Page 1

HEARTSTART XLT
Service Manual
M3500B/
M5500B
Page 2

Page 3

Service Manual
M3500B HeartStart XLT/
M5500B Heartstart 4000
Defibrillator/Monitor
Page 4

Notice
About This Edition
Edition 2
Printed in the USA
Publication number M3500-90900
The information in this manual applies
to the M3500B HeartStart XLT Release
Main 34 and earlier, and to the
Heartstart 4000 Release Main 34 and
earlier. This information is subject to
change without notice.
Philips Medical Systems shall not be
liable for errors contained herein or for
incidental or consequential damages in
connection with the furnishing, performance, or use of this material.
Edition History
Edition 1.1, March 28, 2000
Edition 2, February 2003
Copyright
Copyright © 2003
Philips Electronics North America
Corporation
3000 Minuteman Road
Andover, MA 01810-1099 USA
(978) 687-1501
All rights are reserved. Reproduction in
whole or in part is prohibited without
the prior written consent of the copyright holder.
WARNING
Radio Frequency (RF) interference
from nearby transmitting devices may
seriously degrade performance of the
M3500B/M5500B defibrillator/monitor. Electromagnetic compatibility with
surrounding devices should be assessed
prior to using the defibrillator.
CAUTION
Use of supplies or accessories other
than those recommended by Philips
Medical Systems may compromise
product performance.
THIS PRODUCT IS NOT INTENDED
FOR HOME USE.
IN THE U.S., FEDERAL LAW
RESTRICTS THIS DEVICE TO SALE
ON OR BY THE ORDER OF A PHYSICIAN.
Medical Device Directive
The M3500B/M5500B Defibrillator/
Monitor complies with the requirements
of the Medical Device Directive 93/42/
EEC and carries the
accordingly.
Authorized EU-representative:
Philips Medizinsysteme Böblingen
GmbH
Hewlett Packard Str. 2
71034 Böbingen
Germany
Canada EMC:ICES-001
0123
mark
ii
Page 5

Conventions
This manual uses the following text conventions:
NO TE Notes contain additional information on servicing this product.
CAUTION Caution statements describe conditions or actions that can result in damage to
the equipment or loss of data.
WARNING W arning statements describe conditions or actions that can result in personal injury
or loss of life.
Text represents messages that appear on the display
Softkey
represents softkey labels that appear on the display
above or below the button to which they correspond
iii
Page 6

Page 7

Contents
Introduction
Overview ............................................................................................................................... 1-1
Defibrillator/Monitor ...................................................................................................... 1-1
Batteries, Power Modules, Battery Charger Adapter ..................................................... 1-2
Installation ...................................................................................................................... 1-2
Upgrades ......................................................................................................................... 1-2
Preventive Maintenance .................................................................................................. 1-2
Repair Philosophy ...........................................................................................................1-3
Defibrillator/Monitor ................................................................................................ 1-3
Batteries, Power Modules, Battery Charger Adapter ............................................... 1-3
Performance Verification and Safety Tests
Overview ............................................................................................................................... 2-1
Mandatory Testing ................................................................................................................ 2-1
External Repairs/No Trouble Found ...............................................................................2-1
Printer .............................................................................................................................. 2-2
Internal Repairs ...............................................................................................................2-2
Test and Inspection Matrix ................................................................................................... 2-3
Test Equipment ..................................................................................................................... 2-8
Configuration and Diagnostic Modes ................................................................................. 2-10
Configuration Mode ...................................................................................................... 2-10
Diagnostic Mode ........................................................................................................... 2-11
Performance Verification .................................................................................................... 2-12
Visual Inspection .......................................................................................................... 2-12
Functional Checks ......................................................................................................... 2-13
ECG Functional Checks .......................................................................................... 2-13
Shock Advisory Functional Check ......................................................................... 2-14
Synchronized Cardioversion Functional Check ..................................................... 2-14
Functional Check ........................................................................................... 2-15
Sp0
2
Diagnostic Tests .................................................................................................................. 2-16
The System Log ............................................................................................................ 2-16
Extended Self Test ........................................................................................................ 2-17
User Interface Tests ...................................................................................................... 2-19
To check the Controls (keys): ................................................................................. 2-19
To check the display: .............................................................................................. 2-20
To check the audio output: ...................................................................................... 2-20
To check the printer: ............................................................................................... 2-21
ECG Tests ..................................................................................................................... 2-22
ECG Status messages .............................................................................................. 2-23
DC Offset ................................................................................................................ 2-23
ECG amplifier tests ................................................................................................. 2-23
PCI function ............................................................................................................ 2-24
v
Page 8

Contents
Pacing Test ....................................................................................................................2-25
Defibrillator Test (AC Power At 200 J) ........................................................................ 2-27
Defibrillator Test (Battery Power At 200 J) ................................................................. 2-28
Defibrillator Disarm Test ..............................................................................................2-29
Safety Tests ...................................................................................................................2-30
Earth Leakage ......................................................................................................... 2-30
Patient Lead Leakage ..............................................................................................2-30
Battery Capacity Test ..........................................................................................................2-31
Troubleshooting
Overview ............................................................................................................................... 3-1
Repair Philosophy ...........................................................................................................3-1
Equipment Required ....................................................................................................... 3-1
Troubleshooting and Repair Methodology ........................................................................... 3-2
Interview the User ..................................................................................................... 3-2
Identify the Problem ................................................................................................. 3-2
Perform the Repair ....................................................................................................3-2
Test the Unit .............................................................................................................. 3-2
Initial Assessment ................................................................................................................. 3-3
Attempt Power Up .................................................................................................... 3-3
Evaluate the Response .............................................................................................. 3-3
Diagnosing External Failures ................................................................................................ 3-4
Capture the Configuration Data ................................................................................ 3-4
Print the System Log ................................................................................................. 3-4
Rule out external components and improper use ...................................................... 3-4
Diagnosing Internal Failures ................................................................................................. 3-5
Run Self Tests ........................................................................................................... 3-5
Use the Troubleshooting Tables ............................................................................... 3-5
Configuration and Diagnostic Modes ............................................................................. 3-5
Accessing Configuration Mode ...................................................................................... 3-5
Accessing Diagnostic Mode ........................................................................................... 3-6
Printing the System Log ........................................................................................... 3-6
Troubleshooting Tables ........................................................................................................ 3-8
Using the Tables ............................................................................................................. 3-8
Unit Unresponsive ................................................................................................................ 3-9
Error Codes ......................................................................................................................... 3-11
System Messages ................................................................................................................3-13
Momentary Messages ......................................................................................................... 3-16
Audio Tones .................................................................................................................. 3-17
Extended Self Test Failures .......................................................................................... 3-18
vi
Page 9

Contents
Operational Problems ......................................................................................................... 3-19
ECG Monitoring ........................................................................................................... 3-19
SpO2 Monitoring ........................................................................................................... 3-21
Defibrillation and Cardioversion .................................................................................. 3-22
Pacing ............................................................................................................................ 3-24
Printer ............................................................................................................................ 3-25
Display .......................................................................................................................... 3-26
Audio ............................................................................................................................ 3-27
Keys .............................................................................................................................. 3-28
Battery and Power Modules .......................................................................................... 3-29
Data Card ......................................................................................................................3-31
Calling for Service - Philips HeartStart XLT ..................................................................... 3-32
United States of America .............................................................................................. 3-32
Latin America ............................................................................................................... 3-32
Canada .......................................................................................................................... 3-32
Other International Areas .............................................................................................. 3-33
Calling for Service - Laerdal Heartstart 4000 .....................................................................3-34
United States of America ......................................................................................... 3-34
International Customers ................................................................................................ 3-34
Removal and Replacement
Overview ............................................................................................................................... 4-1
Servicing Notes ..................................................................................................................... 4-1
Key Components ............................................................................................................. 4-1
Removal, Handling, and Replacement ........................................................................... 4-1
Flex Circuit Connections .......................................................................................... 4-1
Flex Circuit Handling ............................................................................................... 4-2
Internal Connections ................................................................................................. 4-2
Cable and Assembly Placement ................................................................................ 4-2
Instrument Reassembly ............................................................................................. 4-2
Tool Requirements ................................................................................................................ 4-3
User-replaceable Parts and Accessories ................................................................................4-4
Manual Door ................................................................................................................... 4-4
Removal .................................................................................................................... 4-4
Replacement ..............................................................................................................4-4
Carrying Case ................................................................................................................ 4-7
Removal .................................................................................................................... 4-7
Replacement ..............................................................................................................4-8
User Maintenance ................................................................................................................. 4-9
Cleaning the Printer Printhead ........................................................................................ 4-9
vii
Page 10

Contents
External Assemblies ........................................................................................................... 4-10
Printer Assembly ........................................................................................................... 4-11
Removal .................................................................................................................. 4-11
Replacement ............................................................................................................4-12
Printer Sliding Door ...................................................................................................... 4-13
Removal .................................................................................................................. 4-13
Replacement ............................................................................................................4-13
Printer Platen .................................................................................................................4-14
Removal .................................................................................................................. 4-14
Replacement ............................................................................................................4-14
Battery Cover ................................................................................................................ 4-15
Removal .................................................................................................................. 4-15
Replacement ............................................................................................................4-16
Main Fuse ..................................................................................................................... 4-17
Removal .................................................................................................................. 4-17
Replacement ............................................................................................................4-17
Battery Eject Assembly ................................................................................................ 4-17
Removal .................................................................................................................. 4-17
Replacement ............................................................................................................4-18
Data Card Door ............................................................................................................. 4-18
Removal .................................................................................................................. 4-18
Replacement ............................................................................................................4-18
Labels .................................................................................................................................. 4-19
Label Descriptions ........................................................................................................ 4-19
Case Label Set ........................................................................................................ 4-19
Branding Label Set ................................................................................................. 4-21
Ambient Light Sensor Label ...................................................................................4-21
Speaker Label Set ................................................................................................... 4-22
Removing and Replacing Labels .................................................................................. 4-22
Removal .................................................................................................................. 4-22
Replacement ............................................................................................................4-22
Opening the Sealed Case .................................................................................................... 4-23
Discharging the Power Supply Capacitors ................................................................... 4-23
Primary Method ......................................................................................................4-23
Secondary Method: ................................................................................................. 4-23
Separating the Case ..................................................................................................... 4-25
Discharging the Defibrillator Capacitor ....................................................................... 4-27
Primary Method ......................................................................................................4-27
Secondary Method .................................................................................................. 4-28
Identifying Internal Subassemblies ..................................................................................... 4-29
viii
Page 11

Contents
Top Case Assemblies .......................................................................................................... 4-30
Lithium Backup Battery ................................................................................................ 4-30
Removal .................................................................................................................. 4-30
Cleaning .................................................................................................................. 4-30
Replacement ............................................................................................................4-30
Disconnecting the Control PCA ................................................................................... 4-31
From the Rest of the Unit ....................................................................................... 4-31
From the Display .................................................................................................... 4-31
Reconnecting the Control PCA ..................................................................................... 4-31
To the Display ......................................................................................................... 4-31
To the Rest of the Unit ............................................................................................ 4-32
Control Stack ................................................................................................................ 4-33
Removal .................................................................................................................. 4-33
Replacement ............................................................................................................4-33
Control PCA ................................................................................................................. 4-34
Removal .................................................................................................................. 4-34
Replacement ............................................................................................................4-35
LCD Display Assembly ................................................................................................ 4-37
Removal .................................................................................................................. 4-37
Replacement ............................................................................................................4-37
SpO2 PCA ..................................................................................................................... 4-38
Removal .................................................................................................................. 4-38
Replacement ............................................................................................................4-39
ECG Connector .............................................................................................................4-40
Removal .................................................................................................................. 4-40
Replacement ............................................................................................................4-41
SpO2 Connector ............................................................................................................ 4-42
Removal .................................................................................................................. 4-42
Replacement ............................................................................................................4-43
Manual Keypad Assembly ............................................................................................ 4-44
Removal .................................................................................................................. 4-44
Replacement ..................................................................................................................4-47
Interface PCA ............................................................................................................... 4-50
Removal .................................................................................................................. 4-50
Replacement ............................................................................................................4-52
Speaker .......................................................................................................................... 4-55
Removal .................................................................................................................. 4-55
Replacement ............................................................................................................4-55
Top Case Assembly ............................................................................................................ 4-56
Description ..............................................................................................................4-56
Removal and replacement ....................................................................................... 4-56
ix
Page 12

Contents
Bottom Case Assemblies .................................................................................................... 4-58
Battery PCA .................................................................................................................. 4-58
Removal .................................................................................................................. 4-58
Replacement ............................................................................................................4-59
Defibrillator Capacitor .................................................................................................. 4-60
Removal .................................................................................................................. 4-60
Replacement ............................................................................................................4-61
Power PCA ................................................................................................................... 4-62
Removal .................................................................................................................. 4-62
Replacement ............................................................................................................4-63
Power Connector ........................................................................................................... 4-64
Removal .................................................................................................................. 4-64
Replacement ............................................................................................................4-64
Patient Connector .......................................................................................................... 4-65
Removal .................................................................................................................. 4-65
Replacement ............................................................................................................4-65
Bottom Case Assembly ....................................................................................................... 4-66
The Language Support Tool ............................................................................................... 4-67
Using the Support Tool ................................................................................................. 4-67
Closing the case .................................................................................................................. 4-69
Disposing of the M3500B/M5500B ................................................................................... 4-70
Disposing of the SLA Battery ....................................................................................... 4-70
Replacement Parts
Overview ............................................................................................................................... 5-1
Ordering Replacement Parts ........................................................................................... 5-1
Ordering Supplies and Accessories ................................................................................ 5-1
Key Components ................................................................................................................... 5-1
Calling for Service - Philips HeartStart XLT ....................................................................... 5-2
United States of America ................................................................................................ 5-2
Latin America ................................................................................................................. 5-2
Canada ............................................................................................................................ 5-2
Other International Areas ................................................................................................ 5-3
Calling for Service - Laerdal Heartstart 4000 .......................................................................5-4
United States of America ........................................................................................... 5-4
International Customers .................................................................................................. 5-4
Special Tools ......................................................................................................................... 5-4
M3500B Unit Exchange Program ......................................................................................... 5-5
Logistics .................................................................................................................... 5-5
Replacement Parts Tables ..................................................................................................... 5-6
Electrical Assemblies ............................................................................................................ 5-7
Control PCA ................................................................................................................... 5-7
Other Replacement PCAs ............................................................................................... 5-8
Other Electrical Assemblies ............................................................................................ 5-8
Individual Electrical Parts ............................................................................................... 5-8
x
Page 13

Contents
Mechanical Assemblies ........................................................................................................ 5-9
Manual Door ................................................................................................................... 5-9
Manual Keypad Assembly ............................................................................................ 5-10
Other Mechanical Assemblies ...................................................................................... 5-12
Connectors .................................................................................................................... 5-12
Individual Mechanical Parts ......................................................................................... 5-13
Labels .................................................................................................................................. 5-14
Case Label Sets ............................................................................................................. 5-14
Other Labels .................................................................................................................. 5-15
Supplies & Accessories ...................................................................................................... 5-16
Key Components .................................................................................................................5-20
Theory of Operation
Overview ............................................................................................................................... 6-1
PCA Descriptions ................................................................................................................. 6-2
Control PCA ................................................................................................................... 6-2
Interface PCA ................................................................................................................. 6-3
Power PCA ..................................................................................................................... 6-3
SpO2 PCA .......................................................................................................................6-3
Battery PCA ....................................................................................................................6-4
Battery ............................................................................................................................. 6-4
Printer .............................................................................................................................. 6-4
System Level Interconnections ............................................................................................. 6-5
System Functional Descriptions ........................................................................................... 6-6
Signal and Data Flow ...................................................................................................... 6-6
ECG Monitoring Functions ............................................................................................ 6-7
ECG - Pads ................................................................................................................ 6-7
ECG - 3/5-lead cable ................................................................................................. 6-7
Patient impedance functions ..................................................................................... 6-8
SpO2 Monitoring Functions ........................................................................................... 6-8
Defibrillation Functions .................................................................................................. 6-9
Charging .................................................................................................................... 6-9
Delivering a shock .................................................................................................... 6-9
Delivering synchronized cardioversion .................................................................. 6-10
Pacing Functions ...........................................................................................................6-11
Audio Functions ............................................................................................................ 6-12
Display Functions ......................................................................................................... 6-12
Contrast - manual control ....................................................................................... 6-12
Contrast - automatic control ................................................................................... 6-12
Backlight ................................................................................................................. 6-12
Indicator Functions ....................................................................................................... 6-13
Key Functions ............................................................................................................... 6-14
Main Keys ...............................................................................................................6-14
Other Keys ..............................................................................................................6-14
xi
Page 14

