PHILIPS E8 Training

PSSG
PHILIPS SERVICE SOLUTIONS GROUP
PHILIPS TECHNICAL
TRAINING
PHILIPS
TECH
VIDEOTA PE S
MANUALS
COLOR TV
CHASSIS
Philips Technical Training (USA)
401 E. Old Andrew Johnson hwy
PO box 555
Jefferson City, TN 37760
PH: 865-475-0397
FAX: 865-475-0221
TRAINING
EMAIL: Technical.Training@Philips.com
E8

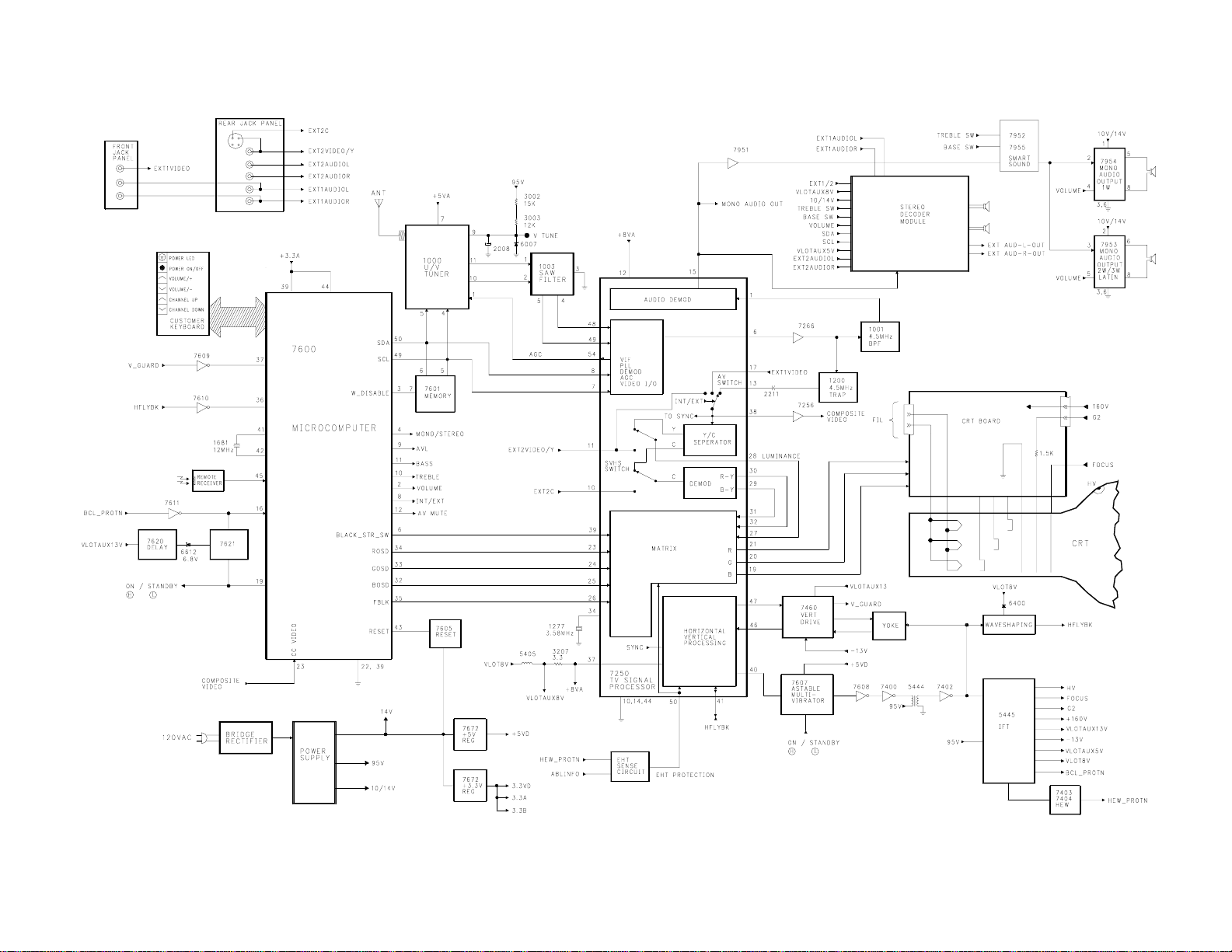
E8 OVERALL BLOCK FIGURE 1
The E8 series chassis is the
Small Screen TV chassis produced
by Philips Consumer Electronics
Company for the 1999-2000 model
year. The E8 is used with 13,
19, and 20 inch CRT's. The E8
Tuning System features a 181
channel Tuning System with OnScreen Display. The Tuning System
uses two IC's mounted on the main
chassis. It consists of a
Microcomputer IC and Memory IC.
