Philips HEF4938BT, HEF4938BP Datasheet
DATA SH EET
Preliminary specification
File under Integrated Circuits, IC04
January 1995
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
HEF4938B
Dual precision monostable
multivibrator
For a complete data sheet, please also download:
•The IC04 LOCMOS HE4000B Logic
Family Specifications HEF, HEC
•The IC04 LOCMOS HE4000B Logic
Package Outlines/Information HEF, HEC
January 1995 2
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Dual precision monostable multivibrator HEF4938B
FEA TURES
• Separate reset inputs
• Triggering from leading or
trailing edge
• ICCcategory: MSI
DESCRIPTION
The HEF4938B is a dual
retriggerable-resettable monostable
multivibrator. Each multivibrator has
an active LOW trigger/retrigger input
(
I0), an active HIGH trigger/retrigger
input (I1), an overriding active LOW
direct reset input (CD), an output (O)
and its complement (O), and two pins
(CTCand RCTC) for connecting the
external timing components Ct and
Rt. Typical pulse width variation over
temperature range is ±0.2%.
The HEF4938B may be triggered by
either the positive or the negative
edges of the input pulse and will
produce an accurate output pulse
with a pulse width range of 10 µsto
infinity. The duration and accuracy of
the output pulse are determined by
the external timing components
Ctand Rt. The output pulse width (T)
is equal to Rt× Ct. The linear design
techniques in LOCMOS guarantee
precise control of the output pulse
width. A LOW level at CDterminates
the output pulse immediately.
Schmitt-trigger action in the inputs
makes the circuit highly tolerant for
slower rise and fall times.
FUNCTION TABLE
Notes
1. H = HIGH voltage level
2. L = LOW voltage level
INPUTS OUTPUTS
I
0
I
1
C
D
O O
↑ LH
H↑H
XXL L H
3. X = state is immaterial
4. ↑ = positive-going transition
5. ↓ = negative-going transition
6. = positive output pulse
7. = negative output pulse
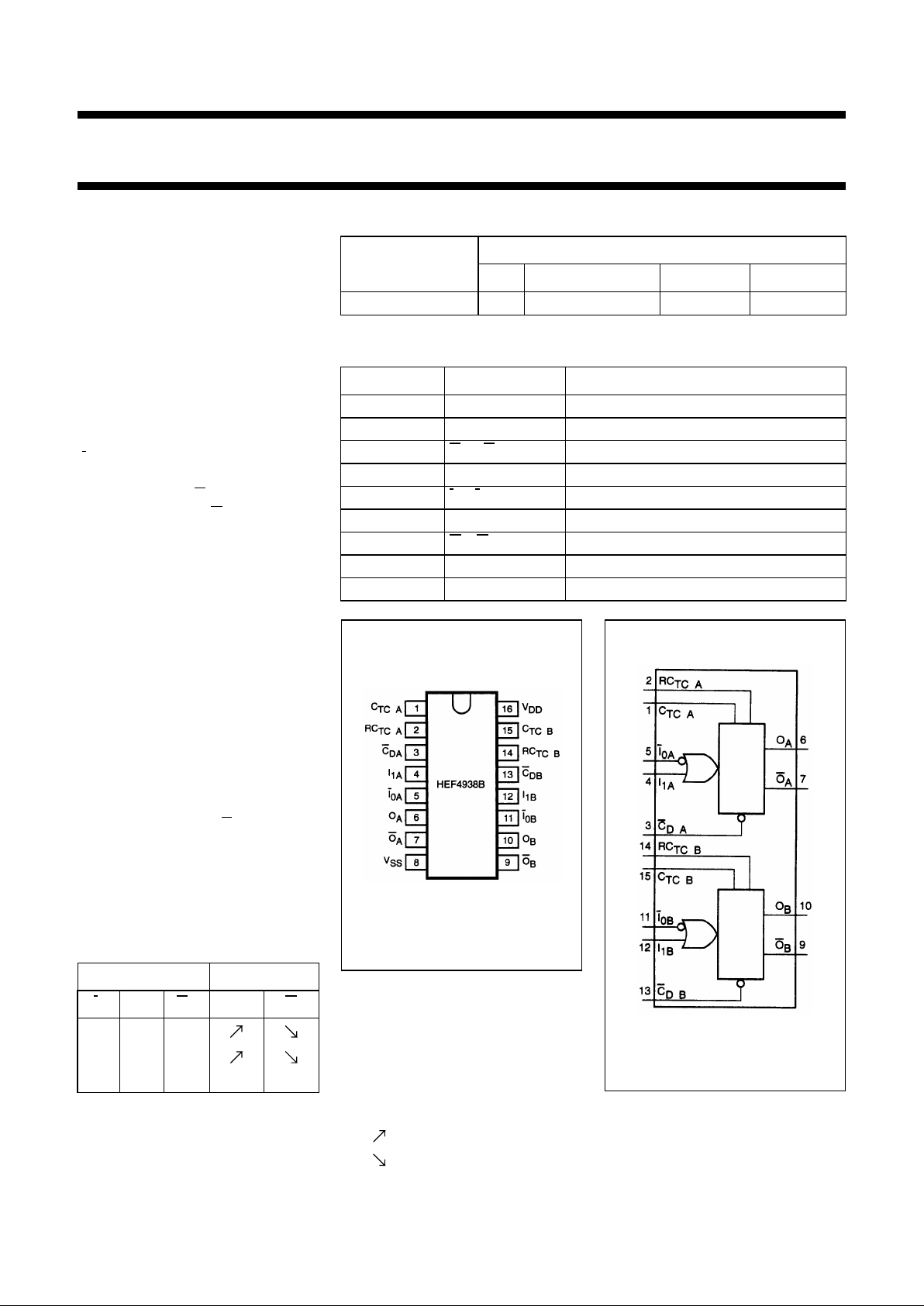
ORDERING AND PACKAGE INFORMATION
PIN DESCRIPTION
TYPE NUMBER
PACKAGES
PINS PIN POSITION MATERIAL CODE
HEF4938B 16 DIL plastic SOT38Z
PIN NO. SYMBOL NAME AND FUNCTION
1, 15 C
TC A,CTC B
external capacitor connections
2, 14 RC
TC A
,RC
TC B
external capacitor/resistor connections
3, 13
CDA, C
DB
direct reset input (active LOW)
4, 12 I
1A,I1B
input (LOW-to-HIGH triggered)
5, 11
I0A, I
0B
input (HIGH-to-LOW triggered)
6, 10 O
A,OB
output
7, 9
OA, O
B
complementary output (active LOW)
8V
SS
ground (0 V)
16 V
DD
positive supply voltage
Fig.1 Pin configuration.