Contents
Printing Functions ......................................................................................................... 6-15
Contrast ................................................................................................................... 6-15
Out of paper/door open ........................................................................................... 6-15
Battery/Power Functions ............................................................................................... 6-16
Contacts/Battery Type ............................................................................................ 6-16
Charging .................................................................................................................. 6-16
Lithium Backup Battery ................................................................................................ 6-18
Data Card ......................................................................................................................6-18
Specifications
Overview ............................................................................................................................... 7-1
Specifications ........................................................................................................................ 7-1
Defibrillator .................................................................................................................... 7-1
Manual Mode ............................................................................................................ 7-2
AED Mode ................................................................................................................ 7-3
ECG Monitoring ............................................................................................................. 7-3
Frequency Response: ................................................................................................ 7-4
Patient Isolation: ....................................................................................................... 7-4
Display ............................................................................................................................ 7-4
Thermal Array Printer ..................................................................................................... 7-4
Continuous Real Time Strip: .................................................................................... 7-4
Battery and Battery Power Modules ............................................................................... 7-5
Noninvasive Pacing ........................................................................................................ 7-6
SpO2/Pulse Oximetry ...................................................................................................... 7-6
Accuracy with: .......................................................................................................... 7-6
Event Storage ..................................................................................................................7-6
Internal Event Summary: .......................................................................................... 7-6
Data Card Event Summary: ...................................................................................... 7-6
General ............................................................................................................................ 7-7
Environmental ................................................................................................................. 7-7
Waveforms - 150J ................................................................................................................. 7-8
150J, 25 ohms .............................................................................................................. 7-8
150J, 50 ohms .............................................................................................................. 7-8
Waveforms -150J (continued) .............................................................................................. 7-9
150J, 75 ohms ............................................................................................................... 7-9
150J, 100 ohms ............................................................................................................ 7-9
Waveforms -150J (continued) ............................................................................................ 7-10
150J, 125 ohms (2ms/div) ........................................................................................ 7-10
150J, 125 ohms (5 ms/div) .......................................................................................... 7-10
xii
Page 15

Contents
Waveforms - 200J ............................................................................................................7-11
Waveforms - 200J (continued) ........................................................................................... 7-12
Waveforms - 200J (continued) ...................................................................................... 7-13
Symbol Definitions .............................................................................................................7-14
Safety Considerations ......................................................................................................... 7-16
Electromagnetic Compatibility ........................................................................................... 7-18
Reducing Electromagnetic Interference ........................................................................ 7-18
Restrictions for Use ...................................................................................................... 7-18
Immunity Level ............................................................................................................. 7-19
xiii
Page 16

Page 17

1Introduction
This Service Manual provides the information needed to successfully service
the Philips M3500B HeartStart XLT and the Laerdal M5500B Heartstart 4000
Defibrillator/Monitors. The intended users of this manual are technical personnel who have been trained in the safe and proper servicing of the M3500B/
M5500B.
Overview
In this chapter, you’ll find general information that you should become familiar with before servicing the M3500B/M5500B. Detailed information regarding controls, operation, and capabilities of the instrument can be found in the
Instructions for Use that was shipped with the product. We recommend you
review the Instructions for Use before servicing this device. This Service
Manual assumes you are familiar with the controls and with basic operations.
1
Defibrillator/Monitor
The M3500B/M5500B is a biphasic, semi-automatic external defibrillator.
This portable, lightweight device offers two modes of operation for defibrillation:
z Semi-Automatic External Defibrillation (AED) Mode
z Manual Mode
In AED Mode, the M3500B/M5500B analyzes the patient’s ECG and advises
the clinician whether or not to deliver a shock. In Manual Mode, the M3500B/
M5500B turns control of the defibrillation process over to the clinician. The
clinician analyzes the patient’s ECG, decides if defibrillation is advised, and
determines the energy setting for defibrillation. Manual Mode also allows the
clinician to perform synchronized cardioversion and offers optional noninvasive pacing (using a monophasic waveform).
Defibrillation is performed through multifunction defib electrode pads. In
addition, both AED and Manual Mode offer monitoring through pads, 3-lead
ECG monitoring electrodes, or optional 5-lead ECG monitoring electrodes.
Optional pulse oximetry (SpO
well.
) monitoring is available in both modes, as
2
1-1
Page 18
Overview
The M3500B/M5500B automatically stores critical events, such as shocks
and alarm violations, in its internal memory. An Event Summary may be
printed at any time. The M3500B/M5500B also enables you to store data and
events on an M3510A/M5510A Data Card for downloading to the Event
Review Data Management System.
Batteries, Power Modules, Battery Charger Adapter
The M3500B/M5500B is powered by a rechargeable Sealed Lead Acid (SLA)
battery (M3516A/M5516A). Proper care of these batteries will ensure that
they have the energy required to operate the M3500B/M5500B and deliver the
appropriate therapy (See "Battery Maintenance" section in Instructions for
Use).
Batteries may be charged either in the defibrillator or in the Battery Charger
Adapter (M3506A/M5506A). In either case, power for charging can be provided by the AC Power Module (M3517A/M5517A), or by the DC Power
Module (M3518A/M5518A).
NO TE The defibrillator will take longer to charge when powered with either power
module without a battery installed. The recommended practice is to use a battery in conjunction with the power module to ensure optimal performance.
For information on either the power modules or the adapter, see the documentation supplied with the power module or adapter.
Installation
The M3500B/M5500B does not require installation. The Instructions for Use
describes the setup required before placing the device into service, as well as
configuration options.
Upgrades
Upgrades are available to add specific functionality to units in the field. As of
the publication of this manual, these upgrades are:
z M3514A Pacing Upgrade (adds pacing)
z M3515A SpO2 upgrade.
Consult your sales representative or dealer or distributor for the latest details.
Preventive Maintenance
Preventive maintenance and periodic operational checks are intended to be
performed by the user. Both topics are covered in the Maintenance chapter of
the Instructions for Use.
1-2 Introduction
Page 19

Overview
Repair Philosophy
Defibrillator/Monitor
The repair philosophy of the M3500B/M5500B is subassembly replacement.
Examples of subassemblies are the printer, the Control Printed Circuit Assembly (PCA), and selected connectors and other items. Repairs that involve
replacing components on a PCA are not supported.
CAUTION Individual component replacement should not be attempted outside of a fac-
tory authorized repair facility. Component level repair is extremely difficult
due to the extensive use of surface mount technology and the high parts-density on the circuit boards. Unauthorized component replacement can impair
performance of the M3500B/M5500B.
Batteries, Power Modules, Battery Char ger Adapter
The repair philosophy for the SLA battery (M3516A/M5516A), AC Power
Module (M3517A/M5517A), DC Power Module (M3518A/M5518A), and
the Battery Charger Adapter (M3506A/M5506A) is unit replacement. These
accessories are not repaired in the field.
1
For information on ordering replacements, see "Supplies & Accessories" on
page 5-16.
M3500B/M5500B Service Manual 1-3
Page 20

Page 21

2 Performance Verification and Safety Tests
Overview
This chapter describes the tests and inspections required to verify performance of the M3500B/M5500B Defibrillator/Monitor.
The information is presented in the following sequence:
Test Matrix A list of the tests required to verify per-
formance of the M3500B/M5500B,
along with expected test results.
Test Equipment A list of commercially available test, cal-
ibration and simulation devices needed
to perform performance verification
tests.
Performance Verification Step-by-step instructions for performing
each of the Performance Verification
Tests.
Mandatory Testing
The Performance Verification Tests in this chapter are intended to verify
proper operation of the M3500B/M5500B following repair. The level of testing required corresponds to the type of repair performed, and is divided into 3
categories:
2
z External/No Trouble Found
z Printer
z Internal
External Repairs/No Trouble Found
External Repairs are those involving the repair or replacement of one or
more of the items below. No Trouble Found applies when no malfunction
can be found, or when the problem appears to be due to improper use. In
either situation, the key point is that the case has not been opened.
z ECG cable
z SpO
z Battery
cable or sensor
2
2-1
Page 22

Mandatory Testing
z Labels
z AC or DC Power module
z Consumables (ECG monitoring electrodes, multifunction defibrilla-
tion pads, printer paper)
z Main fuse (on Battery PCA)
z Manual Door Assembly
z Data Card Door Assembly
z Battery Eject Assembly
The following testing is required after an External Repair or when the outcome of the service is No Trouble Found (when the case has not been
opened):
z Perform the Visual Inspection (page 2-12).
z Run the Extended Self Test (page 2-17).
z Print and Verify the System Log (page 2-16).
Printer
If the printer was replaced, and the case was not opened, the following tests
are required:
z Perform the Visual Inspection (page 2-12).
z Run the Extended Self Test (page 2-17).
z Run the Printer Test (page 2-21).
z Print and Verify the System Log (page 2-16).
Internal Repairs
If the case was opened (regardless of what the repair involved), all of the Performance Verification Tests must be performed, beginning with "Visual
Inspection" on page 2-12.
2-2 Performance Verification and Safety Tests
Page 23
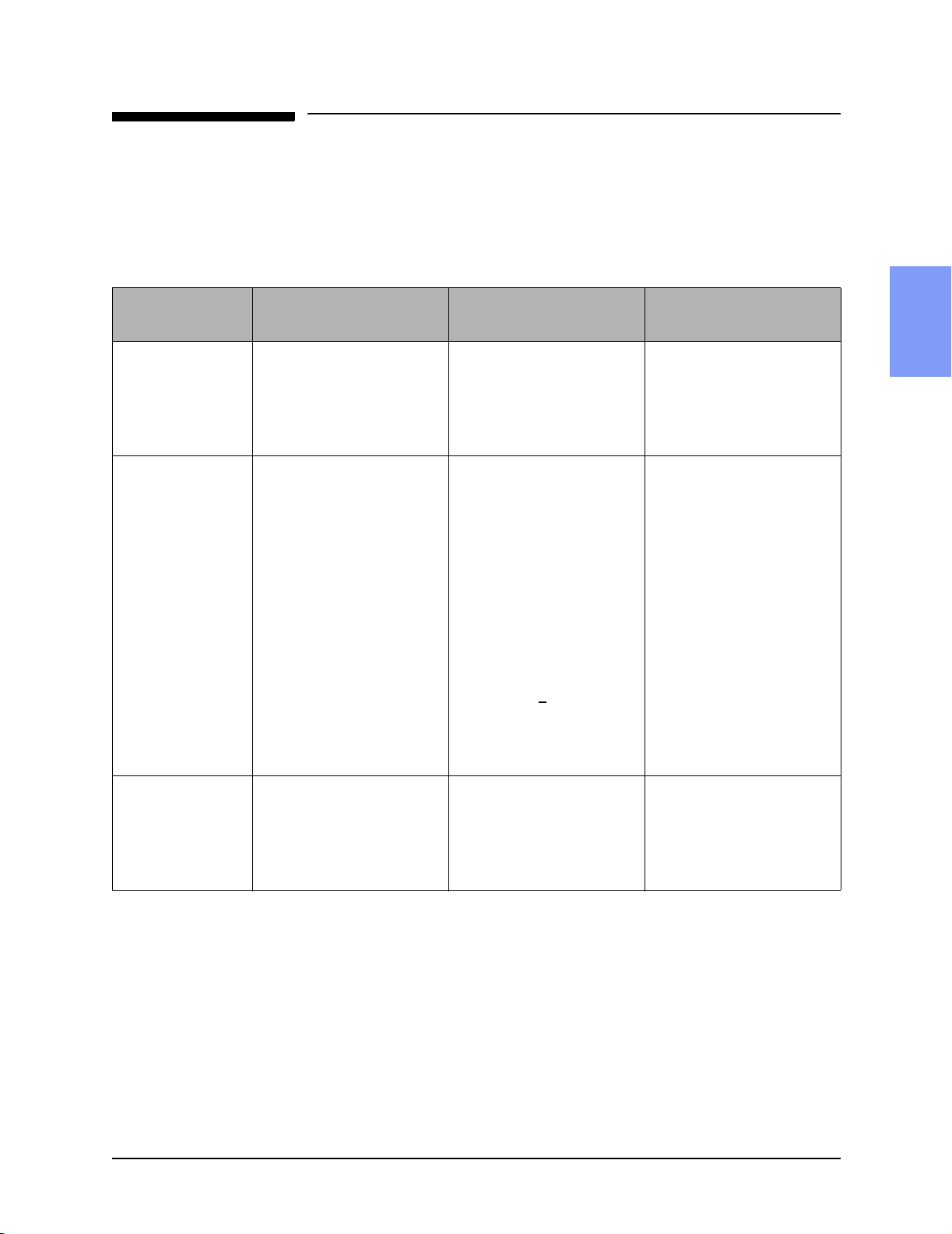
Test and Inspection Matrix
The matrix in Table 2-1 summarizes performance verification tests and
inspections for the M3500B/M5500B; including test name, test or inspection
to perform, expected test results, and data to record.
Table 2-1 Performance Verification and Safety Tests
Test and Inspection Matrix
Test Group Name
Visual Inspection
(VI)
Functional
Checks (F)
Test or Inspection to
Perform
Inspect unit, accessories,
cables, etc. as described on
page 2-12.
In normal Operating Mode,
perform the following functional checks:
• ECG (page 2-13). • Waveform clear on dis-
• Shock Advisory (page 2-
14).
• Synchronized Cardiover-
sion (page 2-14).
• SpO
(page 2-15). • 95% -100%
2
Expected Test Results
• If no unusual damage, no
corrosion, no missing
items,
then Visual Inspection
passes
• If all functions respond as
expected:
play; HR correct on display;
HR alarm works. Leads off,
pads off indicators as
expected.
• Shock Advised only when
appropriate
• Shock delivered with cor-
rect timing (<
60msec)
Data to Record
P (pass) or F (fail)
Example VI:p
Example F:p
2
then Functional test passes
Extended Self
Test (X)
In Diagnostic Mode, run the
Extended Self Test (page 2-
17). Includes Data Card Test
and time/date check.
If "Pass" reported on all
tests applicable to the device
configuration and options,
then Extended Self test
passes
Example X:p
M3500B/M5500B Service Manual 2-3
Page 24
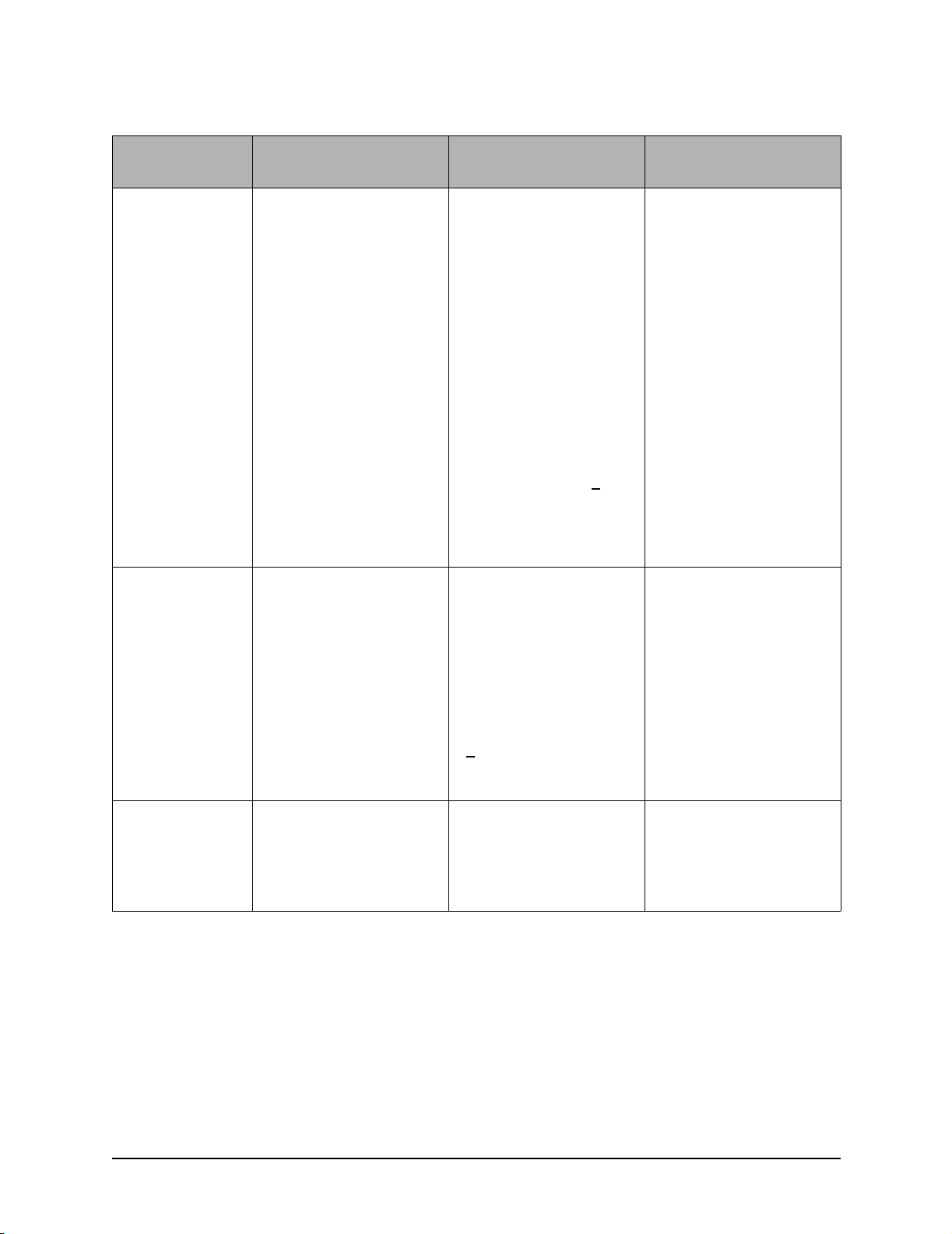
Test and Inspection Matrix
Table 2-1 Performance Verification and Safety Tests (Continued)
Test Group Name
User Interface
Tests (U)
ECG Tests (E) In Diagnostic Mode, run the
Test or Inspection to
Perform
• In Diagnostic Mode, run
the following tests
(page 2-19):
• Controls Test • All keys respond as
• Display Test • Display goes dark, then
• Audio Test • Alerts, alarms, and tones
• Printer Test • Print quality is adequate;
ECG Tests (page 2-22):
Expected Test Results
If all responses as expected: Example: U:p
expected
light. Black vertical bar
scrolls across the screen
from left to right.
are clearly heard
no stray marks or lines
• Print speed: 25 mm +
(1.25mm)
then User Interface test
passes
If all data within limits, all
checks pass:
5%
Data to Record
P (pass) or F (fail)
Example:E:p
• Status messages (lead,
pad, DSP)
PCI measurement If all PCI measurements are
• PCI - Test Load attached • 50 ± 30 Ω
• PCI - Pads open • >
Pacing Test (P) In Diagnostic Mode, run the
Pacing Test (page 2-25):
• 200 mA • 200 mA± 20 mA
• "Good" displayed for all
three status messages
within the following ranges:
2000 Ω
then ECG test passes
If measurement is within the
following limit:
then Pacing test passes
Example: P:p
2-4 Performance Verification and Safety Tests
Page 25
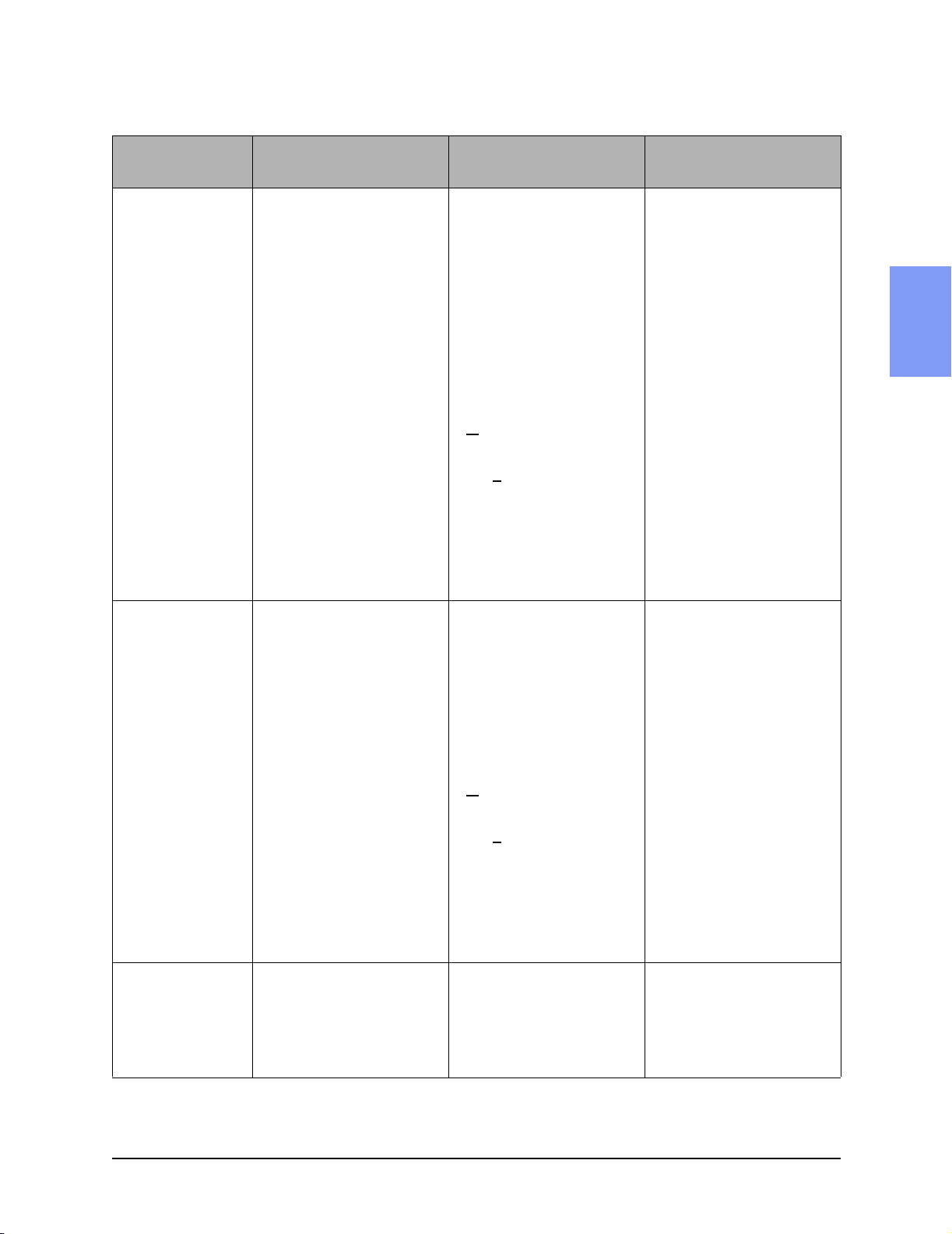
Table 2-1 Performance Verification and Safety Tests (Continued)
Test and Inspection Matrix
Test Group Name
Defibrillator Test AC or DC P ower
Module (DM)
(Required only
when AC or DC
power module
used.)
Test or Inspection to
Perform
Using only the AC or DC
power module, enter Diagnostic Mode and run the
Defibrillator Test (at
200Joules) (page 2-27):
Displayed by
M3500B/M5500B:
• Available Energy after
Shock
• Msec to charge • <
• Delivered energy • Actual delivered energy
• Impedance • 42 to 57 Ω
• Defib errors • None (0)
Expected Test Results
If the measurements are as
follows:
• 0
15000 msec
200 +
7%
then the Defibrillator test
(Power Module) passes
Data to Record
P (pass) or F (fail)
Example: DM:p
2
Defibrillator Test Battery Power
(DB)
Defibrillator
Disarm Test (D)
Using only battery power,
enter Diagnostic Mode and
run the Defibrillator Test (at
200Joules) (page 2-28).
Displayed by
M3500B/M5500B
• Available Energy after
Shock
• Msec to charge • <
• Delivered energy • Actual delivered energy
• Impedance • 42 to 57 Ω
• Defib errors • None (0)
Enter Diagnostic Mode and
run the Defibrillator Disarm
Test (page 2-29)
If the measurements are as
follows:
• 0
3000 msec
200 +
7%
then the Defibrillator test
(Battery Power) passes
If all readings as expected
Available energy - failure >0
No errors reported
then the Defibrillator Disarm
test passes
Example: DB:p
Example: D:p
M3500B/M5500B Service Manual 2-5
Page 26

