Philips bga2001 DATASHEETS

DISCRETE SEMICONDUCTORS
DATA SH EET
M3D124
BGA2001
Silicon MMIC amplifier
Product specification
Supersedes data of 1999 Jul 23
1999 Aug 11
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Silicon MMIC amplifier BGA2001
FEATURES
• Low current, low voltage
• Very high power gain
• Low noise figure
• Integrated temperature compensated biasing
• Supply and RF output pin combined.
APPLICATIONS
• RF front end
• Wideband applications, e.g. analog and digital cellular
telephones, cordless telephones (PHS, DECT, etc.)
• Radar detectors
• Low noise amplifiers
• Satellite television tuners (SATV)
• High frequency oscillators.
DESCRIPTION
Silicon MMIC amplifier consisting of an NPN double
polysilicontransistorwithintegratedbiasingforlowvoltage
applications in a plastic, 4-pin dual-emitter SOT343R
package.
PINNING
PIN DESCRIPTION
1 GND
2 RF in
3 GND
4V
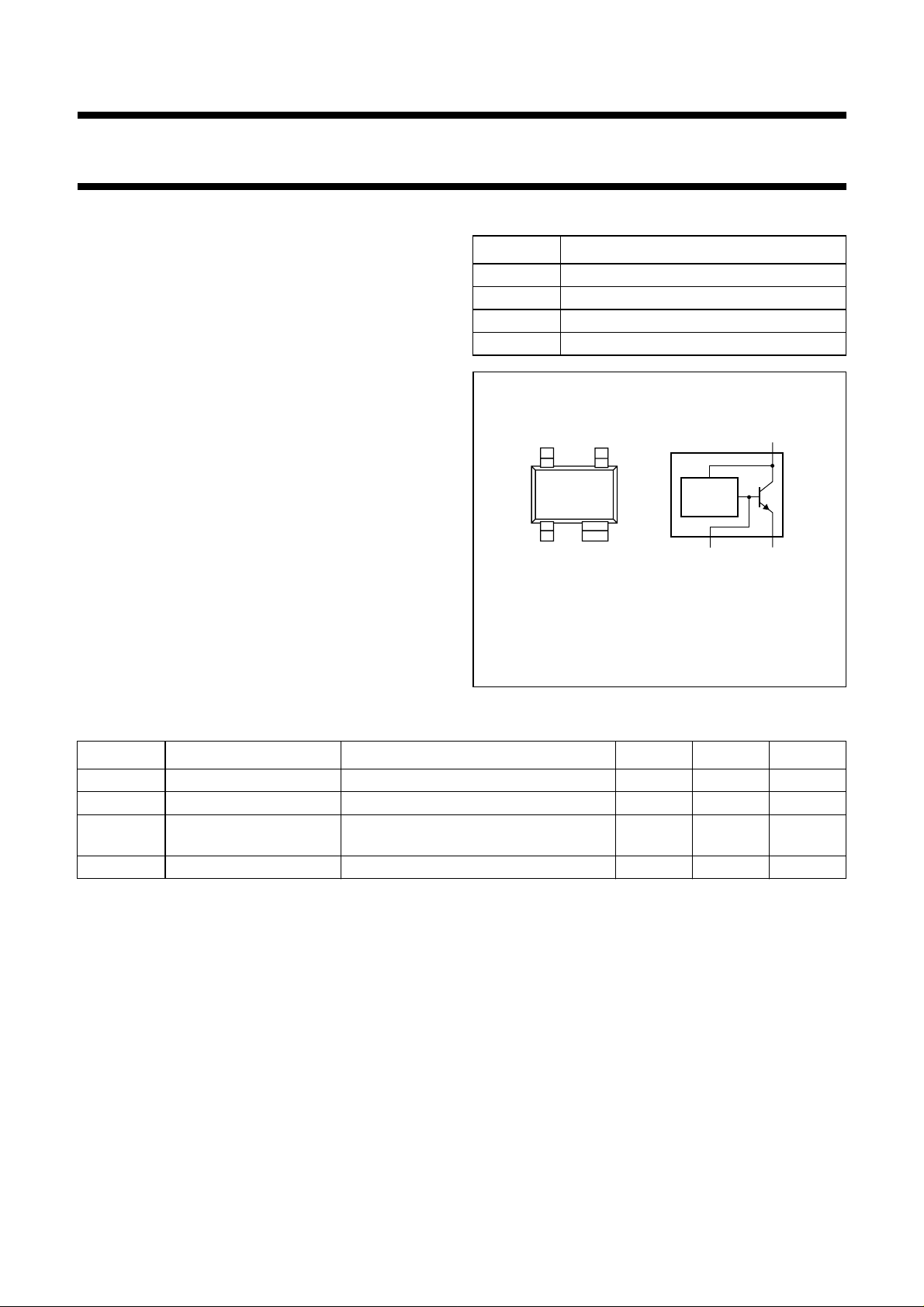
handbook, halfpage
21
Top view
Marking code: A1.
+ RFout
S
43
MAM430
BIAS
CIRCUIT
RFin GND
Fig.1 Simplified outline (SOT343R) and symbol.
VS+RFout
QUICK REFERENCE DATA
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS TYP. MAX. UNIT
V
S
I
S
MSG maximum stable gain V
NF noise figure V
DC supply voltage RF input AC coupled − 4.5 V
DC supply current V
T
= 2.5 V; RF input AC coupled 4.5 − mA
VS-OUT
= 2.5 V; f = 1.8 GHz;
VS-OUT
=25°C
amb
= 2.5 V; f = 1.8 GHz; ΓS= Γ
VS-OUT
19.5 − dB
1.3 − dB
opt
1999 Aug 11 2

