Philips CR2427S Datasheet

DISCRETE SEMICONDUCTORS
DATA SH EET
CR2427S
Video driver hybrid amplifier
Product specification
File under Discrete Semiconductors, SC05
Philips Semiconductors
1995 Feb 09
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Video driver hybrid amplifier CR2427S
FEATURES
• Typical transition times (10 to 90%)
with CL= 8.5 pF:
– at 35 V (p-p) swing
tr= 2.2 ns; tf= 2.0 ns
– at 40 V (p-p) swing
tr= 2.3 ns; tf= 2.1 ns
– at 50 V (p-p) swing
tr= 2.5 ns; tf= 2.2 ns
• Low power consumption
• Minimum small signal
bandwidth 130 MHz
• Very fast slew rate; 15000 V/µs
• Excellent grey-scale linearity
• Unconditional stability
• Gold metallization ensures
excellent reliability.
APPLICATIONS
It is designed for application in
cathode-ray tube (CRT) drivers in
high-resolution colour and
monochrome monitors.
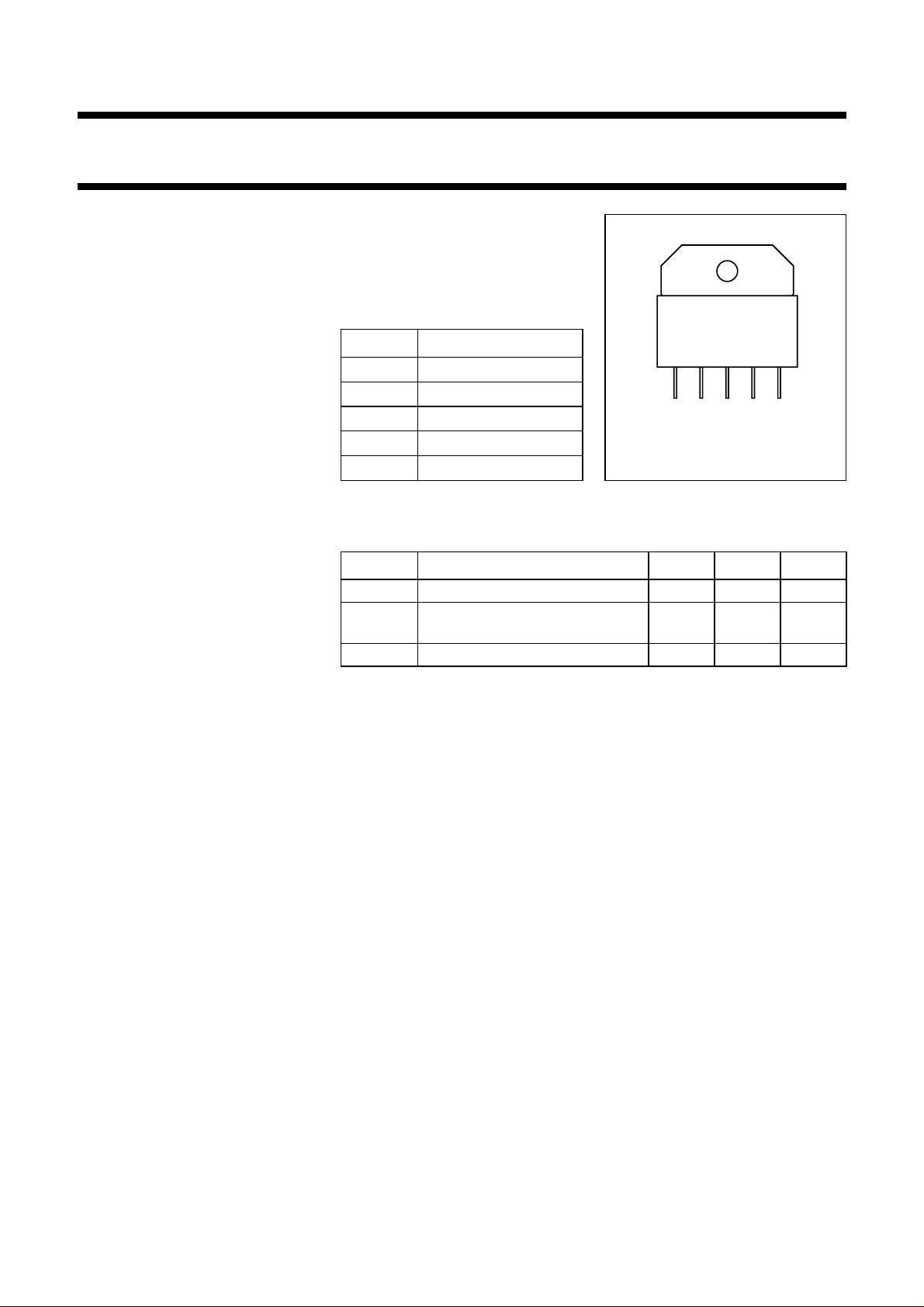
DESCRIPTION
Hybrid amplifier module mounted in
handbook, 2 columns
SOT348 package.
