Philips DVDR-610, DVDR-615, DVDR-616 Service manual

DVD-Video Recorder DVDR610, DVDR615 & DVDR616
DVDR610/00/02/05/19/33, DVDR615/00/02/05/19/33
DVDR616/00/02/05
Contents Page Contents Page
1 Technical Specifications and Connection
Facilities
2 Safety Information, Gene ra l Notes 5
3 Directions for Use 7
4 Mechanical Instructions 9
5 Diagnostic Software 13
6
Block Diagrams, Waveforms, Wiring Diagram
Wiring Diagram 80
Waveforms 82
Testpoints 84
7
Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
MOBO:Fronted Video (FV) (Diagram 1) 87
MOBO: In / Out Video (IOV) (Diagram 2) 88
MOBO: In / Out Audio (IOA) (Diagram 3) 89
MOBO: Power Supply (PS) (Diagram 4) 90
MOBO: Multi Sound Processing (M SP)(Diagram 5) 91
MOBO: Cinch Out (CINCH) (Diagram 6) 92
MOBO: Follow Me (FOME) (Diagram 7) 93
MOBO: Audio Converter( DA C_A DC ) (Diagram 9) 94
MOBO: Color UniT (CU) (Diagram 10) 95
MOBO: IR Blaster (IRB) (Diagram 11) 96
MOBO: Digital In/Out 1(DIGIO1) (Diagram 12) 97
MOBO: Digital In/Out 2(DIGIO2) (Diagram 10) 104
MOBO: Keyboard (KEY) (Diagram 11) 105
MOBO: Standby (STBY) (Diagram 12) 107
MOBO: Open / C lose (OPCL) (Diagram 13) 109
MOBO: 5-Way Switch (5WSW) (Diagram 14) 110
FEBE: FE OPU Interface (Diagram 1) 111
FEBE: Fe Cheetah 2 Pre-processing (Diagram 2) 112
FEBE: FE Laconic Pre-processing (Diagram 3) 113
FEBE: FE Drivers (Diagram 4) 114
FEBE: FE Centaurus 1.5 Processor (Diagram 5) 115
FEBE: FE Supply / BE Interface (Diagram 6) 116
FEBE: FE Tray Motor / Swich Conn. (Diagram 7) 117
©
Copyright 2004 Philips Consumer Electronics B.V. Eindhoven, The Netherlands.
All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a
retrieval system or transmitted, in any form or by any means, electronic,
mechanical, photocopying, or otherwise without the prior permission of Philips.
2
77
87
FEBE: BE Chrysalis (Diagram 8) 118
FEBE: BE Flash, EEPROM & SDRAM (Diagram 9) 119
FEBE: BE DV In IEEE1394 (Diagram 10) 120
FEBE: BE Video In Processing (VIP) (Dia gram 11) 121
FEBE: BE Audio & Video In/Out (Diagram 12) 122
FEBE: BE Supply, Reset, UART, Enc. (Diagram 13) 123
LECO: Fe Opu Interface (Diagram 1) 134
LECO: Fe Pre-Processing (Diagram 2) 135
LECO: Febe Power Supply (Diagram 3) 136
LECO: Fe Drivers (Diagram 4) 137
LECO: Fe Processor (Diagram 5) 138
LECO: FeBe Interface (Diagram 6) 139
LECO: Be Debug Connectors (Diagra m 7) 140
LECO: Be LECO (Diagram 8) 141
LECO: Memory (Diagram 9) 142
LECO: IEE1934 (Diagram 10) 143
LECO: Be Video In (Diagram 11) 144
LECO: Be Audio/Video Out (Diagram 12) 144
LECO: Be Pheriphery (Diagram 13) 146
8 Alignments 157
9 Circuit-, IC Descriptions and List
of Abbreviations
10 Spare Parts List 219
10 Revision List 228
158
Published by KC 0428 Service PaCE Printed in the Netherlands Subject to modification EN 3122 785 14181
Version 1.1
EN 2 DVDR610/615/6161.
Technical Specifications and Connection Facilities
1. Technical Specifications and Connection Facilities
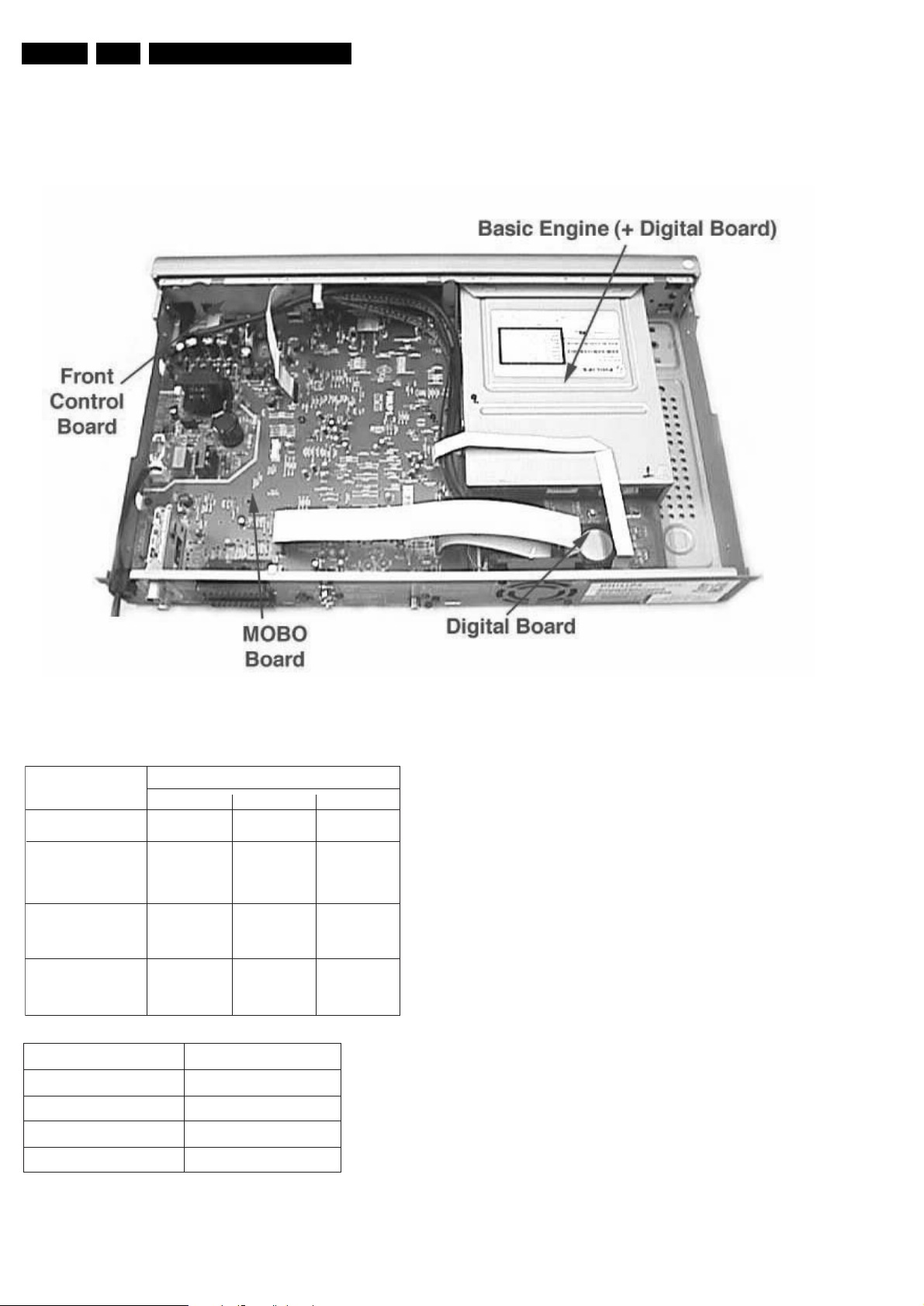
1.1 PCB Locations
1.2 Diversity Matrix and Read and Write speed 1.3 General:
Mains voltage : 198V-276V
Mains frequency : 43 Hz - 63Hz
Power consumption (record) : 27 W
Power consumption (AV loop through) : < 15W
Power consumption low power
stand-by : < 3 W
1.4 RF Tuner
Test equipment:Fluke 54200 TV Signal generator
Test streams:PAL BG Philips Standard test pattern
1.4.1 System:
PAL B/G, PAL D/K, SECAM L/L’, PAL I
1.4.2 RF - Loop Through:
Frequency range : 45 MHz - 860 MHz
Gain: (ANT IN - ANT OUT) : -6 dB to 0dB
1.4.3 Radio Interference:
input voltage /3 tone method (+40
dB min) : no limit
Module / Pcb Application
MOBO 04 E1
12NC: 3139 248 82891
VAU8041/11
DS version: E2_AV3_4
12NC: 9305 025 84111
FEBE pcb: 3104 128 09271
Drive: AV3.5
VAU8041/21
DS version: E1_AV3_4
12NC: 9305 025 84121
pcb: 3104 128 09281
Drive: AV3.5
LECOLITE U4.01L
DS version: OL22FEBE
12NC: 3139 247 10942
pcb: 3139 248 83791
Drive: D4.0
DVDR610/0x/19/33
Type of Disc (Function)
Read Speed CD
Read Speed DVD
Write Speed DVD+RW
Write Speed DVD+R
VFM RANGE
DVDR615/0x/19/33
x
x
x
x
x
Disc Rotation Speed
CAV 7x
CAV 4x
ZCAV 2.4x
ZCAV2.4x
DVDR616/0x/19/33
x
x
1.4.4 Receiver:
PLL tuning with AFC for optimum reception