Test and Inspection Matrix
Table 2-1 Performance Verification and Safety Tests (Continued)
Test Group Name
Safety Tests Indicate test results as
Earth Leakage
Current (S1)
(Required only
when AC Power
module is used.)
Patient Lead
Leakage (S3)
(Required only
when AC Power
module is used.)
Test or Inspection to
Perform
follows:
Earth Leakage Current NC
(Normal Condition)
Earth Leakage SF
(Single Fault - open neutral)
ECG Patient Cable If readings are as expected:
• Source
(Normal Condition) - aa
Expected Test Results
Note: All Safety tests include
both Normal and Reverse
Polarity conditions.
If NC maximum leakage
current:
300 uA (UL), <500 uA
<
and
If SF maximum leakage
current:
< 1000 uA
then S1 test passes
• <
10 uA
Data to Record
P (pass) or F (fail)
Example: S1:p/200/300
S3:p/aa/bb/cc/dd/ee/ff/ggg/
hhh/iii
Example: S3:p/9/49/49/10/
50/50/100/499/750
• Source (Single Fault
Condition - open earth,
open neutral) - bb
• With Mains on applied part
(Single Fault condition) - cc
SPO
2
• Source
(Normal Condition) - dd
• Source (Single Fault
Condition - open earth,
open neutral) - ee
With Mains on applied part
(Single Fault condition) - ff
• <
50 uA
• <
50 uA
then Safety Patient Lead
Leakage test passes
If readings are as expected:
• <
10 uA
• <
50 uA
• <
50 uA
then Safety Patient SPO2
Leakage test passes.
2-6 Performance Verification and Safety Tests
Page 27

Table 2-1 Performance Verification and Safety Tests (Continued)
Test and Inspection Matrix
Test Group Name
Note: When recording test results, separate results within a test by slashes; separate tests by a semicolon (;); and
do not use empty spaces. For example:
VI:p;F:p;X:p;U:p;E:p;P:p;DM:p;DB:p;D:p;S1:p/200/300;S3:p/9/49/49/10/50/50/100/499/750
Test or Inspection to
Perform
Pads If readings are as expected:
• Source
(Normal Condition) - ggg
• Source (Single Fault
Condition) - hhh
• With Mains on applied part
(Single Fault condition) - iii
Expected Test Results
<
100 uA
<
500 uA
<
5000 uA
then Safety Pads Test
passes
Data to Record
P (pass) or F (fail)
2
M3500B/M5500B Service Manual 2-7
Page 28

Test Equipment
Test Equipment
Table 2-2 lists the equipment needed to perform the Performance Verification
tests, and provides specifications for commercially available analyzers and
simulators. Test equipment is called out within each test procedure when
needed. In addition, a digital voltmeter is also useful.
A 50 ohm test load is available from Philips Medical Systems (M1781A).
Table 2-2 Equipment List
Equipment/Test Specifications
ECG Simulator
Calibrated Leads
• Amplitude accuracy ±2%
• Rate accuracy ±2%
Calibrated Paddles
• Amplitude accuracy ±2%
• Rate accuracy ±2%
Defibrillator Analyzer
Waveform compatibility Meets all specs below using biphasic
Load resistance: 50 Ω ±1% (non-inductive)
Maximum energy: ≥ 200 joules
Maximum voltage: ≥ 2500 V
Maximum current: ≥50 A
Measurement accuracy:
• ≥ 20 joules: ≤ ±2% of reading
• < 20 joules: ≤ ±0.4 joules
ECG simulator
ECG simulator
truncated exponential waveform.
Cardioversion measurement range: –150 to +150 ms
2-8 Performance Verification and Safety Tests
Page 29

Table 2-2 Equipment List
Equipment/Test Specifications
Pacer tester
Load impedance: ≤400 Ω
Test Equipment
Current
• 10 mA–50 mA: <±2 mA
• 50 mA–200 mA: <±4%
Rate
• 30–180 ppm: <±0.5%
Waveform duration accuracy:
• 30–180 ppm: ±1ms
measurement accuracy
measurement accuracy
2
M3500B/M5500B Service Manual 2-9
Page 30

Configuration and Diagnostic Modes
Configuration and Diagnostic Modes
The instructions below describe how to enter Configuration Mode and Diagnostic Mode.
Configuration Mode
These instructions describe briefly how to enter Configuration Mode. See the
Instructions for Use for details on configuration settings and what effect they
have.
CAUTION Inserting or removing the Data Card while the unit is on can corrupt the Data
Card and prevent the unit from powering on again. If this occurs, see Chapter
3, Troubleshooting.
1. Power off.
Make sure the unit’s power is off.
2. Insert the Data Card.
If you intend to save the configuration to a Data Card (or load the configuration from a Data Card), insert the Data Card now. To avoid possible
confusion, designate one Data Card as the "Configuration Card" and label
it clearly. Keep this card physically separate from cards used by the clinical staff for data storage.
3. Enter Configuration Mode.
Press softkeys 4 and 5 at the same time, and hold them down while turning the power on. See Figure 2-1 for softkey numbering.
4. Select and manage Configuration choices.
z To select a configuration, press the and softkeys to move up
or down the list until the desired Settings item is highlighted. Then
press the softkey to access those settings.
z To print out a strip with all the current configuration choices, select
Print All Settings and press .
z To store the configuration settings on a data card, select Save Settings
to Data Card and press . When prompted with Save Settings to
Data Card? press .
z To load configuration settings from a Data Card, select Load Settings
from Data Card and press . When prompted with Load Settings
from Data Card? press .
ENTER
ENTER
ENTER
SAVE
ENTER
LOAD
5. Exit Configuration Mode.
z To exit Configuration Mode, turn the unit off.
z Wait 2 seconds. Remove the Data Card by pressing the black eject
button and pulling the Data Card from the compartment.
2-10 Performance Verification and Safety Tests
Page 31

Figure 2-1 Softkey Numbers
Configuration and Diagnostic Modes
Contrast
ECG Size
Volume
Diagnostic Mode
These instructions describe how to enter Diagnostic Mode. Once in Diagnostic Mode, you can:
z Print the System Log (see "Printing the System Log" on page 3-6).
z Run the Extended Self Test (see "Diagnostic Tests" on page 2-16).
z Run other Diagnostic Tests (see "Diagnostic Tests" on page 2-16).
1. Power off.
Make sure the power is off.
2. Enter Diagnostic Mode.
Press softkeys 4 and 6 at the same time, and hold them down while turning the power on. See Figure 2-1.
3. Wait for the Diagnostic software to initialize.
This will take several seconds. The unit is ready to proceed when the
screen cursor responds to softkey inputs.
2
4. Select the desired test or function.
z To select a test, press the and softkeys to move up or down
the list until the desired test is highlighted. Then press the
ENTER
softkey to start that test.
5. Exit Diagnostic Mode.
To exit Diagnostic Mode, turn the unit off.
M3500B/M5500B Service Manual 2-11
Page 32

Performance Verification
Performance Verification
This section gives instructions for running Performance Verification tests on
the M3500B/M5500B. The tests are sequenced to check more basic functions
first, and then build on that to check more complex functions. We recommend
you perform these tests in this sequence. If desired, you can make copies of
the Test Results Matrix (page 2-3) and use it to record results.
The Performance Verification is divided into four sections:
Visual Inspection Items that should be inspected each
time the defib is serviced.
Functional Checks A series of checks in normal operating
mode to assess general performance.
Diagnostic Tests A series of tests using the built-in Diag-
nostic Test menu. Describes how to
access Diagnostic Mode, and how to
run each of the Diagnostic Tests.
Safety Tests Tests of safety related parameters such
as leakage current.
Visual Inspection
1. Inspect the entire unit, especially power cords, printer, battery, cables, and
sensors for signs of the following.
z Wear or damage to patient cables and associated strain reliefs.
z Mechanical damage to case, membrane switches, speaker cover,
ambient light sensor cover, display window.
z Loose or missing hardware.
z Evidence of liquid spill. Check inside the printer bucket and clean out
any accumulation using gloves and an approved cleaner.
z Residue on the thermal printhead.
z Printer roller wear.
z Wear or damage to power cord and associated strain relief.
z Corrosion on connector pins, printer parts, or battery contacts.
Pass: Only normal wear, no damage serious enough to inhibit
performance. No corrosion visible.
2. Check ECG electrodes and defibrillator pads for freshness (data code or
expiration date) and condition.
Pass: Electrodes and pads are within their expiration date and
appear usable. Packaging is unopened and shows no tears or punctures.
No corrosion visible on connector sockets, electrodes, or pads.
2-12 Performance Verification and Safety Tests
Page 33

Performance Verification
Functional Checks
The following functional checks exercise the basic functions of the defibrillator/monitor. They are intended as a broad check of the unit’s performance, and
are designed to complement (not replace) the Diagnostic Tests described later.
If all elements of a test pass, record that test as a PASS and return to the main
diagnostic menu by pressing . If there is any failure, begin troubleshooting and repairing the unit as needed. See "Troubleshooting"
on page 3-1.
MAIN
ECG Functional Checks
This section describes how to check the operation of the ECG functions. Each
of the ECG checks assumes the unit and the simulator are still set up as they
were at the end of the previous ECG check.
To check ECG display and Heart Rate (HR) functions:
1. Connect the ECG simulator to both the Pads input and the 3- or
5-lead ECG cable. Set the simulator for normal sinus rhythm (NSR), 1mV
amplitude, at some nominal rate (e.g., 60 bpm).
2. Set the M3500B/M5500B to Manual operating mode (not Diagnostic
Mode).
3. Using the softkey, verify that the display shows a normal
ECG with a clean baseline for both Pads and Lead II.
4. Verify the Heart Rate (HR) displayed is correct.
5. Disconnect the ECG simulator from the pads cable and verify that the display shows a dashed line in place of the waveform and that the unit both
alarms and gives the Pads Off message.
6. If using a 5-lead ECG cable, set the defibrillator to monitor from the V
lead.
7. Disconnect each of the ECG leads from the simulator one at a time, and
verify that the display shows a dashed line in place of the waveform and
that the unit both alarms and gives the Leads Off message.
LEAD SELECT
2
To check ECG printing functions:
1. Reconnect the simulator.
2. Print a strip and verify that the strip shows a normal ECG with a clean
baseline.
3. Verify that the date, time, and configuration information printed at the top
of the strip is correct.
M3500B/M5500B Service Manual 2-13
Page 34

