresses
• Addresses with
host number all 0s
or 1s
255.255.255.0 Any address is valid.
0.0.0.0 Same as the parameter
IP Address, except that
the address 0.0.0.0. is
allowed.
DHCP Settings
Parameter & Description Default Value Range
#
DHCP Server
Specifies the use of a DHCP server.
For details, refer to "Detailed Explanations".
#
DHCP Server Port No.
Specifies the port number for DHCP communications by the
DHCP server.
Generally, there is no need to change the default value.
#
DHCP Client Port No.
Specifies the port number for DHCP communications by the
card (the DHCP client).
Generally, there is no need to change the default value.
#
DHCP Lease Time (min) 1-1440min
This parameter is provided for engineer use only.
Don't use Use,
Don't use
67 1 to 65535
68 1 to 65535
1440 0 (disable),
1 to 1440
Programming Guide 11
Page 12

2.2 Programming
HTTP Settings
Parameter & Description Default Value Range
#
HTTP Port No.
Specifies the port number for HTTP communications by the
card.
Generally, there is no need to change the default value.
80 1 to 65535
QSIG Connectionless Tunneling Settings
Parameter & Description Default Value Range
#
QSIG Connectionless Tunneling Port No.
Specifies the port number for connectionless tunneling
between cards at different locations in a QSIG network.
Generally, there is no need to change the default value.
Notes
• Connectionless tunneling enables the PBXs on a
QSIG network to use enhanced networking
features. (For more information about these
features, refer to the relevant sections of the Hybrid
IP-PBX documentation.)
• If you are using a gatekeeper, and "Routed" is
specified for the parameter Call Signaling Model
(see "2.2.2 H.323 Parameters"), connectionless
tunneling is not possible. In this case, the PBX
cannot use the enhanced networking features.
1718 1 to 65535
Others
Parameter & Description Default Value Range
#
LAN Disconnect Threshold Time (s)
Specifies the time (in seconds) until disconnection from the
LAN is recognized.
For example, even if a LAN cable is disconnected during a
call, reconnecting the cable within this time period maintains
the call.
5 1 to 10
Detailed Explanations
DHCP Server
When using the DHCP feature, the IP address settings of the card (IP address, subnet mask, and
default gateway) will be assigned by a DHCP server.
However, keep in mind that the maintenance of the card is performed through a web browser from a
PC; hence you must know the IP address of the card. Therefore, it is necessary to set up the DHCP
12 Programming Guide
Page 13

2.2 Programming
server to assign a static IP address to the card from a pool of IP addresses that is defined in advance.
For more information about DHCP server settings, consult your network administrator.
In addition, it is also necessary to specify the values for the parameters under IP Address Settings
as they will be assigned by the DHCP server.
Programming Guide 13
Page 14

2.2 Programming
2.2.2 H.323 Parameters
1. Click 1.2 H.323 Detailed Settings in the main menu.
2. Assign each parameter referring to the descriptions below.
At any time during the session, you can:
• Click ALL CLEAR to return all parameters to their previous values.
• Click MENU to return to the main menu (see "2.1 Main Menu for the Administrator").
• Click LOGOUT to log out from the IP-GW16 Maintenance Utility (see "2.5.2 Log Out").
3. Click OK.
You will see a confirmation screen.
Note
4. Confirm your entry and click OK.
To return to the previous screen, click CANCEL.
14 Programming Guide
If your entry contains an invalid value, you will be prompted to correct your input. Enter
correct values for the parameters shown in red and try again.
Page 15

2.2 Programming
Parameter Descriptions
The parameters indicated with "#" must be changed while the VoIP Gateway Card is in the "STOP" status (see
"2.3.1 Status Control"). The changes must be followed by a reboot to become effective (see "2.5.1 Reboot").
The parameters indicated with "*" must be changed while the card is in the "STOP" status (see "2.3.1 Status
Control"). The changes do not have to be followed by a reboot to become effective.
Port No. Settings
Parameter & Description Default Value Range
#
H.225 Port No.
Specifies the port number for the H.225 protocol (call control)
in an H.323 protocol suite.
Generally, there is no need to change the default value.
#
H.245 Port No.
Specifies the port number for the H.245 protocol (negotiation
of channel usage and capabilities) in an H.323 protocol suite.
32 consecutive ports, starting with the specified port, will be
used (by default, 1721 to 1752).
Generally, there is no need to change the default value.
#
RAS Port No.
Specifies the port number for the H.225 protocol (RAS) in an
H.323 protocol suite.
Generally, there is no need to change the default value.
#
RTP/RTCP Port No.
Specifies the port number for RTP/RTCP. 64 consecutive
ports, starting with the specified port, will be used (by default,
5004 to 5067).
Generally, there is no need to change the default value.
1720 1 to 65535
1721 1 to 65504
1719 1 to 65535
5004 1 to 65472
Programming Guide 15
Page 16

2.2 Programming
Voice CODEC Settings
Parameter & Description Default Value Range
*
Voice CODEC Priority 1st–4th
Specifies the type of CODEC for voice communications.
Choose the appropriate CODEC for the network environment
(e.g., bandwidth, CODEC conditions of the remote terminal).
When using multiple CODECs, set them in an appropriate
priority order.
Prior to establishing a call, a negotiation takes place over the
network and the CODEC to be used will be decided
depending on the setting of this parameter.
For details about relations between bandwidth and CODEC,
refer to "Detailed Explanations" in "2.2.3 Voice
Communication Parameters".
Note
When the Fast Connect feature (see under "Others"
below) is disabled, the communicating cards must have
the same first priority CODEC set.
1st: G.729A
2nd: No default
3rd: No default
4th: No default
G.723.1,
G.729A,
G.711Mu,
G.711A
Gatekeeper Settings
Parameter & Description Default Value Range
#
Gatekeeper
Specifies the use of a gatekeeper.
For details, refer to "Detailed Explanations".
*
Primary Gatekeeper IP Address
Specifies the IP address of the primary gatekeeper.
*
Primary Gatekeeper Port No.
Specifies the port number of the primary gatekeeper.
*
Secondary Gatekeeper IP Address
Specifies the IP address of the secondary gatekeeper.
Set this parameter when setting up a secondary gatekeeper
as a redundant backup system.
*
Secondary Gatekeeper Port No.
Specifies the port number of the secondary gatekeeper.
Set this parameter when setting up a secondary gatekeeper
as a redundant backup system.
Don't use Use,
Don't use
192.168.1.3 The following addresses
are invalid:
• Class D addresses
• Class E addresses
• Loopback
addresses
1719 1 to 65535
192.168.1.4 The following addresses
are invalid:
• Class D addresses
• Class E addresses
• Loopback
addresses
1719 1 to 65535
16 Programming Guide
Page 17