Technical Specifications and Connection Facilities
EN 3DVDR610/615/616 1.
Frequency range: : 45.25 MHz - 857 MHz
Sensitivity at 40 dB S/N : ≥ 60dBµV at 75Ω
(video unweighted )
1.4.5 Video Performance:
Channel 25 / 503,25 MHz,
Test pattern: PAL BG PHILIPS standard test pattern,
RF Level 74 dBV
Measured on SCART 1
Frequency response: : 0.1- 4.00 MHz ± 3dB
Group delay ( 0.1 MHz - 4.4 MHz ) : 0 nsec ± 150nsec
1.4.6 Audio Performance:
Audio Performance Analogue - HiFi:
Frequency response at SCART 1
(L+R) output: : 100 Hz - 12 kHz / 0±
3dB
S/N according to DIN 45405, 7, 1967 :
and PHILIPS standard test pattern
video signal: : ≥ 50dB, unweighted
Harmonic distortion ( 1 kHz, ± 25
kHz deviation ): : ≤ 1.5%
Audio Performance NICAM:
Frequency response at SCART
1(L+R) output: : 40 Hz - 15 kHz 0 ±
3dB
S/N according to DIN 45405, 7, 1967 :
and PHILIPS standard test pattern
video signal: : ≥ 60 dB unweighted
Harmonic distortion (1 kHz): : ≤ 0.5 %
1.4.7 Tuning
Automatic Search Tuning
scanning time without antenna : typ. 3 min.
stop level (vision carrier) : ≥ 37dBµV
Maximum tuning error of a recalled
program : ± 62.5 kHz
Maximum tuning error during
operation : ± 100 kHz
Tuning Principle
automatic B,G, I, DK and L/L’detection
manual selection in "STORE" mode
1.5 Analogue Inputs / Outputs
1.5.1 SCART 1 (Connected to TV)
Pin Signals:
1 - Audio R 1.8V RMS
2 - Audio R
3 - Audio L 1.8V RMS
4 - Audio GND
5 - Blue/Chroma GND
6 - Audio L
7 - Blue out/
Chroma in 0.7Vpp ± 0.1V into 75 Ohm (*)
8 - Function
switch <2V = TV
>4.5V / <7V = asp. ratio 16:9 DVD
>9.5V / <12V = asp. ratio 4:3 DVD
9 - Green GND
10 - P50 control
11 - Green 0.7Vpp ± 0.1V into 75 Ohm (*)
12 - Nc
13 - Red/Chroma GND
14 - fast switch GND
15 - Red out/
Chroma out 0.7Vpp ± 0.1V into 75 Ohm (*)
± 3dB 0.3Vpp Chroma (burst)
16 - fast switch
RGB/ CVBS or Y <0.4V into 75 Ohm = CVBS
>1V / <3V into 75 Ohm = RGB
17 - Y/CVBS GND OUT
18 - Y/CVBS GND IN
19 - CVBS/Y 1Vpp ± 0.1V into 75 Ohm (*)
20 - CVBS/Y
21 - Shield
1.5.2 SCART 2 (Connected to AUX)
Pin Signals:
1 -Audio R 1.8V RMS
2-Audio R
3 -Audio L 1.8V RMS
4 -Audio GND
5 -Blue/Chroma GND
6 -Audio L
7 -Blue in/
Chroma out ± 3dB 0.3Vpp Chroma (burst)
8 -Function
switch
9 -Green GND
10 -P50 control
11 -Green in
12 -Nc
13 -Red/Chroma GND
14 -fa st s w i t c h GN D
15 -Red in/Chroma in
16 -fast switch
RGB/ CVBS or
Y
17 -CVBS GND OU T
18 -CVBS GND IN
19 -CVBS/Y/RGB
sync 1Vpp ± 0.1V into 75 Ohm (*)
20 -CVBS/Y
21 -Shield
(*) for 100% white
1.5.3 Audio/Video Front Input Connectors
Audio - Cinch
Input voltage : 2.2 Vrms
Input impedance : >10kΩ
Video - Cinch
Input voltage : 1 Vpp ± 3dB
Input impedance : 75 Ω
Video - YC (Hosiden)
According to IEC 933-5
Superimposed DC-level on pin 4 (load > 100kΩ)
< 2.4V is detected as 4:3 aspect ratio
> 3.5V is detected as 16:9 aspect ratio
Input voltage Y : 1Vpp ± 3dB
Input impedance Y : 75 Ω
Input voltage C : burst 300 mVpp ± 3
dB
Input impedance C : 75 Ω
1.5.4 Audio/Video Output rear Connectors
Audio- Cinch
Output voltage : 2Vrms max.
Output impedance : >10kΩ
Video- Cinch
Output voltage : 1 Vpp ± 3dB

EN 4 DVDR610/615/6161.
Technical Specifications and Connection Facilities
Output impedance : 75 Ω
Video - YC (Hosiden)
According to IEC 933-5
Superimposed DC-level on pin 4 (load > 100kohm)
< 2.4V is detected as 4:3 aspect ratio
> 3.5V is detected as 16:9 aspect ratio
Output voltage Y : 1Vpp +10/-15%
Output voltage C : 300mVpp +1/-4dB
1.6 Video Performance
All outputs loaded with 75 Ohm
SNR measurements over full bandwidth without weighting.
1.6.1 SCART (RGB)
SNR : > -65 dB on all output
Bandwidth : 4.8 MHz ± 2dB
1.7 Audio Performance CD
1.7.1 Cinch Output Rear
Output voltage 2 channel mode : 2Vrms ± 2dB
Channel unbalance (1kHz) : <1dB
Crosstalk 1kHz : >95dB
Crosstalk 16Hz-20kHz : >87dB
Frequency response 20Hz- 20kHz : ±0.2dB max
Signal to noise ratio : >85 dB
Dynamic range 1kHz : >83dB
Distortion and noise 1kHz : >83dB
Distortion and noise 16Hz-20kHz : >75dB
Intermodulation distortion : >70dB
Mute : >95dB
Outband attenuation: : >40dB above 30kHz
Specification of consumer use digital VCR’s using 6.3 mm
magnetic tape - dec.1994
Mechanical connection according:
Annex A of 61883-1
1.10 P50 System Control
Via SCART pin nr 10
1.11 Dimensions and Weight
Height of feet : 5.5mm
Apparatus tray closed : WxDxH :435 x 285x 65mm
Apparatus tray open : WxDxH :435 x 422x 65mm
Weight without packaging : app. 4 kg ± 0.5 kg
Weight in packaging : a pp. 6.5 kg
1.12 Laser Output Power & Wavelength
1.12.1 DVD
Output power during reading : 0.8mW
Output power during writing : 2 0mW
Wavelength : 6 60nm
1.12.2 CD
Output power : 0 .3mW
Wavelength : 7 80nm
1.7.2 Scart Audio
Output voltage 2 channel mode : 1.6Vrms ± 2dB
Channel unbalance (1kHz) : <1dB
Crosstalk 1kHz : >85dB
Crosstalk 16Hz-20kHz : >70dB
Frequency response 20Hz- 20kHz : ± 0.2dB max
Signal to noise ratio : >80 dB
Dynamic range 1kHz : >75dB
Distortion and noise 1kHz : >75dB
Distortion and noise 16Hz-20kHz : >50dB
Intermodulation distortion : >70dB
Mute (spin-up, pause, access) : >80dB
Outband attenuation: : >40dB above 25kHz
1.8 Digital Output
1.8.1 Coaxial
CDDA/ LPCM (incl MPEG1) : according IEC958
MPEG2, AC3 audio : according IEC1937
DTS : according IEC1937,
amendment 1
1.9 Digital Video Input (IEEE 1394)
1.9.1 Applicable Standards
Implementation according:
IEEE Std 1394-1995
IEC 61883 - Part 1
IEC 61883 - Part 2 SD-DVCR (02-01-1997)