Performance Verification
Shock Advisory Functional Check
This section describes how to check the Shock Advisory function.
1. Connect the ECG simulator to the pads cable. Set the simulator for normal sinus rhythm (NSR), 1mV amplitude, at some nominal rate (e.g., 60
bpm).
2. Set the M3500B/M5500B to AED Mode and press .
ANALYZE
3. Verify that the defibrillator responds with No Shock Advised.
4. Set the simulator to Asystole (or turn the simulator off) and press
ANALYZE
. Verify that the defibrillator still responds with No Shock
Advised.
5. Set the simulator to VF (Ventricular Fibrillation) and press .
ANALYZE
Verify that the defibrillator responds with Shock A dvised and charges up to
150J. If the unit is configured to do so, verify that it automatically prints a
strip of the event.
WARNING Do not discharge the stored energy unless you are certain the simulator contains a
50 ohm test load.
6. If the simulator contains a 50 ohm test load, discharge the stored energy
into the test load. If it does not, or you are not sure, wait until the defibril-
lator reports Shock cancelled before proceeding with other tests.
Synchronized Cardioversion Functional Check
This section describes how to check the operation of the synchronized cardioversion function.
1. Connect the ECG simulator to the ECG cable. Connect the defibrillator
analyzer to the pads cable.
2. Set the simulator for normal sinus rhythm (NSR), 1mV amplitude, at
some nominal rate (e.g., 60 bpm).
3. Set the defibrillator to Manual Mode, and press SYNC.
4. Verify that sync markers appear on the display, at the peak or on the falling side of the QRS complex. Adjust the size of the displayed ECG as
needed to view it more clearly.
5. Select an energy of 5 J. Press then press and hold until
CHARGE SHOCK
the shock is delivered (at next QRS).
6. Verify on the defibrillator analyzer that the shock was delivered, and was
5J +
2J.
7. If the unit is configured to do so, verify that it prints a strip with the correct information on it (waveform, text).
8. Verify on the defibrillator analyzer that the delay between the peak of the
QRS and the delivered shock was <
2-14 Performance Verification and Safety Tests
60 msec.
Page 35

Performance Verification
Sp02 Functional Check
This check only needs to be performed if SpO2 is installed.
1. Attach the SpO
2. Activate Manual Mode and press the SpO
3. The SpO
is less than 95%, check that your finger is fully inserted into the sensor
and properly positioned.
2
transducer to your finger.
2
softkey to turn SpO2 on.
2
value displayed should be in the range of 95-100%. If the value
2
M3500B/M5500B Service Manual 2-15
Page 36

Diagnostic Tests
Diagnostic Tests
The M3500B/M5500B includes an extensive set of diagnostic tests, which
test the major hardware components of the defibrillator.
The System Log
These instructions describe how to print the system log, which includes the
unit’s serial number, hardware configuration, and a listing of error codes. The
System Log should be printed each time a Performance Verification Test is
run.
1. Enter Diagnostic Mode as described in "Diagnostic Mode" on page 2-11.
2. Select Print Log and press .
ENTER
3. The printer will print the System Log strip.
4. Check the printout to verify the printed results are consistent with the
hardware in place. Check options installed (SpO
serial number (on the bottom of the case). If the printout is not correct,
investigate and resolve the source of the mismatch. Then reset the hardware options and serial number as needed using the Support Software
Tool. See "The Language Support Tool" on page 4-67.
5. If there are errors reported in the System Log:
a. Check the time and date stamps to see if they are recent errors or not.
Consult Table 3-2 "Error Codes" on page 3-11 to identify the errors.
Then begin troubleshooting as needed (see the "Troubleshooting"
chapter.)
b. Check that the time and date are correct. If they are not correct, access
Configuration Mode and reset them.(If there are no errors, the time
and date are not displayed.) See "Configuration Mode" on page 2-10.
Figure 2-2 Sample System Log Printout
SYSTEM LOG
Firmware Versions Error Codes
Main: 34 90007 18:33 19 Jan 2000
DSP: 02
196: 57.00
Key: 06
SpO2: 02.42 01.04
, pacing) and the unit’s
2
Language: English
Serial Number: US01000241
Options: Pacer SpO2
Shocks: 2
2-16 Performance Verification and Safety Tests
Page 37

Diagnostic Tests
Extended Self Test
The Extended Self Test checks that all internal processors are operating and
communicating with each other. The instructions below describe how to run
the Extended Self Test.
If all results are as described, the unit passes this test. Return to the main
Diagnostic Test menu by pressing .
If there is any failure, begin troubleshooting and repairing the unit as needed.
See "Troubleshooting" on page 3-1, and Table 3-6 "Extended Self Test Failures" on page 3-18.
NO TE Make sure that no one touches the unit during the self test as that can generate
an erroneous Not Tested or Fail message.
1. Connect the test load to the pads cable.
2. Access the Diagnostic Test menu as described in "Diagnostic Mode"
above.
MAIN
2
3. Select Extended Self Test and press . The printout should appear
ENTER
similar to Figure 2-3.
Figure 2-3 Sample Extended Self Test Printout
EXTENDED SELF TEST 18:48 1/19/2000
ROM: Pass
RAM: Pass
System: Pass
Data Card: Not Tested
CODEC: Pass
IRDA: Not Tested
Timebase: Pass
Defib: Pass
FE: Pass
SpO2: Pass
Pacer: Pass
4. Check the printout to verify that the time and date are correct. If they are
not, reset them using the Configuration Mode. See "Configuration Mode"
on page 2-10.
5. The results of the following tests will appear on the display and on the
printout:
z ROM
Tests the Read Only Memory (ROM).
z RAM
Tests the Random Access Memory (RAM).
M3500B/M5500B Service Manual 2-17
Page 38

Diagnostic Tests
z SYSTEM
Tests the integrity of the core processing system and checks
the Lithium backup battery.
z Data Card
The Data Card test writes a small file to the data card, reads it back
and checks it, then erases that file. If no Data Card is present, the
test result will be Not Tested.
z CODEC
The processor turns on the CODEC (coding/decoding) chip (used
for voice prompts), and gets an acknowledgement that it’s ready to
receive data. It does not give the CODEC data to process.
z IRDA
Tests the infrared communications port. If no active infrared device
is within range, the test result will be Not Tested.
z Timebase
The Timebase test compares the Real Time clock to the System
clock to check for discrepancies. It does not test the SpO
clock
2
or the Biphasic clock.
z DEFIB
The Defib test charges the defibrillator capacitor and then disarms it.
It does not deliver the energy outside the unit. The pads cable and
test load must be connected for the test to run; otherwise the test
result will be Not Tested.
z FE
The Front End (FE) test checks that the main processor is
communicating with the Digital Signal Processor (DSP), and that
the DSP is communicating with both ECG front ends (pads and
leads). It does not test the quality of the ECG measurement.
z SP02 (if SpO
This tests that communication with the SpO
option installed)
2
PCA is working. It
2
does this by reading the software revision back from the PCA.
It does not test the quality of the SpO
z Pacer (if Pacing option installed)
measurement.
2
The Pacer test has the Pacer deliver current into the test box, and
measures that the current delivered was what was expected. The
pads cable and test load must be connected for the test to run;
otherwise the test result will be Not Tested.
2-18 Performance Verification and Safety Tests
Page 39

Diagnostic Tests
User Interface Tests
The User Interface Tests check the functions that provide information to the
user, or receive inputs from the user. Each of the User Interface checks
assumes the unit and the simulator are still set up as they were at the end of
the previous User Interface check.
If all results are as described, the unit passes that test. Return to the main
Diagnostic Test menu by pressing .
If there is any failure, begin troubleshooting and repairing the unit as needed.
See "Troubleshooting" on page 3-1 and the following specific tables:
z Table 3-11 "Operational Problems - Printer" on page 3-25.
z Table 3-12 "Operational Problems - Display" on page 3-26.
z Table 3-13 "Operational Problems - Audio Tones/Voice Prompts" on
page 3-27.
z Table 3-14 "Operational Problems - Keys" on page 3-28.
MAIN
2
To check the Controls (keys):
1. Access the Diagnostic Test menu as described in "Diagnostic Mode" on
page 2-11.
2. Select Controls Test and press . The screen will display a map of
the front panel keys.
3. Press each of the numbered softkeys in turn. See Figure 2-1 on page 2-11
for numbering of softkeys. Each softkey number on the display should be
highlighted each time that key is pressed. Don’t press Softkey #4 at
this time. This will return you to the Main diagnostic mode menu.
4. Check each of the Contrast, ECG Size, and Volume softkeys. See Figure 2-1
on page 2-11 for location of these keys.Each key should show a highlighted ("plus") when the up arrow on the key is pressed, and show a
highlighted ("minus") when the down arrow is pressed.
5. Check each of the printer control keys (Print Strip, Print Summary, and
Mark Event). Each corresponding softkey label on the display should be
highlighted each time that key is pressed.
6. Check each of the Manual keys (under the Manual door). The displayed
labels for Manual, Sync, Pacer, Start/Stop and Mode should be highlighted
each time that key is pressed. The displayed labels for Rate and Output
should show a highlighted ("plus") when the up arrow on the key is
pressed, and show a highlighted ("minus") when the down arrow is
pressed.
+
-
ENTER
MAIN
+
-
M3500B/M5500B Service Manual 2-19
Page 40

Diagnostic Tests
To check the display:
1. Select Display Test and press .
ENTER
2. The display should turn completely dark, then completely light, then a
black vertical bar should scroll across the screen from left to right.
3. The display should then show Ambient Light Reading: with a number.
Under bright office lighting the reading would typically be about 10 or 15.
Cover the ambient light sensor tightly with your finger; the reading
should decrease (to near 0).
4. The display will also show softkey labels for and
BACKLIGHT OFF
. Press each key and verify that the backlight on the dis-
BACKLIGHT ON
play cycles on and off.
5. The display will also show a softkey label. Press this softkey
TEST LEDs
and verify that the indicators in the Manual keypad each light in turn.
To check the audio output:
1. Select Audio Test and press .
ENTER
2. The screen will display Audio Test menu. Press the and softkeys
to move up or down the list to select the desired test. Then press
ENTER
to begin that test.
Check the Shutdown Warning and the Voice Prompt; the other responses
are for reference. The results should be as described below.
Press to end the test and return to the main audio test menu.
CANCEL
z Message Alert - a repeating series of 3 short tones, followed by a
pause.
z Heart Rate Alarm - 1 sustained tone of moderately high pitch.
z Charge Done Tone - 1 sustained tone of lower pitch than the Heart Rate
Alarm
z Auto Disarm Warning - a repeating series of 1 short tone and a pause
z Shutdown Warning - a repeating series of tones of alternating high/low
pitch
z Voice Prompt - the prompt is repeated 3 times, each time with increas-
ing volume. Voice should be clear and understandable.
2-20 Performance Verification and Safety Tests
Page 41

To check the printer:
Diagnostic Tests
1. Select Printer Test and press . Press to end the test and
ENTER CANCEL
return to the main Diagnostic Test menu.
2. Verify that the test patterns on the strip are as indicated in
Figure 2-4. Watch for white lines (printhead elements stuck off) or black
lines (printhead elements stuck on). Check area "A" for stray marks or
lines.
3. The area of Figure 2-4 labeled "C" contains printouts of all characters and
symbols. Verify that they are readable.
4. Measure between the long tick marks (B in Figure 2-4) to verify paper
speed. Distance should be 25mm +
5. Open the printer door and press the key. The unit should sound a
5% (+1.25 mm).
Print
Strip
series of 3 tones indicating a printer problem.
6. Take out the paper, close the door, and press the key. The unit
Print
Strip
should sound a series of 3 tones indicating a printer problem.
Figure 2-4 Printer Test Output
2
Diagonal lines
Vertical bars
Diamonds
M3500B/M5500B Service Manual 2-21
Page 42

Diagnostic Tests
ECG Tests
These instructions describe how to test the ECG functions.
Each of the ECG tests assumes the unit and the simulator are still set up as
they were at the end of the previous ECG test.
If all results are as described, the unit passes that portion of the test. Return to
the main Diagnostic Test menu by pressing .
If there is any failure, begin troubleshooting and repairing the unit as needed.
See "Troubleshooting" on page 3-1 and Table 3-7 "Operational Problems ECG Monitoring (Pads or Leads)" on page 3-19.
1. Access the Diagnostic Test menu as described in "Diagnostic Mode" on
page 2-11.
MAIN
2. Select ECG Test and press .
ENTER
3. The display should look similar to Figure 2-5:
Figure 2-5 ECG Test Display
MAIN ENTER
ECG TEST
Selected Lead: Lead II
AC Line Filter: 60 Hz On
Leads FE Status: Good
Pads FE Status: Good
DSP Status: Good
DC Offset: xxxx
Peak to Peak:
Diagnostic: 1050
Monitor: 1090
PCI: 51 Off
Checking settings
In areas with 50 Hz power, the AC Line Filter should be set to 50 Hz. If the set-
ting is incorrect, access the Configuration Mode and correct it. See "Configuration Mode" on page 2-10.
The PCI setting should always be Off (factory set default). If it is On, press the
Volume Up and Down arrow keys simultaneously to turn it Off. (See Figure 2-
1 on page 2-11.) The software feature this setting controls is not used in the
M3500B/M5500B.
2-22 Performance Verification and Safety Tests
Page 43

Diagnostic Tests
Changing settings
To change the settings of Selected lead or AC Line filter, press the and
softkeys to highlight the parameter, then press (and release) to select
ENTER
it. After a few seconds the highlighted selection will begin to blink, and the
and softkeys will allow you change the selection to another of the
values available. When the value you want is displayed, press to set
ENTER
that value. The available choices for Selected Lead will depend on whether
the unit is configured for 3-lead or 5-lead ECG monitoring.
NO TE These changes are only temporary, and will not override the configuration set
by the user in the Configuration screens.
ECG Status messages
The 3 status messages (Lead FE, Pad FE, DSP) should all be GOOD.
z The Leads FE test checks that communication is working between the
Leads Front End (FE) and the Digital Signal Processor (DSP).
z The Pads FE test checks that communication is working between the
Pads FE and the DSP.
z The DSP test checks that communication is working between the DSP
and the rest of the monitor.
DC Offset
This test is for manufacturer’s use only and should be ignored.
ECG amplifier tests
These tests measure both the gain and the noise of the two ECG amplifiers
(Leads and Pads). Both use the Peak to Peak reading.
The Peak to Peak reading measures the peak to peak amplitude of the signal
appearing on the selected ECG input. If the simulator’s calibrated output is
1.0 mV, then the Peak to Peak reading should be 1000 +
10% (+100) for both
Monitor and Diagnostic. If the simulator output is calibrated to some other
value, the displayed value should be (1000 x simulator output) +
10%.
2
NO TE The diagnostic frequency response is only available when using the ECG
Leads input. When the unit is set to Pads, the display will indicate dashes
(-----) for the Diagnostic P e ak -t o Peak value.
M3500B/M5500B Service Manual 2-23
Page 44

Diagnostic Tests
To test amplifier gain:
1. Connect the ECG simulator to the pads cable. Set the simulator output for
sine wave, 2 Hz or 10 Hz, 1 mV peak-to-peak.
2. Following the instructions under "Changing settings" on page 2-23, set
Selected lead to Pads. Only the Monitor frequency response will be avail-
able.
3. Wait for the displayed value under Monitor to stabilize.
4. The displayed value should be 1000 +
10% (+100). Record this as "aaaa".
5. Connect the ECG simulator to the ECG leads cable.
6. Following the instructions under "Changing settings", set Selected lead to
Lead II.
7. Wait for the displayed value under Diagnostic to stabilize.
8. The displayed value should be 1000 +
To test amplifier noise:
10% (+100). Record this as "bbbb".
1. Turn the simulator off. Leave it connected to the ECG cable, and leave
Selected lead set to Lead II.
2. Wait for the displayed value under Diagnostic to stabilize.
3. The displayed value should be 0 +
30 uV. Record this as "cc".
If the unit exhibits more than 30 uV of noise, try repositioning the cable
or unit to minimize external interference. See "Reducing Electromagnetic
Interference" on page 7-18. Also try various combinations of having the
ECG simulator turned on or off, and (if applicable) whether the simulator
is plugged into the AC mains.
4. Following the instructions under "Changing settings", set Selected lead to
Pads.
5. Connect the simulator to the pads cable.
6. Wait for the displayed value under Monitor to stabilize.
7. The displayed value should be 0 +
30 uV. Record this as "dd".
PCI function
This test checks the PCI (Patient Contact Impedance) function. The PCI mea-
surement is used to detect Pads Off.
1. Connect the test load to the pads cable.
2. The PCI setting should always be Off (factory set default). If it is On, press
the Volume Up and Down arrow keys simultaneously to turn it Off. (See
Figure 2-1 on page 2-11.) The software feature this setting controls is not
used in the M3500B/M5500B.
3. The PCI measurement should read 50 ohms +
30 ohms. Record this
as "ee".
4. Disconnect the test load and leave the end of the cable open. The PCI
measurement should read >
2000 ohms (full scale). Record this
as "ffff".
2-24 Performance Verification and Safety Tests
Page 45