2.2 Programming
Parameter & Description Default Value Range
*
Gatekeeper Connection Checking Interval (min) 01440min
Specifies the time (in minutes) between periodic checks of
connection to the gatekeeper.
When the primary gatekeeper fails, these checks can detect
the failure. In this case, the connection automatically
switches to the secondary gatekeeper if it is available, so that
the network remains functional.
*
Call Signaling Model
Specifies whether to carry out a call control (H.225) process
directly between the cards or through a gatekeeper.
Direct call control is typically preferred because it involves
less network load.
00 (disable),
1 to 1440
Direct Direct,
Routed (via
Gatekeeper)
Others
Parameter & Description Default Value Range
#
Fast Connect
Specifies the use of the Fast Connect feature.
Using Fast Connect simplifies the communication process so
that calls can be established quickly.
Generally, there is no need to change the default value.
Use Use,
Don't use
Detailed Explanations
Gatekeeper
The following are the general functions of a gatekeeper:
• Dialed number-to-IP address translation
• Authentication
• Bandwidth control
It is possible to employ a VoIP network without the use of a gatekeeper, because the card is equipped
with internal address translation capabilities. However, should the network contain dozens of cards,
maintenance of address translation tables in individual cards can become a strain.
A gatekeeper is useful in this case, because with the gatekeeper it is possible to consolidate the
maintenance. (However, you still need to program each card on the network with its own address
translation information. For details, refer to "2.2.6 Address Translation Table—GW Entry" and "2.2.7
Address Translation Table—DN2IP Entry".) For more information about gatekeeper functions,
consult the documentation of the gatekeeper.
When using a gatekeeper, make sure to choose a compatible model. For more information about
gatekeeper compatibility with the card, consult a certified dealer.
Programming Guide 17
Page 18

2.2 Programming
2.2.3 Voice Communication Parameters
1. Click 1.3 Voice Communication Detailed Settings in the main menu.
2. Assign each parameter referring to the descriptions below.
At any time during the session, you can:
• Click ALL CLEAR to return all parameters to their previous values.
• Click MENU to return to the main menu (see "2.1 Main Menu for the Administrator").
• Click LOGOUT to log out from the IP-GW16 Maintenance Utility (see "2.5.2 Log Out").
3. Click OK.
18 Programming Guide
Page 19
2.2 Programming
You will see a confirmation screen.
Note
If your entry contains an invalid value, you will be prompted to correct your input. Enter
correct values for the parameters shown in red and try again.
4. Confirm your entry and click OK.
To return to the previous screen, click CANCEL.
Parameter Descriptions
QoS Field Settings
The parameters below are used to set the ToS (Type of Service) field in the header of IP packets to control
QoS of VoIP communications.
For more information about QoS, refer to "A1.4 QoS (Quality of Service)" of the VoIP Gateway Card Getting
Started. For the actual setting values, consult your network administrator.
Parameter & Description Default Value Range
ToS
Specifies the value in the ToS field by a generic term.
For details, refer to "Detailed Explanations".
DSCP
Specifies the value in the ToS field by a DSCP for DiffServ.
HEX
Specifies the value in the ToS field by a hexadecimal number.
Priority: 0 0 to 7
Normal Normal,
Monetary Cost,
Reliability,
Throughput,
Delay
No default 0 to 63
No default 00 to FF
Jitter Buffer Settings
When voice signals are packetized and transmitted, individual packets can take different paths through the
network and arrive at the destination at varied timings. This is referred to as "jitter", and it can cause
degradation in speech quality. To compensate for jitter problems, the "jitter buffer" accumulates the packets
temporarily for processing.
The parameters below are used to adjust the size of the jitter buffer. However, in general, there is no need to
change the default values.
Jitter buffer Settings (G.711/G.729A/G.723.1 for Voice)
Parameter Default Value Range
Jitter Buffer Minimum (ms)
Jitter Buffer Maximum (ms)
Jitter Buffer Default (ms)
Jitter Buffer Recovery Start (ms)
Jitter Buffer Recovery Period (s)
20 10 × n (n = 2–10)
500 10 × n (n = 2–50)
20 10 × n (n = 2–10)
200 10 × n (n = 2–10)
10 1 to 20
Programming Guide 19
Page 20

2.2 Programming
Jitter buffer Settings (G.711 for Fax)
Parameter Default Value Range
Jitter Buffer Minimum (ms)
Jitter Buffer Maximum (ms)
50 10 × n (n = 4–10)
500 10 × n (n = 4–50)
CODEC Frame Settings
The parameters below are used to set the interval between packet transmissions for each type of CODEC. It
is recommended that all VoIP Gateway Cards in a VoIP network have the same settings for these parameters.
For details, refer to "Detailed Explanations".
Parameter Default Value Range
G.723.1 Packet Sending Interval (ms)
G.729A Packet Sending Interval (ms)
G.711 Packet Sending Interval (ms)
30 30, 60, 90
20 20, 30, 40, 60
20 20, 30, 40, 60
Echo Canceller Settings
Parameter & Description Default Value Range
Echo Canceller
Specifies the length of the echo canceller (in milliseconds)
when using the echo cancellation feature (G.168), or disables
the feature.
Echo is the audible duplication of a caller's voice on the return
path; when echo exists, the caller hears his or her own voice
after some delay. The echo canceller eliminates this echo.
Generally, the default length of 48 ms will suffice. However, if
an echo is still heard, it is recommended that you set the
length to 128 ms.
Note
There are various factors that may cause an echo. In
some cases, this feature does not eliminate the echo
entirely.
48 48, 128, Don't use
20 Programming Guide
Page 21

2.2 Programming
Gain Level Settings
The parameters below are used to adjust the gain level. However, in general, there is no need to change the
default values.
Parameter & Description Default Value Range
Gain Level PCM → LAN (dB)
Specifies the gain level (in decibels) output from the PBX,
through the card, to the LAN.
Gain Level LAN → PCM (dB)
Specifies the gain level (in decibels) output from the LAN,
through the card, to the PBX.
0 -14 to 6
0 -14 to 6
Voice Activity Detection (VAD) Settings
Parameter & Description Default Value Range
G.723.1/G.729A/G.711 VAD
Specifies the use of the VAD feature for each available
CODEC (G.723.1, G.729A, and G.711).
The VAD conserves bandwidth by detecting silent periods
during a call and suppressing the packets of silence from
being sent to the network.
Notes
• To use the VAD feature for a certain CODEC, be
sure to enable it for that CODEC on both the local
and remote cards.
• To use the VAD feature between the KX-TDA0490
and KX-TDA5480/KX-TDA0484, you must enable it
for the G.723.1 CODEC. Otherwise, the VAD feature
cannot be used between these cards (although calls
can be made and received as normal).
Use Use,
Don't use
Others
Parameter & Description Default Value Range
G.723.1 Rate
Specifies the rate of the G.723.1 CODEC.
DTMF Detection
Specifies the use of the DTMF detection feature.
DTMF detection enables end-to-end DTMF relay over the
network.
For details, refer to "Detailed Explanations".
6.3Kbps 5.3Kbps,
6.3Kbps
Use Use,
Don't use
Programming Guide 21
Page 22

2.2 Programming
Parameter & Description Default Value Range
FAX Signal Detection
Specifies the use of the fax signal detection feature.
Fax signal detection enables end-to-end fax signal relay over
the network.
For details, refer to "Detailed Explanations".
DTMF Detection Level (dB) -46-0dB
Specifies the level (in decibels) of DTMF detection.
Generally, there is no need to change the default value.
Detailed Explanations
QoS Field Settings
The following diagrams show the bit values of the ToS field in the IP header in relation to the setting
values for the parameters under QoS Field Settings:
ToS
0
0
0
Priority: 0
0
0
1
Priority: 1
0
1
0
Priority: 2
0
1
1
Priority: 3
1
0
0
Priority: 4
1
0
1
Priority: 5
1
1
0
Priority: 6
1
1
1
Priority: 7
0
0
0
0
1
Don't use Use,
-20 -46 to 0
0
0
0
1
0
0
0
0
1
0
0
Normal
1
Monetary Cost
0
Reliability
0
Throughput
0
Delay
Don't use
Bit 8
Bit 0
IP Header Version IHL Total Length
Type of Service
....
....
....
Reserved
Bit 15
Bit 32
IP Packet
22 Programming Guide
Page 23