Safety Information, General Notes
2. Safety Information, General Notes
EN 5DVDR610/615/616 2.
2.1 Safety Instructio ns
2.1.1 General Safety
Safety regulations require that during a repair:
• Connect the unit to the mains via an isolation transformer.
• Replace safety components, indicated by the symbol ,
only by components identical to the original ones. Any
other component substitution (other than original type) may
increase risk of fire or electrical shock hazard.
Safety regulations require that after a repair, you must return
the unit in its original condition. Pay, in particular, attention to
the following points:
• Route the wires/cables correctly, and fix them with the
mounted cable clamps.
• Check the insulation of the mains lead for external
damage.
• Check the electrical DC resistance between the mains plug
and the secondary side:
1. Unplug the mains cord, and connect a wire between
the two pins of the mains plug.
2. Set the mains switch to the 'on' position (keep the
mains cord unplugged!).
3. Measure the resistance value between the mains plug
and the front panel, controls, and chassis bottom.
4. Repair or correct unit when the resistance
measurement is less than 1 MΩ.
5. Verify this, before you return the unit to the customer/
user (ref. UL-standard no. 1492).
6. Switch the unit ‘off’, and remove the wire between the
two pins of the mains plug.
2.1.2 Laser Safety
This unit employs a laser. Only qualified service personnel may
remove the cover, or attempt to service this device (due to
possible eye injury).
2.2 Warnings
2.2.1 General
• All ICs and many other semiconductors are susceptible to
electrostatic discharges (ESD, ). Careless handling
during repair can reduce life drastically. Make sure that,
during repair, you are at the same potential as the mass of
the set by a wristband with resistance. Keep components
and tools at this same potential.
Available ESD protection equipment:
– Complete kit ESD3 (small tablemat, wristband,
connection box, extension cable and earth cable) 4822
310 10671.
– Wristband tester 4822 344 13999.
• Be careful during measurements in the live voltage section.
The primary side of the power supply (pos. 1005), including
the heatsink, carries live mains voltage when you connect
the player to the mains (even when the player is 'off'!). It is
possible to touch copper tracks and/or components in this
unshielded primary area, when you service the player.
Service personnel must take precautions to prevent
touching this area or components in this area. A 'lightning
stroke' and a stripe-marked printing on the printed wiring
board, indicate the primary side of the power supply.
• Never replace modules, or components, while the unit is
‘on’.
2.2.2 Laser
• The use of optical instruments with this product, will
increase eye hazard.
• Only qualified service personnel may remove the cover or
attempt to service this device, due to possible eye injury.
• Repair handling should take place as much as possible
with a disc loaded inside the player.
• Text below is placed inside the unit, on the laser cover
shield:
Laser Device Unit
Type : Semiconductor laser
GaAlAs
Wavelength : 650 nm (DVD)
: 780 nm (VCD/CD)
Output Power : 20 mW
(DVD+RW writing)
:0.8 mW
(DVD reading)
:0.3 mW
(VCD/CD reading)
Beam divergence : 60 degree
Figure 2-1
Note: Use of controls or adjustments or performance of
procedure other than those specified herein, may result in
hazardous radiation exposure. Avoid direct exposure to beam.
CAUTION VISIBLE AND INVISIBLE LASER RADIATION WHEN OPEN AVOID EXPOSURE TO BEAM
ADVARSEL SYNLIG OG USYNLIG LASERSTRÅLING VED ÅBNING UNDGÅ UDSÆTTELSE FOR STRÅLING
ADVARSEL SYNLIG OG USYNLIG LASERSTRÅLING NÅR DEKSEL ÅPNES UNNGÅ EKSPONERING FOR STRÅLEN
VARNING SYNLIG OCH OSYNLIG LASERSTRÅLNING NÄR DENNA DEL ÄR ÖPPNAD BETRAKTA EJ STRÅLEN
VARO! AVATTAESSA OLET ALTTIINA NÄKYVÄLLE JA NÄKYMÄTTÖMÄLLE LASER SÄTEILYLLE. ÄLÄ KATSO SÄTEESEEN
VORSICHT SICHTBARE UND UNSICHTBARE LASERSTRAHLUNG WENN ABDECKUNG GEÖFFNET NICHT DEM STRAHL AUSSETSEN
DANGER VISIBLE AND INVISIBLE LASER RADIATION WHEN OPEN AVOID DIRECT EXPOSURE TO BEAM
ATTENTION RAYONNEMENT LASER VISIBLE ET INVISIBLE EN CAS D'OUVERTURE EXPOSITION DANGEREUSE AU FAISCEAU
!
Figure 2-2
2.2.3 Notes
Dolby
Manufactered under licence from Dolby Laboratories. “Dolby”,
“Pro Logic” and the double-D symbol are trademarks of Dolby
Laboratories. Confidential Unpublished Works.
©1992-1997 Dolby Laboratories, Inc. All rights reserved.
Figure 2-3
Trusurround
TRUSURROUND, SRS and symbol (fig 2-4) are trademarks of
SRS Labs, Inc. TRUSURROUND technology is manufactured
under licence frm SRS labs, Inc.
Figure 2-4

EN 6 DVDR610/615/6162.
Video Plus
“Video Plus+” and “PlusCode” are registered trademarks of the
Gemstar Development Corporation. The “Video Plus+” system
is manufactored under licence from the Gemstar Development
Corporation.
Figure 2-5
Macrovision
This product incorporates copyright protection technology that
is protected by method claims of certain U.S. patents and other
intellectual property rights owned by Macrovision Corporation
and other rights owners.
Use of this copyright protection technology must be autorized
by Macrovision Corporation, and is intended for home and
other limited viewing uses only unless otherwise authorized by
Macrovision Corporation. Reverse engineering or disassembly
is prohibited.
Safety Information, General Notes

Directions For Use
3. Directions For Use
The following excerpt of the Quick Use Guide serves as an introduction to the set.
The complete Direction for Use can be downloaded in different languages from the internet site of Philips Customer Care Center:
www.p4c.philips.com
EN 7DVDR610/615/616 3.

EN 8 DVDR610/615/6163.
Directions For Use

Mechanical Instructions
4. Mechanical Instructions
EN 9DVDR610/615/616 4.
4.1 Dismantling and Assembly of the Set
For item numbers please see the exploded views in chapter 10.
4.1.1 Front Panel Assembly
– After removing the top cover, remove tray front 134+138,
see picture 4-1
– Remove the three screws 188
– Release the two snap hooks on the sides and remove the
front assembly
– Remove the 4 screws 186 to remove the front plate 184,
see picture 4-2
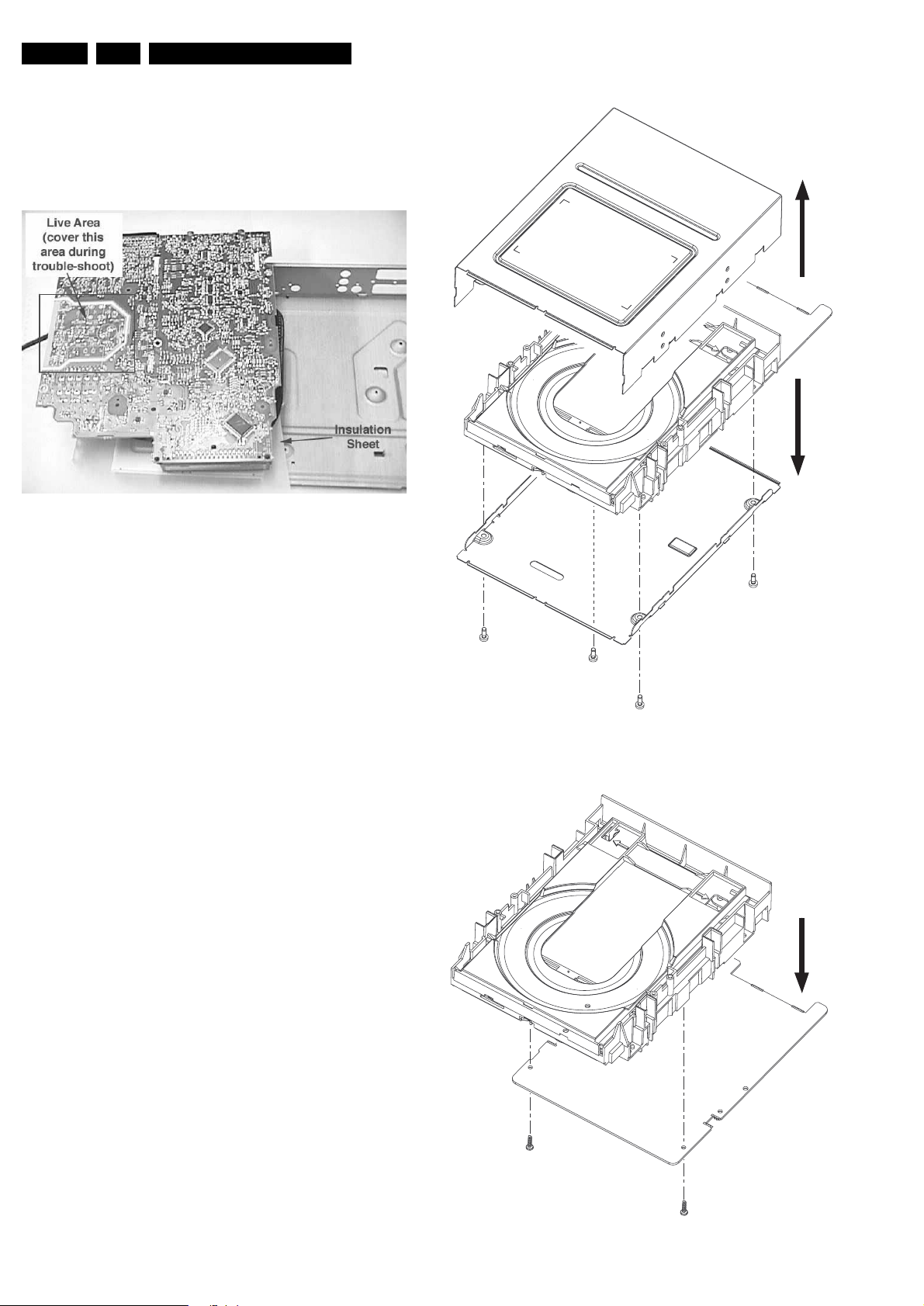
4.1.2 Basic Engine
– Remove the Front Panel Assembly as given in 4.1.1
– Remove the 6 screws 260, 269 to free the Basic Engine
– Remove the dust cover assembly 147 and 148
– Loosen 2 screws to remove bracket 256
– Loosen 4 screws to remove the Basic Engine metal casing
– Place the Basic Engine in the service position
Figure 4-3
Figure 4-1
Figure 4-2
Figure 4-4
EN 10 DVDR610/615/6164.
4.1.3 MOBO Board
– Remove the Front Panel assembly as given in 4.1.1
– Remove 6 screws 246 and 254
– Remove 4 screws 270
– Service position is achieved by flipping the MOBO board
above the Basic Engine
Mechanical Instructions
2
2
Figure 4-5
4.2 Dismantling and assembly of the Basic Engine
4.2.1 General
Follow the dismantling instructions in described order.
Do not place the unit with its PCB on a hard surface (e.g. table),
as it could damage the components on it.
Always place something soft (a towel or foam cushion) under it.
Never touch the lens of the OPU.
Take sufficient ESD measures during handling.
4.2.2 Dismantling the FEBE Board / Lecolite (LECO) Board
– Remove 4 screws to remove the metal case 150+180
– Remove 2 screws to separate the P.C. board 179 or 180
from the main Loader/Drive assembly
Note: After exchange of the PCB (or the Drive mechanism)
the complete Basic Engine has to be adjusted! Refer to
chapter 8 for adjustment instructions!
1
1
1
1
Figure 4-6 Basic Engine Module dismantling
2
1
1
Figure 4-7 Remove P.C. board