Diagnostic Tests
Pacing Test
These instructions describe how to test the pacing function. This test only
needs to be run if the Pacing option is installed.
If all results are as described, the unit passes the test. Return to the main Diagnostic Test menu by pressing .
If there is any failure, begin troubleshooting and repairing the unit as needed.
See "Troubleshooting" on page 3-1 and Table 3-10 "Operational Problems Pacing" on page 3-24.
1. Connect the defibrillator to the Pacer tester.
2. From the Diagnostic Menu, select Pacer Test and press . The dis-
play should look similar to Figure 2-6.
Figure 2-6 Pacer Test Display
MAIN
PACER TEST
Pacer Status: Off
MAIN
ENTER
2
Selected Rate: 70
Selected Output: 30
Delivered mA: 0
3. Press . The LED to the left of the button will illuminate. The
Pacer
screen display of Pacer Status will change to Stopped.
4. Press . Pacer Status will change to Pacing, and pacing will
Start
Stop
begin at the default settings of 70 beats per minute (bpm) and 30 mA.
5. The Pacer should be delivering a current of 30mA +
5mA. Record the
delivered current indicated by the Pacer tester as "aa".
6. The display on the M3500B/M5500B should read the delivered current as
measured by the Pacer tester ("aa") +
M3500B/M5500B Service Manual 2-25
5 mA.
Page 46

Diagnostic Tests
7. Using the button, increase the rate to 180 bpm.
8. Using the button, increase the output to 200 mA.
9. The Pacer should be delivering a current of 200mA +
Rate
Output
20mA. Record the
delivered current indicated by the Pacer tester as "bbb".
10. The display on the M3500B/M5500B should read the delivered current as
measured by the Pacer tester ("bb") +
11. Turn off Pacing by pressing the button.
20 mA.
Pacer
2-26 Performance Verification and Safety Tests
Page 47

Diagnostic Tests
Defibrillator Test (AC Power At 200 J)
These instructions describe how to test the defibrillation function when powered only by the AC Power Module (no battery installed).
This test is required only if the defibrillator is connected to AC power during
normal use.
If all results are as described, the unit passes the test. Return to the main Diagnostic Test menu by pressing .
If there is any failure, begin troubleshooting and repairing the unit as needed.
See "Troubleshooting" on page 3-1 and Table 3-9 "Operational Problems Defibrillation and Synchronized Cardioversion" on page 3-22.
1. Turn defibrillator off and remove the battery. Connect the AC Power
Module.
2. Connect the defibrillator analyzer to the pads cable. Set the analyzer to
measure delivered energy. If needed, reset the analyzer’s display to
read 0.
3. Turn the defibrillator on, and from the Diagnostic Menu, Select the Defib
Meas Test and press .
MAIN
ENTER
2
4. Use the softkey to select 200J. Then press the
CHARGE SHOCK
Readings from defibrillator analyzer:
Read the delivered energy indicated by the defibrillator analyzer. It should be
200J +
Readings from M3500B/M5500B display:
The results displayed by the M3500B/M5500B should be as follows:
Available Energy: Not recorded - failure if >0.
ms to Charge: <
Delivered Energy: Actual delivered energy ("aaa") +
Impedance: 42 to 57 ohms (Record as "dd")
Peak Current: Ignore. Derived from same measurements as delivered
Defib Errors: Not recorded - failure if any reported.
ENERGY SELECT
softkey to charge the defibrillator. Press .
15% (+30J). Record as "aaa".
15000 (Record as "bbbbb")
7%(Record as "ccc")
energy and impedance
M3500B/M5500B Service Manual 2-27
Page 48

Diagnostic Tests
Defibrillator Test (Battery Power At 200 J)
These instructions describe how to test the defibrillation function when powered only by a fully charged battery, with no AC Power Module connected.
This test is always required when performing the full Performance Verification test.
If all results are as described, the unit passes the test. Return to the main Diagnostic Test menu by pressing . If there is any failure, begin trouble-
shooting and repairing the unit as needed. See "Troubleshooting" on
page 3-1 and Table 3-9 "Operational Problems - Defibrillation and Synchronized Cardioversion" on page 3-22.
1. Turn defibrillator off. Insert the battery and disconnect the AC Power
Module.
2. Connect the defibrillator analyzer to the pads cable. Set the analyzer to
measure delivered energy. If needed, reset the analyzer’s display to read
0.
3. Turn the defibrillator on, and from the Diagnostic Menu, Select the Defib
Meas Test and press .
MAIN
ENTER
4. Use the softkey to select 200J. Then press the
CHARGE SHOCK
Readings from defibrillator analyzer:
ENERGY SELECT
softkey to charge the defibrillator. Press .
Read the delivered energy indicated by the defibrillator analyzer. It should be
200J +
15% (+30J). Record as "aaa".
Readings from M3500B/M5500B display:
The results displayed by the M3500B/M5500B should be as follows:
Available Energy: Not recorded - failure if >0.
ms to Charge: <
3000 (Record as
"bbbb")
Delivered Energy: Actual delivered energy ("aaa") +
7%(Record as "ccc")
Impedance: 42 to 57 ohms (Record as "dd")
Peak Current: Ignore. Derived from same measurements as delivered
energy and impedance
Defib Errors: Not recorded - failure if any reported.
NO TE If the "ms to Charge" measurement is too high (unit takes too long to charge),
verify that the battery is fully charged. If it is, the battery may simply be old.
The 3000 ms specification is defined for a new, freshly charged M3516A/
M5516A. Replace the battery with one that is new and fully charged, and
repeat the test.
2-28 Performance Verification and Safety Tests
Page 49

Diagnostic Tests
Defibrillator Disarm Test
These instructions describe how to test the disarm function.
If all results are as described, the unit passes the test. Return to the main Diagnostic Test menu by pressing . If there is any failure, begin trouble-
shooting and repairing the unit as needed. See "Troubleshooting" on
page 3-1.
1. Connect the defibrillator analyzer to the pads cable. If needed, reset the
analyzer’s display to read 0.
MAIN
2. From the Diagnostic Menu, Select the Defib Meas Test and press .
3. Use the softkey to select 200J. Then press the
CHARGE DISARM
Readings from defibrillator analyzer:
Read the delivered energy indicated by the defibrillator analyzer. It should
be 0J or be blank.
Readings from M3500B/M5500B display:
The results displayed by the M3500B/M5500B should be as follows:
Available Energy Not recorded - failure if >0.
Msec to charge Ignore - tested earlier
Delivered energy Blank
Impedance Blank
Peak current Blank
Defib errors Not recorded - failure if any reported.
ENERGY SELECT
softkey to charge the defibrillator. Press .
ENTER
2
M3500B/M5500B Service Manual 2-29
Page 50

Diagnostic Tests
Safety Tests
This section covers tests of the defibrillator’s electrical safety.
These safety tests only need to be performed if the customer normally uses the
defibrillator with the AC Power Module connected. If the defibrillator is normally used on battery power only, these tests do not need to be performed.
Using the procedures called out by the manufacturer of the analyzer in use,
measure and record the following data. Only test at the AC Mains (line) voltage used in the customer’s facility - there is no need to test both 120VAC and
240VAC. Also, test both Normal and Reverse Polarity line connections, and
record the worst case value.
Earth Leakage
z Normal Condition - < 500 uA (< 300 uA for UL)
Record as "aaa".
z Single Fault Condition - < 1000 uA
Record as "bbbb".
Patient Lead Leakage
Test both Leads (C) and pads (B) inputs.
z Source (Normal Condition) - < 10 uA (C), < 100 uA (B)
Record as "ccc".
z Source (Single Fault Condition) - < 50 uA (C), < 500 uA (B)
Record as "ddd".
z With Mains on Applied Part (Single Fault Condition) - < 50 uA (C),
<
5000 uA (B)
Record as "eeee".
z Auxiliary (Normal Condition) - < 10 uA (C), < 100 uA (B)
Record as "fff".
z Auxiliary (Single Fault Condition) - < 50 uA (C), < 500 uA (B)
Record as "ggg".
2-30 Performance Verification and Safety Tests
Page 51

Battery Capacity Test
Battery Capacity Test
The Battery Capacity Test is not part of the routine Performance Verification.
This test is part of the routine checks that the user performs. See the Instruc-
tions for Use for details. It is included here for reference.
To perform a Battery Capacity Test:
1. Turn the M3500B/M5500B off.
2. Place a "Test in Progress" label on the unit to indicate to others that it may
not be used.
3. Insert a charged battery.
4. If an AC or DC power module is connected, unplug the power module
Mark
from the HeartStart XLT. While pressing , press On to start the test.
5. Allow the test to proceed to completion. The test takes approximately
three hours and is complete when test results print out and the device
turns itself off.
6. Review the test results and take the appropriate action, as follows:
Event
2
Table 2-3 Battery Capacity Test Results
If Then
Elapsed Time >
and
Low Battery Time > 10 minutes
Elapsed Time < 2.5 hours
or
Low Battery Time < 10 minutes
NO TE If the message "Unsupported Battery" appears, replace the battery with the
2.5 hours
1. The battery passed the test.
2. Record "pass CT" and the date on
the label on the bottom of the battery.
3. Recharge the battery before use.
1. The battery failed the test.
2. Record "fail CT" and the date on the
label on the bottom of the battery.
3. Discard the battery appropriately.
M3516A battery. See Table 3-15 on page 3-29.
M3500B/M5500B Service Manual 2-31
Page 52

Page 53

3 Troubleshooting
Overview
This chapter provides information for troubleshooting problems with the
M3500B/M5500B. The "Troubleshooting and Repair Methodology" section
of this chapter (page 3-2) provides an overview of the steps needed to isolate
and repair unit problems.
Repair Philosophy
The repair philosophy of the M3500B/M5500B is subassembly replacement.
Examples of subassemblies are the printer, the Control PCA, and selected
connectors and other items. Repairs that involve replacing components on a
PCA are not supported.
CAUTION Individual component replacement should not be attempted outside of a fac-
tory authorized repair facility. Component level repair is extremely difficult
due to the extensive use of surface mount technology and the high parts-density on the circuit boards. Unauthorized component replacement can impair
performance of the M3500B/M5500B.
3
Equipment Required
Troubleshooting requires the same test equipment as does Performance Verification. See "Test Equipment" on page 2-8.
3-1
Page 54

Troubleshooting and Repair Methodology
Troubleshooting and Repair Methodology
The M3500B/M5500B is designed to be a sealed, water resistant unit. We
recommend you follow the steps below so the sealing surfaces are not disturbed unless absolutely necessary:
Interview the User
If possible, talk directly with the user who reported the problem. Identify
what they were doing when the problem occurred, and exactly what happened. What was on the display? What tones or voice prompts were heard?
Were there operational problems?
Identify the Problem
First, evaluate the unit’s condition using the steps in "Initial Assessment" on
page 3-3. Then use "Diagnosing External Failures" on page 3-4 to identify
problems that can be resolved without further troubleshooting. Finally, if
needed use "Diagnosing Internal Failures" on page 3-5 to isolate the problem
to a particular subassembly.
If no trouble is found, proceed to the "Performance Verification and Safety
Tests" chapter for instructions on tests to run.
Perform the Repair
Follow the procedures in the "Removal and Replacement" chapter to replace
any defective subassemblies.
When the repair is complete, it is good practice to check the repair by attempting to reproduce the specific problem found. It is also advisable to print the
System Log again to check that no errors have been logged after the repair.
Test the Unit
Use the procedures found in the "Performance Verification and Safety Tests"
chapter to verify that the unit is operating properly overall. Be sure the testing
performed is appropriate for the level of repair.
3-2 Troubleshooting
Page 55

Initial Assessment
Initial Assessment
Use the following steps to isolate the problem to a particular subassembly.
Attempt Power Up
Assess the unit’s condition by performing the following steps.
1. Disconnect the Power Module (if connected).
2. Insert a fully charged battery into the unit.
3. If the unit is used with a Data Card, insert a new, empty M3510A/
M5510A Data Card into the unit.
4. Attempt to power up the unit by pressing On.
Evaluate the Response
The unit will respond in one of the following 3 ways:
No response
IF The unit emits no sounds, and no changes are visible on
the display.
THEN Troubleshoot further using Table 3-1 on page 3-9.
("Unit Unresponsive").
Minimal response
IF Unit provides only a slight response, such as a click or chirp
from the speaker, or a change in the contrast or the borders
of the display.
THEN Replace the Control PCA (see "Removal and Replacement"
on page 4-1).
Return to this section and begin again with
"Attempt Power Up".
Powers Up
IF The unit powers up to one of the following states:
a. It can generate tones or voice prompts, or display text
or graphics, or respond to keypresses.
b. The screen is blank except for an error message such
as Defib Failure - Cycle Power.
3
THEN Proceed to "Diagnosing External Failures" on page 3-4.
M3500B/M5500B Service Manual 3-3
Page 56

Diagnosing External Failures
Diagnosing External Failures
Many times, a problem will be the result of external failures such as defective
cables, depleted batteries, or improper operation. Use the steps below to rule
out these external failures before looking for an internal failure in the unit.
Capture the Configuration Data
Store the unit’s configuration data on a Data Card or print out the current configuration, if possible. See "Accessing Configuration Mode" on page 3-5.
Print the System Log
Print out the System Log if possible, and use any error codes to help isolate
the problem. See "Printing the System Log" on page 3-6.
NO TE The M3500B/M5500B log of error codes only reports the last 10 errors. If
new errors are created at this stage they may overwrite the existing codes and
valuable clues to the reported problem might be lost.
Rule out external components and improper use
Referring to Table for Supplies and Accessories, make sure the unit has:
z An undamaged, fully charged M3516A/M5516A battery.
z A new, dry roll of Philips 40457C/D printer paper. Printer paper may
jam if paper is wet. Also, printer may be damaged if wet paper is
allowed to dry while in contact with printer elements.
z Cables and sensors which are approved by Philips and known to be
good. Also make sure that all external cables are fully inserted in their
receptacles.
z A new, empty Data Card of the correct type (M3510A/M5510A).
Plugging in the wrong type of card (e.g., a modem card) can cause
startup failures.
To help identify problems which may be caused by external components or by
improper use, refer to:
z Table 3-3 ("System Messages") and Table 3-4 ("Momentary Mes-
sages"). While both sets of messages are intended for the end user and
are found in the Instructions for Use, they are included here for reference.
z The individual tables describing Operational Problems associated
with each function (defibrillation, ECG, etc.). The Operational Problems tables describe failures to operate properly and indicate what
corrective actions the service person should take.
3-4 Troubleshooting
Page 57

Diagnosing Internal Failures
Diagnosing Internal Failures
The following steps will help you isolate an internal failure to a particular
subassembly.
Run Self Tests
To run the Self Tests, perform the following steps:
1. Enter Diagnostic Mode. See "Accessing Diagnostic Mode" on page 3-6.
2. Run the Extended Self Test. See "Extended Self Test" on page 2-17.
3. Run the individual Diagnostic Tests that are applicable to the problem.
Diagnostic Tests are described starting with "User Interface Tests" on
page 2-19.
Use the Troubleshooting Tables
Use the Tables provided starting on page 3-8 to isolate the problem based on
factors such as:
z Error codes reported in the System Log (Table 3-2, page 3-11).
3
z Extended Self Test failures (Table 3-6, page 3-18).
z Operational problems (starting with Table 3-7 on page 3-19).
Configuration and Diagnostic Modes
Some of the Troubleshooting procedures look for responses from the unit that
are dependent on that unit’s configuration. Similarly, many procedures
require that the unit be in Diagnostic Mode. Follow the instructions given
below to enter these modes.
Accessing Configuration Mode
These instructions describe briefly how to enter Configuration Mode. See the
Instructions for Use for details on configuration settings and what effect they
have.
1. Make sure the power is off.
2. If you intend to save the configuration to a Data Card (or load the configuration from a Data Card), insert the Data Card now.
3. Press softkeys 4 and 5 at the same time, and hold them down while turning the power on. See Figure 3-1 for softkey numbering.
z To select a configuration, press the and softkeys to move up
or down the list until the desired Settings item is highlighted. Then
press the softkey to access those settings.
ENTER
z To print out a strip with all the current configuration choices, select
Print All Settings and press .
M3500B/M5500B Service Manual 3-5
ENTER
Page 58

Diagnosing Internal Failures
z To store the configuration settings on a data card, select Save Settings
to Data Card and press . When prompted with Save Settings to
Data Card? press .
z To load configuration settings from a Data Card, select Load Settings
from Data Card and press . When prompted with Load Settings
from Data Card? press .
z To exit Configuration Mode, turn the unit off. Wait 2 seconds.
ENTER
SAVE
ENTER
LOAD
Remove the Data Card by pressing the black eject button and pulling
the Data Card from the compartment.
Figure 3-1 Softkey Numbers
Contrast
ECG Size
Volume
Accessing Diagnostic Mode
These instructions describe how to enter Diagnostic Mode. The Diagnostic
Mode allows printing of the System Log (see "Printing the System Log" on
page 3-6). It also allows running the Extended Self Test and other Diagnostic
Tests. For details of running these tests, see "Diagnostic Tests" on page 2-16.
1. Make sure the power is off.
2. Press softkeys 4 and 6 at the same time, and hold them down while turning the power on. See Figure 3-1 for softkey numbering.
3. Wait for the Diagnostic software to initialize. This will take several
seconds. The unit is ready to proceed when the screen cursor
responds to softkey inputs.
z To select a function, press the and softkeys to move up or
down the list until the desired function is highlighted. Then press the
ENTER
z To exit Diagnostic Mode, turn the instrument off.
softkey to begin that function.
Printing the System Log
These instructions describe how to print the system log, which includes the
unit’s serial number, hardware configuration, and a listing of error codes.
1. Enter Diagnostic Mode as described in "Accessing Diagnostic Mode".
3-6 Troubleshooting
Page 59