DSCP
2.2 Programming
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
....
....
....
....
0
....
0
1
....
DSCP: 0
DSCP: 1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
Bit 8
Bit 0
IP Header Version IHL Total Length
Type of Service
....
....
0
1
DSCP: 62
DSCP: 63
....
HEX
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
1
....
1
....
0
1
Bit 8
....
1
1
....
....
1
1
1
1
....
....
1
1
....
1
1
1
1
ReservedReserved
HEX: 0
HEX: 1
HEX: FE
HEX: FF
Bit 15
Bit 32
IP Packet
Bit 15
Bit 0
IP Header Version IHL Total Length
CODEC Frame Settings
The amount of required bandwidth depends on the type of CODEC and the selected packet sending
interval. The tables below show the amount of bandwidth required for one VoIP channel in each case:
Required Bandwidth for Voice Communication via LAN
CODEC
G.711 87.2 kbps 79.5 kbps 75.6 kbps 71.7 kbps —
G.729A 31.2 kbps 23.5 kbps 19.6 kbps 15.7 kbps —
G.723.1 5.3 kbps — 20.8 kbps — 13.1 kbps 10.5 kbps
G.723.1 6.3 kbps — 21.9 kbps — 14.1 kbps 11.6 kbps
Bit 32
Type of Service
IP Packet
....
....
....
Packet Sending Interval
20 ms 30 ms 40 ms 60 ms 90 ms
Programming Guide 23
Page 24

2.2 Programming
Required Bandwidth for Voice Communication via WAN (PPP: Point-to-Point Protocol)
G.711 84 kbps 77.3 kbps 74 kbps 70.7 kbps —
G.729A 28 kbps 21 kbps 18 kbps 14.7 kbps —
G.723.1 5.3 kbps — 18.7 kbps — 12 kbps 9.8 kbps
G.723.1 6.3 kbps — 19.7 kbps — 13.1 kbps 10.8 kbps
When assessing your bandwidth requirements, keep in mind that the longer the packet sending
interval, the smaller the amount of required bandwidth, and vice versa.
However, also consider that the shorter the packet sending interval, the clearer the expected speech
quality, because delays in packet transmissions will be small. When the packet sending interval is
long, delays are more likely to occur, resulting in overall degradation in speech quality with more
pauses and loss in voice communications.
Therefore, it is recommended that you select the shortest packet sending interval that network
bandwidth can accommodate.
DTMF Detection
A VoIP network does not guarantee accurate end-to-end transmission of DTMF signals because the
DTMF signals are coded/decoded during VoIP communications, in the same way as voice signals. In
addition, packets can get lost during transmission.
To compensate for this problem, it is possible to enable DTMF detection for the VoIP Gateway Card
to carry out accurate end-to-end DTMF relay over the network. Upon detecting DTMF signals from
the PBX, the card encodes the signals and then sends them to the destination, instead of as voice
signals. Then at the destination, the card regenerates the DTMF signals from the received encoded
signals, and then sends them to the PBX.
Note that when this feature is enabled, the sending of packets is delayed by approximately 30 ms.
Therefore, it is recommended that you disable this feature unless DTMF detection is necessary.
CODEC
Packet Sending Interval
20 ms 30 ms 40 ms 60 ms 90 ms
FAX Signal Detection
When sending fax signals using a CODEC other than G.711, the signals cannot be received
accurately at the destination because they are coded/decoded over the VoIP network, in the same
way as voice signals.
To compensate for this problem, it is possible to enable fax detection for the card. Upon detecting fax
signals (CED tones) from the PBX, the card automatically switches the CODEC to G.711 to
communicate with the card at the destination. With the G.711 CODEC, it is possible to assure errorfree fax communications to a certain extent.
To further assure fax communications, it is strongly recommended that the communicating fax
machines be equipped with the ECM (Error Correction Model) feature, an automatic error correction
feature. When, for example, the receiving fax machine detects errors in transmission, it can have the
sending fax machine resend the relevant data.
When using the fax detection feature, the communicating cards must share the same value (either
"G.711Mu" or "G.711A") for the parameter Voice CODEC Priority (see "Voice CODEC Settings" in
"2.2.2 H.323 Parameters").
Notes
• To carry out fax communications between the KX-TDA0490 and KX-TDA5480/KX-TDA0484
24 Programming Guide
VoIP Gateway Cards, it is necessary to disable the "FAX High Reliable Method" for the KX-
Page 25

2.2 Programming
TDA5480/KX-TDA0484 card. (For more information about this feature, refer to the KXTDA5480/KX-TDA0484 Programming Guide.)
• Fax communications cannot take place between the KX-TDA0490 and KX-TDA0480 VoIP
Gateway Cards.
• Fax communications in the Super G3 mode are not guaranteed.
Programming Guide 25
Page 26

2.2 Programming
2.2.4 VoIP Gateway/IP-PBX Interface Parameters
1. Click 1.4 VoIP Gateway/IP-PBX Interface Settings in the main menu.
2. Assign each parameter referring to the descriptions below.
At any time during the session, you can:
• Click ALL CLEAR to return all parameters to their previous values.
• Click MENU to return to the main menu (see "2.1 Main Menu for the Administrator").
• Click LOGOUT to log out from the IP-GW16 Maintenance Utility (see "2.5.2 Log Out").
3. Click OK.
You will see a confirmation screen.
Note
If your entry contains an invalid value, you will be prompted to correct your input. Enter
correct values for the parameters shown in red and try again.
4. Confirm your entry and click OK.
To return to the previous screen, click CANCEL.
Parameter Descriptions
The parameters indicated with "*" must be changed while the VoIP Gateway Card is in the "STOP" status (see
"2.3.1 Status Control"). The changes do not have to be followed by a reboot to become effective.
Dialing Settings
Parameter & Description Default Value Range
*
First Digit Time (s) 5-30s
Specifies the length of time (in seconds) within which the first
digit of a dial number must be dialed after seizing a VoIP
gateway trunk (CO line).
Generally, there is no need to change the default value.
*
Inter-Digit Time (s) 1-10s
Specifies the length of time (in seconds) within which
subsequent digits of a dial number must be dialed.
Generally, there is no need to change the default value.
20 5 to 30
5 1 to 10
26 Programming Guide
Page 27

2.2 Programming
Parameter & Description Default Value Range
*
Digit End Code
# 0 to 9, #, *
Specifies the delimiter code to be used to signal the end of a
dial number.
Generally, there is no need to change the default value.
Others
Parameter & Description Default Value Range
Network CODEC of IP-PBX
The value of this parameter is set automatically as
appropriate to the setting of the PBX.
There is no need to change the value.
Not applicable G.711 Mu-Law,
G.711 A-Law
Programming Guide 27
Page 28

2.2 Programming
2.2.5 Hunt Pattern Parameters
1. Click 1.5 Hunt Pattern (for Incoming Calls) in the main menu.
2. Assign each parameter referring to the descriptions below.
At any time during the session, you can:
• Click ALL CLEAR to return all parameters to their previous values.
• Click MENU to return to the main menu (see "2.1 Main Menu for the Administrator").
• Sort the hunt patterns in the table at the bottom of the screen:
• Delete the desired hunt pattern from the table at the bottom of the screen:
• Click LOGOUT to log out from the IP-GW16 Maintenance Utility (see "2.5.2 Log Out").
28 Programming Guide
a. Click the desired sort key and sort order from the Sort Option lists.
b. Click SORT.
a. Select the appropriate check box for the hunt pattern you want to delete.
b. Click DELETE.
Page 29