4.2.3 Dismantling the Tray
– Remove the encasing as described in 4.2.2
– Disengage the two holders that fix the tray [1] and pull out
the tray [2]
Mechanical Instructions
EN 11DVDR610/615/616 4.
1
2
Figure 4-8 Remove Tray
4.2.4 DVD-M (Drive Mechanism)
1
1
1
1
Figure 4-9 Remove DVD-M
4.2.5 Re - assembly
To re-assemble the module, do all processes in reverse order.
Take care of the following:
• Heat Paths:Put the 5 heat paths (gray rubber pieces) back
to their position on the ICs.
• Complete module: Place all wires/cables in their original
positions
• Emergency opening slot: Be sure that the slot for the
emergency tray opener is covered by adhesive tape!
2
1
Caution: Never try to align or repair the DVD-Module itself!
Only the factory can do this properly. Service engineers are
only allowed to exchange the sledge motor assy.
After Exchanging the DVD-M (or the PCB) the complete drive
has to be adjusted! Refer to chapter 8 for adjustment
instructions!
– Remove encasing and P.C. board as described in 4.2.2
– Remove the Sealing strip 5 by uncatching it
– Loosen the 4 screws/washer [1] to remove the DVD-M [2]
Figure 4-10 Heat Paths
EN 12 DVDR610/615/6164.
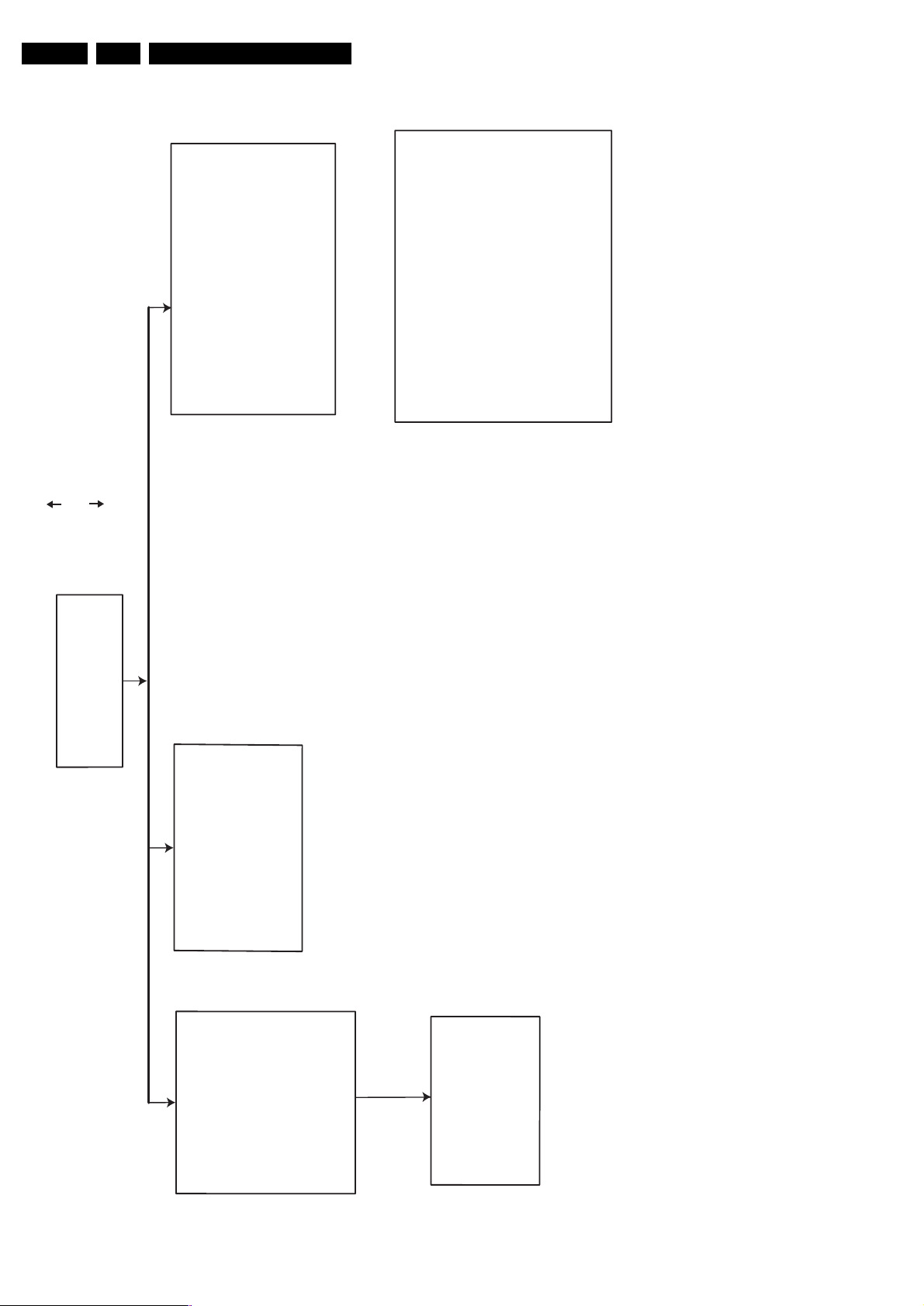
4.3 Dismantling Instructions
Remove all the connections
DVDR BASIC ENGINE 1004
⇒
⇒ Remove Front Panel assembly
mounting
demounting
Remove 6 screws 260 and 269
Remove 2 screws 262
(assembly -> support bracket 256)
(assembly -> frame 224)
⇒
⇒
Mechanical Instructions
Uncatch dust cover assembly 147 + 148
from DVDR Basic Engine
⇒
In case the loader is defective and cannot be
opened electrically, you can open the tray
tray front 134 + 138
Manual opening of tray and removal of
It is possible to unlock the tray by means
of a screwdriver via a slot in the
⇒
as follows:
front and frame at the underside.
Open the unlocked tray.
.
Push the white pin of the slider at the
underside of the basic engine to the left
(seen from the front)
⇒
Remove 7 screws 220 & 240
Cover 196
⇒
DISMANTLING INSTRUCTIONS
See exploded view for item numbers
to remove
Lift the cover
⇒
→
demount the board
(board frame)
MOBO board 1001
Front Panel Assembly
the
open the tray and remove
⇒
- Remove the Front Panel assembly
- Remove the connections
- Remove 6 screws 246, 254
→
tray front 134 + 138
remove 3 screws 188
⇒
(board => backplate)
⇒ remove 4 screws 270
⇒
frame 224)
remove 4 screws 186 to
unlock the front from the
frame by releasing 2 snaps
on left and right
(front assy
⇒
⇒
remove the plate front 184
front)
→
Remove screws 172
of DV input cable
(board
Remove 2 screws 176
⇒
⇒
Front Control board
TR 06003_003
demount the board
⇒
300504
Figure 4-11

5. Diagnostic Software
Diagnostic Software
EN 13DVDR610/615/616 5.
Due to the complexity of the DVD recorder, the time to find a
defect in the recorder can become long. To reduce this time,
the recorder has been equipped with Diagnostic and Service
software (DS). The DS offers functionality to diagnose the
DVDR hardware and tests the following:
• Interconnections between components
• Accessibility of components
• Functionality of the audio and video paths
This functionality can be accessed via several interfaces:
1. End user/Dealer script interface
2. Command Interface
5.1 End User/Dealer Script Interface
5.1.1 Description
The End user/Dealer script interface gives a diagnosis on a
stand alone DVD recorder. During this mode, a number of
hardware tests (nuclei) are automatically executed to check if
the recorder is faulty. The diagnosis is simply a "fail" or "pass"
message. If the message "FAIL" appears on the display, there
is apparently a failure in the recorder. If the message "PASS"
appears, the nuclei in this mode have been executed
successfully. There can be still a failure in the recorder
because the nuclei in this mode don't cover the complete
functionality of the recorder.
5.1.2 Structure
Unplug the power cord
Hold key <PLAY> pressed
while you plug the recorder
During the test, the display will show
the a sequence of nuclei under test
SET O.K.?
NO
YES
To exit DEALER SCRIPT, unplug the power cord
Figure 5-1
The End use/Dealer script executes all diagnostic nuclei that
do not need any user interaction and are meaningful on a
standalone DVD recorder.
TR 18029_001
120304
5.1.3 Contents
Included tests: 1.DS_ANAB_COMMUNICATIONECHO_NUC
2.DS_DCB_COMMUNICATIONECHO_NUC
3. DS_BROM_COMMUNICATION_NUC
4. DS_SYS_SETTINGSDISPLAY_NUC
5. DS_CHR_DEVTYPEGET_NUC
6. DS_CHR_INT_PIC_NUC
7. DS_CHR_DMA_NUC
8. DS_BROM_WRITEREAD_NUC
9. DS_NVRAM_COMMUNICATION_NUC
10. DS_NVRAM_WRITEREAD_NUC
11. DS_SDRAM_WRITEREADFAST_NUC
12. DS_FLASH_WRITEREAD_NUC
13.DS_FLASH_CHECKSUMPROGRAM_NUC
14.DS_SYS_HARDWAREVERSIONGET_NUC
15. DS_VIP_DEVTYPEGET_NUC
16. DS_VIP_COMMUNICATION_NUC
17. DS_DVIO_LINKDEVTYPEGET_NUC
18. DS_DVIO_PHYDEVTYPEGET_NUC
19. DS_DVIO_LINKCOMMUNICATION_NUC
20. DS_DVIO_PHYCOMMUNICATION_NUC
21.DS_PSCAN_COMMUNICATIONDENC_NUC
22.DS_PSCAN_COMMUNICATIONDEINTERLACER_NUC
23. DS_BE_COMMUNICATIONECHO_NUC
24.DS_ANAB_COMMUNICATIONIICNVRAM_NUC
25.DS_ANAB_COMMUNICATIONIICTUNER_NUC
26.DS_ANAB_COMMUNICATIONIICSOUNDPROCESSOR_NUC
27.DS_ANAB_COMMUNICATIONIICAVSELECTOR_NUC
28. DS_ANAB_CHECKSUMPROGRAM_NUC