Diagnosing Internal Failures
2. Select Print Log and press .
ENTER
3. The printer will print the System Log strip. See Figure 3-2.
4. Check the printout to verify the printed results are consistent with the
hardware in place. Verify options installed (SpO2, pacing) and the unit’s
serial number (on the bottom of the case). If the printout is not correct,
investigate and resolve the source of the mismatch. Then reset the hardware options and serial number as needed using the Support Software
Tool. See "The Language Support Tool" on page 4-67.
5. If there are errors reported in the System Log:
a. Check the time and date stamps to see if they are recent errors or not.
Consult Table 3-2 "Error Codes" on page 3-11 to identify the errors.
Then begin troubleshooting as needed (see the "Troubleshooting"
chapter.)
b. Check that the time and date are correct. If they are not correct, access
Configuration Mode and reset them. See "Accessing Configuration
Mode" on page 3-5.
Figure 3-2 Sample System Log Printout
SYSTEM LOG
Firmware Versions Error Codes
Main: 34 90007 18:33 19 Jan 2000
DSP: 02
196: 57.00
Key: 06
SpO2: 02.42 01.04
3
Language: English
Serial Number: US0100241
Options: Pacer SpO2
Shocks: 2
M3500B/M5500B Service Manual 3-7
Page 60

Troubleshooting Tables
Troubleshooting Tables
Below are the troubleshooting tables provided.
Table 3-1 "Unit Unresponsive"
Table 3-2 "Error Codes"
Table 3-3 "System Messages"
Table 3-4 "Momentary Messages"
Table 3-5 "Audio Tones"
Table 3-6 "Extended Self Test Failures"
Table 3-7 "Operational Problems - ECG Monitoring (Pads or Leads)"
Table 3-8 "Operational Problems - SpO
Table 3-9 "Operational Problems - Defibrillation and Synchronized Cardio-
version"
Table 3-10 "Operational Problems - Pacing"
Table 3-11 "Operational Problems - Printer"
Table 3-12 "Operational Problems - Display"
Table 3-13 "Operational Problems - Audio Tones/Voice Prompts"
Table 3-14 "Operational Problems - Keys"
Table 3-15 "Operational Problems - Battery, AC or DC Power Modules, Bat-
tery Charger Adapter"
Table 3-16 "Power Module Indicator Matrix"
Table 3-17 "Operational Problems -Data Card"
Monitoring"
2
Using the Tables
The tables will often suggest more than one cause for a symptom, and more
than one solution for each cause.
The causes are arranged in order of the approximate probability of their
occurrence. Investigate the causes proposed in the order given. If one cause
turns out not to be the problem, try the next.
For each cause there may also be multiple solutions given. These are arranged
in the recommended order of their implementation. Try the first solution, and
if that does not fix the problem, try the next.
Before replacing any parts, check to see if the cables and flex circuits are
properly connected. See "Servicing Notes" on page 4-1.
3-8 Troubleshooting
Page 61

Table 3-1 Unit Unresponsive
Test Result Possible Causes Corrective Actions
Unit Unresponsive
Unit Unresponsive
Isolate the fault by following the steps in Table 3-1. Before replacing any
parts, check to see if the cables and flex circuits are properly connected. See
"Servicing Notes" on page 4-1.
1. Connect Power Module to
power source ONLY (AC
Mains or DC) and
observe indicators on
Power Module
(see Figure 3-3 on page
3-30).
2. Connect Power Module to
unit.
3. Attempt to power up unit. "Power’ indicator turns
"Power’ indicator turns
RED.
’Power’ indicator turns
GREEN.
"Power’ indicator turns
RED.
’Power’ indicator stays
GREEN.
RED.
Power Source voltage low.
Failure in Power
Module.
Short in unit’s 12 volt
wiring.
Short on Power PCA. Replace Power PCA.
Short on Control
PCA.
Failure on Power
PCA.
Failure on Control
PCA.
Check/correct source voltage.
Replace Power Module.
Proceed to step 2.
1. Check/replace Battery
PCA
2. Check/replace wiring to
Power PCA
Replace Control PCA.
Proceed to step 3.
Replace Power PCA.
Replace Control PCA.
3
’Power’ indicator stays
GREEN.
Proceed to step 4.
M3500B/M5500B Service Manual 3-9
Page 62

Unit Unresponsive
Table 3-1 Unit Unresponsive (Con tinued)
Test Result Possible Causes Corrective Actions
4. Observe unit’s response. Unit powers up to some
working state.
Unit still unresponsive. Short or other failure
5. Attempt to power up unit. Unit powers up to some
working state.
Unit still unresponsive. Short or other failure
Main fuse open. 1. Replace Main Fuse
2. Replace Power PCA and
Main Fuse.
Open in battery wiring.
somewhere in unit.
Short in printer or display.
somewhere in unit.
1. Check/replace Battery
PCA
2. Check/replace wiring to
Power PCA
Disconnect printer and display from Control PCA at
Control PCA. Then proceed to step 5.
Isolate the fault by reconnecting one at a time and
powering up again. Then
replace the display or printer
as needed.
1. Replace Control PCA.
2. Replace Power PCA.
3. Replace Interface PCA.
If all above unsuccessful,
return unit for bench repair.
3-10 Troubleshooting
Page 63

Error Codes
Error Codes
The System Log provides error codes in 5 digit hexadecimal format. Before
replacing any parts, check to see if the cables and flex circuits are properly
connected. See "Servicing Notes" on page 4-1.
NO TE Confirm any errors by running the self-tests again, making sure that no one
touches the unit during the test.
Table 3-2 Error Codes
Error Code Meaning Possible Solutions
00000 - 00400 Defib failure - charging circuits. 1. Replace Power PCA.
2. Replace Control PCA.
01000 Defib failure - biphasic processor. 1. Replace Power PCA.
2. Replace Control PCA.
3
02000 Leads front end failure. 1. Replace Interface PCA.
2. Replace Control PCA.
04000 Pacer failure. Replace Power PCA.
08000 Processor error. Replace Control PCA.
10000 - 1FFFF System monitor failure. 1. Cycle power.
2. Replace Control PCA.
10001 Processor Synchronization Error Cycle power.
10004 Synchronization Time Out Cycle power.
• If error does not repeat, run ALL
Performance Verification Tests. If
unit passes all tests, the unit can
be returned to service.
• If error repeats, replace Control
PCA.
20000 - 2FFFF Front end failure. 1. Replace Control PCA.
2. Replace Interface PCA.
30000 - 3FFFF Pacer failure. 1. Replace Power PCA.
2. Replace Control PCA.
40000 - 4FFFF Monitor processor failure. 1. Replace Control PCA.
2. Replace Interface PCA.
50000 - 5FFFF SpO
60000 - 6FFFF Advisory Failure. Replace Control PCA.
problem. 1. Replace SpO2 PCA.
2
2. Replace Interface PCA.
3. Replace Control PCA.
M3500B/M5500B Service Manual 3-11
Page 64

Error Codes
Table 3-2 Error Codes (Continued)
Error Code Meaning Possible Solutions
80000 - 8FFFF IRDA failure. 1. Replace Interface PCA.
2. Replace Control PCA.
90000 - 90002 Self Test failure - RAM/ROM or Gate
Array.
90003 Self Test failure - Data Card circuits. Replace Control PCA.
90004 and 90005 Self Test failure - Codec/time base. 1. Replace lithium battery.
90006 Self Test failure - SpO
90007 and 90008 Self Test failure - Pacer or
Defib.This error can be caused by
pressing the Pacer key during the
self-test.
90009 Self Test failure - Front End. 1. Replace Power PCA.
9000A Lithium backup battery failure. 1. Replace lithium battery.
A0000-A7FFF Data Card failure. 1. Replace Data Card.
2.
1. Replace lithium battery.
2. Replace Control PCA.
2. Replace Control PCA.
1. Replace SpO2 PCA.
2. Replace Control PCA.
3. Replace Interface PCA.
1. Run the self-test again, making
sure not to touch the unit during
the test.
2. Replace Power PCA.
3. Replace Control PCA.
2. Replace Control PCA.
3. Replace Interface PCA.
2. Replace Control PCA.
2. Replace Control PCA.
A8000 - AFFFF Data Archival error. 1. Replace Data Card.
2. Replace Control PCA.
B0000 - BFFFF Audio failure. Replace Control PCA.
F0000 - FFFFF RAM/ROM failure. Replace Control PCA.
F0002 Promo Mode failure. Replace Control PCA.
F0003 Keyscanner failure. 1. Replace Keyscan PCA.
2. Replace Control PCA.
F0004 System Communication error. Replace Control PCA.
F0007 System Communication error Cycle power.
3-12 Troubleshooting
Page 65

Table 3-3 System Messages
Message Description Corrective Action
System Messages
System Messages
System messages remain on the display until the specified action is taken or
no longer relevant. They are intended for the end user and appear in the
Instructions for Use. They are duplicated here for the reference of the service
person.
Before replacing any parts, check to see if the cables and flex circuits are
properly connected. See "Servicing Notes" on page 4-1.
Attach Pads Cable
Configuration Lost
Data Card Disabled
ECG Fault
Monitor Failure - Cycle
Power
Low Battery
Leads Off
The pads cable is not properly attached to
the device.
The configuration is reset to the default
settings.
The PC card is not in use because it is full,
incompatible, absent, or inserted after the
M3500B/M5500B was turned on.
The ECG data acquisition system failed
and data is unavailable from the 3- or 5lead monitoring electrodes.
An error has occurred in the monitoring
subsystem.
The battery has sufficient capacity remaining to provide only about ten minutes of
monitoring time and six shocks before the
M3500B/M5500B shuts off.
The monitoring electrodes are not applied
or are not making proper contact with the
patient.
Check the cable connection
1. Reconfigure the M3500B/M5500B.
2. If problem reoccurs, service the unit.
See "Troubleshooting" on page 3-1 and
Table 3-6 on page 3-18.
If possible, turn the M3500B/M5500B off
for more than 2 minutes, then insert a
new, empty, M3510A/M5510A Data Card
and turn the device on.
Service the unit. See "Troubleshooting" on
page 3-1 and Table 3-7 on page 3-19.
Turn power off, then on. If message reappears, service the unit. See "Troubleshooting" on page 3-1.
Replace the battery with a fully charged
M3516A/M5516A battery.
Check that the monitoring electrodes are
properly applied.
3
The ECG cable is not connected. Check that the ECG cable is properly con-
nected.
No Pads
The internal cable from the ECG connector to the Interface PCA is disconnected
Failure on the Interface PCA. Replace the Interface PCA.
The multifunction defibrillation electrode
pads are not properly connected to the
M3500B/M5500B.
Check the internal cable.
Check the pads cable connection.
M3500B/M5500B Service Manual 3-13
Page 66

System Messages
Table 3-3 System Messages (Continued)
Message Description Corrective Action
Pads Cable Off
Pads Off
Defib Failure - Cycle
Power
Pacer Failure
Pacer Output Low
System Failure Service Unit
SpO2 Cable Off
The pads cable is not connected to the
defibrillator.
Failure on Power PCA. Replace Power PCA.
The pads are not making proper contact
with the patient.
Failure on Power PCA. Replace Power PCA.
An error has occurred in the defibrillator
subsystem.
The pacing system is not functioning. Service the unit. See "Troubleshooting" on
High patient impedance is resulting in the
pacer delivering less current to the patient
than specified in the output current setting.
A serious malfunction has occurred. Service the unit. See "Troubleshooting" on
The SpO2 cable is not connected to the
device.
Check that the pads cable connector is
locked in place.
Make sure the pads are properly applied
to the patient.
Turn power off, then on. If message reappears, service the unit. See "Troubleshooting" on page 3-1 and Table 3-9 on
page 3-18.
page 3-1 and Table 3-10 on page 3-24.
Check the pads are applied properly.
page 3-1.
Attach the SpO2 cable to the M3500B/
M5500B.
SpO2 Light Interf
Non Pulsatile
SpO2 Failure
SpO2 Low Signal
The level of ambient light is so high that
the sensor cannot obtain an SpO2 read-
ing, or the sensor or cable is damaged.
The patient’s pulse is absent or too weak
to be detected.
A failure has occurred in the SpO2
circuitry
SpO2 signal is too low to give an accurate
reading.
1. Cover the sensor with an opaque material.
2. Check the sensor and cable for damage; try another sensor and cable.
1. Check that the sensor is applied properly.
2. Make sure the sensor site has a pulse.
3. Relocate the sensor to a site with
improved circulation.
4. Try another sensor.
1. Replace the SpO2 PCA.
2. Ensure that the flex circuit from the
SpO2 PCA to the Interface PCA is connected.
3. Replace the SpO2 Connector.
1. Check the sensor is applied properly.
2. Try another sensor type.
3-14 Troubleshooting
Page 67

Table 3-3 System Messages (Continued)
Message Description Corrective Action
System Messages
SpO2 Noisy Signal
SpO2 Sensor Fail
System Failure - Cycle
Power
Service Unit
Excessive patient movement, electrical
interference, or optical interference is
present.
The SpO2 cable is not connected to the
device; or the cable or sensor are broken.
A serious error has occurred. Turn power off, then on. If message reap-
Appears during the Shift/System Check 1. Replace Data Card.
1. Minimize patient movement or apply the
sensor to a site with less movement.
2. Secure the sensor cable loosely to the
patient.
3. Reduce sources of electrical or optical
interference.
1. Attach the cable to the M3500B/
M5500B
2. Replace cable and/or sensor.
pears, service unit. See "Troubleshooting" on page 3-1.
2. Replace lithium battery.
3. Replace Control PCA.
.
3
M3500B/M5500B Service Manual 3-15
Page 68

Momentary Messages
Momentary Messages
Momentary messages are temporary and only appear on the display for a few
seconds. They are intended for the end user and appear in the Instructions
for Use. They are duplicated here for the reference of the service person.
Before replacing any parts, check to see if the cables and flex circuits are
properly connected. See "Servicing Notes" on page 4-1.
Table 3-4 Momentary Messages
Message Possible Cause Corrective Action
Attach Leads
Attach Pads
Defib Disarmed
No Shock Delivered
Check Printer
Data Card Full
An attempt was made to begin pacing in
Demand Mode without ECG leads
attached to the patient.
The multifunction defib electrode pads are
not making proper contact with the patient.
The pads connection is compromised. Check the pads are applied to the patient
The mode is changed from Manual to
AED while the defibrillator is charged.
SHOCK SHOCK
of the defibrillator being charged.
DISARM
Patient impedance is too high or too low. 1. Make sure pads are applied properly.
Printer paper is absent or jammed; the
printer door is not closed properly.
The incident is more than 2 hours in duration, causing the Data Card to fill.
is not pressed within 30 seconds
is pressed.
Attach leads to patient
1. Check the pads are applied to the
patient, as directed on the package.
2. Replace pads if the prompt continues.
properly.
If a shock is indicated, deliver the shock
before changing modes.
To deliver a shock, press within
30 seconds of the defibrillator being
charged.
None.
2. Replace the pads.
3. Replace the pads cable.
1. Reload printer paper.
2. Make sure the door is closed properly.
None. A new Data Card can not be
inserted during an incident.
Data Card Interrupted
Data Card Not In Service
Incompatible Data
Card
An empty Data Card was not inserted for
the incident; the Data Card filled sooner.
No data is being recorded on the Data
Card because the Data Card was
removed during an incident.
The Data Card is inserted while the
M3500B/M5500B is on.
A Data Card other than the M3510A is
inserted.
Use one empty Data Card per incident/
patient to decrease the chance of the card
filling.
• During incident, none. The Data Card
cannot be inserted during an incident.
• After incident, remove card, turn
power off, insert card, turn power on.
None. A Data Card must be inserted prior
to turning the M3500B/M5500B on for the
current patient.
Use only M3510A/M5510A Data Cards.
3-16 Troubleshooting
Page 69

Table 3-4 Momentary Messages (Continued)
Message Possible Cause Corrective Action
Momentary Messages
No Data Card Present
Key Inactive
Stop Pacer
A Data Card is not in the M3500B/
M5500B.
The key pressed is currently inactive (i.e.
Sync Pace
AED Mode).
Mode
are being delivered.
Audio Tones
The M3500B/M5500B emits tones to alert you to its status.
Table 3-5 Audio Tones
Tone Meaning Suggested Action
At power on, a low tone of approx. 1
second followed by a series of
higher pitched, short tones.
At power on, a continuous beep of
about 7 seconds.
Turn the M3500B/M5500B off and insert a
Data Card prior to the first event for the
patient.
Use the appropriate mode for the key.
and are inactive in
is pressed while pacing pulses
Normal power on sequence. None needed.
System failure - processors not
communicating.
Stop pacing before changing the pacing
mode.
Turn power off, then on. If problem
reoccurs, replace Control PCA.
3
At any time, a repeating tone that
alternates between two frequencies.
The unit emits this tone beginning 1
minute before shutdown due to low
battery charge.
1. Connect a Power Module or
replace the battery with one that
is fully charged.
2. Replace Power Module.
3. Service the unit. See "Troubleshooting" on page 3-1.
M3500B/M5500B Service Manual 3-17
Page 70