2.2 Programming
3. Click ENTRY.
A maximum of 16 hunt patterns can be created.
4. Click OK.
You will see a confirmation screen.
Note
If your entry contains an invalid value, you will be prompted to correct your input. Enter
correct values for the parameters shown in red and try again.
5. Confirm your entry and click OK.
To return to the previous screen, click CANCEL.
Parameter Descriptions
The parameters indicated with "*" must be changed while the VoIP Gateway Card is in the "STOP" status (see
"2.3.1 Status Control"). The changes do not have to be followed by a reboot to become effective.
Hunt Group
Parameter & Description Default Value Range
*
Port1–8
Assigns a hunt group to a VoIP gateway port.
For details, refer to "Detailed Explanations".
Hunt group 1 Hunt group 1 to 8
Hunt Pattern Entry
The parameters below are used to create hunt patterns.
For details, refer to "Detailed Explanations".
Parameter & Description Default Value Range
*
Hunt Pattern No.
Specifies the number for the hunt pattern to be created.
When changing the current settings of an existing hunt
pattern, first delete the hunt pattern and then re-create with
new values.
*
Receive Leading Number
Specifies the leading digits in received numbers by which to
determine the hunt group to direct incoming calls.
For example, to direct incoming calls with numbers starting
with "9", specify the number "9" in this parameter. Likewise,
to direct incoming calls with numbers starting with "1", specify
the number "1".
However, if you want to direct incoming calls with numbers
starting with "950" and "951" to separate hunt groups, it is
necessary to make 2 hunt patterns with respective numbers,
"950" and "951".
No default 1 to 16
No default Max. 30 digits
Programming Guide 29
Page 30

2.2 Programming
Parameter & Description Default Value Range
*
Hunt Group (Priority1)
Specifies the hunt group to which incoming calls are directed
first.
*
Hunt Group (Priority2)–(Priority8)
Specifies the hunt group to which incoming calls are directed
when the hunt group specified in the previous priority level is
busy.
Detailed Explanations
The card and the PBX are connected with 8 VoIP gateway ports, each of which has 2 communication
channels, in much the same way as an ISDN BRI port.
PBX (PBX Code: 950)
VoIP Gateway Card
Por t 1
Channel 1
Channel 2
Por t 2
1 1 to 8
- 1 to 8,
- (disable)
Extn. Group A
Extn. 101 ... Extn. 199
Channel 1
IP Network
Channel 2
....
Extn. Group B
Por t 8
Channel 1
Channel 2
Hunt pattern programming determines the VoIP gateway ports through which to route incoming calls,
depending on the received numbers. The following examples provide 2 different methods of hunt
pattern programming.
Extn. 201 ... Extn. 299
30 Programming Guide
Page 31

2.2 Programming
Example 1
The following configuration is used to allocate 8 VoIP gateway ports (16 channels) to route incoming
calls to both extension groups A and B.
When there are 16 incoming calls to extension group A in this configuration, no call can be routed to
extension group B.
Hunt Group
Port1 Hunt group 1
Port2 Hunt group 1
::
Port8 Hunt group 1
Hunt Pattern Entry
Hunt Pattern No. 1
Receive Leading Number 9
Hunt Group (Priority1) 1
Hunt Group (Priority2) -
::
Hunt Group (Priority8) -
Dials "950-101".
Dials "950-102".
Dials "950-103".
Dials "950-104".
....
Dials "950-115".
IP Network
PBX (PBX Code: 950)
VoIP Gateway Card
Por t 1
Channel 1
Channel 2
Por t 2
Channel 1
Channel 2
....
Por t 8
Channel 1
Extn. Group A
Extn. 101 ... Extn. 199
Extn. Group B
Dials "950-116".
Dials "950-201".
Channel 2
Extn. 201 ... Extn. 299
Programming Guide 31
Page 32

2.2 Programming
Example 2
The following configuration is used to divide 8 VoIP gateway ports (16 channels) into 2 groups of 4,
and then allocate each group to individual extension groups. Specifically, with this configuration, calls
to extension group A are routed through the first group of ports (consisting of ports 1 to 4). Likewise,
calls to extension group B are routed through the second group of ports (consisting of ports 5 to 8).
When all 8 channels in the first group of ports are being used, this configuration rejects the 9th call to
extension group A. However, the other 8 channels in the second group of ports remain available to
route calls to extension group B.
Hunt Group
Port1 Hunt group 1
::
Port4 Hunt group 1
Port5 Hunt group 2
::
Port8 Hunt group 2
Hunt Pattern Entry—1
Hunt Pattern No. 1
Receive Leading Number 9501
Hunt Group (Priority1) 1
Hunt Group (Priority2) -
::
Hunt Group (Priority8) -
Hunt Pattern Entry—2
Hunt Pattern No. 2
Receive Leading Number 9502
Hunt Group (Priority1) 2
Hunt Group (Priority2) -
::
Hunt Group (Priority8) -
32 Programming Guide
Page 33

Dials "950-101".
2.2 Programming
PBX (PBX Code: 950)
VoIP Gateway Card
Por t 1
Channel 1
Dials "950-102".
....
Dials "950-107".
Dials "950-108".
Dials "950-109".
Dials "950-201".
Dials "950-202".
....
Dials "950-207".
Dials "950-208".
IP Network
Channel 2
....
Por t 4
Channel 1
Channel 2
Por t 5
Channel 1
Channel 2
....
Por t 8
Channel 1
Channel 2
Extn. Group A
Extn. 101 ... Extn. 199
Extn. Group B
Extn. 201 ... Extn. 299
It is possible to program the PBX to allocate separate groups of VoIP gateway ports to individual
extension groups A and B for making outgoing calls. With this programming, each extension group,
A and B, can have a group of ports for its exclusive use.
For example:
• The VoIP gateway ports that extension group A uses to make outgoing calls: ports 1 to 4
• The VoIP gateway ports that extension group B uses to make outgoing calls: ports 5 to 8
Note
The example above details the configuration to route incoming calls to 2 separate hunt groups,
each of which is associated with an individual extension group. However, note that various other
types of configurations are possible. For example, it is possible to route calls to 8 separate hunt
groups, so that you can distribute the calls to 8 different extension groups.
Programming Guide 33
Page 34

2.2 Programming
2.2.6 Address Translation Table—GW Entry
1. Click 1.6 DN2IP (Dialed Number to IP Address Translation) in the main menu.
2. Click 1.6.1 GW Entry.
3. Assign each parameter referring to the descriptions below.
At any time during the session, you can:
• Click MENU to return to the main menu (see "2.1 Main Menu for the Administrator").
• Click PREVIOUS to return to the previous screen.
• Sort the gateway entries in the table at the bottom of the screen:
• Delete the desired gateway entry from the table at the bottom of the screen:
34 Programming Guide
a. Click the desired sort key and sort order from the Sort Option lists.
b. Click SORT.
a. Select the appropriate check box for the gateway entry you want to delete.
Page 35