EN 14 DVDR610/615/6165.
r
s
0
r
s
05
00
Diagnostic Software
5.2 Player Script Interface
5.2.1 Trade Mode
TRADE MODE
When the recorder is in Trade Mode, the recorder cannot be
controlled by means of the front key buttons, but only by means
of the remote control.
IF TRADE MODE OFF
UNPLUG THE RECORDER
PRESS 2 KEYS
SIMULTANEOUSLY
<STOP> + <OPEN/CLOSE>
PLUG THE RECORDER
RECORDER IS IN TRADE MODE
WHEN PRESSING FRONT
KEYS, THE RECORDER
DOESN'T RESPOND
IF TRADE MODE ON
UNPLUG THE RECORDER
PRESS 2 KEYS
SIMULTANEOUSLY
<STOP> + <OPEN/CLOSE>
PLUG THE RECORDER
RECORDER IS IN NORMAL MODE
WHEN PRESSING FRONT
KEYS, THE RECORDER
WILL RESPOND
CL 16532095_071.eps
Figure 5-2
5.2.2 Virgin mode
If you want that the recorder starts up in Virgin mode, follow this
procedure:
• Unplug the recorder
• plug the recorder again while you keep the STAND BY/ON
key pressed
• the set starts up in Virgin mode.
5.3 Menu and Command Mode Interface
5.3.1 Nuclei Numeration
Each nucleus has a unique number of four digits. This number
is the input of the command mode.
[ XX YY ]
Nucleus number
Nucleus group numbe
Figure 5-3
Group number Group name
0Scripts
1 Codec (e.g. Chrysalis, Leco)
2 Boot EE PR O M
3NVRAM
4 SDRAM
5Flash
6 Video Input Processor
7DVIO
8* Progressive Scan
9 Basic Engine
10* Display and Control Board
11* Analogue Board
12 System
13* Electronic Program Guide Board
14* PCMCIA
150801
CL 06532152_012.ep
05120
15* HDMI
16 Analogue Slave Processor
17 Analogue Board EEPROM
18 Video Matrix
19 Audio Matrix
20 Front End
21* Hard Disk
22* Digital Terrestrial Tuner Module
* Not applicable for DVDR610, DVDR615 & DVDR616 Range
5.3.2 Error Handling
Each nucleus returns an error code. This code contains six
numerals, which means:
[ XX YY ZZ ]
Error code
Nucleus number
Nucleus group numbe
Figure 5-4
The nucleus group numbers and nucleus numbers are the
same as above.
5.3.3 Command Mode Interface
Set-Up Physical Interface Components
Hardware required:
•Service PC
• one free COM port on the Service PC
• special cable to connect DVD recorder to Service PC
The service PC must have a terminal emulation program (e.g.
Hyperterminal) installed and must have a free COM port (e.g.
COM1). Activate the terminal emulation program and check
that the port settings for the free COM port are: 19200 bps, 8
data bits, no parity, 1 stop bit and no flow control. The free COM
port must be connected via a special cable to the RS232 port
of the DVD recorder. This special cable will also connect the
test pin, which is available on the connector, to ground (i.e.
activate test pin).
Code number of PC interface cable: 3122 785 90017
Activation of Diagnostic Software
1. Pull the mains cord from the recorder and reconnect it
again (reboot).
2. The next welcome message will appear on the PC:
Welcome screen D&S program
Figure 5-5
Now, the prompt 'DS:>' will appear. The diagnostic software is
now ready to receive commands. The commands that can be
given are the numbers of the nuclei. If you see above shown
screen, continue with paragraph 'Nuclei Codes'.
CL 06532152_013.ep
12

Diagnostic Software
EN 15DVDR610/615/616 5.
3. It is possible that the next messages will appear when
starting the DVD+RW for the first time
Error messages D&S program
Figure 5-6a
Error messages D&S program
Enter "Y" to program a safe string. With this automatically
generated string the board will work in principle but it has to be
checked if all board settings were detected correctly.
Diversity String Input
4. Execute nucleus 1226 to enter the string. Please see
chapter 8.4 for details
Nucleus 1226 execution with string
Figure 5-7
5. To check if the hardware info is filled correctly, you can
execute nucleus 1228.
Nucleus 1228 info example
Figure 5-6b
In these cases, the boot EEPROM of the Digital Board does not
contain the required string with the hardware information. To
update the Digital Board with the correct string, nucleus 1226
must be executed.
See next section 'Diversity String Input'.
There can also be the next error message.
Figure 5-8
6. Exit the 'Terminal' program.
Figure 5-6c
7. Reboot the DVD recorder to allow the software to start.
EN 16 DVDR610/615/6165.
Diagnostic Software
Command overview Digital Board
Below you will find an overview of the nuclei, their numbers,
and their error codes. This overview is preliminary and subject
to modifications.
Note: AV3 in the overview includes also the AV3.5 drive.
CODEC HOST CONTROLLER (CHR)
Nucleus Name DS _CHR_DevTypeGet
Nucleus Number 100
Description Retrieves the device id, the module ids and revisions of the Codec and returns them to the
stdout port.
Technical -
Determine the codec id by means of comparing version ids of the modules.-
Read the module-id register of every module and display it to the user.
Execution Time Less than 1 second.
User Input None
Error Number Description
10000 Getting the information succeeded
10001 Wrong codec id detected
Example DS:> 100
010000:
Device ID 710 0
Codec ID PNX7100_C
F-BCU (0x0102) 1.0 INTC (0x011d) 1.0 PCI-XIO(0x0113) 1.0
SIF (0x013b) 1.0 EJTAG (0x0104) 0.1 S-BCU (0x0102) 1.0
(0x010a) 1.0 CONFIG (0x013f) 1.1 RESET (0x0123) 1.0
DEBUG (0x0116) 0.0 UART0 (0x0107) 0.1 UART1 (0x0107) 0.1
UART2 (0x0107) 0.1 UART3 (0x0107) 0.1 I2C0 (0x0105) 0.1
I2C1 (0x0105) 0.1 GPIO (0x013c) 1.0 SYNC (0x013a) 1.0
DISP0 (0xa015) 1.12 DISP1 (0xa00f) 1.1 OSD (0x0136) 0.1
SPU (0xa00e) 0.0 MIXER (0x0137) 1.0 DENC (0x0138) 1.0
CCIR (0x0139) 1.0 VDEC (0x0133) 0.2 PARSER (0xa00d) 0.0
DV (0xa00c) 0.0 BEI (0xa00a) 0.1 IDE (0xa009) 0.1
SGDX (0xa008) 1.0 B YT E (0xa00b) 0.1 OUTPUT (0xa003) 1.0
ACOMP (0xa000) 1.0 VFE (0xa001) 0.1 VCOMP (0xa002) 1.0
SCR (0x0000) 0.0 SIFF (0xa011) 0.1 WMD (0xa010) 0.0
AUDIO0 (0xa015) 1.12 AUDIO1 (0xa00f) 1.1 PSCAN (0xa018) 0.1
Test OK @
Nucleus Name DS_CHR_TestImageOn
Nucleus Number 101
Description Generates a test-image of a selected video standard on selected video output on the digital
Technical -Validate the user input.
Execution Time 6 seconds.
board. When no input is given, the default values will be used (see user input description below). Make sure to use the proper nuclei to route the video signal on the analogue board to get
the videosignal to the proper output.
-Initialise the SYNC module.
-Initialise the DISPLAY module.
-Initialise the MIXER module.
-Initialise the DENC module.
-Set the selected video standard.
-Generate the selected test image in memory.
-Start the DISPLAY module.
-Start the MIXER module.
-Start the DENC module according to the selected test image id.
Diagnostic Software
Nucleus Name DS_CHR_TestImageOn
User Input The user has to decide which test image, video standard and video output must be used:
Test image id:
0 VERTICAL_C OLOURBAR (default)
1 HORIZONTAL_COLOURBAR
2 WHITE
3 YELLOW
4 CYAN
5 GREEN
6 MAGENTA
7 RED
8 BLUE
9 BLACK
10GRAY
11TEST_IMAGE_FOR_PROGRESSIVE_ SC AN
Video standard:
PAL (default)
NTSC
Video output
ALL CVBS and YC and RGB (default)
CVBS
YC
RGB
YUV
PSCAN progressive scan
Error Number Description
10100 Generating the test image succeeded.
10101 Invalid input was provided.
10102 The Codec SYNC-module cannot be initialised.
10103 The Codec MIXER-module cannot be initialised.
10104 The Codec VPP-module cannot be initialised.
10105 The Codec DENC-module cannot be initialised.
10106 T he digital board hardware information is corrupt
Example DS:> 101
010100:
Test OK @
EN 17DVDR610/615/616 5.
DS:> 101 0 pal cvbs
010100:
Test OK @
DS:> 101 4 ntsc yc
010100:
Test OK @
Nucleus Name DS_CHR_TestImageOff
Nucleus Number 102
Description Switches the test-image off.
Technical -
Execution Time Less than 1 second.
User Input None
Error Number Description
Example DS:> 102
Nucleus Name DS_CHR_SineOn
Nucleus Number 103
Description Generate an audio sine signal on the audio output of the digital board. Note: Left channel
Stop the DENC module.
10200 Stopping the test image generation succeeded
10201 The Codec DENC-module failed.
010200:
Test OK @
6kHz, right channel 12 kHz sine. Make sure to route the signal first.