Momentary Messages
Extended Self Test Failures
Should the unit report a FAIL in the Extended Self Test, resolve it using the
solutions below.
Table 3-6 Extended Self T e s t Failures
Failure Possible Cause Suggested Solution
RAM
ROM
System
CODEC
IRDA
Timebase
System FAIL 10
Data Card
Pacer
Defib
FE
SpO2
Failure on Control PCA. Replace Control PCA.
Lithium backup battery failure. Replace lithium battery.
Data Card full, or incompatible, or
defective.
Failure on Control PCA. Replace Control PCA.
Failure on Power PCA. Replace Power PCA.
Failure on Control PCA. Replace Control PCA.
Failure on Control PCA. Replace Control PCA.
Failure on Power PCA. Replace Power PCA.
Failure on Interface PCA. Replace Interface PCA.
Failure on SpO2 PCA. Replace SpO2 PCA.
Failure on Control PCA. Replace Control PCA.
Replace Data Card with new, empty
M3510A/M5510A.
3-18 Troubleshooting
Page 71

Operational Problems
These tables describe problems that may arise while using the M3500B/
M5500B.
ECG Monitoring
The following table covers problems that might arise while monitoring ECG.
Table 3-7 Operational Problems - ECG Monitoring (Pads or Leads)
Symptom Possible Cause Suggested Solution
Operational Problems
Noisy trace - constant noise on the
baseline.
Noisy trace - intermittent bursts of
noise or random spikes.
Noisy trace - low frequency, periodic.
Flat line - no waveform, no
Off
or Pads Off message.
Leads
Incorrect configuration - power line
frequency (50 or 60 Hz) or Filter settings.
Nearby source of constant interference.
Failure in ECG front end. Pads: Replace Power PCA.
Failure in signal processing circuits. Replace Control PCA.
Nearby source of time-varying interference, such as radio transmitter
(paging, walkie-talkies) or X-Ray
system.
Failure in ECG front end. Pads: Replace Power PCA.
Failure in signal processing circuits. Replace Control PCA.
More than one instrument connected to the patient and active.
Short in internal ECG wiring or front
end.
Check/change configuration as
needed.
Try moving cable/leads; try relocating unit.
Leads: Replace Interface PCA.
Try moving cable/leads; try relocating unit.
Leads: Replace Interface PCA.
Only have one active instrument on
the patient at a time.
Pads:
1. Replace Power PCA.
2. Replace Patient Connector +
its internal cable.
3
Leads:
1. Replace Interface PCA.
2. Replace ECG connector +
internal ECG cable.
Failure in signal processing circuits. Replace Control PCA.
M3500B/M5500B Service Manual 3-19
Page 72

Operational Problems
Table 3-7 Operational Problems - ECG Monitoring (Pads or Leads) (Continued)
Symptom Possible Cause Suggested Solution
Leads Off message even though
ECG cable has been replaced and
is properly connected to the simulator.
Pads Off message even though
pads cable has been replaced and
is properly connected to the simulator.
Trace distorted. Failure in ECG front end. Pads: Replace Power PCA.
Open in internal Leads ECG wiring
or front end, due to:
Cable from ECG Connector to Interface PCA has bad connection.
Defective ECG Connector or cable
to Interface PCA.
Defective Interface PCA Replace Interface PCA.
Open in internal Pads ECG wiring or
front end, due to:
Cable from Patient Connector to
Power PCA has bad connection.
Defective Patient Connector or
cable to Power PCA.
Defective Power PCA. Replace Power PCA.
Reconnect cable properly. See "Servicing Notes" on page 4-1.
Replace ECG Connector.
Reconnect cable properly. See "Servicing Notes" on page 4-1.
Replace Patient Connector + its
internal cable.
Leads: Replace Interface PCA.
Failure in signal processing circuits. Replace Control PCA.
One or more ECG controls don’t
respond (e.g., select lead or ECG
size).
Poor Leads ECG signal quality. The monitoring electrodes are not
Failure in keypress detection/processing.
Failure in keys/connections. Replace Top Case Assembly.
making proper contact with the
patient.
The monitoring electrodes are outdated or dried-out.
Radio frequency interference (RFI)
is causing artifact.
1. Replace Control PCA.
2. Replace Interface PCA.
Check that the monitoring electrodes are properly applied. If necessary, prepare the patient’s skin
and apply new electrodes.
Check the date code on the electrodes. Do not open the electrode
package until immediately prior to
use.
Relocate or turn off equipment that
may be causing RFI.
3-20 Troubleshooting
Page 73

Table 3-7 Operational Problems - ECG Monitoring (Pads or Leads) (Continued)
Symptom Possible Cause Suggested Solution
Operational Problems
Poor Pads ECG signal quality. The multifunction pads are not mak-
ing proper contact with the patient.
The multifunction pads are outdated
or dried-out.
Radio frequency interference (RFI)
is causing artifact.
QRS beeper inaudible or beeps do
not occur with each QRS complex.
Fails ECG Test in Diagnostic Mode. Failure in Pads ECG front end or
The QRS beeper is configured to
Off.
The volume is set too low. Adjust the volume.
The amplitude of the QRS complex
is too small to detect.
signal processing.
Failure in Leads ECG front end or
signal processing.
Check that the pads are properly
applied. If necessary, prepare the
patient’s skin and apply new pads.
Check the date code on the pads.
Do not open the pads package until
immediately prior to use.
Relocate or turn off equipment that
may be causing RFI.
Configure the QRS beeper to On.
Adjust the size of the ECG.
3
1. Replace Power PCA.
2. Replace Control PCA.
1. Replace Control PCA.
2. Replace Interface PCA.
SpO2 Monitoring
The following table covers problems that might arise while monitoring SpO2.
Table 3-8 Operational Problems - SpO2 Monitoring
Symptom Possible Causes Suggested solution
No response - no value on screen,
no pleth bar.
Reads obviously wrong value. Same as above. Same as above.
Noisy/intermittent signal Same as above. Same as above.
Bad internal connection. Carefully reseat flex cables between
SpO2 connector and SpO2 PCA,
and between SpO2 PCA and Inter-
face PCA. See "Servicing Notes" on
page 4-1.
SpO
PCA failure. Replace SpO2 PCA.
2
Control PCA failure. Replace Control PCA.
Interface PCA failure. Replace Interface PCA
M3500B/M5500B Service Manual 3-21
Page 74

Operational Problems
Defibrillation and Cardioversion
The following table covers problems that might arise while defibrillating or
delivering synchronized cardioversion.
Table 3-9 Operational Problems - Defibrillation and Synchronized Cardioversion
Message or Symptom Possible Causes Suggested solution
Won’t charge in Manual Mode. • Pads connector or internal wir-
ing failure.
• Power PCA failure.
• Control PCA failure.
• Interface PCA failure.
CHARGE key failure.
•
Won’t charge in AED Mode. • Pads connector or internal wir-
ing failure.
• Power PCA failure.
• Control PCA failure.
• Interface PCA failure.
CHARGE key failure.
•
Diagnose as follows:
1. Try AED Mode.
• Charges OK: Go to step 3.
• Still not charge: Go to step 2.
2. Verify Pads Off and Cable Off
detection by unplugging pads,
cable.
• Detects both OK: Go to step 3.
• Either Pads Off or Cable Off fail:
replace 1) Pads connector 2)
Power PCA.
3. In Diagnostic Mode, run Controls
Test and test
• Key tests OK: Replace Control
PCA.
• Key not OK: Replace 1) Inter-
face PCA 2) Top Case Assembly 3) Control PCA.
Diagnose as follows:
1. Try Manual Mode
• Charges OK: Go to step 3.
• Still not charge: Go to step 2.
2. Verify Pads Off and Cable Off
detection by unplugging pads,
cable.
• Detects OK: Go to step 3.
• Either Pads Off or Cable Off fail:
replace 1) Pads connector 2)
Power PCA.
3. In Diagnostic Mode, run Controls
Test and test
• Key tests OK: Replace Control
PCA.
• Key not OK: Replace 1) Inter-
face PCA 2) Top Case Assembly 3) Control PCA.
CHARGE key.
CHARGE key.
3-22 Troubleshooting
Page 75

Operational Problems
Table 3-9 Operational Problems - Defibrillation and Synchronized Cardioversion (Continued)
Message or Symptom Possible Causes Suggested solution
Won’t discharge. • Control PCA failure.
• Interface PCA failure.
• SHOCK key failure.
Charges, but disarms when press
Shock.
Charges, but disarms spontaneously.
Patient impedance sensed as too
high or too low during energy delivery due to:
• Pads losing contact with patient.
• Pads failure.
• Pads cable failure.
Power PCA failure. Replace Power PCA
Control PCA failure. Replace Control PCA
1. Unit sensed
Off
due to:
• Pads losing contact with patient.
• Pads failure.
• Pads cable failure.
• Power PCA failure.
• Control PCA failure.
• Interface PCA failure.
Pads Off or Cable
Diagnose as follows:
1. In Diagnostic Mode, run Controls
Test and test SHOCK key.
• Key tests OK: Replace Control
PCA.
• Key not OK: Replace 1) Inter-
face PCA 2) Top Case Assembly 3) Control PCA.
Replace pads, pads cable.
Replace pads, pads cable.
Diagnose further as follows:
In Diagnostic Mode, run Controls
Test and test
• Key tests OK: Replace 1) Power
PCA 2) Control PCA.
• Key not OK: Replace 1) Inter-
face PCA 2) Top Case
Assembly3) Control PCA.
DISARM key.
3
DISARM key failure (intermittent)
2.
Charges slowly - about 4-5 sec.
instead of 2-3 sec.
Battery too old or not fully charged. Replace with new, fully charged bat-
tery. Also run Battery Capacity Test
on suspect battery (see page 2-31).
Unit senses unsupported battery
due to:
• Unsupported battery in use
• Battery PCA failure.
• Power PCA failure.
• Control PCA failure.
Use only supported battery
(M3516A/M5516A).
Diagnose further as follows:
In Diagnostic Mode, start Battery
Capacity Test (see page 2-31).
Unsupported battery" on dis-
• "
play: Stop test. Replace 1)
Battery PCA 2) Power PCA 3)
Control PCA.
• No message on display: Stop
test. Replace 1) Power PCA 2)
Control PCA.
M3500B/M5500B Service Manual 3-23
Page 76

Operational Problems
Table 3-9 Operational Problems - Defibrillation and Synchronized Cardioversion (Continued)
Message or Symptom Possible Causes Suggested solution
Doesn’t deliver correct energy into
Defibrillator Analyzer or delivers no
energy at all. (Should also get mes-
No shock delivered or Defib
sage -
.)
failure
Doesn’t measure its own delivered
energy correctly.
Not synchronizing even though
ECG waveform OK on display.
Fails
Defib Meas Test in Diagnostic
Mode (other then symptoms above).
Control PCA failure. Replace Control PCA.
Power PCA failure. Replace Power PCA.
Power PCA failure. Replace Power PCA.
Control PCA failure. Replace Control PCA.
Control PCA failure. Replace Control PCA.
Power PCA failure. Replace Power PCA.
Control PCA failure. Replace Control PCA.
Pacing
The following table covers problems that might arise while performing external pacing.
Table 3-10 Operational Problems - Pacing
Message or Symptom Possible Causes Suggested solution
Doesn’t deliver correct current into
Pacer Tester or delivers no current
at all.
Doesn’t measure its own delivered
current correctly.
Doesn’t pace at correct rate. Control PCA failure. Replace Control PCA.
Pacer hardware not installed. mes-
sage even though Pacer is present.
Unit fails either the Shift System
Check or Extended Self Test, or
reports error code 90007.
Control PCA failure. Replace Control PCA.
Power PCA failure. Replace Power PCA.
Power PCA failure. Replace Power PCA.
Control PCA failure. Replace Control PCA.
Bad connections - Manual Keypad
flex circuits to Interface PCA.
Test sequence is interrupted. Run the test again, making sure that
Reconnect flex circuits properly.
See "Servicing Notes" on page 4-1.
no one touches the unit during the
test.
3-24 Troubleshooting
Page 77

Printer
The following table covers problems that might arise while printing. Before
replacing any parts, check to see if the cables and flex circuits are properly
connected. See "Servicing Notes" on page 4-1. Also check for damage to the
printer ribbon cable where the ribbon is captured in the connectors.
Table 3-11 Operational Problems - Printer
Symptom Possible Causes Suggested solution
Operational Problems
Paper won’t move. Paper improperly loaded or
jammed, or paper is wet.
Printer failure. Replace printer.
Paper moves then stops. Door improperly latched. Check door latch.
Paper improperly loaded or
jammed.
Paper moves but printing is faint or
absent.
Paper moves but print quality poor
or some dots missing.
Loud buzzing or grinding noise. Door improperly latched. Check door latch.
Waveforms or text distorted even
though they look OK on display.
Door improperly latched. Check door latch.
Dirty printhead. Clean printhead.
Printer failure. Replace printer.
Control PCA failure. Replace Control PCA.
Dirty printhead. Clean printhead. See"Cleaning the
Printer failure. Replace printer.
Printer failure. Replace Printer.
Control PCA failure. Replace Control PCA.
Reload paper or clear jam. If paper
is wet, replace with fresh dry roll.
Reload paper or clear jam.
Printer Printhead" on page 4-9.
3
Black line running along paper. Dots (printhead elements) stuck on
due to:
Printer failure. Replace Printer.
Control PCA failure. Replace Control PCA.
White line running along paper. Dirt on printhead. Clean printhead. See "Cleaning the
Printer Printhead" on page 4-9.
Dots (printhead elements) stuck off
due to:
Printer failure. Replace Printer.
Control PCA failure. Replace Control PCA.
Fails Printer Test in Diagnostic
Mode (other then symptoms above).
Printer failure. Replace Printer.
Control PCA failure. Replace Control PCA.
M3500B/M5500B Service Manual 3-25
Page 78

Operational Problems
Display
The following table covers problems that might arise with the LCD display.
Before replacing any parts, check to see if the cables and flex circuits are
properly connected. See "Servicing Notes" on page 4-1.
Table 3-12 Operational Problems - Display
Symptom Possible Causes Suggested solution
No response - all white or all black. Contrast misadjusted. Adjust contrast.
Control PCA failure. Replace Control PCA.
Display failure. Replace Display.
Display is blank but backlight works. Bad connections involving Display
Data Cable.
Display failure. Replace Display.
Control PCA failure. Replace Control PCA.
Backlight doesn’t light in dark ambient conditions.
• Display failure.
• Control PCA failure.
• Ambient light sensor failure.
1. Check/reseat data cable.
2. Replace data cable
Diagnose as follows:
In Diagnostic Mode, run Display
Test and press
BACKLIGHT ON and
BACKLIGHT OFF softkeys.
• Backlight does not respond:
Replace 1) Display 2) Control
PCA.
• Backlight responds normally:
test Ambient Light Sensor
(below).
In Diagnostic Mode, run Display
Test and check ambient light readings.
• Normal: Replace 1) Display 2)
Control PCA.
• Abnormal or not responding:
Replace 1) Control PCA 2)
Interface PCA.
Contrast does not adjust for ambient
temperature.
Fails Display Test in Diagnostic
Mode (display problem other then
symptoms above).
Fails Display Test in Diagnostic
Mode (ambient light readings).
Fails Display Test in Diagnostic
Mode (backlight).
Display failure. Replace Display.
Control PCA failure. Replace Control PCA.
Display failure. Replace Display.
Control PCA failure. Replace Control PCA.
Control PCA failure. Replace Control PCA.
Interface PCA failure. Replace Interface PCA.
Display failure. Replace Display.
Control PCA failure. Replace Control PCA.
3-26 Troubleshooting
Page 79

Table 3-12 Operational Problems - Display (Continued)
Symptom Possible Causes Suggested solution
Operational Problems
Fails Display Test in Diagnostic
Mode (indicator LEDs).
Control PCA failure. Replace Control PCA.
Manual Keypad failure. Replace Manual Keypad.
Audio
The following table covers problems that might arise with the audio tones or
voice prompts. Before replacing any parts, check to see if the cables and flex
circuits are properly connected. See "Servicing Notes" on page 4-1.
Table 3-13 Operational Problems - Audio Tones/Voice Prompts
Symptom Possible Causes Suggested solution
No audio at all. Speaker failure. Replace Speaker Assembly.
Control PCA failure. Replace Control PCA.
Audio is distorted. Damage to speaker label. Replace speaker label.
Speaker failure. Replace Speaker Assembly.
Control PCA failure. Replace Control PCA.
Buzzing noise when audio active. Damage to speaker label. Replace speaker label.
3
Debris between speaker and
speaker label.
Speaker hardware loose. Tighten hardware as needed.
Speaker failure. Replace Speaker Assembly.
Control PCA failure. Replace Control PCA.
Tones present but no voice prompt
(in AED Mode).
Voice prompt present but no tones. Control PCA failure. Replace Control PCA.
Control PCA failure. Replace Control PCA.
Remove speaker label, clean out
debris, install new speaker label.
M3500B/M5500B Service Manual 3-27
Page 80