2.2 Programming
Note
If the gateway entry is registered to a DN2IP entry (see "2.2.7 Address Translation
Table—DN2IP Entry"), no check box will be shown for the gateway entry.
b. Click DELETE.
• Click LOGOUT to log out from the IP-GW16 Maintenance Utility (see "2.5.2 Log Out").
4. Click ENTRY.
A maximum of 512 gateway entries can be created.
5. Click OK.
You will see a confirmation screen.
Note
If your entry contains an invalid value, you will be prompted to correct your input. Enter
correct values for the parameters shown in red and try again.
6. Confirm your entry and click OK.
To return to the previous screen, click CANCEL.
Parameter Descriptions
The parameters indicated with "*" must be changed while the VoIP Gateway Card is in the "STOP" status (see
"2.3.1 Status Control"). The changes do not have to be followed by a reboot to become effective.
GW Entry
The parameters below are used to create gateway entries for both local and remote cards on the network, as
a preliminary step to programming the address translation table (DN2IP).
For a programming example, refer to "3.2.5 Programming the Address Translation Table" of the VoIP Gateway
Card Getting Started.
Note
If you are using a gatekeeper, create the gateway entry only for the local card.
Parameter & Description Default Value Range
*
GW No.
Specifies the number for the gateway entry to be created.
When changing the current settings of an existing gateway
entry, first delete the gateway entry and then re-create with
new values.
*
Comment
Specifies the comment for the gateway entry.
*
IP Address
Specifies the IP address of the card.
0 0 to 511
No default Max. 16 characters
No default The following addresses
are invalid:
• Class D addresses
• Class E addresses
• Loopback
addresses
Programming Guide 35
Page 36

2.2 Programming
Parameter & Description Default Value Range
*
Group No.
Specifies the number of the gateway group to which the
gateway entry belongs.
Grouping is useful when there is more than one card installed
in a PBX, because it allows you to use the automatic route
redirection feature. For details, refer to "Detailed
Explanations" in the next section, "2.2.7 Address Translation
Table—DN2IP Entry".
0 0 (belong to no group),
1 to 256
36 Programming Guide
Page 37

2.2.7 Address Translation Table—DN2IP Entry
1. Click 1.6 DN2IP (Dialed Number to IP Address Translation) in the main menu.
2. Click 1.6.2 DN2IP Entry.
2.2 Programming
3. Assign each parameter referring to the descriptions below.
At any time during the session, you can:
• Click MENU to return to the main menu (see "2.1 Main Menu for the Administrator").
• Click PREVIOUS to return to the previous screen.
• Sort the DN2IP entries in the table at the bottom of the screen:
a. Click the desired sort key and sort order from the Sort Option lists.
b. Click SORT.
• Delete the desired DN2IP entry from the table at the bottom of the screen:
a. Select the appropriate check box for the DN2IP entry you want to delete.
b. Click DELETE.
• Click LOGOUT to log out from the IP-GW16 Maintenance Utility (see "2.5.2 Log Out").
4. Click ENTRY.
Programming Guide 37
Page 38

2.2 Programming
A maximum of 512 DN2IP entries can be created.
5. Click OK.
You will see a confirmation screen.
Note
If your entry contains an invalid value, you will be prompted to correct your input. Enter
correct values for the parameters shown in red and try again.
6. Confirm your entry and click OK.
To return to the previous screen, click CANCEL.
Parameter Descriptions
The parameters indicated with "*" must be changed while the VoIP Gateway Card is in the "STOP" status (see
"2.3.1 Status Control"). The changes do not have to be followed by a reboot to become effective.
DN2IP Entry
The parameters below are used to create DN2IP entries based on the gateway entries created previously (see
"2.2.6 Address Translation Table—GW Entry"). The DN2IP entries associate dialed numbers and IP address
of the destination; therefore, a caller can reach the destination by dialing the number without knowing the
destination IP address.
For a programming example, refer to "3.2.5 Programming the Address Translation Table" of the VoIP Gateway
Card Getting Started.
Note
If you are using a gatekeeper, create the DN2IP entries only for the local card. In this case, you can create
up to 4 DN2IP entries per card.
Note that if you are not using a gatekeeper, there is no maximum number of DN2IP entries.
Parameter & Description Default Value Range
*
Leading Number
Specifies the leading digits in dialed numbers by which to
associate calls with the appropriate destination.
For example, to associate calls with dialed numbers "950xxxx" and "951-xxxx" with separate destinations, it is
necessary to make 2 DN2IP entries with respective numbers,
"950" and "951".
*
Remaining Number of Digits
Specifies the number of digits to be dialed following the
leading number to access the destination.
For example, if the dialed numbers are either "950-xxxx" or
"951-xxxx" and the numbers "950" and "951" are specified for
the parameter Leading Number respectively, specify the
number "4" in this parameter.
*
GW No/Group No. Selection
Specifies the type of destination when making calls: a
gateway or a gateway group.
No default Max. 30 digits
0 0 to 29
GW GW,
Group
38 Programming Guide
Page 39

2.2 Programming
Parameter & Description Default Value Range
*
GW No/Group No.
Specifies the number of the destination gateway or gateway
group.
Detailed Explanations
Automatic Route Redirection
When more than one card is installed in a PBX, you can assign them to a single gateway group.
Grouping allows you to logically combine the channels of multiple cards in a PBX (there are 16
channels per card). This aids the effective use of channels in a PBX.
The following diagram and tables provide an example of this configuration.
Example of Configuration
In the diagram below, there are 2 cards (cards B and C) installed in PBX 2.
PBX 1
• PBX Code: 951
• Extension Number: 3 digits
Card A
IP Address: 192.168.1.1
IP Network
GW No: 0,
Group No.: 1
• PBX Code: 952
• Extension Number: 4 digits
Gateway Group 1
IP Address: 192.168.1.2
IP Address: 192.168.1.3
GW No: 0 to 511,
Group No.: 1 to 256
PBX 2
Card B
Card C
Example of Gateway Entry Programming
Through gateway entry programming, cards B and C are grouped into a single gateway group.
Parameter Card A Card B Card C
GW No 0 1 2
Comment IP-GW Card A IP-GW Card B IP-GW Card C
IP Address 192.168.1.1 192.168.1.2 192.168.1.3
Group No. 0 11
Example of DN2IP Entry Programming
When DN2IP entries are programmed as in the table below, calls through card A arrive at gateway
group 1, which includes cards B and C.
Parameter To Card A To Gateway Group 1
(Cards B and C)
Leading Number 951 952
Programming Guide 39
Page 40

2.2 Programming
Remaining Number of Digits 3 4
GW No/Group No. Selection GW Group
GW No/Group No. 0 1
The automatic route redirection feature activates in this configuration. If a call is made through card
A to gateway group 1 when all 16 channels of card B are busy, card A automatically redirects the call
to card C.
This is possible because by grouping, PBX 1 sees PBX 2 as having a combined set of 32 channels,
not 2 separate sets of 16 channels.
Note
Parameter To Card A To Gateway Group 1
(Cards B and C)
The automatic route redirection feature cannot be used in a network where a gatekeeper is used.
For details about gatekeeper settings, refer to "Gatekeeper Settings" in "2.2.2 H.323
Parameters".
40 Programming Guide
Page 41

2.2.8 Initialization
1. Click 1.7 Initialization in the main menu.
2. Click OK to initialize all parameters to the default values.
To abort initialization, click CANCEL. You will be taken back to the main menu (see "2.1 Main
Menu for the Administrator").
2.2 Programming
Initialization has to be followed by a reboot to make the default values effective for the
parameters indicated with "#" (e.g., IP address of the VoIP Gateway Card). If not followed by a
reboot, the current setting values will remain effective instead.
3. Click MENU to return to the main menu (see "2.1 Main Menu for the Administrator").
4. Refer to "2.5.1 Reboot" and finish the reboot.
Note
If you have forgotten the IP address or log-in password of the VoIP Gateway Card, follow the
procedure detailed in "C1 Initializing the VoIP Gateway Card" of the VoIP Gateway Card Getting
Started to return all settings to the factory default.
Programming Guide 41
Page 42