EN 18 DVDR610/615/6165.
Diagnostic Software
Technical - De-mute the analogue board
Execution Time Less than 1 second
User Input None
Error Number Description
Example DS:> 103
Nucleus Name DS_CHR_SineOff
Nucleus Number 104
Description Stop generating the audio sine signal
Technical - Reset the audio block of the Codec
Execution Time Less than 1 second.
User Input None
Error Number Description
Example DS:> 104
- Set fifo parameters for audio
- Set the volume
- Set the I2S outputs and configuration paths
- Set the decoder mode
- Configure the audio decoder
- Put the AC3 audio in the fifo
- Send ‘prepare’ command to the audio decoder
- Send ‘play’ command to the audio decoder
10300 The sine signal was successfully generated
10301 The analogue board could not be de-muted
10302 The audio decoder did not initialise
10303 The dsp2 of the audio decoder did not configure
10304 The dsp1 of the audio decoder did not configure
10305 There was a delay-error before starting
10306 Wrong input was given to the decoder function
10307 Wrong input was given to the decoder function @@@@@
10308 The audio decoder did not get into the 'prepared' state
010300:
Test OK @
10400 Switching off the audio sine signal succeeded
10401 Failed to reset the audio decoder
010400:
Test OK @
Nucleus Name DS_CHR_SineBurst
Nucleus Number 105
Description Generate an audio sine signal on the audio output of the digital board for 4 seconds.
Technical - Call the DS_CHR_SineOn nucleus
Execution Time 4 seconds
User Input None
Error Number Description
Example DS:> 105
Nucleus Name DS_CHR_MuteOn
Nucleus Number 106
Description Mute the audio outputs of the digital board
Technical - Send the 'Mute' command to the audio decoder
Execution Time Less than 1 second.
User Input None
Error Number Description
Note: Left channel 6kHz, right channel 12 kHz sine with some known hick-ups
- Delay for 4 seconds
- Call the DS_CHR_SineOff nucleus
10500 The sine signal burst was successfully generated
10501 The delay did not succeed during the burst
10502 The audio sine could not be generated
010500:
Test OK @
10600 Muting the audio succeeded
Diagnostic Software
EN 19DVDR610/615/616 5.
Example DS:> 106
Nucleus Name DS_CHR_MuteOff
Nucleus Number 107
Description De-mute the audio outputs of the digital board
Technical - Send the ‘DeMute’ command to the audio decoder
Execution Time Less than 1 second.
User Input None
Error Number Descr iption
Example DS:> 107
Nucleus Name DS_CHR_DvLedOn
Nucleus Number 108
Description Check the connection to the DV-LED on the digital board by switching it on
Technical - Write to the PIO pin to light the DV LED
Execution Time Less than 1 second.
User Input None
Error Number Descr iption
Example DS:> 108
010600:
Test OK @
10700 De-muting the audio succeeded
010700:
Test OK @
10800 Switching the DV-LED on succeeded
10801 Switching the DV-LED on failed
010800:
Test OK @
Nucleus Name DS_CHR_DvLedOff
Nucleus Number 109
Description Switch off the DV-LED on the digital board
Technical - Write to the PIO pin to switch off the DV LED
Execution Time Less than 1 second.
User Input None
Error Number Descr iption
10900 Switching the DV-LED off succeeded
10901 Switching the DV-LED off failed
Example DS:> 109
010900:
Test OK @
Nucleus Name DS_CHR_MacroVisionOn
Nucleus Number 110
Description Turn on MacroVision.
Technical - Set some registers of the DENC module in the Codec.
Execution Time Less than 1 second.
User Input None
Error Number Descr iption
11000 Turning on MacroVision succeeded
11001 Turning on MacroVision failed
Example DS:> 110
011000:
Test OK @
Nucleus Name DS_CHR_MacroVisionOff
Nucleus Number 111
Description Turn off MacroVision.
Technical - Set some registers of the DENC module in the Codec.
Execution Time Less than 1 second.
User Input None
Error Number Descr iption
11100 Turning off MacroVision succeeded

EN 20 DVDR610/615/6165.
11101 Turning off MacroVision failed
Example DS:> 111
011100:
Test OK @
Nucleus Name DS_CHR_Peek
Nucleus Number 112
Description Peek a value on a specified address
Technical - Check the user input
- Read out the address specified
- Check whether the address to be read is aligned on 4 bytes
Execution Time Less than 1 second.
User Input The address to peek on
Error Number Description
11200 Peeking on the specified address succeeded
11201 Peeking on the specified address failed, wrong user input
11202 Peeking on the specified address failed due to misalignment
Example DS:> 112 0xa0700000
011200: Value read = 0x000001BD
Test OK @
Nucleus Name DS_CHR_Poke
Nucleus Number 113
Description Poke a value on a specified address
Technical - Check the user input
- Change the value on the address specified
- Check whether the address to be modified is aligned on 4 bytes
Execution Time Less than 1 second.
User Input The address to poke and the value: <address><value>
Error Number Description
11300 Poking the specified address succeeded
11301 Poking the specified address failed, wrong user input
11302 Poking the specified address failed due to misalignment
Example DS:> 113 0xa0700000 0xaabbccdd
011300:
Test OK @
Diagnostic Software
Nucleus Name DS_CHR_INT_PICInterrupts
Nucleus Number 114
Description Test all interrupts of the priority interrupt controller
Technical - Install interrupt handlers
Execution Time Less than 1 second.
User Input Error Number Description
Example DS:> 114
Nucleus Name DS_CHR_DMA_TestDMA
Nucleus Number 115
Description Test the memory to memory DMA transfer
Technical - Create a block with known data in memory
Execution Time Less than 2 seconds.
User Input Error Number Description
- Generate interrupts
- Test whether all interrupts were received
11400 Testing all the PIC interrupts succeeded
11401 Testing all the PIC interrupts failed
011400:
Test OK @
- Copy this block to the consecutive area using 3 different DMAs
- Check whether all DMAs transferred the data properly
11500 The testing of the DMAs succeeded
11501 The initialisation of the DMAs failed for one or more DMA
11502 One or more DMAs failed the test

Diagnostic Software
EN 21DVDR610/615/616 5.
Example DS:> 115
011500:
Test OK @
Boot EEPROM (BROM)
Nucleus Name DS_BROM_Communication
Nucleus Number 200
Description Check the communication between the IIC controller of the Chrysalis and the boot EE-
PROM
Technical - Initialise IIC
Execution Time Less than 1 second.
User Input None
Error Number Descr iption
Example DS:> 200
- Read something from th e EEPROM
20000 The data is properly read so the communication is OK
20001 The IIC bus was not accessible
20002 There was a timeout reading the device
20003 The IIC acknowledge was not received
20004 An IIC-bus error occurred
20005 The IIC bus initialisation failed
20006 An unexpected IIC error occurred
020000:
Test OK @
Nucleus Name DS_BROM_WriteRead
Nucleus Number 201
Description Check whether the Boot EEPROM can be written to and read from
Technical - Initialise IIC
- Write something to the
- Read from the same location and check whether it is the same as written
Execution Time Less than 1 second.
User Input None
Error Number Descr iption
20100 The write-read test succeeded
20101 The write-read test failed
20102 An IIC-bus error occurred
20103 There was a timeout reading the device
20104 The IIC bus was not accessible
20105 The IIC acknowledge was not received
20106 Got unknown IIC bus error
20107 The IIC bus initialisation failed
Example DS:> 201
020100:
Test OK @
EEPROM
NVRAM
Nucleus Name DS_NVRAM_Communication
Nucleus Number 300
Description Check the communication between the IIC controller of the Codec and the EEPROM
Technical - Initialise IIC
Execution Time Less than 1 second.
User Input None
Error Number Descr iption
- Read from a location in NVRAM
30000 Something is properly read so the communication is OK
30001 The IIC bus was not accessible
30002 There was a timeout reading the device
30003 The IIC acknowledge was not received
30004 The communication with the device failed
30005 The IIC bus initialisation failed
30006 @@@@@@