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Silicon MMIC amplifier BGA2001
LIMITING VALUES
In accordance with the Absolute Maximum Rating System (IEC 134).
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. MAX. UNIT
V
S
I
S
P
tot
T
stg
T
j
THERMAL CHARACTERISTICS
SYMBOL PARAMETER VALUE UNIT
R
th j-s
CHARACTERISTICS
RF input AC coupled; T
supply voltage RF input AC coupled − 4.5 V
supply current (DC) forced by DC voltage on RF input − 30 mA
total power dissipation Ts≤ 100 °C − 135 mW
storage temperature −65 +150 °C
operating junction temperature − 150 °C
thermal resistance from junction to soldering point 350 K/W
=25°C; unless otherwise specified.
j
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
I
S
supply current V
MSG maximum stable gain V
2
|s
|
21
P
L
insertion power gain V
load power at 1 dB gaincompression point;
NF noise figure V
IP3
(in)
input intercept point; note 1 V
V
V
I
VS-OUT
V
I
VS-OUT
I
VS-OUT
V
I
VS-OUT
V
I
VS-OUT
I
VS-OUT
ΓS= Γ
V
I
VS-OUT
ΓS= Γ
I
VS-OUT
V
I
VS-OUT
=1V − 0.7 − mA
VS-OUT
= 2.5 V 3 4.5 6 mA
VS-OUT
= 4.5 V − 11 − mA
VS-OUT
VS-OUT
= 2.5 V;
− 22 − dB
= 4 mA; f = 900 MHz
VS-OUT
= 2.5 V;
− 19.5 − dB
= 4 mA; f = 1.8 GHz
VS-OUT
= 2.5 V;
− 18 − dB
= 4 mA; f = 900 MHz
VS-OUT
= 2.5 V;
− 14 − dB
= 4 mA; f = 1.8 GHz
−−2−dBm
= 2.5 V;
VS-OUT
= 4.4 mA; f = 900 MHz;
VS-OUT
= 2.5 V;
− 1.3 − dB
= 4 mA; f = 900 MHz;
opt
VS-OUT
= 2.5 V;
− 1.3 − dB
= 4 mA; f = 1.8 GHz;
opt
VS-OUT
= 2.5 V;
−−7.4 − dBm
= 4.4 mA; f = 900 MHz
VS-OUT
= 2.5 V;
−−4.5 − dBm
= 4.5 mA;
f = 1800 MHz
Note
1. See application note: RNR-T45-99-B-0513.
1999 Aug 11 3

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Silicon MMIC amplifier BGA2001
handbook, halfpage
12
handbook, halfpage
I
VS-OUT
(mA)
10
8
6
100 pF
GND
BGA2001
IN
C
RF in
L1
V
S-OUT
GND
MGS605
R1
V
C
RF out
Fig.2 Typical application circuit.
S
MGS607
(8)
(7)
(6)
(5)
200
handbook, halfpage
P
tot
(mW)
150
100
50
0
0 50 100 200
16
handbook, halfpage
I
VS-OUT
(mA)
12
8
150
Ts (
Fig.3 Power derating curve.
MGS606
°C)
MGS608
80
T
amb
VS-OUT
(4)
(3)
(2)
(1)
°C)
(
as
4
2
0
−40 0 40 120
(1) V
(2) V
(3) V
(4) V
Fig.4 Bias current (I
VS-OUT
VS-OUT
VS-OUT
VS-OUT
=1V
= 1.5 V
=2V
= 2.5 V
(5) V
(6) V
(7) V
(8) V
=3V
VS-OUT
= 3.5 V
VS-OUT
=4V
VS-OUT
= 4.5 V.
VS-OUT
) as a function of
VS-OUT
ambient temperature with V
parameter; typical values.
1999 Aug 11 4
4
0
0
15
Fig.5 Bias current (I
voltage at the output pin (V
typical values.
234
VS-OUT
V
VS-OUT
(V)
) as a function of
);
VS-OUT
 Loading...
Loading...