2.3 Maintenance
2.3 Maintenance
2.3.1 Status Control
1. Click 2.1 Change RUN/STOP status in the main menu.
Current RUN/STOP Status shows the current status of the VoIP Gateway Card.
2. Click RUN or STOP for Status after changing.
If you want to forcibly change the status from "RUN" to "STOP" while there are ongoing calls,
click the Yes check box for Forced Disconnect when executing STOP. This will allow you to
place the card in the "STOP" status even when there are ongoing calls.
At any time during the session, you can:
• Click MENU to return to the main menu (see "2.1 Main Menu for the Administrator").
• Click LOGOUT to log out from the IP-GW16 Maintenance Utility (see "2.5.2 Log Out").
3. Click OK.
You will see a confirmation screen.
4. Click OK.
You will see a result screen.
Note
5. Click OK.
You will be taken back to the Change RUN/STOP status screen.
42 Programming Guide
If the operation is not successful, you will see an error screen. Click OK to return to the
previous screen, and then try again.
Page 43

2.3.2 Maintenance Settings
1. Click 2.2 Maintenance Settings in the main menu.
2.3 Maintenance
2. Assign each parameter referring to the descriptions below.
At any time during the session, you can:
• Click ALL CLEAR to return all parameters to their previous values.
• Click MENU to return to the main menu (see "2.1 Main Menu for the Administrator").
• Click LOGOUT to log out from the IP-GW16 Maintenance Utility (see "2.5.2 Log Out").
3. Click OK.
You will see a confirmation screen.
Note
If your entry contains an invalid value, you will be prompted to correct your input. Enter
correct values for the parameters shown in red and try again.
4. Confirm your entry and click OK.
To return to the previous screen, click CANCEL.
Parameter Descriptions
The parameters indicated with "*" must be changed while the VoIP Gateway Card is in the "STOP" status (see
"2.3.1 Status Control"). The changes do not have to be followed by a reboot to become effective.
Username/Password Settings
Parameter & Description Default Value Range
Username for Administrator
Administrator-level log-in user name.
Administrator Max. 16 characters
Programming Guide 43
Page 44

2.3 Maintenance
Parameter & Description Default Value Range
Password
Administrator-level log-in password.
Password (Confirmation)
Confirmation of the administrator-level log-in password.
Administrator Max. 16 characters
No default Max. 16 characters
Programming Auto Disconnect Time Settings
Parameter & Description Default Value Range
Programming Auto Disconnect Time (min) 1-30min
Specifies the time (in minutes) until programming is
automatically terminated.
If the specified period of time passes with no programming
input, programming will automatically be terminated. This
prevents problems caused by continuation of log-in status in
cases such as being unable to log out due to the sudden
failure of a PC.
10 1 to 30
Periodic Diagnosis Time Interval Settings
Parameter & Description Default Value Range
*
Periodic Diagnosis Time Interval (min) 0-1440min
Specifies the time (in minutes) between periodic selfdiagnoses to test operation as described in "2.3.3 Diagnosis".
If failures are detected during the self-diagnosis, the card will
alert the PBX.
60 0 (no periodic
diagnosis),
1 to 1440
44 Programming Guide
Page 45

2.3 Maintenance
Version
Parameter & Description Default Value Range
IP-GW16 Program Version
Indicates the version of the VoIP Gateway Card's main
program.
The main program controls the VoIP protocol.
DSP Program Version
Indicates the version of the VoIP Gateway Card's DSP
program.
The DSP program controls a DSP device, which controls
speech and audio processing.
DSP Device Version
Indicates the version of the VoIP Gateway Card's DSP
device.
The DSP device is a processor that controls speech and
audio processing.
Display only
Programming Guide 45
Page 46

2.3 Maintenance
2.3.3 Diagnosis
This function is used to carry out the self-diagnostic program manually.
If failures are detected, there is a potential for trouble with the operation of the VoIP Gateway Card.
1. Click 2.3 Diagnosis in the main menu.
2. Click DIAGNOSIS to carry out the self-diagnostic program.
3. Do one of the following:
• Click DIAGNOSIS to carry out the self-diagnostic program again.
• Click MENU to return to the main menu (see "2.1 Main Menu for the Administrator").
• Click LOGOUT to log out from the IP-GW16 Maintenance Utility (see "2.5.2 Log Out").
46 Programming Guide
Page 47

2.3.4 Log Information
The function to collect log information is provided for engineer use only. However, in the case that a
need should arise, this section provides the procedure for collecting the log information.
1. Click 2.4 Log Information in the main menu.
2. Click OK.
Log information is displayed.
2.3 Maintenance
3. Click Download (All) to download the log information.
Programming Guide 47
Page 48

2.4 Data Management
2.4 Data Management
It is strongly recommended that you download the configuration data and the address translation
table (DN2IP) data from the VoIP Gateway Card for backup and archive purposes.
The following sections provide the procedures for downloading and uploading.
2.4.1 Upload of Configuration Data
Before uploading the data, place the card in the "STOP" status (see "2.3.1 Status Control").
1. Click 3.1 Upload of Configuration data (PC → VoIP Gateway) in the main menu.
2. Click Browse and choose a file to upload.
At any time during the session, you can:
• Click MENU to return to the main menu (see "2.1 Main Menu for the Administrator").
• Click LOGOUT to log out from the IP-GW16 Maintenance Utility (see "2.5.2 Log Out").
3. Click UPLOAD (PC→VoIP Gateway).
The upload operation starts.
Notes
• If the upload operation is executed while the card is in the "RUN" status, you will see an
error screen. Click Change RUN/STOP status Screen and place the card in the
"STOP" status (see "2.3.1 Status Control"), and then upload the data again.
• If the operation is not successful for other reasons, you will see another error screen.
Click OK to return to the previous screen, and then upload the data again.
48 Programming Guide
Page 49

4. Do one of the following:
• Click REBOOT to make the changes effective now.
You will see a confirmation screen. Refer to "2.5.1 Reboot" and finish the reboot.
• Click OK to return to the previous screen without rebooting.
However, remember to reboot the card at the end of the programming session to make
changes effective.
2.4 Data Management
Programming Guide 49
Page 50

2.4 Data Management
2.4.2 Download of Configuration Data
1. Click 3.2 Download of Configuration data (VoIP Gateway → PC) in the main menu.
2. Click DOWNLOAD.
At any time during the session, you can:
• Click MENU to return to the main menu (see "2.1 Main Menu for the Administrator").
• Click LOGOUT to log out from the IP-GW16 Maintenance Utility (see "2.5.2 Log Out").
3. Specify the file name and the folder in which to save the file.
50 Programming Guide
Page 51