EN 22 DVDR610/615/6165.
Diagnostic Software
Example DS:> 300
Nucleus Name DS_NVRAM_WriteRead
Nucleus Number 301
Description Check whether the EEPROM can be written to and read from
Technical - Initialise IIC
Execution Time Less than 1 second
User Input None
Error Number Description
Example DS:> 301
Nucleus Name DS_NVRAM_Clear
Nucleus Number 302
Description Make the EEPROM empty, containing all zeroes.
Technical - Initialise IIC
Execution Time 16 seconds
User Input None
Error Number Description
Example DS:> 302
030000:
Test OK @
- Backup data from location to modify
- Write to location and read it back again
- Write back the backed up data to the location to leave the NVRAM as found
30100 The write-read test succeeded
30101 The IIC bus could not be initialised
30102 There was an NVRAM IO error
30103 The value could not be read back from the NVRAM
030100:
Test OK @
- Create a memory block filled with zeroes
- Write this block to the NVRAM
30200 The clearing of the NVRAM succeeded
30201 There was an IIC error
30202 Clearing the NVRAM failed
030200:
Test OK @
Nucleus Name DS_NVRAM_Modify
Nucleus Number 303
Description Modifies one or more locations in NVRAM and updates the checksum of the section
Technical - Initialise IIC
Execution Time Less than 1 second
User Input 1. The location that must be modified
Error Number Description
modified
- Decode user input
- Modify the NVRAM as indicated
- Validate the NVRAM by calculating the checksum and storing it
i.e. "ALL" "BOOT" "DIAGNOS TICS" "DOWNLOAD" "CONFIG" "RECORDER" or
no string if an offset from the base address of the NVRAM is required
2. The offset and data which to put on the selected location
<offset> <length> <data>
30300 Modifying the NVRAM contents succeeded
30301 Unable to initialise NVM
30302 Modifying the NVRAM contents failed
30303 length out of range
30304 unable to decode length
30305 offset out of range
30306 unable to decode offset
30307 unknown location specified
30308 no location is specified
30309 number of values incorrect
30310 There was an IIC error

Diagnostic Software
EN 23DVDR610/615/616 5.
Example DS:> 303 DIAGNOSTICS 5 1 0x5a
Nucleus Name DS_NVRAM_Read
Nucleus Number 304
Description Read out one or more locations in the NVRAM
Technical - Initialise IIC
Execution Time Less than 1 second
User Input 1. The location which must be read i.e. "ALL" "BOOT" "DIAGNOSTICS" "DOWN LOAD"
Error Number Descr iption
Example 304 DIAGNOSTICS 0 6
030300: Section is modified successfully
Test OK @
- Decode user input
- Read from the NVRAM and return this info to the user
"CONFIG" "RECORDER" or no string if an offset from the base address of the NVRAM
is required
2. The offset and number of bytes to read
<offset> <length>
30400 Value read
30401 Unable to initialise NVM
30402 Reading the NVRAM contents failed
30403 length out of range
30404 unable to decode length
30405 offset out of range
30406 unable to decode offset
30407 unknown location specified
30408 no location is specified
030400: Value read = 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x5A
Test OK @
SDRAM
Nucleus Name DS_SDRAM_WriteRead
Nucleus Number 400
Description Check all data lines, address lines and memory locations of the SDRAM
Technical - Test the databus
Execution Time 11 seconds for 32 Mb
User Input None
Error Number Descr iption
Example DS:> 400
Nucleus Name DS_SDRAM_WriteReadFast
Nucleus Number 401
Description Check all data lines and address lines of the SDRAM
Technical - Test the databus
Execution Time Less than 1 second
User Input None
Error Number Descr iption
Example DS:> 401
- Test the address bus
- Test the integrity of the device itself (memory locations)
23 seconds for 64 Mb
40000 The write-read test succeeded
40001 The data bus contains an error
40002 The address bus contains an error
40003 The SDRAM itself contains an error
040000:
Test OK @
- Test the addressbus
40100 The write-read test succeeded
40101 The data bus contains an error
40102 The address bus contains an error
040100:
Test OK @
EN 24 DVDR610/615/6165.
Nucleus Name DS_SDRAM_Write
Nucleus Number 402
Description Write to a specific memory address
Technical - Decode the user input and check its ranges and alignment on 4 bytes
- Write the data to the SDRAM
Execution Time Less than 1 second
User Input 1. The location that must be modified
( SDRAM starts at address 0xA0000000 )
2. The value to put on the selected location
Error Number Description
40200 Writing to the SDRAM succeeded
40201 Writing to the SDRAM failed; Wrong user input
40202 Address is not dividable by 4
Example DS:> 402 0xa1000010 0xad112222
040200:
Test OK @
Nucleus Name DS_SDRAM_Read
Nucleus Number 403
Description Read from a specific memory address
Technical - Decode the user input and check the ranges
- Read from the SDRAM and return this info to the user
Execution Time Less than 1 second
User Input The location from which the data must be read
( SDRAM starts at address 0xA0000000 )
Error Number Description
40300 Reading from the SDRAM succeeded
40301 Reading from the SDRAM failed; Wrong user input
40302 Address is not dividable by 4
Example DS:> 403 0xa1000010
040300: Value read = 0xAD112222
Test OK @
Diagnostic Software
FLASH
Nucleus Name DS_FLASH_DevTypeGet
Nucleus Number 500
Description Get the device (revision) type information of the FLASH IC. (type, manufacturer, device ID
and size)
Technical - Set the timing for the flash writing
Execution Time Less than 1 second
User Input None
Error Number Description
Example DS:> 500
Nucleus Name DS_FLASH_WriteRead
Nucleus Number 501
Description Check whether the FLASH can be written to and read from
Technical - Find the test segment in flash
Execution Time Less than 1 seconds.
User Input None
Error Number Description
- Write a command sequence to determine device type information
- Return the information to the user
50000 Getting the information from the FLASH succeeded
50001 Getting the information from the FLASH failed
050000: Found FLASH memory:
NOR AMD 29DL640G 8MB,NOR AMD 29DL640G 8MB
Test OK @
- Read the data into SDRAM
- Modify the data
- Write this data from SDRAM to FLASH and verify it by reading back again
50100 The FLASH write-read test succeeded
50101 The test segment could not be found
50102 All bits is the TEST region are filled with 0 (region exhausted)

Diagnostic Software
50103 The WriteRead test failed
50104 The Write Failed
Example DS:> 501
050100:
Test OK @
Nucleus Name DS_FLASH_Read
Nucleus Number 502
Description Read from a specific memory address in FLASH
Technical - Decode the user input and check the ranges and whether the address is aligned on
4 bytes
- Read the data and return this to the user
Execution Time Less than 1 seconds.
User Input The location from which data must be read
( FLASH starts at address 0xB8000000 )
Error Number Description
50200 Reading the FLASH succeeded
50201 Reading the FLASH failed; Wrong user input
50202 Address is not dividable by 4
Example DS:> 502 0xb8000000
050200: Value read = 0x3C08A000
Test OK @
EN 25DVDR610/615/616 5.
Nucleus Name DS_FLASH_ChecksumProgram
Nucleus Number 503
Description Check the checksum of the application partitions by recalculating and comparing partition
Technical - Determine the number of segments
Execution Time 6 seconds
User Input None
Error Number Description
Example DS:> 503
Nucleus Name DS_FLASH_CalculateChecksum
Nucleus Number 504
Description Calculate the checksum over all memory addresses. Used to check entire FLASH contents
Technical - Run the checksum calculation algorithm all flash memory addresses
Execution Time 6 seconds
User Input None
Error Number Description
Example DS:> 504
checksums
- Find the application in each segment and determine its checksum
- Check whether the checksums stored match the newly calculated
50300 The checksum is valid, the test succeeded
50301 The checksum is invalid
050300:
BootCode checksum is: 0xBABE5B6F, which is correct
Diagnostics checksum is : 0xBABEBAFF, which is correct
Download checksum is: 0xBABEEDBF, which is correct
Application checksum is : 0xBABE8EEC, which is correct
Test OK @
50400 Calculating the checksum over all addresses succeeded
050400: The Checksum = 0xBABE30A4
Test OK @
Nucleus Name DS_FLASH_CalculateChecksumFast
Nucleus Number 505
Description Calculate a checksum over a selected number of address locations
Technical - Run the checksum calculation algorithm on a selected number of flash memory
Execution Time 6 seconds
User Input None
Error Number Description
addresses
50500 Calculating the checksum over selected addresses succeed-
ed