Operational Problems
Keys
The following table covers problems that might arise with the keypads.
Before replacing any parts, check to see if the cables and flex circuits are
properly connected. See "Servicing Notes" on page 4-1.
Table 3-14 Operational Problems - Keys
Symptom Possible Causes Suggested solution
ON key doesn’t respond.
One or more of the Main Keys fails
to respond (OFF, 1, 2, 3).
One or more of the other keys don’t
respond (display controls, printer
controls, manual/pacing).
• Key failure.
• Interface PCA failure.
• Control PCA failure.
• Key failure.
• Interface PCA failure.
• Control PCA failure.
Refer to Table 3-1 "Unit Unresponsive".
Diagnose as follows:
In Diagnostic Mode, run Controls
test and identify all unresponsive
keys.
• Some keys don’t respond:
Replace 1) Control PCA 2)
Interface PCA 3) Top Case
Assembly.
• All keys don’t respond: Replace
1) Control PCA 2) Interface
PCA
Diagnose as follows:
In Diagnostic Mode, run Controls
test and identify all unresponsive
keys.
• Some keys don’t respond:
Replace 1) Interface PCA 2)
Control PCA 3) Top Case
Assembly.
• All keys don’t respond: Replace
1) Interface PCA 2) Control
PCA.
Fails Controls Test in Diagnostic
Mode
See symptoms above.
3-28 Troubleshooting
Page 81

Operational Problems
Battery and Power Modules
The following table covers problems that might arise with the Battery or
Power Module. Refer to Figure 3-3 to identify the indicators. Refer to Table 316 for the different combinations of indicator illuminations.
Table 3-15 Operational Problems - Battery, AC or DC Power Modules, Battery Charger Adapter
Symptom Possible Causes Suggested solution
Low battery life (depletes quickly in
use).
Charging indicator doesn’t come on
when Power Module plugged into
Battery Charger Adapter or into
M3500B/M5500B.
Fails Battery Capacity Test Battery old, worn out, or failed. Replace battery.
Done indicator doesn’t come on
even after plenty of charging time
(>14.5 hours).
Very frequent use - not charging
long enough between uses.
Battery failure. Run Battery Capacity Test (see
Power module failure. Replace Power Module.
Failure on Control PCA, Power
PCA, or Battery PCA.
Power module failure. Replace Power Module.
Failure on Control PCA. Replace Control PCA.
Performing System/Shift Test resets
the Power Module’s charging clock thus "Done" never illuminates even
though battery is charged.
Battery failure. Run Battery Capacity Test (see
Charge fully between uses. Use
spare batteries and adapters as
needed to allow complete charging.
"Battery Capacity Test" on page 2-
31). If battery fails test, replace bat-
tery.
Replace 1) Control PCA 2) Power
PCA 3) Battery PCA.
Use spare batteries and adapters as
needed to allow complete charging.
"Battery Capacity Test" on page 2-
31). If battery fails test, replace bat-
tery.
3
Power Module failure. Replace Power Module.
"Unsupported Battery" message
appears on the screen
• Not an M3516A battery.
• Battery damage.
• Failure on battery PCA.
• Use an M3516A battery only.
• Replace the battery.
• Replace the Battery PCA.
M3500B/M5500B Service Manual 3-29
Page 82

Operational Problems
Figure 3-3 Power Module Indicators
Table 3-16 Power Mod ule Indicator Matrix
INDICATORS SYSTEM STATE MEANING
Charge Done
Indicator
Charging Indicator
Power Indicator
POWER
CHARG-
ING
R = RED G = GREEN
DONE
Con-
nected
to Mains
(AC/DC) ?
Y = YES N = NO --- = don’t care
Con-
nected
M3500B/
M5500B ?
Battery in
Place?
Unit Power
ON ?
OR = ORANGE/AMBER
OFF OFF OFF N --- --- --- Normal
G OFF OFF Y --- --- --- Normal
G OFF OFF Y Y N --- Normal
G OR OFF Y Y Y --- Battery is charging.
G G OFF Y Y Y --- Battery 90% charged.
G G G Y Y Y --- Battery fully charged.
R OFF OFF Y Y --- --- If Power light was green before
connecting to unit, fault in
M3500B/M5500B.
R OFF OFF Y N --- --- Mains voltage low or
Fault in Power Module.
3-30 Troubleshooting
Page 83

Data Card
The following table covers problems that might arise with the Data Card.
Table 3-17 Operational Problems -Data Card
Symptom Possible Cause Corrective Action
Operational Problems
Data card is not recognized when
plugged in.
Data on the card corrupted. The card was removed while the
Fails Data Card Test in Diagnostic
Mode
Unit power is already on. Card is
only recognized during power-up
sequence.
Card is full or not a supported type. Use a new, empty M3510A/M5510A
unit power on.
Card is full or not a supported type. Use a new, empty M3510A/M5510A
Failure on Control PCA. Replace Control PCA.
Turn power off for 2 minutes, then
on again.
Data Card.
Only remove card after power is
turned off. Delete corrupted files
using the Event Review Data Management System.
Data Card.
3
M3500B/M5500B Service Manual 3-31
Page 84

Calling for Service - Philips HeartStart XLT
Calling for Service - Philips HeartStart XLT
For telephone assistance, call the Philips Medical Systems Response Center
nearest to you, or visit our website at: www.medical.philips.com/cms.
United States of America
Medical Response Center
Latin America
Medical Response Center
Canada
Medical Response Center
Tel: (800) 548-8833
Tel: 954-835-2600
Tel: 800-323-2280
3-32 Troubleshooting
Page 85

Calling for Service - Philips HeartStart XLT
Other International Areas
Australia France
Tel: 131147 Tel: 0803 35 34 33
Germany Italy
Tel: 0180 5 47 50 00 Tel: 800-825087
Netherlands United Kingdom
Tel: 31 20 547 2555
Fax: 31 29 547 2949
Belgium (for Dutch) Belgium (for French)
Tel: 32 2 525 7102
Fax: 32 2 525 71 91
Spain Poland
Tel: 34 902 30 40 50
Fax: 34 91 326 39 66
Austria Finland
Tel: 43 1 60101 820 Tel: 09 6158 0400
Switzerland Russia
Tel: 0800 80 10 23 Tel: 7 095 933 0339
Tel: 00 44 7002 432584
Tel: 32 2 525 710 3
Fax: 32 2 525 71 91
Tel: 48 22 5710499
Fax: 7 095 933 0338
3
M3500B/M5500B Service Manual 3-33
Page 86

Calling for Service - Laerdal Heartstart 4000
Calling for Service - Laerdal Heartstart 4000
For telephone assistance, call the Laerdal office nearest to you, or visit our
website at: www.medical.philips.com/cms.
United States of America
Laerdal Medical Corporation Tel: (800) 547-4781
International Customers
Tel: 61-3-95694055 Tel: 44-1689-876634
Tel: 946-71-700 Tel: 47-51511700
Australia United Kingdom
Norway Other Internationa l Areas
3-34 Troubleshooting
Page 87

4 Removal and Replacement
Overview
This chapter provides procedures for removing and replacing the subassemblies that are available as replacement parts.
Servicing Notes
Following are some important points to keep in mind whenever servicing the
M3500B/M5500B.
Key Components
Replacement assemblies marked with an asterisk (" * ") in the Replacement
Parts tables contain one or more Key Components. Key Components require
detailed tracking, by recording the key component part number and either the
key component’s date code or its serial number. This data must be recorded
for both the failed assembly and the replacement assembly.
4
Philips Medical Systems service personnel must record this information on
the Customer Service Order (CSO).
The Key Components that are part of the replacement assemblies are listed in
Table 5-15 on page 5-20.
Removal, Handling, and Replacement
The following sections give details of how to successful work with the internal assemblies of the M3500B/M5500B.
Flex Circuit Connections
In order for flex connections to function properly, they must be disconnected
and reconnected as follows:
z Always unlatch the PCA-mounted connector before removing the
flex, and hold the latch open while reinserting the flex into the connector.
4-1
Page 88

Servicing Notes
z When reconnecting, align the flex carefully in its receptacle, making
sure it is both centered from side to side in the connector, and oriented
at 90 degrees to the connector.
z Be sure the flex is fully seated in the connector and the connector is
properly latched.
Flex Circuit Handling
The flex circuits are delicate and can be damaged by improper handling:
z Do not bend sharply.
z Do not scrape the contact surface against other parts.
z Handle the flex with bent tip needle nose pliers whose jaws are cov-
ered with a soft material (such as plastic tubing or tape).
Internal Connections
Whenever troubleshooting indicates a particular PCA may be at fault, it is
always good practice to check all the connections to that PCA carefully before
replacing the PCA.
Cable and Assembly Placement
How the wires and cables are routed and dressed inside the chassis plays an
important role in two areas: in preventing long term wear problems, and in
reducing electromagnetic and radio frequency interference emitted by the
defibrillator.
z When you disassemble any part of the defibrillator, pay special atten-
tion to how cables and wires are routed.
z When you reassemble the defibrillator, be sure to route and dress all
cables and wires as they were originally.
z Return all components to their former position within the case.
Instrument Reassembly
If you do not reassemble the instrument correctly, the instrument may no
longer be properly sealed. This could result in water damage to the defibrillator. Be sure to maintain the water-resistant seal by:
z Replacing all gaskets in their proper locations.
z Correctly assembling all parts that mate with gaskets (making sure
the gaskets are not wrinkled or pinched).
z Replacing all screws.
z Making sure that screws are not cross-threaded and that they are
tightened firmly.
4-2 Removal and Replacement
Page 89

Tool Requirements
Tool Requirements
The following tools are needed to perform the procedures given.
z Torx T10 and T15 drivers (or Torx driver kit, Philips part number
5181-1933). T15 driver shaft should be at least 2.25" long and less
than 5/16" in diameter to reach down to recessed case screws.
z Phillips #1 screwdriver.
z Small straight bladed screwdriver.
z Straight tip needle nose pliers or tweezers.
z Bent tip needle nose pliers whose jaws are covered with a soft mate-
rial (such as plastic tubing or tape).
z Fine nose wire cutters.
z Utility knife.
z High voltage discharge tool for discharging the defibrillator capacitor
(Philips part number M2475-69572).
z Clip leads (at least 2, each approx. 10-18").
z Language Support Tool (see Table 5-2 on page 5-7 part numbers)
4
M3500B/M5500B Service Manual 4-3
Page 90

User-replaceable Parts and Accessories
User-replaceable Parts and Accessories
The Instructions for Use gives detailed instructions on replacing the following:
z Patient cables & sensors
z Battery
z Printer paper
For the convenience of the service person, instructions on replacing the Manual Door and the Carrying Case are duplicated here.
Manual Door
The following instructions detail how to remove and replace the Manual
Door. Refer to Table 5-6 on page 5-9 to select the correct replacement.
Removal
1. Open the door to a vertical position as shown in Figure 4-1.
2. Pull the hinge end of the door away from the case. It will snap free.
Replacement
1. If you are installing a new door, install the new labels as follows
a. Clean both top and bottom door surfaces with isopropyl alcohol.
Allow them to dry.
b. Lay the door on a clean flat surface with its underside facing up (the
side that is concealed when the door is closed).
c. The new door will come with labels both for units with Pacing and
without Pacing. Select the correct label for your unit.
d. Peel the new Manual Operation label off the backing material.
e. Starting with the top edge, align the label carefully with the recess on
the door and roll it down slowly into place. When installed, it should
be as shown in Figure 4-3.
f. Press firmly all over, especially the edges, to adhere the new label
into place.
g. Turn the door over to expose its top surface.
h. Peel the new Manual label off the backing material.
i. Starting with the top edge, align the label very carefully with the
recess on the door and roll it down slowly into place.
j. Press firmly all over, especially the edges, to adhere the new label
into place.
2. Align the door with the door hinges as shown in Figure 4-1.
4-4 Removal and Replacement
Page 91

User-replaceable Parts and Accessories
3. Push, as shown in Figure 4-2, until the door snaps into place.
Figure 4-1 Aligning the Manual Door
Figure 4-2 Snapping the Door in Place
4
M3500B/M5500B Service Manual 4-5
Page 92

User-replaceable Parts and Accessories
Figure 4-3 Attaching the Door Labels
Top label
Label
4-6 Removal and Replacement
Page 93

User-replaceable Parts and Accessories
Carrying Case
Removal
To remove the carrying case from the M3500B/M5500B, follow steps 1
through 7 as shown in Figure 4-4. Note the screws are Phillips head, not Torx.
Also, after loosening the captive screws (step 6), lay the unit flat and lift the
defibrillator up off the mounting plates to disengage it from the 2 locating pins
in the carrying case. Then slide it out of the carrying case as shown in step 7.
Figure 4-4 Removing the Carrying Case
4
M3500B/M5500B Service Manual 4-7
Page 94

User-replaceable Parts and Accessories
Replacement
To install the carrying case on the M3500B/M5500B, follow steps 1 through 7
as shown in Figure 4-5. Slide the unit into the case as shown in step 1, then
lower it onto the 2 locating pins in the case before tightening the screws in
step 2.
Figure 4-5 Installing the Carrying Case
Printer ribbon cable
4-8 Removal and Replacement
Page 95

User Maintenance
User Maintenance
The Instructions for Use gives detailed instructions on maintaining and
cleaning the M3500B/M5500B, including:
z Operational Checks
z Battery Maintenance
z Cleaning Instructions
For the convenience of the service person, instructions on cleaning the printer
printhead are duplicated here. Instructions on running the Battery Capacity
Test are duplicated on page 2-31.
Cleaning the Printer Printhead
If the printout has light or varying density printing, clean the printhead to
remove any buildup of paper residue.
To clean the printhead:
1. Slide the printer door to the right until the paper roller pops up.
2. Pull up on the plastic removal tab to remove the roll of paper.
3. Clean the printhead surface (above the brush) with a cotton swab dipped
in isopropyl alcohol.
4. Replace the roll of paper.
4
M3500B/M5500B Service Manual 4-9
Page 96

External Assemblies
External Assemblies
This section describes how to remove and replace assemblies that are external
to the sealed case.
Not all the assemblies described here are available as replacement parts; see
the "Replacement Parts" chapter.
CAUTION Be sure to work in a static safe environment. The work surface and area sur-
rounding it must be static free. Use a static control wrist band, in conjunction
with an antistatic pad which is grounded per the manufacturer’s instructions.
4-10 Removal and Replacement
Page 97

External Assemblies
Printer Assembly
The following steps describe how to remove and replace the printer assembly.
Removal
1. Disconnect the Power Module and remove the battery.
2. Discharge the power supply capacitors by turning the power on. You will
hear a click from the speaker.
3. Open the door over the paper by moving the sliding door in the direction
of the arrow and lifting up the platen and roller.
4. Loosen the (2) T10 screws now visible on the top and bottom edges of the
printer assembly at the left end. See Figure 4-6.
5. Peel up the label with the arrow on it.
6. Loosen the (2) T10 screws under the label
7. Pull the printer assembly and its screws straight upward
8. Unlatch the ribbon cable and unplug it as shown in Figure 4-7.
Figure 4-6 Removing the Printer Label and Screws
Label
Sliding Door
4
M3500B/M5500B Service Manual 4-11
Page 98

External Assemblies
Platen
Platen Springs
Hinge Pins
Figure 4-7 Removing the Printer
Sliding
Door
Printer
ribbon
cable
Replacement
1. The replacement printer ships with a grey sliding door and a grey platen
installed. They must be replaced with the yellow sliding door and yellow
platen that came in the printer kit. Refer to "Printer Sliding Door" and
"Printer Platen" on page 4-13.
2. Open the paper door on the new printer. Leave the paper door open until
the screws under the label are tightened.
3. Put the 4 screws in the holes in the new printer. Get the 2 screws back in
the holes under the label with tweezers or fine nose pliers.
4. Reconnect the ribbon cable. Be sure to engage the 2 latches on the ends of
the ribbon connector.
5. Lower the printer straight down into the instrument.
6. Tighten all screws.
7. Clean the surface where label will be placed with alcohol. Allow it to dry.
8. Replace the label.
4-12 Removal and Replacement
Page 99

External Assemblies
Printer Sliding Door
Removal
a. Turn the printer upside down on a flat surface. Orient it so that the
sliding door is nearest you. Note how the 2 springs are installed on
the sliding door and how the metal door limit is used to stop the travel
of the sliding door (the springs are identical).
b. Using a pair of needle-nose pliers, remove and save both springs.
c. Lift the metal door travel limiter up and slide the door forward, away
from the printer.
d. Slide the door out on its rails as far as it will go. Pull the retaining
clips on one side of the door out away from the side of the printer
frame to unsnap the door from the printer.
Replacement
a. Starting at the end of the rails furthest out from the printer, hook the
retaining clips on one side of the door over the rail and snap the clips
on the other side of the door into place. This is made easier by pulling
out on the retaining clips to spread them further apart, and by squeezing the printer frame to deflect the rails toward each other.
b. Lift the metal door travel limiter up and slide the door in toward the
printer all the way to the end of its rails.
c. Reattach the two springs, with their round ends hooked through the
holes in the frame, and their angled ends hooked over the lugs on the
underside of the door. Note that the springs should be behind the
metal door limit.
4
M3500B/M5500B Service Manual 4-13
Page 100

External Assemblies
Printer Platen
Removal
a. Open the printer. If you have just removed the sliding door, it will
already be open.
b. Note the two platen springs (they are not identical), and how they are
located. Their longer ends fit into grooves in the platen; their shorter
ends fit through a slot in the printer frame.
c. Grasp the body of the printer just below the hinge pins and squeeze
the body so that the hinge pins move in. Disengage one pin first, then
the other.
d. Lift the platen assembly from the hinges. Keep track of the springs.
Replacement
a. Reinstall the springs on their correct hinge pins.
b. Grasp the body of the printer just below the hinge pins and squeeze
the body so that the hinge pins move in. First engage one pin to the
new platen, then the other. Be sure the springs are installed correctly.
4-14 Removal and Replacement
 Loading...
Loading...