2.4.3 Upload of Address Translation Table
Before uploading the data, place the card in the "STOP" status (see "2.3.1 Status Control").
1. Click 3.3 Upload of DN2IP data (PC → VoIP Gateway) in the main menu.
2.4 Data Management
2. Click Browse and choose a file to upload.
At any time during the session, you can:
• Click MENU to return to the main menu (see "2.1 Main Menu for the Administrator").
• Click LOGOUT to log out from the IP-GW16 Maintenance Utility (see "2.5.2 Log Out").
3. Click UPLOAD (PC→VoIP Gateway).
The upload operation starts.
Notes
• If the upload operation is executed while the card is in the "RUN" status, you will see an
error screen. Click Change RUN/STOP status Screen and place the card in the
"STOP" status (see "2.3.1 Status Control"), and then upload the data again.
• If the operation is not successful for other reasons, you will see another error screen.
Click OK to return to the previous screen, and then upload the data again.
4. Do one of the following:
• Click REBOOT to make the changes effective now.
You will see a confirmation screen. Refer to "2.5.1 Reboot" and finish the reboot.
• Click OK to return to the previous screen without rebooting.
Programming Guide 51
Page 52

2.4 Data Management
However, remember to reboot the card at the end of the programming session to make
changes effective.
52 Programming Guide
Page 53

2.4.4 Download of Address Translation Table
1. Click 3.4 Download of DN2IP data (VoIP Gateway → PC) in the main menu.
2. Click DOWNLOAD.
At any time during the session, you can:
• Click MENU to return to the main menu (see "2.1 Main Menu for the Administrator").
• Click LOGOUT to log out from the IP-GW16 Maintenance Utility (see "2.5.2 Log Out").
3. Specify the file name and the folder in which to save the file.
2.4 Data Management
Programming Guide 53
Page 54

2.5 Others
2.5 Others
2.5.1 Reboot
1. Click REBOOT in the main menu.
2. Click REBOOT.
To return to the main menu, click CANCEL (see "2.1 Main Menu for the Administrator").
Note
If the reboot operation is not successful, you will see an error page.
3. To continue programming, click LOGIN Screen and log in again.
You will see the log-in screen (see "1.1 Starting the IP-GW16 Maintenance Utility").
54 Programming Guide
Page 55

2.5.2 Log Out
1. Click LOGOUT in the main menu.
2. Click OK to log out.
2.5 Others
Programming Guide 55
Page 56

2.5 Others
56 Programming Guide
Page 57

Section 3
Installer Functions
This section provides operating instructions for the IP-GW16
Maintenance Utility when logged in as the Installer.
Programming Guide 57
Page 58

3.1 Main Menu for the Installer
3.1 Main Menu for the Installer
The IP-GW16 Maintenance Utility provides the following menu to a user logged in as the Installer.
Maintenance
Menu Section Reference
1.1 Change RUN/STOP status 3.2.1 Status Control
1.2 Maintenance Settings 3.2.2 Maintenance Settings
Data Management
Menu Section Reference
2.1 Upload of Firmware data (PC → VoIP
Gateway)
2.2 Handling of Firmware Page 3.3.2 Handling of Firmware Page
Others
Menu Section Reference
REBOOT 3.4.1 Reboot
LOGOUT 3.4.2 Log Out
3.3.1 Upload of Firmware Data
58 Programming Guide
Page 59

3.2 Maintenance
3.2.1 Status Control
1. Click 1.1 Change RUN/STOP status in the main menu.
Current RUN/STOP Status shows the current status of the VoIP Gateway Card.
2. Click RUN or STOP for Status after changing.
If you want to forcibly change the status from "RUN" to "STOP" while there are ongoing calls,
click the Yes check box for Forced Disconnect when executing STOP. This will allow you to
place the card in the "STOP" status even when there are ongoing calls.
At any time during the session, you can:
• Click MENU to return to the main menu (see "3.1 Main Menu for the Installer").
• Click LOGOUT to log out from the IP-GW16 Maintenance Utility (see "3.4.2 Log Out").
3. Click OK.
You will see a confirmation screen.
4. Click OK.
You will see a result screen.
3.2 Maintenance
Note
If the operation is not successful, you will see an error screen. Click OK to return to the
previous screen, and then try again.
5. Click OK.
You will be taken back to the Change RUN/STOP status screen.
Programming Guide 59
Page 60

3.2 Maintenance
3.2.2 Maintenance Settings
1. Click 1.2 Maintenance Settings in the main menu.
2. Assign each parameter referring to the descriptions below.
At any time during the session, you can:
• Click ALL CLEAR to return all parameters to their previous values.
• Click MENU to return to the main menu (see "3.1 Main Menu for the Installer").
• Click LOGOUT to log out from the IP-GW16 Maintenance Utility (see "3.4.2 Log Out").
3. Click OK.
You will see a confirmation screen.
Note
If your entry contains an invalid value, you will be prompted to correct your input. Enter
correct values for the parameters shown in red and try again.
4. Confirm your entry and click OK.
To return to the previous screen, click CANCEL.
Parameter Descriptions
Username/Password Settings
Parameter & Description Default Value Range
Username for Installer
Installer-level log-in user name.
Installer Max. 16 characters
Password
Installer-level log-in password.
Password (Confirmation)
Confirmation of the installer-level log-in password.
60 Programming Guide
Installer Max. 16 characters
No default Max. 16 characters
Page 61

3.2 Maintenance
Version
Parameter & Description Default Value Range
IP-GW16 Program Version
Indicates the version of the VoIP Gateway Card's main
program.
The main program controls the VoIP protocol.
DSP Program Version
Indicates the version of the VoIP Gateway Card's DSP
program.
The DSP program controls a DSP device, which controls
speech and audio processing.
DSP Device Version
Indicates the version of the VoIP Gateway Card's DSP
device.
The DSP device is a processor that controls speech and
audio processing.
Display only
Programming Guide 61
Page 62

3.3 Data Management
3.3 Data Management
The upload and update operations of the firmware data are closely related. First follow the procedure
as described in "3.3.1 Upload of Firmware Data" to upload new firmware data to the VoIP Gateway
Card, and then go on to "3.3.2 Handling of Firmware Page" to update the card with the newly
uploaded firmware data.
3.3.1 Upload of Firmware Data
Before uploading the data, place the card in the "STOP" status (see "3.2.1 Status Control").
1. Click 2.1 Upload of Firmware data (PC → VoIP Gateway) in the main menu.
2. Do the following to upload the firmware data to the temporary buffer in the VoIP Gateway Card:
a. Click Browse and choose a file to upload.
At any time during the session, you can:
•Click MENU to return to the main menu (see "3.1 Main Menu for the Installer").
•Click LOGOUT to log out from the IP-GW16 Maintenance Utility (see "3.4.2 Log Out").
b. Click UPLOAD (PC→VoIP Gateway).
The upload operation starts.
Note
If the upload operation is executed while the card is in the "RUN" status, you will see an
error screen. Click Change RUN/STOP status Screen and place the card in the
"STOP" status (see "3.2.1 Status Control"), and then upload the data again.
62 Programming Guide
Page 63

3.3 Data Management
Firmware Status shows the current firmware status of page 0 and page 1, and Startup
Page shows the current active page on startup. For details about these parameters, refer to
"3.3.2 Handling of Firmware Page".
3. Do the following to update the desired page with the uploaded firmware data:
a. Click the option for the page whose current firmware status is not "Main Operation Mode"
for Select Page.
b. Click OK.
You will see a confirmation screen.
c. Click OK.
4. Do one of the following:
• Click REBOOT to start up the VoIP Gateway Card with the updated page and confirm that
the upload operation has been carried out successfully.
You will see a reboot confirmation screen. Refer to "3.4.1 Reboot" and finish the reboot.
Note
After the reboot, the card starts up with the updated page temporarily so that you can
confirm the result of the upload operation. If you reboot again, the card does not start
up with the updated page, but starts up with the page whose current firmware status is
"Main Operation Mode".
Programming Guide 63
Page 64