EN 26 DVDR610/615/6165.
Diagnostic Software
Example DS:> 505
050500: The Checksum = 0xBABEB064
Test OK @
Video Input Processor (VIP)
Nucleus Name DS_VIP_DevTypeGet
Nucleus Number 600
Description Get the device (revision) type information of the VIP IC
Technical - Initialise IIC
- Read out the device (revision) type information of the VIP IC
Execution Time Less than 1 second
User Input None
Error Number Description
60000 Getting the information from the VIP succeeded
60001 The IIC bus initialisation failed
60002 The was an error getting the information from the VIP
60003 Type not according to type stored in HW diversity string
Example DS:> 600
Nucleus Name DS_VIP_Communication
Nucleus Number 601
Description Check the communication between the IIC controller of the Codec and the VIP IC
Technical - Initialise IIC
Execution Time Less than 1 second
User Input None
Error Number Description
Example DS:> 601
060000: Found SAA7118
Test OK @
- Read data from a location in the VIP
60100 Communicating with the VIP succeeded
60101 The IIC bus was not accessible
60102 There was a timeout reading the device
60103 The IIC acknowledge was not received
60104 The communication with the device failed
60105 The IIC bus initialisation failed
060100:
Test OK @
Nucleus Name DS_VIP_ClockO utputOn
Nucleus Number 602
Description Switch the clock output on
Technical - Initialise IIC
Execution Time Less than 1 second
User Input None
Error Number Description
Example DS:> 602
Nucleus Name DS_VIP_ClockOutputOff
Nucleus Number 603
Description Switch the clock output off
Technical - Initialise IIC
Execution Time Less than 1 second
User Input None
Error Number Description
- Set the clock output through IIC
60200 Switching the clock output on succeeded
60201 Switching the clock output on failed
060200:
Test OK @
- Reset the clock output through IIC
60300 Switching the clock output off succeeded
60301 Switching the clock output off failed

Diagnostic Software
EN 27DVDR610/615/616 5.
Example DS:> 603
Nucleus Name DS_VIP_SelectInput
Nucleus Number 604
Description Select an input video path to be switched to the analogue output pin (AOUT) of the VIP
Technical - Check the user input
Execution Time Less than 1 second
User Input The input to select, see table below.
Error Number Description
Example DS:> 604 1
Table 5-1
Channel number Description
1 CVBS_Y_IN_A
2 CVBS_OUT_B
3 CVBS_Y_IN_B
4 CVBS_Y_IN_C
6C_IN
8G_IN
9Y_IN
13 B_IN
14 U_IN
18 R_IN
19 V_IN
Available channels for input of the 7118 and their description
060300:
Test OK @
- Initialise IIC
- Read out the VIP id
- Write the set of registers required for the input specified
60400 Selecting the input of the VIP succeeded
60401 The user provided wrong input
60402 The VIP was not accessible
60402 An unsupported VIP was found
060400:
Test OK @
Table 5-2
Channel number Description
1 CVBS_Y_IN_B
2 CVBS_OUT_B_VIP
4C_IN_VIP
7 CVBS_Y_IN_B
Digital Video Input Output (DVIO)
Nucleus Name DS_DVIO_LinkDevTypeGet
Nucleus Number 700
Description Get the device (revision) type information of the 1394 Link layer IC
Technical - Initialise the PIO pins on the Codec
Execution Time Less than 1 second
User Input None
Error Number Description
Example DS:> 700
Nucleus Name DS_DVIO_PhyDevTypeGet
Nucleus Number 701
Available channels for input of the 7115 and their description
- Read out the ID register
70000 Getting the information from the link layer IC succeeded
70001 Getting the information from the link layer IC failed
70002 Type not according to type stored in HW diversity string
070000: Device type of the link layer IC: ffc00301
Test OK @

EN 28 DVDR610/615/6165.
Description Get the device (revision) type information of the 1394 Physical layer IC
Technical - Initialise the PIO pins of the Codec-Write the PHY
- access regist er in the Link chip to indicate phy read access
- Wait until the link chip has obtained the value from the phy-chip
- Read this out and filter the data to be returned to the user
Execution Time Less than 1 second
User Input None
Example DS:> 701
070100: Physical layer IC: VendorID: 0x006037, ProductID: 0x412801
Test OK @
Nucleus Name DS_DVIO_LinkCommunication
Nucleus Number 702
Description Check the acc essibility of the 1394 Link layer IC by writing to and reading from a specific
address
Technical - Initialise the PIO pins of the chrysalis
- Write a pattern to the CYCTM register of the link chip
- Read back and verify the pattern
Execution Time Less than 1 second
User Input None
Error Number Description
70200 Communicating with the link layer IC succeeded
70201 Communicating with the link layer IC failed
70202 Result of nucleus not according to HW diversity string
Example DS:> 702
070200:
Test OK @
Diagnostic Software
Nucleus Name DS_DVIO_PhyCommunication
Nucleus Number 703
Description Check the accessibility of the 1394 Physical layer IC by writing to and reading from a spe-
Technical - Initialise the PIO pins of the Codec
Execution Time Less than 1 second
User Input None
Error Number Description
Example DS:> 703
Nucleus Name DS_DVIO_Routing
Nucleus Number 704
Description Route a DV stream containing an audio and video signal through the physical and link layer
Technical - Initialise the DMA to transfer 5 frames PAL/NTSC
Execution Time 6-10 seconds (6 when OK, 10 when no stream or error)
User Input None
cific address
- Initialise IIC
- Write the data to be written to the phy-chip to the link chip first
- Wait until the link chip indicates that the data has been written to the PHY
- Write the PHY-access register in the Link chip to indicate PHY read access
- Wait until the link chip has obtained the value from the PHY-chip
- Test whether the value read back equals the one previously written
70300 Communicating with the physical layer IC succeeded
70301 The physical layer IC was not accessible
70302 Communicating with the physical layer IC failed
70303 Result of nucleus not according to HW diversity string
070300:
Test OK @
ICs to the Codec. This test works for both NTSC and PAL.
- Initialise the DV demultiplexer
- Initialise the 1394 interface and start reception of the DV stream
- Check whether the stream was copied to memory properly by the byte input interface
(port to memo r y type DMA)

Diagnostic Software
Error Number Description
70400 Routing the signals succeeded
70401 The 1394 link chip could not be initialised properly
70402 There was a syntax error in the DV stream
70403 DMA could not copy DV stream to memory. Stream connect-
ed?
70404 DMA not working properly
Example DS:> 704
070400:
Test OK @
Nucleus Name DS_DVIO_DetectNode
Nucleus Number 705
Description Check whether a DV node can be detected by the hardware. This test works for both NTSC
and PAL.
Technical - Initialise the 1394 interface
- Detect whether a node is in range
Execution Time 3 or 5 seconds (3 when OK, 5 when no stream or error)
User Input None
Error Number Description
70500 The node was detected OK
70501 The 1394 link chip could not be initialised properly
70502 Unable to write to 1394 PHY chip
70503 Unable to read from 1394 PHY chip
70504 No node was detected
Example DS:> 705
070500:
Test OK @
EN 29DVDR610/615/616 5.
Nucleus Name DS_DVIO_DetectStream
Nucleus Number 706
Description Check whether a DV stream can be detected by the hardware. T his test works for bot h
Technical - Initialise the 1394 interface
Execution Time 3 or 5 seconds (3 when OK, 5 when no stream or error)
User Input None
Error Number Description
Example DS:> 706
NTSC and PAL.
- Start receiving the stream
- Detect whether the stream is OK
70600 The stream was detected
70601 The 1394 link chip could not be initialised properly
70602 No stream detected
070600:
Test OK @
Progressive Scan (PSCAN)
Nucleus Name DS_P SCAN_DencDevTypeGet
Nucleus Number 800
Description Retrieve the device type information from the progressive scan DENC IC
Technical Execution Time Less than 1 second
User Input None
Error Number Description
80000 Retrieving the device type information succeeded
80001 The IIC bus was not accessible
80002 There was a timeout reading the device
80003 The IIC acknowledge was not received
80004 Communicating with the progressive scan DENC-IC failed
80005 The initialisation of the IIC bus failed
Example DS:> 800
080000: Device Type xxxx t.b.d.
Test OK @

EN 30 DVDR610/615/6165.
Nucleus Name DS_PSCAN_CommunicationDenc
Nucleus Number 801
Description Check the communication between the IIC controller of the chrysalis and the progressive
scan DENC-IC
Technical - Initialise IIC
- Write data to a register of the DENC through IIC
Execution Time Less than 1 second
User Input None
Error Number Description
80100 Communicating with the progressive scan DENC-IC succeed-
80101 The IIC bus was not accessible
80102 There was a timeout reading the device
80103 The IIC acknowledge was not received
80104 Communicating with the progressive scan DENC-IC failed
80105 The initialisation of the IIC bus failed
80106 The read data is not the same as the written data
80107 No chip was expected
Example DS:> 801
080100:
Test OK @
Nucleus Name DS_PSCAN_TestImageOn
Nucleus Number 802
Description Generate the test images that are present on the progressive scan IC.
Technical - Determine whether the user wanted a HATCH or a FRAME image pattern
- Initialise the PIO pins of the Codec
- Initialise IIC
- Reset the DENC
- Enable the 27Mhz clock
- Send all settings for the pattern to the DENC through IIC
Execution Time Less than 1 second
User Input In case of ADV7196:
When no input is given “HATCH” is the default
-“HATCH”
-“FRAME”
Remark:
“HATCH” is a crosshatch test pattern (horizontal and vertical white lines are display ed
against a black background)
“FRAME” is a uniform coloured frame/field test pattern (default white).
In case of FLI2300: Nothing.
Error Number Description
80200 The generation of the test image succeeded
80201 Unable to initialise
80202 Unable to reset DENC
80203 Unable to generate image
80204 No chip was expected
Example DS:> 802 HATCH
080200:
Test OK @
Diagnostic Software
ed
PSCAN IC
Nucleus Name DS_PSCAN_TestImageOff
Nucleus Number 803
Description Switch off the generated test image
Technical - Initialise IIC
- Send the default DENC settings to the DENC through IIC
Execution Time Less than 1 second
User Input None
Error Number Description
80300 Turning off the test image succeeded
80301 Unable to initialise
80302 IIC Error during writing PSCAN IC
80303 No chip was expected
PSCAN IC
 Loading...
Loading...