The Microcomputer communicates
with the Memory IC, the Customer
Keyboard, the Remote Receiver, the
U/V Tuner, the TV Signal
Processor, the Stereo Decoder
(optional), and the Power On-Off
circuitry. The Memory IC retains
the settings for favorite
stations, customer control
settings, feature settings, and
factory setup data.
The chassis features a Very Large
Scale Integration (VLSI) IC for TV
Signal Processing. This IC
performs Video IF, Sound IF,
AFT/AGC control, Horizontal Signal
Processing, Vertical Signal
Processing, Horizontal/Vertical
Synchronization, Chroma/Luminance
Processing, and Video Switching
between internal and external
inputs. On-Screen Graphics from
the Microcomputer are placed on
the main signal within the TV
Signal Processor. Automatic
Volume Level (AVL) from the
Microcomputer is sent to the TV
Signal Processor (Mono Sets) and
to the Stereo Module (DBX Stereo
Sets via the I2C bus). AVL for
Normal Stereo is switched by Pin
9 of the Microcomputer, 7600.
The Mono version has a 1 watt
audio amplifier. The Normal
Stereo version has a 2x1 watt
amplifier. The DBX Stereo version
has a 2x3 watt amplifier. Latin
American versions of this chassis
may have a 2 or 3 watt Mono
amplifier.
The E8 chassis features a
Switching Mode Power Supply. A
"HOT" ground reference is used in
the primary side of the power
supply. "COLD" (signal)ground is
used from the secondary of the
power supply and throughout the
rest of the chassis. AN ISOLATION
TRANSFORMER IS REQUIRED WHEN DOING
SERVICE ON ANY CHASSIS.
SIGNAL FLOW
The incoming TV RF signal is
applied to the U/V Tuner via the
Antenna and RF input. The
45.75MHz IF signal is developed
within the U/V Tuner, then
amplified by an IF Preamplifier
located inside the Tuner. The
amplified IF signal is sent from
Pins 10 and 11 of the U/V Tuner
to the SAW filter, 1003. The SAW
filter produces bandpass shaping
for the IF signal before it is
applied to the TV Signal
Processing Integrated Circuit,
7250, for processing. AFT voltage
is developed within 7250. These
voltage values are then sent to
the microcomputer via the I2C bus
for Tuner Oscillator frequency
correction.
Sound IF signal processing for the
E8 chassis is performed by
coupling the 4.5MHz Sound IF
signal from 7250 Pin 6 through
transistor 7266 and a 4.5MHz band
PAGE 1
PAGE 2
FIGURE 1 - E8 BLOCK

pass filter 1001 to Pin 1 of 7250.
In the Mono version, Baseband
Audio from Pin 15 of 7250 is
buffered by transistor 7951 before
being applied to Bass and Treble
circuits. The outputs of the Base
and Treble circuits are applied to
a 1 watt amplifier 7954 in the US
version or a 2 or 3 watt amplifier
7953 in the Latin version. In sets
equipped with a Stereo module,
Baseband Audio from Pin 15 of 7250
is fed to the Stereo Decoder
module. The DBX Stereo Decoder
module has internal/external
switching, AVL switching,
volume control, and alignment
settings via the I2C bus (SDA &
SCL). Internal/external switching,
AVL switching, and volume control
for the Normal Stereo module are
performed through individual
control lines from the
Microcomputer. Audio Output
Amplifiers for both the DBX and
Normal Stereo versions are located
on the Stereo module. AVL
switching for the Mono version is
performed in 7250 via the I2C bus.
Volume for the Mono set is
controlled in the Audio Output
Amplifier 7954 or 7953 by a
control line from the
Microcomputer 7600 Pin 2. Volume
for the Normal Stereo is
controlled in the Stereo Module by
a control line from the
Microcomputer 7600 Pin 2. Volume
control for the DBX Stereo is
controlled in the Stereo Module by
the Microcomputer via the I2C bus.
Composite Video from Pin 6 of 7250
is buffered by 7266 and sent to
1200, a 4.5MHz trap, to remove any
sound. The Video is then applied
to Pin 13 of 7250. The
Internal/External switch selects
between Pin 13, the External Video
source on Pin 17, or the External
Two Video source on Pin 11. The
selected Video is fed to an
internal Y/C separator inside
7250. Luminance and Chromance is
fed to an internal SVHS switch
which selects between internal Y/C
or external Y/C on Pins 11 and 10.