3.3 Data Management
• Click CANCEL to return to the main menu without starting up the card with the updated
5. Switch the firmware status of the updated page from "NEW" to "Main Operation Mode".
After the previous step (with or without a reboot), the firmware status of the updated page is still
"NEW". To set the updated page as the active page on startup, you must change its firmware
status to "Main Operation Mode". For instructions, refer to "3.3.2 Handling of Firmware Page".
The following is a sample image of the screen in which you can set the active page on startup:
page.
64 Programming Guide
Page 65

3.3.2 Handling of Firmware Page
1. Click 2.2 Handling of Firmware Page in the main menu.
For details about the parameters on this screen, refer to the descriptions below.
2. Click Main Operation Mode for Operation to set the desired page as the active page on startup.
3.3 Data Management
Note
Do not click Empty, as it is an option provided for engineer use only.
At any time during the session, you can:
• Click MENU to return to the main menu (see "3.1 Main Menu for the Installer").
• Click LOGOUT to log out from the IP-GW16 Maintenance Utility (see "3.4.2 Log Out").
3. Click the option for the page in the "NEW" status for Select Page to specify it as the target page
of the operation.
4. Click OK.
You will see a confirmation screen.
5. Click OK.
You will see a result screen.
6. Click OK.
You will be taken back to the Handling of Firmware Page screen.
Parameter Descriptions
Parameter & Description Default Value Range
IP-GW16 Program Version
Indicates the version of the VoIP Gateway Card's main
program in the firmware data of the corresponding page.
Display only
DSP Program Version
Indicates the version of the VoIP Gateway Card's DSP
program in the firmware data of the corresponding page.
Display only
Programming Guide 65
Page 66

3.3 Data Management
Parameter & Description Default Value Range
Firmware Status
Indicates the current firmware status of the corresponding
page. There are 3 kinds of status indications:
• Main Operation Mode: Active firmware data on startup
under normal operation.
• OLD: Firmware data uploaded to the card before the
firmware data in the "Main Operation Mode" status was
uploaded.
• NEW: Firmware data uploaded to the card after the
firmware data in the "Main Operation Mode" status was
uploaded.
Note
The status indications "OLD" and "NEW" are irrelevant to
the version of the firmware data.
Startup Page
Indicates (with an "x" sign) the active page on startup.
Generally, the startup page is the firmware data whose status
is "Main Operation Mode".
The exception is when the card undergoes a reboot after a
firmware data upload operation; in this case, the card starts
up with the page in the "NEW" status. This is for the purposes
of confirming the result of the upload operation. If you reboot
again, the card starts up with the page in the "Main Operation
Mode" status.
To set the updated page as the active page on startup, you
must change its firmware status to "Main Operation Mode".
Display only
Display only
Operation
Specifies whether to set the page (selected with the
parameter Select Page) as the active page on startup ("Main
Operation Mode"), or delete the page ("Empty").
"Empty" is an option provided for engineer use only.
Select Page
Specifies the target page of the operation selected with the
parameter Operation.
Not applicable Empty,
Main Operation Mode
Not applicable Page-0,
Page-1
66 Programming Guide
Page 67

3.4 Others
3.4.1 Reboot
1. Click REBOOT in the main menu.
2. Click REBOOT.
To return to the main menu, click CANCEL (see "3.1 Main Menu for the Installer").
3.4 Others
Note
If the reboot operation is not successful, you will see an error page.
3. To continue programming, click LOGIN Screen and log in again.
You will see the log-in screen (see "1.1 Starting the IP-GW16 Maintenance Utility").
Programming Guide 67
Page 68

3.4 Others
3.4.2 Log Out
1. Click LOGOUT in the main menu.
2. Click OK to log out.
68 Programming Guide
Page 69

Index
Programming Guide 69
Page 70

Index
A
Automatic Route Redirection 39
B
Bandwidth 23
C
Call Signaling Model 17
20, 23
42, 59
Change RUN/STOP status
CODEC Frame Settings
D
Default Gateway 11
DHCP Settings
Diagnosis
Dialing Settings
DiffServ
Digit End Code
DN2IP (Dialed Number to IP Address Translation)
DN2IP Entry
Download of Address Translation Table
Download of Configuration Data
DSCP
DSP Program Version
DTMF Detection
DTMF Detection Level
DTMF Relay
19
19, 23
46
11
26
27
37, 38
21, 24
21, 24
53
50
65
22
E
Echo Canceller 20
ECM (Error Correction Model)
Empty
66
24
F
Fast Connect 17
FAX Signal Detection
Firmware Status
First Digit Time
22, 24
66
26
G
G.168 20
G.711A
G.711Mu
G.723.1
G.723.1 Rate
G.723.1/G.729A/G.711 VAD
G.729A
Gatekeeper Settings
GW Entry
16
16
16
16
34, 35
21
21
16
H
H.225 Port No. 15
14
15
14
65
12
H.245 Port No.
H.323
H.323 Detailed Settings
Handling of Firmware Page
HTTP Settings
34, 37
Hunt Pattern (for Incoming Calls)
28
I
Initialization 41
11
19, 22
26
11
65
Inter-Digit Time
IP Address
IP Address Settings
IP Header
IP-GW16 Program Version
J
Jitter Buffer Settings 19
Jitter buffer Settings (G.711 for Fax)
Jitter buffer Settings (G.711/G.729A/G.723.1 for Voice)
20
L
LAN 23
LAN Disconnect Threshold Time
55, 68
47
Log Information
Log Out
12
M
Main Menu for the Administrator 8
66
43, 60
58
Main Menu for the Installer
Main Operation Mode
Maintenance Settings
N
Network CODEC of IP-PBX 27
Network Settings, General
10
P
Packet Sending Interval 20, 23, 24
Periodic Diagnosis Time Interval Settings
Port No. Settings
PPP (Point-to-Point Protocol)
Programming Auto Disconnect Time Settings
15
24
44
44
Q
QoS Field Settings 19, 22
QSIG Connectionless Tunneling Settings
12
R
RAS Port No. 15
Reboot
RTP/RTCP Port No.
54, 67
15
S
Startup Page 66
Subnet Mask
Super G3 Mode
11
25
T
ToS 19, 22
19
70 Programming Guide
Page 71

U
Upload of Address Translation Table 51
Upload of Configuration Data
Upload of Firmware Data
Username/Password Settings
48
62
43, 60
V
VAD (Voice Activity Detection) 21
Version
Voice CODEC Settings
Voice Communication Detailed Settings
VoIP Gateway/IP-PBX Interface Settings
45, 61
16
Index
18
26
Programming Guide 71
Page 72

Panasonic Consumer Electronics Company
Division of Panasonic Corporation of North America
One Panasonic Way
Secaucus, NJ 07094
Panasonic Puerto Rico, lnc.
Ave. 65 de Infantería, Km. 9.5
San Gabriel Industrial Park
Carolina, Puerto Rico 00985
http://www.panasonic.com/csd
Copyright:
This material is copyrighted by Panasonic Communications Co., Ltd., and may be reproduced for internal use
only. All other reproduction, in whole or in part, is prohibited without the written consent of Panasonic
Communications Co., Ltd.
© 2005 Panasonic Communications Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved.
PSQX3381YA
KK0105AH1015
 Loading...
Loading...