PINNING
PIN DESCRIPTION
1
2
3
4
5
input
ground
supply voltage (V
ground
output
)
S
15
Front view
MBB932
Fig.1 SOT348.
LIMITING VALUES
In accordance with the Absolute Maximum Rating System (IEC 134).
SYMBOL PARAMETER MIN. MAX. UNIT
V
S
T
mb
supply voltage (DC) − 70 V
operating mounting base
−20 +100 °C
temperature; note 1
T
stg
storage temperature −40 +125 °C
Note
1. To ensure proper thermal contact, a layer of heatsink compound should be
applied between module and heatsink.
1995 Feb 09 2
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Video driver hybrid amplifier CR2427S
CHARACTERISTICS
T
=25°C; CL= 8.5 pF; R1 = 215 Ω; C1 = 50 pF (see Fig.10); unless otherwise specified.
mb
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
= 60 V; 40 V (p-p) output swing with 30 V (DC) offset; unless otherwise specified
V
S
I
S
V
I
V
O
t
r
t
f
= 65 V; 50 V (p-p) output swing with 32.5 V (DC) offset; unless otherwise specified
V
S
I
S
V
I
V
O
t
r
t
f
V
= 60 V or 65 V; 40 V (p-p) or 50 V (p-p) output swing with 30 V (DC) or 32.5 V (DC) offset;
S
unless otherwise specified
P
tot
B
s
V
tilt
V
os
NLN non-linearity V
A
V
V
G
supply current input and output open 39 45 51 mA
input voltage (DC) input and output open 1.3 1.6 1.9 V
output voltage (DC) input and output open 28 31 34 V
rise time transient response 10 to 90%; note 1 − 2.3 2.9 ns
fall time transient response 10 to 90%; note 1 − 2.1 2.6 ns
supply current input and output open − 50 57 mA
input voltage (DC) input and output open 1.4 1.75 2.1 V
output voltage (DC) input and output open 29 32 35 V
rise time transient response 10 to 90%; note 2 − 2.5 3.2 ns
fall time transient response 10 to 90%; note 2 − 2.2 3.2 ns
total power dissipation 50 MHz square wave − 4.6 6 W
small signal bandwidth between −3 dB points; note 3 130 145 − MHz
low frequency tilt voltage 1 kHz square wave − 1.3 1.5 V
overshoot voltage varied by C1; see Fig.10 − 310%
= 5 to 55 V − 25%
O
DC voltage gain 50 Ω source; note 4 11.2 12.4 13.2
insertion gain 50 Ω source; note 5 160 180 200
Notes
1. Input signal is a nominal 100 kHz square wave of 3.25 V (p-p), with 1.5 V (DC) offset (50 Ω source).
2. Input signal is a nominal 100 kHz square wave of 3.4 V (p-p), with 1.65 V (DC) offset (50 Ω source).
3. Sine wave output signal: 1 V (p-p).
4. Measured V
(Figs 2 and 6) at input test circuit (see Fig.10).