Fig.2 Functional diagram.
January 1995 3
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Dual precision monostable multivibrator HEF4938B
This text is here in white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here in
_white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here inThis text is here in
white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader. white to force landscape pages to be ...
This text is here in white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here in
_white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here inThis text is here in
white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader. white to force landscape pages to be ...
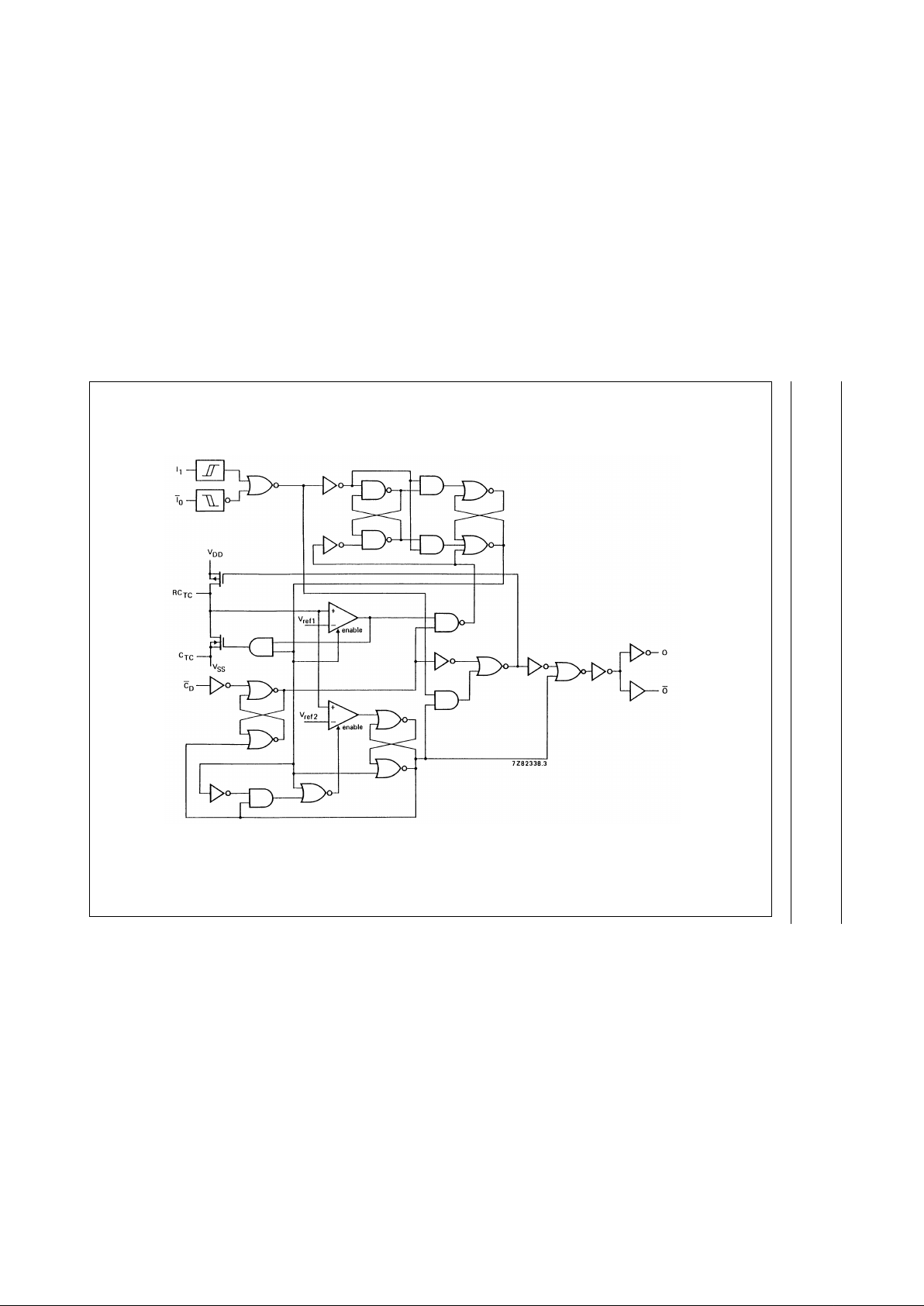
Fig.3 Logic diagram.
 Loading...
Loading...