Internally selected "C" Chromance
is fed to an internal Demodulator
which outputs R-Y and B-Y on Pins
30 and 29. Internally selected
"L" Luminance is output on Pin 28.
R-Y, B-Y, and "L" are fed to the
Matrix circuit on Pins 31, 32, and
27.
Red, Green, and Blue On-Screen
display signals from the
Microcomputer 7600 Pins 34, 33,
and 32 are fed to the Signal
Processor 7250 Pins 23, 24, and
25. Fast Blanking from 7600 Pin 35
is fed to 7250 Pin 26.
Brightness, Picture, Sharpness,
Color, and Tint control voltages
are developed within 7250 from the
Tuning System Microcomputer 7600
via the I2C bus. The Red, Green,
and Blue signals developed by the
signal processor, 7250, are output
on Pins 21, 20, and 19 and applied
to the CRT board. On the CRT
board, these signals are amplified
before being applied to the CRT.
The White Balance controls for the
CRT set-up are controlled within
7250 by the Microcomputer via the
I2C bus. Adjustments are
performed with the set in the
Service Test Mode. Always use the
procedures in the Service Manual
for setting up the CRT circuits
(White Balance). The White Balance
is set by adjusting the White Tone
adjustments in the Service Test
PAGE 3

Mode.
Horizontal and Vertical signals
are also developed within 7250.
Adjustment for Horizontal and
Vertical Geometry are done with
the Remote Transmitter via the
Service Test Mode. There is no
adjustment for the Horizontal
Oscillator. The Horizontal circuit
is a count down type of system
that gets its base frequency from
the 3.58MHz circuit.
When the set is turned On, the Low
on Pin 19 of 7600 is removed
allowing the On/Standby line to go
High. The High is applied to
7607, the Astable Multivibrator,
which is powered by the +5VD
supply. The Astable Multivibrator
7607 provides Horizontal Drive to
drivers 7608 and 7400. The drive
is then applied to 7402, the
Horizontal Output transistor,
which drives the Horizontal
Deflection Yoke and the IFT. The
IFT develops high voltage, focus
voltage, and filament voltage for
the CRT. Scan derived voltages
produced by the IFT are 160 volts,
VLOTAUX13V 13 volts, -13 volts,
VLOTAUX5V 5 volts, and VLOT8V 8
volts. The scan derived VLOT8V,8
volt supply, produces the +8VA
supply which is applied to Pin 37
of 7250 to power the Horizontal
and Vertical sections of the IC.
The Horizontal Oscillator section
of 7250 does not operate until the
Scan circuit is working.
Horizontal Drive on Pin 40 is
applied to 7607 to synchronize the
Astable Multivibrator to the
correct frequency.
The Shutdown circuits of the set
monitor for excessive Beam
Current, excessive High Voltage,
or a Low +13 volt supply
(VLOTAUX13V). The BCL_PROTN
circuit of the IFT monitors for
excessive Beam Current. If the
BCL_PROTN line goes High,
transistor 7611 will turn On,
causing Pin 16 of 7600 to go Low,
turning the set Off. Transistors
7403 and 7404 monitor the
secondary of the IFT for excessive
voltage. If the output of the IFT
should go too high, the HEW_PROTN
line will go High, causing Pin 50
of 7250 to go High. This will
shut the Horizontal Oscillator
Off. Transistor 7621 and Zener
Diode 6612 monitors the 13 volt
(VLOTAUX13V) line. If the 13 volt
supply should go Low or fail, 7621
will turn On, causing Pin 16 of
7600 to go Low, turning the set
Off. Transistor 7620 provides a
power On delay for this circuit.
E8 CHASSIS POWER SUPPLY BLOCK
(Figure 2)
When a 120Vac source is connected
to the E8 chassis, approximately
160Vdc is developed by the bridge
rectifier circuit. The 160 volts
dc goes through 5545 to the FET
switch. The start voltage for the
switching mode power supply is
taken from the hot leg of the
input ac.
The power supply includes a single
integrated circuit, operating as a
free-running switching mode power
supply. The frequency of operation
varies with the circuit load.
There is no separate power supply
for standby; instead, the power
supply turns On when ac is
applied. The switching regulator
IC starts switching when the
PAGE 4
 Loading...
Loading...