O/VI
5. Measured VO/VI (Figs 3 and 7) at input module (see Fig.10).
1995 Feb 09 3
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Video driver hybrid amplifier CR2427S
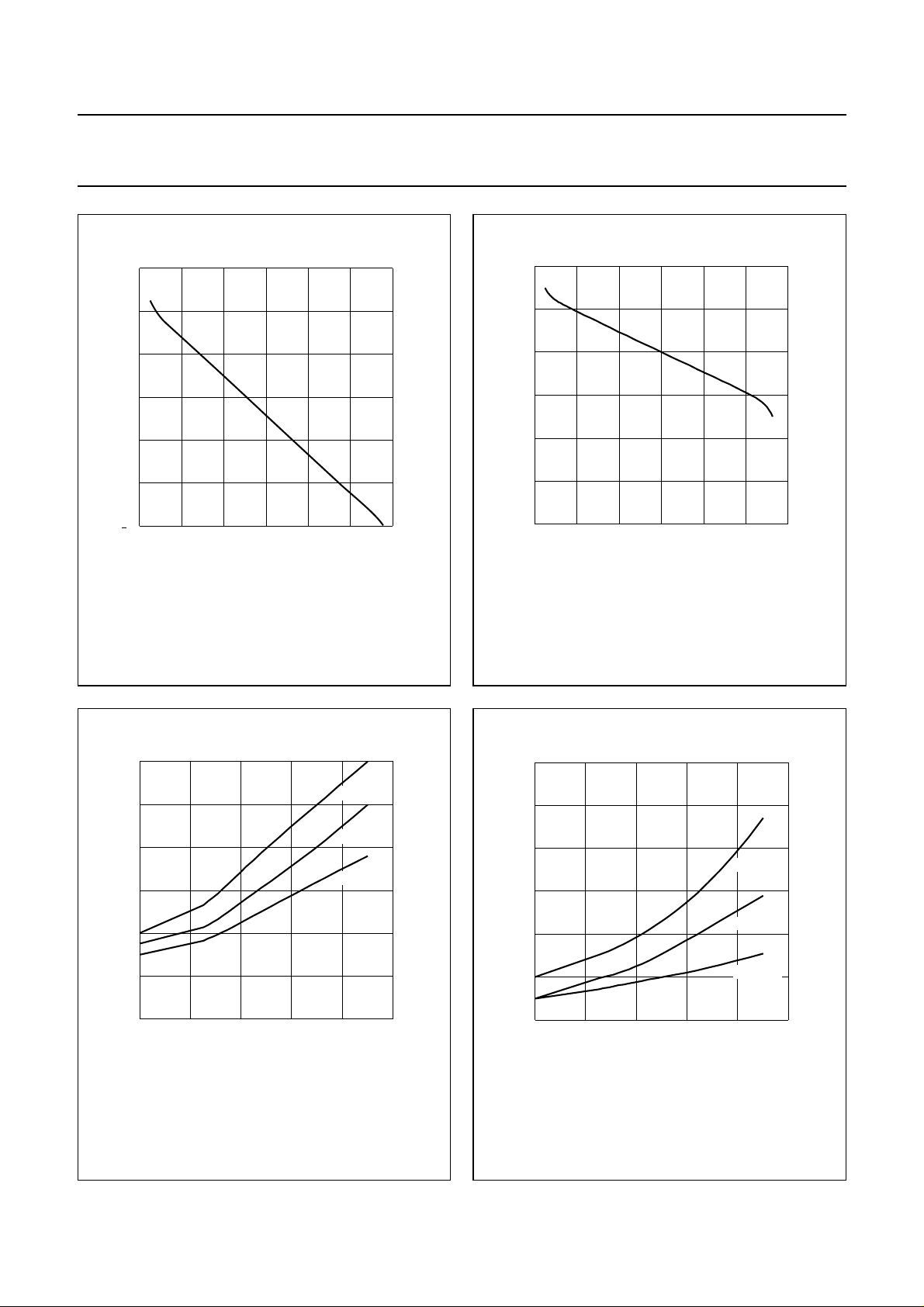
handbook, halfpage
5
V
I
(V)
3
1
1
020
VS=60V; Tmb=25°C; CL= 8.5pF; R1 = 215 Ω; C1 = 50 pF;
40 V (p-p) output swing with 30 V (DC) offset (see Fig.10).
40 60
VO(V)
Fig.2 Input voltage at input test-circuit as a
function of output voltage; typical values.
MLB868
1.8
handbook, halfpage
V
I
(V)
1.6
1.4
1.2
0 204060
VS=60V; Tmb=25°C; CL= 8.5 pF; R1 = 215 Ω; C1 = 50 pF;
40 V (p-p) output swing with 30 V (DC) offset (see Fig.10).
V (V)
O
Fig.3 Input voltage at input module as a function
of output voltage; typical values.
MLB867
3.0
handbook, halfpage
t
r
(ns)
2.6
2.2
1.8
6 8 10 12 14 16
VS=60V; Tmb=25°C; CL= 8.5 pF; R1 = 215 Ω; C1 = 50 pF;
40, 35, 30 V (p-p) output swing with 30 V (DC) offset.
MRA627 - 1
40 V (p-p)
35 V (p-p)
30 V (p-p)
L
Fig.4 Rise time transient response as a function
of load capacitance; typical values.
3.0
handbook, halfpage
t
f
(ns)
2.6
2.2
1.8
(pF)C
6 8 10 12 14 16
VS=60V; Tmb=25°C; CL= 8.5 pF; R1 = 215 Ω; C1 = 50 pF;
40, 35, 30 V (p-p) output swing with 30 V (DC) offset.
MRA628 - 1
40 V (p-p)
35 V (p-p)
30 V (p-p)
CL(pF)
Fig.5 Fall time transient response as a function of
load capacitance; typical values.
1995 Feb 09 4
 Loading...
Loading...